Page 1

Ordering number : ENN*6715
CMOS IC
LC875164A/48A/32A
8-Bit Single Chip Microcontroller with
64/48/32K-Byte ROM and 1024 -Byte RAM On Chip
Preliminary
Overview
The LC875164A/48A/32A microcontroller is 8-bit single chip microcontroller with the following on-chip functional blocks:
- CPU: Operable at a minimum bus cycle time of 100ns
- 64K/48K/32K bytes ROM
- 1024 byte RAM
- two high performance 16 bit timer/counters (can be divided into 8 bit units)
- two 8 bit timers with prescalers
- timer for use as date/time clock
- two synchronous serial I/O ports (with automatic block transmit/receive function)
- one asynchronous/synchronous serial I/O port
- 12-bit PWM × 2
- 8-channel × 8-bit AD converter
- high speed 8-bit parallel interface
- 19-sour ce 10-vec tored interrupt system
All of the above functions are fabricated on a single chip.
Features
(1) Read Only Memory
- 65536 × 8 bits (LC875164A)
- 49151 × 8 bits (LC875148A)
- 32512 × 8 bits (LC875132A)
Ver.1.03
O3098
91400 RM (IM) HK / SY No.6715-1/25
Page 2

LC875164A/48A/32A
(2) Bus Cycle Time
- 100ns (10MHz)
Note: The bus cycle time indicates ROM read time.
(3) Minimum Instruction Cycle Time : 300ns (10MHz)
(4) Ports
- Input/output ports
Each bit data direction programmable 59 (P1n,P2n,P3n,P70 to P73,P8n,PAn,PBn,PCn,S2Pn)
Nibble data direction programmable 8 (P0n)
- Input ports 2 (XT1,XT2)
- PWM Output po rts 2 (PWM0,PWM1)
- Oscillator pins 2 (CF1,CF2)
- Reset pin 1 (
RES)
- Power supply 6 (VSS1 to 3,VDD1 to 3)
(5) Timers
- Timer0: 16 bit timer/counter with capture register
Mode 0: 2 channel 8 bit timer with programmable 8 bit prescaler and 8 bit capture register
Mode 1: 8 bit timer with 8 bit programmable prescaler and 8 bit capture register + 8 bit counter with 8 bit
capture register
Mode 2: 16 bit timer with 8 bit programmable prescaler and 16 bit capture register
Mode 3: 16 bit counter with 16 bit capture register
- Timer1: PWM/16 b it timer/counter (with togg le output)
Mode 0: 8 bit timer (with toggle output) + 8 bit timer counter (with toggle output)
Mode 1: 2 channel 8 bit PWM
Mode 2 : 1 6 bit timer/counter (wit h toggle outp ut)
Mode 3: 16 bit timer (with toggle output) Lower order 8 bits can be used as PWM output.
- Timer4: 8-bit timer with 6-bit prescaler
- Timer5: 8-bit timer with 6-bit prescaler
- Base timer
1. The clock signal can be selected from any of the following: sub-clock (32.768kHz crystal oscillator), system
clock, and prescaler output for timer 0.
2. Interrupts can be selected to occur at one of five different times.
(6) SIO
- SIO0: 8 bit synchronous serial interface
1. LSB first/MSB first function available
2. Internal 8-bit baud-rate generator (maximum transmit clock period 4/3 T
3. Continuous automatic data communications (1 - 256 bits)
- SIO1: 8 bit asynchronous/synchronous serial interface
Mode 0: Synchronous 8 bit serial IO (2-wire or 3-wire, transmit clock 2 - 512 T
Mode 1: Asynchronous serial IO (half duplex, 8 data bits, 1 stop bit, baud rate 8 - 2048 T
Mode 2: Bus mode 1 (start bit, 8 data bits, transmit clock 2 - 512 T
Mode 3: Bus mode 2 (start detection, 8 data bits, stop detection)
- SIO2: 8 bit synchronous serial interface
1. LSB-first
2. Built in 8-bit baud-rate generator (Maximum clock period 4/3 T
3. Continuous automatic data communication (1 - 32 bytes)
(7) AD converter
- 8-bits × 8-channels
(8) PWM
- 2 channel synchronous variable 12 bit PWM
(9) Parallel interface
RD , WR , CS0 - CS2 Outputs (reversible polarity)
- RS,
- read/write possible in 1 T
CYC
CYC
CYC
)
CYC
)
CYC
CYC
)
)
)
No.6715-2/25
Page 3

LC875164A/48A/32A
(10) Remote control receiver circuit (connected to P73/INT3/T0IN terminal)
- Noise rejection function (noise rejection filter time constant can selected from 1/32/128 T
(11) Watchdog timer
- The watchdog timer period set by external RC.
- Watchdog timer can be set to produce interrupt, system reset
(12) Interrupts
- 19-source, 10-vectored interrupts:
1. Three level (low, high and highest) multiple interrupts are supported. During interrupt handling, an equal or
lower level interrupt request is refused.
2. If interrupt requests to two or more vector addresses occur at once, the higher level interrupt takes precedence.
In the case of equal priority levels, the vector with the lowest address takes precedence.
No. Vector Selectable Level Interrupt signal
1 00003H X or L INT0
2 0000BH X or L INT1
3 00013H H or L INT2/T0L/INT4
4 0001BH H or L INT3/INT5/Base timer
5 00023H H or L T0H
6 0002BH H or L T1L/T1H
7 00033H H or L SIO0
8 0003BH H or L SIO1/ SIO2
9 00043H H or L ADC
10 0004BH H or L Port 0/T4/T5/PWM0, 1
• Priority Lev el : X > H > L
• For equal priority levels, vector with lowest address takes precedence.
(13) Subroutine stack levels
- 512 levels max. Stack is located in RAM
(14) Multiplication and division
- 16 bit × 8 bit (executed in 5 cycles)
- 24 bit × 16 bit (12 cycles )
- 16 bit ÷ 8 bit (8 cycles)
- 24 bit ÷ 16 bit (12 cycles)
(15) Oscillation circuits
- On-chip RC oscillation circuit used for system clock
- On-chip CF oscillation circuit used for system clock
- On-chip Crystal oscillation circuit used for system clock and time-base clock
(16) Standby function
- HALT mode
HALT mode is used to reduce power consumption. Program execution is stopped. Peripheral circuits still operate.
1. Oscillation circuits are not stopped automatically
2. Release on system reset
- HOLD mode
HOLD mode is used to reduce the power dissipation. Both program execution and peripheral circuits are stopped.
1. CF, RC and crystal oscillation circuits stop automatically
2. Release occurs on any of the following conditions
•input to the reset pin goes low
•a specified level is input to at least one of INT0, INT1, INT2, INT4, INT5
•an interrupt condition arises at port 0
CYC
)
No.6715-3/25
Page 4

