Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA5145
Brushless DC motor drive circuit
Product specification
Supersedes data of March 1992
File under Integrated Circuits, IC11
Philips Semiconductors
June 1994
Page 2
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
FEATURES
• Full-wave commutation (using push/pull drivers at the
output stages) without position sensors
• Built-in start-up circuitry
• Three push-pull outputs:
– output current 2.0 A (typ.)
– built-in current limiter
– soft-switching outputs for low Electromagnetic
Interference (EMI)
• Thermal protection
• Flyback diodes
• Tacho output without extra sensor
• Motor brake facility
• Direction control input
• Reset function
• Transconductance amplifier for an external control
transistor.
APPLICATIONS
• General purpose spindle driver e.g.:
– Hard disk drive
– Tape drive
– Optical disk drive.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA5145 is a bipolar integrated circuit used to drive
3-phase brushless DC motors in full-wave mode. The
device is sensorless (saving of 3 hall-sensors) using the
back-EMF sensing technique to sense the rotor position.
It includes bidirectional control, brake function and has a
special circuit built-in to reduce the EMI (soft switching
output stages).
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Measured over full voltage and temperature range.
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
P
V
VMOT
supply voltage note 1 4 − 18 V
input voltage to the output driver
note 2 1.7 − 16 V
stages
V
I
DO
LIM
drop-out output voltage IO= 100 mA − 0.90 1.05 V
current limiting V
= 10 V; RO= 1.2 Ω 1.8 2.0 2.5 A
VMOT
Notes
1. An unstabilized supply can be used.
2. V
= VP; +AMP IN = −AMP IN = 0 V; all outputs IO = 0 mA.
VMOT
ORDERING INFORMATION
PACKAGE
TYPE NUMBER
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
TDA5145 28 DIL plastic SOT117-1
TDA5145T 28 SOL plastic SOT136-1
June 1994 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
BLOCK DIAGRAM
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
Pin numbers for both DIL and SOL packages are identical.
June 1994 3
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBB
Fig.1 Block diagram.
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
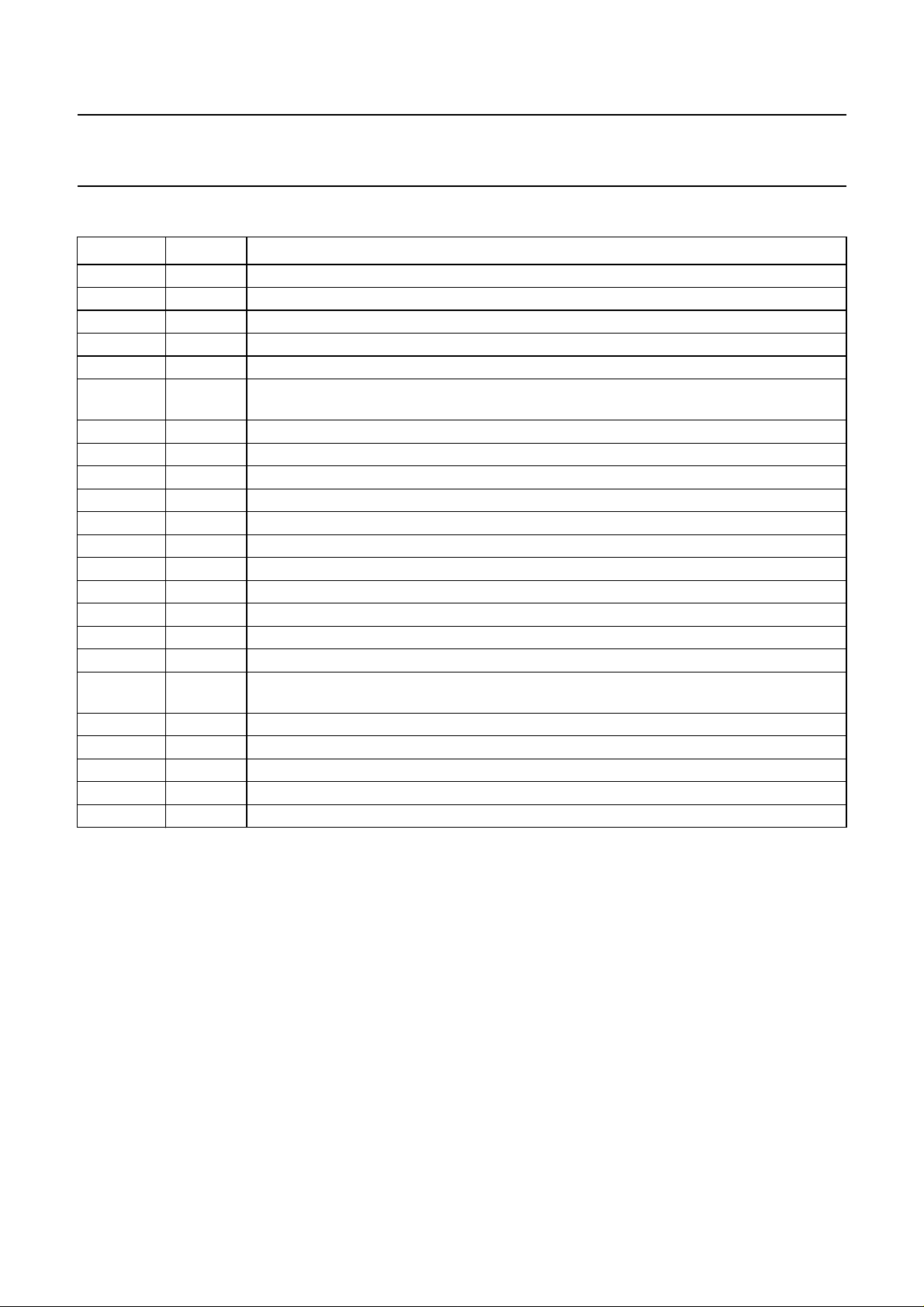
PINNING
SYMBOL PIN
MOT1 1 and 2 driver output 1
TEST 3 test input/output
n.c. 4 not connected
MOT2 5 and 6 driver output 2
VMOT 7 and 8 input voltage for the output driver stages
BRAKE 9 brake input; this pin may not be left floating, a LOW level voltage must be applied to disable
DIR 10 direction control input; this pin may not be left floating
FG 11 frequency generator: output of the rotation speed (open collector digital output)
GND2 12 ground supply return for control circuits
V
P
