Page 1

MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE
Programming Guide
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
www.danfoss.com/drives
Page 2

Page 3

Contents Programming Guide
Contents
1 Introduction
1.2 Abbreviations
1.3 Software Version and Approvals
1.4 Disposal Instruction
2 Safety
2.1 Safety Symbols
2.2 Qualified Personnel
2.3 Safety
3 Programming
3.1 How to Programme
3.2 Status Menu
3.3 Quick Menu
3.4 Main Menu
4 Parameter Descriptions
4.1 Parameter Group 0: Operation/Display
3
5
5
5
6
6
6
6
8
8
9
9
10
11
11
4.2 Parameter Group 1: Load/Motor
4.3 Parameter Group 2: Brakes
4.4 Parameter Group 3: Reference/Ramps
4.5 Parameter Group 4: Limits/Warnings
4.6 Parameter Group 5: Digital In/Out
4.7 Parameter Group 6: Analog In/Out
4.8 Parameter Group 7: Controllers
4.9 Parameter Group 8: Communication
4.10 Parameter Group 13: Smart Logic
4.11 Parameter Group 14: Special Functions
4.12 Parameter Group 15: Drive Information
4.13 Parameter Group 16: Data Readouts
4.14 Parameter Group 18: Extended Motor Data
5 Parameter Lists
5.1 Parameter Overview
5.2 Parameter Lists
5.2.1 Conversion Index 56
14
19
21
25
28
32
36
37
41
46
48
49
51
52
52
56
5.2.2 Change During Operation 56
5.2.3 2-Set-up 56
5.2.4 Type 56
5.2.5 0-** Operation/Display 57
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 1
Page 4

Contents
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
5.2.6 1-** Load/Motor 57
5.2.7 2-** Brakes 58
5.2.8 3-** Reference/Ramps 58
5.2.9 4-** Limits/Warnings 59
5.2.10 5-** Digital In/Out 59
5.2.11 6-** Analog In/Out 60
5.2.12 7-** Controllers 60
5.2.13 8-** Comm. and Options 61
5.2.14 13-** Smart Logic 61
5.2.15 14-** Special Functions 61
5.2.16 15-** Drive Information 62
5.2.17 16-** Data Readouts 62
5.2.18 18-** Extended Motor Data 63
6 Troubleshooting
Index
64
70
2 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 5

Introduction Programming Guide
1 Introduction
The nameplate sticker is located on the top of each
frequency converter and shows the ratings, serial number,
warnings catalog number, and other relevant data for each
unit. See Table 1.1 for details, how to read the type code
string.
1
1
Illustration 1.1 Nameplate Sticker
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 3
Page 6

Introduction
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
1
1.1.1 Type Code
Illustration 1.2 Type Code Definition
Description Pos. Possible choice
Product group 1-3 Frequency converters
Series and product type 4-6 Micro Drive
Power size 7-10 0.18–22 kW
Mains voltage 11-12 S2: Single phase 200–240 V AC
T2: 3-phase, 200–240 V AC
T4: 3-phase, 380–480 V AC
Enclosure 13-15 IP20/Chassis
RFI filter 16-17 HX: No RFI filter
H1: RFI filter class A1/B
H3:RFI filter A1/B (reduced cable length1))
Brake 18 B: Brake chopper included (from 1.5 kW and up)
X: No brake chopper included
Display 19 X: No Local Control Panel
N: Numerical Local Control Panel (LCP)
P: Numerical Local Control Panel (LCP)) with potentiometer
Coating PCB 20 C: Coated PCB
X. No coated PCB
Mains option 21 X: No mains option
Adaptation A 22 X: No adaptation
Adaptation B 23 X: No adaptation
Software release 24-27 SXXX: Latest release - standard software
Table 1.1 Type Code Description
1) See the VLT® Micro Drive FC 51 Design Guide.
4 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 7
Introduction Programming Guide
1.2 Abbreviations
1.3
Software Version and Approvals
1
1
Abbreviations
a
AWG American wire gauge
Auto Tune Automatic motor tuning
°C
I Current A Amp
I
LIM
IT mains Mains supply with star point
Joule Energy J=N∙m ft-lb, Btu
°F
FC Frequency converter
f Frequency Hz Hz
kHz Kilohertz kHz kHz
LCP Local control panel
mA Milliampere
ms Millisecond
min Minute
MCT Motion Control Tool
M-TYPE Motor type dependent
Nm Newton metres in-lbs
I
M,N
f
M,N
P
M,N
U
M,N
PELV Protective extra low voltage
Watt Power
Pascal Pressure
I
INV
RPM Revolutions per minute
s Second
SR Size related
T Temperature C F
t Time s s,hr
T
LIM
U Voltage V V
Terms SI units I-P units
Acceleration
Celsius
Current limit
in transformer floating to
ground
Fahrenheit
Nominal motor current
Nominal motor frequency
Nominal motor power
Nominal motor voltage
Rated inverter output current
Torque limit
2
m/s
W
Pa =
N/m²
2
ft/s
Btu/hr,
hp
psi, psf,
ft of
water
Software Version
Programming Guide
VLT® Micro Drive
FC 51 Series
This Programming Guide can be used for all VLT
Micro Drive FC 51 frequency converters with
software version 3.1X.
The software version number can be read in
15-43 Software Version.
Table 1.3 Software Version and Approvals
1.4 Disposal Instruction
Equipment containing electrical components
must not be disposed of together with domestic
waste.
It must be separately collected with electrical
and electronic waste according to local and
currently valid legislation.
®
Table 1.2 Abbreviations
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 5
Page 8

Safety
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
2 Safety
22
2.1 Safety Symbols
The following symbols are used in this manual:
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that could
result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that could
result in minor or moderate injury. It can also be used to
alert against unsafe practices.
NOTICE
Indicates important information, including situations that
can result in damage to equipment or property.
2.2 Qualified Personnel
WARNING
UNINTENDED START
When the frequency converter is connected to AC mains,
DC supply, or load sharing, the motor may start at any
time. Unintended start during programming, service, or
repair work can result in death, serious injury, or
property damage. The motor can start via an external
switch, a serial bus command, an input reference signal
from the LCP, or after a cleared fault condition.
To prevent unintended motor start:
Disconnect the frequency converter from the
•
mains.
Press [Off/Reset] on the LCP before
•
programming parameters.
Fully wire and assembly the frequency
•
converter, motor, and any driven equipment
before connecting the frequency converter to
AC mains, DC supply, or load sharing.
Correct and reliable transport, storage, installation,
operation, and maintenance are required for the troublefree and safe operation of the frequency converter. Only
qualified personnel are allowed to install or operate this
equipment.
Qualified personnel are defined as trained staff, who are
authorised to install, commission, and maintain equipment,
systems, and circuits in accordance with pertinent laws and
regulations. Additionally, the qualified personnel must be
familiar with the instructions and safety measures
described in these operating instructions.
2.3
Safety
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE
Frequency converters contain high voltage when
connected to AC mains input, DC supply, or load sharing.
Failure to perform installation, start-up, and maintenance
by qualified personnel can result in death or serious
injury.
Installation, start-up, and maintenance must be
•
performed by qualified personnel only.
WARNING
DISCHARGE TIME
The frequency converter contains DC-link capacitors,
which can remain charged even when the frequency
converter is not powered. Failure to wait the specified
time after power has been removed before performing
service or repair work, could result in death or serious
injury.
1. Stop the motor.
2. Disconnect FC 51 from mains (and external DC
supply, if present).
3. Wait for 4 minutes (M1, M2 and M3) and 15 min
(M4 and M5) for discharge of the DC-link.
4. Disconnect DC bus terminals and brake
terminals (if present).
5. Remove motor cable.
WARNING
LEAKAGE CURRENT HAZARD
Leakage currents exceed 3.5 mA. Failure to ground the
frequency converter properly can result in death or
serious injury.
Ensure the correct grounding of the equipment
•
by a certified electrical installer.
6 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 9
Safety
Programming Guide
WARNING
EQUIPMENT HAZARD
Contact with rotating shafts and electrical equipment
can result in death or serious injury.
Ensure that only trained and qualified
•
personnel perform installation, start up, and
maintenance.
Ensure that electrical work conforms to national
•
and local electrical codes.
Follow the procedures in this document.
•
CAUTION
INTERNAL FAILURE HAZARD
An internal failure in the frequency converter can result
in serious injury, when the frequency converter is not
properly closed.
Ensure that all safety covers are in place and
•
securely fastened before applying power.
2 2
NOTICE
HIGH ALTITUDES
For installation at altitudes above 2000 m, contact
Danfoss regarding PELV.
NOTICE
Use on Isolated Mains
For details about the use of the frequency converter on
isolated mains, refer to section RFI Switch in the design
guide.
Follow the recommendations regarding the installation
on IT-mains. Use relevant monitoring devices for ITmains to avoid damage.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 7
Page 10
Programming
3 Programming
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
3.1 How to Programme
33
3.1.1 Programming with MCT 10 Set-up
Software
The frequency converter can be programmed from a PC
via RS485 com-port by installing the MCT 10 Set-up
Software.
This software can either be ordered using code number
130B1000 or downloaded from the Danfoss Web site:
www.danfoss.com/BusinessAreas/DrivesSolutions/softwaredownload
Refer to VLT
Operating Instructions.
3.1.2
®
Motion Control Tools MCT 10 Set-up Software,
Programming with the LCP 11 or LCP
12
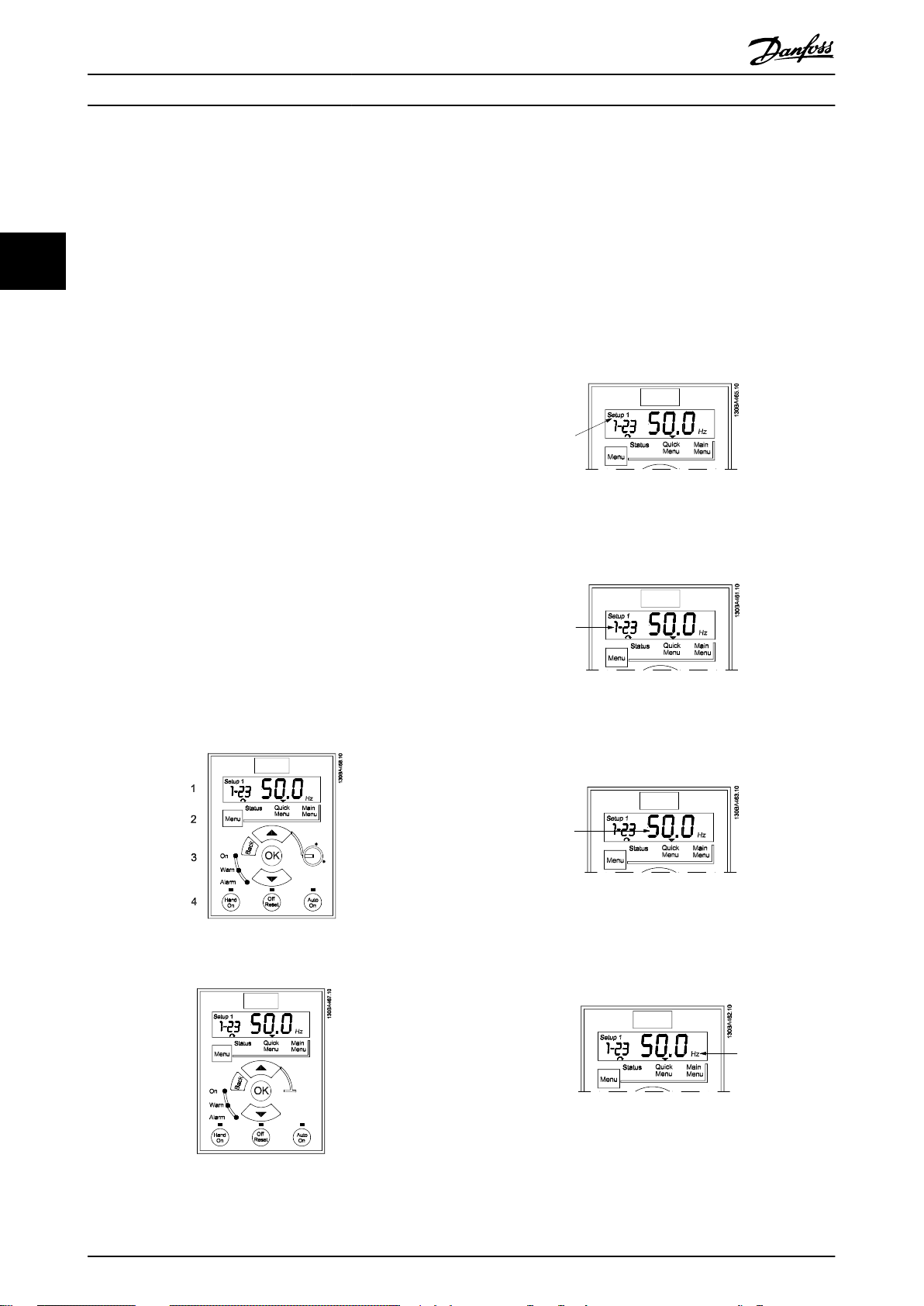
The LCP is divided into four functional groups:
1. Numeric display.
2. Menu key.
3. Navigation keys.
4. Operation keys and indicator lights (LEDs).
The display
Different information can be read from the display.
Set-up number shows the active set-up and the edit set-
up. If the same set-up acts as both active and edit set-up,
only that set-up number is shown (factory setting).
When active and edit set-up differ, both numbers are
shown in the display (Set-up 12). The number flashing,
indicates the edit set-up.
Illustration 3.3 Indicating Set-up
The small digits to the left are the selected parameter
number.
Illustration 3.4 Indicating Selected Parameter Number
Illustration 3.1 LCP 12 with Potentiometer
Illustration 3.2 LCP 11 without Potentiometer
The large digits in the middle of the display show the
value of the selected parameter.
Illustration 3.5 Indicating Value of Selected Parameter
The right side of the display shows the unit of the selected
parameter. This can be either Hz, A, V, kW, hp, %, s or
RPM.
Illustration 3.6 Indicating Unit of Selected Parameter
8 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 11
130BA466.10
Programming Programming Guide
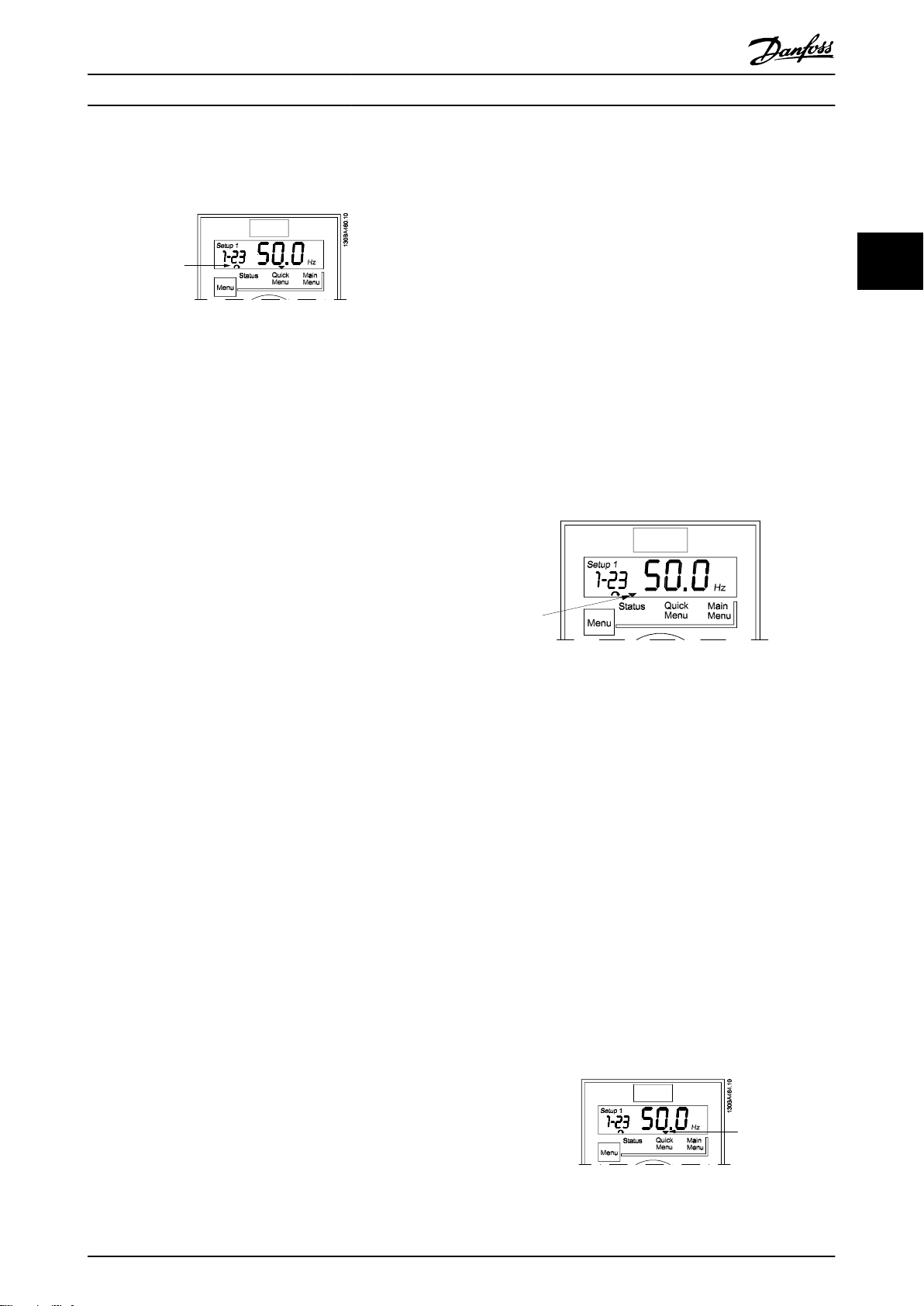
Motor direction is shown to the bottom left of the display
- indicated by a small arrow pointing either clockwise or
counterclockwise.
Illustration 3.7 Indicating Motor Direction
Press the [Menu] key to select one of the following menus
Status Menu
The Status Menu is either in Readout Mode or Hand on
Mode. In Readout Mode the value of the currently selected
readout parameter is shown in the display.
In Hand on Mode the local LCP reference is displayed.
Quick Menu
Displays Quick Menu parameters and their settings.
Parameters in the Quick Menu can be accessed and edited
from here. Most applications can be run by setting the
parameters in the Quick Menus.
Main Menu
Displays Main Menu parameters and their settings. All
parameters can be accessed and edited here.
LED (indicator lights)
Green LED: The frequency converter is on.
•
Yellow LED: Indicates a warning. See
•
chapter 6 Troubleshooting.
Flashing red LED: Indicates an alarm. See
•
chapter 6 Troubleshooting.
Navigation keys
[Back]: For moving to the previous step or layer in the
navigation structure.
[▲] [▼]: For maneuvering between parameter groups,
parameters and within parameters.
[OK]: For selecting a parameter and for accepting changes
to parameter settings.
Pressing [OK] for more than 1 s enters Adjust mode. In
Adjust mode, it is possible to make fast adjustment by
pressing [▲] [▼] combined with [OK].
Press [▲] [▼] to change value. Press [OK] to shift between
digits quickly.
To exit Adjust mode, press [OK] more than 1 s again with
changes saving or press [Back] without changes saving.
Operation keys
A yellow light above the operation keys indicates the
active key.[Hand On]: Starts the motor and enables control
of the frequency converter via the LCP.
[Off/Reset]: The motor stops except in alarm mode. In that
case the motor will be reset.
[Auto On]:
control terminals or serial communication.
[Potentiometer] (LCP 12): The potentiometer works in two
ways depending on the mode in which the frequency
converter is running.
In Auto Mode the potentiometer acts as an extra
programmable analog input.
In Hand on Mode the potentiometer controls local
reference.
The frequency converter is controlled either via
3.2 Status Menu
After power up, the Status Menu is active. Press [Menu] to
toggle between Status, Quick Menu and Main Menu.
[▲] and [▼] toggles between the choices in each menu.
The display indicates the status mode with a small arrow
above “Status”.
Illustration 3.8 Indicating Status Mode
3.3 Quick Menu
The Quick Menu gives easy access to the most frequently
used parameters.
1. To enter the Quick Menu, press [Menu] key until
indicator in display is placed above Quick Menu.
2.
Press [▲] [▼] to select either QM1 or QM2, then
press [OK].
3.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameters
in the Quick Menu.
4. Press [OK] to select a parameter.
5.
Press [▲] [▼] to change the value of a parameter
setting.
6. Press [OK] to accept the change.
7.
To exit, press either [Back] twice to enter Status,
or press [Menu] once to enter Main Menu.
Illustration 3.9 Indicating Quick Menu Mode
3 3
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 9
Page 12

