Page 1
- 1 -
HM17CM256
128XRGBX82 OUTPUT LCD DRIVER IC
with built-in RAM
■
INSTRUCTION
HM17CM256 is a dot-Matrix LCD drive IC with 82
commons (80 + 2 icons) and 384 segments (128 X
RGB) drive ports for 256 colors driving.
This IC stores the serial or parallel BIT data
transferred by the microcomputer on the built-in
RAM (81,920 bits for graphic + 2048 bits for icons)
and generates the signals to drive LCD panel.
Color graphic display is achieved by selecting 8
gray (256 color) levels out of 32 gray palettes
independently.
This IC is suitable for battery-operated system,
hand-carrying information equipment by ensuring
low power consumption, low power supply (1.7V ~ )
and a wide range of operating voltage.
And 164 x 128 display (maximum) is possible with
master and slave application.
■
FEATURES
256 color bitmap LCD driver
LCD drive outputs 128×RGB segments, 80 commons for graphic and 2 commons for icons
Display RAM capacity 81,920bits (for graphic usage)
2,048bits (for icon usage)
Gradation display 8 gradations can be selected from 32 gradations by PWM control
Black/White display 82 × (128 × 3) bits display is possible
8 bit BUS interface directly connectable with 68 / 80 series CPU
RAM data length 8 BIT / 16 BIT selectable
Serial interface available
Programmable duty / bias ratio with command
Various instruction set
display data read/write, display ON/OFF, positive/negative display, page address set
display start line address set, partial display, bias select,
column address set, all display ON/OFF, boosting selection, n line inversion mode
read modified write, power save …
Built-in voltage booster (programmable) : 7 × boosting
Built-in voltage regulator
Controllable contrast with built-in electric volume (128 steps)
Low current consumption
Logic supply 1.7V ~ 3.3V
LCD drive supply 5.0V ~ 18.0V
C-MOS silicon process
Package bumped chip / bare chip
Preliminary Specification(0.3)
HM17CM256
EXTERNAL SHAPE
01/02/09
Page 2
HM17CM256
- 2 -
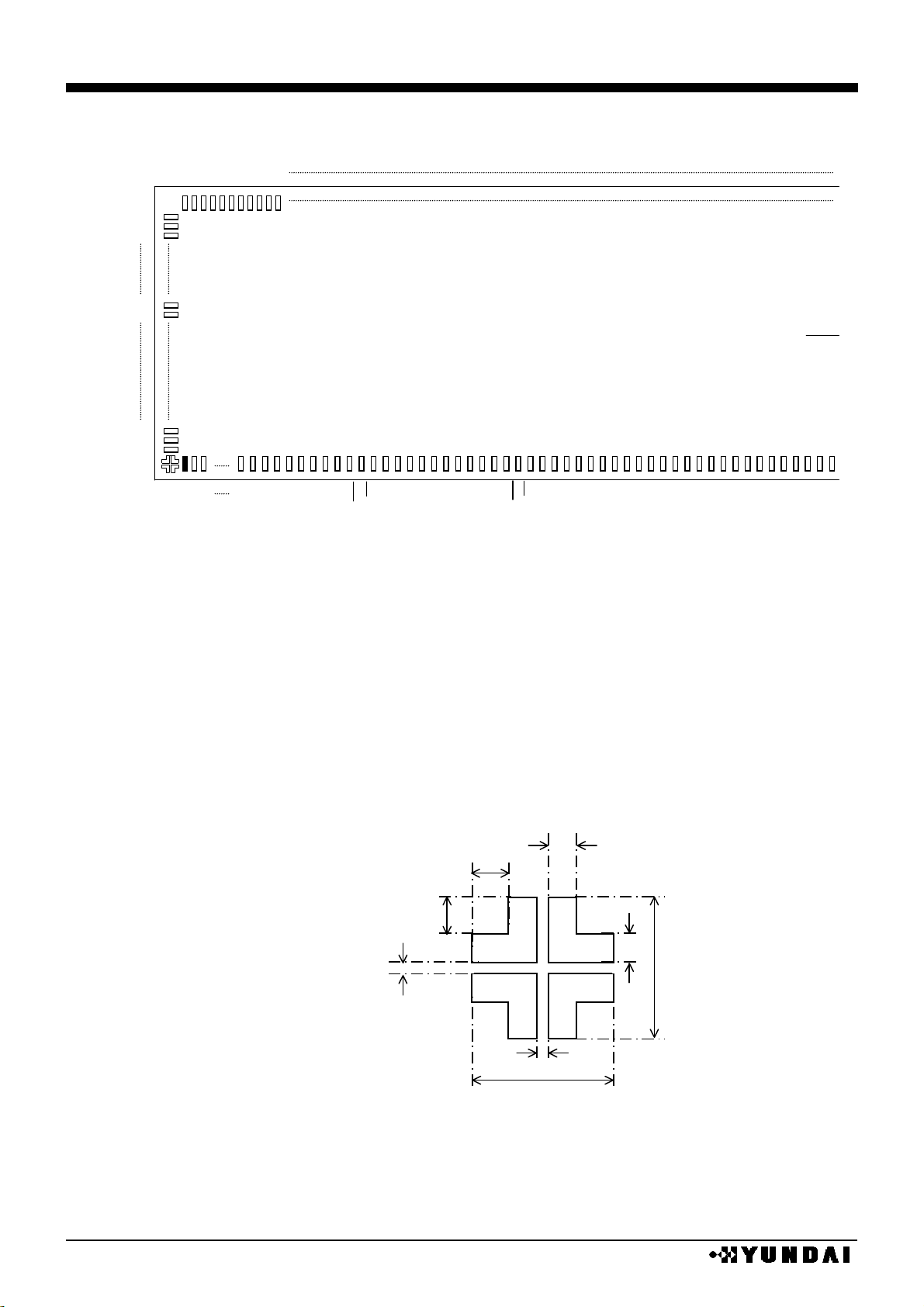
PAD LAYOUT
note 1) The (L) (R) (C) mark after port name is internally shorted.
note 2) DMYport is opened electrically.
chip center : X= 0
µµ
m, Y= 0µµm
chip size : with scribe lane : 19.84mm x 2.48mm ,
main chip : 19.74mm x 2.38mm
chip thickness : 625µµm ±± 25µµm
bump size : 100µµm x 32µµm, 100µµm x 80µµm
bump pitch : 50µµm(Min)
bump height : 18 ±± 3µµm
bump material : Au
align mark appearance and size
a : 30µµm
b : 6µµm
c : 120µµm
d : 27µµm
coordinates of align marks
(X= - 9732µµm, Y= -1052µµm)
(X= 9732µµm, Y= -1052µµm)
1
DMY
5
(R)
SEGA
125
DMY
5
(L)
SEGB
125
SEGC
125
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
COM40
SEGSC3
SEGSA2
DMY6(R)
DMY6(L)
DMY7(R)
DMY7(L)
COM66
DMY
0
(R)
DMY
0
(L)
COM
67
RES
COM
79
CLK
FR
FLM
CL
V
SS
(R)
V
SS
(C)
V
SS
(L)
D
15
D
13
D
12
D
14
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
/SPOL
D
3
/SMODE
D
2
/EXCS
D
1
/SDA
D
0
/SCL
V
DD
(R)
V
DD
(C)
V
DD
(L)
RD
WR
V
SSA
(R)
V
SSA
(C)
SEL68
V
SSA
(L)
P/S
V
DDA
M/S
V
SS
(R)
V
SS
(C)
RS
V
SS
(L)
CSB
V
DD
(R)
V
DD
(C)
V
DD
(L)
TEST
V
SSA
(R)
V
SSA
(C)
COMI
1
V
SSA
(L)
Page 3
HM17CM256
- 3 -
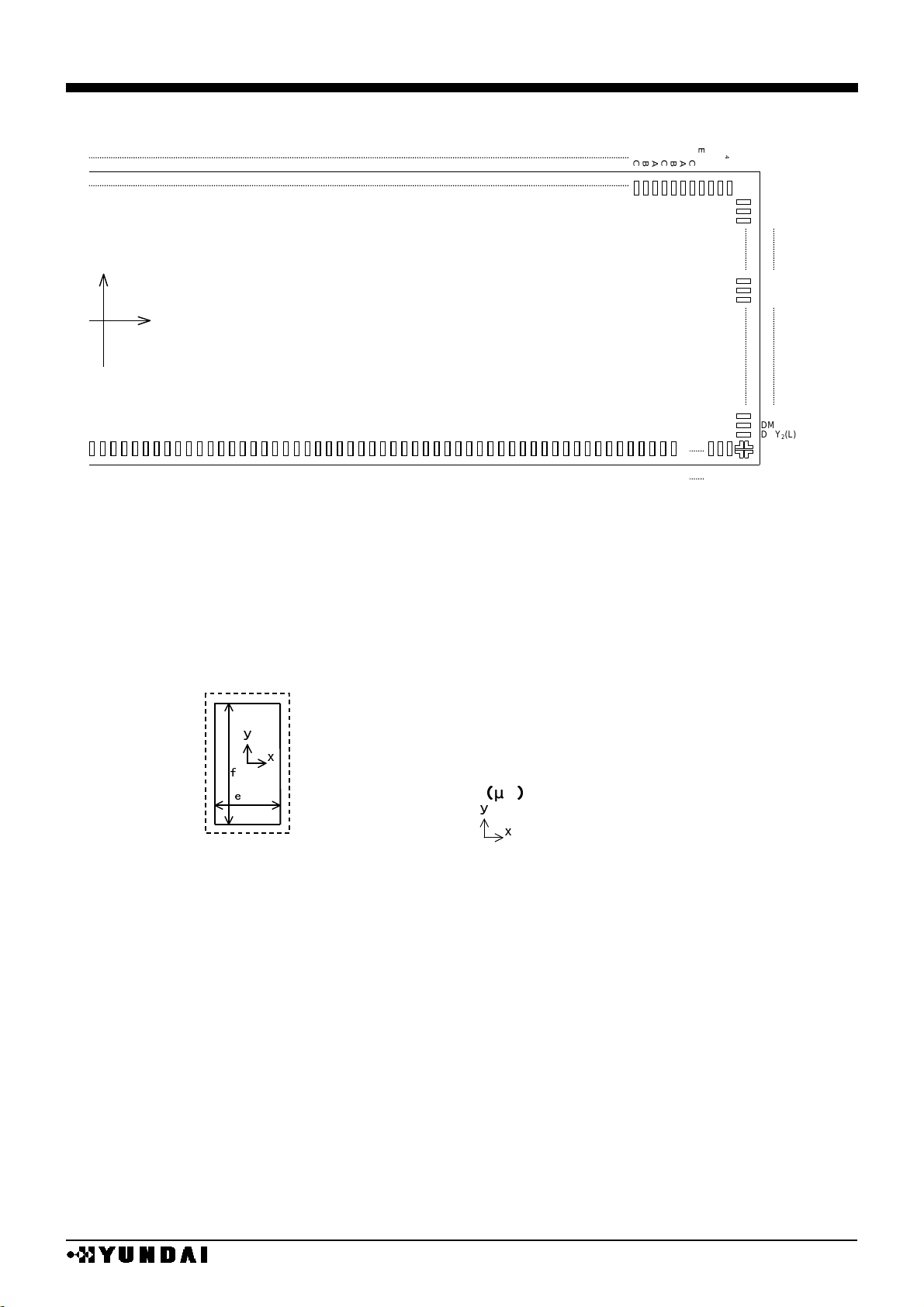
All sorts of PAD open
1. open size (e, f)=(66, 86)
17~118
2. open size (e, f)=(18, 86)
1~16, 119~596
Original point mark of left picture is presented
at the table of pad coordinates.
unit
µµ
m
DMY2(L)
DMY2(R)
COM25
COM0
COMI0
SEGSA0
SEGSC1
DMY3(L)
DMY3(R)
DMY
4
(R)
SEGA
0
DMY
4
(L)
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
2
SEGB
2
SEGC
2
X
Y
COM
39
V
EE
(R)
V
EE
(C)
V
EE
(L)
V
REF
V
BA
(R)
V
BA
(L)
V
REG
(R)
V
REG
(L)
C
1
+(R)
C
1
+(L)
V
SSH
(R)
V
SSH
(C)
OSC
2
V
SSH
(L)
OSC
1
V
LCD
(L)
V
LCD
(R)
V
1
(L)
V
1
(R)
V
2
(L)
V
2
(R)
V
3
(L)
V
3
(R)
V
4
(L)
V
4
(R)
V
SSH
(R)
V
SSH
(C)
V
SSH
(L)
C
1
-(R)
C
1
-(L)
C
2
+(R)
C
2
+(L)
C
2
-(R)
C
2
-(L)
C
3
+(R)
C
3
+(L)
C
3
-(R)
C
3
-(L)
C
4
+(R)
C
4
+(L)
C
4
-(R)
C
4
-(L)
C
5
+(R)
C
5
+(L)
C
5
-(R)
C
5
-(L)
C
6
+(R)
C
6
+(L)
C
6
-(R)
C
6
-(L)
V
OUT
(R)
V
OUT
(L)
V
LCD
(L)
V
LCD
(R)
DMY
1
(L)
COM
26
DMY
1
(R)
Page 4
HM17CM256
- 4 -
■
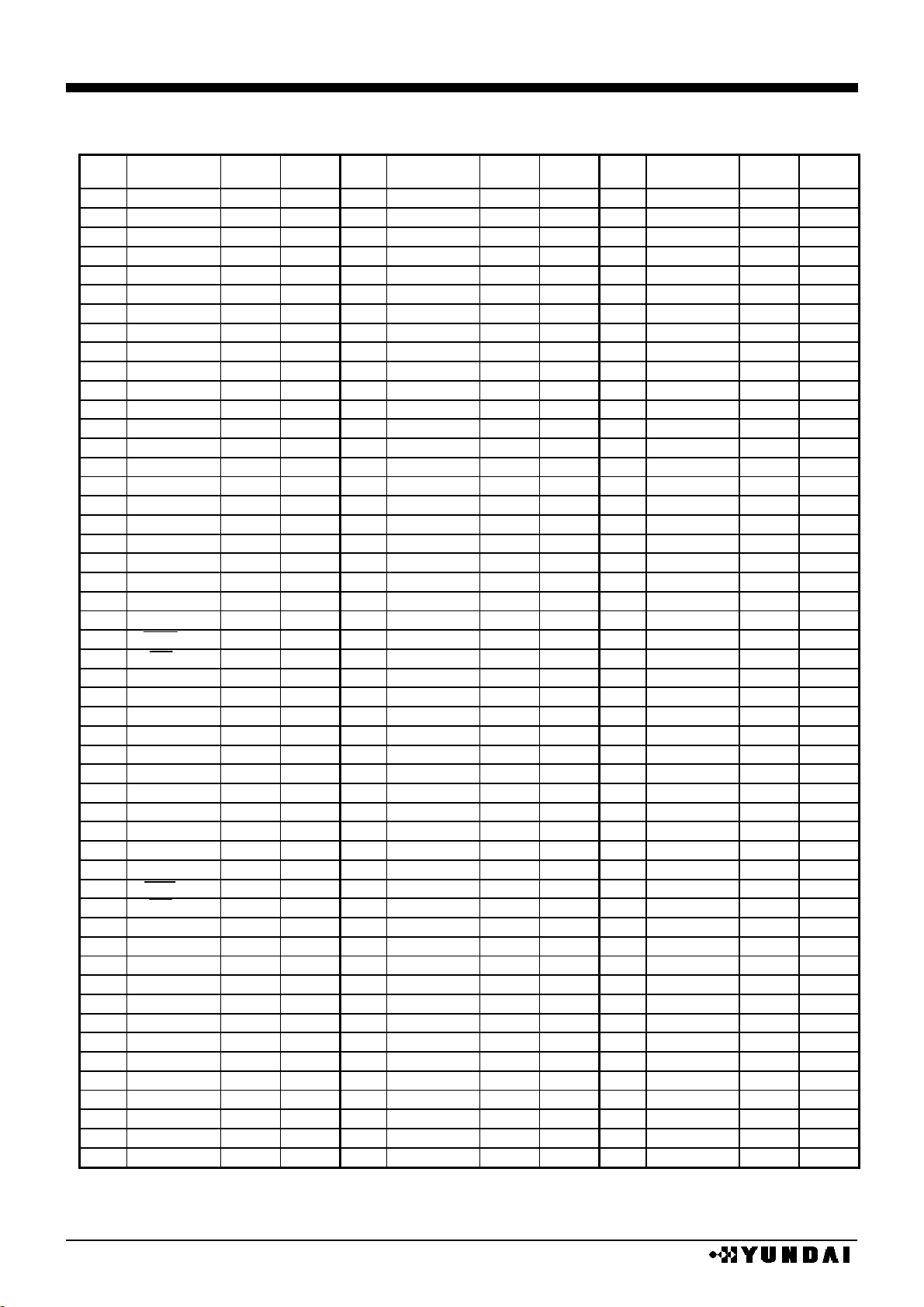
PAD coordinates 1
chip size 19840µm x 2480µm ( chip center : 0µm x 0µm )
PAD
No.
Pin name
X(µm)
Y(µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
1
DMY0(L)
-9625
-1068
52
D10
-2550
-1068
103
C4+(L)
6120
-1068
2
DMY0(R)
-9575
-1068
53
D11
-2380
-1068
104
C4+(R)
6290
-1068
3
COM67
-9525
-1068
54
D12
-2210
-1068
105
C4-(L)
6460
-1068
4
COM68
-9475
-1068
55
D13
-2040
-1068
106
C4-(R)
6630
-1068
5
COM69
-9425
-1068
56
D14
-1870
-1068
107
C5+(L)
6800
-1068
6
COM70
-9375
-1068
57
D15
-1700
-1068
108
C5+(R)
6970
-1068
7
COM71
-9325
-1068
58
VSS(L)
-1472
-1068
109
C5-(L)
7140
-1068
8
COM72
-9275
-1068
59
VSS(C)
-1340
-1068
110
C5-(R)
7310
-1068
9
COM73
-9225
-1068
60
VSS(R)
-1190
-1068
111
C6+(L)
7480
-1068
10
COM74
-9175
-1068
61
CL
-1020
-1068
112
C6+(R)
7650
-1068
11
COM75
-9125
-1068
62
FLM
-850
-1068
113
C6-(L)
7820
-1068
12
COM76
-9075
-1068
63
FR
-680
-1068
114
C6-(R)
7990
-1068
13
COM77
-9025
-1068
64
CLK
-510
-1068
115
V
LCD
(L)
8160
-1068
14
COM78
-8975
-1068
65
OSC1
-340
-1068
116
V
LCD
(R)
8330
-1068
15
COM79
-8925
-1068
66
OSC2
-107
-1068
117
V
OUT
(L)
8500
-1068
16
COMI1
-8875
-1068
67
V
SSH
(L)
74
-1068
118
V
OUT
(R)
8670
-1068
17
V
SSA
(L)
-8670
-1068
68
V
SSH
(C)
196
-1068
119
COM39
8875
-1068
18
V
SSA
(C)
-8500
-1068
69
V
SSH
(R)
318
-1068
120
COM38
8925
-1068
19
V
SSA
(R)
-8330
-1068
70
V
LCD
(L)
510
-1068
121
COM37
8975
-1068
20
TEST
-8171
-1068
71
V
LCD
(R)
680
-1068
122
COM36
9025
-1068
21
VDD(L)
-7990
-1068
72
V1(L)
850
-1068
123
COM35
9075
-1068
22
VDD(C)
-7820
-1068
73
V1(R)
1020
-1068
124
COM34
9125
-1068
23
VDD(R)
-7650
-1068
74
V2(L)
1190
-1068
125
COM33
9175
-1068
24
RES
-7480
-1068
75
V2(R)
1360
-1068
126
COM32
9225
-1068
25
CS
-7310
-1068
76
V3(L)
1530
-1068
127
COM31
9275
-1068
26
RS
-7140
-1068
77
V3(R)
1700
-1068
128
COM30
9325
-1068
27
VSS(L)
-6970
-1068
78
V4(L)
1870
-1068
129
COM29
9375
-1068
28
VSS(C)
-6800
-1068
79
V4(R)
2040
-1068
130
COM28
9425
-1068
29
VSS(R)
-6630
-1068
80
V
REG
(L)
2210
-1068
131
COM27
9475
-1068
30
M/S
-6448
-1068
81
V
REG
(R)
2380
-1068
132
COM26
9525
-1068
31
V
DDA
-6290
-1068
82
VBA(L)
2550
-1068
133
DMY1(L)
9575
-1068
32
P/S
-6120
-1068
83
VBA(R)
2693
-1068
134
DMY1(R)
9625
-1068
33
SEL68
-5950
-1068
84
V
REF
2879
-1068
135
DMY2(L)
9726
-900
34
V
SSA
(L)
-5780
-1068
85
VEE(L)
3060
-1068
136
DMY2(R)
9726
-850
35
V
SSA
(C)
-5610
-1068
86
VEE(C)
3230
-1068
137
COM25
9726
-800
36
V
SSA
(R)
-5440
-1068
87
VEE(R)
3400
-1068
138
COM24
9726
-750
37
WR
-5270
-1068
88
V
SSH
(L)
3570
-1068
139
COM23
9726
-700
38
RD
-5111
-1068
89
V
SSH
(C)
3740
-1068
140
COM22
9726
-650
39
VDD(L)
-4930
-1068
90
V
SSH
(R)
3910
-1068
141
COM21
9726
-600
40
VDD(C)
-4760
-1068
91
C1+(L)
4102
-1068
142
COM20
9726
-550
41
VDD(R)
-4590
-1068
92
C1+(R)
4250
-1068
143
COM19
9726
-500
42
D0/SCL
-4420
-1068
93
C1-(L)
4420
-1068
144
COM18
9726
-450
43
D1/SDA
-4250
-1068
94
C1-(R)
4590
-1068
145
COM17
9726
-400
44
D2/EXCS
-3995
-1068
95
C2+(L)
4760
-1068
146
COM16
9726
-350
45
D3/SMODE
-3740
-1068
96
C2+(R)
4930
-1068
147
COM15
9726
-300
46
D4/SPOL
-3570
-1068
97
C2-(L)
5100
-1068
148
COM14
9726
-250
47
D5
-3400
-1068
98
C2-(R)
5270
-1068
149
COM13
9726
-200
48
D6
-3230
-1068
99
C3+(L)
5440
-1068
150
COM12
9726
-150
49
D7
-3060
-1068
100
C3+(R)
5610
-1068
151
COM11
9726
-100
50
D8
-2890
-1068
101
C3-(L)
5780
-1068
152
COM10
9726
-50
51
D9
-2720
-1068
102
C3-(R)
5950
-1068
153
COM9
9726
0
Page 5
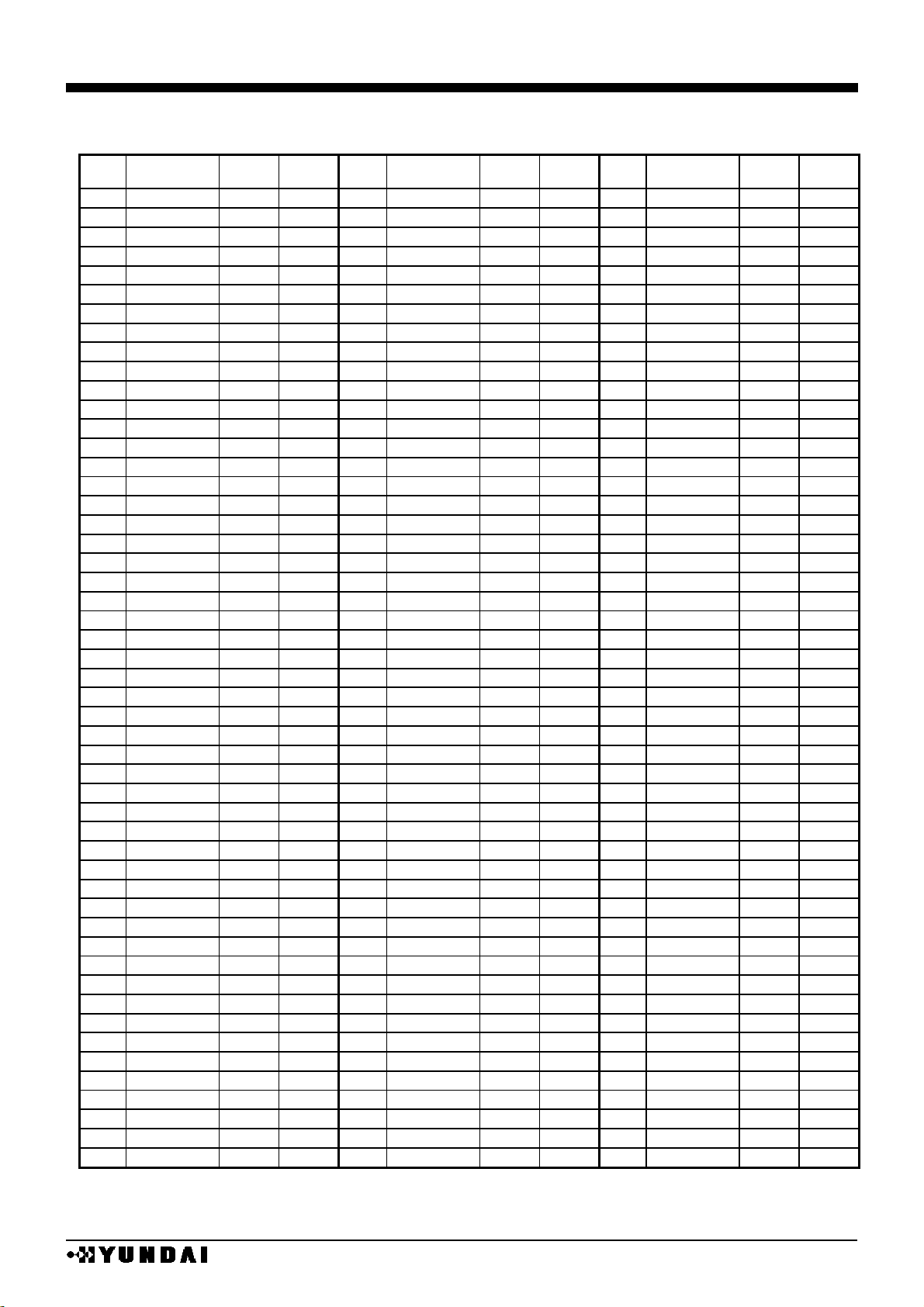
HM17CM256
- 5 -
■
PAD coordiantes 2
chip size 19840µm x 2480µm ( chip center : 0µm x 0µm )
PAD
No.
Pin name
X(µm)
Y(µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
154
COM8
9726
50
205
SEGB10
8025
1068
256
SEGB27
5475
1068
155
COM7
9726
100
206
SEGC10
7975
1068
257
SEGC27
5425
1068
156
COM6
9726
150
207
SEGA11
7925
1068
258
SEGA28
5375
1068
157
COM5
9726
200
208
SEGB11
7875
1068
259
SEGB28
5325
1068
158
COM4
9726
250
209
SEGC11
7825
1068
260
SEGC28
5275
1068
159
COM3
9726
300
210
SEGA12
7775
1068
261
SEGA29
5225
1068
160
COM2
9726
350
211
SEGB12
7725
1068
262
SEGB29
5175
1068
161
COM1
9726
400
212
SEGC12
7675
1068
263
SEGC29
5125
1068
162
COM0
9726
450
213
SEGA13
7625
1068
264
SEGA30
5075
1068
163
COMI0
9726
500
214
SEGB13
7575
1068
265
SEGB30
5025
1068
164
SEGSA0
9726
550
215
SEGC13
7525
1068
266
SEGC30
4975
1068
165
SEGSB0
9726
600
216
SEGA14
7475
1068
267
SEGA31
4925
1068
166
SEGSC0
9726
650
217
SEGB14
7425
1068
268
SEGB31
4875
1068
167
SEGSA1
9726
700
218
SEGC14
7375
1068
269
SEGC31
4825
1068
168
SEGSB1
9726
750
219
SEGA15
7325
1068
270
SEGA32
4775
1068
169
SEGSC1
9726
800
220
SEGB15
7275
1068
271
SEGB32
4725
1068
170
DMY3(L)
9726
850
221
SEGC15
7225
1068
272
SEGC32
4675
1068
171
DMY3(R)
9726
900
222
SEGA16
7175
1068
273
SEGA33
4625
1068
172
DMY4(L)
9675
1068
223
SEGB16
7125
1068
274
SEGB33
4575
1068
173
DMY4(R)
9625
1068
224
SEGC16
7075
1068
275
SEGC33
4525
1068
174
SEGA0
9575
1068
225
SEGA17
7025
1068
276
SEGA34
4475
1068
175
SEGB0
9525
1068
226
SEGB17
6975
1068
277
SEGB34
4425
1068
176
SEGC0
9475
1068
227
SEGC17
6925
1068
278
SEGC34
4375
1068
177
SEGA1
9425
1068
228
SEGA18
6875
1068
279
SEGA35
4325
1068
178
SEGB1
9375
1068
229
SEGB18
6825
1068
280
SEGB35
4275
1068
179
SEGC1
9325
1068
230
SEGC18
6775
1068
281
SEGC35
4225
1068
180
SEGA2
9275
1068
231
SEGA19
6725
1068
282
SEGA36
4175
1068
181
SEGB2
9225
1068
232
SEGB19
6675
1068
283
SEGB36
4125
1068
182
SEGC2
9175
1068
233
SEGC19
6625
1068
284
SEGC36
4075
1068
183
SEGA3
9125
1068
234
SEGA20
6575
1068
285
SEGA37
4025
1068
184
SEGB3
9075
1068
235
SEGB20
6525
1068
286
SEGB37
3975
1068
185
SEGC3
9025
1068
236
SEGC20
6475
1068
287
SEGC37
3925
1068
186
SEGA4
8975
1068
237
SEGA21
6425
1068
288
SEGA38
3875
1068
187
SEGB4
8925
1068
238
SEGB21
6375
1068
289
SEGB38
3825
1068
188
SEGC4
8875
1068
239
SEGC21
6325
1068
290
SEGC38
3775
1068
189
SEGA5
8825
1068
240
SEGA22
6275
1068
291
SEGA39
3725
1068
190
SEGB5
8775
1068
241
SEGB22
6225
1068
292
SEGB39
3675
1068
191
SEGC5
8725
1068
242
SEGC22
6175
1068
293
SEGC39
3625
1068
192
SEGA6
8675
1068
243
SEGA23
6125
1068
294
SEGA40
3575
1068
193
SEGB6
8625
1068
244
SEGB23
6075
1068
295
SEGB40
3525
1068
194
SEGC6
8575
1068
245
SEGC23
6025
1068
296
SEGC40
3475
1068
195
SEGA7
8525
1068
246
SEGA24
5975
1068
297
SEGA41
3425
1068
196
SEGB7
8475
1068
247
SEGB24
5925
1068
298
SEGB41
3375
1068
197
SEGC7
8425
1068
248
SEGC24
5875
1068
299
SEGC41
3325
1068
198
SEGA8
8375
1068
249
SEGA25
5825
1068
300
SEGA42
3275
1068
199
SEGB8
8325
1068
250
SEGB25
5775
1068
301
SEGB42
3225
1068
200
SEGC8
8275
1068
251
SEGC25
5725
1068
302
SEGC42
3175
1068
201
SEGA9
8225
1068
252
SEGA26
5675
1068
303
SEGA43
3125
1068
202
SEGB9
8175
1068
253
SEGB26
5625
1068
304
SEGB43
3075
1068
203
SEGC9
8125
1068
254
SEGC26
5575
1068
305
SEGC43
3025
1068
204
SEGA10
8075
1068
255
SEGA27
5525
1068
306
SEGA44
2975
1068
Page 6
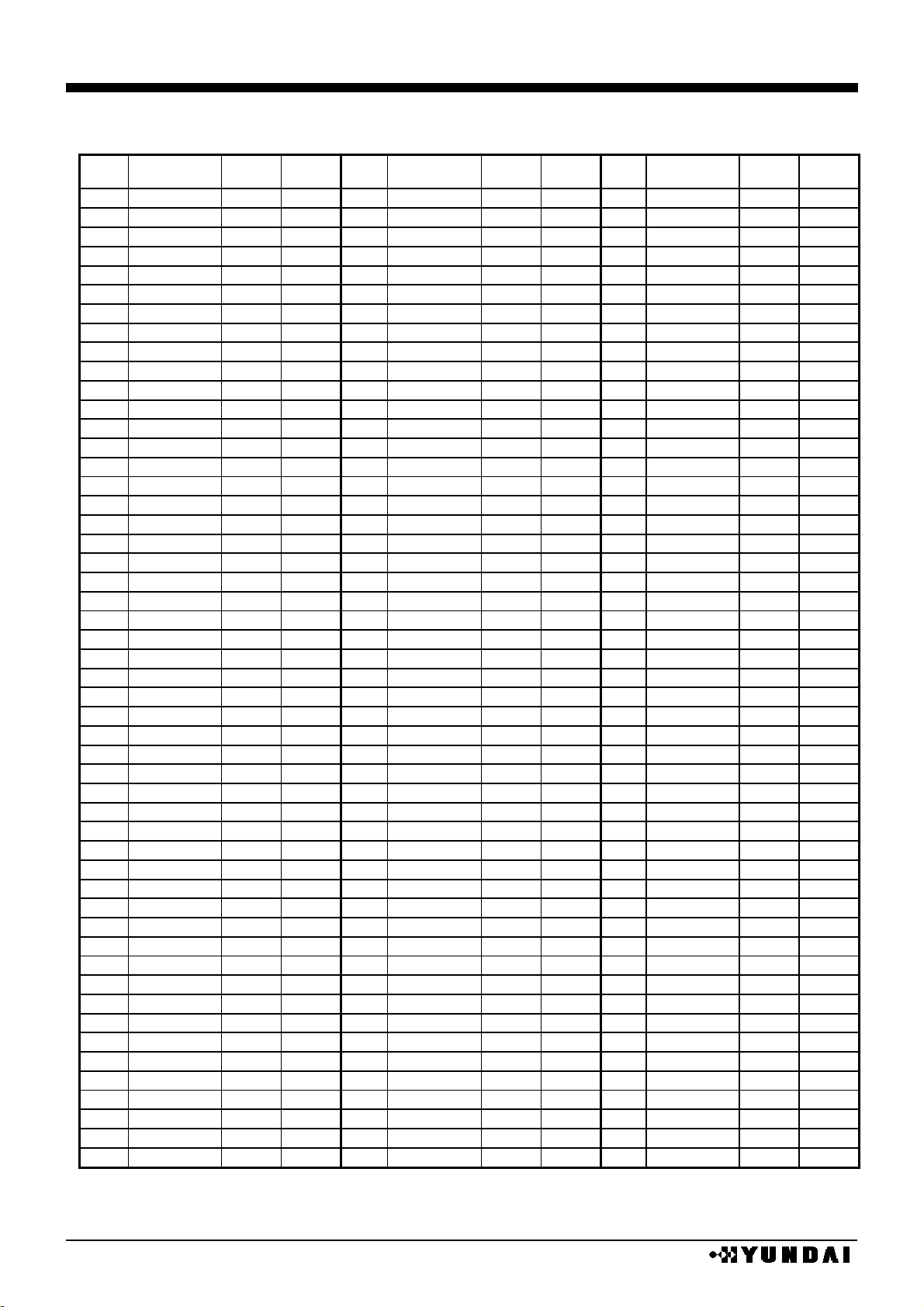
HM17CM256
- 6 -
PAD coordinates 3
chip size 19840µm x 2480µm (chip center : 0µm x 0µm )
PAD
No.
Pin name
X(µm)
Y(µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
307
SEGB44
2925
1068
358
SEGB61
375
1068
409
SEGB78
-2175
1068
308
SEGC44
2875
1068
359
SEGC61
325
1068
410
SEGC78
-2225
1068
309
SEGA45
2825
1068
360
SEGA62
275
1068
411
SEGA79
-2275
1068
310
SEGB45
2775
1068
361
SEGB62
225
1068
412
SEGB79
-2325
1068
311
SEGC45
2725
1068
362
SEGC62
175
1068
413
SEGC79
-2375
1068
312
SEGA46
2675
1068
363
SEGA63
125
1068
414
SEGA80
-2425
1068
313
SEGB46
2625
1068
364
SEGB63
75
1068
415
SEGB80
-2475
1068
314
SEGC46
2575
1068
365
SEGC63
25
1068
416
SEGC80
-2525
1068
315
SEGA47
2525
1068
366
SEGA64
-25
1068
417
SEGA81
-2575
1068
316
SEGB47
2475
1068
367
SEGB64
-75
1068
418
SEGB81
-2625
1068
317
SEGC47
2425
1068
368
SEGC64
-125
1068
419
SEGC81
-2675
1068
318
SEGA48
2375
1068
369
SEGA65
-175
1068
420
SEGA82
-2725
1068
319
SEGB48
2325
1068
370
SEGB65
-225
1068
421
SEGB82
-2775
1068
320
SEGC 48
2275
1068
371
SEGC65
-275
1068
422
SEGC82
-2825
1068
321
SEGA49
2225
1068
372
SEGA66
-325
1068
423
SEGA83
-2875
1068
322
SEGB49
2175
1068
373
SEGB66
-375
1068
424
SEGB83
-2925
1068
323
SEGC49
2125
1068
374
SEGC66
-425
1068
425
SEGC83
-2975
1068
324
SEGA50
2075
1068
375
SEGA67
-475
1068
426
SEGA84
-3025
1068
325
SEGB50
2025
1068
376
SEGB67
-525
1068
427
SEGB84
-3075
1068
326
SEGC50
1975
1068
377
SEGC67
-575
1068
428
SEGC84
-3125
1068
327
SEGA51
1925
1068
378
SEGA68
-625
1068
429
SEGA85
-3175
1068
328
SEGB51
1875
1068
379
SEGB68
-675
1068
430
SEGB85
-3225
1068
329
SEGC51
1825
1068
380
SEGC68
-725
1068
431
SEGC85
-3275
1068
330
SEGA52
1775
1068
381
SEGA69
-775
1068
432
SEGA86
-3325
1068
331
SEGB52
1725
1068
382
SEGB69
-825
1068
433
SEGB86
-3375
1068
332
SEGC52
1675
1068
383
SEGC69
-875
1068
434
SEGC86
-3425
1068
333
SEGA53
1625
1068
384
SEGA70
-925
1068
435
SEGA87
-3475
1068
334
SEGB53
1575
1068
385
SEGB70
-975
1068
436
SEGB87
-3525
1068
335
SEGC53
1525
1068
386
SEGC70
-1025
1068
437
SEGC87
-3575
1068
336
SEGA54
1475
1068
387
SEGA71
-1075
1068
438
SEGA88
-3625
1068
337
SEGB54
1425
1068
388
SEGB71
-1125
1068
439
SEGB88
-3675
1068
338
SEGC54
1375
1068
389
SEGC71
-1175
1068
440
SEGC88
-3725
1068
339
SEGA55
1325
1068
390
SEGA72
-1225
1068
441
SEGA89
-3775
1068
340
SEGB55
1275
1068
391
SEGB72
-1275
1068
442
SEGB89
-3825
1068
341
SEGC55
1225
1068
392
SEGC72
-1325
1068
443
SEGC89
-3875
1068
342
SEGA56
1175
1068
393
SEGA73
-1375
1068
444
SEGA90
-3925
