Page 1

Operating Guide
Safe Torque Off
VLT® Frequency Converters
vlt-drives.danfoss.com
Page 2

Page 3

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Contents
1
Introduction 5
1.1
Purpose of this Operating Guide 5
Additional Resources 5
1.2
Functional Overview 5
1.3
1.3.1
Introduction 5
1.3.2
Products Covered and Identification 5
1.4
Applied Standards and Compliance 6
Safety 7
2
Safety Symbols 7
2.1
Qualified Personnel 7
2.2
Responsibilities of Users of Safety-related Power Drive Systems PDS(SR) 7
2.3
Protective Measures 7
2.4
Contents
Safety Precautions 7
2.5
Installation 10
3
3.1
Safety Instructions 10
3.2
Installing STO 10
3.3
Installation in Combination with VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 11
4
Commissioning 13
4.1
Safety Instructions 10
4.2
Activating STO 13
4.3
Parameter Settings for STO Used With VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 13
4.4
Automatic/Manual Restart Behavior 13
4.5
STO Commissioning Test 14
4.5.1
Restart Prevention for STO Application 14
4.5.2
Automatic Restart of STO Application 14
4.6
System Configuration Security 14
4.7
Service and Maintenance 14
4.7.1
Performing Functional Tests 15
5
Application Examples 16
5.1
SISTEMA Data 16
5.2
Emergency Stop of Drive with STO - Category 1, PL c, SIL1 16
5.3
Emergency Stop of Drive with STO Using Safety Relay - Category 3, PL d, SIL2 17
5.4
Emergency Stop of Drive with STO, Safety Relay, and Output Contactor - Category 4, PL e, SIL3 18
5.5
Emergency Stop of Multiple Drives - Category 3, PL d, SIL2 19
AQ313340186453en-000201/130R0544 | 3Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 4

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
6
STO Technical Data 21
Notices Regarding Technical Data 21
6.1
6.2
European Directives 21
Safety Standards 21
6.3
6.4
Safety Function 21
6.5
Safety Performance 21
Appendix 22
7
Abbreviations 22
7.1
Conventions 22
7.2
Contents
AQ313340186453en-000201/130R05444 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 5

