Page 1
1
Standard ICs
Dual operational amplifier
BA728 / BA728F / BA728N
The BA728, BA728F, and BA728N are ICs with two independently functioning operational amplifiers featuring internal phase compensation. These products offer a wide range of operating voltages, from 3 to 18V ( ± 1.5 to 9V) and
are high-performance operational amplifiers which can be driven from a single power supply within the in-phase
mode input range, including a negative power supply.
•
Applications
Ground sensing small-signal amplifiers
Control amplifiers requiring high phase margin, such as motor drivers
Amplifiers operated on low voltages
Capacitive loaded amplifiers
•
Features
1) Can be driven from a single power supply.
2) Low power.
3) Pin layout is the same as that of the general-
purpose 4558 operational amplifier.
4) When driven from a single power supply, the power
supply voltage ranges from 3 to 18V.
5) When driven from a dual power supply, the power
supply voltage ranges from ± 1.5 to ± 9V.
6) Output is protected against short-circuits.
7) Output block is operated as a class AB to minimize crossover distortion.
8) Low input bias current of 10nA (typ.).
9) Each package contains two operational amplifiers.
10) Internal phase compensation provided.
•
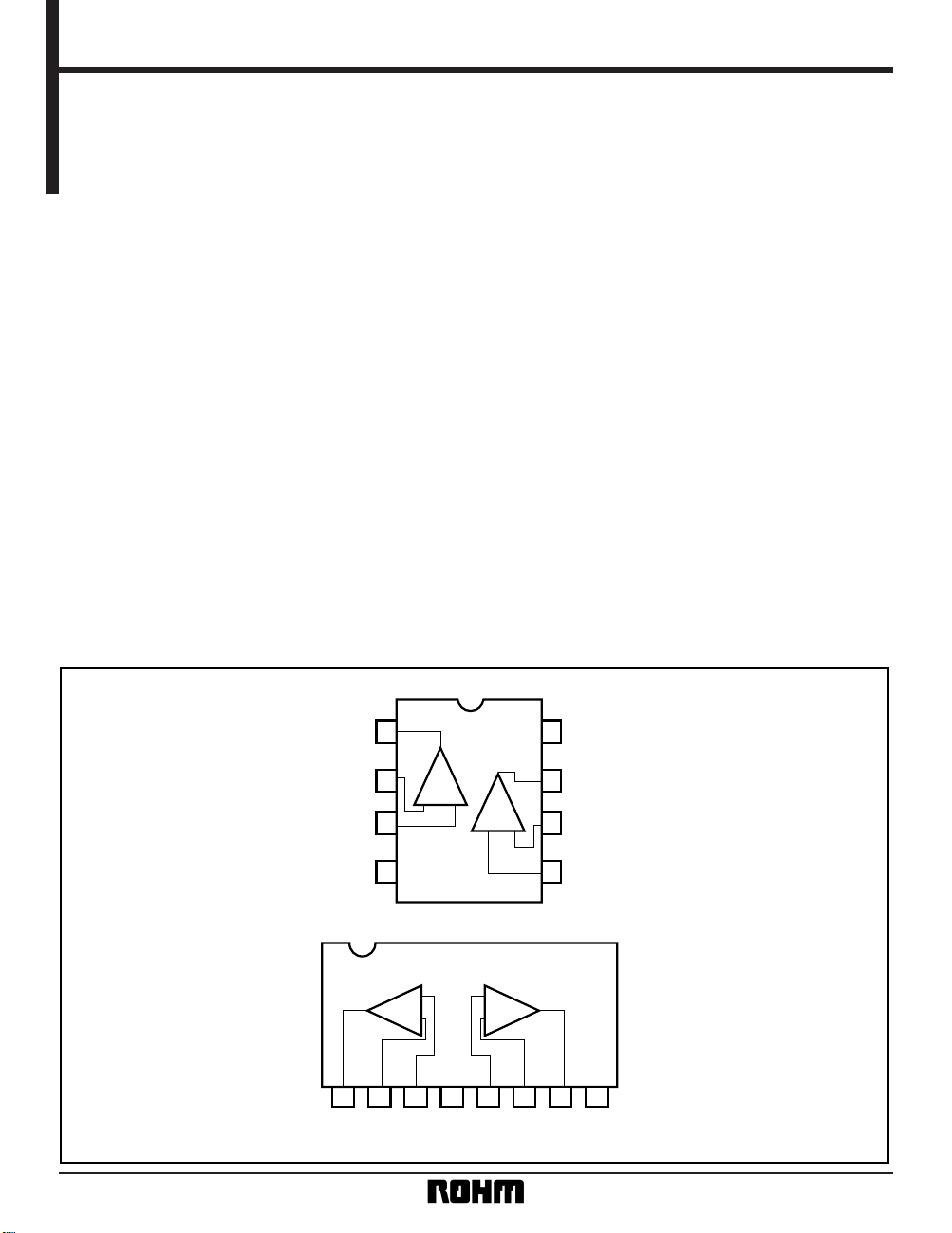
Block diagram
OUT1
– IN1
+ IN1
V
EE
VCC
OUT2
– IN2
+ IN2
1
2
3
4
1
8
7
6
5
OUT1
2
– IN1
3
+ IN1
4
V
EE
5
+ IN2
6
– IN2
7
OUT2
8
V
CC
+ –
+
+
– +
1ch
2ch
2ch1ch
––
BA728 / BA728F
BA728N
Page 2
2
Standard ICs BA728 / BA728F / BA728N
•
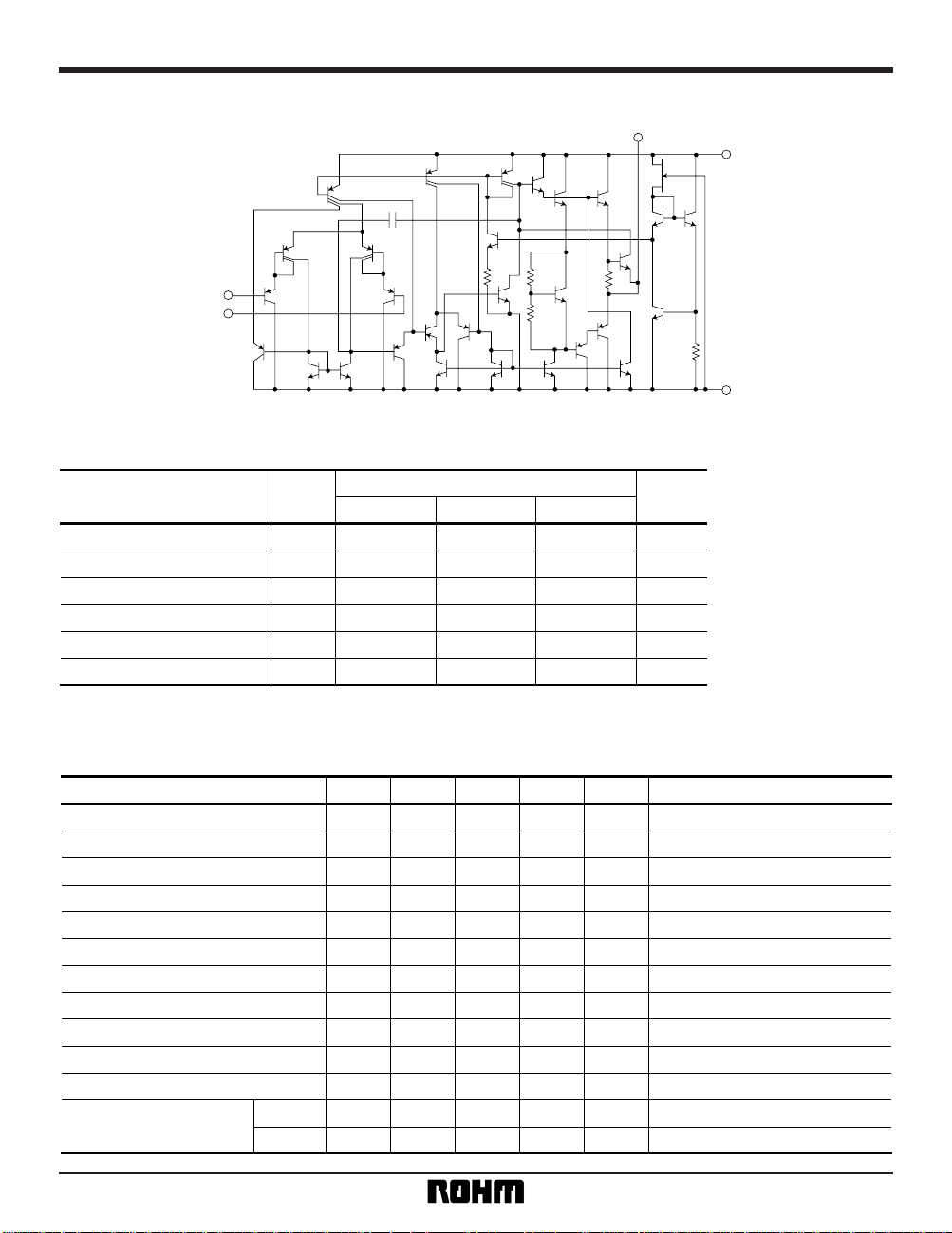
Internal circuit configuration
+ IN
– IN
Q
1
Q4 Q5
Q2
Q3
Q6
Q13
Q16
Q10
Q11
Q12
Q14
Q21
R3
R2
R6
R4
R5
R1
Q20
Q17
Q15
Q22
Q23
Q28
Q25
Q24
Q19
Q18
Q27 Q29
Q26
Q7
Q8
Q9
C1
VEE
VCC
OUT
•
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol
Limits
Unit
BA728 BA728F BA728N
V
CC 18 ( ± 9) 18 ( ± 9) 18 (
± 9) V
Pd 800
∗
550
∗
550
∗
mW
V
ID VCC V
V
I – 0.3 ~ + VCC V
Topr – 20 ~ + 75 – 20 ~ + 75 – 20 ~ + 75 °C
Tstg – 55 ~ + 125 – 55 ~ + 125 – 55 ~ + 125 °C
V
CC VCC
– 0.3 ~ + VCC – 0.3 ~ + VCC
Power supply voltage
Power dissipation
Differential input voltage
Common-mode input voltage
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
∗
Refer to Pd characteristics diagram.
