Page 1

E2U0036-28-81
¡ Semiconductor
This version: Aug. 1998
Previous version: Nov. 1996
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
MSM7583
p/4 Shift QPSK MODEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The MSM7583 is a CMOS IC for the p/4 shift QPSK modem developed for the digital cordless
telephone systems.
The device, which contains one system of modulator and two systems of demodulater, is
optimized for applications for cell stations in a cordless telephone system.
FEATURES
• Single +5 V Power Supply: 4.5 V to 5.5 V
(Modulator Block)
• Built in Root Nyquist Filter for Baseband Limitting (50% Roll-off)
• Ramp Bit for Burst Signal Rise-up (Fall-down) : 2 Symbols
• Built-in D/A converters for Analog Outputs of Quadrature Signal I/Q Components and
22
I + Q
• Differential I/Q Analog Output Type
• I/Q Output, DC Offset/Amplitude Adjustable
(Analog) Power Envelope Output.
(Demodulator Block)
• Built-in Diversity-corresponding Demodulation Circuit: 2 Systems
• Full Digital p/4 Shift QPSK Demodulation System
• Input IF Signal Frequency Selectable: 1.2/10.7/10.75/10.8 MHz
• Built-in Clock Recovery: 4 Circuits
• Transmit/Receive Independent Power-down Control capability
• Built-in Precise Analog Voltage Reference
• MCU Serial Interface for Mode Setting and Built-in Test Circuit
• Test Modes: Eye Pattern/AFC Compensating Signal/Phase Detection Signal Monitoring
Capability
• Transmission Speed: 384 kbps
• Low Power Consumption
Operating Mode: 16 mA Typ./Modulator (VDD = 5.0 V)
28 mA Typ./Demodulator (VDD = 5.0 V)
Whole Power-down Mode: 0.03 mA Typ. (VDD = 5.0 V)
• Package:
64-pin plastic QFP (QFP64-P-1414-0.80-BK)(Product name : MSM7583GS-BK)
1/23
Page 2
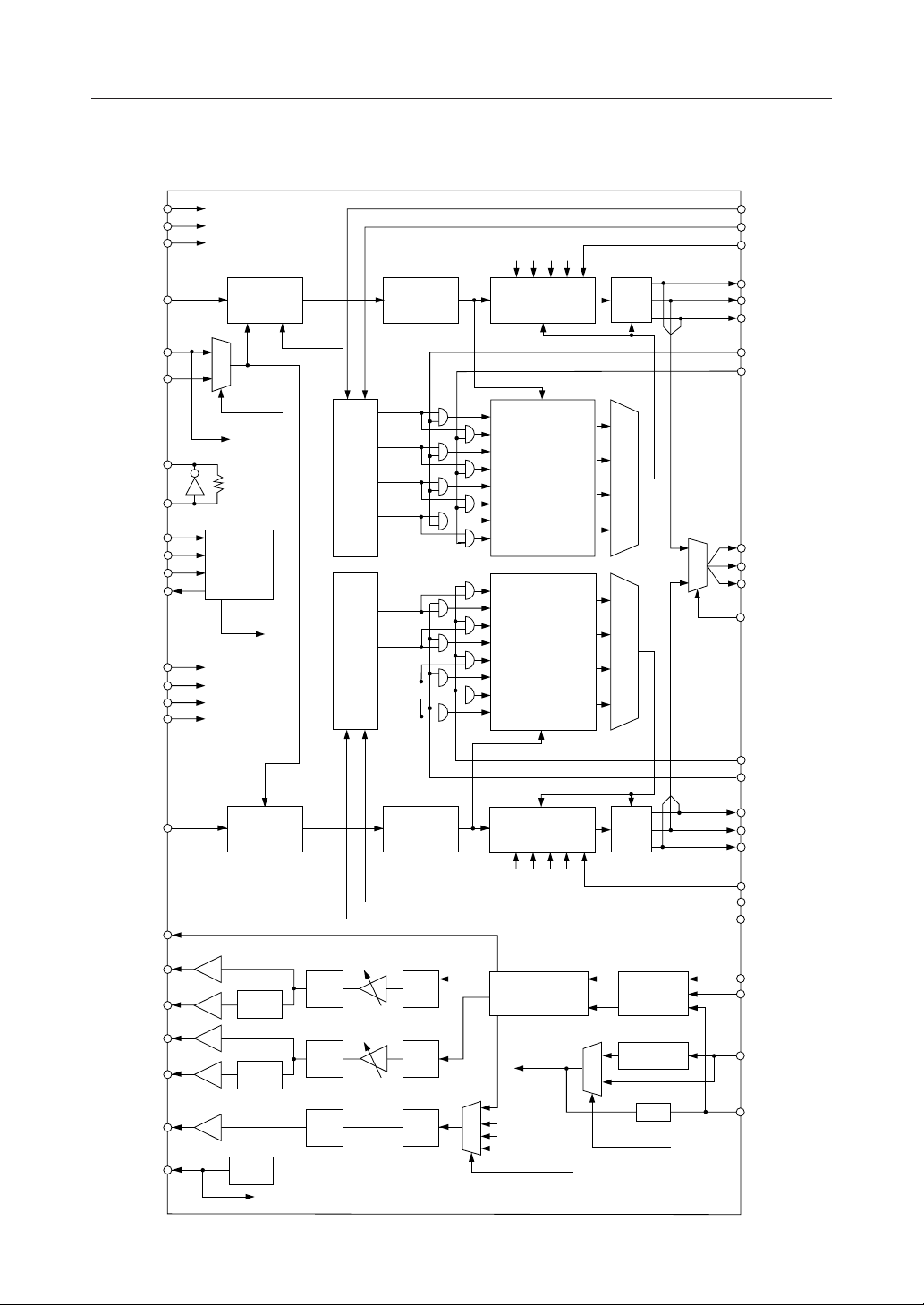
BLOCK DIAGRAM
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
V
DGND
AGND
IFIN1
MCK
IFCK
DEN
EXCK
DIN
DOUT
PDN0
PDN1
PDN2
RESET
DD
SL41
SL41
SL41
SL41
Phase Detector Delay Detector
IFSEL0
S
(From CR)
AFC
Decision
E
L
IFSEL1
(From CR)
To each block
X2
X1
Control
Register
To each block
SL11
SL21
D
E
SL31
C
SL41
DPLL
S
E
L
S
E
L
SL11
D
SL21
E
C
SL31
SL41
DPLL
S
E
L
SLS11
SLS21
AFC1
RXD1
RXC1
RXSC1
RCW1
RPR1
RXD0
RXC0
RXSC0
RXSEL
IFN2
BST0
ENV
SG
RPR2
RCW2
RXCS2
Phase Detector Delay Detector
AFC
Decision
RXC2
RXD2
SL42
SL32
SL22
SL12
AFC2
SLS21
SLS22
I+
I–
Q+
Q–
+1
DC Offset
–1
Adjust
LPF
I output gain adjust
D/A
Root Nyquist
LPF
S/P
MAPPING
TXD
TXW
+1
DC Offset
–1
Adjust
+1
LPF
Q output gain adjust
LPF
VREF
To internal SG
D/A
D/A
3.84 MHz
To D/A
To monitor
output of
each block
TEST1, TEST0 (From CR)
S
E
L
PLL
1/10
TXCEL (From CR)
384 kHZ
TXCI
TXCO
2/23
Page 3
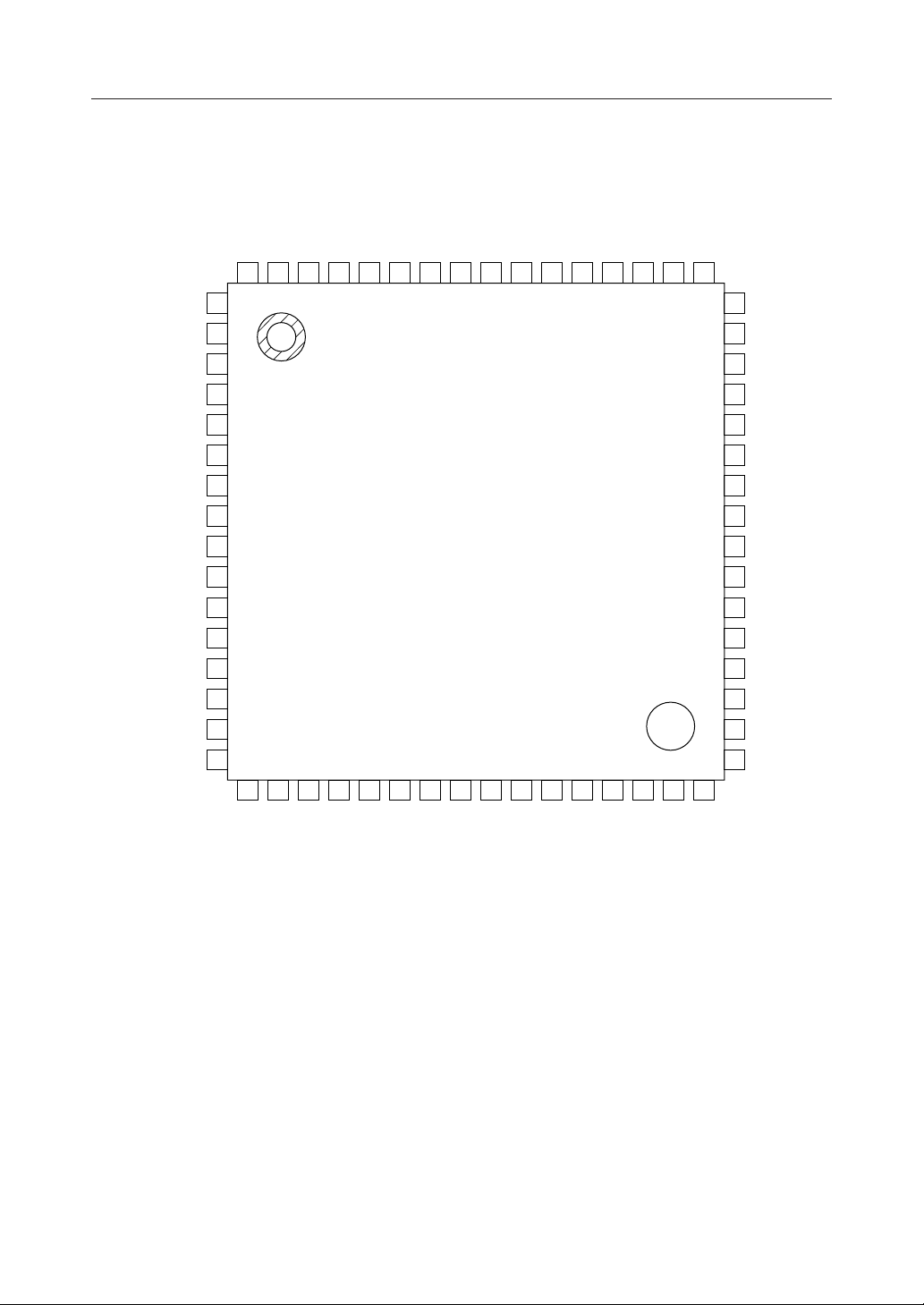
PIN CONFIGURATION (TOP VIEW)
NC
X2
X1
RPR2
AFC2
64
63
62
61
60
1
NC
2
IFCK
3
MCK
4
DGND
5
IFIN2
6
DGND
7
IFIN1
8
DGND
9
V
DD
10
DOUT
11
DIN
12
EXCK
13
DEN
14
RESET
15
PDN0
16 33
PDN1
RCW2
59
RPR1
58
AFC1
57
RCW1
56
RXSC0
55
RXC0
54
RXD0
53
RXSEL
52
RXSC2
51
RXC2
50
RXD2
49
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
NC
SLS22
SLS12
RXSC1
RXC1
RXD1
SLS21
SLS11
V
DD
ENV
Q–
Q+
I–
I+
SG
AGND
NC : No connect pin
17
NC
18
PDN2
19
BSTO
20
TXW
21
22
23
24
TXD
TXCO
64-Pin Plastic QFP
TXCI
NC
25
NC
26
NC
27
NC
28
NC
29
NC
30
NC
31
NC
32
NC
3/23
Page 4

