Page 1
MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE
Technical Information
Steering
PVED-CL Communication
Protocol, version 1.38
powersolutions.danfoss.com
Page 2
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
July 2014 Danfoss layout. BA
07 September, 2010 New standard backpage. AD
10 February, 2010 Two new positions 11176,77 in the table - minor change. AC
08 February, 2010 Position 11152 in the table - minor change. AB
28 January, 2010 First edition. For PVED-CL software release version 1.38 AA
2 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 3

Technical Information
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Contents
Introduction
Purpose of the document .............................................................................................................................................................5
Conventions ...................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Reference documents.....................................................................................................................................................................5
Definitions and abbreviations......................................................................................................................................................5
Communications
J1939/ISOBUS compliance............................................................................................................................................................6
Network Management Protocol (NMP)...............................................................................................................................6
Identification.................................................................................................................................................................................6
Application layer......................................................................................................................................................................... 6
Diagnostics....................................................................................................................................................................................6
Proprietary messages ............................................................................................................................................................... 7
11bit ID messages.......................................................................................................................................................................8
Proprietary protocol........................................................................................................................................................................ 9
General............................................................................................................................................................................................9
Communication with sensors and steering devices.......................................................................................................9
Configuration............................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Secondary configuration device......................................................................................................................................... 10
Status.............................................................................................................................................................................................10
Control..........................................................................................................................................................................................10
Guidance......................................................................................................................................................................................11
Diagnostics..................................................................................................................................................................................13
Communication with sensors and steering devices
Steering wheel absolute angle and speed........................................................................................................................... 14
High priority steering device position....................................................................................................................................14
Low priority steering device position.....................................................................................................................................14
Primary steered wheel angle/position...................................................................................................................................15
Redundant steered wheel angle/position............................................................................................................................15
High priority external set-point controller............................................................................................................................15
Vehicle speed.................................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Configuration
GetParameter ................................................................................................................................................................................. 17
GetParameterResponse...............................................................................................................................................................17
SetParameter...................................................................................................................................................................................17
SetParameterResponse................................................................................................................................................................18
RestoreDefaults.............................................................................................................................................................................. 18
RestoreDefaultsResponse...........................................................................................................................................................19
CommitData.....................................................................................................................................................................................19
CommitDataResponse ................................................................................................................................................................ 20
EnterCalibrationMode..................................................................................................................................................................20
Status
GetCurrentMode............................................................................................................................................................................ 22
GetCurrentModeResponse.........................................................................................................................................................22
StartStopStatus...............................................................................................................................................................................22
Status..................................................................................................................................................................................................23
StartStopOperationStatus...........................................................................................................................................................24
OperationStatus ............................................................................................................................................................................ 25
TimeReport.......................................................................................................................................................................................26
Control
SetSpoolPosition ...........................................................................................................................................................................27
SetFlow ............................................................................................................................................................................................. 27
StartValveAutoCalibration..........................................................................................................................................................28
ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.......................................................................................................................................................29
SelectProgram.................................................................................................................................................................................30
SelectProgramResponse............................................................................................................................................................. 31
DisableSteeringDevice.................................................................................................................................................................31
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 3
Page 4

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Contents
DisableSteeringDevice Response.............................................................................................................................................32
Guidance
GuidanceSystemCommand....................................................................................................................................................... 33
GuidanceMachineStatus............................................................................................................................................................. 33
Diagnostics (proprietary)
GetErrorEntry...................................................................................................................................................................................35
GetErrorEntryResponse ...............................................................................................................................................................35
ClearErrorEntries.............................................................................................................................................................................36
Commit Error Code........................................................................................................................................................................37
4 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 5
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Introduction
Purpose of the document
This document has been created in order to present the communication protocol implemented in PVEDCL – a controller in the Electro-hydraulic Power Steering system. The document describes the CAN
messages which enables the PVED-CL and relevant sensor to be connected to a J1939 network.
Conventions
As suggested in J1939 protocol documentation, the little-endian layout applies to all multi-byte
•
numerical values, any exception requires an explicit note.
Unless otherwise mentioned, all signed numerical values are encoded in two’s complement format.
•
The CAN Data field byte numbers start from 1.
Reference documents
Refering to literature:
Reference Title/author
[PVED] Controller for Electro-Hydraulic Steering PVED, User Manual, 11079550.
[J1939] SAE J1939 Top Level
[J1939-21] SAE J1939 Data Link Layer
[J1939-71] SAE J1939 Application Layer
[J1939-73] SAE J1939 Diagnostic Layer
[J1939-81] SAE J1939 Network Management
Definitions and abbreviations
Definitions and abbreviations
Term Description
DTC Diagnostic Trouble Code
EHPS Electro-Hydraulic Power Steering
MMI Man-Machine Interface
XID Extended Message Identifier
PVED-CL Proportional Valve Digital – Closed Loop – here the valve controller
SPN Suspect Parameter Number
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 5
Page 6

