Page 1
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
1
10-DIGIT SCIENTIFIC CALCULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The SC3445 is a one-chip CMOS LSI for a hand calculator with
mathematical functions and a 10 digits variable mode exponential
type liquid crystal display.
FEATURES
* Built-in ROM capacity: 64 X63 X8 bits
* Built-in RAM capacity: 12X16X4 bits
* RC oscillator Internal operation: 100kHz (3V TYP. Resistance:
200KΩ)
* Current consumption:
Display: 80µA (3V TYP)
Off: 3µA(3Vmax)
* LCD driver: 1/4 duty, 1/3 bias
* Single power supply: 2.7V to 3.3V
* Automatic power off
* Operand: 4 bits
* C-MOS metal gate process.
* Not designed or rated as radiation hardened.
* Not programmable (on chip programmed ROM).
* A memory that holds up to 40 steps to make for easy repeated
calculations.
SC3445
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
13
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
25
262728293031
* A full complement of 46 mathematical
functions.
* Automatic priority of operations logic
and parentheses nesting up to 7
deep for simplified calculations.
* Memory protection with power off (3
memories and program memory).
* A handy storage memory for
conversion calculations.
* An automatic power off feature to
preserve battery life.
Page 2
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
2
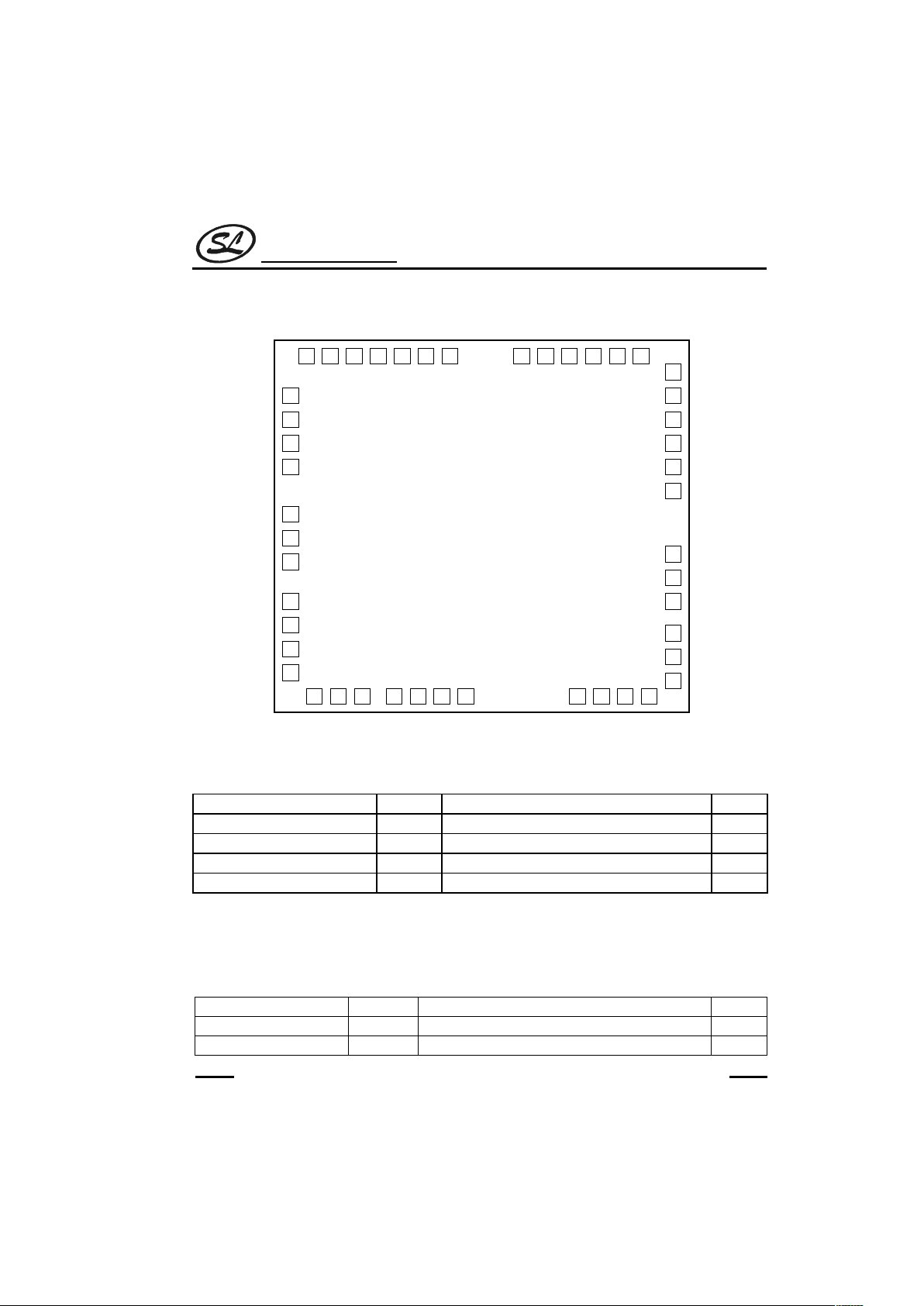
PAD ASSIGNMENT
K4
H2 H3 b12 a12 b11 a11 b10 a10 b9 a9 b8
a8
b7
a7
b6
a6
b5
a5
b4
a4
b3
a3
b2
a2b1a1H4S1
K3
K2
K1
CI
CO
GND
TE
S10
S9
S8
S7 S6 S5 S4 S3 S2
H1V
GG
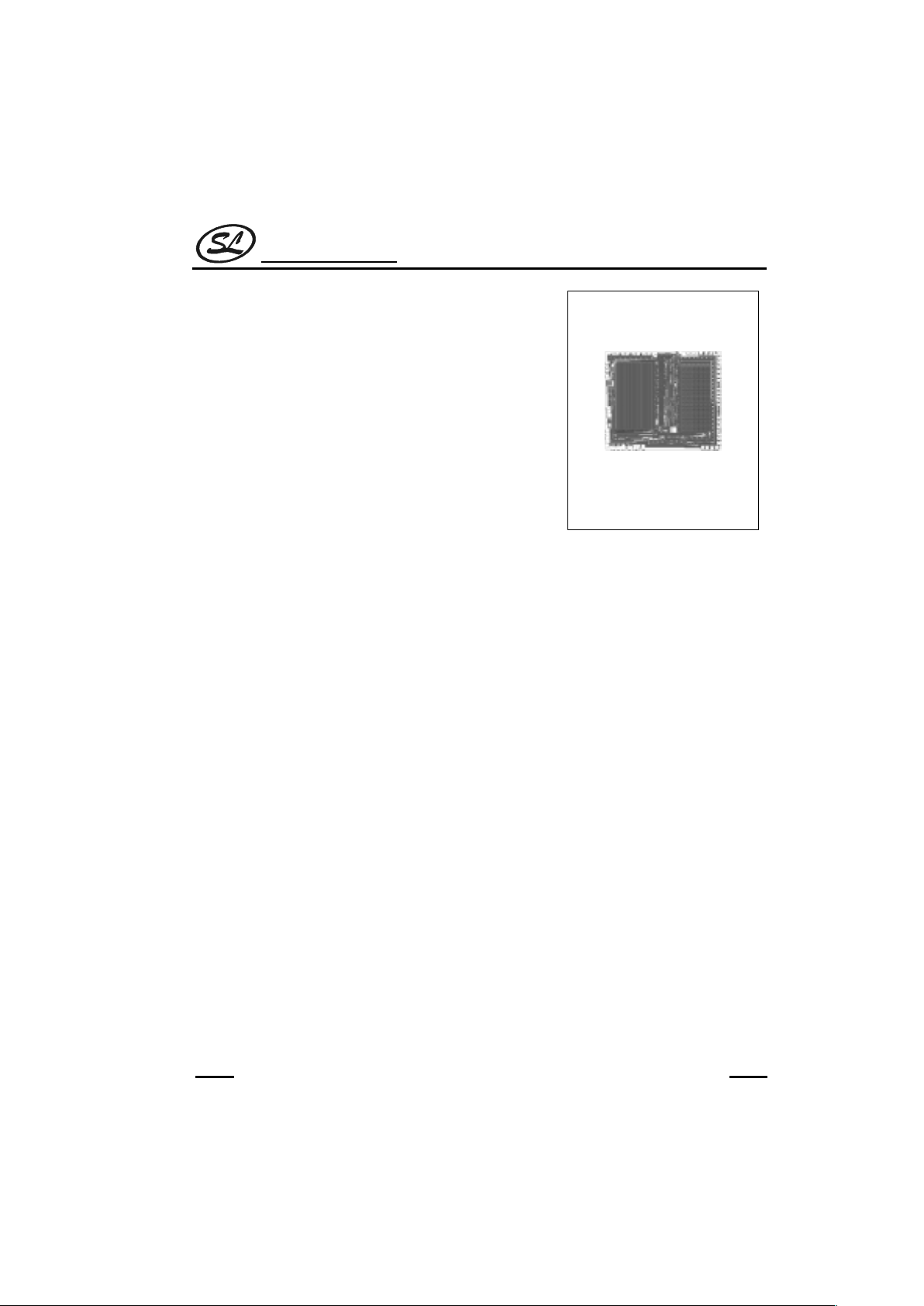
SC3445
size:5.63 x 4.93 mm
2
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATING
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Terminal 1 Voltage VT1 -0.3~-4.0
Note1
V
Terminal 2 Voltage VT2 -0.3~VGG+0.3
Note2
V
Operating Temperature Topr 0~50 °C
Storage Temperature T
STG
-55~+150 °C
Note: 1. The maximum voltage can be applied to the VGGterminal.
2. The maximum voltage that can be applied to all terminals other than V
GG
terminal with respect to the
GND terminal.
OPERATING CONDITIONS
Characteristic Symbol Value Unit
Supply Voltage V
CC
-3 ± 0.3 V
Oscillator Resistor RF 200 ± 10 kΩ
Page 3
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
3
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
(Ta=25°C, V
DD
=3.0V,Unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol Test conditions Min Typ Max Unit
-V
IH
0.6
Input Voltage
note1
-V
IL
VGG+0.6
V
Input Current
note1
I
IH
VIH=0V 25 µA
-V
OH
IOH=30µA0.3
Output Voltage 1
note2
-V
OL
No load VGG+0.3
V
-V
OA
No load 0 0.3
-V
OB
No load 0.7 1.3
-V
OC
No load 1.7 2.3
Output Voltage 2
note3
-V
OD
No load 2.7 3.0
C
Display Frequency
note3
f
D
55 Hz
Current Consumption 1
note4
I
GG1
Display shows (DEG 0.) µA
Current Consumption 2
note4
I
GG2
In power off mode 3 µA
Note: 1. Applies to terminals K1~K4, and TE
2. Applies to terminals S1~S10.
3. Applies to terminals H1~H4, a1~a12, and b1~b12
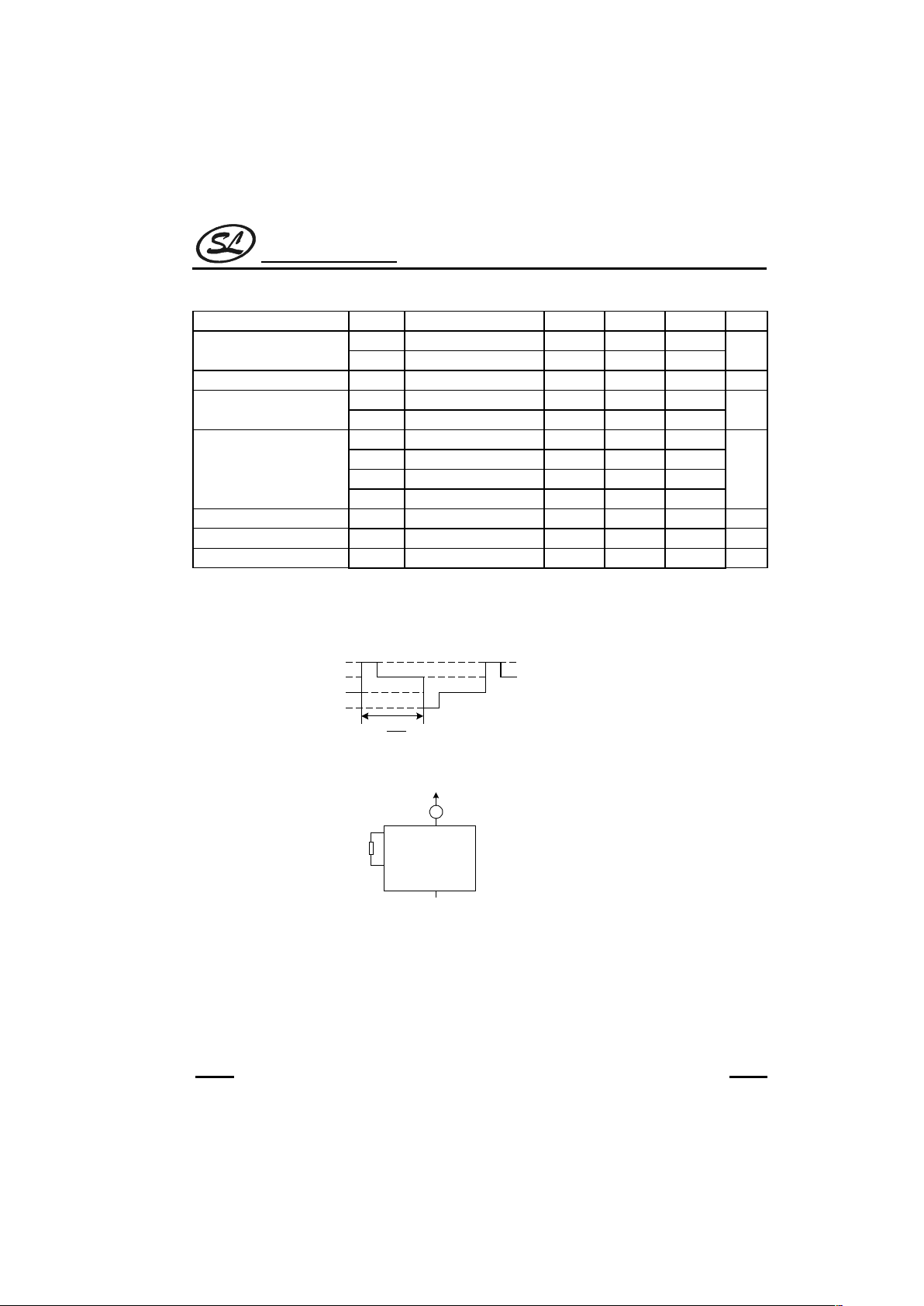
Typical wave form
V
OA
V
OB
V
OC
V
OD
fd
1
4. Measurements were made with the circuit shown in the figure below.
CI
CO
V
GG
GND
A
0V
-3V
R
f
LI-3301
Page 4
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
4
PIN DESCRIPTION
Pin No. Symbol Description Pin No. Symbol Description
1 K4 Key input 25 b2 Segment signal
2 H2 Common signal 26 a2 Segment signal
3 H3 Common signal 27 b1 Segment signal
4 b12 Segment signal 28 a1 Segment signal
5 a12 Segment signal 29 H4 Common signal
6 b11 Segment signal 30 H1 Common signal
7 a11 Segment signal 31 VGG -3 volt power source
8 b10 Segment signal 32 S1 Key strobe
9 a10 Segment signal 33 S2 Key strobe
10 b9 Segment signal 34 S3 Key strobe
11 a9 Segment signal 35 S4 Key strobe
12 b8 Segment signal 36 S5 Key strobe
13 a8 Segment signal 37 S6 Key strobe
14 b7 Segment signal 38 S7 Key strobe
15 a7 Segment signal 39 S8 Key strobe
16 b6 Segment signal 40 S9 Key strobe
17 a6 Segment signal 41 S10 Key strobe
18 b5 Segment signal 42 TE T est use
19 NC -- 43 GND 0 volt power source
20 a5 Segment signal 44 C0 Oscillator use
21 b4 Segment signal 45 C1 Oscillator use
22 a4 Segment signal 46 K1 Key input
23 b3 Segment signal 47 K2 Key input
24 a3 Segment signal 48 K3 Key input
Page 5
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
5
KEY SPECIFICATIONS
2ndF
DRG
K1EXP
COMP
sin
Lny
x
cos
log
tan
x
2
OFF
(
ON/C
CE
)
7
4
1
0
8
5
2
+/-
9
6
3
x
-
+
RM
M+
=
∑
x
2
s
δ
DATA
n!
1/x
tan
-1
cos
-1
sin
-1
10
x
3
Y
x
e
x
K1
x
HYP
π
DMS
RND
LRN
DEG
FE
TAB OFFB STAT
[X] HLT
K2
K2
x
x
CD CAD
n
∑
x
M
x
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
1. KEY SPECIFICATIONS
(1). 2ndF Second function select key
* The key is used to select the second function on those keys having two functions.
* Pressing the key twice in a row acts to clear the 2
nd
function selection.
* 2F shows on the display when the second function has been selected.
(Example)
e
x
1 . 2 3 2ndF Ln
gives e
1.23
as a result.
1/x
4 2ndF 2ndF x
2
Gives 42as a result.
Note 1. Specifying the 2
nd
function only applies to the key pressed immediately thereafter.
2. The 1
st
and 2ndfunctions will hereafter be expressed as shown below.
(Example)
1/x
x
2
→
1: x
2
(1stfunction)
2: 2ndF 1/x (2md function)
Page 6

