Page 1
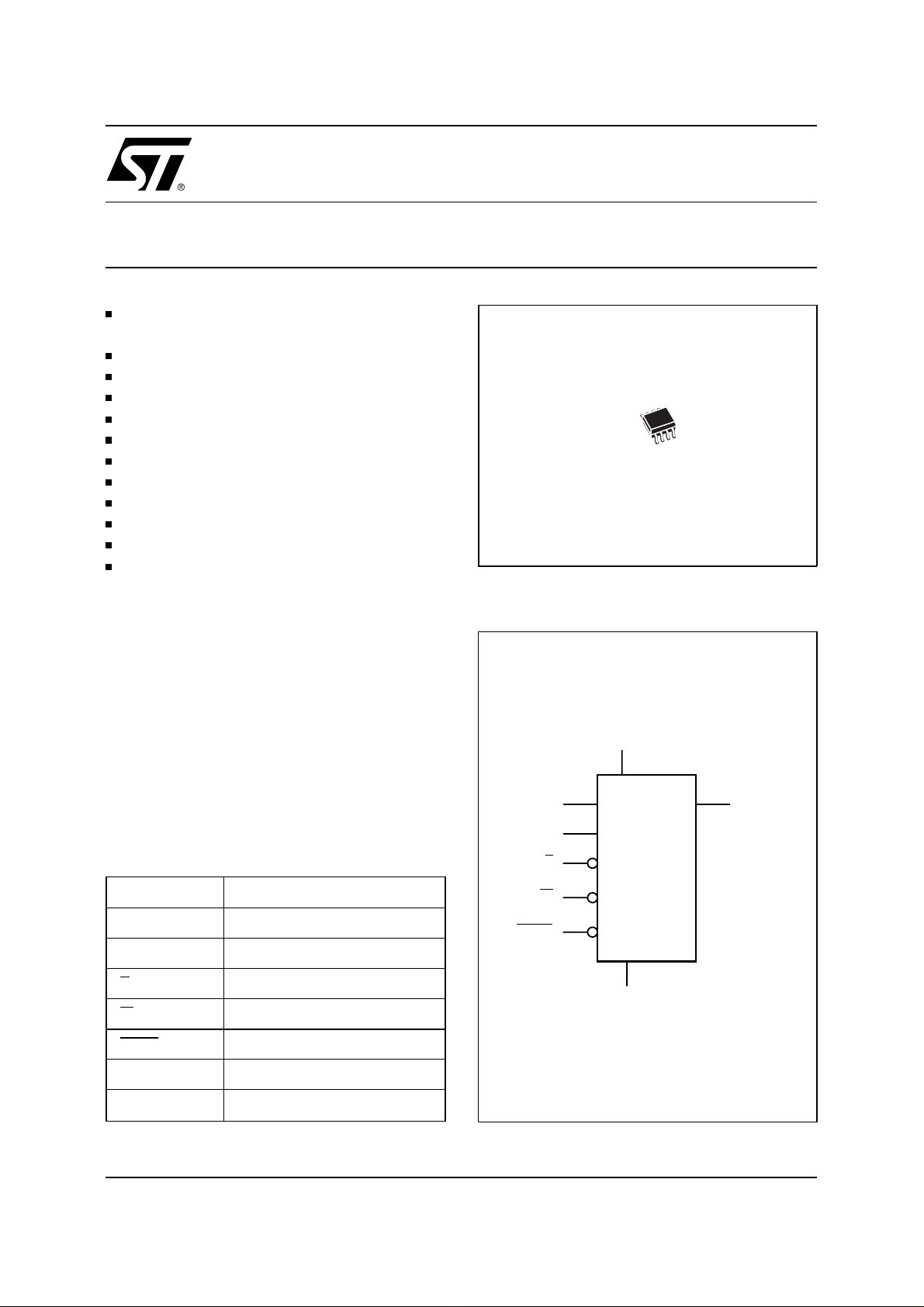
2 Kbit Serial SPI EEPROM with High Speed Clock
HIGH SPEED CLOCK RATE:
– 2.1 MHz Max
1,000,000 ERASE/WRITE CYCLES
40 YEARS DA TA RETE NT ION
SINGLE 4.5V to 5.5V SUPPLY VOLTAGE
SPI BUS COMPATIBLE SERIAL INTERFACE
BLOCK WRITE PROTECTION
STATUS REGISTER
16 BYTE PAGE MODE
WRITE PROTECT
SELF-TIMED PROGRAMMING CY CLE
E.S.D.PROTECTION GREATER than 4000V
SUPPO RTS POSITIVE CLOCK SPI MODES
ST95022
8
1
SO8 (M)
150mil Width
Figure 1. Logic Diagram
DESCRIPTION
The ST95022 is an high speed 2 Kbit Electrically
Erasable Programmable Memory (EEPROM) fabricated with STMicroelectronics’s High Endurance
Single Polysilicon CMOS technology. The memory
is accessed by a simple SPI bus compatible serial
interface. The bus signals are a serial clock input
(C), a serial data input (D) and a serial data output
(Q).
