Page 1
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
Order this document
by MBR150/D
. . . employing the Schottky Barrier principle in a large area metal–to–silicon
power diode. State–of–the–art geometry features epitaxial construction with
oxide passivation and metal overlap contact. Ideally suited for use as rectifiers
in low–voltage, high–frequency inverters, free wheeling diodes, and polarity
protection diodes.
• Low Reverse Current
• Low Stored Charge, Majority Carrier Conduction
• Low Power Loss/High Efficiency
• Highly Stable Oxide Passivated Junction
Mechanical Characteristics:
• Case: Epoxy, Molded
• Weight: 0.4 gram (approximately)
• Finish: All External Surfaces Corrosion Resistant and Terminal Leads are
Readily Solderable
• Lead and Mounting Surface Temperature for Soldering Purposes: 220°C
Max. for 10 Seconds, 1/16″ from case
• Shipped in plastic bags, 1000 per bag
• Available Tape and Reeled, 5000 per reel, by adding a “RL’’ suf fix to the
part number
• Polarity: Cathode Indicated by Polarity Band
• Marking: B150, B160
MAXIMUM RATINGS
Rating Symbol MBR150 MBR160 Unit
Peak Repetitive Reverse Voltage
Working Peak Reverse Voltage
DC Blocking Voltage
RMS Reverse Voltage V
Average Rectified Forward Current (2)
(V
R(equiv)
see Note 3, TA = 55°C)
Nonrepetitive Peak Surge Current
(Surge applied at rated load conditions, halfwave, single phase, 60 Hz, TL = 70°C)
Operating and Storage Junction Temperature Range (Reverse Voltage applied) TJ, T
Peak Operating Junction Temperature (Forward Current applied) T
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS (Notes 3 and 4)
Thermal Resistance, Junction to Ambient R
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS (T
Maximum Instantaneous Forward Voltage (1)
(iF = 0.1 A)
(iF = 1 A)
(iF = 3 A)
Maximum Instantaneous Reverse Current @ Rated dc Voltage (1)
(TL = 25°C)
(TL = 100°C)
(1) Pulse Test: Pulse Width = 300 µs, Duty Cycle ≤ 2.0%.
(2) Lead Temperature reference is cathode lead 1/32″ from case.
v 0.2 VR(dc), TL = 90°C, R
Characteristic Symbol Max Unit
Characteristic Symbol Max Unit
= 80°C/W, P.C. Board Mounting,
θJA
= 25°C unless otherwise noted) (2)
L
V
RRM
V
RWM
V
R
R(RMS)
I
O
I
FSM
stg
J(pk)
θJA
v
F
i
R
MBR160 is a
Motorola Preferred Device
SCHOTTKY BARRIER
RECTIFIERS
1 AMPERE
50, 60 VOL TS
CASE 59–04
PLASTIC
50 60 Volts
35 42 Volts
1 Amp
25 (for one cycle) Amps
*
65 to +150 °C
150 °C
80 °C/W
0.550
0.750
1.000
0.5
5
Volt
mA
Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value.