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
PIN AND FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTIONS
TXD
Transmit data input for 384 kbps.
TXCI
Transmit clock input.
When the control register CR0 - B6 is “0”, a 384 kHz clock pulse synchronous with TXD should
be input to this pin. This clock pulse should be continuous because this device uses APLL to
generate internal clock pulses.
When CR0 - B6 is “1”, a 3.84 MHz clock pulse should be input to this pin. When the 3.84 MHz
clock pulse is applied to TXCI, TXCO outputs a 384 kHz clock pulse, which is generated by
dividing the TXCI input by 10. The transmit data, synchronous 384 kHz clock pulse, should be
input to the TXD. In this case the device does not use APLL, and the 3.84 MHz clock pulse need
not be continuous. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
TXCO
Transmit clock output.
When CR0 - B6 is “0”, TXCO outputs the 384 kHz clock pulse (APLL output) for monitoring
purposes. When CR0 - B6 is “1”, this pin outputs a 384 kHz clock pulse generated by dividing
the TXCI input by 10. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
TXW
Transmit data window signal input.
The transmit timing signal for the burst data is input to the device through this pin. If TXW pin
is “1”, modulation data is output. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
I+, I–
Quadrature modulation signal I component differential analog outputs.
The level of the outputs is 500 mVpp with 1.6 Vdc as center value. The output pin load
conditions are: R ≥ 10 kW, C £ 20 pF. The gain of these pins can be adjusted using the control
registers CR1 - B7 to B4, and the offset voltage at the I– pin can be adjusted using CR3 - B7 to
B3.
Q+, Q–
Quadrature modulation signal Q component differential analog outputs.
The level of the outputs is 500 mVpp with 1.6 Vdc as center value. The output pin load
conditions are: R ≥ 10 kW , C £ 20 pF. The gain of these pins can be adjusted using the control
registers CR1 - B3 to B0, and the offset voltage at the Q– pin can be adjusted using CR4 - B7 to
B3.
4/23
Page 5
ENV
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Quadrature modulation signal envelope (
22
I + Q
) output.
Its output level is 500 mVpp with 1.6 Vdc as a center value. The output pin load conditions are:
R ≥ 10 kW , C £ 20 pF. The gain of this output can be adjusted using the control registers CR2
- B7 to B4.
This pin is also used to monitor eye pattern, AFC compensating signal, and phase detection of
the demodulator block during the test mode. Refer to the description of the control register for
details.
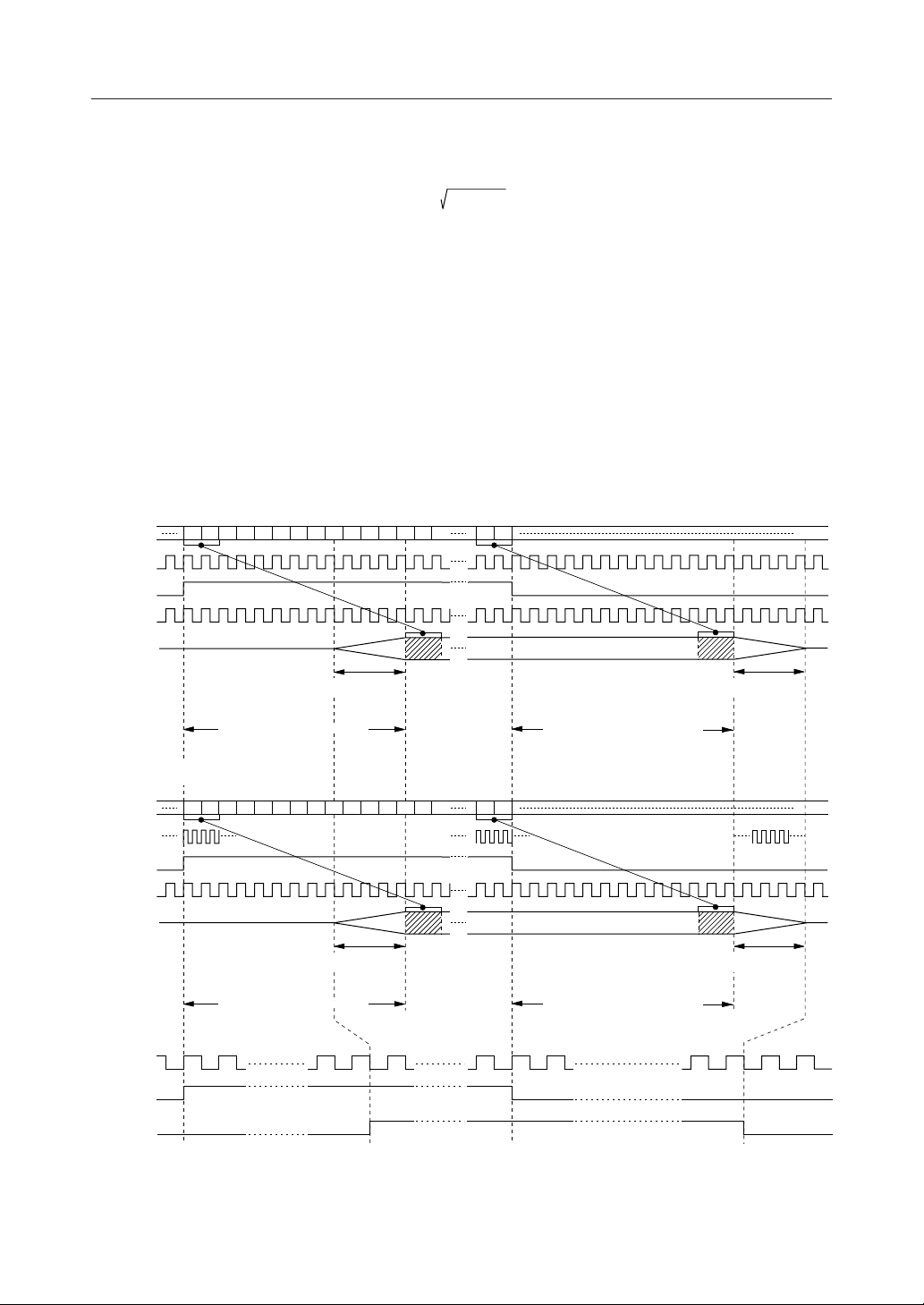
BSTO
Modulation burst window signal output.
The burst position for the I/Q baseband modulation output is output. (Refer to Fig. 1.)
(1) CR0 - B6 ="0".
TXD
TXCI
(384 kHz)
TXW
TXCO
(384 kHz)
I, Q
D0 D1
D2 D3 D4 D5D6D7 D8D9
Delay of 6.25 symbols
Ramp rise-up
2 symbols
