Page 1
1
Multimedia ICs
SYNC separator IC with AFC
BA7062F
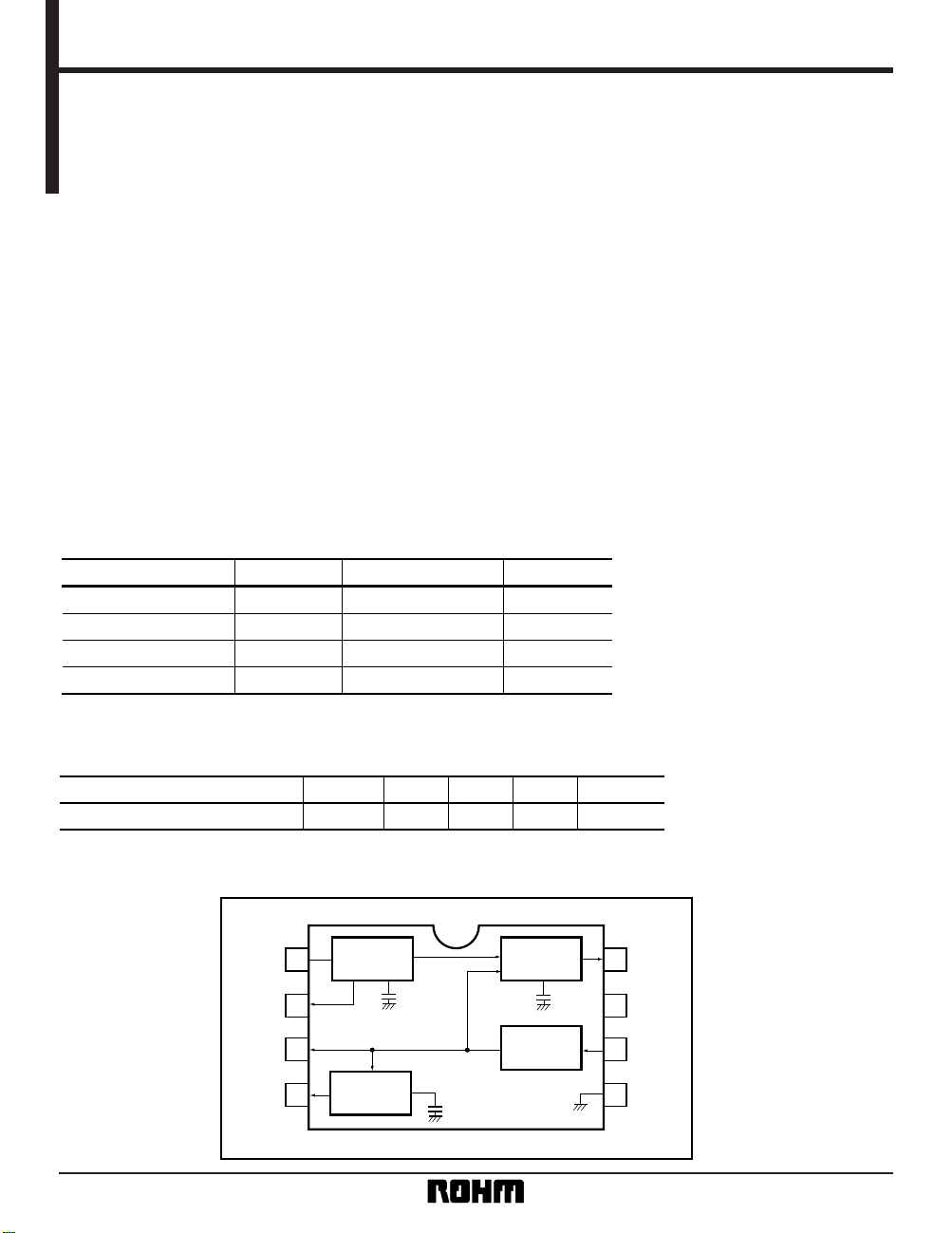
The BA7062F separates the synchronization signals from a video signal and outputs the horizontal and vertical synchronization signals (H
D and VD), and the composite synchronization signal (Sync-out).
