
E2U0053-28-81
¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Aug. 1998
Previous version: Apr. 1997
MSM7728
Single Rail Linear CODEC
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM7728 is a single-channel linear CODEC CMOS IC for voice signals that contains filters
for A/D and D/A conversions.
Designed especially for a single-power supply and low-power applications, the device is
optimized for applications for the analog interfaces of audio signal processing DSPs and digital
wireless systems.
The analog outputs include the speaker drive output, earphone drive output and ringer output.
Therefore, the sound interface can be configured with a few external circuits.
FEATURES
• Single power supply : 2.5 V to 3.6 V
• Low power consumption
Operating mode : 36 mW Typ.
Power down mode : 0.003 mW Typ.
• Digital signal input/output interface : 14-bit serial code in 2's complement format
• Transmission clock frequency : 112 kHz min., 2048 kHz max.
• Filter characteristics : Complies with ITU-T Recommendation G.714
• Built-in PLL eliminates a master clock
• Built-in PB tone signal generator
• Built-in service tone generator
• Built-in ringer tone generator
• General latch output: 1 bit
• Both transmit and receive gain adjustable by external control
• Receive interface: Speaker direct drive output
Earphone interface output : 600 W, 1 mW max.
Ringer output : 70 nF, 4 V
• Transmit gain adjustable using an external resistor
• Transmit microphone amplifier is eliminated by the gain setting of a maximum of 36 dB.
• Built-in reference voltage supply
• Serial 8-bit processor interface
• Package:
30-pin plastic SSOP (SSOP30-P-56-0.65-K) (Product name: MSM7728GS-K)
PP
1/23
¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
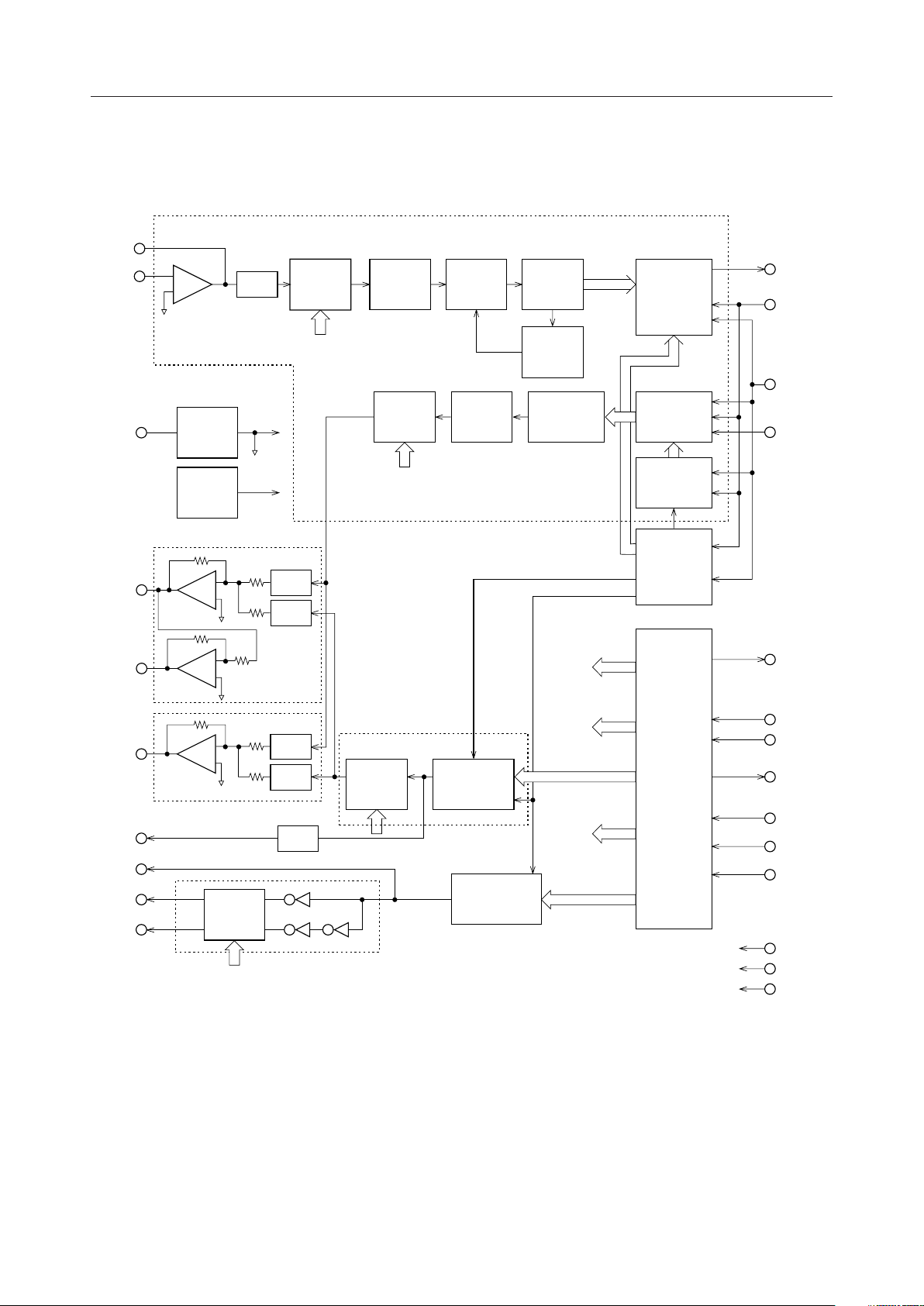
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MAO
MAIN
SGC
SPKP
SPKN
CODEC
–
+
GEN
GEN
SW1
SG
VR
SPK
–
+
–
+
VOL1
SW 2
SW 4
RC
LPF
VOL2
8th
BPF
5th
LPF
14 BIT
ADCONV
AUTO
ZERO
14 BIT
DACONV
SW CONTROL
TCONT
RCONT
RTIM
PLL
PCMOUT
SYNC
BCLK
PCMIN
LA
EAR
TOUT
LED
RINGP
RINGN
EAR
–
+
VOL4
SW 3
SW 5
SW 6
Tone GEN
VOL3
PB Tone
SERVICE Tone
RINGER
Tone
VOL CONTROL
POWER-DOWN
CONTROL
MCU
INF.