Rev 1
Rectifier Device Data
Motorola, Inc. 1996
1
Page 2
10
7.0
5.0
3.0
2.0
1.0
0.7
0.5
0.3
0.2
TJ = 150°C
100°C
25°C
10
5.0
2.0
1.0
0.5
0.2
TJ = 150°C
125°C
100°C
75°C
0.1
0.05
0.02
0.01
, REVERSE CURRENT (mA)
R
I
0.005
25°C
0.002
0.001
50 6010 20 30
40 700
VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
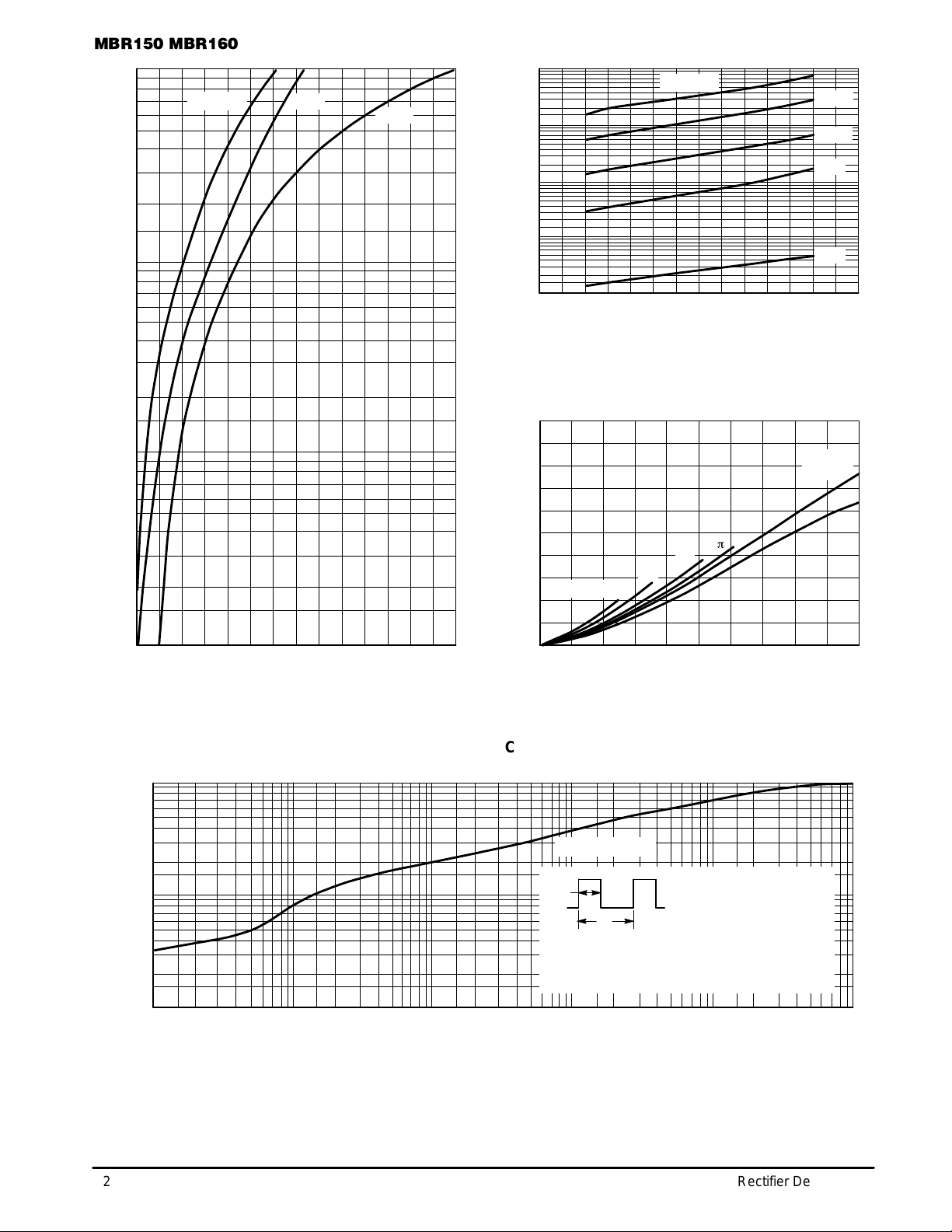
Figure 2. T ypical Reverse Current*
*The curves shown are typical for the highest voltage device in the voltage grouping. Typical reverse current for lower voltage selections can
be estimated from these same curves if VR is sufficiently below rated VR.