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
6
(2). LRN
COMP
1: The compute key
2: The key used to set and clear program mode.
• When not in program mode, this key is used to execute the steps in program memory and
to restart execution after it has stopped to allow variable entry or viewing of the display.
• Used to set and clear the program mode.
When program mode is selected LRN shows on the display. A maximum of 40 program
steps may be stored in memory.
(3). TAB
F-E
1: Used to switch between display modes.
2: Used to set the number of digits displayed after the decimal point.
• Pressing the key causes the display to switch back and forth between floating point and
exponential display modes while either a final or intermediate result is being displayed.
• Used to set the number of digits displayed after the decimal point in either final of
intermediate results. However, the display is an underflow type in which high order digits
take precedence.
2ndF
TAB
0~6
Digits are displayed to the right of the decimal point.
2ndF
TAB
7, 8, 9, ⋅
The floating point format is selected.
Note: The 1: and 2: keys are inactive immediately after or during numerical input.
(4). OFFB
OFF
1: Power off key
2: Backup memory power off key
* Both 1 and 2 turn power off.
• ON/C is used to turn power on with the memory, program memory, and all register
contents cleared.
• ON/C is used to turn power on with the contents of all memories as they were prior to
power off.
(This is the same as when the automatic power off occurs.)
(Example)
Display
ON/C
123
X 2ndF OFFB
123.
ON/C
56088.
456 =
Page 7

