Page 1

NTE7133
Integrated Circuit
Horizontal and Vertical Deflection Controller
for VGA/XGA and Autosync Monitors
Description:
The NTE7133 is an integrated circuit in a 20–Lead DIP type package. This device is designed to provide an economical solution in VGA/XGA and autosync monitors by incorporating complete horizontal and vertical small signal processing. VGA–dependent mode detection and setting are performed
on–chip.
Features:
D VGA Operation Fully Implemented Including Alignment–Free Vertical and E/W Amplitude
Pre–Settings
D 4th VGA Mode Easy Applicable (XGA, Super VGA)
D Autosync Operation Externally Selectable
D Low Jitter
D All Adjustments DC–Controllable
D Alignment–Free Oscillators
D Sync Separators for Video or Horizontal and Vertical TTL Sync Levels Regardless or Polarity
D Horizontal Oscillator with P
D Constant Vertical and E/W Amplitude in Multi–Frequency Operation
D DC–Coupling to Vertical Power Amplifier
D Internal Supply Voltage Stabilization with Excellent Ripple Rejection to Ensure Stable Geometrical
Adjustments
for Sync and P
LL1
for Flyback
LL2
Absolute Maximum Ratings:
Supply Voltage (Pin1), V
Voltage (Pin3, Pin7), V3, V
Voltage (Pin8), V
8
Voltage (Pin5, Pin6, Pin9, Pin10, Pin13, Pin14, Pin18), V
Current (Pin2), I
Current (Pin3), I
Current (Pin7), I
Current (Pin8), I
2
3
7
8
Electrostatic Handling for All Pins (Note 1), V
Operating Junction Temperature, T
Operating Ambient Temperatrure Range, T
Storage Temperature Range, T
Thermal Resistance, Junction–to–Ambient (In Free Air), R
P
7
n
esd
J
A
stg
thJA
Note 1. Equivalent to discharging a 200pF capacitor through a 0Ω series resistor.
–0.5 to +16V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–0.5 to +16V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–0.5 to +7V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–0.5 to +6.5V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±10mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
100mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
20mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–10mA. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
±400V. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
+150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