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Introduction
1 Introduction
1.1 Purpose of this Operating Guide
This Operating Guide provides information for use of Danfoss VLT® FC Series drives in functional safety applications. The manual
includes information about functional safety standards, Danfoss VLT® FC Series Safe Torque Off (STO) function, the related installation and commissioning, and service and maintenance for STO.
VLT® is a registered trademark for Danfoss A/S.
1.2 Additional Resources
This manual is targeted at users already familiar with the VLT® drives. It is intended as a supplement to the manuals and instructions
available for download at
unit, and observe the instructions for safe installation.
www.danfoss.com. Read the instructions shipped with the drive and/or drive option before installing the
1.3 Functional Overview
1.3.1 Introduction
The Safe Torque Off (STO) function is a component in a safety control system. STO prevents the unit from generating the power
required to rotate the motor.
N O T I C E
Select and apply the components in the safety control system appropriately to achieve the required level of operational safety.
Before integrating and using STO in an installation, carry out a thorough risk analysis on the installation to determine whether the
STO functionality and safety levels are appropriate and sufficient.
The VLT® drive is available with:
•
Safe Torque Off (STO), as defined by EN IEC 61800-5-2.
•
Stop category 0, as defined in EN 60204-1.
The drive integrates the STO functionality via control terminal 37.
The VLT® drive with STO functionality is designed and approved suitable for the requirements of:
•
Category 3 in EN ISO 13849-1.
•
Performance Level "d" in EN ISO 13849-1.
•
SIL 2 in IEC 61508 and EN 61800-5-2.
•
SILCL 2 in EN 62061.
1.3.2 Products Covered and Identification
The STO function is available for the following drive types:
•
VLT® HVAC Drive FC 102.
VLT® Refrigeration Drive FC 103.
•
•
VLT® AQUA Drive FC 202.
•
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301, enclosure size A1.
•
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302.
•
VLT® Decentral Drive FCD 302.
•
VLT® Parallel Drive Modules.
Identification
•
Confirm that the drive is configured with the STO function by checking the unit type code on the nameplate.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 5Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 6
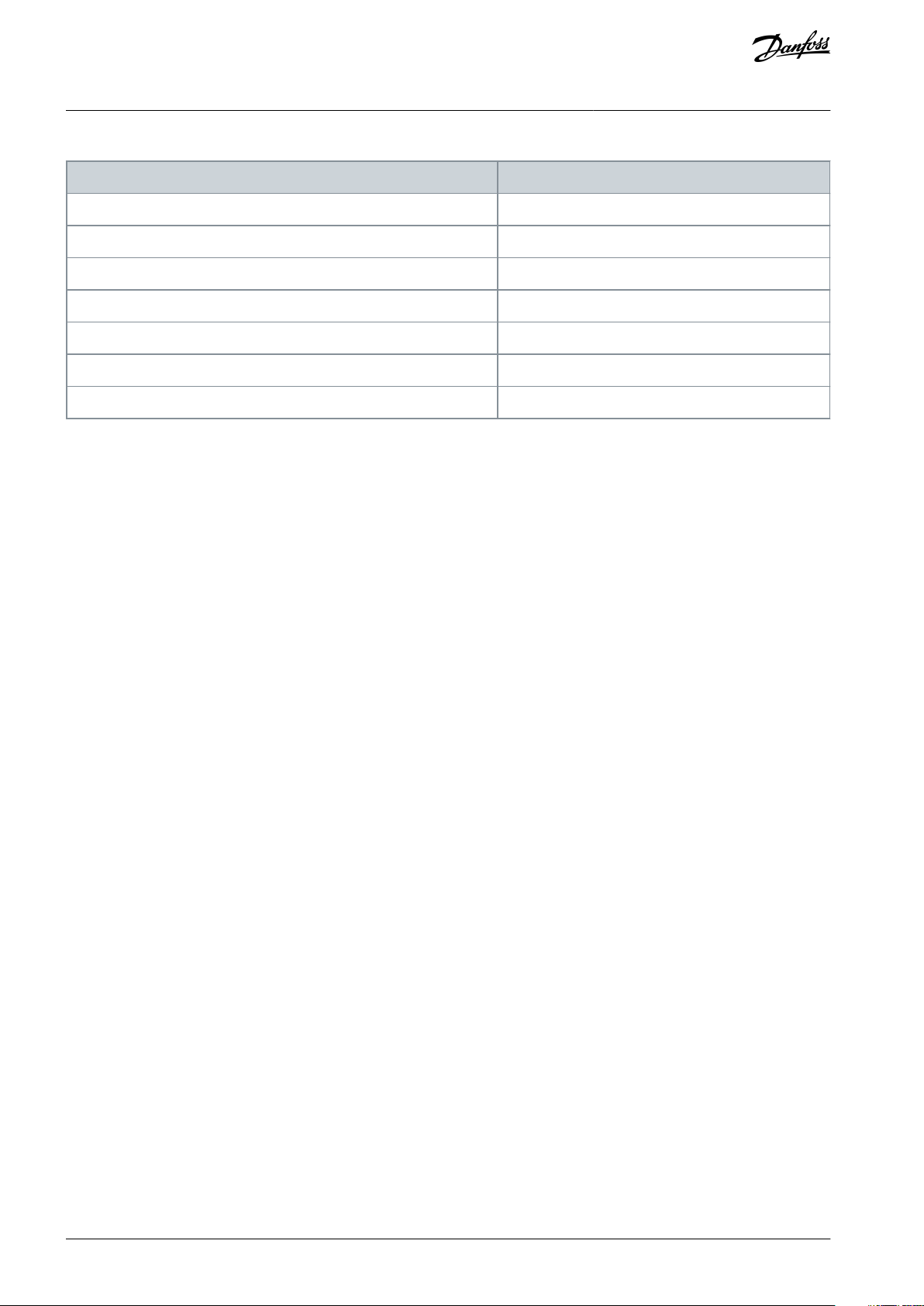
Product
Type code
VLT® HVAC Drive FC 102
T or U at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® Refrigeration Drive FC 103
T at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® AQUA Drive FC 202
T or U at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301, enclosure size A1
T at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302
X, B, or R at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® Decentral Drive FCD 302
X, B, or R at digit 18 of the type code.
VLT® Parallel Drive Modules
T or U at digit 18 of the type code.
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Table 1: Type Code Identification
Introduction
1.4 Applied Standards and Compliance
Using the STO on terminal 37 requires that the user fulfills all provisions for safety, including relevant laws, regulations, and guidelines.
The integrated STO function complies with the following standards:
•
IEC/EN 60204-1: 2016 Stop category 0 - uncontrolled stop.
•
IEC/EN 61508: 2010 SIL2.
•
IEC/EN 61800-5-2: 2016.
•
IEC/EN 62601: 2015 SIL CL2.
•
EN ISO 13849-1: 2015 Category 3 PL d.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R05446 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 7

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
2 Safety
2.1 Safety Symbols
The following symbols are used in this manual:
D A N G E R
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious injury.
W A R N I N G
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or serious injury.
C A U T I O N
Indicates a hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in minor or moderate injury.
N O T I C E
Indicates information considered important, but not hazard-related (for example, messages relating to property damage).
Safety
2.2 Qualified Personnel
The products must only be assembled, installed, programmed, commissioned, maintained, and decommissioned by persons with
proven skills. Persons with proven skills:
•
Are qualified electrical engineers, or persons who have received training from qualified electrical engineers and are suitably
experienced to operate devices, systems, plant, and machinery in accordance with the general standards and guidelines for
safety technology.
•
Are familiar with the basic regulations concerning health and safety/accident prevention.
•
Have read and understood the safety guidelines given in this manual and also the instructions given in the operating guide of
the drive.
•
Have good knowledge of the generic and specialist standards applicable to the specific application.
2.3 Responsibilities of Users of Safety-related Power Drive Systems PDS(SR)
Users of safety-related Power Drive Systems (PDS(SR)) are responsible for:
•
Hazard and risk analysis of the application.
•
Identifying safety functions required and allocating SIL or PLr to each of the functions.
•
Other subsystems and the validity of signals and commands from these subsystems.
•
Designing appropriate safety-related control systems (hardware, software, parameterization, and so on).
2.4 Protective Measures
Qualified and skilled personnel must be available for installing and commissioning the safety engineering systems.
Procedure
1.
Install the drive in an IP54 cabinet as per IEC 60529, or in an equivalent environment. In special applications, a higher IP
rating may be necessary.
2.
Ensure short-circuit protection of the cable between terminal 37 and the external safety device according to ISO 13849-2
table D.4.
3.
Install additional measures (for example, a safety holding brake) if external forces influence the motor axis (for example
suspended loads).
2.5 Safety Precautions
See the Safety chapter in the relevant operating guides for general safety precautions.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 7Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 8

