Page 1

Technical Information
Gear Pumps
Group 4
www.danfoss.com
Page 2

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
October 2019 First edition 0101
2 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 3

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Contents
General Information
Overview..............................................................................................................................................................................................4
Group 4 gear pumps attributess.................................................................................................................................................4
Pump displacements.......................................................................................................................................................................4
Pump design...................................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Technical data for TAP4NN........................................................................................................................................................... 5
Determination of nominal pump sizes.....................................................................................................................................6
Product Code
Model code.........................................................................................................................................................................................7
A Family.......................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
B Displacement............................................................................................................................................................................7
C Rotation...................................................................................................................................................................................... 7
D Project version......................................................................................................................................................................... 7
E Mounting flange...................................................................................................................................................................... 7
F Drive gear................................................................................................................................................................................... 8
G Rear cover.................................................................................................................................................................................. 8
H Inlet size; I Outlet size............................................................................................................................................................ 8
J Ports positions & Special body............................................................................................................................................ 9
K Seals..............................................................................................................................................................................................9
L Screws..........................................................................................................................................................................................9
M Set valve.....................................................................................................................................................................................9
N Type mark.................................................................................................................................................................................. 9
O Mark position.........................................................................................................................................................................10
System Requirements
Pressure............................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Speed..................................................................................................................................................................................................11
Hydraulic fluids............................................................................................................................................................................... 12
Temperature and viscosity......................................................................................................................................................... 12
Filtration............................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Filters.............................................................................................................................................................................................13
Selecting a filter.........................................................................................................................................................................13
Reservoir...................................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Line sizing......................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Pump drive.......................................................................................................................................................................................14
Pump drive data form.................................................................................................................................................................. 15
Pump Life..........................................................................................................................................................................................16
Product Options
Shaft, flange, and port configurations....................................................................................................................................17
Mounting flanges...........................................................................................................................................................................17
Shaft options....................................................................................................................................................................................17
Port configurations........................................................................................................................................................................18
Porting............................................................................................................................................................................................... 19
Dimensions
TAP4NN - 01FA, 01DA, and 01BA............................................................................................................................................. 21
TAP4NN - 02RA, and 02GA..........................................................................................................................................................22
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 3
Page 4
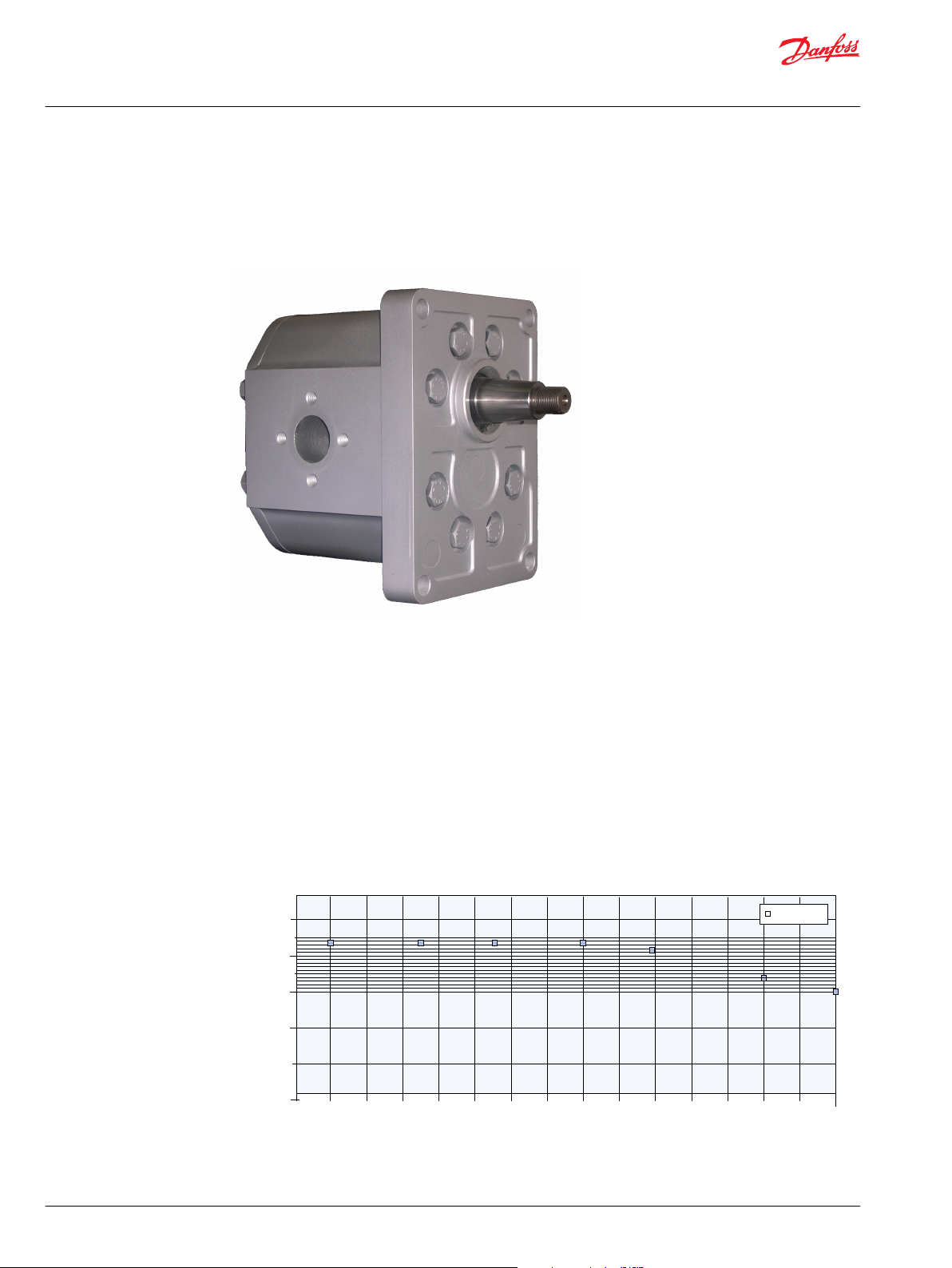
Displacement (cm3/rev)
Rated pressure
(bar)
200
150
100
50
0
250
50 60 70 80 90 100 110 120 130 140 150 160 170 180 190 200
TAP4NN
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
General Information