0° to +70°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
–55° to +150°C. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
65K/W. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Page 2
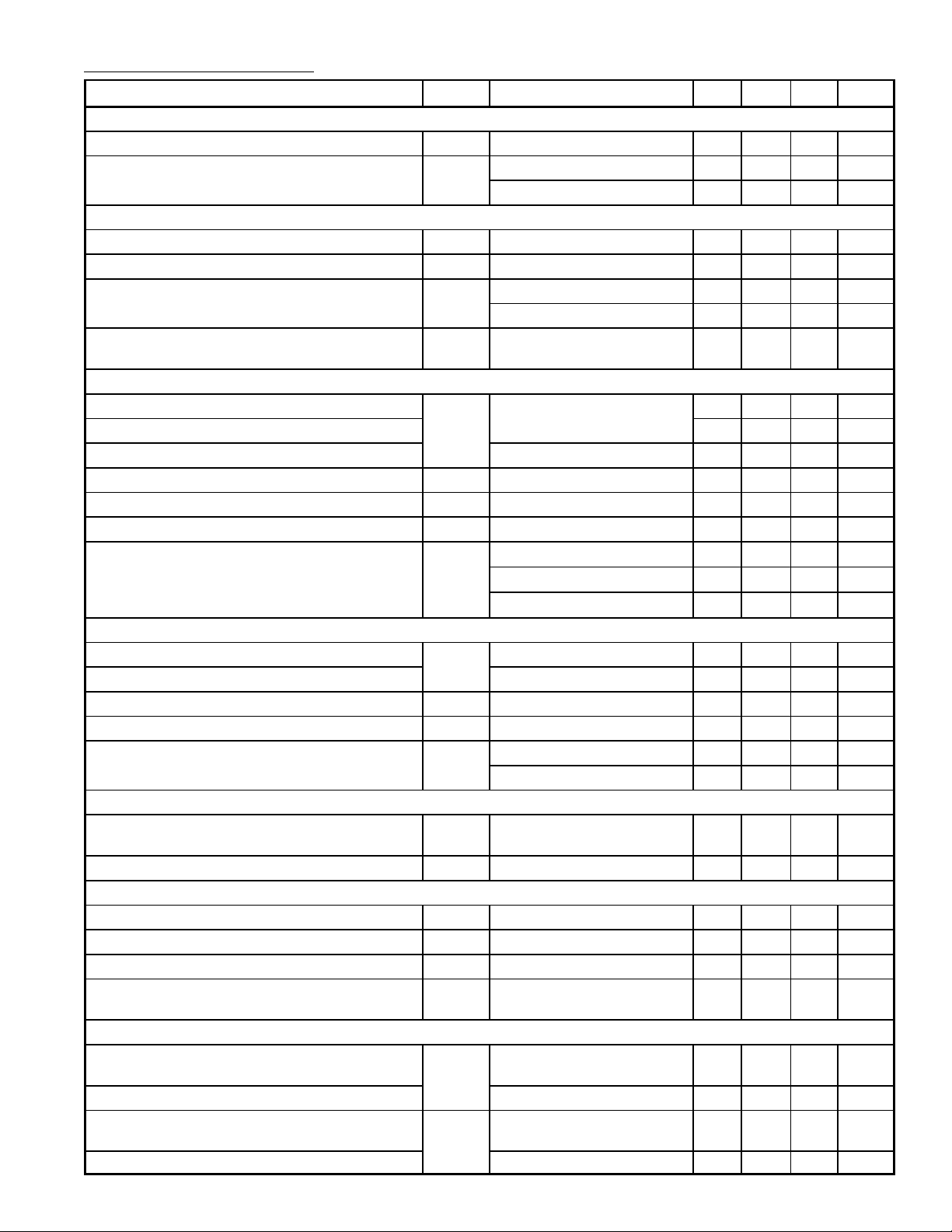
Electrical Characteristics: (VP = 12V, TA = +25°C unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Supply
Positive Supply Voltage (Pin1) V
Supply Current I
P
I18 = –1.05mA – 36 44 mA
P
I18 = –3.388mA – 40 49 mA
Internal Reference Voltage
Internal Reference Voltage V
ref
Temperature Coefficient TC TA = +20° to +100°C – – ±90 10–6/K
Power Supply Ripple Rejection PSRR f = 1kHz Sine Wave 60 75 – dB
f = 1MHz Sine Wave 25 35 – dB
Supply Voltage (Pin1) to Ensure All Internal
V
P
Reference Voltages
Composite Sync Input (AC–Coupled, V10 = 5V)
Sync Amplitude of Video Input Signal (Pin9) V
i sync
Sync on Green – 300 – mV
Top Sync Clamping Level 1.1 1.28 1.5 V
Slicing Level Above Top Sync Level Sync on Green, RS = 50Ω 90 120 150 mV
Allowed Source Resistance for 7% Duty Cycle R
Differential Input Resistance r
Charging Current of Coupling Capacitor I
Vertical Sync Integration Time to Generate
Sync Pulse
t
V
S
9
9
int
> 200mV – – 1.5 kΩ
i sync
During Sync – 80 – Ω
V9 > 1.5V 1.3 2.0 3.0 µA
fH = 31kHz, I18 = –1.050mA 7 10 13 µs
fH = 64kHz, I18 = –2.169mA 3.5 5.0 6.5 µs
fH = 100kHz, I18 = –3.388mA 2.5 3.4 4.5 µs
Horizontal Sync Input (DC–Coupled, TTL–Compatible)
Sync Input Signal (Peak Value, Pin9) V
u sync
Slicing Level 1.2 1.4 1.6 V
Minimum Pulse Width t
Rise Time and Fall Time tr, t
Input Current I
p
f
V9 = 0.8V – – –200 µA
9
V9 5.5V – – 10 µA
Automatic Horizontal Polarity Switch (H–Sync on Pin9)
Horizontal Sync Pulse Width Related to t
H
t
p H/tH
(Duty Cycle for Automatic Polarity Correction)
Delay Time for Changing Sync Polarity t
p
Vertical Sync Input (DC–Coupled, TTL–Compatible,,V–Sync on Pin10)
Sync Input Signal (Peak Value, Pin10) V
i sync
Slicing Level 1.2 1.4 1.6 V
Input Current I
Maximum Vertical Sync Pulse Width for
t
p V
0 < V10 < 5.5V – – ±10 µA
10
Automatic Vertical Polarity Switch
Horizontal Mode Detector Output (VGA Mode)
Output Saturation Voltage LOW
V
I7 = 6mA – 0.275 0.33 V
7
(For Modes 1, 2, and 3)
Output Voltage HIGH Mode 4 – – V
Load Current to Force VGA Mode–Dependent
I
Modes 1, 2, and 3 2 – 6 mA