1068
343
SEGB56
1125
1068
394
SEGB73
-1425
1068
445
SEGB90
-3975
1068
344
SEGC56
1075
1068
395
SEGC73
-1475
1068
446
SEGC90
-4025
1068
345
SEGA57
1025
1068
396
SEGA74
-1525
1068
447
SEGA91
-4075
1068
346
SEGB57
975
1068
397
SEGB74
-1575
1068
448
SEGB91
-4125
1068
347
SEGC57
925
1068
398
SEGC74
-1625
1068
449
SEGC91
-4175
1068
348
SEGA58
875
1068
399
SEGA75
-1675
1068
450
SEGA92
-4225
1068
349
SEGB58
825
1068
400
SEGB75
-1725
1068
451
SEGB92
-4275
1068
350
SEGC58
775
1068
401
SEGC75
-1775
1068
452
SEGC92
-4325
1068
351
SEGA59
725
1068
402
SEGA76
-1825
1068
453
SEGA93
-4375
1068
352
SEGB59
675
1068
403
SEGB76
-1875
1068
454
SEGB93
-4425
1068
353
SEGC59
625
1068
404
SEGC76
-1925
1068
455
SEGC93
-4475
1068
354
SEGA60
575
1068
405
SEGA77
-1975
1068
456
SEGA94
-4525
1068
355
SEGB60
525
1068
406
SEGB77
-2025
1068
457
SEGB94
-4575
1068
356
SEGC60
475
1068
407
SEGC77
-2075
1068
458
SEGC94
-4625
1068
357
SEGA61
425
1068
408
SEGA78
-2125
1068
459
SEGA95
-4675
1068
Page 7
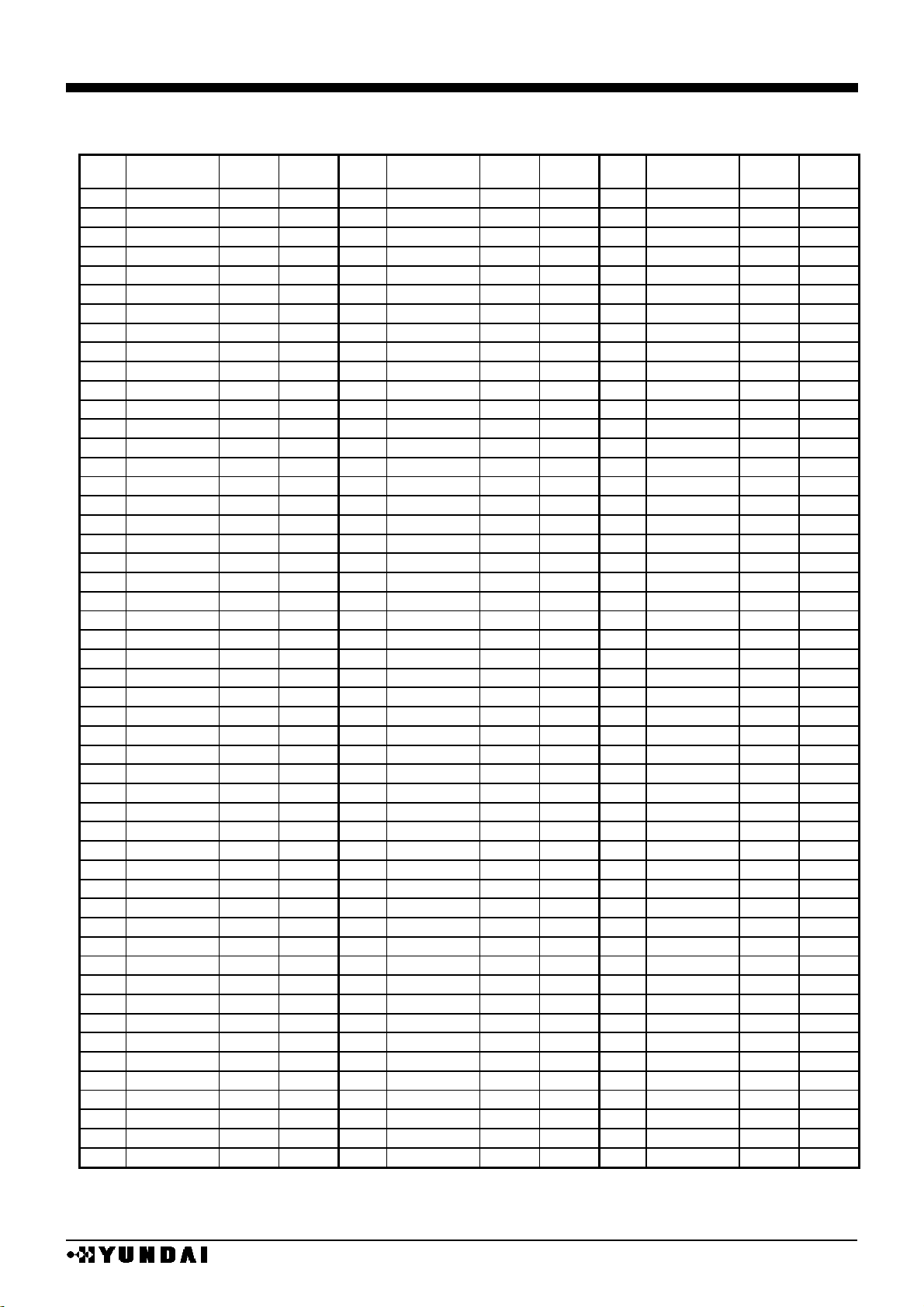
HM17CM256
- 7 -
■
PAD coordinates 4
chip size 19840µm x 2480µm (chip center : 0µm x 0µm )
PAD
No.
Pin name
X(µm)
Y(µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
PAD
No.
Pin name
X (µm)
Y (µm)
460
SEGB95
-4725
1068
511
SEGB
112
-7275
1068
562
SEGSA2
-9726
800
461
SEGC95
-4775
1068
512
SEGC
112
-7325
1068
563
SEGSB2
-9726
750
462
SEGA96
-4825
1068
513
SEGA
113
-7375
1068
564
SEGSC2
-9726
700
463
SEGB96
-4875
1068
514
SEGB
113
-7425
1068
565
SEGSA3
-9726
650
464
SEGC96
-4925
1068
515
SEGC
113
-7475
1068
566
SEGSB3
-9726
600
465
SEGA97
-4975
1068
516
SEGA
114
-7525
1068
567
SEGSC3
-9726
550
466
SEGB97
-5025
1068
517
SEGB
114
-7575
1068
568
COM40
-9726
500
467
SEGC97
-5075
1068
518
SEGC
114
-7625
1068
569
COM41
-9726
450
468
SEGA98
-5125
1068
519
SEGA
115
-7675
1068
570
COM42
-9726
400
469
SEGB98
-5175
1068
520
SEGB
115
-7725
1068
571
COM43
-9726
350
470
SEGC98
-5225
1068
521
SEGC
115
-7775
1068
572
COM44
-9726
300
471
SEGA99
-5275
1068
522
SEGA
116
-7825
1068
573
COM45
-9726
250
472
SEGB99
-5325
1068
523
SEGB
116
-7875
1068
574
COM46
-9726
200
473
SEGC99
-5375
1068
524
SEGC
116
-7925
1068
575
COM47
-9726
150
474
SEGA
100
-5425
1068
525
SEGA
117
-7975
1068
576
COM48
-9726
100
475
SEGB
100
-5475
1068
526
SEGB
117
-8025
1068
577
COM49
-9726
50
476
SEGC
100
-5525
1068
527
SEGC
117
-8075
1068
578
COM50
-9726
0
477
SEGA
101
-5575
1068
528
SEGA
118
-8125
1068
579
COM51
-9726
-50
478
SEGB
101
-5625
1068
529
SEGB
118
-8175
1068
580
COM52
-9726
-100
479
SEGC
101
-5675
1068
530
SEGC
118
-8225
1068
581
COM53
-9726
-150
480
SEGA
102
-5725
1068
531
SEGA
119
-8275
1068
582
COM54
-9726
-200
481
SEGB
102
-5775
1068
532
SEGB
119
-8325
1068
583
COM55
-9726
-250
482
SEGC
102
-5825
1068
533
SEGC
119
-8375
1068
584
COM56
-9726
-300
483
SEGA
103
-5875
1068
534
SEGA
120
-8425
1068
585
COM57
-9726
-350
484
SEGB
103
-5925
1068
535
SEGB
120
-8475
1068
586
COM58
-9726
-400
485
SEGC
103
-5975
1068
536
SEGC
120
-8525
1068
587
COM59
-9726
-450
486
SEGA
104
-6025
1068
537
SEGA
121
-8575
1068
588
COM60
-9726
-500
487
SEGB
104
-6075
1068
538
SEGB
121
-8625
1068
589
COM61
-9726
-550
488
SEGC
104
-6125
1068
539
SEGC
121
-8675
1068
590
COM62
-9726
-600
489
SEGA
105
-6175
1068
540
SEGA
122
-8725
1068
591
COM63
-9726
-650
490
SEGB
105
-6225
1068
541
SEGB
122
-8775
1068
592
COM64
-9726
-700
491
SEGC
105
-6275
1068
542
SEGC
122
-8825
1068
593
COM65
-9726
-750
492
SEGA
106
-6325
1068
543
SEGA
123
-8875
1068
594
COM66
-9726
-800
493
SEGB
106
-6375
1068
544
SEGB
123
-8925
1068
595
DMY7(L)
-9726
-850
494
SEGC
106
-6425
1068
545
SEGC
123
-8975
1068
596
DMY7(R)
-9726
-900
495
SEGA
107
-6475
1068
546
SEGA
124
-9025
1068
496
SEGB
107
-6525
1068
547
SEGB
124
-9075
1068
497
SEGC
107
-6575
1068
548
SEGC
124
-9125
1068
498
SEGA
108
-6625
1068
549
SEGA
125
-9175
1068
499
SEGB
108
-6675
1068
550
SEGB
125
-9225
1068
500
SEGC
108
-6725
1068
551
SEGC
125
-9275
1068
501
SEGA
109
-6775
1068
552
SEGA
126
-9325
1068
502
SEGB
109
-6825
1068
553
SEGB
126
-9375
1068
503
SEGC
109
-6875
1068
554
SEGC
126
-9425
1068
504
SEGA
110
-6925
1068
555
SEGA
127
-9475
1068
505
SEGB
110
-6975
1068
556
SEGB
127
-9525
1068
506
SEGC
110
-7025
1068
557
SEGC
127
-9575
1068
507
SEGA
111
-7075
1068
558
DMY5(L)
-9625
1068
508
SEGB
111
-7125
1068
559
DMY5(R)
-9675
1068
509
SEGC
111
-7175
1068
560
DMY6(L)
-9726
900
510
SEGA
112
-7225
1068
561
DMY6(R)
-9726
850
Page 8
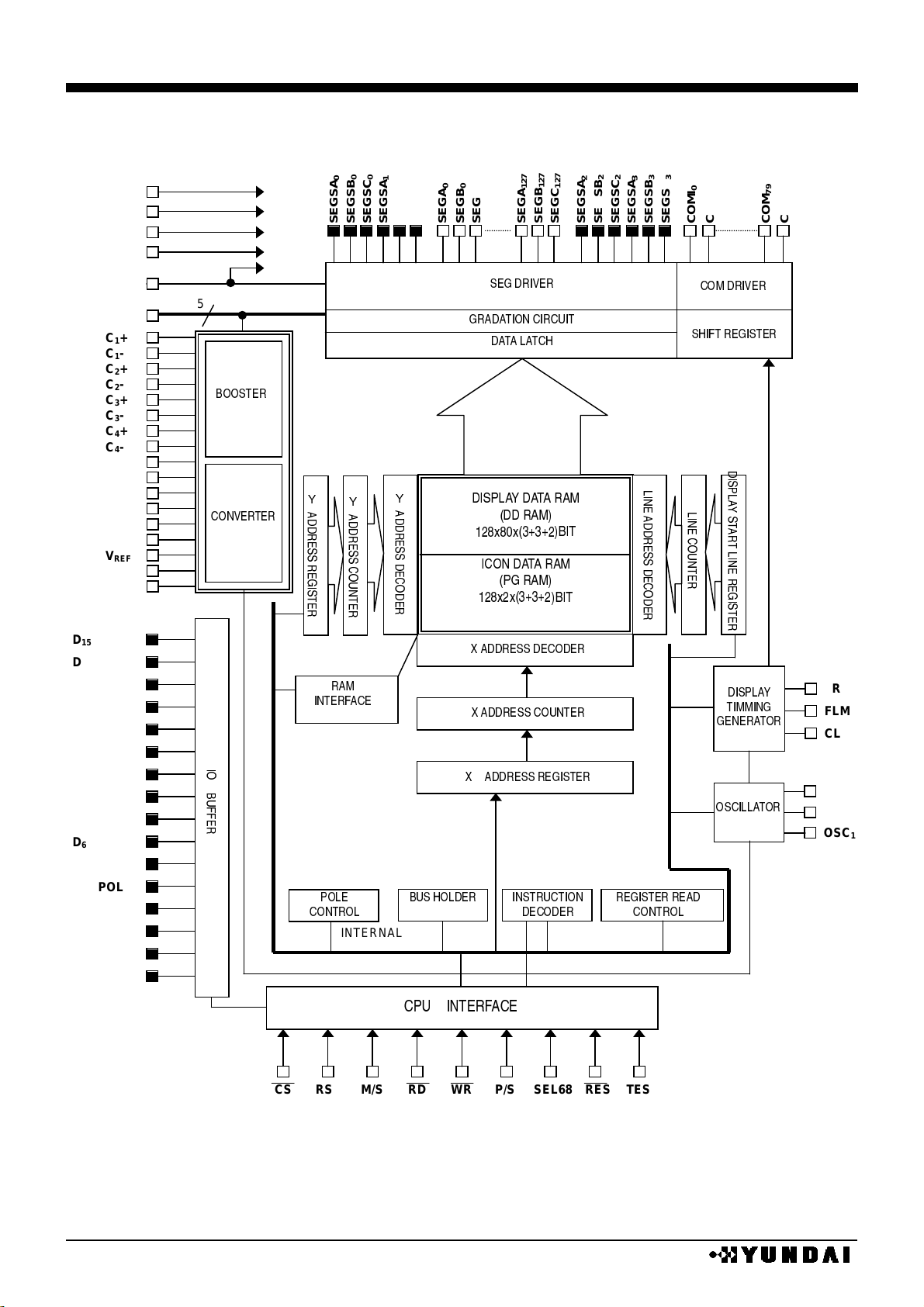
HM17CM256
- 8 -
BLOCK DIAGRAM
VSS
VDD
V
LCD
, V1 ~V4
V
OUT
VBA
VEE
INTERNAL BUS
CLK
FR
FLM
CL
5
RS
P/S
SEL68
CS
WR
RD
TEST
RES
M/S
C1-
C1+
C2+
C2-
V
REF
C3+
C3-
C4+
C4-
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
COMI
0
COM
0
COM
79
COMI
1
OSC1
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
C5+
C5-
C6+
C6-
D7
D4/SPOL
D6
D15
D14
D13
D12
D5
D11
D10
D9
D8
D3/SMODE
D0/SCL
D2/EXCS
D1/SDA
V
SSH
OSC2
V
REG
V
DDA
V
SSA
D
$
%
S
"
T
T
'
+
(
)
)
"
'
*
*
"
'
G
&
"
*
'
R
D
+
+
(
)
()
)
)
"
"
'
'
*
*
*
"
)
*
#$
%
#$
!&
"
)
"
'
'
H I J K L M N O P Q H N
, - . / 0 1 2 , 1 3 1 4 1 5
6
, , 4 1 5 7
6 = > = >
8 9 : ; : < ;
- @ A B , 1 3 1 4 1 5
6
/ C 4 1 5 7
8 9 : ; 9 ;
7 ? - 3
9
6 = > = >
7 ? - 3
9
!"
()
)
"
'
*
*
"
)
#$
"
)
'
D
R
)
*E
(F
&
!"
*
&
(
'
#$%
!"
!&
"
"
'
'
G
&
"
*
'
Page 9
HM17CM256
- 9 -
■
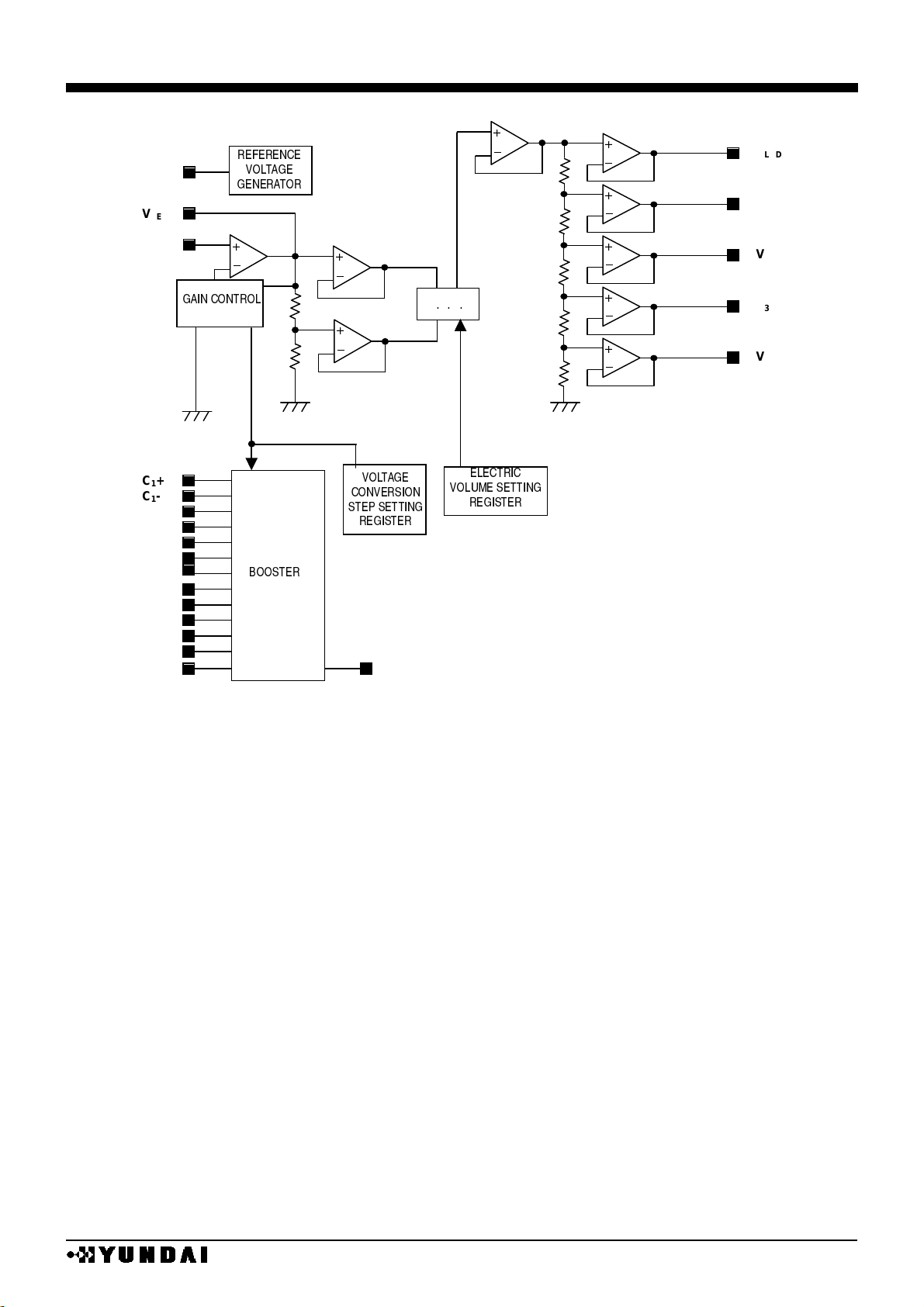
POWER CIRCUIT BLOCK DIAGRAM
VBA
V
REF
V
OUT
VEE
C1+
C1-
C2+
C2-
C3+
C3-
C
4
+
C4-
C5+
C5-
C6+
C6-
V W V W V
E.V.R.
V
REG
V
V W V W V W V
V1
V2
V3
V4
V
LCD
V
R
D
U
D
D
W
D
W
W
Page 10
HM17CM256
- 10 -
■
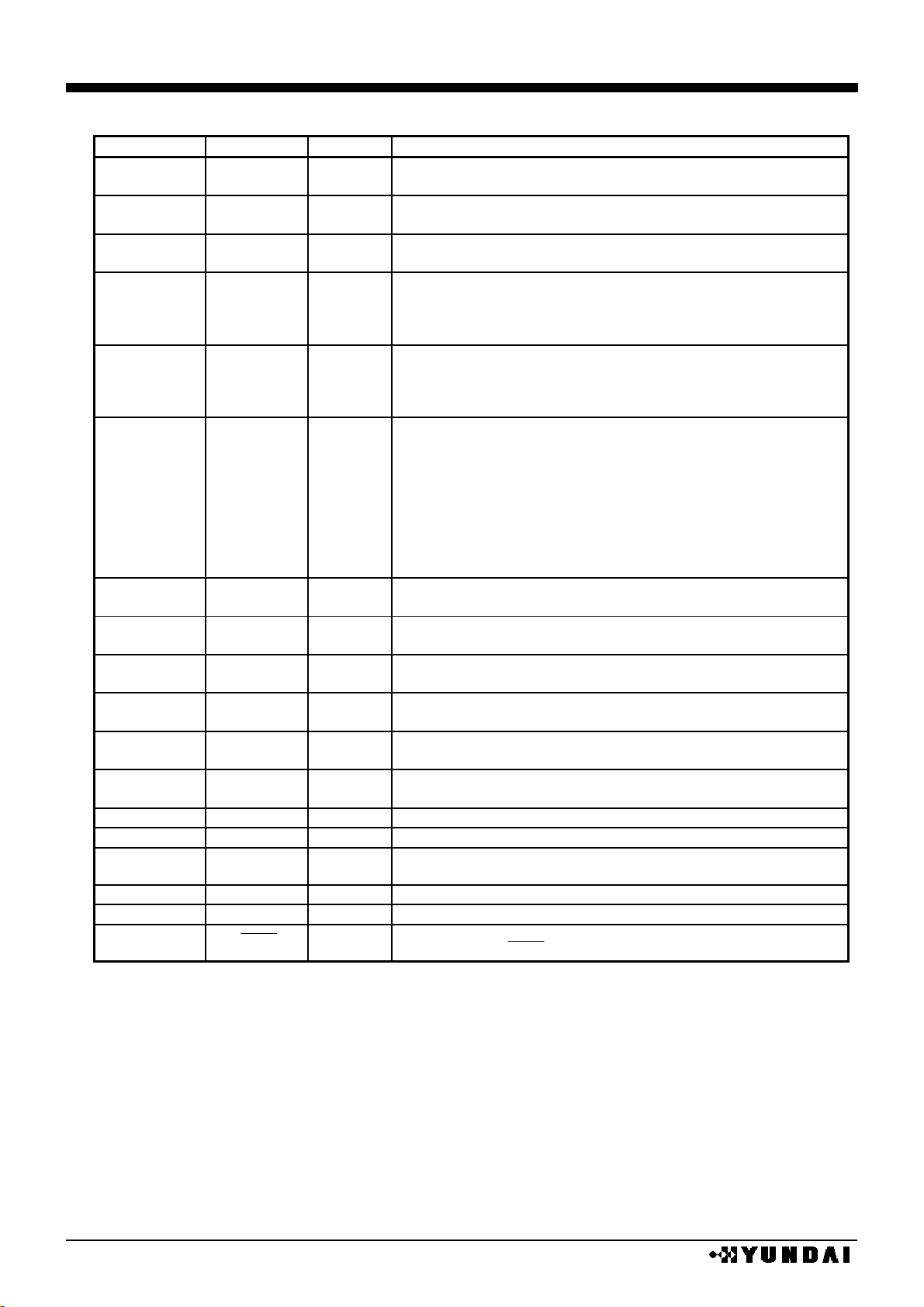
PIN DESCRIPTION 1
No.
NAME
I/O
FUNCTION
21,22,23,
39,40,41
VDD
supply
Power pin for logic
27,28,29,
58,59,60
VSS
supply
GND pin for logic
67,68,69,
88,89,90
V
SSH
supply
High voltage GND pin
31
V
DDA
supply
This pin is internally connected to VDD pin.
This pin is used when the voltage of each input pin is fixed to
VDD level.
caution) Do not use to main power pin.
17,18,19,
34,35,36
V
SSA
supply
This pin is internally connected to VSS pin.
This pin is used when the voltage of each input pin is fixed to
VSS level.
caution) Do not use to main power pin.
70,71,115,116
72,73
74,75
76,77
78,79
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
supply/O
LCD driver supply voltage
•
LCD driver power supply port when external power supply
is used. When external power is used, voltages should
have following relations.
VSS<V4<V3<V2<V1<V
LCD
•
V
LCD
, V1~V4 voltages are generated by voltage booster at
master mode operation under power circuit ON.
•
When internal power supply is used, capacitors must be
connected between V
LCD
, V1~V4 and VSS.
91,92
93,94
C1+
C1-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
95,96
97,98
C2+
C2-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
99,100
101,102
C3+
C3-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
103,104
105,106
C4+
C4-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
107,108
109,110
C5+
C5-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
111,112
113,114
C6+
C6-
O
Capacitor connection pin for voltage converter
82,83
VBA
O
Reference voltage output pin for voltage regulating.
84
V
REF
I
Reference voltage input pin for voltage regulating.
85,86,87
VEE
supply
Voltage supply pin for boosted voltage generation.
VDD level at normal status.
117,118
V
OUT
supply/O
Internal DC/DC converter output pin.
80,81
V
REG
O
Voltage regulator output pin.
24
RES
I
Reset pin
Reset when RES= “L”
Page 11
HM17CM256
- 11 -
■
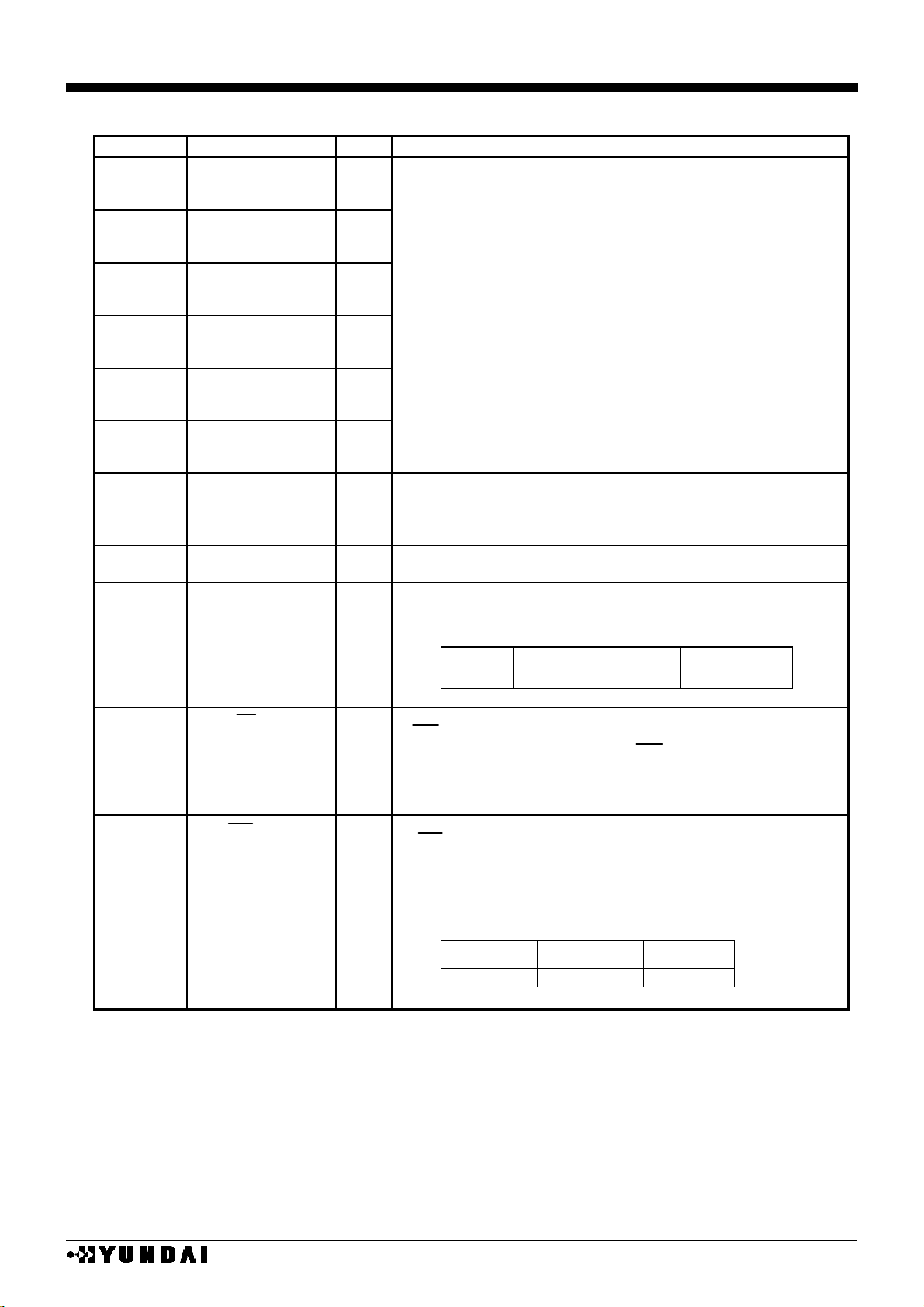
PIN DESCRIPTION 2
No.
NAME
I/O
FUNCTION
42
D0/SCL
I/O
43
D1/SDA
I/O
44
D2/EXCS
I/O
45
D3/SMODE
I/O
46
D4/SPOL
I/O
47,48,49
D5,D6,D7
I/O
•
When parallel interface is selected (P/S=”H”), data line is
connected to MPU data bus with 8bit bi-directional bus
•
When serial interface is selected (P/S=”L”),
D0 and D1(SCL, SDA) are used as serial interface pins
and various sets are taken by serial interface use mode of
D2, D3, D4.
SDA : serial data input pin
SCL : data transfer clock
EXCS : extension chip selection I/O pin
SMODE : serial transfer mode setting input pin
SPOL : RS polarity selection pin when 3 line serial interface is
selected.
SDA data is shifted at the rising edge of SCL
Internal serial/parallel conversion into 8-bit data occurs at the
rising edge of 8th clock of SCL.
Set to “L” after data transfer or during non-access time
50,51,52,53
54,55,56,57
D8,D9,D10,D11,
D12,D13,D14,D15
I/O
Connect to data bus to MPU with 8bit bi-directional bus.
Used as MSB 8bit data bus in the 16bit data RAM transfer
mode
Set to “L” or “H” when not used.
25
CS
I
Chip selection pin.
Data in-out is possible when CS = “L”.
Input data selection pin.
Distinguish bus data from CPU whether instruction or display
data.
RS H L
class
instruction
display data
26
RS
I
38
RD (E)
I
<80 series CPU interface (P/S=”H”,SEL68=”L”)>
RD signal connection port of 80 series CPU.
Data bus goes to output state at RD = “L”.
<68 series CPU interface (P/S=”H”,SEL68=”H”)>
Enable signal connection port of 68 series CPU.
Active status when this signal is at “H”.
<80 series CPU interface (P/S=”H”,SEL68=”L”)>
WR signal connection port of 80 series CPU.
Active at “L” and data bus signal is taken at the rising edge
of WR.
<68 series CPU interface (P/S=”H”,SEL68=”H”)>
Read write control signal , R/W connection port of 68-
series MPU.
R/W
H
L
status
read
write
37
WR (R/W)
I
Page 12
HM17CM256
- 12 -
■
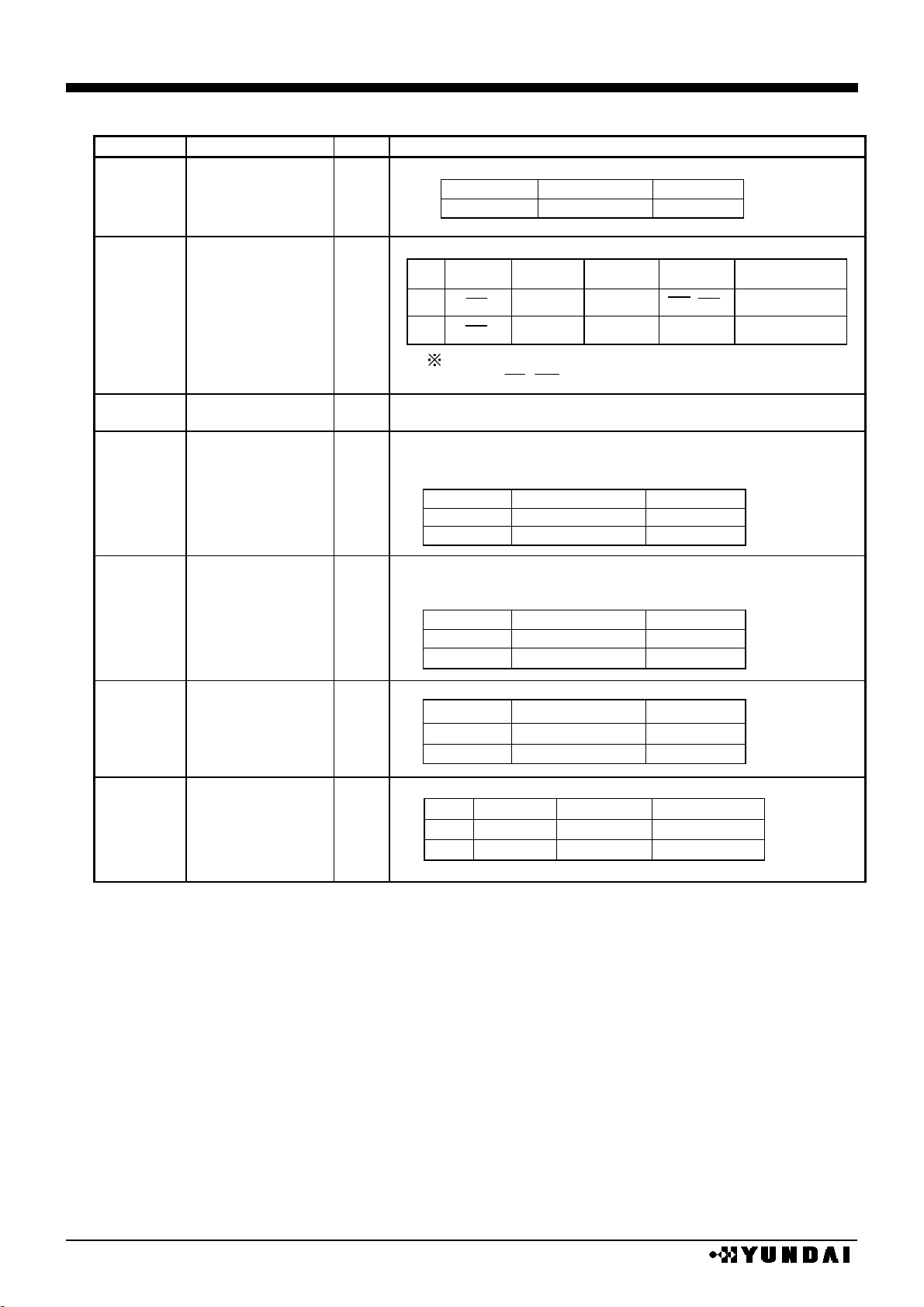
PIN DESCRIPTION 3
No.
NAME
I/O
FUNCTION
CPU interface selection port
SEL68
H
L
status
68 series
80 series
33
SEL68
I
Serial / parallel interface selection port
P/S
chip
select
data/
command
data
read/
write
serial clock
H
CS
RS
D0~D7
RD, WR
-
L
CS
RS
SDA(D1)
write only
SCL (D0)
32
P/S
I
P/S = “L” :serial interface selection ,D15~D5 goes to Hi-Z
state. Fix RD, WR to “H” or “L”.
20
TEST
I
Test port.
Fix to ”L”.
Latching signal pin of display data.
Display line counter is counted up at the rising edge and LCD
driving signal is generated at the falling edge
M/S
status
CL
H
master
output
L
slave
input
61
CL
I/O
LCD synchronous signal (first line marker) I/O pin.
Display start address is loaded in the display line counter at
FLM = “H”.
M/S
status
FLM
H
master
output
L
slave
input
62
FLM
I/O
Alternated display signal of LCD driver output I/O pin.
M/S
status
FR
H
master
output
L
slave
input
63
FR
I/O
Master / slave mode selection pin
M/S
mode
oscillator
Power supply
H
master
enable
enable
L
slave
disable
disable
30
M/S
I
Fix to “H” or “L” according to operating mode.
X
Page 13
HM17CM256
- 13 -
PIN DESCRIPTION 4
No.
NAME
I/O
FUNCTION
Segment drive port
Segment output from display RAM data
mode
Non-lighted
lighted
Normal
0
1
Reverse
1
0
The output level is selected among V
LCD
, V2, V3, VSS by the
combination of FR signal and RAM data
(B/W mode)
FR signal
display RAM data
Normal mode
V2
V
LCD
V3
VSS
Reverse mode
V
LCD
V2
VSS
V3
174~557
SEGA0~SEGA
127
,
SEGB0~SEGB
127
,
SEGC0~SEGC
127
O
164~169,
562~567
SEGSA0~SEGSA3,
SEGSB0~SEGSB3,
SEGSC0~SEGSC3
O
Dummy segment driver output
Located at both side of segment drivers, used for edge
display.
Common driver output
The output level is selected among V
LCD
, V1, V4 and VSS by
the combination of FR and scan data.
data
FR
Output level
H H
VSS
L H V1
H L
V
LCD
L L V4
162~137,
132~119,
568~594,
3~15
COM0~COM79
O
163
COMI0
O
Common drive output for icon display
16
COMI1
O
Common drive output for icon display
65,
66
OSC1,
OSC2
I
O
External reference clock input pin
Open when using internal oscillator clock or used as slave
device.
In this case, OSC1 goes to VSS level.
Connect external oscillating source to OSC1 port or connect
resistor between OSC1 and OSC2 when using external
oscillator.
Input / output pin for display timing clock
Output clock from master device is applied to slave chip
through CLK pin when used as master / slave mode.
M/S
mode
CLK
H master
output
L slave
input*
64
CLK
I/O
*input from master chip’s CLK output
(port No. 1,2,133,134,135,136,170,171,172,173,558,559,560,561,595,596 is dummy port.)
Page 14
HM17CM256
- 14 -
■
FUNCTION DESCRIPTION
(1) CPU interface
(1-1) Selection of interface type
HM17CM256
receives data through 8 bit parallel I/O(D0~D7)
16 bit parallel I/O(D0~D15) or
divided into serial data input (SDA, SCL). Parallel or serial selection is decided by P/S pin setting.
Parallel or serial selection is possible as following table.
Reading out from internal register or RAM is not possible at serial interface mode.
TABLE
P/S
Type
CS
RS
RD
WR
SEL68
SDA
SCL
data
H
Parallel input
CS
RS
RD
WR
SEL68
D0~D7 (D0~D15)
L
Serial input
CS
RS - -
-
SDA
SCL
-
caution 1) “-” mark item : Fix to ”H” or ”L”
(1-2) Parallel input
In the parallel interface mode selected by P/S port, parallel data is transferred from the
8bit/16bit MPU through data bus. SEL68 port setting makes 80-series or 68-series interface
selection
TABLE
SEL68
CPU type
CS
RS
RD
WR
data
H
68 series CPU
CS
RS
E
R/W
D0~D7 (D0~D15)
L
80 series CPU
CS
RS
RD
WR
D0~D7 (D0~D15)
(1-3) Data identification
Combinations of RS, RD, and WR signals identify contents of 8bit data bus.
TABLE
68 series
80 series
RS
R/W
RD
WR
FUNCTION
1 1 0
1
Read out from internal register
1 0 1
0
Write in to internal register
0 1 0
1
Read display data
0 0 1
0
Write display data
(1-4) Serial interface
2 types of serial interface (3 line type mode, 4 line type mode) are available by selecting
SMODE pin.
TABEL
SMODE
Serial interface mode
H
