Page 1

MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE
Instruction Manual
Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Page 2

Safety Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Safety
WARNING
EQUIPMENT HAZARD!
The vertical bypass/non bypass panel contains dangerous
voltages when connected to mains voltage. It is strongly
recommended that all electrical work conform to the
National Electrical Code (NEC) and all national and local
regulations. Installation, start-up and maintenance should
be performed only by qualified personnel. Failure to follow
the NEC or local regulations could result in death or
serious injury.
Motor control equipment and electronic controls are
connected to hazardous mains voltages. Extreme care
should be taken to protect against shock. The user must
be protected against supply voltage and the motor must
be protected against overload in accordance with
applicable national and local regulations. Be sure
equipment is properly grounded. Wear safety glasses
whenever working on electric control or rotating
equipment.
WARNING
UNINTENDED START!
When the vertical bypass/non bypass panel is connected
to AC input power, the motor may start at any time. The
drive, panel, motor, and any driven equipment must be in
operational readiness. Failure to be in operational
readiness when panel and drive are connected to AC input
power could result in death, serious injury, or equipment
or property damage.
Grounding
Correct protective grounding of the equipment must be
established in accordance with national and local codes.
Ground currents are higher than 3mA.
Safety Guidelines
1. Disconnect the drive and vertical bypass/non
bypass panel from mains before commencing
service work
2. DO NOT touch electrical parts of the vertical
bypass/non bypass panel or drive when mains is
connected. After mains has been disconnected,
wait 15 minutes before touching any electrical
components or read the label on vertical
bypass/non bypass panel.
3. The user must be protected against supply
voltage and the motor must be protected against
overload in accordance with applicable national
and local regulations.
4. While programming parameters, the motor may
start without warning. Activate the [Off] key on
the LCP when changing parameters.
5. The [Off] key on the LCP does not isolate the
drive from mains voltage and is not to be used as
a safety switch.
Warning against unintended start
When the vertical bypass/non bypass panel is connected
to mains, the motor may be started by means of an
external switch, a serial bus command, an input reference
signal, or a cleared fault condition. Use appropriate
cautions to guard against an unintended start.
WARNING
GROUNDING HAZARD!
For operator safety, it is important to ground drive, vertical
bypass panel, and motor properly. Follow the grounding
guidelines of local and national codes. Failure to follow
grounding guidelines could result in death or serious
injury.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 3

Safety Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 4

Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Contents
1 Introduction
1.1.1 Purpose of the Manual 2-1
1.1.2 Overview 2-1
1.1.3 Typical Bypass Operation 2-1
1.2 Bypass Circuits
1.2.1 Three-contactor Bypass 2-1
1.3 Bypass Options
1.3.1 Common Run/Stop with Bypass 2-2
1.3.2 Automatic Bypass 2-2
1.3.3 Run Permissive in Bypass 2-2
1.3.4 Basic Fire Mode in Bypass 2-2
1.3.5 Advanced Fire Mode in Bypass 2-2
1.3.6 Overload Protection 2-2
1.4 Bypass Platform Configurations
1.5 Switch Mode Power Supply
1.5.1 Control Transformer 2-3
1.6 Disconnects
2-1
2-1
2-2
2-3
2-3
2-3
1.6.1 Main Disconnect 2-3
1.6.2 Mode Selector Switch 2-4
1.6.3 Panel Configurations 2-5
1.6.4 Panel Voltage and Frame Ratings 2-6
1.7 Power Component Functions
1.7.1 Power Fusing 2-6
2 Pre-installation
2.1.1 Receiving Inspection 3-1
2.1.2 Pre-installation Check 3-1
2.1.3 Installation Site Check 3-1
2.2 Harsh Environments
2.2.1 Airborne Liquids 3-2
2.2.2 Airborne Solids 3-2
2.2.3 Corrosive Chemicals 3-2
3 Installation
3.1.1 Tools Required 4-1
2-6
3-1
3-2
4-1
3.1.2 Drive Fuses 4-1
3.1.3 Internal Main Panel Fuses 4-5
3.2 Mechanical Installation
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
4-5
Page 5

Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3.2.1 Lifting 4-5
3.2.2 Hoist or Overhead Lift 4-5
3.2.3 Forklift 4-5
3.2.4 Shipping Weights 4-5
3.3 Cooling
3.4 Electrical Installation
3.4.1 Component Identification & Customer Connection 4-8
3.4.2 Wire and Cable Access 4-16
3.4.3 Wire Size 4-19
3.4.4 Wire Type Rating 4-21
3.4.5 Terminal Tightening Torques 4-21
3.4.6 Input Line Connection 4-25
3.4.7 Motor Wiring 4-25
3.4.8 Grounding (Earthing) 4-26
3.4.9 Control Wiring 4-26
3.4.10 Serial Communication Bus Connection 4-26
3.4.11 Drive Control Terminals 4-27
4 Start Up
4.1.1 Inspection Prior to Start Up 5-2
4.1.2 Start Up Procedure 5-2
4-6
4-7
5-1
5 Electromechanical Bypass (EMB2) Operation
5.1.1 Typical Control Connections for Common HVAC Applications 6-1
5.1.2 EMB2 Auto Bypass 6-3
5.1.3 EMB2 Common Run/Stop 6-3
5.1.4 EMB2 Run Permissive 6-4
5.1.5 EMB2 Overload 6-4
5.1.6 EMB2 Safety Interlock 6-5
5.1.7 EMB2 Fire Mode 6-5
5.1.8 EMB2 Fault Reporting 6-5
5.1.9 EMB2 Switches 6-6
6 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation
6.1 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation
6.1.1 Overview 7-1
6.1.2 ECB Control Card 7-2
6.1.3 ECB Drive or Bypass Selection 7-5
6.1.4 ECB Programming 7-7
6-1
7-1
7-1
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 6

Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.5 ECB Hand/OFF/Auto 7-8
6.1.6 ECB Mode of Operation 7-8
6.1.7 Bypass Status Word Bit Examples 7-10
6.1.8 ECB Auto Bypass 7-10
6.1.9 ECB Run Permissive 7-11
6.1.10 ECB Overload 7-11
6.1.11 ECB Safety Interlock 7-12
6.1.12 ECB Common Run/Stop 7-12
6.1.13 ECB Advanced Fire Mode 7-13
6.1.14 ECB Fault Reporting 7-13
7 Start Up Troubleshooting
7.1.1 Option Panel Alarm and Warnings 8-1
8 Appendix
8.1.1 Dimensions 9-1
8.1.2 Mechanical Diagrams 9-2
8.1.3 Typical Wiring Diagrams 9-6
8-1
9-1
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 7
Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Contents | Figure
Figure 1.1: Basic Non Bypass Circuit 1-2
Figure 1.2: Basic Bypass Circuit 1-3
Figure 2.1: Sample Panel Label 2-1
Figure 3.1: Proper Lifting Method 3-5
Figure 3.2: Side Cooling Clearance 3-6
Figure 3.3: Cooling Airflow 3-6
Figure 3.4: Power Connections 3-7
Figure 3.5: P2 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram 3-8
Figure 3.6: P2 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-9
Figure 3.7: P3 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-10
Figure 3.8: P3 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-11
Figure 3.9: P4 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-12
Figure 3.10: P4 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-13
Figure 3.11: P5 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-14
Figure 3.12: P5 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram. 3-15
Figure 3.13: Bypass Panel Conduit Entry Diagram 3-16
Figure 3.14: Non Bypass Panel Conduit Entry Diagram 3-16
Figure 3.15: P2 Panel 3-17
Figure 3.16: P3 Panel 3-17
Figure 3.17: P4 Panel 3-18
Figure 3.18: P5 Panel 3-19
Figure 3.19: Control Terminals Location 3-26
Figure 3.20: Removable Drive Connectors and Terminals 3-27
Figure 5.1: Customer Side EMB2 Control Card Terminal Connections 5-2
Figure 5.2: Sample Overload Device 5-5
Figure 6.1: Local Control Panel (LCP) 6-1
Figure 6.2: ECB Control Card Terminal Connections 6-3
Figure 6.3: Bypass Trip Time Delay 6-10
Figure 6.4: Drive Display with Bypass Start Time Delay Active 6-11
Figure 6.5: Sample Overload Device 6-12
Figure 8.1: P2 Bypass 8-2
Figure 8.2: P2 Non-bypass 8-3
Figure 8.3: P3 P4 P5 Bypass 8-4
Figure 8.4: P3 P4 P5 Non-bypass 8-5
Figure 8.5: EMB2 with Control Relay, Part 1 8-6
Figure 8.6: EMB2 with Control Relay, Part 2 8-7
Figure 8.7: EMB2, Part 1 8-8
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 8
Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.8: EMB2, Part 2 8-9
Figure 8.9: ECB, Part 1 8-10
Figure 8.10: ECB, Part 2 8-11
Figure 8.11: ECB with Control Relays, Part 1 8-12
Figure 8.12: ECB with Control Relays, Part 2 8-13
Figure 8.13: Non-bypass 8-14
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 9
Contents Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Contents | Table
Table 1.1: Contactor Operation 1-2
Table 1.2: Bypass Configurations 1-3
Table 1.3: Tier Definitions and Features 1-5
Table 1.4: Panel Voltage and Frame Ratings 1-6
Table 3.1: Tools Required 3-1
Table 3.2: Drive Fuses 208 V 3-1
Table 3.3: Drive Fuses 230 V 3-2
Table 3.4: Drive Fuses 460 V 3-3
Table 3.5: Drive Fuses 600 V 3-4
Table 3.6: Sample Fuse Rating Label 3-5
Table 3.7: Approximate Shipping Weights 3-5
Table 3.8: Reference Designator Definitions 3-8
Table 3.9: Wire Size Chart, 208 and 230 V 3-20
Table 3.10: Wire Size Chart 460 and 600 V 3-21
Table 3.11: Tightening Torques, 208 and 230 V 3-22
Table 3.12: Tightening Torques, 460 V 3-23
Table 3.13: Tightening Torques, 600 V 3-24
Table 3.14: Sample Tightening Torque and Wire Rating Label 3-25
Table 3.15: Drive Control Terminals Functions 3-27
Table 4.1: Inspection prior to Startup 4-2
Table 5.1: EMB2 Default Parameter Settings for Common HVAC Applications 5-1
Table 5.2: Common Functions for Controlling Motor using Bypass and Typical Terminal Connections. 5-1
Table 6.1: Parameter Group 5-** Factory Default Settings 6-2
Table 6.2: ECB Card Terminals 6-4
Table 6.3: LCP Control Keys Programming 6-8
Table 6.4: Bypass Parameter Functions 6-9
Table 6.5: Parameter 31-10 Bypass Status Word Bit Definitions 6-9
Table 7.1: Panel Alarms and Warnings (ECB only) 7-1
Table 7.2: Panel Status Display (ECB only) 7-1
Table 7.3: Fault Table 7-2
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 10

Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
1 Introduction
1.1.1 Purpose of the Manual
This manual is intended to provide detailed information for
the installation and operation of the vertical panel used in
conjunction with a Danfoss variable frequency drive (VFD).
To enable efficient handling of the equipment,
requirements are provided for installation of mechanical,
electrical, control wiring, proper grounding, and environmental considerations. Pre-start and start up procedures
are detailed. Also included is a detailed overview of the
panel bypass function. In addition, identification of other
optional components and their operation and start up
troubleshooting instructions are included. For the electronically controlled bypass, additional programming and
operation information is provided.
Overview
1.1.2
A variable frequency drive regulates the speed and
operation of an electric motor. The drive is programmable
and offers many features and savings compared to
operating a motor from unregulated line voltage. The
panel is a protective enclosure in which the drive and
various optional components are assembled and mounted.
The vertical non bypass panel is always configured with a
disconnect switch and fuses to protect the drive. The
vertical bypass panel allows switching between running
the motor from the drive (variable speed) or across the line
input power (constant speed).
The vertical bypass panel comes with one of two control
options:
The electromechanical bypass (EMB2)
•
Electronically controlled bypass (ECB)
•
The EMB2 is operated by a selector switch on the front of
the panel. The EMB2 controls a motor by switching
between drive control, operation in bypass, or off. In
addition, a test selection is available, which disengages the
motor from the drive but keeps the drive operational while
the motor runs in bypass. The switching function activates
contactors to provide power to the motor through the
drive or bypass circuitry, as required.
inputs, and status reporting. The VFD’s logic circuitry is
backed up by an independent panel-mounted power
supply so that, even if the drive loses power, control and
communication functions are maintained. Programming
and display are provided by the LCP. An important feature
of the ECB is the ability to accept commands from a
building automation system (BAS) and to report
operational status in return.
See more detailed descriptions of the EMB2 in 5 Electrome-
chanical Bypass (EMB2) Operation and ECB in 6 Electronically
Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation of this manual.
Typical Bypass Operation
1.1.3
With contactors M1 and M2 closed and contactor M3
open, the motor is running in drive control. Opening
contactor M2 removes power to the motor but allows the
drive to remain under power. This is referred to as test
mode. With contactors M1 and M2 open and contactor M3
closed, the motor is running in bypass from the line input
power.
1.2
Bypass Circuits
1.2.1 Three-contactor Bypass
The bypass circuit consists of a bypass contactor (M3)
interlocked with a drive output contactor (M2), a drive
input contactor (M1), and an overload relay. For the EMB2,
a door mounted Drive/OFF/Bypass/Test Selector switch is
used to electrically select whether the motor is powered
by the drive, connected to the full speed bypass, or
disconnected from both. The test position applies power
to the motor through the bypass (M3 closed) contactor but
removes power from the drive (M2 open) while keeping
the drive powered (M1 closed). A Pilot light indicates when
in bypass. For the ECB, control selection is made through
the drive keypad by pressing the DRIVE BYPASS key and
selecting from the available options shown. Display data
indicates when in bypass. The circuitry may be supplied
with either an input disconnect switch or an input circuit
breaker.
1 1
The ECB also uses contactors to provide power to the
motor through the drive or bypass circuitry. However, the
ECB contains a local processor that interacts with the
drive’s control logic for programmable options, remote
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 1-1
Page 11
T3
T2
T1
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR.
INPUT
POWER
EARTH
GROUND
TYPE 1 ENCLOSURE
130BX360.11
W/98
U/96
V/97
VFD
L1
L2
L3
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
DISCONNECT
DS1
DRIVE
1L1
1L2
1L3
2L1
2L2
2L3
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
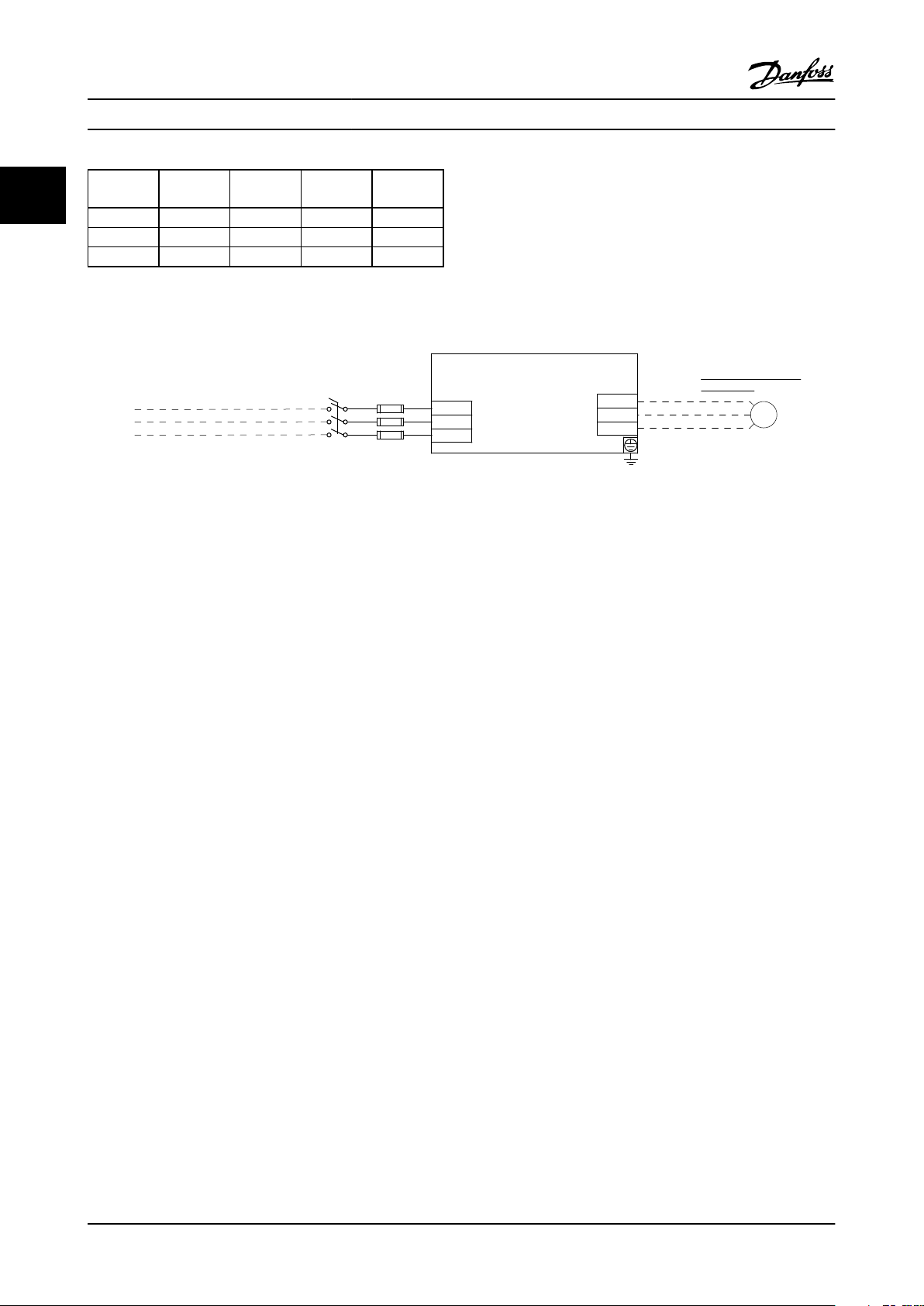
Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
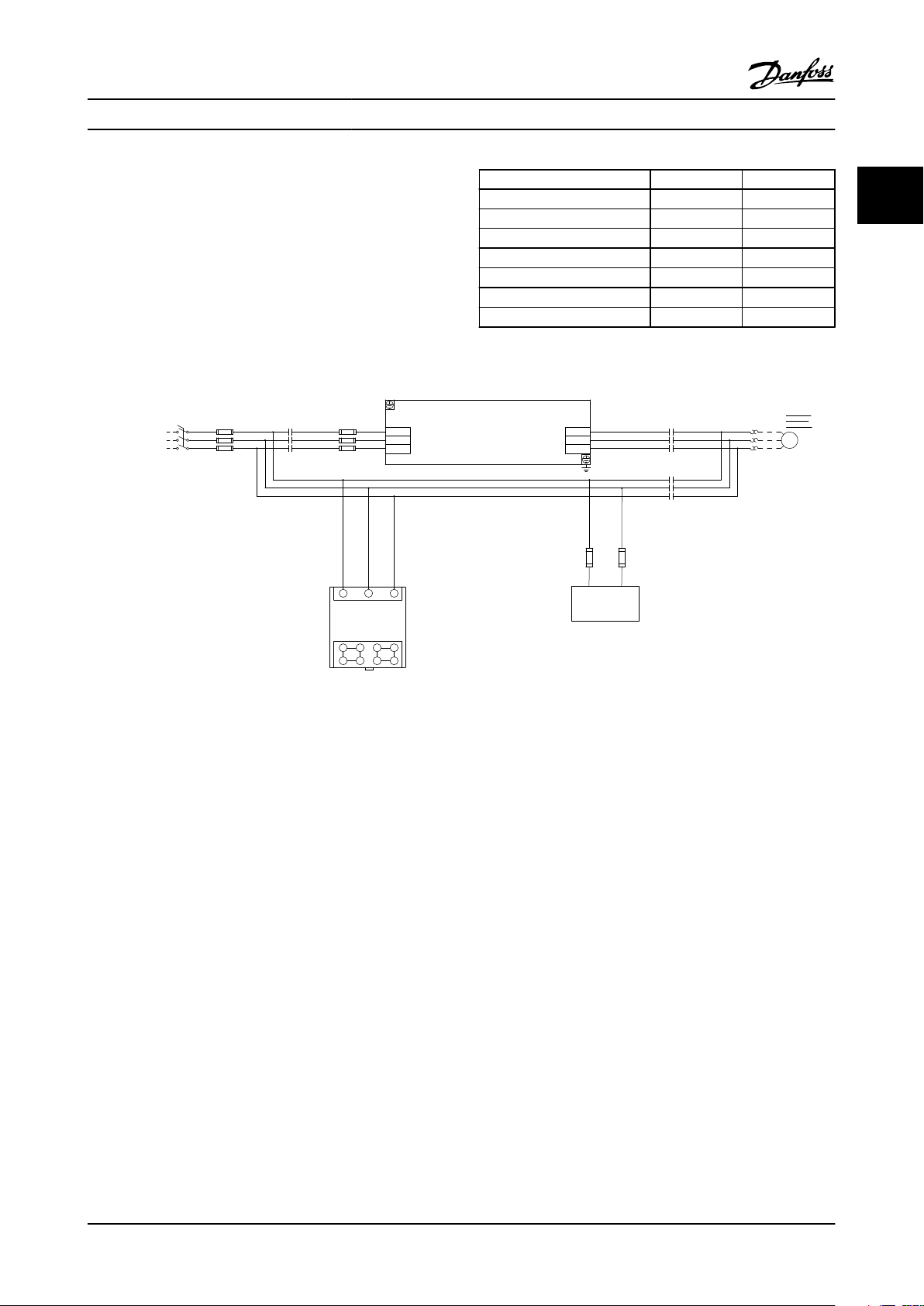
Contactor Drive Mode OFF Bypass
11
M1 Closed Open Open Closed
M2 Closed Open Open Open
M3 Open Open Closed Closed
Table 1.1 Contactor Operation
Figure 1.1 Basic Non Bypass Circuit
Mode
1.3 Bypass Options
1.3.1 Common Run/Stop with Bypass
Test Mode
Basic Fire Mode in Bypass
1.3.4
This option switches the panel to bypass whenever a
remote fire mode signal is given to the VFD through the
input terminals. In either drive or bypass, fire mode is
Allows a remote signal to initiate operation in either drive
control or bypass depending upon the position of the
bypass selector switch.
intended to ignore common safety and overload inputs for
emergency situations. The motor will continue to run in
bypass until fire mode is removed or the drive, panel, or
motor fails. External safety signals and motor overload are
1.3.2 Automatic Bypass
ignored when in fire mode.
This feature automatically transfers the motor from drive to
1.3.5 Advanced Fire Mode in Bypass
bypass without operator intervention when a fault
condition trips the drive, after a programmable time-out
period. The VFD’s internal fault circuitry controls this
action. The time delay permits all automatically resettable
faults to clear prior to transfer to bypass. Run permissive or
safety circuit signals override the auto bypass function and
The advanced fire mode allows for a variety of
programmable responses to an external fire mode
command signal. Bypass options are programmed through
the drive’s fire mode parameters. See 6.1.13 ECB Advanced
Fire Mode.
may prevent or delay bypass operation.
Overload Protection
1.3.6
Run Permissive in Bypass
1.3.3
This thermally activated device provides mechanical
With run permissive active, the drive sends a run request
and waits for a remote response before commanding the
motor to start. The response indicates the system is safe to
operate.
overload protection for the motor while in bypass
operation. It measures motor current and is set to the full
load amps (FLA) of the motor. A 1.2 x FLA service factor is
built-in and maintained, meaning that should the motor
current increase above that value, the overload will
calculate the level of increase to activate timing for the trip
function. The higher the current draw, the quicker the trip
response. The overload provides Class 20 motor protection.
1-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 12
W/98
U/96
V/97
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
INPUT
POWER
2T1
2T2
2T3
M2
M3
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR
1T1
1T3
1T2
OL1
T1
T3
T2
MK902
2
6
24 V DC SMPS
MK901
1
5
MK903 MK904
374
8
- +
EARTH
GROUND
Type 1 Enclosure
VFD
EARTH
GROUND
2L3
M1
2L1
2L2
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
TRANSFORMER
CONTROL
600V
600V
3L3
3L1
3L2
130BX361.11
MAIN DISCONNECT
DS1
Fuse
Fuse
Fuse
1L1
1L2
1L3
L2
L3
L1
Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Control Features EMB2 ECB
1.4 Bypass Platform Configurations
The two bypass platform configurations are ECB and EMB2.
The features available as options with each platform are
listed in Table 1.2. The ECB, also listed below, has all option
features available. See 5 Electromechanical Bypass (EMB2)
Operation for additional details on the EMB2 and
Safety Interlock X X
Common Start / Stop X X
Automatic Bypass X X
Run Permissive X X
Basic Fire Mode X X
Advanced Fire Mode X
Serial Communication X
6 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation for the
ECB.
Table 1.2 Bypass Configurations
1 1
1.5 Switch Mode Power Supply
The VFD’s logic circuitry is backed up by an independent
panel-mounted switch mode power supply so if the drive
loses power, control and communication functions are
maintained. The SMPS converts three-phase AC input
power to 24 V DC control power. Since the SMPS draws
power from all three phases, it offers immunity protection
from most phase-loss and brown-out conditions. The SMPS
is internally protected from short circuit on its output and
three board-mounted fuses provide additional protection.
The SMPS is not designed for external use and may take
up to 5 sec. to initialize at power-up. The SMPS will
maintain a 24 V DC output with a low input line voltage.
The 200 Volt SMPS will maintain the 24 V DC output with
a line voltage as low as 150 V AC and the 600 V SMPS to
335 V AC. Refer to Figure 1.2.
Figure 1.2 Basic Bypass Circuit
Control Transformer
1.5.1
A control transformer is included on larger horsepower
units where the contactor coils are AC. The control
transformer steps down the line input voltage to 120V AC.
The coils of AC contactors are isolated from the Switch
Mode Power Supply via relays.
1.6 Disconnects
1.6.1 Main Disconnect
The main disconnect removes line input power to the
drive and bypass. A main disconnect is available in four
options.
Fused disconnect. Two-position (ON/OFF) rotary
•
switch, padlock compatible, with three fuses, one
on each phase, built into the switch. For safety,
the switch must be in the OFF position before
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 1-3
Page 13

Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
the option panel door can be opened. (Bypass
11
1.6.2
The mode selector switch is used for 3-contactor bypass
on EMB2 units. The selector switch allows the operator to
select from four modes of operation.
Drive mode: When drive mode is selected, the M1 and M2
contactors are closed allowing power to flow in and out of
the drive to the motor.
Off mode: This mode opens all contactors removing any
power to the motor.
Bypass mode:When bypass mode is selected, the M3
contactor closes and allows the motor to run directly from
the input line power.
Test mode:Test mode closes the M1 and M3 contactors
and allows the motor to be powered by the input line
power. This also allows the drive to power up without
being connected to the motor. Refer to Figure 1.2.
panel only.)
Disconnect without fuses. For user-supplied fuses
•
option. (Bypass panel only.)
Main circuit breaker. A thermal/ magnetic current
•
interrupt device using an ON/TRIP/OFF/RESET
switch. When in the ON position, a trip fault
removes power from the drive/bypass circuit and
the switch moves to the TRIP setting. The switch
must be moved to the RESET position
momentarily after the fault has been cleared to
reset the circuit breaker. (Bypass panel only.)
Main Disconnect with drive fuses. Non-bypass
•
panel two-position (ON/OFF) rotary switch that
disconnects the main AC line power to the drive
only.
Mode Selector Switch
1-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 14
130BX363.10
130BX365.10
130BX362.10
130BX364.10
Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
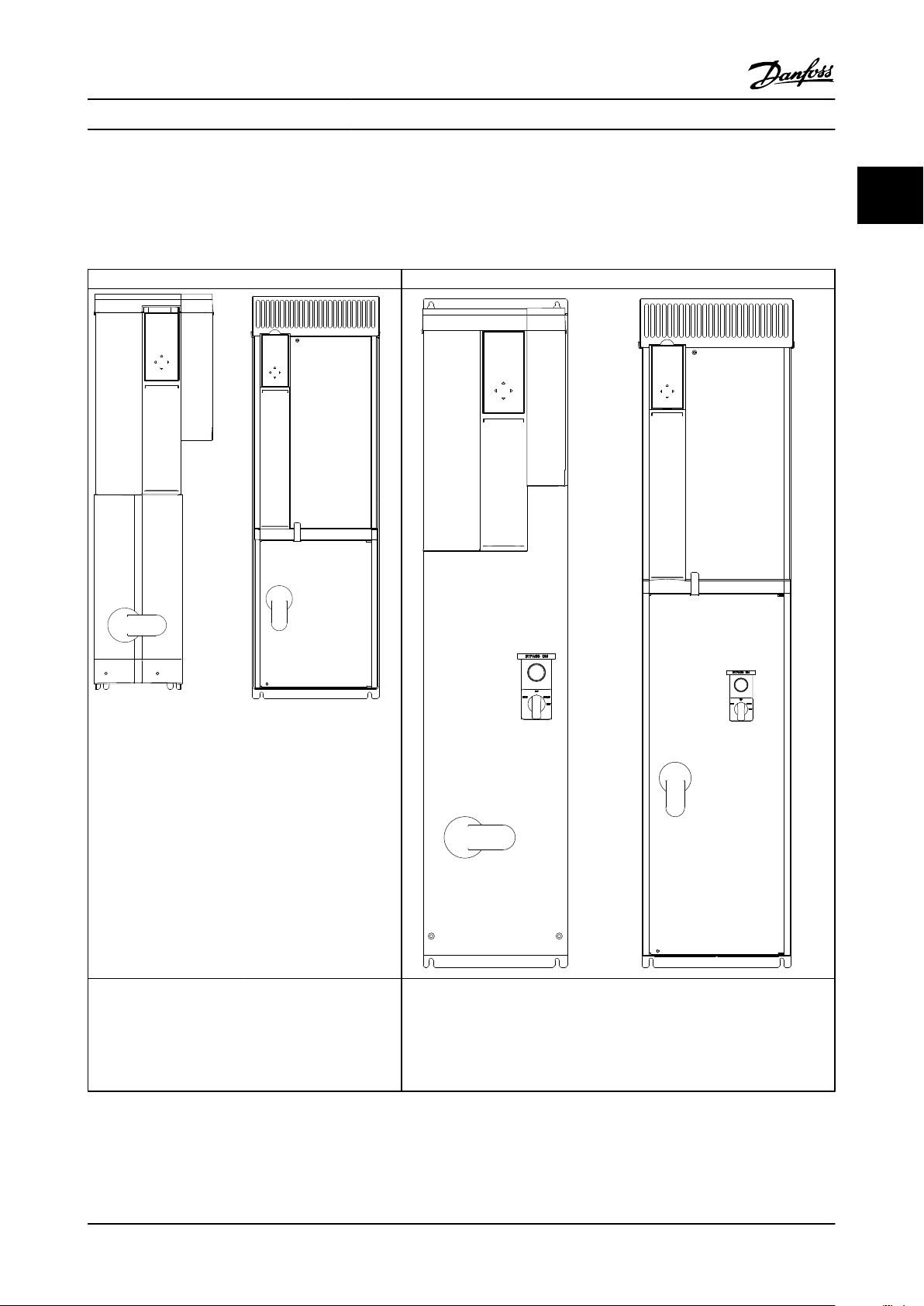
1.6.3 Panel Configurations
The VLT FC Drive Series comes in two panel enclosure types. One is the non bypass and the other is the bypass. See
Table 1.3 for descriptions and available options.
Non bypass Bypass
1 1
Drive plus both of the following:
1. Fuses
2. Disconnect
Table 1.3 Tier Definitions and Features
Drive with bypass:
1. Fuses
2. Disconnect/Circuit Breaker
3. Contactors
4. Power Supply
5. Control Module
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 1-5
Page 15
Introduction Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
1.6.4 Panel Voltage and Frame Ratings
11
Table 1.4Table 1.5 defines the voltage and hp ratings of the frames sizes for the panel. See 8 Appendix for overall and
mounting dimensions.
Panel P2
(B3 - Drive)
Volts VAC HP (KW)
208 & 230 7.5 (5.5) - 15 (11) 7.5 (5.5) - 15 (11) 7.5 (5.5) - 10 (7.5)
460 & 600 15 (11) - 25 (18.5) 15 (11) -25 (18.5) 15 (11) - 20 (15)
Panel P3
(B4 - Drive)
Volts VAC HP (KW)
208 20(15)
230 20 (15) - 25 (18.5)
460 & 600 30 (22) - 50 (37) 30 (22) - 50 (37) 25 (18.5) - 40 (30)
Panel P4
(C3 - Drive)
Volts VAC HP (KW)
208 25 (18.5) - 40 (30)
230 30 (22) - 40 (30)
460 & 600 60 (45) - 75 (55) 60 (45) - 75 (55) 50 (37) - 60 (45)
Panel P5)
(C4 - Drive)
Volts VAC HP (KW)
208 & 230 50 (37) - 60 (45) 50 (37) - 60 (45) 40 (30) - 50 (37)
460 & 600 100 (75) - 125 (90) 100 (75) - 125 (90) 75 (55) - 100 (75)
Bypass Non Bypass
FC102/202/322 FC102/202/322 FC302
Bypass Non Bypass
FC102/202/322 FC102/202/322 FC302
20 (15) - 25 (18.5) 15 (11) - 20 (15)
Bypass Non Bypass
FC102/202/322 FC102/202/322 FC302
30 (22) - 40 (30) 25 (18.5) - 30 (22)
Bypass Non Bypass
FC102/202/322 FC102/202/322 FC302
Table 1.4 Panel Voltage and Frame Ratings
1.7
Power Component Functions
1.7.1 Power Fusing
For main panel power fuses, only use the specified fuse or
an equivalent replacement. For drive fuses only use the
specified fuse. See the fuse ratings label on the inside
cover of the unit or Table 3.2Table 3.3, Table 3.3Table 3.4,
Table 3.4Table 3.5 and Table 3.5Table 3.6.
Main fusing
Main fuses are located ahead of the drive and bypass.
Main fuses are designed to protect the circuitry within the
bypass panel but is not adequate to protect the drive.
Main fuses are dual-element, time-delay types and mount
inside the bypass enclosure.
Drive fusing
Drive fuses are located ahead of the drive and are a fastacting type. Drive fuses are standard in all bypass and nonbypass panels.
5,000 or 100,000 amp SCCR
The bypass panel supplied with a non fusible Main
Disconnect Switch is 5,000 amps short-circuit current rating
(SCCR). The bypass panel supplied with a Fusible
disconnect or circuit breaker is 100,000 amp SCCR. The
non bypass panel supplied with a non-fusible Main
Disconnect is 100,000 amp SCCR. See the panel label for
SCCR rating.
NOTE!
The 600 V circuit breaker option is 5,000 amp (SCCR).
1-6 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 16