WRN
RDN
CDOUT
CDIN
DCLK
RSTN
V
DD
AG
DG
2/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
SPKP
SPKN
EAR
RINGP
RINGN
TOUT
LED
LA
NC
RDN
CDOUT
WRN
DCLK
CDIN
DG
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
NC: No connection
30
29
28
27
26
25
24
23
22
21
20
19
18
17
16
AG
NC
NC
SGC
MAO
MAIN
NC
V
DD
NC
NC
RSTN
SYNC
BCLK
PCMOUT
PCMIN
30-Pin Plastic SSOP
3/23
¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
PIN AND FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
V
DD
Power supply pin for 2.5 to 3.6 V (Typically 3.0 V).
AG
Analog signal ground.
DG
Ground pin for the digital signal circuits.
This ground is separated from the analog signal ground in this device. The DG pin must be
connected to the AG pin on the printed circuit board.
SGC
Bypass capacitor pin for generating the signal ground voltage level.
Insert a 0.1 mF capacitor with excellent high frequency characteristics between the AG pin and
the SGC pin.
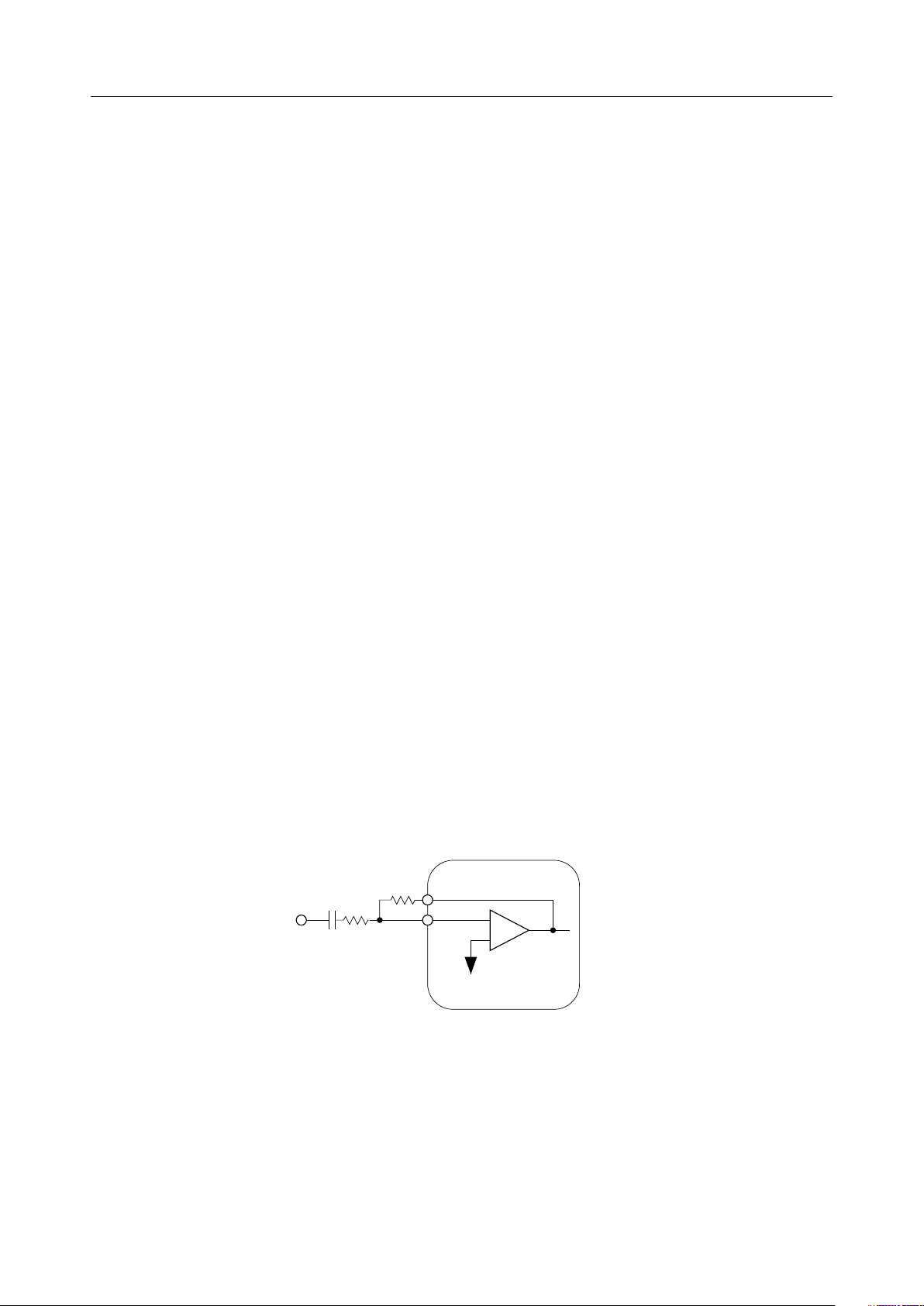
MAIN, MAO
Transmit microphone input and level adjustment.