The H
D and VD pulse widths are different.
•
Applications
TVs and VCRs
•
Features
1) Built-in AFC circuit.
2) Low power dissipation (approx. 21mW).
3) Low external parts count.
4) SOP 8-pin package.
5) Horizontal free-run frequency does not require adjustment.
1
2
3
4
8
7
6
5
PHASE
COMP
H.OSC
SYNC
SEPA
V.SEPA
•
Block diagram
•
Absolute maximum ratings (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Limits Unit
8.0 V
350
∗
mW
°C
°C
V
CC Max.
Pd
Topr
Tstg
– 20 ~ + 75
– 55 ~ + 125
Power supply voltage
Power dissipation
Operating temperature
Storage temperature
∗
When mounted on a 50mm × 50mm PCB, reduced by 3.5mW for each increase in Ta of 1°C over 25°C.
•
Recommended operating conditions (Ta = 25°C)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
V
CC 4.5 — 5.5 VOperating power supply voltage
Page 2
2
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
VCC
1pin
1k
12k
100µA
Fig. 1
2pin
V
CC
200
5k
Fig. 2
3pin
200
Fig. 3
VCC
4pin
200
10k
Fig. 4
VCC
6pin
100
10µA
Fig. 5
VCC
8pin
1k
3k
3k 3k
3k 3k 3k
Fig. 6
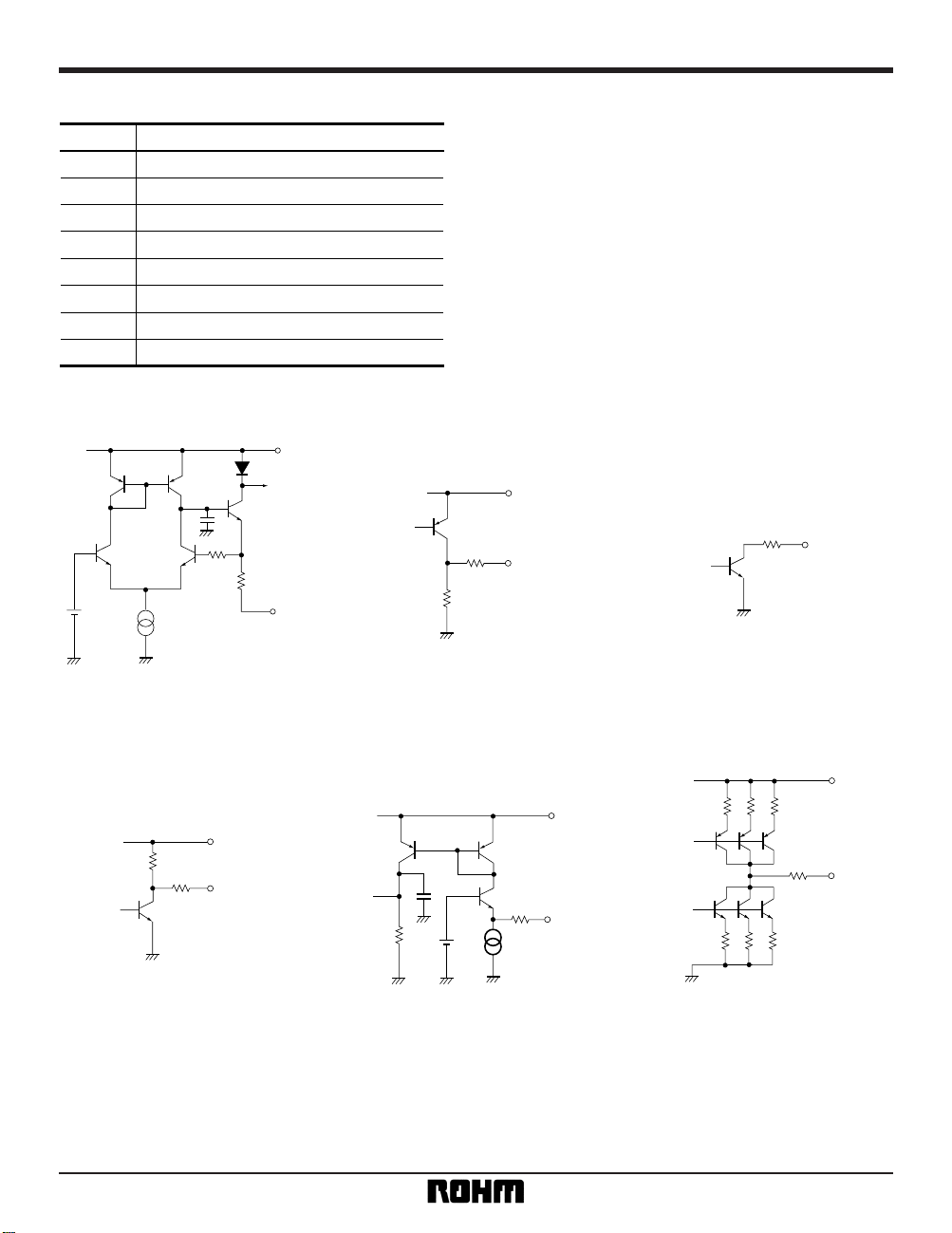
•
Input / output circuits
•
Pin descriptions
Pin No.