3 line type
L
4 line type
Y
Page 15
HM17CM256
- 15 -
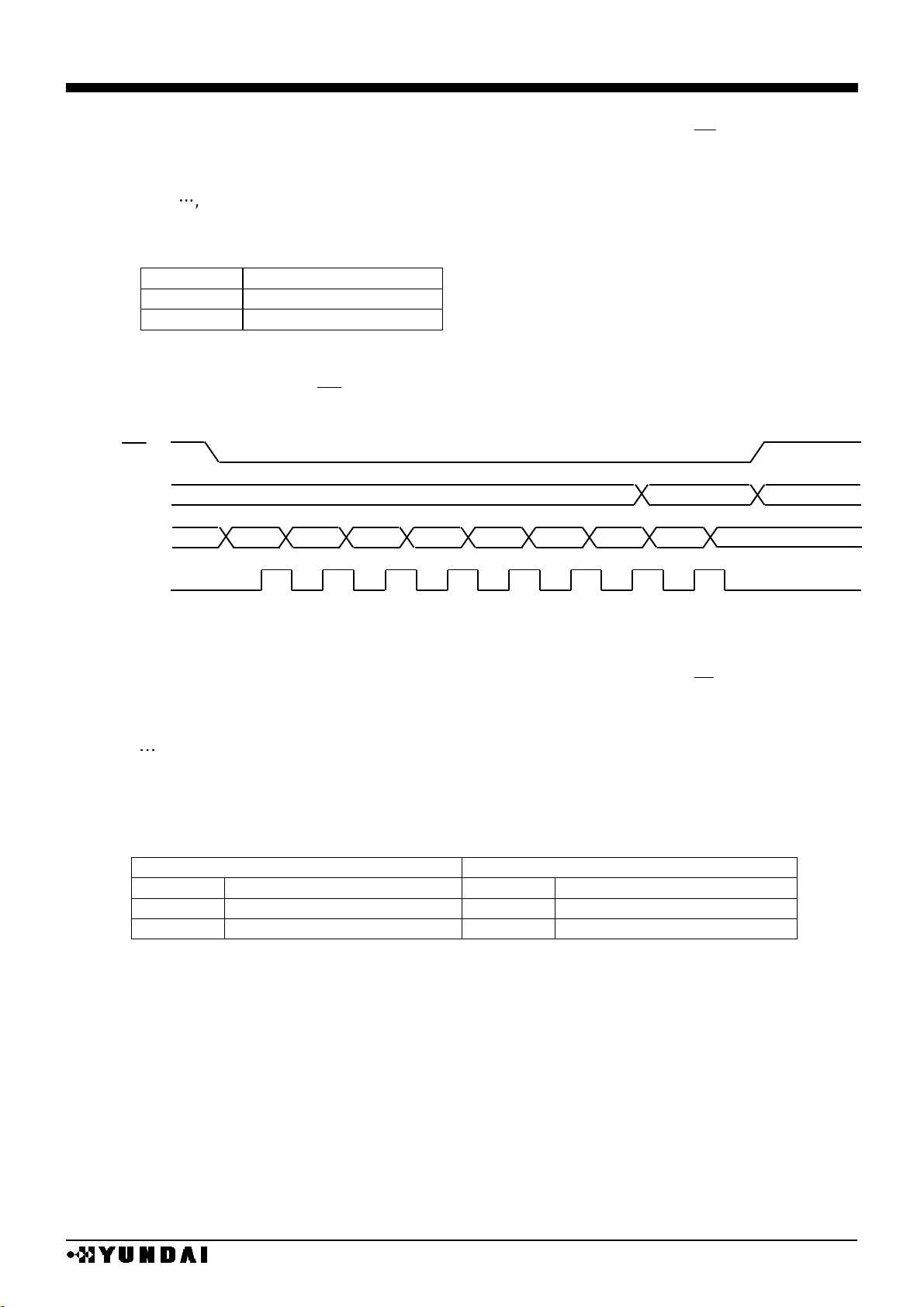
(1-5) 4 line type serial interface
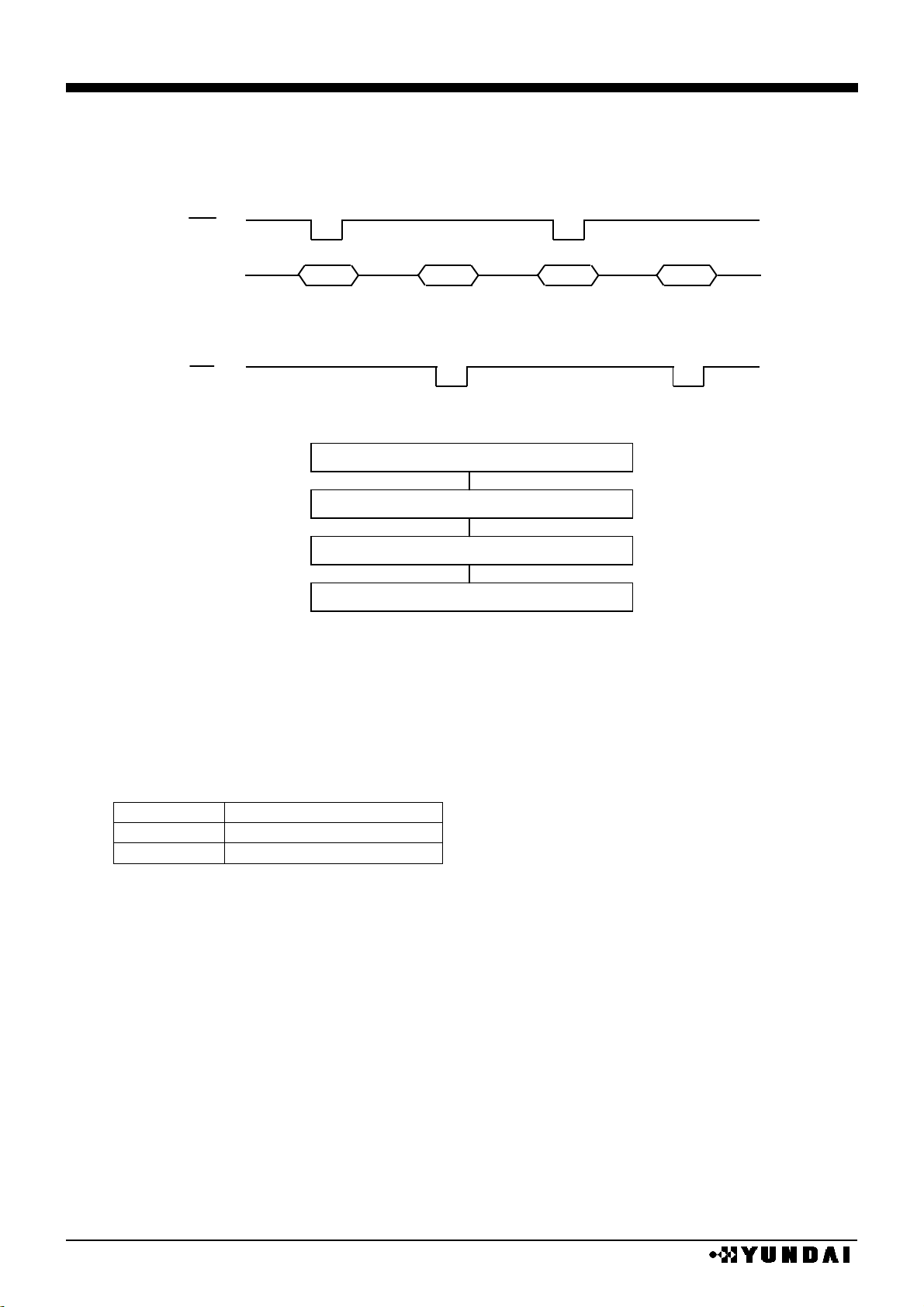
4 line serial interface by SDA and SCL is possible at chip selection state (CS=”L”)
When chip is not selected, internal shift register and counter are reset to initial value.
Serial input data from SDA are latched at the rising edge of serial clock (SCL) in the sequence
of D7,
, D1, D0 and converted into 8-bit parallel data at the rising edge of 8th serial clock.
Serial data (SDA) are identified to display data or command by RS input.
TABLE
RS
Data contents
H
command
L
Display data
Make serial clock (SCL) “L” at the non-access period and after 8bit data transfer.
SDA and SCL signals are sensitive to external noise. To prevent mal-function, chip selector
state should be released (CS = “H”) after 8bit data transfer as shown in the following figure.
4 line serial interface
(1-6) 3 line type serial interface
3-line serial interface by SDA and SCL is possible at chip selection state (CS=”L”)
When chip is not selected, internal shift register and counter are reset to initial value.
Input data from SDA are latched at the rising edge of serial clock (SCL) in the sequence of RS,
D
7
, ,D1, D0, and converted to 8bit parallel data and handled at the rising edge of 9th serial
clock.
Serial data (SDA) are identified to display data or command by RS bit data at the rising of first
serial clock (SCL) and state of command data bit polarity shift pin (SPOL).
TABLE
SPOL=L
SPOL=H
RS
Data identify
RS
Data identify
L
Display data
L
command
H
command
H
Display data
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
VALID
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
8
CS
RS
SDA
SCL
Z
[
Page 16
HM17CM256
- 16 -
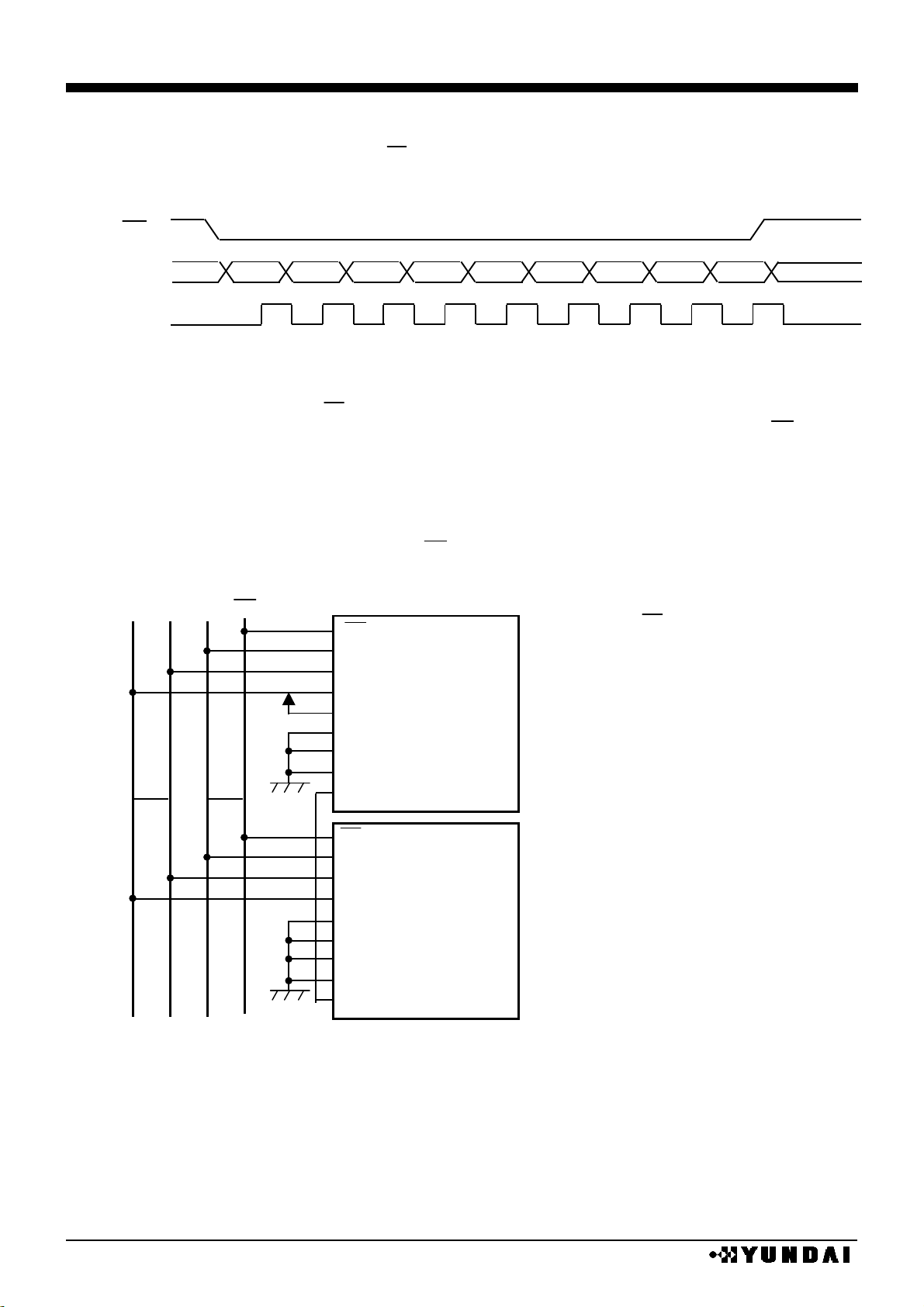
Serial clock (SCL) should go to “L” at the non-access period and after 9bit data transfer.
SDA and SCL signals are sensitive to external noise. To prevent miss operation chip
selector state should be released (CS = “H”) after 9bit data transfer as shown in the following
figure
.
3line serial interface
(1-7) One systematization of CS when serial interface is selected
In the multi-chip operation (master/slave) mode with serial I/F connection, one CS signal
controls two chips to reduce control signal.
Connect extended chip selection port (EXCS) of master chip to EXCS port ( input at slave
device and output at master device mode ) of slave chip.
When EXCS is “L”, master chip cannot accept command except for EXCS control; at this
point, only slave chip can be controlled.
Slave device control is possible when CS = “L” period within EXCS = “L” state.
RS
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
CS
SDA
SCL
D0
9
SDA
CS
SCL
RS
M/S
P/S
SMODE
SPOL
EXCS
(MASTER)
SDA
CS
SCL
RS
M/S
P/S
SMODE
SPOL
EXCS
(SLAVE)
CS
SDA
SCL
RS
EXCS: expand CS signal ( input port )
Master device : output port
Slave device : input port
(input port)
P/S=0: serial I/F
P/S=1: parallel I/F
P/S: parallel . serial selection port
(input port)
M/S=0: slave operation
M/S=1: master operation
M/S: master . slave selection port
(input port)
SMODE=0: 4 line serial I/F
SMODE=1: 3 line serial I/F
SMODE: serial I/Fmode selection port
(input port)
Access display RAM at SPOL=0:RS=0
Access display RAM at SPOL=1:RS=1
SPOL:command data bit polarity selection port
At 3 line serial I/F mode
Page 17
HM17CM256
- 17 -
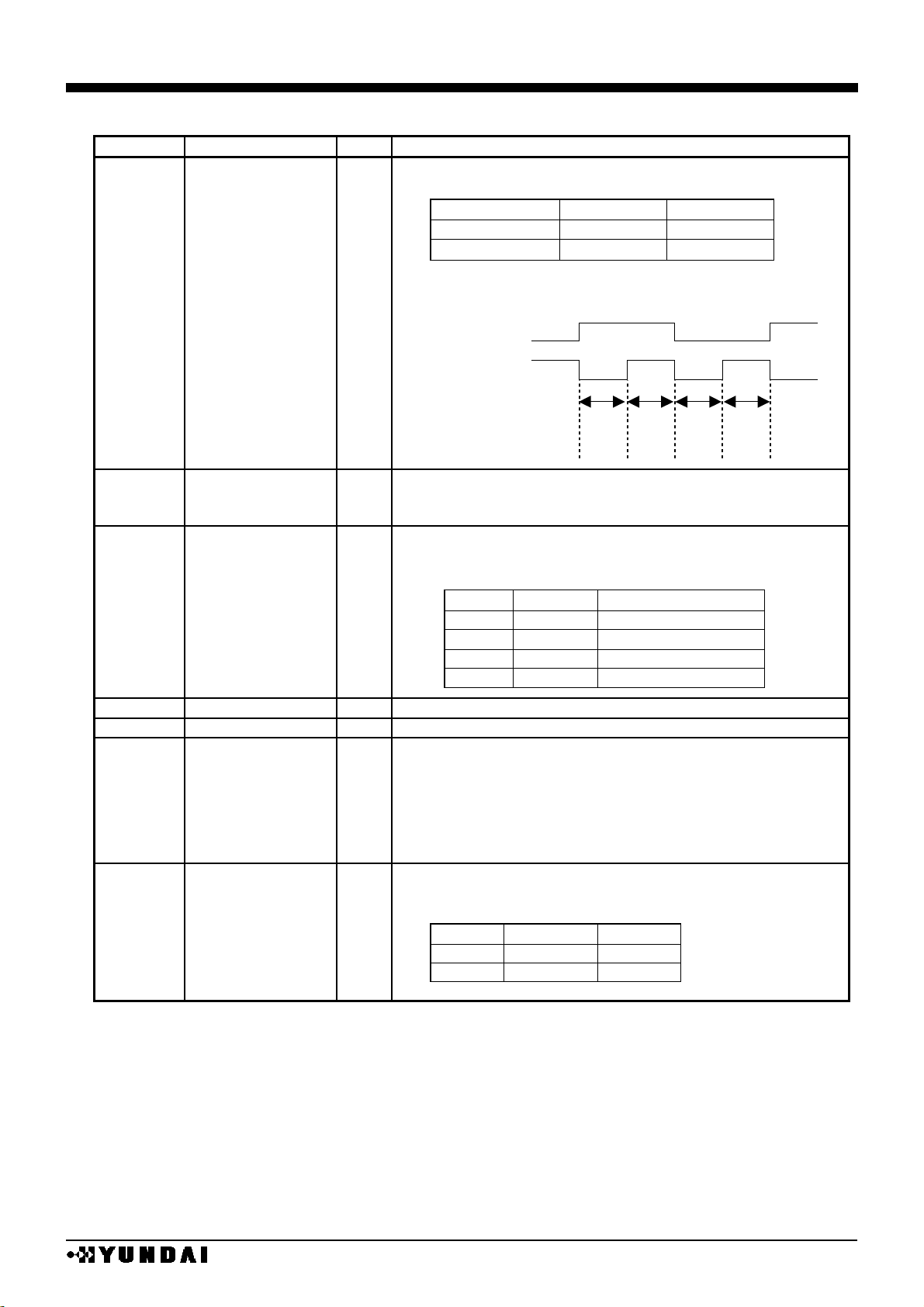
(2) DDRAM and internal register access
DDRAM and internal register are accessed by data bus D0~D7(D0~D15), chip select pin (CS),
DDRAM / register select pin (RS), read / write control pin (RD) or WR pin.
When CS=“H”, it is in non-selective state and DDRAM and internal register access is impossible.
During access, Set CS=“L”.
Access selection to DDRAM or internal register is controlled by RS input.
TABLE
RS
Data contents
L
Display RAM data
H
Internal command register
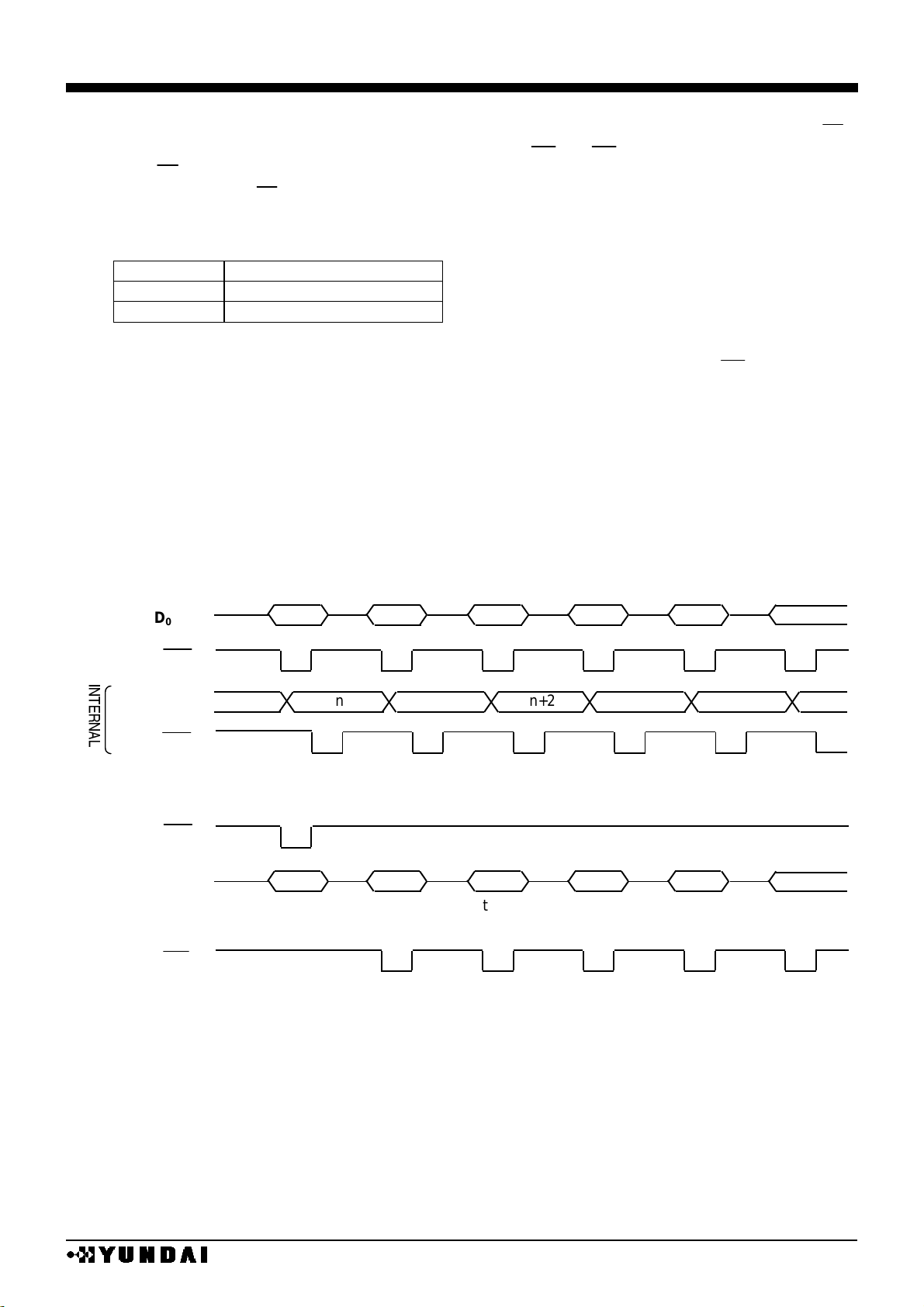
Write process starts after address setting and then the data on the 8bit data bus D0~D
7
or 16bit
data bus D0~D15 will be written in by CPU. The data is written at the rising edge of WR (80 series) or
falling edge of E (68 series).
Internally, bus holder data is processed to data bus and data are written to bus holder from CPU
until next cycle.
After address setting, data of assigned address are read at the 1st and 3rd clock, which means it
needs dummy read at the 2nd clock.
There are rules at reading data out of display RAM, after address setting, the data of assigned
address is shown directly after the end of the read command, so pay attention that assigned data is
available at 2nd timing step.
In other words, 1 cycle dummy read is needed after address setting and write cycle.
DATA WRITE IN OPERATION
DATA READ OUT OPERATION
caution) When 16 bit mode, do write in and read out by 16 bit not only RAM access but also command
setting.
n
n+2
D0~D15
WR
BUS HOLDER
WR
n
n+1
n+2
n+3
n+4
n+1
n+3
n+4
D0~D7(D0~D15)
RD
n n n+1
n+2
WR
address set
n
dummy
read
data read
n address
data read
n+1 address
data read
n+2 address
\]^
_`
]a
b
Page 18
HM17CM256
- 18 -
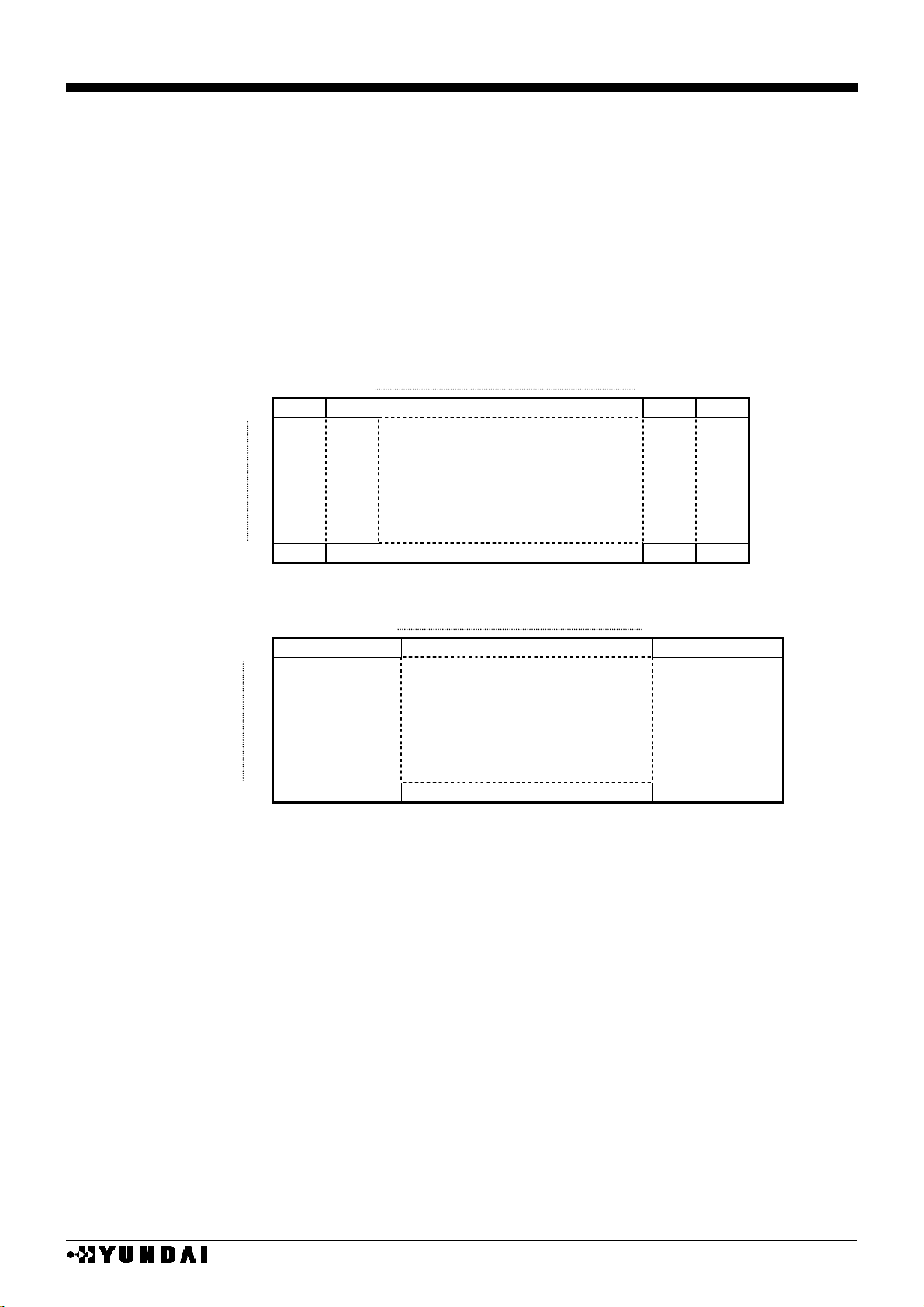
(3) Read out of internal register
Read out is possible not only from DDRAM, but also from the internal register. Addresses for
read (0~FH) are allocated in each register.
Read out is executed after writing read-out register address to internal register.
Internal register read out sequence
When register is read out, upper 4 bit data are “1111”.
Non-used bits of active registers are “0”.
When non-used registers are read out, upper 4 bits are “1111” and lower 4 bits are “0000”.
(4) 16 bit data access to DDRAM
It is possible to write in DDRAM by 16-bits access with the data of 16 bits data bus D0~D15.
16 bits data access mode is possible by setting the value of WLS register to “1”.
TABEL
WLS
Acess mode
L
8 bit
H
16 bit
Each command should be set to 8-bits(D0~D7) as well as to 16-bit access mode.
16-bit access is available at display RAM access.
(5) Display start line register
When displaying the DDRAM data, it is the contents of Y address register that is corresponding to
display start line.
The data of Y address is displayed on the display start line depending on the value of the shift
command register and the display start line register.
The data of this register are preset to the display line counter per FLM signal transition.
Line counter is counted up in synchronization with CL input and generates line address that read
out 384bit data from DDRAM to LCD driver circuit.
D0~D7
M
N
WR
Address set
for
register read
Internal
register read
Address set
for
register read
Internal
register read
m
n
RD
RE register set:100
Internal register read address set
set RE of register to be read out
Internal register read
Page 19
HM17CM256
- 19 -
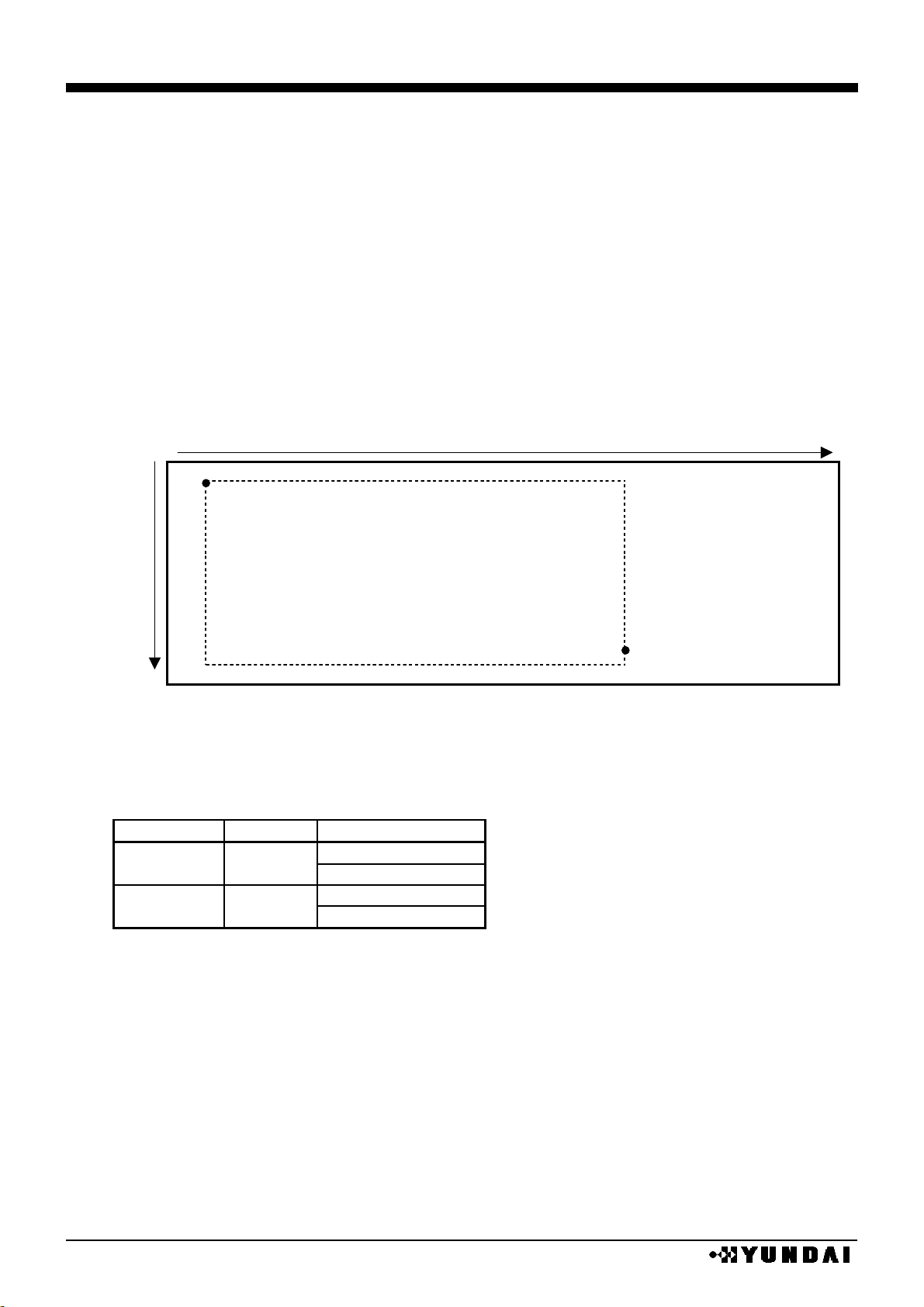
(6) DDRAM addressing
This IC includes display memory Bit mapped that is composed of 1024 bit of X direction
(8bit×128) and 82bit of Y direction.
In gray mode, neighboring 3-bit data or 2-bit data are displayed by segment driver with 8 grays or
4 grays, respectively.
3 outputs of segment driver compose 1 pixel of RGB and 128×82 pixels are displayed with 256
color (8gray×8gray×4gray).
Address area of X direction is varied according to accessed data length. The area of X direction
is 0H~7FH at 8bit access mode and 0H~3FH at 16bit access mode.
•
8BIT access
X-address
0H
1H 7EH
7FH
0 H
8bit
8bit 8bit
8bit
Y-address
51H
8bit
8bit 8bit
8bit
•
16 BIT access
X-address
0H
3FH
0 H
16bit
16bit
Y-address
51H
16bit
16bit
In the Black & white mode, the MSBs of 3 bit and 2 bit corresponding with RGB are used to
display data. And so, 128x82 dot gray display or 384 x 82 B/W mode display is possible.
Display RAM is accessed with X address and Y address from CPU by 8 bit or 16 bit unit.
X address and Y address can be increased automatically by setting status of control register.
The address is increased per every read and write of display RAM by CPU. ( Please see detail
description at command function.)
X direction is selected by X address and Y direction is selected by Y address. Please do not set
the address on non-effective area and it is forbidden to set address on outside area in each case.
384bit display data of Y direction are read out to display latch at rising edge of CL signal per 1 line
cycle and this data comes out from display latch at falling edge of CL signal.
Display start line address register is preset to line counter at “H” state of FLM signal which changes
per one frame cycle and the address is counted up with synchronized CL input.
Display line address counter is synchronized by timing signals of LCD driver, and it operates
independently with X, Y address counters.
Page 20
HM17CM256
- 20 -
(7) Window address assign of display RAM
This IC can be accessed to display RAM by window area designation in addition to access to
display RAM designated by X and Y address.
Through address space of all display address, specific area of RAM can be accessed by
designated two points.
The start point of two point addresses is assigned by normal X address and Y address register and
the end point of them is done by X end address and Y end address register value. Designated
inner addresses depend on WLS bit.
Read modified write action can be taken by AIM=“1”.
In case of using window area accessing mode, you must set start point X address, Y address in
sequence and end point X address, Y address in sequence after executing Win command (WIN=“1”,
auto increase mode AXI=“1”, AYI=“1”) and then access to Display RAM.
And set start point and end point not to be designated to access the outside of available address
area. Address set value should be taken to set AX ≤ EX ( end point of X address ) and AY≤EY
( end point of Y address ).
X direction
(X, Y)
address designation
end address designation
Window display area
(X, Y)
All display RAM area
(8) display RAM data and LCD
Display RAM data related with one dot of LCD is dependent on REV register. Normal display and
reverse display by REV register are set up as follows.
TABLE
REV
Display
RAM data
0
L
normal
1
0
H
reverse
1
(9) Segment display output order/reverse set up
The order of display outputs, SEGA0, SEGB0, SEGC0 to SEGA
127
, SEGB
127
, and can be reversed
by reversing access to display RAM from MPU by using REF register, lessen the limitation in placing
IC when assembling an LCD panel module.
Y direction
Page 21
HM17CM256
- 21 -
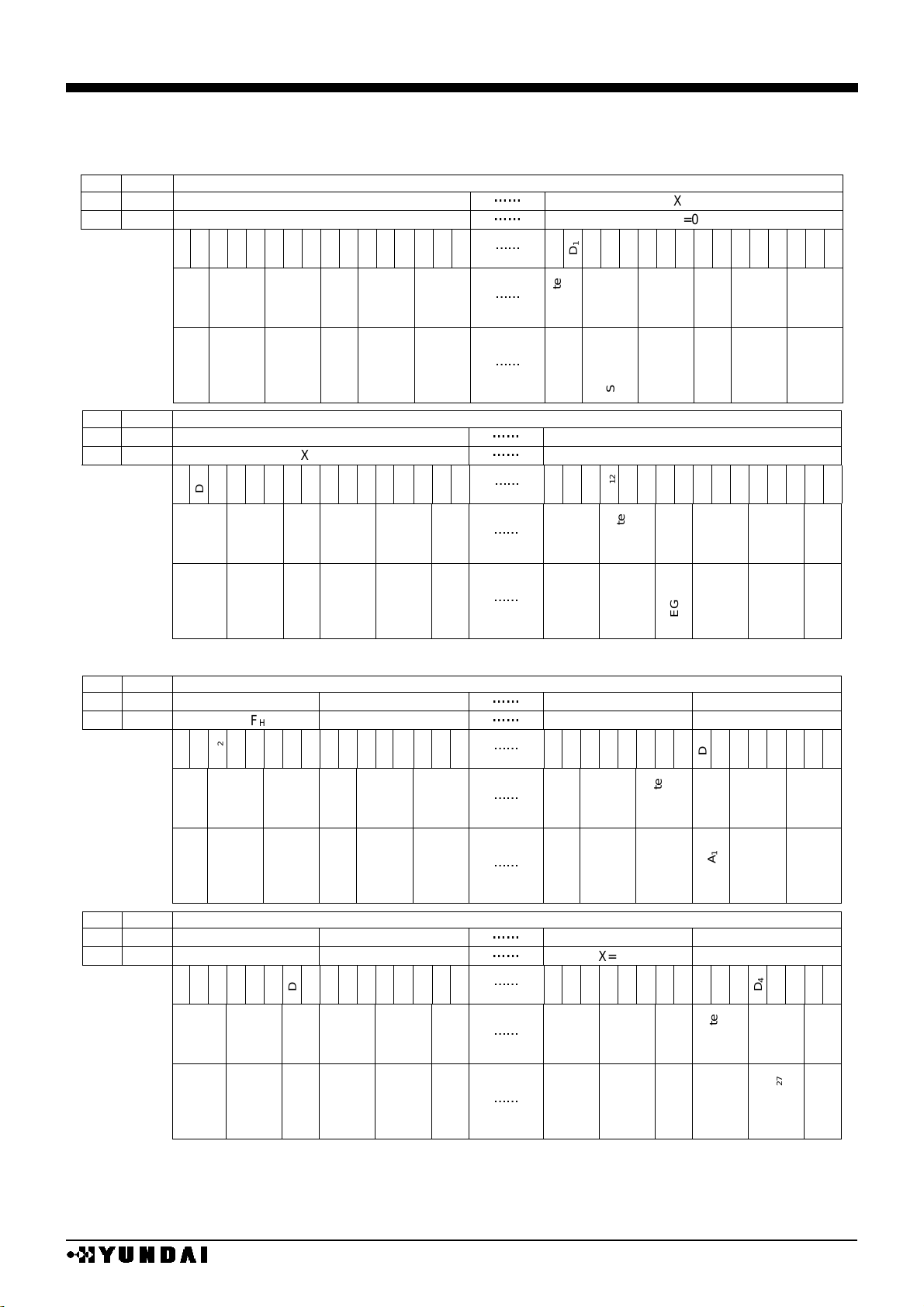
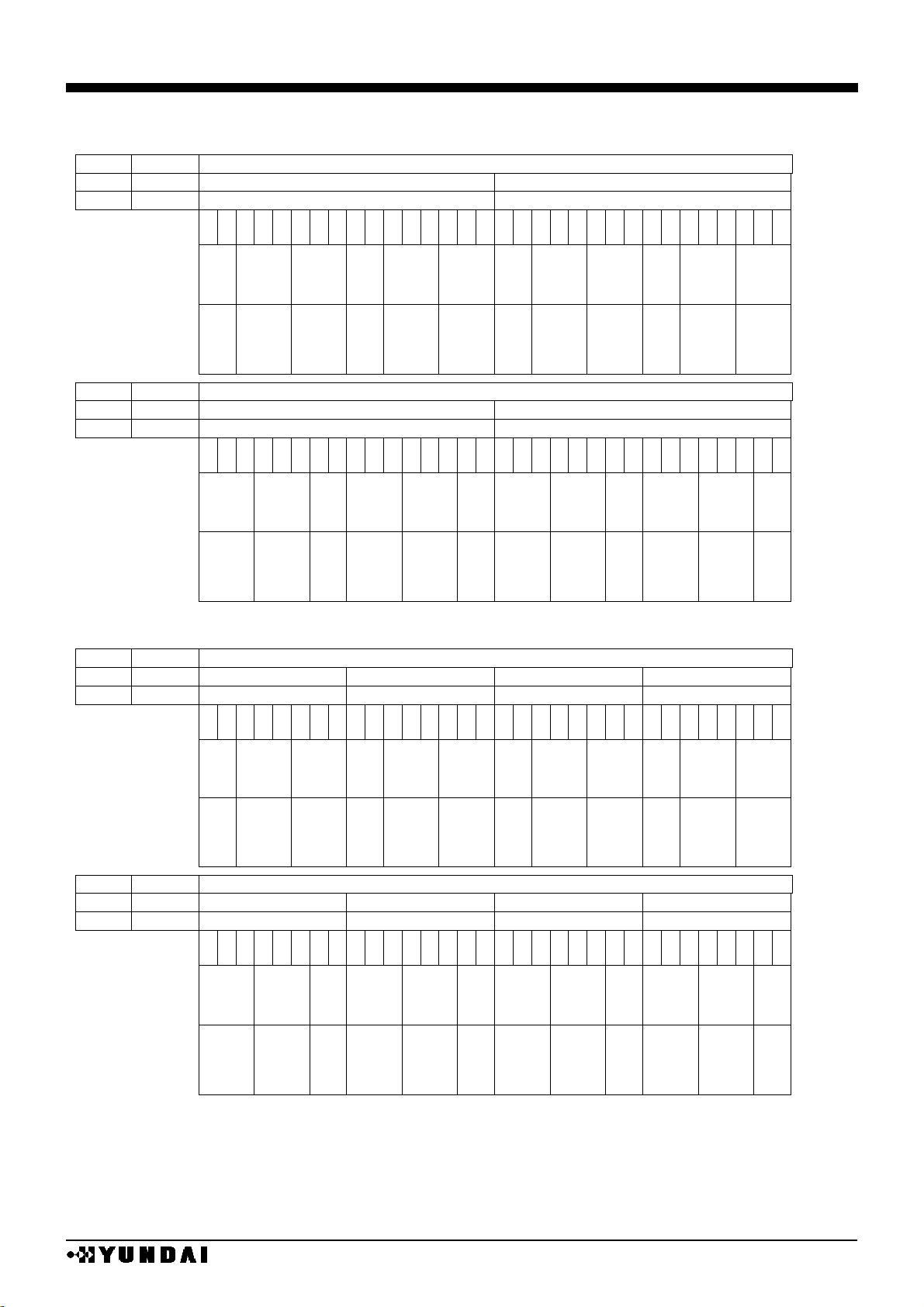
(10) Relation between Display RAM and address
•
RAM address and bitmap
COLOR / 16 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0
0
X=00H
X=3FH
1
1
X=3FH
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
SEGA0
SEGB0
SEGC0
SEGA1
SEGB1
SEGC1
SEGA126
SEGB126
SEGC126
SEGA127
SEGB127
SEGC127
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0
1
X=00H
X=3FH
1
0
X=3FH
X=00H
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
COLOR / 8 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0 0 X=00H
X=01H
X=7EH
X=7FH
1 1 X=7FH
X=7EH
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
palette
A
palette B palette
C
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0 1 X=00H
X=01H
X=7EH
X=7FH
1 0 X=7FH
X=7EH
X=01H
X=00H
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
palette C palette
B
palette
A
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
c c
c c
d d
d d
d d
e e
e e
d d
d d
d d
e e
e e
d d
d d
d d
e e
e e
d d
d d
d d
Page 22
HM17CM256
- 22 -
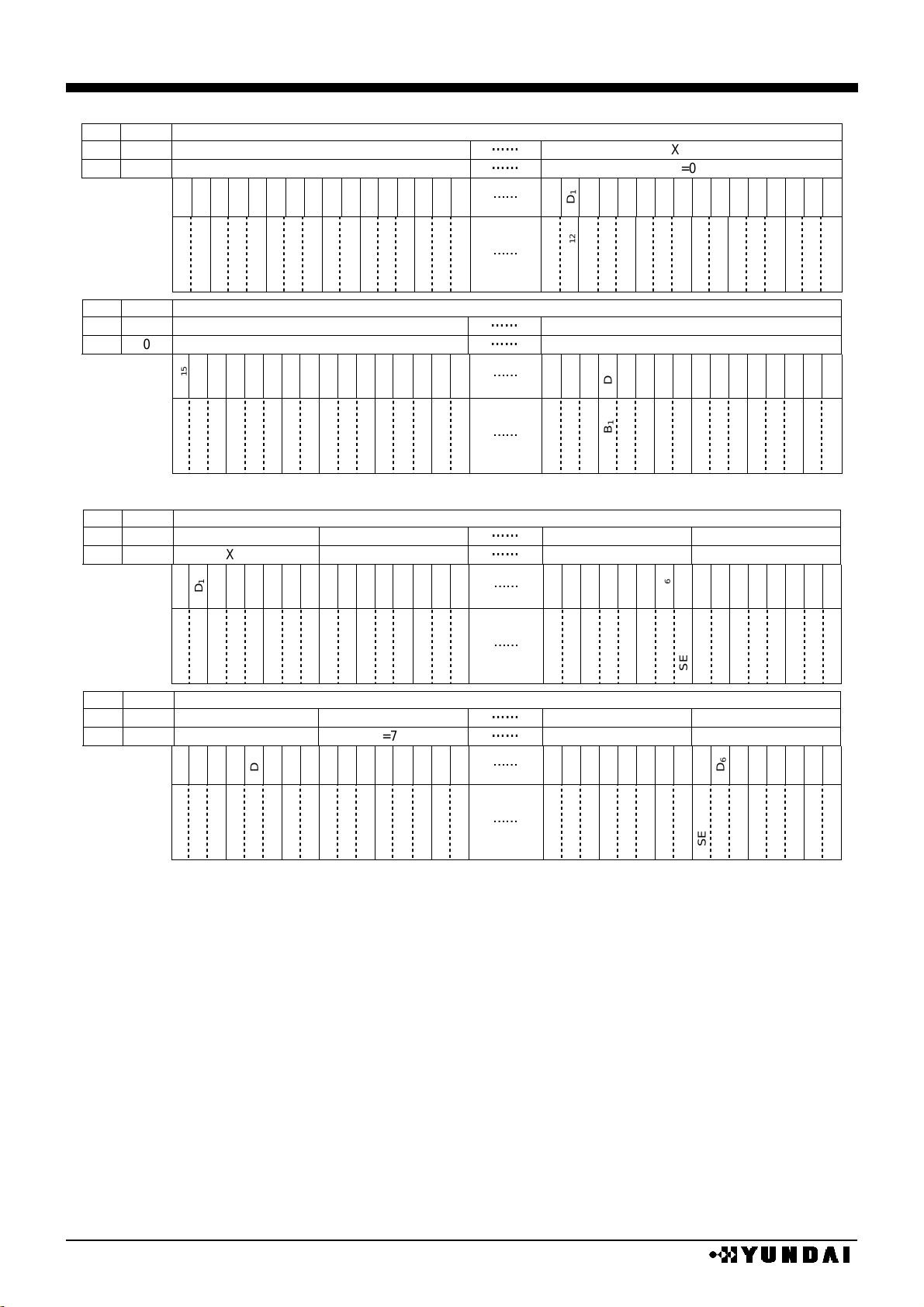
BLACK & WHITE / 16 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0
0
X=00H
X=3FH
1
1
X=3FH
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0
1
X=00H
X=3FH
1
0
X=3FH
X=00H
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
BLACK & WHITE / 8 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0 0 X=00H
X=01H
X=7EH
X=7FH
1 1 X=7FH
X=7EH
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
REF
SWAP
X address / bit / segment assign
0 1 X=00H
X=01H
X=7EH
X=7FH
1 0 X=7FH
X=7EH
X=01H
X=00H
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
SEGA
0
SEGB
0
SEGC
0
SEGA
1
SEGB
1
SEGC
1
SEGA
126
SEGB
126
SEGC
126
SEGA
127
SEGB
127
SEGC
127
f f
f f
g g
g g
f f
f f
g g
g g
f f
f f
g g
g g
f f
f f
g g
g g
Page 23
HM17CM256
- 23 -
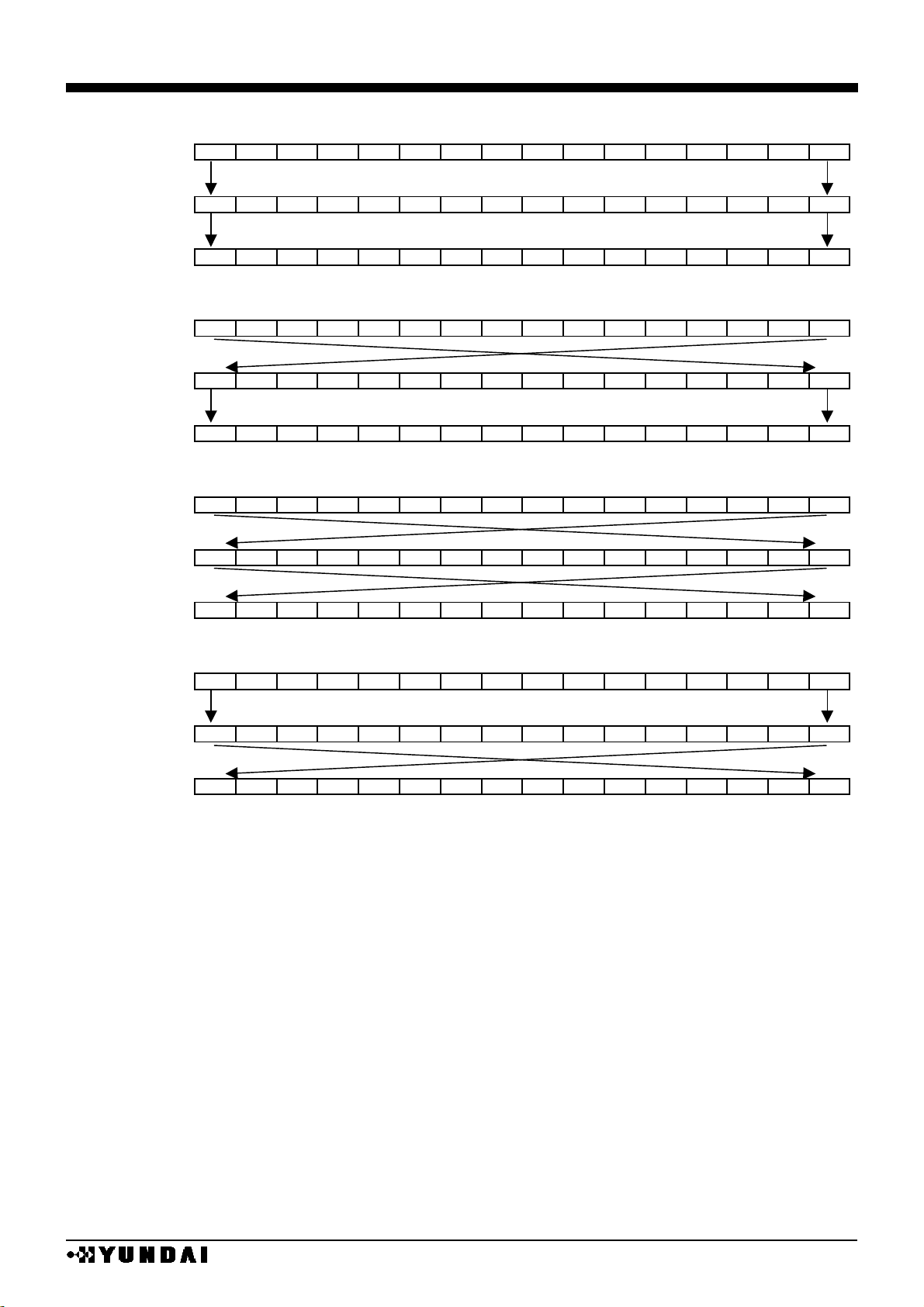
•
WRITE IN / READ IN BITMAP ( 16 BIT MODE )
REF=0, SWAP=0
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
REF=0, SWAP=1
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
REF=1, SWAP=0
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
REF=1, SWAP=1
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
SEG8
SEG9
SEG10
SEG11
SEG12
SEG13
SEG14
SEG15
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
Page 24
HM17CM256
- 24 -
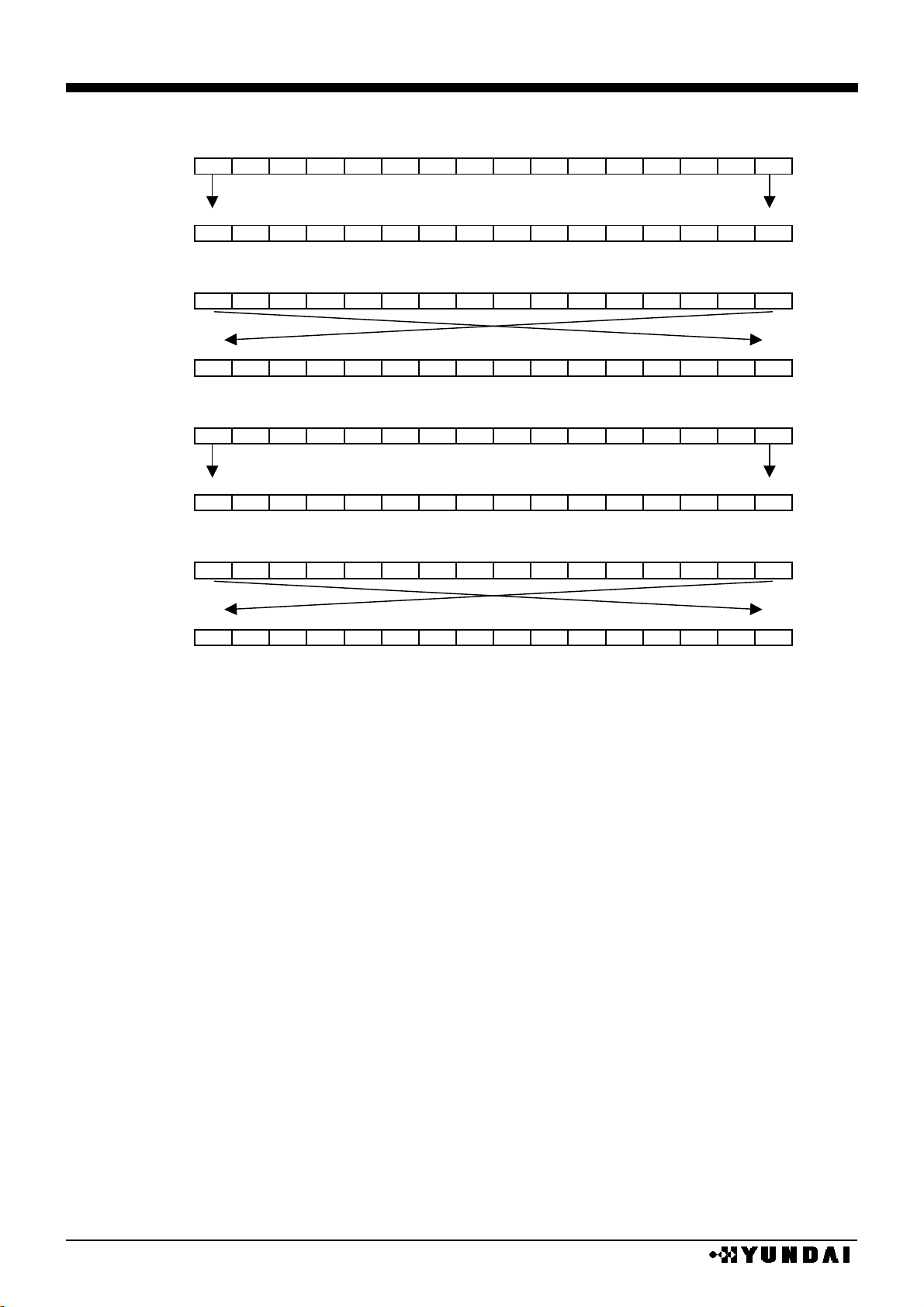
•
READ OUT AFTER WROTE IN DATA ( 16 BIT MODE )
REF=0, SWAP=0
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
REF=0, SWAP=1
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (4F27H)
REF=1, SWAP=0
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
REF=1, SWAP=1
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 (E4F2H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
0 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (4F27H)
Page 25