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
7
(5). STAT
ON/C
1: Power on / clear key
2: Sets and clears the statistical mode
• OFF, 2ndF OFFB or automatic power off sequences followed by pressing this key turns
power on.
* Clears an error condition
Statistical mode set (STAT) clear (
STAT
) and program mode set (LRN) clear (
LRN
)
sequences cause the following:
* STAT LRN: Except for statistical data all values in program memory, calculation
commands and data input is cleared.
*STAT
LRN
: Except for statistical data and program memory all calculation commands
and data input is cleared.
*
STAT
LRN: Except for data memory, program memory, calculation commands and
data input is cleared.
*
STAT LRN
: Except for data and program memory all calculation commands and data
input is cleared.
* If pressed during execution of program commands the execution is halted. (Hold until
the display comes on.)
• Both sets and clears the statistical mode
* When statistical mode is set the STAT symbol appears and except for program memory,
all contents, including the memories, are cleared and the keys take on the meanings as
shown below.
* When statistical mode is cleared, all contents, including the memories, are cleared,
except for the program memory and the number being displayed and the STAT symbol
disappear.
K1
K1
x
K2
K2
x
M
x
RM
M+
CD
CAD
n
Σ
x
x
∑
x
2
s
DATA
δ
STATSTAT
Page 8
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
8
(6). HYP
DRG
1: Selects angular units.
2: Selects hyperbolic functions.
• This key selects angular units for use with trigonometric and inverse trigonometric function
calculations.
Pressing the key cycles through
DEG RAD GRAD DEG
DEG : Treatthe input as a base 10 decimal degree value. [ ° ]
RAD : Treat the input as a radian value. [rad]
GRAD : Treat the input as a grade value. [ g ]
(90°=π/2 rad=100g)
• Selects and clears the hyperbolic function mode.
* When the hyperbolic function mode is selected HYP is displayed.
(Example)
2
2ndF HYP SIN
→ Sinh2
3
2ndF HYP 2ndF HYP SIN
→ Sin 3
4
2ndF HYP 2ndF SIN
-1
→ Sinh-14
(7).
HYP
HYP
sin
sin
-1
1: Trigonometric function key 1: Hyperbolic function key
2: Inverse trigonometric function 2: Inverse hyperbolic function key
(8).
cos
cos
-1
(9).
HYP
tan
tan
-1
1: Press to perform trigonometric calculations (sin cos tan).
(Example)
Set DEG
30 SIN
→ 0.5
2: Press to perform inverse trigonometric calculations (sin
-1
cos-1tan-1)
(Example)
Set DEG
30 2ndF TAN
-1
→ 45.
HYP
1: Press to perform hyperbolic function calculations. (sinh cosh tanh)
(Example)
2 2ndF HYP SIN
→ 3.626860408
2: Press to perform inverse hyperbolic function calculations. (sinh
-1
cosh-1tanh-1)
(Example)
3 2ndF HYP 2ndF SIN
-1
→ 1.818446459
Page 9
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
9
(12).
CE
n!
1: Clear entry key
2: Factorial key
• Used to correct a mistaken numerical entry.
(Example)
1.23CE
→ 0.
1.24 → 1.24
• Used to perform factorial calculations.
(Example)
5 2ndF n!
→ 120.
(13).
y
x
Y
x
1: Power key
2: Root key
• Used to raise Y to the x power.
(Example)
24→ 2YX4=
→ 16.
• Used to take the X root of Y.
(Example)
4
16
→ 16 2ndF
x
Y
4=
→ 2.
(14).
Ln
e
x
1: Natural logarithm key
2: Exponential key
• Used to calculate logarithms to the base e (≈2.718281828).
(Example)
Ln 2 → 2Ln
→ 0.693147181
• Used to raise e to a given power.
(Example)
e4→ 4 2ndF e
x
→ 54.59815003
(15).
log
10
x
1: Common logarithm key
2: Common anti-logarithm key
•. Used to calculate logarithms to the base 10.
(Example)
Log 2 → 2 Log
→ 0.301029996
• Used to calculate the anti-logarithm in base 10
(Example)
10
1.2
→ 1.2 2ndF 10
x
→ 15.84893193
Page 10
Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
10
(16).
(
[]
1: Open parenthesis key
2: Specify variable key
• Used to open parentheses when they are used in a calculation.
(Example)
2 x ((22–6)÷ )3=
2( )22-6) ÷ 4) Y
X
3=
→ 128.
• When entering a program into memory it is pressed just before a variable would be
entered.
* By specifying a variable it is possible to have the execution of program steps
stopped momentarily to allow variable input.
(17).
)
HLT
1: Close parenthesis key
2: Temporarily halt calculation key
• Used to close parentheses when they are used in a calculation.
• The execution of program steps can be temporarily halted to allow the viewing of
intermediate results or to interrupt calculations by pressing 2ndF HLT when
entering program steps.
(18).
EXP
π
1: Exponent select key
2: π key
• Used to enter the exponent part of a number.
(Example)
1.2x10
-23
→
1.2EXP+/-23
100000 →
EXP 5
• Used to enter the value of π.
(19).
3
1: Square root key
2: Cube root key
• Calculates the square root of a number.
(Example)
2
→ 2
→ 1.41421362
• Calculates the cube root of a number.
(Example)
3
8
→ 8 2ndF
3
→ 2.
Page 11