5.0
0.1
, INSTANTANEOUS FORWARD CURRENT (AMPS)
F
i
4.0
0.07
, AVERAGE FORW ARD
F(AV)
P
3.0
2.0
1.0
POWER DISSIPATION (WATTS)
0
p
5
10
IPK/IAV = 20
1.00
I
, AVERAGE FORW ARD CURRENT (AMPS)
F(AV )
2.0
3.0 4.0 5.0
Figure 3. Forward Power Dissipation
0.05
0.03
0.02
0
0.60.2 0.4 0.8 1.0
1.2
1.4
1.6
vF, INSTANTANEOUS VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
Figure 1. T ypical Forward Voltage
THERMAL CHARACTERISTICS
1.0
0.7
0.5
0.3
0.2
0.1
0.07
(NORMALIZED)
0.05
0.03
0.02
r(t), TRANSIENT THERMAL RESIST ANCE
0.01
0.1 0.2 0.5 1.0 2.0 5.0 10 20 50 100 200 500 1 k 2 k 5 k 10 k
t, TIME (ms)
Figure 4. Thermal Response
Z
= Z
θ
JL
P
pk
t
1
[D + (1 – D)
θ
JL
• r(t)
•
P
pk
DUTY CYCLE, D = tp/t
PEAK POWER, Ppk, is peak of an
equivalent square power pulse.
TIME
r(t1 + tp) + r(tp) – r(t1)]
θ
JL(t)
t
p
∆
TJL = Ppk • R
where
∆
TJL = the increase in junction temperature above the lead temperature
r(t) = normalized value of transient thermal resistance at time, t, from Figure 4, i.e.:
r(t) = r(t1 + tp) = normalized value of transient thermal resistance at time, t
1
+ tp.
1
SQUARE
WAVE
dc
2
Rectifier Device Data
Page 3

90
g
R
80
70
°
60
50
40
, THERMAL RESISTANCE,
30
JL
q
JUNCTION–TO–LEAD ( C/W)
R
20
10
Figure 5. Steady–State Thermal Resistance Figure 6. T ypical Capacitance
200
BOTH LEADS TO HEA T SINK,
EQUAL LENGTH
100
C, CAPACITANCE (pF)
80
70
60
50
40
30
20
MAXIMUM
TYPICAL
3/81/8 1/4 1/2 5/8 7/8 1.0 60 7010 20 30 40
L, LEAD LENGTH (INCHES)
3/40
TJ = 25°C
f = 1 MHz
50 800
VR, REVERSE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
10090
NOTE 3 — MOUNTING DATA:
Data shown for thermal resistance junction–to–ambient
(R
for the mounting shown is to be used as a typical
θJA)
guideline values for preliminary engineering or in case the tie
point temperature cannot be measured.
T ypical Values for R
Mounting
Method
1 52 65 72 85 °C/W
2 67 80 87 100 °C/W
3 — 50 °C/W
Lead Length, L (in)
1/8 1/4 1/2 3/4
in Still Air
θJA
θJA
NOTE 4 — THERMAL CIRCUIT MODEL:
(For heat conduction through the leads)
T
C(K)
R
θ
L(K)Rθ
T
L(K)
T
S(K)
A(K)
R
θ
S(A)Rθ
T
A(A)
T
L(A)
L(A)Rθ
T
C(A)TJ
J(A)
R
P
θJ(K)
D
Use of the above model permits junction to lead thermal
resistance for any mounting configuration to be found. For a
given total lead length, lowest values occur when one side of
the rectifier is brought as close as possible to the heat sink.
Terms in the model signify:
TA = Ambient Temperature TC = Case Temperature
TL = Lead Temperature TJ = Junction Temperature
RθS = Thermal Resistance, Heat Sink to Ambient
RθL = Thermal Resistance, Lead to Heat Sink
RθJ = Thermal Resistance, Junction to Case
PD = Power Dissipation
Mounting Method 1
P.C. Board with
1–1/2″ x 1–1/2″
copper surface.
LL
Mounting Method 2
LL
VECTOR PIN MOUNTING
Mounting Method 3
P.C. Board with
1–1/2″ x 1–1/2″
copper surface.
L = 3/8
″
BOARD GROUND
PLANE
(Subscripts A and K refer to anode and cathode sides,
respectively.) Values for thermal resistance components are:
RθL = 100°C/W/in typically and 120°C/W/in maximum.