MAIN is connected to the inverting input of the op-amp, and MAO is connected to the output
of the op-amp. This amplifier can set up a gain to a maximum of 36dB by using an external
resistor.
Level adjustment should be performed in a way below.
A transmit level of +6, 0, –6, or –12dB can be selected using control data from the processor
interface.
When CODEC is turned off, the MAO output goes high impedance.
R1 : variable
R2 > 20 kW
C1 > 1/(2 ¥ 3.14 ¥ 30 ¥ R1) (F)
Gain = R2/R1 < 63
Microphone input
C1
R1
R2
MAO
MAIN
–
+
SG
4/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
SPKP, SPKN
These pins are used for speaker driving.
The SPKN output is reversed in phase against the SPKP output when the gain is 1.
The receive output signal amplitude is 2.2VPP at maximum.
These outputs swing around the SG potential (signal ground potential, VDD/2) and can drive the
minimum 0.6kW load in pushpull driving mode.
The maximum output amplitude is 4.4VPP in pushpull driving mode (a load is inserted between
SPKN and SPKP).
Control data from the processor interface allows selecting the D/A conversion output, PB tone
output, or service tone output and also can provide a level control and mute control. When SPK
is turned off, the SG potential is output with high resistance.
EAR
Analog output for external accessary circuit.
This output swings around the SG potential and can drive the minimum 0.6kW against the SG
potential.
Control data from the processor interface allows selecting the D/A conversion output, PB tone
output, or service tone output and also can provide a level control and mute control. When EAR
is turned off, the SG potential is output with high resistance.
BCLK
Shift clock signal input for PCMIN and PCMOUT.
The frequency is equal to the data signaling rate.
SYNC
Synchronizing signal input.
In the transmit section, the PCM output signal from the PCMOUT pin is output synchronously
with this synchronizing signal. This synchronizing signal triggers the PLL and synchronizes all
timing signals of the transmit section.
In the receive section, 14 bits required are selected from serial input of PCM signals on the PCMIN
pin by the synchronizing signal.
Signals in the receive section are synchronized by this synchronizing signal. This signal must be
synchronized in phase with the BCLK.
When this signal frequency is 8 kHz, the transmit and receive paths have the frequency
characteristics specified by ITU-T G. 714. The frequency characteristics for 8 kHz are specified in
this data sheet.
For different frequencies of the SYNC signal, the frequency values in this data sheet should be
translated according to the following equation:
Frequency values described in the data sheet
8 kHz
¥ the SYNC frequency values to be actually used
5/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
PCMIN
PCM signal input.
A serial PCM signal input to this pin is converted to an analog signal synchronously with the
SYNC signal and BCLK signal.
The data signaling rate of the PCM signal is equal to the frequency of the BCLK signal.
The PCM signal is shifted at the falling edge of the BCLK signal. The PCM signal is latched into
an internal register when shifted by 14 bits.
The top of the data (MSD) is identified at the rising edge of SYNC.
The input signal should be input in the 14-bit 2's complement format.
The MSD bit represents the polarity of the signal with respect to the signal ground.
PCMOUT
PCM signal output.
The PCM output signal is output starting with MSD in sequential order, synchronously with the
rising edge of the BCLK signal.
MSD may be output at the rising edge of the SYNC signal, depending on the timing between
BCLK and SYNC.
This pin is in a high impedance state except during 14-bit PCM output. It is also high impedance
when the CODEC is turned off.
A pull-up resistor must be connected to this pin, because its output is configured as an open
drain.
The output coding format is in 14-bit 2's complement.
The MSD represents a polarity of the signal with respect to the signal ground.
Input/Output Level
+Full scale
+1
0
–1 1111 1111 1111 11
–Full scale
Table 1
PCMIN/PCMOUT
MSD
0111 1111 1111 11
0000 0000 0000 01
0000 0000 0000 00
1000 0000 0000 00
6/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
WRN, RDN, DCLK, CDIN, CDOUT
Serial control ports for microcontroller interface.
