Page 1

INTEGRATED CIRCUITS
DATA SH EET
SAA8115HL
Digital camera USB interface
Preliminary specification
Supersedes data of 1999 Jun 28
File under Integrated Circuits, IC22
2000 Jan 27
Page 2

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
CONTENTS
1 FEATURES
2 APPLICATIONS
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
5 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
6 BLOCK DIAGRAM
7 PINNING
8 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
8.1 Video synchronization
8.2 Frame rate converter and SDRAM interface
8.3 Video formatter: downsampler and cutter
8.4 Compression engine
8.5 Transfer buffer
8.6 USB video FIFO
8.7 PSIE-MMU, I2C-bus interface and USB RAM
space
8.8 ATX interface
8.9 Audio
8.10 Sensor pulse pattern generator
8.11 Power management
8.12 Power supply
9 CONTROL REGISTER DESCRIPTION
9.1 SNERT (UART)
9.2 I2C-bus interface
10 LIMITING VALUES
11 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
12 OPERATING CHARACTERISTICS
13 TIMING
14 APPLICATION INFORMATION
15 PACKAGE OUTLINE
16 SOLDERING
16.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
16.2 Reflow soldering
16.3 Wave soldering
16.4 Manual soldering
16.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for
wave and reflow soldering methods
17 DEFINITIONS
18 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
19 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I2C COMPONENTS
2000 Jan 27 2
Page 3

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
1 FEATURES
• VGA (progressive mode), CIF and medium resolution
(PAL non-interlaced mode) CCD sensors compliant
• D1 digital video input (8 bits YUV 4:2:2time
multiplexed)
• Internal Pulse Pattern Generator (PPG) dedicated for
VGA Panasonic, CIF and medium resolution Sharp
sensors or compatibles, and frame rate selection
• Frame rate converter
• SDRAM interface for high quality VGA snapshot
(uncompressed 4:2:2 or 4:2:0)
• Downsampler and scaler (programmable formatter for
CIF, QCIF, sub-QCIF, SIF and QSIF) controlled via
SNERT (UART) interface
• Flexible compression engine controlled via SNERT
(UART) interface
• Selectable outputframe rate (up to 15 fps in VGA, up to
30 fps in CIF and QCIF)
• Video packetizer FIFO
• I2C-bus interface for communication between the USB
protocol hardware and the external microcontroller
• Microphone/audio input to USB (microphone supply,
controllable gain and ADC)
• Integrated analog bus driver (ATX)
• Integrated main oscillator
• Integrated 5 V power supply and reset circuit including
functionalities for bus-powered USB device
• Programmable (frequency and duty cycle) switch mode
power signal for CCD supply
• Miscellaneous functions (e.g. power management, PLL
for audio frequencies).
2 APPLICATIONS
Low-cost desktop video applications with USB interface.
3 GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The SAA8115HL is the second generation of integrated
circuitapplicablein PC video cameras to convert D1 video
signals and analog audio signals to properly formatted
USB packets.
Thispowerful successor of the SAA8117HL can handle up
to 15 fps in VGA format or 30 fps in CIF format. High
snapshot quality is achievable using the SDRAM interface
to an external memory.
It is designed as a back-end of the SAA8112HL (general
cameradigital processing IC) and is optimized for use with
the TDA8784 to TDA8787 (camera pre-processing ICs).
2000 Jan 27 3
Page 4
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
4 ORDERING INFORMATION
TYPE
NUMBER
NAME DESCRIPTION VERSION
PACKAGE
SAA8115HL LQFP144 plastic low profile quad flat package; 144 leads; body 20 × 20 × 1.4 mm SOT486-1
5 QUICK REFERENCE DATA
Measured over full voltage and temperature range
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
V
DDD
V
DDA
V
DDA_USB
I
DD(tot)
V
I
V
O
f
clk
P
tot
T
stg
T
amb
T
j
digital supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage from USB note 1 4.0 5.0 5.5 V
total supply current V
input signal levels 3.0V<V
output signal levels 3.0V<V
= 3.3 V −−tbf mA
DDD
< 3.6 V low voltage TTL compatible V
DDD
< 3.6 V low voltage TTL compatible V
DDD
clock frequency − 48 − MHz
total power dissipation T
=25°C −−tbf mW
amb
storage temperature −55 −−°C
ambient temperature 0 25 70 °C
junction temperature T
=70°C −40 − +125 °C
amb
Note
1. This concerns pins VBUS1 and VBUS2.
2000 Jan 27 4
Page 5
This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
ha
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2000 Jan 27 5
ndbook, full pagewidth
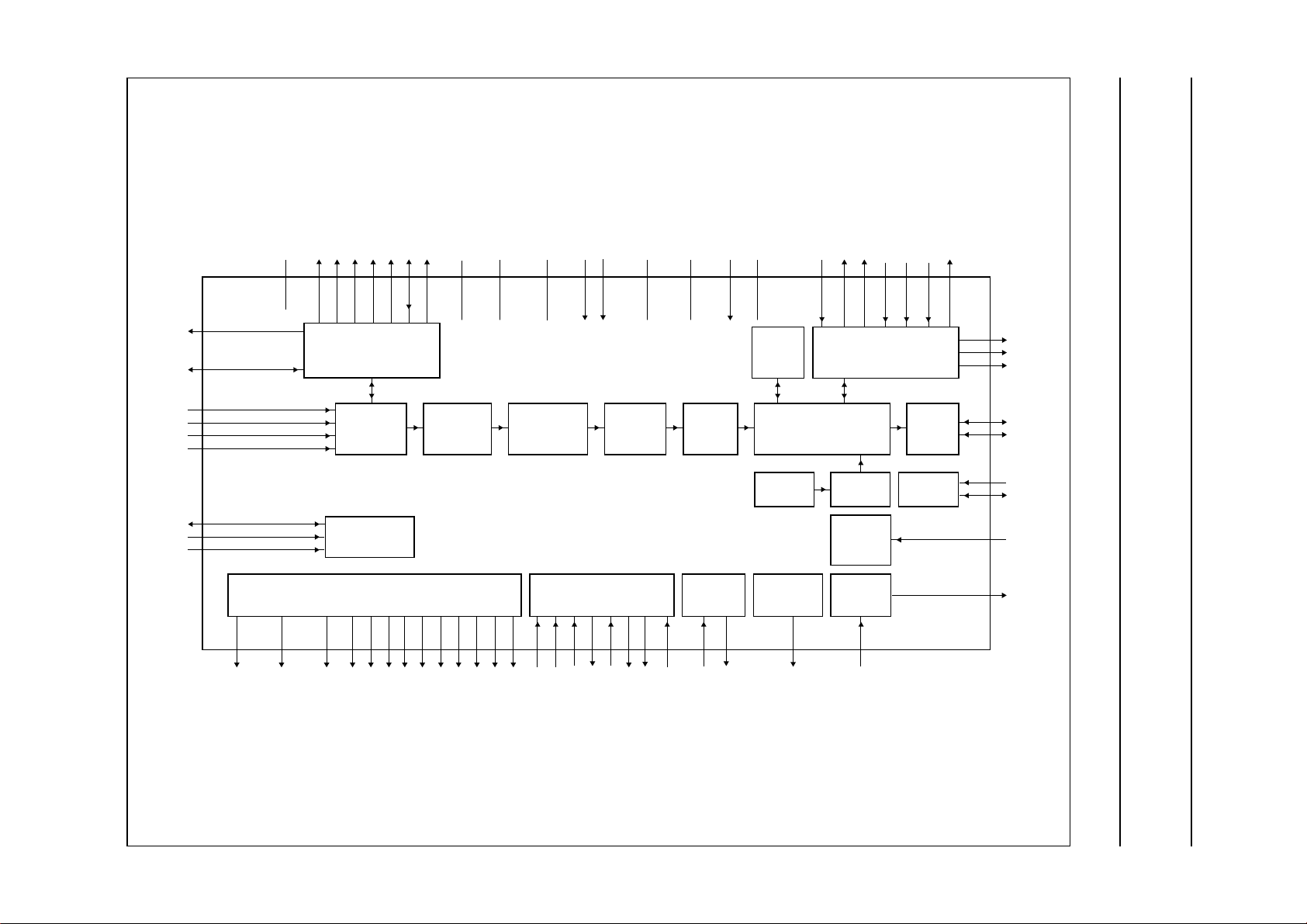
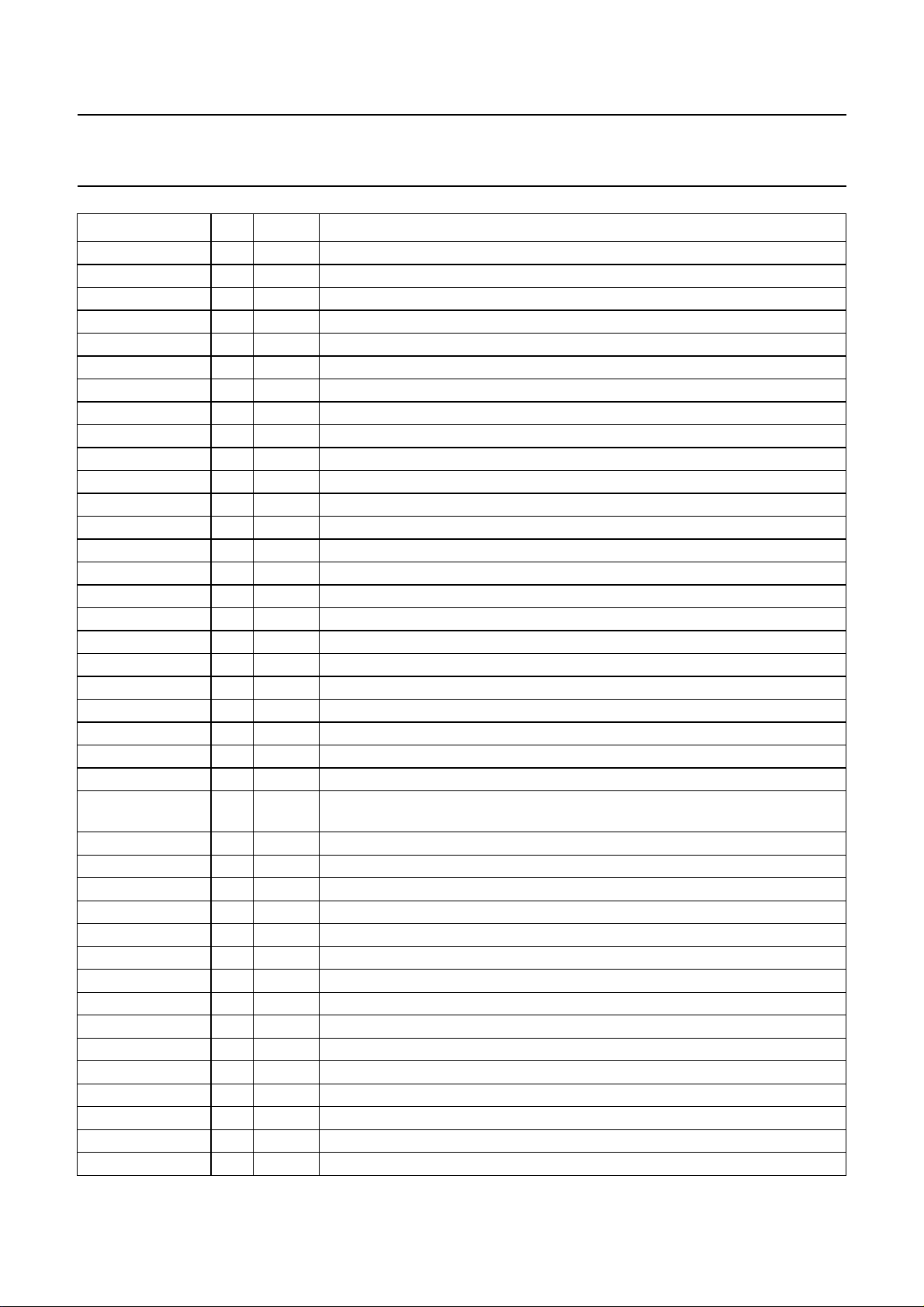
6 BLOCK DIAGRAM
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
AD10
to AD0
DQ15
to DQ0
YUV7
to YUV0
LLC
HREF
SNDA
SNCL
SNRES
48, 47, 45, 44,
42, 39, 38, 40,
41, 43, 46
77, 76, 75, 74, 67, 65,
62, 60, 61, 63, 64, 66,
70, 71, 72, 73
28, 27, 26, 25
22, 21, 20, 19
30
31
32
VS
34
35
36
139, 140,
143, 144
A1 to A4
DDD3
to V
DDD1
V
24,
53,
102
137, 138,
136, 135
B1 to B4
CASB
RASB52SDCLK
WEB57CLKEN55CSB
56
58
SDRAM
INTERFACE
FRAME RATE
CONVERTER
SNERT
INTERFACE
PULSE PATTERN GENERATOR
3, 2,
1, 4
C1 to C4
(PPG)
5RG8
SHUTTER
DQM
51
59
FORMATTER
12
10FS9
DCP
FCDS
VIDEO
13
BCP
DD6
to V
DD1
V
7, 16,
37, 50,
69, 141
DDA6
to V
DDA1
V
82, 84,
85, 122,
124, 125
COMPRESSION
ENGINE
17
11HD15VD14
CLK1
CLK2
M3 to M0
RESET
DGND1 to DGND4
115, 116,
33
23, 29,
54, 101
117, 118
TRANSFER
BUFFER
SAA8115HL
DC-TO-DC CONVERTER
94
92
91
90
87
3V3
VBUS1
VBUS2
LXUP
LXDOWN
AGND1 to AGND6
79, 88,
93, 119,
123, 134
114
113
95
OFF
POR
SWITCHED5V
GND1 to GND7
6, 18,
49, 68,
78, 98,
142
USB
VIDEO
FIFO
MAIN
OSCILLATOR
121
120
XIN
RESERVED1 to
RESERVED6
REF1 to REF3
83, 86,
126,
89, 96,
127,
97, 129
128
USB
RAM
SPACE
AUDIO
MICROPHONE
SUPPLY
XOUT
PLL
133
MICSUPPLY
SUSPEND
GENPOR
100 109
103
POWER MANAGEMENT
PSIE MMU
AUDIO
ADC
AUDIO
VARIABLE
GAIN
AMPLIFIER
AUDIO
LOW NOISE
AMPLIFIER
132
MICIN
CLOCKON
TRC
112
SNAPSHOT
SUSPREADYNOT
110
111
ATX
2
I
C-BUS
INTERFACE
SMP
108
99
104
105
80
81
106
107
130
131
FCE349
UCINT
UCPOR
UCCLK
ATXDP
ATXDM
SCL
SDA
VGAIN
LNAOUT
Fig.1 Block diagram.
Page 6
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
7 PINNING
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
C3 1 O horizontal CCD transfer pulse output
C2 2 O horizontal CCD transfer pulse output (FH1)
C1 3 O horizontal CCD transfer pulse output (FH2)
C4 4 O horizontal CCD transfer pulse output
SHUTTER 5 O shutter control output for CCD charge reset
GND1 6 P ground 1 for output buffers
V
DD1
7 P supply voltage 1 for output buffers
RG 8 O reset output for CCD output amplifier gate
FS 9 O data sample-and-hold pulse output to TDA8784/87 (SHD)
FCDS 10 O preset sample-and-hold pulse output to TDA8784/87 (SHP)
CLK1 11 O pixel clock to TDA8784/87 and SAA8112HL
DCP 12 O dummy clamp pulse output to TDA8784/87
BCP 13 O optical black clamp pulse output to TDA8784/87
VD 14 O vertical definition pulse to SAA8112HL
HD 15 O horizontal definition pulse to SAA8112HL
V
DD2
16 P supply voltage 2 for output buffers
CLK2 17 O double pixel clock to SAA8112HL
GND2 18 P ground 2 for output buffers
YUV0 19 I multiplexed YUV bit0
YUV1 20 I multiplexed YUV bit1
YUV2 21 I multiplexed YUV bit2
YUV3 22 I multiplexed YUV bit3
DGND1 23 P digital ground 1 for input buffers, predrivers and for the digital core
V
DDD1
24 P digital supply voltage 1 for input buffers, predrivers and one part of the digital
core
YUV4 25 I multiplexed YUV bit4
YUV5 26 I multiplexed YUV bit5
YUV6 27 I multiplexed YUV bit6
YUV7 28 I multiplexed YUV bit7
DGND2 29 P digital ground 2 for input buffers, predrivers and for the digital core
LLC 30 I line-locked clock input (delayed CLK2) for YUV-port from SAA8112HL
HREF 31 I horizontal reference input for YUV-port from SAA8112HL
VS 32 I vertical synchronization input for YUV-port from SAA8112HL
RESET 33 I Power-on reset input (for video processing and PPG)
SNDA 34 I/O data input/output for SNERT-interface (communication between SAA8115HL
and SAA8112HL)
SNCL 35 I clock input for SNERT-interface (communication between SAA8115HL and
SAA8112HL)
SNRES 36 I reset input for SNERT-interface (communication between SAA8115HL and
SAA8112HL)
2000 Jan 27 6
Page 7
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
V
DD3
37 P supply voltage 3 for output buffers
(1)
DESCRIPTION
AD4 38 O SDRAM output address bit 4
AD5 39 O SDRAM output address bit 5
AD3 40 O SDRAM output address bit 3
AD2 41 O SDRAM output address bit 2
AD6 42 O SDRAM output address bit 6
AD1 43 O SDRAM output address bit 1
AD7 44 O SDRAM output address bit 7
AD8 45 O SDRAM output address bit 8
AD0 46 O SDRAM output address bit 0
AD9 47 O SDRAM output address bit 9
AD10 48 O SDRAM output address bit 10
GND3 49 P ground 3 for output buffers
V
DD4
50 P supply voltage 4 for output buffers
CSB 51 O SDRAM chip select output
RASB 52 O SDRAM row address strobe output
V
DDD2
53 P digital supply voltage 2 for the switchable digital core
DGND3 54 P digital ground 3 for input buffers, predrivers and for the digital core
CLKEN 55 O SDRAM clock enable output
CASB 56 O SDRAM column address strobe output
WEB 57 O SDRAM write enable output
SDCLK 58 O SDRAM clock output
DQM 59 I/O SDRAM data mask enable
DQ8 60 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 8
DQ7 61 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 7
DQ9 62 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 9
DQ6 63 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 6
DQ5 64 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 5
DQ10 65 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 10
DQ4 66 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 4
DQ11 67 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 11
GND4 68 P ground 4 for output buffers
V
DD5
69 P supply voltage 5 for output buffers
DQ3 70 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 3
DQ2 71 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 2
DQ1 72 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 1
DQ0 73 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 0
DQ12 74 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 12
DQ13 75 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 13
DQ14 76 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 14
DQ15 77 I/O SDRAM data I/O bit 15
2000 Jan 27 7
Page 8
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
GND5 78 P ground 5 for output buffers
AGND1 79 P analog ground 1 for ATX (transceiver)
ATXDP 80 I/O positive driver of the differential data pair input/output (ATX)
ATXDM 81 I/O negative driver of the differential data pair input/output (ATX)
V
DDA1
82 P analog supply voltage 1 for ATX
RESERVED1 83 − test pin 1 (should not be used)
V
V
DDA2
DDA3
84 P analog supply voltage 2 for bandgap (reference)
85 P analog supply voltage 3 for bandgap, comparator and ring oscillator
RESERVED2 86 − test pin 2 (should not be used)
3V3 87 I 3V3 detector input signal
AGND2 88 P analog ground 2 for N-switch
RESERVED3 89 − test pin 3 (should not be used)
VBUS1 90 I supply voltage input 1 from the USB
VBUS2 91 I supply voltage input 2 from the USB
LXDOWN 92 O LX coil node output (5 V downconverter)
AGND3 93 P analog ground 3 for N-switch
LXUP 94 I LX coil node input (5 V upconverter)
SWITCHED5V 95 O 5 V switched power supply
RESERVED4 96 − test pin 4 (should not be used)
RESERVED5 97 − test pin 5 (should not be used)
GND6 98 P ground 6 for output buffers
UCINT 99 O interrupt output from USB to microcontroller
SUSPEND 100 O control output from USB protocol hardware to microcontroller
DGND4 101 P digital ground 4 for input buffers, predrivers and for the digital core
V
DDD3
102 P digital supply voltage 3 for input buffers, predrivers and one part of the digital
core
GENPOR 103 I Power-on reset input (for USB protocol hardware)
UCPOR 104 O control output from USB protocol hardware to microcontroller
UCCLK 105 O clock output from USB protocol hardware to microcontroller
2
SCL 106 I slave I
SDA 107 I/O slave I
C-bus clock input
2
C-bus data input/output
SMP 108 O switch mode power pulse output for CCD supplies
CLOCKON 109 O control output for main oscillator switched on
SNAPSHOT 110 I input for remote wake-up (snapshot)
SUSPREADYNOT 111 I input from microcontroller for SUSPEND mode
TRC 112 I threshold control input for enabling clock
POR 113 O 3.3 V supply domain ready indicator output
OFF 114 I disable 5 V switchable supply domain input
M3 115 I test mode control input signal bit 3
M2 116 I test mode control input signal bit 2
M1 117 I test mode control input signal bit 1
2000 Jan 27 8
Page 9
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
SYMBOL PIN TYPE
(1)
DESCRIPTION
M0 118 I test mode control input signal bit 0
AGND4 119 P analog ground 4 for crystal oscillator (48 MHz, 3rd overtone)
XIN 120 I oscillator input
XOUT 121 O oscillator output
V
DDA4
122 P analog supply voltage 4 for crystal oscillator (48 MHz, 3rd overtone)
AGND5 123 P analog ground 5 for PLL
V
V
DDA5
DDA6
124 P analog supply voltage 5 for PLL
125 P analog supply voltage 6 for amplifier and ADC
REF1 126 I reference voltage 1 (used in the ADC)
REF2 127 I reference voltage 2 (used in the ADC)
REF3 128 I reference voltage 3 (used in the amplifier and the ADC)
RESERVED6 129 O test pin 6 (should not be used)
VGAIN 130 I variable gain amplifier input
LNAOUT 131 O low noise amplifier output
MICIN 132 I microphone input
MICSUPPLY 133 O microphone supply output
AGND6 134 P analog ground 6 for amplifier and ADC
B4 135 O vertical CCD load pulse output (VH1X)
B3 136 O vertical CCD load pulse output (VH3X)
B1 137 O vertical CCD load pulse output
B2 138 O vertical CCD load pulse output
A1 139 O vertical CCD transfer pulse output (V1X)
A2 140 O vertical CCD transfer pulse output (V2X)
V
DD6
141 P supply voltage 6 for output buffers
GND7 142 P ground 7 for output buffers
A3 143 O vertical CCD transfer pulse output (V3X)
A4 144 O vertical CCD transfer pulse output (V4X)
Note
1. I = input, O = output and P = power supply.
2000 Jan 27 9
Page 10