Programming
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
3.4 Main Menu
The Main Menu gives access to all parameters.
1. To enter the Main Menu, press [Menu] key until
indicator in display is placed above Main Menu.
33
2.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameter
groups.
3. Press [OK] to select a parameter group.
4.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameters
in the specific group.
5. Press [OK] to select the parameter.
6.
Press [▲] [▼] to set/change the parameter value.
7. Press [OK] to accept the value.
8.
To exit, press either [Back] twice to enter Quick
Menu, or press [Menu] once to enter Status.
Illustration 3.10 Indicating Main Menu Mode
10 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 13
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4 Parameter Descriptions
4.1 Parameter Group 0: Operation/Display
0-03 Regional Settings
Option: Function:
In order to meet the needs for different default
settings in different parts of the world, 0-03
Regional Settings, is implemented in the
frequency converter. The selected setting
influences the default setting of the motor
nominal frequency.
[0 ] * Interna-
tional
[1] US
Sets default of 1-23 Motor Frequency, to 50 Hz,
shows 1-20 Motor Power in kW.
Sets default of 1-23 Motor Frequency, to 60 Hz,
shows 1-20 Motor Power in HP.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed while
motor runs.
0-04 Operating State at Power-up (Hand Mode)
Option: Function:
This parameter controls whether or not the
frequency converter start running the motor
when powering up after a power down in
Hand mode.
NOTICE
If LCP with potentiometer is mounted,
reference is set according to actual
potentiometer value.
[0] Resume Frequency converter starts in same Hand or
Off State as when powered off.
Local reference is stored and used after
power-up.
[1] * Forced
Stop,
Ref=Old
[2] Forced
Stop, Ref=0
Frequency converter powers up in Off State
meaning that motor is stopped after power
up.
Local reference is stored and used after
power-up.
Frequency converter powers up in Off State
meaning that motor is stopped after power
up.
Local reference is set to 0. Thus motor will not
start running before local reference has been
increased.
4.1.1 0-1* Set-up Handling
User-defined parameters and miscellaneous external inputs
(eg. bus, LCP, analog/digital inputs, feedback, etc.) controls
the functionality of the frequency converter.
A complete set of all parameters controlling the frequency
converter is called a set-up. The frequency converter
contains 2 set-ups, Set-up 1 and Set-up 2.
Furthermore, a fixed set of factory settings can be copied
into one or more set-ups.
Some of the advantages of having more than one set-up
in the frequency converter are
Run motor in one set-up (Active Set-up) while
•
updating parameters in another set-up (Edit Setup)
Connect various motors (one at a time) to
•
frequency converter. Motor data for various
motors can be placed in different set-ups.
Rapidly change settings of frequency converter
•
and/or motor while motor is running (eg. ramp
time or preset references) via bus or digital
inputs.
The Active Set-up can be set as Multi Set-up where the
active set-up is selected via input on a digital input
terminal and/or via the bus control word.
NOTICE
Factory Set-up cannot be used as active set-up.
0-10 Active Set-up
Option: Function:
Active Set-up controls the motor.
Shifts between set-ups can only happen when
the motor is coasted
•
OR
the set-ups between which the shift
•
happens are linked to each other (see
0-12 Linked Set-ups).
If changing between set-ups that are not linked,
the change will not happen before motor is
coasted.
NOTICE
The motor is only considered stopped
when it is coasted.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 11
Page 14
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
0-10 Active Set-up
Option: Function:
[1 ]*Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[9] Multi
Set-up
Set-up 1 is active.
Set-up 2 is active.
Select the active set-up via digital input and/or
bus, see 5-1* Digital Inputs choice [23].
0-11 Edit Set-up
44
Option: Function:
The Edit Set-up is for updating parameters in
the frequency converter from either LCP or
bus. It can be identical or different from the
Active Set-up.
All set-ups can be edited during operation,
independently of the active set-up.
[1 ] * Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[9] Active
Set-up
Update parameters in Set-up 1.
Update parameters in Set-up 2.
Update parameters in set-up selected as Active
Set-up (see 0-10 Active Set-up).
0-12 Link Set-ups
Option: Function:
The link ensures synchronizing of the “not
changeable during operation” parameter values
enabling shift from one set-up to another during
operation.
If the set-ups are not linked, a change between
them is not possible while the motor is running.
Thus the set-up change does not occur until the
motor is coasted.
[0] Not
linked
[1 ]*Linked Copy parameters “not changeable during
Leaves parameters unchanged in both set-ups
and cannot be changed while motor runs.
operation” parameter values into presently
selected Edit Set-up.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed while
motor runs.
0-31 Custom Readout Min Scale
0-32 Custom Readout Max Scale
Range: Function:
100.0* [0.00–
9999.00]
It is possible to create a customized readout
related to the output frequency of the unit.
The value entered in 0-32 Custom Readout
Max Scale will be shown at the frequency
programmed in 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit.
The readout can be shown in the LCP
display when in Status Mode or it can be
read in 16-09 Custom Readout
4.1.2 0-4* LCP
The frequency converter can operate in the following three
modes: Hand, Off and Auto.
Hand: The frequency converter is locally operated and does
not allow any remote control. By activating Hand a start
signal is given.
OFF: The frequency converter stops with a normal stop
ramp. When Off is chosen the frequency converter can
only be started by pressing either Hand or Auto on the
LCP.
Auto: In Auto-mode the frequency converter can be
remote controlled (bus/digital).
0-40 [Hand On] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled [Hand On] key has no function.
[1 ] * Enabled [Hand On] key is functional.
0-41 [Off/Reset] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disable Off/Reset [Off/Reset] key has no function.
[1 ] * Enable Off/Reset Stop signal and reset of any faults.
[2] Enable Reset Only Reset only. Stop (Off) function is
disabled.
0-42 [Auto On] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled [Auto On] key has no function.
[1 ] * Enabled [Auto On] key is functional.
Range: Function:
0.00 * [0.00–
9999.00 ]
It is possible to create a customized readout
related to the output frequency of the unit.
The value entered in 0-31 Custom Readout
Min Scale will be shown at 0 Hz. The readout
can be shown in the LCP display when in
Status Mode or it can be read in 16-09
Custom Readout
4.1.3 0-5* Copy/Save
0-50 LCP Copy
Option: Function:
The detachable LCP of the frequency
converter can be used for storing
setups, and thus for transferring data
when moving parameter settings from
one frequency converter to another.
NOTICE
LCP Copy can only be activated
from the LCP and ONLY when the
motor is coasted.
12 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 15
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
0-50 LCP Copy
Option: Function:
[0] * No copy
[1] All to LCP Copy all setups from the frequency
converter into the LCP.
[2] All from LCP Copy all setups from LCP to frequency
converter.
[3] Size independent
from LCP
Copy non motor size dependent data
from LCP to frequency converter.
0-51 Set-up Copy
Option: Function:
Use this function to copy a set-up content
into the Edit Set-up.
In order to be able to make a set-up copy
ensure that
the motor is coasted
•
0-10 Active Set-up, Active Set-up, is
•
set to either [1] Set-up 1 or [2] Set-up
2
NOTICE
The keyboard/parameter database are
blocked while Set-up Copy is running.
[0 ]*No Copy Copy function is inactive
0-61 Access to Main/Quick Menu w/o Password
Option: Function:
[0] * Full access
[1] LCP: Read Only
[2] LCP: No Access
Select [0] Full Access to disable the
password in 0-60 (Main) Menu Password.
Select [1] Read Only to block unauthorized
editing of Main/Quick menu parameter.
Select [2] No Access to block unauthorized
editing and viewing of Main/Quick menu
parameter.
4 4
[1] Copy from
Set-up 1
[2] Copy from
Set-up 2
[9] Copy from
Factory Setup
Copy from Set-up 1 to edit set-up chosen in
0-11 Edit Set-up.
Copy from Set-up 2 to edit set-up chosen in
0-11 Edit Set-up.
Copy from Factory Settings to edit set-up
chosen in 0-11 Edit set-up.
4.1.4 0-6* Password
0-60 (Main) Menu Password
Range: Function:
Use password for protection against unintended
change of sensitive parameters, eg. motor
parameters.
0 * [0-999] Enter the password for access to Main Menu via
the [Main Menu] key. Select the number that
should allow for changing other parameter values.
0 means there is no password.
NOTICE
A password has affect on the LCP - not on the bus
communication.
NOTICE
Pressing [Menu], [OK] and [▼] will unlock the password.
This will automatically enter the parameter editing
screen in Quick Menu or Main Menu.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 13
Page 16
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.2 Parameter Group 1: Load/Motor
1-05 Hand Mode Configuration
Option: Function:
1-00 Configuration Mode
Option: Function:
Use this parameter for selecting the
application control principle to be used when
a Remote Reference is active.
NOTICE
44
Changing this parameter resets 3-00
Reference Range, 3-02 Minimum
[0] Speed
Open
Loop
Reference and 3-03 Maximum Reference
to their default values.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while motor runs.
[0 ] * Speed
Open
Loop
[3] Process Enables process closed loop control. See
For normal speed control (References).
parameter group 7-3* Process PI Control for
further information on PI-controller.
1-01 Motor Control Principle
[2]*As
configuration in
1-00
Configuration
Mode.
4.2.1 1-2* Motor Data
This parameter is only relevant when 1-00
Configuration Mode is set to [3] Process Closed
Loop. The parameter is used for determining the
reference or setpoint handling when changing
from Auto Mode to Hand Mode on the LCP.
In Hand Mode the drive always runs in Open
Loop configuration regardless of setting in 1-00
Configuration Mode. Local potentiometer (if
present) or Arrow up/down determines output
frequency limited by Motor Speed High/Low
Limit (4-14 Motor Speed High Limit and 4-12
Motor Speed Low Limit).
If 1-00 Configuration Mode is set to [1] Open Loop
function is as described above.
If 1-00 Configuration Mode is set to [3] Process
Closed Loop changing from Auto mode to Hand
mode results in a setpoint change via local
potentiometer or Arrow up/down. The change is
limited by Reference Max/Min (3-02 Minimum
Reference and 3-03 Maximum Reference).
Option: Function:
[0] U/f Is used for parallel connected motors and/or special
motor applications. The U/f settings are set in 1-55
U/f Characteristic -U and 1-56 U/f Characteristic -F.
NOTICE
When running U/f control slip- and load
Enter the correct motor nameplate data (power, voltage,
frequency, current and speed).
Run AMT, see 1-29 Automatic Motor Tuning (AMT).
Factory settings for advanced motor data, parameter group
1-3* Adv. Motor Data, are automatically calculated.
compensations are not included.
[1] * VVC+ Normal running mode, including slip- and load
compensations.
NOTICE
Parameters in parameter group 1-2* Motor Data cannot
be adjusted while motor runs.
1-03 Torque Characteristics
Option: Function:
With more torque characteristics it is
possible to run low energy consuming, as
well as high torque applications.
[0 ] * Constant
Torque
[2] Automatic
Energy
Optimisation
Motor shaft output provides constant
torque under variable speed control.
This function automatically optimizes
energy consumption in centrifugal pump
and fan applications. See 14-41 AEO
Minimum Magnetisation.
1-20 Motor Power [kW]/[HP] (P
Option: Function:
Enter motor power from nameplate
data.
Two sizes down, one size up from
nominal VLT rating.
[1] 0.09 kW/0.12 HP
[2] 0.12 kW/0.16 HP
[3] 0.18kW/0.25 HP
[4] 0.25 kW/0.33 HP
[5] 0.37kW/0.50 HP
[6] 0.55 kW/0.75 HP
[7] 0.75 kW/1.00 HP
[8] 1.10 kW/1.50 HP
[9] 1.50 kW/2.00 HP
[10] 2.20 kW/3.00 HP
[11] 3.00 kW/4.00 HP
[12] 3.70 kW/5.00 HP
[13] 4.00 kW/5.40 HP
m.n
)
14 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 17
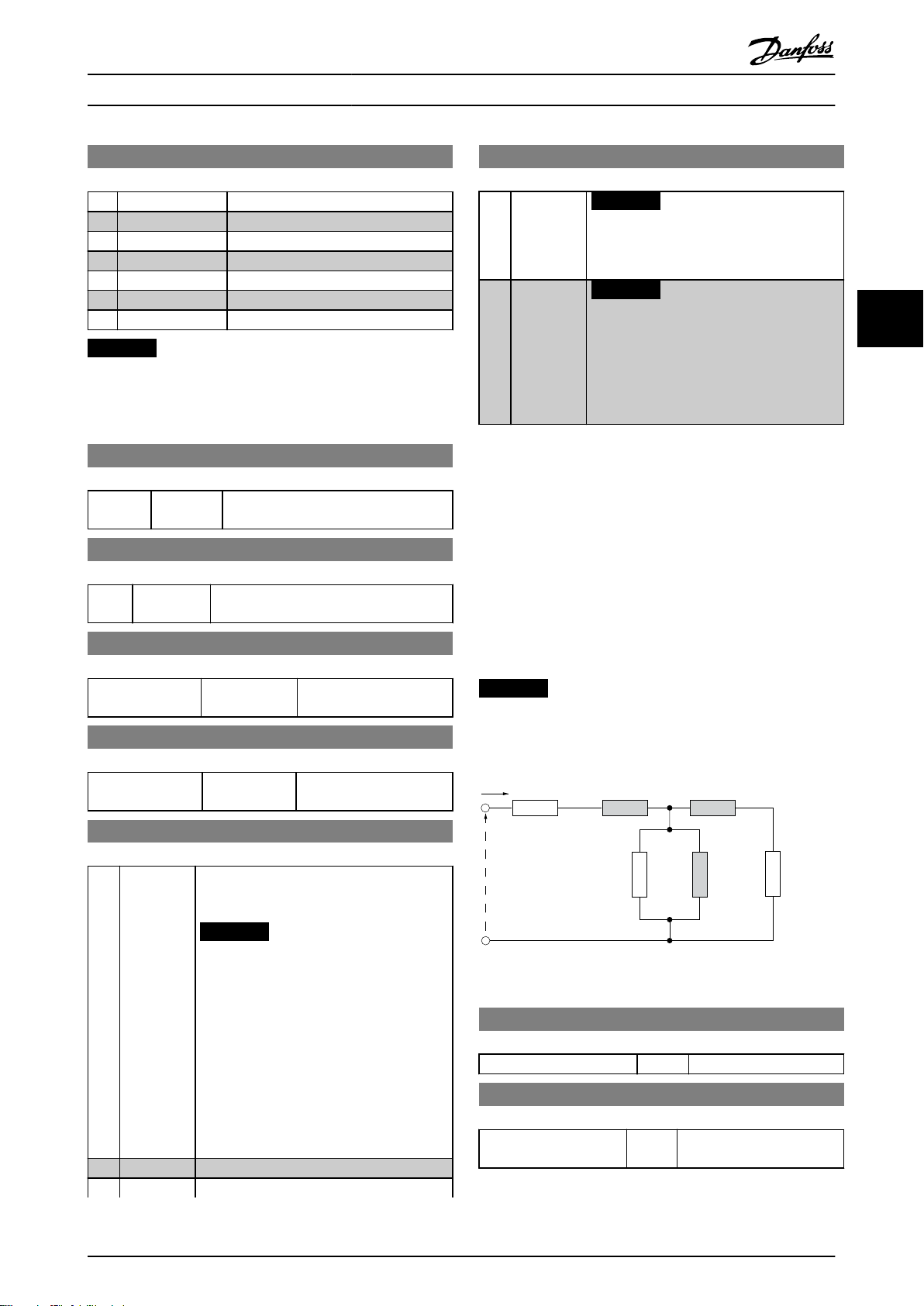
130BA375.11
R
S
P 1-30
R
1s
X
h
P1-35
R
1
X
2
X
1
U
1
I
1
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-20 Motor Power [kW]/[HP] (P
m.n
)
Option: Function:
[14] 5.50 kW/7.50 HP
[15] 7.50 kW/10.0 HP
[16] 11.00 kW/15.00 HP
[17] 15.00 kW/20.00 HP
[18] 18.50 kW/25.00 HP
[19] 22.00 kW/29.50 HP
[20] 30.00 kW/40.00 HP
NOTICE
Changing this parameter affects parameters 1-22 Motor
Voltage to 1-25 Motor Frequency, 1-30 Stator Resistance,
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance and 1-35 Main Reactance.
1-22 Motor Voltage (U_
Range: Function:
230/400 V [50-999 V] Enter motor voltage from nameplate
1-23 Motor Frequency (f_
Range: Function:
50 Hz* [20-400 Hz] Enter motor frequency from nameplate
data.
1-24 Motor Current (I_
Range: Function:
M-type dependent* [0.01-100.00 A] Enter motor current from
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed (n_
Range: Function:
M-type Dependent* [100–9999
RPM]
data.
m.n
m.n
)
)
)
m.n
nameplate data.
)
m.n
Enter motor nominal speed
from nameplate data.
1-29 Automatic Motor Tuning (AMT)
Option: Function:
NOTICE
To gain optimum tuning of the
frequency converter, run AMT on a cold
motor.
[3] Complete
AMT with
Rotating
motor
NOTICE
When set to this option, the motor will
rotate.
With this option, 1-35 Main Reactance (X2) is
also optimized, other than parameters 1-30
Stator Resistance (Rs) and 1-33 Stator Leakage
Reactance (X1).
4.2.2 1-3* Adv. Motor Data
Adjust advanced motor data using one of these methods:
1. Run AMT on cold motor. The frequency converter
measures value from motor.
2. Enter X1 value manually. Obtain value from motor
supplier.
3. Use Rs, X1, and X2 default setting. The frequency
converter establishes setting based on motor
nameplate data.
NOTICE
These parameters cannot be changed while the motor
runs.
4 4
1-29 Automatic Motor Tuning (AMT)
Option: Function:
Use AMT to optimise motor performance.
When 1-01 Motor Control Principle is set to [0]
U/f, AMT does not work.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed
while the motor runs.
1. Stop the frequency converter - make
sure that the motor is at standstill
2.
Select [2] Enable AMT
3. Apply start signal
- Via LCP: Press [Hand On]
- Or in Remote On mode: Apply
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 15
[0] * Off AMT function is disabled.
[2] Enable AMT AMT function starts running.
start signal on terminal 18
Illustration 4.1 Advanced Motor Data Parameters
1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
Range: Function:
Depending on motor data* [Ohm] Set stator resistance value.
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1)
Range: Function:
Depending on motor
data*
[Ohm] Set stator leakage reactance
of motor.
Page 18
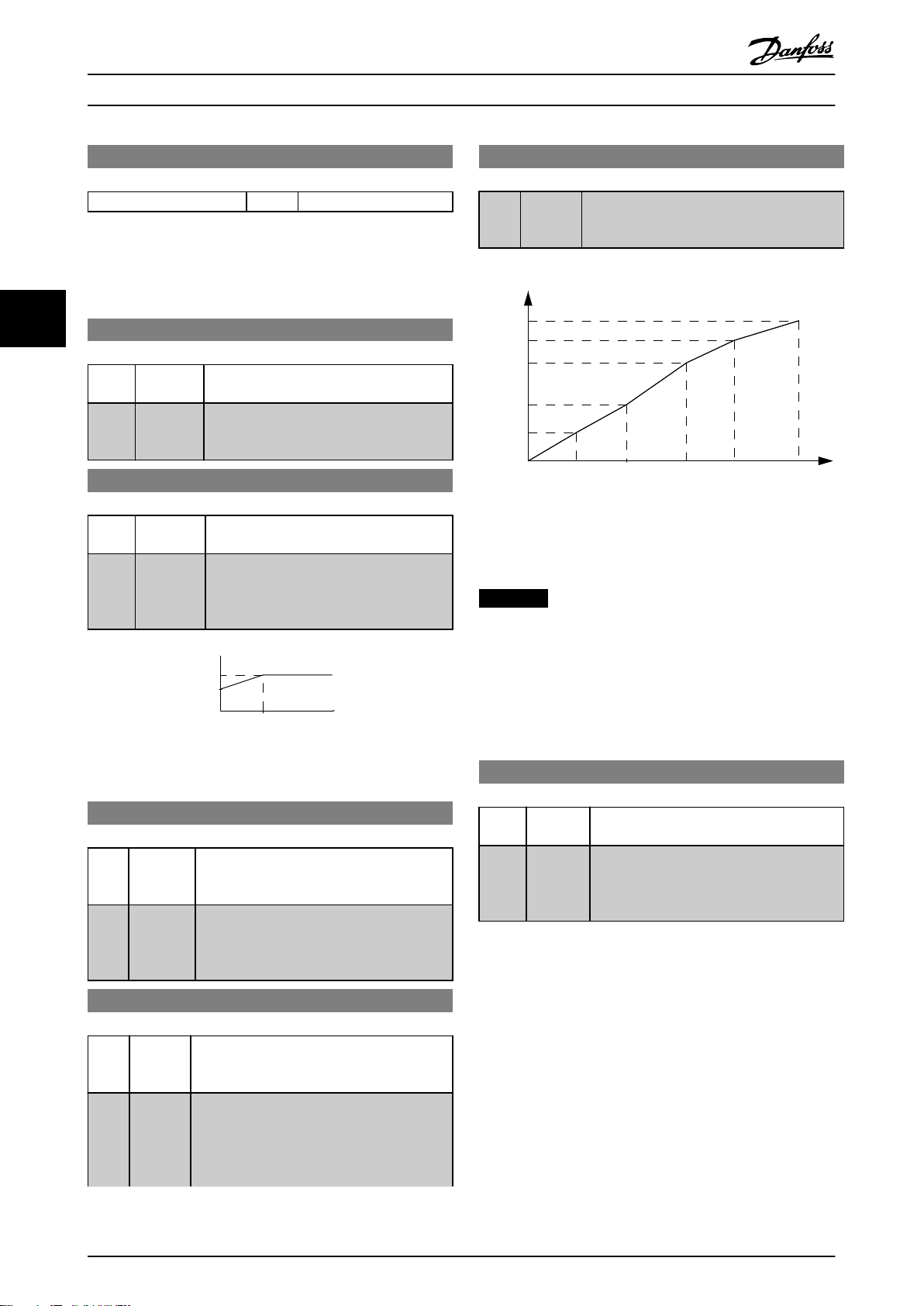
Magn. current
130BD016.10
Hz
Par.1-50
Par.1-51
100%
Par.1-52 RPM
Motor Voltage
Par 1-55 [x]
Output Frequency
Par 1-56 [x]
1-55[5]
1-55[4]
1-55[3]
1-55[2]
1-55[1]
1-55[0]
1-56
[0]
1-56
[1]
1-56
[2]
1-56
[3]
1-56
[4]
1-56
[5]
130BD017.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
1-35 Main Reactance (X2)
Range: Function:
Depending on motor data* [Ohm] Set motor main reactance.
4.2.3 1-5* Load Independent Setting
1-56 U/f Characteristic - F
Range: Function:
Simplify U/f characteristics by merging 2 or
more points (voltages and frequencies),
respectively, are set equal.
This parameter group is for setting the load independent
motor settings.
44
1-50 Motor Magnetization at Zero Speed
Range: Function:
This parameter enables different thermal
load on motor when running at low speed.
100 %* [ 0–300%] Enter a percentage of rated magnetizing
current. If setting is too low, motor shaft
torque may be reduced.
1-52 Min. Speed Normal Magnetizing [Hz]
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–10.0
Hz]
Use this parameter along with 1-50 Motor
Magnetizing at Zero Speed.
Set frequency required for normal
magnetizing current. If frequency is set
lower than motor slip frequency, 1-50 Motor
Magnetizing at Zero Speed is inactive.
Illustration 4.3 U/f Characteristics
NOTICE
For 1-56 U/f characteristics - F the following applies
[0] ≦ [1] ≦ [2] ≦ [3] ≦ [4] ≦ [5]
Illustration 4.2 Parameters 1-50 and 1-52
1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
Range: Function:
This parameter is an array parameter [0-5]
and is only functional when 1-01 Motor
Control Principle is set to [0] U/f.
0.0 V* [0.0–
999.9 V]
Enter voltage at each frequency point to
manually form a U/f characteristic matching
motor. Frequency points are defined in 1-56
U/f characteristics - F.
1-56 U/f Characteristic - F
Range: Function:
This parameter is an array parameter [0-5] and
is only functional when 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [0] U/f.
0.0
Hz*
[0.0–
1000.0
Hz]
Enter frequency points to manually form a U/f
characteristic matching motor. Voltage at each
point is defined in 1-55 U/f Characteristic - U.
Make a U/f characteristic based on 6 definable
voltages and frequencies, see Illustration 4.3.
4.2.4 1-6* Load Dependent Setting
Parameters for adjusting the load-dependent motor
settings.
1-60 Low Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
Use this parameter to gain optimum U/f
characteristic when running at low speed.
100 %* [0–199%]Enter percentage in relation to load when
motor runs at low speed.
Change-over point is automatically calculated
based on motor size.
16 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 19
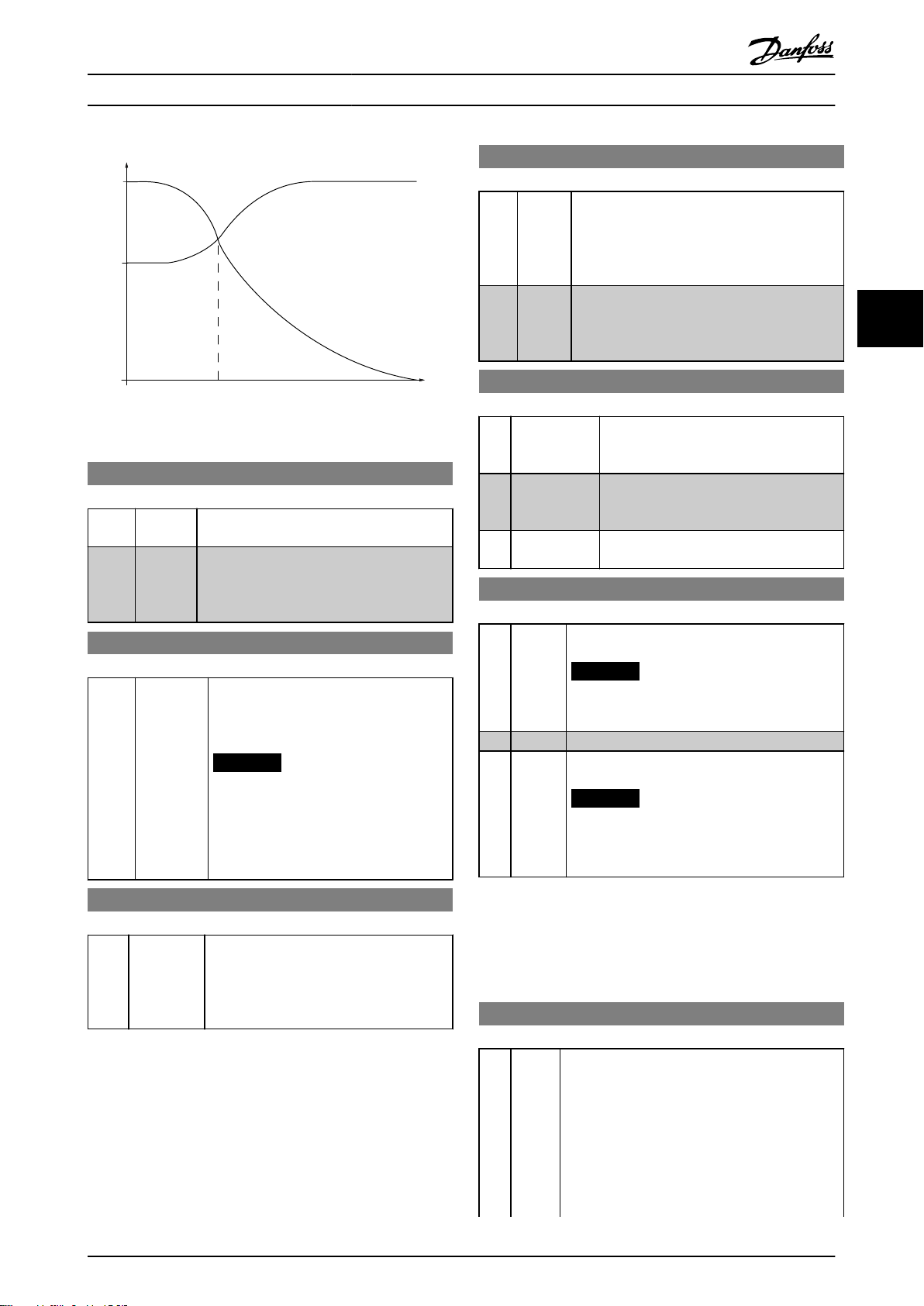
130BD018.10
60%
0%
100%
U
m
Changeover
f
out
Par.1-60 Par.1-61
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
Illustration 4.4 Load Compensation Characteristics
1-61 High Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
Use this parameter to obtain optimum load
compensation when running at high speed.
100 %* [0–199%]Enter percentage to compensate in relation
to load when motor runs at high speed.
Change-over point is automatically calculated
based on motor size.
1-62 Slip Compensation
Range: Function:
100 %* [-400–399%]Compensation for load dependent motor
slip.
Slip compensation is calculated automatically based on rated motor speed, n
M,N
.
NOTICE
This function is only active when 1-00
Configuration Mode, is set to [0]
Speed Open Loop and when 1-01
Motor Control Principle, is set to [1]
+
VVC
1-71 Start Delay
Range: Function:
The start delay defines the time to pass from a
start command is given until the motor starts
accelerating.
Setting start delay to 0.0 s disables 1-72 Start
Function, when start command is given.
0.0s* [0.0–
10.0 s]
Enter the time delay required before
commencing acceleration.
1-72 Start Function is active during Start delay
time.
1-72 Start Function
Option: Function:
[0] DC Hold/Delay
Time
[1] DC Brake/
Delay Time
[2] * Coast/Delay
Time
Motor is energised with DC holding current
(2-00 DC Hold Current) during start delay
time.
Motor is energised with DC braking current
(2-01 DC Brake Current) during start delay
time.
Inverter is coasted during start delay time
(inverter off).
1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
The Flying Start parameter is used to catch a
spinning motor after eg. mains drop-out.
NOTICE
This function is not suitable for hoisting
applications.
[0] * Disabled Flying start is not required.
[1] Enabled Frequency converter enabled to catch spinning
motor.
NOTICE
When flying start is enabled 1-71 Start
Delay, and 1-72 Start Function, have no
function.
4 4
1-63 Slip Compensation Time
Range: Function:
0.10 s [0.05–5.00s]Enter slip compensation reaction speed. A
high value results in slow reaction whereas
a low value results in quick reaction.
If low-frequency resonance problems arise,
use longer time setting.
4.2.5 1-7* Start Adjustments
Considering the need for various start functions in different
applications, it is possible to select a number of functions
in this parameter group.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 17
4.2.6 1-8* Stop Adjustments
To meet the need for various stop functions in different
application these parameters offer some special stop
features for the motor.
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
The selected function at stop is active in following
situations:
Stop command is given and output
•
speed is ramped down to Min. Speed for
Function at Stop.
Start command is removed (standby), and
•
output speed is ramped down to Min.
Speed for Function at Stop.
Page 20
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
DC-brake command is given, and DC-
•
brake time has passed
While running and calculated output
•
speed is below Min. Speed for Function at
Stop.
[0] * Coast The inverter is coasted.
44
[1] DC
hold
The motor is energised with a DC current. See 2-00
DC Hold Current for more information.
1-82 Min. Speed For Function at Stop [Hz]
NOTICE
When the ETR function has been selected the drive will
store the recorded temperature at power down and this
temperature will resume at power up regardless of the
elapsed time. Changing 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
back to [0] No Protection will reset the recorded
temperature.
1-93 Thermistor Resource
Option: Function:
Select the thermistor input terminal.
[0]*None No thermistor is connected.
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–20.0 Hz]
Set the speed at which to activate 1-80
Function at Stop.
[1] Analog
Input 53
Connect thermistor to analog input terminal 53.
NOTICE
Analog input 53 cannot be selected for
4.2.7 1-9* Motor Temperature
other purposes when selected as
thermistor resource.
With an estimated motor temperature monitor the
frequency converter is able to estimate motor temperature
without having a thermistor mounted. It is thus possible to
receive a warning or an alarm, if motor temperature
exceeds upper operational limit.
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
Using ETR (Electronic Terminal Relay) the
motor temperature is calculated based on
frequency, speed and time. Danfoss
recommends using The ETR function, if a
thermistor is not present.
NOTICE
ETRElectronic Overload calculation is
[6] Digital
input 29
Connect thermistor to digital input terminal 29.
While this input functions as thermistor input, it
will not respond to the function chosen in 5-13
Digital Input 29. The value of 5-13 Digital Input 29
remains unchanged in parameter database while
function is inactive.
Input Digital/
Analog
Digital 10 V
Analog 10 V
Table 4.1 Threshold Cut-out Values
Supply
Voltage
Threshold Cut-
out
Values
<800 Ω ⇒ 2.9
kΩ
<800 Ω ⇒ 2.9
kΩ
based on motor data from parameter
group 1-2* Motor Data.
[0] * No
Protection
[1] Thermistor
Warning
[2] Thermistor
Trip
[3] ETR Warning If calculated upper limit of motor
[4] ETR Trip If 90% of calculated upper limit of motor
Disables temperature monitoring.
A thermistor connected to either digital or
analog input gives a warning if upper limit
of motor temperature range is exceeded,
(see 1-93 Thermistor Resource).
A thermistor connected to either digital or
analog input gives an alarm and makes the
frequency converter trip if upper limit of
motor temperature range is exceeded, (see
1-93 Thermistor Resource.
temperature range is exceeded, a warning
occurs.
temperature range is exceeded, an alarm
occurs and the frequency converter trips.
18 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 21
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.3 Parameter Group 2: Brakes
4.3.1 2-0* DC-Brake
The purpose of DC-brake function is to brake a rotating
motor by applying DC-current to the motor.
2-00 DC Hold Current
Range: Function:
This parameter either holds the motor (holding
torque) or pre-heats the motor.
The parameter is active if DC Hold has been
selected in either 1-72 Start Function or 1-80
Function at Stop.
50%* [0–
150%]
Enter a value for holding current as a
percentage of the rated motor current set in
1-24 Motor Current. 100% DC holding current
corresponds to I
M,N
.
NOTICE
Avoid 100% current too long as it may overheat the
motor.
2-01 DC Brake Current
Range: Function:
50%* [0–
150%]
2-02 DC-Braking Time
Range: Function:
10.0 s* [0.0–60 s]
Set DC-current needed to brake rotating motor.
Activate DC-brake in one of the four following
ways:
1.
DC-brake command, see 5-1* Digital
Inputs choice [5]
2.
DC Cut-in function, see 2-04 DC-Brake
Cut-in Speed
3. DC-brake selected as start function, see
1-72 Start Function
4.
DC-brake in connection with Flying
Start, 1-73 Flying Start.
DC-braking time defines the period during
which DC-brake current is applied to the
motor.
Set the time DC-braking current, set in 2-01
DC Brake Current, must be applied.
2-04 DC-Brake Cut-in Speed
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–400.0
Hz]
Set DC-brake cut-in speed to activate DC
braking current, set in 2-01 DC Brake
Current, when ramping down.
When set to 0 the function is off.
4.3.2 2-1* Brake Energy Function
Use the parameters in this group for selecting dynamic
braking parameters.
2-10 Brake Function
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Resistor brake is only functional in
frequency converters with integrated
dynamic brake. An external resistor must
be connected.
Resistor brake
The resistor brake limits voltage in the
intermediate circuit when the motor acts as
generator. Without brake resistor, the frequency
converter eventually trips.
The resistor brake consumes surplus energy
resulting from motor braking. A frequency
converter with brake, stops a motor faster than
without a brake, which is used in many
applications. Requires connection of external
brake resistor.
An alternative to the resistor brake is the AC
brake.
AC brake
The AC brake consumes surplus energy by
creating power loss in the motor.
It is important to keep in mind that an increase
in power loss causes motor temperature to rise.
* Off No brake function.
[0]
[1] Resistor
Brake
[2] AC Brake AC brake is active.
2-11 Brake Resistor (Ohm)
Range: Function:
5 Ω* [5–5000 Ω] Set brake resistor value.
Resistor brake is active.
4 4
NOTICE
If DC-brake is activated as start function, DC-brake time
is defined by start delay time.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 19
2-14 Brake Voltage Reduce
Range: Function:
0* [0–
100]
Change this parameter affects the value of 2-11
Brake Resistor (Ohm).
Use this parameter to set the voltage reduction for
resistor braking. It is only active when 2-10 Brake
Function is set to [1] Resistor Brake. This function is
valid for 400 v, 5.5–15 kW units.
Page 22
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
2-16 AC Brake, Max Current
Range: Function:
100.0%* [0.0–150.0%] Enter max. permissible current for ACbraking to avoid overheating of motor.
100% equals motor current set in 1-24
Motor Current.
2-17 Over-Voltage Control
Option: Function:
44
[0] * Disabled The OVC is not active/required.
[1] Enabled,
not at stop
[2] Enabled OVC is running, also when a stop signal is
Use overvoltage control (OVC) to reduce the
risk of the frequency converter tripping due to
an over voltage on the DC link caused by
generative power from the load.
An over-voltage occurs eg. if the ramp down
time is set too short compared to the actual
load inertia.
OVC is running unless a stop signal is active.
active.
2-22 Activating Mechanical Brake
Range: Function:
If the motor is stopped using ramp, the
mechanical brake is activated when motor speed is
less than Active Brake Speed.
Motor is ramped down to stop in the following
situations:
A start command is removed (stand by)
•
A stop command is activated
•
Quick-stop is activated (Q-stop ramp is
•
used)
0
[0–
Select motor speed at which mechanical brake
Hz*
400
activates when ramping down.
Hz]
Mechanical brake automatically activates if
frequency converter trips or reports an alarm.
NOTICE
If Resistor Brake has been chosen in 2-10 Brake Function
the OVC is not active even though enabled in this
parameter.
4.3.3 2-2* Mechanical Brake
For hoisting applications an electro-magnetic brake is
required. The brake is controlled by a relay, which releases
the brake when activated.
The brake activates if the frequency converter trips or a
coast command is given. Furthermore, it activates when
motor speed is ramped down below the speed set in 2-22
Active Brake Speed.
2-20 Release Brake Current
Range: Function:
0.00 A* [0.00–100 A] Select motor current at which mechanical
brake releases.
NOTICE
If start delay time has passed, and
motor current is below Release
brake current, frequency converter
trips.
20 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 23
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.4 Parameter Group 3: Reference/Ramps
Parameters for reference handling, definition of limitations,
and configuration of the frequency converter's reaction to
changes
4.4.1 3-0* Reference Limits
Parameters for setting the reference unit, limits and ranges.
3-00 Reference Range
Option: Function:
Select the range of reference and feedback
signals.
[0] * Min to
Max
[1] -Max to
+Max
3-02 Minimum Reference
Range: Function:
0.00* [-4999-4999] Enter value for minimum reference.
3-03 Maximum Reference
Range: Function:
60.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
to US; 50.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
to International *
Reference setpoint ranges can have positive
values only.
Select this if running in Process Closed Loop.
Ranges can have both positive and negative
values.
If potentiometer is used to adjust motor running
in both direction, set reference range to –Max
Reference to Max Reference by par.=[1] Choose
hand on mode by LCP. Adjust the potentiometer
to minimum, the motor can run in anti-clockwise
with max speed. Then adjust the potentiometer
to maximum, the motor will ramp down to 0 and
run clockwise with max speed.
The sum of all internal and external
references are clamped (limited) to the
minimum reference value, 3-02 Minimum
Reference.
Maximum Reference is
adjustable in the range
Minimum Reference–4999.
[-4999–
4999]
Enter value for Maximum
Reference.
The sum of all internal and
external references are
clamped (limited) to the
maximum reference value,
3-03 Maximum Reference.
4.4.2 3-1* References
Parameters for setting up the reference sources. Select the
preset references for the corresponding digital inputs in
parameter group, 5-1* Digital Inputs.
3-10 Preset Reference
Option: Function:
Each parameter set-up contains 8 preset
references which are selectable via 3 digital
inputs or bus.
[18]
Bit2
0 0 0 0
0 0 1 1
0 1 0 2
0 1 1 3
1 0 0 4
1 0 1 5
1 1 0 6
1 1 1 7
Table 4.2 Parameter Group 5-1* Digital
Inputs Option [16], [17] and [18]
[0.00]*-100.00–
100.00%
Enter the different preset references using
array programming.
Normally, 100%=value set in 3-03 Maximum
Reference.
However, there are exceptions if 3-00 Reference
Range is set to [0] Min - Max.
Example 1:
3-02 Minimum Reference is set to 20 and 3-03
Maximum Reference is set to 50. In this case
0%=0 and 100%=50.
Example 2:
3-02 Minimum Reference is set to -70 and 3-03
Maximum Reference is set to 50. In this case
0%=0 and 100%=70.
3-11 Jog Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Jog speed is a fixed output speed and
overrules the selected reference speed, see
parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs option [14].
If the motor is stopped while in jog mode, the
jog signal acts as a start signal.
Removing the jog signal makes the motor run
according to the selected configuration.
5.0Hz [0.0–
400.0
Hz]
Select speed to function as jog speed.
[17]
Bit1
[16]
Bit0
[16]
Bit0
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 21
Page 24