T ab le 1. Signal Names
C Serial Clock
D Serial Data Input
Q Serial Data Output
S Chip Select
W Write Protect
HOLD Hold
V
CC
Supply Voltage
W
HOLD
V
CC
D
C
S
ST95022
V
SS
Q
AI01722
V
SS
February 1999 1/16
Ground
Page 2
ST95022
T ab le 2. Absolute Maximum Ratings
Symbol Parameter Value Unit
T
A
T
STG
T
LEAD
V
O
V
V
CC
V
ESD
Notes:
1. Except for the rating "Operating T emperature Range", stresses above those listed in the Table "Absolute Maximum Ratings"
2. Depends on range.
3. MIL-STD-883C, 3015.7 (100pF, 1500Ω)
4. EIAJ IC-121 (Condition C) (200pF , 0Ω)
Ambient Operating Temperature
Storage Temperature –65 to 150 °C
Lead Temperature, Soldering (SO8 package) 40 sec 215 °C
Output Voltage –0.3 to VCC +0.6 V
Input Voltage with respect to Ground –0.3 to 6.5 V
I
Supply Voltage –0.3 to 6.5 V
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Human Body model)
Electrostatic Discharge Voltage (Machine model)
may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress rating s only and operation of the device at these or any other
conditions above those indicated in the Operating sections of this specification is not implied. Exposure to Absolute Maximum
Rating conditions for extended periods may affect device reliability. Refer also to the STMicroelectronics SURE Program and
other relevant quality documents.
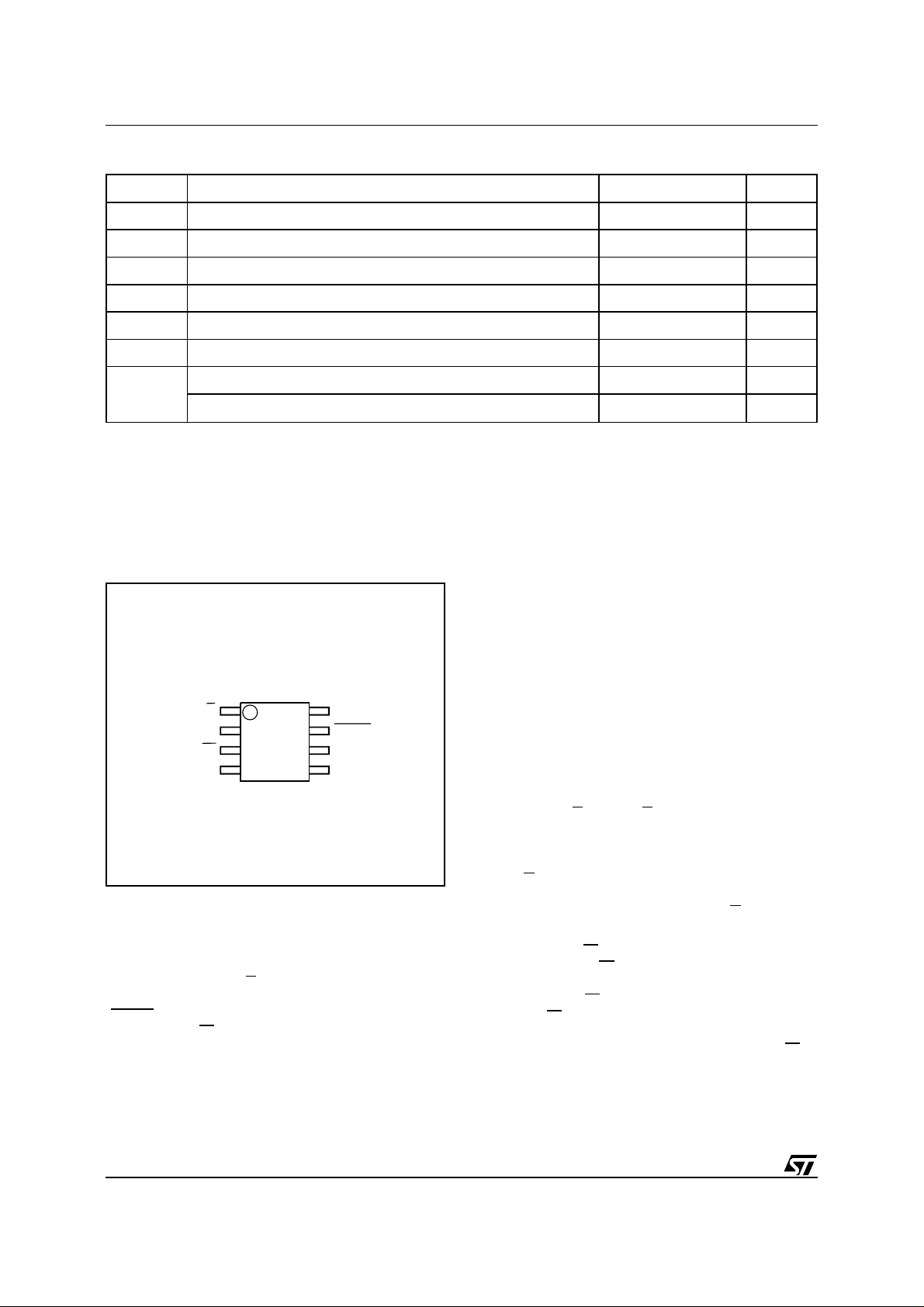
Figure 2B. SO Pin Connections
(1)
(2)
(3)
(4)
–40 to 125 °C
4000 V
500 V
SIGNALS DESCRIPTION
Serial Output (Q).