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
handbook, full pagewidth
SHUTTER
GND1
V
DD1
RG
FCDS
CLK1
DCP
BCP
VD
HD
V
DD2
CLK2
GND2
YUV0
YUV1
YUV2
YUV3
DGND1
V
DDD1
YUV4
YUV5
YUV6
YUV7
DGND2
LLC
HREF
RESET
SNDA
SNCL
SNRES
DD3
DD6
V
A2A1B2B1B3B4AGND6
143
142
141
140
139
AD4
AD5
AD3
AD2
AD6
138
AD1
137
AD7
136
AD8
135
AD0
MICSUPPLY
134
133
AD9
AD10
MICIN
132
V
GND3
LNAOUT
VGAIN
131
130
DD4
CSB
RESERVED6
REF3
129
SAA8115HL
RASB
V
A4A3GND7
144
C3
1
C2
2
C1
3
C4
4
5
6
7
8
FS
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
VS
32
33
34
35
36
3738394041424344454647484950515253545556575859606162636465666768697071
V
128
DDD2
REF2
REF1
127
126
CLKEN
DGND3
DDA6VDDA5
V
125
124
WEB
CASB
DDA4
AGND5
V
123
122
DQM
SDCLK
XOUT
XIN
AGND4M0M1M2M3
121
120
119
DQ8
DQ7
DQ9
118
DQ6
117
DQ5
116
DQ10
115
DQ4
OFF
114
DQ11
POR
113
GND4
TRC
SUSPREADYNOT
SNAPSHOT
112
111
110
DD5
DQ3
DQ2
V
CLOCKON
109
108
107
106
105
104
103
102
101
100
99
98
97
96
95
94
93
92
91
90
89
88
87
86
85
84
83
82
81
80
79
78
77
76
75
74
73
72
DQ1
SMP
SDA
SCL
UCCLK
UCPOR
GENPOR
V
DDD3
DGND4
SUSPEND
UCINT
GND6
RESERVED5
RESERVED4
SWITCHED5V
LXUP
AGND3
LXDOWN
VBUS2
VBUS1
RESERVED3
AGND2
3V3
RESERVED2
V
DDA3
V
DDA2
RESERVED1
V
DDA1
ATXDM
ATXDP
AGND1
GND5
DQ15
DQ14
DQ13
DQ12
DQ0
FCE350
Fig.2 Pin configuration.
2000 Jan 27 10
Page 11