LC875164A/48A/32A
- X’tal HOLD mode
X’tal HOLD mode is used to reduce power consumption. Program execution is stopped. All peripheral circuits
except the base timer are stopped.
1. CF and RC oscillation circuits stop automatically
2. Crystal oscillator is maintained in its state at HOLD mode inception.
3. Release occurs on any of the following conditions
•input to the reset pin goes low
•a specified level is input to at least one of INT0, INT1, INT2, INT4, INT5
•an interrupt condition arises at port 0
•an interrupt condition arises at the base-timer
(17) Factory shipment
- delivery form QIP80E
- delivery form SQFP80
(18) Development Tools
- Evaluation chip : LC876099
- Emulator : EVA87000 + ECB875100 (Evaluation chip board) + POD875100 (P O D)
No.6715-4/25
Page 5
LC875164A/48A/32A
#
#
#
#
N
N
Pin Assignment
65
PB4/D4
PB3/D3
PB2/D2
PB1/D1
PB0/D0
VSS3
VDD3
PC7/A7
PC6/A6
PC5/A5
PC4/A4
PC3/A3
PC2/A2
PC1/A1
PC0/A0
PA0/CS2#
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
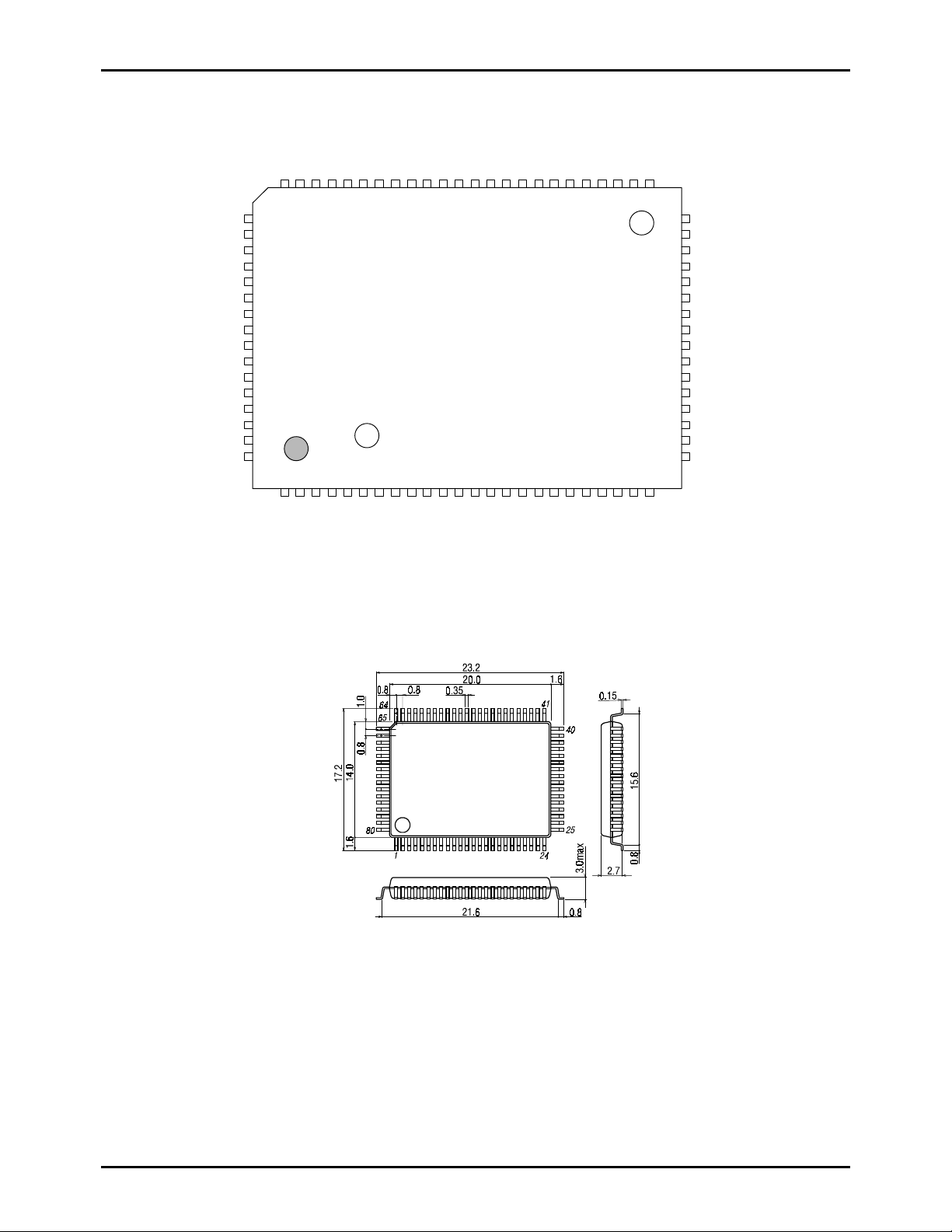
Package Dimension
(unit : mm)
3174
PB5/D5
PB6/D6
PB7/D7
P27/INT5/T1IN
P26/INT5/T1IN
P25/INT5/T1IN
P24/INT5/T1IN
P23/INT4/T1IN
P22/INT4/T1IN
P21/INT4/T1IN
P20/INT4/T1IN
P07
P06
P05
P04
P03
P02
P01
P00
VSS2
VDD2
PWM0
PWM1
64 63 62 61 60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41
LC875164A/48A/32A
QIP80
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24
CF1
VSS1
CF2
VDD1
P80/AN0
P81/AN1
P82/AN2
P83/AN3
P84/AN4
P85/AN5
P86/AN6
PA1/CS1
PA2/CS0
XT1
XT2
PA5/RS
PA4/RD
PA3/WR
P70/INT0/T0LCP
P71/INT1/T0HCP
RES#
P73/INT3/T0I
P72/INT2/T0I
SI2P3/SCK20
40
39
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
P87/AN7
SI2P2/SCK2
SI2P1/S12/SB2
SI2P0/SO2
P17/T1PWMH/BUZ
P16/T1PWML
P15/SCK1
P14/SI1/SB1
P13/SO1
P12/SCK0
P11/SI0/SB0
P10/SO0
P34
P33
P32
P31
P30
SANYO : QIP-80E
No.6715-5/25
Page 6
Pin Assignment
#
N
PB6/D6
PB5/D5
PB4/D4
PB3/D3
PB2/D2
PB1/D1
PB0/D0
VSS3
VDD3
PC7/A7
PC6/A6
PC5/A5
PC4/A4
PC3/A3
PC2/A2
PC1/A1
PC0/A0
PA0/CS2#
PA1/CS1#
PA2/CS0#
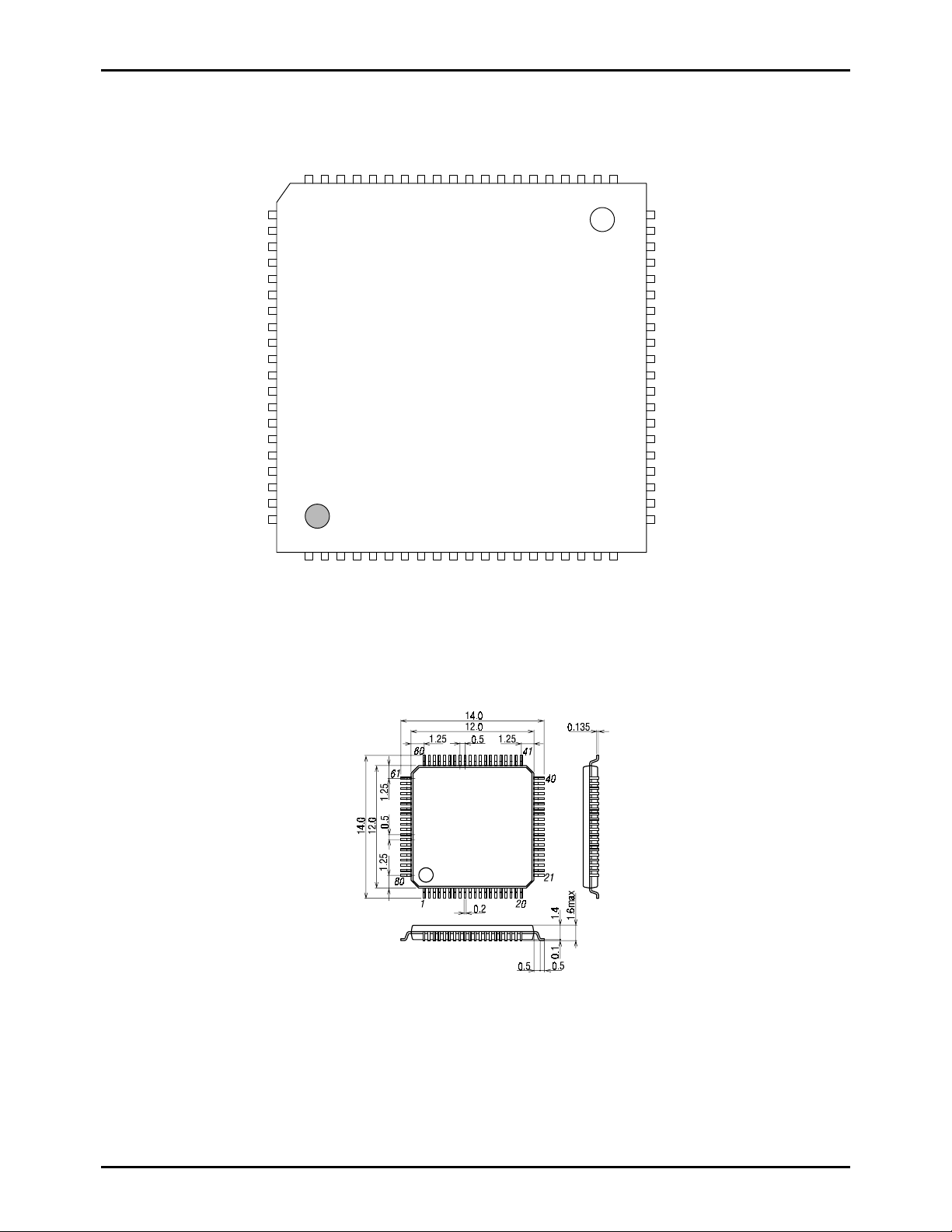
Package Dimension
(unit : mm)
3220
LC875164A/48A/32A
PB7/D7
P27/INT5/T1IN
P26/INT5/T1IN
P25/INT5/T1IN
P24/INT5/T1IN
P23/INT4/T1IN
P22/INT4/T1IN
P21/INT4/T1IN
P20/INT4/T1IN
P07
P06
P05
P04
P03
P02
P01
60 59 58 57 56 55 54 53 52 51 50 49 48 47 46 45 44 43 42 41
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20
PA5/RS
PA4/RD
PA3/WR#
LC875164A/48A/32A
SQFP80
XT1
RES#
P73/INT3/T0IN
P72/INT2/T0I
P70/INT0/T0LCP
P71/INT1/T0HCP
XT2
VSS1
CF1
CF2
VDD1
P80/AN0
P81/AN1
P00
VSS2
VDD2
PWM0
40
PWM1
39
SI2P3/SCK20
38
SI2P2/SCK2
37
SI2P1/SI2/SB2
36
SI2P0/SO2
35
P17/T1PWMH/BUZ
34
P16/T1PWML
33
P15/SCK1
32
P14/SI1/SB1
31
P13/SO1
30
P12/SCK0
29
P11/SI0/SB0
28
P10/SO0
27
P34
26
P33
25
P32
24
P31
23
P30
22
P87/AN7
21
P86/AN6
P82/AN2
P83/AN3
P84/AN4
P85/AN5
SANYO : SQFP-80
No.6715-6/25
Page 7
LC875164A/48A/32A
QIP NAME SQFP QIP NAME SQFP
1
2
3
4
5 PA5/RS 3 45 VSS2 43
6 P70/INT0/T0LCP 4 46 P00 44
7 P71/INT1/T0HCP 5 47 P01 45
8 P72/INT2/T0IN 6 48 P02 46
9 P73/INT3/T0IN 7 49 P03 47
10
11 XT1 9 51 P05 49
12 XT2 10 52 P06 50
13 VSS1 11 53 P07 51
14 CF1 12 54 P20/INT4/T1IN 52
15 CF2 13 55 P21/INT4/T1IN 53
16 VDD1 14 56 P22/INT4/T1IN 54
17 P80/AN0 15 57 P23/INT4/T1IN 55
18 P81/AN1 16 58 P24/INT5/T1IN 56
19 P82/AN2 17 59 P25/INT5/T1IN 57
20 P83/AN3 18 60 P26/INT5/T1IN 58
21 P84/AN4 19 61 P27/INT5/T1IN 59
22 P85/AN5 20 62 PB7/D7 60
23 P86/AN6 21 63 PB6/D6 61
24 P87/AN7 22 64 PB5/D5 62
25 P30 23 65 PB4/D4 63
26 P31 24 66 PB3/D3 64
27 P32 25 67 PB2/D2 65
28 P33 26 68 PB1/D1 66
29 P34 27 69 PB0/D0 67
30 P10/SO0 28 70 VSS3 68
31 P11/SI0/SB0 29 71 VDD3 69
32 P12/SCK0 30 72 PC7/A7 70
33 P13/SO1 31 73 PC6/A6 71
34 P14/SI1/SB1 32 74 PC5/A5 72
35 P15/SCK1 33 75 PC4/A4 73
36 P16/T1PWML 34 76 PC3/A3 74
37 P17/T1PWMH/BUZ 35 77 PC2/A2 75
38 SI2P0/SO2 36 78 PC1/A1 76
39 SI2P1/SI2/SB2 37 79 PC0/A0 77
40 SI2P2/SCK2 38 80
PA1/
PA2/
PA3/
PA4/
RES
CS1
CS0
WR
RD
79 41 SI2P3/SCK20 39
80 42 PWM1 40
1 43 PWM0 41
2 44 VDD2 42
8 50 P04 48
PA0/
CS2
78
No.6715-7/25
Page 8
LC875164A/48A/32A
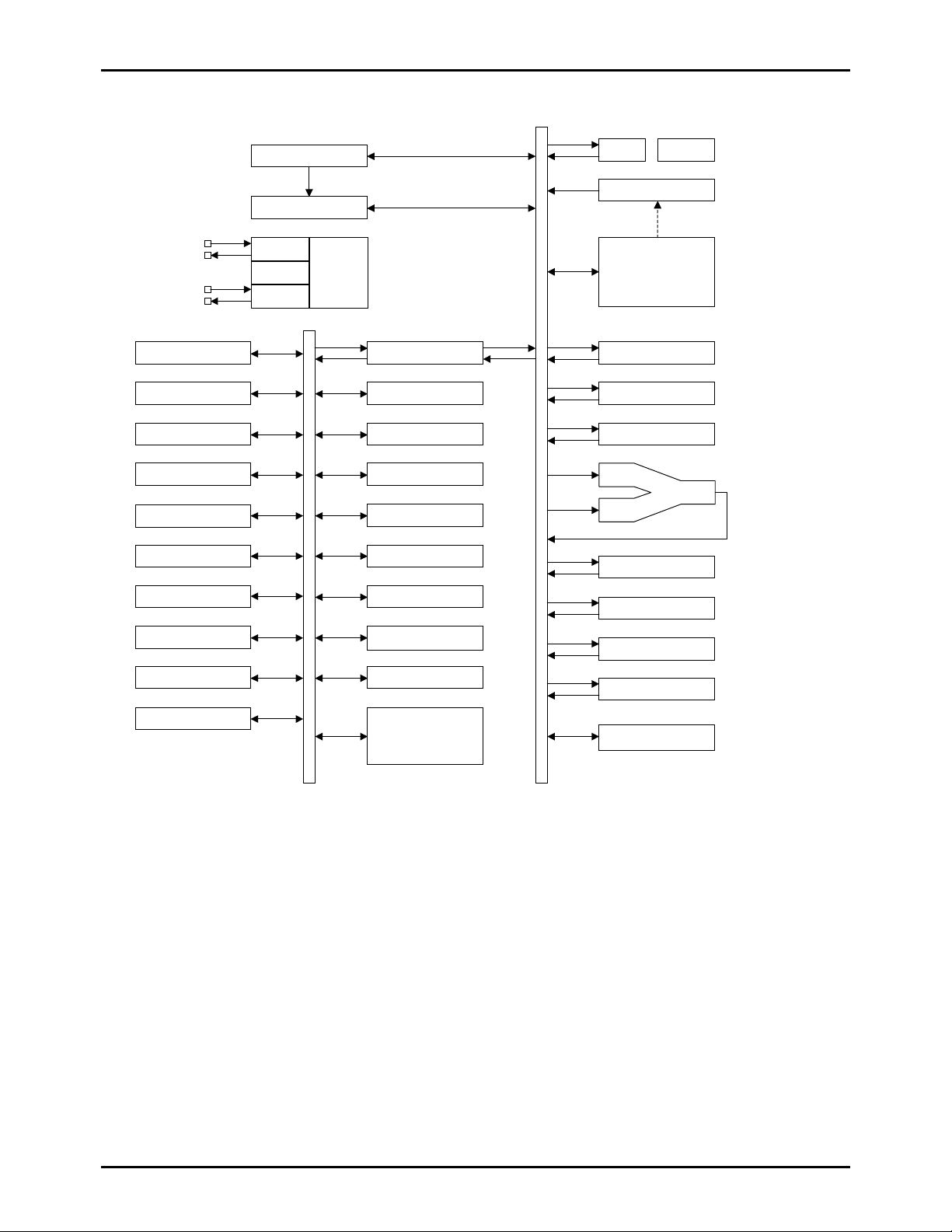
System Block Diagram
SIO0
SIO1
SIO2
Timer 0
Timer 1
Timer 4
Timer 5
PWM0
PWM1
Base Timer
Interrupt control
Standby control
CF
RC
Xtal
IR PLA
ROM
Clock
Generator
Noise Rejection Filter
Port 2 INT4,,5
Bus Interface
Port 0
Port 1
Port 3
Port 7
Port 8
ADC
INT0-3
Parallel interface
Port A
Port B
Port C
PC
ACC
B Register
C Register
ALU
PSW
RAR
RAM
Stack Pointer
Watch Dog Timer
No.6715-8/25
Page 9