The output pin is used to transfer data serially out of the ST95022. Data is shifted
out on the falling edge of the serial clock.
Serial Input (D).
The input pin is used to transfer
data serially into the device. It r eceives instructions,
ST95022
1
SV
2
3
W
SS
4
8
7
6
5
AI01723
CC
HOLDQ
C
DV
addresses, and the data to be written. Input is
latched on the rising edge of the serial clock.
Serial Clock (C).
The serial clock provides the
timing of the serial interface. Instructions, addresses, or data present at the input pin are latched
on the rising edge of the clock input, while data on
the Q pin changes after the falling edge of the clock
input.
Chip Select (
S).
When
S is high, the ST95022 is
deselected and the D output pin is at high impedance and, unless an internal write operation is
underway the ST95022 will be in the standby power
S low enables the ST95022, placing it in the
mode.
active power mode. It should be noted that af ter
S is required
DESCRIPTION
(cont’d)
The device connected to the bus is selected when
the chip select input (
S) goes low. Communications
with the chip can be interrupted with a hold input
HOLD). The write operation is disabled by a write
(
protect input (
W).
Data is clocked in during the low to high transition
of clock C, data is clocked out during the high to
low transition of clock C.
power-on, a high to low transition on
prior to the start of any operation.
Write Protect (
protection. When
W).
This pin is for hardware write
W is low, writes to the ST95022
memory are disabled but any other operations stay
enabled. When
available.
W is high, all writes operations are
W going low at any time before the last
bit D0 of the data stream will reset the write enable
latch and prevent programming. No action on
on the write enable latch can interrupt a write cycle
which has commenced.
W or
2/16
Page 3
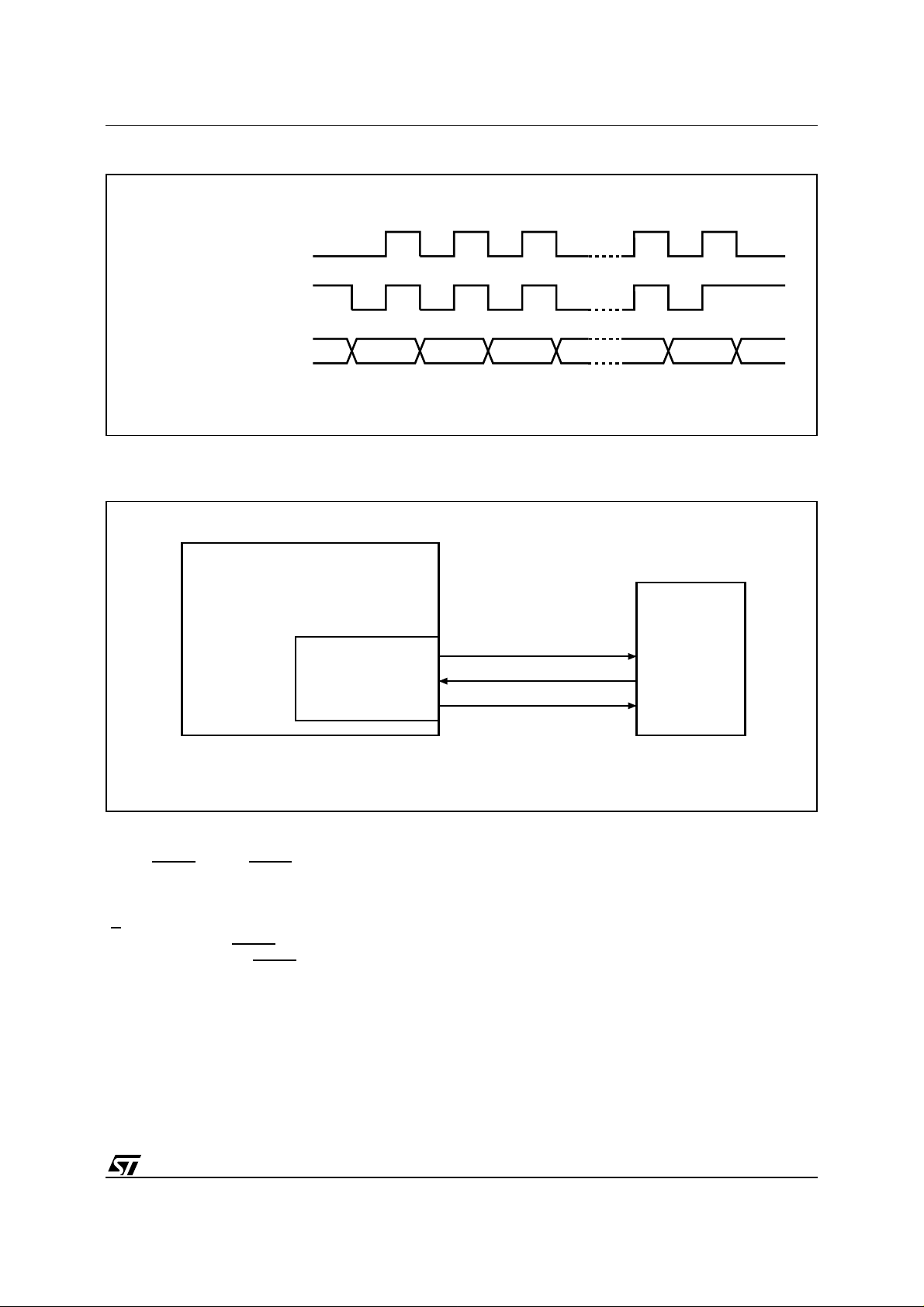
Figure 3. Data and Clock Timing
ST95022
CPOL
CPHA
0
1
0
1
C
C
D or Q
MSB LSB
Figure 4. Microcontroller and SPI Interface Set-up
MICROCONTROLLER
(ST6, ST7, ST9)
SPI Interface with
(CPOL, CPHA) =
('0', '0') or ('1', '1')
SCK
SDI
SDO
C
Q
D
AI01438
ST95xx0
HOLD ).
Hold (
HOLD pin is used to pause
The
serial communications with a ST95022 without resetting the serial sequence. To take the Hold condition into account, the product must be selected
(
S = 0). Then the Hold state is validated by a high
to low transition on
the communications,