Overview
The Danfoss Group 4 is a range of peak performance fixed-displacement gear pumps. Constructed of a
high-strength extruded aluminum body with aluminum cover and flange, all pumps are pressurebalanced for exceptional efficiency.
Group 4 gear pumps attributess
Pump displacements
•
Wide range of displacements from 60 to 200 cm3/rev [from 3.66 to 12.2 in3/rev]
•
Continuous pressure rating up to 220 bar [3191 psi]
•
Speeds up to 3000 min-1 (rpm)
•
SAE and European standard mounting flanges
•
High quality case hardened steel gears
•
Multiple pump configurations in combination with SNP1NN, SNP2NN and SNP3NN
Quick reference chart for pump displacements vs. rated pressure
4 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 5
C
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
General Information
Pump design
TAP4NN
The TAP4NN gear pump is available in a displacement range from 60.0 to 200.0 cm3/ rev [from 3.66 to
12.2 in3/rev]. Suitable for applications where the pressure is lower than 220 bar[3191 psi] continuous, the
TAP4NN range is released into SAE and European configurations.
TAP4NN 01BA
Technical data for TAP4NN
TAP4NN pump model Frame size
60 85 106 130 148 180 200
Displacement
Peak pressure
Rated pressure
Minimum speed
Maximum speed
Weight
Moment of inertia ofrotating
components
Theoretical flow at maximum
speed
cm3/rev [in3/rev]
bar [psi] 230
min-1 (rpm) 650 650 600 550 500 500 480
kg [lb]
x 10-6 kg•m
[x 10-6 lbf•ft2]
l/min
[US gal/min]
58.0
[3.54]
[3335]
220
[3190]
3000 3000 2500 2500’ 2400 2400 2400
13.45
[29.65]
2
682,7
16193,6
174.0
[46.0]
83.3
[5.08]
230
[3335]
220
[3190]
14.4
[31.75]
839
19901,1
249.9
[66.0]
103.4
[6.31]
230
[3335]
220
[3190]
14.9
[32.85]
965,2
22894,5
258.5
[68.3]
126.1
[7.69]
230
[3335]
220
[3190]
15.75
[34.72]
1106,5
26246,2
315.2
[83.3]
143.8
[8.77]
220
[3190]
210
[3045]
17.2
[37.92]
1216,4
28853,0
345.1
[91.2]
174.1
[10.62]
180
[2610]
170
[2465]
17.25
[38.03]18[39.68]
1216,4
28853,0
417.8
[110.4]
194.3
[11.86]
160
[2320]
150
[2175]
1530,3
36298,7
466.3
[123.2]
Caution
The rated and peak pressure mentioned are for pumps with flanged ports only. When threaded ports are
required a derated performance must be considered. To verify the compliance of an high pressure
application with a threaded ports pump apply to a Danfoss representative.
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 5
Page 6
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
General Information
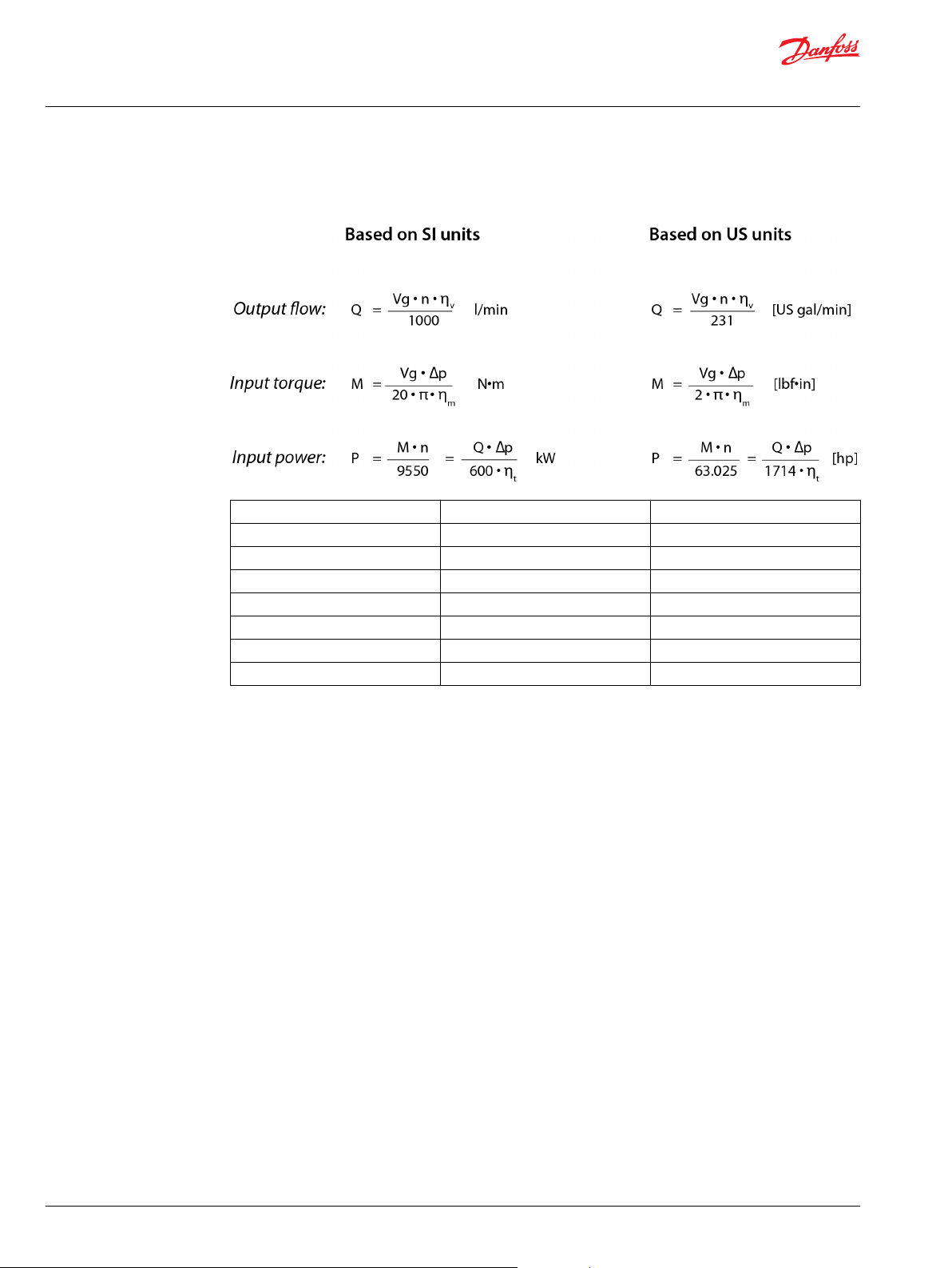
Determination of nominal pump sizes
Use these formula to determine the nominal pump size for a specific application:
Vg = Displacement per rev. cm3/rev [in3/rev]
pHD = Outlet pressure bar [psi]
p
= Inlet pressure bar [psi]
ND
Δp = pHD – p
n = Speed min-1 (rpm)
ηv = Volumetric efficiency
ηm = Mechanical (torque) efficiency
ηt = Overall efficiency (ηv • ηm)
ND
bar [psi]
6 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 7
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Code
Model code
A Family
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
● ● ● ● ● ● / /
TAP4NN
Group 4 pumps from 60 up to 200 cc
B Displacement
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
060
085
106
130
148
180
200
58 cc
83,3 cc
103,4 cc
126,1 cc
143,8 cc
174,1 cc
194,3 cc
C Rotation
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
L
R
Left rotation
Right rotation
/ ● ● ● /
/ ● /
D Project version
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● /
N
Std Version of Project
E Mounting flange
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
Code Description (Type of flange • Type of drive gear • Preferred ports for configuration)
01
02
F1
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 7
European 4 bolt - Pilot Ø63,5
SAE C 2 bolt - Pilot Ø127
European 4 bolt - Pilot Ø63,5 (special FIAT-ALLIS)
Page 8