HM17CM256
- 25 -
•
WRITE IN / READ IN BITMAP ( 8 BIT MODE )
REF=0, SWAP=0
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
REF=0, SWAP=1
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
REF=1, SWAP=0
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
REF=1, SWAP=1
WRITE IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
SEGMENT DATA
SEG0
SEG1
SEG2
SEG3
SEG4
SEG5
SEG6
SEG7
READ IN DATA
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
Page 26

HM17CM256
- 26 -
•
READ OUT AFTER WROTE IN DATA ( 8 BIT MODE )
REF=0, SWAP=0
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
REF=0, SWAP=1
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (27H)
REF=1, SWAP=0
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
REF=1, SWAP=1
D15
D0
WRITE IN DATA
1 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 (E4H)
D15
D0
READ IN DATA
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 (27H)
Page 27
HM17CM256
- 27 -
•
DUMMY SEGMENT REGISTER ADDRESS AND BITMAP
COLOR / 16 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0
0
X=00H
X=01H
1
1
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0
1
X=00H
X=01H
1
0
X=01H
X=00H
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D1
D
0
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
COLOR / 8 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0 0 X=00H
X=01H
X=02H
X=03H
1 1 X=03H
X=02H
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
Palette
A
Palette B Palette
C
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0 1 X=00H
X=01H
X=02H
X=03H
1 0 X=03H
X=02H
X=01H
X=00H
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
Palette C Palette
B
Palette
A
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
Page 28
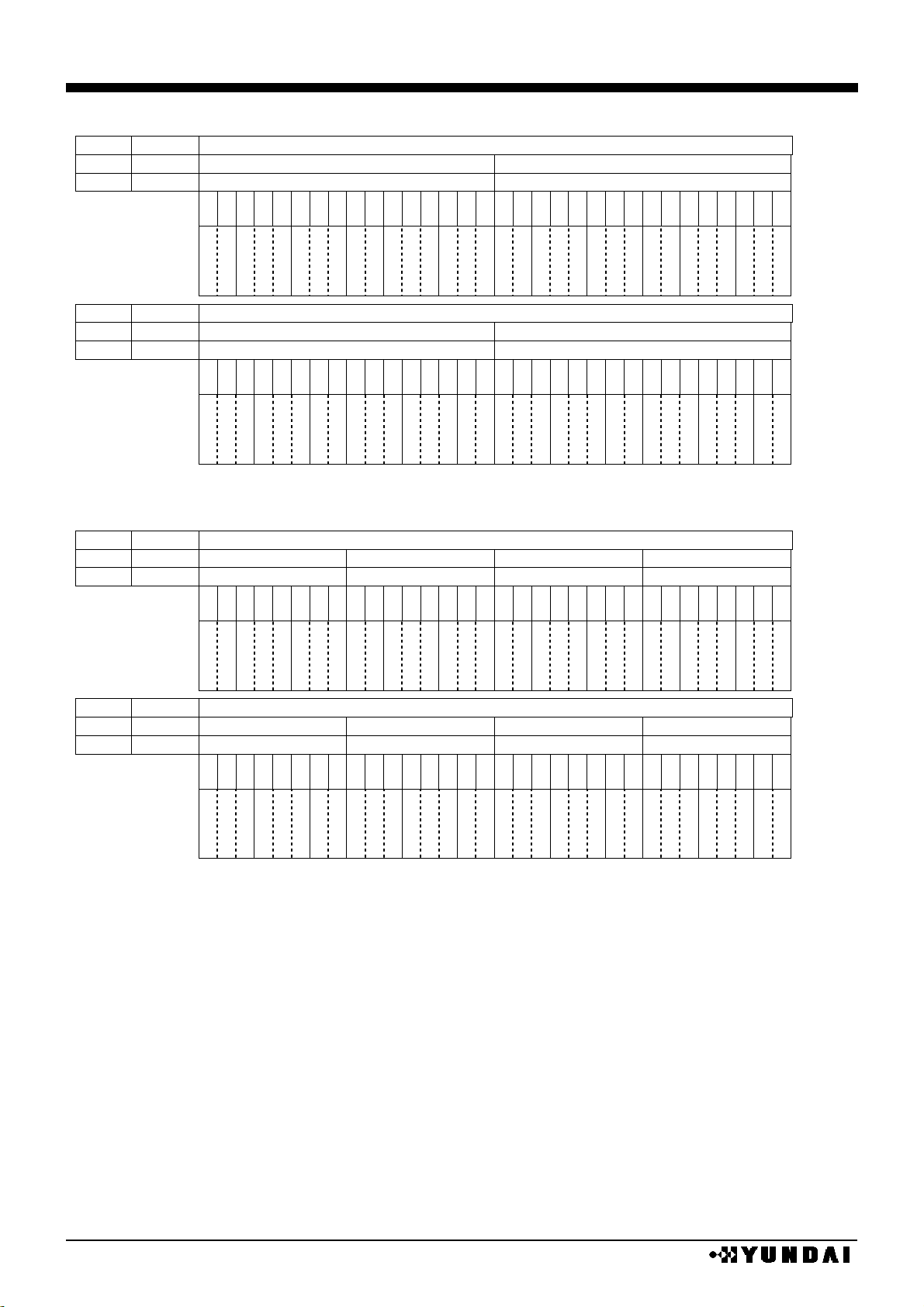
HM17CM256
- 28 -
•
BLACK 7 WHITE / 16 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0
0
X=00H
X=01H
1
1
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
8
D
9
D
10
D
11
D
12
D
13
D
14
D
15
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0
1
X=00H
X=01H
1
0
X=01H
X=00H
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
15
D
14
D
13
D
12
D
11
D
10
D
9
D
8
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
•
BLACK & WHITE / 8 BIT MODE
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0 0 X=00H
X=01H
X=02H
X=03H
1 1 X=03H
X=02H
X=01H
X=00H
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
D
0
D
1
D
2
D
3
D
4
D
5
D
6
D
7
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
REF
SWAP
X address / bit segment assign
0 1 X=00H
X=01H
X=02H
X=03H
1 0 X=03H
X=02H
X=01H
X=00H
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
D
7
D
6
D
5
D
4
D
3
D
2
D
1
D
0
SEGSA
0
SEGSB
0
SEGSC
0
SEGSA
1
SEGSB
1
SEGSC
1
SEGSA
2
SEGSB
2
SEGSC
2
SEGSA
3
SEGSB
3
SEGSC
3
Page 29
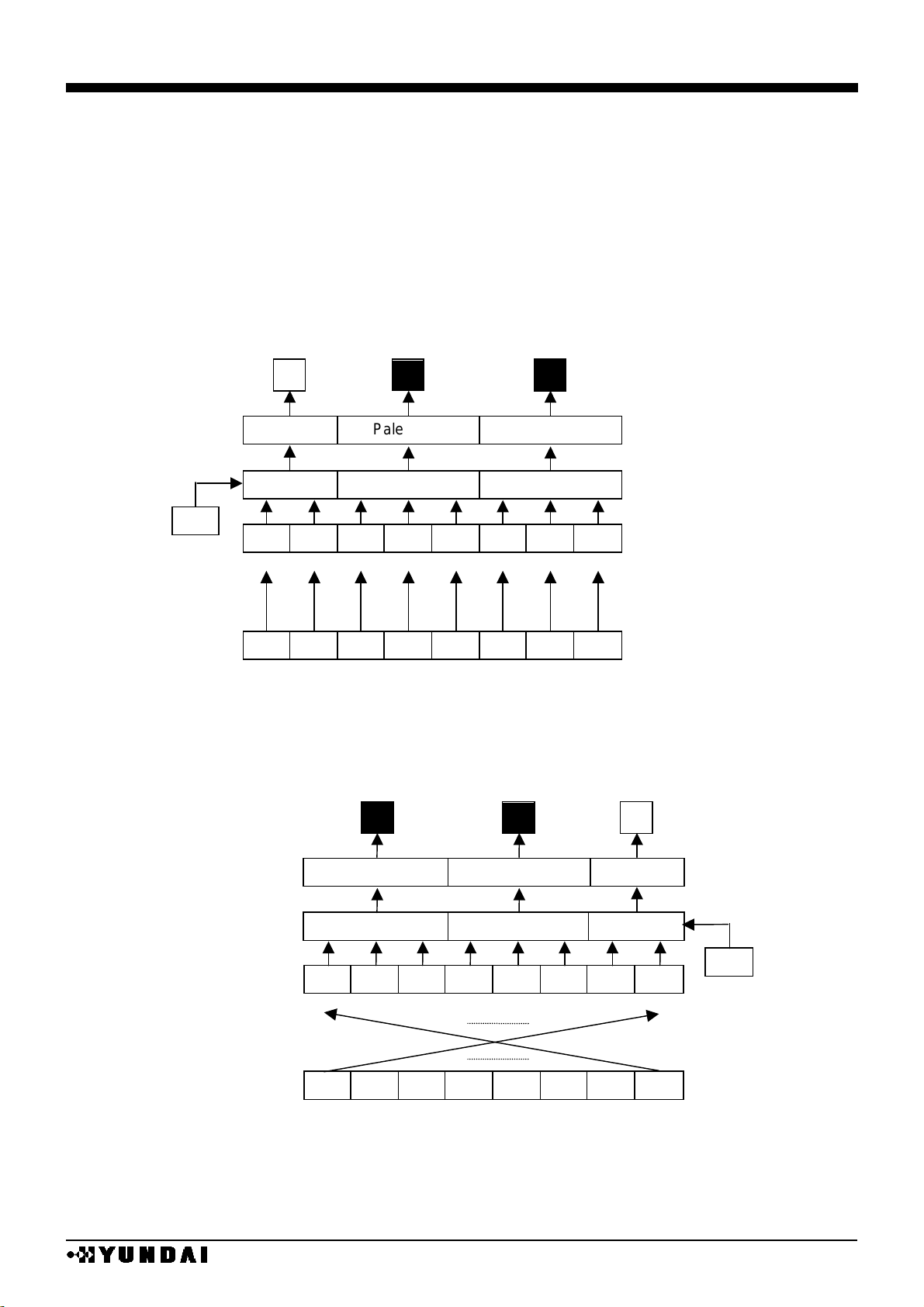
HM17CM256
- 29 -
(11) display data structure and gradation control
For the purpose of gradation control, information per pixel requires multiple bits. This IC has 3 bit
or 2 bit data per output to achieve the gradation display.
This IC is connected to an STN color LCD panel by three segment port units and one pixel consists
of three outputs of segment driver, and so 256 color ( 3 bits x 3 bits x 2 bits ) display on 128 x 82
pixels is realized.
Since one pixel data can be processed by one time access to memory, the data can be rewritten
fast and naturally.
The weight of each data bit is dependent on the status of SWAP register bit and REF register
when data is written to the display RAM.
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 0) or (1, 1)
notice) internal access X address :nH~7FH (access when REF=”0”)
:7FH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 1) or (1, 0)
notice) internal access X address :nH~7FH (access when REF=”0”)
:7FH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
SEGAi
SEGBi
Aj
Palette Bj
0
0
Palette Aj
1 0 0
SEGCi
Palette Cj
1 1 1
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7 0 GLSB circuit
Gradation palette
i=0~127
j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :nH
Gradation
control circuit.
Display RAM data
SEGAi
SEGBi
1 1 1 0 0
SEGCi
Palette Aj
Palette Bj
Palette Cj
1 0 0
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
Gradation palette
i=0~127
j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :nH
Gradation
control circuit
Display RAM data
0
GLSB circuit
h i j k
Page 30
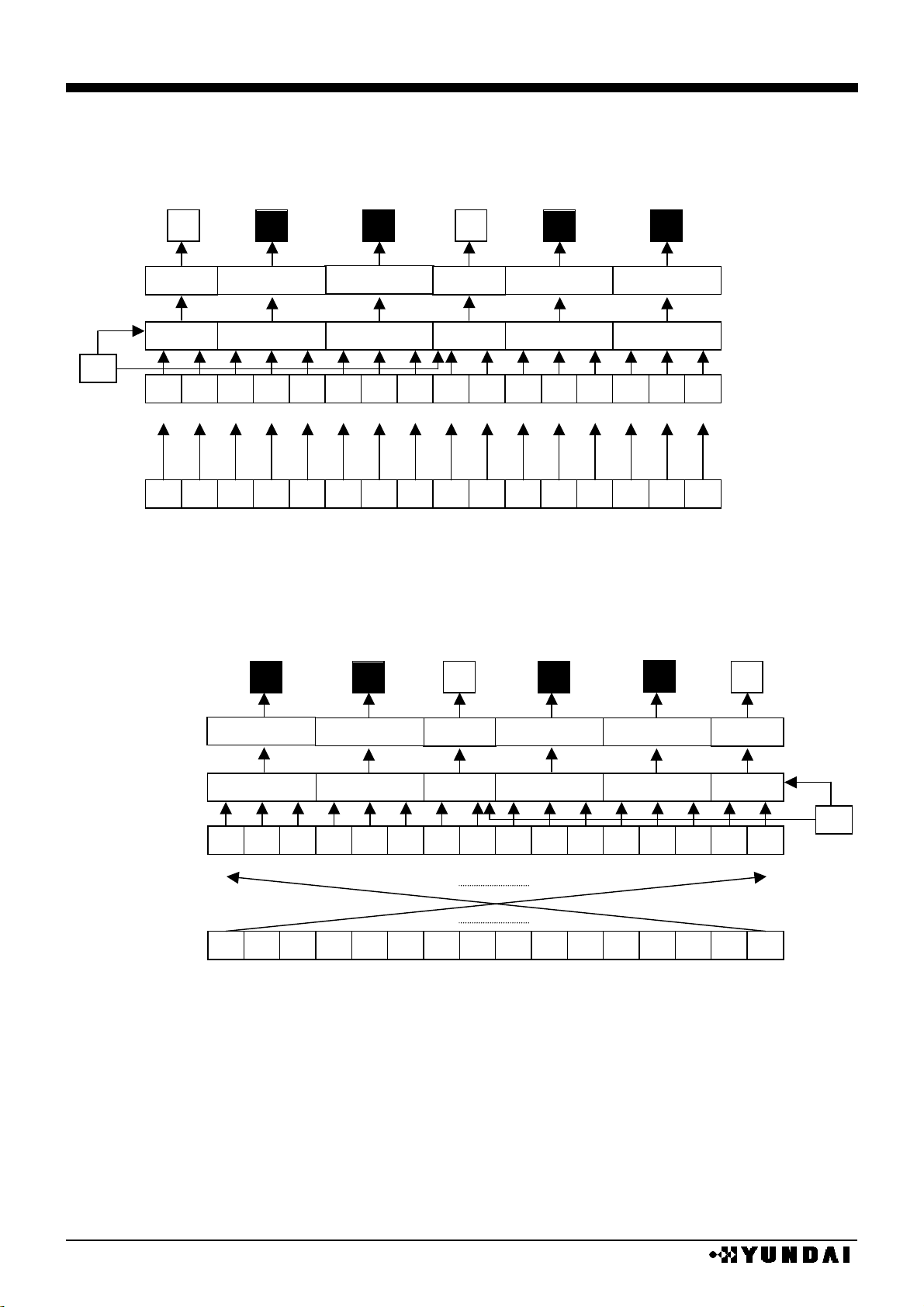
HM17CM256
- 30 -
When display RAM is accessed by 16 bit data width, the weight of each data bit is dependent on
the status of SWAP register and REF register, the same method as 8 bit access
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 0) or (1, 1)
notice) internal access X address :nH~3FH (access when REF=”0”)
:3FH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 1) or (1, 0)
notice) internal access X address :nH~3FH (access when REF=”0”)
:3FH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
GLSB circuit
CPU access data
X address :nH
1
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
MSB
1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
SEGAi
SEGBi
0
Palette Aj
SEGCi
Palette Cj
Gradation palette
i=0~126
j=0~7
Gradation
control ciruit
Display RAM data
0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 SEGBi+1
Palette Bj
Palette Cj
Palette Bj
Palette Aj
SEGAi+1
SEGCi+1
1 1 0 0 SEGAi
SEGBi
1
Palette Aj
SEGCi
Palette Cj
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
GLSB circuit
Gradation palette
i=0~126
j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :nH
Graydation
control ciruit
Display RAM data
1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 1 0
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
MSB
SEGBi+1
Palette Bj
Palette Cj
Palette Bj
Palette Aj
SEGAi+1
SEGCi+1
1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 1 1 1 0 0 0
D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
D8
D9
D10
D11
D12
D13
D14
D15
Page 31