1
2H
D
3
4V
D
5
6
7
8
Horizontal oscillator resistor
H
D output
SYNC output (open collector)
V
D output
GND
Video input
Power supply
Phase comparator output
Function
Page 3
3
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
•
Electrical characteristics (unless otherwise noted, Ta = 25°C and VCC = 5V)
Parameter Symbol Min. Typ. Max. Unit
I
Q
2.0 4.1 6.2 mA
V
syn-Min.
— 0.08 0.15 V
P-P
V
P-L
— 0.1 0.3 V
V
P-H
4.7 4.9 — V
f
H-O
13.9 15.7 17.5 kHz
± 2.1 ± 2.9 ——kHz
T
HPH
– 1.0 0 + 1.0 µs
T
HD
10.5 11.5 12.5 µs
T
VD
200 260 320 µs
∆f
CAP
Quiescent current
Minimum SYNC separation level
Pulse voltage, Low
Pulse voltage, High
Capture range
Lock-in phase
H
D pulse width
V
D pulse width
Conditions
2pin
4pin
2pin – 6pin
Pin 3 open
Pin 6 terminated with 75
Ω resistor
2, 4 pin
2, 4 pin
No input signal, I
1
= open
䊊 Not designed for radiation resistance.
(Horizontal)
free-running frequency
•
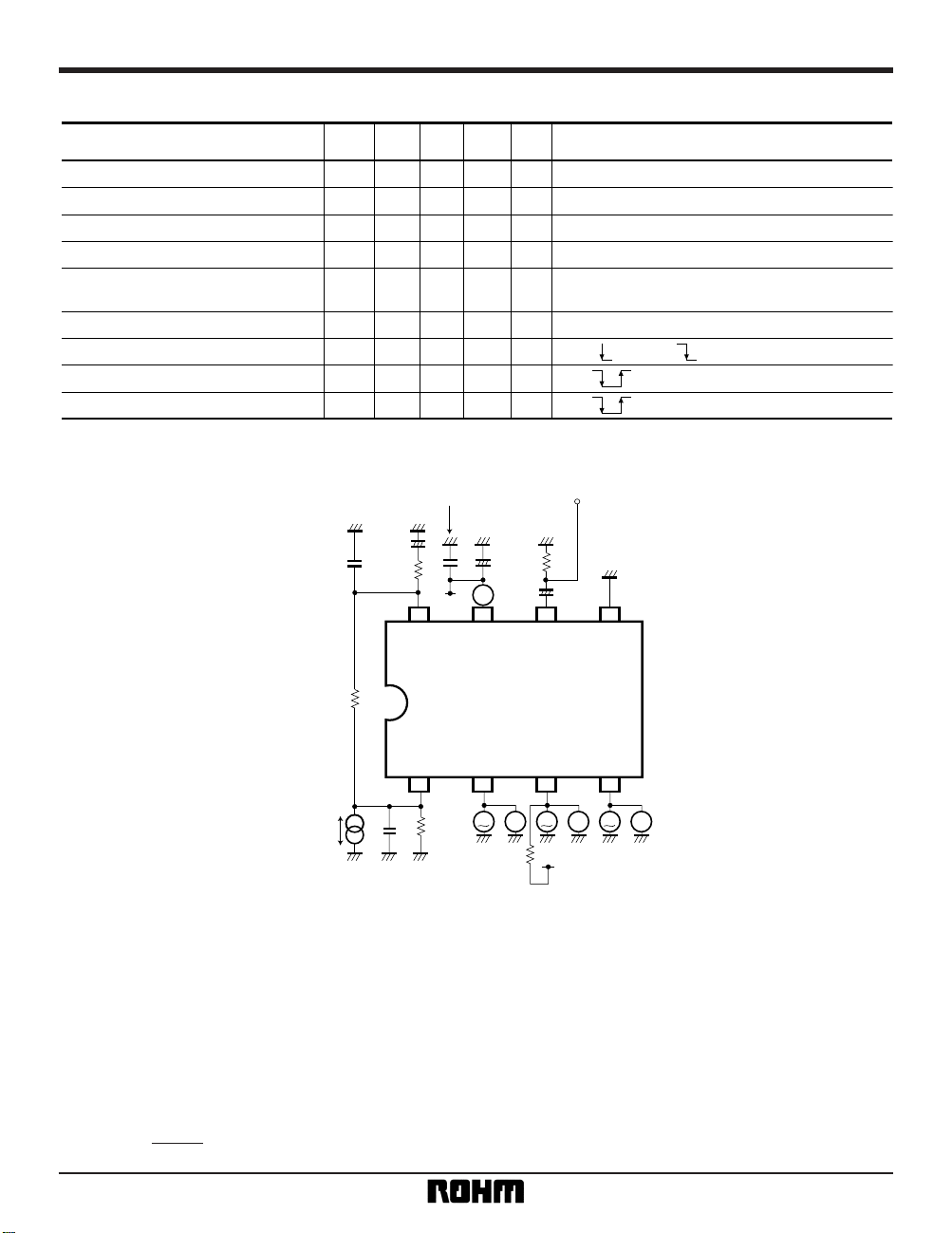
Measurement circuit
8 7 6 5
1 2 3 4
II
100p
130k
V
T
V
T
V
T
1µ
1µ
1µ
75
Video In
+
+
+
A
47µ
0.022µ
39k
VCC
2200p
470k
10k V
CC
Fig. 7
•
Circuit operation
(1) Synchronization separation circuit
Detects the charging current to a externally-connected
capacitor, and performs synchronization separation.
(2) Horizontal oscillation circuit
When a video signal is input, it is synchronized with