Relative
Z=X+X*Y/100
Resulting
actual
reference
Y
X
130BA059.12
Z
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
3-12 Catch Up/Slow Down Value
Range: Function:
0% * [0–
100%]
44
The Catch-up/Slowdown function is activated by
an input command (see 5-1* Digital Inputs,
choice [28]/[29]). If the command is active, the
Catch-up/Slowdown value (in %) is added to the
reference function as follows:
Reference
=
Reference
+
Reference
−
Reference
Catchup Slowdown
×
100
Reference
=
Catchup Slowdown
×
100
Reference
When the input command is inactivated, the
reference returns to its original value ie.
Reference=Reference + 0.
3-14 Preset Relative Reference
Range: Function:
0.00%
[-100.00–
100.00%]
Define fixed value in % to be added to
variable value defined in 3-18 Relative Scaling
Reference Source.
The sum of fixed and variable values (labeled
Y in illustration below) is multiplied with
actual reference (labeled X in illustration). This
product is added to actual reference
+ X ×
100
Y
X
3-16 Reference 2 Source
Option: Function:
See 3-15 Reference 1 Source for
description.
[0] No Function No reference signal is defined.
[1] Analog Input 53 Use signals from analog input 53 as
reference.
[2] * Analog Input 60 Use signals from analog input 60 as
reference.
[8] Pulse input 33 Use signals from pulse input as
reference, see parameter group 5-5*
Pulse Input.
[11] Local Bus
Use signals from local bus as reference.
Reference
[21] LCP Potenti-
ometer
Use signals from LCP potentiometer as
reference.
3-17 Reference 3 Source
Option: Function:
See 3-15 Reference 2 Source for
description.
[0] No Function No reference signal is defined.
[1] Analog Input 53 Use signals from analog input 53 as
reference.
[2] Analog Input 60 Use signals from analog input 60 as
reference.
[8] Pulse input 33 Use signals from pulse input as
reference, see parameter group 5-5*
Illustration 4.5 Formula for Actual
Reference
[11] * Local Bus
Pulse Input.
Use signals from local bus as reference.
Reference
[21] LCP Potenti-
ometer
Use signals from LCP potentiometer as
reference.
3-15 Reference 1 Source
Option: Function:
3-15 Reference 1 Source, 3-16 Reference 2
Source and 3-17 Reference 3 Source define
up to three different reference signals. The
sum of these reference signals defines the
actual reference.
[0] No Function No reference signal is defined.
[1] * Analog Input53Use signals from analog input 53 as
reference, see parameter group 6-1* Analog
Input 1.
[2] Analog Input60Use signals from analog input 60 as
reference, see parameter group 6-2* Analog
Input 2.
[8] Pulse input 33 Use signals from pulse input as reference,
see parameter group 5-5* Pulse Input.
[11] Local Bus
Reference
[21] LCP Potenti-
ometer
Use signals from local bus as reference, see
parameter group 8-9* Bus Feedback.
Use signals from LCP potentiometer as
reference, parameter group 6-8* LCP
Potentiometer.
3-18 Relative Scaling Reference Source
Option: Function:
Select the source for a variable value to
be added to the fixed value defined in
3-14 Preset Relative Reference.
[0] * No Function The function is disabled
[1] Analog Input 53 Select analog input 53 as relative scaling
reference source.
[2] Analog Input 60 Select analog input 60 as relative scaling
reference source.
[8] Pulse Input 33 Select pulse input 33 as relative scaling
reference source.
[11] Local Bus
Reference
[21] LCP Potenti-
ometer
Select local bus ref. as relative scaling
reference source.
Select LCP potentiometer as relative
scaling reference source.
22 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 25

