Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
TDA4504B
Small signal combination for
multistandard colour TV
Product specification
File under Integrated Circuits, IC02
February 1992
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
FEATURES
• Gain controlled vision IF amplifier
• Synchronous demodulator for negative and positive
demodulation
• AGC detector operating on peak sync amplitude for
negative demodulation and on peak white level for
positive demodulation
• Tuner AGC
• AFC circuit with two control polarities and on/off-switch
• Video preamplifier
• Video switch to select either the internal video signal or
an external video signal
• Horizontal oscillator and synchronization circuit with two
control loops
• Vertical synchronization (divider system), ramp
generator and driver with automatic amplitude
adjustment for 50 and 60 Hz
• Transmitter identification (mute)
• Sandcastle pulse generation
• VCR/auto VCR switch
• Start-up circuit
• Vertical guard
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Having the capability to demodulate IF signals with either
positive or negative-going video information, the
TDA4504B (Fig.1) is contained within a 32 pin
encapsulation. It includes a three-stage vision IF amplifier,
mute circuit, AFC and AGC circuitry, fully synchronised
horizontal and vertical timebases with drive circuits and
integral three-level sandcastle pulse generator.
A functional colour tv receiver can thus be realized with the
addition of a tuner, audio demodulator and amplifier,
chroma decoder and respective line and field deflection
circuitry.
ORDERING INFORMATION
EXTENDED
TYPE NUMBER
TDA4504B 32 DIL plastic SOT201
Note
1. SOT201-1; 1996 November 29
PINS PIN POSITION MATERIAL CODE
PACKAGE
(1)
February 1992 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard
colour TV
TDA4504B
February 1992 3
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
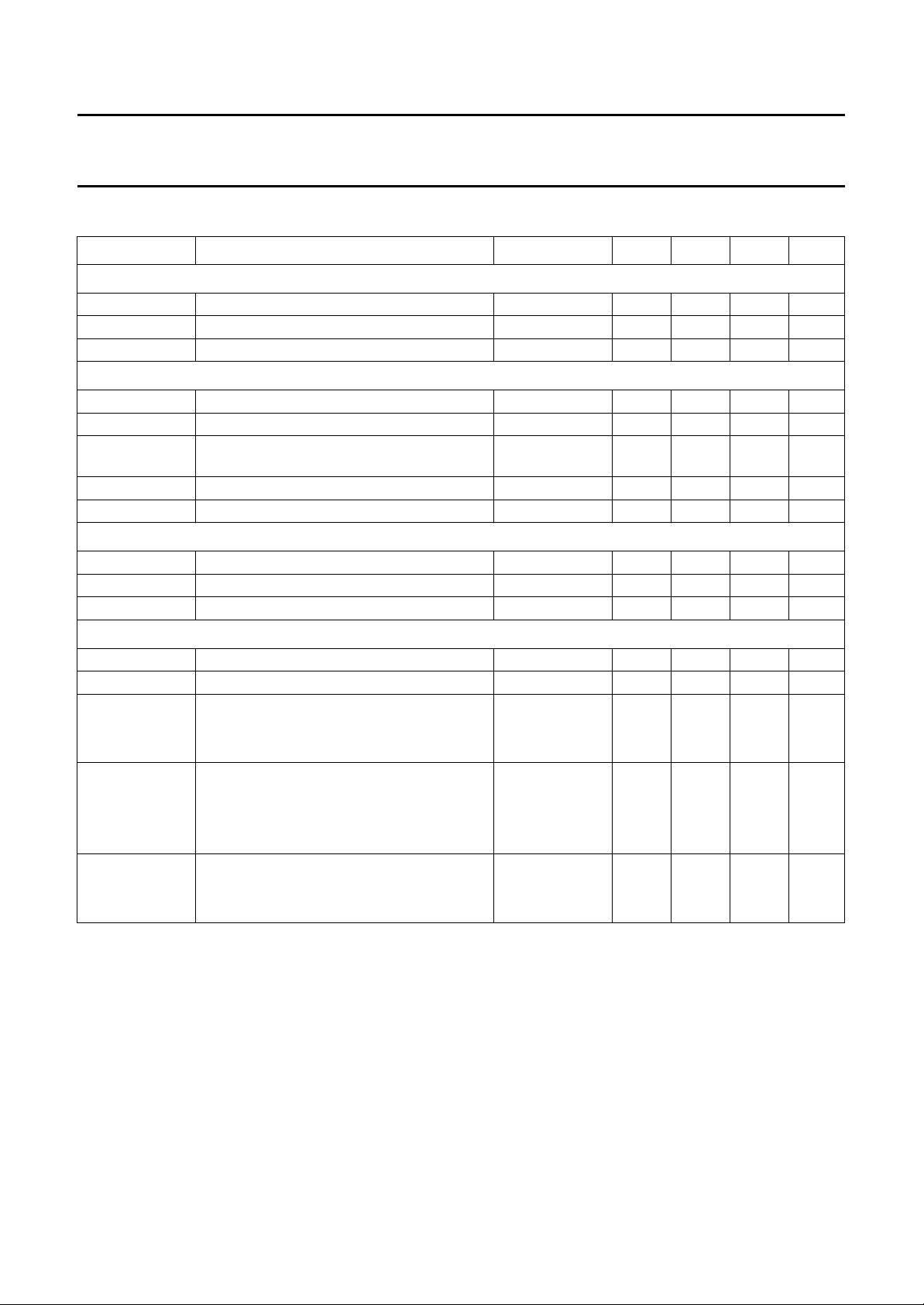
QUICK REFERENCE DATA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
8
I
8
I
12
Video
V
9-10
G
9-10
S/N signal to noise ratio V
V
21
Video switch
16
(p-p)
V
13(p-p)
V
15(p-p)
Sync
V
28
I
30
V
30
V
14
V
5
V
5(p-p)
positive supply voltage pin 8 10 12 13.2 V
supply current pin 8 90 115 140 mA
start current pin 12 − 6.5 9 mA
IF sensitivity (RMS value) 25 40 65 µV
IF gain control range − 74 − dB
input signal =
i
− 58 − dB
10 mV
AFC output voltage swing 10.5 − 11.5 V
video output amplitude − 2 − V
internal video input − 2 − V
external video input − 1 − V
video output − 2.5 − V
sync pulse input amplitude (p-p) 200 −−mV
flyback input current 0.1 − 2mA
sandcastle output during burst key 8 −−V
- during hor. blanking 4 4.4 5 V
- during vert. blanking 2.1 3.3 3.7 V