7
Vertical and Parabola Amplitudes
Output Current Mode 4 – 0 – mA
9.2 12.0 16.0 V
6.0 6.25 6.5 V
9.2 – 16.0 V
1.7 – – V
700 – – ns
10 – 500 ns
– – 30 %
0.3 – 1.8 ms
1.7 – – V
– – 300 µs
P
V
Page 3
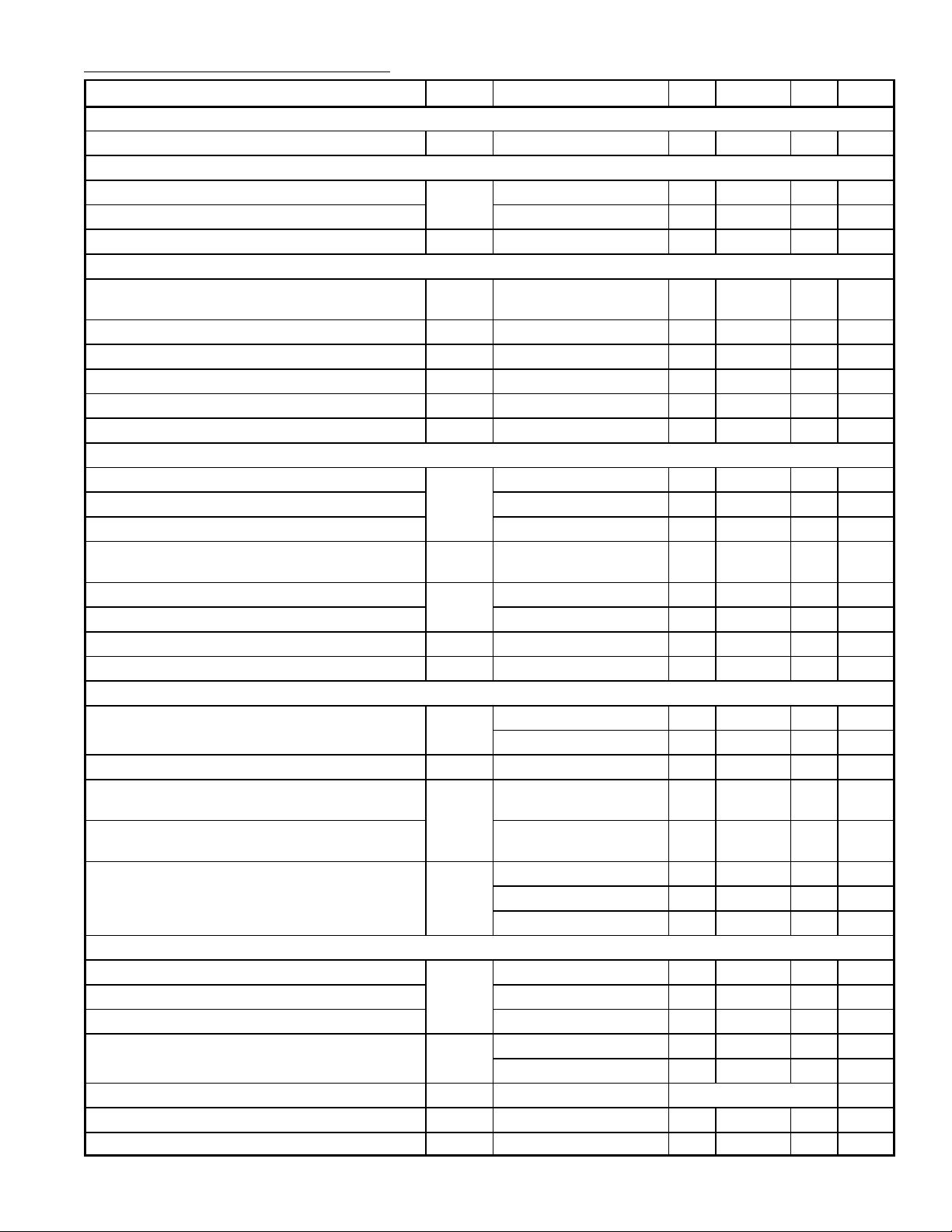
Electrical Characteristics (Cont’d): (VP = 12V, TA = +25°C unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
VGA/Autosync Mode Switch
Input Voltage LOW to Force Autosync Mode V
Horizontal Comparator P
LL1
Upper Control Voltage Limitation V
7
17
Lower Control Voltage Limitation
Control Current I
17
Horizontal Oscillator
Center Frequency f
OSC
R18 = 2.4kΩ (Pin18),
C19 = 10nF (Pin19)
Deviation of Center Frequency ∆f
OSC
Temperature Coefficient TC – +200 +300 10–6/K
Relative Holding/Catching Range ϕH/t
External Oscillator Current I
Voltage at Reference Current Input (Pin18) V
Horizontal P
LL2
Upper Clamping Level of Flyback Input V
H
18
18
I2 = 6mA – 5.5 – V
2
Lower Clamping Level of Flyback Input I2 = –1mA – –0.75 – V
H–Flyback Slicing Level – 3.0 – V
Delay Between Middle of Sync and Middle of
H–Flyback Related to t
H
Upper Control Voltage Limitation V
td/t
H
20
Lower Control Voltage Limitation – 4.8 – V
Control Current I
P
Control range Related to t
LL2
H
∆t/t
20
H
Horizontal Output (Open–Collector)
Output Voltage LOW V
I3 = 20mA – – 0.3 V
3
I3 = 60mA – – 0.8 V
tH Duty Cycle tp/t
Threshold to Activate Too Low Supply Voltage
H
V
Horizontal Output OFF – 5.6 – V
P
Protection
Threshold to Activate Too Low Supply Voltage
Horizontal Output ON – 5.8 – V
Protection
Jitter of Horizontal Output ∆t
f = 31kHz – – 3.5 ns
H
f = 64kHz – – 1.9 ns
f = 100kHz – – 1.2 ns
Horizontal Clamping/Blanking Generator Output
Output Voltage LOW V
8
Blanking Output Voltage Internal V Blanking 1.6 1.9 2.2 V
Clamping Output Voltage H–Sync on Pin9 5.15 5.4 5.65 V
Internal Sink Current for All Output Levels I
H and V Scanning 2.3 2.9 3.5 mA
8
External Load Current – – –3.0 mA
Clamping Pulse Start t
Clamping Pulse Width t
8
clp
Steepness of Rise and Fall Times S – 60 75 ns/V
0 – 50 mV
– 5.9 – V
– 5.1 – V
– ±0.083I
18
– µA
– 31.45 – kHz
– – ±3.0 %
±6.0 ±6.5 ±7.3 %
–0.5 – –4.3 mA
2.35 2.5 2.65 V
– 3.0 – %
– 6.2 – V
– ±0.083I
18
– µA
30 – – %
42 45 48 %
– – 0.9 V
With End of H–Sync
0.8 1.0 1.2 µs
Page 4