HOLD when C is low . T o r esume
HOLD is brought high while
C is low. During the Hold condition D, Q , and C are
at a high impedance state.
When the ST95022 is under the Hold condition, it
is possible to deselect the device. However, the
serial communications will remain paused after a
reselect, and the chip will be reset.
AI01439
The ST95022 can be driven by a microcontroller
with its SPI peripheral running in either of the two
following modes: (CPOL, CPHA) = (’0’, ’0’) or
(CPOL, CPHA) = (’1’, ’1’).
For these two modes, input data is latched in by the
low to high transition of clock C, and output data is
available from the high to low transition of Clock
(C).
The difference between (CPOL, CPHA) = (0, 0) and
(CPOL, CPHA) = (1, 1) is the stand-by polarity: C
remains at ’0’ for (CPOL, CPHA) = (0, 0) and C
remains at ’1’ for (CPOL, CPHA) = ( 1, 1) when there
is no data transfer.
3/16
Page 4

ST95022
OPERATIONS
All instructions, addresses and data are shifted in
and out of the chip MSB first. Data input (D) is
sampled on the first rising edge of clock (C) after
the chip select (
S) goes low. Prior to any operation,
a one-byte instruction code must be entered in the
chip. This code is entered via the data input (D),
and latched on the rising edge of the clock input
(C). T o enter an instruction code, the product must
have been previously selected (
S = low). Table 3
shows the instruction set and format for device
operation. If an invalid instruction is sent (one not
contained in Table 3), the chip is automatically
deselected.
Write Enable (WREN) and Write Disable (WR DI)
The ST95022 contains a write enable latch. This
latch must be set prior to every WRITE or WRSR
operation. The WREN instruction will set the latch
and the WRDI instruction will reset the latch. The
latch is reset under the following conditions:
W pin is low
–
– Power on
– WRDI instruction executed
– WRSR instruction executed
– WRITE instruction executed
As soon as the WREN or WRDI instruction is
received by the ST95022, the circuit executes the
instruction and enters a wait mode until it is deselected.
Read Status Register (RDSR)
The RDSR instruction provides access to the status
register. The status register may be read at any
time, even during a write to the memory operation.
As soon as the 8th bit of the status register is read
out, the ST95022 enters a wait mode (data on D is
not decoded, Q is in Hi-Z) until it is deselected.