LC875164A/48A/32A
Pin Assignment
Pin Name I/O Pin Function Option
VSS1
VSS2
VSS3
VDD1
VDD2
VDD3
Port 0
P00 - P07
Port 1
P10 - P17
Port 2 •8-bit Input/output port
P20 - P27
Port 3
P30 - P34
Port 7 •4-bit Input/output port
P70 - P73
- Negative power supply No
- Positive power supply No
I/O •8-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified in nibble units
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified in nibble units
•HOLD-release input
•Input for port 0 interrupt
I/O •8-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified fo r each bit
•Other functions
P10: SIO0 data output
P11: SIO0 data input/bus input/output
P12: SIO0 clock input/output
P13: SIO1 data output
P14: SIO1 data input/bus input/output
P15: SIO1 clock input/output
P16: Timer 1 PWML output
P17: Timer 1 PWMH o utput/Buzzer output
I/O
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
P20-P23: INT4 input/HOLD release input/timer 1 event input
P24-P27: INT5 input/HOLD release input/timer 1 event input
Interrupt receiver format
INT4
INT5
I/O •5-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
I/O
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
P70: INT0 input/HOLD release input/Timer0L capture input
P71: INT1 input/HOLD release input/Timer0H capture input
P72: INT2 input/HOLD release input/timer 0 event input
P73: INT3 input(noise rejection filter attached input)
Interrupt receiver format
Rising Falling Rising/
INT0
INT1
INT2
INT3
/Timer 0L capture input/Timer 0H capture input
/Timer 0L capture input /Timer 0H capture input
Rising Falling Rising/
Yes
Yes
/Output for watchdog timer
/Timer0L capture input
/timer 0 event input/Timer0H capture input
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
falling
Yes
Yes
falling
No
No
Yes
Yes
H level L level
No
No
H level L level
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No
Yes
Yes
No
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
(Continued)
No.6715-9/25
Page 10