video transmitter identification
- no signal condition − 0.3 − V
- 50 Hz signal − 12 − V
- 60 Hz signal − 9 − V
vert. feedback
- DC voltage 2.9 3.3 3.7 V
- AC voltage − 1 − V
February 1992 4
Page 5

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
PINNING
PIN DESCRIPTION
1 black level internal video
2 AGC take over (output)
3 vertical ramp generator (output)
4 vertical drive (output)
5 vertical feedback (input)
6 tuner AGC (input)
7 ground
8 supply voltage
9 vision IF (input)
10 vision IF (input)
11 IF AGC (output)
12 start horizontal oscillator (output)/AFC polarity switch (input)
13 external video (input)
14 mute/50 / 60 Hz (output)
15 video switch (output)
16 internal video (input)
17 VCR switch (input)
18 video switch (input)
19 ground for some critical parts
20 video amplifier (output)
21 AFC (output)
22 AFC S/H, AFC switch (input)
23 vision demodulator tuned circuit
24 vision demodulator tuned circuit
25 coincidence detector/transmitter identification
26 horizontal oscillator
27 phase 1 detector (output)
28 sync separator (input)
29 horizontal drive (output)
30 sandcastle output/horizontal flyback (input)
31 phase 2 detector (output)
32 AGC system switch (input)
February 1992 5
Page 6

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Vision IF amplifier, demodulator
and video amplifier
Each of the three AC-coupled IF
stages permit the omission of DC
feedback and possess a control
range in excess of 20 dB.
The IF amplifier, which is completely
symmetrical, is followed by a passive
synchronous demodulator providing a
regenerated carrier signal. This is
limited by a logarithmic limiter circuit
prior to its application to the
demodulator.
A noise clamp circuit is provided at
the video input (pin 16) to limit
interference pulses below the sync tip
level and is more efficient than a
noise inverter in providing improved
picture stability during the presence of
interference.
The video amplifier has good linearity
and bandwidth figures.
AFC-circuit
Obtaining the AFC reference signal
from the demodulator tuned circuit
presents the advantage of utilizing a
single tuned circuit and one
adjustment. However, since the
frequency spectrum of the signal
applied to the demodulator is
determined by the characteristic of
the SAW filter, the resultant
asymmetrical spectrum with respect
to the vision carrier causes the AFC
output voltage to be dependent upon
the video signal. The TDA4504B thus
contains a sample-and-hold circuit.
With negative-going vision signals the
AFC is active only during the sync
pulse period. When positive-going
signals are applied to the device,
however, the AFC is continuously
active but filtered to ensure only a
small by-pass current is present in the
sample-and-hold circuit.