130BA168.10
Ramp (X) S-Ramp
Ratio at Accel.End
Jerk compensated
Ramp (X)
Up Time
Ramp (X)
S-Ramp
Ratio at
Accel.End
Linear
Speed
Ramp (X)
Down Time
Ramp (X)
S-Ramp
Ratio at
Dec.End
Ramp (X) S-Ramp
Ratio at Dec.End
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.4.3 3-4* Ramp 1
3-42 Ramp1 Ramp-down Time
Range: Function:
A linear ramp is characterized by ramping up at a constant
speed until the desired motor speed has been reached.
Some overshoot may be experienced when reaching
speed, which may cause speed jerks for a short while
before stabilizing.
An S-ramp accelerates more smoothly thus compensating
for jerks when the speed is reached.
See Illustration 4.6 for a comparison of the two ramp types.
Size
related*
[0.05-3600.00s]Enter ramp down time from rated
motor frequency (f
Frequency to 0 Hz.
Select a ramp down time that does
not cause overvoltage in the inverter
due to regenerative operation of
motor. Furthermore, regenerative
torque must not exceed limit set in
4-17 Torque Limit in Generator Mode.
M,N
4.4.4 3-5* Ramp2
See parameter group 3-4* Ramp 1 for a description of
ramp types.
NOTICE
Ramp2 - alternative ramp times:
Changing from Ramp1 to Ramp2 is done via the digital
input. See 5-1* Digital Inputs, option [34].
Illustration 4.6 Ramp Type Comparison
Ramp Times
Ramp up: Acceleration time from 0 to nominal motor
frequency (1-23 Motor Frequency).
Deceleration time from nominal motor frequency (1-23
Motor Frequency) to 0.
Limitation
Too short ramp up time can result in Torque limit warning
(W12) and/or DC over voltage warning (W7). Ramping is
stopped when the frequency converter has reached Torque
limit motor mode (4-16 Torque Limit in Motor Mode).
Too short ramp down time can result in Torque limit
warning (W12) and/or DC over voltage warning (W7).
Ramping is stopped when the frequency converter reaches
the Torque limit generator mode (4-17 Torque Limit in
Generator Mode) and/or the internal DC over voltage limit.
3-40 Ramp1 Type
Option: Function:
[0] * Linear Constant acceleration/deceleration.
[2] S-ramp Smooth jerk compensated acceleration/
deceleration.
3-41 Ramp1 Ramp-up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 23
[0.05-3600.00 s] Enter ramp-up time from 0 Hz to
rated motor frequency (f
1-23 Motor Frequency.
Select a ramp-up time ensuring
that torque limit is not exceeded,
see 4-16 Torque Limit in Motor
Mode.
M,N
) set in
3-50 Ramp2 Type
Option: Function:
[0] * Linear Constant acceleration/deceleration.
[2] S-ramp Smooth jerk compensated acceleration/
deceleration.
3-51 Ramp2 Ramp-up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.05-3600.00 s] Enter ramp-up time from 0 Hz to
rated motor frequency (f
1-23 Motor Frequency.
Choose a ramp-up time ensuring
that torque limit is not exceeded,
see 4-16 Torque Limit in Motor
Mode.
3-52 Ramp2 Ramp-down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related
[0.05-3600.00s]Enter ramp down time from rated
motor frequency (f
Frequency to 0 Hz.
Choose a ramp down time that does
not cause over-voltage in inverter
due to regenerative operation of
motor. Furthermore, regenerative
torque must not exceed limit set in
4-17 Torque Limit in Generator Mode.
M,N
) in 1-23 Motor
) set in
M,N
) in 1-23 Motor
4 4
Page 26

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.4.5 3-8* Other Ramps
This section contains parameters for Jog and Quick Stop
Ramps.
With a Jog Ramp it is possible to both ramp up and down
whereas, it is only possible to ramp down with the Quick
Stop Ramp.
44
3-80 Jog Ramp Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.05-3600.00s]A linear ramp applicable when Jog
is activated. See parameter group
5-1* Digital Inputs, option [14].
Ramp up time = Ramp down time.
Jog Ramp time starts upon
activation of a jog signal via a
selected digital input or serial
communication port.
3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time
Range: Function:
Size related* [0.05-3600.00 s] A linear ramp applicable when
Q-stop is activated. See
parameter group 5-1* Digital
Inputs, option [4].
24 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 27