Writing data to 8-bit control registers allows controling the transmit speech path/receive speech
path mute, transmit speech path/receive speech path level, PB tone, service tone, and ringer.
WRN is the write control signal input, RDN is the read control signal input, DCLK is the clock
signal input for data shift, CDIN is the control data input, CDOUT is the control data output.
When reset (RSTN=0), the control registers are reset to the initial values as described in "Control
Data Description".
The initial values remains unchanged until control data is written after reset.
Writing of control data: When WRN is at digital "0", data that is entered in CDIN is shifted at the
rising edge of the DCLK signal pulse and is latched in an internal control register.
Reading of control data: When RDN is at digital "0", control data is output from CDOUT at the
rising edge of a DCLK signal pulse.
See Figure 2 for write and read timings.
RINGP, RINGN
Ringer (sounder) drive outputs.
The sounder can be structured by putting a piezo-electric type sounding body (equivalent
capacitance: less than 70nF) between RINGP and RINGN.
LED
Ringer digital level output. This pin is used for LED blinking synchronous with the ringer.
LA
General latch output. This output is used as a control signal for a peripheral circuit because this
output can be set to digital "0" or "1" by writing data from a microcontroller interface.
TOUT
PB tone/service tone output. When SW6 is in the ON state, tone is output.
The output resistance of this pin is approximately 10kW, which should be taken into account
when using it externally.
RSTN
Control register reset signal input. When this pin is set to digital "0" level.
All control registers are reset to the initial values.
Be sure to reset the control registers after turning on the power.
7/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
Parameter
Power Supply Voltage
Analog Input Voltage
Digital Input Voltage
Storage Temperature
Symbol
V
DD
V
AIN
V
DIN
T
STG
Condition
AG = DG = 0 V
AG = DG = 0 V
AG = DG = 0 V
—
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter
Power Supply Voltage
Operating Temperature
Analog Input Voltage
High Level Input Voltage
Low
Level
Input Voltage
Clock Frequency
Symbol
V
DD
Ta
V
AIN
V
IH
V
IL
F
C
Condition
—
—
Gain = 1
SYNC, BCLK, PCMIN, WRN,
RDN, DCLK, CDIN, RSTN
BCLK
Min.
2.5
–30
—
0.45 ¥
V
DD
0
14 ¥ Fs
Rating
–0.3 to +7.0
–0.3 to V
–0.3 to V
–55 to +150
Typ.
3.0
+25
—
—
—
—
DD
DD
+ 0.3
+ 0.3
128 ¥ Fs
Max.
3.6
+85
1.4
V
DD
0.16 ¥
V
DD
Unit
V
V
V
°C
Unit
V
°C
V
PP
V
V
kHz
Sync Pulse Frequency
Clock Duty Ratio
Digital Input Rise Time
Digital Input Fall Time
Sync Signal Timing
High Level Sync Pulse Width *1
Low Level Sync Pulse Width *1
PCMIN Setup Time
PCMIN Hold Time
Digital Output Load
DCLK Pulse Width
WRN Timing
t
t
R
t
t
t
t
t
t
P
F
SYNC
S
BCLK
D
C
SYNC, BCLK, PCMIN, WRN,
t
Ir
t
RDN, DCLK, CDIN, RSTN
If
t
BCLKÆSYNC, See Fig.1
XS
t
SYNCÆBCLK, See Fig.1
SX
SYNC, See Fig.1
WSH
SYNC, See Fig.1 1 BCLK — — —
WSL
Refer to Fig.1
t
DS
t
Refer to Fig.1
DH
Pull-up resistor
DL
C
DL
DCLK Low width, See Fig.2
WCL
DCLK High width, See Fig.2
WCH
DCLKÆWRNL, See Fig.2
WR1
WRNLÆDCLK, See Fig.2
WR2
DCLKÆWRNH, See Fig.2 50 — —
WR3
WRNHÆDCLK, See Fig.2 50 — —
WR4
WRN
—
4.0
40
—
—
100
100
1 BCLK
100
100
0.5
—
50
50
50
50
9DCLK — —WRN Period ——
8.0
50
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
12
60
50
50
—
—
—
—
—
—
100
—
—
—
—
kHz
%
ns
ns
ns
ns
—
ns
ns
kW
pF
ns
ns
ns
*1 For example, the minimum pulse width of SYNC is 488 ns when the frequency of BCLK is
2048 kHz.
8/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS (Continued)
Parameter
RDN Timing
CDIN Setup Time
CDIN Hold Time
Symbol
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RD3
t
RD4
P
RDN
t
CDS
t
CDH
Condition
DCLKÆRDNL, See Fig.2
RDNLÆDCLK, See Fig.2
DCLKÆRDNH, See Fig.2 50 — —
RDNHÆDCLK, See Fig.2 50 — —
See Fig.2
See Fig.2
Transmit gain stage, Gain = 0 dB
Analog Input Allowable DC Offset
Allowable Jitter Width
PCM Data Output Delay Time
Control Data Output Delay Time ns—
V
off
Transmit gain stage, Gain = 20 dB
—
SYNC, BCLK
t
SD
t
XD1
t
XD2
t
XD3
t
CD1
t
CD2
= 50 pF + 1 LSTTL
C
L
Pull-up resistor = 500 W
Min.