CAP-CD 14 external capacitor connection for adaptive communication delay timing
CAP-DC 15 external capacitor connection for adaptive communication delay timing copy
CAP-ST 16 external capacitor connection for start-up oscillator
CAP-TI 17 external capacitor connection for timing
+AMP IN 18 non-inverting input of the transconductance amplifier
−AMP IN 19 inverting input of the transconductance amplifier
n.c. 20 not connected
RESET 21 reset input; this pin may not be left floating, a LOW level voltage must be applied to disable
AMP OUT 22 transconductance amplifier output (open collector)
MOT3 23 and 24 driver output 3
n.c. 25 not connected
MOT0 26 input from the star point of the motor coils
GND1 27 and 28 ground (0 V) motor supply return for output stages
(1)
this function
13 supply voltage
this function
DESCRIPTION
Note
1. Pin numbers for both DIL and SOL packages are identical.
June 1994 4
Page 5
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
The TDA5145 offers a sensorless three phase motor drive
function. It is unique in its combination of sensorless motor
drive and full-wave drive. The TDA5145 offers protected
outputs capable of handling high currents and can be used
with star or delta connected motors. It can easily be
adapted for different motors and applications. The
TDA5145 offers the following features:
• Sensorless commutation by using the motor EMF.
• Built-in start-up circuit.
• Optimum commutation, independent of motor type or
motor loading.
• Built-in flyback diodes.
• Three phase full-wave drive.
• High output current (2.0 A).
• Outputs protected by current limiting and thermal
protection of each output transistor.
• Low current consumption by adaptive base-drive.
• Soft-switching pulse output for low radiation.
• Accurate frequency generator (FG) by using the
motor EMF.
• Direction of rotation controlled by one pin.
• Uncommitted operational transconductance amplifier
(OTA), with a high output current, for use as a control
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
amplifier.
• Brake function.
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
P
V
I
supply voltage − 18 V
input voltage; all pins except
VI< 18 V −0.3 VP + 0.5 V
VMOT
V
VMOT
V
O
V
I
VMOT input voltage −0.5 17 V
output voltage
AMP OUT and FG GND V
MOT0, MOT1, MOT2 and MOT3 −1V
input voltage CAP-ST, CAP-TI,
− 2.5 V
P
VMOT
+ V
DHF
V
V
CAP-CD and CAP-DC
T
stg
T
amb
P
tot
V
es
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
operating ambient temperature 0 +70 °C
total power dissipation see Figs 3 and 4 −− W
electrostatic handling see Chapter “Handling” − 2000 V
June 1994 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
3.08
1.75
P
(W)
6
tot
4
2
0
50
0 200
50 100 150
70
T ( C)
handbook, halfpage
Fig.3 Power derating curve (SOT117-1; DIL28).