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
8 FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
8.1 Video synchronization
The video synchronization module is capable of locking to
the video signal implementing a horizontal gate signal
HREF (HREF = HIGH when data is valid) and a VS signal
indicating the start of a new video frame.
8.2 Frame rate converter and SDRAM interface
An optional SDRAM (external) can be accessed using the
SDRAM interface which is integrated in the SAA8115HL.
Pinning and functionality is based on the NEC
µPD4516161 (16 Mbits) and the NEC µPD4564163
(64 Mbits).
When used, the memory is placed at the video input of the
SAA8115HL before prefilter, scaler and compression
engine. At this point only YUV 4 : 2 : 2 formatted data is
available.
The use of the SDRAM is twofold:
• Lowering the frame rate. The memory enables to store
one frame of video accumulated at a specific rate and to
read it out at a lower frame rate. For interline VGA
sensors, the input frame rate is either 30 fps or 15 fps.
It can be lowered with a factor of 2, 3, 6, 16 or 32.
For CIF or medium resolution PAL, the input frame rate
is only 30 fps
• Enhanced snapshot mode. Storage of full size VGA
pictures in 4:2:2 format which can be retrieved upon
dedicated software command.
8.3 Video formatter: downsampler and cutter
Horizontally a downsampling from 512 or 640 to either
384, 320, 192 or 160 or from 352 to 176 is necessary.
The horizontal downsampling is performed with the use of
a Variable Phase Delay filter (VPD-4). This filter can
realize the needed downsample factors. To avoid aliasing,
this module also contains a prefilter which has four modes:
• No filter for medium resolution PAL (512 × 288) to CIF
(352 × 288) or SIF (320 × 240)
• Prefilter A (3 taps) for VGA (640 × 480) to CIF or SIF,
CIF to QCIF (176 × 144) or QSIF (160 × 120)
• Prefilter B (7 taps) for medium resolution PAL to QCIF
or QSIF
• Prefilter A combined with prefilter B-comb (13 taps) for
VGA to QCIF or QSIF.
Prefilter B-comb is similar to prefilter B but inserts extra
taps with amplification 0.
The vertical downsampling in PAL mode is from CIF to
QCIF only. This is done via a vertical filter A (3 taps).
In VGA mode a 4 taps polyphase filter is applied to scale
from 640 × 480 to CIF and QCIF.
From a full size QCIF picture a sub-QCIF (128 × 96) cut
can be made. For the zoomed sub-QCIF format, the origin
(upperleftcorner)isprogrammable via SNERT in 13 steps
(both horizontally and vertically), so that an electronic pan
and tilt is possible.
The incoming 4:2:2data is vertically filtered to 4:2:0,
in order to be sent over USB, by throwing away colour
samples.In the even lines the V-samples are discarded, in
the odd lines the U-samples.
This block is used to achieve the required output format
from the specified sensor formats (see Fig.3). It works for
YUV4 : 2 : 2only. In RAW mode this block is by-passed to
create a full resolution snapshot.
2000 Jan 27 11
Page 12

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
8.4 Compression engine
The compression engine module (see Fig.3) can process
VGA, CIF, SIF, QCIF and QSIF but has optimal
performance with CIF resolution (30 fps) and VGA
resolution (5 fps). The algorithm is Philips proprietary.
The compression ratio is continuously programmable by
setting the maximum number of bits which can be used for
4 compressed lines, a so-called band (see Table 1). It is
possible to reduce the YUV input data by scaling down
(divide by 2 or divide by 4 operations) to 7 or 6 bits per
sample. For compression with an output rate below 2 bpp
(bits per pixel) it leads to performance improvement.
handbook, full pagewidth
YUV7 to YUV0
PREFILTER_A_ON_OFF
PREFILTER
A
PREFILTER
VIDEO_OUTPUT_FORMAT
B
For a number of compression ratios, performance is also
improved thanks to different quantization tables which are
defined and stored in a ROM. The required table must be
selected via software.
Real time decoding can be done in software on any
Pentium platform.
UV_EXCHANGE
PAL_VGA
to
transfer
DOWN
SCALER
COMPRESSION
ENGINE
buffer
PREFILTER_B_ON_OFF
PREFILTER B_COMB_ON_OFF
COMPRESSION_MODE
VP_C_ BITCOST_(MSB/LSB)
FCE430
Fig.3 The video formatter and compression engine.
Table 1 Data rate performed by compression engine
FORMAT ADVISED DATA RATE MAXIMUM DATA RATE
CIF/SIF 2 bpp 12 bpp (uncompressed)
QCIF/QSIF 6 bpp uncompressed
VGA high quality 3 bpp 4 bpp
VGA 1.5 bpp 3 bpp
RAW VGA high quality 4 bpp 4 bpp
2000 Jan 27 12
Page 13
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
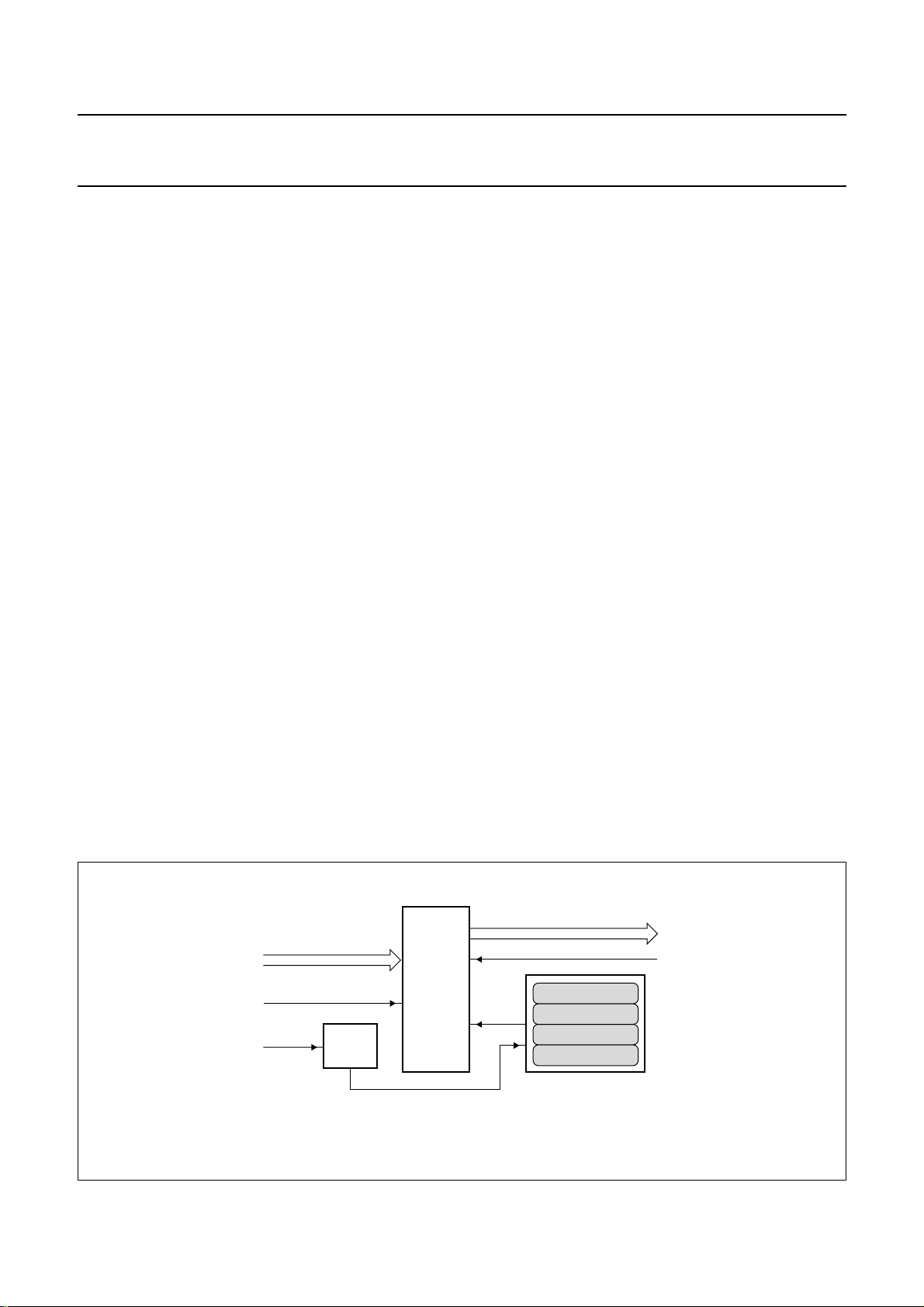
8.5 Transfer buffer
The transfer buffer module (see Fig.4) takes care of a
smooth transfer of the data to the FIFO of the USB.
Moreover the transfer buffer can insert inband
synchronization words in the video data stream. This
function can be switched on and off with
INBAND_CONTROL in register VP_TR_CONTROL
(0x36). The synchronization words can only be used with
non-compressed data stream and are formatted like
0x00 0xFF 0x<framecounter>7<linecounter>9.
(Subscript denotes the number of bits and the frame
counter is circular incrementing).
The non-compressed data is formatted like:
4:2:0:<optional sync word><Y0><Y1><Y2><Y3>
<C0><C2><Y4><Y5><Y6><Y7><C4><C6>....,
4:2:2: <optional sync word><Y0><Y1><Y2><Y3>
<U0><V0><U2><V2><Y4>....,
whereC denotes U-data in the even lines (0, 2, 4 etc.) and
V-data in the odd lines (1, 3, 5 etc.).
8.6 USB video FIFO
The USB video FIFO is programmed via the I2C-bus
(see Fig.5). The FIFO is designed to achieve three
differentpacketscontainingvideoonthe isochronous USB
channel.Videodataiscontained in a chain ofequallysized
USB packets, except for the last packet of a video frame
which is always smaller. The video frames can be
separated from each other by one or more 0-length
packets. For low frame rates (below 10 frames per
second) there are always 0-length packets in the stream.
The host can synchronize on the smaller packets for the
high frame rates and on the 0-length packets for the low
frame rates.
For every mode the FIFO must be adjusted. There are
three parameters to program the video FIFO:
• PACKET_SIZE (0x06): this value indicates the length of
all packets with video data except for the last packet of
a video frame
• FIFO_OFFSET (0x04): this value indicates the number
of data in the FIFO before a new packet will be
transmitted over USB
• READ_SPACING (0x07): this value indicates the
number of 12 MHz clock cycles between read actions
from the FIFO.
Moreover the FIFO is enabled and disabled with
FIFO_ACTIVE (0x05).
The write process to the FIFO is controlled by the transfer
buffer and not programmable.
The read process is executed in the PSIE-MMU and is
driven by the USB frame interval (1 ms). Every frame
interval the PSIE-MMU tries to read PACKET_SIZE bytes
from the FIFO. This read process will not be started when
a new video frame is stored in the FIFO and there are less
thanFIFO_OFFSETbyteswritten.Theread process stops
if the next bytes are of another video frame, or if the
read-pointer would overtake the write-pointer.
READ_SPACING determines the read rate. Its value can
easily be determined with the formula:
READ_SPACING
12000
<
---------------------------------------PACKET_SIZE
handbook, full pagewidth
data from transfer buffer
write
WRITE
SYNC
Ptr_to_start_Vframe
FIFO
Fig.4 USB video FIFO.
2000 Jan 27 13
data to PSIE-MMU
read
read
enable
FIFO_OFFSET
PACKET_SIZE
READ_SPACING
FIFO_ACTIVE
FCE431
Page 14
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
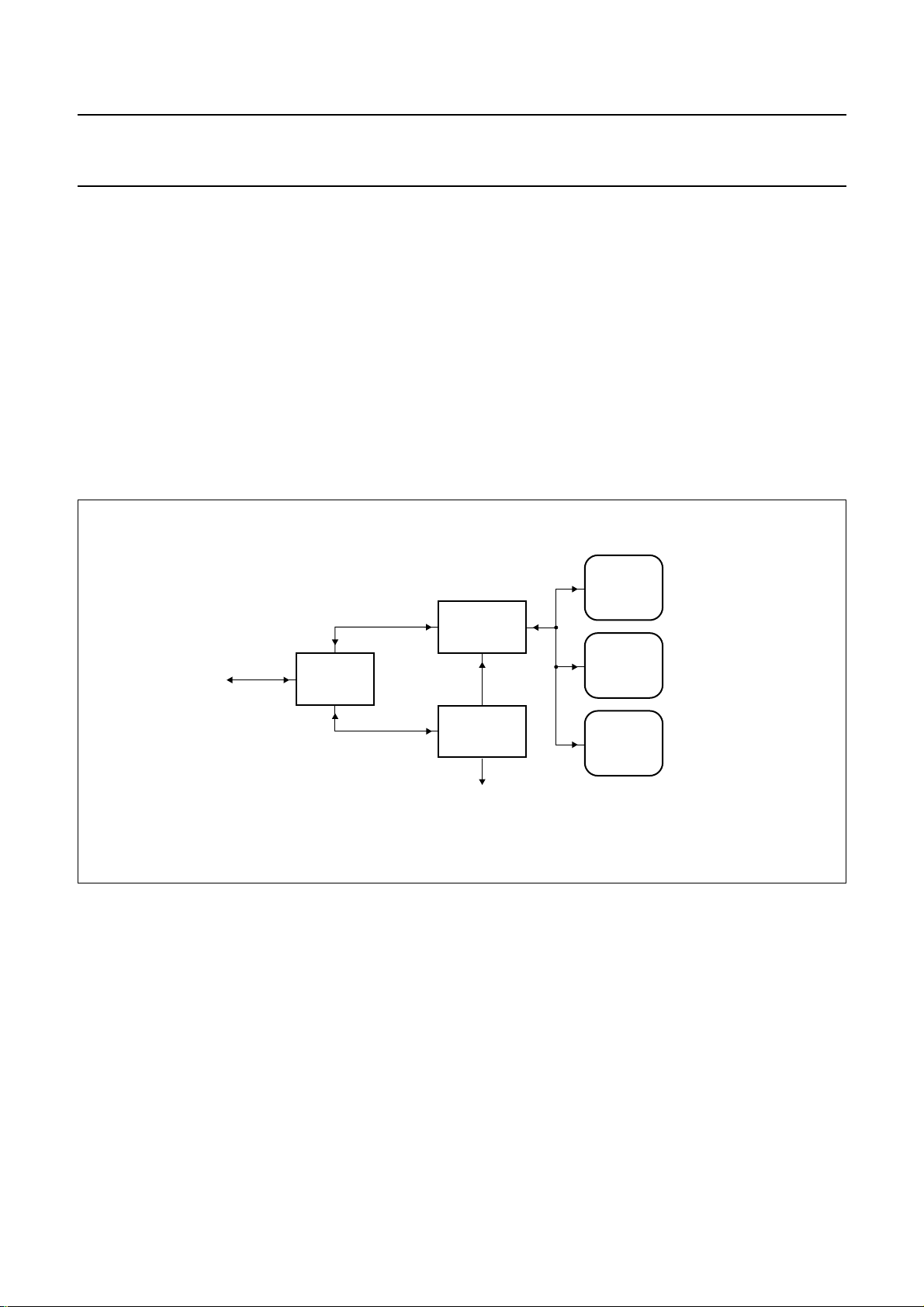
8.7 PSIE-MMU, I2C-bus interface and USB RAM
space
The Programmable Serial Interface Engine (PSIE) and
Memory Management Unit (MMU) is the heart of the USB
protocol hardware (see Fig.5). It formats the actual
packets that are transferred to the USB and passes the
incoming packets to the right end-point buffers. These
buffers are allocated as part of the USB RAM space.
ThemicrocontrollercommunicatesviatheI2C-buswiththe
PSIE-MMU. The I2C-bus protocol distinguishes three
register spaces. These spaces are addressed via different
commands. The command is sent to the command
address.
handbook, full pagewidth
PI_Address + 0X
to/from
microcontroller
I2C-BUS
INTERFACE
Depending on the command it is sent to the PSIE-MMU
and/or to the command interpreter which configures the
(de-)mux to open the path to the right register space.
Subsequent write/reads to/from the data address store or
retrieve data from the register space selected by the
command.
8.8 ATX interface
The SAA8115HL contains an analog bus driver, called the
ATX. It incorporates a differential and two single-ended
receivers and a differential transmitter.
The interface to the bus consists of a differential data pair
(ATXDM and ATXDP).
PSIE-MMU
REGISTER
SPACE
(DE)MUX
SET MODE
REGISTER
SPACE
PI_Address + 10
Fig.5 I2C-bus interface and register map.
8.9 Audio
The SAA8115HL contains a microphone supply and an
amplifier circuit composed of two stages: a Low Noise
Amplifier (LNA)andavariablegainamplifier.TheLNAhas
a fixed gain of 26 dB while the variable gain amplifier can
be programmed between 0 and 30 dB by steps of 2 dB.
The gain control can be done via either the SNERT
interface or the I2C-bus interface (see Table 57).
The serial interface must be first selected using bit SIS
(see Table 57). The frequency transfer characteristic of
theaudiopathmustbecontrolledviaexternalhigh-passor
low-pass filters.
COMMAND
INTERPRETER
to
PSIE-MMU
NON USB
AND
VIDEO FIFO
REGISTERS
FCE432
The PLL converts the 48 MHz to 256fs(fs= audio sample
frequency). There are three modes for the PLL to achieve
the sample frequencies of 48, 44.1 or 32 kHz
(see Table 2).
The bitstream ADC samples the audio signal. It runs at an
oversample rate of 256 times the base sample rate. In the
application, the bitstream can be converted to parallel
16-bit samples. This conversion is programmable with
respect to the effective sample frequency (dropping
sample results in a lower effective sample frequency) and
sample resolution. As a result the effective sample rate
can be determined.
2000 Jan 27 14
Page 15