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Safety
W A R N I N G
FALL PROTECTION REQUIRED
External forces acting on the motor, for example suspended loads, and unintended movements, for example caused by gravity,
can cause hazards. Not taking any measures to protect against falling loads can lead to death or serious injury.
Equip the motor with extra measures for fall protection, for example, install extra mechanical brakes.
-
W A R N I N G
NO ELECTRICAL SAFETY
STO (that is, removal of 24 V DC voltage supply to terminal 37) does not provide electrical safety. The STO function itself is not
sufficient to implement the Emergency-Off function as defined by EN 60204-1. Using the STO function to implement Emergency-
Off may lead to personal injury.
Emergency-Off requires measures of electrical isolation, for example, by switching off mains via an extra contactor.
-
W A R N I N G
RISK OF ELECTRICAL SHOCK
The STO function does NOT isolate mains voltage to the drive or auxiliary circuits. Only perform work on electrical parts of the
drive or the motor after isolating the mains voltage supply and waiting for the discharge time to elapse, as specified in the Safety
chapter in the Operating Guide of the relevant drive. Failure to isolate the mains voltage supply from the unit and waiting the
time specified could result in death or serious injury.
Do not stop the drive by using the STO function. If a running drive is stopped by using the function, the unit trips and stops
-
by coasting. If this limitation is not acceptable, for example because it causes danger, use the appropriate stopping mode to
stop the drive and machinery before using the STO function. Depending on the application, a mechanical brake may be required.
STO is suitable for performing mechanical work on the drive system or affected area of a machine only. It does not provide
-
electrical safety. STO must not be used as a control for starting and/or stopping the drive.
W A R N I N G
RESIDUAL ROTATION
The STO function can be used for asynchronous, synchronous, and permanent magnet motors. Two faults can occur in the power
semiconductor of the drive. When using synchronous or permanent magnet motors, a residual rotation can result from the faults.
The rotation can be calculated to angle = 360/(number of poles). The application using synchronous or permanent magnet mo-
tors must consider this residual rotation and ensure that it does not pose a safety risk. The situation is not relevant for asynchro-
nous motors.
C A U T I O N
After installing STO, perform a commissioning test. A passed commissioning test is mandatory after the 1st installation and after
each change to the safety installation.
C A U T I O N
AUTOMATIC RESTART
Automatic restart behavior is only allowed in 1 of the 2 situations:
The unintended restart prevention is implemented by other parts of the STO installation.
-
A presence in the dangerous zone can be physically excluded when STO is not activated. In particular, observe paragraph
-
6.3.3.2.5 of ISO 12100:2010.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R05448 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 9

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
N O T I C E
Perform a risk assessment for each stop function to determine the selection of a stop category in accordance with EN 60204-1:
Stop Category 0 is achieved with immediate removal of power to the actuator, resulting in an uncontrolled coast to stop.
-
STO according to EN 61800-5-2 accomplished a Stop Category 0 stop.
Stop Category 1 is achieved with power available to the machine actuators to achieve the stop. Power is removed from the
-
actuators when the stop is achieved according to EN 61800-5-2 Safe Stop 1 (SS1).
Stop Category 2 is a controlled stop with power available to the machine actuators. A holding position under power follows
-
the stop.
N O T I C E
When designing the machine application, timing and distance must be considered for a coast to stop (Stop Category 0 or STO).
For more information regarding stop categories, refer to EN 60204-1.
Safety
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 9Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 10