130BX366.10
Pre-installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
2 Pre-installation
2.1.1 Receiving Inspection
Inspect the packaging and equipment closely when
received. Any indication of careless handling by the carrier
should be noted on the delivery receipt, especially if the
equipment will not be immediately uncrated. Obtain the
delivery person’s signed agreement to any noted damages
for any future insurance claims. Ensure that the model
number and power match the order and intended use for
the drive.
IMPORTANT!
LOST OR DAMAGED GOODS
INSPECT THIS SHIPMENT IMMEDIATELY UPON ARRIVAL
If goods are received short or in damaged condition, insist
on a notation of the loss or damage across the face of the
freight bill. Otherwise no claim can be enforced against
the transportation company. If concealed loss or damage is
discovered, notify your carrier at once and request an
inspection. This is absolutely necessary. Unless you do this
the carrier will not entertain any claim for loss or damage.
The agent will make an inspection and can grant a
concealed damage notation. If you give the transportation
company a clear receipt for equipment that has been
damaged or lost in transit, you do so at your own risk and
expense.
Danfoss is willing to assist you to collect claims for loss or
damage, but willingness on our part does not make us
responsible for collection of claims or replacement of
material. The actual filing and processing of the claim is
your responsibility.
2.1.2
Pre-installation Check
1. Compare panel model number to what was
ordered.
2. Ensure each of the following are rated for the
same voltage:
Drive
•
Panel
•
Power line
•
Motor
•
3. Ensure that the panel output rating is equal to or
greater than motor total full load current for full
motor performance.
Motor power size and panel must match
•
for proper overload protection.
If panel rating is less than motor; full
•
motor output cannot be achieved.
4. Check motor wiring:
Any disconnect between drive and
•
motor should be interlocked to drive
safety interlock circuit to avoid
unwanted drive trips.
Do not connect power factor correction
•
capacitors between the drive and motor.
Two speed motors must be wired
•
permanently for full speed.
Y-start, Δ-run motors must be wired
•
permanently for run.
2
2
Figure 2.1 Sample Panel Label
Ensure that the model number and power match the order
and intended use for the drive.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 2-1
Installation Site Check
2.1.3
Because the panel relies on the ambient air for
•
cooling, it is important to observe the limitations
on ambient air temperature. Derating concerns
start above 104°F (40°C) and 3300 feet (1000m)
elevation above sea level.
It is important with multiple panels to check wall
•
strength. Make sure that the proper mounting
screws or bolts are used.
Ensure that the wall or floor area for installation
•
will support the weight of the unit.
If construction work continues after the
•
equipment is mounted, it is important to keep
the interior free from concrete dust and similar
Page 17
2
Pre-installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
dirt. If the unit does not have power applied to it,
supply a protective covering. It is important to
ensure that the components stay as clean as
possible. It may be necessary to clean the interior
once construction is completed.
Keep drawings and manuals accessible for
•
detailed installation and operation instructions. It
is important that the manuals be available for
equipment operators.
2.2 Harsh Environments
The mechanical and electrical components within the
panel can be adversely affected by the environment. The
effects of contaminants in the air, either solid, liquid, or
gas, are difficult to quantify and control.
Airborne Liquids
2.2.1
Liquids in the air can condense in components. Water
carried in the air is easily measured as relative humidity,
but other vapors are often more difficult to measure or
control. Steam, oil and salt water vapor may cause
corrosion of components. In such environments, use TYPE
12 enclosures to limit the exchange of outside air into the
option enclosure. Extremely harsh environments may
require a higher level of protection.
Airborne Solids
2.2.2
Particles in the air may cause mechanical, electrical or
thermal failure in components. A TYPE 1 enclosure
provides a reasonable degree of protection against falling
particles, but it will not prevent the fan from pulling dirty
air into the enclosure.
Corrosive Chemicals
2.2.3
In environments with high temperatures and humidity,
corrosive gases such as sulfur, nitrogen and chlorine
compounds cause corrosion to occur in components.
Indications of corrosion are blackened copper or rust on
steel or oxidized aluminum. In such environments, it is
recommended that the equipment be mounted in a
cabinet with fresh air ventilation and that corrosive
compounds be kept away. A non-ventilated cabinet fitted
with an air conditioner as a heat exchanger may be used.
Conformal coated circuit boards may be specified to
reduce the corrosive effects of a harsh environment.
2-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 18
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 Installation
3.1.1 Tools Required
In addition to the standard tool kit, the tools in Table 3.1
are recommended for installation of the panel.
Drive Fuses
3.1.2
Spreader bar capable of lifting up to 750 lbs.
Max diameter 0.5 in.
Forklift, crane, hoist or other lifting device capable of handling
up to 750 lbs. (Qualified device operator available for operating
the equipment.)
Metric Socket Set: 7 - 19mm
Socket Extensions: 4, 6, and 12 inch
Torx driver set: T10 - T40
Torque wrench: 6 - 375 lbs-in
Allen Wrenches:1/8, 3/16, 1/4, & 5/16 inches
Metric or English wrenches: 7 - 19mm
Table 3.1 Tools Required
TOOLS
To maintain UL, the drive fuses should be replaced only with the fuses specified in , , , and . If an alternate drive fuse is
desired please consult the factory. See the specifications label inside the cover of the unit for acceptable replacement drive
fuses. A sample of this data can be seen in Table 3.6
208 V AC
HP (KW)
7.5 (5.5) 24.2
10 (7.5) 30.8
15 (11) 46.2
20 (15) 59.4 P3
25 (18.5) 74.8
30 (22) 88
40 (30) 114
50 (37) 143
UL Motor
Current
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P3 - Non Bypass P4
- Bypass
Panel
P2
P4
Main Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34035600 (LPJ-40-
SP)
34035700 (LPJ-50-
SP)
34042800 (LPJ-70-
SP)
34042900 (LPJ-90-
SP)
34043100 (LPJ-125-
SP)
34043200 (LPJ-150-
SP)
34043300 (LPJ-175-
SP)
34042300 (LPJ-250-
SP)
Drive Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
176F8953 (JJN-50)
176F8953 (JJN-50)
176F8955 (JJN-60)
176F8957 (JJN-80)
176F8960 (JJN-125)
176F8960 (JJN-125)
174N6538 (JJN-150)
174N6839 (JJN-200)
Transformer Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34046200 (FNQ-
R-1.25)
Panel
(FC302)
Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Drive Fuse
(FC302) Danfoss
(Bussman)
176F8953
(JJN-50)
176F8955
(JJN-60)
176F8957
(JJN-80)
176F8960
(JJN-125)
176F8960
(JJN-125)
174N6538
(JJN-150)
174N6839
(JJN-200)
174N6840
(JJN-250)
3 3
60 (45) 169
Table 3.2 Drive Fuses 208 V
P5
34042300 (LPJ-250-
SP)
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-1
174N6840 (JJN-250)
34046200 (FNQ-
R-1.25)
Page 19
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
230 V AC
Panel
HP (KW)
7.5 (5.5) 22
33
10 (7.5) 28
15 (11) 42
20 (15) 54
25 (18.5) 68
30 (22) 80
40 (30) 104
50 (37) 130
60 (45) 154
UL Motor
Current
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Main Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34042600 (LPJ-35-
SP)
34042700 LPJ-45-
SP
34042800 (LPJ-70-
SP)
34042900 (LPJ-90-
SP)
34043000 (LPJ-100-
SP)
34043100 (LPJ-125-
SP)
34043200 (LPJ-150-
SP)
34043400 (LPJ-200-
SP)
34042300 (LPJ-250-
SP)
Drive Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
176F8953 (JJN-50)
176F8953 (JJN-50)
176F8955 (JJN-60)
176F8957 (JJN-80)
176F8960 (JJN-125)
176F8960 (JJN-125)
174N6538
(JJN-150)
174N6839
(JJN-200)
174N6840
(JJN-250)
Transformer Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34046200 (FNQ-
R-1.25)
34046200 (FNQ-
R-1.25)
Panel
(FC302)
Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Drive Fuse
(FC302) Danfoss
(Bussman)
176F8953
(JJN-50)
176F8955
(JJN-60)
176F8957 JJN-80
176F8960
(JJN-125)
176F8960
(JJN-125)
174N6538
(JJN-150)
174N6839
(JJN-200)
174N6840
(JJN-250)
Table 3.3 Drive Fuses 230 V
3-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 20
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
460 V AC
HP (KW)
15 (11) 21
20 (15) 27
25 (18.5) 34
30 (22) 40
40 (30) 52
50 (37) 65
60 (45) 77
75 (55) 96
100 (75) 124
125 (90) 156
UL Motor
Current
Panel
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Main Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34042600 (LPJ-35-
SP)
34035600 (LPJ-40-
SP)
34035700 (LPJ-50-
SP)
34035800 (LPJ-60-
SP)
176U5037 (LPJ-80-
SP)
34043000 (LPJ-100-
SP)
34043100 (LPJ-125-
SP)
34043200 (LPJ-150-
SP)
34043400 (LPJ-200-
SP)
34042300 (LPJ-250-
SP)
Drive Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
176F8952 (JJS-40)
176F8952 (JJS-40)
176F8954 (JJS-50)
176F8956 (JJS-60)
176F8958 (JJS-80)
176F8959 (JJS-100)
176F8961 (JJS-125)
176F9078 (JJS-150)
34051200 (JJS-200)
00002051 (JJS-250)
Transformer
Fuse
(FC102/202/322
) Danfoss
(Bussman)
34046000 (FNQ-
R-0.60)
34046000 (FNQ-
R-0.60)
Panel
(FC302) Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Drive Fuse
(FC302) Danfoss
(Bussman)
176F8952
(JJS-40)
176F8954
(JJS-50)
176F8956
(JJS-60)
176F8958
(JJS-80)
176F8959
(JJS-100)
176F8961
(JJS-125)
176F9078
(JJS-150)
34051200
(JJS-200)
00002051
(JJS-250)
3 3
Table 3.4 Drive Fuses 460 V
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-3
Page 21
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
600 V AC
Panel
HP (KW)
15 (11) 17
UL Motor
Current
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
33
20 (15) 22
25 (18.5) 27
30 (22) 32
40 (30) 41
50 (37) 52
60 (45) 62
75 (55) 77
100 (75) 99
125 (90) 125
P2
P3
P4
P5
Main Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
34035500 (LPJ-30-
SP)
34042600 (LPJ-35-
SP)
34042700 (LPJ-45-
SP)
34035700 (LPJ-50-
SP)
34035800 (LPJ-60-
SP)
176U5037 (LPJ-80-
SP)
34043000 (LPJ-100-
SP)
34043100 (LPJ-125-
SP)
34043200 (LPJ-150-
SP)
34043400 (LPJ-200-
SP)
Drive Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss (Bussman)
176F9076 (JJS-35)
176F9076 (JJS-35)
176F9077 (JJS-45)
176F8954 (JJS-50)
176F8956 (JJS-60)
176F8958 (JJS-80)
176F8959 (JJS-100)
176F8961 (JJS-125)
176F9078 (JJS-150)
130G0488 (JJS-175)
Transformer
Fuse
(FC102/202/322)
Danfoss
(Bussman)
34053600 (FNQ-
R-0.50)
34053600 (FNQ-
R-0.50)
Panel
(FC302) Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Drive Fuse
(FC302) Danfoss
(Bussman)
176F9076
(JJS-35)
176F9077
(JJS-45)
176F8954
(JJS-50)
176F8956
(JJS-60)
176F8958
(JJS-80)
176F8959
(JJS-100)
176F8961
(JJS-125)
176F9078
(JJS-150)
130G0488
(JJS-175)
Table 3.5 Drive Fuses 600 V
3-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 22
130BX367.10
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3.1.3 Internal Main Panel Fuses
Use only the specified fuse or an equivalent replacement for the internal main fuses. See the specifications label inside the
cover of the unit for acceptable replacement main fuses. A sample of this can be seen in Table 3.6.
Fuse Description Manufacturer Part Number/Size
F13A & C Primary Transformer Bussmann FNQ-R-0.50
F15A, B, & C Main Fuses Bussmann LPJ-30-SP
F16A, B, & C Drive Fuses Bussmann JJS-35
F900, F901,F902 SMPS - Power Supply Bussmann FWH-020A6F, 500V
Table 3.6 Sample Fuse Rating Label
3.2 Mechanical Installation
3 3
3.2.1 Lifting
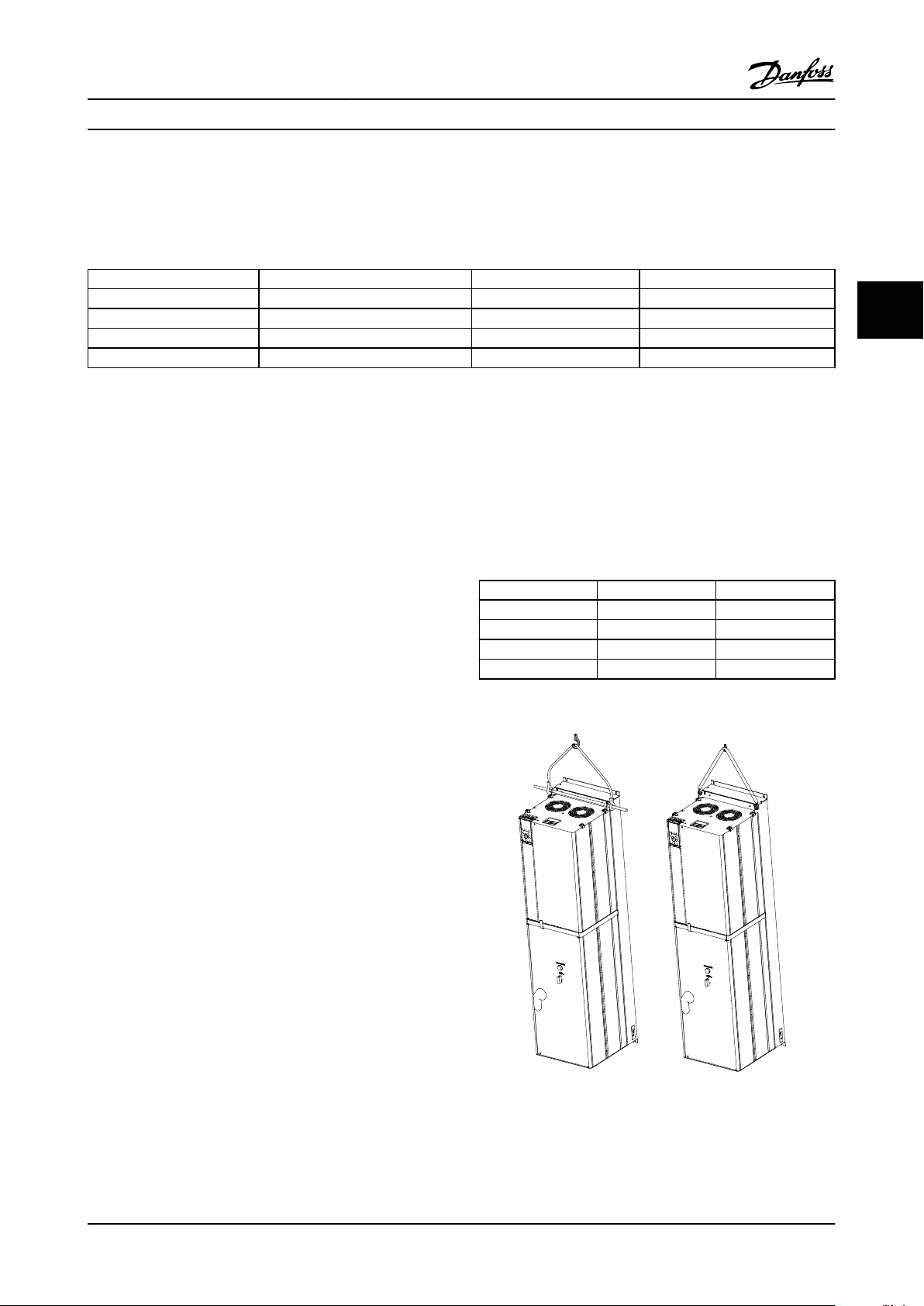
Check the weight of the unit before attempting to lift.
Ensure that the lifting device is suitable for safely lifting
the panel. If necessary, plan for a hoist, crane or forklift
with appropriate rating to move the units.
3.2.2 Hoist or Overhead Lift
Use a solid steel spreader bar for lifting. Slide the
•
spreader bar through the two (2) lifting holes on
the panel. Lifting rings are 0.59in (15mm) in
diameter (see Figure 3.1). If VFD mounting screws
interfere with the spreader bar, lifting hooks can
be used instead of the lifting bar.
Connect the spreader bar to a hoist or other
•
lifting device.
Carefully lift the unit and secure it to the wall.
•
Refer to 8 Appendix for dimensional drawings to
determine fasteners size and location.
Forklift
3.2.3
Shipping Weights
3.2.4
Weights listed in Table 3.7 are approximate for base units.
Options can add or reduce weight of unit. Weights listed
are in lbs.
Frame Non Bypass Panel Bypass Panel
P2 36 84
P3 66 106
P4 106 167
P5 155 248
Table 3.7 Approximate Shipping Weights
Only a competent lift operator with additional
•
support personnel should attempt moving the
unit.
Carefully position forklift and ensure stability prior
•
to lift.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-5
Figure 3.1 Proper Lifting Method
Page 23
38.1 [1.5]
130BX368.10
50.8 [2.0] min
101.6 [4.0] min
FLOOR
CEILING
AIRFLOW
AIRFLOW
130BX369.12
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
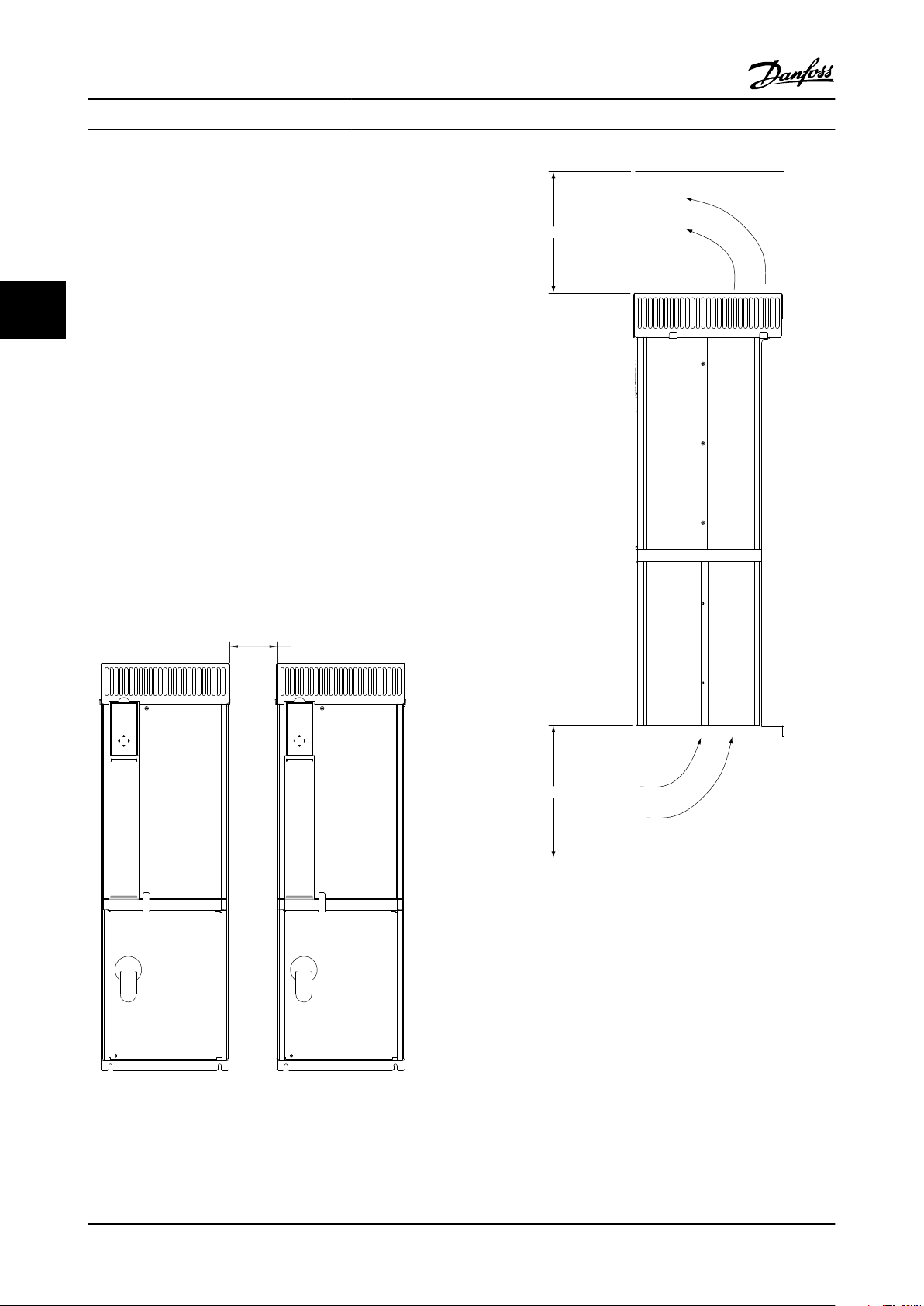
3.3 Cooling
Only mount the drive and panel vertically.
•
Panels rely on the ambient air for cooling. It is
•
important to observe the limitations on ambient
33
air temperature. The maximum ambient
temperature for all bypass panels is 40°C and
45°C for non bypass panels. Derating concerns
start above 3300 feet elevation above sea level.
Most panels may be mounted side-by-side
•
without additional side clearance. However, the
P2 (B3 frame size) units require 1.5 in. minimum
clearance between units (see Figure 3.2).
Top and bottom clearance is required for cooling
•
(see Figure 3.3). Generally, 2 to 10 inches (50 to
250mm) minimum clearance is required,
depending upon the hp (kW) of the unit. See the
dimensional drawings in 8 Appendix for specific
requirements.
No additional back plate is required for drives
•
with the bypass and non bypass panels.
Figure 3.2 Side Cooling Clearance
Figure 3.3 Cooling Airflow
3-6 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 24
Motor
Line Power
Stop
Start
Speed
Control
130BX370.10
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3.4 Electrical Installation
WARNING
•
•
EQUIPMENT HAZARD!
Rotating shafts and electrical equipment can be hazardous.
It is strongly recommended that all electrical work conform
to all national and local regulations. Installation, start-up
and maintenance should be performed only by qualified
personnel. Failure to follow local regulations could result in
death or serious injury.
•
Control wiring should always be isolated from the high
voltage power wiring.
Avoid getting metal chips into electronics.
Power into the panel (and ground back to the
distribution panel)
Power from the panel to the motor and earth
insulated motor ground
Control wiring
3 3
Motor control equipment and electronic controls
•
are connected to hazardous line voltages.
Extreme care should be taken to protect against
electrical hazard.
Correct protective grounding of the equipment
•
must be established. Ground currents are higher
than 3mA.
A dedicated ground wire is required.
•
Wear safety glasses whenever working on electric
•
control or rotating equipment.
NOTE!
Make all power connections with a minimum of 60°C/
140°F rated copper wire.
WARNING
INDUCED VOLTAGE!
Run output motor cables from multiple drives separately.
Induced voltage from output motor cables run together
can charge equipment capacitors even with the equipment
turned off and locked out. Failure to run output motor
cables separately could result in death or serious injury.
Follow the connection procedures as illustrated in the
drawing provided with the unit.
NOTE!
Run input power, motor wiring and control wiring in three
separate metallic conduits or raceways for high frequency
noise isolation. Failure to isolate power, motor and control
wiring could result in less than optimum drive and
associated equipment performance.
Because the motor wiring carries high frequency
•
electrical pulses, it is important that no other
wires are run together. If the incoming power
wiring is run in the same conduit as the motor
wiring, these pulses can couple electrical noise
back onto the building power grid.
At least three separate conduits must be connected to the
panel (Figure 3.4).
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-7
Figure 3.4 Power Connections
Page 25
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
(ECB OPTION ONLY)
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUST. CONNECTION
POWER TO MOTOR
T1 T2 T3
CUST. CONNECTION
EMB2 CONTROL WIRES
14
15
17
7
10
4,5,6
12
8
19
18
1
2
11
13
130BX372.12
27
26
CUST. CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
TERMINAL BLOCK 1
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT & OUTPUT
GROUND
CUST. CONNECTION
ECB CONTROL WIRES
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
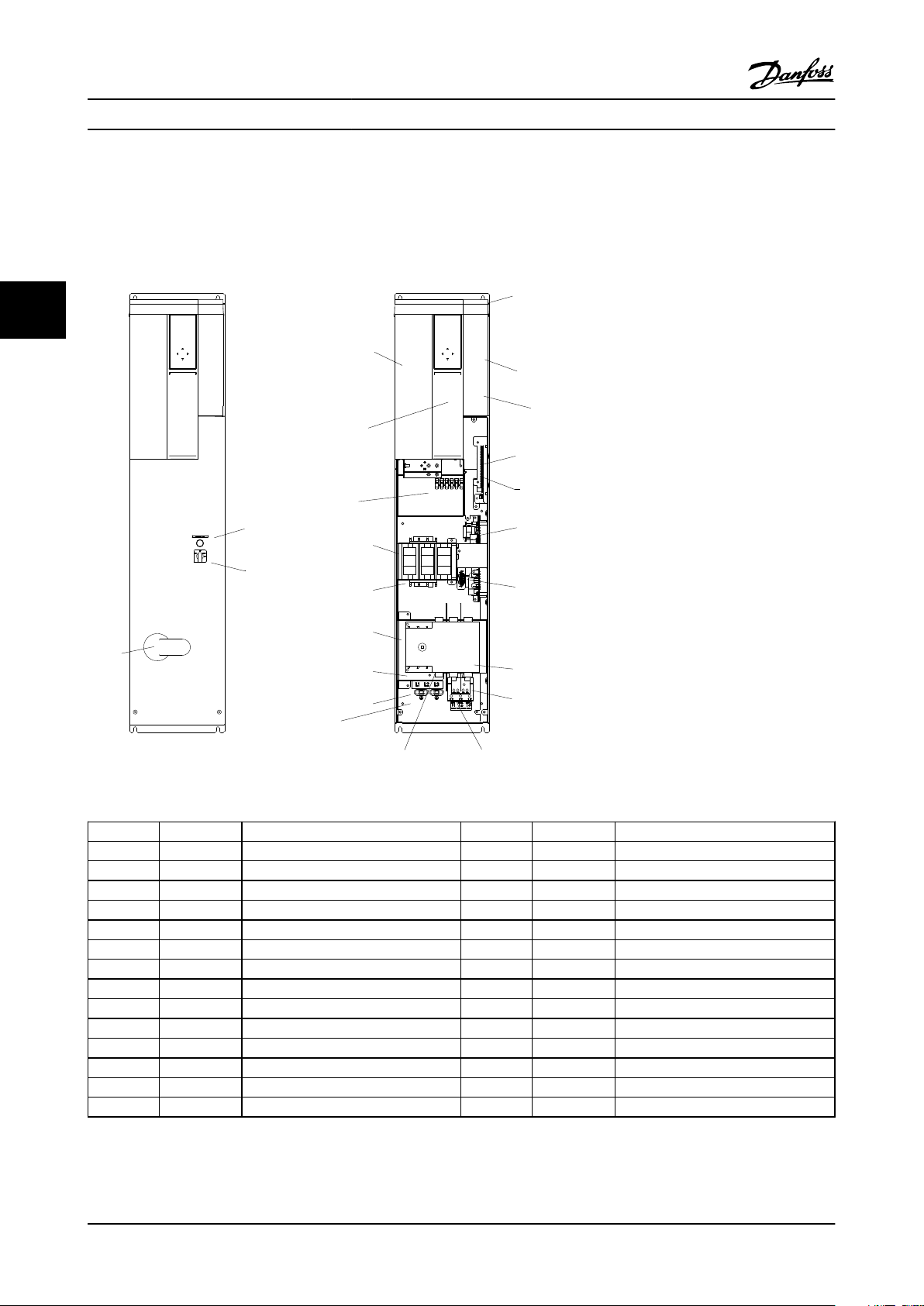
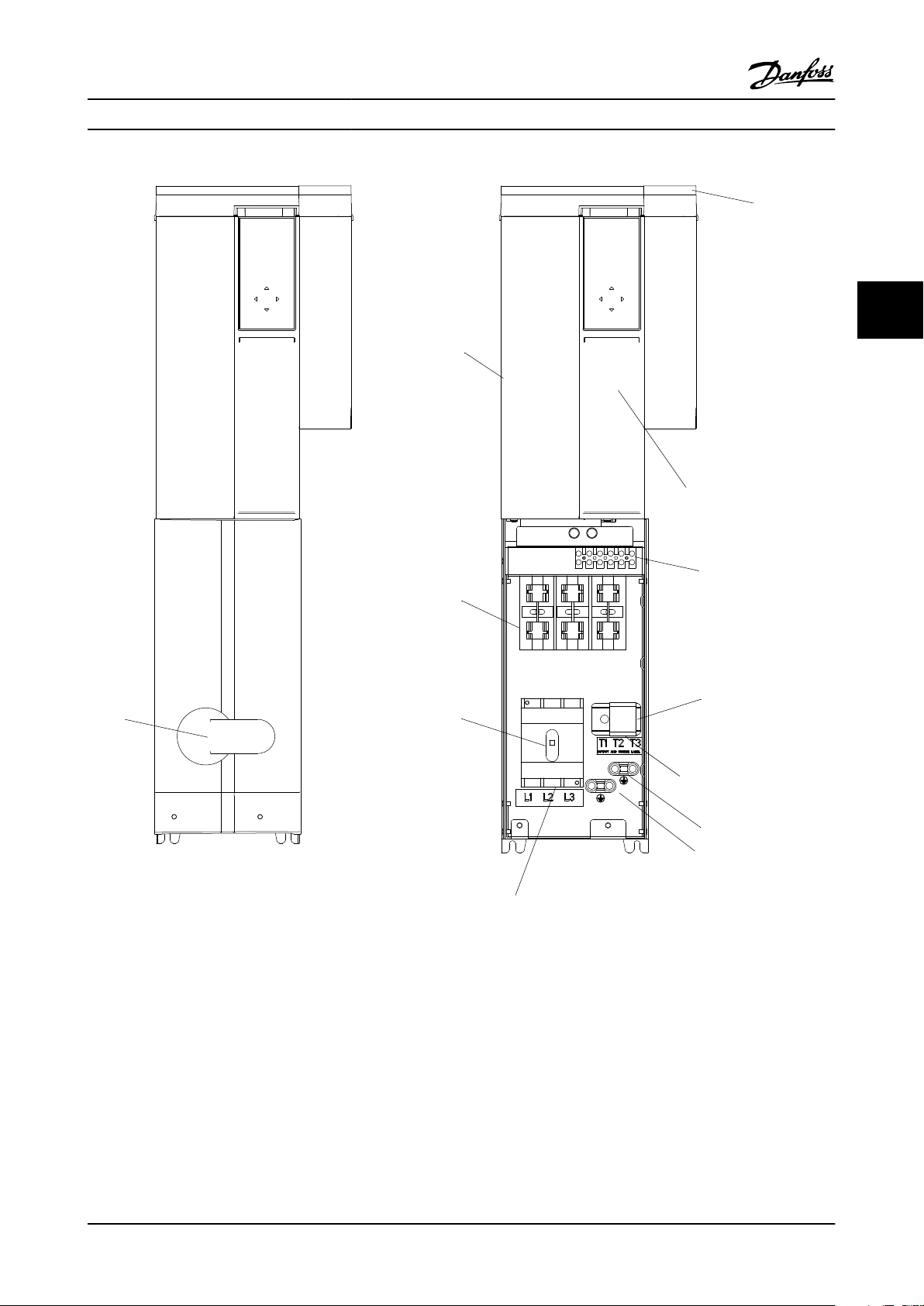
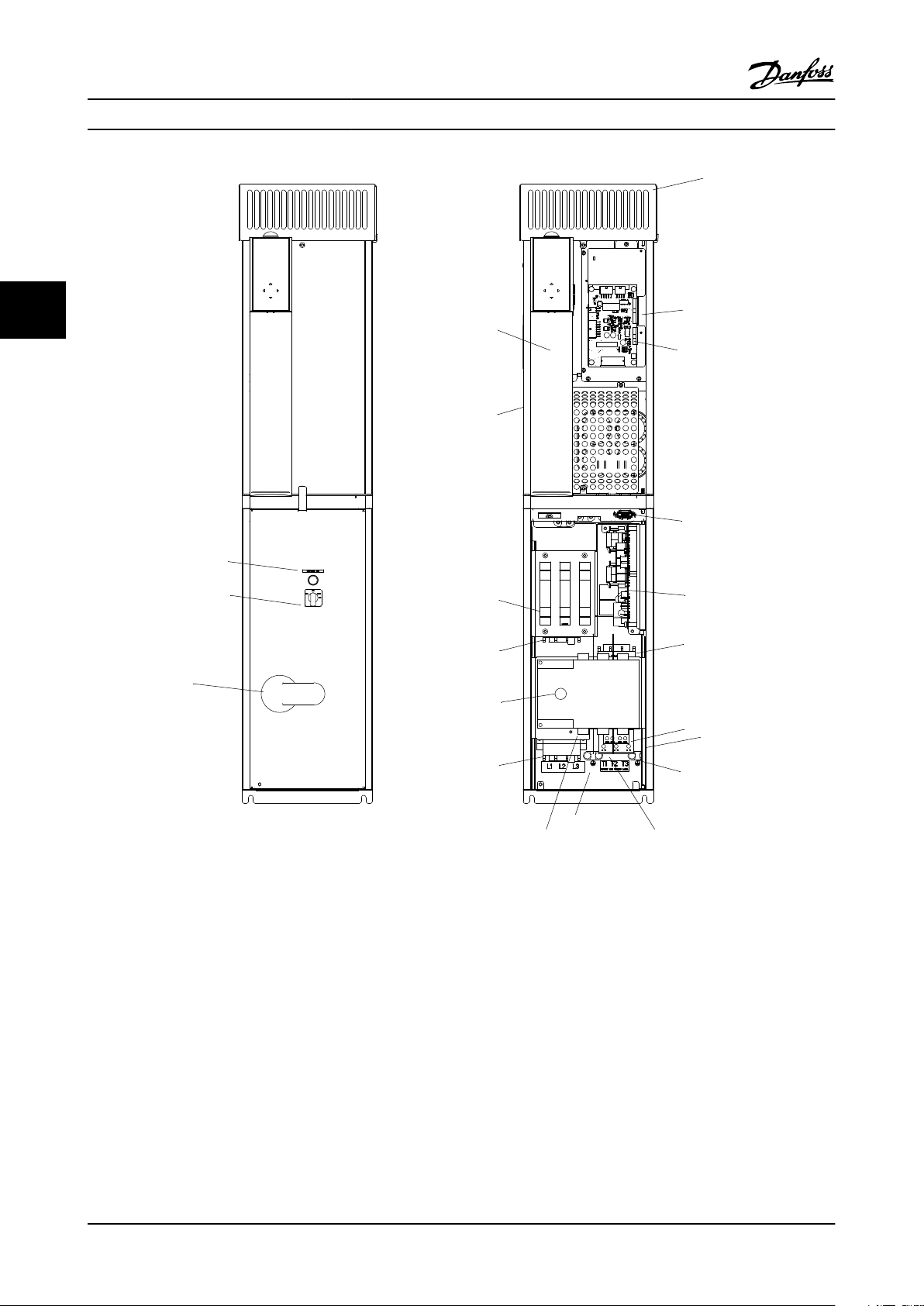
3.4.1 Component Identification & Customer Connection
Mechanical layout drawings are intended to provide the installer or equipment user with component identification and
location for that specific unit. Figure 3.5 represents a typical layout drawing. Table 3.8 provides definitions for drawing
reference designators. (Not all reference designators are shown.)
33
Figure 3.5 P2 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram
ID
1 24 V DC Panel 24 V DC SMPS 15 S1 Auto Bypass Selector Switch
2 HPC High Pot Connector 16 TF 120 V AC control transformer
3 F13 T1 primary fuse 17 VFD Variable frequency drive
4 CB1 Main Circuit Breaker 18 EMB2 Control Module
Device Definition ID Device Definition
5 DS1 Main or Drive Disconnect 19 ECB Control Module
6 F15 Main fuse 20 TB1-C Terminal block 1 - Control
7 F16 Drive fuse 21 TB1-P Terminal block 1 - Power
8 GND Ground terminal 22 PR1 Control Relay for M1 Contactor
9 LCP LCP 23 PR2 Control Relay for M2 Contactor
10 M1 Drive Input contactor 24 PR3 Control Relay for M3 Contactor
11 M2 Drive Output contactor 25 UVM Under voltage module
12 M3 Bypass contactor 26 TC Top Cover
13 OL1 Overload for Motor 27 DH Disconnect Handle
14 PL1 Bypass indicator light
Table 3.8 Reference Designator Definitions
3-8 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 26
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUST. CONNECTION
POWER TO MOTOR
T1 T2 T3
5
7
17
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
TERMINAL BLOCK 1
21
8
130BX374.11
27
26
CUST. CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT AND OUTPUT GROUND
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.6 P2 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
See
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-9
Page 27
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
CUST. CONNECTION
EMB2 / ECB CONTROL WIRES
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUST. CONNECTION
POWER TO MOTOR
T1 T2 T3
14
15
18 OR 19
2
1
11
13
8
12
4,5,6
10
7
17
130BX375.12
27
26
CUST. CONNECTION
OUTPUT GROUND
CUST. CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT GROUND
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
33
Figure 3.7 P3 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
See
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
3-10 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 28

CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUST.CONNECTION
POWER TO MOTOR
T1 T2 T3
17
5
8
7
130BX376.12
CUST. CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUST. CONNECTION
OUTPUT GROUND
26
27
CUST. CONNECTION
INPUT GROUND
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.8 P3 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
See
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-11
Page 29

(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT POWER
T1 T2 T3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
EMB/ECB CONTROL WIRES
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
18 OR 19
10
11
13
1
8
12
4,5,6
7
17
14
15
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT AND OUTPUT GROUND
26
130BX378.12
27
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
33
Figure 3.9 P4 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
See
3-12 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 30

CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT POWER
T1 T2 T3
17
7
5
8
130BX380.12
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT GROUND
26
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL TERMINALS
27
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT GROUND
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.10 P4 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
See
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-13
Page 31

CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT POWER
T1 T2 T3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
EMB/ECB CONTROL WIRES
18 OR 19
10
11
2
25
13
1
8
22
23
24
3 & 16
4,5,6
12
7
17
14
15
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
(EMB2 OPTION ONLY)
130BX381.11
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT & OUTPUT GROUND
27
26
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
33
Figure 3.11 P5 Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
See
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
3-14 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 32

CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT POWER
L1 L2 L3
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT POWER
T1 T2 T3
17
7
5
8
26
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
DRIVE CONTROL
TERMINALS
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
INPUT GROUND
CUSTOMER CONNECTION
OUTPUT GROUND
130BX382.12
27
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.12 P5 Non Bypass Mechanical Layout Diagram.
Table 3.8 for reference designator definitions.
See
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-15
Page 33

POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
130BX383.12
BYPASS PANEL CONDUIT ENTRY DIAGRAM
USE EITHER CONDUIT PLATE FOR CONVENIENCE
CONTROL WIRES
POWER WIRES
130BX384.12
NON BYPASS PANEL CONDUIT ENTRY DIAGRAM
USE EITHER CONDUIT PLATE FOR CONVENIENCE
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3.4.2 Wire and Cable Access
Refer to through for wire routing and termination
•
locations.
Removable access knockout covers are provided
•
for cable connections (see Figure 3.13 and
33
Figure 3.14).
Access holes are provided for input power, motor
•
leads, and control wiring.
Run input power, motor wiring, and control
•
wiring in three separate conduits for isolation.
NOTE!
RUN INPUT POWER, MOTOR WIRING AND CONTROL
WIRING IN THREE SEPARATE METALLIC CONDUITS OR
RACEWAYS FOR HIGH FREQUENCY NOISE ISOLATION.
FAILURE TO ISOLATE POWER, MOTOR AND CONTROL
WIRING COULD RESULT IN LESS THAN OPTIMUM DRIVE
AND ASSOCIATED EQUIPMENT PERFORMANCE.
Figure 3.13 Bypass Panel Conduit Entry Diagram
The drive always resides in the upper section of
•
the panel. Connections to the ECB and EMB2 are
in this area except on the P2 bypass panels.
Power connections are typically towards the
•
bottom side of the panel.
Control wiring should be isolated from power
•
components inside the unit as much as possible.
Danfoss has included hardware to allow for the
separation.
See the mechanical layout drawings in through
•
for connection details and recommended wire
routing.
Figure 3.14 Non Bypass Panel Conduit Entry Diagram
3-16 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 34

INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
Non Bypass
Bypass
130BX387.11
CONTROL WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
Bypass
Non Bypass
130BX388.11
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.15 P2 Panel
Figure 3.16 P3 Panel
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-17
Page 35

CONTROL WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
Bypass
Non Bypass
130BX389.12
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
33
Figure 3.17 P4 Panel
3-18 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 36

CONTROL WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
CONTROL WIRES
INPUT POWER WIRES
OUTPUT POWER WIRES
Non Bypass
Bypass
130BX390.11
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3 3
Figure 3.18 P5 Panel
Wire Size
3.4.3
WARNING
ELECTROCUTION AND FIRE HAZARDS WITH IMPROPERLY INSTALLED AND GROUNDED FIELD WIRING!
Improperly installed and grounded field wiring poses FIRE & ELECTROCUTION hazards. To avoid these hazards, you MUST
follow requirements for field wiring installation and grounding as described in the National Electrical Codes (NEC) and your
local/state electrical codes. All field wiring MUST be performed by qualified personnel.
Failure to follow these requirements could result in death or serious injury.
NOTE!
Make all power connections with minimum 60 or 75°C/140 or 155°F rated copper wiring for installations in North America.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-19
Page 37

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
208 V AC
Panel
HP (KW)
7.5 (5.5) 24.2
10 (7.5) 30.8 8 AWG 10 AWG 60
33
15 (11) 46.2
20 (15) 59.4 P3 3 AWG 10 AWG 60
25 (18.5) 74.8
30 (22) 88
40 (30) 114
50 (37) 143
60 (45) 169 4/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
HP (KW)
7.5 (5.5) 22
10 (7.5) 28 8 AWG 10 AWG 60
15 (11) 42
20 (15) 54
25 (18.5) 68
30 (22) 80
40 (30) 104
50 (37) 130
60 (45) 154 3/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
UL Motor
Current
UL Motor
Current
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3 - Non Bypass
P4 -Bypass
P4
P5
Panel
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Panel (FC302)
Non Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
230 V AC
Panel (FC302) Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Maximum Field
Wiring Size Class
B or C
8 AWG 10 AWG 60
4 AWG 10 AWG 60
2 AWG 8 AWG 60
2 AWG 8 AWG 60
1/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
3/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
Maximum Field
Wiring Size
Class B or C
10 AWG 10 AWG 60
6 AWG 10 AWG 60
4 AWG 10 AWG 60
3 AWG 8 AWG 60
3 AWG 8 AWG 60
1 AWG 6 AWG 75
2/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
Field Ground
Wiring Size Class
B or C
Field Ground
Wiring Size
Class B or C
Minimum
Temperature Wire
Rating "°C" Copper
Conductor
Minimum
Temperature Wire
Rating "Degree C"
Copper Conductor
Table 3.9 Wire Size Chart, 208 and 230 V
3-20 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 38
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
460 V AC
Panel
HP (KW) UL Motor Current
15 (11) 21
20 (15) 27 8 AWG 10 AWG 60
25 (18.5) 34
30 (22) 40
40 (30) 52 4 AWG 10 AWG 60
50 (37) 65
60 (45) 77
75 (55) 96
100 (75) 124
125 (90) 156 3/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
HP (KW) UL Motor Current
15 (11) 17
20 (15) 22 10 AWG 10 AWG 60
25 (18.5) 27
30 (22) 32
40 (30) 41 6 AWG 10 AWG 60
50 (37) 52
60 (45) 62
75 (55) 77
100 (75) 99
125 (90) 125 2/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Panel
(FC102/202/322)
Non Bypass &
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Panel (FC302) Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
600 VAC
Panel (FC302) Non
Bypass
P2
P3
P4
P5
Maximum Field
Wiring Size Class
B or C
10 AWG 10 AWG 60
6 AWG 10 AWG 60
6 AWG 10 AWG 60
3 AWG 8 AWG 60
1 AWG 8 AWG 60
1 AWG 8 AWG 60
2/0 AWG 6 AWG 75
Maximum Field
Wiring Size Class
B or C
10 AWG 10 AWG 60
8 AWG 10 AWG 60
8 AWG 10 AWG 60
4 AWG 10 AWG 60
3 AWG 8 AWG 60
1 AWG 8 AWG 60
1 AWG 8 AWG 60
Field Ground
Wiring Size Class
B or C
Field Ground
Wiring Size Class
B or C
Minimum
Temperature Wire
Rating "°C" Copper
Conductor
3 3
Minimum
Temperature Wire
Rating "Degree C"
Copper Conductor
Table 3.10 Wire Size Chart 460 and 600 V
Wire Type Rating
3.4.4
The wire style rating specifications are provided inTable 3.9 and Table 3.10
•
Terminal Tightening Torques
3.4.5
Tighten all connections to the torque specifications provided in Table 3.11 and Table 3.12
•
The torque specifications are also located on the tightening torque and wire rating label inside the panel cover.
•
See Table 3.14 for a sample of the torque and wire rating data.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-21
Page 39

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Torque lb-in
Overload T1,
Single Motor
L1, L2, & L3
Circuit Breaker
Disconnect Switch
Disconnect Switch
(N-m)
T2, & T3
Torque lb-in
Torque lb-in
L2, & L3 Torque
Fusible UL98 L1,
L1, L2, & L3 Torque
(w/o Fuses) UL508A
(N-m)
(N-m)
lb-in (N-m)
lb-in (N-m)
(N-m)
Torque lb-in
Ground Wire
Fusible UL98 L1,
T2, & T3
Torque lb-in
L2, & L3 Torque
UL508A L1, L2, &
Torque lb-in
lb-in (N-m)
L3 Torque lb-in
(N-m)
(N-m)
(N-m)
200 (22.5) 500 (56.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
33
Overload T1,
Single Motor
L1, L2, & L3
Circuit Breaker
Disconnect Switch
(w/o Fuses)
Disconnect Switch
Ground Wire
208 V
Non Bypass Bypass
Input Output Input Output
(N-m)
T3 Torque lb-in
Motor T1, T2, &
Drive
Disconnect
L3 Torque lb-in
Switch L1, L2, &
Non Bypass
Panel (FC302)
Non Bypass & Bypass
Panel (FC102/202/322)
(N-m)
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
P2
P2
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 45 (5) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P3
70 (7.9) 40 (4.5) 55 (6.2) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
200 (22.5) 40 (4.5) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
200 (22.5) 88.5 (10) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
P5
200 (22.5) 88.5 (10) 200 (22.5) 500 (56.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
230 V
124/212.4
(14/24) *Note 1
200 (22.5)
P5
Non Bypass Bypass
Input Output Input Output
(N-m)
T3 Torque lb-in
Motor T1, T2, &
Drive
Disconnect
& L3 Torque
Switch L1, L2,
Non Bypass
Panel (FC302)
Non Bypass & Bypass
Panel (FC102/202/322)
lb-in (N-m)
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
P2
P2
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 45 (5) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P3
55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P3
70 (7.9) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
70 (7.9) 40 (4.5) 55 (6.2) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
200 (22.5) 88.5 (10) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
200 (22.5) 88.5 (10) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
P5
P5
*Note 1 - Tightening of terminals for different cable dimensions x/y, where x <0.147in sq [95mm sq] and y>0.147 in sq [95mm sq]
15 (11)
20 (15) P3 - Non Bypass 55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
30 (22)
40 (30)
50 (37)
10 (7.5) 55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
HP (KW)
3-22 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
7.5 (5.5)
25 (18.5) P4 - Bypass
60 (45)
HP (KW)
7.5 (5.5)
10 (7.5) 55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
15 (11)
20 (15)
25 (18.5)
30 (22)
40 (30)
50 (37)
60 (45) 200 (22.5) 124 (14) 200 (22.5) 500 (56.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
Table 3.11 Tightening Torques, 208 and 230 V
Page 40

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
(N-m)
Torque lb-in
Ground Wire
Overload T1, T2,
L1, L2, & L3
L2, & L3 Torque
& T3 Torque lb-
Torque lb-in
lb-in
in (N-m)
(N-m)
(N-m)
Single Motor
Circuit Breaker
Fusible UL98 L1,
Disconnect Switch
3 3
460 V
Non Bypass Bypass
Input Output Input Output
Disconnect
Switch (w/o
Fuses) UL508A
Motor T1, T2, &
Drive
Disconnect
Non Bypass
Panel (FC302)
Non Bypass & Bypass
Panel (FC102/202/322)
L1, L2, & L3
T3 Torque lb-in
Switch L1, L2, &
Torque lb-in
(N-m)
L3 Torque lb-in
(N-m)
(N-m)
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
P2
P2
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 45 (5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 30 (3.3) 45 (5) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P3
P3
55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
70 (7.9) 88.5 (10) 55 (6.2) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
200 (22.5) 88.5 (10) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
200 (22.5) 124 (14) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
P5
P5
*Note 1 - Tightening of terminals for different cable dimensions x/y, where x <0.147in sq [95mm sq] and y>0.147 in sq [95mm sq]
HP (KW)
15 (11)
20 (15) 55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (0.8) 30 (3.3) 40 (4.5) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
25 (18.5)
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-23
30 (22)
40 (30) 55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 50 (5.6) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
50 (37)
60 (45)
75 (55)
100 (75)
125 (90) 200 (22.5) 124 (14) 200 (22.5) 500 (56.5) 274 (31) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
Table 3.12 Tightening Torques, 460 V
Page 41

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
(N-m)
Torque lb-in
Ground Wire
33
lb-in (N-m)
Overload T1,
Single Motor
T2, & T3 Torque
(N-m)
L1, L2, & L3
Torque lb-in
Circuit Breaker
Torque lb-in
L1, L2, & L3
T3 Torque lb-in
(N-m)
(N-m)
Torque lb-in
(N-m)
600 V
Non Bypass Bypass
Disconnect
Switch Fusible
Disconnect
Switch (w/o
Fuses) UL508A
Motor T1, T2, &
UL98 L1, L2, & L3
Drive
Input Output Input Output
3-24 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Disconnect
Non Bypass
Panel (FC302)
Non Bypass & Bypass
Panel (FC102/202/322)
HP (KW)
(N-m)
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (.79) 17 (1.92) 62 (7) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
L3 Torque lb-in
Switch L1, L2, &
P2
15 (11)
P2
20 (15) 55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (.79) 30 (3.3) 62 (7) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
55 (6.2) 16 (1.8) 7 (.79) 30 (3.3) 62 (7) 24 (2.7) 40 (4.5)
25 (18.5)
55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 7 (.79) 30 (3.3) 62 (7) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P3
30 (22)
P3
40 (30) 55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 30 (3.3) 62 (7) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
55 (6.2) 40 (4.5) 18 (2) 120 (13.5) 62 (7) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
50 (37)
55 (6.2) 88.5 (10) 55 (6.2) 120 (13.5) 62 (7) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P4
60 (45)
70 (7.9) 88.5 (10) 55 (6.2) 200 (22.5) 62 (7) 50 (5.6) 40 (4.5)
P5
75 (55)
200 (22.5) 124 (14) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
P5
100 (75)
*Note 1 - Tightening of terminals for different cable dimensions x/y, where x <0.147in sq [95mm sq] and y>0.147 in sq [95mm sq]
125 (90) 200 (22.5) 124 (14) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 200 (22.5) 275 (31) 40 (4.5)
Table 3.13 Tightening Torques, 600 V
Page 42

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Field Connection Tightening Torque lb-in (N-m) Temperature & Type Rating
L1, L2, L3/Ground 25 (2.8) 25 (2.8) Use 75°C Copper Conductor
2T1, 2T2, 2T3/Ground 25 (2.8) 25 (2.8) Use 75°C Copper Conductor
TB1 25 (2.8) 25 (2.8) Use 75°C Copper Conductor
Table 3.14 Sample Tightening Torque and Wire Rating Label
3.4.6 Input Line Connection
CAUTION
Run input power, motor wiring and control wiring in three
separate metallic conduits or raceways for high frequency
noise isolation. Failure to isolate power, motor and control
wiring could result in less than optimum drive and
associated equipment performance.
Connect 3-phase AC input power wire to
•
terminals L1, L2, and L3. See the connection
drawing inside the cover of the unit.
Depending on the configuration of the
•
equipment, input power may be connected to a
circuit breaker or disconnect switch.
Torque terminals in accordance with the
•
information provided inTable 3.11 and Table 3.12
on the label inside the panel cover.
Use with Isolated Input Source. Many utility
•
power systems are referenced to earth ground.
Although not as common, the input power may
be an isolated source. All drives may be used
with an isolated input source as well as with
ground reference power lines.
Motor Wiring
3.4.7
WARNING
ELECTROCUTION AND FIRE HAZARDS WITH
IMPROPERLY INSTALLED AND GROUNDED FIELD
WIRING!
Improperly installed and grounded field wiring poses FIRE
& ELECTROCUTION hazards. To avoid these hazards, you
MUST follow requirements for field wiring installation and
grounding as described in the National Electrical Codes
(NEC) and your local/state electrical codes. All field wiring
MUST be performed by qualified personnel. Failure to
follow these requirements could result in death or serious
injury.
WARNING
INDUCED VOLTAGE!
Run output motor cables from multiple drives separately.
Induced voltage from output motor cables run together
can charge equipment capacitors even with the equipment
turned off and locked out. Failure to run output motor
cables separately could result in death or serious injury.
NOTE!
Run input power, motor wiring and control wiring in three
separate metallic conduits or raceways for high frequency
noise isolation. Failure to isolate power, motor and control
wiring could result in less than optimum drive and
associated equipment performance.
Connect the 3-phase motor wiring to bypass
•
terminals T1 (U), T2 (V), and T3 (W). See the
connection drawing inside the cover of the unit.
Depending on the configuration of the
•
equipment, motor wiring may be connected to
overload or terminal block.
Torque terminals in accordance with the
•
information provided on the connection diagram
inside the cover of the unit.
Motor wiring should never exceed the following
•
maximum distances: 300m (1000 ft) for
unshielded, 150m (500 ft) for shielded.
Motor wiring should always be as short as
•
practical.
3 3
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-25
Page 43

130BX224.10
1
2
3
4
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
3.4.8 Grounding (Earthing)
WARNING
GROUNDING HAZARD!
for operator safety, it is important to ground the option
panel properly. Failure to do so could result in death or
33
serious injury.
NOTE!
It is the responsibility of the user or certified electrical
installer to ensure correct grounding (earthing) of the
equipment in accordance with national and local electrical
codes and standards.
Follow all local and national codes for proper
•
electrical equipment grounding (earthing).
Correct protective grounding of the equipment
•
must be established. Ground currents are higher
than 3 mA.
A dedicated ground wire is required for input
•
ground.
Connect the ground wire directly to a reliable
•
earth ground. Grounding studs are provided on
the back plate of the panel for grounding.
Do not use conduit connected to the panel as a
•
replacement for a ground wire.
A high strand count ground wire is preferred for
•
dissipating high frequency electrical noise.
Keep the ground wire connections as short as
•
possible.
Ground the motor to the panel with insulated
•
wire run inside metal conduit with motor leads.
Figure 3.19 Control Terminals Location
1. EIA-485 terminal
2. Jumper wire
3. Control terminals
4. Grounded restraining clips
3.4.10
Serial Communication Bus
Connection
The ECB reports serial communication data to host systems
through the drive. Connection to the serial communication
network is made either through the EIA-485 terminals on
the drive (see Figure 3.19) or, for other protocols, terminals
located on the communication option card. For option
card connection, see the option card instructions provided
with the unit.
For ECB serial communication protocols using the
Control Wiring
3.4.9
Detailed instructions for terminal connection, control
wiring installation, and operation are shown in Section 5
Electromechanical Bypass (EMB2) Operation and Section 6
Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation.
It is recommended that control wiring is rated for
•
600 V for 480 V and 600 V drives and 300 V for
200-240 V drives.
Isolate control wiring from high power
•
components in the drive.
See 3.4.2 Wire and Cable Access for details.
•
3-26 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
•
EIA-485 terminals, make connections in the
following manner.
NOTE!
It is recommended to use braided-shielded, twisted-pair
cables to reduce noise between conductors.
1. Connect signal wires to terminal (+) 68 and
terminal (-) 69 on control terminals of drive. (See
the drive support materials for wire size and
tightening torque.)
2. Terminate shield to grounded restraining clip
provided by stripping wire insulation at point of
contact.
3. If shielded cabling is used, do not connect the
end of the shield to terminal 61.
Page 44