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 2 ADC clock frequencies and sample frequencies
CLOCK
(MHz)
8.1920 1 32 4.096
11.2996 1 44.1 5.6448
12.2880 1 48 6.144
Note
1. Not supported.
Table 3 Typical SAA8115HL compatible sensors
DIVIDING
NUMBER
2 16 2.048
4 8 1.042
8 note 1 note 1
2 22.05 2.8224
4 11.025 1.4112
8 5.5125 0.7056
2 24 3.072
4 12 1.536
8 6 0.768
SAMPLE
FREQUENCY
(kHz)
ADCCLOCK
(MHz)
8.10 Sensor pulse pattern generator
The SAA8115HL incorporates a Pulse Pattern Generator
(PPG) function. The PPG can be used for medium
resolution PAL, CIF and VGA CCD-sensors (see Table 3).
Depending on the sensor type, an external inverter driver
should be required to convert the 3.3 V pulses into a
voltage suitable for the used CCD-sensor.
The active video size is 512 × 288 for medium resolution
PAL, 352 × 288 for CIF and 640 × 480 for VGA. The total
H × V size are 685 × 292 for medium resolution PAL/CIF
and 823 × 486 for VGA. It should be noted that additional
HD pulses are added during the vertical blanking interval
to reach a total of 312 lines in PAL and CIF modes and
525 lines in VGA mode as required by the SAA8112HL.
A high level of flexibility is available for the PPG thanks to
19 internal registers (see Section 9.1.3).
SENSOR TYPE BRAND PART NUMBER
VGA Sony ICX098AK
Panasonic MN3777PP and MN37771PT
Sharp LZ24BP
Medium resolution PAL Sony ICX054, ICX086 and ICX206
Panasonic MN37210FP
Sharp LZ2423B and LZ2423H
Toshiba TCD5391AP
CIF Sharp LZ244D and LZ2547
Other sensors all the sensors fully compatible with the above mentioned sensors
2000 Jan 27 15
Page 16

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
8.11 Power management
USB requires the device to switch power states.
The SAA8115HL contains a power management module
since the complete camera may not consume more than
500 µA during the power state called SUSPEND. This
requires that even the crystal oscillator must be switched
off. The SAA8115HL is not functional except for some
logic that enables the IC to wake-up the camera. After
wake-up of the SAA8115HL first the clock to the
microcontroller is generated and thereafter an interrupt is
generated to wake-up the microcontroller. Therefore the
clock of the microcontroller is generated by the
SAA8115HL.
Thepowermanagementmodulealsosetsaflaginregister
SET_MODE_AND_READ(PSIE_MMU_STATUS).After a
reset the microcontroller should check this register via the
I2C-bus and find the cause of the wake-up. Different
causes may require different start-up routines.
The internal video processing core uses another supply
domain which can be switched off during SUSPEND
mode.
The PPG is switched off by setting
PPG_RESUME_MODE (0x08) and resetting PAL_VGA
(0x09).
The SAA8115HL has the feature to autonomously
wake-up from SUSPEND mode, but requires
microcontroller interference before going in SUSPEND
mode (via the signal on pin SUSPREADYNOT).
SincethemainoscillatoroftheSAA8115HLisswitchedoff
during SUSPEND mode, precautions are needed to avoid
undefined states when the clock is switched on. This is
ensuredviathepins CLOCKON and TRC. Pin CLOCKON
goes HIGH as soon as the main oscillator is switched on.
The oscillator will need some time to make a stable
48 MHz signal. However, the clock is only passed through
to other parts of the SAA8115HL when the level on
pin TRC reaches a certain threshold. The time needed to
reach the threshold can be trimmed with an external
RC circuit.
8.12 Power supply
A power supply regulator is integrated in the device. This
DC-to-DC converter transforms the USB supply voltage
(range from 4.0 to 5.5 V) into a stable 5 V supply voltage.
This power domain is switchable. The power circuit also
generates a reset signal when the external 3.3 V supply
voltage is stable and in range.
In non CIF modes the power consumption is reduced by
resetting COMPRESSION_MODE (0x2F) and
COMPRESSION_CLOCK (0x09).
2000 Jan 27 16
Page 17
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9 CONTROL REGISTER DESCRIPTION
This specification gives an overview of all registers.
9.1 SNERT (UART)
The SAA8115HL is partly controlled via SNERT. The frame rate converter, the SDRAM interface, the video formatter,
the compression engine, the PPG, the SMP and the audio functions are controlled via SNERT. This SNERT interface
works independently from the frame rate and can always be operated in the full frequency range.
Via SNERT the following registers are accessible (see Table 4).
Table 4 SNERT write registers SAA8115HL
ADDRESS FUNCTION
00 write register soft reset (see Table 5)
01 to 05 write registers Frame Rate Converter (FRC) including the SDRAM interface
06 and 07 reserved
08 to 1A write registers Pulse Pattern Generator (PPG)
1B to 1F reserved
20 to 38 write registers video formatter and compression engine
39 to 3C reserved
3D and 3E write registers Switch Mode Power (SMP)
3F write register audio variable gain amplifier
9.1.1 G
Table 5 Detailed description of SNERT general register 0x00
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXX reserved
ENERAL REGISTER
BIT SNERT REGISTER 00: SOFT_RESET
RESET_VP_C
1 compression engine in reset state
0 compression engine operating
RESET_VP_VF
1 formatter engine in reset state
0 formatter engine operating
RESET_FRC
1 frame rate converter engine in reset state (by default)
0 frame rate converter engine operating
2000 Jan 27 17
Page 18

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.1.2 FRAME RATE CONVERTER AND SDRAM INTERFACE REGISTERS
Table 6 Detailed description of SNERT FRC and SDRAM register 0x01
BIT SNERT REGISTER 01: FRC_CONTROL_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
X X X number of active lines after rising edge of VS signal; range: 0 to 6 (by default 0)
FRAMERATE_DIVIDER_SELECT_BIT
1 1 1 undefined
1 1 0 32 (30 fps in; 0.9375 fps out)
1 0 1 16 (15 fps in; 0.9375 fps out)
1 0 0 6 (30 fps in; 5 fps out)
0 1 1 3 (30 fps in; 10 fps out) or (15 fps in; 5 fps out)
0 1 0 2 (30 fps in; 15 fps out) or (15 fps in; 7.5 fps out)
0 0 1 1 (1 fps in; 1 fps out) (by default)
0 0 0 undefined
LLC_CLKFREQ
1 24 MHz (by default)
0 12 MHz
Table 7 Detailed description of SNERT FRC and SDRAM register 0x02
BIT SNERT REGISTER 02: FRC_CONTROL_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X X X reserved
REFRESH_MODE
1 automatic SRAM refresh
0 precharge command as implicit refresh (by default)
REFRESH_CLOCK (MSBs)
X X see Table 9
INPUT_FORMAT
1 1 undefined
1 0 medium resolution
0 1 CIF
0 0 VGA (by default)
2000 Jan 27 18
Page 19

