Page 1

HA12215F
Audio Signal Processor for Cassette Deck
(Dolby B-type NR with Recording System)
ADE-207-253D (Z)
Target Specification
5th Edition
Oct. 1999
Description
HA12215F is silicon monolithic bipolar IC providing Dolby noise reduction system*1, music sensor
system, REC equalizer system and each electronic control switch in one chip.
Note: 1. Dolby is a trademark of Dolby Laboratories Licensing Corporation.
A license from Dolby Laboratories Licensing Co r por ation is required for the use of this IC.
Functions
• Dolby B-NR × 2 channel
• REC equalizer × 2 channel
• Music sensor × 1 channel
• Pass amp. × 2 channel
• Each electronic control switch to change REC equalizer, bias, etc.
Features
• REC equalizer is very small number of external parts and have 6 types of frequency characteristics
built-in.
• 2 types of input for PB, 1 type of input for REC.
• 70µ - PB equalizer changing system built-in.
• Dolby NR with dubbing double cassette decks.
Unprocessed signal output available from recording out terminals during PB mode.
• Provide stable music sensor system, available to design music sensing time and level.
• Controllable from direct micro-computer output.
• Bias oscillator control switch built-in.
• NR ON / OF F and REC / PB fully electronic control switch ing built-in.
• Normal-speed / high-speed, Normal / Crom / Metal and PB equalizer fully electronic control switching
built-in.
• Available to reduce substrate-area because of high integration and small external parts.
Page 2

HA12215F
Ordering Information
Operating Voltage
Product VCC (V) VEE (V) Note
HA12215F +6.0 to +7.5 –7.5 to –6.0 | V
Standard Level
Product Package PB-OUT Level REC-OUT Level Dolby Level
HA12215F FP-56 580 mVrms 300 mVrms 300 mVrms
Function
+ VEE | < 1.0 V
CC
Music
Product Dolby B-NR REC-EQ
HA12215F ❍❍❍❍❍❍
Note: Depending on the employed REC / PB head and test tape characteristics, there is a rare case that
the REC-EQ characteristics of this LSI can not be matched to the required characteristics because of
built-in resistors which determined the REC-EQ parameters in this case, please inquire the
responsible agent because the adjustment built-in resistor is necessary.
Sensor Pass Amp.
REC / PB
Selection ALC
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 2 of 69
Page 3
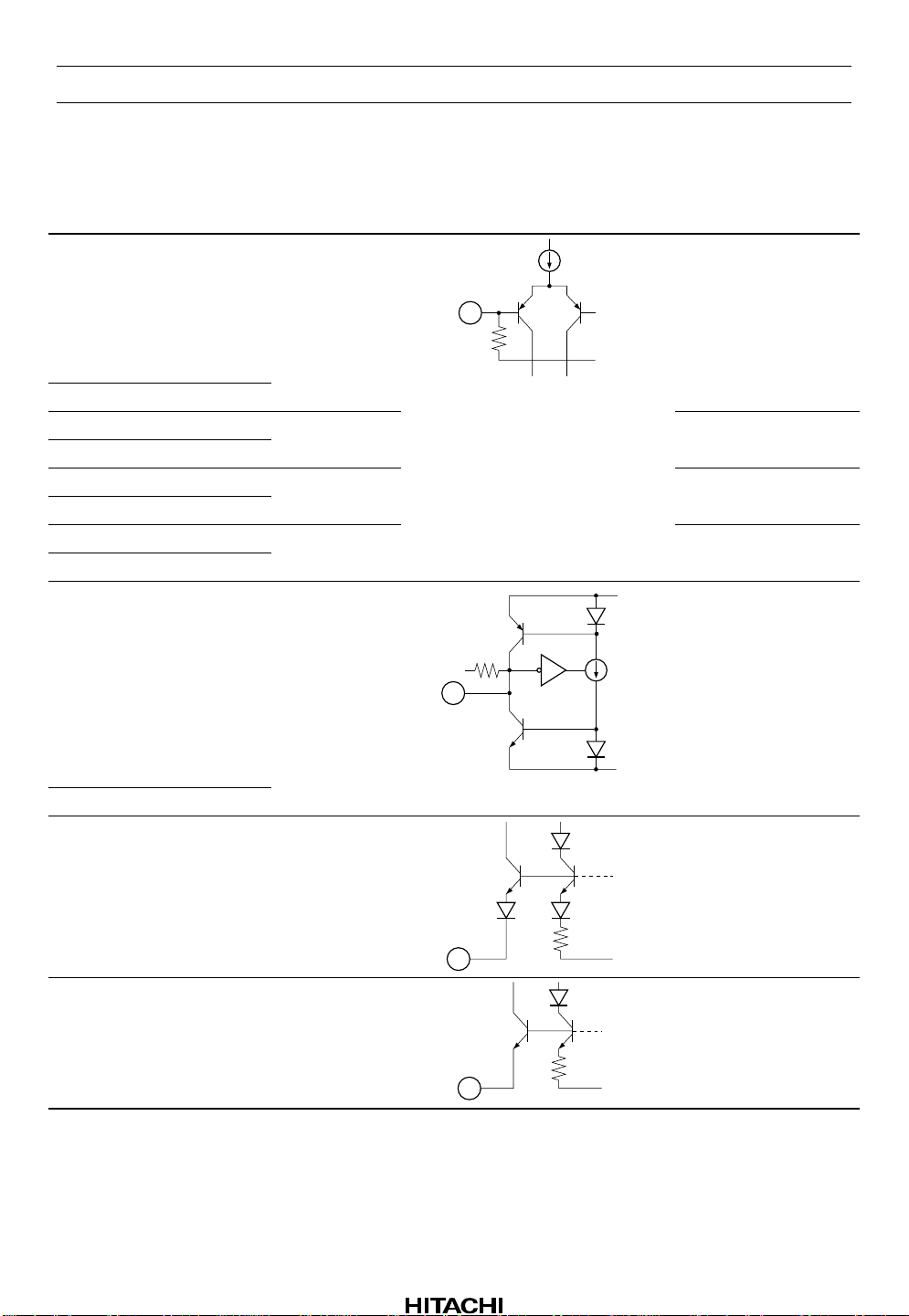
HA12215F
Pin Description, Equivalent Circuit (VCC = ±7 V, A system of split supply voltage,
Ta = 25°C, No Signal, The value in the show typical value.)
Pin No. Terminal Name Note Equivalent Circuit Pin Description
51 AIN (R) V = GND
V
100k
GND
48 AIN (L)
53 BIN (R) V = GND PB B Deck input
46 BIN (L)
56 RIN (R) V = GND REC input
43 RIN (L)
5 EQIN (R) V = GND REC equalizer input
38 EQIN (L)
1DET (R) V = V
+2.7V
EE
V
PB A Deck input
Time constant pin for
CC
Dolby-NR
42 DET (L)
2 BIAS1 V = VEE+0.6V
41 BIAS2 V = VEE+1.3V
V
V
EE
Dolby bias current
input
V
V
EE
REC equalizer bias
current input
V
V
EE
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 3 of 69
Page 4
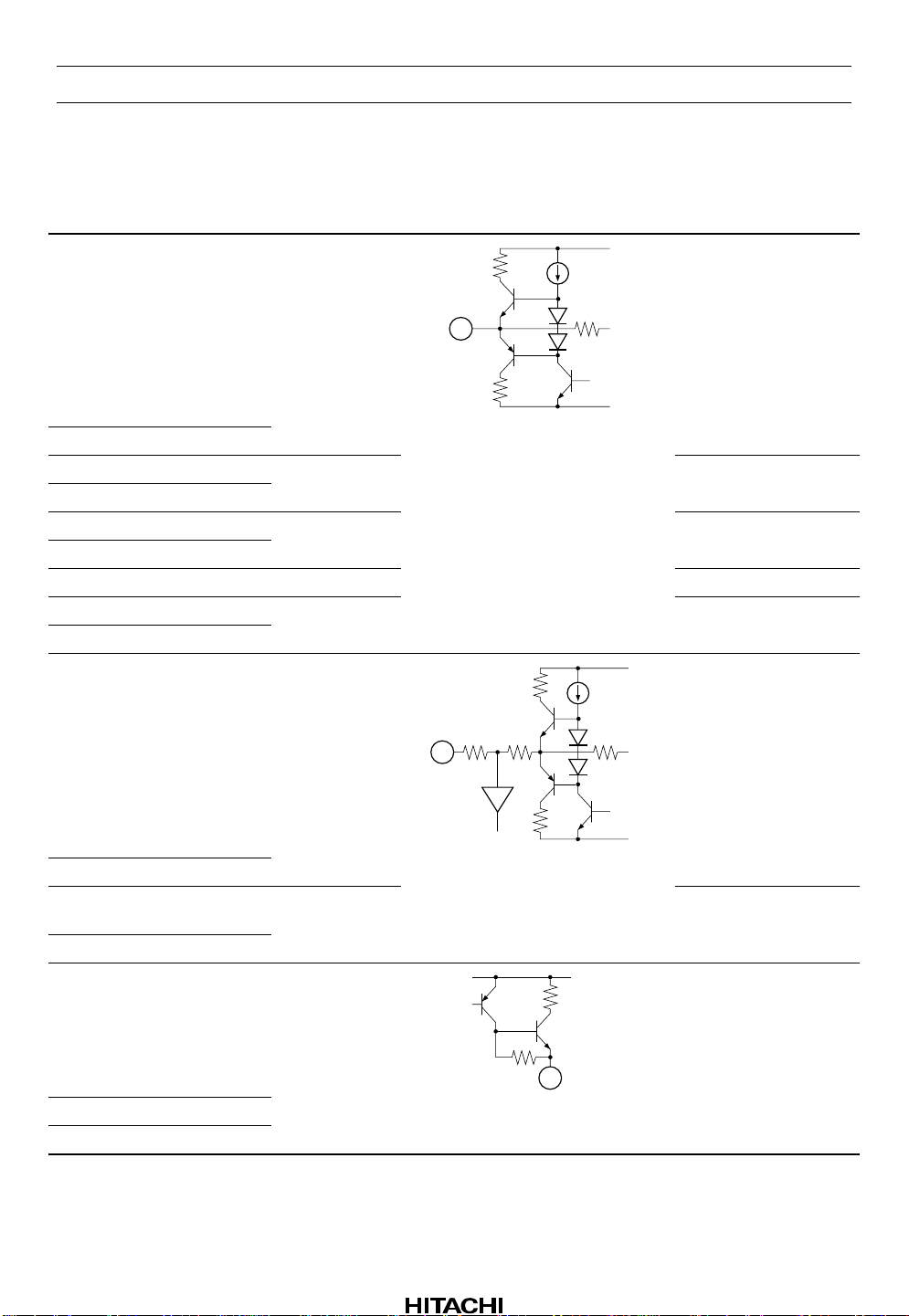
HA12215F
Pin Description, Equivalent Circuit (VCC = ±7 V, A system of split supply voltage,
Ta = 25°C, No Signal, The value in the show typical value.) (cont)