D13D12D11D10
Dn-1 D
n
Ramp fall-down
2 symbols
Delay of 6.25 symbols
(2) CR0 - B6 ="1".
TXD
D0 D1
TXCI
(3.84 MHz)
TXW
TXCO
(384 kHz)
I, Q
TXCI
(384 kHz)
12 8910 N
TXW
BSTO
D2 D3 D4 D5D6D7 D8D9
Ramp rise-up
2 symbols
Delay of 6.25 symbols
Figure 1 Transmitter Timing Diagram
D13D12D11D10
Dn-1 D
n
Ramp fall-down
2 symbols
Delay of 6.25 symbols
N+1 N+2 N+16 N+17 N+18 N+19
5/23
Page 6
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
SG
Internal reference voltage output.
The output voltage is about 2.0 V. A bypass capacitor should be connected between this pin
and the AGND pin. The external SG voltage, if necessary should be used via buffer.
RESET
Control register reset.
When this pin is set to "0", the register is reset to the initial value.
The reset signal input width is 200 ns or more.
PDN0, PDN1, PDN2
Inputs for power-down control.
PDN0 controls the standby/communication modes, PDN1 controls the modulator, and PDN2
controls the demodulator. Refer to Table 1 for details.
Table 1 Power Down Control
PDN1
0
0—1
100
111
Standby Mode
Communication
Mode
V
DD
PDN0
+5 V power supply voltage.
AGND
Analog signal ground.
PDN2
—0
Function
All power-down.
Modulator power is off (VREF and PLL power is also off).
Demodulator power is on.
Modulator power is off (VREF and PLL power is on).
I and Q outputs are in a high-impedance state.
Only demodulator clock recovery block power is on.
Modulator power is on.
Only demodulator clock recovery block power is on.
Modulator power is off (VREF and PLL power is on).
I and Q outputs are in a high-impedance state.
Demodulator power is on.
Modulator power is on.
Demodulator power is on.
Mode
Mode A
Mode B
Mode C
Mode D110
Mode E101
Mode F
DGND
Digital signal ground.
AGND and DGND are not connected in the device. This pin should be tied to the AGND pin
on the PCB as close as possible from the device.
AGND and DGND should be connected as close as prossible on the PC board.
6/23
Page 7
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
MCK
Master clock input.
The clock frequency is 19.2 MHz.
IFIN1, IFIN2
Modulated signal inputs for the demodulator block.
Select the IF frequency from 1.2 MHz, 10.7 MHz, 10.75 MHz, and 10.8 MHz based on CR0 - B4
and B3. IFIN1 is for Channel 1, and IFIN2 for Channel 2.
IFCK
Clock signal input for demodulator block IF frequency (10.7 MHz or 10.75 MHz).
If the IF frequency is 10.7 MHz, 19.0222 MHz should be supplied. When it is 10.75 MHz, 19.1111
MHz should be supplied. When the IF frequency is 1.2 MHz or 10.8 MHz, set this pin to “0”
or “1”. (Refer to Fig. 2.)
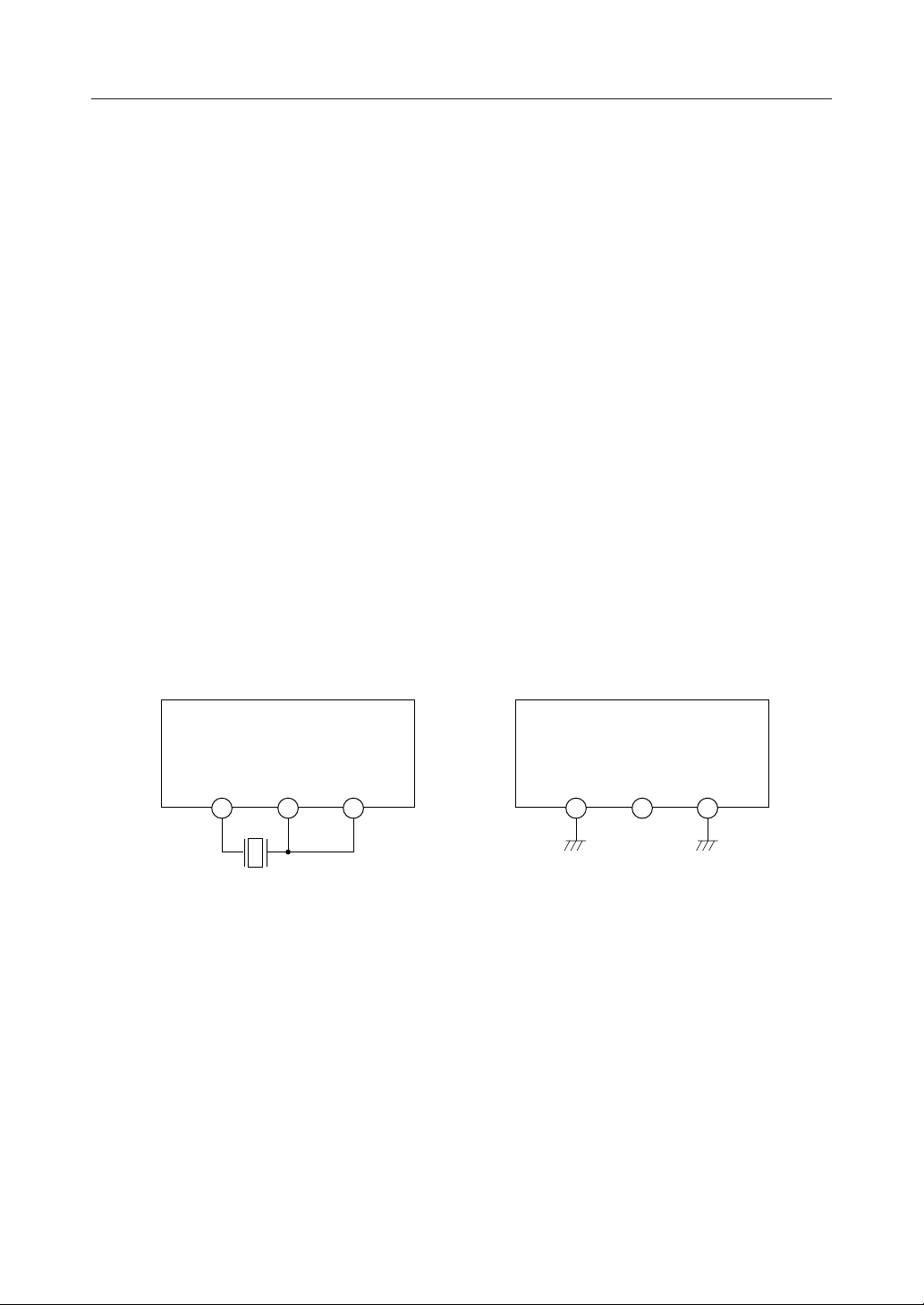
X1, X2
Crystal oscillator connection pins.
When supplying a 19.0222 MHz or 19.1111 MHz clock to IFCK, use these pins. (Refer to Fig. 2.)
When IFIN = 10.7 MHz or 10.75 MHz
MSM7583
IFCKX2X1
19.0222 MHz or 19.1111 MHz
Figure 2 How to Use IFCK, X1, and X2
When IFIN = 1.2 MHz or 10.8 MHz
MSM7583
IFCKX2X1
7/23
Page 8