HANDLING
amb
MBD866
o
MBD557
o
T ( C)
amb
P
(W)
1.62
3
tot
2
1
0
50
0 200
50 100 150
Fig.4 Power derating curve (SOT136-1; SO28L).
Every pin withstands the ESD test according to
“MIL-STD-883C class 2”
. Method 3015 (HBM 1500 Ω, 100 pF) 3 pulses +
and 3 pulses − on each pin referenced to ground.
CHARACTERISTICS
= 14.5 V; T
V
P
=25°C; unless otherwise specified.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
I
P
V
VMOT
supply voltage note 1 4 − 18 V
supply current note 2 − 6.8 7.8 mA
input voltage to the output driver
see Fig.1 1.7 − 16 V
stages
Thermal protection
T
SD
local temperature at temperature
130 140 150 °C
sensor causing shut-down
∆T reduction in temperature before
after shut-down − T
− 30 − K
SD
switch-on
June 1994 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
MOT0; centre tap
V
I
I
I
V
CSW
∆V
CSW
input voltage −0.5 − V
input bias current 0.5 V < VI< V
comparator switching level note 3 ±20 ±25 ±30 mV
variation in comparator switching
levels
V
hys
comparator input hysteresis − 75 −µV
MOT1, MOT2 and MOT3; see Fig.5
V
∆V
DO
OL
drop-out output voltage IO= 100 mA − 0.9 1.05 V
variation in saturation voltage
between lower transistors
∆V
OH
variation in saturation voltage
between upper transistors
I
LIM
t
r
t
f
V
DHF
V
DLF
I
DM
current limiting V
rise time switching output V
fall time switching output V
diode forward voltage (diode DH)I
diode forward voltage (diode DL)I
peak diode current note 5 −− 2.5 A
+AMP IN and −AMP IN
V
I
input voltage −0.3 − VP− 1.7 V
differential mode voltage without
‘latch-up’
I
b
C
I
V
offset
input bias current −− 650 nA
input capacitance − 4 − pF
input offset voltage −− 10 mV
AMP OUT (open collector)
I
V
V
sink
sat
O
output sink current 40 −−mA
saturation voltage II=40mA − 1.5 2.1 V
output voltage −0.5 − +18 V
SR slew rate R
G
tr
transfer gain 0.3 −−S
DIR
V
IH
V
IL
I
IL
I
IH
HIGH level input voltage 4 V < VP< 18 V 2.0 −−V
LOW level input voltage 4 V < VP<18V −− 0.8 V
LOW level input current −−20 −µA
HIGH level input current − 20 −µA
VMOT
− 1.5 V −10 −−µA
VMOT
−− 3mV
I
= 1000 mA − 1.6 1.85 V
O
IO= 100 mA −− 180 mV
IO= −100 mA −− 180 mV
= 10 V; RO= 1.2 Ω 1.8 2.0 2.5 A
VMOT
= 15 V; see Fig.6 5 10 15 µs
VMOT
= 15 V; see Fig.6 10 15 20 µs
VMOT
=−500 mA;
O
−− 1.5 V
notes 4 and 5; see Fig.1
= 500 mA;
O
−1.5 −−V
notes 4 and 5; see Fig.1
−− ±V
= 330 Ω; CL=50pF − 60 − mA/µs
L
P
V
V
June 1994 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
RESET
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage reset mode;
4V<VP<18V
V
IL
LOW level input voltage normal mode;
4V<VP<18V
I
IL
I
IH
LOW level input current VI= 2.0 V −−20 −µA
HIGH level input current VI= 0.8 V − 20 −µA
BRAKE
V
IH
HIGH level input voltage brake mode;
4V<VP<18V
V
IL
LOW level input voltage normal mode;
4V<VP<18V
I
IL
I
IH
LOW level input current VI= 2.0 V −−20 −µA
HIGH level input current VI= 0.8 V − 20 −µA
FG (open collector)
V
OL
V
OH(max)