LC875164A/48A/32A
Name I/O Function description Option
Port 8
P80 - P87
Port A
PA0 - PA5
Port B
PB0 - PB7
Port C
PC0 - PC7
SIO2 Port
SI2P0
- SI2P3
PWM0 O PWM0 output port No
PWM1 O PWM1 output port No
RES
XT1 I •Input for 32.768kHz c rystal osci l lation
XT2 I/O •Output for 32.768kHz c r ystal oscil lation
CF1 I Input terminal for ceramic oscillator No
CF2 O Output terminal for ceramic oscillator No
I/O •8-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
P80-P87: AD input port
I/O •6-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
PA0: Parall el interface output
PA1: Parallel interface output
PA2: Parallel interface output
PA3: Parallel interface output
PA4: Parallel interface output
PA5: Parallel interface output RS
I/O •8-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
PB0-PB7: Parallel interface data input/ output; address output
I/O •8-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Use of pull-up resistor can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
PC0-PC7: Parallel interface address output
I/O •4-bit Input/output port
•Data direction can be specified for each bit
•Other functions
SI2P0: SIO2 data output
SI2P1: SIO2 data output/bus input/output
SI2P2: SIO2 clock input/output
SI2P3: SIO2 clock output
I Reset terminal No
•Other function
Input port
When not in use, connect to VDD1.
•Other function
General purpose input port
When not in use, set to oscillation mode and leave open circuit
CS2
CS1
CS0
WR
RD
No
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
No
No
No.6715-10/25
Page 11