Technical Information
Communications
J1939/ISOBUS compliance
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
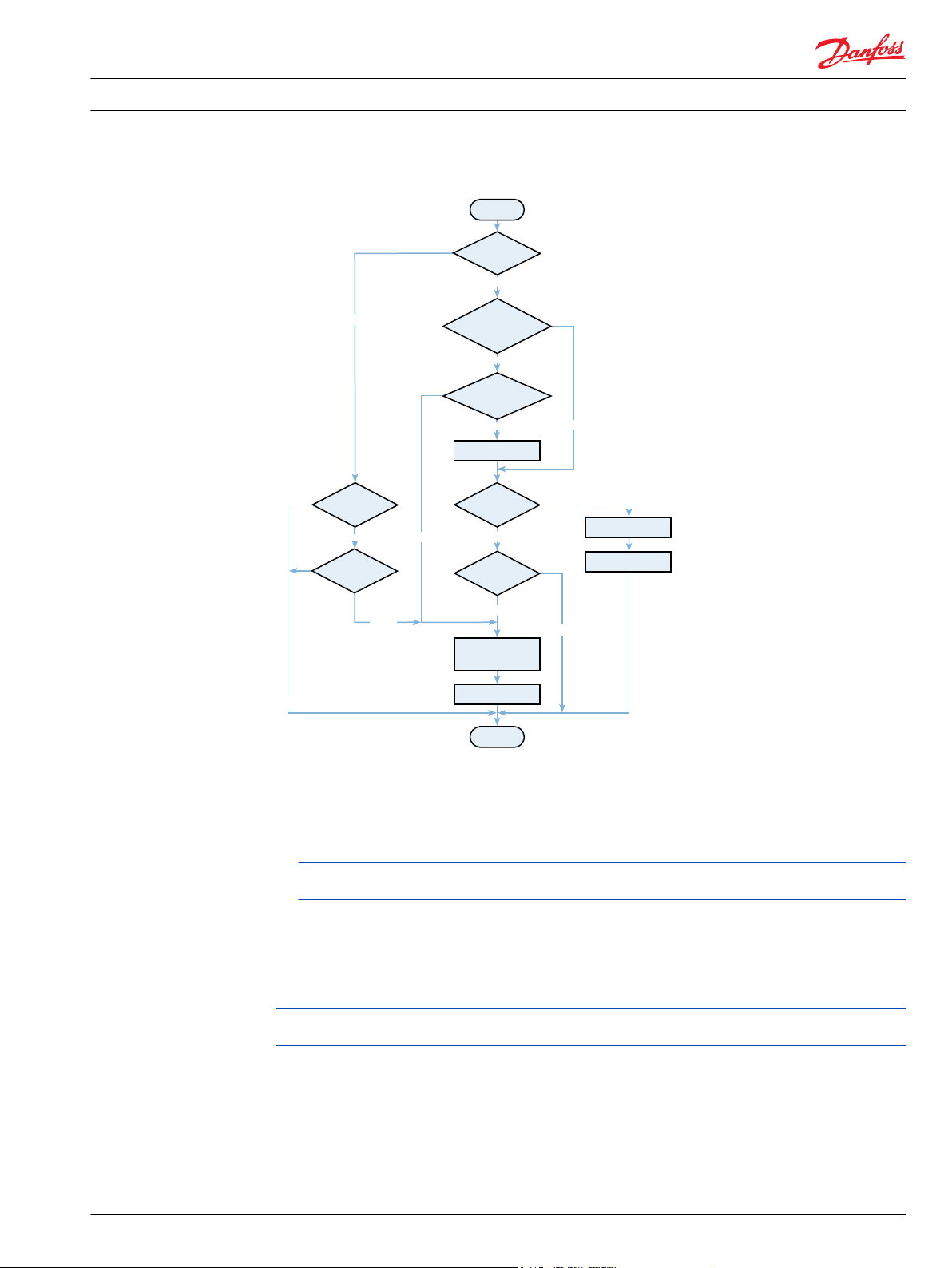
Network Management Protocol (NMP)
To make PVED-CL able to work in CAN J1939 networks, the following parts of NMP have been
implemented:
Address Claimed
•
Request for Address Claimed response
•
PVED-CL claims it address on power-on, after any won address arbitration and when requested to do so.
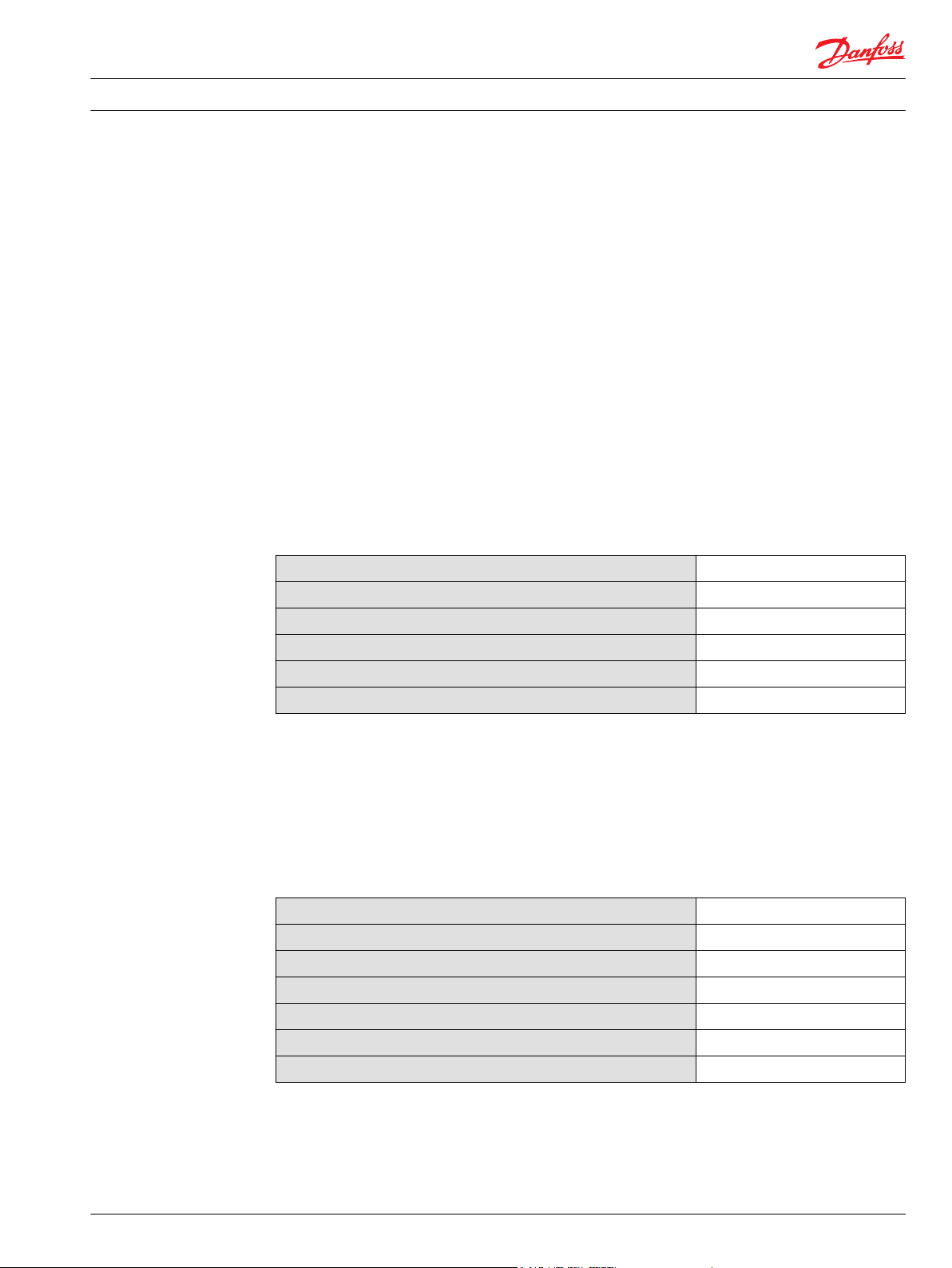
However, please note that because of some platform and software architecture constraints, PVED-CL may
claim its address even when it’s not needed. This is triggered by a RequestParameterGroup message –
no matter which node has sent it and which one the message is addressed to – as illustrated on figure
below.
Identification
There are 2 items which identify PVED-CL:
Source Address – available in all 29bit ID messages sent by PVED-CL
•
NAME – broadcast while claiming the address
•
Apart from this, the protocol supports the following proprietary identification:
PVED Serial Number available as a read-only parameter at index 65001
•
Sales Order Number at index 65002
•
Software Version Number at index 65003
•
Parameter Definition File at index 65004
•
SoftwareID (pgn65242) and ComponentID (pgn65259) defined by [J1939-71] are not available.
Application layer
Some steering functionality requires the Wheel Based Vehicle Speed signal (spn84) available in
pgn65265 – for more detailed information see Vehicle speed on page 15. The standardized guidance
messages are available in pgn44288 (Guidance System Command) and pgn44032 (Guidance Machine
Status). Further details see GuidanceSystemCommand on page 33.
PVED-CL supports Request PG message, but recognizes only requests for Address Claimed (pgn60928),
DM1 (pgn65226), DM2 (pgn65227) and DM3 (pgn65228). All other requests, if addressed explicitly to
PVED-CL, are answered with NACK (pgn59392).
Please note the following limitations:
Only 4 ACK/NACK messages can be buffered for transmission. Other requests will be ignored
•
If Request PG messages are sent too fast (with an interval less than 20 ms), some messages may be
•
lost.
Diagnostics
PVED-CL supports the following items defined by the J1939 diagnostic protocol [J1939-73]:
DM1 – Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes
•
DM2 – Previously Active Diagnostic Trouble Codes
•
DM3 – Diagnostic Data Clear/Reset for Previously Active DTCs
•
A request for DM3 results in resetting the Occurrence Counts for Previously Active DTCs.
6 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 7
No
No
No
Yes
No
No
START
Request PG?
Request to
global destination
or PVED-CL?
Request for
Address Claimed?
Process the request
Timer marked
as active?
Yes
Timer`s value
exceeds limit?
Yes
Signal that Address
Claimed message
has to be sent out
Mark timer inactive
STOP
Timer marked
as active?
Yes
Timer’s value
exceeds limit?
Reset timer`s value
Mark timer active
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
No
Technical Information
Communications
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Reception of request parameter group message
Due to software architectural limitations, the following deviations apply:
If DM1 message (expected to be sent every 1s) is a long message and a long upon-the-request
•
DM1/DM2 is being sent out, the transmission of the cyclic message will be skipped
If DM2 is a long message – more than one CAN message is needed – it will always be transmitted to
•
the global destination (preceded with the Broadcast Announce Message)
Proprietary error codes are available for deep diagnostics. Further details can be found in Diagnostics
(proprietary) on page 35.
Proprietary messages
Both proprietary A and B messages are in use. PDU1 proprietary messages (pgn61184) are used for
configuration and control commands as well as GetCurrentMode and GetCurrentModeResponse
messages, whereas PDU2 format is used for broadcast status messages.
PVED-CL uses a separate CAN buffer for receiving data from each node it can communicate with. This
means there’s no dependency between messages with pgn61184 sent from different nodes.
As three different status messages can be broadcast, three proprietary PDU2 parameter group numbers
are needed.
These numbers are as follows:
(65280 + offset_base)
•
(65280 + offset_base + 1)
•
(65280 + offset_base + 2)
•
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 7
Page 8