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
RXD1, RXC1, RXSC1
Channel 1 receive data, receive clock, and receive symbol clock output pins.
During power-on, these output pins are at the output level of the clock recovery circuit selected
by a combination of SLS11 and SLS21 (described later). (Refer to Fig. 3.)
RXD2, RXC2, RXSC2
Channel 2 receive data, receive clock, and receive symbol clock output pins.
During power-on, these output pins are at the output level of the clock recovery circuit selected
by a combination of SLS12 and SLS22 (described later). (Refer to Fig. 3.)
SLS11, SLS21, SLS12, SLS22
Receiver slot select signal pins of Channel 1 (SLS11, SLS21) and Channel 2 (SLS12, SLS22).
The MSM7583 has four sets of clock recovery circuits and four AFC information storage
registers. One of the sets is selected according to a combination of the signals at these pins.
(Refer to Fig. 3.)
Channel 1 (SLS21, SLS11) = (0, 0): Slot 1, (0, 1): Slot 2
(1, 0): Slot 3, (1, 1): Slot 4
Channel 2 (SLS22, SLS12) = (0, 0): Slot 1, (0, 1): Slot 2
(1, 0): Slot 3, (1, 1): Slot 4
RXD1 (RXD2)
RXC1 (RXC2)
RXSC1 (RXSC2)
SLS21 (SLS22)
SLS11 (SLS12)
The recovery data and clock pulse are
selected asynchronously by the SLS signals.
Figure 3 RXD, RXC, and RXSC Timing Diagram
RXD0, RXC0, RXSC0
Receive data, receive clock, and receive symbol clock outputs.
These pins are at the output level selected by RXSEL (described below).
8/23
Page 9