12/13
37
e30ba874.11
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Installation
3 Installation
3.1 Safety Instructions
C A U T I O N
ELECTRICAL HAZARD
The operator or electrical installer is responsible for proper grounding and compliance with all applicable national and local safe-
ty regulations.
See 2.5 Safety Precautions and the Operating Guide of the relevant drive. Also, always observe the instructions provided by the
motor manufacturer.
3.2 Installing STO
For motor connection, AC mains connection, and control wiring, follow the instructions for safe installation in the Operating Guide
of the drive. See 2.5 Safety Precautions and the relevant drive. For installation with the Ex-certified VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB
112, see 3.3 Installation in Combination with VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112.
Procedure
1.
Remove the yellow jumper wire between control terminals 37 and 12 or 13.
Cutting or breaking the yellow jumper is not sufficient to avoid short-circuiting, see jumper in Illustration 1.
Illustration 1: Jumper between Terminals 12/13 (24 V) and 37 (all Drives Except FCD 302)
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054410 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 11

e30bc393.11
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Installation
Illustration 2: Jumper between Terminals 13 (24 V) and 37 (FCD 302)
2.
For example, connect an external safety monitoring relay via an NO safety function to terminal 37 (STO) and either terminal
12 or 13 (24 V DC).
Connection and application examples are found in the chapter Application Examples.
3.
Complete wiring according to the instructions given in the Operating Guide of the drive.
3.3 Installation in Combination with VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112
N O T I C E
The combination of VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 and STO function is only available for VLT® HVAC Drive FC 102, VLT®
Refrigeration Drive FC 103, VLT® AQUA Drive FC 202, VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302, and VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301 enclosure
size A1.
VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 uses terminal 37 as its safety-related switch-off channel.
•
Ensure that the output X44/12 of MCB 112 is AND-ed with the safety-related sensor (for example, emergency stop button and
safeguard switch) that activates STO. This means that the output to STO terminal 37 is high (24 V) only if both the signal from
MCB 112 output X44/12 and the signal from the safety-related sensor are high. If at least 1 of the 2 signals is low, the output to
terminal 37 must be low too.
•
Ensure that the safety device with AND-logic complies with the needed safety level.
•
Short-circuit protect the connection from the output of the safety device with safe AND-logic to the STO terminal 37.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 11Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 12

e30ba967.13
Digital input
PTC
sensor
Non-hazardous area
Hazardous
area
X44/
PTC Thermistor Card
MCB 112
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 101112
Safety device
Manual restart
SIL 2
Safe AND input
Safe output
Safe input
DI DI
STO
Par. 5-19
Terminal 37 Safe Stop
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 20 37
e.g. Par 5-15
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Installation
Illustration 3: Combination of an STO Application and an MCB 112 Application
The illustration shows a restart input for the external safety device. This means that in this installation, parameter 5-19 Terminal 37
Safe Stop can be set to value [7] PTC 1 & Relay W or [8] PTC 1 & Relay A/W. Refer to VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 Operating
Guide for further details.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054412 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 13

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Commissioning
4 Commissioning
4.1 Safety Instructions
C A U T I O N
ELECTRICAL HAZARD
The operator or electrical installer is responsible for proper grounding and compliance with all applicable national and local safe-
ty regulations.
See 2.5 Safety Precautions and the Operating Guide of the relevant drive. Also, always observe the instructions provided by the
motor manufacturer.
4.2 Activating STO
The STO function is activated by removing the voltage at terminal 37 of the drive. By connecting the drive to external safety devices
providing a safe delay, an installation for a Safe Stop 1 can be obtained. External safety devices must fulfill Cat./PL or SIL when connected to terminal 37. The STO function can be used for asynchronous, synchronous, and permanent magnet motors.
When the STO function (terminal 37) is activated, the drive issues an alarm, trips the unit, and coasts the motor to a stop. Manual
restart is required. Use the STO function to stop the drive in emergency stop situations. In normal operating mode when STO is not
required, use the standard stop function instead. Ensure that requirements according to ISO 12100 paragraph 6.3.3.2.5 are fulfilled
before using the automatic restart function.
4.3 Parameter Settings for STO Used With VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112
When MCB 112 is connected, more selections are available for parameter 5-19 Terminal Safe Stop (options [4] PTC 1 Alarm to [9] PTC 1
& Relay W/A).
•
Selections [1] Safe Stop Alarm and [3] Safe Stop Warning are still available, but for installations without MCB 112 or any external
safety devices. If [1] Safe Stop Alarm or [3] Safe Stop Warning are selected and MCB 112 is triggered, the drive issues alarm 72,
Dangerous Failure and coasts the motor safely without automatic restart.
•
Do not select [4] PTC 1 Alarm and [5] PTC 1 Warning when an external safety device is used. Only use those selections when only
MCB 112 uses the STO. If selection [4] PTC 1 Alarm or [5] PTC 1 Warning is selected and the external safety devices triggers STO,
the drive issues alarm 72, Dangerous Failure and coasts the motor safely without automatic restart.
•
Select [6] PTC 1 & Relay A to [9] PTC 1 & Relay W/A for combining external safety devices and MCB 112.
C A U T I O N
AUTOMATIC RESTART
Selections allow automatic restart when the external safety device is deactivated. Before selecting [7] PTC 1 & Relay W or [8] PTC 1
& Relay A/W, ensure that:
The unintended restart prevention is implemented by other parts of the STO installation, or
-
A presence in the dangerous zone can be physically excluded when STO is not activated. In particular, paragraph 6.3.3.2.5 of
-
ISO 12100:2010 must be observed.
See VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 Operating Guide for further information.
4.4 Automatic/Manual Restart Behavior
The STO default state prevents unintended restarts (restart prevention behavior). To terminate STO and resume normal operation,
follow the procedure below.
Procedure
1.
Reapply 24 V DC to terminal 37.
2.
Give a reset signal via bus, digital I/O, or [Reset] key.
Set the STO function to automatic restart by setting the value of parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe Stop from default value
[1] Safe Stop Alarm to value [3] Safe Stop Warning.
Automatic restart means that STO is terminated and normal operation is resumed when the 24 V DC is applied to terminal
37. No reset signal is required.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 13Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 14