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Code
F Drive gear
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
BA
DA
FA
GA
RA
Taper 1:8-M20x1,5-Key 6,375
Spline DIN 5482 B35x31xL44
Parallel Ø30-Key 8x7xL50
Parallel Ø31,75-Key 7,962x7x36
Splined-SAE J498-14T-12/24-SAE C 2 bolt
G Rear cover
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
P1
H Inlet size; I Outlet size
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● ● ● /
A4
A5
A6
31x30,18x58,72x7/16-14UNC
37,5x35,71x69,85x1/2-13UNC
50x42,88x77,77x1/2-13UNC
Standard cover for pump
CB
CC
CD
CE
CF
CG
CH
CK
CL
F7
F8
F9
30x56xM10
32x62xM10
36x62xM10
32x62xM12
38x72,5xM12
40x72,5xM12
45x72,5xM12
48x72,5xM12
56x92xM12
1-1/4 GAS
1-1/2 GAS
1-3/4 GAS
8 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 9

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Code
GE
GF
GK
32x62x7/16-14UNC
38x72,5x1/2-13UNC
48x72,5x1/2-13UNC
J Ports positions & Special body
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
NN
SD
G9
I5
L0
LI
Std position from cataloge
Body width side ports=151mm (Std for 02 Flange)
Ports distance from flange=79 - Special
Ports distance from flange =95 - Special
Ports distance from flange =100 - Special
Ports distance from flange =104,5 - Special
K Seals
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● /
N
L Screws
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
N
M Set valve
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
NNN
N Type mark
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
N
A
Z
Standard NBR seals
/ ● /
Std burnished screws
/ / ● ● ●
No valve
/ / ●
Standard Danfoss Marking
Standard Danfoss Marking+Customer Code
Without Marking
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 9
Page 10

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Code
O Mark position
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ / ●
N
A
Std Marking position (on top)
Special Marking position on the bottom
10 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 11

Peak pressure
Rated pressure
Reaction time (100 ms max)
Time
Pressure
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Pressure
The inlet vacuum must be controlled in order to realize expected pump life and performance. The system
design must meet inlet pressure requirements during all modes of operation. Expect lower inlet
pressures during cold start. It should improve quickly as the fluid warms.
Max. continuous vacuum
Max. intermittent vacuum
Max. pressure
bar abs. [in. Hg] 0.8 [23.6]
0.6 [17.7]
3.0 [88.5]
Peak pressure is the highest intermittent pressure allowed. The relief valve overshoot (reaction time)
determines peak pressure. It is assumed to occur for less than 100 ms. The accompanying illustration
shows peak pressure in relation to rated pressure and reaction time (100 ms maximum).
Rated pressure is the average, regularly occurring, operating pressure that should yield satisfactory
product life. The maximum machine load demand determines rated pressure. For all systems, the load
should move below this pressure.
System pressure is the differential of pressure between the outlet and inlet ports. It is a dominant
operating variable affecting hydraulic unit life. High system pressure, resulting from high load, reduces
expected life. System pressure must remain at, or below, rated pressure during normal operation to
achieve expected life.
Speed
Maximum speed is the limit recommended by Danfoss for a particular gear pump when operating at
rated pressure. It is the highest speed at which normal life can be expected.
The lower limit of operating speed is the minimum speed. It is the lowest speed at which normal life can
be expected. The minimum speed increases as operating pressure increases. When operating under
higher pressures, a higher minimum speed must be maintained, as illustrated here.
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 11
Page 12

Rated
P
1
Pressure
0
N MaxN
2
Speed
Operating
envelope
1
C
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Speed versus pressure
Where:
N1 = Minimum speed at 100 bar
N2 = Minimum speed at 180 bar
Hydraulic fluids
Temperature and viscosity
Ratings and data for TAP4NN gear pumps are based on operating with premium hydraulic fluids
containing oxidation, rust, and foam inhibitors. These fluids must possess good thermal and hydrolytic
stability to prevent wear, erosion, and corrosion of internal components. They include:
•
•
•
•
Use only clean fluid in the pump and hydraulic circuit.
Never mix hydraulic fluids.
Temperature and viscosity requirements must be concurrently satisfied. Use petroleum / mineralbased fluids.
High temperature limits apply at the inlet port to the pump. The pump should run at or below the
maximum continuous temperature. The peak temperature is based on material properties. Don’t exceed
it.
Cold oil, generally, doesn’t affect the durability of pump components. It may affect the ability of oil to
flow and transmit power. For this reason, keep the temperature at 16 °C [60 °F] above the pour point of
the hydraulic fluid.
Minimum (cold start) temperature relates to the physical properties of component materials.
Minimum viscosity occurs only during brief occasions of maximum ambient temperature and severe duty
cycle operation. You will encounter maximum viscosity only at cold start. During this condition, limit
speeds until the system warms up. Size heat exchangers to keep the fluid within these limits. Test
regularly to verify that these temperatures and viscosity limits aren’t exceeded. For maximum unit
efficiency and bearing life, keep the fluid viscosity in the recommended viscosity range.
Hydraulic fluids following DIN 51524, part 2 (HLP) and part 3 (HVLP) specifications
API CD engine oils conforming to SAE J183
M2C33F or G automatic transmission fluids
Certain agricultural tractor fluids
Caution
12 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 13