Electrical Characteristics (Cont’d): (VP = 12V, TA = +25°C unless otherwise specified)
Parameter Symbol Test Conditions Min Typ Max Unit
Vertical Oscillator (V
Vertical Free–Running Frequency f
Nominal Vertical Sync Range f
Voltage on Pin15 V
Delay Between Sync Pulse and Start of Vertical
Scan in VGA/XGA Mode
Delay Between Sync Pulse and Start of Vertical
Scan in Autosync Mode
Control Current for Amplitude Control I
Capacitor for Amplitude Control C
Vertical Differential Output
Differential Output Current Between Pin5 and
Pin6 (Peak–to–Peak Value)
Maximum Offset Current Error Io = 1mA – – ±2.5 %
Maximum Linearity Error – – ±1.5 %
Vertical Amplitude Adjustment (In Percent of Output Signal)
Input Voltage V
Adjustment Current I
VGA Mode–Dependent Pre–Settings Activated
by an External Resistor on Pin7
Mode 1
Mode 2 101.6 102.2 102.8 %
Mode 3 – 100 – %
Mode 4 – 100 – %
Autosync Operation
(VGA Operation Disabled)
E/W Output (Note 2)
Bottom Output Signal During Mid–Scan (Pin11) V
Top Output Signal During Flyback 4.2 4.5 4.8 V
Temperature Coefficient of Output Signal TC – – 250 10–6/K
E/W Amplitude Adjustment (Parabola)
Input Voltage (Pin14) V
Adjustment Current I
= 6.25V)
ref
o
V
15
t
d
12
12
I
o
13
13
∆Io/∆t
11
14
14
R15 = 22kΩ, C16 = 0.1µF – 42 – Hz
No fo Adjustment 50 – 110 Hz
R15 = 22kΩ 2.8 3.0 3.2 V
Measured on Pin8,
500 575 650 µs
Activated by an External
Resistor on Pin7
Measured on Pin8,
240 300 360 µs
V7 < 50mV
– ±200 – µA
– – 0.18 µF
Mode 3, I13 > –135µA,
0.9 1.0 1.1 mA
R15 = 22kΩ
– 5.0 – V
Iomax (100%) –110 –120 –135 µA
Iomin (Typically 58%) – 0 – µA
Table 2,Note 2 116.1 116.8 1 17.4 %
Table 2, Note 2,
– 100 – %
V7 < 50mV
Internally Stabilized 1.05 1.2 1.35 V
– 5.0 – V
100% Parabola –110 –120 –135 µA
Typicall 28% Parabola – 0 – µA
Note 2. ∆Io/∆t relative to value of Mode 3.
Note 3. Parabola amplitude tracks with mode–dependent vertical amplitude but not with vertical
amplitude adjustment. Tracking can be achieved by a resistor from ver tical am pli tude
potentiometer to Pin14.
Page 5

Functional Description:
Horizontal Sync Separator and Polarity Correction
An AC–coupled video signal or a DC–coupled TTL sync signal (H only or composite sync) is input
on Pin9. Video signals are clamped with top sync on 12.8V, and are sliced at 1.4V. This results in a