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Communications
where the offset_base is any value within the range [0…253] and can be selected with the configuration
tool. It’s OEM’s responsibility to make sure that offset_base is not programmed to a value that results in
pgns other nodes may use for different purposes.
Due to a relatively high number of exchanged messages, it’s recommended to implement a separate CAN
bus for the EHPS system only.
11bit ID messages
Most of the communication between PVED-CL and sensors/steering devices is performed with 11bit ID
messages. This makes the sensors simpler and allows them to be used in networks with other protocols.
8 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 9
Technical Information
Communications
Proprietary protocol
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
General
Because J1939 documents do not define a standard communication protocol for systems like EHPS, a
proprietary one has been defined on top of the existing common mechanisms described in previous
section. The proprietary protocol covers issues related to the communication with sensors, configuration,
status information, etc. Detailed information is available in the following sections.
The following general rules apply:
the time delay between messages marked as “when needed” shall not be less than 100 ms
•
PVED-CL shall respond within 200 ms, with exception for CommitDataResponse – 5000 ms
•
a response timeout shall be 500 ms (does not apply to CommitDataResponse message)
•
a not allowed command is ignored what results in no response sent back. Timeout policy shall apply
•
as a proprietary protocol is in use, default message priority shall be set to 6
•
PVED-CL’s can receive messages from selected nodes only. The source addresses of the vehicle speed
sensor, the MMI controller, the high priority external set-point controller as well as the configuration tool
and PVED-CL itself are configurable.
The default factory programmed values
Node
PVED-CL
High priority external set-point controller
Vehicle speed sensor
MMI controller
Configuration/diagnostic tool
Default Source Address
19
28
251
252
253
Communication with sensors and steering devices
In general, most of this type communication is performed with 11bit ID messages. More details about
message formats can be found in chapter Communication with sensors and steering devices on page 9.
A sensor is expected to periodically broadcast the data. A lack of data from the mapped sensor (with
exception for high priority set-point controller) causes PVED-CL to fail silent or enter the reduced mode,
depending on the configuration data. The timeouts are as follows:
The timeouts
Sensor or Steering Device:
Steering wheel sensor
High priority steering device
Low priority steering device
Primary steered wheel angle/position sensor
Redundant steered wheel angle/position sensor
Vehicle speed sensor
Timeout [ms]
100
100
100
60
60
160
Configuration
PVED-CL’s configuration memory contain parameters which identify the system components and control
the device’s behaviour. These parameters can be set up with a configuration tool.
The following operations are available:
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 9
Page 10

Technical Information
Communications
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
retrieving a parameter value
•
setting a parameter value
•
committing data to non-volatile memory
•
entering the calibration mode
•
restoring factory defaults
•
Secondary configuration device
Beside the configuration tool, the high priority external set-point controller has an access to the
parameter data, too. However, this device’s rights are limited to only reading the configuration settings.
Status
The information about control and sensor variables as well as PVED-CL’s current time and mode can be
found in periodically broadcast status messages. For further details see chapter Status on page 22.
Control
Control messages have been implemented to make the operator able to enable/disable steering devices
dynamically. This is especially useful when e.g. a joystick is mounted on the armrest and can be
unintentionally activated while getting on/off the machine. Disabling a steering device prevents the
controller from using the device set-points for steering. Default power-on state can be configured with
proper parameters stored in non-volatile memory.
The figure below shows the steering device disabling/enabling procedure. State transitions are
receptions of disable steering device commands and/or message timeouts which are set to 200 ms. For
further details see Control on page 27.
The numbers in octagons show where a response is sent back (DisableSteeringDeviceResponse
message):
1. Response data: enabling armed
2. Response data: device enabled
3. Response data: device disabling armed
4. Response data: device disabled
The current state of the device will be reported back if a command does not follow what’s on the figure.
Note that there are independent state machines implemented for each steering device which can be
disabled.
10 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 11