t
THL
LOW level output voltage IO= 1.6 mA −− 0.4 V
maximum HIGH level output voltage V
HIGH-to-LOW transition time CL= 50 pF; RL=10kΩ− 0.5 −µs
ratio of FG frequency and
commutation frequency
δ duty factor − 50 − %
2.0 −−V
−− 0.8 V
2.0 −−V
−− 0.8 V
P
−−V
− 1:2 −
CAP-ST
I
sink
I
source
V
SWL
V
SWH
CAP-TI
I
sink
I
source
V
SWL
V
SWM
V
SWH
CAP-CD
I
sink
I
source
I
sink/Isource
V
IL
V
IH
output sink current 1.5 2.0 2.5 µA
output source current −2.5 −2.0 −1.5 µA
LOW level switching voltage − 0.20 − V
HIGH level switching voltage − 2.20 − V
output sink current − 28 −µA
output source current 0.2 V < V
0.3V<V
< 0.3 V −−57 −µA
CAP-TI
< 2.2 V −−5−µA
CAP-TI
LOW level switching voltage − 50 − mV
MIDDLE level switching voltage − 0.30 − V
HIGH level switching voltage − 2.20 − V
output sink current 10.6 16.2 22 µA
output source current −5.3 −8.1 −11 µA
ratio of sink to source current 1.85 2.05 2.25
LOW level input voltage 850 875 900 mV
HIGH level input voltage 2.3 2.4 2.55 V
June 1994 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
CAP-DC
I
sink
I
source
I
sink/Isource
V
IL
V
IH
Notes
1. An unstabilized supply can be used.
2. V
VMOT=VP
3. Switching levels with respect to MOT1, MOT2 and MOT3.
4. Drivers are in the high-impedance OFF-state.
5. The outputs are short-circuit protected by limiting the current and the IC temperature.
output sink current 10.1 15.5 20.9 µA
output source current −20.9 −15.5 −10.1 µA
ratio of sink to source current 0.9 1.025 1.15
LOW level input voltage 850 875 900 mV
HIGH level input voltage 2.3 2.4 2.55 V
, all other inputs at 0 V; all outputs at VP; IO= 0 mA.
Fig.5 Switching levels with respect to MOT1, MOT2 and MOT3.
Fig.6 Output transition time measurement.
June 1994 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
APPLICATION INFORMATION
(1) Value selected for 3 Hz start-up oscillator frequency.
Fig.7 Application diagram without use of the operational transconductance amplifier (OTA).
Introduction (see Fig.8)
Full-wave driving of a three phase motor requires three
push-pull output stages. In each of the six possible states
two outputs are active, one sourcing (H) and one sinking
(L). The third output presents a high impedance (Z) to the
motor, which enables measurement of the motor
back-EMF in the corresponding motor coil by the EMF
comparator at each output. The commutation logic is
responsible for control of the output transistors and
selection of the correct EMF comparator. In Table 1 the
sequence of the six possible states of the outputs has
been depicted.
The zero-crossing in the motor EMF (detected by the
comparator selected by the commutation logic) is used to
calculate the correct moment for the next commutation,
that is, the change to the next output state. The delay is
calculated (depending on the motor loading) by the
adaptive commutation delay block.
Because of high inductive loading the output stages
contain flyback diodes. The output stages are also
protected by a current limiting circuit and by thermal
protection of the six output transistors.
Table 1 Output states.
STATE MOT1
(1)
MOT2
(1)
MOT3
(1)
1ZLH
2HLZ
3HZL
4ZHL
5LHZ
6LZH
Note
1. H = HIGH state;
L = LOW state;
Z = high-impedance OFF-state.
The detected zero-crossings are used to provide speed
information. The information has been made available on
the FG output pin. This is an open collector output and
provides an output signal with a frequency that is half the
commutation frequency.
The system will only function when the EMF voltage from
the motor is present. Therefore, a start oscillator is
June 1994 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
provided that will generate commutation pulses when no
zero-crossings in the motor voltage are available.
A timing function is incorporated into the device for internal
timing and for timing of the reverse rotation detection.
The TDA5145 also contains an uncommitted
transconductance amplifier (OTA) that can be used as a
control amplifier. The output is capable of directly driving
an external power transistor.
The TDA5145 is designed for systems with low current
consumption: use of I2L logic, adaptive base drive for the
output transistors (patented).
Adjustments
The system has been designed in such a way that the
tolerances of the application components are not critical.
However, the approximate values of the following
components must still be determined:
• The start capacitor; this determines the frequency of the
start oscillator.
• The two capacitors in the adaptive commutation delay
circuit; these are important in determining the optimum
moment for commutation, depending on the type and
loading of the motor.
• The timing capacitor; this provides the system with its
timing signals.
T
HE START CAPACITOR (CAP-ST)
f
osc
=
1
---------------------------------- K
I× p×
t
---------------------- -
2π
J
where:
K
= torque constant (N.m/A)
t
I = current (A)
p = number of magnetic pole-pairs
J = inertia J (kg.m2)
Example: J = 72 × 10−6kg.m2, K = 25 × 10−3N.m/A,p=6
and I = 0.5 A; this gives f
= 5 Hz. If the damping is high
osc
then a start frequency of 2 Hz can be chosen or
t = 500 ms, thus C = 0.5/2 = 0.25 µF (choose 220 nF).