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.5 Parameter Group 4: Limits/Warnings
Parameter group for configuring limits and warning.
4.5.1 4-1* Motor Limits
Use these parameters for defining the speed, torque and
current working range for the motor.
4-10 Motor Speed Direction
Option: Function:
If terminals 96, 97 and 98 are connected to U,
V and W respectively, the motor runs clockwise
when seen from the front.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while
the motor is running
[0]*Clockwise The motor shaft rotates in clockwise direction.
This setting prevents the motor from running
in counterclockwise direction. If 1-00 Configu-
ration Mode is set to close loop control, 4-10
Motor Speed Direction will be automatically set
to clockwise.
[1] Counter-
clockwise
[2]*Both With this setting the motor can run in both
The motor shaft rotates in counterclockwise
direction. This setting prevents the motor from
running in clockwise direction.
directions. However, the output frequency is
limited to the range: Motor Speed Low Limit
(4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit) to Motor Speed
High Limit (4-14 Motor Speed High Limit). If 1-00
Configuration Mode is set to open loop control,
4-10 Motor Speed Direction will be automatically
set to both direction
4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0-400.0 Hz]
Set the Minimum Motor Speed Limit
corresponding to the minimum output
frequency of the motor shaft.
NOTICE
As the minimum output frequency
is an absolute value, it cannot be
deviated from.
4-16 Torque Limit in Motor Mode
Range: Function:
150 %* [0-400%] Set the torque limit for motor operation.
The setting is not automatically reset to
default when changing settings in 1-00
Configuration Mode to 1-25 Load & Motor.
4-17 Torque Limit in Generator Mode
Range: Function:
100 %* [0-400%] Set the torque limit for generator mode
operation.
The setting is not automatically reset to
default when changing settings in 1-00
Configuration Mode to 1-25 Load & Motor.
4.5.2 4-4* Adjustable Warnings 2
4-40 Warning Freq. Low
Range: Function:
Size
related*
4-41 Warning Freq. High
Use this parameter to set a higher limit for the frequency range.
When the motor speed exceeds this limit, the display reads
SPEED HIGH. Warning bit 9 is set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The
output relay or the digital output can be configured to indicate
this warning. The LCP warning indicator light is not turned on
when this parameter set limit is reached.
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0 - 400 Hz]
[ 0 400
Hz]
Use this parameter to set a lower limit for
the frequency range.
When the motor speed drops below this
limit, the display reads SPEED LOW. Warning
bit 10 is set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The
output relay or the digital output can be
configured to indicate this warning. The LCP
warning indicator light is not turned on
when this parameter set limit is reached.
4 4
4-14 Motor Speed High Limit
Range: Function:
65.0 Hz* [0.0-400.0 Hz]
Set the Maximum Motor Speed
corresponding to the maximum output
frequency of the motor shaft.
NOTICE
As the maximum output
frequency is an absolute value, it
cannot be deviated from.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 25
Page 28

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.5.3 4-5* Adjustable Warnings
4-55 Warning Reference High
Range: Function:
Parameter group containing adjustable warning limits for
current, speed, reference and feedback.
Warnings are shown in display, programmed output or
serial bus.
4-50 Warning Current Low
44
Range: Function:
Use this parameter to set a lower limit for
the current range.
If current drops below the set limit, warning
bit 8 is set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word.
Output Relay can be configured to indicate
this warning. LCP warning light does not
light when this parameter's set limit is
reached.
0.00A* [0.00–
100.00A]
Set value for low current limit.
4-51 Warning Current High
4-56 Warning Feedback Low
Range: Function:
-4999* [-4999 4999]
4-57 Warning Feedback High
Range: Function:
4999* [-4999 -
4999]
Range: Function:
Use this parameter to set an upper limit for
the current range.
If current exceeds the set limit, warning bit
7 is set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word.
Output Relay can be configured to indicate
this warning. LCP warning light does not
light when this parameter's set limit is
4-58 Missing Motor Phase Function
Option: Function:
100.00A* [0.00–
100.00 A]
reached.
Set upper current limit.
4-54 Warning Reference Low
Range: Function:
-4999.000* [-4999.000–
Depends on the
value of 4-55
Warning
Reference High]
4-55 Warning Reference High
Range: Function:
4999* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Use this parameter to set a higher limit for
the reference range.
When the actual reference exceeds this limit,
the display reads Reference High. Warning bit
19 is set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The output
relay or the digital output can be configured
to indicate this warning. The LCP warning
Use this parameter to set a lower
limit for the reference range.
When the actual reference falls
below this limit, the display reads
Reference Low. Warning bit 20 is
set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word.
Output Relay can be configured to
indicate this warning. LCP warning
light does not light when this
parameter set limit is reached.
[0] Off Function is disabled.
[1] * On Function is enabled.
4.5.4 4-6* Speed Bypass
In some applications mechanical resonance may occur.
Avoid resonance points by creating a bypass. The
frequency converter ramps through the bypass area
thereby passing mechanical resonance points quickly.
indicator light is not turned on when this
parameter set limit is reached.
Use this parameter to set a lower limit for the
feedback range.
When the feedback drops below this limit, the
display reads Feedback Low. Warning bit 6 is
set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The output relay
or digital output can be configured to
indicate this warning. The LCP warning
indicator light does not light when this
parameter set limit is reached.
Use this parameter to set a higher limit for the
feedback range.
When the feedback exceeds this limit, the
display reads Feedback High. Warning bit 5 is
set in 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The output relay
or digital output can be configured to indicate
this warning. The LCP warning indicator light
does not light when this parameter set limit is
reached.
A missing motor phase causes the motor torque to
drop. This monitor may be disabled for special
purposes (eg. small motors running pure U/f mode),
but as there is a risk of overheating the motor,
Danfoss strongly recommends that the function is On.
A missing motor phase causes the frequency converter
to trip and report an alarm.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed while
motor runs.
26 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 29

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4-61 Speed Bypass From [Hz]
Array [2]
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–
400.0 Hz]
Enter either the lower or upper limit of the
speeds to be avoided.
It does not matter whether Bypass From or
Bypass To is the upper or lower limit,
however the Speed Bypass function is
disabled if the two parameters are set to
the same value.
4-63 Speed Bypass To [Hz]
Array [2]
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–400.0
Hz]
Enter either the upper or lower limit of
the speed area to be avoided.
Make sure to enter the opposite limit of
that in 4-61 Speed Bypass From [Hz].
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 27
Page 30

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.6 Parameter Group 5: Digital In/Out
The following describes all digital input command
functions and signals.
4.6.1 5-1* Digital Inputs
Parameters for configuring the functions for the input
terminals.
44
The digital inputs are used for selecting various functions
in the frequency converter. All digital inputs can be set to
the following:
[0] No
Operation
[1] Reset Reset the frequency converter after a Trip/
[2 ] Coast Inverse Coasting stop, inverted input (NC). The
[3] Coast and
reset inv.
[4] Quick stop
inverse
[5] DC-brake inv. Inverted input for DC braking (NC). Stops
[6] Stop inv. Stop inverted function. Generates stop
[8] Start Select start for a start/stop command.
[9] Latched start Motor starts if a pulse is applied for min. 2
[10] Reversing Change direction of motor shaft rotation.
[11] Start
reversing
[12] Enable start
forward
[13] Enable start
reverse
The frequency converter will not react to
signals transmitted to the terminal.
Alarm. Not all alarms can be reset.
frequency converter leaves the motor in free
mode.
Reset and coasting stop inverted input (NC).
The frequency converter resets and leaves
the motor in free mode.
Inverted input (NC). Generates a stop in
accordance with the quick-stop ramp time
set in 3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time. When
motor stops, shaft is in free mode.
motor by energizing it with DC current for a
certain time period, see 2-01 DC Brake
Current. Function is only active when value in
2-02 DC-Braking Time is different from 0.
function when selected terminal goes from
logical level “1” to “0”. Stop is performed
according to selected ramp time.
1 = Start, 0 = stop.
ms. Motor stops when Stop inverse is
activated.
Reversing signal only changes direction of
rotation; it does not activate start function.
Select [2] Both directions in 4.10 Motor Speed
Direction.
0 = normal, 1 = reversing.
Use for start/stop and for reversing at the
same time. Signals on start [8] are not
allowed at the same time.
0 = stop, 1 = start reversing.
Use if motor shaft must rotate clockwise at
start.
Use if motor shaft must rotate counterclockwise at start.
[14] Jog
[16] Preset
reference bit
0
[17] Preset
reference bit
1
[18] Preset
reference bit
2
[19] Freeze
reference
[20] Freeze
output
[21] Speed up Select Speed up and Speed down if digital
[22] Speed down Same as Speed-up [21].
[23] Setup select
bit 0
[28] Catch up Select Catch up/Slow down to increase or
[29] Slow down Same as Catch up [28]
[34] Ramp bit 0
Use for activating jog speed. See 3-11 Jog
Speed.
Preset reference bit 0, 1 and 2 enables a
choice between one of the eight preset
references according to below.
Same as preset reference bit 0 [16], see 3-10
Preset Reference.
Same as preset reference bit 0 [16].
Freeze actual reference. The frozen reference
is now the point of enable/condition for
Speed up and Speed down to be used. If
Speed up/down is used, speed change
always follows ramp 2 (3-51 Ramp2 Ramp-up
Time and 3-52 Ramp2 Ramp-down Time) in
the range 3-02 Minimum Reference - 3-03
Maximum Reference.
Freeze the actual motor frequency (Hz). The
frozen motor frequency is now the point of
enable/condition for Speed up and Speed
down to be used. If Speed up/down is used,
the speed change always follows ramp 2 in
the range 4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit - 4-14
Motor Speed High Limit.
NOTICE
When freeze output is active, the
frequency converter cannot be
stopped via a low [8] Start signal. Stop
the frequency converter via a terminal
programmed for Coasting Inverse [2]
or Coast and reset, inverse [3].
control of the up/down speed is desired
(motor potentiometer). Activate this function
by selecting either Freeze reference or Freeze
output. When Speed-up is activated for less
than 400 ms. the resulting reference will be
increased by 0.1%. If Speed-up is activated
for more than 400 ms. the resulting reference
will ramp according to ramp 2 in 3-51 Ramp2
Ramp-up Time.
Set 0-10 Active set-up to Multi set-up.
Logic 0 = set up 1, Logic 1 = Set up 2.
reduce the resulting reference value by the
percentage set in 3-12 Catch Up/Slow Down
Value
Logic 0=Ramp1, see parameter group 3-4*
Ramp1
Logic 1=Ramp2, see parameter group 3-5*
Ramp2.
28 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 31

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
[60] Counter A
(up)
[61] Counter A
(down)
[62] Reset
counter A
[63] Counter B
(up)
[64] Counter B
(down)
[65] Reset
counter B
Input for counter A.
Input for counter A.
Input for reset of counter A.
Input for counter B.
Input for counter B.
Input for reset of counter B.
5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[8] * Start Select function from available digital input range.
See parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs for choices.
5-11 Terminal 19 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[10] * Reversing Select function from available digital input
range.
See parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs for
choices.
5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[1] * Reset Select function from available digital input range.
See parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs* for choices.
5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[14] * Jog Select function from available digital input range.
See parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs for choices.
5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[16] * Preset bit 0 Select function from available digital input
range.
See parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs for
choices.
4.6.2 5-3* Digital Outputs
5-34 On Delay, Digital Output
Enter the delay time before the digital output is switched on.
The digital output (terminal 42/45) condition must not be
interrupted during the delay time.
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s]
5-35 Off Delay, Digital Output
Enter the delay time before the digital output is switched off.
The digital output (terminal 42/45) condition must not be
interrupted during the delay time.
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s]
4.6.3 5-4* Relays
Parameter group for configuring timing and output
functions for relays.
[0] No Operation Default for all digital and relay outputs.
[1] Control Ready Control board receives supply voltage.
[2] Drive Ready Frequency converter is ready for
operation and applies supply signal on
control board.
[3] Drive Ready,
Remote
[4] Enable/No
Warning
[5] Drive Running Motor is running.
[6] Running/No
Warning
[7] Run in Range/No
Warning
[8] Run on ref/No
Warning
[9] Alarm An alarm activates output.
[10] Alarm on
Warning
[12] Out of Current
Range
[13] Below Current,
low
[14] Above Current,
high
[16] Below Frequency,
low
[17] Above
Frequency, high
[19] Below Feedback,
low
[20] Above Feedback,
high
[21] Thermal Warning Thermal warning is present when
Frequency converter is ready for
operation in Auto On-mode.
Frequency converter is ready for
operation. No start or stop command is
given. No warnings are present.
Motor runs, and no warning are present.
Motor runs within programmed current
ranges, see 4-50 Warning Current Low
and 4-51 Warning Current High. No
warnings are present.
Motor runs at reference speed.
An alarm or warning activates output.
Motor current is outside range set in
4-50 Warning Current Low and 4-51
Warning Current High.
Motor current is lower than set in 4-50
Warning Current Low.
Motor current is higher than set in 4-51
Warning Current High.
Motor speed is lower than set in 4-40
Warning Frequency Low.
Motor speed is higher than set in 4-41
Warning Frequency High.
Feedback is lower than set in 4-56
Warning Feedback Low.
Feedback is higher than set in 4-57
Warning Feedback High.
temperature exceeds limit in motor,
frequency converter, brake resistor or
thermistor.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 29
Page 32

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
[22] Ready, No
Thermal Warning
[23] Remote Ready,
No Thermal
Warning
[24] Ready, VoltageOKFrequency converter is ready for
44
[25] Reverse Motor runs/is ready to run clockwise
[26] Bus OK Active communication (no time-out) via
[28] Brake, No Warn Brake is active, and no warnings are
[29] Brake Ready/No
Fault
[30] Brake Fault (IGBT) Protects frequency converter if fault on
[32] Mech. Brake
Control
[36] Control Word Bit11Bit 11 in control word controls relay.
[41] Below Reference,
low
[42] Above Reference,
high
[51] Local Reference
Active
[52] Remote
Reference Active
[53] No Alarm
[54] Start Cmd Active
[55] Running Reverse
[56] Drive in Hand
Mode
[57] Drive in Auto
Mode
[60] Comparator 0
[61] Comparator 1
[62] Comparator 2
[63] Comparator 3
Frequency converter is ready for
operation and no over-temperature
warning is present.
Frequency converter is ready for
operation in Auto mode, and no overtemperature warning is present.
operation and mains voltage is within
specified voltage range.
when logic = 0 and counter clockwise
when logic = 1. Output changes as soon
as reversing signal is applied.
serial communication port.
present.
Brake is ready for operation, and no
faults are present.
brake modules is present. Use relay to
cut out main voltage from frequency
converter.
Enables control of external mechanical
brake, see parameter group 2-2*
Mechanical Brake.
Reference is lower than set in 4-54
Warning Reference Low.
Reference is higher than set in 4-55
Warning Reference High.
See parameter group 13-1* Comparators.
If comparator 0 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-1* Comparators.
If comparator 1 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-1* Comparators.
If comparator 2 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-1* Comparators.
If comparator 3 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[70] Logic Rule 0
[71] Logic Rule 1
[72] Logic Rule 2
[73] Logic Rule 3
[81] SL Digital Output
B
See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
Logic Rule 1 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
Logic Rule 2 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
Logic Rule 3 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
Logic Rule 3 is evaluated as TRUE,
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
See 13-52 SL Control Action. When Smart
Logic Action [39] Set dig. out. A high is
executed, input goes high. When Smart
Logic Action [33] Set dig. out. A low is
executed, input goes low.
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[0] * No Operation Select function from available relay output
range.
5-41 On delay, Relay
Option: Function:
[0.01 s] * 0.00–
600.00 s
Enter the delay of the relay cut-in time. If
the Selected Event condition changes
before the On delay timer expires, the
relay output is unaffected. The function to
control the relay see 5-40 Function Relay.
5-42 Off delay, Relay
Option: Function:
[0.01 s] * 0.00–
600.00 s
Enter the delay of the relay cut-off time. If
the Selected Event condition changes
before the off delay timer expires, the
relay output is unaffected. The function to
control the relay see 5-40 Function Relay.
4.6.4 5-5* Pulse Input
Set 5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input to choice [32] pulse input.
Now terminal 33 handles a pulse input in the range from
Low frequency, 5-55 Terminal 33 Low Frequency, to 5-56
Terminal 33 High Frequency. Scale frequency input via 5-57
Terminal 33 Low Ref./Feedb. Value and 5-58 Terminal 33 High
Ref./Feedb. Value.
5-55 Terminal 33 Low Frequency
Range: Function:
20 Hz* [20–4999
Hz]
Enter low frequency corresponding to low
motor shaft speed (i.e. low reference
value) in 5-57 Terminal 33 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value.
30 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 33

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
5-56 Terminal 33 High Frequency
Range: Function:
5000 Hz* [21–5000
Hz]
Enter high frequency corresponding to
high motor shaft speed (i.e. high
reference value) in 5-58 Terminal 33 High
Ref./Feedb. Value.
5-57 Terminal 33 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
0.000* [-4999–4999] Set reference/feedback value
corresponding to low pulse frequency
value set in 5-55 Terminal 33 Low
Frequency.
5-58 Terminal 33 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
60.000 Hz if parameter
0-03 is set to US;
50.000 Hz if parameter
0-03 is set to International*
[-4999-4999] Set reference/feedback
value corresponding to
high pulse frequency
value set in 5-56 Terminal
33 High Frequency.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 31
Page 34

Ref./Feedback
[RPM]
Analog input
High Ref./
Feedb. Value'
Low Ref./
Feedb. Value'
'Low Voltage'or
'Low Current'
'High Voltage'or
'High Current'
130BD019.10
1 V 5 V 10 V
300
600
900
1200
1500
[V]
150
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
44
4.7 Parameter Group 6: Analog In/Out
Parameter group for configuring analog inputs and
outputs.
NOTICE
Micro switch 4 in position U:
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage and 6-11 Terminal 53 High
Voltage are active.
Micro switch 4 in position I:
4.7.1 6-0* Analog I/O Mode
6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current and 6-13 Terminal 53 High
Current are active.
Parameter group for setting up the analog I/O configuration.
6-00 Live Zero Timeout Time
Range: Function:
The Live Zero function is used for monitoring the
signal on an analog input. If the signal disappears,
a Live Zero warning is reported.
10 s* [1–99
s]
Set delay time before Live Zero Timeout Function is
applied (6-01 Live Zero Timeout Time).
If the signal reappears during the set delay, timer
will be reset.
When live zero is detected, the frequency
converter freezes output frequency and starts Live
Zero Timeout timer.
Illustration 4.7 S200 Switches 1–4
6-01 Live Zero Timeout Function
Option: Function:
Function is activated if input signal is below
50% of value set in 6-10 Terminal 53 Low
Voltage, 6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current or 6-22
Terminal 60 Low Current.
[0] * Off Function is disabled.
[1] Freeze
output
[2] Stop Frequency converter ramps down to 0 Hz.
[3] Jogging Frequency converter ramps to jog speed, see
[4] Max Speed Frequency converter ramps to Motor Speed
[5] Stop and
Trip
Output frequency remains at value it had
when live zero was detected.
Remove live zero error condition before
restarting frequency converter.
3-11 Jog Speed.
High Limit, see 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit.
Frequency converter ramps down to 0 Hz and
then trips. Remove live zero condition and
activate reset before restarting the frequency
converter.
Illustration 4.8 Parameters for Configuring Analog Inputs
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage
Range: Function:
NOTICE
The value must be set to min. 1 V in
4.7.2 6-1* Analog Input 1
Parameters for configuring scaling and limits for analog
input 1 (terminal 53).
32 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
0.07 V* [0.00–
9.90 V]
order to activate the Live Zero
Timeout function in 6-01 Live Zero
Timeout Function.
This scaling value should correspond to
minimum reference value set in 6-14
Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb. Value. See also
chapter 4.4 Parameter Group 3: Reference/
Ramps.
Enter low voltage value.
Page 35