Pin No. Terminal Name Note Equivalent Circuit Pin Description
3 PBOUT (R) V = GND
V
CC
V
V
EE
40 PBOUT (L)
4 RECOUT (R) V = GND REC output
39 RECOUT (L)
7 EQOUT (R) V = GND REC equalizer output
36 EQOUT (L)
28 MAOUT V = GND MS Amp. output *
8 ROUT (R) V = GND Input Amp. output
35 ROUT (L)
52 ABO (R) R1 = 15 k
R2 = 12 k
PB output
Time constant pin for
V
CC
PB equalizer (70µ)
1
47 ABO (L)
6 BOOST (R) R1 = 4.8 k
R2 = 4.8 k
37 BOOST (L)
31 BIAS (M) V = VCC – 0.7V
32 BIAS (C)
33 BIAS (N)
Note: 1. MS: Music Sensor
V
R2R1
V
EE
Time constant pin for
low boost
V
CC
REC bias current
output
V
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 4 of 69
Page 5
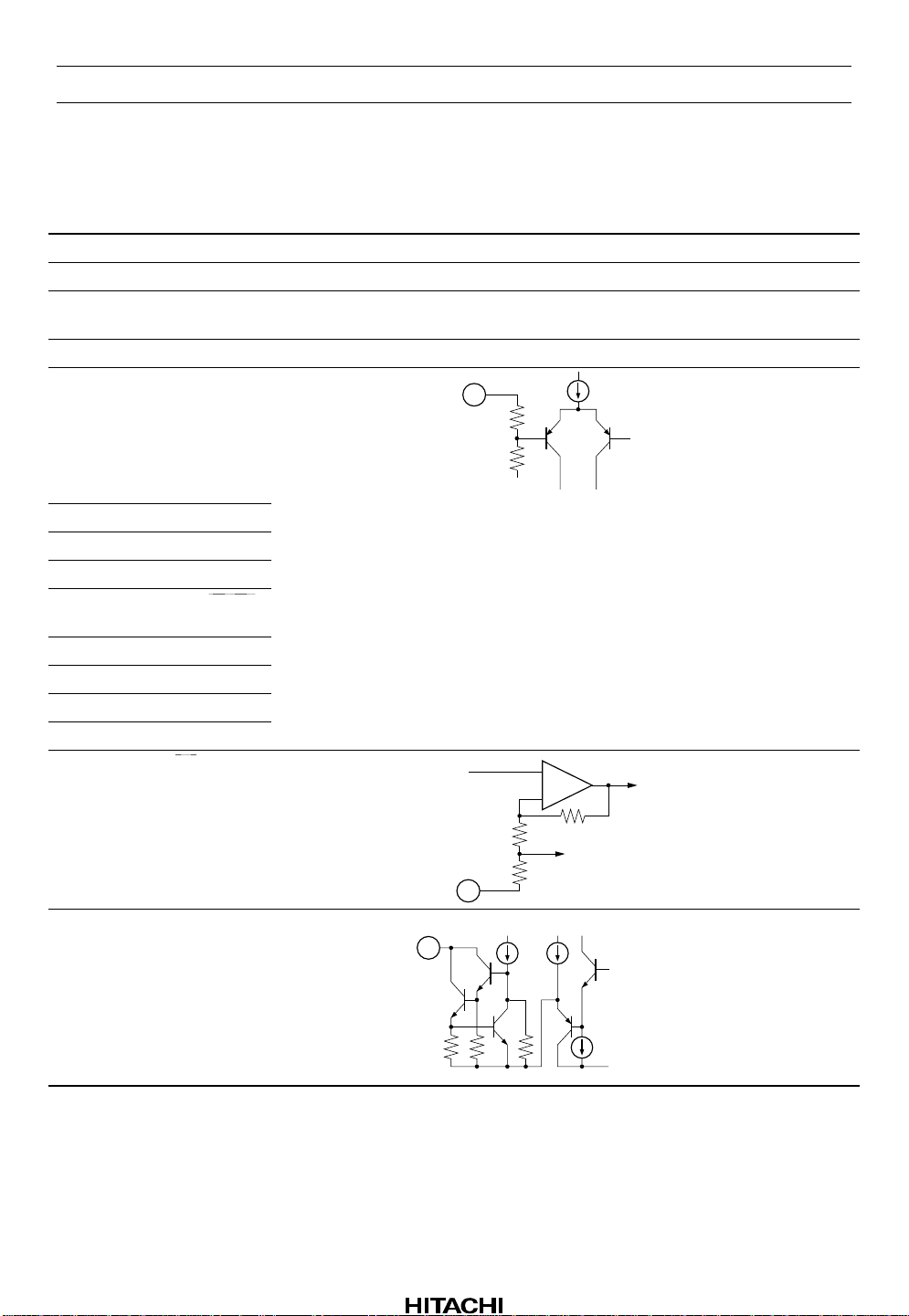
HA12215F
Pin Description, Equivalent Circuit (VCC = ±7 V, A system of split supply voltage,
Ta = 25°C, No Signal, The value in the show typical value.) (cont)
Pin No. Terminal Name Note Equivalent Circuit Pin Description
21 V
CC
V = V
CC
49 GND V = 0V GND pin
50 V
EE
V = V
EE
45, 54 NC No connection No connection
15 ALC ON/OFF I = 50 µA
V
I
22 k
100 k
GND
16 PB A/B
17 A 120/70
18 NORM/HIGH
19 B NORM/CROM/
METAL
20 BIAS ON/OFF
22 RM ON/OFF
23 NR ON/OFF
25 LM ON/OFF
24 REC/PB/PASS
2.5 V
+
−
Power supply
Negative power
supply
Mode control input
Mode control input
26 MSOUT I = 0 µA
Note: 1. MS: Music Sensor
100 k
100 k
22 k
V
V
V
CC
I
MSGND
V
EE
MS output (to MPU) *
1
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 5 of 69
Page 6
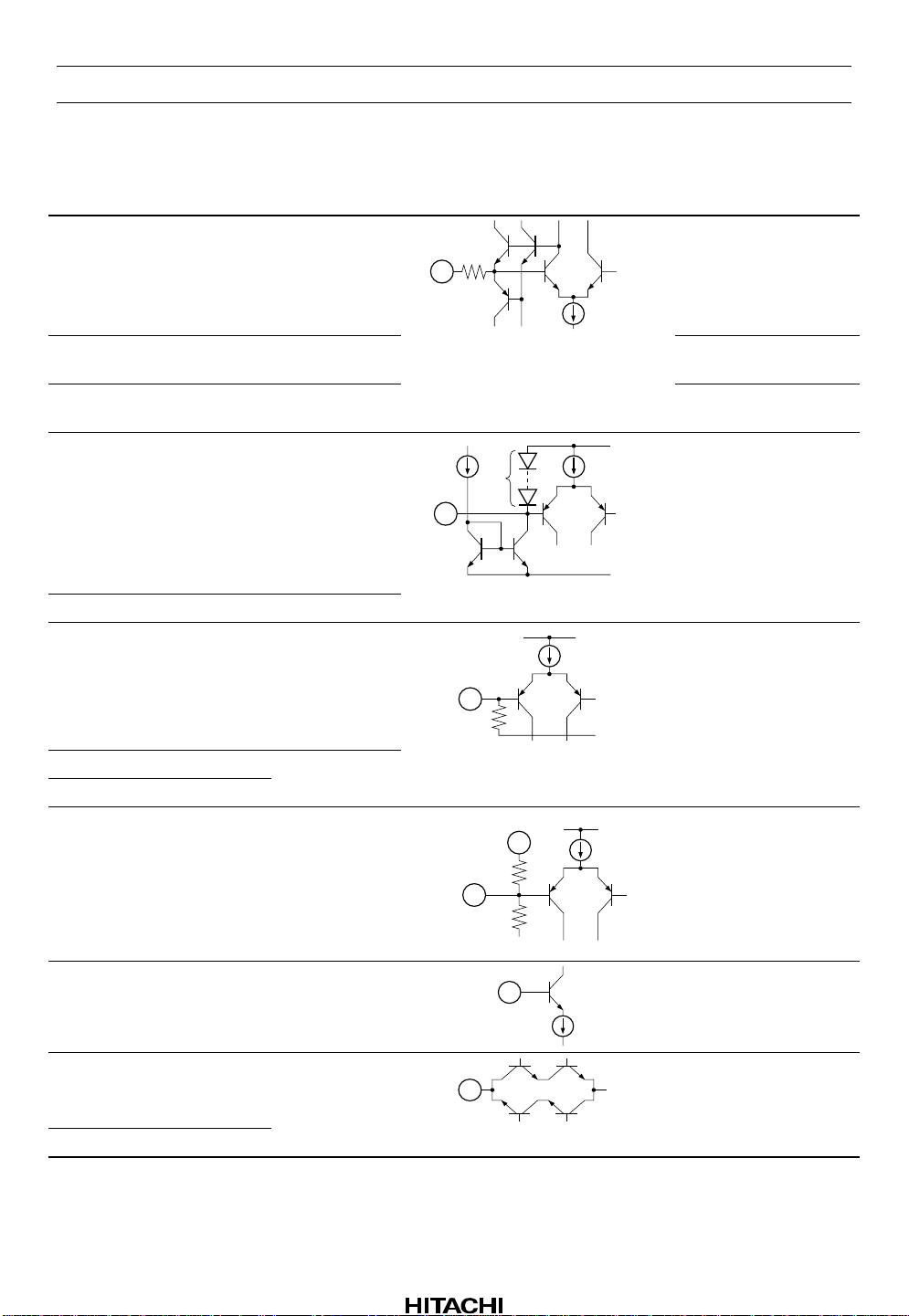
HA12215F
Pin Description, Equivalent Circuit (VCC = ±7 V, A system of split supply voltage,
Ta = 25°C, No Signal, The value in the show typical value.) (cont)
Pin No. Terminal Name Note Equivalent Circuit Pin Description
10 GPCAL R = 110 kΩ
R
2.5 V
11 RECCAL R = 110 kΩ REC gain calibration
12 ALCCAL R = 140 kΩ ALC operation level
14 MSDET n = 6
0 µA
V
CC
n
V
EE
13 ALCDET n = 2
27 MSIN R = 50 kΩ
V
CC
GP gain calibration
terminal
terminal
calibration terminal
Time constant pin for
1
MS *
MS input *
1
9 ALCIN (R) R = 100 kΩ
34 ALCIN (L)
30 MAI V = GND
29 MS GND I = ±100 µA
55 ALC (R) V = GND
44 ALC (L)
Note: 1. MS: Music Sensor
V
R
GND
MAOUT
V
CC
MS Amp. input *
1
100 k
V
8.2 k
GND
MS output voltage
level control pin *
I
1
Variable impedance
V
for attenuation
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 6 of 69
Page 7
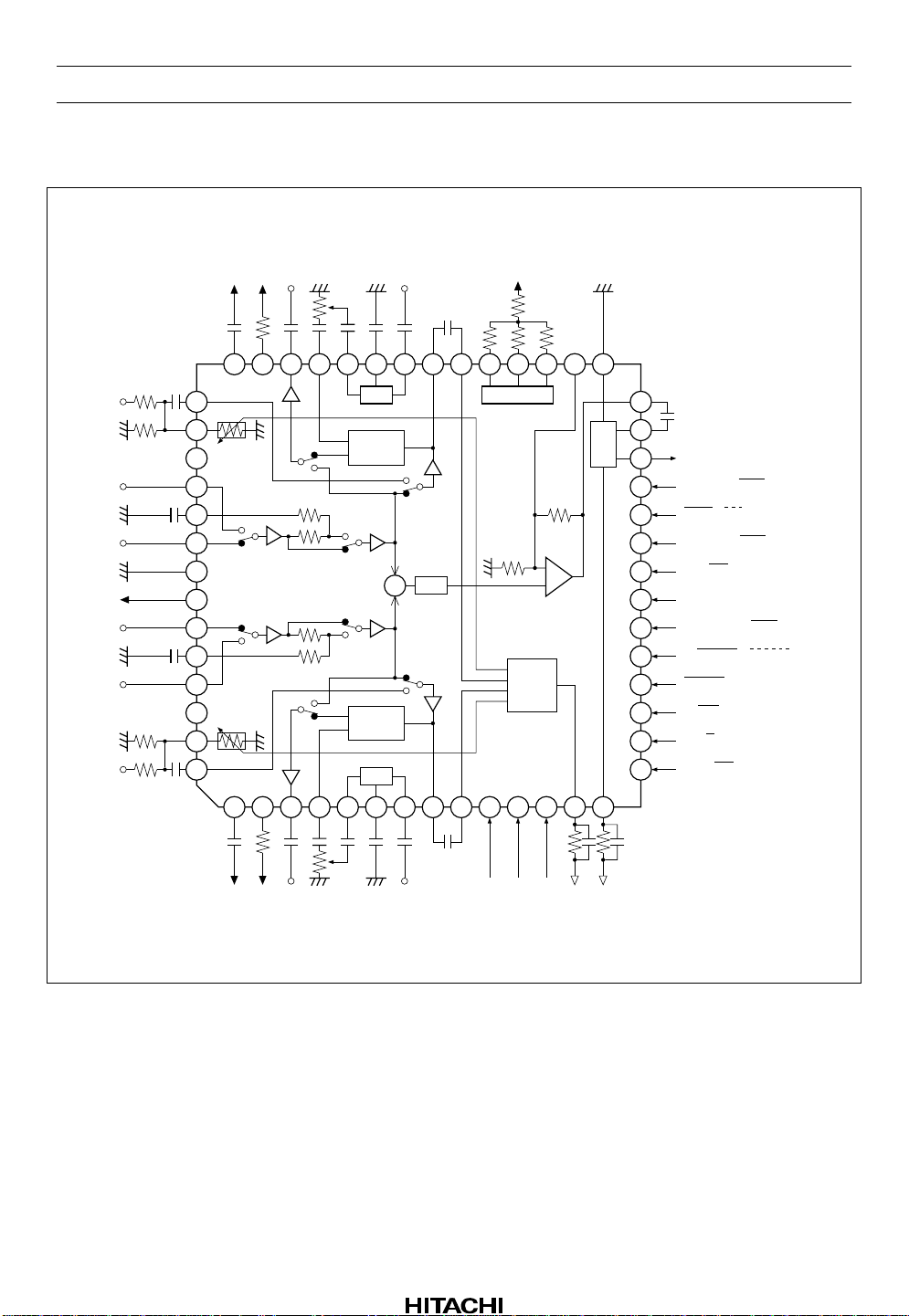
Block Diagram
DET (L)
BIAS2
42 41 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 2940
PBOUT (L)
RECOUT (L)
EQIN (L)
BOOST (L)
EQOUT (L)
ROUT (L)
ALCIN (L)
BIAS (N)
BIAS (C)
BIAS (M)
MAI
HA12215F
MSGND
RIN (L)
ALC (L)
BIN (L)
ABO (L)
AIN (L)
GND
V
AIN (R)
ABO (R)
BIN (R)
ALC (R)
RIN (R)
43
44
45NC
46
47
48
49
EE
50
51
52
53
54NC
55
56
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
BIAS1
DET (R)
PBOUT (R)
EQ
Dolby
B-NR
Dolby
B-NR
EQ
EQIN (R)
RECOUT (R)
BOOST (R)
+
LPF
EQOUT (R)
ROUT (R)
BIAS
GPCAL
ALCIN (R)
−
+
ALC
ALCCAL
RECCAL
MS
MSDET
ALCDET
28
MAOUT
27
MSIN
26
MSOUT
25
LM ON / OFF
24
REC / PB / PASS
23
NR ON / OFF
22
RM ON / OFF
21
V
CC
20
BIAS ON / OFF
B NORM / CROM / METAL
19
NORM / HIGH
18
17
A 120 / 70
16
PB A / B
15
ALC ON / OFF
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 7 of 69
Page 8