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 8 Detailed description of SNERT FRC and SDRAM register 0x03
BIT SNERT REGISTER 03: FRC_ROWWIDTH
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXspecifies the width of the row of the SDRAM
95 for PAL sensors
159 for VGA sensors (by default)
63 for CIF sensors
Table 9 Detailed description of SNERT FRC and SDRAM register 0x04
BIT SNERT REGISTER 04: FRC_REFRESH_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXspecifies the number of clock cycles between two refresh cycles
246 for PAL sensors
395 for VGA sensors (by default)
239 for CIF sensors
Table 10 Detailed description of SNERT FRC and SDRAM register 0x05
BIT SNERT REGISTER 05: FRC_STOPWRITE
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXnumber of lines in a frame
243 for VGA sensors (by default)
146 for PAL or CIF sensors
2000 Jan 27 19
Page 20

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.1.3 PULSE PATTERN GENERATOR REGISTERS
Table 11 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x08
BIT SNERT REGISTER 08: PPG_CONTROL_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X X X reserved
SHUTTER_UPDATE_BUFFER
1 during the vertical blanking (shutter speed is buffered)
0 immediately (by default)
PPG_RESUME_MODE
1 switched off (except vertical transfer pulses in case of VGA sensors)
0 operating (by default)
PPG _FRAMERATE
1 1 X undefined
101 5fps
1 0 0 10 fps
0 1 1 15 fps
0 1 0 20 fps
0 0 1 24 fps
0 0 1 30 fps (by default)
2000 Jan 27 20
Page 21

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 12 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x09
BIT SNERT REGISTER 09: PPG_CONTROL_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
COMPRESSION_CLOCK
1 1 X X reserved
1011 24MHz
1010 19.2 MHz
1001 16MHz
1000 12MHz (by default)
0111 9.6MHz
0110 8.0MHz
0101 6.0MHz
0100 4.8MHz
0011 4.0MHz
0010 2.4MHz
0001 2.0MHz
0000 off
VGA_SENSOR_TYPE (valid if MSB set to logic 0)
1 1 VGA (Sony and Panasonic)
1 0 VGA (Sharp)
0 X reserved
PAL_VGA
1 PAL or CIF timing
0 VGA timing (by default)
2000 Jan 27 21
Page 22

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 13 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0A
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0A: PPG_H_CTRL
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
RG_SHORT
1 RG pulse width is set to half of nominal value
0 RG pulse width is set to nominal value
FH2_CTRL (non FT mode); note 1
1 X 1 no horizontal blanking
1 X 0 no horizontal blanking, pulse inverted
0 1 1 blanked to HIGH, starts HIGH
0 1 0 blanked to LOW, starts LOW
0 0 1 blanked to LOW, starts HIGH
0 0 0 blanked to HIGH, starts LOW
FH1_CTRL (non FT mode); note 1
1 X 1 no horizontal blanking, pulse inverted
1 X 0 no horizontal blanking
0 1 1 blanked to HIGH, starts LOW
0 1 0 blanked to HIGH, starts HIGH
0 0 1 blanked to HIGH, starts LOW
0 0 0 blanked to LOW, starts HIGH
Note
1. If bits [5 to 3] equal bits [2 to 0] then FH2 is the inverse of FH1.
2000 Jan 27 22
Page 23

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 14 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0B
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0B: PPG_V_INV
76543210 PARAMETER
A4_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
A3_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
A2_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
A1_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
B4_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
B3_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
B2_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
B1_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
2000 Jan 27 23
Page 24

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 15 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0C
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0C: PPG_H_INV
76543210 PARAMETER
CLK2_INV
1 inverted pulses
0 nominal pulses
CLK1_INV
1 inverted pulses
0 nominal pulses
FS_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
FCDS_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
FR_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
C3_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
C2_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
C1_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
2000 Jan 27 24
Page 25

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 16 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0D
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0D: PPG_MISC_INV
76543210 PARAMETER
SELECT_A2
1 A2 is HIGH during read-out gate in line 2
0 A2 is LOW during read-out gate in line 2
SELECT_A3
1 A3 equals A4 (in case of VGA type 1 sensors)
0 A3 equals A2
C4_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
CR_INV
1 positive pulses
0 negative pulses
BCP_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
DCP_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
HD_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
VD_INV
1 negative pulses
0 positive pulses
Table 17 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0E
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0E: PPG_SHUTTERSPEED_V_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of line number (9 bits)
Table 18 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x0F
BIT SNERT REGISTER 0F: PPG_SHUTTERSPEED_H_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits)
2000 Jan 27 25
Page 26

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 19 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x10
BIT SNERT REGISTER 10: PPG_SHUTTERSPEED_MSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXX reserved
SENSOR_TYPE
1 Sony
0 Sharp
X X MSBs of pixel number (10 bits)
X MSBs of line number (9 bits)
Table 20 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x11
BIT SNERT REGISTER 11: PPG_BCP_START_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where BCP starts
Table 21 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x12
BIT SNERT REGISTER 12: PPG_BCP_STOP_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where BCP stops
Table 22 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x13
BIT SNERT REGISTER 13: PPG_DCP_START_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where DCP starts
Table 23 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x14
BIT SNERT REGISTER 14: PPG_DCP_STOP_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where DCP stops
Table 24 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x15
BIT SNERT REGISTER 15: PPG_BCP_DCP_MSB
76543210 PARAMETER
X X MSBs of PPG_DCP_STOP
X X MSBs of PPG_DCP_START
X X MSBs of PPG_BCP_STOP
X X MSBs of PPG_BCP_START
2000 Jan 27 26
Page 27

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 25 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x16
BIT SNERT REGISTER 16: PPG_B3_START_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where B3 starts
Table 26 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x17
BIT SNERT REGISTER 14: PPG_B3_STOP_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where B3 stops
Table 27 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x18
BIT SNERT REGISTER 18: PPG_B4_START_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where B4 starts
Table 28 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x19
BIT SNERT REGISTER 19: PPG_B4_STOP_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX8LSBs of pixel number (10 bits) where B4 stops
Table 29 Detailed description of SNERT PPG register 0x1A
BIT SNERT REGISTER 1A: PPG_B3_B4_MSB
76543210 PARAMETER
X X MSBs of PPG_B4_STOP
X X MSBs of PPG_B4_START
X X MSBs of PPG_B3_STOP
X X MSBs of PPG_B3_START
2000 Jan 27 27
Page 28

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.1.4 VIDEO FORMATTER AND COMPRESSION ENGINE REGISTERS
Table 30 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x20
BIT SNERT REGISTER 20: VP_VF_CONTRL_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X X reserved
UV_EXCHANGE
X exchange chrominance irregularities if needed
SCALE_DATA: limits the number of bits of the video signal
1 1 undefined
1 0 6 bits
0 1 7 bits
0 0 8 bits
PREFILTER_B_COMB_ON_OFF (if filter B is on)
1 prefilter B_COMB with 13 taps
0 prefilter B_COMB with 7 taps
PREFILTER_B_ON_OFF
1 on with 7 taps
0 bypassed
PREFILTER_A_ON_OFF
1 on with 3 taps
0 bypassed
2000 Jan 27 28
Page 29

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 31 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x21
BIT SNERT REGISTER 21: VP_VF_CONTRL_1
76543210 PARAMETER
420_FIL_BYPASS: 4 :2:0 formatter mode
1 throw away samples
0 average UV samples
VGA_RAW: data mode
1 raw data, no scaling or 4:2:0 formatting
0 YUV data
VIDEO_OUTPUT_FORMAT
1 1 1 undefined
110 SIF
1 0 1 QSIF
1 0 0 undefined
011 VGA
010 CIF
0 0 1 QCIF
0 0 0 sub-QCIF
VIDEO_INPUT_FORMAT
1 1 1 undefined
1 1 0 square SIF (sensors with square pixels)
1 0 1 CIF (sensors with 12/11 pixel ratio format)
1 0 0 medium resolution PAL
0 1 1 undefined
0 1 0 undefined
0 0 1 undefined
000 VGA
Table 32 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x22
BIT SNERT REGISTER 22: VP_VF_VCOEF_C0_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 0 phase 0
Table 33 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x23
BIT SNERT REGISTER 23: VP_VF_VCOEF_C0_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 0 phase 1
2000 Jan 27 29
Page 30

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 34 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x24
BIT SNERT REGISTER 24: VP_VF_VCOEF_C0_2
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 0 phase 2
Table 35 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x25
BIT SNERT REGISTER 25: VP_VF_VCOEF_C1_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 1 phase 0
Table 36 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x26
BIT SNERT REGISTER 26: VP_VF_VCOEF_C1_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 1 phase 1
Table 37 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x27
BIT SNERT REGISTER 27: VP_VF_VCOEF_C1_2
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 1 phase 2
Table 38 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x28
BIT SNERT REGISTER 28: VP_VF_VCOEF_C2_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 2 phase 0
Table 39 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x29
BIT SNERT REGISTER 29: VP_VF_VCOEF_C2_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 2 phase 1
2000 Jan 27 30
Page 31

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 40 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x2A
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2A: VP_VF_VCOEF_C2_2
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 2 phase 2
Table 41 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x2B
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2B: VP_VF_VCOEF_C3_0
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 3 phase 0
Table 42 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x2C
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2C: VP_VF_VCOEF_C3_1
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 3 phase 1
Table 43 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x2D
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2D: VP_VF_VCOEF_C3_2
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
XXXXXXXvertical filter coefficient tap 3 phase 2
Table 44 Detailed description of SNERT video formatter register 0x2E
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2E: VP_VF_LIMITER
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXoutput of the video formatter is clipped to this maximum value
2000 Jan 27 31
Page 32

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 45 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x2F
BIT SNERT REGISTER 2F: VP_VF_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
QTABLE_SELECT: quantization table select
XXXX range [0 : 15]
DC_COEFF_LENGTH
1 1 undefined
1 0 8 bits
0 1 7 bits
0 0 6 bits
COMPRESSION_MODE
1on
0 off (by default)
Table 46 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x30
BIT SNERT REGISTER 30: VP_C_YMASK
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXoperates an AND between this value and the compression engine input; can be
used to set bit positions in the Y signal to 0 (by default 0x00)
Table 47 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x31
BIT SNERT REGISTER 31: VP_C_UVMASK
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXoperates an AND between this value and the compression engine input; can be
used to set bit positions in the UV signal to 0 (by default 0x00)
Table 48 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x32
BIT SNERT REGISTER 32: VP_C_BITCOST_MSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXset the compression ratio; the bitcost determines the maximum number of bits
generated by the compression algorithm for 4 subsequent lines
Table 49 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x33
BIT SNERT REGISTER 33: VP_C_BITCOST_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXset the compression ratio; the bitcost determines the maximum number of bits
generated by the compression algorithm for 4 subsequent lines
2000 Jan 27 32
Page 33

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 50 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x34
BIT SNERT REGISTER 34: VP_C_THRESHOLD_MSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXoutput of the video formatter is clipped to this maximum value
Table 51 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x35
BIT SNERT REGISTER 35: VP_C_THRESHOLD_LSB
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXthreshold must be set to:
(number of UV blocks per band) × (DC_COEFF_LENGTH + 2)
Table 52 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x36
BIT SNERT REGISTER 36: VP_TR_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
VGA_FORMAT
1 4:2:2 (uncompressed only)
0 4:2:0
INBAND_CONTROL
1on
0 off
LLC_OUT_DIV: select the rate at which the video data is transmitted to the
USB core
XXXXX range [1 to 31]
Table 53 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x37
BIT SNERT REGISTER 37: VP_TR_SQCIF_OFFSET
76543210 PARAMETER
VERTICAL_OFFSET
XXXX range 3 × [0 to 15]
HORIZONTAL_OFFSET
XXXX range 4 × [0 to 12]
Table 54 Detailed description of SNERT compression engine register 0x38
BIT SNERT REGISTER 38: VP_VS_V_SHIFT
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXshift internal line counter with respect to VS pulse
2000 Jan 27 33
Page 34