Disabling
armed
Device
disabled
Enabling
armed
Device
enabled
Command data:
enable device
Command data:
arm disabling
(Command data !-
disable device)
or
(disabling timeout)
(Command data !-
enable device)
or
(enabling timeout)
Command data:
arm enabling
Command data:
disable device
4
4
3
2
2
1
Technical Information
Communications
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Device enable/disable state transitions
Guidance
The high priority external set-point controller does not communicate with the PVED-CL the same way as
other steering devices do. The set-point controller is expected to provide PVED-CL with ISOBUS curvature
commands. This approach needs a special group of messages described in Guidance on page 33 and
the state machine shown on the figure Guidance Engage and Disengage State Machine below. Please note
that the state machine is executed only when PVED-CL is in the operational mode, or reduced mode and
the high priority external set-point controller is mapped.
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 11
Page 12
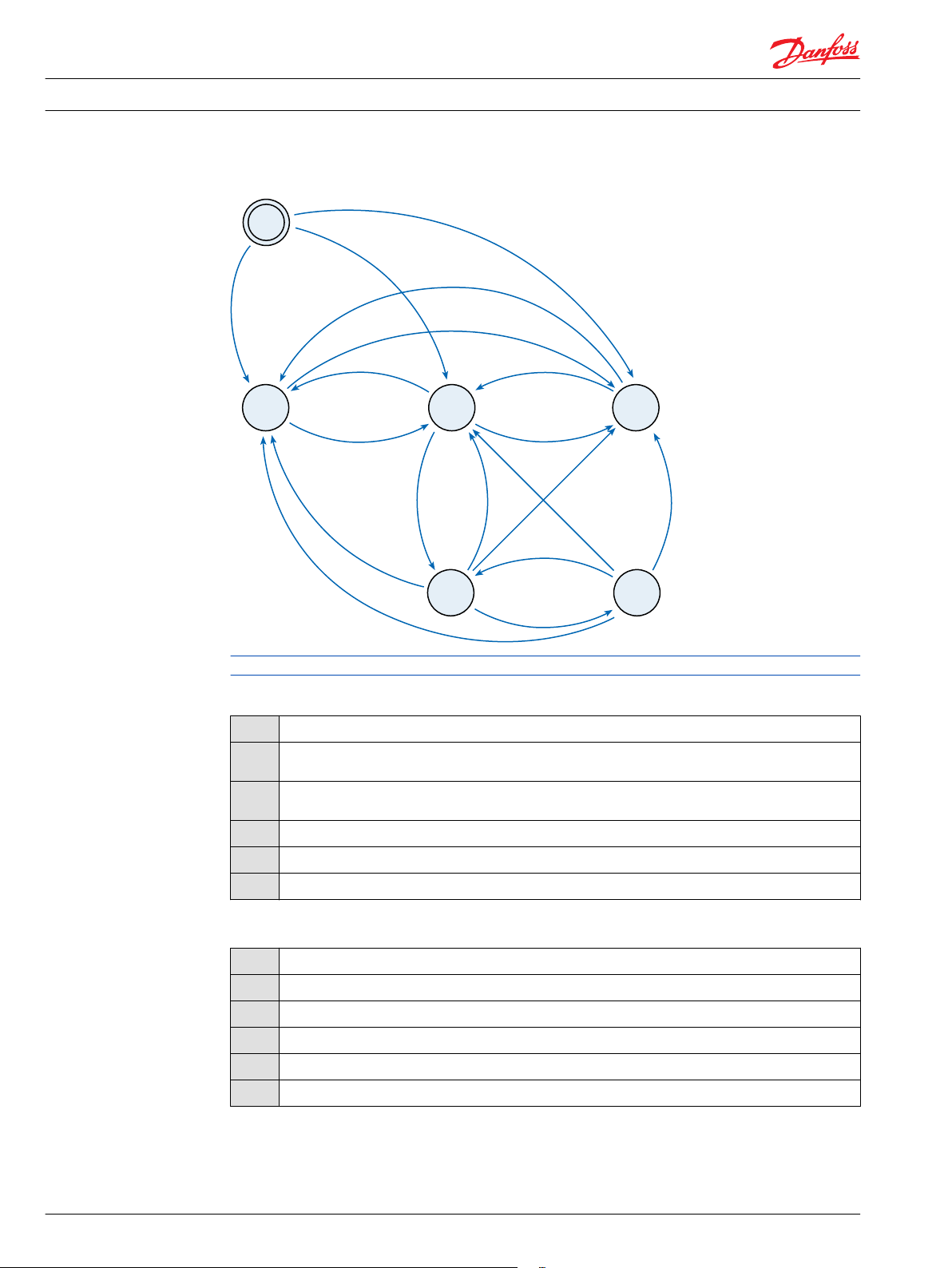
(not A) and B
1
not (A or B)
not (A or B)
not (A or B)
not (A or B)
not (A or B)
A
A
A
A
A
E
E
(not A) and B
(not A) and B
(not A) and B and C
(not A) and B and C
(not A) and B and D
and F
2 3
6
5
4
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Communications
Guidance engage and disengage state machine
Please note that no active transaction means no state change happens.
State definitions
1
2
3
4
5
6
Initialization
High priority set-point controller disabled (device disable functionality available in PVED-CL). If other
steering device is selected, PVED-CL follows set-points from this device
PVED-CL requests the high priority set-point controller for a message reset. It waits for at least one
GuidanceSystemCommand message not intended for steering
PVED-CL waits for curvature requests intended for steering
PVED-CL follows curvature requests
PVED-CL follows set-points from other steering device
Conditions
A
B
C
D
E
F
High priority set-point controller disabled (device disable functionality available in PVED-CL)
No other steering device selected or set-points (from other steering device) below threshold
New curvature request received, but not intended for steering
New curvature request received, intended for steering
Timeout – no new curvature request has been received for 200 ms
Steering wheel disengage ability check has been passed or is disabled
12 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 13

Technical Information
Communications
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Flags available in status messages (guidance machine status)
State Request Reset
Command Status
1 No status message transmitted
2 00 – reset not required 11 – not available 11 – not available 01 – active
3 01 – reset required 01 – correct position or
4 00 – reset not required 01 – correct position or
5 00 – reset not required 01 – correct position 01 – system is ready 00 – inactive
6 00 – reset not required 00 – incorrect position 00 – system is not ready 00 – inactive
1)
Error indication is reported if the steering wheel disengage ability check (if enabled) has failed. This means that too
much time has passed since a steering wheel position change has last exceeded the defined position change
threshold. Both the position change threshold and the timeout value can be configured as required by the
application.
To allow removable set-point controllers to be used, vehicle specific data can be stored in the PVED-CL‘s
configuration memory. For further details refer to PVED-CL User Manual, 11079550.
Steering Input Position
Status
10 – error indication
10 – error indication
1)
1)
Machine can Execute
Commands
00 – system is not ready 00 – inactive
00 – system is not ready 00 – inactive
Mechanical System
Lockout
Diagnostics
Although PVED-CL supports J1939 diagnostic protocol [J1939-73], there exists a proprietary way of
informing about errors. The configuration/diagnostic tool has an access to the event logs maintained by
PVED-CL’s software, which is intended to make the debugging easier as well as to help an OEM or a
support team to tune the system. Detailed information about the interface is provided in the chapter
Diagnostics (proprietary) on page 35.
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 13
Page 14

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Communication with sensors and steering devices
Steering wheel absolute angle and speed
The message data represents the absolute position of the steering wheel and the position change.
CAN message
CAN id.
Occurrence
Sent by
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095 position – reflects 0 – 359.9121 deg. with the
3 – – ignored by PVED-CL
4, 5 SIGNED16 -4095 – 4095 position change – reflects -359.9121 – 359.9121 deg.
6-8 – – ignored by PVED-CL
0x301 (11bit)
every 5, 10 (recommended) or 20 ms
steering wheel angle sensor
resolution of 0.0879 deg. Rolls over after a full turn
with the resolution of 0.0879 deg
High priority steering device position
The message data represents the position of the high priority steering device.
CAN message
CAN id.
Occurrence
Sent by
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095
Low priority steering device position
The message data represents the position of the low priority steering device.
CAN message
CAN id.
Occurrence
Sent by
0x304 (11bit)
every 80 ms or less (recommended 10 ms)
high priority steering device
Position:
0
2047
4095
0x406 (11bit)
every 80 ms or less (recommended 10 ms)
low priority steering device
– left end lock
– neutral position
– right end lock
14 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 15
Technical Information
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Communication with sensors and steering devices
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095
Primary steered wheel angle/position
The message data represents either the position of the steering actuator or the steered wheel angle
CAN message
CAN id.
Occurrence
Sent by
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095 Position:
Position:
0
2047
4095
0x105 (11bit)
every 40 ms or less (recommended: 10 ms)
primary steered wheel angle/position sensor
– left end lock
– neutral position
– right end lock
0 – left end lock
2047 – neutral position (vehicle’s moving straight
ahead)
4095 – right end lock
Redundant steered wheel angle/position
The message data represents either the position of the steering actuator or the steered wheel angle.
CAN message
CAN id.
Occurrence
Sent by
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095
High priority external set-point controller
The communication with the high priority external set-point controller is performed in a special way, with
messages described in Guidance on page 11.
Vehicle speed
This is a standard message used for broadcasting the information about the vehicle speed [J1939 – 71].
0x205 (11bit)
every 40 ms or less (recommended: 10 ms)
redundant steered wheel angle/position sensor
Position:
0
2047
4095
– left end lock
– neutral position (vehicle’s moving straight ahead)
– right end lock
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 15
Page 16