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
6-11 Terminal 53 High Voltage
Range: Function:
This scaling value should correspond to
maximum reference value set in 6-15
Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb. Value.
10.0 V* [0.10–10.00V]Enter high voltage value.
6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current
Range: Function:
NOTICE
The value must be set to min. 2 mA
in order to activate the Live Zero
Timeout function in 6-01 Live Zero
Timeout Function.
This reference signal should correspond
to minimum reference value set in 6-14
Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb. Value.
0.14
mA*
6-13 Terminal 53 High Current
Range: Function:
20.00 mA* [0.00–20.00
6-14 Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
0.000* [-4999–
[0.00–
19.90 mA]
mA]
4999]
Enter the low current value.
This reference signal should
correspond to the maximum reference
value set in 6-15 Terminal 53 High Ref./
Feedb. Value.
Enter high current value.
The scaling value corresponding to the
low voltage/low current set in 6-10
Terminal 53 Low Voltage and 6-12 Terminal
53 Low Current.
Enter analog input scaling value.
6-16 Terminal 53 Filter Time Constant
Range: Function:
A first-order digital low pass filter time
constant for suppressing electrical noise in
terminal 53. A high time constant value
improves dampening but also increases
time delay through the filter.
0.01 s* [0.01–10.00s]Enter time constant.
6-19 Terminal 53 Mode
Option: Function:
Select the input to be present on terminal
53.
NOTICE
6-19 Terminal 53 Mode MUST be set
according to Micro switch 4 setting.
[0] * Voltage Mode
[1] Current Mode
4.7.3 6-2* Analog Input 2
Parameters for configuring scaling and limits for analog
input 2, terminal 60.
6-22 Terminal 60 Low Current
Range: Function:
NOTICE
The value must be set to min. 2 mA
to activate the Live Zero Timeout
function in 6-01 Live Zero Timeout
Time.
This reference signal should correspond
to minimum reference value set in 6-24
Terminal 60 Low Ref./Feedb. Value.
0.14
mA*
[0.00–
20.00 mA]
Enter the low current value.
4 4
6-15 Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
The scaling value
corresponding to the high
voltage/high current set in
6-11 Terminal 53 High
Voltage and 6-13 Terminal
53 High Current.
60.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is
set to US; 50.000 Hz
if parameter 0-03 is
set to International
*
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 33
[-4999.000–
4999.000]
Enter analog input scaling
value.
6-23 Terminal 60 High Current
Range: Function:
This reference signal should
correspond to the high current value
set in 6-25 Terminal 60 High Ref./Feedb.
Value.
20.00 mA* [0.00–20.00
mA]
Enter high current value.
6-24 Terminal 60 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
The scaling value corresponding to the
low current set in 6-22 Terminal 60 Low
Current.
0.000* [-4999–4999] Enter analog input scaling value.
Page 36

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
6-25 Terminal 60 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
The scaling value
corresponding to the high
current set in 6-23
Terminal 60 High Current.
60.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
44
to US; 50.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
to International *
[-4999-4999] Enter analog input scaling
value.
6-26 Terminal 60 Filter Time Constant
Range: Function:
A first-order digital low pass filter time
constant for suppressing electrical noise in
terminal 60. A high time constant value
improves dampening, but also increases
time delay through the filter.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed
while motor runs.
0.01 s* [0.01–
10.00 s]
Enter time constant.
6-82 LCP Potentiometer High Ref. Value
Range: Function:
The scaling value
corresponding to the
maximum reference feedback
value set in 3-03 Maximum
Reference.
60.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
to US; 50.000 Hz if
parameter 0-03 is set
to International *
[-4999–
4999]
Enter high reference value.
The reference value
corresponding to potentiometer turned fully clockwise
(200 degrees).
4.7.5 6-9* Analog Output
These parameters are for configuring the analog outputs of
the frequency converter.
6-90 Terminal 42 Mode
Option: Function:
[0] * 0-20 mA Range for analog outputs is 0-20 mA
[1] 4-20 mA Range for analog outputs is 4-20 mA
[2] Digital
output
Functions as slow reacting digital output. Set
value to either 0 mA (off) or 20 mA (on), see
6-92 Terminal 42 Digital Output.
4.7.4 6-8* LCP Potentiometer
The LCP potentiometer can be selected either as Reference
Resource or Relative Reference Resource.
NOTICE
In Hand mode, the LCP potentiometer functions as local
reference.
6-80 LCP Potmeter Enable
Option: Function:
If LCP Potmeter is disabled, [▲] [▼] can adjust
local reference, and Potmeter value does not give
any reference in Auto/Hand mode.
[0] Disabled
[1] * Enable
6-81 LCP Potentiometer Low Ref. Value
Range: Function:
The scaling value corresponding to 0.
0.000* [-4999–4999] Enter low reference value.
The reference value corresponding to
potentiometer turned fully counterclockwise (0 degrees).
6-91 Terminal 42 Analog Output
Option: Function:
Select the function for terminal
42 as an analog output.
[0] * No Operation
[10] Output Frequency [0-100
Hz]
[11] Reference (REF min-max)
[12] Feedback (FB min-max)
[13] Motor Current (0-I
[16] Power (0-P
[19] DC Link Voltage (0–1000
V)
[20] Bus Reference [0.0%
-100.0%]
nom
max
)
3-02 Minimum Reference to 3-03
Minimum Reference.
)
16-37 Inv. Max. Current is I
1-20 Motor Power is P
The analog output will follow
the reference value set on the
RS-485 bus.
6-92 Terminal 42 Digital Output
Option: Function:
See parameter group 5-4* Relays, for
choices and descriptions.
[0] * No Operation
[80] SL Digital
Output A
See 13-52 SL Control Action. When Smart
Logic Action [38] Set dig. out. A high is
executed, input goes high. When Smart
Logic Action [32] Set dig. out. A low is
executed, input goes low.
nom
.
max
(motor).
34 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 37

130BD020.10
(mA)
0%
20
0/4
100%
Current
Analogue
output
Min Scale
par. 6-93
Variable
for
output
example:
Speed
(RPM)
Analogue
Output
Max Scale
par. 6-94
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
6-93 Terminal 42 Output Min. Scale
Range: Function:
0.00% [0.00-200.0%] Scale minimum output of selected analog
signal at terminal 42 as percentage of
maximum signal value. E.g. if 0 mA (or 0
Hz) is desired at 25% of maximum output
value, program 25%. Scaling values up to
100% can never be higher than
corresponding setting in 6-94 Terminal 42
Output Min. Scale.
4 4
Illustration 4.9 Analog Output Parameters
6-94 Terminal 42 Output Max. Scale
Range: Function:
100.00%* [0.00–
200.00%]
Scale maximum output of selected analog
signal at terminal 42. Set value to
maximum value of current signal output.
Scale output to give a current lower than
20 mA at full scale; or 20 mA at an
output below 100% of maximum signal
value.
If 20 mA is the desired output current at
a value between 0-100% of the full-scale
output, programme percentage value in
the parameter, i.e. 50% = 20 mA. If a
current between 4 and 20 mA is desired
at maximum output (100%), calculate
percentage value as follows:
20
desired maximum current
mA
i.e.
10 mA =
20
× 100 = 200%
10
× 100 %
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 35
Page 38

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.8 Parameter Group 7: Controllers
Parameters group for configuring application controls.
4.8.1 7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedback
Select feedback sources and handling for Process PI
Control.
7-33 Process PI Proportional Gain
Option: Function:
[0.01] * 0.00–10.00 Enter the value for the P proportional gain,
i.e. the multiplication factor of the error
between the setpoint and the feedback
signal.
NOTICE
0.00=Off.
44
NOTICE
Set 3-15 Reference 1 Source to [0] No Function in order to
use Analog Input as a feedback signal.
In order to use analog input as a feedback resource, do
not use the same resource as reference resource in
parameters 3-15, 3-16 and 3-17.
7-20 Process CL Feedback Resources
Option: Function:
Select input to function as feedback
signal.
[0] * No Function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 60
[8] Pulse Input 33
[11] Local Bus
4.8.2 7-3* Process PI Control
7-34 Process PI Integral Time
Range: Function:
9999.00 s* [0.10–
9999.00 s]
The integrator provides an increasing
gain at a constant error between the
set point and the feedback signal. The
integral time is the time needed by the
integrator to reach the same gain as
the proportional gain.
7-38 Process Feed Forward Factor
Range: Function:
0%* [0–
400%]
The FF factor sends a part of the reference
signal around the PI controller which then only
affects part of the control signal.
By activating the FF factor less overshoot and
high dynamics are gained when changing the
setpoint.
This parameter is always active when 1-00
Configuration Mode is set to [3] Process.
7-30 Process PI Normal/Inverse Control
Option: Function:
[0] * Normal Feedback larger than setpoint results in a speed
reduction.
Feedback less than setpoint results in a speed
increase.
[1] Inverse Feedback larger than setpoint results in a speed
increase.
Feedback less than setpoint results in a speed
reduction.
7-31 Process PI Anti Windup
Option: Function:
[0] Disable Regulation of a given error continues even when
the output frequency cannot be increased/
decreased.
[1] * Enable PI-controller ceases from regulating a given error
when the output frequency cannot be increased/
decreased.
7-32 Process PI Start Speed
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0–200.0 Hz] Until the set motor speed has been
reached, the frequency converter
operates in open loop mode.
7-39 On Reference Bandwidth
Range: Function:
5% [0–200% ] Enter the value for the On Reference
Bandwidth.
The PI control error is the difference between
setpoint and feedback and when this is less
than the value set in this parameter the On
Reference is active.
36 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 39

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.9 Parameter Group 8: Communication
Parameter group for configuring communication.
4.9.1 8-0* General Settings
Use this parameter group for configuring the general
settings for communication.
8-01 Control Site
Option: Function:
[0] * Digital and
Control Word
[1] Digital Only Use digital input as control.
[2] Control Word
Only
8-02 Control Word Source
Option: Function:
[0] None Function is inactive
[1] * FC RS-485 Monitoring control word source is done via
8-03 Control Word Timeout Time
Range: Function:
1.0 s* [0.1–6500 s] Enter time to pass before control word
8-04 Control Word Timeout Function
Option: Function:
[0] * Off No function.
[1] Freeze Output Freeze output until communication
[2] Stop Stop with auto restart when communication
[3] Jogging Run motor at jog frequency until communi-
[4] Max. Speed Run motor at max. frequency until
[5] Stop and Trip Stop motor, then reset frequency converter
Use both digital input and control word
as control.
Use control word only as control.
NOTICE
The setting in this parameter
overrules settings in 8-50 Coasting
Select to 8-56 Preset Reference
Select.
serial communication port RS-485.
timeout function (8-04 Control Word
Timeout Function) must be carried out.
Select the action to be taken in case of a
timeout.
resumes.
resumes.
cation resumes.
communication resumes.
in order to restart either via LCP or digital
input.
8-06 Reset Control Word Timeout
Option: Function:
Resetting the control word timeout will
remove any timeout function.
[0] * No Function Control word timeout is not reset.
[1] Do Reset Control word timeout is reset, and parameter
goes into [0] No Function state.
4.9.2 8-3* FC Port Settings
Parameters for configuring the FC Port.
8-30 Protocol
Option: Function:
Select the protocol to be used. Note that
changing protocol will not be effective until
after powering off the frequency converter.
[0] * FC
[2] Modbus RTU
8-31 Address
Range: Function:
Select the address for the bus.
1* [1 - Protocol-dependent] FC-bus range is 1-126.
Modbus range is 1-247.
8-32 FC Port Baud Rate
Option: Function:
Select baud rate for FC Port.
NOTICE
Changing baud rate will be effective
after responding to any ongoing busrequests.
[0] 2400 Baud
[1] 4800 Baud
[2] * 9600 Baud When choosing FC bus in 8-30
[3] * 19200 Baud When choosing Modbus in 8-30
[4] 38400 Baud
8-33 FC Port Parity
Option: Function:
This parameter only affects Modbus
as FC bus always has even parity.
[0] * Even Parity (1 stopbit)
[1] Odd parity
[2] No Parity (1 stopbit)
[3] No Parity (2 stopbit)
8-35 Minimum Response Delay
Range: Function:
0.010 s* [0.001-0.500 s] Specify minimum delay time between
receiving a request and transmitting a
response.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 37
Page 40

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
8-36 Max Response Delay
Range: Function:
5.000 s* [0.010-10.00 s] Specify maximum permissible delay
time between transmitting a request
and receiving a response. Exceeding
this time delay causes control word
timeout.
44
4.9.3 8-4* FC MC Protocol Set
8-42 FC Port PCD Write Configuration
Range: Function:
Size
related
[0] * None
[1] [302] Minimum Reference
[2] [303] Maximum Reference
[3] [312] Catch up/Slow Down
[4] [341] Ramp 1 Ramp up time
[5] [342] Ramp 1 Ramp down
[6] [351] Ramp 2 Ramp up time
[7] [352] Ramp 2 Ramp down
[8] [380] Jog Ramp Time
[9] [381] Quick Stop Time
[10] [412] Motor Speed Low Limit
[11] [414] Motor Speed High Limit
[12] [416] Torque Limit Motor
[13] [417] Torque Limit Generator
[14] FC Port CTW
[15] FC Port REF
[0–9999 ] Select the parameters
to be assigned to the
telegrams of PCDs.
The number of
available PCDs
depends on the
telegram type. The
values in PCDs are
then written to the
selected parameters
as data values.
Value
time
time
[Hz]
[Hz]
Mode
Mode
8-43 FC Port PCD Read Configuration
Array [16]
Option: Function:
[5] 1601 Reference [Unit]
[6] 1602 Reference %
[7] 1603 Status Word
[8] 1605 Main Actual Value [%]
[9] 1609 Custom Readout
[10] 1610 Power [kW]
[11] 1611 Power [hp]
[12] 1612 Motor Voltage
[13] 1613 Frequency
[14] 1614 Motor Current
[15] 1615 Frequency [%]
[16] 1618 Motor Thermal
[17] 1630 DC Link Voltage
[18] 1634 Heatsink Temp.
[19] 1635 Inverter Thermal
[20] 1638 SL Controller State
[21] 1650 External Reference
[22] 1651 Pulse Reference
[23] 1652 Feedback [Unit]
[24] 1660 Digital Input 18,19,27,33
[25] 1661 Digtial Input 29
[26] 1662 Analog Input 53(V)
[27] 1663 Analog Input 53(mA)
[28] 1664 Analog Input 60
[29] 1665 Analog Output 42 [mA]
[30] 1668 Freq. Input 33 [Hz]
[31] 1671 Relay Output [bin]
[32] 1672 Counter A
[33] 1673 Counter B
[34] 1690 Alarm Word
[35] 1692 Warning Word
[36] 1694 Ext. Status Word
Select the parameters to be
assigned to PCD's of
telegrams. The number of
available PCDs depends on
the telegrams. This table is
not for [0] array and [1]
array . For these two arrays,
index 1 is fixed to [7] and
index 2 is fixed to [8]. These
two arrays cannot be
changed by end user.
8-43 FC Port PCD Read Configuration
Array [16]
Option: Function:
[0] * None
[1] 1500 Operation Hours
[2] 1501 Running Hours
[3] 1502 kWh Counter
[4] 1600 Control Word
38 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 41

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.9.4 8-5* Digital/Bus
Parameters for configuring control word Digital/Bus
merging.
NOTICE
Parameters are only active when 8-01 Control Site, is set
to [0] Digital and control word.
8-50 Coasting Select
Option: Function:
Select control of coasting function via digital
input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-51 Quick Stop Select
Option: Function:
Select control of quick stop function via
digital input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-52 DC Brake Select
Option: Function:
Select control of DC brake via digital input
and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-53 Start Select
Option: Function:
Select control of start function via digital
input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-54 Reversing Select
Option: Function:
Select control of reversing function via digital
input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-55 Set-up Select
Option: Function:
Select control of set-up selection via digital
input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
8-56 Preset Reference Select
Option: Function:
Select control of Preset Reference selection
via digital input and/or bus.
[0] Digital Input Activation via a digital input.
[1] Bus Activation via serial communication port.
[2] LogicAnd Activation via serial communication port and
a digital input.
[3] * LogicOr Activation via serial communication port or a
digital input.
4.9.5 8-8* Bus communication diagnostics
These parameters are used for monitoring the Bus
communication via the Port.
8-80 Bus Message Count
Range: Function:
0 N/A* [0-0 N/A] This parameter shows the number of valid
telegrams detected on the bus.
8-81 Bus Error Count
Range: Function:
0 N/A* [0-0 N/A] This parameter shows the number of
telegrams with faults (e.g. CRC fault),
detected on the bus.
8-82 Slave Messages Rcvd
Range: Function:
0 N/A* [0-0 N/A] This parameter shows the number of valid
telegrams addressed to the slave, sent by the
frequency converter.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 39
Page 42