LC875164A/48A/32A
Port Output Configuration
Output configuration and pull-up resistor options are shown in the following table.
Input is possible even when port is set to output mode.
Terminal
Option
applies to:
each bit
P20-P27
P30-P34
each bit
PB0-PB7(*)
PC0-PC7
P70 - None Nch-open drain Programmable
P71-P73 - None CMOS Programmable
P80-P87 - None Nch-open drain None
SI2P0, SI2P2
- None CMOS None
SI2P3
PWM0,
PWM1
SI2P1 - None CMOS (When used as standard port)
XT1 - None Input only None
XT2 - None Output for 32.768kHz crystal oscillation None
Option Output Format Pull-up resistor
1 CMOS Programmable (Note 1) P00-P07 1 bit units
2 Nch-open drain None
1 CMOS Programmable P10-P17
2 Nch-open drain Programmable
1 CMOS Programmable PA0-PA5
2 Nch-open drain Programmable
Nch-open drain (When used for SIO2 data)
None
Note 1 Programmable pull-up resisters of Port 0 can be attatched in nibble units (P00-03, P04-07).
(*) When in parallel interface mode, PB0-PB7 output format is CMOS, regardless of any selected option.
Note: Connect as follows to reduce noise on VDD and increase the back-up time.
VSS1, VSS2 and VSS3 must be connected together and grounded.
The voltage of Port 7 should be fixed.
Example 1 : In hold mode, during backup, port output ‘H’ level is supplied from the back-up capacitor.
Power
Supply
Back-up capacitor
LSI
VDD1
VDD2
VDD3
VSS1 VSS2 VSS3
Example 2 : During backup in hold mode output is not held high and its value in unsettled.
Power
Supply
Back-up capaci t or
LSI
VDD1
VDD2
VDD3
VSS1 VSS2 VSS3
No.6715-11/25
Page 12

LC875164A/48A/32A
1. Absolute Maximum Ratings at Ta=25°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Supply voltage VDDMAX VDD1, VDD2,
VDD3
VDD1=VDD2
=VDD3
Input voltage VI(1) XT1, XT2, CF1 -0.3
Output voltage VO(1) PWM0, PWM1 -0.3
Input/output
voltage
VIO(1) Ports 0, 1, 2
Ports 3, 7, 8
-0.3
Ports A, B, C
SI2P00-SI2P03
PWM0, PWM1
High
level
output
current
output
current
IOPH(1) Ports 0, 1, 2, 3
Ports A, B, C
SI2P00-SI2P03
PWM0, PWM1
•CMOS output
•For each pin.
IOPH(2) P71-P73 For each pin. -5
Total
output
current
IOAH(1)
Σ
IOAH(2)
Σ
P71-P73 The total of all pins. -5
Port 1
The total of all pins. -30
PWM0, PWM1
Port 3
SI2P00-SI2P03
Ports 0, 2 The total of all pins. -20
Port B The total of all pins. -20
Ports A, C The total of all pins. -20
For each pin. 20
Ports 1, 2, 3
Ports A, B, C
SI2P00-SI2P03
Low
level
output
current
Peak
output
current
IOAH(3)
Σ
IOAH(4)
Σ
IOAH(5)
Σ
IOPL(1) P02-P07
PWM0, PWM1
IOPL(2) P00, P01 For each p in. 30
IOPL(3) Ports 7, 8 For each pin. 5
Total
output
current
IOAL(1)
Σ
IOAL(2)
Σ
IOAL(3)
Σ
Port 7 The total of all pins. 15
Port 8 The total of all pins. 15
Port 1
The total of all pins. 50
PWM0, PWM1
Port 3
SI2P00-SI2P03
Ports 0, 2 The total of all pins. 70
Port B The total of all pins. 40
Ports A, C The total of all pins. 40
Ta=-30 to +70°C
SQFP80
Maxim un power
dissipation
Operating
IOAL(4)
Σ
IOAL(5)
Σ
IOAL(6)
Σ
Pdmax QIP80E
Topg -30 70
temperature
range
Storage
Tstg -55 125
temperature
range
Ratings
VDD[V]
min. typ. max.
-0.3 +7.0
-10 Peak
350 mW
VDD+0.3
VDD+0.3
VDD+0.3
unit
V
mA
C
°
No.6715-12/25
Page 13

LC875164A/48A/32A
2. Recommended Operating Range at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Operating
supply voltage
range
VDD(1) VDD1=VDD2
=VDD3
0.294µs ≤ t
200µs
0.588µs ≤ t
CYC
CYC
≤
≤
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
4.5 6.0
2.5 6.0
200µs
HOLD voltage VHD VDD1=VDD2
=VDD3
RAM and the
register data are
2.0 6.0
kept in HOLD mode.
Input high
voltage
VIH(1) •Ports 1, 2
•P71-P73
2.5 - 6.0
0.3VDD
+0.7
•P70 port input
/interrupt
VIH(2) •Ports 0, 8
•Ports A, B, C
VIH(3) Port 70 Watchdog
2.5 - 6.0
2.5 - 6.0 0.9VDD VDD
0.3VDD
+0.7
timer input
0.75VDD
Input low
voltage
VIH(4) XT1, XT2, CF1,
RES
VIL(1) •Ports 1, 2
•P71-P73
2.5 - 6.0
2.5 - 6.0 VSS
•P70 port input
/interrupt
VIL(2) •Ports 0, 8
2.5 - 6.0 VSS
•Ports A, B, C
VIL(5) Port 70 Watchdog
2.5 - 6.0 VSS
timer input
cycle time
External
system clock
frequency
VIL(6) XT1, XT2, CF1,
RES
CYC
t
FEXCF(1) CF1
2.5 - 6.0 VSS
4.5 - 6.0 0.294 200 Operation
2.5 - 6.0 0.588 200
4.5 - 6.0 0.1 10 •CF2 open circuit
•system clock
divider set to 1/1
•external clock
2.5 - 6.0
DUTY=50±5%
•CF2 open circuit
•system clock
divider set to 1/2
4.5 - 6.0 0.2 20.4
2.5 - 6.0
(Note 1) The oscillation constant is shown in Tables 1 and 2.
unit
VDD
VDD
VDD
0.1VDD
+0.4
0.15VDD
+0.4
0.8VDD
-1.0
0.25VDD
µ
MHz
V
s
No.6715-13/25
Page 14