HM17CM256
- 31 -
DISPLAY RAM BITMAP AT BLACK & WHITE MODE (MON=”1”)
The MSBs of display RAM data ( 3 bit, 2 bit ) is used as display data at black and white mode.
example) 8 bit width access ( the same method as 16 bit width access)
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 0) or (1, 1)
notice) internal access X address :nH (access when REF=”0”)
:7FnH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
•
ACCESS when (REF, SWAP)=(0, 1) or (1, 0)
notice) internal access X address :nH (access when REF=”0”)
:7FnH~nH (access when REF=”1”)
SEGAi
SEGBi
Aj
Palette Bj
0 0 Palette Aj
1 0 0
SEGCi
Palette Cj
1 1 1
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7 0 GLSB circuit
Gradation palette
i=0~127
j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :nH
Gradation control circuit.
Display RAM data
SEGCi
SEGBi
1 1 1 0 0
SEGAi
Palette Cj
Palette Bj
Palette Aj
1 0 0
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7
Gradation palette
i=0~127
j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :nH
Gradation control circuit
Display RAM data
0
GLSB circuit
l
m n o p
Page 32

HM17CM256
- 32 -
gradation level table (MON=”1”, Black & white mode)
(MSB)RAM data (LSB)
Gradation level
RAM data
GLSB
Gradation level
0 0 0 0 0 0 *
0
0 0 1 0 0 1 *
0
0 1 0 0 1 0 *
1
0 1 1 0 1 1 *
1
1 0 0
1
* : Don’t Care
1 0 1 1
1 1 0
1
1 1 1
1
(12) GRADATION LSB CONTROL
At 256 colors input mode, this IC provides segment driver output for 8-gradation display using
successive 3 bits of data and that for 4-gradation display using successive 2 bits of data.
The segment driver output for the 4-gradation display uses 2 bits written to the corresponding RAM
area and 1 bit supplemented by the gradation LSB circuit, and then selects 4 gradations from 8gradations.
At fixed gradation mode, the segment driver output for the 4-gradation display result in a gradation
level of 0 regardless of gradation LSB register, when 2 bits of data on the display RAM are “00”.
When 2 bits of data on the display RAM is “11”, a gradation level of 7/7 is selected regardless of
gradation LSB register. The other gradation levels are selected depending on 2 bits of data on the
display RAM and the gradation LSB register.
One bit of data is supplemented by setting the gradation LSB register (GLSB).
For this register, the bit information specified for only one time setting is used as the LSB of the
RAM for all the 4-gradation segment drivers.
Gradation LSB = “0”: Set 0 as the LSB of the RAM for 4-gradation segment drivers.
Gradation LSB = “1”: Set 1 as the LSB of the RAM for 4-gradation segment drivers.
(13) GRADATION PALETTE
This IC has two gradation display modes, the fixed gradation display mode and the variable
gradation display mode.
Select mode by setting the gradation display mode register (PWM command) to the purpose.
PWM=”0” : variable gradation mode among 32-level gradations.
PWM=”1” : fixed 8 gradation mode
To select the best gradation level suited to LCD panel at variable gradation display mode, use the
gradation palette register among 32-level gradation palettes. Segment driver outputs are set by
selected 8-level gradation palette.
The gradation palette register provides three registers ( palette Aj, Bj, and Cj : j=0∼7 ) for the
segment driver outputs, SEGAi(0∼127), SEGBi(0∼127), and SEGCi(0∼127) . Each register
consists of a 5-bit register, selecting 8 gradations from the 32 gradation pattern.
Segment driver selects 4 gradations among 8 gradation by 2 bits wrote-in RAM and 1bit calibrated
by GLSB.
Page 33