With weak input signals the drive
signal will contain considerable noise
which also possesses an
asymmetrical frequency spectrum
and could create an offset in the AFC
output voltage. The inclusion of a
notch in the demodulator tuned circuit
minimises this effect.
The sample-and-hold circuit is
followed by a high impedance output
amplifier. Thus the AFC control
gradient depends upon the load
impedance.
The AFC polarity switch is combined
with the start circuit (pin 12). It has a
negative slope when pin 12 is open or
connected to the main supply and a
positive slope when pin 12 is
grounded. The AFC is disabled when
the sample connection (pin 22) is
grounded.
February 1992 6
Page 7

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
AGC circuit
For signals employing negative modulation the AGC detector operates on peak sync level but upon peak white content
with those having positive modulation. Selection is facilitated by the system switch (pin 32):
pin 32 HIGH/open: positive modulation
pin 32 LOW: negative modulation
The AGC detector currents are:
positive modulation negative modulation
charge 1 µA55µA
discharge 3 mA 1.5 mA
With a 6.8 µF AGC capacitor, the video tilt will be < 10% for positively modulated signals and < 2% for negative
modulation.
To obtain a rapid AGC action when executing a search tuning operation with the circuit set for peak white AGC, the
charge current is held at 55 µA until the detection of a transmitted signal.
The transmitter identification
A mute signal is generated to disable the audio preamplifier of an audio demodulator during the absence of a
transmission signal. When the video switch is in the internal mode, the identification of a transmitted signal is derived
from the coincidence detector.
In the external mode the IF part of the circuit has its own identification system. The system relies upon the detection of
sync. pulses on the incoming IF signal. The separated horizontal sync pulse charges the capacitor on pin 25 which drives
the mute output (pin 14).
The connection of a 1 MΩ resistor between pin 25 and V
50/60 Hz information derived from the internal vertical divider section
(see 50/60 Hz truth table).
MUTE Truth Table:
Input signal
Pins 9 and 10
pin 25 9.5 V 9.5 V 0.3 V 9.5 V 9.5 V 9.5 V 0.3 V
pin 28 50 Hz 60 Hz none 50 Hz 60 Hz none 50/60 Hz
pin 18 LOW LOW LOW/
pin 14 12 V 9 V 0.3 V 12 V 9 V 12 V 0.3 V
50 Hz 60 Hz none 50/60 Hz 50/60 Hz 50/60 Hz none
HIGH
results in the mute information being overruled by the
CC
HIGH HIGH HIGH HIGH
February 1992 7
Page 8

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
50/60 Hz Information
In the external video mode and with a resistor of 1 MΩ from pin 25 to VCC the mute is overruled by the 50/60 Hz
information from the divider system.
50/60 Hz Truth Table:
Input Signal
Pin 9/10
Pin 25 9.5 9.5 0.3 9.5 9.5 9.5
Pin 28 50 Hz 60 Hz None 50 Hz 60 Hz None
Pin 18 LOW LOW LOW HIGH HIGH HIGH
Pin 14 12 9 0.3 12 9 12
VCR switch
Flywheel horizontal synchronization is desirable when receiving weak signals marred by noise but is usually unnecessary
when receiving stronger off-air signals unless certain types of interference or multipath reception are apparent. Due to
the inherent instability of VCR signals, however, the horizontal time constant should be shorter to prevent loss of
horizontal synchronization in the early part of the scan. Provision is therefore incorporated to automatically switch the
short time constant such that a strong signal instigates the 'VCR' mode and a weak signal triggers the 'TV' mode.
The connection of a switch to pin 17 provides for this to be accomplished manually and may take the form of an auxiliary
switching function associated with a designated program selector button.
The TDA4504B has a separate pin (pin 17) for the VCR switch:
pin 17 HIGH: VCR mode fast time constant; ungated
pin 17 n.c.: auto VCR mode
pin 17 LOW: TV mode slow time constant; gated
Video-switch
50 Hz 60 Hz None Don’t care Don’t care Don’t care
Video output from the demodulator is filtered to remove the audio carrier and DC-coupled to pin 16. If AC-coupling is
employed the internal noise clamp will operate on sync. tips.
The TDA4504B provides the opportunity for a direct video connection (e.g. via a peritel connector) to be made to the
device at pin 13. Selection between internal and external video is made by applying a switching potential to pin 18.
Video switch:
pin 18 LOW: internal video
pin 18 HIGH: external video
Gain reduction
To prevent crosstalk between the IF stages and the horizontal oscillator when the device is operated in its external video
mode with no RF input, the TDA4504B incorporates an option to reduce IF gain by 20 dB. This is accomplished by
connecting a 39 kΩ resistor between pin 17 and ground. Omission of this component results in the IF amplifier remaining
at full gain.
