Page 1
SM1126 Series
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS INC.
OVERVIEW
The SM1126 Series are melody ICs for use in mobile
telecommunications equipment. A maximum of 15
melodies can be stored in programmable ROM and
one in built-in read/write SRAM.
FEATURES
■
2.0 to 3.6 V supply voltage
■
Maximum of 16 melody selections (15 in ROM +
1 in SRAM)
■
Level hold playback mode
■
External reference clock input versions and builtin RC oscillator versions available, set by masterslice option (RC oscillator versions require an
external resistor and capacitor).
■
Selectable clock frequencies (fixed for all melodies)
• External clock input versions (6 frequencies)
- 32.768 kHz system: 32.768, 65.536 and
131.072 kHz
- 38.4 kHz system: 38.4, 76.8 and 153.6 kHz
• Built-in RC oscillator versions (1 frequency)
- 131.072 kHz
■
2-pin serial data melody selection and 1-pin melody playback control
■
Parity check function
■
Delivery pattern alarm
■
Power save function
• External clock input versions
Clock gating in non-play modes
• Built-in RC oscillator versions
Oscillator stopped in non-play modes
Melody IC with Built-in SRAM
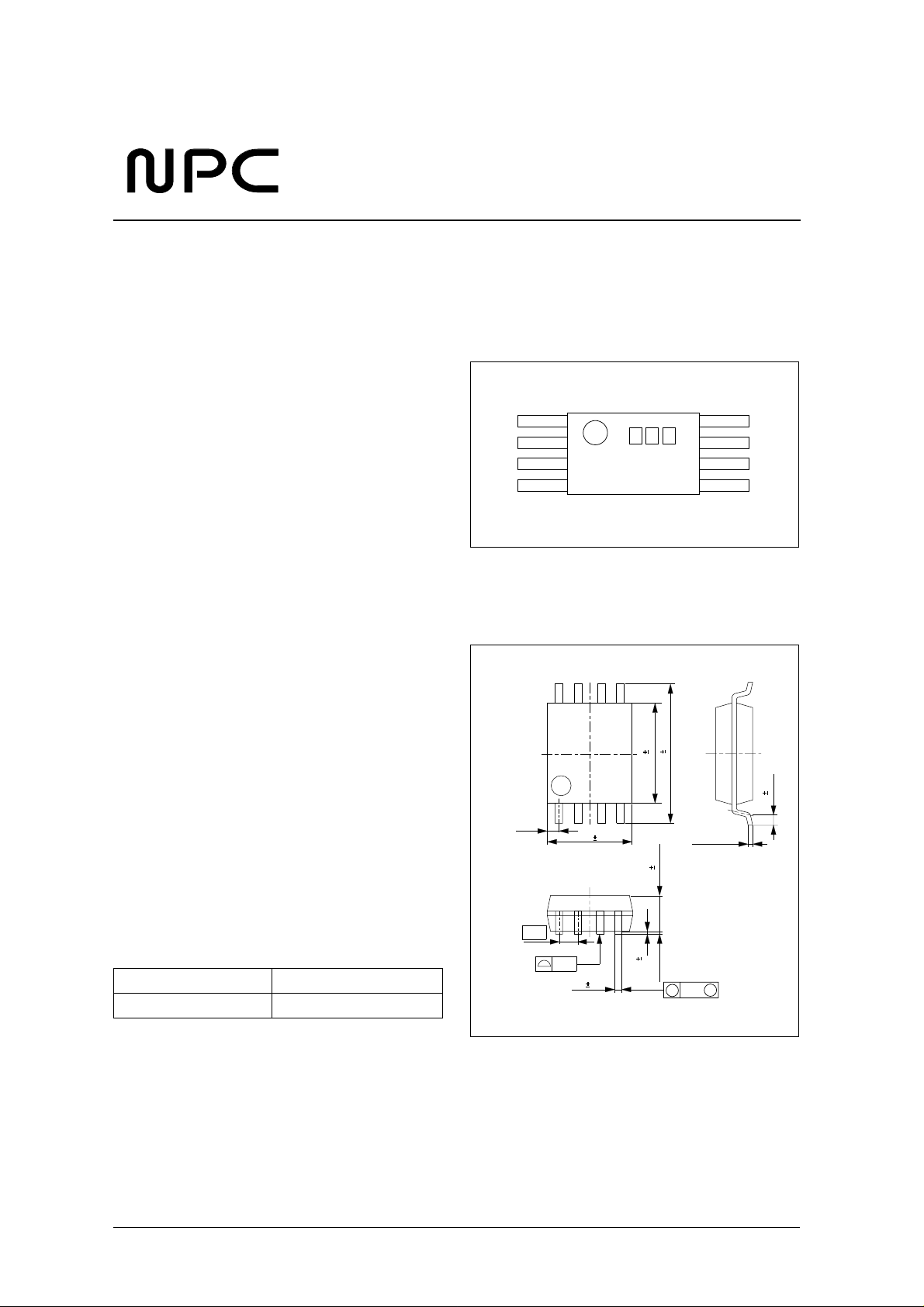
PINOUT
(T op V iew)
8-pin VSOP
OSC
SIO
SC
ST
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit: mm)
0.575 TYP
1
2
3
4
3.1 0.3
1126××
4.4 0.2
1.15 0.05
8
7
6
5
6.4 0.3
0.15
+ 0.1
− 0.05
VSS
VDD
MTO
TEST
0.5 0.2
ORDERING INFORMATION
De vice Pack ag e
SM1126 ×× V 8-pin VSOP
0.65
0.10
0.22 0.1
0.1 0.05
0.12
+
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—1
M
Page 2
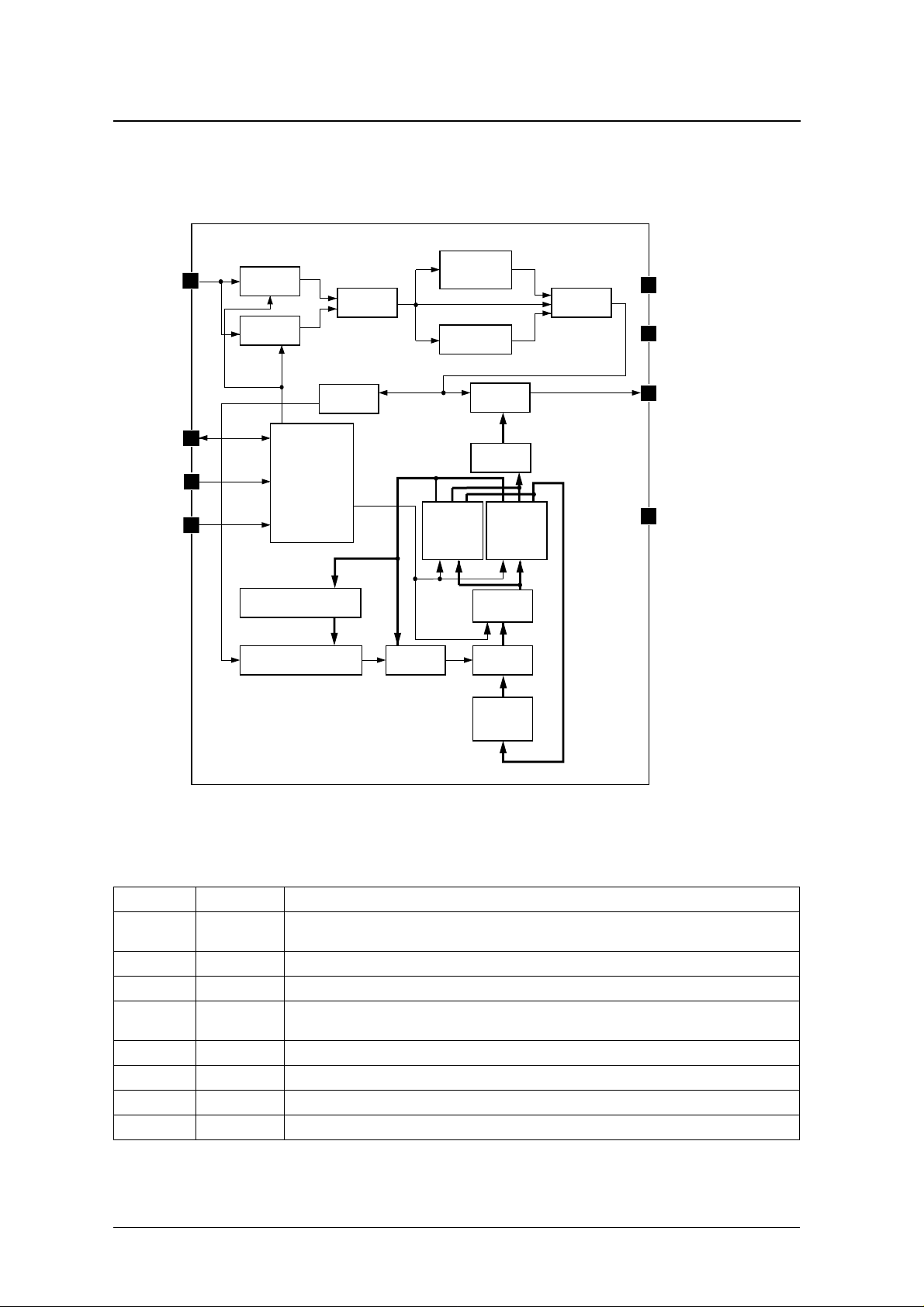
BLOCK DIAGRAM
OSC
OSC
SM1126 Series
Frequency
Master slice Master slice
SW1
Multiplier
SW2
VSS
SIO
SC
ST
Gate
Divider
Control
Circuit
Tempo Latch
Tempo Counter
Rhythm
Counter
Divider
Main
RAM
Scale
Counter
Scale
ROM
Main
ROM
MultiPlexer
Address
Counter
Start
Address
Latch
VDD
MTO
TEST
(Pull-down resistance
built-in)
PIN DESCRIPTION
Number Name Function
1 OSC
2 SIO Playback control serial interface data input. During parity check, the G flag is output while ST is HIGH.