HA12215F
Parallel-Data Format
MODE
Pin No. Pin Name Lo Mid Hi
15 ALC ON/OFF ALC ON — ALC OFF Lo
16 PB A/B Ain *
1
—Bin *1Lo
17 A 120/70 *1 — *1 Lo
22 RM ON/OFF REC MUTE ON — REC MUTE OFF Lo
20 BIAS ON/OFF BIAS OFF — BIAS ON Lo
23 NR ON/OFF NR OFF — NR ON Lo
24 REC/PB/PASS REC MODE PB MODE REC MODE PASS Mid
25 LM ON/OFF LINE MUTE OFF — LINE MUTE ON Lo
18 NORM/HIGH Normal speed — High speed Lo
19 B NORM/CROM/
METAL
REC EQ Normal *
Bias Normal
1
REC EQ CROM *
Bias CROM
1
REC EQ METAL *
Bias METAL
Note: 1. PB EQ logic
PB EQ Logic
“Pin Open”
1
Lo
PB
A 120
120/70 B NORM
120120
NORM / CROM / METAL Lo Hi
NORM NORM
Lo Lo FLAT FLAT
Lo Hi or Mid FLAT 70 µ
Hi Lo 70 µ FLAT
Hi Hi or Mid 70 µ 70 µ
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 8 of 69
Page 9
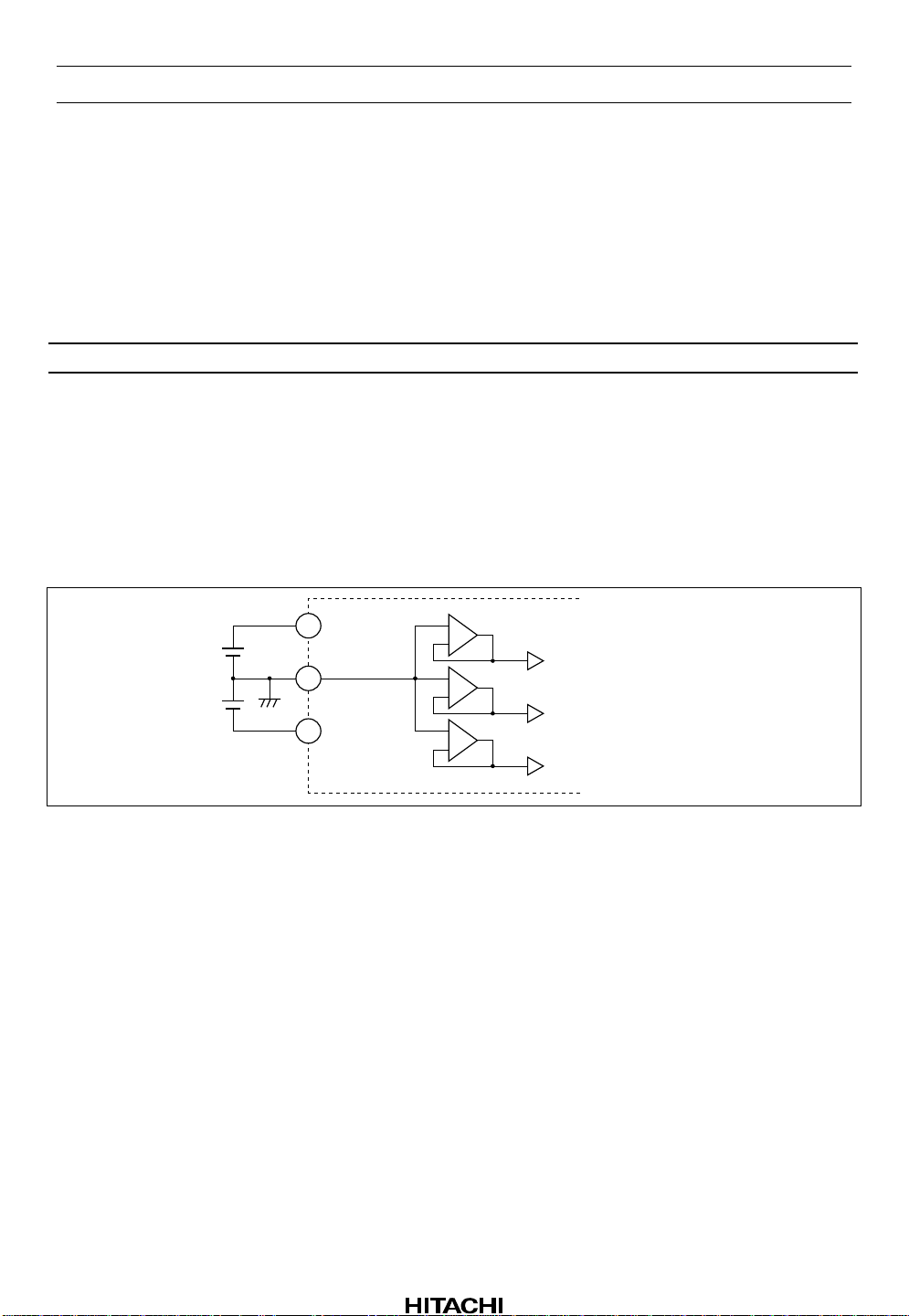
HA12215F
Functional Description
Power Supply Range
HA12215F is designed to operate on split supply.
Table 1 Supply Voltage
Product VCC (V) VEE (V) Note
HA12215F +6.0 to +7.5 –7.5 to –6.0 | V
Note: The lower limit of supply voltage depends on the line output reference level.
The minimum value of the overload margin is specified as 12 dB by Dolby Laboratories.
Reference Voltage
The reference voltage are provided for the left channel and the right channel separately. The block diagram
is shown as figure 1.
+ VEE | < 1.0 V
CC
21
V
49
50
CC
GND
V
EE
V
CC
V
EE
+
−
L channel reference
+
−
Music sensor reference
+
−
R channel reference
Figure 1 Reference Voltage
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 9 of 69
Page 10
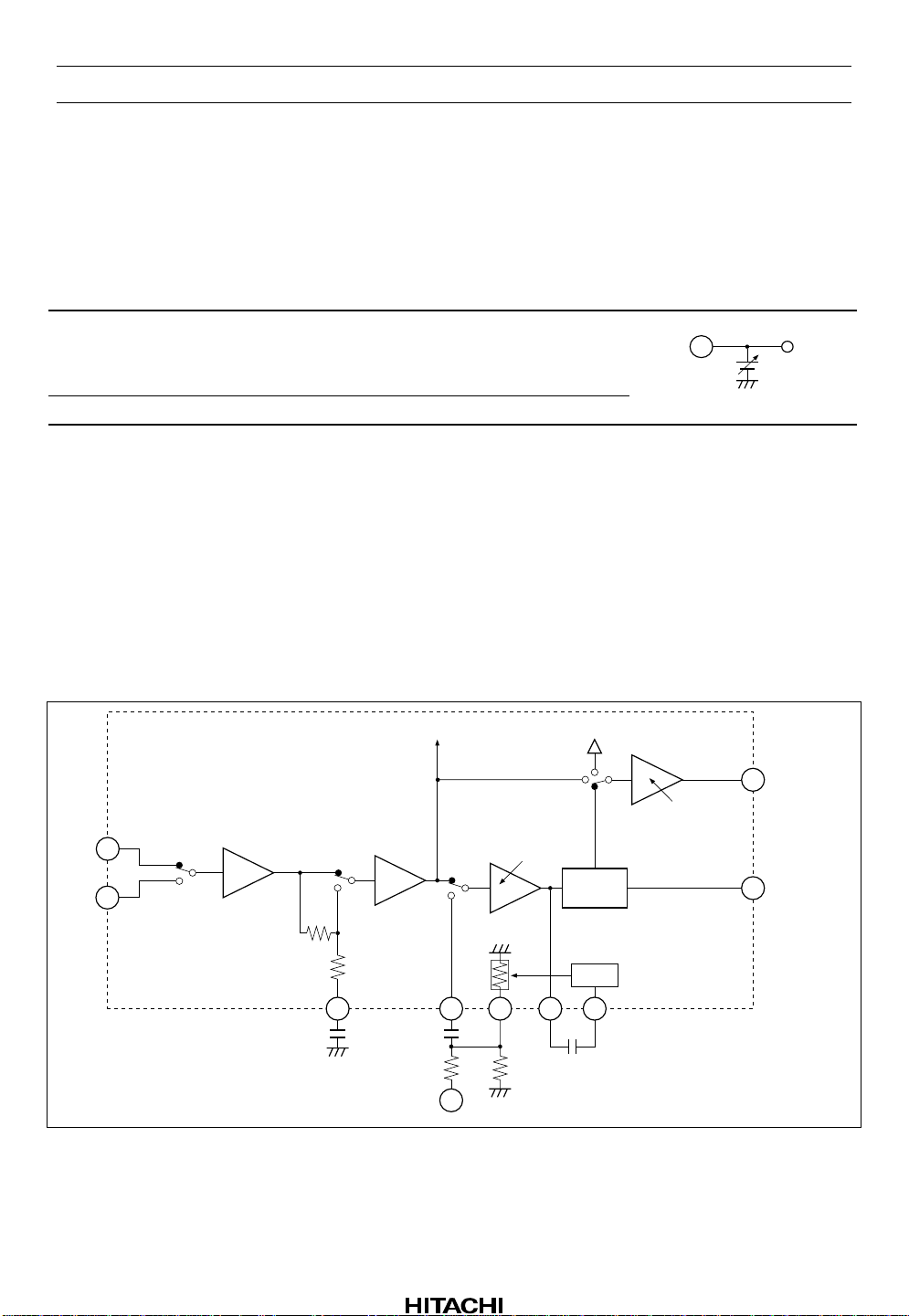
HA12215F
Operating Mode Control
HA12215F provide fully electronic switching circuits. And each operating mode control is controlled by
parallel data (DC voltage).
Table 2 Control Voltage
Pin No. Lo Mid Hi Unit Test Condition
15, 16, 17, 18,
20, 22, 23, 25
–0.2 to 1.0 — 4.0 to V
CC
V
Input Pin Measure
19, 24 –0.2 to 1.0 2.0 to 3.0 4.0 to V
CC
Notes: 1. Each pins are on pulled down with 100 kΩ inter nal resi stor.
Therefore, it will be low-level when each pins are open.
But pin 24 is mid-level when it is open.
2. Over shoot level and under shoot level of input signal must be the standardized (High: V
Low: –0.2 V).
3. For reduction of pop noise, connect 1 µF to 22 µF capacitor with mode control pins.
But it is impossible to reduce completely in regard to Line mute, therefore, use external mute at
the same time.
Input Block Diagram and Lev e l Diagram
The each level shown above is typical value
when offering PBOUT level to PBOUT pin.
AIN
BIN
25.9mVrms
21.3dB
300mVrms
4700pF
R3
12k
C2
FLAT
(120µ)
70µs
R4
15k
25.5mVrms
200mVrms
MS REF
300mVrms
PB/REC,
PASS=0dB/21.4dB
0dB
PB
REC
PASS
C1
0.1µF
R1
15k
RIN
R2
2.2k
PASS
300mVrms
0.1µF
V
Dolby
B-NR
ALC
C3
REC
PB
PASS/REC,
PB=5.7dB/5.7dB
300mVrms
,
CC
PBOUT
580mVrms
RECOUT
300mVrms
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 10 of 69
Figure 2 Input Block Diagram
Page 11
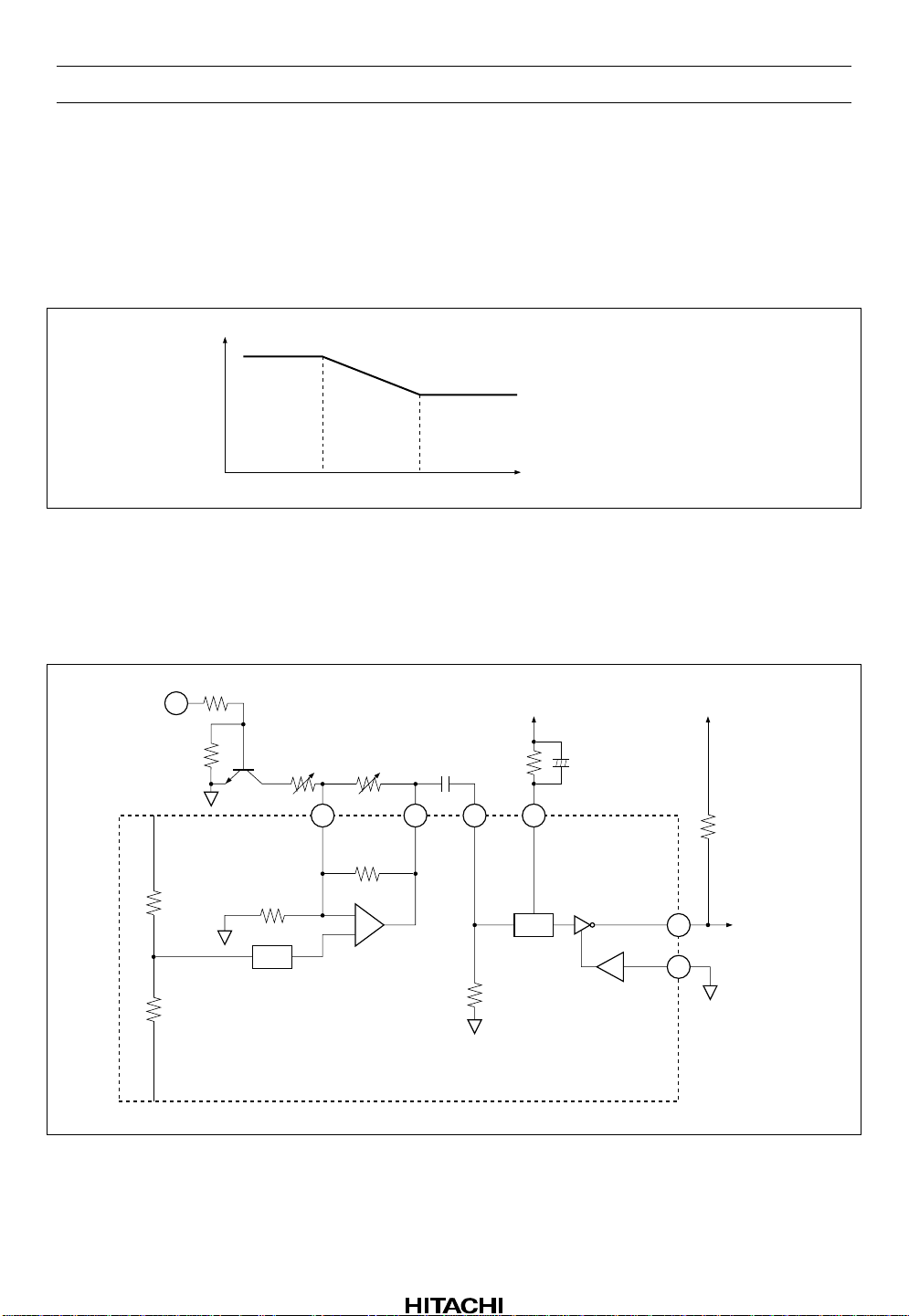
HA12215F
PB Equalizer
By switching logical input level of pin 17 (for Ain) and pin 19 (for Bin), you can equalize corresponding to
tape position at play back mode.
With the capacity C2 capacitance that we showed for figure 2 70 µs by the way figure seem to 3 they are
decided.
G
V
t1 = C2 ⋅ (12k + 15k)
t2 = C2 ⋅ 15k
t1 t2
Figure 3 Frequency Characteristic of PB Equalizer
The Sensitivity Adjustment o f Music Sensor
f
Adjusting MS Amp gain by external resistor , the sensitivity of music sensor can set up.
REP
V
CC
DET
MS
DET
+
C13
0.33µ
MS OUT
GND
PB (L)
−6dB
PB (R)
8.2k
LPF
25kHz
MAI
100k
−
+
MS AMP
C16
1000p
MA
OUT
R13
330k
MSIN
50k
Figure 4 Music Sensor Block Diagram
D V
CC
R
L
Microcomputer
GND
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 11 of 69
Page 12
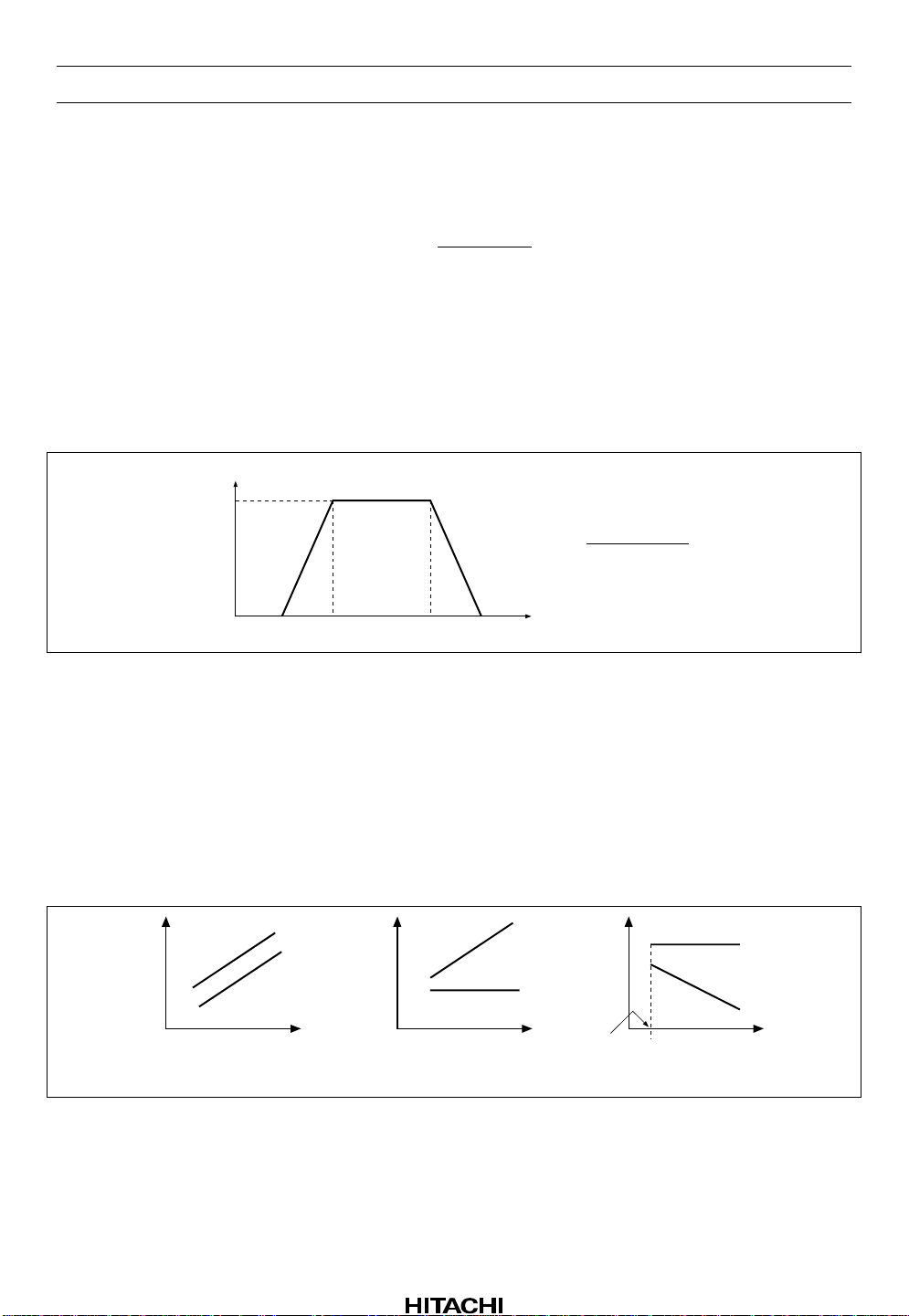
HA12215F
The Sensitivity of Music Sensor
A standard level of MS input pin 25.9 mVrms, therefore, the sensitivity of music sensor (S) can request
it, by lower formulas.
A = MS Amp Gain*
B = PB input Gain × (1/2)*
C = Sensed voltage
20log (A × B) = D [dB]
C = 130 [mVrms] (Intenally voltage in a standard)
PB input Gain = 21.3 [dB]
Notes: 1. When there is not a regulation outside.
2. Case of one-sided channel input.
But necessary to consider the same attenuation quantity practically, on account of A(B) h ave made
frequency response.
37.7dB
1
2
S = 20log
S = 14 − D [dB]
G
V
C
25.9 ⋅ A ⋅ B
[dB]
f1 =
f2 = 25k [Hz]
f
f1 f2
1
2π ⋅ C16 ⋅ 50k
[Hz]
Figure 5 Frequency Characteristic of MSIN
Occasion of the external component of figure 4, f1 is 3.18 kHz.
Time constant of detection
Figure 6(1) generally shows that detection time is in proportion to value of capacitor C13. But, with
Attack*
2
and Recovery*3 the detection time differs exceptionally.
Notes 2. Attack : Non- music to Music
3. Recovery : Music to Non-music
Recovery
Attack