50
50
Typ.
—
—
9DCLK — —RDN Period ——
50
50
–100
–10
—
20
20
20
20
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
—
50 — —
50 — —
Max.
—
—
—
—
+100
+10
1000
100
100
100
100
Unit
ns
ns
ns
mV
mV
ns
ns
9/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
DC and Digital Interface Characteristics
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
DD
Min.
—
—
—
Typ.
20
12
70
Max.
—
—
200
0.45 ¥
V
—
DD
V
DD
0.16 ¥
0.0
—
—
—
—
—
V
2.0
0.5
DD
0.0 0.2 0.4 V
V
– 0.2 V
DD
—
—
10
Unit
mA
mA
mA
V
V
mA
mA
mA
Parameter
Symbol
Power Supply Current
High Level Input Voltage
Low Level Input Voltage
High Level Input Leakage Current
Low Level Input Leakage Current
Digital Output Low Voltage V
Digital Output High Voltage V
Digital Output Leakage Current
Input Capacitance
Condition
Operating mode,
I
DD1
No signal
I
Power-off mode
DD2
V
IH
SYNC, BCLK, PCMIN, WRN,
RDN, CDIN, DCLK, RSTN
V
IL
I
IH
I
IL
PCMOUT pull-up resistor = 500 W
OL
LA, LED, CDOUT I
LA, LED, CDOUT I
OH
I
O
C
IN
—
—
—
— —5—pF
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
V
= 3.6 V
DD
= 3.0 V
V
DD
= 0.4mA
OL
= 1mA
OH
Transmit Analog Interface Characteristics
Parameter
Input Resistance
Output Load Resistance
Output Load Capacitance
Output Amplitude
Offset Voltage
Symbol
R
INX
R
LGX
C
LGX
V
OGX
V
OSGX
MAIN 10
MAO with respect to SG
potential
MAO with respect to SG potential
(DC Gain = 1)
Receive Analog Interface Characteristics
Parameter
Output Resistance
Output Load Resistance
Output Load Capacitance
Offset Voltage
Symbol
R
SP
SPKP, SPKN —
O
ROER EAR — — 100 W
ROTO TOUT — 10 — kW
SPKP-SPKN 600 — — W
R
LSP
R
EAR with respect to SG potential
LER
C
Output open
LAO
V
OAO
SPKP, SPKN, EAR, TOUT with
V
OSA
respect to SG potential
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
DD
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
—
30
—
–0.7
–20
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
DD
—
—
—
—
—
—
30
+0.7
+20
MW
kW
pF
V
mV
Condition Min. Typ. Max. Unit
—
10
W
600 — — W
—
—
50
pF
–1.1 — +1.1 VSPKP, SPKN, EAROutput Amplitude
–100 — +100 mV
10/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
AC Characteristics
Parameter
Overall Frequency Response
Transmit Frequency Response
(Expected Value)
Receive Frequency Response
(Expected Value)
Overall Signal to Distortion Ratio 1020 dB
Transmit Signal to Distortion Ratio
(Expected Value)
Receive Signal to Distortion Ratio
(Expected Value)
Symbol
Loss 1
Loss 2
Loss 3
Loss 4
Loss 5
Loss 6
Loss T1
Loss T2
Loss T3
Loss T4
Loss T5
Loss T6
Loss R1
Loss R2
Loss R3
Loss R4
Loss R5
SD 1 57.0 — —3
SD 2 57.0 — —0
SD 3 50.0 — —–10
SD 4
SD 5
SD 6
SD T1 58 — —3
SD T2 58 — —0
SD T3 58 — —–10
SD T4 38 — —–30
SD T5 28 — —–40
SD T6 23 — —–45
SD R1 60 — —
SD R2 60 — —
SD R3 60 — —
SD R4 40 — —
SD R5 30 — —
SD R6 25 — —
Freq.
(Hz)
60 20 — —
300 –0.2 — +0.4
1020 Reference value
2020 –0.2 — +0.4
3000 –0.2 — +0.4
3400 0 — 1.6
60 20 — —
300 –0.15 — +0.2
1020 Reference value
2020 –0.15 — +0.2
3000 –0.15 — +0.2
3400 0 — 0.8
300 –0.15 — +0.2
1020 Reference value
2020 –0.15 — +0.2 dB0
3000 –0.15 — +0.2
3400 0.0 — 0.8
1020 dB
1020 dB
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
Level
(dBm0)
3
0
–10
–30
–40
–45
DD
Condition
Analog to
Analog
Analog to
Analog
*1
=
V
DD
2.7 to 3.3 V
*1
*1
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
32.0 — —–30
23.0 — —–40
20.0 — —–45
dB0
dB0
*1 Psophometric filter is used.