3 SC Playback control serial interface clock input
4ST
5 TEST Test input. Pull-down resistor built-in. Leave open or connect to VSS.
6 MTO Playback melody signal output
7 VDD Supply
8 VSS Ground
Built-in RC oscillator option: External resistor and capacitor connection pins
External clock input option: External reference clock input (gate circuit b uilt-in)
Play mode: Playback start/stop control signal input
Write mode: Serial interface data write control signal input
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—2
Page 3
−
−
−
−
°
°
−
° C
−
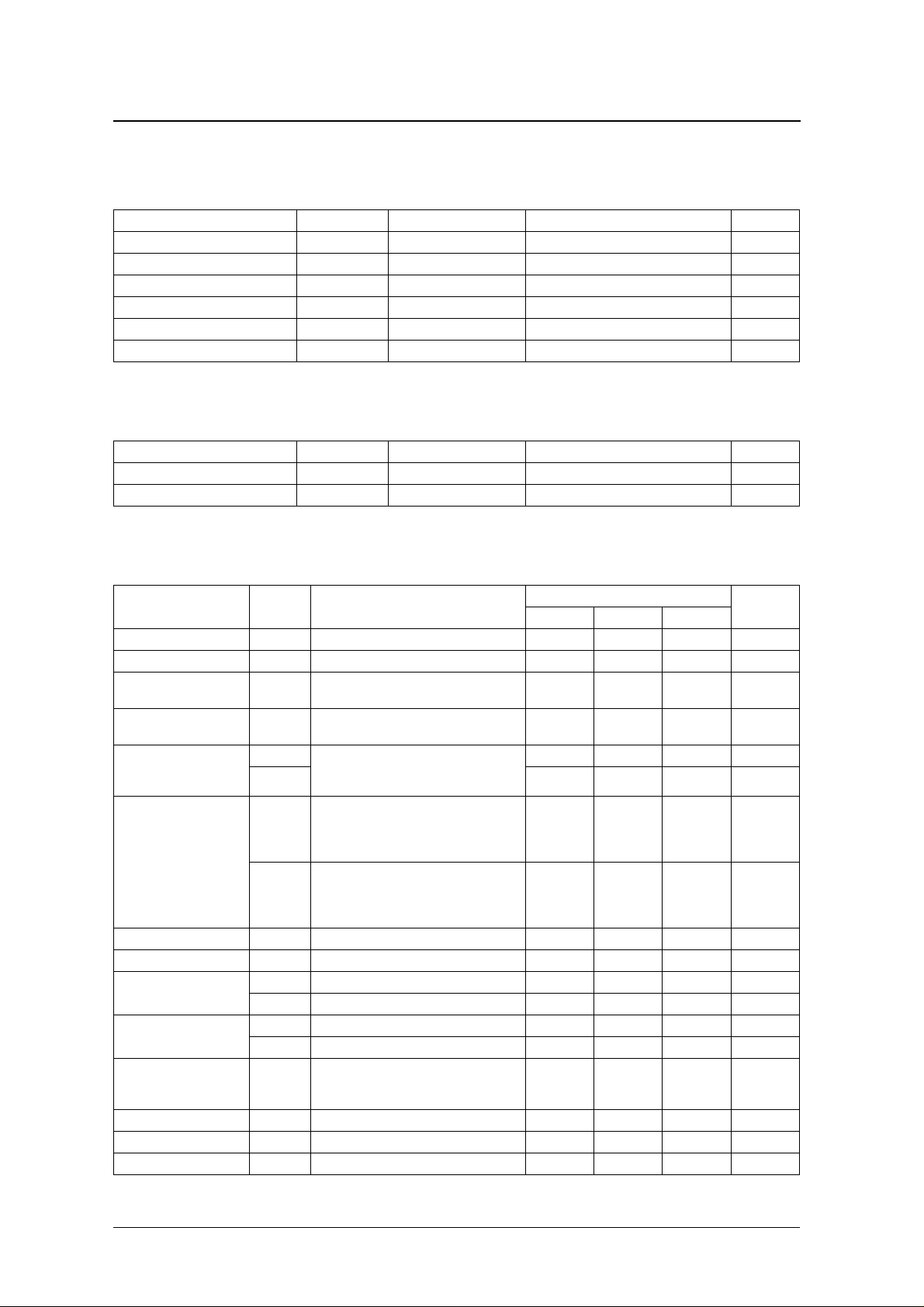
SPECIFICATIONS
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Parameter Symbol Condition Rating Unit
Supply voltage range V
Input voltage range V
Power dissipation P
Storage temperature range T
Soldering temperature T
Soldering time t
Recommended Operating Conditions
V
= 0 V
SS
Parameter Symbol Condition Rating Unit
Supply voltage V
Operating temperature T
DD
V
SS
IN
D
stg
sld
sld
DD
opr
−
SM1126 Series
−
∆
0.3 to 5.0 V
V
SS
0.2 to V
+ 0.2 V
DD
100 mW
40 to 125
255
C
C
10 s
2.0 to 3.6 V
20 to 70
DC Characteristics
T
= − 20 to 70 ° C, V
a
Parameter Symbol Condition
Supply voltage V
Current consumption (1) I
Current consumption (2) I
Current consumption (3) I
Input voltage
Input current (1)
Input current (2) I
Start voltage V
Output voltage (1)
Output voltage (2)
Oscillator frequency f
Frequency stability
Oscillator start voltage V
Oscillator stop voltage V
= 0 V, V
SS
DD
DD1
DD2
DD3
V
V
I
IH1
IH
IL
= 2.0 to 3.6 V
DD
Non-playback mode, T
External clock input option: Playback mode,
MTO pin open
Built-in RC oscillator option: Playback mode,
MTO pin open
External clock input option: ST, SIO, SC and
OSC pins, Built-in RC oscillator option: ST ,
SIO and SC pins
V
= V
IH
DD
External clock input option: ST, SIO, SC and
OSC pins, Built-in RC oscillator option: ST ,
SIO and SC pins
V
= 0 V , T
IL
External clock input option: ST, SIO, SC and
I
IL1
OSC pins, Built-in RC oscillator option: ST ,
SIO and SC pins
TEST pin, V
IH2
TEST pin – – 0.1 V