LC875164A/48A/32A
3. Electrical Characteristics at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Input high
current
IIH(1) •Ports 0, 1, 2
IIH(2) XT1, XT2 When specified as an
IIH(3) CF1 VIN=VDD 2.5 - 6.0 15
•Ports 3, 7, 8
•Ports A, B, C
•SI2P00-SI2P03
RES
•
•PWM0, PWM1
•Output disable
•Pull-up resistor off
•VIN=VDD
(including off state
leak current of
output Tr.)
input port.
VIN=VDD
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
2.5 - 6.0 1
2.5 - 6.0 1
unit
A
µ
Input low
current
Output high
current
Output low
current
Pull-up
resistor
Hysteresis
voltage
Pin
capacitance
IIL(1) •Ports 0, 1, 2
IIL(2) XT1, XT2 When specified as an
IIL(3) CF1 VIN=VSS 2.5 - 6.0 -15
VOH(1) •Ports 0, 1, 2, 3
VOH(2) •SI2P00-SI2P03
VOH(3) IOH=-5.0mA 4.5 - 6.0 VDD-1
VOH(4)
VOH(5) Port 7 IOH=-1.0mA 2.5 - 6.0 V DD-1
VOL(1) •Ports 0, 1, 2, 3
VOL(2) IOL=1.6mA 2.5 - 6.0 0.4
VOL(3)
VOL(4) P00, P01 IOL=30mA 4.5 - 6.0 1.5
VOL(5) IOL=1mA 4.5 - 6.0 0.4
VOL(6)
VOL(7) IOL=15mA 4.5 - 6.0 1.5
VOL(8)
Rpu •Ports 0, 1, 2, 3
VHIS
CP All pins •Every other te rminal
•Ports 3, 7, 8
•Ports A, B, C
•SI2P00-SI2P03
RES
•
•PWM0, PWM1
•Ports B, C
•PWM0, PWM1
Port A
•Ports B, C
•SI2P00-SI2P03
•PWM0, PWM1
Ports 7, 8
Port A
•Port 7
•Ports A, B, C
RES
•Output disable
•Pull-up resistor off
•VIN=VSS
(including off state
leak current of
output Tr.)
input port
VIN=VSS
IOH=-2.0mA 4.5 - 6.0 VDD-1
IOH=-0.1mA 2.5 - 6.0
IOH=-1.0mA 2.5 - 6.0
IOL=10mA 4.5 - 6.0 1.5
IOL=1.0mA 2.5 - 6.0 0.4
IOL=0.5mA 2.5 - 6.0
IOL=2mA 2.5 - 6.0 0.4
VOH=0.9VDD 4.5 - 5.5 15 40 70
4.5 - 5.5 0.1VDD V
connected to VSS.
•f=1MHz
•Ta=25°C
2.5 - 6.0 -1
2.5 - 6.0 -1
VDD-0.5
VDD-0.5
4.5 - 5.5 10 pF
V
V
kΩ
No.6715-14/25
Page 15

LC875164A/48A/32A
4. Serial Input/Output Characteristics at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Cycle t
pulse width
SCK
SCKL
t
SCKLA
t
(1)
(1)
(1)
SCK0(P12),
SI2P2
Refer to figure 6 2.5 - 6.0
SCKH
t
(1)
pulse width
SCKHA
t
(1)
Input clock
Cycle t
SCK
(2)
SCK1(P15) Refer to figure 6 2.5 - 6.0
Low level
SCKL
t
(2) 1
pulse width
High level
SCKH
t
(2)
pulse width
Serial clock
Cycle t
Low level
pulse width
SCK
SCKL
t
(3)
(3)
SCK0(P12),
SI2P2
SI2P3
SCKLA
t
(2)
•Use pull- up resistor
(1kΩ) when output
is open drain.
•Refer to figure 6
SCK0(P12)
SIO0
SI2P2, SI2P3
SIO2
High level
pulse width
Output clock
SCKHA
t
(3)
(2)
1/2
SCK0(P12)
SIO0
SI2P2, SI2P3
SCKH
t
SIO2
Cycle t
Low level
SCK
(4)
SCKL
t
SCK1(P15) •CMOS output option
•Refer to figure 6
(4) 1/2
pulse width
High level
SCKH
t
(4)
pulse width
time
Data hold
time
Serial input
tsDI
thDI
SB0(P11),
SB1(P14),
SI2P1
SI0
SI1
•Data set-up to
SI0CLK
•Refer to figure 6
Output delay
time
Serial output
tdD0 SO0(P10),
SO1(P13),
SB0(O11),
SB1(P14),
SI2P0,
SI2P1
•Data set-up to
SI0CLK
•When port is open
drain: Time delay
from SI0CLK traili ng
edge to the SO data
change.
•Refer to figure 6
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
2
1 Low level
1
1 High level
3(SIO0)
2
1
2.5 - 6.0
4/3
1/2
3/4
1
2
7/4
2.5 - 6.0
2 t
1/2
4.5 - 6.0 0.03 Data set-up
2.5 - 6.0
4.5 - 6.0 0.03
2.5 - 6.0
4.5 - 6.0
2.5 - 6.0
1/3tCYC
+0.05
1/3tCYC
+0.05
unit
CYC
t
tSCK
CYC
tSCK
µ
s
No.6715-15/25
Page 16

LC875164A/48A/32A
5. Parallel Input/Output Characteristics at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Note: Port A terminals used as RS,
WR, RD
and CS should be set to CMOS format.
Please refer to figures 8 and 9 for parallel output timing waveforms.
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Write cycle, Read
cycle
Address set-up
time
Address hold time
RS set-up tie
CS
set-up time
RS
hold time
CS
hold time
WR
’H’ pulse width
WR
’L’ pulse width
tC(1) 2.5 - 6.0 1 tCYC
tsA(1)
tsA(2)
thA(1)
thA(2)
tsRS(1)
tsRS(2)
tsRS(3)
tsCS(1)
tsCS(2)
thRS(1)
thRS(2)
thRS(3)
thCS(1)
thCS(2)
tWRH(1)
tWRH(2)
tWRL(1)
tWRL(2)
WR (PA3), PB0-PB7
•
(PA4), PC0-PC7
•
RD
RD (PA4), PC0-PC7
RD (PA4), PC0 -PC7 From change of RD
(PA3), PC0-PC7 From change of
WR
(PA3), RS(PA5),
WR
(PAX)
CS
(PA4), RS(PA5)
RD
(PA4), RS(PA5)
RD
RD (PA4), CS(PAX) From c hange in CS
WR (PA3),
(PAX)
CS
(PA3), RS(PA5) From change in WR
WR
RD (PA4), RS(PA5),
CS(PAX)
RD (PA4), RS(PA5),
(PAX)
CS
(PA4), RS(PA5) From change in RD
RD
(PA3), RS(PA5) From change in WR
WR
(PA3)
WR
(PA3)
WR
(PA3)
WR
(PA3)
WR
From address set-up
until control signal
changes
until address change
until address change
From change of RS,
until change in
CS
WR
from change of RS
until change in
until change in
From change in
until change in
until change in RS
From change in
until change in RS,
CS
until change in
until change in
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 2/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
WR
RD
RD
CS
WR
RD
CS
CS
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 2/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 5 ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 2/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 0 ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 0 ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 0 ns
-30ns
-30ns
-15ns
-15ns
-15ns
-15ns
-15ns
-5ns
-5ns
-5ns
-5ns
tCYC
tCYC
1/6
tCYC
2/3
tCYC
1/6
tCYC
1/3
tCYC
(Continued)
unit
tCYC
& ns
tCYC
& ns
& ns
& ns
tCYC
& ns
No.6715-16/25
Page 17