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Communication with sensors and steering devices
CAN message
Priority
PGN
Occurrence
Sent by
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1 – – ignored by PVED-CL
2, 3 UNSIGNED16 0 – 64255 vehicle speed in 1/256 km/h
4 – 8 – – ignored by PVED-CL
6
65265
every 100 ms
vehicle speed sensor
reflects 0 – 250.996 km/h
16 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 17
Technical Information
Configuration
GetParameter
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
This message is used to retrieve a value of a given parameter. If an unknown parameter value is
requested, no response will be sent back. Timeout policy shall be applied.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA0 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 UNSIGNED16 (see parameter list) parameter index
6
61184
0x0FA0 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration and fault
configuration tool, high priority external set-point controller
PVED-CL
GetParameterResponse
This message is sent upon the GetParameter request and contains both parameter index and parameter
value.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FA1 (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced, calibration and fault
PVED-CL
configuration tool or high priority external set-point controller
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA1 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 UNSIGNED16 (see parameter list) parameter index
5 – 8 UNSIGNED32 (depends on a
parameter)
parameter value
SetParameter
This message is used to set value of a given parameter. Please note that the values are not stored in nonvolatile memory unless CommitData command is sent.
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 17
Page 18
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Configuration
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA2 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 UNSIGNED16 (see parameter list) parameter index
5 – 8 UNSIGNED32 (depends on a
6
61184
0x0FA2 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration
configuration tool
PVED-CL
parameter value
parameter)
SetParameterResponse
Sent back upon the SetParameter request and contains both parameter index and value. If, due to any
reason, parameter value has not been changed, the previous and still valid one is reported.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FA3 (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced, calibration
PVED-CL
configuration tool
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA3 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 UNSIGNED16 (see parameter list) parameter index
5 – 8 UNSIGNED32 (depends on a
parameter)
parameter value
RestoreDefaults
Used to set all parameter values to factory defaults.
Please note that the values are not stored in non-volatile memory unless CommitData command is sent.
CAN message
Priority
18 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
6
Page 19

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Configuration
CAN message (continued)
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA4 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x5C check value
RestoreDefaultsResponse
Sent back to signal the status.
61184
0x0FA4 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration
configuration tool
PVED-CL
CommitData
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FA5 (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced, calibration
PVED-CL
configuration tool
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA5 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x00
0x0FF
- restoring defaults failed
- all parameter values changed to factory
defaults
This is a request for copying all modified parameters to non-volatile memory.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
6
61184
0x0FA6 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 19
Page 20

Technical Information
Configuration
CommitDataResponse
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
CAN message (continued)
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA6 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x5A check value
Sent back to signal any change in the commit process status.
This means the CommitData command may result in several responses, e.g. ready > in progress >
succeeded.
The minimum delay between responses is set to 40 ms.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
configuration tool
PVED-CL
6
61184
0x0FA7 (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced, calibration
PVED-CL
configuration tool
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA7 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8
4, 5 UNSIGNED16 Commit error code If commit operation failed, an error code on the
EnterCalibrationMode
This command is used to force PVED-CL to enter the calibration mode, for further information see PVEDCL User Manual, 11079550 and shall be sent within 200ms after PVED-CL transmits its Address Claimed
message.
Once the system state changes to Calibration, a response – GetCurrentModeResponse with a proper
mode identifier – will be sent back.
20 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
Commit status:
– ready to perform commit operation
– commit operation has just begun
– the operation succeeded
– the operation failed
– parameter cross-check failed
– commit is already in progress
particular parameter cross-check is issued.
If commit operation succeeded, the value is 0.
Please refer to Commit Error Code on page 37.
Page 21

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Configuration
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA8 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x58 check value
6
61184
0x0FA8 (MSB first)
if required, within 200ms after PVED-CL’s Address Claim
only during start-up
configuration tool
PVED-CL
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 21
Page 22

Technical Information
Status
GetCurrentMode
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Used to get the information about the current PVED-CL mode.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FA9 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
6
61184
0x0FA9 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration, fault
configuration tool
PVED-CL
GetCurrentModeResponse
Information about the current mode.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FAA (MSB first)
200 ms after claiming an address (if no address arbitration lost) and upon
request
operational, reduced, calibration, fault
PVED-CL
configuration tool
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAA (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x55
0x0AA
0x0AF
0x0FF
current mode:
– calibration
– operational
– reduced
– fault
StartStopStatus
This command is used to make PVED-CL start/stop sending status information. Power-on state: status
disabled.
22 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 23

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Status
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAB (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x00
6
61184
0x0FAB (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced, calibration
configuration tool
PVED-CL
stop sending status information
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
request for status data set no. 1
request for status data set no. 2
request for status data set no. 3
request for status data set no. 4
Status
Used to broadcast sensor or control variables on the CAN bus. In fault mode broadcasting is stopped to
minimize the bus load and avoid incorrect hazardous actions done by devices that rely on the message.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
65280 + offset_base
n/a
every 40 ms. Only if Status messages are enabled
operational, reduced,calibration
PVED-CL
all nodes
Set no. 1
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 SIGNED16 0 – 1023 AD1 – the raw input of the first ADC channel. Reflects
(0-5) V
3, 4 SIGNED16 0 – 1023 AD2 – the raw input of the second ADC channel.
Reflects (0-5) V
5, 6 SIGNED16 0 – 1023 AD3 – the raw input of the spool position channel
(third ADC channel). Reflects (0-5) V
7, 8 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Xsp – the calculated spool position set-point.
Reflects -7 – 7 mm spool travel
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 23
Page 24