11/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
AC Characteristics (Continued)
Parameter
Symbol
GT 1 –0.4 +0.01 +0.4
GT 2 Reference value
Freq.
(Hz)
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
Level
(dBm0)
3
–10
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
DD
Condition
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
Analog to
Overall Gain Tracking
GT 3 1020 –0.4 0.0 +0.4 dB
GT 4 –1.0 –0.03 +1.0
GT 5 –1.5 +0.15 +1.5
GT T1 –0.3 +0.01 +0.3
GT T2 Reference value
–40
–50
–55
3
–10
Analog
Transmit Gain Tracking
GT T3 1020 –0.3 0.0 +0.3 dB
–40
(Expected Value)
GT T4 –0.6 –0.03 +0.6
GT T5 –1.2 +0.15 +1.2
GT R1 –0.3 –0.06 +0.3
GT R2 Reference value
–50
–55
3
–10
Receive Gain Tracking
GT R3 1020 –0.3 –0.02 +0.3 dB
–40
(Expected Value)
GT R4 –0.6 –0.02 +0.6
GT R5 –1.2 –0.27 +1.2
–50
–55
Transmit Idle Channel Noise
Nidle T
— — –72 –68
—
AIN: no signal
(Expected Value)
Receive Idle Channel Noise
Nidle R
— –76
—
*1
— –74
(Expected Value)
AV T
*2
MAO-PCMOUT
Output Level
(Initial value)
AV
AV
AV Tt –0.2 — +0.2
Output Level
(Deviation of Temperature and Power)
SPK
EAR
1020
0
PCMIN-SPKP
PCMIN-EAR
V
DD
*3
*3
= 2.5
to 3.6 V
Ta = –30
AV Rt –0.2 — +0.2
to +85°C
A to A
Absolute Delay
T
d
1020 — — 0.6 ms0
BCLK
= 128 kHz
t
Transmit Group Delay
Receive Group Delay
Crosstalk Attenuation
T1 — — 0.325
GD
tGD T2 — — 0.1750ms*4
T3 — 0.325
GD
tGD R1
t
R2 2800
GD
CR T 7585—
CR R 80
500
600 to 2600
2800
500 to 2600
1020 dB0
*4
TRANS Æ RECV
RECV Æ TRANS
— 0.00 0.125
— 0.12 0.325
70 —
*1 Psophometric filter is used.
*2 AVT is the input level to output 0dBm0 pattern. VOL1 0dB setting.
AV
AV
is the level to be output from SPKP pin when 0dBm0 pattern is input.
SPK
is the level to be output from EAR pin when 0dBm0 pattern is input.
EAR
*3 VOL2 0dB setting
*4 The minimum value of group delay distortion is referenced.
dBmOp
0.3500.312 0.393
Vrms
0.2750.245 0.309
dB
dB
—t
ms0
12/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
AC Characteristics (Continued)
Symbol
DIS
IMD
PSR T
PSR R
PB Acknowledge Tone Output Level
Service Tone Output Level
PB Acknowledge Tone
Frequency Distortion
Service Tone Frequency Distortion
VOL1
Gain Setting Value
VOL2
Gain Setting Value
VOL3
Gain Setting Value
V PB
V RT
Df
Df
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
Gv
S
PB
RT
11
12
13
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
Freq.
(Hz)
4.6 kHz to
72 kHz
300 to
3400
fa = 470
fb = 320
0 to
50 kHz
SPKP, EAR
VOL3 standard
TOUT
SPKP, EAR
1020 0
1020 0
1020 0
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
Level
(dBm0)
PP
TOUT
DD
ConditionParameter
0 to 4000 Hz
4.6 kHz to
100 kHz
Measured inband
High group
Low group
High group
Low group
VOL3 standard
—
Referenced to
0dB setting
Referenced to
0dB setting
Referenced to
0dB setting
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
30 32 — dBDiscrimination 0
— –37.5 –35 dBm0Out-of-band Spurious 0
— –52 –40 dBm0Intermodulation Distortion –4 2fa – fb
—30—dBPower Supply Noise Rejection Ratio 50 mV
–27 –22 –19
–28 –23 –20
dBV
–16 –11 –8
–17 –12 –9
–18 –15 –13
dBV
–8 –3 –1
–1.5 — +1.5
–1.5 — +1.5
6dBsetting
–6dBsetting
–12dBsetting
6dBsetting
3dBsetting
–3dBsetting
–6dBsetting
–9dBsetting
–12dBsetting
–15dBsetting
12dBsetting
8dBsetting
4dBsetting
–4dBsetting
–8dBsetting
–12dBsetting
–16dBsetting
567
–7 –6 –5
–13 –12 –11
567
234
–4 –3 –2
–7 –6 –5
–10 –9 –8
–13 –12 –11
–16 –15 –14
10.5 12 13.5
6.5 8 9.5
2.5 4 5.5
–5.5 –4 –2.5
–9.5 –8 –6.5
–13.5 –12 –10.5
–17.5 –16 –14.5
%
dB
dB
dB
13/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
Ringing Tone
(Fs = 8 kHz, V
ConditionParameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
= 2.5 V to 3.6 V, Ta = –30°C to +85°C)
DD
Ringing Tone Output Amplitude
Sound volume1
Sound volume2
Sound volume3
Sound volume4
730W between
RINGP and RINGN
Sound volume max.