LC875164A/48A/32A
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
RD
’H’ pulse width
RD
’L’ pulse width
Data write
permission delay
Input data
set-up time
Input data
hold time
Output data
set-up time
Output data
set-up time
hold time
tRDH(1)
tRDH(2)
tRDL(1)
tRDL(2)
tdDT(1)
tdDT(2)
tsDTR(1)
thDTR(1)
tsDTW(1)
tsDTW(2)
thDTW(1) 2.5 - 6.0 0 Output data
thDTW(2)
(PA4)
RD
(PA4)
RD
RD (PA4)
RD (PA4)
(PA4), PB0-PB7
RD
(PA4), PB0-PB7
RD
RD (PA4), PB0-PB7
(PA4), PB0-PB7 From RD leading
RD
(PA4), PB0-PB7
RD
(PA4), PB0-PB7
RD
RD (PA4), PB0-PB7 From
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/2tCYC
Time for permission,
from
RD
edge until input data
set-up
(Note 1)
From input data set-
up to
RD
edge.
(Note 2)
edge until input data
hold
From output data set-
up until
leading
edge
edge until output data
hold
WR
WR
leading
leading
leading
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
-5ns
-5ns
-5ns
-5ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/6tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
2.5 - 6.0 40 ns
2.5 - 6.0 0 ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
-30ns
2.5 - 6.0 1/3tCYC
-30ns
2.5 - 6.0 0
Note 1 : Time until incorrect data of Low is disappeared.
Note 2 : Incorrect data of Low is not output in the period between tRDL(1) - tdDT(1).
6. Pulse input Conditions at T a=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
High/low level
pulse width
tPIH(1)
tPIL(1)
INT0(P70),
INT1(P71),
INT2(P72)
INT4(P20-P23)
•Interrupt accept able
•Events to timer 0
and 1 can be input.
INT5(P24-P27)
tPIH(2)
tPIL(2)
INT3(P73)
(The noise
rejection clock
•Interrupt accept able
•Events to timer 0
can be input.
select to 1/1.)
tPIH(3)
tPIL(3)
INT3(P73)
(The noise
rejection clock
•Interrupt accept able
•Events to timer 0
can be input.
select to 1/32.)
tPIH(4)
tPIL(4)
INT3(P73)
(The noise
rejection clock
•Interrupt accept able
•Events to timer 0
can be input.
select to 1/128.)
tPIL(5)
RES
Reset acceptable
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
2.5 - 6.0 1
2.5 - 6.0 2
2.5 - 6.0 64
2.5 - 6.0 256
2.5 - 6.0 200
1/6
tCYC
1/3
tCYC
1/3
tCYC
1/2
tCYC
-15ns
-15ns
unit
tCYC
& ns
tCYC
& ns
ns
unit
CYC
t
µ
s
No.6715-17/25
Page 18

LC875164A/48A/32A
7. AD Converter Characteristics at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Resolution
Absolute
N 3.0 - 6.0 8 bit
ET (Note 2) 3.0 - 6.0 ±1.5 LSB
AN0(P80)
- AN7(P 87)
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
unit
precision
Conversion
time
Analog input
TCAD
AD conversion time
CYC
=32
t
×
3.0 - 6.0
(ADCR2=0) (Note 3)
AD conversion time
CYC
t
=64
×
3.0 - 6.0 15.10
(ADCR2=1) (Note 3)
VAIN 3.0 - 6.0 VSS VDD V
15.10
(tCYC=
0.588µs)
(tCYC=
0.294µs)
97.92
97.92
(tCYC=
3.06µs)
(tCYC=
1.53µs)
s
µ
voltage range
Analog port
input current
IAINH VAIN=VDD 3.0 - 6.0 1
IAINL
VAIN=VSS 3.0 - 6.0 -1
A
µ
(Note 2) Absolute precision not including quantizing error (±1/2 LSB).
(Note 3) Conversion time means time from executing AD conversion instruction to loading complete digital value to register.
8. Current Dissipation Characteristics at Ta=-30°C to +70°C, VSS1=VSS2=VSS3=0V
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Current flow
during basic
operation
(Note 4)
IDDOP(1) •FmCF=10MHz for
VDD
Ceramic resonator
oscillation
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: CF
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
IDDOP(2) 4.5 - 6.0 7 12
IDDOP(3)
•FmCF=5MHz for
Ceramic resonator
oscillation
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: CF
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
IDDOP(4) 4.5 - 6.0 1 3.0
IDDOP(5)
•FmCF=0Hz
(oscillation stops)
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: Internal
RC oscillation
IDDOP(6) 4.5 - 6.0 40 80
•FmCF=0Hz
(oscillation stops)
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
IDDOP(7)
•System clock: X’tal
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
(Continued)
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
4.5 - 6.0 16 29
2.5 - 4.5 3 8
2.5 - 4.5 0.5 2
2.5 - 4.5 15 46
unit
mA
A
µ
No.6715-18/25
Page 19

LC875164A/48A/32A
Parameter Symbol Pins Conditions
Current flow:
HALT mode
(Note 4)
HOLD mode
(Note 4)
Date/time
clock HOLD
mode
IDDHALT(1) •HALT mode
IDDHALT(2) 4.5 - 6.0 3 5
IDDHALT(3)
IDDHALT(4) 4.5 - 6.0 500 1500
IDDHALT(5)
IDDHALT(6) 4.5 - 6.0 25 70
IDDHALT(7)
IDDHOLD(1) 4.5 - 6.0 0.01 30 Current flow:
IDDHOLD(2)
IDDHOLD(2) VDD1 Date/time clock HOLD
VDD
•FmCF=10MHz for
ceramic resonator
oscillation
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: CF
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
•HALT mode
•FmCF=5MHz for
Ceramic resonator
oscillation
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: CF
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
•HALT mode
•FmCF=0Hz
(oscillation stops)
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: Internal
RC oscillation
•HALT mode
•FmCF=0Hz
(oscillation stops)
•FsX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
•System clock: X’tal
oscillation
•Internal RC oscillation
stopped.
VDD1 HOLD mode
mode
•CF1=VDD or open
circuit (when using
external clock)
•FmX’tal=32.768kHz for
crystal oscillation
Ratings
VDD[V] min. typ. max.
4.5 - 6.0 6 13
2.5 - 4.5 1.2 3
2.5 - 4.5 300 1000
2.5 - 4.5 8 30
2.5 - 4.5 0.01 30
4.5 - 6.0 45 100 Current flo w:
2.5 - 4.5 6 36
(Note 4) The currents of output transistors and pull-up MOS transistors are ignored.
unit
mA
A
µ
A
µ
A
µ
No.6715-19/25
Page 20