The status register format is as follows:
b7 b0
1 1 1 1 BP1 BP0 WEL WIP
BP1, BP0: Read and write bits.
WEL, WIP: Read only bits.
b7 to b4: Read only bits.
During a write to the memory operation to the
memory array, all bits BP1, BP0, WEL, WIP are
valid and can be read. During a write to the status
register, only the bits WEL and WIP are valid and
can be read. The values of BP1 and BP0 read at
that time correspond to the previous contents of the
status register.
The Write-In-Process (WIP) read-only bit indicates
whether the ST95022 is busy with a write operation. When set to a ’1’ a write is in progress, when
set to a ’0’ no write is in progress.
The Write Enable Latch (WEL) read-only bit indicates the status of the write enable latch. When set
to a ’1’ the lat ch is set, when set t o a ’0’ the latch is
reset. The Block Protect (BP0 and BP1) bits indicate the extent of the protection employed. These
bits are set by the user issuing the WRSR instruction. These bits are non-volatile.
Write Status Register (WRSR)
The WRSR instruction allows the user to select the
size of protected memory. The ST95022 is divided
into four 512 bit blocks. The user may read the
blocks but will be unable to write within the pro-
T ab le 3. Instruction Set
Instruction Description Instruction Format
WREN Set Write Enable Latch 0000 0110
WRDI Reset Write Enable Latch 0000 0100
RDSR Read Status Register 0000 0101
WRSR Write Status Register 0000 0001
READ Read Data from Memory Array 0000 0011
WRITE Write Data to Memory Array 0000 0010
Notes:
A = 1, Upper page selected
A = 0, Lower page selected
4/16
Page 5
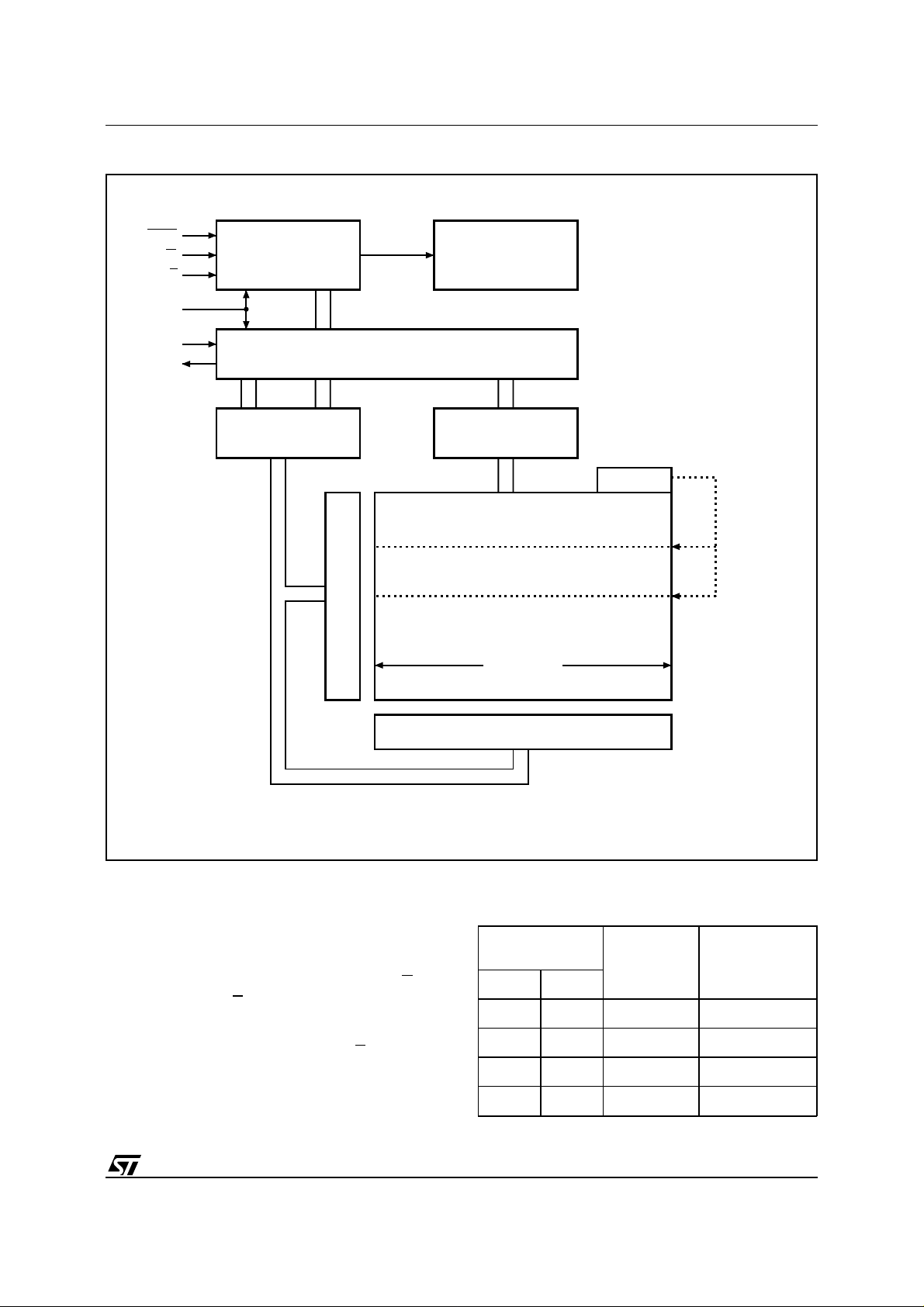
Figure 5. Block Diagram
ST95022
HOLD
W
S
C
D
Q
Control Logic
I/O Shift Register
Address Register
and Counter
Y Decoder
High Voltage
Generator
Data
Register
Status
Block
Protect
16 Bytes
tected blocks. The blocks and respective WRSR
control bits are shown in Table 4.