HM17CM256
- 33 -
GRADATION PALETTE INITIAL VALUE
( palette Aj, palette Bj, palette Cj (j=0~7) )
(MSB)RAM data (LSB)
Register name
Initial value
0 0 0
Gradation palette 0
0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1
Gradation palette 1
0 0 1 0 1
0 1 0
Gradation palette 2
0 1 0 1 0
0 1 1
Gradation palette 3
0 1 1 1 0
1 0 0
Gradation palette 4
1 0 0 0 1
1 0 1
Gradation palette 5
1 0 1 0 1
1 1 0
Gradation palette 6
1 1 0 1 0
1 1 1
Gradation palette 7
1 1 1 1 1
GRADATION PALETTE TABLE (PWM=”0”, variable mode)
( palette Aj, palette Bj, palette Cj (j=0~7) )
Palette
Gradation
remark
Palette
gradation
remark
0 0 0 0 0
0
Palette 0 initial value
1 0 0 0 0
16/31
0 0 0 0 1
1/31
1 0 0 0 1
17/31
Palette 4 initial value
0 0 0 1 0
2/31
1 0 0 1 0
18/31
0 0 0 1 1
3/31
1 0 0 1 1
19/31
0 0 1 0 0
4/31
1 0 1 0 0
20/31
0 0 1 0 1
5/31
Palette 1 initial value
1 0 1 0 1
21/31
Palette 5 initial value
0 0 1 1 0
6/31
1 0 1 1 0
22/31
0 0 1 1 1
7/31
1 0 1 1 1
23/31
0 1 0 0 0
8/31
1 1 0 0 0
24/31
0 1 0 0 1
9/31
1 1 0 0 1
25/31
0 1 0 1 0
10/31
Palette 2 initial value
1 1 0 1 0
26/31
Palette 6 initial value
0 1 0 1 1
11/31
1 1 0 1 1
27/31
0 1 1 0 0
12/31
1 1 1 0 0
28/31
0 1 1 0 1
13/31
1 1 1 0 1
29/31
0 1 1 1 0
14/31
Palette 3 initial value
1 1 1 1 0
30/31
0 1 1 1 1
15/31
1 1 1 1 1
31/31
Palette 7 initial value
GRADATION PALETTE TABLE (PWM=”1”, fixed mode)
(MSB)RAM data(LSB)
gradation
RAM data
GLSB
gradation
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0 0 1
1/7
0 0 1
0
0 1 0
2/7
0 1 0
2/7
0 1 1
3/7
0 1 1
3/7
1 0 0
4/7
1 0 0
4/7
1 0 1
5/7
1 0 1
5/7
1 1 0
6/7
1 1 0
1 1 1
7/7
1 1 1
7/7
Page 34

HM17CM256
- 34 -
(14) DISPLAY TIMMING GENERATOR
The display-timing generator makes a timing clock and timing pulses (CL, FLM, FR and CLK) for
internal operation by inputting the original oscillating clock CK or by the oscillating circuit.
By setting up Master / Slave mode (M/S), the state of timing pulse pins and the timing generator
changes.
Display timing pulse pins and generator status
M/S port
mode
CL port
FR port
FLM port
CLK port
Timing generator status
L
Slave
Input
Input
Input
Input
CL, FLM, FR signal generator stop
H
Master
Output
Output
Output
Output
Operating status
(15) SIGNAL GENERATION OF DISPLAY LINE COUNTER, DISPLAY DATA LATCH CIRCUIT.
The latch signal from line counter clock to display data latch circuit is generated from display clock
(CL). Synchronized with the display clock, the line addresses of Display RAM are generated and
384-bit display data are latched to display-data latching circuit and then output to the LCD drive
circuit (SEG output port).
Read-out of the display data to the LCD drive circuit is completely independent of MPU side and so
MPU can access it with no relationship with the read-out operation of the display data.
(16) GENERATION OF THE ALTERNATED SIGNAL(FR), SYNCHRONOUS SIGNAL(FLM).
The alternated signal (FR) and synchronous signal (FLM) are generated from the display clock
(CL). The FLM generates alternated drive waveform to the LCD drive circuit per frame at normal
state ( inverse FR signal level per 1 frame ). But by setting up data (n-1) on n-line inversion
register and “1” on n-line alternated command (NLIN), n-line inverse waveform can be generated.
When this
HM17CM256
is used in multi-chip application, the signals of CL, FLM, FR and CLK
must be sent from master side to slave side.
(17) DISPLAY DATA LATCH CIRCUIT
This circuit latches the display data from display RAM to LCD driver circuit temporarily per every
common period. Normal / reverse display, display ON/OFF, and display all on command are done
by controlling data in this latch. And no data within display RAM changes.
Page 35

HM17CM256
- 35 -
(18) EXAMPLE OF LCD DRIVING (NORMAL MODE, 1/82 DUTY, BLACK & WHITE DISPLAY MODE)
COM1
COM0
SEG
1
SEG
0
SEG
2
COM1
SEG1
SEG0
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VSS
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VSS
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VSS
COM0
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VSS
FR
FLM
CL
82 1 2 4 3 5 82 1 2 4 3 5 82
1
Page 36

HM17CM256
- 36 -
(19) LCD DRIVER CIRCUIT
This drive circuit generates four levels of LCD drive voltage. The circuit has 384 segment outputs
and 82 common outputs and outputs combined display data and FR signal.
Two of common outputs(COMI0,COMI1) are for pictograph marker display only. The common
drive circuit that has shift register and outputs common scan signals sequentially.
(20) DUMMY SEGMENT DRIVER CIRCUIT
Segment driver circuit has 6 dummy output ( SEGSA0 ~ SEGSA3, SEGSB0 ~ SEGSB3, SEGSC0 ~
SEGSC3 ) at each edge side. Normally, the segment driver output is generated by memorized
RAM data but there are no RAMs but registers for dummy segment driver. There are 8 bit registers
correspond to SEGSA0, SEGSB0, SEGSC
0
and drive LCD with same level to Y direction. ( SEGSA1
~ SEGSA3, SEGSB1 ~ SEGSB3, SEGSC1 ~ SEGSC3 are the same function. )
SEGSA0 ~ SEGSA3 port is used same gradation palette with SEGA0 ~ SEGA
127,
SEGSB0 ~
SEGSB3 with SEGB0 ~ SEGB
127
, and SEGSC0 ~ SEGSC3 with SEGC0 ~ SEGC
127
This circuit is effective at display of boundary or background display. The dummy segment
drivers do not depend on LREV polarity but ALLON and REV command for display
There are 4-byte registers for dummy segment driver, SEGSA0 ~ SEGSA3, SEGSB0 ~ SEGSB3,
SEGSC0 ~ SEGSC3, If you want to access this register, please use DMY =”1” command.
68 series
80 series
RS
DMY
R/W
RD
WR
Function
0 0 1
0
1
Read out display data
0 0 0
1
0
Write in display data
0 1 1
0
1
Read out dummy segment register
0 1 0
1
0
Write in dummy segment register
There are the same rules at read out of dummy segment register as display RAM data read out
sequence. After address setting, the data of assigned address is shown directly after the end of
the read command, so pay attention that assigned data is available at 2nd timing step. In other
words, there needs 1 cycle dummy read after address set and write cycle.
1 cycle dummy read is necessary for after address setting and write cycle.
When access with DMY=”1”, X address is an effective value at address setting. There are 4-byte
and so 00H, 01H, 02H, 03H are effective at 8-bit mode and 00H, 01H are effective at 16-bit mode.
The access bears no relation to Y address setting.
When access with DMY=”1”, it is possible that the data is written into register by increment
operation.
notice) more detail information atqDUMMY SEGMENT REGISTER ADDRESS AND BITMAPrin s(10) Relation
between Display RAM and address
t
Page 37

HM17CM256
- 37 -
ACCESS WITH 8 BIT BUS EXAMPLE : GRAY MODE , ACCESS UNDER (REF, SWAP)=(0, 0)
(21) OSCILLATOR CIRCUIT
HM17CM256 has the CR oscillator. The output of oscillator is used as the timing signal source of
display and boosting clock to the booster. This is valid only in the master operation mode.
When in the master operation mode and if external clock is used, feed the clock to OSC1 pin or
connect resistor between OSC1 and OSC2.
And feedback resistance with command can set the inner oscillator circuit of HM17CM256.
The frame frequency can be altered by changed oscillator frequency according to feedback
resistance length set value. To get optimum frame frequency, please check LCD and then set the
frequency of oscillator.
(22) POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
Gradation
GLSB circuit
Gradation control circuit
Latched data
SEGSA0
SEGSB0
Palette Aj
Palette Bj
0 0 1 0 0
SEGSC0
Palette Cj
1 1 1
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7 0 j=0~7
CPU access data
X address :00H
Gradation palette
Gradation control circuit
SEGSA3
SEGSB3
Palette Aj
Palette Bj
0 0 1 0 0
SEGSC3
Palette Cj
1 1 1
MSB
LSB
MSB
LSB
MSB
0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 D0
D1
D2
D3
D4
D5
D6
D7 0 GLSB circuit
j=0~7
CPU access data
Latched data
X address :03H
Page 38

HM17CM256
- 38 -
This block generates the voltages necessary for driving LCD panel. The power supply circuit
consists of voltage boosting circuit and voltage converting circuit and generates the voltages (V
LCD
,
V1, V2, V3, V4. ) for LCD driving.
For large panel driving, it’s preferable to use external voltage source rather than to use built-in
power supply circuit for good image quality.
When using external voltage source, disable the built-in power supply circuit(AMPON, DCON=‘00’),
supply the V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, V4 and V
OUT
externally and open the C1+, C1-, C2+, C2-, C3+, C3-, C4+, C4-,
C5+, C5-, C6+, C6-, V
REF
, V
REG
, VEE terminals.
According to power supply circuit control command input, the power supply circuit can be enabled
partially. External power supply and partial inner power circuit can be used together. Refer to the
next table.
DCON
AMPON
Boosting circuit
Converting circuit
External voltage input
remark
0 0 Disable
disable
V
OUT
, V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, V4 common
1,3
0 1 Disable
enable
V
OUT
common
2,3
1 1 Enable
enable
−
−
1. All the built-in boosting circuit, converting circuit is not used. Open the ,C1+, C1-, C2+, C2-, C3+, C3-, C4+,
C4-, C5+, C5-, C6+, C6-, V
REF
, V
REG
, VEE terminals, LCD driving voltage should be applied externally.
2.Only the Boosting circuit is not used. Open the C1+,C1-,C2+,C2-,C3+,C3-,C4+,C4-,C5+,C5-,C6+,C6-, V
OUT
terminals, The power for converting circuit must be supplied through V
OUT
terminal and the reference
voltage must be supplied by V
REF
terminal.
3.The conditions between V
OUT
, V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, and V4 are V
OUT
≥
V
LCD
≥
V
1
≥
V
2
≥
V
3
≥
V
4
≥
VSS.
(23) VOLTAGE BOOSTING CIRCUIT
By connecting capacitor CA1 between C1+ and C1-, C2+ and C2-, C3+ and C3-, C4+ and C4-, C5+
and C5- , C6+ and C6-, V
OUT
and VSS , n-time boosted voltage of V
EE
- V
SS
can be generated through
V
OUT
port. The boosting coefficient can be set by command and 2-times/ 3-times / 4-times/ 5-
times/ 6-times/ 7-times boosted voltage is output through V
OUT
port.
At application, specific boosting coefficient is used, refer to the following description.
At 2-times boosting is designed, connect boosting capacitor CA1 between C1+ and C1- , and
open C2+, C2-, C3+, C3-, C4+, C4-, C5+, C5-, C6+, C6- terminals.
At 3-times boosting is designed, connect boosting capacitor CA1 between C1+ and C1- , C2+
and C2- , and open C3+,C3-, C4+, C4-, C5+, C5-, C6+, C6- terminals.
At 4-times boosting is designed, connect boosting capacitor CA1 between C1+ and C1- , C2+
and C2- , C3+ and C3- , and open C4+, C4-, C5+, C5-, C6+, C6- terminals
At 5-times/ 6-times/ 7-times boosting are same structures with upper case.
Special care should be taken so that the voltage of VOUT would not exceed 18V MAX.
VOUT voltage exceeding 18V can cause malfunction and reliability problem.
3-times boosting
7-times boosting
VSS=0V
VEE=3V
V
OUT
=9V
V
OUT
=17.5V
VSS=0V
VEE=2.5V
v
v
v
w
x
y
z
u
u
Page 39

HM17CM256
- 39 -
(24) ELECTRIC VOLUME
The electric volume is within voltage converting circuit and the brightness of LCD can be controlled
by adjusting V
LCD
level with command.
The LCD driving voltage V
LCD
is generated by selecting 1 level within 128 step electric volume
controlled levels by setting 7 bit electric volume register.
(25) VOLTAGE REGULATOR CIRCUIT
The voltage regulator circuit is within voltage converting circuit and generates regulated voltage
using V
REF
input with magnification by adjusting internal resistor. The generated voltage by voltage
regulator is output at V
REG
terminal. Even though boosted voltage variation, generated regulator
voltage is stable because boosting voltage level is higher than the amplified regulator voltage V
REG
.
And so, stable voltage level can be generated even if there is load variation.
V
REG
is used as input voltage of electric volume circuit to generate LCD driving voltage.
(26) REFERENCE VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT
The reference voltage generation circuit is within voltage converting circuit.
This circuit generates reference voltage VBA terminal for using at regulator circuit through. The
output voltage level from VBA terminal is as following description.
V
BA
= VEE x 0.9
The LCD driving voltages can be made by applying reference voltage to reference voltage input
terminal V
REF .
(27) LCD DRIVING VOLTAGE GENERATION CIRCUIT
The generation circuit of LCD driving voltage is within voltage converting circuit and generates
voltages V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, V4 by resistively dividing V
LCD
into 4 levels.
The bias ratio of LCD driving voltages can be one of 1/5, 1/6, 1/7, 1/8, 1/9, 1/10.
When using built-in power supply circuit, you should connect voltage stabilization capacitor CA2 at
each of LCD power terminals. There is need for selecting the coefficient of capacitor CA2 after
display the LCD.
When using external voltage supply, disable the built-in power supply circuit(AMPON, DCON=‘00’),
supply the V
OUT
, V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, V4 voltages externally and open the C1+ , C1- , C2+ , C2- , C3+ , C3- ,
C4+ , C4- , C5+ , C5- , C6+ , C6- , V
EE
, V
REF
, V
REG
terminals.
When using external voltage source and parts of built-in voltage converting circuit, the terminals of
C1+ , C1- , C2+ , C2- , C3+ , C3- , C4+ , C4- , C5+ , C5- , C6+ , C6- should be open because boosting
circuit is not activated, you should supply reference voltage through V
REF
terminal and the voltage for
voltage converting circuit at V
OUT
.
Connecting stabilization capacitor CA
3
at V
REG
terminal is recommended.
Page 40

HM17CM256
- 40 -
value
CA1
1.0 ~ 4.7µF
CA2
1.0 ~ 2.2µF
CA3
0.1µF
caution{ Please use B grade capacitor.
internal power circuit is not used case
internal power circuit / internal reference voltage
generating circuit are activated case.(7 times boosting)
VDD
VEE
VBA
V
REF
V
REG
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
C4-
C4+
V
OUT
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VDD
CA3
VSS
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
VSS
VSS
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
C5-
C5+
C6-
C6+
CA1
CA1
Extnal
power
circuit
VDD
VEE
VBA
V
REF
V
REG
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
C4-
C4+
V
OUT
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VDD
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
C5-
C5+
C6-
C6+
HM17CM256
HM17CM256
Page 41

HM17CM256
- 41 -
value
CA1
1.0 ~ 4.7µF
CA2
1.0 ~ 2.2µF
CA3
0.1µF
caution
Please use B grade capacitor.
Internal power circuit is used case. Reference
voltage input from outside . (7 times boosting)
Internal power circuit is used case.
Temperature compensation by external
thermistor . (7 times boosting )
VDD
VEE
VBA
V
REF
V
REG
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
C4-
C4+
V
OUT
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VDD
CA3
VSS
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
VSS
VSS
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
C5-
C5+
C6-
C6+
CA1
CA1
VDD
VEE
VBA
V
REF
V
REG
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
C4-
C4+
V
OUT
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VDD
CA3
VSS
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
CA1
VSS
VSS
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
C5-
C5+
C6-
C6+
CA1
CA1
HM17CM256
HM17CM256
thermistor
|
Page 42

HM17CM256
- 42 -
value
CA1
1.0 ~ 4.7µF
CA2
1.0 ~ 2.2µF
CA3
0.1µF
caution
Please use B grade capacitor.
Internal power circuit is used case. (boosting circuit is
not used, V
OUT
is supplied from outside)
HM17CM256
VDD
VEE
VBA
V
REF
V
REG
C1-
C1+
C2-
C2+
C3-
C3+
C4-
C4+
V
OUT
V
LCD
V1
V2
V3
V4
VDD
CA3
VSS
VSS
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
CA2
C5-
C5+
C6-
C6+
External
power
circuit
}
Page 43

HM17CM256
- 43 -
(28) PARTIAL DISPLAY FUNCTION
HM17CM256 can realize the partial display at graphic display area on LCD panel.
Partial display is used with lower duty than normal state at driving.
And so, HM17CM256 can drive the LCD panel with lower bias ratio, lower boosting times and
lower LCD driving voltages, and that can drive the LCD panel with lower power consumption.
This function is suitable for calendar or clock display at mobile information apparatus.
PARTIAL DISPLAY IMAGE
Normal display partial display
The next sequence should be followed carefully to realize partial display function.
boosting coefficient
electric volume
bias ratio
duty ratio
display start line setting
display start command
and so on.
HYUNDAI
LCD DRIVER
Low Power and
Low Voltage
LCD DRIVER
Any display states
DISPLAY OFF(ON/OFF=”0”)
built-in power source OFF(DCON=”0”, AMPON=”0”)
WAIT
Setting the power supply circuit
Setting the display-related function
Built-in power source ON(DCON=”1”, AMPON=”1”)
WAIT
Display ON(ON/OFF=”1”)
Partial display state
~
~
~
~
~
~
Page 44

HM17CM256
- 44 -
When using partial display function, the display duty can be selected among 1/17, 1/26, 1/32, 1/38,
1/47, 1/66, 1/77 by setting the LCD duty set command.
The display states such as LCD driving bias ratio, LCD Driving voltage, electric volume setting
value, boosting coefficient should be optimized to the selected LCD and display duty.
(29) DISCHARGE CIRCUIT
The discharge circuit of voltage(V
LCD
, V1~V4) stabilization capacitor is built in the HM17CM256.
To discharge the capacitors, set the DIS register to “1” or set the RES terminal to “0”. When built-
in power supply circuit is used, built-in power supply circuit should be disabled before discharging of
the capacitor is executed. When external power supply(V
LCD
, V1~V4, V
OUT
) is used, external power
supply should be turned off before discharging of the capacitor is executed. Do not turn on the
internal power supply and external power supply (V
LCD
, V1~V4, V
OUT
) during discharging is executed.
(30) RESET CIRCUIT
HM17CM256 is initialized as following description when RES terminal is set to “L”.
INITIAL SETTING CONDITION (default setting)
1. display RAM :unknown
2. X address :00H set
3. Y address :00H set
4. display start line :1 line value 0H
5. display ON/OFF :display OFF
6. positive/negative :positive
7. display duty ratio :1/82
8. n line inversion :n inversion disable
9. COM shift direction :COM0 → COM79, COMI0, COMI1
10. increment mode :increment OFF
11. REF mode :positive
12. data SWAP mode :OFF
13. electric volume :(0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
14. power circuit :OFF
15. display mode :gradation display mode
16. bias ratio :1/10 bias
17. gradation palette 0 :(0, 0, 0, 0, 0)
18. gradation palette 1 :(0, 0, 1, 0, 1)
19. gradation palette 2 :(0, 1, 0, 1, 0)
20. gradation palette 3 :(0, 1, 1, 1, 0)
21. gradation palette 4 :(1, 0, 0, 0, 1)
22. gradation palette 5 :(1, 0, 1, 0, 1)
23. gradation palette 6 :(1, 1, 0, 1, 0)
24. gradation palette 7 :(1, 1, 1, 1, 1)
25. gradation mode :variable mode
26. GLSB :"0"
27. RAM data length :8 bit mode
28. discharge register :"0"
Usually RES terminal is connected reset terminal of CPU, so that the chip can be initialized
simultaneously with CPU. HM17CM256 should be initialized when the power is on.
Page 45

HM17CM256
- 45 -
(31) SUPPLYING POWER AND ON/OFF SEQUENCE
Special care should be taken to the next notice. Supplying the power at LCD driving voltage
terminal when the logic VDD is floating can cause over-current and damage the IC
(31-1) WHEN USING EXTERNAL POWER SUPPLY
power ON sequence
Reset the IC after supplying the logic power at VDD terminal, and then turn on the LCD driving
voltage at the terminals (V
LCD
, V1, V2, V3, V4).
And when internal voltage converter is used, reset the IC after supplying the logic power at
VDD terminal, and then supply power to V
LCD
terminal.
power OFF sequence
Execute HALT command or reset the IC to turn off the outputs of LCD driving output port, and
then turn off the LCD driving voltage after logic power OFF.
Inserting series resistor of 50 ~100Ω or fuse at V
LCD
or V
OUT
terminal (when only internal
voltage converting circuit is used) is recommended to prevent over-current.
This series resistor should be selected carefully because image quality can be dependent on.
(31-2) WHEN USING BUILT-IN POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
power ON sequence
Reset the IC after supplying the logic power at VDD terminal or after supplying power through
voltage common port (VEE) of boosting voltage generation and then operate internal power
circuit by command.
And when internal voltage converter is used, reset the IC after supplying the logic power at
VDD terminal, and then supply power to V
LCD
terminal.
You should turn on the display after the output level of internal power module is set.
If you do not keep this sequence, LCD can display wrong data.
power OFF sequence
To make off state of LCD driving output, cut the source to voltage common port (VEE) of
boosting voltage generation, the logic power at VDD terminal after reset the IC by HALT
command.
If VEE, and VDD are supplied from different power source, VEE terminal should be turned on/off
during VDD terminal voltage maintain voltage level specified in specification sheet.
Specially, when turn off the power, after cut the source to voltage common port (VEE), and then
turn off the logic power at VDD terminal after the voltage levels of VEE, V
OUT
, V
LCD
, V1~V4 become
under LCD on voltage(LCD threshold voltage)level.
Page 46

HM17CM256
- 46 -
(32) COMMAND SETTING EXAMPLE
(32-1) initial setting
electric volume code set
bias ratio set
power control set
(DCON=”1”, AMPON=”1”)
(notice) If the voltage level of VEE and VDD are different, VDD should be inputted first.
(32-2) DATA DISPLAY
display start line set
increment mode set
X address set
Y address set
display data write
display ON/OFF command set(ON/OFF=”1”)
VDD, VEE-VSS power ON
Power stable
RESET input
WAIT
Function setting by command (user setting
End of initial setting
Function setting by command (user setting
End of initialization
Function setting by command (user setting)
Data display
Function setting by command (user setting)
Function setting by command (user setting
Page 47

HM17CM256
- 47 -
(32-3) POWER OFF
HALT command set or reset operation
(all LCD driver output is VSS level)
Discharge command set
(discharge of V
LCD
, V1~V4 capacitor)
Before turning off the power, be sure to execute HALT or RESET command to make LCD
driver output OFF state.
And if VDD and VEE have different potential (V
DD
and VEE are not common), be sure to turn off
VEE first during VDD is supplied.
Any operation states
Function setting by command (user setting
VEE, VDD-VSS power OFF
WAIT
Page 48

HM17CM256
- 48 -
(33) INSTRUCTION
INSTRUCTION TABLE (1)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
display data write in
0 0 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1
Write Data
Write in to display RAM
display data read out.
0 0 0 1 0/1
0/1
0/1
Read Data
Read out from display RAM
X address
(lower) [0H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
AX3
AX2
AX1
AX0
Display RAM X direction set
X address
(upper) [1H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1
*
AX6
AX5
AX4
Display RAM X direction set
Y address
(lower) [2H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0
AY3
AY2
AY1
AY0
Display RAM Y direction set
Y address
(upper) [3H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1
*
AY6
AY5
AY4
Display RAM Y direction set
display start line set
(lower) [4H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
LA3
LA2
LA1
LA0
RAM Y address setting
corresponds to scan start line of
common driver.
display start line set
(upper) [5H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
*
LA6
LA5
LA4
RAM Y address setting
corresponds to scan start line of
common driver.
N line inversion set
(lower) [6H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
N3
N2
N1
N0
quantity setting of line inversion
N line inversion set
(upper) [7H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 * N6
N5
N4
quantity setting of line inversion
display control (1)
[8H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
SHI
FT
MO
N
ALL
ON
ON/
OFF
SHIFT: common shift direction set,
MON: BW/gradation display,
ALLON: all on ,
ON/OFF: display ON/OFF control
display control (2)
[9H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
RE
V
NL
IN
SW
AP
RE
F
REV: display positive / negative,
NLIN: n line inversion ON/OFF,
SWAP: display data swap,
REF: segment positive / negative
increment control
[AH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
WIN
AIM
AYI
AXI
WIN: window selection,
AIM: increment timing selection,
AYI:Y increment,
AXI:X increment
power control
[BH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
AMP
ON
HA
LT
DC
ON
AC
L
AMPON: internal OP Amp. ON,
HALT: power save
DCON: boosting circuit ON, ACL: reset
LCD duty set
[CH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
*
DS2
DS1
DS0
LCD driver duty ratio set
boosting coefficient
set [DH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
*
VU2
VU1
VU0
Boosting times set
bias ratio set
[EH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 * B2
B1
B0
LCD drive bias set
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Page 49