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Fluid viscosity
Maximum (cold start)
Recommended range
Minimum
Temperature
Minimum (cold start)
Maximum continuous
Peak (intermittent)
Filtration
Filters
Use a filter that conforms to Class 22/18/13 of ISO 4406 (or better). It may be on the pump outlet
(pressure filtration), inlet (suction filtration), or reservoir return (return-line filtration).
mm2/s [SUS]
°C [°F]
1000 [4600]
12-60 [66-290]
10 [60]
-20 [-4]
80 [176]
90 [194]
Selecting a filter
When selecting a filter, please consider:
•
contaminant ingression rate (determined by factors such as the number of actuators used in the
system)
•
generation of contaminants in the system
•
required fluid cleanliness
•
desired maintenance interval
•
filtration requirements of other system components
Measure filter efficiency with a Beta ratio (βX). For:
•
suction filtration, with controlled reservoir ingression, use a β
•
return or pressure filtration, use a pressure filtration with an efficiency of β10 = 75
35-45
= 75 filter
βx ratio is a measure of filter efficiency defined by ISO 4572. It is the ratio of the number of particles
greater than a given diameter ( “X“ in microns) upstream of the filter to the number of these particles
downstream of the filter.
Fluid cleanliness level and βx ratio
Fluid cleanliness level (per ISO 4406)
βx ratio (suction filtration)
βx ratio (pressure or return filtration)
Recommended inlet screen size
Class 22/18/13 or better
β
= 75 and β10 = 2
35-45
β10 = 75
100-125 µm [0.004-0.005 in]
The filtration requirements for each system are unique. Evaluate filtration system capacity by monitoring
and testing prototypes.
Reservoir
The reservoir provides clean fluid, dissipates heat, removes entrained air, and allows fluid volume
changes associated with fluid expansion and cylinder differential volumes. A correctly sized reservoir
accommodates maximum volume changes during all system operating modes. It promotes deaeration of
the fluid as it passes through, and accommodates a fluid dwell-time between 60 and 180 seconds,
allowing entrained air to escape.
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 13
Page 14
Pilot cavity
Ø 0.1 [0.004]
Mating spline
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Minimum reservoir capacity depends on the volume required to cool and hold the oil from all retracted
cylinders, allowing for expansion due to temperature changes. A fluid volume of 1 to 3 times the pump
output flow (per minute) is satisfactory. The minimum reservoir capacity is 125% of the fluid volume.
Install the suction line above the bottom of the reservoir to take advantage of gravity separation and
prevent large foreign particles from entering the line. Cover the line with a 100-125 micron screen. The
pump should be below the lowest expected fluid level. Put the return-line below the lowest expected
fluid level to allow discharge into the reservoir for maximum dwell and efficient deaeration. A baffle (or
baffles) between the return and suction lines promotes deaeration and reduces fluid surges.
Line sizing
Choose pipe sizes that accommodate minimum fluid velocity to reduce system noise, pressure drops, and
overheating. This maximizes system life and performance.
Design inlet piping that maintains continuous pump inlet pressure above 0.8 bar absolute during normal
operation. The line velocity should not exceed the values in this table:
Maximum line velocity
Inlet
Outlet
Return
m/s [ft/sec]
2.5 [8.2]
5.0 [16.4]
3.0 [9.8]
Pump drive
Most systems use hydraulic oil containing 10% dissolved air by volume. Under high inlet vacuum
conditions the oil releases bubbles. They collapse when subjected to pressure, resulting in cavitation,
causing adjacent metal surfaces to erode. Over-aeration is the result of air leaks on the inlet side of the
pump, and flow-line restrictions. These include inadequate pipe sizes, sharp bends, or elbow fittings,
causing a reduction of flow line cross sectional area. This problem will not occur if inlet vacuum and rated
speed requirements are maintained, and reservoir size and location are adequate.
Shaft options for Group 4 gear pumps include tapered, splined, or parallel shafts. They are suitable for a
wide range of direct and indirect drive applications for radial and thrust loads.
Plug-in drives, acceptable only with a splined shaft, can impose severe radial loads when the mating
spline is rigidly supported. Increasing spline clearance does not alleviate this condition.
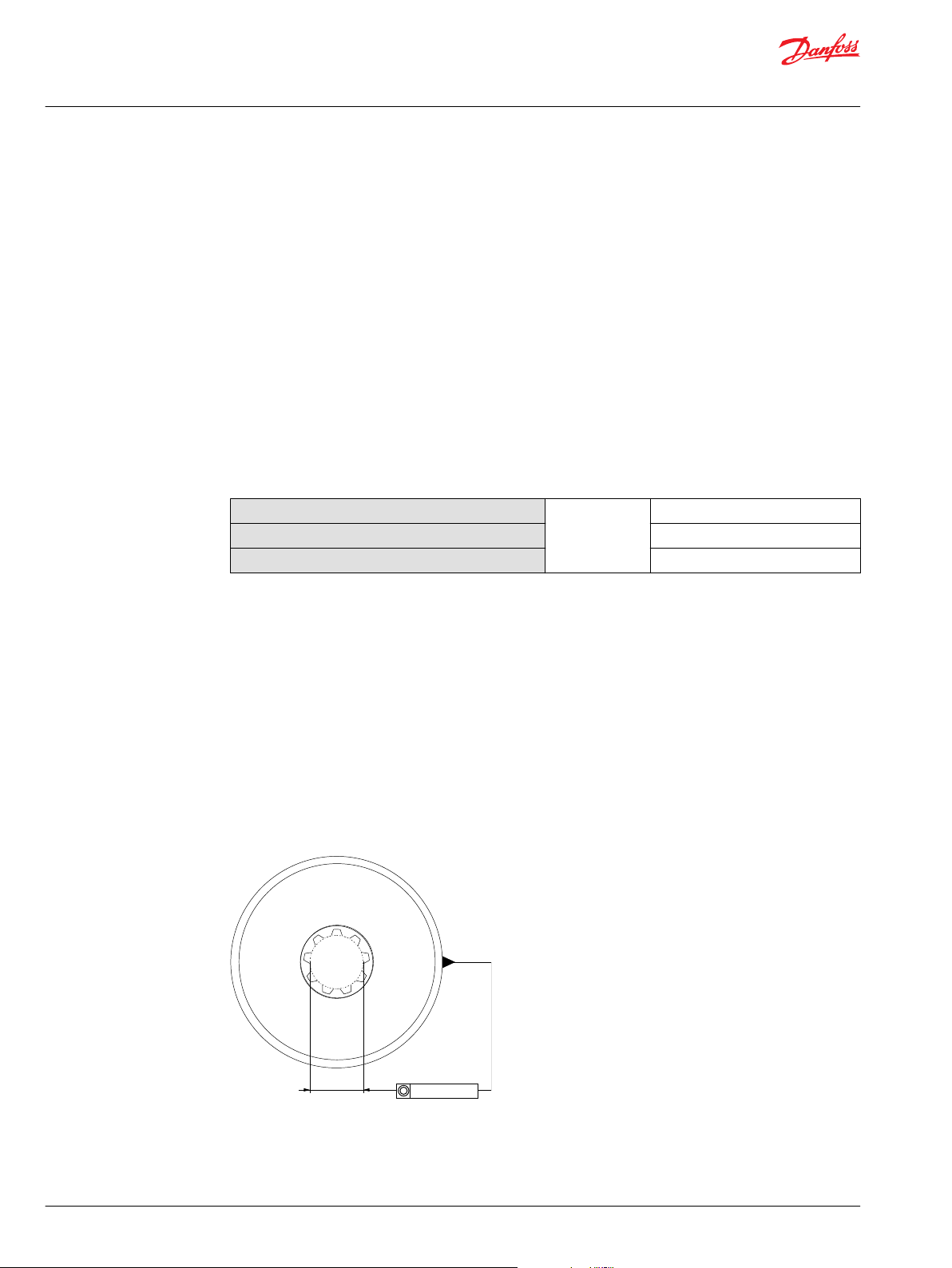
Use plug-in drives if the concentricity between the mating spline and pilot diameter is within 0.1 mm
[0.004 in]. Lubricate the drive by flooding it with oil. A 3-piece coupling minimizes radial or thrust shaft
loads.
14 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 15