130BX231.10
Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Programming
Serial communication point maps, parameter settings, and
other details for bypass option functionality are included in
the serial communication materials supplied with the unit.
Also provided are two Form C relay outputs that
•
are in various locations depending upon the drive
configuration and size.
3.4.11 Drive Control Terminals
Definitions of the drive terminals are summarized in
Table 3.15.
Connector 1 provides four digital inputs; two
•
selectable digital inputs or outputs, 24 V DC
terminal supply voltage, and a common for
optional customer supplied 24 V DC voltage.
Serial communications use EIA-485 connector 2
•
with terminal 68 (+) and 69 (-).
Connector 3 provides two analog inputs, one
•
analog output, 10 V DC supply voltage, and
commons for the inputs and output.
A USB port, connector 4, is also available for use
•
with the MCT 10 Set-up Software available on the
Danfoss website.
Terminal No. Function
01, 02, 03, 04,
05, 06
12, 13 24 V DC digital supply voltage. Useable for digital inputs and external transducers. To use the 24 V DC for digital input
18, 19, 32, 33 Digital inputs. Selectable for NPN or PNP function in parameter 5-00. Default is PNP.
27, 29 Digital inputs or outputs. Programmable for either. Parameter 5-01 for terminal 27 and 5-02 for 29 selects input/output
20 Common for digital inputs. To use for digital input common, program parameter 5-00 for NPN operation.
39 Common for analog output.
42 Analog output. Programmable for various functions in parameter 6-5*. The analog signal is 0 to 20 mA or 4 to 20 mA at
50 10 V DC analog supply voltage. 15 mA maximum commonly used for a potentiometer or thermistor.
53, 54 Analog input. Selectable for voltage (0-10 V) or current (0- or 4-20 mA). Closed is for current and open is for voltage.
55 Common for analog inputs.
61 Common for serial communication. Do not use to terminate shields. See drive support materials for proper shield
68 (+), 69 (-) RS-485 interface. When the drive is connected to an RS-485 serial communication bus, a drive control card switch is
Form-C relay output. Useable for AC or DC voltage and resistive or inductive loads. See drive support materials for
details on voltage and current ratings and relay location.
common, program parameter 5-00 for PNP operation. Maximum output current is 200 mA total for all 24V loads.
function. Default setting is input.
a maximum of 500 Ω.
Switches are located on the drive control card behind the removable LCP. See drive support materials for details.
termination.
provided for termination resistance. ON for termination and OFF for no termination. See drive support materials for
details.
Figure 3.20 Removable Drive Connectors and Terminals
3 3
Table 3.15 Drive Control Terminals Functions
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 3-27
Page 45

Installation Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
33
3-28 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 46

Start Up Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
4 Start Up
1. Input power to the unit must be OFF and locked
out per OSHA requirements. Do not rely on panel
disconnect switches.
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
if input and output connections have been connected
improperly, there is potential for high voltage on these
terminals. If power leads for multiple motors are
improperly run in same conduit, there is potential for
leakage current to charge capacitors within the panel, even
when disconnected from line input. For initial start up,
make no assumptions about power components. Follow
pre-start procedures described below. Failure to do so
could result in death, serious injury or damage to
equipment.
2. Use AC voltmeter to verify there is no voltage on
input terminals L1, L2, and L3, phase-to-phase
and phase-to-ground, and output terminals T1,
T2, and T3, phase-to-phase and phase-to-ground.
3. Use ohmmeter to confirm continuity of the motor
by measuring T1-T2, T2-T3, and T3-T1.
4. Use ohmmeter to confirm open on input by
measuring L1-L2, L2-L3, and L3-L1. Note that if an
isolation transformer is between the power
source and panel, continuity will be present. In
this case, visually confirm that motor and power
leads are not reversed.
5. Inspect the panel for loose connections on
terminals.
6.
CheckTable 3.9 and Table 3.10 for proper ground
wire: panel to main building distribution ground,
and panel to motor ground.
7. Confirm control connections terminated per
connection diagrams supplied with the
equipment.
8. Check for external devices between drive panel
output and motor. It is recommended that no
devices be installed between the motor and
drive.
9. Record motor nameplate data; hp, voltage, full
load amps (FLA), and RPM. It will be needed to
match motor and drive later on.
10. Confirm that incoming power voltage matches
drive label voltage and motor nameplate voltage.
11. For multiple winding motors, the motor must be
wired on run winding, not start winding.
CAUTION
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE!
if motor FLA (full load amperage) is greater than unit
maximum amps, drive and panel must be replaced with
one of appropriate rating. Do not attempt to run the unit.
Failure to match FLA to unit maximum amp rating may
result in equipment damage.
12. Confirm motor FLA is equal to or less than
maximum panel output current. Some motors
have higher than normal NEMA currents.
13. Check that the overload relay is set for FLA of
connected motor. Service factor is built into
overload relay. Relay trips at 120% of setting.
14. For drive start up procedures, see drive
instruction manual.
4 4
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 4-1
Page 47

Start Up Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
4.1.1 Inspection Prior to Start Up
Before applying power to the unit, inspect the entire installation as detailed in Table 4.1.
Inspect For Description
Look for auxiliary equipment, switches, disconnects, or input fuses/circuit breakers that may reside on input
Auxiliary equipment
44
Cable routing
Control wiring
EMC considerations Check for proper installation with regard to electromagnetic capability.
Environmental
conditions
Fusing and circuit
breakers
Grounding
Input and output
power wiring
Panel interior
Proper Cooling
Clearance
Switches Ensure that all switch and disconnect settings are in the proper position.
Vibration Look for any unusual amount of vibration the equipment may be subjected to when mounting panel.
power side of drive or output side to motor. Examine their operational readiness and ensure they are ready in
all respects for operation at full speed. Check function and installation of pressure sensors or encoders (etc.)
used for feedback to drive. Remove power factor correction caps on motor, if present.
Ensure that input power, motor wiring, and control wiring are in three separate metallic conduits for high
frequency noise isolation. Failure to isolate power, motor, and control wiring could result in less than optimum
drive and associated equipment performance.
Check for broken or damaged wires and connections. Check the voltage source of the signals, if necessary. The
use of shielded cable or twisted pair is recommended for serial communication. Ensure the shield is terminated
correctly.
See panel label for the maximum ambient operating temperature. Humidity levels must be less than 95% noncondensing. Attitude less than 3300 feet.
Check that all fuses are inserted firmly and in operational condition and that all circuit breakers are in the open
position.
The panel requires a dedicated ground wire from its chassis to the building ground. It is required that the
motor be grounded to the panel chassis. The use of conduit or mounting of the panel to a metal surface is not
considered a suitable ground. Check for good ground connections that are tight and free of oxidation. Run
insulated motor ground wire back to panel in conduit with motor wires.
Check for loose connections. Check for proper fusing or circuit breakers.
Panel interior must be free of dirt, metal chips, moisture, and corrosion. Check for harmful airborne contaminates such as sulfur based compounds.
Panels require top and bottom clearance adequate to ensure proper air flow for cooling. See Figure 3.2 and
Figure 3.3
Table 4.1 Inspection prior to Startup
Start Up Procedure
4.1.2
1. Perform pre-startup procedure.
2. Ensure that all operator devices are in the OFF
In the following procedures, changing the equipment
between drive mode and bypass mode is required.
Changing modes is different for the ECB and EMB2. The
ECB uses pushbuttons on the drive keypad while the EMB2
uses a selector switch on the front of the panel. Be familiar
with the operation of these devices prior to start up.
position. The main disconnect switch on the front
of the electromechanical bypass panel must be in
the OFF position. The panel door should be
closed.
3. Keep main disconnect switch in the OFF position
and apply voltage to the panel.
4. Confirm that input line voltage is balanced within
WARNING
EQUIPMENT HAZARD!
3%. If not, correct the input voltage imbalance
before proceeding.
The panel contains dangerous voltages when connected to
line voltage. Installation, start-up and maintenance should
be performed only by qualified personnel. Failure to
perform installation, start-up and maintenance by qualified
personnel only could result in death or serious injury.
4-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 48

Start Up Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
CAUTION
MOTOR START!
Ensure that motor, system, and any attached equipment is
ready for start. Failure to do so could result in personal
injury or equipment damage.
5. If a bypass is connected, place the Mode Selector
Switch in drive mode. Apply power by turning
the main disconnect switch to the ON position.
6. Enter drive programming data per the drive
instruction manual.
7. Check motor rotation direction in drive control as
follows.
7a Put panel in drive mode.
7b Hand start drive at minimum speed (see
drive instruction manual for details).
7c Confirm directional rotation.
7d If incorrect, stop the drive, remove
power, and lock out.
7e Reverse connection of T1 & T2 motor
leads. Do not change incoming power
leads.
7f Remove lockout and apply power.
7g Confirm directional rotation.
8. Check motor rotation direction in bypass as
follows.
8a Momentarily bump motor in bypass.
8b Confirm directional rotation.
8c If incorrect, stop drive, remove power,
and lock out.
8d Reverse connection of L1 & L2 input
power leads to the main disconnect. Do
not change motor leads.
8e Confirm directional rotation.
9a Put the unit in drive mode.
9b Check motor current on motor terminals
T1, T2, and T3. Verify the motor amps
are within drive and motor rated current
and are balanced within 3%. If incorrect,
see 7.1 Start Up Troubleshooting for
isolation procedures.
9c Check input current on input terminals
L1, L2, and L3. Verify that current is
within FLA of drive and balanced within
3%. If incorrect, see 7.1 Start Up Trouble-
shooting for isolation procedures.
10. Check motor current in bypass mode on the
motor terminals.
10a Put the unit in bypass mode.
10b Check full load amps on terminals T1,
T2, and T3. Verify the motor amps are
within motor FLA rated current and
balanced within 3%. If incorrect, see
7.1 Start Up Troubleshooting for isolation
procedures.
For steps 11-13, see 5 Electromechanical Bypass (EMB2)
Operation and 6 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB)
Operation for details.
11. Check operation of any optional functions to
confirm that they work, as applicable. Options
may include run permissive, fire mode, common
start/stop, or others.
12. Exercise the safety circuit and verify that the unit
stops running.
13. Exercise the start/stop circuit and verify that the
unit starts and stops with the system in the Auto
mode of operation.
4 4
CAUTION
FULL SPEED OPERATION!
Ensure that the motor, system, and any attached
equipment is ready for full speed operation. The user
assumes all responsibility for assuring the system is able to
safely run at full speed. Failure to ensure that the motor,
system, and any attached equipment is ready for full speed
operation could result in equipment damage.
9. Check motor current in drive mode on the motor
terminals.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 4-3
Page 49
Start Up Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
44
4-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 50

Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
5 Electromechanical Bypass (EMB2) Operation
5.1.1 Typical Control Connections for Common HVAC Applications
Drive Terminal Parameter Number Parameter Name Value Number Value Name Function
27 500 Digital I/O Mode 0 PNP External Interlock
27 501 Term 27 mode 0 Input External Interlock
29 502 Term 29 Mode 1 Output Auto Bypass
18 510 Term 18 digital input 8 Start Common run/stop
19 511 Term 19 digital input 52 Run Permissive Run Permissive
27 512 Term 27 digital input 7 External Interlock External Interlock
29 531 Term 29 digital output 160 No Alarm Auto Bypass
01 & 02 540 [0] Relay 1 function 167 Start Command Active Run Permissive
01 & 02 540 [0] Relay 1 off delay 0.00 seconds Off Delay Run Permissive
Table 5.1 EMB2 Default Parameter Settings for Common HVAC Applications
If the drive is reinitialized, be sure that these settings are maintained or reset for proper bypass.
5
5
Name Function Drive Terminals EMB2 X59 EMB2 X55
Remote Drive Start (with common start/stop) Input Command 3, 4
Remote Drive Start (without common start/stop) Input Command 13, 18
Motor Running on Drive Output Status 04, 05, 06
Run Request (for run permissive) Output Command 11, 12
Run Enable (for run permissive) Input Command 1, 2
Safety Stop Input Command 5, 6
Drive Fault Output Status 5, 6, 7
Fire Mode Input Command 7, 8
Drive Mode Output Status 1, 2
Bypass Mode Output Status 3, 4
Fire Mode Output Status 9, 10
Table 5.2 Common Functions for Controlling Motor using Bypass and Typical Terminal Connections.
Commands enable drive functions. Status reports describe conditions, but do not enable a function.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 5-1
Page 51

(A2)
M3
(A1)
(A2)
(A1)
M2
(A1)
M1
(A2)
1-2
CONTACT
5-6
7-8
3-4
TEST
X
X
X
X
X
BYPASSOFFDRIVE
X
X INDICATES CONTACT CLOSED
CONTACT SEQUENCE CHART FOR S1
POSITION
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X55,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
4
3
M1, M2, AND M3
10
7
9
8
4
6
5
MK 106
EMB2
MK 110
MK 101
4
3
2
7
5
6
8
3
1
2
O.L. RELAY
EXTERNAL
1
2
3
4
1
2
MK 107
1
MK 105
2 3 54 6
MK 100
7
6
5
10
8
9
7
10
12
11
9
24 V SUPPLY
CONTACT
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CONTACTORS
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
5
D/O/B/T SWITCH
BOARD
4321
ON
S100
28
100
M3
73
72
71
70
CR9
RL6
S1
30
(3)
(4)
31
(5)
(6)
S1
40
94
91
TO DRIVE
28
M3
42
M2
33
34
M2
91
90
94
92
83
84
60
RL2
NC
PL2
R
X55
X59
BLUE
100
OL1
(95)
(96)
35
30
BLUE
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
24 VDC, 1 A
RESISTIVE LOAD
MAXIMUM
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
JUMPERED
FACTORY
M3
27
(8)
S1
(7)
S1
91
27
(2)
(1)
100
94
BLUE
(13)
(14)
(32)
(31)
(31)
(32)
43
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
8
NC
NC
NC
DRIVE
MK 103
14
11
13
12
NC
NC
NC
NC
M2
(34)
(33)
M3
(34)
(33)
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
3
4
S105
1
2
ON
(X2)
(X1)
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
12
8
11
9
10
14
13
123
4
162738495101627384
9
MK106
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
9
11
10
12
4321
ON
MK107
MK100
MK105MK103
S105
130B7290
REFERENCE T.B. TERMINAL NUMBERS
S105
1 2
ON
TO SMPS
CONTROL BOARD
(10 POS. TB)
TEST CONNECTOR
1
M2
ALL OFF NO AUTO BYPASS (FACTORY DEFAULT)
AUTOMATIC BYPASS TIME SELECT
ALL ON 15 SEC.
ONLY # 3 ON 300 SEC
ONLY # 2 ON 60 SEC.
ONLY # 1 ON 30 SECONDS
3
4
S100
1
2
ON
CUSTOMER SETTING
NO FUNCTION
NO FUNCTION
RUN PERMISSIVE
COMMON RUN/STOP
4
321
ON
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
MK101
TEST CONNECTOR
MK110
S100
130B7290
EMB2 BOARD
CONTACT CLOSED
MOTOR ON BYPASS
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
FIREMANS OVERRIDE STATUS
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
(COMMON RUN/STOP)
DAMPER END SWITCH
RUN PERMISSIVE
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
FIREMANS OVERRIDE CONTACT
CONTACTS SHOWN
IN FAULT POSITION
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
INTERLOCK
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED SAFETY
REPLACE WITH
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
MOTOR ON DRIVE
INDICATES
DRIVE FAULT STATUS
DAMPER MOTOR CONTROL
(CONTACT)
130BX402.12
Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
5
Figure 5.1 Customer Side EMB2 Control Card Terminal Connections
5-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 52

Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
5.1.2 EMB2 Auto Bypass
General Information
Auto bypass allows a fault condition in the drive to
activate running the motor in bypass without operator
intervention. Activation of the function is through setting
DIP switches (S100) located on the EMB2 bypass control
card (see Figure 5.1). A fault condition enables a delay
timer prior to tripping the drive into bypass. The fault trip
and running in bypass are reported as output from the
bypass control card. The auto bypass function is built in.
Prior to Enabling Auto Bypass
Complete the start-up procedure to verify that
•
the motor rotation direction in bypass is correct
and that the system is ready in all respects for
continuous full speed operation in bypass.
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE!
Remove power to the bypass panel before setting auto
bypass dip switch settings. Bypass can contain high
voltage. Failure to remove power to bypass panel before
setting dip switches could result in death or serious injury.
Operation
With the bypass selector switch in drive and auto
•
bypass enabled, a fault signal from the drive will
activate the auto bypass timer.
If the fault clears before the time delay is
•
complete, the motor remains operating in drive
mode. This allows temporary faults, such as a
momentary under or over voltage, to clear
without transferring the system to bypass.
If the timer completes its cycle before the fault
•
clears, the panel trips into bypass mode and the
motor runs at constant full speed from line input
voltage.
In bypass, the motor will stop if safety or motor
•
overload conditions are exceeded.
Once auto bypass is activated, the only way to
•
reset the unit back to drive is by operator
intervention. Ensure that the fault has been
cleared, then rotate the bypass switch to the OFF
position momentarily before setting it back to the
drive position. This resets the drive and fault
timer.
Auto Bypass Function Setup
Enable auto bypass by closing one or more DIP switches
on switch S100 located on the bypass control card. (Times
are approximate.)
All OFF = no auto bypass operation
•
Switch 1 only ON = 30 sec. delay
•
Switch 2 only ON = 60 sec. delay
•
Switch 3 only ON = 300 sec. delay (maximum)
•
Switch 4 = Always OFF
•
5.1.3 EMB2 Common Run/Stop
General Information
The common run/stop function provides remote run and
stop control of the motor in bypass. Without common run/
stop, the motor would automatically run at full speed
whenever the bypass is activated. The remote signal
provides drive control as well as bypass control, making
this one input common to both. Common run/stop is
enabled by factory default. When used with the run
permissive function, common run/stop permits run request
operation in bypass.
Prior to Enabling Common Run/Stop
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Operation
A user supplied remote start command wired to
•
connector X55, terminals 3 and 4 initiates remote
bypass operation. With common run/ stop,
bypass mode cannot be activated by hand on the
drive keypad or by serial communication.
Common Run/Stop Setup
Wire input terminals 3 and 4 on connector X55
•
per the system application.
To Disable Common Run/Stop
Common run/stop is enabled by factory default
•
when ordered.
To disable the feature, turn switch four on dip
•
switch S105. This allows the bypass to start when
the bypass switch is placed in the bypass
position.
Remove wire from terminal 18 of the drive
•
control terminal and insulate the end of the wire
to prevent shorting. This is required or the drive
will always have a run command.
If applicable, connect remote run/stop input to
•
terminals 12 and 18 on the drive control card.
5
5
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 5-3
Page 53
Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
5
5.1.4 EMB2 Run Permissive
General Information
Run permissive allows a remote signal to notify the drive
to start, indicating the system is safe to operate. Run
permissive works in drive or bypass mode. Run permissive
is enabled by factory default and can be disabled by
switching dip switch #4 on S105 to the on position or
placing a jumper wire between terminal 1 and 2 of the
X55 customer connector.
Prior to Enabling Run Permissive
Complete the start-up procedure to verify that
•
motor rotation direction in bypass is correct and
that the system is ready in all respects for
continuous full speed operation in bypass.
Verify that the drive is programmed for the run
•
permissive function. See the drive support
manual provided for information on
programming the run permissive function.
Operation
A start command can be from local hand start on
•
the drive keypad or a remote auto start signal
through digital input connector X55 terminals 3
and 4, or via the serial communications input.
In response to a start command, an output
•
request is sent from X55 terminals 11 and 12 to
the external equipment (to activate a valve or
damper, for example).
When a return run signal on X55 terminals 1 and
•
2 is received, the motor is started in either drive
or bypass mode, depending upon the bypass
switch position.
Run Permissive Function Setup
Remove the factory-installed jumper wire on
•
connector X55, terminals 1 and 2.
Wire the output run request to connector X55,
•
terminals 11 and 12.
Wire the input run permission to connector X55,
•
terminals 1 and 2 per the system application.
Disable Run Permissive
Run permissive is enabled by factory default
•
when ordered.
To disable the run permissive function, jumper
•
between terminals 1 and 2 on connector X55 or
use dip switch 4 on 5105.
5.1.5
EMB2 Overload
General Information
The overload device provides overcurrent protection for
the motor when running in bypass. The thermally activated
overload monitors motor current and trips to remove
power to the motor if a sustained over-current condition
exists. A Class 20 overload is standard with a variable
setting for motor current. Test and reset buttons are also
provided. In drive mode, the drive provides current sensing
and trip protection. Fuses provide quick action for high
over current conditions.
Prior to Enabling Overload
Verify that the overload current dial setting
•
matches the motor FLA rating on the motor
nameplate.
If the motor FLA is greater or less than the range
•
of the current dial, reconfirm that the motor hp
and voltage are within the option panel (and
drive) rating. If greater than the FLA rating,
replace the panel with one of a proper rating.
CAUTION
MOTOR DAMAGE!
Repeated attempts to reset an overload can cause motor
damage. Correct the overload condition and let the
overload and motor return to normal operating
temperature before resetting. See motor manufacturer’s
recommendations for time between start attempts. Failure
to correct the overload condition and let the motor return
to normal operating temperature could cause motor
damage.
Operation
Overloads are rated by class. The class is defined by the
NEC to determine the maximum time to trip. A Class 20
overload, for example, has a typical trip delay of 20 sec. or
less at 600% current and normal operating temperature.
This allows for high motor inrush current for 20 sec. while
the motor is ramping up to synchronous speed. The trip
time, however, is based on the percentage of overload.
The higher the overload, the shorter the trip time. It is
important that the overload class not exceed the motor
class rating or motor damage could occur.
Overload Function Setup
Set the overload current dial to the FLA of the
•
motor. DO NOT add the service factor of the
motor into the setting. A service factor of 120%
for Class 20 is designed into the overload.
Pressing the test pushbutton verifies the
•
operation of the overload. The overload should
5-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 54

T1
T2 T3
97NO
98NO 95NC
96NC
10
20
30
RESET
TEST
MANUAL
AUTO
TRIP
5
130BX229.10
Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
trip when pressed. Use the reset pushbutton to
reset the overload after the test.
Reset is used to reset the overload after it trips. If
•
the overload is still hot, wait until the motor
reaches normal operating temperature before
resetting. The overload offers a manual (hand) or
auto reset selection. It is highly recommended to
operate in the manual factory setting to prevent
the risk of damage to the motor.
Figure 5.2 Sample Overload Device
5.1.6 EMB2 Safety Interlock
General Information
The safety interlock feature prevents the drive or bypass
from operating. For operation in drive or bypass, the safety
interlock input contact must be closed. Only a fire mode
command to run in bypass overrides this function. Safety
inputs include, but are not limited to, high and low
pressure limit switches, fire alarm, smoke alarm, high and
low temperature switches, and vibration sensors.
Operation
When an external safety input closes, the panel is in
operational mode. When open, power is interrupted to the
drive output and bypass contactors and relays, and the
bypass ignores all run commands except for fire mode
operation. When power is interrupted in drive mode, the
drive display indicates an external fault, meaning the
problem is external to the drive. In some instances, a fault
can be caused by a failure within the panel, which will still
be reported as an external fault from the drive. A factory
installed jumper allows the unit to operate when no safety
input is connected. This jumper must be removed when
connecting a safety interlock in the circuit.
Safety Interlock Function Setup
Remove factory-installed jumper between
•
terminals 5 and 6 on connector X55
Wire safety input to terminals 5 and 6 on
•
connector X55
5.1.7
EMB2 Fire Mode
General Information
Fire mode runs the motor at full speed in bypass and is
intended to ignore common safety, overload, and mode
selector switch inputs in emergency situations. The motor
will continue to run in bypass until fire mode is removed
or the unit fails.
Prior to Enabling Fire Mode
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Operation
Activation of fire mode is accomplished by
•
closing connector X55, input terminals 7 and 8.
When activated, a relay overrides the safety
•
circuit, motor overload, and bypass switch (SW1)
position.
Fire mode is deactivated only when removed or
•
fuses blow.
Fire mode status can be reported through
•
connector X55, terminals 9 and 10, a normally
open dry contact that closes when fire mode is
active.
Fire Mode Function Setup
Wire the fire mode input to connector X55,
•
terminals 7 and 8.
Wire the fire mode status output to connector
•
X55, terminals 9 and 10.
EMB2 Fault Reporting
5.1.8
General Information
A fault indication is provided if the drive experiences a
fault or bypass input power is lost. The EMB2 bypass
control card monitors the drive fault output for status
reporting. The fault contacts are fail-safe, meaning that if
power is removed, a fault condition is automatically
reported. Fault status is not monitored in bypass
operation.
Operation
For the EMB2, fault reporting is monitored through a
Form-C relay (RL2) on the bypass control board. The relay
reports a fault on connector X59 terminals 5, 6, and 7. In
normal operation, the relay is powered and terminal 5 is
closed with terminal 7 open. In a fault condition, power to
the relay is lost and the relay positions automatically
reverse, signaling the fault condition. Terminal 6 is
common to both.
5
5
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 5-5
Page 55