Hsync by the PLL. The horizontal free-running frequency is determined by external resistor R
1.
(3) Vertical synchronization separation circuit
When a video signal is input, synchronization signal
separation is done over the vertical synchronization
pulse interval.
f
H-O = [kHz]
2.05E6
R
1
Page 4

4
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
NTSC signal
Odd-number field
(IN)
(OUT)
Vertical synchronizing pulse interval
V
D
1 / 2H
NTSC signal
Even field (IN)
H
D
Odd field (OUT)
H
D
Even field (OUT)
(1) The rise and fall positions for VD are basically the same for both odd and even fields.
(2) H
D shifts by 1 / 2H during the odd and even field interval.
Fig. 8
•
VIN, HD, and VD timing charts
Page 5

5
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
•
Application example
(1) Connect pin 1 to GND via a 120kΩ (approx.) resistor. Leave pins 2, 4 and 8 open.
(2) SYNC output polarity (pin 3) is positive.
(3) The delay time for rising edge of the SYNC output (pin 3) with respect to the falling edge of Sync for the Vsig
input signal (pin 6) is 850ns (reference value).
(4) The delay time for falling edge of the SYNC output (pin 3) with respect to the rising edge of Sync for the Vsig
input signal (pin 6) is 450ns (reference value).
•
Attached components
Resistor R
1 should have a tolerance of ± 2%, and a temperature coefficient of 100ppm or lower.