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
RXSEL
Receive data, receive clock, and receive symbol clock select signal.
If this pin is set to "0", the output levels of Channel 1 RXD1, RXC1, and RXSC1 are selected to
be output to RXD0, RXC0, and RXSC0. If this pin is set to "1", the output levels of Channel 2
RXD2, RXC2, and RXSC2 are selected to be output to RXD0, RXC0, and RXSC0.
Note that a hazard may sometime occur in RXDO, RXCO, and RXSCO because RXSEL selects
asynchronously.
RPR1, RPR2
High-speed phase clock control signal input pin for the clock recovery circuit.
When each of the pins is “1”, the clock recovery circuit starts in the high-speed phase clock
mode. When the phase difference is less than a defined value, the circuit shifts to the low-speed
phase clock mode automatically. When each of the pins is “0”, the circuit is always in the lowspeed phase clock mode. RPR1 is for Channel 1, and RPR2 for Channel 2.
AFC1, AFC2
AFC operation range specification signal inputs.
As shown in Fig. 4, the AFC information is reset when both AFC and RPR are set to “1”. AFC
operation starts at a certain period after the AFC information is reset. When RPR is set to “1”,
an average number of times that AFC sets to on is low. When RPR is “0”, it is high. When AFC
is “0”, frequency error is not calculated, but the frequency is corrected using an error that is
held. AFC1 is for Channel 1, and AFC2 for Channel 2.
RCW1, RCW2
Clock recovery circuit operation ON/OFF control signal inputs.
When this pin is “0”, DPLL does not make any phase corrections. RCW1 is for Channel 1, and
RCW2 for Channel 2.
(CASE1)
AFC
RPR
(CASE2)
AFC
RPR
AFC information
is reset.
The clock recovery
circuit starts with the previous
AFC information.
Average
number of times
AFC is low.
Average number of times
AFC is high.
“0”
Average number of times
AFC is high.
AFC information
is maintained.
AFC information
is maintained.
Figure 4 AFC Control Timing Diagram
9/23
Page 10

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
,
DEN, EXCK, DIN, DOUT
Serial control ports for the microprocessor interface.
The MSM7583 contains a 6-byte control register. An external CPU uses these pins to read data
from and write data to the control register. DEN is the "Enable" signal input pin. EXCK is a
data shift clock pulse input pin. DIN is an address and data input pin. DOUT is a data output
pin. Figure 5 shows an input/output timing diagram.
DEN
EXCK
W
A2
DIN
A1 A0 B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
DOUT
DEN
EXCK
DIN
DOUT
High Impedance
(a) Data Write Timing Diagram
R A2A1A0
High Impedance
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
(b) Data Read Timing Diagram
Figure 5 MCU Interface Input/Output Timing Diagram
10/23
Page 11