HM17CM256
- 49 -
INSTRUCTION TABLE (2)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
Gradation palette A0 set
(lower) [0H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
PA
03 PA02
PA01
PA00
Set value to gradation palette
A0
Gradation palette A0 set
(upper) [1H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 * *
*
PA04
Set value to gradation palette
A0
Gradation palette A1 set
(lower) [2H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
PA
13 PA12
PA11
PA10
Set value to gradation palette
A1
Gradation palette A1 set
(upper) [3H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 * *
*
PA14
Set value to gradation palette
A1
Gradation palette A2 set
(lower) [4H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
PA
23 PA22
PA21
PA20
Set value to gradation palette
A2
Gradation palette A2 set
(upper) [5H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 * *
*
PA
24
Set value to gradation palette
A2
Gradation palette A3 set
(lower) [6H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
PA
33
PA
32
PA
31
PA
30
Set value to gradation palette
A3
Gradation palette A3 set
(upper) [7H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 * *
*
PA
34
Set value to gradation palette
A3
Gradation palette A4 set
(lower) [8H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
PA
43
PA
42
PA
41
PA
40
Set value to gradation palette
A4
Gradation palette A4 set
(upper) [9H]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 * *
*
PA
44
Set value to gradation palette
A4
Gradation palette A5 set
(lower) [AH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
PA
53
PA
52
PA
51
PA
50
Set value to gradation palette
A5
Gradation palette A5 set
(upper) [BH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 * *
*
PA
54
Set value to gradation palette
A5
Gradation palette A6 set
(lower) [CH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
PA
63
PA
62
PA
61
PA
60
Set value to gradation palette
A6
Gradation palette A6 set
(upper) [DH]
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 * *
*
PA
64
Set value to gradation palette
A6
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Page 50

HM17CM256
- 50 -
INSTRUCTION TABLE (3)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
Gradation palette A7 set
(lower) [0H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
PA
73 PA72
PA71
PA70
Set value to gradation palette
A7
Gradation palette A7 set
(upper) [1H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 * *
*
PA74
Set value to gradation palette
A7
Gradation palette B0 set
(lower) [2H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
PB
03 PB02
PB01
PB00
Set value to gradation palette
B0
Gradation palette B0 set
(upper) [3H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 * *
*
PB04
Set value to gradation palette
B0
Gradation palette B1 set
(lower) [4H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
PB
13 PB12
PB11
PB10
Set value to gradation palette
B1
Gradation palette B1 set
(upper) [5H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 * *
*
PB
14
Set value to gradation palette
B1
Gradation palette B2 set
(lower) [6H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 0
PB
23 PB22
PB21
PB20
Set value to gradation palette
B2
Gradation palette B2 set
(upper) [7H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 * *
*
PB
24
Set value to gradation palette
B2
Gradation palette B3 set
(lower) [8H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 0
PB
33 PB32
PB31
PB30
Set value to gradation palette
B3
Gradation palette B3 set
(upper) [9H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 * *
*
PB
34
Set value to gradation palette
B3
Gradation palette B4 set
(lower) [AH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 0
PB
43 PB42
PB41
PB40
Set value to gradation palette
B4
Gradation palette B4 set
(upper) [BH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 * *
*
PB
44
Set value to gradation palette
B4
Gradation palette B5 set
(lower) [CH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 0
PB
53 PB52
PB51
PB50
Set value to gradation palette
B5
Gradation palette B5 set
(upper) [DH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 * *
*
PB
54
Set value to gradation palette
B5
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Page 51

HM17CM256
- 51 -
INSTRUCTION TABLE (4)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
Gradation palette B6 set
(lower) [0H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 0
PB
63 PB62
PB61
PB60
Set value to gradation palette
B6
Gradation palette B6 set
(upper) [1H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 * *
*
PB64
Set value to gradation palette
B6
Gradation palette B7 set
(lower) [2H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 0
PB
73 PB72
PB71
PB70
Set value to gradation palette
B7
Gradation palette B7 set
(upper) [3H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 * *
*
PB74
Set value to gradation palette
B7
Gradation palette C0 set
(lower) [4H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0
PC
03 PC02
PC01
PC00
Set value to gradation palette
C0
Gradation palette C0 set
(upper) [5H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 * *
*
PC
04
Set value to gradation palette
C0
Gradation palette C1 set
(lower) [6H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 0
PC
13 PC12
PC11
PC10
Set value to gradation palette
C1
Gradation palette C1 set
(upper) [7H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 * *
*
PC
14
Set value to gradation palette
C1
Gradation palette C2 set
(lower) [8H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 0
PC
23 PC22
PC21
PC20
Set value to gradation palette
C2
Gradation palette C2 set
(upper) [9H]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 * *
*
PC
24
Set value to gradation palette
C2
Gradation palette C3 set
(lower) [AH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 0
PC
33 PC32
PC31
PC30
Set value to gradation palette
C3
Gradation palette C3 set
(upper) [BH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 * *
*
PC
34
Set value to gradation palette
C3
Gradation palette C4 set
(lower) [CH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 0
PC
43 PC42
PC41
PC40
Set value to gradation palette
C4
Gradation palette C4 set
(upper) [DH]
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 * *
*
PC
44
Set value to gradation palette
C4
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Page 52

HM17CM256
- 52 -
INSTRUCTION TABLE (5)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D
3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
Gradation palette C5 set
(lower) [0H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 0
PC
53 PC52
PC51
PC50
Set value to gradation palette
C5
Gradation palette C5 set
(upper) [1H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 * *
*
PC54
Set value to gradation palette
C5
Gradation palette C6 set
(lower) [2H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 0
PC
63 PC62
PC61
PC60
Set value to gradation palette
C6
Gradation palette C6 set
(upper) [3H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 * *
*
PC64
Set value to gradation palette
C6
Gradation palette C7 set
(lower) [4H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 0
PC
73 PC72
PC71
PC70
Set value to gradation palette
C7
Gradation palette C7 set
(upper) [5H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 * *
*
PC
74
Set value to gradation palette
C7
Display start command
set
[6H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0
*
SC2
SC1
SC0
Common drive scan start line
set
Serial extension CS
control
[7H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 * *
*
EX
CS
Serial I/F, extension CS port
(EXCS) control
Display selection
control
[8H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 0
PW
M
GL
SB
*
*
Gradation display set
RAM data length set
[9H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 * *
CKS
WL
S
RAM access data length set
8 bit/16 bit selection
Electric volume
control
(lower) [AH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 0
DV3 DV2
DV1
DV0
Electric volume level set
(lower bit)
Electric volume
control
(upper) [BH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1
*
DV6
DV5
DV4
Electric volume level set
(upper bit)
Oscillator Rf control
[DH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 1
FFL RF2
RF1
RF0
RF: oscillator feed back resistor set
FFL: oscillator frequency control
discharge
[EH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 * *
*
DIS
V
LCD
, V1~V4 capacitor
discharge
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Internal register read
address set
[CH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0 0
Register read
address
Internal register read out
address set
Internal register read
0 1 0 1 0/1
0/1
0/1 * * * *
Read Data
Internal register read out
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Notice 4) CKS=0: internal oscillation mode
CKS=1: external oscillation mode
Default CSK=0
Page 53

HM17CM256
- 53 -
INSTRUCTION TABLE (6)
CODE (80 series I/F)
CODE
INSTRUCTION
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
FUNCTION
Window end
X
address
(lower)
[0H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0
EX3 EX2
EX1
EX0
Window mode X direction end
address set
Window end
X
address
(upper
) [1H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1
*
EX6
EX5
EX4
Window mode X direction end
address set
Window end
Y
address
(lower
) [2H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0
EY3 EY2
EY1
EY0
Window mode Y direction end
address set
Window end
Y
address
(upper)
[3H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1
*
EY6
EY5
EY4
Window mode Y direction end
address set
Line inversion start
Address (lower)
[4H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0
LS3 LS2
LS1
LS0
Line inversion start address set
Line inversion start
address (upper)
[5H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1
*
LS6
LS5
LS4
Line inversion start address set
Line inversion end
Address (lower)
[6H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0
LE3 LE2
LE1
LE0
Line inversion end address set
Line inversion end
Address (upper)
[7H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1
*
LE6
LE5
LE4
Line inversion end address set
Line inversion
control [8H]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 * *
BT
LR
EV
LREV,BT: line inversion display set
Dummy segment
driver address set
[9
H
]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 * *
*
DM
Y
Dummy segment driver
address selection
PWM mode control
[AH]
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 0
PW
MS
PW
MA
PW
MB
PW
MC
PWM mode selection
RE register set
[FH]
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1 1
TST
0
RE2
RE1
RE0
RE flag set
Notice 1) * mark is Don’t Care
Notice 2) [ ] The inner side number is an address for internal register read.
Notice 3) The commands that upper/lower register settings are demanded are effective at the point of commands input.
But electric volume is effective after upper and lower register setting.
Page 54

HM17CM256
- 54 -
(34) INSTRUCTION DESCRIPTION
As shown in instruction table, HM17CM256 has abundant command set
.
All the data code and command code are valid only when the chip select signal CS is at “0” state.
The left side of the following command code and data table are the setting of 80 series CPU`
interface. Do not use undefined command code.
(34-1) Write display data on RAM
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 0 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1
Display RAM write data
Writing the 8-bit display RAM data at specified X, Y address.
(34-2) Read display data from RAM
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 0 0 1 0/1
0/1
0/1
Display RAM read data
Reading out the 8-bit display RAM data from specified X, Y address.
One Dummy read cycle is needed after X, Y address is set.
(34-3) X address register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
AX3
AX2
AX1
AX0
( reset :AX3~AX4=0H, read address :0H )
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 *
AX6
AX5
AX4
( reset :AX6~AX4=0H, read address :1H ) * : “Don’t care”
Setting the X direction address address set. The lower 4-bits are set first, and then upper 3-bits are set later.
Please set from lower bit.
(34-4) Y address register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 AY3
AY2
AY1
AY0
( reset :AY3~AY0=0H, read address :2H )
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 *
AY6
AY5
AY4
( reset :AY6~AY4=0H, read address :3H ) * : “Don’t care”
Setting the Y address of display RAM. The lower 4-bits are set first, and then upper 3-bits are set later.
Please set from lower bit.
00H~51H is valid range at Y address(AY6~AY0). Do not use 52H~FFH range. The Y address(AY6~AY0) of
50H,51H is used for ICON display data address.
Page 55

HM17CM256
- 55 -
(34-5) Display start line register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 LA3
LA2
LA1
LA0
(reset:LA3~LA0=0H, read address:4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 1 *
LA6
LA5
LA4
(reset:LA6~LA4=0H, read address:5H) * : “Don’t care”
Setting the line address of COM0. The address stored at the start line register becomes display line at
COM0 line of LCD panel.
The display of LCD panel is done from line address value to the direction of increase.
LA6
LA5
LA4
LA3
LA2
LA1
LA0
Line address
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
0
0 0 0 0 0 0 1
1
:
:
:
:
1 0 0 1 1 1 1
79
(34-6) n line inversion register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 N3
N2
N1
N0
( reset :N3~N0=0H, read address :6H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 *
N6
N5
N4
( reset :N6~N4=0H, read address :7H) * : “Don’t care”
Setting line number to be inversed to register. Setting range is from 2 to 80. N line inversion register
can be effective only when N line inversion command NLIN=‘1
”.
If NLIN=“0”, the polarity of LCD driving voltage is inverted by every other frame.
N6
N5
N4
N3
N2
N1
N0
Inversion line number
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Forbidden *
0 0 0 0 0 0 1
2
:
:
:
:
1 0 0 1 1 1 1
80
n=N-1
* : N0~N6 =”0” is forbidden.
Page 56

HM17CM256
- 56 -
•
Inversion timing
a) when n-line inversion function is OFF(1/82 duty display)
b) when n-line inversion function is ON
(34-7) display control (1) register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
0
SHIFT
MON ALLON
ON/OFF
( reset :{SHIFT, MON, ALLON, ON/OFF}=0H, read address : 8H)
various control setting of display
a) ON/OFF command
Display ON/OFF control
ON/OFF=”0”: display OFF (all ports are VSS level)
ON/OFF=”1”: display ON
b) ALLON command
Setting display data to “1” with independence of RAM data. This command has higher priority than
positive display/negative display command. RAM data is not changed.
ALLON=”0”: normal display state
ALLON=”1”: turn on all the pixel
c) MON command
BW display / gradation display selection
MON=”0”: gradation display mode
MON=”1”: BW display mode
d) SHIFT command
Selection of the shift direction of scan data of common driver output
SHIFT=”0”:COM
0
COM79 shift
SHIFT=”1”:COM
79
COM0 shift
LP
FLM
FR
LP
FR
2 line
82 line
N line control
1 line
3 line
1 line
81 line
2 line
1 line
3 line
1 line
N line
2 line
Page 57

HM17CM256
- 57 -
(34-8) Display control (2) register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 0
1
REV
NLIN SWAP REF
( reset :{REV, NLIN, SWAP, REF}=0H, read address :9H )
various control setting of display
a) REF command
When CPU tries to access display RAM, the relation between X address and write data is changed by
command, normal or headfirst.
The output sequence of display data to segment driver can be controlled by register setting. The IC can
be placed in panel with less constraint at application.
b) SWAP command
When CPU tries to access display RAM, the display data can be swapped.
SWAP=”0”: Normal state, D7~D0 or D15~D0 are written to the RAM.
SWAP=”1”: SWAP mode on : The swapped data of D7~D0 or D15~D0 are written to the RAM.
SWAP=”0”
SWAP=”1”
Write data
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
Internal data
d
7 d6 d5 d4 d3 d2 d1 d0
d
0 d1 d2 d3 d4 d5 d6 d7
Read data
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
D7 D6 D5 D4 D3 D2 D1 D0
c) NLIN command
n line inversion ON/OFF control.
NLIN=”0”: n line inversion OFF. Polarity signal, FR is inverted every other frame.
NLIN=”1”: n line inversion ON. The n lines are inverted according to the contents of n line inversion
register
d) REV command
The relation between RAM data and display data is defined by this command.
REV=”0”: The display data are reflected the RAM data until that time.
REV=”1”: The display data are reflected the opposite data from RAM data.
Page 58

HM17CM256
- 58 -
(34-9) Increment control register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
0
WIN
AIM
AYI
AXI
(reset :{WIN, AIM, AYI, AXI}=0H, read address :AH) * : ”Don’t care”
Sets the display RAM address to increment mode when RAM data is accessed.
Per RAM write or read access, the increment or non-increment settings of X and Y address counter are
possible by AIM, AYI, AXI register setting. When accessing consecutive RAM areas by read or write,
the address increment operation is possible without setting the read or write address by this register setting.
After setting the auto increment register, the X, Y address should be set lower bits first.
Please revise X, Y address register after increment register setting.
When WIN register is set to “1”, the CPU accesses specified area of display RAM. In this case X, Y
address should be used with auto increment mode set (AXI=”1”, AYI=”1”). Do not revise X, Y address
register when it is not auto increment mode.
WIN=”0”: normal display RAM access
WIN=”1”: window area access at display RAM
The window to be accessed is defined by setting the start X, Y address and end X, Y address.
When accessing display with window area mode, please set X, Y start address and then X, Y window
end address.
When accessing consecutive RAM area, it is possible to access next location without setting the address
by using this command. X, Y address is unknown after auto increment setting. When WIN register is set
to “1”, the RAM should be accessed after setting start point address and end point address.
And address setting should be done in sequence of start point of X address and Y address, and then
end point of X address and Y address after WIN command setting ( WIN=”1”).
The relationship between AIM, AYI, AXI register and X, Y address increment mode is as follow.
AIM
Increment timing selection
Remark
0
Both case of writing in and read out display RAM
1
Only when writing in display RAM( read modify)
notice
This mode is valid when read or write is performed on consecutive RAM location.
notice
This mode is valid when read out consecutive data and modifying the data and then write them in again or
read write per access.
AYI
AXI
Increment timing selection
Remark
0
0
No increment
0
1
X address auto increment
1
0
Y address auto increment
1
1
X, Y address auto increment
notice
Regardless of AIM setting, no auto increment for X and Y address
notice
According to AIM setting, auto increment only for X address.
And X address is increased as followed loop according to REF register( SEG output direction setting
register ) value.
∗
) Please refer toRAM address bitmapin(10) relation between display RAM and address
notice
According to AIM setting, auto increment only for Y address
Y address is increased as followed loop regardless of REF register
.
00H
MaxH
Page 59

HM17CM256
- 59 -
notice
According to AIM setting, auto increment for X and Y address
X address is increased to MaxH first and then Y address is increased later.
You should set X address, Y address in sequence, anything else is forbidden.
∗
)
Please refer toRAM address bitmapin(10) relation between display RAM and address
And when X, Y auto increment mode operating, window access is possible. When window mode is
selected ( WIN =”1” ), address is increased as following loop.
a) 8 bit access mode
The increment operating is as above description.
b) 16 bit access mode
Two-byte access is done by single RAM access.
Address is increased after access.
X address is increased as (00H, 01H,
3EH, 3FH) sequence.
51H
00H
MaxH
00H
51H
00H
X address
Y address
START
Address
X address
Y address
END
Address
START
Address
END
Address
Page 60

HM17CM256
- 60 -
(34-10) Power control register set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 0 1
1
AMPON
HALT
DCON
ACL
( reset :{AMPON, HALT, DCON, ACL}=0
H
read address :BH )
a) ACL command
This command initializes internal circuit and it is valid only at master operating.
ACL=”0”: normal state
ACL=”1”: initialization ON
Just after the execution of ACL command (ACL=”1”), D0 bit is set to 1. But as the initialization process
goes on internally, D0 is reset to “0”.
When ACL command is executed, internal reset signal is produced by using local display clock ( clock
from internal oscillator or from external resistor oscillation mode ).
So, after ACL command is executed, it needs to WAIT at least 2 period of the clock for next process
beginning.
ACL command is effective only at master mode operation because it uses original oscillator clock.
It is prohibited for slave mode operation to use the internal oscillator or external oscillator.
So, ACL command is impossible at slave mode. Please reset the slave device at RES terminal, when
needed.
b) DCON command
ON/OFF the internal voltage boosting circuit.
DCON=”0”: boosting circuit OFF
DCON=”1”: boosting circuit ON
c) HALT command
Power save mode ON/OFF control
HALT=”0”: normal state
HALT=”1”: power save state
The power consumption is decreased near static current at power save mode.
States of each sub-block in power save mode are as follow.
•
Oscillator, built-in power supply block stop.
•
Stop driving LCD panel, segment drive, the outputs of common driver are all set to VSS level.
•
Clock input from OSC1 port is disabled.
•
Display RAM data are conserved.
•
Operational modes are preserved as those before power save command was executed.
•
V
LCD
, V1 ~ V4 become high impedance state.
Make display OFF state before power save mode by HALT command.
And when returning from power save mode, you should display ON after oscillator, power circuit is
activated stably.
After display OFF and HALT command, if the display is turned ON before oscillator and power circuit is
not activated stably, wrong display can be appeared.
d) AMPON command
ON/OFF the internal OP. amplifier circuit of power block (voltage regulator block, electric volume,
voltage converting circuit ).
AMPON=”0”: internal power circuit OP. Amplifier OFF
AMPON=”1”: internal power circuit OP. Amplifier ON
¡
Page 61

HM17CM256
- 61 -
(34-11) LCD duty set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 *
DS2
DS1
DS0
( reset :{DS2, DS1, DS0}=0
H
read address :CH) *:”Don’t care”
LCD display duty setting
DS2
DS1
DS0
duty
0 0 0
Y direction 80 dot width display, 1/82 duty
0 0 1
Y direction 75 dot width display, 1/77 duty
0 1 0
Y direction 64 dot width display, 1/66 duty
0 1 1
Y direction 45 dot width display, 1/47 duty
1 0 0
Y direction 30 dot width display, 1/32 duty
1 0 1
Y direction 15 dot width display, 1/17 duty
1 1 0
Y direction 36 dot width display, 1/38 duty
1 1 1
Y direction 24 dot width display, 1/26 duty
Partial display is possible by setting duty operation.
¢
Page 62

HM17CM256
- 62 -
(34-12) Boosting coefficient setting
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 *
VU2
VU1
VU0
( reset :{VU2~VU0}=0
H
read address :DH) * : ”Don’t care”
coefficient setting of boosting circuit
VU2
VU1
VU0
Boosting multiple
0 0 0
No boosting *
0 0 1
2 times boosting operation
0 1 0
3 times boosting operation
0 1 1
4 times boosting operation
1 0 0
5 times boosting operation
1 0 1
6 times boosting operation
1 1 0
7 times boosting operation
1 1 1
forbidden
*V
REG
amplifier gain is 1.
(34-13) Bias setting register
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 *
B2
B1
B0
( reset :{B2~B0}=0
H
read address : EH) * : ”Don’t care”
The bias ratio is selected by this register. 1/10, 1/9, 1/8, 1/7, 1/6, 1/5 biases can be selected by B2, B1
and B0 register.
B2
B1
B0
bias
0 0 0
Operating under 1/9 bias
0 0 1
Operating under 1/8 bias
0 1 0
Operating under 1/7 bias
0 1 1
Operating under 1/6 bias
1 0 0
Operating under 1/5 bias
1 0 1
Operating under 1/10 bias
1 1 0
forbidden
1 1 1
forbidden
(34-14) RE flag state register setting.
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 1 1 1
1
TST0
RE2
RE1
RE0
( reset :{TST0, RE2, RE1, RE0}=0
H
read address :FH)
Setting the register of command extension register(RE2, RE1, RE0). When accessing command
register, the extension register corresponding flag should be set first, and then access it. The TST0
register is that for test, and so please set to “0”.
£
£
¤
Page 63

HM17CM256
- 63 -
(34-15) Gradation palette register setting
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
0
PA03
PA02
PA01
PA00
(read address :0H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 * * *
PA04
( read address :1H) *:”Don’t care”
(reset :PA04~PA00=”00000”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1
0
PA13
PA12
PA11
PA10
( read address :2H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 * * *
PA14
( read address :3H) * : ”Don’t care”
( reset :PA14~PA10=”00101”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0
0
PA23
PA22
PA21
PA20
( read address :4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 * * *
PA24
( read address:5H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PA24~PA20=”01010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1
0
PA33
PA32
PA31
PA30
( read address : 6H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 1 1 * * *
PA34
( read address : 7H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset : PA34~PA30=”01110”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0
0
PA43
PA42
PA41
PA40
( read address :8H)
Page 64

HM17CM256
- 64 -
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 * * *
PA44
( read address :9H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PA44~PA40=”10001”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1
0
PA53
PA52
PA51
PA50
( read address :AH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 * * *
PA54
( read address :BH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PA54~PA50=”10101”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0
0
PA63
PA62
PA61
PA60
( read address :CH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 * * *
PA64
( read address :DH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PA64~PA60=”11010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0
0
PA73
PA72
PA71
PA70
( read address :0H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 * * *
PA74
( read address :1H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PA74~PA70=”11111”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1
0
PB03
PB02
PB01
PB00
( read address :2H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 * * *
PB04
( read address :3H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB04~PB00=”00000”)
Page 65

HM17CM256
- 65 -
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0
0
PB13
PB12
PB11
PB10
( read address :4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 * * *
PB14
( read address :5H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB14~PB10=”00101”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1
0
PB23
PB22
PB21
PB20
( read address :6H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 * * *
PB24
( read address :7H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB24~PB20=”01010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0
0
PB33
PB32
PB31
PB30
( read address :8H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 * * *
PB34
( read address :9H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB34~PB30=”01110”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1
0
PB43
PB42
PB41
PB40
( read address :AH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 * * *
PB44
( read address :BH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB44~PB40=”10001”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0
0
PB53
PB52
PB51
PB50
( read address :CH)
Page 66

HM17CM256
- 66 -
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 0 1 * * *
PB54
( read address :DH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB54~PB50=”10101”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0
0
PB63
PB62
PB61
PB60
( read address :0H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 0 1 * * *
PB64
( read address :1H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB64~PB60=”11010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1
0
PB73
PB72
PB71
PB70
( read address :2H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 1 1 * * *
PB74
( read address :3H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PB74~PB70=”11111”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0
0
PC03
PC02
PC01
PC00
( read address :4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 1 * * *
PC04
( read address :5H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC04~PC00=”00000”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
0
PC13
PC12
PC11
PC10
( read address :6H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1 1 * * *
PC14
( read address :7H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC14~PC10=”00101”)
Page 67

HM17CM256
- 67 -
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0
0
PC23
PC22
PC21
PC20
( read address :8H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 0 1 * * *
PC24
( read address :9H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC24~PC20=”01010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1
0
PC33
PC32
PC31
PC30
( read address :AH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 1 1 * * *
PC34
( read address :BH) * : ”Don’t care”
( reset :PC34~PC30=”01110”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0
0
PC43
PC42
PC41
PC40
( read address :CH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 1 1 1 1 0 1 * * *
PC44
( read address :DH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC44~PC40=”10001”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0
0
PC53
PC52
PC51
PC50
( read address :0H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 * * *
PC54
( read address :1H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC54~PC50=”10101”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1
0
PC63
PC62
PC61
PC60
( read address :2H)
Page 68

HM17CM256
- 68 -
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 * * *
PC64
( read address :3H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC64~PC60=”11010”)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
0
PC73
PC72
PC71
PC70
( read address :4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 * * *
PC74
( read address :5H) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :PC74~PC70=”11111”)
Setting each gradation palette. The gradation level is selected among 32 level.
GRADATION LEVEL TABLE
( palette Aj, palette Bj, palette Cj (j=0~7) 3 kinds )
Palette value
Gradation
level
Remarks
Palette value
Gradation
level
remarks
0 0 0 0 0 0 Initial value of palette 0
1 0 0 0 0
16/31
0 0 0 0 1
1/31
1 0 0 0 1
17/31
Initial value of palette 4
0 0 0 1 0
2/31
1 0 0 1 0
18/31
0 0 0 1 1
3/31
1 0 0 1 1
19/31
0 0 1 0 0
4/31
1 0 1 0 0
20/31
0 0 1 0 1
5/31
Initial value of palette 1
1 0 1 0 1
21/31
Initial value of palette 5
0 0 1 1 0
6/31
1 0 1 1 0
22/31
0 0 1 1 1
7/31
1 0 1 1 1
23/31
0 1 0 0 0
8/31
1 1 0 0 0
24/31
0 1 0 0 1
9/31
1 1 0 0 1
25/31
0 1 0 1 0
10/31
Initial value of palette 2
1 1 0 1 0
26/31
Initial value of palette 6
0 1 0 1 1
11/31
1 1 0 1 1
27/31
0 1 1 0 0
12/31
1 1 1 0 0
28/31
0 1 1 0 1
13/31
1 1 1 0 1
29/31
0 1 1 1 0
14/31
Initial value of palette 3
1 1 1 1 0
30/31
0 1 1 1 1
15/31
1 1 1 1 1
31/31
Initial value of palette 7
Page 69

HM17CM256
- 69 -
(34-16) Display start command set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 0 *
SC2
SC1
SC0
( reset :{SC2, SC1, SC0}=0H, read address :6H) * : “Don’t care”
Setting the scan start output of common driver.
SC2
SC1
SC0
SHIFT=0 starting point of COM.
SHIFT=1 starting point of COM.
0 0 0
COM0~
COM79~
0 0 1
COM15~
COM64~
0 1 0
COM30~
COM49~
0 1 1
COM45~
COM34~
1 0 0
COM60~
COM19~
1 0 1
COM75~
COM4~
1 1 0
forbidden
forbidden
1 1 1
forbidden
forbidden
SHIFT=0:COM increasing direction scanning
SHIFT=1:COM decreasing direction scanning
(34-17) Serial extension CS control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 1 1 * * *
EXCS
( reset :{EXCS}=1H, read address :7H) * : “Don’t care”
Controlling the output of extension CS at serial interface application.
EXCS pin is I/O pin and used as output at master mode device thus can be controlled.
EXCS=”0”:EXCS pin output is set to “L”.
EXCS=”1”:EXCS pin output is set to “H”.
(34-18) display selection control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0
0
PWM
GLSB
*
*
( reset :{PWM, GLSB}=0H, read address :8H) * : “Don’t care”
a) GLSB command
The segment driver outputs corresponding to 4 gradation display actually uses 3 bit data to select 4
gradation levels out of 8 gradation levels, 2 bit data out of RAM area and 1 bit out of Gradation LBS.
This command sets the supplement 1 bit Gradation LSB ( GLSB ) register.
GLSB=”0”: Set the LSB of segment driver corresponding to 4-gradataion display to “0”.
GLSB=”1”: Set the LSB of segment driver corresponding to 4 gradataion display to “1”.
b) PWM command
Selection gradation display mode.
PWM=”0”: Gradation mode is selected variable 8 gradation among 32 levels.
PWM=”1”: Fixed 8 gradation display mode.
Page 70

HM17CM256
- 70 -
(34-19) RAM data length setting
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 0 1 *
*
CKS
WLS
( reset :{WLS}=0H, read address :9H) * : “Don’t care”
WLS: Selection 8 bit access or 16 bit access at RAM access. Access with 16 bits data length is effective
only at RAM access. The other accesses are 8 bits access ( command access ).
WLS=”0”: RAM access is done by 8 bits data length.
WLS=”1”: RAM access is done by 16 bits data length
CKS: Selection the oscillator.
CKS=”0”: internal oscillation mode ( default ).
Internal oscillation mode should be used under condition of OSC1 and OSC2 open.
CKS=”1”: external oscillation mode.
External oscillation mode should be used under the condition of clock input by OSC1 port or resistor
connection between OSC1 and OSC2 port.
(34-20) Electric volume registers setting.
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1
0
DV3
DV2
DV1
DV0
( read address :AH)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 1 1 *
DV6
DV5
DV4
( read address :BH) * : “Don’t care”
( reset :DV6~DV0=00H)
Setting the electric volume code. The voltage range is divided into 127 levels by this register
DV6
DV5
DV4
DV3
DV2
DV1
DV0
Output voltage
0 0 0 0 0 0 0
low
0 0 0 0 0 0 1
:
:
:
:
:
1 1 1 1 1 1 0
:
1 1 1 1 1 1 1
high
The output voltage of V
REG
is determined by Eq. ¥.
V
REG
= V
REF
x N
(N: booster coefficient)
N=1 under the condition of boosting operation is not valid (booster coefficient register, VU=0H ).
The LCD driving voltage V
LCD
is decided by V
REG
level or electric volume value (Eq. ¨).
V
LCD
= 0.5 x V
REG
+ M x (V
REG
- 0.5V
REG
) / 127
( M : DV6~DV0 register value )
To prevent over voltage from being generated by electric volume setting, when the register value is set
to upper side of electric volume, voltage level is not changed immediately.
When the register value is set to lower side of electric volume, the voltage level is changed instantly.
¦ ¦ ¦ ¦ §
© © © © ¨
Page 71