LC875164A/48A/32A
Main system clock osci llation circuit characteristics
The characteristics in the table bellow is based on the following conditions:
1. Use the standard evaluation board SANYO has provided.
2. Use the peripheral parts with indicated value externally.
3. The peripheral parts value is a recommended value of oscillator manufacturer.
Table 1. Main system clock oscillation circuit characteristics using ceramic resonator
Frequency Manufacturer Oscillator
10MHz
5MHz
4MHz
Murata
Kyocera KBR-10.0M 33pF 33pF
Murata
Murata
Kyocera KBR-4.0MSA 33pF 33pF
CSA10.0MTZ 33pF 33pF
CST10.0MTW (30pF) (30pF)
CSA5.00MG 33pF 33pF
CST5.00MGW (30pF) (30pF)
CSA4.00MG 33pF 33pF
CST4.00MGW (30pF) (30pF)
Circuit Parameters Oscillation stabilizing time
C1 C2 Rd1
Operating
supply voltage
range
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms Built in C1,C2
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms Built in C1,C2
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms Built in C1,C2
0Ω
4.5 - 6.0V 0.05ms 0.50ms
0Ω
typ max
Notes
*The oscillation stabilizing time is a period until the oscillation becomes stable after VDD becomes higher than minimum
operating voltage. (Refer to Figure4)
Subsystem clock osci lla tion circuit characteristics
The characteristics in the table bellow is based on the following conditions:
1. Use the standard evaluation board SANYO has provided.
2. Use the peripheral parts with indicated value externally.
3. The peripheral parts value is a recommended value of oscillator manufacturer.
Table 2. Subsystem clock oscillation circu it characteristics using cry s tal oscillator
Frequency Manufacturer Oscillator
32.768kHz Seiko EPSON C-002Rx 12pF 15pF OPEN
Circuit Parameters Oscillation stabilizing time
C3 C4 Rf Rd2
300kΩ
Operating supply
voltage range
4.5 - 6.0V 1.0S 3.0S
typ max
Notes
*The oscillation stabilizing time is a period until the oscillation becomes stable after executing the instruction which starts the
sub-clock oscillation or after releasing the HOLD mode. (Refer to Figure4)
(Notes) •Since the circuit pattern affects the oscillation frequency, place the oscillation-related parts as close
to the oscillation pins as possible with the shortest possible pattern length.
CF2 CF1
XT2 XT1
Rd1
Rf
Rd2
C1
CF
C2
C3
X’tal
C4
Figure 1 Ceramic oscillation circuit Figure 2 Crystal oscillation circuit
0.5VDD
Figure 3 AC timing measurement point
No.6715-20/25
Page 21

,
,
Resonator oscillation
Operation mode
HOLD release signal
Resonator oscillation
Operation mode
Power Supply
RES#
Internal RC
CF1
CF2
XT1
XT2
Internal RC
CF1,CF2
XT1,XT2
LC875164A/48A/32A
Reset time
tmsCF
tmsXtal
Unfixed
Rese t Instruction execution mode
Reset time and oscillation stable time
Without HOLD
Release signal
HOLD release signal VALID
tmsCF
tmsXtal
HOLD HALT
HOLD release signal and oscillation stable time
Figure 4 Oscillation stabilizing time
VDD
VDD limit
GND
No.6715-21/25
Page 22

SI0CLK:
DATAIN:
DATAOUT:
SI0CLK:
DATAIN:
DATAOUT:
SI0CLK:
DATAIN:
DATAOUT:
LC875164A/48A/32A
VDD
RES
R
RES
RES
, R
values such that reset time
RES
(Note) Set C
exceeds 200µs.
RES
C
Figure 5 Reset circuit
DI0 DI7 DI2 DI3 DI4 DI5 DI6 DI8
DO0 DO7 DO2 DO3 DO4 DO5 DO6 DO8
DI1
DO1
Data RAM transmission period
(only SIO0,2)
tSCK
tSCKL tSCKH
thDI tsDI
tdDO
Data RAM transmission period
(only SIO0,2)
tSCKLA tSCKHA
thDI tsDI
tdDO
Figure 6 Serial input/output test condition
tPIL tPIH
Figure 7 Pulse input timing condition
No.6715-22/25
Page 23

LC875164A/48A/32A
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(3)
(3)
(1)
(2)
• Parallel Input/Output timing waveform : Indirect Setting, Read Mode
ADR/DATA:
CS#:
RS:
WR#:
tsRS(1)
tWRH
addr
tsA
thRS
tWRL(1) tsRS(2) tRDL(1) thRS(2)
RD#:
DATAin:
Note: Port A terminals used as RS,
WR, RD
and
• Parallel Input/Output timing waveform : Indirect Setting, Write Mode
ADR/DATA:
CS#:
RS:
WR#:
tWRH
tsA
thRS(1)
tsRS
tWRL(1)
RD#:
DATAin:
Note: Port A terminals used as RS,
WR, RD
and
Figure 8 Indirect mode: Parallel Timing Waveforms
tC
read cycle
tsDTR(1)
tRDH
tdDT
thDTR(1)
CS
should be set to CMOS format.
tC(1)
write cycle
tsRS
tsDTW(1)
CS
should be set to CMOS format.
data H
data addr
thDTW(1)
thRS
tWRL
No.6715-23/25
Page 24

LC875164A/48A/32A
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(1)
(1)
(1)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
(2)
• Parallel Input/Output timing waveform : Direct Setting, Read Mode
ADR:
tsA
CS#:
DATA:
tsCS
WR#:
RD#:
tRDH
DATAin:
Note: Port A terminals used as RS,
WR, RD
and
• Parallel Input/Output timing waveform : Direct Setting, Write Mode
ADR:
tsA
tsCS
DATA:
CS#:
WR#:
RD#:
tWRH
DATAin:
Note: Port A terminals used as RS,
WR, RD
and
Figure 9 Direct Mode: Parallel Input/Output Timing Diagrams
tC(1)
read cycle
addr
tRDL
tsDTR
tdDT
CS
should be set to CMOS format.
tC(1)
write cycle
addr
should be set to CMOS format.
CS
thDTR(1)
thA
thCS
data H
thA
thCS
data
thDTW(2)
tsDTW
tWRL
No.6715-24/25
Page 25

memo:
LC875164A/48A/32A
No.6715-25/25
PS
 Loading...
Loading...