The register map is shown below
Table 2 Control Register Map
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Register
Address
A2
A1 A0
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
ENVPD
Ich
GAIN3
ENV
GAIN3
Ich
Offset4
Qch
Offset4
R/W : Read/Write enable
TXCSEL
Ich
GAIN2
ENV
GAIN2
Ich
Offset3
Qch
Offset3
MODOFF
Ich
GAIN1
ENV
GAIN1
Ich
Offset2
Qch
Offset2
IFSEL1
Ich
GAIN0
ENV
GAIN0
Ich
Offset1
Qch
Offset1
Data
IFSEL0
Qch
GAIN3
—
Ich
Offset0
Qch
Offset0
LOCAL
INV1
ENVSEL
Qch
GAIN2
—
—
—
LOCAL
INV0
TEST1
Qch
GAIN1
—
—
—
TEST0
Qch
GAIN0
—
—
—
R/W
R/WCR0 0 0 0
R/WCR1 0 0 1
R/WCR2 0 1 0
R/WCR3 0 1 1
R/WCR4 1 0 0
R/WCR5 1 0 1 ICT7 ICT6 ICT5 ICT4 ICT1 ICT0
11/23
Page 12

ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATINGS
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Parameter Symbol
Power Supply Voltage
Digital Input Voltage
Storage Temperature
V
DD
V
DIN
T
STG
—
—
—
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
Parameter Symbol
Power Supply Voltage
Operating Temperature
Input High Voltage
Input Low Voltage
Master Clock Frequency
Modulator Input Frequency
Demodulator Input
Frequency
Clock Duty Cycle
IF Input Duty Cycle
Voltage must be fixed
V
DD
Ta
All digital input pins
V
IH
V
All digital input pins
IL
MCK
f
MCK
TXCI (when CR0 - B6 = "0")
f
TXC1
TXCI (when CR0 - B6 = "1")
f
TXC2
IFCK (when IFIN = 10.7 MHz)
f
IFCK1
f
IFCK (when IFIN = 10.75 MHz)
IFCK2
D
MCK, IFCK, TXCI
CCK
D
IFCK
CIF
Condition
—
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
RatingCondition
0 to 7
–0.3 to V
DD
+ 0.3
–55 to +150
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, Ta = –25°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Min. Typ.
4.5
–25
2.2
0
—
—
—
–50 ppm
–50 ppm
19.0222
19.1111
40
45
—
+25
—
—
19.2
384
3.84
50
50
Max.
5.5
+70
V
DD
0.6
—
—
—
+50 ppm
+50 ppm
60
55
Unit
V
V
°C
Unit
V
°C
V
V
MHz
kHz
MHz
MHz
MHz
%
%
DC Characteristics
Parameter Symbol
Power Supply Current
Output High Voltage
Output Low Voltage
Input Leakage Current
Mode A (when VDD = 5.0 V)
I
DD1
Mode B (when V
I
DD2
Mode C (when V
I
DD3
Mode D (when V
I
DD4
Mode E (when V
I
DD5
Mode F (when V
I
DD6
= 0.4 mA
I
V
OH
OH
= –1.6 mA
I
V
OL
I
IH
I
IL
OL
Condition
= 5.0 V)
DD
= 5.0 V)
DD
= 5.0 V)
DD
= 5.0 V)
DD
= 5.0 V)
DD
—
—
(V
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, Ta = –25°C to +70°C)
DD
Min. Typ.
—
—
—
—
—
—
2.8
0.0
—
—
0.03
25.0
8.5
16.0
28.0
35.0
—
—
—
—
Max.
0.06
50.0
17.0
32.0
56.0
70.0
V
DD
0.4
10
10
Unit
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
mA
V
V
mA
mA
12/23
Page 13

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Analog Interface Characteristics
Parameter
Output Resistance Load
Output Capacitance Load
Output DC Voltage Level
Output AC Voltage Level
Offset Voltage Difference V
Output DC Voltage Adjustment Level Range
Output AC Voltage Adjustment Level Range
Out-of-band Spectrum
Symbol
R
LIQ
C
LIQ
V
DC1
V
DC2
V
DC3
V
DC4
V
DC5
V
DC6
V
AC
OFF
DCVL — ±45 — mV—
ACVL — ±4 — %—
P600 60 — — dB600 kHz detuning (*)
P900 65 — — dB900 kHz detuning (*)
Condtion Min.
I+, I–, Q+, Q–, ENV
I+, I–, Q+, Q–, ENV
I+, I–, Q+, Q– (TXW = 0)
I+ (CR0 – B5 = 1)
when not modulated
Q+ (CR0 – B5 = 1)
when not modulated
ENV (TXW = 1, CR0 – B2 = 0, TXD = 0)
ENV (TXW = 1, CR0 – B2 = 1, TXD = 0)
I+, I–, Q+, Q–
(TXW = 0 continuous input)
Difference among
I+, I–, Q+, and Q–
(V
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, Ta = –25°C to +70°C)
DD
Typ.
10
—
1.55
—
—
1.6
— 1.77 V
— 1.67 V
— 1.35 VENV (TXW = 0)
— 1.72 V
— 1.63 V
340
360
–20 — +20 mV
Modulation Accuracy EVM — 1.0 3.0 % rms—
Demodulator IF Input Level IFV 0.5 — V
IFIN Input Impedance
IFIN input level
RIF — 20 — kW—
CIF — 5 — pF—
SG Output Voltage VSG — 2.0 — V—
SG Output Impedance RSG — 2 — kW—
SG´AGND 0.1 mF
SG warm-up Time T
(Rise Time to 90% of max.
SG
— 400 — ms
level.)
Modulator D/A
Conversion Sampling Frequency
Modulator D/A
Conversion Offset Frequency
F
SDA
F
CDA
— 1.92 — MHz—
— 380 — kHz—
Max.
—
20
1.65
—
—
—
—
—
380
DD
Unit
kW
pF
V
mV
V
PP
PP
* Power attenuation at 600 kHz or 900 kHz ±96 kHz as referred to two times of the power in
frequency band of 0 to 96 kHz
13/23
Page 14