Parameter Descriptions
8-83 Slave Error Count
Range: Function:
0 N/A* [0-0 N/A] This parameter shows the number of error
telegrams, which could be executed by the
frequency converter.
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.9.6 8-9* Bus Feedback
44
Parameter for configuring bus feedback.
8-94 Bus Feedback 1
Range: Function:
0* [0x8000-0x7FFF] Bus feedback is delivered via FC or
Modbus by writing the feedback value into
this parameter.
40 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 43

130BD021.10
State 1
Event 1/
Action 1
State 2
Event 2/
Action 2
Start
event P13-01
State 3
Event 3/
Action 3
State 4
Event 4/
Action 4
Stop
event P13-02
Stop
event P13-02
Stop
event P13-02
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.10 Parameter Group 13: Smart Logic
Smart Logic Control (SLC)is a sequence of user-defined
actions (13-52 SL Controller Action [X]) executed by the SLC
when the associated user-defined event (13-51 SL Controller
Event [X]) is set to True.
Events and actions are linked in pairs, meaning that when
an event is true, the linked action is carried out. After this
the next event is evaluated and its belonging action
carried out and so on. Only one event is evaluated at the
time.
If an event is evaluated as False, the SLC takes no action
during the scan interval and no other events are evaluated.
It is possible to programme from 1 to 20 events and
actions.
When the last event/action has been executed, the
sequence starts again from event/action [0].
Illustration 4.10 Example with Three Events/Actions
Starting and stopping the SLC
Start the SLC by selecting [1] On in 13-00 SL Controller
Mode The SLC starts evaluating Event 0, and if this is
evaluated as TRUE, the SLC continues its cycle.
The SLC stops when the Stop Event, 13-02 Stop Event, is
TRUE. The SLC can also be stopped by selecting [0] Off in
13-00 SL Controller Mode.
To reset all SLC parameters select [1] Reset SLC in 13-03
Reset Smart Logic Controller and start programming from
scratch.
4.10.1
Use SLC settings to activate, deactivate and reset the
Smart Logic Control.
[0] * Off Function is disabled.
[1] On SLC is active.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 41
13-0* SLC Settings
13-00 SL Controller Mode
Option: Function:
13-01 Start Event
Option: Function:
Select input to activate Smart Logic
Control.
[0] False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] InRange
[4] OnReference
[7] Out of Current
Range
[8] BelowILow
[9] AboveIHigh
[16] ThermalWarning
[17] MainsOutOfRange Mains voltage is outside the specified
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning A warning is active.
[20] Alarm_Trip A trip alarm is active.
[21] Alarm_TripLock A trip lock alarm is active.
[22] Comparator 0 Use result of comparator 0 in logic
[23] Comparator 1 Use result of comparator 1 in logic
[24] Comparator 2 Use result of comparator 2 in logic
[25] Comparator 3 Use result of comparator 3 in logic
[26] LogicRule 0 Use result of logic rule 0 in logic rule.
[27] LogicRule 1 Use result of logic rule 1 in logic rule.
[28] LogicRule 2 Use result of logic rule 2 in logic rule.
[29] LogicRule 3 Use result of logic rule 3 in logic rule.
[33] DigitalInput_18 Use value of DI 18 in logic rule.
[34] DigitalInput_19 Use value of DI 19 in logic rule.
[35] DigitalInput_27 Use value of DI 27 in logic rule.
[36] DigitalInput_29 Use value of DI 29 in logic rule.
[38] DigitalInput_33
[39] * StartCommand
[40] DriveStopped
Enters False in logic rule.
Enters True in logic rule.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [5]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [7]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [8]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [12]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [13]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [14]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [21]
for description.
voltage range.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [25]
for description.
rule.
rule.
rule.
rule.
This event is True, if frequency
converter is started by any means
(digital input or other).
This event is True, if frequency
converter is stopped or coasted by
any means (digital input or other).
4 4
Page 44

Par. 13-11
Comparator Operator
=
TRUE longer than.
. . .
. . .
Par. 13-10
Comparator Operand
Par. 13-12
Comparator Value
130BD022.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
[0] False
[1] True
[2] Running
44
[3] InRange
[4] OnReference
[7] Out of Current
[8] BelowILow
[9] AboveIHigh
[16] ThermalWarning
[17] MainsOutOfRange Mains voltage is outside the specified
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning A warning is active.
[20] Alarm_Trip A trip alarm is active.
[21] Alarm_TripLock A trip lock alarm is active.
[22] Comparator 0 Use result of comparator 0 in logic
[23] Comparator 1 Use result of comparator 1 in logic
[24] Comparator 2 Use result of comparator 2 in logic
[25] Comparator 3 Use result of comparator 3 in logic
[26] LogicRule 0 Use result of logic rule 0 in logic rule.
[27] LogicRule 1 Use result of logic rule 1 in logic rule.
[28] LogicRule 2 Use result of logic rule 2 in logic rule.
[29] LogicRule 3 Use result of logic rule 3 in logic rule.
[30] SL Timeout0 Use result of timer 0 in logic rule.
[31] SL Timeout1 Use result of timer 1 in logic rule.
[32] SL Timeout2 Use result of timer 2 in logic rule.
[33] DigitalInput_18 Use value of DI 18 in logic rule.
[34] DigitalInput_19 Use value of DI 19 in logic rule.
[35] DigitalInput_27 Use value of DI 27 in logic rule.
[36] DigitalInput_29 Use value of DI 29 in logic rule.
[38] DigitalInput_33
[39] StartCommand
[40] * DriveStopped
42 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
13-02 Stop Event
Option: Function:
Select input to activate Smart Logic
Control.
Enters False in logic rule.
Enters True in logic rule.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [5]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [7]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [8]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [12]
Range
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [13]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [14]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [21]
for description.
voltage range.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [25]
for description.
rule.
rule.
rule.
rule.
This event is True, if frequency
converter is started by any means
(digital input or other).
This event is True, if frequency
converter is stopped or coasted by
any means (digital input or other).
13-03 Reset SLC
Option: Function:
[0] * Do Not Reset Retains all settings programmed in
parameter group 13.
[1] Reset SLC Reset all group 13 parameters to default
settings.
4.10.2 13-1* Comparators
Comparators are used for comparing continuous variables
(i.e. output frequency, output current, analog input etc.) to
fixed preset values.
Illustration 4.11 Comparator Parameters
In addition, there are digital values that will be compared
to fixed time values. See explanation in 13-10 Comparator
Operand. Comparators are evaluated once in each scan
interval. Use the result (TRUE or FALSE) directly. All
parameters in this parameter group are array parameters
with index 0 to 5. Select index 0 toprogramme Comparator
0, select index 1 to programme Comparator 1, and so on.
13-10 Comparator Operand
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select variable to be monitored by
comparator.
[0] * Disabled Comparator is disabled.
[1] Reference Resulting remote reference (not local) as a
percentage.
[2] Feedback Feedback in [Hz].
[3] MotorSpeed Motor speed in Hz.
[4] MotorCurrent Motor current in [A].
[6] MotorPower Motor power in either [kW] or [hp].
[7] MotorVoltage Motor voltage in [V].
[8] DCLinkVoltage DC-link voltage in [V].
[12] AnalogInput53 Expressed as actual value.
[13] AnalogInput60 Expressed as actual value.
[18] PulseInput33 Expressed as actual value.
[20] AlarmNumber Shows number of the alarm.
[30] CounterA Number of counts.
[31] CounterB Number of counts.
Page 45

. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
Par. 13-43
Logic Rule Operator 2
Par. 13-41
Logic Rule Operator 1
Par. 13-40
Logic Rule Boolean 1
Par. 13-42
Logic Rule Boolean 2
Par. 13-44
Logic Rule Boolean 3
130BD023.10
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
13-11 Comparator Operator
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select operator to be used in comparison.
[0] Less Than <
[1] * Approxi-
mately
equals ≈
[2] Greater Than>Inverse logic of option [0].
Result of evaluation is True if variable
selected in 13-10 Comparator Operand is
smaller than fixed value in 13-12 Comparator
Value. Result is False if variable selected in
13-10 Comparator Operand is greater than
fixed value in 13-12 Comparator Value.
Result of evaluation is True if variable
selected in 13-10 Comparator Operand is
approximately equal to fixed value in 13-12
Comparator Value.
Illustration 4.12 Parameters for Logic Rules
Priority of calculation
The results of 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1, 13-41 Logic Rule
Operator 1 and 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 are calculated
first. The outcome (TRUE/FALSE) of this calculation is
combined with the settings of 13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
and 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3, yielding the final result
13-12 Comparator Value
Array [4]
Range: Function:
0.0* [-9999-9999] Enter “trigger level” for variable monitored
by this comparator.
4.10.3 13-2* Timers
Use the timer results to define an event (13-51 SL Controller
Action) or as boolean input in a logic rule (13-40 Logic Rule
Boolean 1, 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 or 13-44 Logic Rule
Boolean 3).
When timer value has elapsed timer changes state from
False to True.
13-20 SLC Controller Timer
Array [3]
Range: Function:
0.0 s* [0.0-3600 s]
Enter value to define duration of the False
output from programmed timer. A timer is
only False if it is started by an action and
until the given timer value has elapsed.
4.10.4 13-4* Logic Rules
Combine up to three boolean inputs (TRUE/FALSE inputs)
from timers, comtors, digital inputs, status bits and events
using the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT. Select
boolean inputs for the calculation in 13-40 Logic Rule
Boolean 1, 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 and 13-44 Logic Rule
Boolean 3. Define the operators used to logically combine
the selected inputs in 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1 and
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 43
(TRUE/FALSE) of the logic rule.
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select first boolean input for selected
logic rule.
[0] * False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] InRange
[4] OnReference
[7] Out of Current
Range
[8] BelowILow
[9] AboveIHigh
[16] ThermalWarning
[17] MainsOutOfRange Mains voltage is outside the specified
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning A warning is active.
[20] Alarm_Trip A trip alarm is active.
[21] Alarm_TripLock A trip lock alarm is active.
[22] Comparator 0 Use result of comparator 0 in logic
[23] Comparator 1 Use result of comparator 1 in logic
[24] Comparator 2 Use result of comparator 2 in logic
[25] Comparator 3 Use result of comparator 3 in logic
[26] LogicRule 0 Use result of logic rule 0 in logic rule.
Enters False in logic rule.
Enters True in logic rule.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [5] for
description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [7] for
description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [8] for
description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [12]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [13]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [14]
for description.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [21]
for description.
voltage range.
See parameter group 5-4* Relays [25]
for description.
rule.
rule.
rule.
rule.
4 4
Page 46

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1
Array [4]
Option: Function:
[27] LogicRule 1 Use result of logic rule 1 in logic rule.
[28] LogicRule 2 Use result of logic rule 2 in logic rule.
[29] LogicRule 3 Use result of logic rule 3 in logic rule.
[30] SL Timeout0 Use result of timer 0 in logic rule.
[31] SL Timeout1 Use result of timer 1 in logic rule.
44
[32] SL Timeout2 Use result of timer 2 in logic rule.
[33] DigitalInput_18 Use value of DI 18 in logic rule.
[34] DigitalInput_19 Use value of DI 19 in logic rule.
[35] DigitalInput_27 Use value of DI 27 in logic rule.
[36] DigitalInput_29 Use value of DI 29 in logic rule.
[38] DigitalInput_33 Use value of DI 33 in logic rule
[39] StartCommand
[40] DriveStopped
This event is True, if frequency
converter is started by any means
(digital input or other).
This event is True, if frequency
converter is stopped or coasted by any
means (digital input or other).
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
Array [4]
Option: Function:
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 and the boolean
input from 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2.
[0] * Disabled
[1] And Evaluates expression [13-40/13-42] AND
[2] Or Evaluates expression [13-40/13-42] OR [13-44].
[3] And not Evaluates expression [13-40/13-42] AND NOT
[4] Or not Evaluates expression [13-40/13-42] OR NOT
[5] Not and Evaluates expression NOT [13-40/13-42] and
[6] Not or Evaluates expression NOT [13-40/13-42] OR
[7] Not and not Evaluates expression NOT [13-40/13-42] AND
[8] Not or not Evaluates expression NOT [13-40/13-42] OR
Ignores 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3.
[13-44].
[13-44].
[13-44].
[13-44].
[13-44].
NOT [13-44].
NOT [13-44].
13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select first logical operator to use on boolean
inputs from 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1 and
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2.
[0] * Disabled
[1] And Evaluates expression [13-40] AND [13-42].
[2] Or Evaluates expression [13-40] OR [13-42].
[3] And not Evaluates expression [13-40] AND NOT [13-42].
[4] Or not Evaluates expression [13-40] OR NOT [13-42].
[5] Not and Evaluates expression NOT [13-40] and [13-42].
[6] Not or Evaluates expression NOT [13-40] OR [13-42].
[7] Not and not Evaluates expression NOT [13-40] AND NOT
[8] Not or not Evaluates expression NOT [13-40] OR NOT
Ignores 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2, 13-43 Logic
Rule Operator 2 and 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean
3.
[13-42].
[13-42].
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select second boolean input for selected logic rule.
See 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1 for choices and
descriptions.
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select second logical operator to use on
boolean inputs calculated in 13-40 Logic Rule
Boolean 1, 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1, and
13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3
Array [4]
Option: Function:
Select third boolean input for selected logic rule.
See 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1 for choices and
descriptions.
4.10.5 13-5* States
13-51 SL Controller Event
Array [20]
Option: Function:
Select boolean input to define Smart Controller Event.
See 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1 for choices and
descriptions.
13-52 SL Controller Action
Array [20]
Option: Function:
Select action corresponding to SLC event.
Actions are executed when corresponding
event (13-51 SL Controller Event) is
evaluated as True.
[0] * Disabled Function is disabled.
[1] No Action No action is taken.
[2] Select Set-up1 Changes active set-up to Set-up 1.
[3] Select Set-up2 Changes active set-up to Set-up 2.
[10] SelectPresetRef0 Selects preset reference 0
[11] SelectPresetRef1 Selects preset reference 1
[12] SelectPresetRef2 Selects preset reference 2
[13] SelectPresetRef3 Selects preset reference 3
[14] SelectPresetRef4 Selects preset reference 4
44 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 47

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
13-52 SL Controller Action
Array [20]
Option: Function:
[15] SelectPresetRef5 Selects preset reference 5
[16] SelectPresetRef6 Selects preset reference 6
[17] SelectPresetRef7 Selects preset reference 7
[18] SelectRamp1 Selects ramp 1
[19] SelectRamp2 Selects ramp 2
[22] Run Issues start command to frequency
converter.
[23] RunReverse Issues start reverse command to
frequency converter.
[24] Stop Issues stop command to frequency
converter.
[25] Qstop Issues quick stop command to frequency
converter.
[26] DCstop Issues DC stop command to frequency
converter.
[27] Coast frequency converter coasts immediately.
All stop commands including coast
command stop the SLC.
[28] Freeze Output Freezes output frequency.
[29] StartTimer0 Starts timer 0.
[30] StartTimer1 Starts timer 1
[31] StartTimer2 Starts timer 2
[32] SetDO42Low Set Digital output 42 low.
[33] SetRelayLow Set Relay low.
[38] SetDO42High Set Digital output 42 high.
[39] SetRelayHigh Set Relay high.
[60] ResetCounterA Resets counter A to 0.
[61] ResetCounterB Resets counter B to 0.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 45
Page 48

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.11 Parameter Group 14: Special Functions
Parameter group for configuring special frequency
converter functions.
4.11.1 14-0* Inverter Switching
14-01 Switching Frequency
44
Option: Function:
Select the switching frequency in order to
minimize e.g. acoustic noise and power loss or
maximizing efficiency.
[0] 2 KHz
[1] * 4 KHz
[2] 8 KHz
[4] 16 KHz
NOTICE
For 18.5 kW and 22 kW frequency converter, the option
[4] is not available.
14-03 Overmodulation
Option: Function:
This feature allows more accurate speed control near
and over nominal speed (50/60 Hz). Another
advantage with overmodulation is the ability of
staying at a constant speed even though main is
dropping.
[0] Off Disables the overmodulation function to avoid torque
ripple on the motor shaft.
[1] * On Connects the overmodulation function to obtain an
output voltage up to 15% greater than mains voltage.
14-20 Reset Mode
Option: Function:
Select reset function after tripping. Once
reset, the frequency converter can be
restarted.
[0] * Manual Reset Perform reset via [Reset] or digital inputs.
[1] AutoReset 1 Performs one automatic reset after tripping.
[2] AutoReset 2 Performs two automatic resets after tripping.
[3] AutoReset 3 Performs three automatic resets after
tripping.
[4] AutoReset 4 Performs four automatic resets after tripping.
[5] AutoReset 5 Performs five automatic resets after tripping.
[6] AutoReset 6 Performs six automatic resets after tripping.
[7] AutoReset 7 Performs seven automatic resets after
tripping.
[8] AutoReset 8 Performs eight automatic resets after
tripping.
[9] AutoReset 9 Performs nine automatic resets after
tripping.
[10] AutoReset 10 Performs ten automatic resets after tripping.
[11] AutoReset 15 Performs fifteen automatic resets after
tripping.
[12] AutoReset 20 Performs twenty automatic resets after
tripping.
[13] Infinite auto
reset
[14] Reset at
power-up
Performs an infinite number of automatic
resets after tripping.
Trip-lock alarm can be reset at power up.
WARNING
UNINTENDED START
When the frequency converter is
connected to AC mains, DC supply, or
load sharing, the motor may start at
any time. Unintended start during
4.11.2 14-1* Mains Monitoring
programming, service, or repair work
can result in death, serious injury, or
This parameter group supplies functions for handling
imbalance on mains.
14-12 Functions at Mains Imbalance
Option: Function:
Operation under severe mains imbalance
conditions reduces drive lift time.
Select function to take place when severe mains
imbalance is detected.
[0] * Trip Frequency converter trips.
[1] Warning Frequency converter issues a warning.
[2] Disabled No action taken.
Parameters for configuring auto reset handling, special trip
handling and control card self-test or initialisation.
property damage. The motor can start
via an external switch, a serial bus
command, an input reference signal
from the LCP, or after a cleared fault
condition.
To prevent unintended motor start:
Disconnect the frequency
•
converter from the mains.
Press [Off/Reset] on the LCP
•
before programming
parameters.
Fully wire and assembly the
•
frequency converter, motor,
and any driven equipment
before connecting the
frequency converter to AC
mains, DC supply, or load
sharing.
46 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 49