C
90
o
a
a
0
o
270
o
180
o
0
o
Inlet port
Inlet port
a
dw
270
o
180
o
90
o
dw
a
P
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Caution
In order to avoid spline shaft damages it is recommended to use carburized and hardened steel
couplings with 80-82 HRA surface hardness.
Allowable radial shaft loads are a function of the load position, load orientation, and operating pressure
of the hydraulic pump. All external shaft loads have an effect on bearing life, and may affect pump
performance.
In applications where external shaft loads can’t be avoided, minimize the impact on the pump by
optimizing the orientation and magnitude of the load. Use a tapered input shaft; don’t use splined shafts
for belt or gear drive applications. A spring-loaded belt tension-device is recommended for belt drive
applications to avoid excessive tension. Avoid thrust loads in either direction.
Pump drive data form
Contact Danfoss if continuously applied external radial or thrust loads occur. Fill out this page and send
the complete form to your Danfoss representative for an assistance in applying pumps with belt or gear
drive. This illustration shows a pump with counterclockwise orientation:
Optimal radial load position
Application data
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 15
Item Value Unit
Pump displacement cm3/rev [in3/rev]
Rated system pressure bar psi
Relief valve setting
Pump shaft rotation left right
Pump minimum speed
Pump maximum speed
Drive gear helix angle (gear drive only) degree
Belt type (gear drive only) V notch
Belt tension (gear drive only) P N lbf
min-1 (rpm)
Page 16

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
System Requirements
Application data (continued)
Item Value Unit
Angular orientation of gear or belt to inlet port
Pitch diameter of gear or pulley dw mm in
Distance from flange to center of gear or pulley a
Pump Life
Pump life is a function of speed, system pressure, and other system parameters (such as fluid quality and
cleanliness).
All Danfoss gear pumps use hydrodynamic journal bearings that have an oil film maintained between the
gear/shaft and bearing surfaces at all times. If the oil film is sufficiently sustained through proper system
maintenance and operating within recommended limits, long life can be expected.
B10 life expectancy number is generally associated with rolling element bearings. It does not exist for
hydrodynamic bearings.
High pressure, resulting from high loads, impacts pump life. When submitting an application for review,
provide machine duty cycle data that includes percentages of time at various loads and speeds. We
strongly recommend a prototype testing program to verify operating parameters and their impact on life
expectancy before finalizing any system design.
ɑ
degree
16 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 17