OPN
V
V
V
V
OH1
OL1
OH2
OL2
SIO pin, I
SIO pin, I
MTO pin, I
MTO pin, I
Built-in RC oscillator option: NPC test board
measurement, V
OSC
C
= 130 pF
O
f/f Built-in RC oscillator option – 0.2 – %/0.1V
Built-in RC oscillator option – – 1.6 V
DOB
Built-in RC oscillator option – – 1.6 V
DOS
= 25 ° C – – 0.5 µA
a
, T
= 25 ° C
a
= 25 ° C
a
= V
IH
DD
= 1 mA, V
OH1
= 1 mA, V
OL1
= 1 mA V
OH2
= 1 mA V
OL2
= 2.4 V V
DD
= 2.4 V V
DD
= 3.0 V, R
DD
= 82 k Ω ,
O
Rating
min typ max
2.0 3.0 3.6 V
– 25 200 µA
– 215 600 µA
V
0.2 – V
DD
V
SS
–V
DD
+ 0.2 V
SS
– – 0.5 µA
– – 0.5 µA
– – 200 µA
0.4 – V
DD
SS
0.4 – V
DD
SS
–V
–V
DD
+ 0.4 V
SS
DD
+ 0.4 V
SS
117.965 131.072 144.179 kHz
Unit
V
V
V
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—3
Page 4
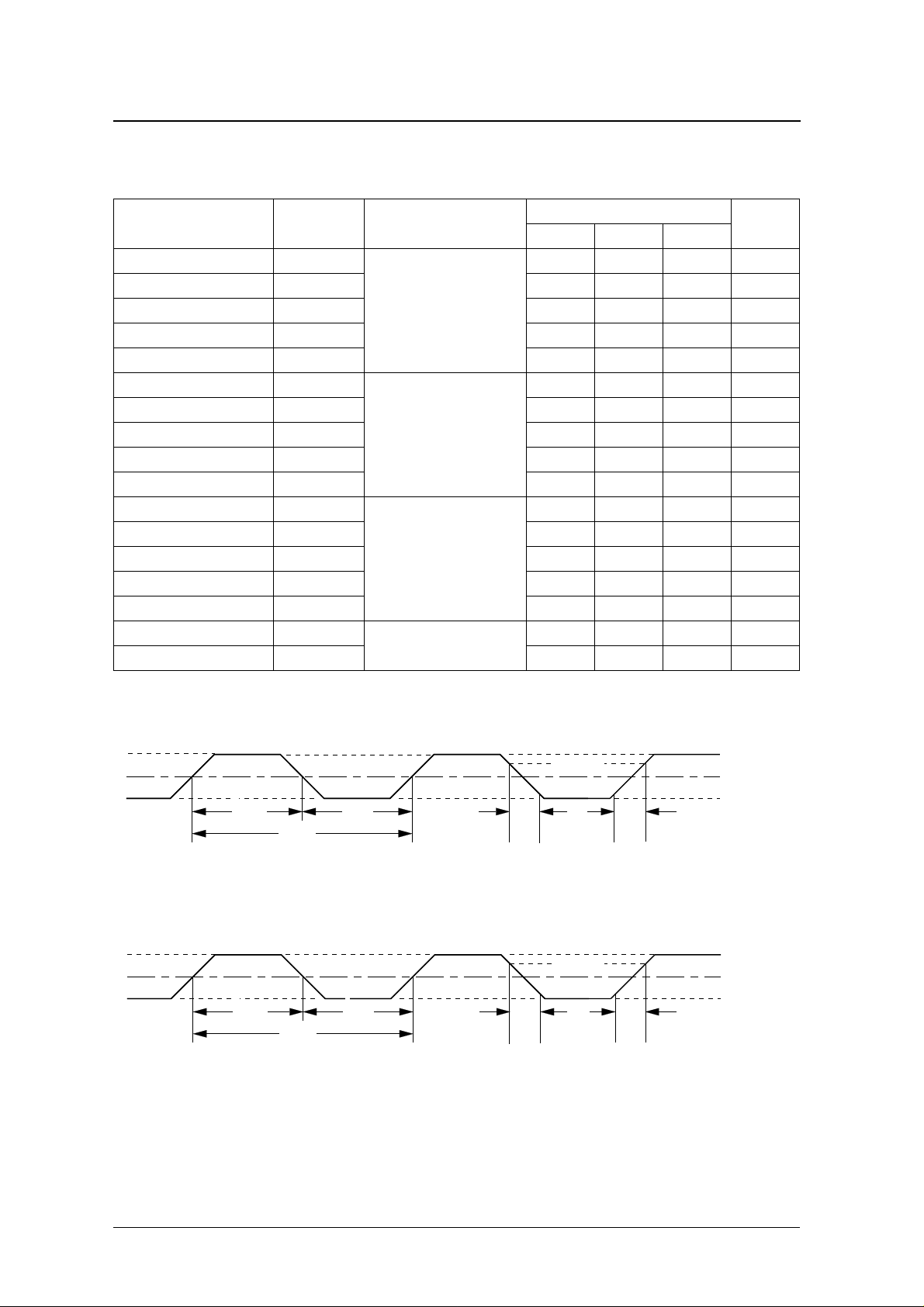
AC Characteristics
T
= − 20 to 70 ° C, V
a
SS
= 0 V, V
= 2.0 to 3.6 V
DD
SM1126 Series
Parameter Symbol Condition
OSC pulse cycle t
OSC HIGH-level pulsewidth t
OSC LOW-level pulsewidth t
OSC pulse rise time t
OSC pulse fall time t
SC pulsewidth t
SC HIGH-level pulsewidth t
SC L OW-level pulsewidth t
SC pulse rise time t
SC pulse fall time t
SIO-SC setup time t
SIO-SC hold time t
ST input write pulsewidth t
ST input write pulse rise time t
ST input write pulse fall time t
SIO output enable delay t
SIO output disable delay t
OSC
OWH
OWL
Or
Of
SC
SWH
SWL
Sr
Sf
DS
DH
WP
Wr
Wf
OE
OD
“OSC input pulse (external clock
input version)” timing
“SC input pulse” timing
“SC-SIO-ST serial input pulse”
timing
“SIO parity check G-flag output
data” timing
Rating
Unit
min typ ma x
4.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
– – 200 ns
– – 200 ns
4.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
– – 200 ns
– – 200 ns
2.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
2.0 – – µs
– – 200 ns
– – 200 ns
– – 600 ns
– – 600 ns
OSC input pulse (external clock input version)
tt
OWH
t
OSC
OWL
SC input pulse
t
SWH
t
SC
t
SWL
OWL
V
0.9VDD
0.1VDD
t
Of
t
Or
0.9VDD
0.1VDD
t
Sf
t
Sr
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—4
Page 5
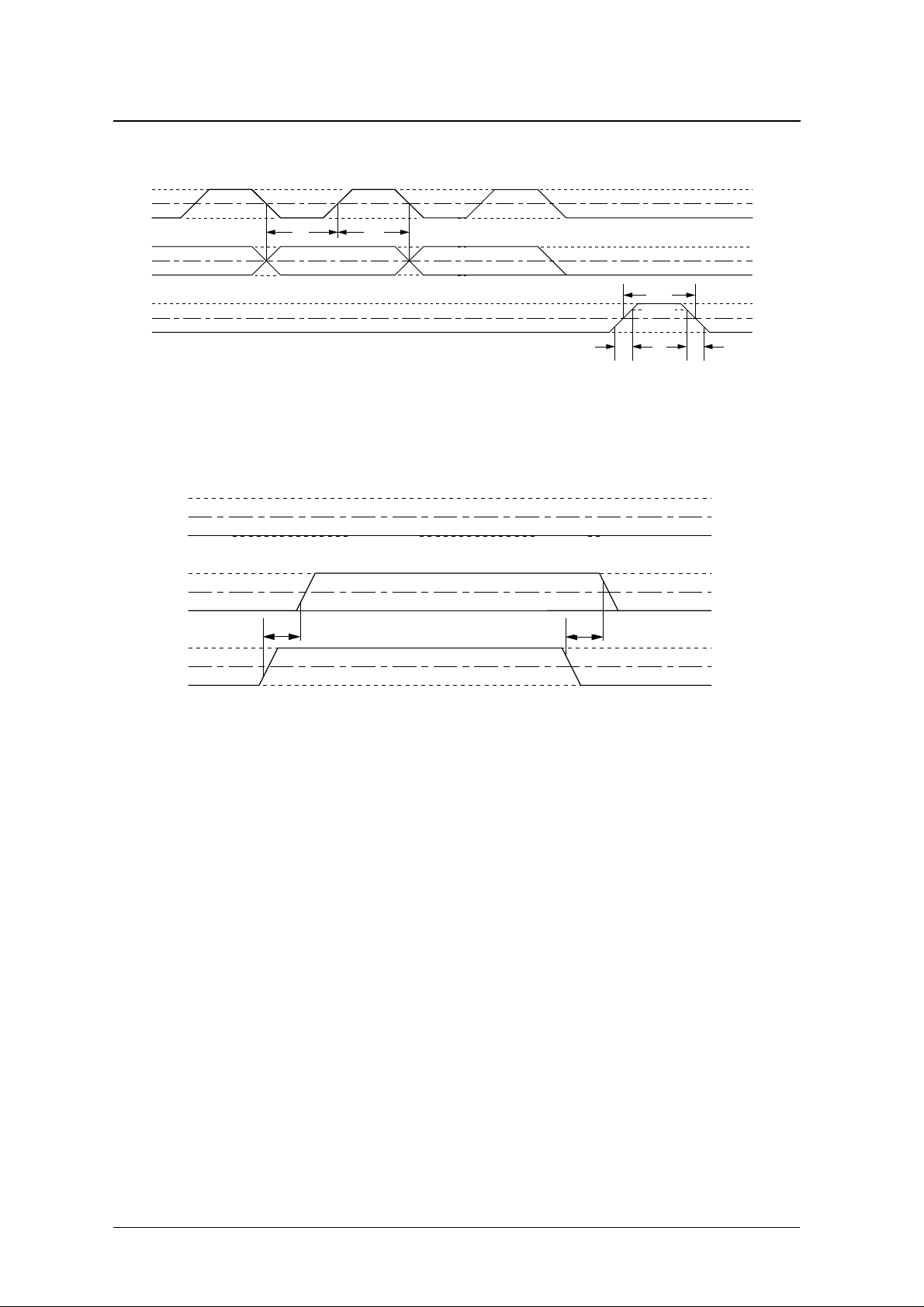