T
HE ADAPTIVE COMMUTATION DELAY (CAP-CD AND
CAP-DC)
In this circuit capacitor CAP-CD is charged during one
commutation period, with an interruption of the charging
current during the diode pulse. During the next
commutation period this capacitor (CAP-CD) is discharged
at twice the charging current. The charging current is
8.1 µA and the discharging current 16.2 µA; the voltage
range is from 0.9 to 2.2 V. The voltage must stay within
this range at the lowest commutation frequency of
interest, f
C
==
:
C1
8.1 10
×
-------------------------f 1.3×
6–
6231
(C in nF)
------------ f
C1
This capacitor determines the frequency of the start
oscillator. It is charged and discharged, with a current of
2 µA, from 0.05 to 2.2 V and back to 0.05 V. The time
taken to complete one cycle is given by:
t
= (2.15 × C) s (with C in µF)
start
The start oscillator is reset by a commutation pulse and so
is only active when the system is in the start-up mode. A
pulse from the start oscillator will cause the outputs to
change to the next state (torque in the motor). If the
movement of the motor generates enough EMF the
TDA5145 will run the motor. If the amount of EMF
generated is insufficient, then the motor will move one step
only and will oscillate in its new position. The amplitude of
the oscillation must decrease sufficiently before the arrival
of the next start pulse, to prevent the pulse arriving during
the wrong phase of the oscillation. The oscillation of the
motor is given by:
June 1994 11
If the frequency is lower, then a constant commutation
delay after the zero-crossing is generated by the discharge
from 2.2 to 0.9 V at 16.2 µA;
maximum delay = (0.076 × C) ms (with C in nF)
Example: nominal commutation frequency = 900 Hz and
the lowest usable frequency = 400 Hz; so:
CAP-CD
6231
------------ 400
(choose 18 nF)
15.6==
The other capacitor, CAP-DC, is used to repeat the same
delay by charging and discharging with 15.5 µA. The same
value can be chosen as for CAP-CD. Figure 9 illustrates
typical voltage waveforms.
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
B
B
BBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBBBB
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
B
BBBBBB
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBB
BBBBBB
BBBBBB
BBBBBB
BBBBBB
June 1994 12
Fig.8 Typical application of the TDA5145 as a scanner driver, with use of OTA.
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
BBBBBBBBBBBBBBB
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
Fig.9 CAP-CD and CAP-DC typical voltage waveforms in normal running mode.
THE TIMING CAPACITOR (CAP-TI)
Capacitor CAP-TI is used for timing the successive steps
within one commutation period; these steps include some
internal delays.
The most important function is the watchdog time in which
the motor EMF has to recover from a negative diode-pulse
back to a positive EMF voltage (or vice versa). A watchdog
timer is a guarding function that only becomes active when
the expected event does not occur within a predetermined
time.
The EMF usually recovers within a short time if the motor
is running normally (<<ms). However, if the motor is
motionless or rotating in the reverse direction, then the
time can be longer (>>ms).
A watchdog time must be chosen so that it is long enough
for a motor without EMF (still) and eddy currents that may
stretch the voltage in a motor winding; however, it must be
short enough to detect reverse rotation. If the watchdog
time is made too long, then the motor may run in the wrong
direction (with little torque).
The capacitor is charged, with a current of 57 µA, from
0.2 to 0.3 V. Above this level it is charged, with a current of
5 µA, up to 2.2 V only if the selected motor EMF remains
in the wrong polarity (watchdog function). At the end, or, if
the motor voltage becomes positive, the capacitor is
discharged with a current of 28 µA. The watchdog time is
the time taken to charge the capacitor, with a current of
5 µA, from 0.3 to 2.2 V.
To ensure that the internal delays are covered CAP-TI
must have a minimum value of 2 nF. For the watchdog
function a value for CAP-TI of 10 nF is recommended.
To ensure a good start-up and commutation, care must be
taken that no oscillations occur at the trailing edge of the
flyback pulse. Snubber networks at the outputs should be
critically damped.
Typical voltage waveforms are illustrated by Fig.10.
June 1994 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
If the chosen value of CAP-TI is too small oscillations can occur in certain positions of a blocked rotor. If the chosen value is too large, then it
is possible that the motor may run in the reverse direction (synchronously with little torque).
Fig.10 Typical CAP-TI and V
voltage waveforms in normal running mode.
MOT1
Other design aspects
There are other design aspects concerning the application
of the TDA5145 besides the commutation function. They
are:
• Generation of the tacho signal FG
• General purpose operational transconductance
amplifier (OTA)
• Motor control
• Direction function
• Brake function
• Reliability.