In the internal video mode the resistor must be disconnected to achieve the auto-VCR mode.
February 1992 8
Page 9

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Horizontal synchronization
The horizontal synchronization circuit
of the TDA4504B has been designed
as follows:
• The retrace of the horizontal
oscillator occurs during the
horizontal retrace and not during
the scan period. This has the
advantage that no interference will
be visible on the screen when
receiving weak input signals. Video
crosstalk will not disturb the phase
of the horizontal locking.
• Reduced frequency shift of the
horizontal oscillator due to noise
since the horizontal phase detector
reference signal is more
symmetrical and independent of
the supply voltage and
temperature.
• The phase detector current ratio for
strong and weak signals is
increased to obtain a better
performance during both VCR
playback and weak signal
reception. The switching level is
also independent of temperature
and supply voltage.
Vertical synchronization
Generation of the vertical sawtooth
(pin 3) is accomplished by a divider
that permits the production of a
vertical frequency of either 50 Hz or
60 Hz with freedom from adjustment,
amplitude correction and maximum
interference/disturbance protection.
A discriminator window checks the
vertical trigger pulse. When the
trigger pulse occurs before count 576,
the divider system operates in the
60 Hz mode otherwise the 50 Hz
mode is selected. (2 clock pulses
equal one horizontal line).
The divider section operates with
different reset windows. These
windows are activated via an up/down
counter. This increases its count by 1
for each occasion the separated
vertical sync pulse is within the
selected window. On each occasion
the vertical sync. pulse is not within
the selected window, the count is
reduced by 1.
LARGE (SEARCH) WINDOW; DIVIDER
RATIO BETWEEN
488 - 722
This mode is valid for the following
conditions:
1 divider locking to another
transmitter
2 divider ratio found, not within
the narrow window limits
3 up/down counter value of the
divider system operating in
narrow window mode, count
falls below 10.
ARROW WINDOW; DIVIDER RATIO
N
BETWEEN
628 (50 H
522 - 528 (60 HZ) OR 622 -
Z)
The divider switches to this mode
when the up/down counter has
reached its maximum value of 15
approved vertical sync pulses. When
the divider operates in this mode and
a vertical sync pulse is missing within
the window, the divider is reset at the
end of the window and the count
lowered by 1. At a counter value
below 10, the divider switches to the
large window mode.
An anti-top flutter pulse is also
generated by the divider system. This
inhibits the horizontal phase-1
detector during the vertical sync
pulse. The width of this pulse
depends upon the divider mode. For
the large window mode the start is
generated at the divider reset. In the
narrow window mode the anti-top
flutter pulse starts at the beginning of
the first equalizing pulse. The anti-top
flutter pulse ends at count 10 for 50
Hz and count 12 for 60 Hz.
When out-of-sync is detected by the
coincidence detector, the divider is
switched to count 625. This results in
a stable vertical amplitude when no
input signal is available.
February 1992 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum System (IEC 134)
SYMBOL PARAMETER MIN. MAX. UNIT
T
stg
T
amb
V
P
P
tot
ESD
All pins meet:
2000 V, 100 pF, 1500 Ω
200 V, 200 pF, 0 Ω
THERMAL RESISTANCE
storage temperature range − 55 + 150 °C
operating ambient temperature range − 25 + 65 °C
positive supply voltage (pin 8) − 13.2 V
total power dissipation − 2.3 W
SYMBOL PARAMETER THERMAL RESISTANCE
R
th j-a
from junction to ambient in free air 30 K/W
February 1992 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
CHARACTERISTICS
=25°C; supply 12 V; carrier 38.9 MHz negative modulation, unless otherwise specified.