Sound volume mid.
Sound volume sma.1
Sound volume sma.2
3.5 — —
1.5 — —
0.5 — —
0.25 — —
V
PP
14/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
TIMING DIAGRAMS
CODEC Interface Timing
Transmit Timing
BCLK 12345678910
t
XS
SYNC
PCMOUT
Receive Timing
BCLK
t
RS
SYNC
PCMIN
t
XD1
t
SX
t
WSH
t
SD
D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8
When t
When t
12345678910
£ 1/2 • Fc, the Delay of the MSD bit is defined by t
XS
< 1/2 • Fc, the Delay of the MSD bit is defined by tSD.
SX
t
SR
t
WSH
D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8
t
XD2
t
t
DS
DH
Figure 1 Basic Timing Diagram
Processor Interface Timing
11
12 13 14 15 16 17
t
WSL
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14MSD
.
XD1
11 12 13 14 15 16 17
t
WSL
D9 D10 D11 D12 D13MSD
D14
t
18 19
XD3
18 19
DCLK
CDIN
WRN
RDN
CDOUT
DCLK
CDIN
WRN
RDN
CDOUT
t
WR1
H
t
RD1
H
Hi-Z
t
WCL
t
WCH
12345678
t
CDS
t
CDH
B3B4A0A1A2 B2 B1 B0
t
WR2
P
WRN
t
WR3
Hi-Z
WRITE Mode
12345678
XXA0A1A2 X X X
t
RD2
t
CD1
P
RDN
t
RD3
B3B4 B2 B1 B0
READ Mode
t
t
WR4
t
RD4
CD2
Figure 2 Processor Timing Diagram
15/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Control Data Description
The MSM7728 has eight registers to control the analog pass switch, volume, and tone via an
external CPU.
The data interface consists of 3-bit address data and 5-bit control data in the serial 8-bit format.
The register map is as shown below.
AD2 AD1 AD0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Read
CR0
CR1
CR2
CR3
CR4
CR5
CR6
CR7
0 0 0 VOL1 VOL2 Enable
0 0 1 VOL3 VOL4 Enable
0 1 0 SW5 SW4 SW3 SW2 SW1 Enable
0 1 1 — — — LA SW6 Enable
1 0 0 PB tone Disable
1 0 1 Service tone Disable
1 1 0 Ringer tone Disable
1 1 1 Power ON/OFF Enable
VOL1, VOL2 gain setting
VOL3, VOL4 gain setting
SW ON/OFF control
Latch output/SW ON/OFF control
PB tone setting ON/OFF control
Service tone setting ON/OFF control
Ringer tone setting ON/OFF control
Power ON/OFF control
Description of Each Register
CR0 - - - VOL1, VOL2 control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
00000
01
10
11
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
0dB (standard)
6dB
VOL1 gain setting
–6dB
–12dB
0dB (standard)
6dB
3dB
–3dB
VOL2 gain setting
–6dB
–9dB
–12dB
–15dB
VOL1 and VOL2:
Simultaneous setting
Standard after reset
is released
16/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
CR1 - - - VOL3, VOL4 control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
001
000
001
010
011
100
101
110
111
00
01
10
11
VOL3 gain setting
Ringer sound
volume
0dB (standard)
12dB
8dB
4dB
–4dB
–8dB
–12dB
–16dB
Middle (standard)
Maximum
Small 1
Small 2
VOL3 and VOL4:
Simultaneous setting
Standard after reset
is released
CR2 - - - SWcontrol
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
0 1 0 1: SW1 ON, SW1 to SW5:
1: SW2 ON,
1: SW3 ON,
1: SW4 ON,
1: SW5 ON,
0: SW1 OFF
0: SW2 OFF
0: SW3 OFF
0: SW4 OFF
0: SW5 OFF
Simultaneous setting
Standard after reset
is released
CR3 - - - SW & latch control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
0 1 1 0: SW6 OFF, SW6 and LA:
0 0 0 1: SW6 ON
0: LA=0,
1: LA=1
Simultaneous setting
SW6: OFF, LA=0
after reset is released
17/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
CR4 - - - PB tone control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
1 0 0 PBtone 697Hz, 1209Hz Output destination of
1 0 0
0 0 9 0h
HEX
Code
PBtone 697Hz, 1336Hz100019 1h
PBtone 697Hz, 1477Hz100109 2h
PBtone 697Hz, 1633Hz100119 3h
PBtone 770Hz, 1209Hz101009 4h
PBtone 770Hz, 1336Hz101019 5h
PBtone 770Hz, 1477Hz101109 6h
PBtone 770Hz, 1633Hz101119 7h
PBtone 852Hz, 1209Hz110009 8h
PBtone 852Hz, 1336Hz110019 9h
PBtone 852Hz, 1477Hz110109 Ah
PBtone 852Hz, 1633Hz110119 Bh
PBtone 941Hz, 1209Hz111009 Ch
PBtone 941Hz, 1336Hz111019 Dh
PBtone 941Hz, 1477Hz111109 Eh
PBtone 941Hz, 1633Hz111119 Fh
PBtone OFF000008 0h
PB tone:
EAR
SPKP
SPKN
PB OFF after reset is
released