SC-SIO-ST serial input pulse
SC
t
DS
SIO
ST
SM1126 Series
t
DH
ST must be set to LOW when switching ST
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
t
WP
0.9VDD
0.1VDD
t
Wr
t
Wf
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
SIO parity check G-flag output data
SC
SIO
ST
INPUT MODE
t
0.1VDD
OE
OUTPUT MODE (G FLAG OUTPUT) INPUT MODE
0.1VDD
ST must be set to LOW when switching ST
0.9VDD
0.9VDD
t
OD
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
V
DD
0.5VDD
V
SS
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—5
Page 6
SM1126 Series
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Control Functions
External reference clock
SM1126 Series devices are available in external clock input versions and built-in RC oscillator versions, set
by master-slice option. In the case of the built-in RC oscillator option, an external resistor and capacitor is
required for the oscillator function.
SM1126 Series devices can operate at 6 selectable reference clock frequencies. All melodies playback at the
fixed speed set by the reference clock frequency. External clock input versions operate at one of 6 selectable
clock frequencies, as shown in table 1. Built-in RC oscillator versions operate at only one oscillator frequencies—131.072 kHz.
Table 1. Reference clock frequencies (external clock)
Frequency
system
32.768 kHz 32.768 kHz 65.536 kHz 131.072 kHz
38.4 kHz 38.4 kHz 76.8 kHz 153.6 kHz
Selectable frequencies
Power-save function
In external clock input versions, the external reference clock input is used during playback mode only and is
otherwise ignored. If a clock signal is input when not in playback mode (when ST is LOW), the gate circuit
switches to cutoff the external reference clock signal from entering the device, preventing unwanted current
flow.
In built-in RC oscillator versions, the oscillator is stopped when not in playback mode (when ST is LOW),
preventing unwanted current flow.
ST
OSC
Figure 1. External clock input version: OSC input during playback mode only
OSC
OSC
ST