T
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supply
V
P
I
P
I
12
V
12
IF Amplifier
V
9-10(RMS)
R
9−10
C
9−10
G
9−10
∆V
20
V
9-10
V
9-10
Video Amplifier (note 5)
V
20
V
20
V
20
V
20
V
20
V
20
Z
20
I
20(int)
I
source
B bandwidth of demodulated output signal 5 6 − MHz
G
d
ϕd differential phase note 8 − 25°
NL video non linearity note 9 − 25%
supply voltage range (pin 8) 10 12 13.2 V
supply current (pin 8) no input 90 115 140 mA
start current (pin 12) note 1 − 6.5 9 mA
start protection level (pin 12) I12 = 12 mA −−16.5 V
input sensitivity (RMS−value) note 2 25 40 65 µV
differential input resistance note 3 − 1300 −Ω
differential input capacitance note 3 − 5 − pF
gain control range − 74 − dB
output signal expansion for 46 dB input signal
note 4 − 1 − dB
variation
maximum input signal 100 170 − mV
input sensitivity at gain reduction note 2 250 400 650 µV
RMS
Zero signal output level note 6
negative modulation 4.7 4.9 5.1 V
positive modulation 2.5 2.7 2.9 V
sync tip (negative modulation) note 7 2.5 2.7 2.9 V
white level (positive modulation) note 7 4.5 4.7 4.9 V
white spot threshold level − 5.5 − V
white spot insertion level − 4 − V
video output impedance − 25 −Ω
internal bias current of NPN emitter follower
1.4 1.8 − mA
output transistor
maximum source current 10 −−mA
differential gain note 8 − 25%
intermodulation note 10
1.1 MHz; blue 50 60 − dB
1.1 MHz; yellow 50 60 − dB
3.3 MHz; blue 55 65 − dB
3.3 MHz; yellow 55 65 − dB
February 1992 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
S/N signal-to-noise ratio note 11
see Fig.5
= 10 mV input signal 52 57 − dB
V
i
end of gain control range 57 62 − dB
V
20
V
20
AGC
I
C11
System switch (note 13)
V
32
I
32
V
32
I
32
IF sync separator
I
I
I
O
V
1
Tuner AGC
V
9-10 (RMS)
V
9-10(RMS)
I
6
V
6
I
6
∆ input signal variation complete tuner control ∆I
V
2
Video Switching Circuit (note 14)
residual carrier signal − 210mV
residual 2nd harmonic of carrier signal − 210mV
allowed leakage of the AGC capacitor −−700 nA
AGC on sync tip level for negative modulation
signals
control voltage 0 − 0.8 V
input current −100 −−500 µA
AGC on white level for positive modulation
signals
control voltage 2 − 12 V
input current 0 − 1mA
input current 0.4 0.6 0.8 mA
output current 22 27 32 µA
clamp level − 3.3 − V
minimum starting point for tuner take-over
−−0.2 mV
(RMS value)
maximum starting point for tuner take-over
100 150 − mV
(RMS value)
maximum tuner AGC output swing V6 = 3 V 4 −−mA
output saturation voltage I6 = 2 mA −−300 mV
leakage current −−1µA
= 2 mA 0.2 2 4 dB
6
minimum voltage tuner take-over −−1V
E
XTERNAL POSITIVE VIDEO INPUT
V
13(p-p)
I
13
V
13
input signal (peak-to-peak value) VO = 2.5 V
input current − 1.5 5 µA
sync tip clamping at 1 mA level 1.65 1.85 2.05 V
February 1992 12
(p-p)
− 1 − V
Page 13

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
INTERNAL VIDEO INPUT
16(p-p) Internal video input signal (peak-to-peak
value)
I
16
V
16
input current − 1.5 5 µA
noise clamping at 1 mA level 2.2 2.4 2.6 V
VIDEO OUTPUT (POSITIVE VIDEO)
V
15(p-p)
positive video output signal (peak-to-peak
value)
V
I
I
15
bias
O
sync tip signal − 3 − V
internal bias current 1 1.5 − mA
maximum output current 5 −−mA
α crosstalk external to internal notes 12 and 15 − 55 − dB
α crosstalk internal to external notes 12 and 15 − 55 − dB
= 2.5 V (p-p) − 2 − V
V
O
2.3 2.5 2.7 V
Video switch
V
18
V
18
I
18
input voltage for internal video −−0.8 V
input voltage for external video 2 − V
maximum current pin 18 = 0 V − 0.05 0.2 mA
AFC-circuit (note 16)
I
22
I
O
I
IL
V
21
I
21
AFC sample and hold switch-off current 0.1 −−mA
output current V22 = 0 V 0.2 0.4 0.8 mA
leakage current −−1µA
AFC output voltage swing 10.5 − 11.5 V
available output current ±0.2 −−mA
control slope − 100 − mV/kHz
V
21
R
O
V
21(p-p)
output voltage AFC off 5.5 6 6.5 V
AFC output resistance
output voltage swing note 12 − 11 − V
control slope note 12 − 80 − mV/kHz
V
21
output voltage shift with respect to
VI = 10 mV
AFC polarity switch
I
12
I
12
I
12
V
12
sink current for negative slope −−1µA
sink current for positive slope 0.1 −−mA
maximum current V12 = 0 V −−1mA
switching level 5 − 7V
(RMS)
P
V
pin 18 = 12 V − 0.25 1 mA
measured at an
− 40 − kΩ
input signal
amplitude of
150 µV(RMS)
note 12 −−2−V
February 1992 13
Page 14

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Sync separator (see Fig.6)