Detection time
C13
(1) (2) (3)
Recovery Recovery
Attack Attack
Detection time
R13
Detection level
Detection time
Input level
Figure 6 Function Characteristic of MS
Like the figure 6(2), Recovery time is variably possible by value of resistor R13. But Attack time gets
about fixed value. Attack time has dependence by input level. When a large signal is inputted, Attack time
is short tendency.
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 12 of 69
Page 13
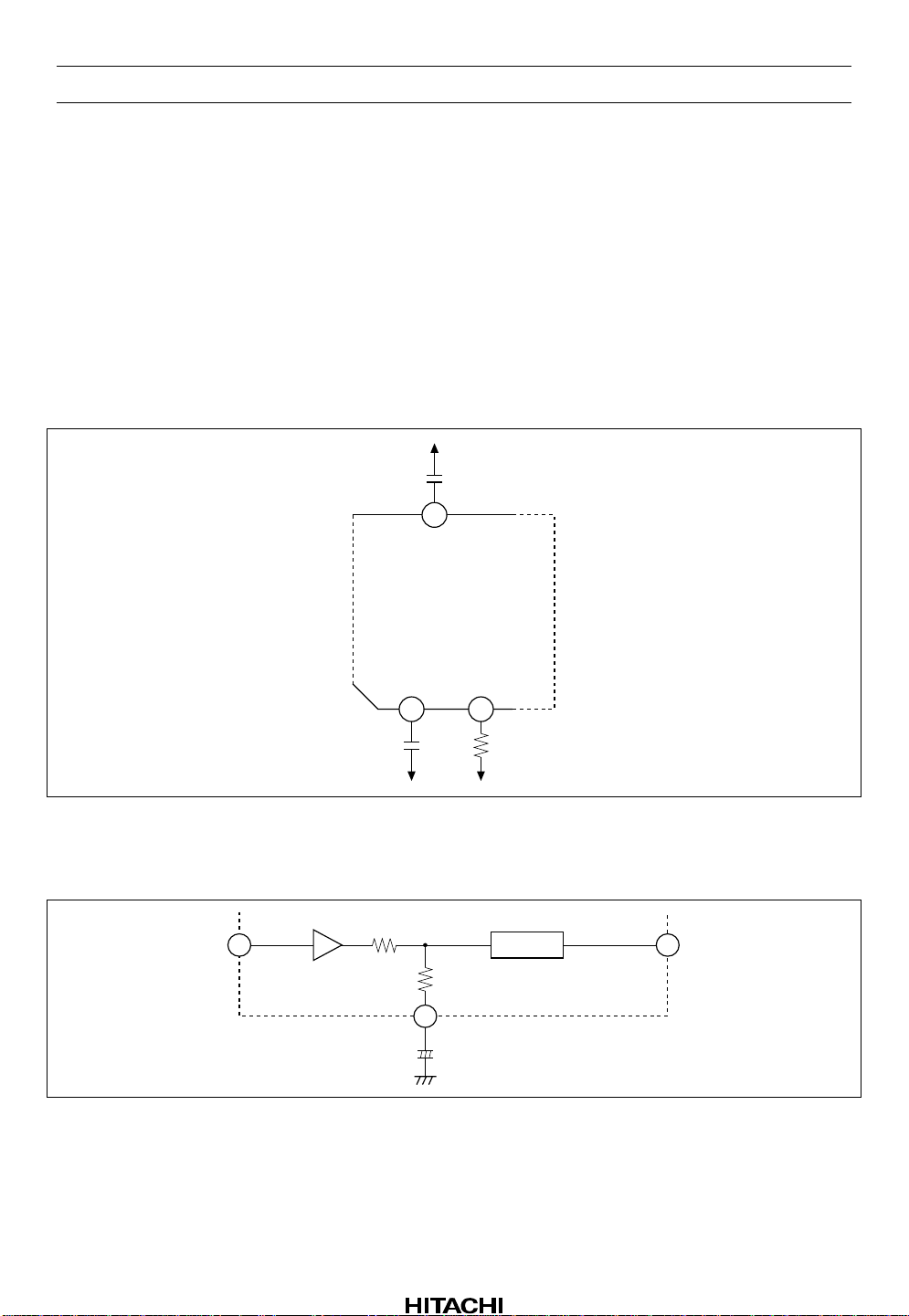
HA12215F
Music Sensor Output (MSOUT)
As for internal circuit of music sensor block, music sensor output pin is connected to the collector of
NPN type directly, output level will be “high” when sensing no signal. And output level will be “low”
when sensing signal.
Connection with microcomputer, it is requested to use external pull up resistor (R
Note: Supply voltage of MSOUT pin must be less than V
voltage.
CC
The Tolerances of External Components
For Dolby NR precision securing, please use external components shown at figure 7. If leak-current are a
few electrolytic-capacitor, it can be applicable to C5 and C23.
V
EE
C23
0.1µ
±10%
42
DET (L)
HA12215F
= 10 kΩ to 22 kΩ)
L
DET (R)
C5
0.1µ
±10%
BIAS1
1
2
R5
33k
±2%
V
EE
Figure 7 Tolerance of External Components
Low-Boost
EQIN
24.6dB
4.8k
4.8k
BOOST
+
C9(C19)
0.47µ
REC EQ
EQOUT
Figure 8 Example of Low Boost Circuit
External components shown figure 8 gives frequency response to take 6 dB boost. And cut off frequency
can request it, by C9 (C19).
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 13 of 69
Page 14
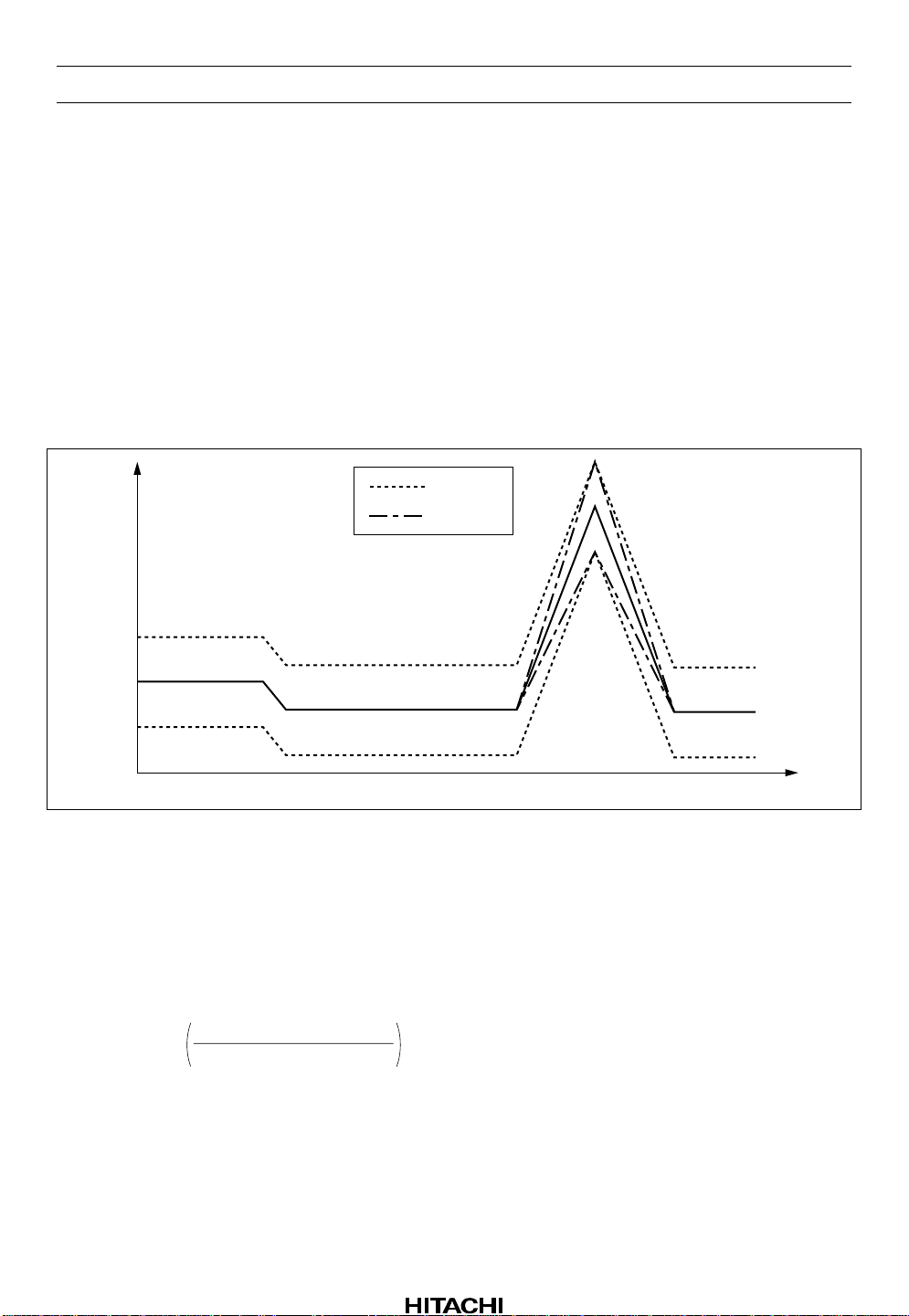
HA12215F
REC Equalizer
The outlines of REC Equalizing frequency characteristics are sh own by figure 9. Those peak level can be
set up by supplying voltage. (0 V to 5 V, GND = 0 V) to pin 10 (GPCAL).
And whole band gain can be set up by supplying voltage (0 V to 5 V, GND = 0 V) to pin 11 (RECCAL).
Both setting up range are ±4.5 dB. In case that you do not need setting up, pin 10, pin 11 should be open
bias.
Note: Depending on the employed REC/PB head and test tape characteristics, there is a rare case that the
REC-EQ characteristics of this LSI can not be matched to the required characteristics because of
built-in resistors which determined the REC-EQ parameters in this care, please inquire the
responsible agent because of the adjustment of built-in resistor is necessary.
RECCAL
GPCAL
Gain (dB)
Frequency (Hz)
Figure 9 Frequency Characteristics of REC Equalizer
Bias Switch
HA12215F built-in DC voltage generator for bias oscillator and its bias switches.
External resistor R19, R20, R21 which corresponded with tape positions and bias out voltage are relater
with below.
.
Vbias = × (VCC − VEE − 0.7) + VEE [V]
.
(R19 or R20 or R21) + R22
R22
Bias switch follows to a logic of pin 19 (B / Norm / Crom / Metal).
Note: A current that flows at bias out pin, please use it less than 5 mA.
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 14 of 69
Page 15
HA12215F
BIAS (N)
Pin 33
BIAS (C)
Pin 32
BIAS (M)
Pin 31
R21
R20
R19
R22
V
Vbias
EE
Figure 10 External Components of Bias Block
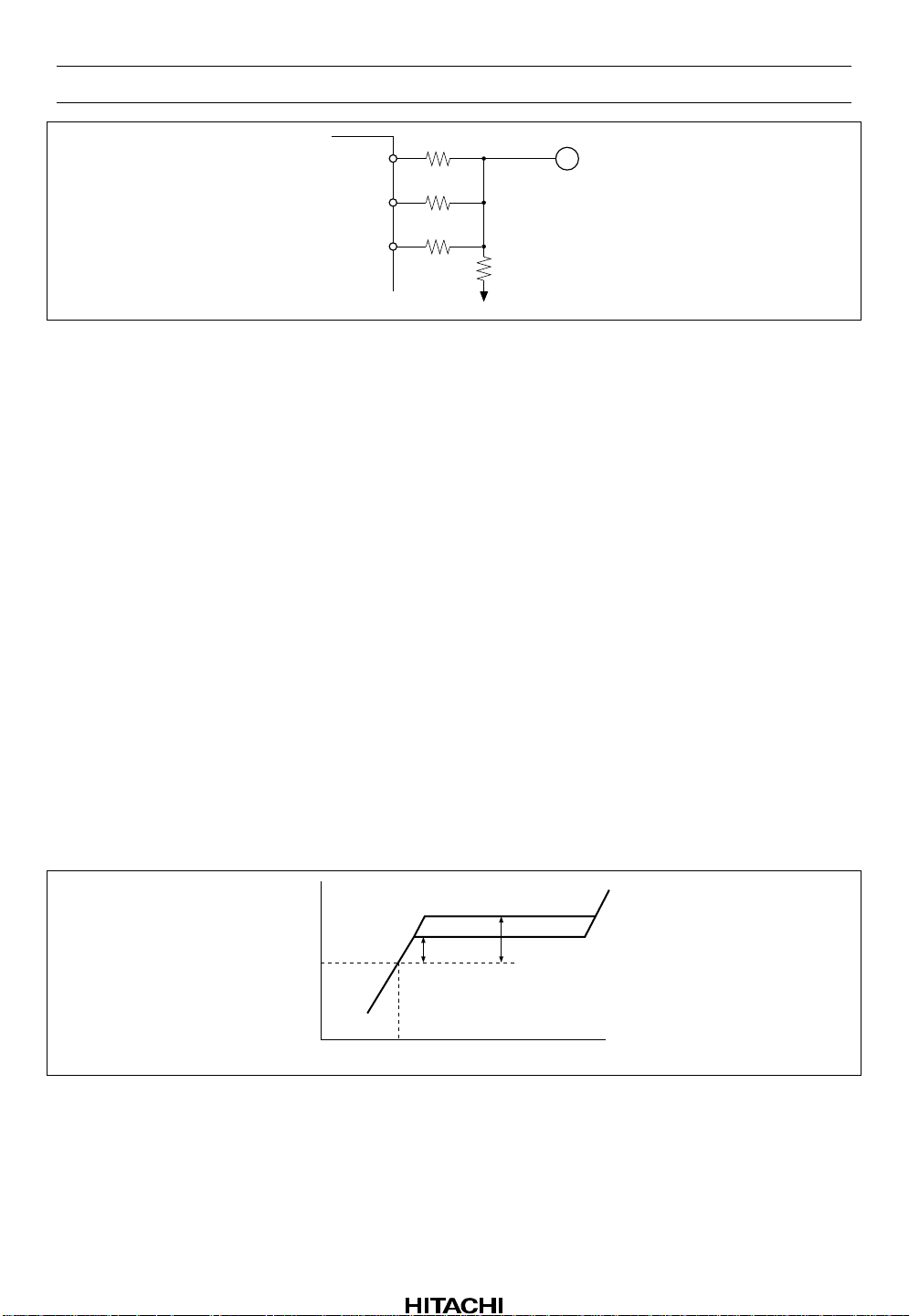
Automatic Level Control
ALC is the input decay rate variable system. It has internal variable resistors of pin 55 (pin 44) by
RECOUT signal that is inputted to p in 9 (pin 34 ) .
The operation is similitude to MS, detected by pin 13.
The signal input pin is pin 56 (pin 43). Resistor R1, R2 and capacitor C2, external components, for the
input circuit are commended as figure 12. There are requested to use value of the block diagram figure for
performance maintenance of S/N, T.H.D. etc.
Figure 11 shows the relation with R1 front RIN point and ROUT.
ALC operation level acts for the center of +4.5 dB at tape position TYPE I, IV and the center of +2.5 dB at
tape position TYPE II, to standard level (300 mVrms).
Then, adopted maximum value circuit, ALC is operated by a large channel of a signal.
ALC ON/OFF can switch it by pin 15. Please do ALC ON, after it does for one time ALC OFF inevitably,
for ALC time to start usefully (when switching PB → PASS, when switching PB → PASS), in order to
reset ALC circuit.
TYPE I, IV
4.5dB
RIN
300mV
ROUT
TYPE II
2.5dB
Figure 11 ALC Operation Level
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 15 of 69
Page 16
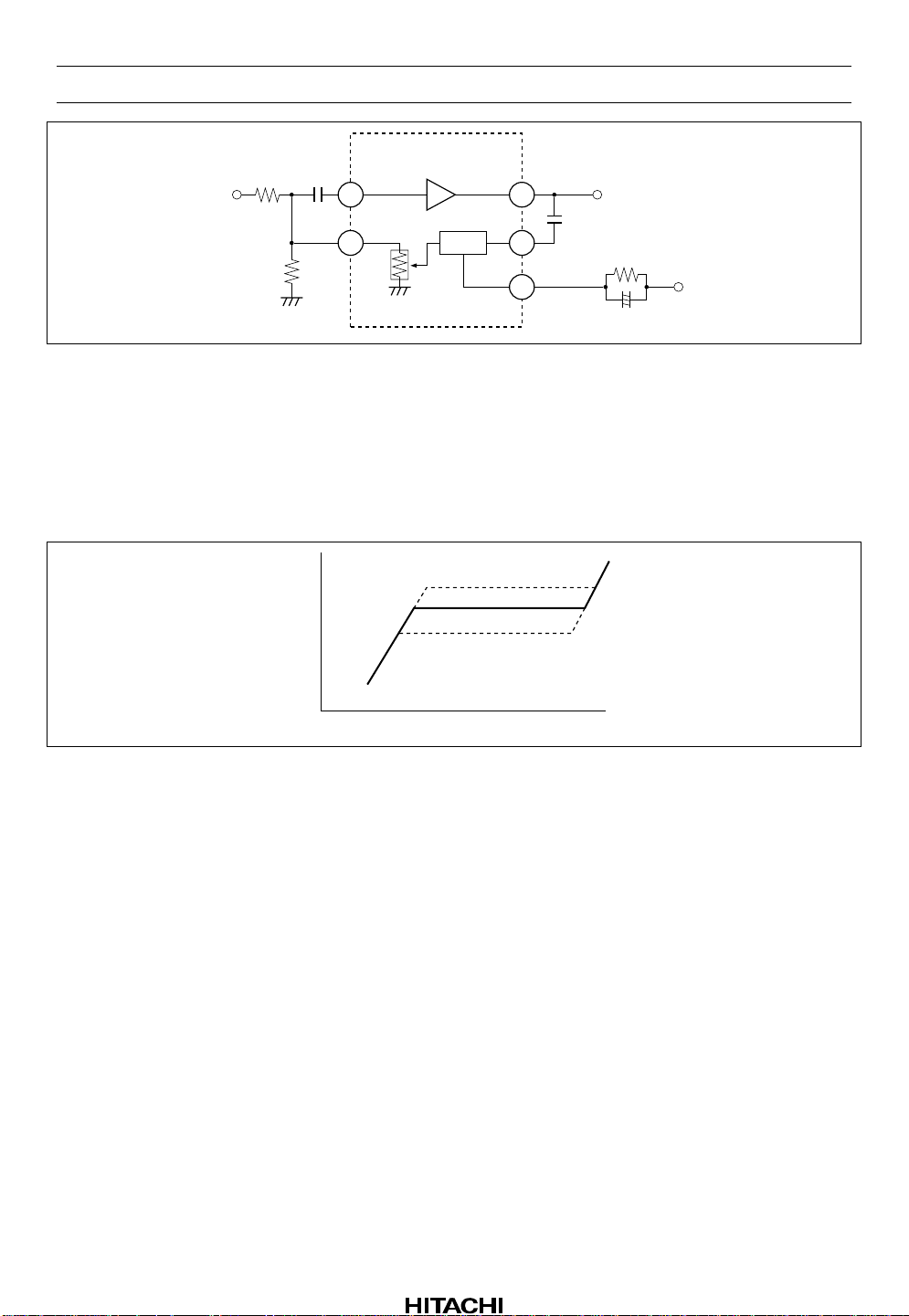
HA12215F
R1
15k
RIN ROUT
25.5mV 21.4dB
C2
0.1µ
R2
2.2k
56
55
ALC
ALC
8 OutputInput
9
13
300mV
C4
ALCIN
ALCDET
R12
C12
V
+
CC
Figure 12 ALC Block Diagram
ALC Operation Level Necessary
ALC operation level is variable to pin 12 bias (ALC-CAL: 0 to 5 V), and its range is ±4.0 dB.
Unnecessary, pin 12 is unforced.
ALC-CAL = 5V
ALC-CAL = 0V
ROUT
RIN
Figure 13 ALC-CAL Characteristics
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 16 of 69
Page 17