5
Electromechanical Bypass (E... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Fault Reporting Function Setup
Fault reporting status is connected to connector
•
X55, output terminals 5, 6, and 7.
5.1.9 EMB2 Switches
Mode selector switch.
A panel mounted Drive/OFF/Bypass/Test selector switch is
used to electrically select whether the motor is controlled
by the drive (M1 and M2 contactors), connected to the
full-speed bypass (M3 contactor), or disconnected from
both. The test position allows for operation in bypass while
providing power to the drive (M1 and M3). See Figure 1.2.
5-6 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 56

130BX230.10
1
3
4
2
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB) Operation
1. LCP Display
6.1 Electronically Controlled Bypass (ECB)
Operation
6.1.1 Overview
Information provided in this section is intended to enable
the user to connect control wiring, program functions, and
operate the ECB and its optional features.
The ECB contains a local processor located on the ECB
control card, which interacts with the drive’s control logic
for programmable options, remote command input, and
output status reporting. Rather than panel-mounted
operator-activated selector switches, as on the electromechanical option panel, ECB control is provided by the
drive’s processor.
The ECB also contains a power supply which provides back
up for the drive’s logic circuitry, so even if the drive loses
power, the control and communication functions are
maintained.
2. Menu keys
3. Menu navigation
4. Control keys
Programming and display are provided by the drive’s local
control panel. (LCP See Figure 6.1)
An important feature of the ECB is the ability to accept
commands from a building automation system (BAS) and
to report operational status in return.
Control wiring connections are made to either the drive’s
control terminals (see Figure 3.20) or terminals provided on
the ECB control card (see Figure 6.2). Drive analog and
digital I/O terminals are multifunctional and need to be
programmed for their intended use while the terminals on
the ECB control card are dedicated for specific functions.
Programming options for drive terminals are seen by
pressing the [Main Menu] key or [Quick Menu] key on the
LCP keypad. Parameter menus appear in the LCP display.
The arrow keys are used for navigating through the
parameter lists. Terminal functions are programmed in
parameter group 5-**. (See Table 6.1 for factory default
parameter settings for drives with an ECB.) Bypass
functions are programmed in parameter group 31-** (see
Table 6.4). See the drive’s supporting materials for detailed
programming instructions.
6 6
Figure 6.1 Local Control Panel (LCP)
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-1
Page 57
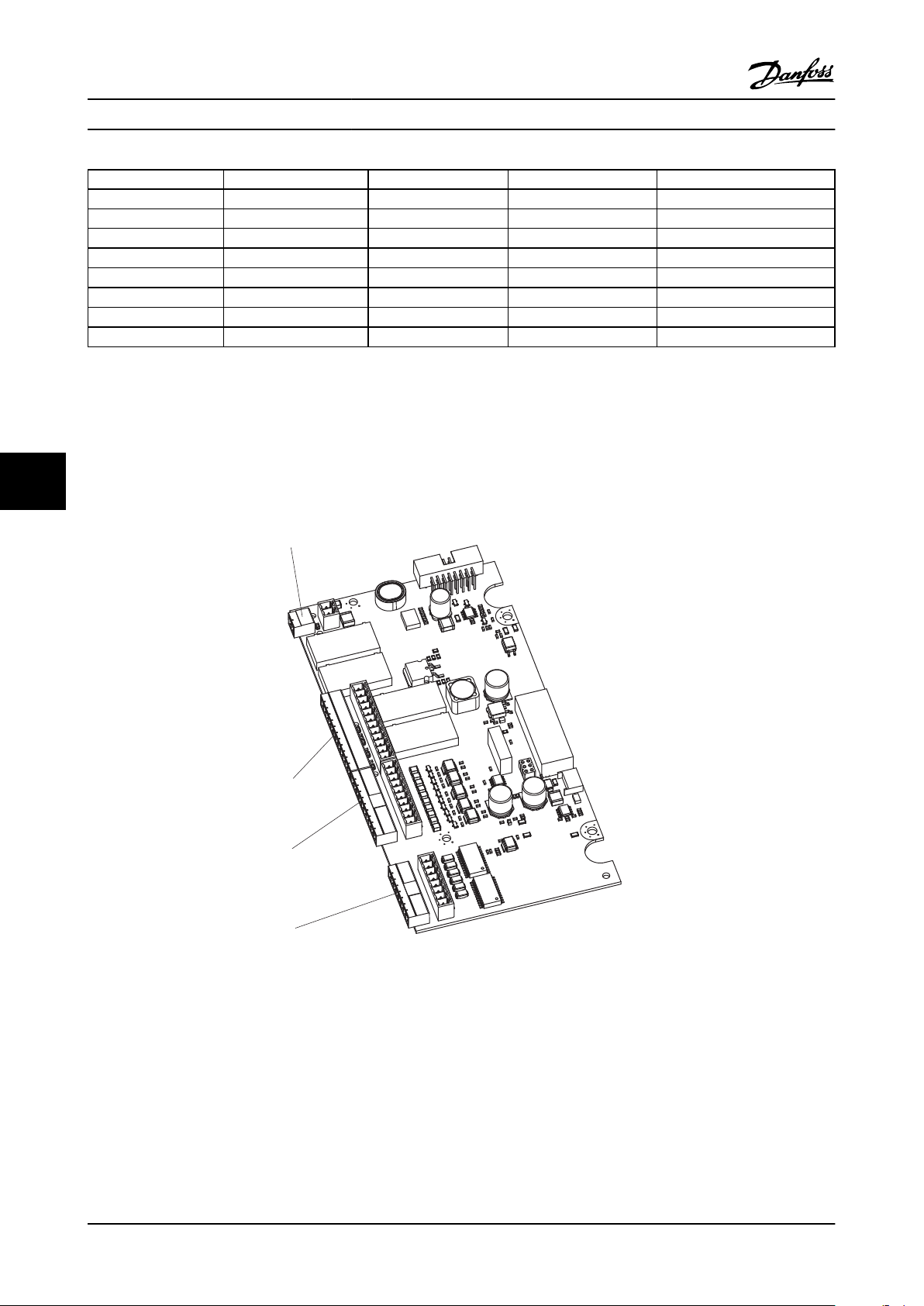
1
130BX232.10
2
3
4
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Parameter Parameter name Setting title Setting Function
5-01 Term 27 Mode Input 0 Customer Interlock
5-02 Term 29 Mode Output 1 Auto bypass
5-10 Term 18 digital input Start 8 Common run/stop
5-11 Term 19 digital input Run Permissive 52 Run Permissive
5-12 Term 27 digital input External Interlock 7 Customer Interlock
5-31 Term 29 digital output No Alarm 160 Auto bypass
5-40(0) Relay 1 function Start Command Active 167 Run Permissive
5-40(0) Relay 1 off delay Off Delay 0.00 S Run Permissive
Table 6.1 Parameter Group 5-** Factory Default Settings
6.1.2 ECB Control Card
The ECB control card (see Figure 6.2) provides input connector X57 for commanding bypass operation remotely and output
connector X59 for reporting the bypass mode of operation, either drive mode or running in bypass.
66
See Table 6.2 for ECB control card terminal types and functions.
1. Terminal X58
2. Terminal X56
3. Terminal X57
4. Terminal X59
6-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 58

9
8
7
6
5
4
2
1
3
4
1
3
2
10
12
11
TEST CONNECTOR
ECB
MK 110
EXTERNAL
6
7
8
3
5
4
2
1
2
1
24 V SUPPLY
BOARD
28
100
16
NC
NC
M3
(A2)
(A1)
(A1)
(A2)
M2
100
7
6
5
10
9
8
+ 24 V
RUNNING
+ 24 V
+ 24 V
15
SAFTY INTERLOCK
M2 STATUS
M3 STATUS
O.L. TRIP
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
O.L. RESET
BYPASS MODE
DRIVE MODE
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
MANUAL
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
BYPASS MODE ENABLE
BYPASS
OVERRIDE
LOAD
LOAD
CONNECTION
CUSTOMER
CUSTOMER
CONNECTION
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
18
COM
COM
COM
COM
COM
MOTOR
CONTACT
0-24 VDC
MAXIMUM 1 AMPS
DC RESISTIVE
22
CUSTOMER
O.L. RESET
BYPASS OVERRIDE
BYPASS
MODE ENABLE
CMS MOTOR SELECTED
DRIVE MODE
BYPASS MODE
40 mA MAX
24 VDC
NC
NC
CUSTOMER
INTERLOCK
SUPPLIED
SAFETY
TB1
100
(95)
(96)
M3
M2
OL1
19
20
21
(14)
(13)
(44)
(43)
X59
X57
X56
X58
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X56,X57,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
BLU
BLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
17
(A1)
(A2)
M1
BLU
BLU
BLU
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
130BX391.11
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6 6
Figure 6.2 ECB Control Card Terminal Connections
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-3
Page 59

Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Input Conn. Term. Function Type
1 Digital input for safety stop User supplied dry contact
2 Common User supplied dry contact
3 Factory use only
4 No function
5 Factory use only
X57
Output Conn. Term. Function
66
X59
Relay Output Term. Function
X56
6 Factory use only
7 Factory use only
8 Digital input for remote bypass enable User supplied dry contact
9 Digital input overrides system to Bypass Mode ignoring all
other inputs and commands, except for safety stop on
terminal 1.
10 Digital input for remote overload reset User supplied dry contact
1 Common for binary I/O
2 Common for binary I/O
3 No function
4 No function
5 Digital output indicates panel is in Drive Mode. 24 VDC digital output
6 Digital output indicates panel is in Bypass Mode 24 VDC digital output
7 Common for binary I/O
8 Common for binary I/O
1 N.O. contact for running in bypass or drive Relay output for user
2 N.O. contact for running in bypass or drive Relay output for user
3-12 Factory use only
User supplied dry contact
Table 6.2 ECB Card Terminals
6-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 60

130BX234.10
1
2
3
130BX235.10
130BX237.10
130BX236.10
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.3 ECB Drive or Bypass Selection
Use the LCP and display to switch between the motor running in drive mode or bypass when operating in local control. The
display in operating mode is shown below.
1. Press [Drive Bypass]. Display changes to show
bypass and drive mode options (shown in Step 2).
2. When running in drive mode, press [OK] on LCP
to activate bypass mode or press CANCEL to
remain in drive mode. In bypass, the motor will
run at full speed.
3. When running in drive mode, press [OK] on the
LCP to activate drive mode or press [Cancel] to
remain in bypass mode.
1 = Display
2 = Info key
3 = Drive/Bypass Option Key
6 6
4. Press [Status] to return to drive status display.
NOTE!
Pressing [Info] at any time displays tips and guidelines for performing the function currently activated.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-5
Page 61

130BX238.10
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
66
6-6 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 62

130BX239.10
130BX240.10
130BX241.10
130BX242.10
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.4 ECB Programming
Use the LCP and display for programming ECB functional options. All programming options appear in numbered
parameters. Parameters are arranged in groups by related functions. Programming is performed by accessing the
parameters through a menu and selecting from displayed options or entering numerical values. See the drives’ supporting
materials for detailed programming instructions.
Access parameters to program bypass functions in accordance with the following instructions:
1. Press [Main Menu] on the LCP to access parameter groups.
(Note that the memory function of the menu returns to the
most recently used function. Use [Back] to return to the main
menu index when necessary.)
2. Press [▲] or [▼] to scroll through parameter groups. A
dotted outline surrounds the selected group. Bypass options
are found in parameter group 31-** Bypass.
6 6
3. Press [OK] to enter the selected parameter group.
4. Press [▲] or [▼] to scroll through the parameter list.
5. Press [OK] again to enter programming mode, which allows
changing parameter options or data. Option is inverse
highlighted.
6. Press [▲] or [▼] to scroll through programmable options.
7. Press [OK] again to activate the selection or [Cancel] to
cancel.
8. For entering numeric values, press [►] or [◄] to select
numeric digit, then Press [▲] or [▼] to scroll through digit
numbers 0-9. Selected digit is inverse highlighted.
9. Press [OK] to activate the selection or [Cancel] to cancel.
10. Press [Status] to return to operational display data or [Back]
to return to parameter menu options.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-7
Page 63

Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.5 ECB Hand/OFF/Auto
General Information
The [Hand on], [Off Reset], and [Auto on] keys on the LCP control both the drive and bypass (see Figure 6.1). [Drive Bypass]
allows the user to locally select drive or bypass mode of operation. It does not necessarily start or stop the motor.
Prior to Enabling Hand/Off/Auto
Complete the start-up procedure to verify that motor rotation direction in bypass is correct and that the system is
•
ready in all respects for continuous full speed operation in bypass.
Programming Key Functions
For [Off Reset] and [Drive Bypass], Table 6.3 lists the parameters that select functions for the control keys. A password
protection can also be assigned in these parameters.
Operation
[Hand on] allows the user to start the motor locally from the LCP. Press the [Hand on] to start the motor locally
•
either in drive or bypass mode.
66
[Off Reset] allows the user to stop the motor locally from the LCP. Press the [Off Reset] to stop the motor locally,
•
either in drive or bypass mode.
[Auto on] allows the motor to be started remotely from digital input or serial communications. Press [Auto on] to
•
activate the remote motor start and stop from a digital input or serial communications in drive or bypass mode.
Press [Drive Bypass] to initiate the display to toggle between drive or bypass mode of operation. Press [OK] to
•
accept the change or [Cancel] to cancel the action.
Parameter No. Key Function
00-44 [Off Reset] This disables or enables the [Off Reset] key on LCP. (0) disabled, (1)
enabled, (2) password Default value is (1) enabled.
00-45 [Drive Bypass] This disables or enables the [Drive Bypass] key on LCP. (0) disabled,
(1) enabled, (2) password Default value is (1) enabled.
Table 6.3 LCP Control Keys Programming
ECB Mode of Operation
6.1.6
General Information
The ECB has four modes of operation: drive, bypass, auto bypass, and test. Each mode is selected through the LCP and
display. Bypass mode select can be accessed directly by pressing [Drive Bypass].
Prior to Enabling Mode of Operation
Complete the start-up procedure and verify motor rotation direction in bypass is correct and that the system is
•
ready in all respects for continuous full speed operation in bypass.
Press [Off Reset] to prevent operation of the motor.
•
Operation
Drive mode: The motor is connected to and controlled by the drive. Contactors M1 and M2 are closed while
•
contactor M3 is open. The motor will not run until a run command is present.
Bypass mode: The motor operates at full speed across the line when a run command is present. Contactor M3 is
•
closed and M1 and M2 are open.
Test mode: Test mode puts the panel into bypass mode and will automatically run in bypass. Contactor M1 is
•
closed, supplying power to the drive for test purposes while M2 is open. Contactor M3 controls the operation of
the motor in bypass, closed to run the motor, open to remove power. The control keys on the LCP will not control
the bypass until test mode is removed.
6-8 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 64

Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Auto bypass mode: When in drive mode, auto bypass is a timed interval that allows a fault condition in the drive
•
to activate running the motor in bypass without operator intervention.
Mode of Operation Select
Mode of operation is programmed through parameter group 31-** . See Table 6.4.
•
Par. No. Selection Function
31-00 Bypass Mode Selects source of motor power.
31-01 Bypass Start Time Delay Sets a delay time for starting in bypass that
31-02 Bypass Trip Time Delay Setting a value other than 0 sec. enables
31-03 Test Mode Activation Setting enabled puts bypass in test mode.
31-10 Bypass Status Word Read-only display, which shows the bypass
31-11 Bypass Running Hours Read only display which shows bypass
(0) Drive (drive mode) (1) Bypass (bypass
mode)
allows for external actions to take place prior
to line starting the motor.
0-60 sec. (default value is 5 sec.)
auto bypass. Bypass trip delay sets the delay
time before switching to bypass mode when
the drive has a fault.
0-300 sec. (default is 0 sec. = OFF)
See the manual for warnings and cautions.
(0) disabled (default value) (1) enabled
status in hex. See the next table for details.
0, 216-1 (default value is 0)
running hours.
6 6
Table 6.4 Bypass Parameter Functions
Bit
0 Test Mode The Test Mode bit will be true when the ECB is in Test Mode.
1 Drive Mode The Drive Mode bit will be true when the ECB is in Drive Mode.
2 Automatic Bypass Mode The Automatic Bypass Mode bit will be true when the ECB is in Automatic Bypass Mode.
3 Bypass Mode The Bypass Mode bit will be true when the ECB is in Bypass Mode.
4 Reserved This bit is reserved for future use.
5 Motor Running from Bypass/Drive The Motor Running from Bypass/Drive Bit will be true when the motor is running from
either the drive or the bypass.
6 Overload Trip The Overload Trip Bit will be true when the ECB detects an overload trip.
7 M2 Contactor Fault The Contactor Fault Bit will be true when an M2 Contactor Fault is detected.
8 M3 Contactor Fault The Contactor Fault Bit will be true when an M3 Contactor Fault is detected.
9 External Interlock The External Interlock Bit will be true when an External Interlock fault is detected.
10 Manual Bypass Override The Manual Bypass Override Bit will be true when the Manual Bypass Override input is true.
Table 6.5 Parameter 31-10 Bypass Status Word Bit Definitions
Description
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-9
Page 65
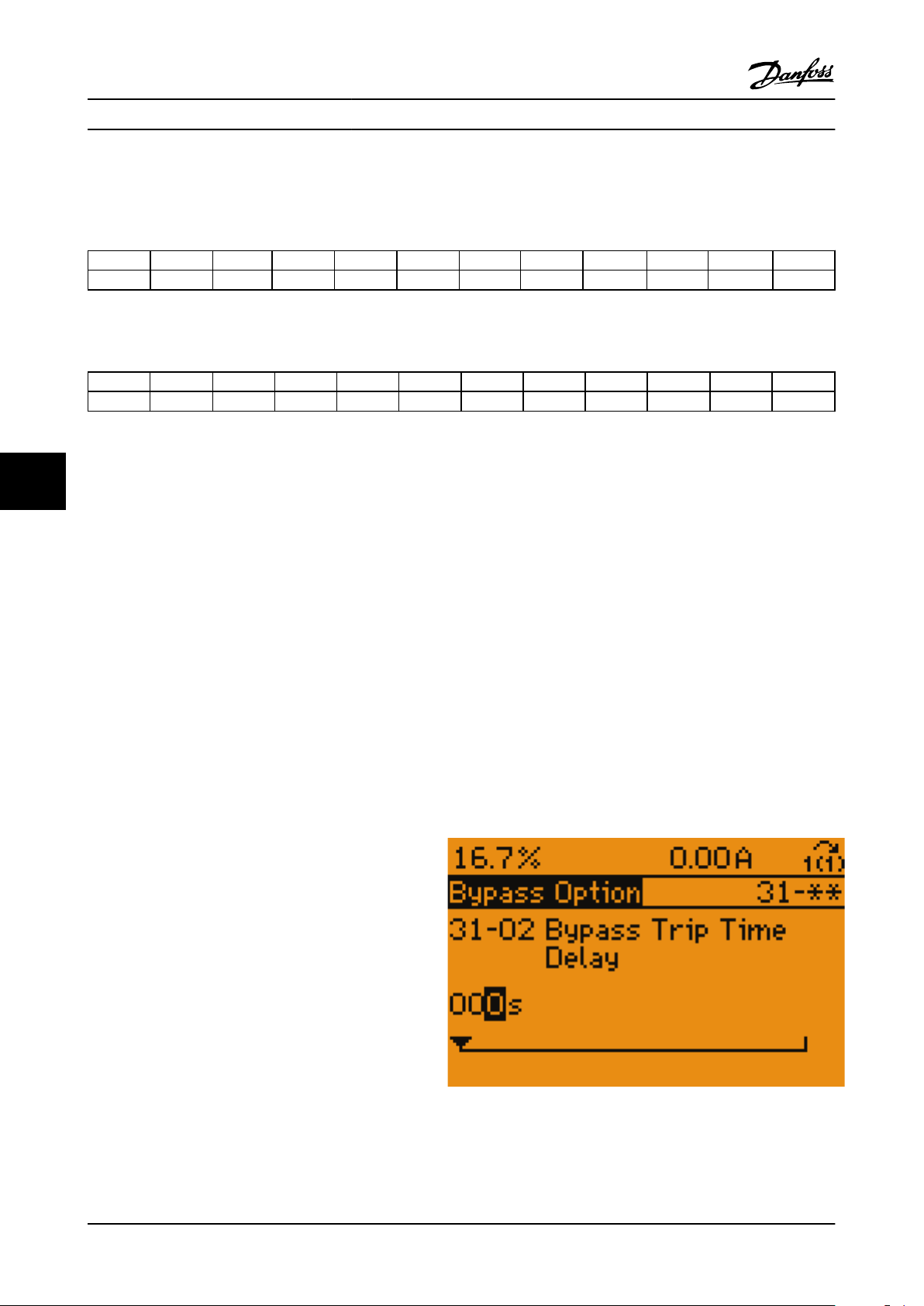
130BX243
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.7 Bypass Status Word Bit Examples
1. Motor running and bypass in drive mode. Status word 22 hexadecimal converts to 00000100010 binary.
Bit 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Binary 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
1. External interlock fault (open) and bypass in bypass mode. Status word 208 hexadecimal converts to 01000001000
binary.
Bit 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0
Binary 0 1 0 0 0 0 0 1 0 0 0
6.1.8 ECB Auto Bypass
66
General Information
Auto bypass allows a fault condition in the drive to
activate running the motor in bypass without operator
intervention. Activation of the function is through setting
timer start parameters in the drive programming. Fault trip
and running in bypass are reported through the drive
display, digital outputs, and serial communications. In
addition, the independently powered ECB card is available
to report bypass status when the drive is inoperable
(control card operative) through its serial communications
or digital outputs.
Prior to Enabling Auto Bypass
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Operation
With the auto bypass function enabled, a fault
•
signal from the drive activates the auto bypass
timer.
If the fault clears before the time delay is
•
complete, the motor remains operating in drive
mode. This allows temporary faults, such as a
momentary under or over voltage, to clear
without transferring the system to bypass.
If the timer completes its cycle before the fault
•
clears, the panel trips into bypass mode and the
motor runs at constant full speed from line input
voltage.
In bypass, the motor will stop:
•
- if the drive receives a remote stop
command
- local stop ([Off]) on the LCP is pressed
•
Auto Bypass Function Setup
Enable auto bypass by changing parameters in group 31 in
the drive extended menu.
•
•
Figure 6.3 Bypass Trip Time Delay
- a remote start command is removed
- a safety is open
- motor overload is tripped
Once auto bypass is activated, the only way to
reset the unit back to drive mode is by operator
intervention. Ensure that the fault has been
cleared, then press [Drive Bypass] and select drive
mode.
31-01, Bypass start time delay. Setting the timer at
anything other than 0 time activates start delay
in bypass. Leave at 30 sec. default or set as
desired up to 60 sec.
31-02, Bypass trip time delay. Setting the timer at
anything other than 0 time activates auto bypass.
Leave at 5 sec. default or set as desired up to 60
sec.
6-10 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 66