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
11
(20).
x
2
1/x
1: Square key
2: Reciprocal key
• Squares a number
(Example)
1.232→ 1.23 X
2
→ 1.5129
Takes the reciprocal of a number.
(Example)
1/8 → 8 2ndF 1/x
→ 0.125
(21).
K1
K1
x
STAT
STAT
CD CAD 1: Storage memory key
1: Correct data key
2: Storage memory input key 2: Clear all data key
STAT
• Used to call recall the contents of storage memory when pressed after the
ON/C,(,+,-,x,÷ ,Y
X
, or 2ndF ,
X
Y
etc.
keys.
* Storage memory contents are recalled even though the result of the
calculation may be 0.
* If pressed when the entered value or the value being displayed is other
than zero, the displayed value and the storage memory contents are
multiplied together.
• Used to enter the displayed value into storage memory.
(Example)
1 . 2 3 2ndF x→K1
2+ K1
→ 1.23
K1
→ 1.5129
=
→ 3.5129
STAT • Press when it is desired to correct data input.
• Press when statistical calculations in new input data are desired.
* All statistical calculation data is cleared.
(22).
K2
K2
x
STAT
STAT
CD CAD 1: Storage memory key
1: Sample number key
2: Storage memory input key 2: Grand total key
STAT
• SeethesectiononstoragememoryK1.
STAT • Recalls the number of data input (number of samples).
• Used to calculate the grand total of input data.
Page 12

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
12
(23).
STAT
STAT
x
M
∑
x
2
x
1: Memory input key 1: Average value key
2: Sum of squares key
STAT
• Used to enter the value displayed into memory.
* The value entered replaces any previously stored value.
* Pressed after pressing ON/C clears the memory.
STAT • Used to calculate the average of the data values.
• Used to calculate the sum of the squares of the data.
(24).
STAT
STAT
RM
S
δ
1: Recall memory key 1: Sample standard deviation key
2: Population standard deviation key
STAT
• Pressed to recall the contents of memory.
* The contents of memory remain unchanged.
STAT • Used to calculate the sample standard deviation (S).
• Used to calculate the population standard deviation (δ).
(25).
STAT
STAT
M+
DATA
1: Memory plus key 1: Data entry key
STAT
• Pressing this key after any of the + , - , x , ÷ ,YX,2ndF,
X
Y
function keys causes the result of the calculation to be added to
memory. Otherwise the displayed value is simply added to memory.
* To subtract from memory, just use the +/- key to change the sign of
the value and press the key.
STAT • Press to enter data for statistical calculations.
(26).
DMS
2: Decimal degrees → degrees, minutes, seconds conversion key.
• Converts degrees in decimal form to degrees, minutes and seconds.
(Example)
12.5125degrees → degrees minutes and seconds.
12.30452ndF →DMS
→ 12.3045
Page 13