∗
The values for the BA728Fare those when it is mounted on a glass epoxy PCB (50mm × 50mm × 1.6mm).
•
Electrical characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = 25°C, VCC = + 6V, VEE = - 6V)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Conditions
V
IO — 210mV
I
IO — 150nA
I
B — 10 250 nA
A
V 86 100 — dB RL ⭌ 2k
Ω
V
ICM — V
± 3.0 ± 4.5 — VR
L ⭌ 2k
Ω
CMRR 70 90 — dB
PSRR — 30 150
µ
V / V
— 0.7 — V /
µ
S
— 0.7 — MHz
CS — 120 — dB
source Isource — 20 — mA
sink Isink — 10 — mA
S. R.
f
T
Unit
A
V = 1, RL = 2k
Ω
V
IN
+
= 1V, VIN– = 0V
V
IN
–
= 1V, VIN+ = 0V
V
OM
4 ~ – 6 4.5 ~ – 6
Input offset voltage
Input offset current
Input bias current
High-amplitude voltage gain
Common-mode input voltage
Maximum output voltage
Common mode rejection ratio
Power supply voltage rejection ratio
Slew rate
Maximum frequency
Channel separation
Maximum output current
Page 3

3
Standard ICs BA728 / BA728F / BA728N
•
Measurement circuits
200
Ω
RS
RS
1
Ω
VS
IC
VEE
VCC
RL
BA728
BA728F
BA728N
(per circuit)
50kΩ
50Ω
V
O2
+
–
1ch
= – 200 log
1000
1
V
O1
VO2
·
Channel separation
Fig. 1 Channel separation measurement circuit
10kΩ
10kΩ
V
O1
+
–
2ch
~
(indicates individual channels
in the same package)
•
Electrical characteristic curves
POWER DISSIPATION: Pd (mW)
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE: Ta (°C)
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
0 25 50 75 100 125 150
BA728
BA728N
Fig.2 Power dissipation vs. ambient
temperature
BA728F
3
2
1
0
010 20
QUIESCENT CURRENT: lQ (mA)
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: V
+
(V)
Fig.3 Quiescent current vs.
power supply voltage
10
20
30
010 20
INPUT BIAS CURRENT: ld (nA)
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: V
+
(V)
Fig.4 Input bias current vs.
power supply voltage
160
10 200
120
80
OPEN LOOP VOLTAGE GAIN: AV (dB)
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: V
+
(V)
Fig.5 Open loop voltage gain vs.
power supply voltage
40
30
20
10
0
– 20
02040 8060
OUTPUT CURRENT: lO (mA)
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE: Ta (°C)
Fig.6 Current control characteristics
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
10M1M100k10k1k100101
OPEN LOOP VOLTAGE GAIN: AV (dB)
FREQUENCY: f (Hz)
Fig.7 Open loop voltage gain vs.
frequency
Page 4

20
15
100k10k1k100 1M
10
5
0
FREQUENCY: f (Hz)
MAXIMUM OUTPUT VOLTAGE: VOM (W)
Fig.8 Maximum output voltage vs.
frequency
4
2
0
1
2
3
1
3
0
20 4030100
VIN (V)
INPUT VOLTAGE
VOUT (V)
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
TIME (µs)
Fig.9 Output response characteristics
10
5
0
– 5
– 10
0 ± 5 ± 10
MAXIMUM OUTPUT VOLTAGE: VOM (V)
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE: V
±
(V)
Fig.10 Maximum output voltage vs.
power supply voltage
(1)Unused circuit connections
If there are any circuits which are not being used, we
recommend making connections as shown in Figure
11, with the non-inverted input pin connected to the
potential within the in-phase input voltage range (V
ICM).
4
Standard ICs BA728 / BA728F / BA728N
•
Operation notes
–
+
VEE
VCC
To potential
in V
ICM
Fig.11 Unused circuit connections
•
External dimensions (Units: mm)
DIP8 SOP8 SIP8
BA728 BA728F BA728N
0.5 ± 0.1
3.2 ± 0.2 3.4 ± 0.3
85
14
9.3
± 0.3
6.5 ± 0.3
0.3
±
0.1
0.51Min.
2.54
0° ~ 15°
7.62
0.4 ± 0.11.27
0.15
0.3Min.
0.15 ± 0.1
0.11
6.2 ± 0.3
4.4 ± 0.2
5.0 ± 0.2
85
41
1.5 ± 0.1
10.5 ± 0.5
1
8
2.54
3.5 ± 0.5
1.3
0.8
0.6
0.3 ± 0.1
2.8 ± 0.2
19.3 ± 0.2
1.2
5.8 ± 0.2
•
Electrical characteristic curve
 Loading...
Loading...