V
28
I
28
First control loop
∆f
RX
∆f
XL
Second control loop (positive edge)
∆td/∆to control sensitivity note 19 − 100 −
td control range − 25 −µs
Phase adjustment (via second control loop)
α maximum allowed phase shift −±2−µs
required sync pulse amplitude note 17 200 750 − mV
input current V28 = 5 V
V28=0V
−
−
8
−10
−
−
µA
mA
PLL holding range −±1500 ±2000 Hz
PLL catching range ±600 ±1500 − Hz
control sensitivity to oscillator note 18 see Fig.7
control sensitivity − 25 −µA/µs
Horizontal oscillator (note 19)
f
ft
free running frequency R = 34.3 kΩ
− 15625 − Hz
C = 2.7 nF
∆f
osc
∆f
osc
spread with fixed external components −−4%
frequency variations with supply voltage from
−−2%
10 to 13.2 V
∆fT frequency variation with temperature note 12 −−1.6 − Hz/K
∆f
fr
maximum frequency deviation at start of
−−10 %
Horizontal output
∆f
osc
frequency variation when only noise is
note 12 −−500 Hz
received
Horizontal output (open collector)
V
V
I
29
OL
sink
output limiting voltage −−16.5 V
output voltage LOW I
= 10 mA − 0.3 0.5 V
sink
maximum sink current 10 −−mA
S output signal duty factor − 46 − %
t
r
t
f
rise time output pulse − 260 − ns
fall times output pulse − 100 − ns
Flyback input and sandcastle output (note 22, Fig.6)
I
30
V
30
required input current during flyback pulse 0.1 − 2mA
output voltage during
burstkey 8 −−V
horizontal blanking 4 4.4 5 V
during vertical blanking 2.1 2.5 2.9 V
February 1992 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
t
W
T
1
T
2
t
Bkt
t
Bkr
VCR switch (non-VCR mode; V
R
17
I
17
VCR switch (auto-VCR mode)
I
17
I
17
VCR switch (VCR mode; V
R
17
I
17
V
9-10(rms)
pulse width
burst key at:
60 Hz 60 Hz 2.9 3.3 3.7 µs
50 Hz 50 Hz 3.2 3.6 4 µs
horizontal blanking flyback pulse
vertical blanking
divider in search window 50 Hz − 21 − lines
60 Hz − 17 − lines
divider in narrow window 50 Hz − 25 − lines
60 Hz − 21 − lines
delay between the start of the sync pulse at
the video output and the burst key pulse
trailing edge 60 Hz −−9.4 µs
rising edge 4.7 5.4 6.1 µs
< 5 V)
17
resistance to ground −−5kΩ
output current pin 17 = 0 V −−0.5 mA
source current −−30 µA
sink current −−30 µA
> 7 V)
17
resistance to V
CC
input current V17 = V
IF input signal for switching from fast to slow
CC
−−5kΩ
−−1mA
− 2.2 − mV
in auto VCR mode (RMS value)
Vertical ramp generator (note 21)
I
3
I
3
V
3(p-p)
input current during scan −−2µA
discharge current during retrace − 0.8 − mA
sawtooth amplitude (peak-to-peak value) − 1.9 − V
t interlace timing of the internal pulses note 12 30 32 34 µs
Vertical output
I
4
V
4
available output current V4 = 4 V −−3mA
maximum available output voltage I4 = 0.1 mA 4.4 5 − V
February 1992 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Vertical feedback input
v
5
V
I
5
∆
5(p-p)
tp
DC input voltage 2.9 3.3 3.7 V
AC input voltage (peak-to-peak value) − 1 − V
input current −−12 µA
internal pre-correction to sawtooth − 3 − %
deviation amplitude 50/60 Hz −−2%
temperature dependency of the amplitude note 12
−−2%
∆T=45°C
Vertical guard (V
∆V
5
active switch level at a deviation with respect
pin 30
= 2.5 V)
to the DC feedback level
guard level LOW − 1.5 − V
guard level HIGH − 2 − V
Coincidence detector/transmitter identification (note 23)
V
25
V
25
V
25
voltage for in-sync condition − 9.8 − V
voltage for no-sync condition no signal − 0.3 − V
switching level to switch the phase detector
from fast to slow
V
25
V
25
hysteresis slow to fast − 0.6 − V
switching level to activate the mute function
(transmitter identification)
V
25
hysteresis mute function − 2.5 − V
Video transmitter identification output
V
14
I
14
I
14
output voltage active no sync;
sink current active −−5mA
output current inactive (transmitter present) −−1µA
50/60 Hz identification (note 24)
V
14
V
14
output voltage at 50 Hz − V
output voltage at 60 Hz − 9 − V
note 22
I = 1 mA
6.2 6.7 7.2 V
2.5 2.8 3.1 V
− 0.3 0.5 V
s
− V
February 1992 16
Page 17

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Notes to the characteristics
1. Supplying a current of 9 mA to pin 12 starts the horizontal oscillator. This current can be obtained via a bleed circuit
from the mains rectifier whilst the main supply for the device (VP) is obtained from the horizontal output stage. The
load current of the driver must be added to the value given above.