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
13
(27).
x
DEG
2: Degrees, minutes and seconds → decimal degrees conversion key
• Converts degrees, minutes and seconds to decimal degrees.
(Example)
12 degrees 30 minutes 45 seconds → degrees
12.30452ndF →DEG
→ 12.5125
(28).
+
-
1: Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division keys
X
• Press the keys in algebraic order to perform addition, subtraction, multiplication
and division (four basic operations).
÷
* The four basic function keys and the power and root keys select the given
functions and they can be used to correct mistaken function entry by simply
pressing the correct key.
(Example)
2+ x 3 =
→ 6.
(29).
=
Equal key
Cause the four basic operations, power and root function performed.
(30).
0~9
Number key
Press to enter numerical Values.
(31).
·
Decimal point key
Used to set the decimal point when entering number.
(32).
+/-
1: Sign change key
Used to change the sign of a display number
2: Exchange key
Used to exchange the display number with the contents of an internal register.
Page 14

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
14
2. DISPLAY SPECIFICATIONS
(1). Display elements
FEM Liquid crystal 1/4 duty 1/3 bias V
P-P
3V fd typ 100 Hz
(2). Display contents
LRN STAT
GRAD M
RAD DEG E
1) Digits displayed
* Floating point display has 10 digits
* Exponential display has an 8 digit mantissa witha2digitexponent.
2) Symbols displayed
STAT : Indicates that statistical mode has been selected.
M : Indicates that a value is stored in memory.
_ : Appears to the left of the mantissa or exponent to indicate that the respective
values are negative
E : Indicates and error condition.
LRN : Indicates that the store program mode has been selected.
GRAD : Indicates that gradient units have been selected.
RAD : Indicates that radian units have been selected.
DEG : Indicates that degree units have been selected.
3) Other
: Displayed when the second function has been selected.
: Displayed when the hyperbolic function has been selected.
: Display when the ( is pressed, it shows the level of nesting
presently existing. (Parentheses display goes to a maximum
of 11 deep)
: Shows the place where 2ndF [ x ] was pressed in program
mode and where execution of program steps halts to allow
variable entry. The number in brackets shows the number of
the place of the variable, and goes from 1-40
Page 15

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
15
E
: Appears when storage memory K1 or K2 is holding the result
of a low priority calculation when either 2ndF x→K1 or 2ndF
x→K2 to indicate an error condition,
E
E
E
: An error message display when a low priority calculation
cannot be saved.
Is it ok to clear program steps?
Is it ok to clear storage memory K1?
Is it ok to clear storage memory K2?
(3). Display format
1) A calculation result that lies within the following range is shown in floating decimal point form.
0.000000001<=1x1<=9999999999.
Results outside this range are displayed in exponential (scientific notation).
However, the floating point display can be changed to scientific notational display by using the F – E key.
2) All calculations are done in exponential form, the result displayed being the mantissa with the 11thplace
rounded off.
3) Using TAB to fix the number of decimal places shown causes the (TAB+ 1) place to the rounded off to fit the
TAB specification.(However, the display is a high order digit priority underflow type.)
(4). Liquid crystal pattern sectioning
Segment
LRN
GRAD
RAD
DEG
STAT
M
E
b12 a12
bi ai (i=1~11)
Common
LRN
GRAD
RAD
DEG
STAT
M
E
H1
H2
H3
H4
(5). Shape of the displayed numbers
Page 16

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
16
(6). Typical display
H1
H2
H3
H4
a1
a2
GRAD
Page 17

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
17
a
2
a
4
b
4
b59b
12
b
2
a
3
bi (i=396~11)
ai (i=5~11)
Page 18

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
18
3. CALCULATION SPECIFICATIONS
(1). Digits in the operation Mantissa Exponent
Data entryLLLLLLLLL 10 digits + 2 digits
OperandLLLLLLLLLL 12 digits + 2 digits
OperatorLLLLLLLLLL 12 digits + 2 digits
ResultLLLLLLLLLLL 11 digits + 2 digits
(The 12
th
place in the mantissa is rounded off in the result.)
(2). Operation typeLLLLLLLLLLHigh order digit priority underflow type.
(3). Calculation order of priority
Because there is automatic priority of operations logic the calculations may be performed as
expresses in the equation. (Calculation order of priority)
1: Function calculations
2: Calculations in ( )
3: Power and root calculations
4: Multiplication and division
5: Addition and subtraction
(Where the priority of two operations is the same they are performed in the order in which they
appear.)
(Example)
Key in and order of operation information for the equation 2 + 3 x (Ln4)³ x ( 5 + 6 ) =
2 +3X4 Y
X
LN 3 (5+6=
1
2
3 4
5
* When execution starts with high priority calculations it is necessary to save low priority calculations,
and for that reason there are 6 internal storage levels supplied.
* These storage levels are also used in calculations involving parentheses; therefore do not exceed 6
levels the calculations may be performed as they appear in the equation.
* The internal storage levels used for low priority calculations may also use storage memories (K1 K2),
and program memory. When saving calculations exceeds 6 levels the error message belowappears.
Page 19

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
19
1:
E
(Ok to clear K2 ?)
2:
E
(Ok to clear K1 ?)
3:
E
(Ok to clear program memory ?)
* Pressing 2ndF causes the display to cycle through 1: → 2: → 3: → 1: giving the user the
choice of which memory to clear.
Pressing CE when it is OK to clear causes the appropriate memory to be cleared, freeing it for saving
calculations and allowing the calculation to proceed
(4). Error conditions
1) The value entered, or intermediate or final results of a calculation exceed 1 x 10¹ºº (Including memory
calculations)
2) Divide by zero error.
3) The number of low priority storage levels exceeds 6 in a parentheses calculation.
* Even if the number of levels is within 6 an error may occur if storage memories K1, K2 or program
memories are being used.
4) When trying 2ndF X→K1 or 2ndF X→K2 while the storage memories are being used for low priority
calculation storage.
5) When trying a calculation out of the range (to be described later) for functional and statistical
calculations.
6) When trying to store over 40 steps while in program storage mode.
(5). Protection
1) Key chattering and bounce protection
Input pulse is stable 2 msec after entry and 40 msec after release at fop=59 KHz
2) Memory and program protection
* The contents of the independent memory, storage memories (K1 and K2) and program memory are all
preserved in the stare just prior to the error condition regardless of the type of error.
* They are also preserved even when power is turned off.
(However, if statistical mode was specified all memories are cleared and used to store data for
statistical calculations) Therefore, the statistical data existing just prior to an error in statistical
calculations is preserved.
3) Backup at power off
* Even if power off occurs by an automatic power off, all contents are preserved, as they were just prior
Page 20