FG
SIGNAL
The FG signal is generated in the TDA5145 by using the
zero-crossing of the motor EMF from the three motor
windings. Every zero-crossing in a (star connected) motor
winding is used to toggle the FG output signal. The FG
frequency is therefore half the commutation frequency. All
transitions indicate the detection of a zero-crossing.
The accuracy of the FG output signal depends on the
symmetry of the motor's electromagnetic construction,
which also effects the satisfactory functioning of the motor
itself.
frequency of 25 × 6 × 6 = 900 Hz, and generates a tacho
signal of 450 Hz.
T
HE OPERATIONAL TRANSCONDUCTANCE AMPLIFIER (OTA)
The OTA is an uncommitted amplifier with a high output
current (40 mA) that can be used as a control amplifier.
The common mode input range includes ground (GND)
and rises to V
− 1.7 V. The high sink current enables the
P
OTA to drive a power transistor directly in an analog
control amplifier.
Although the gain is not extremely high (0.3 S), care must
be taken with the stability of the circuit if the OTA is used
as a linear amplifier as no frequency compensation has
been provided.
The convention for the inputs (inverting or not) is the same
as for a normal operational amplifier: with a resistor (as
load) connected from the output (AMP OUT) to the positive
supply, a positive-going voltage is found when the
non-inverting input (+AMP IN) is positive with respect to
the inverting input (−AMP IN). Confusion is possible
because a ‘plus’ input causes less current, and so a
positive voltage.
Example: a 3-phase motor with 6 magnetic pole-pairs at
1500 rpm and with a full-wave drive has a commutation
June 1994 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
MOTOR CONTROL
DC motors can be controlled in an analog manner using
the OTA.
For the analog control an external transistor is required.
The OTA can supply the base current for this transistor
and act as a control amplifier (see Fig.8).
D
IRECTION FUNCTION
If the voltage at pin 10 is <0.8 V, the motor is running in
one direction (depending on the motor connections). If the
voltage at pin 10 >2.0 V, the motor is running in the other
direction.
BRAKE
FUNCTION
If the voltage at pin 9 is >2.0 V, the motor brakes. In that
condition, the 3 outputs MOT1, MOT2 and MOT3 are
Table 3 Switching sequence after a reset pulse.
DIR
(1)
RESET
(1)
MOT1
(1)
H H Z L H reset
H L Z L H normal direction mode
HLHLZ
HLHZL
HLZHL
HLLHZ
HLLZH
L H H L Z reset
L L H L Z reverse direction mode
LLZLH
LLLZH
LLLHZ
LLZHL
LLHZL
forced at a LOW voltage level and the current limitation is
done internally by the sink drivers.
RESET
FUNCTION
If the voltage at pin 21 is >2.0 V, the output states are
shown in Table 2.
Table 2 Output states if V
RESET
> 2.0 V.
DRIVER OUTPUT STATE
MOT1 Z
MOT2 L
MOT3 H
Note
1. Z = high-impedance OFF-state; L = LOW state;
H = HIGH state.
MOT2
(1)
DIR
(1)
FUNCTION
sequence
sequence
(1)
Note
1. Z = high-impedance OFF-state; L = LOW state; H = HIGH state.
June 1994 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
Table 4 Priority of function.
BRAKE
(1)
TEST
(1)
RESET
(1)
L L L normal
L L H reset
L H L test
L H H test
H L L brake
H L H brake
H H L brake
H H H brake
Note
1. L = LOW state; H = HIGH state.
FUNCTION
RELIABILITY
It is necessary to protect high current circuits and the
output stages are protected in two ways:
• Current limiting of the ‘lower’ output transistors. The
‘upper’ output transistors use the same base current as
the conducting ‘lower’ transistor (+15%). This means
that the current to and from the output stages is limited.
• Thermal protection of the six output transistors is
achieved by each transistor having a thermal sensor
that is active when the transistor is switched on. The
transistors are switched off when the local temperature
becomes too high.
June 1994 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
PACKAGE OUTLINES
handbook, full pagewidth
seating plane
3.9
3.4
1.7
max
28
1
2.54
(13x)
36.0
35.0
1.7 max
0.53
max
15
14
0.51
min
14.1
13.7
max
0.254
4.0
15.80
15.24
5.1
max
M
0.32 max
15.24
17.15
15.90
MSA264
Dimensions in mm.
Fig.11 Plastic dual in-line package; 28 leads (600 mil) (SOT117-1; DIP28).
June 1994 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
handbook, full pagewidth
S
pin 1
index
114
0.9
0.4
(4x)
18.1
17.7
1.27
0.49
0.36
0.1 S
1528
0.25 M
(28x)
2.45
2.25
0.3
0.1
10.65
10.00
detail A
7.6
7.4
1.1
0.5
1.1
1.0
0.32
0.23
0 to 8
MBC236 - 1
A
2.65
2.35
o
Dimensions in mm.