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.1.5 SWITCH MODE POWER REGISTERS
Table 55 Detailed description of SNERT SMP register 0x3D
BIT SNERT REGISTER 3D: SMP_PERIOD
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXperiod of SMP signal in units of 4 × XOSC_PERIOD (0 by default)
Table 56 Detailed description of SNERT SMP register 0x3E
BIT SNERT REGISTER 3E: SMP_LOWTIME
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXlow edge of SMP signal in units of 4 × XOSC_PERIOD (0 by default)
9.1.6 A
Table 57 Detailed description of SNERT audio gain amplifier register 0x3F
76543210 PARAMETER
X X reserved
UDIO VARIABLE GAIN AMPLIFIER
BIT SNERT REGISTER 3F: AUDIO_VGAIN
SIS: serial interface select
1 SNERT
0I
X reserved
XXXXvariable gain settings (0 to 30 dB)
2
C-bus
2000 Jan 27 34
Page 35

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.2 I2C-bus interface
The USB function has its own I2C-bus interface for communication with the microcontroller. The I2C-bus uses two
addresses:
• Command address for writing commands to the Memory Manager (MM)
• Data address for writing/reading data to/from the Memory Manager (MM).
An address is a byte. The 7 MSBs are the actual address, the LSB is the R/W bit. When it is logic 0, data is transferred
from the master to the slave, when it is logic 1, data is written from the slave to the master.
The 6 MSBs of the two addresses are equal and are defined by the PI_Address = 010111 (see Table 58). The LSB of
the address differentiates between the command address and the data address. When bit 1 is logic 1 the address is the
command address (0x5E) and when bit 1 is logic 0 the address is one of the data addresses (0x5C or 0x5D).
2
Table 58 I
C-bus addresses
BIT
76543210
010111000x5C: for writing data to the memory manager
010111010x5D: for reading data from the memory manager
010111100x5E: for writing commands
010111110x5F: not in use
9.2.1 COMMANDS
The commands listed in Table 59 must be sent to the I2C-bus address 0x5E.
2
Table 59 I
76543210
0 0 end-point number select end-point
0 1 end-point number read/write status
1 0 end-point number initialize/read status information
1101 address read/write register bank
11100XXXnot used
11101000set non-USB register
11110000read/write data
11110001acknowledge setup
11110010set buffer empty
11111010set buffer full
11110100read interrupt register
11110101read current frame number
11110110send resume
11110111set status change bits
11110011set mode
C-bus USB command codes
BIT
ADDRESS
FUNCTION
2000 Jan 27 35
Page 36

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 60 Detailed description of set mode and write register overview
BYTE SET_MODE_AND_WRITE
3 N1 timer: programmable timer for power management; counts 12 MHz cycles; must be bigger than number
of cycles needed for the microcontroller to go in power-down state after pinSUSPREADYNOT is made
LOW
2 N2 timer: programmable timer for power management; counts 12 MHz cycles; determines the time between
the microcontroller clock is switched off and the main clock is switched off
1 PSIE-MMU control byte (see Table 61)
Table 61 Detailed description of set mode and write byte 3
BIT PSIE-MMU CONTROL BYTE
76543210 PARAMETER
X X X reserved
interrupt after isochronous audio transfer
1 for each isochronous audio transfer an interrupt to the microcontroller will
be generated; default set to logic 1 upon general Power-on reset and/or
bus reset by the SAA8115HL
0 no interrupts are given to the microcontroller
interrupt after isochronous video transfer
1 for each isochronous video transfer an interrupt to the microcontroller will
be generated; default set to logic 1 upon general Power-on reset and/or
bus reset by the SAA8115HL
0 no interrupts are given to the microcontroller
audio end-point
1 audioend-pointenabled;defaultsetto logic 1 upon general Power-on reset
and/or bus reset by the SAA8115HL
0 audio end-point disabled; the PSIE-MMU will not react on in-tokens on the
audio end-point
video end-point
1 video end-point enabled; default set to logic 1 upon general Power-on reset
and/or bus reset by the SAA8115HL
0 video end-point disabled; the PSIE-MMU will not react on in-tokens on the
video end-point
error debug mode
1 interrupts are generated only in the event the transfer is not successfully
completed; the microcontroller can read data from the interrupt and status
registers to see the cause of this error
0 all successful USB transactions are reported to the microcontroller via an
interrupt; default set to logic 0 upon general power-on reset by the
SAA8115HL
2000 Jan 27 36
Page 37

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 62 Detailed description of set mode and read status byte
BIT PSIE-MMU STATUS BYTE
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXX reserved
remote wake-up status flag
1 remote wake-up when device is in SUSPEND mode
0 no remote wake-up
resume status flag
1 bus resume by the host when device is in SUSPEND mode
0 no bus resume
bus reset status flag
1 bus reset
0 no bus reset
power-up status flag
1 general power-up reset
0 no power-up reset
9.2.2 E
The SAA8115HL has 6 logical end-points which are listed in Table 63.
Table 63 Mapping of logical to physical end-point numbers for used end-points
Control end-point 0 8 0 1
Control end-point 1 8 2 3
Interrupt end-point 2 8 − 4
Interrupt end-point 3 8 − 5
Iso video end-point 4 96.0 − 6
Iso video end-point 5 35.1 − 7
ND-POINTS
END-POINT NAME
LOGICAL
END-POINT
BUFFER SIZE
PHYSICAL END-POINT
OUT IN
2000 Jan 27 37
Page 38

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.2.3 CONTROL TOP REGISTERS
The following registers can be written on I2C-bus address 1 after the command 0xE8 on I2C-bus address 0.
2
Table 64 I
ADDRESS CONTROL TOP REGISTERS (BASE ADDRESS: 0x08)
0x08 clock control
0x09 reset control
0x0A mux block control
0x0B power-on analog modules control
Table 65 Detailed description of I
76543210 PARAMETER
1 sel_ad: clock generated from ADC
0 sel_pll: clock generated from PLL
C-bus control top registers
2
C-bus control top registers 0x08
BIT TOP REGISTER 0x08: CLKSHOP_CONTROL
select ADC clock source
set clock dividers for ADC
0 0 set_divide00: divided by 1
0 1 set_divide01: divided by 2
1 0 set_divide10: divided by 4
1 1 set_divide11: divided by 8
X reserved
disable 48 MHz clock
1 dis_clk_48: disable 48 MHz clock
0 enable clock
disable receiver clock
1 dis_clk_rec: disable receiver clock
0 enable clock
disable ADC clock
1 dis_clk_ad: disable ADC clock
0 enable clock
X reserved
2000 Jan 27 38
Page 39

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 66 Detailed description of I2C-bus control top registers 0x09
BIT TOP REGISTER 0x09: RST_GEN AND PLL_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
set PLL frequency
0 0 fcode00: 256 × 44.1 kHz
0 1 fcode01: 256 × 32 kHz
1 0 fcode10: 256 × 48 kHz
1 1 fcode11: 256 × 44.1 kHz
X X reserved
reset PSIE-MMU top module
1 upc_rst_mmu: resetting the USB protocol block (called PSIE-MMU) during
tests or in case of errors
0 no reset
X reserved
reset ADIF top module
1 upc_rst_adif: resetting the digital audio part during tests or in case of errors
0 no reset
reset AGC module
1 upc_rst_AGC: resetting the AGC control during tests or in case of errors
0 no reset
2
Table 67 Detailed description of I
BIT TOP REGISTER 0x0A: IO_MUX_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXXreserved
C-bus control top registers 0x0A
2000 Jan 27 39
Page 40

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 68 Detailed description of I2C-bus control top registers 0x0B
BIT TOP REGISTER 0x0B: POWER_CONTROL_OF_ANALOG_MODULES
76543210 PARAMETER
power control oscillator module
1 upc_osc_off: power management 48 MHz enabled
0 power management 48 MHz disabled
power control audio module
1 upc_osc_ad_off: power management audio enabled
0 power management audio disabled
power control PLL module
1 upc_pll_off: PLL power-off
0 power-on
X reserved
power control ADC module left channel
1 upc_adl_off: power-off
0 power-on
power control ADC module right channel
1 upc_adr_off: power-off
0 power-on
power control AGC module left channel
1 upc_AGCl_off: power-off
0 power-on
power control AGC module right channel
1 upc_AGCr_off: power-off
0 power-on
2000 Jan 27 40
Page 41

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.2.4 VIDEO FIFO REGISTERS
Table 69 I2C-bus video FIFO registers overview
ADDRESS VIDEO FIFO REGISTERS (BASE ADDRESS: 0x04)
0x04 FIFO offset (8 LSBs)
0x05 FIFO active and FIFO offset (3 MSBs)
0x06 packet size (8 LSBs)
0x07 read spacing and packet size (2 MSBs)
2
Table 70 Detailed description of I
BIT FIFO REGISTER 0x04: FIFO_OFFSET
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXXXX mode_fifo_offset: sets the minimum contents of the FIFO that has to be
C-bus video FIFO registers 0x04
FIFO_OFFSET
reached, before a new video frame will be put on the USB. This value can
be set between 0 and 2047. Total 11 bits with 8 LSBs in this register and
3 MSBs in register 0x05.
2
Table 71 Detailed description of I
BIT FIFO REGISTER 0x05: FIFO_ACTIVE AND FIFO_OFFSET
76543210 PARAMETER
1 mode_active: FIFO is active and the contents of the other mode registers
0 FIFO not active
XXXX reserved
X X X 3 MSBs of the offset value; see also register 0x04
C-bus video FIFO registers 0x05
FIFO_ACTIVE
should not be updated by the microcontroller (maledictive)
FIFO_OFFSET (MSBs)
2000 Jan 27 41
Page 42

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 72 Detailed description of I2C-bus video FIFO registers 0x06
BIT FIFO REGISTER 0x06: PACKET_SIZE
76543210 PARAMETER
PACKET_SIZE
XXXXXXXX mode_packet_size:setsthepacketsizeoftheUSBvideochannel.Packets
can vary in size between 0 and 1023. Total 10 bits with 8 LSBs in this
register and 2 MSBs in register 0x07.
2
Table 73 Detailed description of I
BIT FIFO REGISTER 0x07: READ_SPACING AND PACKET_SIZE
76543210 PARAMETER
XXXXXX mode_read_spacing: sets the periodicity of the read pulses; the periodicity
C-bus video FIFO registers 0x07
READ_SPACING
can be set from 1 to 63 (from ‘000001’ to ‘111111’)
PACKET_SIZE
X X mode_packet_size: 2 MSBs of the value (8 LSBs in register 0x06)
2000 Jan 27 42
Page 43

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
9.2.5 ADIF TOP REGISTERS
Table 74 I2C-bus ADIF top registers overview
ADDRESS ADIF TOP REGISTERS (BASE ADDRESS: 0x0C)
0x0C reserved
0x0D reserved
0x0E VGA control gain
0x0F ADIF control (ADIF2MMU)
2
Table 75 Detailed description of I
BIT ADIF REGISTER 0x0E: GAIN_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
0 reserved
1 gain is controlled directly by bits 3 to 0
X X reserved
0000 0dB
0001 2dB
:::: :
0111 28dB
1111 30dB
C-bus ADIF top registers 0x0E
GAIN_SOURCE_SELECT
GAIN_CONTROL; 0 to 30 dB in steps of 2 dB
2000 Jan 27 43
Page 44

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Table 76 Detailed description of I2C-bus ADIF top registers 0x0F
BIT ADIF REGISTER 0x0F: ADIF_CONTROL
76543210 PARAMETER
X reserved
number of bytes per sample
0 0 0 (reserved)
0 1 1 (8 bits audio samples)
1 0 2 (16 bits audio samples)
1 1 3 (24 bits audio samples)
selection mono/stereo operation
0 mono
1 stereo
selection input for ADC path (ADIF mux)
0 digital input (from I
1 analog input (from Vin_left and Vin_right)
selection high-pass filter (DC filter) for ADC down sample filter
0 high-pass filter off
1 high-pass filter on
selection audio serial input format
00 I
0 1 LSB-justified, 16 bits
1 0 LSB-justified, 18 bits
1 1 LSB-justified, 20 bits
2
S-bus
2
S-bus)
2000 Jan 27 44
Page 45