HA12215F
Absolute Maximum Ratings
Item Symbol Rating Unit Note
Max supply voltage V
Power dissipation Pd 625 mW Ta ≤ 75°C
Operating temperature Topr –40 to +75 °C
Storage temperature Tstg –55 to +125 °C
max 16 V
CC
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 17 of 69
Page 18
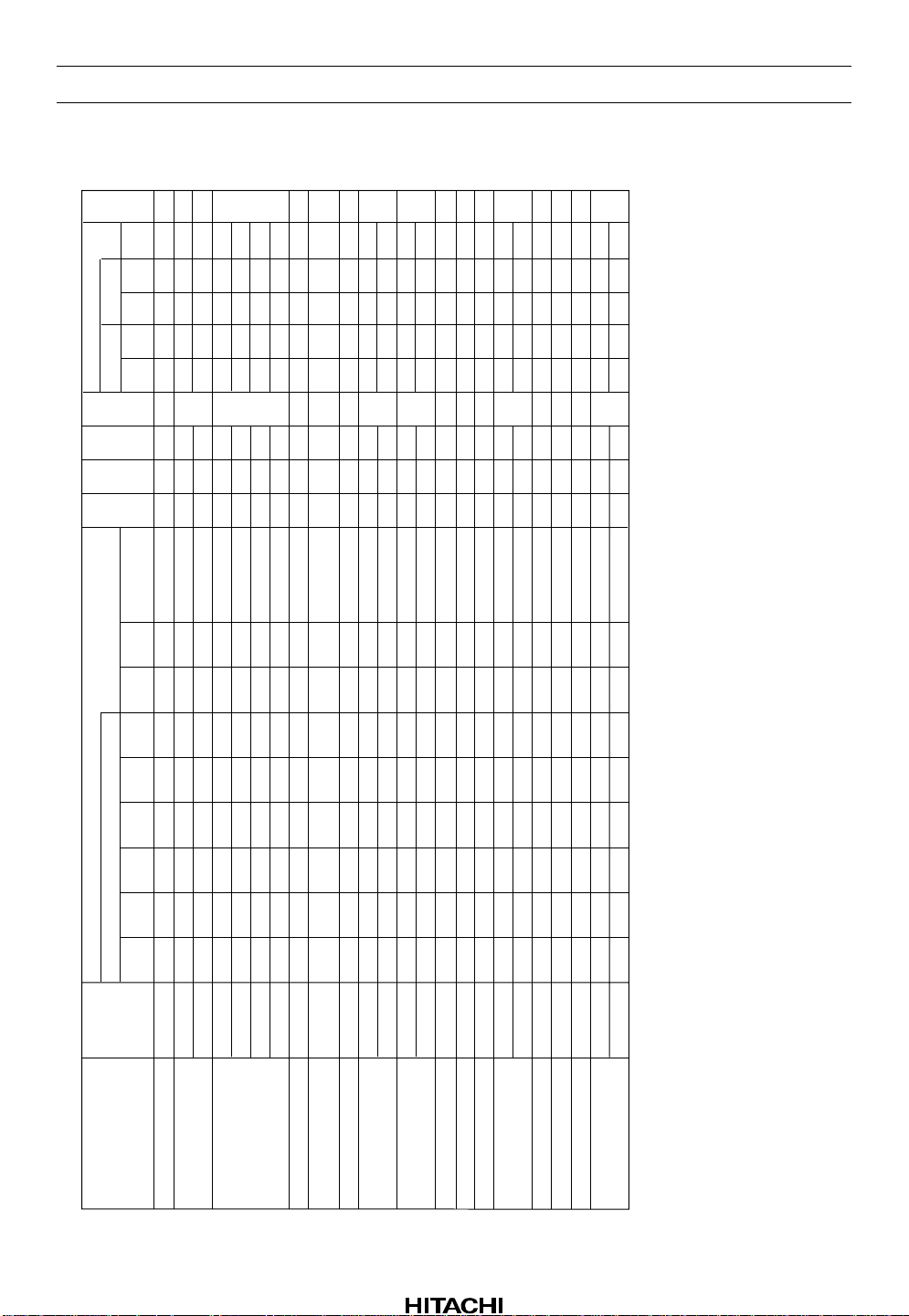
HA12215F
Electrical Characteristics
Remark
Input Output
COM
L
R
L
R
Unit
Max
Typ
Min
404039
334
48/46
51/53
dB
mA
28.5
35.0
27.0
25.5
43
56
28.0
26.5
25.0
393939
444
43
434343
56
565656
dB
5.8
10.0
4.3
8.5
2.8
7.0
= ±7 V, Dolby Level = REC-OUT Level = 300 mVrms = 0 dB)
CC
Other
No signal
(Ta = 25°C, V
RECOUT
level (dB)
fin
(Hz)
0
0
1k1k2k
−20
−30
2k5k5k
3939394040
4
434343
565656
dB 2
4.7
9.7
3.2
8.2
13.0
1.7
6.7
12.0
THD=1%
−20
−30
1k
4
433
dB%dB
0.3
70.0
0.05
64.070.0
Rg=5.1kΩ,
CCIR/ARM
0
1k
1k1k1k1k1k
40
3
48/464348/46
51/535651/53
dB
80.0
85.0
80.0
70.0
70.0
+12
+12
+12
340
48/43
51/56
80.0
70.0
+12
40
3
48/46
51/53
dB
28.5
27.0
25.5
PB
V
G
−
PA
V
G
0
1k
40
3
48/46
51/53
dB
1.0
0.0
−1.0
0
1k
404040
333
48
48/46
51
51/53
dB
dB
27.0
80.0
25.5
70.0
24.0
0
+12
1k
1k
48/46
51/53
23.8
22.3
20.8
0
10k
3
48
48
51
51
V
dB
1.5
−18.0
1.0
−22.0
−26.0
5k
µA
2.0
39
4
43
56
dB
7.0
4.5
2.0
+12
1k
39
4
43
56
5.0
2.5
0.0
+12
1k
B
N/C/M
NORM
NORM
Test Condition Application Terminal
1
IC Condition *
OFF
LINE
MUTE
120
120 OFF
70µ
120µ/
A
A/B
A/B
PB
PB
/PASS
REC/PB
NR
OFFQuiescent current
OFF
ON/OFF
PB
Q
G
I
V
Item Symbol
Input AMP. gain
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
120
120
A
A
REC
REC
ON
OFF
REC
V
G
ENC 2k (1)
B-type
Encode boost
NORM
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
OFF
120
120
120
AAA
REC
REC
REC
ON
ON
ON
ENC 2k (2)
ENC 5k (1)
ENC 5k (2)
NORM
NORM
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
OFF
OFF
120
120
120
120
A
A
A
A/BAA/B
REC
REC
RECPBREC
ONONON
Vo max
Signal handling
OFF
S/N
THD
CTRL (1)
Signal to noise ratio
Total Harmonic Distortion
Channel separation
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
120
120
PB
OFF
OFF
CTRL (2)
CT A/B
Crosstalk
NORM
NORM
NORM
NORM
OFF
120
A
REC/PB
OFF
CT R/P
ON
OFF
OFF
120
120
120
A
A/B
A/B
PBPBPBPBPB
PASS
PASS
OFF
OFF
OFF
V
PA
V
∆G
G
MUTE
Pass AMP. gain
Gain deviation
MUTE ATT.
CROM
NORM/
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
OFF
70
70
120
AAA
A/B
A/B
OFF
OFF
OFF
EQ 1k
EQ 10k
V
V
ONVOL
G
V
G
70µ EQ gain
MS sensing level
NORM,
METAL
NORM
NORM
OFF
OFF
120
120
PB
OFF
OH
I
OFFALC (2) REC A 120 OFF CROM
OFF
= ±6.0 V
2. V
MS output low level
MS output leak current
ALC operate level OFFALC (1) REC A 120 OFF
Notes: 1. Other IC-condition : REC-MUTE OFF, Normal tape, Normal speed, Bias OFF
CC
3. For inputting signal to one side channel
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 18 of 69
Page 19
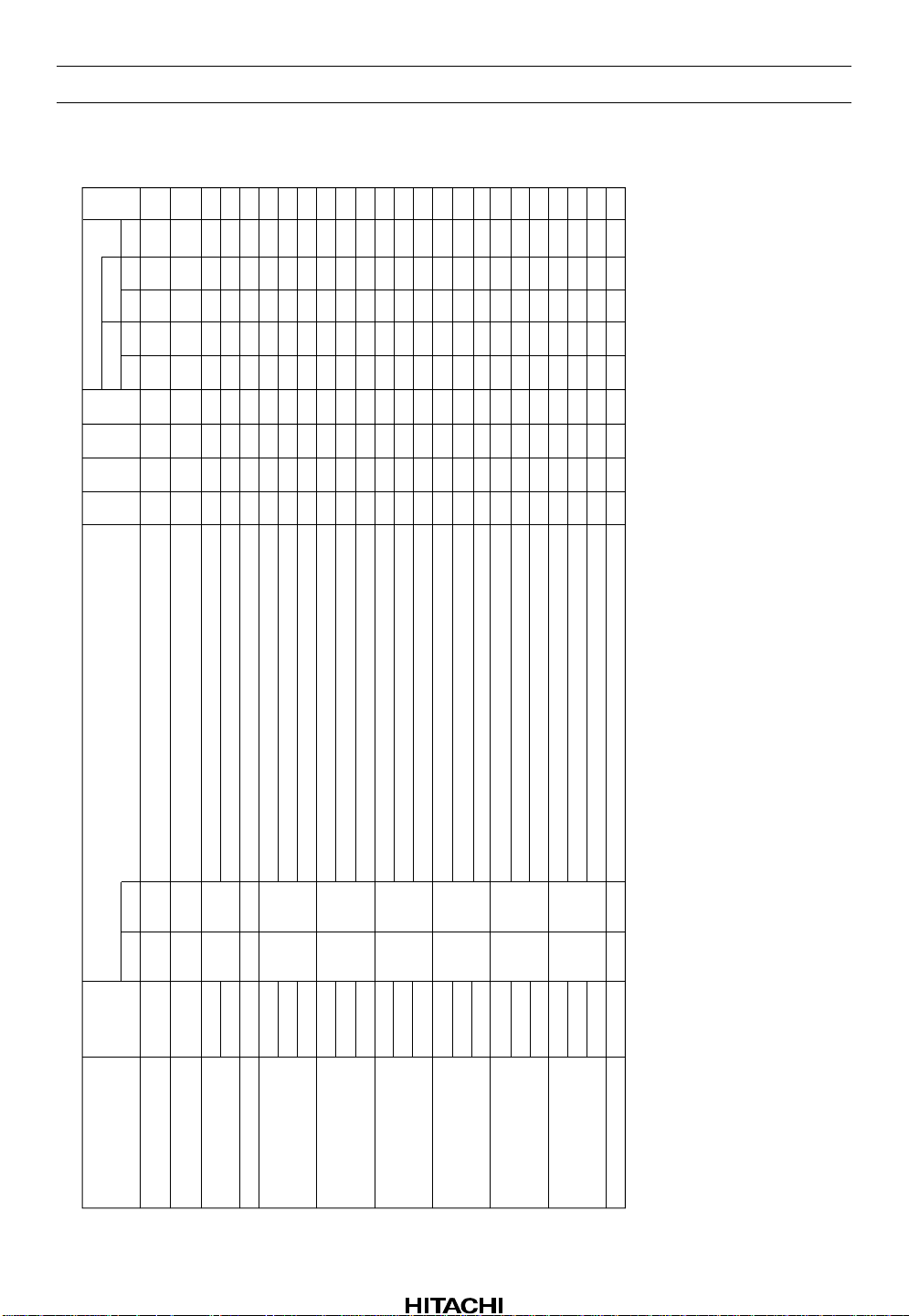
Electrical Characteristics (cont)
HA12215F
= ±7 V)
CC
(Ta = 25°C, V
Remark
COM
L
R
L
Application Terminal
Input Output
R
Unit
Max
Typ
Min
36
7
38
5
538736
dB
dB
58
12.5
55
10.5
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
0.5
538736
538736
%
0.5
0.2
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
%
mV
500
21.8
0
20.3
0.2
18.8
−500
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
dBdBdB
27.9
25.9
23.9
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
35.1
32.6
30.1
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
dBdBdBdBdBdBdB
26.3
32.5
39.0
24.8
30.5
36.5
23.3
28.5
34.0
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
538736
27.1
29.9
33.3
25.6
27.9
30.8
24.1
25.9
28.3
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
18.0
16.5
15.0
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
538736
dB
dB
dB
23.9
28.4
22.9
21.9
25.9
21.4
19.9
23.4
19.9
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
dBdBdB
27.7
25.7
23.7
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
31.9
24.4
29.4
22.9
26.9
21.4
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
538736
538736
dBdBdB
26.0
28.5
70
24.0
26.0
60
22.0
23.5
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
SW22 (L), SW23 (R) OFF
Test Condition
f = 1kHz, THD = 1%,
Rg = 5.1kΩ, A-WTG Filter
(0dB = −5dBs at EQOUT)
NORM
NORM
TAPE SPEED
NORM
NORMEqualizer S/N
Vin max (EQ)
S/N (EQ)
Item Symbol
Equalizer maximum input
Vin = −26dBs = 0dB
f = 1kHz, Vin = −26dBs
NORM
NORM
T.H.D.1 (EQ)
Equalizer total harmonic
f = 3kHz, Vin = −46dBs
No-Signal
f = 1kHz, Vin = −30dBs
T.H.D.2 (EQ)
distortion
f = 8kHz, Vin = −46dBs
NORM
NORM
NORM
NORMG
VEQ-NN1GVEQ-NN2GVEQ-NN3
Vofs (EQ)
Equalizer offset voltage
Equalizer
frequency response
(NORM - NORM)
f = 3kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 12kHz, Vin = −46dBs
CROM NORM
VEQ-CN1GVEQ-CN2GVEQ-CN3GVEQ-MN1GVEQ-MN2GVEQ-MN3GVEQ-NH1
G
Equalizer
f = 3kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 8kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 12kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 8kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 12kHz, Vin = −46dBs
METAL NORM
frequency response
(CROM - NORM)
Equalizer
frequency response
(METAL - NORM)
f = 5kHz, Vin = −46dBs
NORM HIGH
Equalizer
f = 5kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 15kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 20kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 15kHz, Vin = −46dBs
CROM HIGH
VEQ-NH2GVEQ-NH3
VEQ-CH1GVEQ-CH2GVEQ-CH3GVEQ-MH1GVEQ-MH2GVEQ-MH3
G
G
Equalizer
frequency Response
frequency response
(NORM - High)
(CROM - High)
f = 5kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 20kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 15kHz, Vin = −46dBs
f = 20kHz, Vin = −46dBs
METAL HIGH
Equalizer
frequency response
(METAL - High)
f = 1kHz, Vin = −14dBs
REC-MUTE attenuation NORMREC-MUTE NORM
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 19 of 69
Page 20
HA12215F
Electrical Characteristics (cont)
= ±7 V)
CC
Remark
(Ta = 25°C, V
Application Terminal
Input Output
Unit
Min Typ R L R L COMMax
363636
36
777
7
383838
38
555
5
dBdBdB
dB
6.0
−3.0
4.5
−4.5
3.0
−6.0
= 0dB
V EQ-NN1
= 0V
= 5V G
REC-CAL
REC-CAL
V
V
6.0
−3.0
4.5
−4.5
3.0
−6.0
= 0dB
V EQ-NN3
G
= 0V
= 5V
GP-CAL
GP-CAL
V
V
39
4
43
56
dB
−3.0
−4.0
ALC (1) = 0dB
39
4
43
56
dB
4.0
3.0
31 to 33
V
−0.7
CC
V
−1.4
CC
V
31 to 33
15 to 20
V
V
EE
+0.1
1.0
V
EE
V
EE
−0.1
−0.2
V
15 to 20
22 to 25
19, 24
V
3.0
2.0
22 to 25
V
5.3
4.0
Test Condition
Vin = −46dBs,
f = 3kHz,
f = 3kHz, Vin = −46dBs,
NORM
TAPE SPEED
NORM
R-CAL1
R-CAL2
Item Symbol
REC CAL response
= 0V
= 5V
ALC-CAL
ALC-CAL
V
Vin = −46dBs,
Vin = −46dBs,
V
f = 1kHz,
f = 12kHz,
NORM
NORM
GP-CAL1
GP CAL response
f = 1kHz,
f = 12kHz,
NORM
= 2.4kΩ + 270Ω
L
R
NORM
ALC-CAL1
ALC-CAL2
GP-CAL2
Bias on
Bias out maximum level
ALC CAL response
= 2.4kΩ + 270Ω
L
R
ILVIMVIH
Bias off
Bias out offset
Control voltage V
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 20 of 69
Page 21
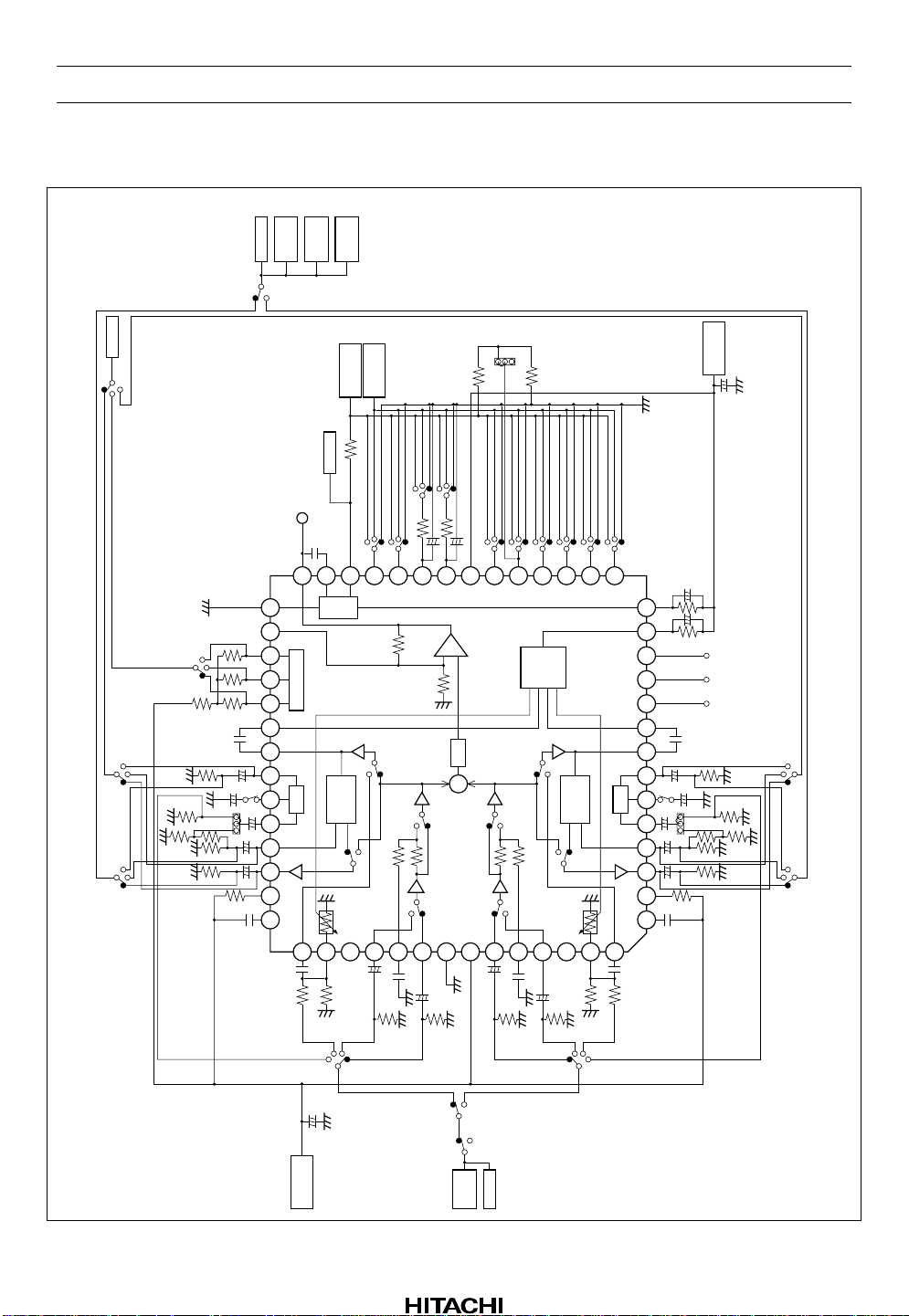
Test Circuit
SW20
Lch
AC VM2
Distortion
Rch
Oscillo
analyzer
scope
Noise
meter
noise meter
with ccir/arm filter
and a-wtg filter
HA12215F
Lch
DC VM1
SW20
Rch
BIAS
EQPB
SW7
EQPB
SW5
REC
REC
JP2
10k
DC +5V
DC +2.5V
SOURCE3
SOURCE4
R18
3.9k
MAOUT
C16
1000p
DC VM2
MSOUT
MSIN
ON
PB
OFF LM ON / OFF
PASS
REC REC / PB / PASS
SW18
SW17
ON
OFF NR ON / OFF
R17
22k
OFF
SW16
R16
22k
++
C15
22µ
282726172520242322
ON RM ON / OFF
SW15
C14
22µ
CC
V
21
R15
ON
R14
B NORM / CROM / METAL
C
OFF BIAS ON / OFF
H
M
N
SW14
SW13
19
18
10k
N NORM / HIGH
70
120 A 120 / 70
SW12
SW11
OFF
ON ALC ON / OFF
A
B PB A / B
SW9
SW10
16
15
MSDET
MS
56
RIN (R)
EQ
ALCDET
ALCCAL
RECCAL
GPCAL
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14
C4
0.1µ
R4
13k
−
C26
0.0047µ
+
AIN (L)
+
ALC
LPF
+
B-NR
Dolby
50
52
+
EE
V
C27
0.47µ
10k
R33
Rch
Lch
SW2
ON
SW1
SG
Audio
OFF
C1
0.47µ
AIN (R)
R1
AC VM1
C2
0.0047µ
BIN (R)
10k
55
53
ALC (R)
+
R3
2.2k
C3
0.47µ
R2
10k
B
R
EQ
A
SW4
R19
270
C
R20
910
BIAS
R21
2k
2.4k
C17
0.47µ
SW21
R22
M
N
ALCIN (L)
ROUT (L)
+
C18
2.2µ
ON
OFF
+
µ
R24
5.1k
C19
0.47
R27
20k
R26
7.5k
16k
R25
C21
10k
R28
C22
22k
R29
EQ
22
SW
JP3
+
µ
C20
0.47
2.2µ
+ +
2.2µ
42 41 39 38 37 36 35 34 33 32 31 30 2940
C23
0.1µ
RIN (L)
13k
R30
43
C24
0.1µ
C29
100µ
+
DC −7V
SOURCE2
B-NR
Dolby
44
45544651474849
+
C25
0.47µ
R31
2.2k
BIN (L)
10k
R32
R
B
A
EQ
SW3
DC +7V
SOURCE1
+
C28
100µ
C13
0.33µ
+
R13
330k
+
C12
10µ
1M
R12
ALCIN (R)
C11
0.47µ
ROUT (R)
+
C10
ON
OFF
+
23
SW
JP1
+
µ
0.47
C8
+
R9
C7
2.2µ
+
R6
C6
2.2µ
R5
33k
C5
0.1µ
10k
REC
R11
2.2µ
µ
C9
R10
5.1k
0.47
R7
20k
R8
7.5k
16k
10k
REC
EQ EQPBPB
SW8
SW6
2. Capacitor tolerance are ±1%.
3. Unit R: Ω, C: F.
Notes: 1. Resistor tolerance are ±1%.
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 21 of 69
Page 22