Fig.12 Plastic small outline package; 28 leads; large body (SOT136-1; SO28L).
June 1994 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
SOLDERING
Plastic small-outline packages
YWAVE
B
During placement and before soldering, the component
must be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. After curing the
adhesive, the component can be soldered. The adhesive
can be applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing.
Maximum permissible solder temperature is 260 °C, and
maximum duration of package immersion in solder bath is
10 s, if allowed to cool to less than 150 °C within 6 s.
Typical dwell time is 4 s at 250 °C.
A modified wave soldering technique is recommended
using two solder waves (dual-wave), in which a turbulent
wave with high upward pressure is followed by a smooth
laminar wave. Using a mildly-activated flux eliminates the
need for removal of corrosive residues in most
applications.
B
Y SOLDER PASTE REFLOW
Reflow soldering requires the solder paste (a suspension
of fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be
applied to the substrate by screen printing, stencilling or
pressure-syringe dispensing before device placement.
Several techniques exist for reflowing; for example,
thermal conduction by heated belt, infrared, and
vapour-phase reflow. Dwell times vary between 50 and
300 s according to method. Typical reflow temperatures
range from 215 to 250 °C.
Preheating is necessary to dry the paste and evaporate
the binding agent. Preheating duration: 45 min at 45 °C.
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS (BY HAND-HELD SOLDERING
R
IRON OR PULSE
-HEATED SOLDER TOOL)
Fix the component by first soldering two, diagonally
opposite, end pins. Apply the heating tool to the flat part of
the pin only. Contact time must be limited to 10 s at up to
300 °C. When using proper tools, all other pins can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 s at between 270
and 320 °C. (Pulse-heated soldering is not recommended
for SO packages.)
For pulse-heated solder tool (resistance) soldering of VSO
packages, solder is applied to the substrate by dipping or
by an extra thick tin/lead plating before package
placement.
Plastic dual in-line packages
BY DIP OR WAVE
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is
260 °C; this temperature must not be in contact with the
joint for more than 5 s. The total contact time of successive
solder waves must not exceed 5 s.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but
the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified storage maximum. If the printed-circuit board has
been pre-heated, forced cooling may be necessary
immediately after soldering to keep the temperature within
the permissible limit.
R
EPAIRING SOLDERED JOINTS
Apply a low voltage soldering iron below the seating plane
(or not more than 2 mm above it). If its temperature is
below 300 °C, it must not be in contact for more than 10 s;
if between 300 and 400 °C, for not more than 5 s.
June 1994 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
June 1994 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
NOTES
June 1994 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
NOTES
June 1994 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Brushless DC motor drive circuit TDA5145
NOTES
June 1994 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors – a worldwide company
Argentina: IEROD, Av. Juramento 1992 - 14.b, (1428)
BUENOS AIRES, Tel. (541)786 7633, Fax. (541)786 9367
Australia: 34 Waterloo Road, NORTH RYDE, NSW 2113,
Tel. (02)805 4455, Fax. (02)805 4466
Austria: Triester Str. 64, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. (01)60 101-1236, Fax. (01)60 101-1211
Belgium: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands,
Tel. (31)40 783 749, Fax. (31)40 788 399
Brazil: Rua do Rocio 220 - 5
CEP: 04552-903-SÃO PAULO-SP, Brazil.
P.O. Box 7383 (01064-970).
Tel. (011)821-2327, Fax. (011)829-1849
Canada: INTEGRATED CIRCUITS:
Tel. (800)234-7381, Fax. (708)296-8556
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS: 601 Milner Ave,
SCARBOROUGH, ONTARIO, M1B 1M8,
Tel. (0416)292 5161 ext. 2336, Fax. (0416)292 4477
Chile: Av. Santa Maria 0760, SANTIAGO,
Tel. (02)773 816, Fax. (02)777 6730
Colombia: IPRELENSO LTDA, Carrera 21 No. 56-17,
77621 BOGOTA, Tel. (571)249 7624/(571)217 4609,
Fax. (571)217 4549
Denmark: Prags Boulevard 80, PB 1919, DK-2300 COPENHAGEN S,
Tel. (032)88 2636, Fax. (031)57 1949
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. (9)0-50261, Fax. (9)0-520971
France: 4 Rue du Port-aux-Vins, BP317,
92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. (01)4099 6161, Fax. (01)4099 6427
Germany: PHILIPS COMPONENTS UB der Philips G.m.b.H.,
P.O. Box 10 63 23, 20043 HAMBURG,
Tel. (040)3296-0, Fax. (040)3296 213.