130BX244.10
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Run Permissive Function Setup
•
•
•
Disable Run Permissive
Figure 6.4 Drive Display with Bypass Start Time Delay Active
•
See the drive manual or support materials for
programming and wiring to the drive control
terminals.
Wire the output run request to the drive output
terminals selected, and program the terminals for
run request.
Wire the input run command to the drive input
terminals selected, and program the terminals for
run permissive.
Disable run permissive through the drive
parameters and terminal programming.
ECB Run Permissive
6.1.9
General Information
With run permissive active, the drive sends a run request
and waits for a remote response before notifying the
motor to start. The response indicates the system is safe to
operate. Run permissive operates from the LCP hand/off/
auto select in drive or bypass mode. Run permissive is
enabled by programming in the drive parameters.
Prior to Enabling Run Permissive
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Verify that the drive is programmed for the run
•
permissive function. See the drive support
materials for programming the run permissive
function.
Operation
A start command can be initiated from local hand
•
start, serial communications, or a remote auto
start signal through digital drive input terminals.
In response to the start command, an output
•
request is sent from the programmable drive
relay to the external equipment (to activate a
valve or damper, for example).
When a return run signal on the digital input is
•
received, the motor is started in either drive or
bypass, depending upon which mode is active.
6.1.10
General Information
An overload device provides overcurrent protection for the
motor when running in bypass. The thermally activated
overload monitors motor current and trips to remove
power to the motor if a sustained overcurrent condition
exists. A Class 20 overload is standard with a variable
setting for motor current. Test and reset buttons are also
provided. In drive mode, the drive provides current sensing
and trip protection. Fuses provide quick action for high
over current conditions.
Prior to Enabling Overload
ECB Overload
Verify that the overload current dial setting
•
matches the motor FLA rating on the motor
nameplate.
If the motor FLA is greater or less than the range
•
of the current dial, reconfirm that the motor HP
and voltage are within the option panel (and
drive) rating. If greater than the FLA rating,
replace the panel with one of a proper rating.
CAUTION
MOTOR DAMAGE!
Repeated attempts to reset overload can cause motor
damage. Correct the overload condition and let the
overload and motor return to normal operating
temperature before resetting. See motor manufacturer’s
recommendations for time between start attempts. Failure
to correct the overload condition and let the motor return
to normal operating temperature could cause motor
damage.
Operation
Overloads and motors are both rated by class. The class is
defined by the NEC to determine the maximum time to
trip. A Class 20 overload, for example, has a typical trip
6 6
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-11
Page 67

T1
T2 T3
97NO
98NO 95NC
96NC
10
20
30
RESET
TEST
MANUAL
AUTO
TRIP
5
130BX229.10
Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
66
delay of 20 sec. or less at 600% current and normal
operating temperature. This allows for high motor inrush
current for 20 sec. while the motor is ramping up to
synchronous speed. The trip time, however, is based on
the percentage of overload. The higher the overload, the
shorter the time.
X57 terminals 1 and 2 allows the unit to operate when no
safety input is connected. This jumper must be removed
when connecting in a safety interlock circuit.
Safety Interlock Function Setup
Remove factory-installed jumper between ECB
•
connector X57 terminals 1 and 2 on drive control
terminals.
Wire safety input to connector X57 terminals 1
•
and 2.
For technicians familiar with connecting to drive
•
terminals 12 and 27 for safety interlock, be aware
that ECB bypass operation will NOT stop with the
external fault report. Use terminals 1 and 2 on
Figure 6.5 Sample Overload Device
6.1.12
connector X57, as indicated, for bypass control.
ECB Common Run/Stop
Overload Function Setup
Set the overload current dial to the FLA of the
•
motor. DO NOT add the service factor of the
motor into the setting. A service factor of 1.2 x
FLA is designed into the overload.
Pressing the test pushbutton verifies the
•
operation of the overload. The overload should
trip when pressed. Use the reset pushbutton to
reset the overload after testing.
Reset is used to reset the overload after it trips. If
•
the overload is still hot, wait until the motor
reaches normal operating temperature before
resetting. The overload offers a manual (hand) or
auto reset selection. It is highly recommended to
operate in the manual factory setting to prevent
the risk of damage to the motor.
General Information
The common run/stop function provides remote run and
stop control of the motor while in either drive or bypass.
Without common run/stop, the motor would automatically
run at full speed whenever the bypass is activated. The
remote signal provides drive control as well as bypass
control, making this one input common to both. Common
run/stop is enabled by factory default. When used with the
run permissive function, common run/stop permits run
request operation in bypass.
Operation
A user supplied remote run command wired to drive
terminals 13 and 18 initiates remote drive or bypass
operation. Common run/stop can also be activated by
hand on the LCP or through serial communication.
Operation in either drive or bypass is determined by drive
or bypass mode selection, not the run/stop command.
6.1.11
General Information
The safety interlock feature prevents the drive or bypass
from operating. Only a fire mode command to run
overrides this function. For operation in drive or bypass
mode, the safety external interlock input contact must be
closed. External inputs include, but are not limited to, high
and low pressure limit switches, fire alarm, smoke alarm,
high and low temperature switches, and vibration sensors.
Operation
ECB Safety Interlock
Prior to Enabling Common Run/Stop
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Common Run/Stop Setup
Wire a remote run/stop to drive input terminals
•
13 and 18 (default run input). Ensure that
parameter 18 is programmed for run (default
setting).
When an external safety input closes on ECB terminals 1
and 2 on connector X57, the option panel is in operational
mode. When open, power to the motor is disabled. The
bypass ignores all run commands except for fire mode
operation, when applicable. The drive display indicates
alarm 221, bypass interlock, meaning the problem is
external to the drive. A factory installed jumper between
6-12 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 68

Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
6.1.13 ECB Advanced Fire Mode
General Information
Drive operation in advanced fire mode is programmable. In
the event the drive does not function, the motor is
operated in bypass at full speed. Fire mode is intended to
ignore common safety and overload inputs in emergency
situations. The fire mode function is built-in. See the drive
support materials for programmable options.
Prior to Enabling Fire Mode
Complete the start-up procedure to verify motor
•
rotation direction in bypass is correct and that
the system is ready in all respects for continuous
full speed operation in bypass.
Verify that the drive is programmed for the fire
•
mode function. See the drive support materials
for programming the fire mode function.
Operation
Activation of fire mode is accomplished by
•
programming the drive for fire mode.
When activated, the ECB ignores safety circuits
•
and motor overload.
Fire mode is deactivated only when the
•
command is removed or the unit fails.
Fire mode status can be reported through serial
•
communications or drive output.
Fire Mode Function Setup
Program drive for fire mode.
•
If required, program a drive output for fire mode
•
status.
See the drive support materials for programming
•
the fire mode function.
The drive monitors the ECB card communication and
detects when communication stops. An ECB card failure or
communication error could cause this. Contact Danfoss
using the phone number on the back of this manual for
technical support if this happens. The phone number can
also be found on the label inside the panel cover.
Fault Reporting Function Setup
Automatic function. No set up required.
•
6 6
6.1.14
General Information
The ECB monitors bypass contactors M2 and M3 and
reports failures to the drive for display and external
reporting. The drive also monitors the ECB card for bypass
communication errors.
Operation
ECB detected faults are reported by the drive in three
ways: Warnings and alarms are displayed on the keypad
display, through serial communication, or through output
relays. The drive provides a form-C fault relay on terminals
01, 02, and 03. The fault contacts are fail-safe, meaning
that if power is removed the contacts close and a fault
condition is reported.
ECB Fault Reporting
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 6-13
Page 69

Electronically Controlled B... Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
66
6-14 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 70

Start Up Troubleshooting Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
7 Start Up Troubleshooting
7.1.1 Option Panel Alarm and Warnings
Code
Number
220 Overload Trip Motor overload has tripped. Indicates excess motor load. Check motor and driven load. To reset,
221 Bypass Interlock Bypass interlock has opened and caused the motor to stop. Correct the problem. Depending on
222 M2 Open Failed ECB: The contactor that connects the drive to the motor failed to open. The motor can not be
223 M2 Close Failed ECB: The contactor that connects the drive to the motor failed to close. The motor can not be
224 M3 Open Failed ECB: The contactor that connects the motor to the power line has failed to open.
226 M3 Close Failed ECB: The contactor that connects the motor to the power line has failed to close. The motor can
227 Bypass Com Error Communication between the main control card and the bypass option has been lost. Motor control
228 APU Low Voltage The Panel Power Supply has failed, or there is a power problem.
229 Motor Disconn. Terminal 3 on connector X57 of the ECB control card shows an open. This generally means that
Table 7.1 Panel Alarms and Warnings (ECB only)
DisplayText
Bypass Run Starts in: Indicates the number of sec. until the motor will be started in bypass. This time delay
Bypass Activates in: Indicates the number of sec. left until the system automatically activates Bypass Mode.
Title Definition
press [Off Reset]. Then, to restart the system, press [Auto on] or [Hand on].
the setting of parameter 14-20, the system will either automatically reset this alarm or require the
[Off Reset] key to be pressed.
operated.
operated.
not be operated.
lost. It will be possible to run the motor using Manual Bypass Override.
neither motor has been selected in contactor motor select. Select a motor.
Definition
can be adjusted using parameter 31-01.
Time delay can be adjusted using parameter 31-02.
7 7
Table 7.2 Panel Status Display (ECB only)
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 7-1
Page 71

Start Up Troubleshooting Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Symptom Possible cause Test Solution
Missing input power See startup guide for voltage checks. Correct voltage at source.
Missing or open fuses or circuit
breaker tripped
Loose connections in panel Perform pre-startup check for loose
Missing customer connections Missing customer connections can cause
Loose customer connections Check all customer connections for
Customer wires incorrectly terminated See customer connection drawing and
No function
Improper voltage applied See pre-startup check list. Correct the voltage mismatch. This
77
Incorrect power connections See pre-startup check list to see if motor
Power disconnect open Verify that the disconnect or circuit
Operator switches off Verify that operator devices are in
OL tripped A tripped OL will disable the motor from
Improper voltage applied See pre-startup check list and correct
Incorrect power connections. Motor and line voltages swapped. Make
Power ground fault Check motor and panel power wires to
Open power
fuses or
circuit
breaker trip
Phase to phase short Motor or panel has a short phase to
Motor overload Motor is overloaded for the application. Perform startup and verify motor
Drive overload Drive is overloaded for the application. Perform startup and verify that drive
Loose connections Perform pre-startup check for loose
See open fuses and tripped circuit
breaker in this section for possible
causes.
connections.
the safety circuit or start signal to be
open.
tightness. Loose customer connections
can act like an open circuit.
make sure wires are connected to correct
terminals.
and power leads were swapped.
breaker is closed.
operating position per startup
procedures.
running. Verify that OL relay is in the
normal operating position per the
manual.
improper voltages.
sure the line in and motor out are on
the correct terminals. See pre-startup
check list.
ground.
phase. Check motor and panel phase to
phase for shorts.
connections.
Reset circuit breaker. If fuses, check for
opens with power removed from panel.
Tighten loose connections in the panel.
See customer connections and make
sure all applicable connections are
made or jumpers installed, especially
customer interlock.
Tighten loose customer connections.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
could potentially damage the panel.
Use caution when applying power.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Set switches to the correct position.
Perform pre-startup checklist and set
OL per instructions.
Correct voltage mismatch. This could
potentially damage the panel. Use
caution when applying power.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Eliminate any ground faults detected.
Eliminate any shorts detected.
current is within specifications. If motor
current is exceeding nameplate FLA,
reduce the load on the motor.
current is within specifications. If not,
reduce the load on the motor.
Tighten loose connections.
Table 7.3 Fault Table
7-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 72

Start Up Troubleshooting Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Symptom Possible cause Test Solution
Repeated
fuse or circuit
breaker fault.
Open control
fuse
Application problem Perform startup procedures. Check
panel output motor current at full
speed and check for excessive over
current.
Panel problem Perform startup procedures. Check
panel input current at full load and
verify it is within acceptable range.
Power problem Monitor incoming power for surges,
sags and overall quality.
Motor problem Test motor for correct function. Repair or replace motor if a problem is
Improper voltage applied See pre-startup check list. Correct voltage mismatch. This could
Customer wires incorrectly terminated See the customer connection drawing
and make sure the wires are connected
to the correct terminals.
Control ground fault Check all control wires for a short to
ground.
Control short Check control wires for a short in
supply voltage.
Improper voltage applied See pre-startup check list. Correct voltage mismatch. This could
If current is too high, reduce the load
on the motor.
If current is too high, reduce the load
on the motor.
Correct any problems found.
found.
potentially damage the panel. Use
caution when applying power.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Correct any ground faults found. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Correct any shorts. This could
potentially cause damage to the panel.
potentially damage the panel. Use
caution when applying power.
7 7
Open SMPS
fuse
Motor
rotation
incorrect
Customer wires incorrectly terminated See the customer connection drawing
and make sure the wires are connected
to the correct terminals.
Control ground fault Check all control wires for a short to
ground.
Control short Check control wires for a short in
supply voltage.
Rotation incorrect in bypass, drive or
both
Motor rotation is backwards in drive
mode, bypass mode, or both.
Correct any wrong connections. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Correct any ground faults found. This
could potentially cause damage to the
panel.
Correct any shorts. This could
potentially cause damage to the panel.
Perform motor rotation procedure in
4 Start Up.
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 7-3
Page 73
Start Up Troubleshooting Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Symptom Possible cause Test Solution
Motor overloaded Motor is drawing too much current for
the application.
Loose connections Look for signs of overheating on
Overload trips
OL not set correctly An improperly set OL can cause the OL
Contamination Remove contactor and check for
Contactor fails
to pull in
77
Contactor fails
to drop out
Mains current
imbalance
greater than
3%
Motor current
imbalance
greater than
3%
Defective coil Compare coil resistance to contactor
Auxiliary contact binding action Remove auxiliary contacts and test
Contamination Remove the contactor and check for
Defective coil Compare coil resistance to functional
Auxiliary contact binding action Remove auxiliary contacts and test
Problem with mains power Rotate incoming power leads into
Problem with option panel Rotate incoming power leads into
Problem with motor or motor wiring Rotate outgoing motor leads one
Problem with option panel Rotate outgoing motor leads one
connections to OL.
to trip too soon. See pre-startup
procedure for correct setting.
contamination.
specification. Inspect the coil for signs
of overheating and damages.
contactor action.
contamination.
contactors of the same size.
contactor action.
option panel one position; A to B, B to
C, and C to A.
option panel one position; A to B, B to
C, and C to A.
position; U to V, V to W, and W to U.
position; U to V, V to W, and W to U.
Perform startup and verify motor current
is within specifications. If not, reduce the
load on the motor.
Perform pre-startup check for loose
connections and tighten. Replace any
overheated components and wires.
Set correct motor current on OL.
If contamination is found, repair or
replace.
If readings are not the same or if there
are visible signs of damage, replace the
coil or contactor.
If contactor operates with auxiliaries
removed, replace auxiliary contacts.
If contamination is found, repair or
replace.
If readings are not the same or there are
visible signs of damage, replace the coil
or contactor.
If the contactor operates with auxiliaries
removed, replace auxiliary contacts.
If the imbalanced leg follows the wire, it
is a power problem. Causes can vary.
Contact an electrician or power expert
for a solution.
If the imbalanced leg stays on the same
option panel input terminal, it is a
problem with the option panel. Contact
the factory for assistance.
If the imbalanced leg follows the motor
lead, the problem is in the motor or
wiring to the motor. Causes can vary.
Contact an electrician or motor expert
for a solution.
If the imbalanced leg stays on the same
option panel output terminal, it is a
problem with the option panel. Contact
the factory for assistance.
7-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 74

Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
8 Appendix
8.1.1 Dimensions
A 8.86 [225.0] 9.11 [231.4] 9.57 [243.0] 9.57 [243.0] 12.69 [322.3] 12.69 [322.2] 15.13 [384.3] 15.13 [384.2]
A1 6.66 [169.1] - - - - - - -
B 29.92 [759.9] 41.77 [1061.0] 34.33 [872.0] 43.23 [1098.0] 39.58 [1005.4] 54.38 [1381.4] 45.79 [1163.1] 59.64 [1514.9]
C 11.45 [290.9] 15.94 [405.0] 11.23 [285.2] 17.70 [449.6] 14.78 [375.5] 17.99 [457.0] 14.78 [375.4] 18.01 [457.5]
D - 1.10 [28.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.59 [15.0]
a 5.51 [140.0] 7.87 [200.0] 7.87 [200.0] 7.87 [200.0] 10.63 [270.0] 10.63 [270.0] 12.99 [330.0] 12.99 [330.0]
b 28.80 [731.5] 41.02 [1042.0] 32.13 [816.0] 41.18 [1046.0] 37.32 [948.0] 51.89 [1318.0] 43.54 [1106.0] 57.09 [1450.0]
c 0.27 [6.8] 0.27 [6.8] 0.33 [8.5] 0.33 [8.5] 0.33 [8.5] 0.33 [8.5] 0.33 [8.5] 0.33 [8.5]
d 0.39 [10.0] 0.43 [11.0] 0.47 [12.0] 0.39 [10.0] 0.47 [12.0] 0.59 [15.0] 0.47 [12.0] 0.59 [15.0]
e 0.49 [12.5] 0.65 [16.5] 0.72 [18.4] 0.61 [15.5] 0.91 [23.0] 0.75 [19.0] 0.94 [24.0] 0.79 [20.0]
f 0.27 [6.9] 0.27 [6.8] - - - - - -
g 0.47 [12.1] 0.47 [12.0] - - - - - h 0.49 [12.5] 0.65 [16.5] - - - - - -
j 0.31 [8.0] 0.31 [8.0] - - - - - -
k 0.32 [8.0] 0.31 [8.0] - - - - - -
P2 NON-
BYPASS
P2 BYPASS
P3 NON-
BYPASS
P3 BYPASS
P4 NON-
BYPASS
P4 BYPASS
P5 NON-
BYPASS
P5 BYPASS
8 8
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-1
Page 75

a
b
k
Øf
Øg
A
c
d
ØD
e
B
C
j
h
SEE DETAIL A
SEE DETAIL B
2X DETAIL A
SCALE 1.000
2X DETAIL B
SCALE 1.000
130BX392.11
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
8.1.2 Mechanical Diagrams
88
Figure 8.1 P2 Bypass
8-2 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 76

A1
a
b
k
j
f
g
c
d
B
h
C
e
SEE DETAIL A
SEE DETAIL B
2X DETAIL A
SCALE 1.000
2X DETAIL B
SCALE 1.000
A
130BX393.10
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.2 P2 Non-bypass
8 8
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-3
Page 77

A
B
b
ae
c
d
ØD
C
SEE DETAIL A
4X DETAIL A
SCALE 1.000
130BX394.10
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
88
Figure 8.3 P3 P4 P5 Bypass
8-4 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 78

ØD
b
ae
c
d
A
B
C
SEE DETAIL A
4X DETAIL A
SCALE 1.000
130BX395.10
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.4 P3 P4 P5 Non-bypass
8 8
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-5
Page 79

INPUT
POWER
EARTH
GROUND
(T2)
(T3)
(T1)
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)(L2)
(L3)
(L2)
(L3)
(L1)
(L1)
2T1
2T2
2T3
M2
M3
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR
(L1)
(L2)
(L3)
1T1
1T3
1T2
OL1
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
T1
T3
T2
GROUND
EARTH
100
28
MK902
2
6
24 V DC SMPS
MK901
1
5
MK903 MK904
374
8
- +
91
CONTROL BOARD T. B.
ADJUSTABLE FREQUENCY
60
100
27 29
DRIVE
(AFD)
90
32 33 37
EARTH
GROUND
W/98
U/96
V/97
92
20
94
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLK 14 AWG
(T3)(L3)
(T1)
(T2)
(L1)
(L2)
M1
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
M3
115VAC
TRANSFORMER
149
CONTROL
600V
150
F13A
WHT
158
155
153
153
153
3CR
2CR
152
1CR
154
BLK 14 AWG
GRN/YEL
151
T1
600V
F13B
(A1)
(A2)
(A1)
M1
(A1)
M2
(A2)
(A2)
BLUE
(6)
(4)
(4)
(6)
(4)
(6)
GD
24V
GD
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
X1
H4
H3
H1
H2
X3
X2
1L3
1L1
1L2
FUSIBLE
L1
L3
L2
DISCONNECT
DF15
F15B
F15C
F15A
MAIN
GRN/YEL
(3)(2)(1)
SEE HIGH POT
83
018402 03
BLUE
BLUE
04 05 06
12 13 18 19
FACTORY SAFETY INTERLOCK JUMPER (ONLY FUNCTIONAL IF ORDERED)
4CR
(2)
(1)
4CR
(C)
(NO)
RED
TO EMB2 CONNECTOR MK103
TO EMB2 CONNECTOR MK103
TO PAGE 2
2L3
2L1
2L2
F16A
F16C
F16B
3L3
3L1
3L2
(4)(5)(6)
SEE HIGH POT
FOR DRIVE INPUT FUSE
REFER TO THE DRIVE
MANUAL
130BX396.11
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
8.1.3 Typical Wiring Diagrams
88
Figure 8.5 EMB2 with Control Relay, Part 1
8-6 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 80

(7)
3CR
(8)
(7)
(8)
2CR
(8)
1CR
(7)
1-2
CONTACT
5-6
7-8
3-4
TEST
X
X
X
X
X
BYPASSOFFDRIVE
X
X INDICATES CONTACT CLOSED
CONTACT SEQUENCE CHART FOR S1
POSITION
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X55,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
4
3
M1, M2, AND M3
10
7
9
8
4
6
5
MK 106
EMB2
MK 110
MK 101
4
3
2
7
5
6
8
3
1
2
O.L. RELAY
EXTERNAL
1
2
3
4
1
2
MK 107
1
MK 105
2 3 54 6
MK 100
7
6
5
10
8
9
7
10
12
11
9
24 V SUPPLY
CONTACT
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CONTACTORS
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
5
D/O/B/T SWITCH
BOARD
4
321
ON
S100
28
100
M3
73
72
71
70
CR9
RL6
S1
30
(3)
(4)
31
(5)
(6)
S1
40
94
91
TO DRIVE
28
M3
42
M2
33
34
M2
91
90
94
92
83
84
60
RL2
NC
PL2
R
X55
X59
BLUE
100
OL1
(95)
(96)
35
30
BLUE
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
24 VDC, 1 A
RESISTIVE LOAD
MAXIMUM
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
JUMPERED
FACTORY
M3
27
(8)
S1
(7)
S1
91
27
(2)
(1)
100
94
BLUE
(13)
(14)
(32)
(31)
(31)
(32)
43
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
8
NC
NC
NC
DRIVE
MK 103
14
11
13
12
NC
NC
NC
NC
M2
(34)
(33)
M3
(34)
(33)
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
3 4
S105
1
2
ON
(X2)
(X1)
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
12
8
11
9
10
14
13
123
4
162738495101627384
9
MK106
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
9
11
10
12
4321
ON
MK107
MK100
MK105MK103
S105
130B7290
REFERENCE T.B. TERMINAL NUMBERS
S105
1 2
ON
TO SMPS
CONTROL BOARD
(10 POS. TB)
TEST CONNECTOR
1
M2
ALL OFF NO AUTO BYPASS (FACTORY DEFAULT)
AUTOMATIC BYPASS TIME SELECT
ALL ON 15 SEC.
ONLY # 3 ON 300 SEC
ONLY # 2 ON 60 SEC.
ONLY # 1 ON 30 SECONDS
3 4
S100
1
2
ON
CUSTOMER SETTING
NO FUNCTION
NO FUNCTION
RUN PERMISSIVE
COMMON RUN/STOP
4321
ON
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
MK101
TEST CONNECTOR
MK110
S100
130B7290
EMB2 BOARD
CONTACT CLOSED
MOTOR ON BYPASS
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
FIREMANS OVERRIDE STATUS
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
(COMMON RUN/STOP)
DAMPER END SWITCH
RUN PERMISSIVE
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
FIREMANS OVERRIDE CONTACT
CONTACTS SHOWN
IN FAULT POSITION
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
INTERLOCK
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED SAFETY
REPLACE WITH
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
MOTOR ON DRIVE
INDICATES
DRIVE FAULT STATUS
DAMPER MOTOR CONTROL
(CONTACT)
130BX401.12
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.6 EMB2 with Control Relay, Part 2
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-7
8 8
Page 81