2. On set AGC.
3. The input impedance has been chosen such that a SAW filter can be employed.
4. Measured with 0 dB = 450 µV.
5. Measured at 10 mV (RMS) 100% input signal.
6. Projected zero point; i.e. with switched demodulator.
7. The output signal amplitude is determined by the AGC detector. For negative modulation the sync tip level is used
as reference. With positive modulation the white level is stabilized
8. Measured according to the test line given in Fig.3.
a) The differential gain is expressed as a percentage of the difference in peak amplitudes between the largest and
smallest value relative to the subcarrier amplitude at blanking level.
b) The differential phase is defined as the difference in degrees between the largest and smallest phase angle.
c) The differential gain and phase are measured with a DSB signal.
9. This figure is valid for the complete video signal amplitude (peak white to black). The non-linearity is expressed as a
percentage of the maximum deviation of a luminance step from the mean step, with respect to the mean step.
10. The test set-up and input conditions are given in Fig.5. The figures are measured at an input signal of 10 mV (RMS).
11. Measure with a source impedance of 75 Ω. The signal-to-noise ratio =
black-to-white
V
20 log
12. These figures are based on sample tests.
13. By means of the system switch, two conditions can be obtained. Negative modulation with sync tip level AGC. This
is obtained with pin 32 connected to ground. Positive modulation with peak white AGC. This is obtained with pin 32
connected to the positive supply.
14. When the video switch is in the external mode the first control loop in the synchronization circuit is not switched to a
long time constant when weak signals are received.
o
----------------------------------------------------------V
nRMS()
atB=5MHz
V
unwanted video black-to-white
15. Defined as ; measured at 4.4 MHz.
20 log()
o
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------ V
wanted video-black-to-white
o
16. The indicated figures are measured at an input signal of 10 mV RMS. The unloaded Q-factor of the reference tuned
circuit is 70.
With very weak input signals the drive signal for the AFC circuit will have a high noise content. This noise input has
a asymmetrical frequency spectrum which will cause an offset of the AFC output voltage. To avoid problems due to
this effect a notch filter can be built into the demodulator tuned circuit. The characteristics given for weak signals are
measured without a notch circuit, with a SAW filter connected in front of the IC input signal such that the input signal
of the IC is 150 µV (RMS value).
17. The minimum value is obtained by connecting a 1.8 kΩ resistor between pins 15 and 28. The slicing level can be
varied by changing the value of this resistor (higher resistor value results in larger value of the minimum sync pulse
amplitude). The slicing level is independent of the video information.
18. Frequency control is obtained by supplying a correction current to the oscillator RC network via a resistor connected
between the phase 1 detector output and the oscillator network. The oscillator can be adjusted to the correct
frequency by short circuiting the sync separator bias network (pin 28) to +V
. To avoid the need of a VCR switch the
P
time constant of the phase detector at strong input signals is sufficiently short to get a stable picture during VCR
playback. During the vertical retrace period the time constant is even shorter so that the head-errors of the VCR are
February 1992 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
compensated at the beginning of scan. During conditions of weak signal (information derived from the AGC circuit)
the time constant is increased to obtain a better noise immunity.
19. This figure is valid for an external load impedance of 82 Ω from pin 31 to the shift adjustment potentiometer.
20. The flyback input and sandcastle output have been combined on one pin. The flyback pulse is clamped to a level of
4.5 V. The minimum current to drive the second control loop is 0.1 mA.
21. The vertical scan is synchronized by means of a divider system. Therefore no adjustment is required for the ramp
generator. The divider detects whether the incoming signal has a vertical frequency of 50 or 60 Hz and corrects the
vertical amplitude.
22. To avoid CRT screen burn due to a collapse of the vertical deflection a continuous blanking level is inserted in the
sandcastle pulse when the feedback voltage of the vertical deflection is not within the specified limits.