Greece: No. 15, 25th March Street, GR 17778 TAVROS,
Tel. (01)4894 339/4894 911, Fax. (01)4814 240
Hong Kong: PHILIPS HONG KONG Ltd., Components Div.,
6/F Philips Ind. Bldg., 24-28 Kung Yip St., KWAI CHUNG, N.T.,
Tel. (852)424 5121, Fax. (852)428 6729
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Components Dept,
Shivsagar Estate, A Block ,
Dr. Annie Besant Rd. Worli, Bombay 400 018
Tel. (022)4938 541, Fax. (022)4938 722
Indonesia: Philips House, Jalan H.R. Rasuna Said Kav. 3-4,
P.O. Box 4252, JAKARTA 12950,
Tel. (021)5201 122, Fax. (021)5205 189
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. (01)640 000, Fax. (01)640 200
Italy: PHILIPS COMPONENTS S.r.l.,
Viale F. Testi, 327, 20162 MILANO,
Tel. (02)6752.3302, Fax. (02)6752 3300.
Japan: Philips Bldg13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku, TOKYO 108,
Tel. (03)3740 5028, Fax. (03)3740 0580
Korea: (Republic of) Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong,
Yongsan-ku, SEOUL, Tel. (02)794-5011, Fax. (02)798-8022
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA,
SELANGOR, Tel. (03)750 5214, Fax. (03)757 4880
Mexico: Philips Components, 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200,
EL PASO, TX 79905, Tel. 9-5(800)234-7381, Fax. (708)296-8556
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB
Tel. (040)783749, Fax. (040)788399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. (09)849-4160, Fax. (09)849-7811
th
floor, Suite 51,
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. (022)74 8000, Fax. (022)74 8341
Pakistan: Philips Electrical Industries of Pakistan Ltd.,
Exchange Bldg. ST-2/A, Block 9, KDA Scheme 5, Clifton,
KARACHI 75600, Tel. (021)587 4641-49,
Fax. (021)577035/5874546.
Philippines: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS PHILIPPINES Inc,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. (02)810 0161, Fax. (02)817 3474
Portugal: PHILIPS PORTUGUESA, S.A.,
Rua dr. António Loureiro Borges 5, Arquiparque - Miraflores,
Apartado 300, 2795 LINDA-A-VELHA,
Tel. (01)14163160/4163333, Fax. (01)14163174/4163366.
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 1231,
Tel. (65)350 2000, Fax. (65)251 6500
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., Components Division,
195-215 Main Road Martindale, 2092 JOHANNESBURG,
P.O. Box 7430 Johannesburg 2000,
Tel. (011)470-5911, Fax. (011)470-5494.
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. (03)301 6312, Fax. (03)301 42 43
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla. S-164 85 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. (0)8-632 2000, Fax. (0)8-632 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. (01)488 2211, Fax. (01)481 77 30
Taiwan: PHILIPS TAIWAN Ltd., 23-30F, 66, Chung Hsiao West
Road, Sec. 1. Taipeh, Taiwan ROC, P.O. Box 22978,
TAIPEI 100, Tel. (02)388 7666, Fax. (02)382 4382.
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong,
Bangkok 10260, THAILAND,
Tel. (662)398-0141, Fax. (662)398-3319.
Turkey:Talatpasa Cad. No. 5, 80640 GÜLTEPE/ISTANBUL,
Tel. (0212)279 2770, Fax. (0212)269 3094
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Limited, P.O. Box 65,
Philips House, Torrington Place, LONDON, WC1E 7HD,
Tel. (071)436 41 44, Fax. (071)323 03 42
United States:INTEGRATED CIRCUITS:
811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. (800)234-7381, Fax. (708)296-8556
DISCRETE SEMICONDUCTORS: 2001 West Blue Heron Blvd.,
P.O. Box 10330, RIVIERA BEACH, FLORIDA 33404,
Tel. (800)447-3762 and (407)881-3200, Fax. (407)881-3300
Uruguay: Coronel Mora 433, MONTEVIDEO,
Tel. (02)70-4044, Fax. (02)92 0601
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing and Sales, Building BAF-1,
P.O. Box 218, 5600 MD, EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands,
Telex 35000 phtcnl, Fax. +31-40-724825
SCD31 © Philips Electronics N.V. 1994
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the
prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of any quotation
or contract, is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed without
notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its
use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license under patent- or
other industrial or intellectual property rights.
Printed in The Netherlands
373061/1500/02/pp24 Date of release: June 1994
Document order number: 9397 735 50011
Philips Semiconductors
 Loading...
Loading...