Figure 2. External clock input version: Continuous OSC input
ST
CR Oscillation
Figure 3. Built-in RC oscillator version
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—6
Page 7

SM1126 Series
Serial inputs
Serial data is input on SIO in sync with the SC clock in 8-bit units when ST is LOW. Data is not accepted
when ST is HIGH. When ST goes HIGH, the 8-bit data is latched. Note that if the input data exceeds 8 bits in
length, the most recent 8 bits are used and any preceding bits are ignored. Data is in MSB first format.
Input data is interpreted as a command or as a data word (in write mode), depending on the current operating
mode of the device. There are 3 types of commands:
■
Playback start command
■
SRAM write command
■
End-of-write command
The SRAM write command is used to invoke write mode operation, and end-of-write command is used to
return to play mode operation. In write mode, however, data is interpreted as data words to be written to
SRAM.
Note that pin SIO is an output pin only when the parity check command is executed. At all other times, SIO
is an input pin.
SIO
Invalid
Data
? ?
B7B6B5
Valid
Data
B3 B2 B1 B0
B4
Invalid
Data
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
?
SC
ST
Pin SC should be LOW when either a LOW-to-HIGH or HIGH-to-LOW transition occurs on pin ST.
Figure 4. Serial input timing
Playback control
The ST pin controls the start of playback. While ST is HIGH, the melody is played repeatedly, and when ST
goes LOW, playback stops. Melodies are selected by input serial data on pins SIO and SC, as shown in table 2.
The melody select command comprises a fixed code (1000) followed by 4 melody select data bits (B3 to B0).
The 8 bits of data are retained even after playback. If serial data is input during playback, the data is ignored
and playback continues.
Invalid
Data
Valid
Data
Invalid
Data
SIO
SC
ST
MTO
B3 B2 B1 B0HL
? ?
Pin SC should be LOW when either a LOW-to-HIGH or HIGH-to-LOW transition occurs on pin ST.
LL
?
?
?
?
Figure 5. Serial data input timing
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—7
?