HA12215F
Characteristic Curves
35
30
(mA)
Q
25
Quiescent Current I
Quiescent Current vs. Split Supply Voltage (REC mode)
RECmode
NR-OFF, ALC ON, REC-MUTE ON, BIAS OFF
NR-OFF, ALC ON, REC-MUTE OFF, BIAS OFF
NR-ON, ALC OFF, REC-MUTE OFF, BIAS ON
Other switch is all Low
20
5
Quiescent Current vs. Split Supply Voltage (PB mode)
35
PBmode
Other switch is all Low
30
(mA)
Q
25
Quiescent Current I
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
NR-OFF, LINE-MUTE OFF, BIAS OFF
NR-ON, LINE-MUTE ON, BIAS OFF
NR-ON, LINE-MUTE OFF, BIAS ON
9
20
5
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 22 of 69
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Page 23

40
VS = ±7.0V
AIN
BIN
30
HA12215F
Input Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (1)
→ RECOUT
20
Gain (dB)
10
0
−10
10
40
VS = ±7.0V
AIN
BIN
30
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Input Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (2)
→ PBOUT
NR-ON
NR-OFF
1M
PASSmode
20
Gain (dB)
10
0
−10
10
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 23 of 69
PBmode
1M
Page 24

HA12215F
40
Input Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (3)
VS = ±7.0V
RECmode
30
20
Gain (dB)
10
0
−10
10
40
VS = ±7.0V
AIN
BIN
PBOUT
RECOUT
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Input Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (4)
→ PBOUT
1M
30
20
Gain (dB)
10
0
−10
10
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 24 of 69
120µ
70µ
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
1M
Page 25