CR5 - - - Service tone control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
1011 0 0
10001B 1h
10010B 2h
10100B 4h
10101B 5h
10110B 6h
11001B 9h
11010B Ah
11011B Bh
00000A 0h
HEX
Code
Frequency
400Hz/16Hz
Above tones stop
Intermittent Time (Note1)
Make Time
Continuous
Continuous
Continuous
Break Time1 Break Time2
—400Hz
—1000Hz
—2000Hz
•
—0.125sec 0.125secB 0h0 0 400Hz
—0.5sec 0.5sec400Hz
—0.25sec 0.25sec400Hz
—
—
—
—1sec 2sec400Hz/16Hz
—0.5sec
—0.032sec 0.032sec400Hz/16Hz
Remarks
Output
destination
of PB tone:
EAR
SPKP
SPKN
18/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
CR6 - - - Ringer tone control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
1101 0 0
10001D 1h
10010D 2h
10011D 3h
10100D 4h
10101D 5h
10110D 6h
10111D 7h
11001D 9h
11010D Ah —
11011D Bh —
00000C 0h
Make time Make time Make timeBreak time1 Break time2
(Note1)
HEX
Code
16Hz alternation of 1kHz/1.3kHz
16Hz alternation of 2kHz/2.6kHz
Frequency
Above tones stop
Intermittent Time (Note1)
Make Time
Continuous
Continuous
Continuous
Continuous
Continuous
Break Time1 Break Time2
—
—
—400Hz
—1kHz
—2kHz
Remarks
—1sec 2secD 0h00
—0.5sec 0.5sec
2.25sec0.25sec 0.25sec
—
—1sec 2sec
Output
destination
of PB tone:
RINGP
RINGN
—0.5sec 0.5sec
2.25sec0.25sec 0.25sec
—
—
CR7 - - - Power-on/off control
A2 A1 A0 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0 Function Remarks
1 1 1 0: CODEC power-off All paths enter a
0: SPK power-off
0: EAR power-off
0: toneGEN power-off
0: SG/VR/PLL power-off
, 1: CODEC power-on
, 1: SPK power-on
, 1: EAR power-on
, 1: toneGEN power-on
, 1: SG/VR/PLL power-on
power-down state
after reset is released
19/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
APPLICATION CIRCUIT
+V
+3 V
MSM7728
Microphone
Speaker
Auxiliary
output
Sounder
General latch
output
0 V
+3 V
M
S
0 to 20 W
LED
0.1 mF
10 mF
*
*
*
MAIN
MAO
SPKP
SPKN
EAR
RINGP
RINGN
LED
LA
SGC
AG
DG
V
DD
PCMOUT
PCMIN
BCLK
SYNC
PDN
DCLK
WRN
RDN
CDIN
CDOUT
PCM output
PCM input
PCM shift clock input
8 kHz SYNC signal input
Reset input
"1" = Operation
"0" = Reset
Controller
* The analog output swings at a maximum of ±1.0 V above and below the V
/2 offset level.
DD
20/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
APPLICATION INFORMATION
Digital pattern for 0 dBm0
The digital pattern for 0 dBm0 is shown below.
(SYNC frequency = 8 kHz, signal frequency = 1 kHz)
S2 S3
SG
Sample No.
S1
S2
S3
S4
S5
S6
S7
S8
S1
MSD D2 D3 D4 D5 D6 D7 D8 D9 D10 D11 D12 D13 D14
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
S4
S5
S6 S7
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
S8
0
1
0
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
0
21/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
NOTES ON USE
• To ensure proper electrical characteristics, use bypass capacitors with excellent high frequency
characteristics for the power supply and keep them as close as possible to the device pins.
• Connect the AG pin and the DG pin as close as possible. Connect them to the system ground
with low impedance.
• Mount the device directly on the PC board. Do not use an IC socket. If use of an IC socket is
unavoidable, use a short lead type socket.
• When mounting the device on a frame, use electro-magnetic shielding, if any electromagnetic wave source such as power supply transformers is surrounding the device.
• Keep the voltage on the VDD pin not lower than –0.3 V to avoid latch-up that may otherwise
occur when power is turned on.
• Use a low noise (particularly, low level type of high frequency spike noise or pulse noise)
power supply to avoid erroneous operation and the degradation of the characteristics of the
device.
22/23

¡ Semiconductor MSM7728
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
(Unit : mm)
SSOP30-P-56-0.65-K
Mirror finish
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
0.19 TYP.
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
23/23
 Loading...
Loading...