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
20
To power off, however, when power off occurs by a 2ndF OFFB, signs of are not
preserved.
4) When an error occurs, to prevent the calculation from continuing all keys except for the ON/C OFF
keys are ignored. (However if the error occurred because calculation priority saves could not be done
even though they were within the 6 levels then the error condition is 4) and the CE key may be used to
clear the error and continue the calculation.)
(6). Automatic power off
* If after pressing a key, another is not pressed for about 8 minutes the power is automatically shut off,
however, going on pressing ON/C key, the power is not shut off.
* All contents are preserved as they were just prior to power off.
(7). TAB (Decimal digit display) function
See the section on the decimal digit display key
(Example)
5
÷
9
=
→
0.555555556
2ndF
TAB
2
→
0.56
2ndF
TAB
5
→
0.5556
2ndF
TAB
1
→
0.6
F–E
→
0.6–0.1
ON/C
→
0.0
2ndF
TAB
Ȏ
→
0.
* As a rule, once the number of decimal digits to be displayed is set it does not change until it is reset.
* Setting or clearing statistical mode, doing 2ndF CAD in statistical mode, or pressing ON/C after OFF
sets floating point mode.
* Using storage memory K1 to save low priority calculations causes the decimal digit display to be cleared
and go to floating point mode.
(8). Auto- clear function
* When the LSI has power applied to it all memory contents and modes are cleared, degree units are
selected and floating point mode is selected. (This is not the same as the ON/C power on)
Page 21

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
21
(9). Types of operations
Addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
Constant calculations * The addend in addition, subtrahend in subtraction multiplicand in
multiplication. The divisor in division and the x value in power (Y
X
) and root
(
X
Y ) calculations takes on the value of the constant.
(Example)
1: 123+ 456=
7:
123÷ 5
=
2: 789+ 456
=
8:
456÷ 5
=
3:
123− 456
=
9:
7
4
=
4:
789− 456
=
10:
8
4
=
5: 123
x456=
11:
_
5
127
=
6: 123x789=
12:
_
5
1024
=
No Key Strokes Display
1:
123 + 456
=
579
2: 789
=
1245.
3:
123 − 456
=
-333.
4: 789
=
333
5:
123 x 456
=
56088.
6: 789
=
97047.
7:
123 ÷ 5
=
24.6
8: 456
=
91.2
9:
7Y
X
4 =
2401
10: 8
=
4096.
11:
1 2 7 2ndF
X
Y
5
=
2.634879413
12: 1024
=
4.
* When chained calculations have been done the last calculation performed and value become the
constant.
(Example)
a+ bxc=
→
+ b c (constant addition)
ab− c
= →−c
(constant subtraction)
a ÷ bx
c= →
a/b x (constant multiplication)
ab÷ c
= →÷c
(constant division)
aY
X
bYXc =
→
YXc (constant power)
aY
X
b
x
y c =
→
x
y c
(constant root)
Page 22

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
22
Memory calculations
Independent memory
* Input and output to the independent memory is done by pressing x→MMRM+
See the section on key specifications.
(Example)
123x2
456x3
789x4
+) 1234
Total
Key strokes Display
ON/C
X→M
M0.
123 x 2
M+
M 246.
456 x 3
M+
M 1368.
789 x 4
M+
M 3156.
1234
M+
M 1234.
RM
M 6004.
Storage memory
LLLLLLSee the section on key specifications
* Conversion function LLLthe storage memory have conversion capabilities
(Example)
1 dollar equals 210 yen
• How much is 6 dollars in yen?
• How many dollars is equal to 5 objects at 5250 yen each?
NO
Key strokes Display
2 1 0 2ndF X→K1
210.
1:
6K1
1260.
2:
5250 X 5 ÷ k1 =
125.
* Selecting statistical mode clears the independent memory and memories K1 and K2 making them
available for statistical data use.
Calculations with parentheses
* Parentheses are used when it is desired to perform calculations in an order than usually followed for
the +, −, ×, ÷,Y
x
,
x
y
operations.
* In other words the “(“ forces those operations prior to it to be pending until the calculations inside the
parentheses are performed.
Page 23

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
23
* Parentheses may be used in a chained calculation as long as the total of levels pending due to
the automatic priority logic and parentheses does not exceed 6.
* Parentheses may be nested up to 7 deep in one level.
* Up to 11 are displayed after pressing the ( key.
* Pressing ( right after numerical entry, function calculation or memory recall gives the same
results as pressing × (.
* If ( is the first part of an equation it may be omitted.
* A ) immediately after = of m+ may be omitted.
(Level usage example)
a+bxcyx(dH(e+f))=4levelusage
123 4
(Example)
• 72 x ( ( ( 56 + 23 ) x 2 ) − 72 ÷ 4)=
• 2+ 3x(3+4x(2+3x(sin30÷ 2)
2
))=
(Less than 10 program steps are used and there are numbers in storage memories
K1 and K2.)
NO Key strokes Display
1:
72 (
((
[[[
56 +
23 ) x 2 )
158.
− 72 ÷ 4=
10080.
2:
2+
3(3+
3.
4(
0ToSTo2
CE
2+3(
0ToSTo1
CE
0ToL
CE
[[[
30SIN
÷ 2)
0.25
X
2
=
37.25
Function calculations
See the Key specifications section
* Trigonometric functions (sin cos tan)
* Inverse trigonometric functions (sin
-1
cos–1tan-1)
* Decimal, minutes seconds → decimal degrees (→DEG)
* Decimal degrees → degrees, minutes, seconds (→DMS)
* Hyperbolic functions (sinh cosh tanh)
* Inverse hyperbolic functions (sinh
-1
cosh-1tanh-1)
Page 24

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
24
* Logarithm functions (Ln Log)
* Exponent functions (e
x10x
)
* Power functions (Y
X
)
* Square root
(
x )
* Cube root
(
3
x )
* Square (x
2
)
*Reciprocal
(
x1 )
* Root functions
(
x
y )
* Factorial (n!)
Statistical calculations
* Use 2ndF STAT to set the statistical mode.
* Since statistical mode cannot be set while in program mode you must first press 2ndF LRN to
leave program mode before specifying statistical mode.
* When statistical mode is selected the independent memory and storage memories K1 and K2 are
cleared and used for storing statistical data.
* Data and it’s frequency may be input. If a mistake is made in inputting data use the CD key to
make corrections. See example 1:
* When in statistical calculation mode low priority calculation storage can have a maximum of 4
levels.
* Toclear all statistical data press 2ndF CAD.
* Toclear statistical calculation mode press 2ndF STAT .
Average x=
∑
n
x
Sample standard deviation s =
1n
nxx
2
−
∑
−
(Used to infer the population standard deviation by extracting sample data from the population.)
Population standard deviation δ =
n
nxx
2
∑
−
(Used to find the standard deviation taking the whole population as the sample. Also used to find
the standard deviation when the sample is taken as the population.)
(Example)
• The average score and standard deviation is found from the data in the table below
which has the results of a test for 35 people.
Score 2030405060708090100
Number of people 1 1 2 4 4 8 9 5 1
Page 25