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Commissioning
4.5 STO Commissioning Test
After installation and before first operation, perform a commissioning test of the installation, using STO. Perform the test again after
each modification of the installation or application involving the STO.
N O T I C E
A successful commissioning test of the STO function is required after the initial installation and after each subsequent change to
the installation or application involving the STO.
•
For applications without automatic restart after a safe stop, follow the instructions in 4.5.1 Restart Prevention for STO Applica-
tion.
•
For applications with automatic restart after a safe stop, follow the instructions in 4.5.2 Automatic Restart of STO Application.
4.5.1 Restart Prevention for STO Application
Applications where parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe Stop is set to default value [1] Safe Stop Alarm or combined STO and VLT® PTC
Thermistor Card MCB 112 where parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe Stop is set to [6] PTC 1 & Relay A or [9] PTC 1 & Relay W/A.
Procedure
Remove the 24 V DC voltage supply to terminal 37 using the interrupt device while the drive runs the motor (that is, mains
1.
supply is not interrupted).
Check that:
2.
The motor coasts.
a.
b.
The mechanical brake activates (if connected).
c.
The LCP (if mounted) shows Alarm 68, Safe Stop.
Reapply 24 V DC to terminal 37.
3.
Ensure that the motor remains in the coasted state, and that the mechanical brake (if connected) remains activated.
4.
Send a reset signal via bus, digital I/O, or [Reset] key.
5.
Ensure that the motor is operational again.
6.
When all given steps are passed, the commissioning test is successfully completed.
4.5.2 Automatic Restart of STO Application
Applications where parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe Stop is set to [3] Safe Stop Warning or combined STO and VLT® PTC Thermistor
Card MCB 112 where parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe Stop is set to [7] PTC 1 & Relay W or [8] PTC 1 & Relay A/W.
Procedure
Remove 24 V DC voltage supply to terminal 37 by the interrupt device while the drive runs the motor (that is, mains supply
1.
is not interrupted).
Check that:
2.
The motor coasts.
a.
The mechanical brake activates (if connected).
b.
c.
The LCP (if mounted) shows Warning 68, Safe Stop.
Reapply 24 V DC to terminal 37.
3.
Ensure that the motor is operational again.
4.
When all the given steps are passed, the commissioning test is successfully completed.
N O T I C E
See the warning on the restart behavior in 2.5 Safety Precautions.
4.6 System Configuration Security
•
Security measures are the responsibility of the user.
•
The drive parameters can be password-protected.
4.7 Service and Maintenance
It is required for PL d or SIL2 to conduct a functional test every 12 months to detect any failure or malfunction of the STO functionality. For lower PL or SIL, it is a recommendation.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054414 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 15

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
4.7.1 Performing Functional Tests
Procedure
1.
Remove 24 V DC voltage supply at terminal 37.
2.
Check if the LCP shows Alarm 68, Safe Stop or Warning 68, Safe Stop.
3.
Verify that the drive trips the unit.
4.
Verify that the motor is coasting and comes to a complete stop.
5.
Verify that the motor cannot be started.
6.
Reconnect 24 V DC supply to terminal 37.
7.
Verify that the motor is not started automatically and restarts only by giving a reset signal via bus, digital I/O, or [Reset] key.
Commissioning
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 15Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 16

FC
1
e30bg733.11
37
2
+24 V
1
Emergency stop button.
2
Short-circuit protected cable.
e30bg734.11
SB emergency
stop device
SB FC 300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
from Danfoss VLT library
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Application Examples
5 Application Examples
5.1 SISTEMA Data
SISTEMA (Safety Integrity Software Tool for the Evaluation of Machine Applications) is a software utility that provides developers
and testers of safety-related machine controls with comprehensive support in the evaluation of safety in the context of ISO 13849-1.
Functional safety data are available from a data library for use with the SISTEMA calculation tool from the ISA (Institute for Occupational Safety and Health of the German Social Accident Insurance), and data for manual calculation. SISTEMA is available for download at www.danfoss.com in the Service and support/downloads sections.
5.2 Emergency Stop of Drive with STO - Category 1, PL c, SIL1
Illustration 4: Application Example, Emergency Stop with STO, Category 1, PL c, SIL1
Safety function
If there is an emergency, the emergency stop device is activated. The STO function of the drive is activated. Following a stop or
emergency stop command, the drive is halted.
Design features
•
The circuit can be used up to Category 1, PL c (ISO 13849-1) or SIL1 (EN 62061 and IEC 61508).
•
The STO function is activated via 1 NC positively operated switch contact (according to IEC 60947-1, IEC 60947-5-1, and IEC
60947-5-5).
•
The PL c, the complete safety functions have to be calculated (MTTFd).
•
Use the basic safety principles.
•
Devices used for activation of STO must be suitable for the selected Category, PL, or SIL.
When implementing the emergency stop, pay attention to the following tips:
•
Any non-safety related standards should be fulfilled for the application and its components.
•
The application designer is responsible for selecting suitable components.
•
To fulfill PL c, the MTTFd and DC for the whole safety function have to be calculated.
•
The B
value of the emergency stop device shall be known. The B
10d
value has to be high enough to fulfill MTTFd correspond-
10d
ing to PL c.
Implementation in SISTEMA using Danfoss VLT library
As an example, use the subsystem "VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302/FCD 302 Safe Torque Off (Terminal 37)". There is no need to edit
all the parameters which are set in the library.
Illustration 5: Safety-related Block Diagram
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054416 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 17