When the WRSR instruction and the 8 bits of the
Status Register are latched-in, the internal write
cycle is then triggered by the ris ing edge of
This rising edge of
S must appear no later than the
S.
16th clock cycle of the WRSR instruction of the
Status Register content (it must not appear a 17th
clock pulse before the rising edge of
S), otherwise
the internal write sequence is not performed.
X Decoder
T ab le 4. Write Protected Block Size
Status Register
Bits
BP1 BP0
0 0 none none
0 1 C0h - FFh Upper quarter
1 0 80h - FFh Upper half
1 1 00h - FFh Whole memory
Array
Addresses
Protected
Protected
AI01272
Block
5/16
Page 6

ST95022
Figure 6. Read Operation Sequence
S
21 345678910111213141516171819
0
C
INSTRUCTION BYTE ADDRESS
A7
D
HIGH IMPEDANCE
Q
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
Read Operation
The chip is first selected by putting
S low. The serial
one byte read instruction is followed by a one byte
address (A7-A0), each bit be ing latched-in during
the rising edge of the clock (C). Then the data
stored in the memory at the selected address is
shifted out on the Q output pin; each bit being
shifted out during the falling edge of the clock (C).
The data stored in the memory at the next address
can be read in sequence by continuing to provide
clock pulses. The byte address is automatically
incremented to the next higher address after each
byte of data is shifted out. When the highest address is reached, the address counter rolls over to
0h allowing the read cycle to be continued indefinitely. The read operation is terminated by deselecting the chip. The chip can be deselected at any
time during data output. Any read attempt during a
write cycle will be rejected and will deselect the
chip.
20 21 22 23
DATA OUT
7 65432 0
1
AI01558
Byte Write Operation
Prior to any write attempt, the write enable latch
must be set by issuing the WRE N instruction. First
the device is selected (
S = low) and a serial WREN
instruction byte is issued. Then the product is deselected by taking
S high. After the WREN instruction byte is sent, the ST95022 will set the write
enable latch and then remain in st andby until it is
deselected. Then the write state is entered by
selecting the chip, issuing two bytes of instruction
and address, and one byte of data.
Chip Select (
S) must remain low for the entire
duration of the operation. The product must be
deselected just after the eighth bit of data has been
latched in. If not, the write process is cancelled. As
soon as the product is deselected, the self-timed
write cycle is initiated. While the write is in progress,
the status register may be read to check BP1, BP0,
WEL and WIP. WIP is high during the self-timed
write cycle. When the cycle is completed, the write
enable latch is reset.
6/16
Page 7

Figure 7. Write Enable Latch Sequence
S
C
D
Q
21 34567
0
HIGH IMPEDANCE
ST95022
AI01441
Figure 8. Byte Write Operation Sequence
S
21 345678910111213141516171819
0
C
INSTRUCTION BYTE ADDRESS
D
HIGH IMPEDANCE
Q
A7
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
20 21 22 23
DATA BYTE
7 65432 0
1
AI01559
7/16
Page 8

ST95022
Figure 9. Page Write Operation Sequence
S
21 345678910111213141516171819
0
C
20 21 22 23
INSTRUCTION BYTE ADDRESS
A7
D
S
2625 27 28 29 30 31
C
DATA BYTE 2
D
7 6 321054
A6 A5 A4 A3 A2 A1 A0
8+8N
9+8N
DATA BYTE N
7
6 3210247 65432
5 4
Figure 10. RDSR: Read Status Register Sequence
10+8N
11+8N
12+8N
13+8N
DATA BYTE 1
7 65432 0
14+8N
15+8N
136
137
138
139
DATA BYTE 16
140
141
1
1
142
7
143
0
AI01560
8/16
S
21 3456789101112131415
0
C
INSTRUCTION
D
Q
HIGH IMPEDANCE
STATUS REG. OUT
7 6543210
MSB
AI01444
Page 9

Figure 11. WRSR: Wri te Status Register Sequence
S
21 3456789101112131415
0
C
INSTRUCTION STATUS REG.