?
?
?
?
?
Page 8

SM1126 Series
Table 2. Serial data melody select
B3 B2 B1 B0 ST Melody B3 B2 B1 B0 ST Melody
→
→
→
LLLLL
LLLHL
LLHLL
LLHHL
LHLLL → H 5th melody H H L L L → H 13th melody
LHLHL → H 6th melody H H L H L → H 14th melody
LHHLL → H 7th melody H H H L L → H 15th melody
LHHHL → H 8th melody HHHHL → H SRAM melody
SIO
#n1 Data
H 1st melody H L L L L → H 9th melody
H 2nd melody H L L H L → H 10th melody
H 3rd melody H L H L L → H 11th melody
→ H 4th melody H L H H L → H 12th melody
#n2 Data
SC
ST
MTO
#n1 Play
#n1 Play
#n1 Play
#n2 Play
Melody plays repeatedly when ST is HIGH, and stops immediately when ST goes LOW.
Figure 6. Melody repetition timing
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—8
Page 9

SM1126 Series
,
,
Playback timing diagrams
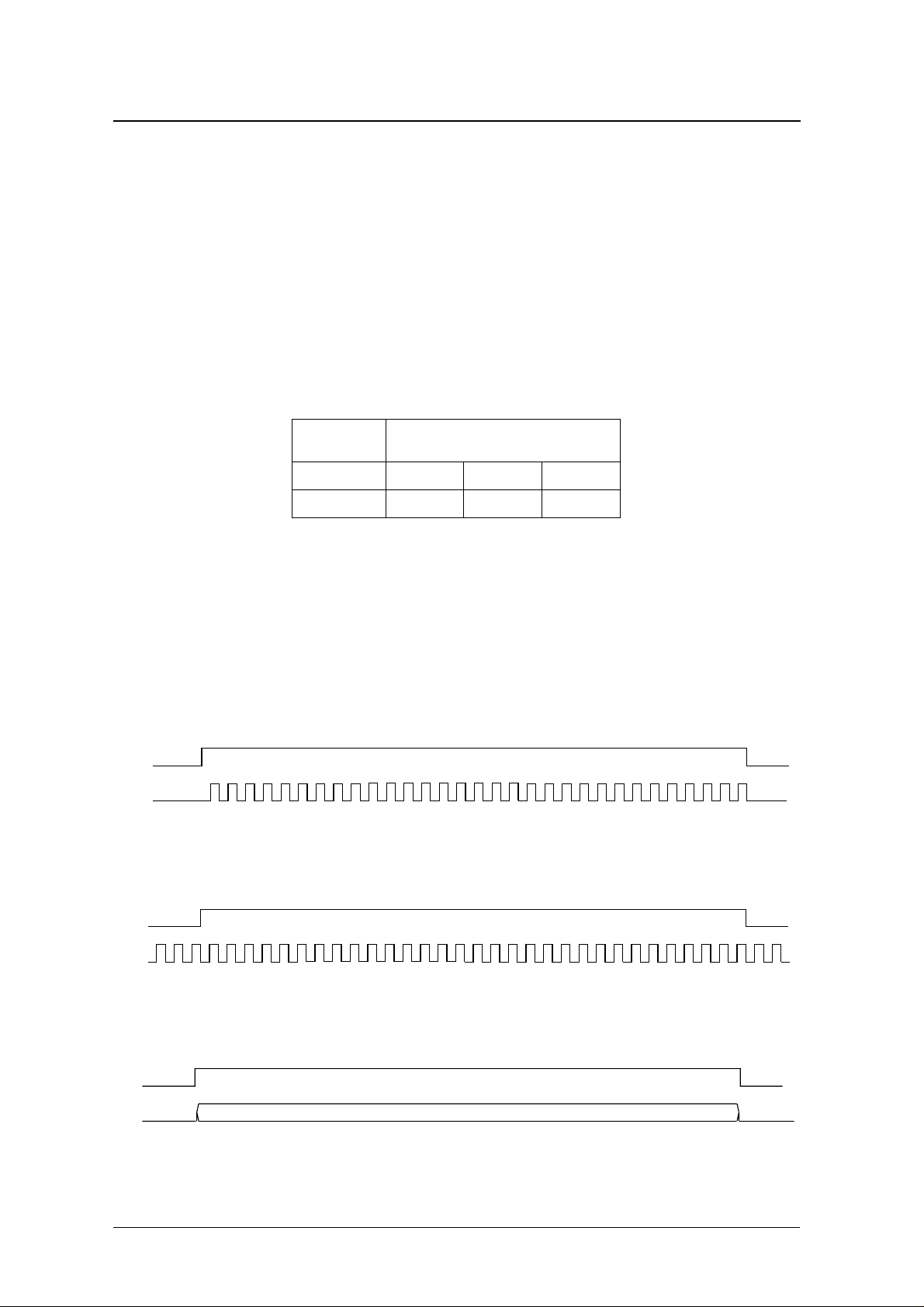
Playback start
Playback starts after an interval tST after ST goes HIGH.
When the reference clock frequency is 32.768 kHz, tST = (256 ± 1 oscillator cycles) + 1/128 seconds.
When the reference clock frequency is 38.4 kHz, tST = (300 ± 1 oscillator cycles) + 1/128 seconds.
Play Start Command
MSB LSB
SIO
SC
ST
OSC
*Internal
Clock
256(300) 1 Clock
1/128 sec
MTO
,,,
Figure 7. Playback start timing
Playback stop
Playback stops immediately when ST goes LOW. In external clock input versions, the IC internal clock also
stops when ST goes LOW, regardless of whether or not there is a clock input signal on pin OSC. In built-in RC
oscillator versions, the oscillator also stops when ST goes LOW.
ST
OSC
*Internal
Clock
MTO
,,,,,,,,,,,,,,,
Figure 8. Stop timing
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—9
Page 10

SM1126 Series
Write Mode Control
Write sequence
The SM1126 Series devices can accept data words written to the built-in SRAM to play any melody. The
SRAM write sequence is described below.