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
25
What does the average score and standard deviation become if the person who scored 20 instead
scored 30,and the 2 people who scored 40 had scored 50 instead?
Key Display Note
2ndF
STAT
STAT 0 .
20
DATA
STAT 1 . Note1
40
DATA
STAT 2 . Note1 Note2
CD
STAT 1 . Note1 Note3
30
DATA
STAT 2 . Note1 Note4
40 X
2
DATA
STAT 4 . Note1
50 X
4
DATA
STAT 8 . Note1 Note5
61 X
5
DATA
STAT 1 3 . Note1 Note6
CD
STAT 8 . Note1
60 X
4
DATA
STAT 12. Note1
70 X
8
DATA
STAT 20. Note1
80 X
9
DATA
STAT 29. Note1
90 X
5
DATA
STAT 34. Note1
100
DATA
STAT 35.
X
STAT 68.57142857
S
STAT 18.49369641
2ndF
δ
STAT 18.22758618
20
CD
STAT 34. Note1
40 X
2
CD
STAT 32. Note1
30
DATA
STAT 33. Note1
50 X
2
DATA
STAT 35. Note1
X
STAT 69.42857143
S
STAT 16.96759145
Note 1: Sample number displayed.
Note 2: 40 was mistakenly entered instead of 30.
Note 3: The 40 is cancelled.
Note 4: The data is corrected to 30.
Note 5: A mistake was made in the input data.
Note 6: The 61 x 5 persons data is cancelled.
Page 26

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
26
• What is the average and standard deviation of the table below?
No Data Standard deviation Frequency
1 4245125 -4875 1
2 4246380 -3620 2
3 4247635 -2365 3
4 4248890 -1110 5
5 4250145 145 8
6 4251400 1400 6
7 4252655 2655 4
8 4253910 3910 2
In cases like this where there are many digits and n
∑x∑
2
x exceeds 12 digits inside
calculator, the low order digits are truncated which causes the accuracy of the standard
deviation and other results to decrease. It is therefore recommend that in cases like this a
suitable working mean is used to find the deviation and then this deviation be used as data to
find the average value and standard deviation.
Shownisthedeviationwhen4250000istakenastheworkingaverageforabove table.
Key strokes Display
2ndF
CAD
STAT 0 .
4875+/−
DATA
STAT 1 .
3620+/− x2
DATA
STAT 3 .
2365+/− x3
DATA
STAT 6 .
1110+/− x5
DATA
STAT 11.
145 X 8
DATA
STAT 19.
1400 X 6
DATA
STAT 25.
2655 X 4
DATA
STAT 29.
3910 X 2
DATA
STAT 31.
S
STAT 2185.379202
x
STAT 104.516129
+ 4250000
=
STAT 4250104.516
Page 27

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
27
Program memory
(Program memory)
* Set program mode by pressing 2ndF LRN. This causes the “LRN” symbol to be displayed and the
entire program memory to be cleared. The program steps are then entered by simply pressing
the keys in the same order that you would normally.
(Do not select program mode except when you want to enter a program. The stored values are
cleared when program mode is selected.)
* 2ndF [ x ] : Avariable is specified by pressing these keys before entering a number that is to be
a variable. 0 ~ 9 , • ,EXP,+/−, CE, F – E Pressed immediately thereafter
will not be recorded.
* 2ndF HTL: Place this in memory at those points where it is desired to view intermediate results
or interrupt calculations.
* There are a maximum of 40 steps. (as a rule 1 key is 1 step) Hyperbolic and inverse hyperbolic
functions like 2ndF HYP 2ndF SIN (sinh
-1
) require 2 steps.
* 2ndF, COMP, 2ndF LRN, OFF, 2ndF OFFB, ON/C, 2ndF STAT, 2ndF CAD cannot be placed
in memory. (Pressing OFF, ON/C 2ndF CAD while entering a program causes the entire
program memory to be cleared.)
* If a mistake is made while entering the program, press ON/C and reenter the program starting
from the beginning.
* When you are finished entering the program press 2ndF LRN this causes the “LRN
” symbol to
disappear and the calculator to leave program mode.
(Execution of a calculation using a program)
* Pressing COMP causes the recorded program to be executed step by step.
* The program halts temporarily at those places where 2ndF [ X ] , 2ndF HLT is recorded .After
entering a variable, checking the display, or making a calculation pressing the COMP key causes
the calculation to start once again.
* Be careful to avoid hitting keys that are unrelated to the program when entering a variable or
viewing the display since doing so before the program starts calculation again may affect the
calculations of the program.
* To stop a calculation being executed by the program hold the ON/C key down until the display is
again active.
Page 28

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
28
(Example)
• A plot of r = 5 sin 2V in polar coordinates for 10 degree increments.
Key strokes Display Note
ON/C
x→M
LRN 0 .
2ndF
LRN
LRN 0 . Start of memory
5 2ndF x→K1 2
2ndF
LRN 2 F Specify 2ndfunction
x→K2 MR K2
SIN
LRN 0 .
K1 2ndF ↨ 10
M+
LRN 10.
2ndF
↨
LRN 0 .
θ =0°
2ndF LRN
0 . Program end
COMP
1.710100717
θ =10°
COMP
3.213938049
θ =20°
COMP
4.330127019
θ =30°
(This example takes 13 program steps.)
• Calculates the area of a triangle given the length of the sides.
Heron’s formula S (area) =
c)b)(sa)(ss(s −−−
S=1/2(a+b+c)
i).a=3 b=4 c=5
ii).a=4 b=5 c=6
Key strokes Display
2ndF LRN
LRN 0 .
2ndF [x] 3 x→M+
LRN 3 .
2ndF [x] 4 2ndF x→ K1
LRN 4 .
+ 2ndF [x]
LRN [ 3 ]
5 2ndF x→K2 ) ÷ 2
LRN 2 .
- K1 2ndF ↨ 2ndF x→K1
LRN 6 .
2ndF ↨ )(K1-
LRN 6 .
MR) (K1–K2
LRN 5 .
)K1=
LRN 6 .
2ndF LRN
0.
COMP
[1]
4COMP
[2]
5COMP
[3]
V6COMP
9.921567417
(This example takes 30 program steps.)
Page 29