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Digital Interface Characteristics
Parameter
Transmitter Digital
Input/Output Setting Time
Receiver Digital Input/Output
Setting Time
Serial Port Digital
Input/Output Setting Time
EXCK Clock Frequency
Symbol
t
SX
t
XS
t
DS
t
DH
t
XD1
t
XD2
t
XD3
t
XD4
t
RD1
t
RD2
t
RS1
t
RS4
t
RW
t
M1
t
M2
t
M3
t
M4
t
M5
t
M6
t
M7
t
M8
t
M9
t
M10
t
M11
f
EXCK
Condtion
C load = 50 pF Fig. 6
C load = 50 pF Fig. 7
to
C load = 50 pF Fig. 8
= 4.5 V to 5.5 V, Ta = –25°C to +70°C)
(V
DD
Other
Min. Typ. Max. Unit
200 — —
200 — —
0 — 200
0 — 200
0 — 200 ns
0 — 200 ns
10 — — ms
10 — — ms
50 — — ns
50 — — ns
50 — — ns
50 — — ns
100 — — ns
50 — — ns
50 — — ns
0 — 100 ns
50 — — ns
50 — — ns
0 — 50 ns
——10MHz— EXCK
ns
ns
ns
ns
14/23
Page 15

TIMING DIAGRAM
Transmit Data Input Timing
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
TXCI [TXCO*]
1 2 3 N-2 N-1 N N+1
(384 kHz)
t
t
SX
XS
TXW
t
t
DS
DH
TXD
123 N-2 N-1 N
*[ ]: When CR0 - B6 = "1", TXCO is indicated.
Transmit Clock (TXCO) Output Timing (when CR0 - B6 = 1)
TXCI
(3.84 MHz)
TXCO
(384 kHz)
2345678910
1
t
XD1
t
XD2
Transmit Burst Position Output (BSTO) Timing
TXCI
(384 kHz)
TXW
BSTO
1
2 9 10 N
t
XD3
N+1
XS
N+16
tSXt
t
XD1
N+17 N+18
t
XD4
SLS1
SLS2
RCW
AFC
RPR
RXC
RXD
Figure 6 Transmit (Modulator) Digital Input/Output Timing
t
t
RS2
RS1
t
t
RS4
RS3
t
RW
t
RD1
Figure 7 Receiver (Demodulator) Digital Input/Output Timing
t
RD2
15/23
Page 16

MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
DEN
EXCK
DIN
DOUT
t
M1tM3
t
M2
t
M5
123456
t
t
M4
M6
t
M7
W/R A2 A1 A0 B7
t
M8
B7
Figure 8 Serial Control Port Interface
11 12
t
M9
B1 B0
B1 B0
t
M11
t
M10
16/23
Page 17

FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
Control Registers
(1) CR0 (basic operation mode setting)
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
B7
CR0
Initial value (*)
* The initial value is set when a reset signal is supplied at RESET.
ENVPD TXCSEL MODOFF IFSEL1 IFSEL2 ENVSEL TEST1 TEST0
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
0000000
B7: Transmit envelope output power down control
0/Envelope output ON
1/Envelope output OFF
B6: Transmit timing clock selection
0/TXCI input: 384 kHz.
TXCO output: 384 kHz output from APLL
Transmit data TXD is input in synchronization with the rising edge of
TXCI (APLL is on.)
1/TXCI input: 3.84 MHz.
TXCO output: 384 kHz (one-tenth of the TXCI frequency)
Transmit data TXD is input in synchronization with the rising edge of
TXCO (APLL is off.)
B5: Modulation on/off control
1/modulation OFF (with phase fixed)
0/modulation ON.
B4, B3: Receiver input IF frequency selection
(0, 0), (0, 1): 1.2 MHz
(1, 0) : 10.8 MHz
(1, 1) : 10.7 MHz/10.75 MHz
B2: Transmit envelope (I2 + Q2 or
When B1, B0 is (0, 0) : 0/
22
I + Q
22
I + Q
) output selection
output
1/I2 + Q2 output
When B1, B0 is other than (0, 0) : 0/Channel 1 receive monitor output
1/Channel 2 receive monitor output
B1, B0: Test mode selection bits. Each monitor output is output to the transmit ENV pin.
(0, 0): transmit envelope (I2 + Q2 or
22
I + Q
) output
(0, 1): receiver phase detection signal output
(1, 0): receiver delay detection signal output
(1, 1): receiver internal AFC information output
17/23
Page 18

(2) CR1 (I, Q gain adjustment)
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
CR1
Initial value
B7
Ich
GAIN3
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Ich
GAIN2
0000000
Ich
GAIN1
Ich
GAIN0
Qch
GAIN3
Qch
GAIN2
B7 to B4: I+/I- output gain setting, in 3 mV steps (Refer to Table 3.)
B3 to B0: Q+/Q- output gain setting, in 3 mV steps (Refer to Table 3.)
(3) CR2 (ENV gain adjustment)
CR2
Initial value
B7
ENV
GAIN3
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
ENV
GAIN2
0000000
ENV
GAIN1
ENV
GAIN0
————
B7 to B4: ENV output gain setting, in 9 mV steps (Refer to Table 3.)
B3 to B0: Not used
Table 3 I, Q, and ENV Output Gain Values
I and Q Amplitude
(value relative to the reference
(1.000) at (0, 0, 0, 0))
1.042
1.036
1.030
1.024
1.018
1.012
1.006
1.000
0.994
0.988
0.982
0.976
0.970
0.964
0.958
0.952
CR2
B7 B6 B5 B4
0
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
0
(value relative to the reference
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
B6B2B5B1B4
B7
B3
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CR1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
B0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
0
0
Qch
GAIN1
ENV Amplitude
(1.000) at (0, 0, 0, 0))
1.126
1.108
1.090
1.072
1.054
1.036
1.018
1.000
0.982
0.964
0.946
0.928
0.910
0.892
0.874
0.856
Qch
GAIN0
18/23
Page 19