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Status
Set no. 2
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Yact – scaled steering actuator position.
Reflects -100.0% – 100.0% where 0.0% indicates the
middle of the cylinder
3, 4 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Yset – commanded actuator position set-point
(closed loop control) or commanded actuator speed
set-point (open loop control)
5, 6 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Q – the port flow command.
Reflects the range 100% at CL port to 100% at CR
port
7, 8 UNSIGNED16
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
Set no. 3
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Xsp – the calculated spool position set-point.
3, 4 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Scaled spool position. Reflects -7 – 7 mm spool travel
5, 6 UNSIGNED16 0 – 4095 wheel angle (scaled Yact)
7, 8 UNSIGNED16 0 - 59999 timestamp – a value of a millisecond timer that starts
Selected device:
– no device selected
– steering wheel
– reserved
– high priority steering device
– low priority steering device
– high priority set-point controller
Reflects -7 – 7 mm spool travel
0 – left endlock
2047 – pointing straight ahead
4095 – right endlock
counting upon PVED-CL power-on and rolls over
after one minute. 1 ms unit, accuracy equal to 5 ms
Set no. 4
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 9990 Sensor supply voltage [mV]
3, 4 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Scaled spool Position
5, 6 SIGNED16 -50 – 451 PVED-CL temperature [deg. C]
7, 8 UNSIGNED16 13 – 35534 Battery supply voltage [mV]
StartStopOperationStatus
The command is used to make PVED-CL start/stop sending operation status information. Power-on state:
operation status enabled.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
24 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Reflects -7 – 7 mm spool travel
6
61184
0x0FAC (MSB first)
Page 25

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Status
CAN message (continued)
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAC (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x00
OperationStatus
Used for broadcasting the information about selected device, chosen program and steering devices
status.
when required
operational, reduced, fault
configuration tool
PVED-CL
0x0FF
stop sending operation status information
request for operation status
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
65280 + offset_base + 1
n/a
every 240 ms. Only if Operation Status messages are enabled
operational, reduced, fault
PVED-CL
all nodes
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1 UNSIGNED8
0x0AA
0x0AF
0x0FF
2 UNSIGNED8
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
3 UNSIGNED8 (depends on the selected device) Active program.
4 UNSIGNED8
0x00
0x03
0x53
0x0A3
0x0F3
Current mode:
– operational
– reduced
– fault
Selected device:
– no device selected
– steering wheel
– reserved
– high priority steering device
– low priority steering device
– high priority external set-point controller
0x0FF if no device is selected
High priority steering device status:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 25
Page 26
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Status
Data field (continued)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
5 UNSIGNED8
0x00
0x04
0x54
0x0A4
0x0F4
6 UNSIGNED8
0x00
0x05
0x55
0x0A5
0x0F5
7 bits 8 - 5 all zeros Not used
Reduced mode caused by problems with:
bit 4
0
1
bit 3
0
1
bit 2
0
1
bit 1
0
1
Low priority steering device status:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
High priority external set-point controller:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
Wheel angle sensor signal:
– no
– yes
Vehicle speed signal:
– no
– yes
High priority steering device:
– no
– yes
Low priority steering device:
– no
– yes
TimeReport
This message is used to provide other nodes with an absolute measure of time since the PVED-CL was
booted. It can be used for diagnostic purposes and for resolving any rollover ambiguities in the
timestamp information available in the Status message – set no. 3.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
65280 + offset_base + 2
n/a
every 1 s
operational, reduced
PVED-CL
all nodes
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 59999 timestamp – a value of a timer that starts counting
3 – 6 UNSIGNED32 0 – 357913 number of rollovers, since boot, of a millisecond
upon PVED‑CL power-on and rolls over after one
minute.
1 ms unit. Accuracy equal to 5 ms.
timer
26 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 27

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
SetSpoolPosition
Used to transmit the spool position set-point to the PVED-CL.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAD (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 requested spool position, reflects -7 – 7 mm spool
6
61184
0x0FAD (MSB first)
when required
calibration
configuration tool
PVED-CL
travel
SetFlow
Used for transmitting a flow request to the PVED-CL. The flow request is converted to a spool position
with dead-band compensation. Use the SetFlow command for black-box testing the PVED-CL flow
characteristic in operational mode without knowledge to the actual dead-band settings.
Open-loop mode converts the flow request directly to the corresponding spool position with dead-band
compensation.
Closed-loop mode converts the flow request as for open-loop mode but adds the programmed closed
loop spool position offset (ClosedLoopXspOffset at parameter index 748) to the spool position. This
allows testing the valve output flow when used in Guidance mode.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB8 (MSB first)
when required
calibration
configuration tool
PVED-CL
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB8 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 27
Page 28

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
Data field (continued)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
3, 4 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000
-1000
-1
1
1000
5 UNSIGNED8 0
255
StartValveAutoCalibration
Used for performing an auto-calibration of the PVED-CL to the valve. The valve dead-bands are
automatically found and stored in the PVED-CL.
Auto-calibration may be useful for fine-tuning the PVED-CL and the valve when installed in its final
environment.
This ensures optimum open-loop and closed-loop steering performances.
Auto-calibration is also useful if the PVED-CL needs to be replaced in the field.
requested flow
– corresponds to max flow to the left
– corresponds to minimum flow to the left
– corresponds to minimum flow to the right
– corresponds to max flow to the right
Apply open-loop flow-to-spool-position scaling
Apply closed-loop flow-to-spool-position scaling
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB6 (MSB first)
when required
calibration
MMI
PVED-CL
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB6 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3, 4 UNSIGNED16 0 – Max XspStartSearch – the spool position set-point (Xsp)
at which the auto-calibration starts.
Max = 250 + XspCalibrationOffset
XspCalibrationOffset is the parameter value stored at
parameter index 758.
5 UNSIGNED8 1 – 255 XspIncrementSize – the spool position set-point
increment size (∆Xsp) while searching for the
specified minimum steered wheel position (Yact)
difference.
6 UNSIGNED8 1 – 255 YactDiffThreshold – the minimum steered wheel
position (Yact) difference threshold
The difference is measured in the time-out period.
7, 8 UNSIGNED16 1 – 65535 Time-out period - defines the time [ms] that each
spool position set-point is active in before the next
increment.
28 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 29
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
Data field (continued)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
The spool position set-point unit is a scaled value in the range -1000 to 1000, corresponding from -7 to 7 mm
nominally.
The scaled steering actuator position/steered wheel position (Yact) range is -1000 to 1000, corresponding to the
steered wheel end-lock positions. Requires that the wheel angle sensor is correctly calibrated.
ValveAutoCalibrationStatus
The message is transmitted as a response to the StartValveAutoCalibration command. Allows monitoring
the progress and status of the valve auto-calibration.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB7 (MSB first)
During auto-calibration after each time-out period, at commit state change, at status
information change
Calibration
PVED-CL
MMI
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB7 (MSB
first)
3 UNSIGNED8
0x00
0x01
0x02
0x03
0x04
0x05
0x06
0x07
0x08
0x09
0x0A
0x0B
0x0C
0x0D
0x0E
0x0F
0x10
0x11
0xA0
0xA1
0xAA
0xFF
4, 5 SIGNED16 -1000 – 1000 Xsp - current main spool position
extended message identifier (XID)
Related to StartValveAutoCalibration command:
− invalid auto-calibration request
− invalid starting spool position set-point request
− invalid spool position set-point increment size request
− invalid minimum wheel angle difference threshold request
− invalid time-out period value request
Auto-calibration status/error codes:
− invalid wheel position for further auto-calibration related activities
− missing steering wheel sensor signal
− steering wheel in use
− missing steered wheel feedback sensor signal
− wheels found moving for the starting spool position set-point
– wheels not moving at maximum allowed spool position (right
direction)
– wheels not moving at maximum allowed spool position (left
direction)
– unable to update dead-band parameters
− the previously requested commit data process has not finished yet
− commit data process has failed due to the cross-parameter check
failure
− commit data process has failed due to the EEPROM write failure
− commit data process has not started on time
− commit data process has not finished on time
– unknown error (contact technical support)
− the commit data process has started
– auto-calibration in progress
− auto-calibration completed
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 29
Page 30