fixed absolute slicing level of 120mV relative to top sync.
DC–coupled TTL sync signals are also sliced at 1.4V, however with the clamping circuit in current limitation. The polarity of the separated sync is detected by internal integration of the signal, then the polarity is corrected.
The polarity information is fed to the VGA mode detector. The corrected sync is the input signal for
the vertical sync integrator and the P
LL1
stage.
Vertical Sync Separaztor, Polarity Correction and Vertical Sync Integrator
DC–coupled vertical TTL sync signals may be applied to Pin10. They are sliced at 1.4V. The polarity
of the separated sync is detected by internal integration, then polarity is corrected. The polarity information is fed to the VGA mode detector. If Pin10 is not used, it must be connected to GND.
The separated V
signal from Pin10, or the integrated composite sync signal from Pin9 (TTL or
i sync
video) directly triggers the vertical oscillator.
VGA Mode Detector and Mode Output
The three standard VGA modes and a 4th not fixed mode are decoded by the polarities of the horizontal and the vertical sync input signals. An external resistor (from VP to Pin7) is necessary to match
this function. In all three VGA modes the correxct amplitudes are activated. The presence of the 4th
mode is indicated by HIGH on Pin7. This signal can be used externally to switch any horizontal or
vertical parameters.
VGA Mode Detector Input
For autosync operation the voltage on Pin7 must be externally forced to a level of < 50mV. Vertical
amplitude pre–settings for VGA are then inhibited. The delay time between vertical trigger pulse and
the start of vertical deflection changes from 575 to 300µs (575µs is needed for VGA). The vertical
amplitude then remains constant in a frequency range from 50 to 110Hz.
Clamping and V–Blanking Generator
A combined clamping and V–blanking pulse is available on Pin8. The lower level of 1.9V is the blanking signal derived from the vertical blanking pulse from the internal vertical oscillator.
Vertical blanking equals the delay between vertical sync and the start of vertical scan. By this, an optimum blanking is acheived for VGA/XGA as well as for multi–frequency operation (selectable via
Pin7).