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
29
• Finds the trajectory of a bullet fired at an initial velocity of Voand angle of…
x=Vocosθt
y=V
o
sinθt − 1/2gt
2
g=9.8[m/sec2]
1). V
o
= 130 [m/sec ] what happens if θ =25° ? (Calculate results every 0.5 seconds.)
2). What about the position after the lapse of 10 seconds with the angle changed to θ=40°
from step 1) above?
Key strokes
130
2ndF
25
2ndF
ON/C
2ndF TAB 2
2ndF LRN
0.5
M+ MR 2ndF HLT K1
x K2 cos = 2ndF HLT
MR K1 K2 SIN -
9.8
x
x MR x
2
2 =
2ndF LRN
COMP
COMP
COMP
COMP
COMP
COMP
LRN
Display
COMP
COMP
COMP
130.
25.
0.
0.00
65.00
58.19
27.47
26.25
0. 00
117.82
50.04
1.50
176.73
71.39
Note
V
t=0
programming starts
xt=0.5
yt=0.5
programming ends
t=1
x
y
t=1.5
x
y
t=10
(There were 27 steps in this example.)
K1
x
K2
x
Mx
LRN
LRN
LRN
LRN
0.00
1.00
x
M
x
9.52ndF
K2
x
4.0
y
10.00
995.86
345.62
(10). Range of calculations
* Input values, addition, subtraction, multiplication and division
Input values, operand and operators
± 1x10
-99
~ ± 9.999999999x1099and 0
Results
± 1x10
-99
~ ± 9.9999999x1099and 0
Page 30

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
30
Function calculations
Function Range of calculation
Sin x DEG
x
<1x10
11
Cos x RAD
x
<1745329252
Tan x GRAD
x≤1.111111111x10
11
Sin–1x
Cos
–1
x
x≤1
Tan-1x
x
<1x10
100
In x
Log x
1x10
–99
≤
x<1x10
100
E
x
x≤230.2585092
10
x
x
<100
3
x
x
<1x10
100
x
0 ≤
x
<1x10
100
X
2
x
<1x10
50
1/x
1x10
-99
≤x <1x10
100
x ≠0
n!
0 ≤
n
≤ 6 9 (n is an integer)
→DEC
→DMS
x
<1x10
100
1x10
-99
≤
y<1x10
100
Y
X
xCIny
≤ 230.2585092
1x10
-99
≤
y<1x10
100
X
Y
1/xCIny
≤ 230.2585092
Sinh x
Cosh x
Tanh x
x
≤ 230.2585092
Sinh–1x
x
<1x10
50
Cosh-1x1<=x<1x10
50
Tanh-1x
x
<1
0<= n <1x10
100
x
<1x10
50
∑x
<1x10
100
0 ≤ ∑x
2
<1x10
100
Summation
calculations
x:n≠ 0s:1<nσ:0<n
Note:1.tanx:| x |≠90 (20 ~ 1)° , π/2 (2n ~ 1) rad, 100 (2n ~ 1) grad where n is a natural number.
2. For calculations that lie within the calculation range, final or intermediate results that have
an absolute value less than 1 x 10
-99
are treated as 0 in the calculation.
Page 31

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
31
(11). Function accuracy
* As a rule the error is ±1 in the last place of the displayed value (the mantissa in scientific notation mode) for
calculations within range.
1) Error of ± 1innexttothelastcanoccurfory
x
x
y
,
3
x
,10xand trigonometric functions in RAD mod. For
trigonometric functions in the RAD mode the error becomes gradually larger as | x | approaches a zero point
or exceeds 2π.
2) The accuracy of sinhx, tanhx, sinh-1x, cosh-1x, tanh-1x becomes worse as a zero point is approached.
* The error in a function increases and the accuracy gets worse as a singularity or inflection point is
approached.
TYPICAL APPLICATION
K4
H2
H3
b12
a12
b11
a11
b10
a10
b9
a9
b8
a8b7a7b6a6b5a5b4a4b3a3b2
a2
b1
a1
H4
S1
K3K2K1CICOGNDTES10S9S8S7
S6
S5
S4
S3
S2
H1
V
GG
SC3445
size:5.63 x 4.93mm
2
L R N
GARD
R A D
D E G
STAT
M
E
Key-board Key-board
STAT
ON/C
n!
CE
HLT
)
xK
2
K
2
nx
xK
1
K
1
CD CAD
[x]
(
tan
-1
tan
OFFB
OFF
TAB
F-E
cos
-1
cos
10
x
Log
1/x
x
2
LRN
COMP
sin
-1
sin
e
x
Ln
3
2nd F
HYP
DRG
3
y
y
x
EXP
RM
S
xM
xx
2
M+
DATA
=
x
DMS
-
+
DEG
9
6
3
8
5
2
7
4
1
0
+/-
S1S3S5S7S9S2S4S6S8S10K1K2K3K4
3V
200k
Page 32

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
32
CHIP TOPOGRAPHY
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
1
2345678 9101112
13
14
15
16
17
18
20
21
22
23
24
25
262728293031
Size: 5.63 x 4.93 mm
2
Page 33

Silan
Semiconductors
SC3445
HANGZHOU SILAN MICROELECTRONICS JOINT-STOCK CO.,LTD
Rev: 1.0 2001.06.11
33
PAD COORDINATES
(Unit: µm)
Pin
No.
Symbol X Y
Pin
No.
Symbol X Y
1K4
-2675.0 -2020.0
25 B2
2680.0 2091.0
2H2
-2391.0 -2340.0
26 A2
2280.0 2340.0
3H3
-2126.0 -2340.0
27 B1
2074.0 2340.0
4B12
-1896.0 -2340.0
28 A1
1819.0 2340.0
5A12
-1611.0 -2340.0
29 H4
1463.0 2340.0
6B11
-1343.0 -2340.0
30 H1
1205.0 2340.0
7A11
-1192.0 -2340.0
31 VGG
818.0 2340.0
8B10
-946.0 -2340.0
32 S1
-660.0 2301.0
9A10
1921.0 -2340.0
33 S2
-923.0 2301.0
10 B9
2125.0 -2340.0
34 S3
-1166.0 2301.0
11 A9
2362.0 -2340.0
35 S4
-1429.0 2301.0
12 B8
2566.0 -2340.0
36 S5
-1672.0 2301.0
13 A8
2682.0 -2115.0
37 S6
-1935.0 2301.0
14 B7
2682.0 -1911.0
38 S7
-2178.0 2301.0
15 A7
2682.0 -1700.0
39 S8
-2691.0 1857.0
16 B6
2682.0 -1316.0
40 S9
-2691.0 1659.0
17 A6
2677.0 -1080.0
41 S10
-2691.0 1464.0
18 B5
2677.0 -875.0
42 TE
-2691.0 1222.0
19 NC
-- --
43 CO
-2641.0 -396.0
20 A5
2675.0 1005.0
44 CI
-2587.0 -559.0
21 B4
2675.0 1209.0
45 GND
-2574.0 -780.0
22 A4
2675.0 1445.0
46 K1
-2675.0 -1479.0
23 B3
2675.0 1650.0
47 K2
-2675.0 -1673.0
24 A3
2675.0 1887.0
48 K3
-2675.0 -1853.0
Note: The original point of the coordinate is the die center.
 Loading...
Loading...