12
VS = ±7.0V
Dolby B-NR
10
8
6
Encode Boost (dB)
4
HA12215F
Encode Boost vs. Frequency
−40dB
−30dB
−20dB
2
0
100
0
−2
−4
−6
Decode Cut (dB)
−8
−10dB
0dB
1k 20k10k
Frequency (Hz)
Decode Cut vs. Frequency
0dB
−10dB
−20dB
−30dB
−10
−12
100
−40dB
VS = ±7.0V
Dolby B-NR
1k 20k10k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 25 of 69
Page 26

HA12215F
Signal Handling (1)
30
RECmode
Rin → RECOUT = 300mVrms = 0dB
f = 1kHz, T.H.D. = 1%
NR-OFF
NR-ON
25
Vomax (dB)
20
15
5
⋅
⋅
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
25
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
BIN
f = 1kHz, T.H.D. = 1%
NR-OFF
NR-ON
PASSmode
20
Vomax (dB)
15
10
5
Signal Handling (2)
⋅
⋅
PBmode
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 26 of 69
Page 27

Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (1)
85
80
f = 1kHz, RECmode
Rin → RECOUT = 300mVrms = 0dB
Rin → PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
75
Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
70
65
5
NR-OFF
NR-ON
NR-OFF
NR-ON
CCIR/ARM filter
678
RECOUT
PBOUT
Split Supply Voltage (V)
HA12215F
9
Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (2)
85
80
75
f = 1kHz, PBmode
AIN
Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
70
65
5
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
BIN
AIN, NR-OFF
BIN, NR-OFF
AIN, NR-ON
BIN, NR-ON
CCIR/ARM filter
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 27 of 69
Page 28

HA12215F
Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (3)
85
80
75
f = 1kHz, PBmode
AIN
Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
70
65
5
→ RECOUT = 300mVrms = 0dB
BIN
AIN, NR-OFF
BIN, NR-OFF
AIN, NR-ON
BIN, NR-ON
CCIR/ARM filter
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (4)
85
80
75
f = 1kHz, PASSmode
AIN
Signal to Noise Ratio (dB)
70
65
5
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
BIN
AIN, Lch
BIN, Lch
AIN, Rch
BIN, Rch
CCIR/ARM filter
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 28 of 69
Page 29

HA12215F
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Split Supply Voltage (1)
1.0
RECmode, NR-OFF
RIN → RECOUT = 300mVrms
100Hz (30kHz LPF)
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
10kHz (400Hz HPF + 80kHz LPF)
RIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
5
(RECmode, NR-OFF)
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Split Supply Voltage (2)
1.0
RECmode, NR-ON
RIN → RECOUT = 300mVrms
100Hz (30kHz LPF)
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
10kHz (400Hz HPF + 80kHz LPF)
RIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
5
(RECmode, NR-ON)
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 29 of 69
Page 30

HA12215F
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Split Supply Voltage (3)
1.0
PBmode, NR-OFF
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms
BIN
100Hz (30kHz LPF)
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
10kHz (400Hz HPF + 80kHz LPF)
AIN
→ RECOUT = 300mVrms
BIN
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
5
(PBmode, NR-OFF)
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Split Supply Voltage (4)
1.0
PBmode, NR-ON
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms
BIN
100Hz (30kHz LPF)
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
10kHz (400Hz HPF + 80kHz LPF)
AIN
→ RECOUT = 300mVrms
BIN
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
5
(PBmode, NR-ON)
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 30 of 69
Page 31

HA12215F
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Split Supply Voltage (5)
1.0
PASSmode, NR-OFF
AIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms
100Hz (30kHz LPF)
1kHz (400Hz HPF + 30kHz LPF)
10kHz (400Hz HPF + 80kHz LPF)
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
5
(PASSmode, NR-OFF)
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (1)
10
RECmode, NR-OFF
= ±7.0V
V
S
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
RIN → RECOUT = 300mVrms = 0dB
1.0
T.H.D. (%)
0.1
0.01
−10
(RECmode, NR-OFF)
Output Level Vout (dB)
15 201050−5
25
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 31 of 69
Page 32

HA12215F
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (2)
10
RECmode, NR-ON
= ±7.0V
V
S
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
RIN → RECOUT = 300mVrms = 0dB
1.0
T.H.D. (%)
0.1
0.01
−10
(RECmode, NR-ON)
Output Level Vout (dB)
15 201050−5
25
10
PBmode, NR-OFF
V
S
AIN
BIN
1.0
T.H.D. (%)
0.1
0.01
−10
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (3)
(PBmode, NR-OFF)
= ±7.0V
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
15 201050−5
Output Level Vout (dB)
25
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 32 of 69
Page 33

HA12215F
10
PBmode, NR-ON
V
S
AIN
BIN
1.0
T.H.D. (%)
0.1
0.01
−10
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (4)
(PBmode, NR-ON)
= ±7.0V
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
15 201050−5
Output Level Vout (dB)
25
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (5)
10
PASSmode, NR-OFF
= ±7.0V
V
S
AIN
BIN
1.0
T.H.D. (%)
0.1
0.01
−10
(PASSmode, NR-OFF)
100Hz
1kHz
10kHz
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
Output Level Vout (dB)
15 201050−5
25
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 33 of 69
Page 34

HA12215F
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency (1)
RECmode, NR-OFF, VS = 7.0V
RIN
RECOUT = 300mVrms
10dB
0dB
10dB
0.01
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
100 1k 10k 100k
RECmode, NR-ON, VS = 7.0V
RIN
RECOUT = 300mVrms
10dB
0dB
10dB
Frequency (Hz)
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency (2)
0.01
100 1k 10k 100k
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 34 of 69
Frequency (Hz)
Page 35

PBmode, NR-OFF, VS = ±7.0V
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms
BIN
10dB
0dB
−10dB
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
HA12215F
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency (3)
0.01
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
100 1k 10k 100k
PBmode, NR-ON, VS = ±7.0V
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms
BIN
10dB
0dB
−10dB
Frequency (Hz)
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency (4)
0.01
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 35 of 69
Page 36

HA12215F
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Frequency (5)
PASSmode, NR-OFF, VS = ±7.0V
AIN
→ PBOUT = 580mVrms
BIN
10dB
0dB
−10dB
0.01
100 1k 10k 100k
−20
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
RIN → RECOUT, Vin = +12dB
RECmode, R → L
−40
−60
−80
Channel Separation (dB)
−100
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (1)
NR-ON
NR-OFF
−120
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 36 of 69
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 37

−20
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
RIN → PBOUT, Vin = +12dB
RECmode, R → L
−40
−60
−80
Channel Separation (dB)
−100
HA12215F
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (2)
NR-ON / OFF
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
RIN → RECOUT, Vin = +12dB
RECmode, L → R
−40
−60
−80
Channel Separation (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (3)
NR-ON
NR-OFF
−120
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 37 of 69
Page 38

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
−80
Channel Separation (dB)
−100
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (4)
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
RIN → PBOUT, Vin = +12dB
RECmode, L → R
−120
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
R → L
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (1)
NR-OFF
NR-ON
−100
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 38 of 69
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 39

Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (2)
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → RECOUT, Vin = +10dB
R → L
−20
−40
HA12215F
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
−100
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
R → L
−20
−40
NR-ON / OFF
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (3)
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
−100
NR-OFF
NR-ON
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 39 of 69
Page 40

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (4)
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → RECOUT, Vin = +10dB
R → L
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
−100
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
L → R
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
NR-ON / OFF
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (5)
NR-OFF
−80
−100
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 40 of 69
NR-ON
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 41

0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → RECOUT, Vin = +10dB
L → R
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
HA12215F
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (6)
NR-ON / OFF
−100
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
L → R
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (7)
NR-OFF
NR-ON
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 41 of 69
Page 42

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (8)
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → RECOUT, Vin = +10dB
L → R
−80
−100
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
PASSmode, R → L
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
NR-ON / OFF
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (1)
−80
−100
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 42 of 69
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 43

0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
PASSmode, R → L
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
HA12215F
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (R→L) (2)
−100
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
AIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
PASSmode, L → R
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (3)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 43 of 69
Page 44

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
Channel Separation (dB)
−80
Channel Separation vs. Frequency (L→R) (4)
0
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
BIN → PBOUT, Vin = +10dB
PASSmode, L → R
−100
−20
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
PBmode, PBOUT
Vin = +12dB, AIN → BIN
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (AIN→BIN) (1)
NR-OFF
NR-ON
−120
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 44 of 69
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 45

−20
VS = ±5.0V, ±7.0V, ±8.0V
PBmode, PBOUT
Vin = +12dB, BIN → AIN
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
HA12215F
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (BIN→AIN) (2)
NR-OFF
NR-ON
−120
−20
VS = ±7.0
PBmode, RECOUT
Vin = +12dB, AIN → BIN
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (AIN→BIN) (3)
NR-ON / OFF
−120
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 45 of 69
Page 46

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (BIN→AIN) (4)
VS = ±7.0
PBmode, RECOUT
Vin = +12dB, BIN → AIN
NR-ON / OFF
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
AIN → RECOUT
Vin = +12dB
PBmode → PASSmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PBmode→PASSmode) (1)
−120
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 46 of 69
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 47

−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
BIN → RECOUT
Vin = +12dB
PBmode → PASSmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
HA12215F
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PBmode→PASSmode) (2)
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
RIN → RECOUT, Lch
Vin = +12dB
PASSmode → PBmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PASSmode→PBmode) (3)
−120
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 47 of 69
Page 48

HA12215F
−20
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (RECmode→PASSmode) (Rch) (1)
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
RIN → PBOUT, Rch
Vin = +12dB
RECmode → PASSmode
8V
5V
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
RIN → PBOUT, Lch
Vin = +12dB
RECmode → PASSmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (RECmode→PASSmode) (Lch) (2)
5V
8V
100k
−120
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 48 of 69
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
100k
Page 49