e30bg775.11
12
37
3
2
FC
4
1
1
Safety relay (Category 3, PL d, SIL 2)
2
Emergency stop button
3
Reset button
4
Short-circuited protected cable (if not inside installation IP54 cabinet). See ISO 13489-2, Table D.4 for further information
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
5.3 Emergency Stop of Drive with STO Using Safety Relay - Category 3, PL d, SIL2
Application Examples
Illustration 6: Installation Example Achieving a Stop Category 0 (EN 60204-1) with Safety Cat. 3/PL "d" (ISO 13849-1) or SIL2 (EN 62061 and IEC
61508)
Safety function
If there is an emergency, the emergency stop device is activated. The STO function of the drive is activated. Following a stop or
emergency stop command, the drive is halted.
Design features
•
The circuit can be used up to Category 3, PL s (ISO 13849-1) or SIL2 (EN 62061 and IEC 61508).
•
For PL d, the complete safety functions have to be calculated (MTTFd).
•
Use the basic safety principles.
•
The device used for activation of STO and safety relay must be suitable for the selected category PL and SIL.
When implementing the emergency stop, pay attention to the following tips:
•
Any non-safety related standards should be fulfilled for the application and its components.
•
The application designer is responsible for selecting suitable components.
•
The cable shown as bold in
•
To fulfill PL d, the MTTFd and DC for the whole safety function have to be calculated.
This setup can be used if a dual positive switching device is used. Depending on the safety relay, it is also possible to connect several activation devices to 1 STO.
Illustration 6 has to be short-circuit protected according to ISO 13849-2 table D.4.
Implementation of SISTEMA using Danfoss VLT library
As an example, use the subsystem "VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302/FCD 302 Safe Torque Off (Terminal 37)". There is no need for
editing all the parameters which are set in the library.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 17Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 18

e30bg776.11
SB emergency
stop device
SB FC 300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
from Danfoss
VLT library
SB safety relay
e30bg777.11
12
37
3
2
FC
4
1
M
K1
K1
K1
+24 V
1
Safety relay (Category 4, PL e, SIL 3)
2
Emergency stop button
3
Reset button
4
Short-circuit protected cable (if not inside installation IP54 cabinet). See ISO 13849-2, Table D.4 for further information.
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Illustration 7: Safety-related Block Diagram
Application Examples
5.4 Emergency Stop of Drive with STO, Safety Relay, and Output Contactor - Category 4, PL e, SIL3
Illustration 8: Drive with STO, Safety Relay, and Output Contactor, Category 4, PL e, SIL3
Safety function
If there is an emergency, the emergency stop device is activated. The STO function in the drive is activated. Following a stop or
emergency stop command, the drive is halted.
Where the safety control system must be in accordance with PL e ISO 13849-1 or SIL3 (EN 62061 and IEC 61508), it requires a 2channel stop for the STO function. One channel can be implemented by the STO input on the drive and the other by a contactor,
which may be connected in either the drive input or output power circuits. The contactor must be monitored through an auxiliaryguided contact, shown as K1 in
Illustration 8.
Design features
•
The circuit can be used up to category 4 and PL e.
•
For PL e, the complete safety functions have to be calculated (MTTFd).
•
Use basic safety principles.
•
Device used for activation of STO and safety relay must be suitable for the selected category, PL or SIL.
When implementing the emergency stop, pay attention to the following tips:
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054418 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 19