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
10 LIMITING VALUES
In accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 60134).
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. MAX. UNIT
V
DDA
V
DDA_USB
V
DDD
V
n
T
stg
T
amb
T
j
Note
1. This concerns pins VBUS1 and VBUS2.
analog supply voltage −0.5 +4.0 V
analog supply voltage from USB note 1 −0.5 +5.5 V
digital supply voltage −0.5 +4.0 V
voltage on
pins AGND and DGND −0.5 +4.0 V
all other pins −0.5 VDD+ 0.5 V
storage temperature −55 +150 °C
ambient temperature 0 70 °C
junction temperature −40 +125 °C
11 THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS VALUE UNIT
R
th(j-a)
thermal resistance from junction to ambient in free air 45 K/W
12 CHARACTERISTICS
V
DDD=VDDA
= 3.3 V ±10%; T
=0to70°C.
amb
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Supplies
V
DDDn
V
DDAn
V
DDA_USB
V
DGND
V
AGND
I
DDDn
I
DDAn
digital supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage 3.0 3.3 3.6 V
analog supply voltage from USB note 1 4.0 5.0 5.5 V
digital ground supply −0.3 0.0 +0.3 V
analog ground supply −0.3 0.0 +0.3 V
digital supply current T
analog supply current T
=25°C −−tbf mA
amb
=25°C −−tbf mA
amb
Data and control inputs
V
IL
V
IH
LOW-level input voltage −−0.8 V
HIGH-level input voltage 2.0 −−V
Data and control outputs
V
OL
V
OH
LOW-level output voltage 0 − 0.1V
HIGH-level output voltage 0.9V
DDD
− V
DDD
DDD
V
V
2000 Jan 27 45
Page 46

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Microphone supply
I
DD0
V
ref
V
O
I
O
Low noise amplifier
TRANSFER FUNCTION
R
i
I
DD1
A amplification 27 28 29 dB
V
o(rms)
THD total harmonic distortion note 2 −−69 −63 dB
V
OO1
BIASING
I
ref1
Variable gain amplifier
supply current − 0.85 1.2 mA
input reference voltage at1⁄2V
output voltage V
DDA
DDA
= 3.3 V − 3.0 − V
− 1.65 − V
output current −−2.0 mA
input impedance 3.5 5.0 − kΩ
supply current − 0.85 1.2 mA
output voltage (RMS value) −−800 mV
output offset voltage − 0.0 1.0 mV
reference current − 10 −µA
TRANSFER FUNCTION
R
I
DD2
i
input impedance 7.0 10.5 13 kΩ
supply current − 0.45 0.6 mA
A amplification 0.0 − 32 dB
THD total harmonic distortion note 3 −−88 −82 dB
note 4 −−65 −57 dB
V
OO2
output offset voltage A = 0 dB − 1.0 2.0 mV
A = 30 dB − 14 30 mV
B
IASING
I
ref2
reference current − 10 −µA
Audio PLL
f
i(clk)
f
o(clk)
clock input frequency − 48 − MHz
clock output frequency note 5 − 11.2996 − MHz
B bandwidth − 2.3 − kHz
ζ damping − 0.98 −
Audio ADC (∑∆ converter)
I
NPUTS
f
i
V
i(rms)
input signal frequency 1 − 20 kHz
input voltage (RMS value) − 800 − mV
TRANSFER FUNCTION
N order of the ∑∆ − 3 −
N
bit
number of output bits − 1 −
2000 Jan 27 46
Page 47

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
N
bit(eq)
DR
i
f
clk
δ clock frequency duty factor − 50 − %
THD total harmonic distortion −−70 −55 dB
ATX transceiver
D
RIVER CHARACTERISTICS IN FULL SPEED MODE: PINS ATXDP AND ATXDM
f
o(sample)
t
r
t
f
t
match
V
cr
Z
o
RECEIVER CHARACTERISTICS IN FULL SPEED MODE: PINS ATXDP AND ATXDM
f
i(sample)
f
i(D)
t
frame
DC-to-DC converter
equivalent output resolution (bit) − 16 −
dynamic range at input note 6 − 96.6 − dB
clock frequency −−5.6448 MHz
sample output frequency 4 − 48 kHz
rise transition time CL=50pF 4 − 20 ns
fall transition time CL=50pF 4 − 20 ns
transition time matching note 7 90 − 110 %
output signal crossover voltage 1.3 − 2.0 V
driver output impedance steady state drive 30 − 42 Ω
sample input frequency 5 − 55 kHz
data input frequency rate − 12.00 − Mbits/s
frame interval − 1.000 − ms
5VUP AND DOWN CONVERTER (SWITCHABLE SUPPLY DOMAIN)
V
O
V
ripple
I
L
R
DSON_P1
output voltage 4.9 5.0 5.1 V
ripple on output voltage − 20 − mV
load current −−150 mA
PMOS switch-on resistance; down
note 8 − 1.0 −Ω
converter
R
DSON_N1
NMOS switch-on resistance; down
note 8 − 4.5 −Ω
converter
R
DSON_P2
PMOS switch-on resistance; up
note 8 − 1.1 −Ω
converter
R
DSON_N2
NMOS switch-on resistance; up
note 8 − 4.6 −Ω
converter
2000 Jan 27 47
Page 48

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
Notes
1. This concerns pins VBUS1 and VBUS2.
2. The distortion is measured at 1 kHz, V
3. The distortion is measured at 1 kHz, V
4. The distortion is measured at 1 kHz, V
5. Frequencies depend on PLL settings (see Table 2).
= 600 mV.
o(rms)
= 600 mV and A=0dB.
o(rms)
= 600 mV and A = 30 dB.
o(rms)
match
input voltage
t
r
100%×=
-- t
f
6. Defined here as:
20
7. Transition time matching:
------------------------------------------------------------------------------ -log×
equivalent input noise voltage
t
8. Including metal and contact resistance on chip and bonding wire resistance.
2000 Jan 27 48
Page 49

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
13 TIMING
V
DDD=VDDA
SYMBOL PARAMETER CONDITIONS MIN. TYP. MAX. UNIT
Data input related to LLC (see Fig.6)
INS YUV0 TO YUV7, HREF, VS
P
t
su(i)(D)
t
h(i)(D)
PPG high-speed pulses for Sony ICX098AK VGA CCD-sensor (see Fig.7)
t
d1
t
d2
t
d3
t
d4
t
d5
t
d6
t
d7
t
d8
t
WH(C1)
t
WL(C2)
t
WL(FCDS)
t
WL(FS)
t
WL(RG)
t
WL(CLK1)
t
WH(CLK2)
t
r
t
f
= 3.3 V ±10%; T
=0to70°C.
amb
data input set-up time 5 −−ns
data input hold time 3 −−ns
delay between falling edgeC2 and rising edge C1 −3.5 −2.5 −1.5 ns
delay between rising edge C2 and falling edge C1 0 1.5 3 ns
delay between falling edgeC1 and rising edge FCDS 20.5 21.5 22.5 ns
delay between rising edge C1 and rising edge FS 21.5 22.5 23.5 ns
delay between rising edge C1 and falling edge RG 0 1.5 3 ns
delay between falling edgeCLK1 and rising edge C1 0 0.5 2 ns
delay between rising edge CLK1 and falling edge C1 2.5 3.0 3.5 ns
delay between rising edge CLK2 and rising edge C1 1 1.5 2 ns
C1 pulse width HIGH 80 81 − ns
C2 pulse width LOW 84 85 − ns
FCDS pulse width LOW 17 18.5 − ns
FS pulse width LOW 41 42 − ns
RG pulse width LOW 42 43 − ns
CLK1 pulse width LOW 84 84.5 − ns
CLK2 pulse width HIGH 39 40 − ns
rise time note 1
pulse C1 − 4 − ns
pulse C2 − 4 − ns
pulse RG − 4 − ns
pulse FCDS − 4 − ns
pulse FS − 4 − ns
fall time note 1
pulse C1 − 4 − ns
pulse C2 − 4 − ns
pulse RG − 4 − ns
pulse FCDS − 4 − ns
pulse FS − 4 − ns
Note
1. C
= 11 pF; T
L
amb
=25°C.
2000 Jan 27 49
Page 50

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
handbook, full pagewidth
LLC
handbook, full pagewidth
data input
C1
C2
FCDS
Fig.6 Data input timing.
t
WH(C1)
50% 50%
t
d1
50% 50%
t
WL(C2)
50% 50%
t
su(i)D
t
d2
t
h(i)D
FCE606
50%
t
WL(FCDS)
FS
RG
CLK1
CLK2
t
d5
50% 50%
50% 50%
50%
t
d6
t
d8
t
WL(RG)
t
t
WH(CLK2)
WL(CLK1)
50%
Fig.7 PPG high-speed pulses for Sony ICX098AK VGA CCD-sensor.
2000 Jan 27 50
t
d3
50% 50%
t
d7
t
WL(FS)
t
d4
FCE607
Page 51

This text is here in white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here in
a
_white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader.This text is here inThis text is here in
white to force landscape pages to be rotated correctly when browsing through the pdf in the Acrobat reader. white to force landscape pages to be ...
2000 Jan 27 51
ndbook, full pagewidth
14 APPLICATION INFORMATION
Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
V-DRIVER
CCD9 to CCD0
TDA878xSENSOR
FS, FCDS, DCP, BCP, CLK1
C1 to C4, CR, RG
A1 to A4, B1 to B4
SMP
RESET
SDATA
SCLK
STROBE
DATA7 to DATA0
M
EPPROM
(optional)
PSEN
ALE
AD10 to AD8
AD15 to AD11
SDAE
SAA8112HL
DSP AND
MICROCONTROLLER
UCM
EEPROM
SCLE
SCL
SDA
YUV7 to YUV0
HREF
VS
LLC
HD
VD
CLK1
CLK2
SNRES
SNCL
SNDA
SUSPEND
SUSPREADYNOT
UCINT
UCPOR
UCCLK
SDRAM
(optional)
DQ15 to DQ0
AD10 to AD0
RASB
CASB
SAA8115HL
USB INTERFACE
FCE464
DQM
WEB
CLKEN
CLOCKON
TRC
CSB
SMP
Fig.8 Typical USB camera application.
Page 52

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
15 PACKAGE OUTLINE
LQFP144: plastic low profile quad flat package; 144 leads; body 20 x 20 x 1.4 mm
c
y
X
A
SOT486-1
108
109
pin 1 index
144
1
w M
b
e
p
D
H
D
DIMENSIONS (mm are the original dimensions)
mm
A
max.
1.6
0.15
0.05
1.45
1.35
0.25
cE
p
0.27
0.20
0.17
0.09
UNIT A1A2A3b
73
72
Z
E
e
H
E
E
A
2
A
A
1
w M
b
p
detail X
37
36
v M
Z
D
A
B
v M
B
0 5 10 mm
scale
(1)
(1) (1)(1)
D
20.1
19.9
eH
H
20.1
19.9
0.50
22.15
21.85
D
E
22.15
21.85
LL
p
0.75
0.45
0.080.2 0.081.0
Z
1.40
1.10
D
(A )
3
L
p
L
Zywv θ
E
o
1.40
7
o
1.10
0
θ
Note
1. Plastic or metal protrusions of 0.25 mm maximum per side are not included.
OUTLINE
VERSION
IEC JEDEC EIAJ
REFERENCES
SOT486-1 136E23 MS-026
2000 Jan 27 52
EUROPEAN
PROJECTION
ISSUE DATE
99-12-03
00-01-19
Page 53