HM17CM256
- 71 -
(34-21) Oscillator circuit Rf control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0 0 0 1 1 0
1
FFL
Rf2
Rf1
Rf0
( resetª{FFL, Rf2, Rf1, Rf0}=0H, read address : DH)
The feedback resistance of oscillator circuit can be changed by setting this register.
The frame frequency is changed according to the frequency of oscillator, and the oscillation frequency is
determined by the resistor value.
When you set the frame rate, please check the state of LCD display.
Rf 2
Rf 1
Rf 0
Feedback resistance size
0 0 0
Reference value
0 0 1
0.8 x reference value
0 1 0
0.9 x reference value
0 1 1
1.1 x reference value
1 0 0
1.2 x reference value
1 0 1
forbidden
1 1 0
forbidden
1 1 1
forbidden
FFL command«Setting oscillator frequency ( frame frequency f
FLM
). ( refer to DC characteristic )
FFL=0« normal oscillator frequency ( set frame frequency, f
FLM
to 73Hz(Typ))
FFL=1« high speed oscillator frequency ( set frame frequency, f
FLM
to 150Hz(Typ))
* The value of typical frame frequency f
FLM
Typ is under following condition.
•
Display mode : variable gradation display
•
1/82 Duty
•
{Rf2, Rf1, Rf0}=0H
(34-22) Discharge control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 1 0 * * *
DIS
( reset ¬{DIS}=0H, read address ¬EH) * : “Don’t care”
The capacitors connected between V
LCD~V4
and VSS can be discharged by this control. Please refer
to capacitor setting example.
DIS=”0” discharge stop
DIS=”1” start discharge
Page 72

HM17CM256
- 72 -
(34-23) Set read address of internal register
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 0
0
RA3
RA2
RA1
RA0
( reset :{RA3, RA2, RA1, RA0}=BH)
Before executing the internal register data read command the address of register should be specified
first. For example, when display control (1) is being read out, { RA3, RA2, RA1, RA0 } = 8H should be
specified first.
Because selected register is corresponded with RE flag, please set RE flag first and then read out the
register.
Refer to the command function description and the lists of commands for the address of each register.
(34-24) Internal register data read
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 0/1
0/1
0/1 * * *
*
Internal register data read
* : “Don’t care”
This command is used to read out internal register data. Before executing this command, RE flag and
the address for internal register to read should be set first.
(34-25) Window end X address set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 0 EX3
EX2
EX1
EX0
( reset :{EX3~EX0}=0H, read address :0H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 *
EX6
EX5
EX4
( reset :{EX6~EX4}=0H, read address :1H) * : “Don’t care”
When the window area of RAM is specified(WIN=“1”) to access, the end X address of the window is set
by this command. The lower 4 bits of address should be set first and then upper 3 bits are set later
(34-26) Window end Y address set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 0 EY3
EY2
EY1
EY0
( reset :{EY3~EY0}=0H, read address :2H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 1 1 *
EY6
EY5
EY4
( reset :{EY6~EY4}=0H, read address :3H) * : “Don’t care”
When window area of RAM is specified(WIN=“1”) to access , the end Y address of the window is set by
this command. The lower 4 bits of address should be set first and then upper 3 bits are set later.
Page 73

HM17CM256
- 73 -
(34-27) Line inversion start address set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 0 LS3
LS2
LS1
LS0
( reset :{LS3~LS0}=0H, read address :4H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 *
LS6
LS5
LS4
( reset :{LS6~LS4}=0H, read address :5H) * : “Don’t care”
When the start address of negative display is set on, it is set by this command. The lower 4 bits of
address should be set first and then upper 3 bits are set later. The possible range is LS=00H~4FH .
The other values are forbidden. Please set the value under the condition, LS≤LE.
(34-28) Line inversion end address set
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 LE3
LE2
LE1
LE0
( reset :{LE3~LE0}=0H, read address :6H)
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 1 1 *
LE6
LE5
LE4
( reset :{LE6~LE4}=0H, read address :7H) * : “Don’t care”
When the end address of negative display is set on, it is set by this command. The lower 4 bits of
address should be set first and then upper 3 bits are set later.
The possible range is LS=00H~4FH . The other values are forbidden. Please set the value under the
condition, LS≤LE.
(34-29) Line inversion control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 0 * * BT
LREV
( reset :{PSC, BT, LREV}=0H, read address :8H) * : “Don’t care”
Setting the status of line inversion display tone.
LREV command : line inversion display ON/OFF setting.
LREV=”0”: normal display
LREV=”1”: line inversion display ON. The area specified by line inversion start/stop address is
blinked.
The blink type display is controlled by BT command.
When line inversion display is ON(LREV=”1”), line inversion start address(LSi) and line inversion stop
address(LEi) should be set as following condition.
LSi ≤ LEi - (1)
And following condition is forbidden.
LEi < LSi - (2)
Page 74

HM17CM256
- 74 -
BT command : inversion timing selection at line inversion display
BT=”0”: Negative tone display in specified area
BT=”1”: The image of specified area is blinked by every 32 frame.
¯ ¯ ¯ °
Display example (BT=”1”)
And be cautious that LREV and BT commands have no influence on dummy segment driver circuit.
And the image selected by COMI0, COMI1 is excluded.
HYUNDAI
LCD DRIVER
Low Power and
Low Voltage
HYUNDAI
LCD DRIVER
Low Power and
Low Voltage
Line inversion display example (LREV=”1”,BT=”1”)
(34-30) Dummy segment driver address selection ( Refer to dummy segment drive related description. )
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 0 1 * * *
DMY
( reset :{DMY}=0H, read address :8H) * : “Don’t care”
When data is to be written to dummy segment driver, this register is active (DMY=”1”).
DMY=”0”: normal display RAM access
DMY=”1”: display data access to dummy segment driver
Normal segment drivers acquire display data from display RAM, but dummy segment drivers acquire
display data from corresponding register not from display RAM. The capacity of register is 4 bytes.
That is correspond to SEGSA0~SEGSA
3
SEGSB0~SEGSB
3
SEGSC0~SEGSC3 output.
When accessing with DMY = “1”, address setting is valid by only X address. There is 4 byte capacity,
and so 00H, 01H, 02H, 03H is valid at 8 bits mode and 00H, 01H is valid at 16 bits mode. There is no
Changes per
every 32 frame.
line inversioin start address
line inversioin end address
Changes per
every 32 frame.
®
° ¯ ¯ ¯ °
° ¯ ¯ ¯ °
° ° ° ° °
° ¯ ¯ ¯ °
° ¯ ¯ ¯ °
° ¯ ¯ ¯ °
¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
¯ ¯ ¯ ¯ ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
¯ ° ° ° ¯
° ° ° ° °
²
²
±
±
Page 75

HM17CM256
- 75 -
relation with Y address setting value.
To access with DMY = “1”, register data write-in is possible with increment mode.
(34-31) PWM mode control
CS
RS
RD
WR
RE2
RE1
RE0
D7
D6
D5
D4
D3
D2
D1
D0
0 1 1 0 1 0 1 1 0 1
0
PWMS
PWMA
PWMB
PWMC
( reset :{PWMS, PWMA, PWMB, PWMC}=0H, read address :8H) * : “Don’t care”
PWM mode selection. ( Refer to following wave diagram. )
PWMS=”0”: Selection PWM type1.
PWMA, PWMB, PWMC=”0” : PWM type1-O is selectable for each A, B, C data.
PWMA, PWMB, PWMC=”1” : PWM type1-E is selectable for each A, B, C data.
PWMS=”1”: Selection PWM type2.
a) PWM type1 (PWMS=”0”)
b) PWM type2 (PWMS=”1”)
odd line
even line
´ µ ´
“H”
“L”
V
LCD
V2
V2
Type-O
Type-E
CL
SEG
V
LCD
“H”
“L”
CL
SEG
V2
V
LCD
³
µ
µ
Page 76

HM17CM256
- 76 -
(35) Relation between each setting and COM / display RAM
The COM port number corresponds to Y address of display RAM by SHIFT command, LCD duty
command, common display start position command and display start line setting command.
•
When display start address was set to “0”.
According to LCD duty and display start common line address, the port of COM line and
display RAM address ( MY ) is changed by 15 line unit.
When SHIFT register is set to “0” common line shift to upward direction, and when the value is
“1”, common line shift to downward direction. When display start address (LA6~LA0) is set to
“0”, the “MY” corresponds to starting position is “0”. The MY shift upward direction as display
goes on.
In any case, COMI0=MY80, COMI1=MY81 .
•
When display start line was set except for “0”
According to LCD duty and display start common line address, the port of COM line and
display RAM address, MY is changed by 15 line unit.
When SHIFT register is set to “0” common line shift to upward direction, and when the value is
“1”, common line shift to downward direction. When display start address (LA6~LA0) is set to
except for “0”, the “MY” corresponds to starting position is shift by the amount of set value.
The MY shift upward direction as display goes on but MY is set to “0” after MY=79.
In any case, COMI0=MY80, COMI1=MY81 .
Page 77

HM17CM256
- 77 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/82 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“000” (1/82 duty)
“000” (1/82 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0 65
50
35
20 5 79
64
49
34
19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5 79
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14 79
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20
79
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
79
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35 79
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44 79
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
79
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
79
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65 79
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74 79
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79
79
64
49
34
19 4 0
65
50
35
20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
¶
· · · · · · · ·
Page 78

HM17CM256
- 78 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/77 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“001” (1/77 duty)
“001” (1/77 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0 65
50
35
20 5
64
49
34
19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5
74
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 74
COM10 74
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
74
COM25
74
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39 74
COM40 74
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
74
COM55
74
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69 74
COM70 74
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
74
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 64
49
34
19 4 0
65
50
35
20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
¸
¹ ¹ ¹ ¹ ¹ ¹ ¹ ¹
Page 79

HM17CM256
- 79 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/66 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“010” (1/66 duty)
“010” (1/66 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0
50
35
20 5 49
34
19
4
COM1 63
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
63
COM14
COM15 0
COM16
63
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20
COM21 63
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28 63
COM29
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
COM36
63
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
63
COM44
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
COM51 63
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58 63
COM59
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
63
COM64 0
COM65
COM66
63
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78 63
COM79
49
34
19 4 0 50
35
20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
º
» » » » » » » »
Page 80

HM17CM256
- 80 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/47 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“011” (1/47 duty)
“011” (1/47 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0 35
20 5
34
19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5
44
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 44
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20 44
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
44
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
44
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39 44
COM40 44
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
44
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
44
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59 44
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70 44
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
44
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 34
19 4 0
35
20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
¼
½ ½ ½ ½ ½ ½ ½ ½
Page 81

HM17CM256
- 81 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/32 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common back scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“100” (1/32 duty)
“100” (1/32 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0
20 5 19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5 29
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
29
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20
29
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24 29
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
29
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35 29
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44 29
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
29
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55 29
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
29
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
29
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74 29
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79
19 4 0 20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
¾
¿ ¿ ¿ ¿ ¿ ¿ ¿ ¿
Page 82

HM17CM256
- 82 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/17 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“101” (1/17 duty)
“101” (1/17 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0 5 4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5
14
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 14
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
14
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20 14
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29 14
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
14
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
14
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50 14
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59 14
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65
14
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70 14
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
14
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 4 0 5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
À
Á Á Á Á Á Á Á Á
Page 83

HM17CM256
- 83 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/38 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“110” (1/38 duty)
“110” (1/38 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0 35
20 5
34
19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
35
COM15 0
35
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 0
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29 35
COM30 0 35
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
35
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
35
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0 35
COM50 35
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 0
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
35
COM65
35
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 0
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 34
19 4 0
35
20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Â
à à à à à à à Ã
Page 84

HM17CM256
- 84 -
display start line set to “0” , 1/26 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“111” (1/26 duty)
“111” (1/26 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000000” (display start point 0)
“0000000” (display start point 0)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 0
20 5 19
4
COM1
COM2
COM3
23
COM4 0
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11 23
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 0
COM16
COM17
COM18 23
COM19 0
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
23
COM24
COM25
COM26
23
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 0
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 0
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38 23
COM39
COM40
COM41 23
COM42
COM43
COM44
COM45 0
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 0
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
23
COM54
COM55
COM56
23
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 0
COM61 23
COM62
COM63
COM64 0
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68 23
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 0
COM76
23
COM77
COM78
COM79
19 4 0 20
5
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ä
Å Å Å Å Å Å Å Å
Page 85

HM17CM256
- 85 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/82 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“000” (1/82 duty)
“000” (1/82 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5 70
55
40
25
10 4 69
54
39
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 0 5
COM5
79
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 79 0
COM10 0 79
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
79 0
COM25 0
79
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39 79 0
COM40 0 79
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
79 0
COM55 0
79
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69 79 0
COM70 0 79
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
79
COM75 0 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 4 69
54
39
24 9 5
70
55
40
25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Æ
Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç Ç
Page 86

HM17CM256
- 86 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/77 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“001” (1/77 duty)
“001” (1/77 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5 70
55
40
25
10 69
54
39
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5
79
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 79
COM10 79
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
79
COM25
79
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39 79
COM40 79
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
79
COM55
79
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69 79
COM70 79
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
79
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 69
54
39
24 9 5
70
55
40
25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
È
É É É É É É É É
Page 87

HM17CM256
- 87 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/66 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“010” (1/66 duty)
“010” (1/66 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5
55
40
25
10
54
39
24
9
COM1 68
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
68
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
68
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20
COM21 68
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28 68
COM29
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
COM36
68
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
68
COM44
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
COM51 68
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58 68
COM59
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
68
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
68
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78 68
COM79
54
39
24 9 5 55
40
25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ê
Ë Ë Ë Ë Ë Ë Ë Ë
Page 88

HM17CM256
- 88 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/47 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“011” (1/47 duty)
“011” (1/47 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5 40
25
10 39
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5
49
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 49
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20 49
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
49
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
49
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39 49
COM40 49
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
49
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
49
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59 49
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70 49
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
49
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 39
24 9 5
40
25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ì
Í Í Í Í Í Í Í Í
Page 89

HM17CM256
- 89 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/32 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“100” (1/32 duty)
“100” (1/32 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5
25
10
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5 34
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
34
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20
34
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24 34
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29
34
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35 34
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44 34
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
34
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55 34
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
34
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
34
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74 34
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79
24 9 5 25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Î
Ï Ï Ï Ï Ï Ï Ï Ï
Page 90

HM17CM256
- 90 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/17 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“101” (1/17 duty)
“101” (1/17 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5 10 9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5
19
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9 19
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
19
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20 19
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29 19
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
19
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
19
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50 19
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59 19
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
19
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70 19
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
19
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 9 5 10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ð
Ñ Ñ Ñ Ñ Ñ Ñ Ñ Ñ
Page 91

HM17CM256
- 91 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/38 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“110” (1/38 duty)
“110” (1/38 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5 40
25
10 39
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
COM4 5
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11
COM12
COM13
COM14
40
COM15 5
40
COM16
COM17
COM18
COM19 5
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
COM24
COM25
COM26
COM27
COM28
COM29 40
COM30 5 40
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
40
COM36
COM37
COM38
COM39
COM40
COM41
COM42
COM43
COM44
40
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5 40
COM50 40
COM51
COM52
COM53
COM54
COM55
COM56
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 5
COM61
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
40
COM65
40
COM66
COM67
COM68
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 5
COM76
COM77
COM78
COM79 39
24 9 5
40
25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ò
Ó Ó Ó Ó Ó Ó Ó Ó
Page 92

HM17CM256
- 92 -
display start line set to “5” , 1/26 duty by DS2~DS0 register
SHIFT set value
SHIFT=”0” (common forward scan)
SHIFT=”1” (common backward scan)
DS2
DS1
DS0
“111” (1/26 duty)
“111” (1/26 duty)
SC2
SC1
SC0
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
“000”
“001”
“010”
“011”
“100”
“101”
LA6
LA0
“0000101” (display start point 5)
“0000101” (display start point 5)
COMI0
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
80
COM0 5
25
10
24
9
COM1
COM2
COM3
28
COM4 5
COM5
COM6
COM7
COM8
COM9
COM10
COM11 28
COM12
COM13
COM14
COM15 5
COM16
COM17
COM18 28
COM19 5
COM20
COM21
COM22
COM23
28
COM24
COM25
COM26
28
COM27
COM28
COM29
COM30 5
COM31
COM32
COM33
COM34 5
COM35
COM36
COM37
COM38 28
COM39
COM40
COM41 28
COM42
COM43
COM44
COM45 5
COM46
COM47
COM48
COM49 5
COM50
COM51
COM52
COM53
28
COM54
COM55
COM56
28
COM57
COM58
COM59
COM60 5
COM61 28
COM62
COM63
COM64 5
COM65
COM66
COM67
COM68 28
COM69
COM70
COM71
COM72
COM73
COM74
COM75 5
COM76
28
COM77
COM78
COM79
24 9 5 25
10
COMI1
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
81
The number on the table means MY ( Y direction shift address ).
The COM electrodes without MY number are driving with non-selection level signal.
The Marked line is display start line.
Ô
Õ Õ Õ Õ Õ Õ Õ Õ
Page 93

HM17CM256
- 93 -
■
ABSOLUTE MAXIMUM RATING
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
PORT
RATINGS
UNIT
supply voltage (1)
VDD
VDD
-0.3 ~ +4.0
V
supply voltage (2)
VEE
VEE
-0.3 ~ +4.0
V
supply voltage (3)
V
OUT
V
OUT
-0.3 ~ +20.0
V
supply voltage (4)
V
REG
V
REG
-0.3 ~ +20.0
V
supply voltage (5)
V
LCD
V
LCD
-0.3 ~ +20.0
V
supply voltage (6)
V1, V2, V3, V4
V1, V2, V3, V4
-0.3 ~ V
LCD
+ 0.3
V
input voltage
VI
VSS(0V)
reference
Ta = +25°C
*1
-0.3 ~ V
DD
+ 0.3
V
Storage temperature
T
stg
-45 ~ +125
°
C
*1 D0~D15, CS, RS, M/S, RD, WR, OSC1, LP, FLM, FR, CLK, RES, TEST port
■
RECOMMENDED OPERATING CONDITIONS
ITEM
SYMBOL
PORT
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
REMARK
V
DD1
1.7
3.3
V
*1
V
DD2
VDD
2.4
3.3
V
*2
supply voltage
VEE
VEE
2.4
3.3
V
*3
V
LCD
V
LCD
5
18.0
V
*4
V
OUT
V
OUT
18.0
V
V
REG
V
REG
V
OUT
x 0.9
V
Recommended
operating voltage
V
REF
V
REF
2.1
3.3
V
*5
Operation
temperature
T
opr
-30
85
°
C
*1 The case when internal reference voltage generation circuit (V
BA
output) is not used.
The voltage compare to VSS port.
*2 The case when internal reference voltage generation circuit (V
BA
output) is used.
The voltage compare to VSS port.
*3 When the boosting circuit is used, supply voltage VEE should be used within the limit.
When driving LCD panel by use of internal boosting circuit, it is possible to short VDD and VEE.
*4 Please keep the relation, V
SS
< V4 < V3 < V2 < V1 < V
LCD
≤
V
OUT
.
*5 When the internal voltage regulator circuit is used, reference voltage V
REF
should be used within the limit.
Please keep the relation V
REF
≤
VEE .
Page 94

HM17CM256
- 94 -
■
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
•
DC Characteristics 1
Unless otherwise noted VSS = 0V, V
DD
= +1.7~+3.3V, Ta = -30~+85°C
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
PORT
High level input voltage
VIH
0.8 VDD
VDD
V
*1
Low level input voltage
VIL 0
0.22 VDD
V
*1
High level output voltage
V
OH1
IOH = -0.4mA
VDD - 0.4
V
*2
Low level output voltage
V
OL1
IOL = 0.4mA
0.4
V
*2
High level output voltage
V
OH2
IOH = -0.1mA
VDD - 0.4
V
*3
Low level output voltage
V
OL2
IOL = 0.1mA
0.4
V
*3
Input leakage current
ILI
VI = VSS or VDD
-10
10
µ
A
*4
Output leakage current
ILO
VI = VSS or VDD
-10
10
µ
A
*5
V
LCD
= 10V
1 2
LCD driver output
ON resistance
R
ON1
|ÖVON| = 0.5V
V
LCD
= 6V
2 4
kΩ
*6
Static current
I
STB
CS=V
DD,
Ta=25°C
VDD = 3V
15
µ
A
*7
f
OSC1
372
*8
f
OSC2
84
*9
f
OSC3
FFL = “0”
(normal
mode)
TBD
12
TBD
*10
f
OSC4
762.6
*8
f
OSC5
172.2
*9
Oscillator frequency
f
OSC6
VDD = 3V
Ta = 25°C
FFL = “1”
(high speed
mode)
TBD
24.6
TBD
kHz
*10
fr1
Rf=6.2kΩ
775.2
fr2
Rf=20kΩ
373.9
fr3
Rf=51kΩ
167.8
fr4
Rf=110kΩ
84.3
fr5
Rf=390kΩ
25.8
oscillator frequency
by External resistor
fr6
Rf=820kΩ
TBD
12.6
TBD
kHz
Boosting output
voltage
V
OUT
N x boosting (N=2~7)
RL = 30kΩ (between V
OUT ,VSS
)
N * V
EE
* 0.95
V
*11
Current consumption (1)
I
DD1
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (2)
I
DD2
VDD = 2.5V
7 x boosting (all ON)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (3)
I
DD3
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (4)
I
DD4
VDD = 2.5V 7x
boosting
(cross check)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (5)
I
DD5
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (6)
I
DD6
VDD = 3.0V
6
x boosting (all ON)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (7)
I
DD7
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (8)
I
DD8
VDD = 3.0V 6x
boosting
(cross check)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (9)
I
DD9
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (10)
I
DD10
VDD = 3.0V
5
x boosting (all ON)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (11)
I
DD11
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (12)
I
DD12
VDD = 3.0V 5x
boosting
(cross check)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (13)
I
DD13
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (14)
I
DD14
VDD = 3.0V
4
x boosting (all ON)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (15)
I
DD15
FFL = “0”
TBD
TBD
Current consumption (16)
I
DD16
VDD = 3.0V 4x
boosting
(cross check)
FFL = “1”
TBD
TBD
µ
A
*12
VBA output voltage
VBA
VEE = 2.4~3.3V
TBD
0.9 VEE
TBD
V
*13
V
REG
output voltage
V
REG
V
EE
= 2.4~3.3V
V
REF
= 0.9 x VEE
N
x boosting
(N=2~7)
TBD
(V
REF
x N)
TBD
V
*14
Page 95

HM17CM256
- 95 -
■
ELECTRICAL CHARACTERISTICS
•
DC Characteristics 1
Unless otherwise noted VSS = 0V, V
DD
= +1.7~+3.3V, Ta = -30~+85°C
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN
TYP
MAX
UNIT
PORT
V
LCD
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V
V1
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V
V2
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V
V3
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V
Output voltage
V4
TBD
TBD
TBD
TBD
V
•
Oscillator frequency,f
OSC
at each mode, relation external clock frequency,fCK to LCD frame frequency,f
FLM
Display duty (1/D)
ITEM
Used
clock
Display mode
1/82, 1/77, 1/66
1/47, 1/38, 1/32, 1/26
1/17
PORT
Variable
gradation display
f
OSC
/ (62*D)
f
OSC
/ (62*D*2)
f
OSC
/ (62*D*4)
Fixed gradation
display
f
OSC
/ (14*D)
f
OSC
/ (14*D*2)
f
OSC
/ (14*D*4)
Using internal
oscillator
circuit
f
OSC
BW display
f
OSC
/ (2*D)
f
OSC
/ (2*D*2)
f
OSC
/ (2*D*4)
Variable
gradation display
fCK / (62*D)
fCK / (62*D*2)
fCK / (62*D*4)
Fixed gradation
display
fCK / (14*D)
fCK / (14*D*2)
fCK / (14*D*4)
Input external
clock
fCK
BW display
fCK / (2*D)
fCK / (2*D*2)
fCK / (2*D*4)
FLM
Page 96

HM17CM256
- 96 -
Applied port (* Remark Solves)
*1 D0~D15, CS, RS, M/S, RD, WR, P/S, SEL68, CLK, CL, FLM, FR, RES ports
*2 D0~D15 ports
*3 CL, FLM, FR, CLK ports
*4 CS, RS, M/S, SEL68, RD, WR, P/S, RES, OSC1 ports
*5 applicable at D0~D15, CL, FLM, FR, CLK = high impedance state
*6 SEGA0~SEGA
127
, SEGB0~SEGB
127
, SEGC0~SEGC
127
, COM0~COM79, COMI0, COMI1 ports
resistance when being supplied 0.5V between each output ports and power port (V
LCD, V1, V2, V3, V4
)
applicable under bias ratio = 1/9
*7 VDD ports
VDD current when source clock is stopped, chip selection (CS=VDD) is non-selection state and no load.
*8 oscillator frequency when internal oscillator circuit is used ( gradation display mode).
applicable under Rf register of oscillator circuit, {Rf2, Rf1, Rf0} = “000”
*9 oscillator frequency when internal oscillator circuit is used ( fixed gradation display mode).
applicable under Rf register of oscillator circuit, {Rf2, Rf1, Rf0} = “000”
*10 oscillator frequency when internal oscillator circuit is used ( BW display mode).
applicable under Rf register of oscillator circuit, {Rf2, Rf1, Rf0} = “000”
*11 V
OUT
port
N x boosting (N=2~7). applicable under internal oscillator circuit and internal power circuit are ON state
VEE = 2.4~3.3V, electric volume is MAX(“1111111”).
bias = 1/5~1/10, 1/82 duty, no load at LCD driver port.
RL = 30kΩ(between V
OUT ,VSS
), CA1= CA2=1.0µF, CA3=0.1µF, DCON=“1”, AMPON=“1”
*12 applicable under internal oscillator circuit and internal power circuit are ON state and no access from
CPU.
electric volume is “1111111”.
Display is all ON and cross check pattern display ( variable gradation display mode), and no load at LCD
driver port.
Test condition : VDD=VEE=V
REF
, CA1=CA2=1.0µF, CA3=0.1µF, DCON=“1”, AMPON=“1”, NLIN=”0”,
1/82 duty.
*13 V
REG
output voltage when VBA output is connected to V
REF
input, V
REG
gain is N=1.
*14 V
REG
port
VEE= 2.4~3.3V, V
REF
= 0.9 VEE, bias= 1/5~1/10, 1/82 duty, electric volume is “1111111”×
Cross hatch state and no load at LCD driver port.
Boosting coefficient N is 2~7 times
Test condition : CA1=CA2=1.0µF, CA3=0.1µF, DCON=“1”, AMPON=“1”, NLIN=”0”×
Page 97

HM17CM256
- 97 -
■
AC CHARACTERISTICS
•
SYSTEM BUS READ / WRITE TIMING (80 series CPU interface)
(write timing)
(VDD=2.7∼3.3V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLW8
t
WRHW8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
WR
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=2.4∼2.7V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLW8
t
WRHW8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
WR
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=1.7∼2.4V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLW8
t
WRHW8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
WR
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
notice) All timing reference is 20% and 80% of VDD and 80%.
t
CYC8
t
AS8
CS
WR
RS
D0 ∼ D15
t
AH8
t
WRLW8
t
WRHW8
t
DS8
t
DH8
Page 98

HM17CM256
- 98 -
read timingÙ
(VDD=2.7∼3.3V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLR8
t
WRHR8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
RD
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=2.4∼2.7V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLR8
t
WRHR8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
RD
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=1.7∼2.4V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH8
t
AS8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Write ”L” pulse width
Write ”H” pulse width
t
CYC8
t
WRLR8
t
WRHR8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
RD
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS8
t
DH8
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
notice) All timing reference is 20% and 80% of VDD and 80%.
t
AS8
CS
RS
D0 ∼ D15
t
RDD8
t
RDH8
t
CYC8
RD
t
WRLR8
t
WRHR8
t
AH8
Ø
Page 99

HM17CM256
- 99 -
•
SYSTEM BUS READ / WRITE TIMING (68 series CPU interface)
(write timingÚ
(VDD=2.7∼3.3V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELW6
t
EHW6
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=2.4∼2.7V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELW6
t
EHW8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=1.7∼2.4V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELW6
t
EHW6
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
notice) All timing reference is 20% and 80% of VDD and 80%.
t
AS6
CS
RS
t
AH6
R/W
(WR)
D0 ∼ D15
t
EHW6
t
ELW6
t
DS6
t
DH6
t
CYC6
E
(RD)
Page 100

HM17CM256
- 100 -
(read timing)
(VDD=2.7∼3.3V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELR6
t
EHR6
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=2.4∼2.7V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELR6
t
EHR8
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
(VDD=1.7∼2.4V, Ta=-30∼+85°C)
ITEM
SYMBOL
CONDITION
MIN.
MAX.
UNIT
PORT
Address hold timing
Address setup timing
t
AH6
t
AS6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
CS
RS
System cycle timing
Enable ”L” pulse width
Enable ”H” pulse width
t
CYC6
t
ELR6
t
EHR6
TBD
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
ns
E
Data setup timing
Data hold timing
t
DS6
t
DH6
TBD
TBD
ns
ns
D0 ∼ D15
notice) All timing reference is 20% and 80% of VDD and 80%.
t
AS6
CS
RS
t
AH6
R/W
(WR)
D0 ∼ D15
t
EHR6
t
ELR6
t
RDD6
t
RDH6
t
CYC6
E
(RD)
 Loading...
Loading...