(4) CR3 (I– output offset voltage adjustment)
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
CR3
Initial value
B7
Ich
Offset4
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Ich
Offset3
0000000
Ich
Offset2
Ich
Offset1
Ich
Offset0
B7 to B3: I– output pin offset voltage adjustment (Refer to Table 4.)
B2 to B0: Not used
(5) CR4 (Q– output offset voltage adjustment)
CR4
Initial value
B7
Qch
Offset4
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
Qch
Offset3
0000000
Qch
Offset2
Qch
Offset1
Qch
Offset0
B7 to B3: Q– output pin offset voltage adjustment (Refer to Table 4.)
B2 to B0: Not used
Table 4 I and Q Channel Offset Adjustment Values
CR3, CR4
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3
1
1
1
0
1
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
1
1
0
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
1
0
0
0
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
I and Q offset
(mV)
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
1
0
+45
+42
+39
+36
+33
+30
+27
+24
+21
+18
+15
+12
+9
+6
+3
0
B7 B6 B5 B4 B3
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
CR3, CR4
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
1
1
1
1
0
0
0
0
———
———
I and Q offset
(mV)
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
1
1
0
1
1
0
0
0
–3
–6
–9
–12
–15
–18
–21
–24
–27
–30
–33
–36
–39
–42
–45
–48
19/23
Page 20

(6) CR5 (IC test)
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
CR5
Initial value
B7
ICT7 ICT6 ICT5 ICT4
0
B6 B5 B4 B3 B2 B1 B0
LOCAL
INV1
0000000
LOCAL
INV0
ICT1 ICT0
B7 to B4: ICT7 to ICT4. Device test control bits.
B3, B2 : Local inverting mode setting bits. (Used when the phase of the demodulator IF
input to this device is inverted.)
(1, 1) = local inverting mode
(0, 0) = normal mode
B1, B0 : ICT1, ICT0. Device test control bits.
Note: CR5 - B7 to B4, B1, and B0 are used to test the device. They should be set to “0” during
normal operation.
State Transition Time
Note: The transition time is 1 ms or
less unless otherwise stated
Standby mode (PDN0 = 0)
Communication mode (PDN0 = 1)
PDN1 = 1
PDN2 = 0
Mode A Mode B
PDN1 = 0
PDN2 = 0
5 ms
Mode C Mode EMode D
PDN1 = 0
PDN2 = 0
1 ms
PDN1 = 0
PDN2 = 1
5 ms40 ms
PDN1 = 0
PDN2 = 1
5 ms
Mode F
PDN1 = 1
PDN2 = 1
40 ms
Figure 9 Power-Down State Transition Time
20/23
Page 21

APPLICATION CIRCUIT
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
19.2 MHz input
Demodulator 2
IF input
Demodulator 1
IF input
Control register
control signal
Reset signal
Power
down
control
signal
V
DD
Demodulator 1
control
signal
Demodulator 2
control
signal
1
2
3
4
C5
5
6
C4
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
646362616059585756555453525150
X2
X1
NC
NC
IFCK
MCK
DGND
IFIN2
DGND
IFIN1
DGND
V
DD
DOUT
DIN
EXCK
DEN
RESET
PDN0
PDN1
NC
PDN2
171819202122232425262728293031
BSTO
RPR2
TXW
AFC2
TXD
RCW2
RPR1
AFC1
RCW1
RXSC0
RXC0
MSM7583GS-BK
TXCO
TXCINCNCNCNCNCNCNCNC
RXD0
RXSEL
RXC2
RXSC2
49
RXD2
NC
SLS22
SLS12
RXSC1
RXC1
RXD1
SLS21
SLS11
V
ENV
Q–
Q+
SG
AGND
NC
32
Receive symbol clock output
Receive clock output
Receive data output
Receive channel select signal
Receive symbol clock 2 output
Receive clock 2 output
Receive data 2 output
48
47
46
45
44
43
42
41
40
DD
39
V
DD
38
37
36
I–
35
I+
34
33
C3 C2 C1
Demodulator 2
control signal
Receive symbol clock 1
output
Receive clock 1 output
Receive data 1 output
Demodulator 1
control signal
Modulator Q
component
output
Modulator I
component
output
V
DD
To orthogonal modulator
Burst window output
Modulator data window
Modulator input data
Modulator 384 kHz input
C1 = 10 mF
C2 = C3 = 0.1 mF
C4 = C5 = 1000 pF
Figure 10 Example of Circuit Configuration
21/23
Page 22

Demodulator Control Timing Diagram (Example)
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
Demodulator
unit Modulator
G
R1
Slot 1
Slot 2
G
input data
Timing for CS
PDN2
SLS2
SLS1
"0"
"0"
AFC
RXD
R1
RXC
240 bits 625 ms
(1) Control channel/synchronous burst (SS + PR = 64 bits)
RXD
G G G G G G G G R R R R
SS SS PR PR ------------- UWPR ------------- CRCR
AFC
RPR
R2
G
"0"
"1"
R2
R3
"1"
"0"
R3
Slot 3
Slot 4
G
R4
G
"1"
"1"
R4
64 bits
G G G G G G G G
RCW
(2) Communication channel (SS + PR = 8 bits)
RXD
G G G G G G G G R R R R
AFC
RPR
"0"
RCW
* AFC and RCW may be controlled at the same timing.
56 bits
8 bits
SS SS PR PR
Loss than 30 bits
-----
UWPR ------------- CRCR
G G G G G G G G
G: Guard bit
R: Ramp bit
SS: Start symbol bit
PR: Preamble bit
UW: Unique word bit
CR: CRC bit
22/23
Page 23

PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
QFP64-P-1414-0.80-BK
Mirror finish
MSM7583¡ Semiconductor
(Unit : mm)
Package material
Lead frame material
Pin treatment
Solder plate thickness
Package weight (g)
Epoxy resin
42 alloy
Solder plating
5 mm or more
0.87 TYP.
Notes for Mounting the Surface Mount Type Package
The SOP, QFP, TSOP, SOJ, QFJ (PLCC), SHP and BGA are surface mount type packages, which
are very susceptible to heat in reflow mounting and humidity absorbed in storage.
Therefore, before you perform reflow mounting, contact Oki’s responsible sales person for the
product name, package name, pin number, package code and desired mounting conditions
(reflow method, temperature and times).
23/23
 Loading...
Loading...