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Options
Shaft, flange, and port configurations
Motor Code Flange Shaft Port
TAP4NN 01BA
TAP4NN 01DA
TAP4NN 01FA
TAP4NN 02RA
TAP4NN 02GA
pilot Ø 63.5 mm
[2.5 in]
European 01, 4-
bolt
pilot Ø 63.5 mm
[2.5 in]
European 01, 4-
bolt
pilot Ø 63.5 mm
[2.5 in]
European 01, 4-
bolt
pilot Ø 127 mm
[5.0 in] SAE C, 2-
bolt
pilot Ø 127 mm
[5.0 in] SAE C, 2-
bolt
1:8 tapered
Spline DIN 5482
B35x31xL44
Parallel Ø30-Key
8x7xL50
Splined-SAE
J498-14T
Parallel Ø31,75-
Key 7,962x7x36
European
flanged port +
pattern
European
flanged port +
pattern
European
flanged port +
pattern
Vertical four bolt
flanged port
Vertical four bolt
flanged port
Mounting flanges
Danfoss offers many types of industry standard mounting flanges. This table shows order codes for each
available mounting flange and its intended use:
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
Code Description
01
02
F1
European 4 bolt - PilotØ63,5
SAE C 2 bolt - Pilot Ø127
European 4 bolt - Pilot Ø63,5 (special FIAT-ALLIS)
Shaft options
Direction is viewed facing the shaft. Group 4 pumps are available with a variety of splined, parallel, and
tapered shaft ends. Not all shaft styles are available with all flange styles.
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● /
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 17
Page 18

C
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Options
Port configurations
Shaft Mounting flange code with maximum torque in
Code Description 01 02
BA
DA
FA
GA
RA
Taper 1:8-M20x1,5-Key 6,375 970 [8585]
Spline DIN 5482 B35x31xL44 850 [7523]
Parallel Ø30-Key 8x7xL50 710 [6284]
Parallel Ø31,75-Key 7,962x7x36 750 [6638]
Splined-SAE J498-14T-12/24-SAE C 2 bolt 800 [7080]
Nm [lb•in]
Danfoss recommends mating splines conform to SAE J498 or DIN 5482. Danfoss external SAE splines have
a flat root side fit with circular tooth thickness reduced by 0.127 mm [0.005 in] in respect to class 1 fit.
Dimensions are modified to assure a clearance fit with the mating spline.
Caution
Shaft torque capability may limit allowable pressure. Torque ratings assume no external radial loading.
Applied torque must not exceed these limits, regardless of stated pressure parameters. Maximum torque
ratings are based on shaft torsional fatigue strength.
Various port configurations are available on Group 4 pumps. They include:
•
SAE split flange ports
•
European standard flanged ports
•
Gas threaded ports (BSPP)
For a table of dimensions see Porting on page 19.
Available port configurations
A B C D E F G H I J K L M N O
/ ● ● ● ● /
Code Description
A4 31x30,18x58,72x7/16-14UNC
A6 50x42,88x77,77x1/2-13UNC
CB 30x56xM10
CC 32x62xM10
CD 36x62xM10
CE 32x62xM12
CF 38x72,5xM12
CG 40x72,5xM12
CH 45x72,5xM12
CK 48x72,5xM12
CL 56x92xM12
SAE flanged portA5 37,5x35,71x69,85x1/2-13UNC
Flanged port with thd holes in + pattern
18 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 19

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Options
F7 1-1/4 GAS
F9 1-3/4 GAS
GE 32x62x7/16-14UNC
GK 48x72,5x1/2-13UNC
Porting
Threaded GAS (BSPP)F8 1-1/2 GAS
Flanged port with the holes in + pattern UN threadGF 38x72,5x1/2-13UNC
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 19
Page 20

Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Product Options
Ports dimensions
Port type A C E
Dimensions a b d c g h i f
Type (displacement)
060
085
106
130
148
180
200
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
Inlet
Outlet
38.1
[1.5]
31.8
[1.25]
38.1
[1.5]
31.8
[1.25]
50.8
[2.0]
38.1
[1.5]
50.8
[2.0]
38.1
[1.5]
50.8
[2.0]
38.1
[1.5]
50.8
[2.0]
38.1
[1.5]
50.8
[2.0]
38.1
[1.5]
35.71
[1.4]
30.18
[1.19]
35.71
[1.4]
30.18
[1.19]
42.88
[1.69]
35.71
[1.4]
42.88
[1.69]
35.71
[1.4]
42.88
[1.69]
35.71
[1.4]
42.88
[1.69]
35.71
[1.4]
42.88
[1.69]
35.71
[1.4]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
7/16 - 14UNC 56 [2.2] 30 [1.18] M10 1-1/4 Gas (BSPP)
58.72
[2.31]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
7/16 - 14UNC 56 [2.2] 30 [1.18] M10 1-1/4 Gas (BSPP)
58.72
[2.31]
1/2 -13 UNC
77.77
[3.06]
1/2 -13 UNC 56 [2.2] 30 [1.18] M10 1-1/4 Gas (BSPP)
69.85
[2.75]
1/2 -13 UNC
77.77
[3.06]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
1/2 -13 UNC
77.77
[3.06]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
1/2 -13 UNC
77.77
[3.06]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
1/2 -13 UNC
77.77
[3.06]
1/2 -13 UNC
69.85
[2.75]
62
[2.44]
62
[2.44]
62
[2.44]
72.5
[2.85]
62
[2.44]
72.5
[2.85]
62
[2.44]
92
[3.62]
72.5
[2.85]
92
[3.62]
72.5
[2.85]
36 [1.42] M10 1-1/2 Gas (BSPP)
36 [1.42] M10 1-1/2 Gas (BSPP)
36 [1.42] M10 1-1/2 Gas (BSPP)
45 [1.77] M12 1-3/4 Gas (BSPP)
36 [1.42] M10 1-1/2 Gas (BSPP)
45 [1.77] M12 1-3/4 Gas (BSPP)
36 [1.42] M10 1-1/2 Gas (BSPP)
56 [2.2] M12 N/A
45 [1.77] M12 N/A
56 [2.2] M12 N/A
45 [1.77] M12 N/A
20 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 21