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
A typical successful valve auto-calibration message sequence:
MMI.StartValveAutoCalibration → PVED-CL
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
...
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
PVED-CL.SetParameterResponse.right dead-band value (index 738) → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
PVED-CL.SetParameterResponse.left dead-band value (index 737) → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
PVED-CL.SetParameterResponse.right maximum value (index 747) → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration in progress → MMI
PVED-CL.SetParameterResponse.left maximum value (index 729) → MMI
PVED-CL.CommitDataResponse.Commit operation has just begun → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.Commit process has started → MMI
PVED-CL.CommitDataResponse.Commit succeeded → MMI
PVED-CL.ValveAutoCalibrationStatus.auto-calibration completed → MMI
SelectProgram
Used for requesting the program change for a defined steering device.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FAE (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced
MMI
PVED-CL
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAE (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8
0 – 9
20 – 24
25 – 29
30 – 34
program number for:
– steering wheel
– high priority steering device
– low priority steering device
– high priority external set-point controller
30 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 31
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
SelectProgramResponse
The message is transmitted upon the SelectProgram command to inform whether the program
transition was successful. If the transition has not been allowed, the active program number will point at
the previous and still valid program.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FAF (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 as for SelectProgram requested program number
4 UNSIGNED8 as for SelectProgram active program number (for the requested device) or
6
61184
0x0FAF (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced
PVED-CL
MMI
0x0FF if a non-existing program has been requested
DisableSteeringDevice
The command is used to disable/enable any mapped steering device, but steering wheel.
The message is ignored if the OSP (hydraulic backup) is not present.
Disabled devices are not taken into account while making a decision which steering device should
control the vehicle. However, the plausibility checks related to these devices will be performed.
Please note that disabling the device currently selected for steering results in “no device selected”
condition.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Mode
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB0 (MSB first)
when required
operational, reduced
MMI
PVED-CL
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB0 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 31
Page 32

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Control
Data field (continued)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
3 SIGNED16
0x53
0x03
0x0A3
0x54
0x04
0x0A4
0x55
0x05
0x0A5
DisableSteeringDevice Response
The message is transmitted upon the DisableSteeringDevice command to inform whether the
operation succeeded.
However, as DisableSteeringDevice command is ignored when the OSP is not present, in this case no
response will be sent back.
Command:
– arm high priority steering device enabling/
disabling
– enable high priority steering device
– disable high priority steering device
– arm low priority steering device enabling/disabling
– enable low priority steering device
– disable low priority steering device
– arm high priority external set-point con. enabling/
disabling
– enable high priority external set-point controller
– disable high priority external set-point controller.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Mode
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB1 (MSB first)
upon request, on timeout
operational, reduced
PVED-CL
MMI
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB1 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 0x00
0x03
0x53
0x0A3
0x0F3
4 UNSIGNED8 0x00
0x04
0x54
0x0A4
0x0F4
5 UNSIGNED8 0x00
0x05
0x55
0x0A5
0x0F5
High priority steering device status:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
Low priority steering device status:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
High priority external set-point controller:
– device not mapped
– device enabled
– device enabled. Change armed
– device disabled
– device disabled. Change armed
32 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 33

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Guidance
GuidanceSystemCommand
This message conforms to ISO 11783-7 guidance commands. It is used for auto-steering and commands
the vehicle to follow the transmitted curvature course.
Negative curvature values will cause the vehicle to drive left.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Mode
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 64255 curvature command
3 bits 8-3 all ones reserved
bits 2, 1 00
4 – 8 – all ones reserved
3
44288
n/a
when required, every 100 ms or faster. PVED-CL sample period is 20 ms
operational, reduced
high priority external set-point controller
PVED-CL
(-8032 to 8031.75) km-1 with resolution 0.25 km-1
and offset -8032 km-1
steering command status:
01
10
11
– not intended for steering
– intended for steering
– error indication
– not available
GuidanceMachineStatus
This message conforms to ISO 11783-7 guidance commands. It is used to report current vehicle’s
estimated curvature as well status flags.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Mode
Sent by
Sent to
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 33
3
44032
n/a
every 80 ms, only if the high priority external set-point controller is mapped
operational, reduced
PVED-CL
high priority external set-point controller
Page 34

Technical Information
Guidance
PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0 – 64255 Estimated curvature: (-8032 to 8031.75) km-1 with
resolution 0.25 km-1 and offset -8032 km
3 bits 8, 7 00
01
10
11
bits 6, 5 00
01
10
11
bits 4, 3 00
01
10
11
bits 2, 1 00
01
10
11
4 – 8 – all ones Reserved
Request reset command status:
– reset not required
– reset required
– error indication
– not available
Steering input position status:
– incorrect position
– correct position
– error indication
– not available
Machine can execute commands:
– system is not ready
– system is ready
– error indication
– not available
Mechanical system lockout:
– not active
– active
– error indication
– not available
-1
Please note that when PVED-CL requests the GPS reset (byte 3, bits 8-7), it waits for at least one
GuidanceSystemCommand message not intended for steering.
34 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 35

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Diagnostics (proprietary)
GetErrorEntry
The command is used to retrieve the data stored in error buffers.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB3 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 1 – 16 buffer index (the oldest error at index 1)
4 UNSIGNED8 0
3
61184
0x0FB3 (MSB first)
when needed
operational, reduced, calibration and fault
configuration tool
PVED-CL
Request details
1
2
– error code
– timestamp when error occurred since power on
– PVED-CL PCB temperature when error occurred
GetErrorEntryResponse
The message presents data available in the error log.
CAN message
Priority
PGN
XID
Occurrence
Modes
Sent by
Sent to
6
61184
0x0FB4 (MSB first)
upon request
operational, reduced, calibration and fault
PVED-CL
configuration tool
Data field (error identification data)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB4 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 1 – 16 buffer index (the oldest error at index 1)
4 UNSIGNED8 0 error code details
5 UNSIGNED8
0
0x55
0xAA
0xFF
error severity:
– caution
– nominal
– critical
– wrong index or no information available
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 35
Page 36

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Diagnostics (proprietary)
Data field (error identification data) (continued)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
6–7 UNSIGNED16 0 – 0xFFFE
0xFFFF
Data field (timestamp)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB4 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 1 – 16 buffer index (the oldest error at index 1)
4 UNSIGNED8 1 timestamp details
5–8 UNSIGNED32
0 – 0xFFFFFFFE
0xFFFFFFFF
Data field (temperature)
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB4 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
3 UNSIGNED8 1 – 16 buffer index (the oldest error at index 1)
4 UNSIGNED8 2 temperature details
5–6 SIGNED16
-50 – 150
150 – 450
-32768
– error code
– wrong index or information not available
timestamp:
– the value of a timer which starts counting upon
PVED-CL power-on, observed when the error
occurred
– wrong index or no information available
PVED temperature:
– temperature in oC, observed when the error
occurred
– temperature sensor provided data, but was likely
to be damaged by being oveheated
– wrong index or no information available
ClearErrorEntries
Used for clearing all error entries in the persistent error buffer.
CAN message
Priority 6
PGN 61184
XID 0x0FB5 (MSB first)
Occurrence when needed
Modes operational, reduced, calibration
Sent by configuration tool
Sent to PVED-CL
Data field
Bytes Encoding Value/Range Description
1, 2 UNSIGNED16 0x0FB5 (MSB first) extended message identifier (XID)
36 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 37