1. Write the SRAM write command (11011111) to invoke write mode.
2. Write the tempo word (parity check ON/OFF selectable).
3. Write all necessary melody data words (parity check ON/OFF selectable).
4. Write the melody end word (parity check ON/OFF selectable).
5. Optionally, write extra data words (these are ignored).
6. Write the end-of-write command (10111111) to return to play mode.
7. If parity check was ON, write the parity check command (01111111) to perform an error check.
The built-in SRAM can store 64 words, so all melody and end words must fit within this limit. Note that the
tempo word is not stored in SRAM, but in a separate register. Playback of melodies stored in SRAM begins
from the SRAM leading address and continues until the end word is detected, at which point playback continues again from the SRAM leading address. All data in SRAM after the end word is ignored.
Input write command (11011111)
Write tempo word
Write melody word (s)
Write end word
Write optional invalid data
Input end-of-write command (10111111)
Play mode
Write mode
Input write command (11011111)
Write tempo word
Write melody word (s)
Write end word
Write optional invalid data
Input end-of-write command (10111111)
Input parity check command (01111111)
Example 1. Parity check selected
Figure 9. Write control sequence
Play mode
Example 2. Parity check not selected
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—10
Page 11

SM1126 Series
Write command
The SRAM write command (11011111), shown below, is used to invoke write mode.
PLAY mode changed to WRITE mode
Address set to tempo-word register
SIO
SC
ST
1111
10
11
Figure 10. Write command timing
Tempo word
The tempo word controls the melody playback speed. The tempo word comprises a fixed code (000) followed by the tempo code (T4 to T0), as shown below. The tempo word is always the first word written after
invoking write mode, and all subsequent words are melody data words.
SIO
SC
ST
ADDRESS
WRITE command
No Address
0T4
Changed to WRITE mode
00 T3T2T1T0
write Tempo-word
Tempo Register Address
RAM Address
Figure 11. Tempo word timing
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—11
Page 12

SM1126 Series
Melody words
Melody words contain all the information needed for playback of a single note, including the note duration
and type (name or rest). Each melody word comprises a 3-bit length code (R2 to R0) followed by a 5-bit type
code (S4 to S0).
SIO
SC
ST
ADDRESS
(n-1)th data
write (n-1)th Data
(n)th data
write (n)th data
nn-1
n+1
Figure 12. Melody word timing
End word
The end word (01011111) indicates the end of the melody. When the end word is detected during melody
playback, operation returns to the SRAM leading address. All data in SRAM after the end word is ignored.
SIO
SC
01
01 1111
write END-WORD
next word
write next word
ST
ADDRESS
m+1m
m+2
Figure 13. End word timing
End-of-write command
The end-of-write command (10111111) is used to return to play mode from write mode. This command
should be executed when power is first applied to set play mode.
WRITE mode changed to PLAY mode
SIO
SC
ST
1111
01
11
Figure 14. End-of-write command timing
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—12
Page 13

SM1126 Series
Parity check command
Data words (tempo word, melody words, end word) can have an optional parity bit added, forming 9-bit data
words, for a parity check function. The parity check command is executed in play mode, immediately after the
end-of-write command is executed.
The parity bit is added at the beginning of the data word. Note that the last 8 bits are always the valid data
bits. The parity check function performs an odd parity check (an odd number of 1s within the 9-bit data). If the
parity check command is not executed, play mode operation continues using the valid 8 bits of data in each
data word.
The parity check sequence is described below.
1. The internal G flag (Good flag) is set to 1 when the write command is executed.
2. When writing data words, the G flag remains set to 1 for odd parity , but is set to 0 if even parity is detected.
3. The G flag remains set to 1 only if all data words have odd parity.
4. Write the end-of-write command to return to play mode.
5. Write the parity check command.
6. When ST is HIGH, the SIO pin functions as the G flag output.
7. When ST goes LOW, the G flag output is released.
SIO
SC
ST
MODE
SIO Condition
G Flag
END-WRITE mode command
011111
WRITE mode
11
Parity Check Command
110111
PLAY mode
Input
Figure 15. Parity check timing
When G Flag = 1
When G Flag = 0
11
Output
Input
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—13
Page 14

SM1126 Series
Command summary
Command MSB Bit 6 Bit 5 Bit 4 Bit 3 Bit 2 Bit 1 L S B
Melody start command 1000B3B2B1B0
Write command 11011111
Tempo word 0 0 0 T4 T3 T2 T1 T0
Melody word R2 R1 R0 S4 S3 S2 S1 S 0
End word 01011111
End-of-write command 10111111
Parity check command 01111111
Musical Specifications
Maximum program steps
A maximum of 256 steps can be programmed into mask-programmable ROM, and a maximum of 64 steps
(including one end word) can be stored in built-in SRAM. Each step represents either a note (sound pitch and
length) a rest, or a tie.
Note length (including rests)
Eight rhythm values for notes and rests can be programmed. Also, 2 or more notes can be musically tied.
Table 3. Rhythm values
Type
Note
Rest
01234567
x e e . q e q . h h .
Å ä ä . . g ä g . .
Code
!
!
Pitch and scale
SM1126 Series devices support 27 pitches from F4 to G6. The pitch varies with the clock frequency, as
shown in the frequency listing in table 4. The reference clock selected at master-slice does not affect the pitch
range.
Also, two pitches higher than G6 can be set as alarm pitches in mask ROM. Note that an alarm pitch option
cannot be specified in SRAM.
The frequency error calculation for a given pitch is shown below.