• When SYNC SEPA output only is used. H
D and VD unused.
Fig. 9
100p
C
4
R1
R2
470k
130k
10k
VD
SYNC
H
D
H.OSC
PHASE
COMP
SYNC
SEPA
8
7
6
1
2
3
4
C3
10k
1µ
R
3C2
+
2200p
C5 C6
47µ 0.022µ
+
C7
C1 R4
330
1µ
R5
470k
+
+
+
5
V.SEPA
Vsig
VCC = 5V
V
CC = 5V
470kR2
R3
10k
8
C
2 C3-2
0.47µ
C
3-1
0.47µ
2200p
1000p
VCC
∗
By configuring the circuit enclosed in the dotted line to that in the
diagram on the right, you can decrease the lock-in time and increase
the capture range.
∗
R1
120k
10k
VD
SYNC
H
D
H.OSC
PHASE
COMP
SYNC
SEPA
8
7
6
1
2
3
4
C5 C6
47µ 0.022µ
+
C7
C1 R4
330
1µ
R5
470k
+
5
V.SEPA
Vsig
VCC = 5V
V
CC = 5V
Fig. 10
1000p
Page 6

6
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
•
Electrical characteristic curves
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
ICC CURRENT (mA)
6
5
4
3
2
1
0
4.0 5.0
6.0
Fig. 11 Quiescent current vs.
power supply voltage
TEMPERATURE (°C)
ICC CURRENT (mA)
VCC = 5V
6.0
5.5
5.0
4.0
4.5
3.5
2.5
3.0
– 25 0 25 50 75
100
Fig. 12 Quiescent current vs.
temperature
HORIZONTAL FREQUENCY (kHz)
16.4
16.2
16.0
15.6
15.4
15.2
15.8
4.5 5.0
5.5
Fig. 13 Horizontal free-running
frequency vs.
power supply voltage
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
Fig. 14 Horizontal free-running
frequency vs. temperature
VCC = 5.0V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
HORIZONTAL FREQUENCY (kHz)
16.6
16.4
16.2
15.8
15.6
15.4
16.0
– 25 0 25 50 75
100
15.2
Fig. 15 HD pulse width vs.
temperature
TEMPERATURE (°C)
HD PULSE WIDTH (µS)
12.0
11.8
11.6
11.2
11.0
10.8
10.6
11.4
– 25 0 25 50 75
100
NTSC
VCC = 5.0V
Fig. 16 VD pulse width vs.
temperature
NTSC
VCC = 5.0V
TEMPERATURE (°C)
VD PULSE WIDTH (µS)
290
280
270
250
240
230
220
260
– 25 0 25 50 75
100
– lock
+ cap
+ lock
– cap
FREQUENCY: f (cap. lock) (kHz)
15
10
20
5.55.04.5
Fig. 17 Capture range / lock range vs.
power supply voltage
POWER SUPPLY VOLTAGE (V)
TEMPERATURE (°C)
– lock
+ cap
+ lock
– cap
FREQUENCY: f (cap. lock) (kHz)
15
10
20
1000255075– 25
VCC = 5.0V
Fig. 18 Capture range / lock range vs.
temperature
Fig. 19 Time from no signal
to pull in
FREQUENCY (kHz)
SIGNAL - LOCK IN TIME (ms)
100
200
0
300
2018 1914 15 16 1713
VCC = 5.0V
f
LOCK = 15.734kHz
Page 7

7
Multimedia ICs BA7062F
FREQUENCY (kHz)
POWER LOCK IN TIME (ms)
200
100
500
400
300
0
700
600
20
18 19
14
15 16 17
13
VCC = 5.0V
f
LOCK = 15.734kHz
Fig. 20 Time from power on
to pull in
•
Operation notes
• Make the ground line as thick as possible.
• Keep power supply noise to a minimum.
•
External dimensions (Units: mm)
SOP8
0.4 ± 0.11.27
0.15
0.3Min.
0.15 ± 0.1
0.11
6.2 ± 0.3
4.4 ± 0.2
5.0 ± 0.2
85
41
1.5 ± 0.1
 Loading...
Loading...