The upper level of 5.4V is the horizontal clamping pulse with internally fixed pulse width of 0.8µs. A
mono flop, which is triggered by the trailing edge of the horizontal sync pulse, generates this pulse.
If composite sync is applied one clamping pulse per H–period is generated during V–sync. The pahse
of the clamping pulse may change during V–sync.
P
Phase Detector
LL1
The phase detector is a standard one using switched current sources. The middle of the sync is
compared with a fixed point of the oscillator sawtooth voltage. The PLL filter is connected to Pin17.
If composite sync is applied, the distributed control voltage is corrected during V–sync.
Horizontal Oscillator
This oscillator is a relaxation type and requires a fixed capacitor of 10nF at Pin19. By changing the
current into Pin18 the whole frequency range from 13 to 100kHz can be covered.
The current can be generated either by a frequency to voltage converter or by a resistor. A frequency
adjustment may also be added if necessary.
The P
control voltage at Pin17 moduloates via a buffer stage the oscillator thresholds. A high DC–
LL1
loop gaqin ensures a stable phase relationship between horizontal sunc and line flyback pulses.
Page 6

Functional Description (Cont’d):
P
Phase Detector
LL2
This pahse detector is similar to the P
phase detector. Line flyback signals (Pin2) are compared
LL1
with a fixed point of the oscillator sawtooth voltage. Delays in the horizontal deflection circuit are compensated by adjusting the phase relationship between horizontal sync and horizontal output pulses.
A certain amount of phase adjustment is possible by injecting a DC current froma an external source
into the P
filter capacitor on Pin20.
LL2
Horizontal Driver
This open–collector output stage (Pin3) can directly drive an external driver transistor . The saturation
voltage is 300mV at 20mA. To protect the line deflection transistor, the horizontal output stage does
not conduct at VP < 6.4V (Pin1).
Vertical Oscillator and Amplitude Control
This stage is designed for fast stabilization of the vertical amplitude after changes in sync conditions.
The free–running frequency fo is determined by the values of R
VOS
and C
. The recommended
VOS
values should be altered marginally only to preserve the excellent linearity and noise performance.
The vertical drive currents I5 and I6 are in relation to the value of R
quency must be determined only by C
fo =
10.8 x R
1
VOS
x C
VOS
on Pin16.
VOS
. Therefore, the oscillator fre-
VOS
To acheive a stabilized amplitude the free–running frequency fo (without adjustment) must be lower
than the lowest occurring sync frequency. The contributions shown in Table 1 can be assumed.
Table 1. Calculation of fo Total Spread
Contributing Elements %
Minimum Frequency Offset Between fo and the Lowest Trigger Frequency 10
Spread of IC ±3
Spread of R (22kΩ) ±1
Spread of C (0.1µF) ±5
Total 19
Results for 50 to 110Hz application: fo =
50Hz
1.19
= 42Hz
Table 2. VGA Modes
Mode Horizontal/Vertical
Sync Polarity
1 +/– 31.45 70 350 LOW
2 –/+ 31.45 70 400 LOW
3 –/– 31.45 60 480 LOW
4 +/+ Fixed by External Circuitry – – HIGH
Autosync */* Fixed by External Circuitry – – Forced to GND
Horizontal
Frequency
(kHz)
Vertical
Frequency
(Hz)
Number of
Active Lines
Output
Mode Pin7
Page 7

Pin Connection Diagram
V
P
Horiz Flyback Input
Horiz Output
GND (0V)
Vert Output 1/Neg–Going Sawtooth
Vert Output 2/Pos–Going Sawtooth
4th Mode Output/Autosync In
Clamping/Blanking Pulse Out
Horiz Sync/Video In
Vert Sync In
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
20
19
18
17
16 Vert OSC Capacitor
15
14
13
10 11
P
Phase
LL2
Horiz OSC Capacitor
Horiz OSC Resistor
P
Phase
LL1
Vert OSC Resistor
E/W Amp Adj Input (Parabola)
V ert Amp Adj Input
Cap for Amp Control9 12
E/W Output (Parabola to Driver Stage)
20 11
.280 (7.12) Max
110
.995 (25.3) Max
.300 (7.62)
.280
(7.1)
.100 (2.54) .125 (3.17) Min .385 (9.8)
 Loading...
Loading...