23. The functions in-sync/out-of-sync and transmitter identification have been combined on this pin.
The capacitor is charged during the sync pulse and discharged during the time difference between gating (6.5 / µs)
and the sync pulse in the internal video mode. When the circuit is in the external mode the capacitor is charged by
the horizontal sync pulse and discharged continuously with a small current.
24. When the mute is active no 50/60 Hz information is available.
Fig.2 Video output signal.
Fig.3 EBU test signal waveform (line 17).
February 1992 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Input signal conditions
SC =Sound carrier
CC =Chrominance carrier
PC =Picture carrier
All with respect to top sync level
V
at 4.4MHz
o
Value at1.1 MHz : 20
Value at 3.3MHz : 20
----------------------------------- -log 3.6dB+
at 1.1MHz
V
o
V
at 4.4MHz
o
----------------------------------- -log
at 3.3MHz
V
o
Fig.4 Test set-up intermodulation.
February 1992 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Fig.5 Signal-to noise ratio as a function of the input voltage (0 dB = 100 mV).
February 1992 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
50 Hz 60 Hz
- search window - 42 p 34 p
T
1
- narrow window - 50 p 42 p
T
2
- burst key pulse - 3.6 µs 3.3 µs
T
3
1
=
p
--------
2f
H
Fig.6 Timing diagram.
February 1992 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Fig.7 Switching levels coincidence detector.
COINCIDENCE DETECTOR SWITCHING LEVELS
CONDITION
PIN 18
VIDEO SWITCH
CONDITION
PIN 17
VCR SWITCH
Low internal video floating
automatic
VCR
HIGH
forced VCR
LOW
T.V. mode
HIGH or
don't care don't care 11.3 7.6
floating
external video
CONDITION
V
25
>6.7 V
V
25
HOR.OSCILLATOR kHz / S
T2 − T1 T3 = SCAN
and
strong signal 11.3 7.6
weak signal 1.3 1.3
CONTROL SENSITIVITY
< 6.1 V
V
25
and
strong signal 11.3 7.6
weak signal 11.3 7.6
don't care 11.3 7.6
> 6.7 V
V
25
V25< 6.1 V
1.3
11.3
1.3
7.6
February 1992 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Fig.8 Horizontal oscillator control sensitivity.
February 1992 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
Fig.9 Application diagram.
February 1992 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
PACKAGE OUTLINE
DIP32: plastic dual in-line package; 32 leads (600 mil)
D
seating plane
L
Z
32
pin 1 index
e
b
SOT201-1
M
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
1
17
E
c
(e )
M
1
H
1
0 5 10 mm
scale
DIMENSIONS (inch dimensions are derived from the original mm dimensions)
A
A
A
UNIT b
inches
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
max.
mm
5.0 0.51 4.0
0.20 0.020 0.16
OUTLINE
VERSION
SOT201-1
12
min.
max.
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
b
1.7
1.3
0.066
0.051
1
0.53
0.38
0.021
0.015
0.32
0.23
0.013
0.009
REFERENCES
cEe M
(1) (1)
D
41.6
40.6
1.64
1.60
February 1992 25
14.2
13.8
0.56
0.54
16
(1)
Z
1
0.14
0.13
L
M
E
3.6
15.80
3.2
15.24
0.62
0.60
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
17.15
15.90
0.68
0.63
e
w
H
0.252.54 15.24
0.010.10 0.60
ISSUE DATE
90-01-22
95-01-25
max.
2.2
0.087
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Product specification
Small signal combination for multistandard colour TV TDA4504B
SOLDERING
Introduction
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all IC packages. Wave soldering is often preferred when through-hole and
surface mounted components are mixed on one printed-circuit board. However, wave soldering is not always suitable for
surface mounted ICs, or for printed-circuits with high population densities. In these situations reflow soldering is often
used.
This text gives a very brief insight to a complex technology. A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in our
“IC Package Databook”
Soldering by dipping or by wave
The maximum permissible temperature of the solder is 260 °C; solder at this temperature must not be in contact with the
joint for more than 5 seconds. The total contact time of successive solder waves must not exceed 5 seconds.
The device may be mounted up to the seating plane, but the temperature of the plastic body must not exceed the
specified maximum storage temperature (T
be necessary immediately after soldering to keep the temperature within the permissible limit.
(order code 9398 652 90011).
). If the printed-circuit board has been pre-heated, forced cooling may
stg max
Repairing soldered joints
Apply a low voltage soldering iron (less than 24 V) to the lead(s) of the package, below the seating plane or not more
than 2 mm above it. If the temperature of the soldering iron bit is less than 300 °C it may remain in contact for up to
10 seconds. If the bit temperature is between 300 and 400 °C, contact may be up to 5 seconds.
DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
February 1992 26
 Loading...
Loading...