D
HIGH IMPEDANCE
Q
ST95022
AI01445
Page Write Operation
A maximum of 16 bytes of data may be written
during one non-volatile write cycle. All 16 bytes
must reside on the same page. The page write
mode is the same as the byte write mode except
that instead of deselecting the device after the first
byte of data, up to 15 additional bytes can be shifted
in prior to deselecting the chip. A page address
begins with address xxxx 0000 and ends with xxxx
1111. If the address counter reaches xxxx 11 1 1 and
the clock continues, the counter will roll over to the
first address of the page (xxxx 0000) and overwrite
any previously written data. The programming cycle will only start if the
S transition occurs just after
the eighth bit of data of a word is r eceived.
POWER ON STATE
After a Power up the ST95022 is in the following
state:
– The device is in the low power standby state.
– The chip is deselected.
– The chip is not in hold condition.
– The write enable latch is reset.
– BP1 and BP0 are unchanged (non-volatile
bits).
DA TA PROTECTION AND PROTOCOL SAFETY
– All inputs are protected against noise, see Ta-
ble 5.
– Non valid
S and HOL D transitions are not
taken into account.
–
S must come high at the proper clock count in
order to start a non-volatile write cycle (in the
memory array or in the cycle status register),
that is the Chip Select
S must rise during the
clock pulse following the introduction of a multiple of 8 bits.
– Access to the memory array during non-vola-
tile programming cycle is ignored; however,
the programming cycle continues.
– After any of the operations WREN, WRDI,
RDSR is completed, the chip enters a wait
state and waits for a deselect.
– The write enable latch is reset upon power-up.
– The write enable latch is reset when
W is
brought low.
INITIAL DELIVERY STATE
The device is delivered with the memory array in a
fully erased state (all data set at all "1’s" or FFh).
The block protect bits are initialized to 00.
9/16
Page 10

ST95022
T ab le 5. AC Measurement Conditions
Input Rise and Fall Times ≤ 50ns
Input Pulse Voltages 0.2V
Input and Output Timing
Reference Voltages
Output Load CL = 100pF
Note that Output Hi-Z is defined as the point where data is no
longer driven.
T able 6. Input Parameters
(1)
to 0.8V
CC
0.3V
to 0.7V
CC
(TA = 25 °C, f = 2.1 MHz )
CC
CC
Figure 12. AC Testing Input Output
Waveforms
0.8V
CC
0.2V
CC
Symbol Parameter Min Max Unit
C
IN
C
IN
t
LPF
Note:
1. Sampled only, not 100% tested.
Input Capacitance (D) 8 pF
Input Capacitance (other pins) 6 pF
Input Signal Pulse Width Filtered Out 10 ns
T ab le 7. DC Characteristics
(T
= –40 to 125°C; VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V)
A
Symbol Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
0.7V
0.3V
AI00825
CC
CC
I
LI
I
LO
I
CC
I
CC1
V
IL
V
IH
V
OL
V
OH
Note:
1. The device meets output requirements for both TTL and CMOS standards.
Input Leakage Current 2 µA
Output Leakage Current ±2 µA
VCC Supply Current (Active)
C = 0.1 V
= 2.1 MHz, Q = Open
f
C
VCC Supply Current (Standby) S = VCC, VIN = VSS or V
Input Low Voltage – 0.3 0.3 V
Input High Voltage 0.7 V
(1)
Output Low Voltage IOL = 2mA 0.4 V
(1)
Output High Voltage IOH = –2mA VCC –0.6 V
/0.9 VCC ,
CC
CC
CC
2mA
50 µA
CC
V
VCC + 1 V
10/16
Page 11

ST95022
T ab le 8. AC Characteristics
(T
= –40 to 125°C; VCC = 4.5V to 5.5V)
A
Symbol Alt Parameter Test Condition Min Max Unit
f
t
SLCH
t
CHSL
t
CH
t
CL
t
CLCH
t
CHCL
t
DVCH
t
CHDX
t
DLDH
t
DHDL
t
HHCH
t
HLCH
t
CLHL
t
CLHH
t
t
t
t
t
f
C
CSS
CLH
CLL
t
RC
t
FC
DSU
t
DH
t
RI
t
FI
HSU
t
HH
C
(1)
(1)
Clock Frequency D.C. 2.1 MHz
S Active Setup Time (relative to
the rising edge of C)
S Not Active Hold Time (relative
to the rising edge of C)
100 ns
100 ns
Clock High Time 190 ns
Clock Low Time 190 ns
Clock Rise Time 1 µs
Clock Fall Time 1 µs
Data In Setup Time 50 ns
Data In Hold Time 50 ns
Data In Rise Time 1 µs
Data In Fall Time 1 µs
HOLD Setup Time 100 ns
Clock Low Hold Time after HOLD
Active
100 ns
HOLD Hold Time 80 ns
Clock Low Set-up Time before
HOLD Inactive
100 ns
t
CHSH
t
SHCH
t
SHSL
t
SHQZ
t
CLQV
t
CLQX
(2)
t
QLQH
(2)
t
QHQL
t
HHQX
t
HLQZ
t
W
Notes:
1. t
2. Value guaranteed by characterization, not 100% tested in production.
+ tCL ≥ 1/fc
CH
t
t
t
CSH
DIS
t
V
t
HO
t
RO
t
FO
t
LZ
t
HZ
WP
S Active Hold Time (relative to the
rising edge of C)
S Not Active Setup Time (relative
to the rising edge of C)
S Deselect Time 200 ns
Output Disable Time 150 ns
Clock Low to Output Valid 240 ns
Output Hold Time 0 ns
Output Rise Time 100 ns
Output Fall Time 100 ns
HOLD High to Output Low-Z 100 ns
HOLD Low to Output High-Z 200 ns
Write Cycle Time 7 ms
200 ns
100 ns
11/16
Page 12

ST95022
Figure 13. Serial Input Timing
S
C
tDVCH
tSLCH
tSHSL
tCHSHtCHSL
tSHCH
tCHCL
D
Q
Figure 14. Hold Tim ing
S
C
tCHDX
MSB IN
HIGH IMPEDANCE
tCLHL
tCLCH
LSB IN
tDLDH
tDHDL
AI01447
tHLCH
tHHCH
tCLHH
tHHQXtHLQZ
12/16
Q
D
HOLD
AI01448
Page 13

Figure 15. Output Timing
S
C
tCLQX
tCLQV
tCH
tCL
ST95022
tSHQZ
Q
ADDR.LSB IN
D
Figure 16. EEPROM and SPI Bus
D
Q
C
MASTER
CQD
ST95xxx
tQLQH
tQHQL
CQD
ST95xxx
LSB OUT
AI01449B
CQD
ST95xxx
CS3 CS2 CS1
S
S
S
AI01446
13/16
Page 14

ST95022
ORDERING INFORMATION SCHEME
Example: ST95022 M 3 TR
Data Strobe
2 Note 1
Note:
1. Data In is strobed on rising edge of the clock (C) and Data Out is synchronized from the falling edge of the clock.
Package
M SO8
150mil Width
Temperature Range
3 –40 to 125 °C
Option
TR Tape & Reel
Packing
Devices are shipped from the factory with the memory content set at all "1’s" (FFh).
For a list of available options (Package, etc...) or for further information on any aspect of this device, please
contact the STMicroelectronics Sales Office nearest to you.
14/16
Page 15

SO8 - 8 lead Plastic Small Outline, 150 mils body width
ST95022
Symb
Typ Min Max Typ Min Max
A 1.35 1.75 0.053 0.069
A1 0.10 0.25 0.004 0.010
B 0.33 0.51 0.013 0.020
C 0.19 0.25 0.007 0.010
D 4.80 5.00 0.189 0.197
E 3.80 4.00 0.150 0.157
e1.27– –0.050– –
H 5.80 6.20 0.228 0.244
h 0.25 0.50 0.010 0.020
L 0.40 0.90 0.016 0.035
α 0° 8° 0° 8°
N8 8
CP 0.10 0.004
mm inches
Drawing is not to scale.
B
SO-a
h x 45˚
A
C
e
CP
D
N
E
H
1
LA1 α
15/16
Page 16

ST95022
Information furnished is believ ed to be accura te a nd rel i abl e. However, STMicroelec tronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences
of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted
by implication or otherwise under any patent or patent rights of STMicroelectronics. Specifications mentioned in this publication are subject to
change without notice. This publication supersedes and repl aces all information previously supplied. STMicroelectron ics products are not
authorized for use as critical components in life support devices or systems without express written approval of STMicroelectronics.
The ST logo is a registered trademark of STMicroelect roni cs
© 1999 STMicroelectronics - All Rights Reserved
All other names are the property of their respective owners
Australia - Brazil - Canada - China - France - Germany - Italy - Japan - Korea - Malaysia - Malta - Mexico - Morocco - The Netherlands -
Singapore - Spain - Sweden - Switzerland - Taiwan - Thailand - United Kingdom - U.S.A.
STMicroelectronics GROUP OF COMPANIES
http://www.st.com
16/16
 Loading...
Loading...