INPUT
POWER
EARTH
GROUND
MAIN
L1
L3
L2
DISCONNECT
DS1
(T2)
(T3)
(T1)
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)(L2)
(L3)
(L2)
(L3)
(L1)
(L1)
2T1
2T2
2T3
M2
M3
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR
(L1)
(L2)
(L3)
1T1
1T3
1T2
OL1
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
T1
T3
T2
GROUND
EARTH
100
28
MK902
2
6
24 V DC SMPS
MK901
1
5
MK903 MK904
374
8
- +
91
CONTROL BOARD T. B.
ADJUSTABLE FREQUENCY
60
100
27 29
DRIVE
(AFD)
90
32 33 37
EARTH
GROUND
W/98
U/96
V/97
92
20
94
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLK 14 AWG
(T3)(L3)
(T1)
(T2)
(L1)
(L2)
M1
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
BLUE
GD
24V
GD
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
1L3
1L1
1L2
GRN/YEL
(3)(2)(1)
SEE HIGH POT
83
018402 03
BLUE
BLUE
04 05 06
12 13 18 19
FACTORY SAFETY INTERLOCK JUMPER (ONLY FUNCTIONAL IF ORDERED)
TO EMB2 CONNECTOR MK103
TO EMB2 CONNECTOR MK103
TO PAGE 2
2L3
2L1
2L2
F16A
F16C
F16B
3L3
3L1
3L2
(4)(5)(6)
SEE HIGH POT
FOR DRIVE INPUT FUSE
REFER TO THE DRIVE
MANUAL
130BX397.12
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
88
Figure 8.7 EMB2, Part 1
8-8 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 82
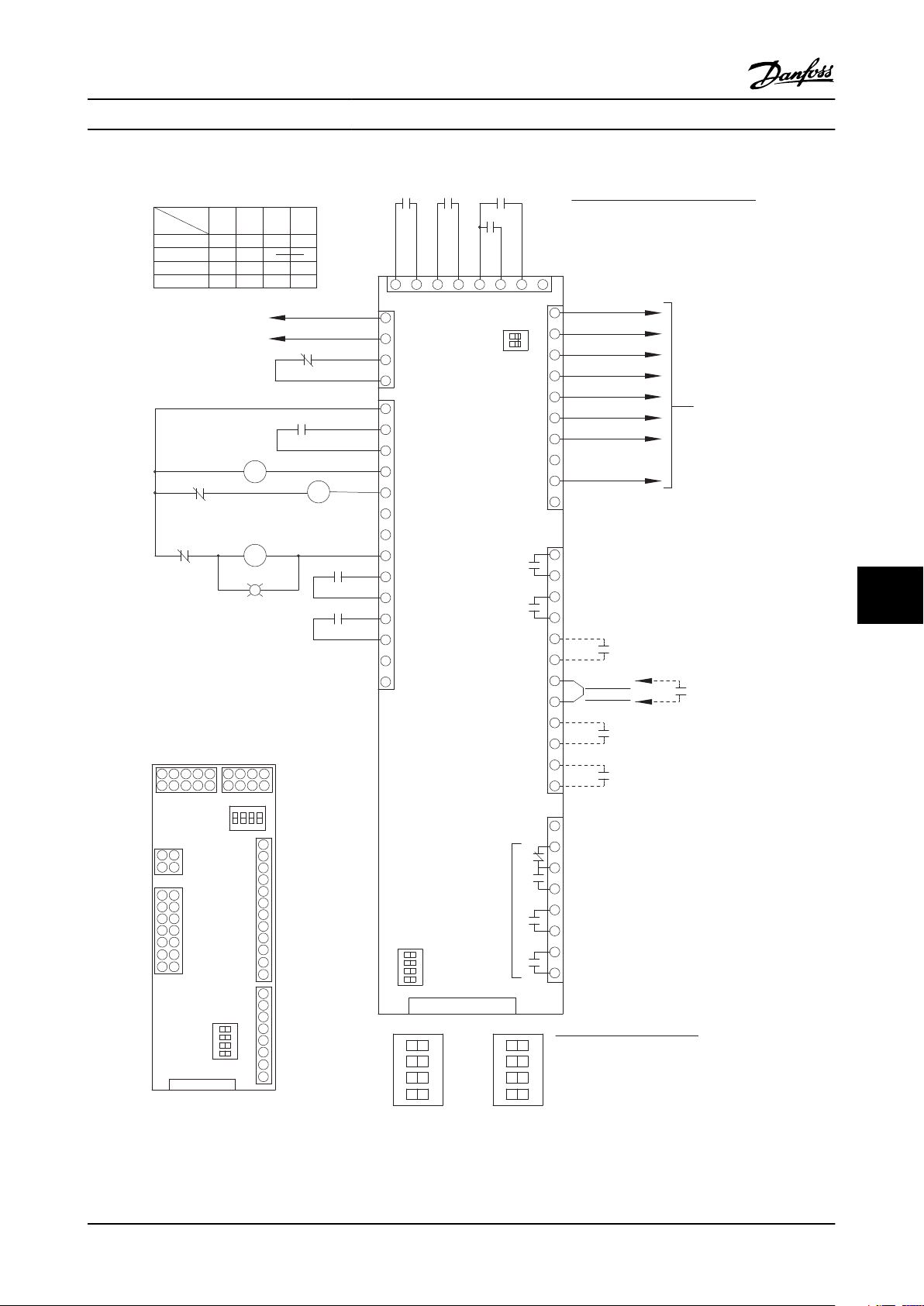
(A2)
M3
(A1)
(A2)
(A1)
M2
(A1)
M1
(A2)
1-2
CONTACT
5-6
7-8
3-4
TEST
X
X
X
X
X
BYPASSOFFDRIVE
X
X INDICATES CONTACT CLOSED
CONTACT SEQUENCE CHART FOR S1
POSITION
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X55,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
4
3
M1, M2, AND M3
10
7
9
8
4
6
5
MK 106
EMB2
MK 110
MK 101
4
3
2
7
5
6
8
3
1
2
O.L. RELAY
EXTERNAL
1
2
3
4
1
2
MK 107
1
MK 105
2 3 54 6
MK 100
7
6
5
10
8
9
7
10
12
11
9
24 V SUPPLY
CONTACT
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CUSTOMER
CONNECTIONS
CONTACTORS
1
2
3
4
6
7
8
5
D/O/B/T SWITCH
BOARD
4321
ON
S100
28
100
M3
73
72
71
70
CR9
RL6
S1
30
(3)
(4)
31
(5)
(6)
S1
40
94
91
TO DRIVE
28
M3
42
M2
33
34
M2
91
90
94
92
83
84
60
RL2
NC
PL2
R
X55
X59
BLUE
100
OL1
(95)
(96)
35
30
BLUE
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
24 VDC, 1 A
RESISTIVE LOAD
MAXIMUM
RESISTIVE LOAD
24 VDC, 1 A
MAXIMUM
JUMPERED
FACTORY
M3
27
(8)
S1
(7)
S1
91
27
(2)
(1)
100
94
BLUE
(13)
(14)
(32)
(31)
(31)
(32)
43
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
8
NC
NC
NC
DRIVE
MK 103
14
11
13
12
NC
NC
NC
NC
M2
(34)
(33)
M3
(34)
(33)
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE/WHT
BLUE
BLUE
BLUE
3
4
S105
1
2
ON
(X2)
(X1)
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
12
8
11
9
10
14
13
123
4
162738495101627384
9
MK106
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
9
11
10
12
4321
ON
MK107
MK100
MK105MK103
S105
130B7290
REFERENCE T.B. TERMINAL NUMBERS
S105
1 2
ON
TO SMPS
CONTROL BOARD
(10 POS. TB)
TEST CONNECTOR
1
M2
ALL OFF NO AUTO BYPASS (FACTORY DEFAULT)
AUTOMATIC BYPASS TIME SELECT
ALL ON 15 SEC.
ONLY # 3 ON 300 SEC
ONLY # 2 ON 60 SEC.
ONLY # 1 ON 30 SECONDS
3
4
S100
1
2
ON
CUSTOMER SETTING
NO FUNCTION
NO FUNCTION
RUN PERMISSIVE
COMMON RUN/STOP
4
321
ON
5
1
4
2
3
7
6
8
MK101
TEST CONNECTOR
MK110
S100
130B7290
EMB2 BOARD
CONTACT CLOSED
MOTOR ON BYPASS
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
CONTACT CLOSED
INDICATES
FIREMANS OVERRIDE STATUS
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
(COMMON RUN/STOP)
DAMPER END SWITCH
RUN PERMISSIVE
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
FIREMANS OVERRIDE CONTACT
CONTACTS SHOWN
IN FAULT POSITION
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
INTERLOCK
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED SAFETY
REPLACE WITH
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
24 VDC, 2A RATED CONTACT
MOTOR ON DRIVE
INDICATES
DRIVE FAULT STATUS
DAMPER MOTOR CONTROL
(CONTACT)
130BX402.12
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.8 EMB2, Part 2
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-9
8 8
Page 83

INPUT
POWER
EARTH
GROUND
(AFD)
DRIVE
ADJUSTABLE FREQUENCY
CONTROL BOARD T. B.
L2
L3
L1
DISCONNECT
DS1
M1
(L2)
(L1)
(L3)
(T2)
(T1)
(T3)
MAIN
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
GROUND
EARTH
(T2)
(T3)
(T1)
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
V/97
U/96
W/98
GROUND
EARTH
(L2)
(L3)
(L2)
(L3)
(L1)
(L1)
2T1
2T2
2T3
M2
M3
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR
(L1)
(L2)
(L3)
1T1
1T3
1T2
OL1
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
T1
T3
T2
04
05
06
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
REQUEST TO RUN
BLK 14 AWG
02
03
01
4
8
MK904
MK901
-
1
5
100
2
6
+
3
7
28
24 V DC SMPS
MK903 MK902
BLU
BLU/WHT
GD
24V
EARTH
GROUND
GD
1L3
1L2
1L1
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 20 37
GRN/YEL
(3)(2)(1)
SEE HIGH POT
FACTORY SAFETY INTERLOCK JUMPER
(ONLY FUNCTIONAL IF ORDERED)
TO PAGE 2
2L3
2L2
2L1
F16B
F16C
F16A
3L3
3L2
3L1
(4)(5)(6)
SEE HIGH POT
FOR DRIVE INPUT FUSE
REFER TO THE DRIVE
MANUAL
130BX398.13
4
5
6
2
3
1
Relay output
terminal block TB1
06
05
04
03
02
01
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
88
Figure 8.9 ECB, Part 1
8-10 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 84

9
8
7
6
5
4
2
1
3
4
1
3
2
10
12
11
TEST CONNECTOR
ECB
MK 110
EXTERNAL
6
7
8
3
5
4
2
1
2
1
24 V SUPPLY
BOARD
28
100
16
NC
NC
M3
(A2)
(A1)
(A1)
(A2)
M2
100
7
6
5
10
9
8
+ 24 V
RUNNING
+ 24 V
+ 24 V
15
SAFTY INTERLOCK
M2 STATUS
M3 STATUS
O.L. TRIP
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
O.L. RESET
BYPASS MODE
DRIVE MODE
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
MANUAL
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
BYPASS MODE ENABLE
BYPASS
OVERRIDE
LOAD
LOAD
CONNECTION
CUSTOMER
CUSTOMER
CONNECTION
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
18
COM
COM
COM
COM
COM
MOTOR
CONTACT
0-24 VDC
MAXIMUM 1 AMPS
DC RESISTIVE
22
CUSTOMER
O.L. RESET
BYPASS OVERRIDE
BYPASS
MODE ENABLE
CMS MOTOR SELECTED
DRIVE MODE
BYPASS MODE
40 mA MAX
24 VDC
NC
NC
CUSTOMER
INTERLOCK
SUPPLIED
SAFETY
TB1
100
(95)
(96)
M3
M2
OL1
19
20
21
(14)
(13)
(44)
(43)
X59
X57
X56
X58
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X56,X57,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
BLU
BLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
17
(A1)
(A2)
M1
BLU
BLU
BLU
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
130BX403.13
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.10 ECB, Part 2
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-11
8 8
Page 85

INPUT
POWER
EARTH
GROUND
(AFD)
DRIVE
ADJUSTABLE FREQUENCY
CONTROL BOARD T. B.
L2
L3
L1
BREAKER
CB1
M1
(L2)
(L1)
(L3)
(T2)
(T1)
(T3)
CIRCUIT
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
GROUND
EARTH
(T2)
(T3)
(T1)
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
V/97
U/96
W/98
GROUND
EARTH
(L2)
(L3)
(L2)
(L3)
(L1)
(L1)
2T1
2T2
2T3
M2
M3
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR
(L1)
(L2)
(L3)
1T1
1T3
1T2
OL1
(T1)
(T3)
(T2)
T1
T3
T2
04
05
06
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
REQUEST TO RUN
BLK 14 AWG
02
03
01
4
8
MK904
MK901
-
1
5
100
2
6
+
3
7
28
24 V DC SMPS
MK903 MK902
BLU
BLU/WHT
GD
24V
EARTH
GROUND
GD
1L3
1L2
1L1
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 20 37
GRN/YEL
(3)(2)(1)
SEE HIGH POT
M3
115VAC
TRANSFORMER
149
CONTROL
600V
150
F13A
WHT
158
155
153
153
153
3CR
2CR
152
1CR
154
BLK 14 AWG
GRN/YEL
151
T1
600V
F13B
(A1)
(A2)
(A1)
M1
(A1)
M2
(A2)
(A2)
(6)
(4)
(4)
(6)
(4)
(6)
X1
H4
H3
H1
H2
X3
X2
4CR
(2)
(1)
4CR
(C)
(NO)
RED
FACTORY SAFETY INTERLOCK JUMPER
(ONLY FUNCTIONAL IF ORDERED)
TO PAGE 2
2L3
2L2
2L1
F16B
F16C
F16A
3L3
3L2
3L1
(4)(5)(6)
SEE HIGH POT
FOR DRIVE INPUT FUSE
REFER TO THE DRIVE
MANUAL
130BX399.13
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
88
Figure 8.11 ECB with Control Relays, Part 1
8-12 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 86

9
8
7
6
5
4
2
1
3
4
1
3
2
10
12
11
TEST CONNECTOR
ECB
MK 110
EXTERNAL
6
7
8
3
5
4
2
1
2
1
24 V SUPPLY
BOARD
28
100
16
NC
NC
100
7
6
5
10
9
8
+ 24 V
RUNNING
+ 24 V
+ 24 V
15
SAFTY INTERLOCK
M2 STATUS
M3 STATUS
O.L. TRIP
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
O.L. RESET
BYPASS MODE
DRIVE MODE
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
MANUAL
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
BYPASS MODE ENABLE
BYPASS
OVERRIDE
LOAD
LOAD
CONNECTION
CUSTOMER
CUSTOMER
CONNECTION
NC
NC
NC
NC
NC
18
COM
COM
COM
COM
COM
MOTOR
CONTACT
0-24 VDC
MAXIMUM 1 AMPS
DC RESISTIVE
22
CUSTOMER
O.L. RESET
BYPASS OVERRIDE
BYPASS
MODE ENABLE
CMS MOTOR SELECTED
DRIVE MODE
BYPASS MODE
40 mA MAX
24 VDC
NC
NC
CUSTOMER
INTERLOCK
SUPPLIED
SAFETY
TB1
100
(95)
(96)
M3
M2
OL1
19
20
21
(14)
(13)
(44)
(43)
X59
X57
X56
X58
USE CLASS 1 CONDUCTORS
CUSTOMER CONNECTIONS X56,X57,X59
CONDUCTOR SIZE 28-14 AWG
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
BLU
BLU/WHT
BLU/WHT
BLU
BLU
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
24 VDC, 0.25 A
CLASS 2 POWER SOURCE
REQUIRED FOR FIELD CONNECTION
17
BLU
BLU
BLU
3CR
(7)
(8)
(8)
(7)
2CR
(8)
(7)
1CR
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
TO PAGE 1
130BX404.12
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
Figure 8.12 ECB with Control Relays, Part 2
MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark 8-13
8 8
Page 87
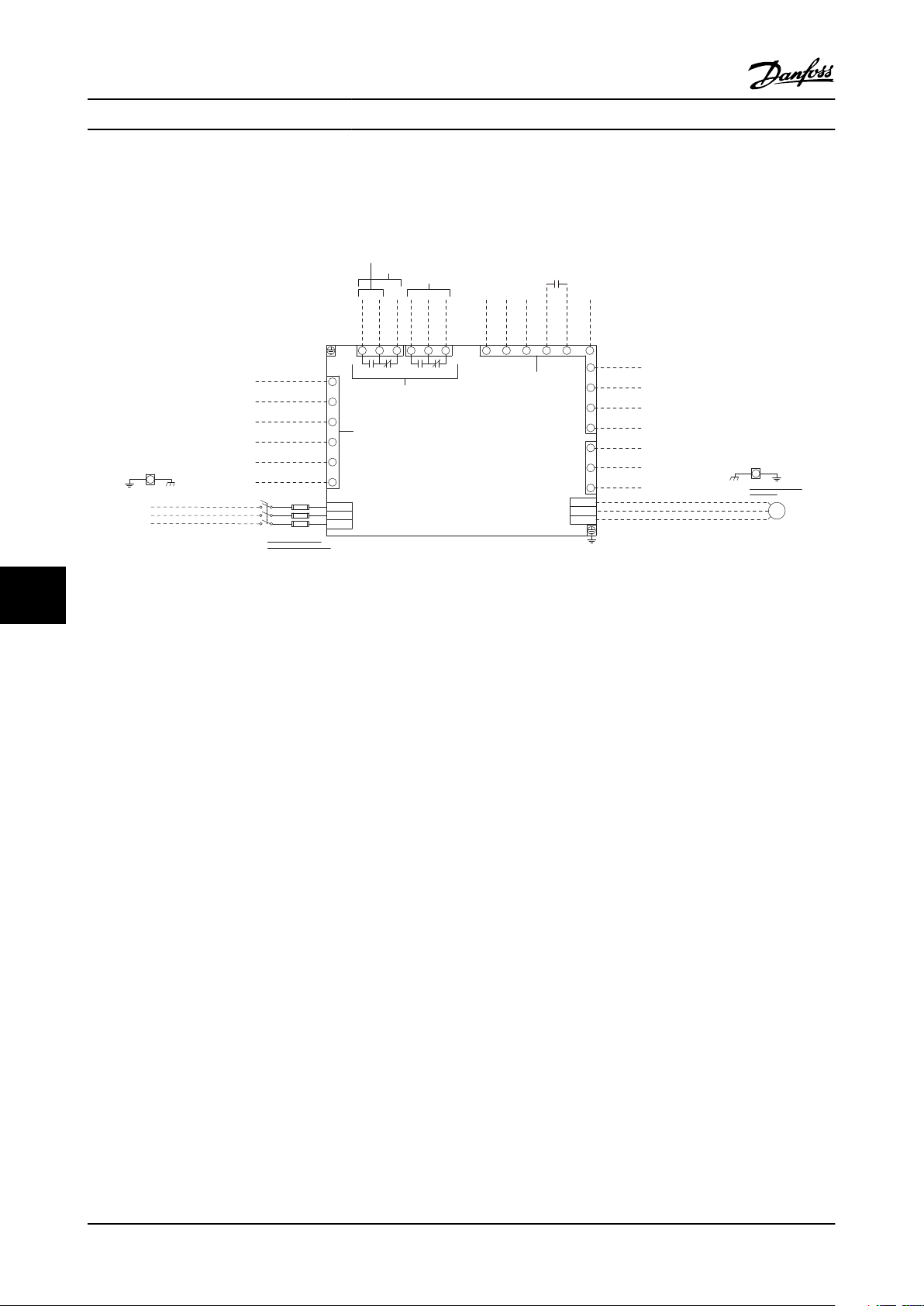
2L1
2L2
2L3
W/98
U/96
V/97
EARTH
GRN
T3
T2
GROUND
T1
CUSTOMER SUPPLIED
AC MOTOR.
INPUT
POWER
L1
L2
L3
EARTH
GROUND GRN
EARTH
GROUND
02 01 03
ADJUSTABLE FREQUENCY
27 20
DRIVE
(AFD)
19 18 12
EARTH
GROUND
13
COAST INVERSE
COMMON
PROG. DIG INPUT
START
05 04 06
29
32
33
37
53
54
55
42
39
+ 24 VOLT (130mA)
JOG
PROG. DIG INPUT
PROG. DIG INPUT
SAFETY INTERLOCK
JUMPERED TO TERMINAL
13 TO RUN W/O
OPTIONAL: FACTORY
68
69
P RS-485
N RS-485
61
COM RS-485
RS-485
INTERFACE
50
CUSTOMER
SUPPLIED
START
+ 24 VOLT (130mA)
ANALOG OUTPUT
COMMON
ANALOG OUTPUT
ANALOG INPUT
ANALOG INPUT COMMON
ANALOG INPUT
+ 10 VOLT OUT (15 mA)
RELAY 1RELAY 2
PROGRAMMABLE
SEE DRIVE MANUAL
PROGRAMMABLE
SEE DRIVE MANUAL
PROGRAMMABLE
SEE DRIVE MANUAL
SAFETY INTERLOCK
RLY 2 NO
RLY 2 COM
RLY 2 NC
RLY 1 NO
RLY 1 COM
RLY 1 NC
240 VAC, 2A
240 VAC, 2A
400 VAC, 2A
1F3
1F2
1F1
REFER TO THE DRIVE
MANUAL FOR FUSE SIZE
DISCONNECT
DS1
DRIVE
1L1
1L2
1L3
L2/92
L1/91
L3/93
130BX400.14
Appendix Vertical Bypass/Non Bypass Panel
88
Figure 8.13 Non-bypass
8-14 MG.13.A1.22 - VLT® is a registered Danfoss trademark
Page 88

www.danfoss.com/drives
130R0264 MG13A122 Rev. 2011-08-10
*MG13A122*
Page 89

 Loading...
Loading...