e30bg778.11
SB emergency
stop device
SB stopping devices
from Danfoss VLT library
SB monitoring
safety relay:
MSR 33
CH channel 1
BL FC 300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
CH channel 2
BL output
contactor:
100S-C
e30bg779.11
12
37
3
2
FC
4
1
12
37
FC
12
37
FC
1
Safety relay (Category 3, PL d, or SIL2)
2
Emergency stop button
3
Reset button
4
Short-circuit protected cable (if not inside an installation IP54 cabinet). See ISO 13849-2, Table D.4 for
further information.
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
•
Any non-safety related standards should be fulfilled for the application and its components.
•
The application designer is responsible for selecting suitable components.
•
The cable shown as bold in Illustration 8 has to be short-circuit protected according to ISO 13849-2, table D.4.
•
To fulfill PL e, the MTTFd and DC for the entire safety function have to be calculated.
Application Examples
This setup can be used if a dual positive switching device is used.
Implementation in SISTEMA using Danfoss VLT library
As an example, use the block "VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302 (Terminal 37)". There is no need for editing all the parameters which
are set in the library.
Illustration 9: Safety-related Block Diagram
5.5 Emergency Stop of Multiple Drives - Category 3, PL d, SIL2
Illustration 10: Multiple Drives with Category 3, PL d, SIL2
Safety function
If there is an emergency, the emergency stop device is activated. The STO function in the drive is activated. Following a stop or an
emergency stop command, the drive is halted.
If it is required to control multiple drives from the same control line, the STO inputs may be interconnected directly.
Connecting inputs together increases the probability of a fault in the unsafe direction since a fault in 1 drive may result in all drives
becoming enabled. However, the probability of a fault is so low, at 1 x 10
requirement for SIL2 for a realistic number of drives. Do not connect more than 20 inputs in parallel.
-10
per hour, that the resulting probability still meets the
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 19Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 20

e30bg780.11
SB emergency
stop device
SB safety relay
from Danfoss VLT library
SB FC300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
from Danfoss VLT library
SB FC300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
from Danfoss VLT library
SB FC300 safe stop
(terminal 37)
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Application Examples
N O T I C E
When using internal 24 V DC supply (terminal 12), the number of parallel inputs (terminal 37) is limited to 3, otherwise the availa-
ble output power is exceeded.
Design features
•
The circuit can be used up to Category 3, PL d, or SIL2.
•
For PL d, the complete safety functions have to be calculated (MTTFd).
•
Use basic safety principles.
•
Device used for activation of STO and safety relay must be suitable for the selected category, PL or SIL.
When implementing the emergency stop, pay attention to the following tips:
•
Any non-safety related standards should be fulfilled for the application and its components.
•
The application designer is responsible for selecting suitable components.
•
The cable shown as bold in Illustration 10 has to be short-circuit protected according to ISO 13849-2, table D.4.
•
To fulfill PL d, the MTTFd and DC for the entire safety function have to be calculated.
This setup can be used if a dual positive switching device is used. Depending on the safety relay, it is also possible to connect several activation devices to one STO.
Implementation in SISTEMA using Danfoss VLT library
As an example, use the subsystem "VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302/FCD 302 Safe Torque Off (Terminal 37)". There is no need for
editing all the parameters which are set in the library. Put the subsystem into the safety function as often as the number of drives
that are present on the single STO line.
Illustration 11: Safety-related Block Diagram
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054420 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 21

Machinery Directive (2006/42/EC)
EN ISO 13849-1, EN IEC 62061, EN IEC 61800-5-2
EMC Directive (2014/30/EU)
EN 50011, EN 61000-6-3, EN 61800-3
Low Voltage Directive (2014/35/EU)
EN 50178, EN 61800-5-1
Safety of Machinery
EN ISO 13849-1, IEC 62061, IEC 60204-1
Functional Safety
IEC 61508-1 to -7, IEC 61800-5-2
Safe Torque Off (STO)
IEC 61800-5-2
Stop Category 0
IEC 60204-1
ISO 13849-1
Category
Cat 3
Diagnostic coverage
DC: 90% (Medium)
Mean time to dangerous failure
MTTFd: 14000 years (high)
Performance level
PL d
IEC 61508/IEC 62061
Safety integrity level
SIL2, SIL CL2
Probability of dangerous failure per hour
PFH: 1E-10/h; 1E-8/h for specific variants (High Demand Mode)
(1)
,
(2)
Probability of dangerous failure on demand
PFD: 1E-10; 1E-4 for specific variants (Low Demand Mode)
(1),(2)
Proof test interval T1
20 years
Mission time TM
20 years
Reaction time
Input to output response time
Maximum 20 ms, 60 ms for specific variants
(1), (2)
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
STO Technical Data
6 STO Technical Data
6.1 Notices Regarding Technical Data
N O T I C E
For technical specifications and operating conditions for the drive, refer to the Operating Guide of the relevant drive.
N O T I C E
The STO signal must be SELV or PELV supplied.
6.2 European Directives
6.3 Safety Standards
6.4 Safety Function
6.5 Safety Performance
1
VLT® HVAC Drive FC 102, VLT® Refrigeration Drive FC 103, VLT® AQUA Drive FC 202, and VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302 high-power drives, enclo-
sure size F:
400 V: 450/500 kW (600/650 hp)–800/1000 kW (1075/1350 hp) (High Overload/Normal Overload).
•
690 V: 630/710 kW (850/950 hp) – 1800/2000 kW (2400/2700 hp) (High Overload/Normal Overload).
•
2
VLT® Parallel Drive Modules:
400 V: 250/315 kW (350/450 hp) – 800/1000 kW (1200/1350 hp) (High Overload/Normal Overload).
•
690 V: 315/400 kW (350/400 hp) – 1000/1200 kW (1150/1350 hp) (High Overload/Normal Overload).
•
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 21Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 22