RθJ = 36°C/W typically and 46°C/W maximum.
NOTE 5 — HIGH FREQUENCY OPERATION:
Since current flow in a Schottky rectifier is the result of majority carrier conduction, it is not subject to junction diode forward and reverse recovery transients due to minority carrier
injection and stored charge. Satisfactory circuit analysis work
may be performed by using a model consisting of an ideal
diode in parallel with a variable capacitance. (See Figure 6.)
Rectification efficiency measurements show that operation
will be satisfactory up to several megahertz. For example,
relative waveform rectification efficiency is approximately 70
percent at 2 MHz, e.g., the ratio of dc power to RMS power in
the load is 0.28 at this frequency, whereas perfect rectification would yield 0.406 for sine wave inputs. However, in contrast to ordinary junction diodes, the loss in waveform efficiency is not indicative of power loss: it is simply a result of
reverse current flow through the diode capacitance, which
lowers the dc output voltage.
Rectifier Device Data
3
Page 4

P ACKAGE DIMENSIONS
B
K
D
A
NOTES:
1. ALL RULES AND NOTES ASSOCIATED WITH
JEDEC DO–41 OUTLINE SHALL APPLY.
2. POLARITY DENOTED BY CATHODE BAND.
3. LEAD DIAMETER NOT CONTROLLED WITHIN F
DIMENSION.
DIM MIN MAX MIN MAX
A 5.97 6.60 0.235 0.260
B 2.79 3.05 0.110 0.120
D 0.76 0.86 0.030 0.034
K 27.94 ––– 1.100 –––
INCHESMILLIMETERS
K
CASE 59–04
ISSUE M
Motorola reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein. Motorola makes no warranty , representation or guarantee regarding
the suitability of its products for any particular purpose, nor does Motorola assume any liability arising out of the application or use of any product or circuit, and
specifically disclaims any and all liability, including without limitation consequential or incidental damages. “T ypical” parameters which may be provided in Motorola
data sheets and/or specifications can and do vary in different applications and actual performance may vary over time. All operating parameters, including “Typicals”
must be validated for each customer application by customer’s technical experts. Motorola does not convey any license under its patent rights nor the rights of
others. Motorola products are not designed, intended, or authorized for use as components in systems intended for surgical implant into the body, or other
applications intended to support or sustain life, or for any other application in which the failure of the Motorola product could create a situation where personal injury
or death may occur. Should Buyer purchase or use Motorola products for any such unintended or unauthorized application, Buyer shall indemnify and hold Motorola
and its officers, employees, subsidiaries, affiliates, and distributors harmless against all claims, costs, damages, and expenses, and reasonable attorney fees
arising out of, directly or indirectly, any claim of personal injury or death associated with such unintended or unauthorized use, even if such claim alleges that
Motorola was negligent regarding the design or manufacture of the part. Motorola and are registered trademarks of Motorola, Inc. Motorola, Inc. is an Equal
Opportunity/Affirmative Action Employer.
How to reach us:
USA/EUROPE/Locations Not Listed: Motorola Literature Distribution; JAPAN: Nippon Motorola Ltd.: SPD, Strategic Planning Office, 4–32–1,
P.O. Box 5405, Denver, Colorado 80217. 303–675–2140 or 1–800–441–2447 Nishi–Gotanda, Shinagawa–ku, Tokyo 141, Japan. 81–3–5487–8488
Mfax: RMFAX0@email.sps.mot.com – TOUCHTONE 602–244–6609 ASIA/PACIFIC: Motorola Semiconductors H.K. Ltd.; 8B Tai Ping Industrial Park,
INTERNET: http://motorola.com/sps
4
– US & Canada ONLY 1–800–774–1848 51 Ting Kok Road, T ai Po, N.T., Hong Kong. 852–26629298
CODELINE TO BE PLACED HERE
◊
Mfax is a trademark of Motorola, Inc.
Rectifier Device Data
MBR150/D
 Loading...
Loading...