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
16 SOLDERING
16.1 Introduction to soldering surface mount
packages
Thistextgivesaverybriefinsightto a complex technology.
A more in-depth account of soldering ICs can be found in
our
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages”
(document order number 9398 652 90011).
There is no soldering method that is ideal for all surface
mount IC packages. Wave soldering is not always suitable
for surface mount ICs, or for printed-circuit boards with
high population densities. In these situations reflow
soldering is often used.
16.2 Reflow soldering
Reflow soldering requires solder paste (a suspension of
fine solder particles, flux and binding agent) to be applied
totheprinted-circuitboardbyscreenprinting,stencillingor
pressure-syringe dispensing before package placement.
Several methods exist for reflowing; for example,
infrared/convection heating in a conveyor type oven.
Throughput times (preheating, soldering and cooling) vary
between 100 and 200 seconds depending on heating
method.
Typical reflow peak temperatures range from
215 to 250 °C. The top-surface temperature of the
packages should preferable be kept below 230 °C.
If wave soldering is used the following conditions must be
observed for optimal results:
• Use a double-wave soldering method comprising a
turbulent wave with high upward pressure followed by a
smooth laminar wave.
• For packages with leads on two sides and a pitch (e):
– larger than or equal to 1.27 mm, the footprint
longitudinal axis is preferred to be parallel to the
transport direction of the printed-circuit board;
– smaller than 1.27 mm, the footprint longitudinal axis
must be parallel to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board.
The footprint must incorporate solder thieves at the
downstream end.
• Forpackageswithleadsonfoursides, the footprint must
be placed at a 45° angle to the transport direction of the
printed-circuit board. The footprint must incorporate
solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
During placement and before soldering, the package must
be fixed with a droplet of adhesive. The adhesive can be
applied by screen printing, pin transfer or syringe
dispensing. The package can be soldered after the
adhesive is cured.
Typical dwell time is 4 seconds at 250 °C.
A mildly-activated flux will eliminate the need for removal
of corrosive residues in most applications.
16.3 Wave soldering
Conventional single wave soldering is not recommended
forsurfacemountdevices(SMDs)orprinted-circuit boards
with a high component density, as solder bridging and
non-wetting can present major problems.
To overcome these problems the double-wave soldering
method was specifically developed.
2000 Jan 27 53
16.4 Manual soldering
Fix the component by first soldering two
diagonally-opposite end leads. Use a low voltage (24 V or
less) soldering iron applied to the flat part of the lead.
Contact time must be limited to 10 seconds at up to
300 °C.
When using a dedicated tool, all other leads can be
soldered in one operation within 2 to 5 seconds between
270 and 320 °C.
Page 54

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
16.5 Suitability of surface mount IC packages for wave and reflow soldering methods
PACKAGE
WAVE REFLOW
(1)
BGA, SQFP not suitable suitable
SOLDERING METHOD
HLQFP, HSQFP, HSOP, HTSSOP, SMS not suitable
(3)
PLCC
, SO, SOJ suitable suitable
LQFP, QFP, TQFP not recommended
SSOP, TSSOP, VSO not recommended
(2)
(3)(4)
(5)
suitable
suitable
suitable
Notes
1. All surface mount (SMD) packages are moisture sensitive. Depending upon the moisture content, the maximum
temperature (with respect to time) and body size of the package, there is a risk that internal or external package
cracks may occur due to vaporization of the moisture in them (the so called popcorn effect). For details, refer to the
Drypack information in the
“Data Handbook IC26; Integrated Circuit Packages; Section: Packing Methods”
.
2. These packages are not suitable for wave soldering as a solder joint between the printed-circuit board and heatsink
(at bottom version) can not be achieved, and as solder may stick to the heatsink (on top version).
3. If wave soldering is considered, then the package must be placed at a 45° angle to the solder wave direction.
The package footprint must incorporate solder thieves downstream and at the side corners.
4. Wave soldering is only suitable for LQFP, TQFP and QFP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.8 mm;
it is definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.65 mm.
5. Wave soldering is only suitable for SSOP and TSSOP packages with a pitch (e) equal to or larger than 0.65 mm; it is
definitely not suitable for packages with a pitch (e) equal to or smaller than 0.5 mm.
2000 Jan 27 54
Page 55

Philips Semiconductors Preliminary specification
Digital camera USB interface SAA8115HL
17 DEFINITIONS
Data sheet status
Objective specification This data sheet contains target or goal specifications for product development.
Preliminary specification This data sheet contains preliminary data; supplementary data may be published later.
Product specification This data sheet contains final product specifications.
Limiting values
Limiting values given are in accordance with the Absolute Maximum Rating System (IEC 134). Stress above one or
more of the limiting values may cause permanent damage to the device. These are stress ratings only and operation
of the device at these or at any other conditions above those given in the Characteristics sections of the specification
is not implied. Exposure to limiting values for extended periods may affect device reliability.
Application information
Where application information is given, it is advisory and does not form part of the specification.
18 LIFE SUPPORT APPLICATIONS
These products are not designed for use in life support appliances, devices, or systems where malfunction of these
products can reasonably be expected to result in personal injury. Philips customers using or selling these products for
use in such applications do so at their own risk and agree to fully indemnify Philips for any damages resulting from such
improper use or sale.
19 PURCHASE OF PHILIPS I
Purchase of Philips I
components in the I2C system provided the system conforms to the I2C specification defined by
Philips. This specification can be ordered using the code 9398 393 40011.
2
C COMPONENTS
2
C components conveys a license under the Philips’ I2C patent to use the
2000 Jan 27 55
Page 56

Philips Semiconductors – a w orldwide compan y
Argentina: see South America
Australia: 3 Figtree Drive, HOMEBUSH, NSW 2140,
Tel. +61 2 9704 8141, Fax. +61 2 9704 8139
Austria: Computerstr. 6, A-1101 WIEN, P.O. Box 213,
Tel. +43 1 60 101 1248, Fax. +43 1 60 101 1210
Belarus: Hotel Minsk Business Center, Bld. 3, r. 1211, Volodarski Str. 6,
220050 MINSK, Tel. +375 172 20 0733, Fax. +375 172 20 0773
Belgium: see The Netherlands
Brazil: see South America
Bulgaria: Philips Bulgaria Ltd., Energoproject, 15th floor,
51 James Bourchier Blvd., 1407 SOFIA,
Tel. +359 2 68 9211, Fax. +359 2 68 9102
Canada: PHILIPS SEMICONDUCTORS/COMPONENTS,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
China/Hong Kong: 501 Hong Kong Industrial Technology Centre,
72 Tat Chee Avenue, Kowloon Tong, HONG KONG,
Tel. +852 2319 7888, Fax. +852 2319 7700
Colombia: see South America
Czech Republic: see Austria
Denmark: Sydhavnsgade 23, 1780 COPENHAGEN V,
Tel. +45 33 29 3333, Fax. +45 33 29 3905
Finland: Sinikalliontie 3, FIN-02630 ESPOO,
Tel. +358 9 615 800, Fax. +358 9 6158 0920
France: 51 Rue Carnot, BP317, 92156 SURESNES Cedex,
Tel. +33 1 4099 6161, Fax. +33 1 4099 6427
Germany: Hammerbrookstraße 69, D-20097 HAMBURG,
Tel. +49 40 2353 60, Fax. +49 40 2353 6300
Hungary: see Austria
India: Philips INDIA Ltd, Band Box Building, 2nd floor,
254-D, Dr. Annie Besant Road, Worli, MUMBAI 400 025,
Tel. +91 22 493 8541, Fax. +91 22 493 0966
Indonesia: PTPhilips DevelopmentCorporation, SemiconductorsDivision,
Gedung Philips, Jl. Buncit Raya Kav.99-100, JAKARTA 12510,
Tel. +62 21 794 0040 ext. 2501, Fax. +62 21 794 0080
Ireland: Newstead, Clonskeagh, DUBLIN 14,
Tel. +353 1 7640 000, Fax. +353 1 7640 200
Israel: RAPAC Electronics, 7 Kehilat Saloniki St, PO Box 18053,
TEL AVIV 61180, Tel. +972 3 645 0444, Fax. +972 3 649 1007
Italy: PHILIPSSEMICONDUCTORS,Via Casati, 23 - 20052 MONZA (MI),
Tel. +39 039 203 6838, Fax +39 039 203 6800
Japan: Philips Bldg 13-37, Kohnan 2-chome, Minato-ku,
TOKYO 108-8507, Tel. +81 3 3740 5130, Fax. +81 3 3740 5057
Korea: Philips House, 260-199 Itaewon-dong, Yongsan-ku, SEOUL,
Tel. +82 2 709 1412, Fax. +82 2 709 1415
Malaysia: No. 76 Jalan Universiti, 46200 PETALING JAYA, SELANGOR,
Tel. +60 3 750 5214, Fax. +60 3 757 4880
Mexico: 5900 Gateway East, Suite 200, EL PASO, TEXAS 79905,
Tel. +9-5 800 234 7381, Fax +9-5 800 943 0087
Middle East: see Italy
Netherlands: Postbus 90050, 5600 PB EINDHOVEN, Bldg. VB,
Tel. +31 40 27 82785, Fax. +31 40 27 88399
New Zealand: 2 Wagener Place, C.P.O. Box 1041, AUCKLAND,
Tel. +64 9 849 4160, Fax. +64 9 849 7811
Norway: Box 1, Manglerud 0612, OSLO,
Tel. +47 22 74 8000, Fax. +47 22 74 8341
Pakistan: see Singapore
Philippines: Philips Semiconductors Philippines Inc.,
106 Valero St. Salcedo Village, P.O. Box 2108 MCC, MAKATI,
Metro MANILA, Tel. +63 2 816 6380, Fax. +63 2 817 3474
Poland: Al.Jerozolimskie 195 B, 02-222 WARSAW,
Tel. +48 22 5710 000, Fax. +48 22 5710 001
Portugal: see Spain
Romania: see Italy
Russia: Philips Russia, Ul. Usatcheva 35A, 119048 MOSCOW,
Tel. +7 095 755 6918, Fax. +7 095 755 6919
Singapore: Lorong 1, Toa Payoh, SINGAPORE 319762,
Tel. +65 350 2538, Fax. +65 251 6500
Slovakia: see Austria
Slovenia: see Italy
South Africa: S.A. PHILIPS Pty Ltd., 195-215 Main Road Martindale,
2092 JOHANNESBURG, P.O. Box 58088 Newville 2114,
Tel. +27 11 471 5401, Fax. +27 11 471 5398
South America: Al. Vicente Pinzon, 173, 6th floor,
04547-130 SÃO PAULO, SP, Brazil,
Tel. +55 11 821 2333, Fax. +55 11 821 2382
Spain: Balmes 22, 08007 BARCELONA,
Tel. +34 93 301 6312, Fax. +34 93 301 4107
Sweden: Kottbygatan 7, Akalla, S-16485 STOCKHOLM,
Tel. +46 8 5985 2000, Fax. +46 8 5985 2745
Switzerland: Allmendstrasse 140, CH-8027 ZÜRICH,
Tel. +41 1 488 2741 Fax. +41 1 488 3263
Taiwan: Philips Semiconductors, 6F, No. 96, Chien Kuo N. Rd., Sec. 1,
TAIPEI, Taiwan Tel. +886 2 2134 2886, Fax. +886 2 2134 2874
Thailand: PHILIPS ELECTRONICS (THAILAND) Ltd.,
209/2 Sanpavuth-Bangna Road Prakanong, BANGKOK 10260,
Tel. +66 2 745 4090, Fax. +66 2 398 0793
Turkey: Yukari Dudullu, Org. San. Blg., 2.Cad. Nr. 28 81260 Umraniye,
ISTANBUL, Tel. +90 216 522 1500, Fax. +90 216 522 1813
Ukraine: PHILIPS UKRAINE, 4 Patrice Lumumba str., Building B, Floor 7,
252042 KIEV, Tel. +380 44 264 2776, Fax. +380 44 268 0461
United Kingdom: Philips Semiconductors Ltd., 276 Bath Road, Hayes,
MIDDLESEX UB3 5BX, Tel. +44 208 730 5000, Fax. +44 208 754 8421
United States: 811 East Arques Avenue, SUNNYVALE, CA 94088-3409,
Tel. +1 800 234 7381, Fax. +1 800 943 0087
Uruguay: see South America
Vietnam: see Singapore
Yugoslavia: PHILIPS, Trg N. Pasica 5/v, 11000 BEOGRAD,
Tel. +381 11 3341 299, Fax.+381 11 3342 553
For all other countries apply to: Philips Semiconductors,
International Marketing & Sales Communications, Building BE-p, P.O. Box 218,
5600 MD EINDHOVEN, The Netherlands, Fax. +31 40 27 24825
© Philips Electronics N.V. SCA
All rights are reserved. Reproduction in whole or in part is prohibited without the prior written consent of the copyright owner.
The information presented in this document does not form part of anyquotationorcontract,is believed to be accurate and reliable and may be changed
without notice. No liability will be accepted by the publisher for any consequence of its use. Publication thereof does not convey nor imply any license
under patent- or other industrial or intellectual property rights.
2000
Internet: http://www.semiconductors.philips.com
69
Printed in The Netherlands 753505/03/pp56 Date of release: 2000 Jan 27 Document order number: 9397750 06568
 Loading...
Loading...