mm
[in]
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Dimensions
TAP4NN - 01FA, 01DA, and 01BA
The drawing shows the TAP4NN standard porting for 01FA, 01DA and 01BA.
TAP4NN – 01FA, 01DA, 01BA dimensions
Frame size 060 085 106 130 148 180 200
Dimension
Inlet
Outlet
Model code examples and maximum shaft torque
Flange/drive gear Model code example Maximum shaft torque
01DA TAP4NN/106LN01DAP1CDCBNNNN/NNNNN 850 [7523]
01FA TAP4NN/148RN01FAP1CHCDNNNN/NNNNN 710 [6284]
01BA TAP4NN/180RN01BAP1CLCH NNNN/NNNNN 970 [8585]
A
84
[3.3]
B
168
[6.61]
C 36 [1.42] 45 [1.77] 56 [2.2]
D 62 [2.44] 72.5 [2.85] 92 [3.62]
E M10 M12 M12
c 30 [1.18] 36 [1.42] 45 [1.77]
d 56 [2.2] 62 [2.44] 72.5 [2.85]
e M10 M10 M12
89
[3.5]
178
[7.0]
93
[3.66]
186
[7.32]
97.5
[3.84]
195
[7.68]
101
[3.98]
202
[7.95]
107
[4.21]
214
[8.42]
For further details on ordering, see Model code on page 7.
111
[4.37]
222
[8.74]
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101 | 21
Page 22

mm
[in]
Technical Information
Gear Pumps Group 4 Technical Information
Dimensions
TAP4NN - 02RA, and 02GA
This drawing shows the standard porting for 02RA and 02GA.
TAP4NN – 02RA, 02GA dimensions
Frame size 060 085 106 130 148 180 200
Dimension
Inlet
Outlet
Flange/drive gear configuration Model code example
02RA TAP4NN/060RN02RAP1A5A4SDNN/NNNNN 800 [7080]
02GA TAP4NN/130LN02GAP1A6A5SDNN/NNNNN 750 [6638]
A
87
[3.42]
B
171
[6.73]
C 38.1 [1.5] 50.8 [2.0]
D 35.71 [1.4] 42.88 [1.69]
E 69.85 [2.75] 77.77 [3.06]
F 1/2-13UNC 1/2-13UNC
c 31.8 [1.25] 38.1 [1.5]
d 30.18 [1.19] 35.71 [1.4]
e 58.72 [2.31] 69.85 [2.75]
f 7/16-14UNC 1/2-13UNC
92
[3.62]
181
[7.13]
96
[3.78]
189
[7.44]
100.5
[3.96]
198
[7.79]
104
[4.1]
205
[8.07]
110
[4.33]
217
[8.54]
Maximum shaft torque
N•m [lb•in]
For further details on ordering, see Model code on page 7.
114
[4.49]
225
[8.86]
22 | © Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
Page 23

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions (US) Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions Trading
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 2080 6201
Products we offer:
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
DCV directional control
•
valves
Electric converters
•
Electric machines
•
Electric motors
•
Gear motors
•
Gear pumps
•
Hydrostatic motors
•
Hydrostatic pumps
•
Orbital motors
•
PLUS+1® controllers
•
PLUS+1® displays
•
PLUS+1® joysticks and
•
pedals
PLUS+1® operator
•
interfaces
PLUS+1® sensors
•
PLUS+1® software
•
PLUS+1® software services,
•
support and training
Position controls and
•
sensors
PVG proportional valves
•
Steering components and
•
systems
Telematics
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electric components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market as well as the
marine sector. Building on our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with you to
ensure exceptional performance for a broad range of applications. We help you and other
customers around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles
and vessels to market faster.
Danfoss Power Solutions – your strongest partner in mobile hydraulics and mobile
electrification.
Go to www.danfoss.com for further product information.
We offer you expert worldwide support for ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also
provide you with comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
©
Danfoss | October 2019 BC319660010597en-000101
 Loading...
Loading...