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Diagnostics (proprietary)
Commit Error Code
Commit Error codes from CommitDataResponse message
Commit Error
Code
11150
11151
11152
11153
11154
11155
11156
11160
11161
11162
11163
11164
11165
11166
11167
11168
Parameter Consistency Check Fail
Vehicle speed dependant parameter conflict.
One or more steering wheel programs do not comply with the rule sts0 ≤ sts1 ≤ sts2 ≤ sts3 ≤ sts4 ≤
sts5.
Vehicle speed dependant parameter conflict.
One or more programs for high priority steering device, low priority steering device or high
priority external set-point controller,
the sensitivity parameters do not comply with the rule sts0 ≥ sts1 ≥ sts2 ≥ sts3 ≥ sts4 ≥ sts5.
OSP and EHPS valve parameter conflict. One or more steering wheel programs do not comply with
the rule that sensitivity parameters (Sts0-Sts5) shall be < OSP (back-up) sensitivity.
OSP and EHPS valve parameter conflict. The backlash parameter Ri shall be ≤ RiOSP.
Closed-loop parameter conflict. YR must be 1000 for programs where the control principle Cp is
“Closed loop”.
Closed-loop parameter conflict. YL must be 1000 for programs where the control principle Cp is
“Closed loop”.
OSP and EHPS valve conflict. For steering wheel programs, Qm must be 1000.
Primary and secondary wheel angle sensor conflict. No primary wheel angle sensor is mapped.
Db and Xysat parameter conflict. Db must be ≥ xysat.
Analogue input AD1 parameter conflict.
For linear (3-point) AD1 calibration the following rule must be followed:
AD1_1000_Left (index 65080) < AD1_Neutral (index 65086) < AD1_1000_Right (index 65083) or
AD1_1000_Left > AD1_Neutral > AD1_1000_Right
For linear (5-point) AD1 calibration the following rule must be followed:
AD1_1000_Left < AD1_500_Left (index 65055) < AD1_Neutral < AD1_500_Right (index
65062) < AD1_1000_Right or
AD1_1000_Left > AD1_500_Left > AD1_Neutral > AD1_500_Right > AD1_1000_Right
Analogue input AD2 parameter conflict.
For linear (3-point) AD2 calibration the following rule must be followed:
AD2_1000_Left (index 65089) < AD2_Neutral (index 65095) < AD2_1000_Right (index 65092) or
AD2_1000_Left > AD2_Neutral > AD2_1000_Right
For linear (5-point) AD2 calibration the following rule must be followed:
AD2_1000_Left < AD2_500_Left (index 65069) < AD2_Neutral < AD2_500_Right (index
65076) < AD2_1000_Right or
AD2_1000_Left > AD2_500_Left > AD2_Neutral > AD2_500_Right > AD2_1000_Right
Closed loop mode with no wheel angle sensor conflict.
Closed loop program for high or low priority steering device or external set-point controller are
configured but no wheel angle sensor is mapped.
J1939 Source address parameter conflict.
PvedSourceAddress, VehicleSpeedSensorSourceAddress, ControlDeviceSourceAddress,
ConfigurationDeviceSourceAddress, and HPExtSourceAddress (index 64003 to 64007) have to
differ from each other.
Device enable/disable initialization conflict.
When no OSP is mapped, all mapped steering devices must be enabled at boot-up (index 64008 to
64010).
Rate limitation parameter conflict.
When fast ramp down is utilized, Tfo (index xy23) and Tfh (index xy24) must be higher than Tfr
(index xy33)
Analogue input mapping conflict. Two sensors are mapped to the same AD input.
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 37
Page 38

Steering_Motion_Threshold • 4095
StwDxActivationThreshold≥
10 • Full_Strk • Period
Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
Diagnostics (proprietary)
Commit Error codes from CommitDataResponse message (continued)
Commit Error
Code
11169
11170
11171
11172
11173
11176
11177
Parameter Consistency Check Fail
AD1/AD2 analogue input compensation error. The 5V ext reference stored for compensation is out
of range.
Articulated vehicle length parameter is out of range. Total length cannot exceed 65535 mm.
Actuator dependant steering sensitivity parameter conflict.
One or more program utilizes actuator dependant steering sensitivity but no wheel angle sensor is
mapped.
Vehicle speed dependant steering sensitivity parameter conflict.
One or more program utilizes vehicle speed dependant steering sensitivity but no wheel speed
sensor is mapped.
StwDxActivationThreshold parameter conflict.
StwDxActivationThresold (index 64022) needs to be greater than or equal to the steering wheel
position difference corresponding to the min motion needed to make the steering wheel selected
for steering. The follow equation shall be true:
Where:
Steering_Motion_Threshold is defined in parameter index 119.
Full_Strk is defined in parameter 111.
Period is the SASA transmission period.
Set Period = 5, 10 or 20 if STWSensor-TransmissionRate is 20, 10 or 5 ms respectively.
STWSensorTransmissionRate is defined in parameter index 65124.
The spool position dead-band parameter (Xspr_0 or Xspl_0) value is out of range for the selected
valve type.
The maximum allowed spool position parameter (Xspr_1000 or Xspl_1000) is out of range for the
selected valve type.
38 11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014
Page 39

Technical Information PVED-CL Communication Protocol, version 1.38 Technical Information
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 39
Page 40

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions US Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 3418 5200
Products we offer:
Comatrol
www.comatrol.com
Schwarzmüller-Inverter
www.schwarzmuellerinverter.com
Turolla
www.turollaocg.com
Valmova
www.valmova.com
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
Bent Axis Motors
•
Closed Circuit Axial Piston
•
Pumps and Motors
Displays
•
Electrohydraulic Power
•
Steering
Electrohydraulics
•
Hydraulic Power Steering
•
Integrated Systems
•
Joysticks and Control
•
Handles
Microcontrollers and
•
Software
Open Circuit Axial Piston
•
Pumps
Orbital Motors
•
PLUS+1® GUIDE
•
Proportional Valves
•
Sensors
•
Steering
•
Transit Mixer Drives
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electronic components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market. Building on
our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with our customers to ensure
exceptional performance for a broad range of off-highway vehicles.
We help OEMs around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring
vehicles to market faster.
Danfoss – Your Strongest Partner in Mobile Hydraulics.
Go to www.powersolutions.danfoss.com for further product information.
Wherever off-highway vehicles are at work, so is Danfoss. We offer expert worldwide support
for our customers, ensuring the best possible solutions for outstanding performance. And
with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also provide comprehensive global
service for all of our components.
Please contact the Danfoss Power Solution representative nearest you.
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to
products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without changes being necessary in specifications already agreed..
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
11079551 • Rev BA • July 2014 www.danfoss.com
Local address:
©
Danfoss A/S, 2013
 Loading...
Loading...