−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
AIN → PBOUT, Rch
Vin = +12dB
PASSmode → RECmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
HA12215F
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PASSmode→RECmode) (Rch) (1)
5V
8V
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
BIN → PBOUT, Rch
Vin = +12dB
PASSmode → RECmode
−40
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PASSmode→RECmode) (Rch) (2)
8V
5V
100k
−120
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 49 of 69
100k
Page 50

HA12215F
−20
−40
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PASSmode→RECmode) (Lch) (3)
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
AIN → PBOUT, Lch
Vin = +12dB
PASSmode → RECmode
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
−120
−20
VS = ±5.0, ±7.0, ±8.0
BIN → PBOUT, Lch
Vin = +12dB
PASSmode → RECmode
−40
5V
8V
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
Crosstalk vs. Frequency (PASSmode→RECmode) (Lch) (4)
100k
−60
−80
Crosstalk (dB)
−100
−120
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 50 of 69
10010 1k 10k
Frequency (Hz)
5V
8V
100k
Page 51

−20
VS = ±7.0V
AIN
→ PBOUT
BIN
Vin = +12dB
−40
PBmode
−60
−80
Line Mute (dB)
−100
HA12215F
Line Mute vs. Frequency
−120
−20
VS = ±7.0V
EQIN → EQOUT
Norm speed, Norm tape
Vin = +14dB
−40
−60
−80
REC Mute Attenuation (dB)
−100
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
REC Mute Attenuation vs. Frequency
−120
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 51 of 69
Page 52

HA12215F
20
VS = ±7.0V
V
CC
RECmode
0
in
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (RECmode) (1)
EQOUT(NN)
−20
−40
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
20
0
VS = ±7.0V
V
in
EE
RECmode
10010 1k 10k 100k
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (RECmode) (2)
RECOUT
NR-ON
PBOUT
RECOUT
NR-OFF
Frequency (Hz)
EQOUT(NN)
−20
−40
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 52 of 69
RECOUT
NR-ON
RECOUT
NR-OFF
PBOUT
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 53

20
VS = ±7.0V
V
PBmode
CC
HA12215F
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (PBmode) (1)
in
0
−20
PBOUT
NR-OFF
−40
PBOUT
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
20
VS = ±7.0V
V
EE
PBmode
0
NR-ON
10010 1k 10k 100k
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (PBmode) (2)
in
EQOUT(NN)
RECOUT
Frequency (Hz)
EQOUT(NN)
PBOUT
NR-OFF
−20
−40
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
10010 1k 10k 100k
PBOUT
NR-ON
RECOUT
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 53 of 69
Page 54

HA12215F
20
VS = ±7.0V
V
CC
PASSmode
0
in
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (PASSmode) (1)
EQOUT(NN)
−20
−40
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
20
0
−20
VS = ±7.0V
V
in
EE
PASSmode
10010 1k 10k 100k
Ripple Rejection Ratio vs. Frequency (PASSmode) (2)
RECOUT
NR-ON
PBOUT
RECOUT
NR-OFF
Frequency (Hz)
EQOUT(NN)
RECOUT
NR-ON
−40
Ripple Rejection Ratio R.R.R. (dB)
−60
−80
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 54 of 69
PBOUT
RECOUT
NR-OFF
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 55

55
VS = ±7.0V
Norm speed
50
45
40
35
30
25
REC-EQ Gain (dB)
20
15
10
HA12215F
Equalizer Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (1)
Crom
Metal
Norm
5
55
VS = ±7.0V
High speed
50
45
40
35
30
25
REC-EQ Gain (dB)
20
15
10
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Equalizer Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (2)
Crom
Metal
Norm
5
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 55 of 69
Page 56

HA12215F
55
50
45
40
35
30
Equalizer Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (RECcal)
VS = ±7.0V
REC-cal
Norm speed, Norm tape
25
REC-EQ Gain (dB)
20
15
10
5
55
VS = ±7.0V
GP-cal
50
Norm speed, Norm tape
45
40
35
30
REC-cal = 5.0V
REC-cal = 2.5V
REC-cal = 0V
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Equalizer Amp. Gain vs. Frequency (GPcal)
GP-cal = 0V
GP-cal = 2.5V
25
REC-EQ Gain (dB)
20
15
10
5
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 56 of 69
GP-cal = 5.0V
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
Page 57

Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (1)
100
NNmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
1kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
5kHz
10kHz
add BOOST C
HA12215F
−20
Output Level Vout (dB)
Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (2)
100
NCmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
1kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
5kHz
10kHz
add BOOST C
5100−5−10−15
15
−20
Output Level Vout (dB)
5100−5−10−15
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 57 of 69
15
Page 58

HA12215F
Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (3)
100
NMmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
1kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
5kHz
10kHz
add BOOST C
−20
Output Level Vout (dB)
Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (4)
100
HNmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
2kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
10kHz
20kHz
add BOOST C
5100−5−10−15
15
−20
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 58 of 69
Output Level Vout (dB)
5100−5−10−15
15
Page 59

Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (5)
100
HCmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
2kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
10kHz
20kHz
add BOOST C
HA12215F
−20
Output Level Vout (dB)
Equalizer Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Output Level (6)
100
HMmode
EQIN → EQOUT
V
= ±7.0V
S
20Hz
2kHz
10
1.0
REC-EQ T.H.D. (%)
0.1
10kHz
20kHz
add BOOST C
5100−5−10−15
15
−20
Output Level Vout (dB)
5100−5−10−15
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 59 of 69
15
Page 60

HA12215F
Equalizer Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (1)
70
65
REC-EQ S/N (dB)
60
f = 1kHz
A-WTG filter
Norm speed
NN
NC
55
5
NM
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Equalizer Signal to Noise Ratio vs. Split Supply Voltage (2)
70
65
REC-EQ S/N (dB)
60
f = 1kHz
A-WTG filter
High speed
HN
HC
55
5
HM
678
Split Supply Voltage (V)
9
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 60 of 69
Page 61

Equalizer Vomax vs. Split Supply Voltage (1)
20
f = 1kHz
add BOOST C
NN
NC
15
10
REC-EQ Vomax (dB)
5
0
5
NM
678
HA12215F
9
Split Supply Voltage (V)
Equalizer Vomax vs. Split Supply Voltage (2)
20
f = 1kHz
add BOOST C
HN
HC
15
10
REC-EQ Vomax (dB)
5
0
5
HM
678
9
Split Supply Voltage (V)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 61 of 69
Page 62

HA12215F
RECcal Correction vs. V
5
f = 3kHz
GP-cal OPEN
4
V
= ±7V
S
Norm speed
3
Norm tape
2
1
0
−1
RECcal Correction (dB)
−2
−3
−4
−5
02 5143
V
REC-cal
REC-cal
(V)
GPcal Correction vs. V
5
4
3
2
1
0
−1
GPcal Correction (dB)
−2
f = 12kHz
−3
REC-cal OPEN
V
= ±7V
S
−4
Norm speed
Norm tape
−5
5
678
V
GP-cal
GP-cal
9
(V)
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 62 of 69
Page 63

ALC Operate Level vs. Input Level
10
f = 1kHz, VS ±7.0V, Both channel input (L, Rch)
RIN → RECOUT, RIN = 192.8mVrms = 0dB
8
TYPE II
TYPE I, IV
cal = 5V
cal = 5V
6
cal = 2.5V
4
cal = 2.5V
HA12215F
2
cal = 0V
0
Output Level RECOUT (dB) 0dB = 300mVrms
cal = 0V
−2
−53020100
51525
Input Level Vin (dB) RIN = 192.8mVrms = 0dB
ALC Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Level (1)
f = 1kHz, V
TYPE I,IV
= ±7.0V
S
(Norm tape, Metal tape)
1.0
Cal = 0V
Cal = 2.5V
Cal = 5V
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0dB = 192.8mVrms
Vin
R4
13kC40.1µ
R3
2.2k
56
55
RIN
ALC
35
0.01
−5
Input Level Vin (dB)
20 25151050
30
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 63 of 69
Page 64

HA12215F
ALC Total Harmonic Distortion vs. Input Level (2)
10
f = 1kHz, V
TYPE II
(Crom tape)
1.0
0.1
T.H.D. (%)
0.01
−5
= ±7.0V
S
Cal = 0V
Cal = 2.5V
Cal = 5V
Input Level Vin (dB)
ALC Operate Level vs. Frequency
20 25151050
30
8
6
4
2
0
−2
Operate Level RECOUT (dB) 0dB = 300mVrms
−4
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 64 of 69
Vin = ±12dB, Both channel input (L, Rch), RIN → RECOUT
TYPE I, IV (Norm tape, Metal tape)
TYPE II (Crom tape)
100 1k 10k 50k
ALC-CAL = 5V
ALC-CAL = 2.5V
ALC-CAL = 0V
Frequency (Hz)
Page 65

Bias Output Voltage vs. Load Current
8
VS = ±7.0V
Bias ON
7
6
Bias Output Voltage (V)
5
0
270Ω
31
V
Load Current I (mA)
I
HA12215F
564321
7
MS Sensing Level vs. Frequency
0
−10
−20
MS Sensing Level (dB)
−30
100 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
VS = ±7.0V, MSOUT
AIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms = 0dB
Lo → Hi
Hi → Lo
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 65 of 69
Page 66

HA12215F
40
30
20
MS Amp. Gain vs. Frequency
VS = ±7.0V
MAOUT
Gain (dB)
10
0
−10
500
VS = ±7.0V, f = 5kHz, MSOUT
AIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms
0dB
−10dB
−20dB
100
MSIN
10010 1k 10k 100k
Frequency (Hz)
No-Signal Sensing Time vs. Resistance
10
No-Signal Sensing Time (ms)
1
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 66 of 69
PBOUT
MSOUT
C13
0.33µ
14 V
CC
R13
100k 1M
Resistance R13 (Ω)
Page 67

100
VS = ±7.0V, f = 5kHz, MSOUT
AIN → PBOUT = 580mVrms
0dB
−10dB
−20dB
10
HA12215F
Signal Sensing Time vs. Capacitance
PBOUT
Signal Sensing Time (ms)
1
MSOUT
14 V
C13
R13
330k
0.01 0.1 0.5
Capacitance C13 (µF)
CC
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 67 of 69
Page 68

HA12215F
Package Dimensions
12.8 ± 0.3
10.0
42
29
43
12.8 ± 0.3
56
1
± 0.08
*0.32
0.30 ± 0.06
0.775 0.775
0.13
M
0.35
0.10
*Dimension including the plating thickness
Base material dimension
14
28
15
+0.1
2.20
−0.09
0.1
0.65
2.54 Max
± 0.04
0.15
*0.17 ± 0.05
Hitachi Code
JEDEC
EIAJ
Weight
(reference value)
0.60
Unit: mm
1.40
0° − 8°
± 0.15
FP-56
0.5 g
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 68 of 69
Page 69

HA12215F
Disclaimer
1. Hitachi neither warrants nor grants licenses of any rights of Hitachi’s or any third party’s patent,
copyright, trademark, or other intellectual property rights for information contained in this document.
Hitachi bears no responsibility for problems that may arise with third party’s rights, includ ing
intellectual property rights, in connection with u se of the information contained in this document.
2. Products and product specifications may be subject to change without notice. Confirm that you have
received the latest product standards or specifications before final design, purchase or use.
3. Hitachi makes every attempt to ensure that its products are of high quality and reliability. However,
contact Hitachi’s sales office before using the product in an application that demands especially high
quality and reliability or where its failure or malfunction may directly threaten human life or cause risk
of bodily injury, such as aerospace, aeronautics, nuclear power, combustion control, transportation,
traffic, safety equipment or medical equipment for life support.
4. Design your application so that the product is used within the ranges guaranteed by Hitachi particularly
for maximum rating, operating supply voltage range, heat radiation characteristics, installation
conditions and other characteristics. Hitachi bears no responsibility for failure or damage when used
beyond the guaranteed ranges. Even within the guaranteed ranges, consider normally foreseeable
failure rates or failure modes in semiconductor devices and employ systemic measures such as failsafes, so that the equipment incorporating Hitachi product does not cause bodily injury, fire or other
consequential damage due to operation of the Hitachi product.
5. This product is not designed to be radiation resistant.
6. No one is permitted to reproduce or duplicate, in any form, the whole or part of this document without
written approval from Hitachi.
7. Contact Hitachi’s sales office for any questions regarding this document or Hitachi semiconductor
products.
Sales Offices
Hitachi, Ltd.
Semiconductor & Integrated Circuits.
Nippon Bldg., 2-6-2, Ohte-machi, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo 100-0004, Japan
Tel: Tokyo (03) 3270-2111 Fax: (03) 3270-5109
URL NorthAmerica : http://semiconductor.hitachi.com/
For further information write to:
Hitachi Semiconductor
(America) Inc.
179 East Tasman Drive,
San Jose,CA 95134
Tel: <1> (408) 433-1990
Fax: <1>(408) 433-0223
Europe : http://www.hitachi-eu.com/hel/ecg
Asia : http://sicapac.hitachi-asia.com
Japan : http://www.hitachi.co.jp/Sicd/indx.htm
Hitachi Europe GmbH
Electronic Components Group
Dornacher Straße 3
D-85622 Feldkirchen, Munich
Germany
Tel: <49> (89) 9 9180-0
Fax: <49> (89) 9 29 30 00
Hitachi Europe Ltd.
Electronic Components Group.
Whitebrook Park
Lower Cookham Road
Maidenhead
Berkshire SL6 8YA, United Kingdom
Tel: <44> (1628) 585000
Fax: <44> (1628) 585160
Hitachi Asia Ltd.
Hitachi Tower
16 Collyer Quay #20-00,
Singapore 049318
Tel : <65>-538-6533/538-8577
Fax : <65>-538-6933/538-3877
URL : http://www.hitachi.com.sg
Hitachi Asia Ltd.
(Taipei Branch Office)
4/F, No. 167, Tun Hwa North Road,
Hung-Kuo Building,
Taipei (105), Taiwan
Tel : <886>-(2)-2718-3666
Fax : <886>-(2)-2718-8180
Telex : 23222 HAS-TP
URL : http://www.hitachi.com.tw
Hitachi Asia (Hong Kong) Ltd.
Group III (Electronic Components)
7/F., North Tower,
World Finance Centre,
Harbour City, Canton Road
Tsim Sha Tsui, Kowloon,
Hong Kong
Tel : <852>-(2)-735-9218
Fax : <852>-(2)-730-0281
URL : http://www.hitachi.com.hk
Copyright Hitachi, Ltd., 2000. All rights reserved. Printed in Japan.
Colophon 2.0
Rev.5, Oct. 1999, page 69 of 69
 Loading...
Loading...