Error calculation: (A4 pitch with 32.768 kHz clock)
Output frequency
-------------------------------------------------
log
1200 log
Output frequency
-------------------------------------------------
2
Reference frequency
×
=
1200
10
Reference frequency
--------------------------------------------------------------log
10
×
2
3986.3 log
3986.3 log
0.63 cent– ≈
Output frequency
-------------------------------------------------
10
Reference frequency
439.839
-------------------
10
440.000
×≈
×≈
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—14
Page 15

SM1126 Series
Table 4. Frequency range
Note code System clock 32.768 kHz system 38.4 kHz system
S4 S3 S2 S1 S 0 Pitch
00000 Rest – – – – – – –
00001 F4 349.228 188 348.596
00010 F#4 369.994 177 370.260 1.24 208 369.231
00011 G4 391.995 167 392.431 1.92 196 391.837
00100 G#4 415.305 158 414.785
00101 A4 440.000 149 439.839
00110 A#4 466.164 141 464.794
00111 B4 493.883 133 492.752
01000 C5 523.251 125 524.288 3.43 147 522.449
01001 C#5 554.365 118 555.390 3.20 139 552.518
01010 D5 587.330 112 585.143
01011 D#5 622.254 105 624.152 5.27 123 624.390 5.93
01100 E5 659.255 99 661.980 7.14 1 1 6 662.069 7.37
01101 F5 698.456 94 697.191
01110 F#5 739.989 89 736.360
01111 G5 783.991 84 780.190
10000 G#5 830.609 79 829.570
10001 A5 880.000 74 885.622 11.02 87 882.759 5.42
10010 A#5 932.328 70 936.229 7.23 8 2 936.585 7.89
10011 B5 987.767 66 992.970 9.10 78 984.615
10100 C6 1046.502 63 1040.254
10101 C#6 1108.731 59 1110.780 3.20 69 1113.043 6.72
10110 D6 1174.659 56 1170.286
10111 D#6 1244.508 53 1236.528
11000 E6 1318.510 50 1310.720
11001 F6 1396.913 47 1394.383
11010 F#6 1479.978 44 1489.455 11.05 52 1476.923
11011 G6 1567.982 42 1560.381
11100 AL1 – – – – – – –
11101 AL2 – – – – – – –
11110 Tie – – – – – – –
11111End word – – – – – – –
Reference
frequency
Frequency
divider
Frequency
(Hz)
Relative
error (cent)
Frequency
divider
3.14 220 349.091
2.17 185 415.135
0.63 175 438.857
5.09 165 465.455
3.97 156 492.308
6.46 131 586.260
3.14 110 698.182
8.51 104 738.462
8.41 98 783.673
2.17 92 834.783 8.68
10.37 73 1052.055 9.16
6.46 65 1181.538 10.11
11.14 62 1238.710
10.26 58 1324.138 7.37
3.14 55 1396.364
8.41 49 1567.347
Frequency
(Hz)
Relative
error (cent)
0.68
3.58
0.70
0.71
4.50
2.64
5.53
2.66
5.78
3.16
0.68
3.58
0.70
5.53
8.08
0.68
3.58
0.70
(Note) A4 is the following note.
ú
&
===
A4 (440Hz)
Pitches AL1 and AL2 are optional alarm pitches which can take any value higher than G6, set in mask ROM.
This option is not supported in SRAM.
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
−
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—15
Page 16

SM1126 Series
Tempo
There are 29 tempos that can be selected for each melody. The tempo does not vary with the clock frequency .
Table 5. Tempo range
Code Frequency divider Tempo
03 4
04 5 256.0
05 6 213.3
06 7 Presto 182.9
07 8
08 9 142.2
09 10 128.0
0A 11
0B 12 106.7
0C 13
0D 14 91.4
0E 15 85.3
0F 16 80.0
10 17
11 18 71.1
12 19 67.4
13 20
14 21 61.0
15 22
16 23 55.7
17 24 53.3
18 25 51.2
19 26 49.2
1A 27 47.4
1B 28 45.7
1C 29 44.1
1D 30 42.7
1E 31 41.3
1F 32 40.0
Prestissimo
Allegro
Moderato
Andante
Adagio
Larghetto
Largo
320.0
160.0
116.4
98.5
75.3
64.0
58.2
Quarter note ( q ) length = {1536 (32.768 kHz system) or 1800 (38.4 kHz system)} × tempo counter frequency
divider ÷ clock frequency
(Ex. 1) Tempo code = 1F (divider = 32), clock frequency = 32.768 kHz (32.768 kHz system)
1536 × 32 ÷ 32768 = 1.5 (seconds)
(Ex. 2) Tempo code = 18 (divider = 25), CLK frequency = 153.6 kHz (38.4 kHz system)
1800 × 25 ÷ 38400 = 1.17 (seconds)
q =
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—16
Page 17

TYPICAL APPLICATION
External Clock Input Versions
SM1126 Series
2.0V to 3.6V
B +
CONTROLLER
Built-in RC Oscillator Versions
2.0 to 3.6V
CONTROLLER
RO
C
OSC
SIO
SC
ST
OSC
SIO
SC
ST
O
VSS
VDD
MTO
TEST
B +
VSS
VDD
MTO
TEST
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—17
Page 18

SM1126 Series
OSCILLATOR FREQUENCY MEASUREMENT
The measurement circuit below shows a SM1126 ×× V with built-in RC oscillator circuit and external RC
oscillator components capacitor C
When ST is switched to V
of the RC oscillator. The output pulse is counted using a frequency counter.
and resistor R
O
, the oscillator starts and outputs a pulse on MTO with a frequency double that
DD
.
O
RO
CO
Switch
Note that the board mounting and wiring will marginally affect the output frequency, even for equivalent values for R
SM1126 V
OSC
SIO
SC
ST
MTO
TEST
V
VSS
DD
Frequency Counter
and C
O
.
O
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS INC. reserves the right to make changes to the products described in this data sheet in order to
improve the design or performance and to supply the best possible products. Nippon Precision Circuits Inc. assumes no responsibility for
the use of any circuits shown in this data sheet, conveys no license under any patent or other rights, and makes no claim that the circuits
are free from patent infringement. Applications for any devices shown in this data sheet are for illustration only and Nippon Precision
Circuits Inc. makes no claim or warr anty that such applications will be suitab le for the use specified without further testing or modification.
The products described in this data sheet are not intended to use for the apparatus which influence human lives due to the failure or
malfunction of the products. Customers are requested to comply with applicable laws and regulations in effect now and hereinafter,
including compliance with export controls on the distribution or dissemination of the products. Customers shall not expor t, directly or
indirectly, any products without first obtaining required licenses and approvals from appropriate government agencies.
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS INC.
4-3, Fukuzumi 2-chome
Koto-ku, Tokyo 135-8430, Japan
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS INC.
Telephone: 03-3642-6661
Facsimile: 03-3642-6698
NC9722BE 1998.12
NIPPON PRECISION CIRCUITS—18
 Loading...
Loading...