Abbreviations
Reference
Description
B
10d
Number of cycles until 10% of the components have a dangerous failure (for pneumatic and
electromechanical components).
Cat.
EN ISO 13849-1
Category, level “B, 1–4”
CCF
Common cause failure
DC
Diagnostic coverage divided into Low, Medium, and High.
FIT
Failure in time: 1E-9/hour
MTTFd
EN ISO 13849-1
Mean time to failure - dangerous. Unit: Years are divided into Low, Medium, and High.
PFH
EN IEC 61508
Probability of dangerous failures per hour. Consider this value if the safety device is operated
in high demand or continuous mode of operation, where the frequency of demands for operation made on a safety-related system is greater than 1 per year.
PFD
EN IEC 61508
Average probability of failure on demand, value used for low demand operation.
PL
EN ISO 13849-1
Discrete level used to specify the ability of safety-related parts of control systems to perform
a safety function under foreseeable conditions. Levels divided into a to e.
PLr
Required performance level (the required performance level for a particular safety function).
SIL
EN IEC 61508
EN IEC 62061
Safety integrity level
STO
EN IEC 61800-5-2
Safe Torque Off
SS1
EN IEC 61800-5-2
Safe Stop 1
SRECS
EN IEC 62061
Safety-related electrical control system
SRP/CS
EN ISO 13849-1
Safety-related parts of control systems
PDS/SR
EN IEC 61800-5-2
Power Drive System (safety-related)
Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
7 Appendix
7.1 Abbreviations
Table 2: Abbreviations Related to Functional Safety
Appendix
7.2 Conventions
•
Numbered lists indicate procedures.
•
Bulleted and dashed lists indicate listings of other information where the order of the information is not relevant.
•
Bolded text indicates highlighting and section headings.
•
Italicized text indicates the following:
-
Cross-reference.
-
Link.
-
Footnote.
-
Parameter name.
-
Parameter option.
-
Parameter group name.
-
Alarms/warnings.
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R054422 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 23

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
••All dimensions in drawings are in metric values (imperial values in brackets).
An asterisk (*) indicates the default setting of a parameter.
Appendix
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544 | 23Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 24

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Index
A
Abbreviations................................................................................................ 22
Alarm.................................................................................................................13
Automatic restart......................................................................................... 13
C
Commissioning test.....................................................................................14
Conventions...................................................................................................22
I
Identification.................................................................................................... 5
M
MCB 112....................................................................................................11, 13
MTTFd...............................................................................................................21
N
Nameplate.........................................................................................................5
P
Parameter settings.......................................................................................13
Q
Qualified personnel........................................................................................7
R
Restart prevention................................................................................ 13, 14
S
Safety device..................................................................................................11
Safety-guard switch.....................................................................................11
Safety-related sensor.................................................................................. 11
Signal................................................................................................................ 11
Index
SIL CL2..........................................................................................................6, 21
SIL2..................................................................................................6, 14, 19, 21
SISTEMA calculation tool...........................................................................16
Standards and directives
EN IEC 61800-5-2....................................................................................5
EN 60204-1.....................................................................................5,8,9,9
EN ISO 13849-1....................................................................................... 5
EN 62061................................................................................. 5,16,17,18
IEC/EN 61508...........................................................................................6
IEC/EN 61800-5-2................................................................................... 6
IEC/EN 62601...........................................................................................6
ISO 13849-1....................................................6,16,17,18,21,21,21,22
IEC/EN 60204-1.......................................................................................6
IEC 60529.................................................................................................. 7
ISO 13849-2......................................................................7,16,17,18,19
ISO 12100............................................................................................8,13
EN 61800-5-2...........................................................................................9
IEC 61508........................................................................16,17,18,21,22
IEC 60947-1............................................................................................16
IEC 60947-5-1........................................................................................16
IEC 60947-5-5........................................................................................16
Machinery directive............................................................................21
IEC 61800-5-2......................................................................21,21,21,22
EN IEC 62061......................................................................................... 21
EMC directive........................................................................................21
EN 50011.................................................................................................21
EN 61000-6-3.........................................................................................21
EN 61800-3.............................................................................................21
Low voltage directive........................................................................ 21
EN 50178.................................................................................................21
IEC 62061....................................................................................21,21,22
IEC 60204-1......................................................................................21,21
IEC 61508-1............................................................................................21
Symbols..............................................................................................................7
T
Type code.......................................................................................................... 5
AQ313340186453en-000201/130R054424 | Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 25

Safe Torque Off
Operating Guide
Index
AQ313340186453en-000201/130R0544 | 25Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
Page 26

Danfoss A/S
Ulsnaes 1
DK-6300 Graasten
vlt-drives.danfoss.com
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogs, brochures, and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This
also applies to products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specifications already agreed. All
trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
*130R0544*
Danfoss A/S © 2021.09
AQ313340186453en-000201 / 130R0544
*M0026501*
 Loading...
Loading...