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
14-21 Automatic Restart Time
Range: Function:
10 s* [0-600 s] Enter time interval from trip to start of
automatic reset function. This parameter is
active when 14-20 Reset Mode, is set to [1] to
[13] Automatic Reset.
14-22 Operation Mode
Option: Function:
Use this parameter for specifying normal
operation or to initialize all parameters,
except 15-03 Power Ups, 15-04 Over Temps
and 15-05 Over Volts.
[0] * Normal
Operation
[2] Initialization Resets all parameters to default settings,
Frequency converter runs normal operation.
except for 15-03 Power Ups, 15-04 Over Temps
and 15-05 Over Volts. Frequency converter
resets during next power-up.
14-22 Operation Mode also reverts to default
setting [0] Normal Operation.
14-26 Action at Inverter Fault
Option: Function:
[0] Trip When the frequency converter detects an over-
voltage, it will trip immediately.
NOTICE
It is recommended to choose [0] Trip in
hoisting applications.
[1] * Warning When the frequency converter detects an over-
voltage, it will give warning immediately. After
protection filter, it will trip.
NOTICE
It is recommended to disable protection
mode in hoisting applications.
4.11.4 14-9* Fault Settings
14-90 Fault Level
Use this parameter to customise fault levels. Only index 7, which
indicates overcurrent faults, is supported.
Option: Function:
[3] * Trip lock Alarm is set to trip lock level. Analog 13
overcurrent alarm cannot be reset without
power cycle.
[4] Trip w.
delayed reset
[5] Flystart The frequency converter tries to catch a
Alarm is configured into trip alarm, which
can be reset after a delay time. For
example, if overcurrent alarm is configured
to this option, it can be reset 3 minutes
after the alarm is reported. Analog 13
overcurrent alarm is changed back to trip
lock if it has been reset for more than 20
times.
motor spinning when starting. If this option
is selected, 1-73 Flying Start s set to [1]
Enabled.
4 4
4.11.3 14-4* Energy Optimising
Parameters for adjusting the energy optimisation level in
both Variable Torque (VT) and AEOAutomatic Energy
Saving mode.
14-41 AEO Minimum Magnetisation
Range: Function:
66 %* [40 - 75%]Enter the minimum allowable magnetisation
for AEO. Selection of a low value reduces
energy loss in the motor, but can also
reduce resistance to sudden load changes.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 47
Page 50

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
4.12 Parameter Group 15: Drive Information
Parameter group containing information on operating
data, hardware configuration, software version, etc.
15-00 Operating Time
Range: Function:
0 days* [0-9999
days]
44
View how many days the frequency
converter has been powered up.
The value is saved at power off and
cannot be reset.
4.12.1 15-3* Fault Log
This parameter group contains a fault log showing reasons
for the ten latest trips.
15-30 Fault Log: Error Code
Range: Function:
0 [0-255]
View error code and look it up in VLT® Micro Drive
FC 51 Quick Guide.
4.12.2 15-4* Drive Identification
15-01 Running Hours
Range: Function:
0* [0- 60000] View running hours of motor.
The value is saved at power off and can be reset
in 15-07 Reset Running Hours Counter.
15-02 kWh Counter
Range: Function:
0 [0-65535] View power consumption in kWh as a mean value
over one hour.
Reset counter in 15-06 Reset kWh Counter.
15-03 Power Ups
Range: Function:
0 [0-2147483647] View number of times frequency converter
has been powered up.
Counter cannot be reset.
15-04 Over Temps
Range: Function:
0 [0-65535] View number of times frequency converter has
tripped due to over temperature.
Counter cannot be reset.
15-05 Over Volts
Range: Function:
0* [0-65535] View number of times frequency converter has
tripped due to over voltage.
Counter cannot be reset.
15-06 Reset kWh Counter
Option: Function:
[0] * Do Not Reset Counter is not reset.
[1] Reset Counter Counter is reset.
Parameters containing read only information about the
hardware and software configuration of the frequency
converter.
15-40 FC Type
Option: Function:
View FC type.
15-41 Power Section
Option: Function:
View power section of frequency converter.
15-42 Voltage
Option: Function:
View voltage of frequency converter.
15-43 Software Version
Option: Function:
View software version of frequency converter.
15-46 Frequency Converter Ordering No
Option: Function:
View ordering number for re-ordering frequency
converter in its original configuration.
15-48 LCP ID No
Option: Function:
View LCP ID number.
15-51 Frequency Converter Serial Number
Option: Function:
View frequency converter serial number.
15-07 Reset Running Hours Counter
Option: Function:
[0] * Do Not Reset Counter is not reset.
[1] Reset Counter Counter is reset.
48 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 51

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.13 Parameter Group 16: Data Readouts
16-00 Control Word
Range: Function:
0* [0-65535] View latest valid control word sent to frequency
converter via serial communication port.
16-01 Reference [Unit]
Range: Function:
0.000* [-4999.000-4999.000] View total remote reference. Total
reference is sum of pulse, analog,
preset, LCP potentiometer, local
bus and freeze reference.
16-02 Reference %
Range: Function:
0.0* [-200.0-200.0%] View total remote reference in percent.
Total reference is sum of pulse, analog,
preset, LCP potentiometer, local bus and
freeze reference.
16-03 Status Word
Range: Function:
0* [0-65535] View status word sent to frequency converter via
serial communication port.
16-13 Frequency
Range: Function:
0.0 Hz* [0.0-6553.5 Hz] View output frequency in Hz.
16-14 Motor Current
Range: Function:
0.00 A* [0.00-655 A] View motor phase current.
16-15 Frequency [%]
Range: Function:
0.00* [0-6553.5%] View a two-byte word reporting actual
motor frequency as a percentage of 4-14
Motor Speed High Limit
16-18 Motor Thermal
Range: Function:
0%* [0-100%] View calculated thermal motor load as
percentage of estimated thermal motor load.
4.13.2 16-3* Drive Status
16-30 DC Link Voltage
Range: Function:
0 V* [0-65535 V] View DC-link voltage.
4 4
16-05 Main Actual Value %
Range: Function:
0.00* [-100.00-100.00%] View two-byte word sent with status
word to bus Master reporting main
actual value.
16-09 Custom Readout
Range: Function:
0.00* [0.00-9999.00%]
Customized readout based on the
settings of 0-31 Custom Readout Min
Scale, 0-32 Custom Readout Max Scale
and 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit
4.13.1 16-1* Motor Status
16-10 Power [kW]
Range: Function:
0 kW* [0-65.535 kW] View output power in kW.
16-11 Power [hp]
Range: Function:
0 hp [0-65.535 hp ] View output power in hp.
16-34 Heat Sink Temp.
Range: Function:
0*
[0-255°C]
View heat sink temperature of frequency
converter.
16-35 Inverter Thermal
Range: Function:
0%* [0-255%] View calculated thermal load on frequency
converter in relation to estimated thermal load
on frequency converter.
16-36 Inv. Nom. Current
Range: Function:
0.00 A* [0.00-655A] View continuous nominal inverter current.
16-37 Inv. Max. Current
Range: Function:
0.00 A* [0.00-655A] View intermittent maximum inverter
current (150%).
16-38 SL Controller State
Range: Function:
0* [0-255] View number of active SLC state.
16-12 Motor Voltage
4.13.3 16-5* Ref. & Feedb.
Range: Function:
0.0* [0.0-65535 V] View motor phase voltage.
16-50 External Reference
Range: Function:
0.0%* [-200.0-200.0%] View sum of all external references in
percent.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 49
Page 52

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
16-51 Pulse Reference
4.13.5 16-8* FC Port
Range: Function:
0.0 %* [-200.0-200.0%] View actual pulse input converted to a
reference in percent.
16-52 Feedback
Range: Function:
0.000* [-4999.000-4999.000] View analog or pulse feedback in
44
Hz.
Parameter for viewing references from FC Port.
16-86 FC Port REF 1
Range: Function:
0* [0x8000-0x7FFF] View currently received reference from FC
Port.
4.13.6 16-9* Diagnosis Read-Outs
4.13.4 16-6* Inputs and Outputs
16-90 Alarm Word
16-60 Digital Input 18, 19, 27, 33
Range: Function:
0* [0-1111] View signal states from active digital inputs.
16-61 Digital Input 29
Range: Function:
0* [0-1] View signal state on digital input 29.
16-62 Analog Input 53 (volt)
Range: Function:
0.00* [0.00-10.00 V] View input voltage on analog input
terminal.
16-63 Analog Input 53 (current)
Range: Function:
0.00* [0.00-20.00 mA] View input current on analog input
terminal.
16-64 Analog Input 60
Range: Function:
0.00* [0.00-20.00 mA] View actual value at input 60 either as
reference or protection value.
Range: Function:
0* [0-0xFFFFFFFF] Via alarm word sent via serial communi-
cation port in hex code.
16-91 Alarm Word 2
Range: Function:
0* [0-0xFFFFFFFFUL] View the alarm word 2 sent via the serial
communication port in hex code.
16-92 Warning Word
Range: Function:
0* [0-0xFFFFFFFF] View warning word sent via serial communi-
cation port in hex code.
16-94 Ext. Status Word
Range: Function:
0* [0-0xFFFFFFFF] View extended warning word sent via serial
communication port in hex code.
16-65 Analog Output 42 [mA]
Range: Function:
0.00 mA* [0.00-20.00 mA] View output current on analog
output 42.
16-68 Pulse Input
Range: Function:
20 Hz* [20-5000 Hz] View input frequency on pulse input
terminal.
16-71 Relay Output [bin]
Range: Function:
0* [0-1] View relay setting.
16-72 Counter A
Range: Function:
0* [-32768-32767] View present value of Counter A.
16-73 Counter B
Range: Function:
0* [-32768-32767] View present value of Counter B.
50 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 53

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.14 Parameter Group 18: Extended Motor
Data
4.14.1 18-8* Motor Resistors
18-80 Stator Resistance (Rs in high resolution)
Range: Function:
0.000 Ohm [0.000–999.900
Ohm]
18-81 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1 in high resolution)
Range: Function:
0.000
Ohm
[0.000–
999.900 Ohm]
Set the stator resistance value.
Enter the value from a motor data
sheet or perform an AMT on a cold
motor.
Set the stator leakage reactance
value. Enter the value from a motor
data sheet or perform an AMT on a
cold motor. The default setting is
calculated by the frequency converter
from the motor nameplate data.
4 4
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 51
Page 54

Parameter Lists
5 Parameter Lists
5.1 Parameter Overview
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
0-** Operation/Display
0-0* Basic Settings
0-03 Regional Settings
*[0] International
[1] US
0-04 Oper. State at Power-up
55
(Hand)
[0] Resume
*[1] Forced stop, ref=old
[2] Forced stop, ref=0
0-1* Set-up Handling
0-10 Active Set-up
*[1] Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[9] Multi Set-up
0-11 Edit Set-up
*[1] Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[9] Active Set-up
0-12 Link Set-ups
[0] Not Linked
*[20] Linked
0-31 Custom Readout Min Scale
0.00–9999.00 * 0.00
0-32 Custom Readout Max Scale
0.00–9999.00 * 100.0
0-4* LCP Keypad
0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP
[0] Disabled
*[1] Enabled
0-41 [Off / Reset] Key on LCP
[0] Disable All
*[1] Enable All
[2] Enable Reset Only
0-42 [Auto on] Key on LCP
[0] Disabled
*[1] Enabled
0-5* Copy/Save
0-50 LCP Copy
*[0] No copy
[1] All to LCP
[2] All from LCP
[3] Size indep. from LCP
0-51 Set-up Copy
*[0] No copy
[1] Copy from set-up 1
[2] Copy from set-up 2
[9] Copy from Factory set-up
0-6* Password
0-60 (Main) Menu Password
0–999 *0
1) M4 and M5 only
52 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
0-61 Access to Main/Quick Menu
w/o Password
*[0] Full access
[1] LCP:Read Only
[2] LCP:No Access
1-** Load/Motor
1-0* General Settings
1-00 Configuration Mode
*[0] Speed open loop
[3] Process
1-01 Motor Control Principle
[0] U/f
*[1] VVC+
1-03 Torque Characteristics
*[0] Constant torque
[2] Automatic Energy Optim.
1-05 Local Mode Configuration
[0] Speed Open Loop
*[2] As config in par. 1-00
1-2* Motor Data
1-20 Motor Power [kW] [hp]
[1] 0.09 kW/0.12 hp
[2] 0.12 kW/0.16 hp
[3] 0.18 kW/0.25 hp
[4] 0.25 kW/0.33 hp
[5] 0.37 kW/0.50 hp
[6] 0.55 kW/0.75 hp
[7] 0.75 kW/1.00 hp
[8] 1.10 kW/1.50 hp
[9] 1.50 kW/2.00 hp
[10] 2.20 kW/3.00 hp
[11] 3.00 kW/4.00 hp
[12] 3.70 kW/5.00 hp
[13] 4.00 kW/5.40 hp
[14] 5.50 kW/7.50 hp
[15] 7.50 kW/10.00 hp
[16] 11.00 kW/15.00 hp
[17] 15.00 kW/20.00 hp
[18] 18.50 kW/25.00 hp
[19] 22.00 kW/29.50 hp
[20] 30.00 kW/40.00 hp
1-22 Motor Voltage
50-999 V *230–400 V
1-23 Motor Frequency
20–400 Hz *50 Hz
1-24 Motor Current
0.01–100.00 A *Motortype dep.
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
100–9999 rpm *Motortype dep.
1-29 Automatic Motor Tuning
(AMT)
*[0] Off
[2] Enable AMT
[3] Complete AMT with Rotating
motor
1-3* Adv. Motor Data
1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
[Ohm] * Dep. on motor data
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance
(X1)
[Ohm] * Dep. on motor data
1-35 Main Reactance (Xh)
[Ohm] * Dep. on motor data
1-5* Load Indep. Setting
1-50 Motor Magnetisation at 0
Speed
0–300% *100%
1-52 Min Speed Norm. Magnet.
[Hz]
0.0–10.0 Hz *0.0Hz
1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
0-999.9 V
1-56 U/f Characteristic - F
0-400 Hz
1-6* Load Depen. Setting
1-60 Low Speed Load Compensation
0–199% *100%
1-61 High Speed Load Compensation
0–199% *100%
1-62 Slip Compensation
-400–399% *100%
1-63 Slip Compensation Time
Constant
0.05–5.00 s *0.10 s
1-7* Start Adjustments
1-71 Start Delay
0.0–10.0 s *0.0 s
1-72 Start Function
[0] DC hold/delay time
[1] DC brake/delay time
*[2] Coast/delay time
1-73 Flying Start
*[0] Disabled
[1] Enabled
1-8* Stop Adjustments
1-80 Function at Stop
*[0] Coast
[1] DC hold
1-82 Min Speed for Funct. at
Stop [Hz]
0.0–20.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
1-9*Motor Temperature
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
*[0] No protection
[1] Thermistor warning
[2] Thermistor trip
[3] Etr warning
[4] Etr trip
1-93 Thermistor Resource
*[0] None
[1] Analog input 53
[6] Digital input 29
2-** Brakes
2-0* DC-Brake
2-00 DC Hold Current
0–150% *50%
2-01 DC Brake Current
0–150% *50%
2-02 DC Braking Time
0.0–60.0 s *10.0 s
2-04 DC Brake Cut In Speed
0.0–400.0 Hz *0.0Hz
2-1* Brake Energy Funct.
2-10 Brake Function
*[0] Off
[1] Resistor brake
[2] AC brake
2-11 Brake Resistor (ohm)
Min/Max/default: Powersize dep.
2-14 Brake Voltage reduce
0 - Powersize dep.* 0
2-16 AC Brake, Max current
0-150% *100%
2-17 Overvoltage Control
*[0] Disabled
[1] Enabled (not at stop)
[2] Enabled
2-2* Mechanical Brake
2-20 Release Brake Current
0.00–100.0 A *0.00 A
2-22 Activate Brake Speed [Hz]
0.0–400.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
3-** Reference / Ramps
3-0* Reference Limits
3-00 Reference Range
*[0] Min - Max
[1] -Max - +Max
3-02 Minimum Reference
-4999–4999 *0.000
3-03 Maximum Reference
-4999–4999 *50.00
Page 55

Parameter Lists Programming Guide
3-1* References
3-10 Preset Reference
-100.0–100.0% *0.00% 3-11 Jog
Speed [Hz]
0.0–400.0 Hz *5.0 Hz
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value
0.00–100.0% * 0.00%
3-14 Preset Relative Reference
-100.0–100.0% *0.00%
3-15 Reference Resource 1
[0] No function
*[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog input 60
[8] Pulse input 33
[11] Local bus ref
[21] LCP Potentiometer
3-16 Reference Resource 2
[0] No function
[1] Analog in 53
*[2] Analog in 60
[8] Pulse input 33
*[11] Local bus reference
[21] LCP Potentiometer
3-17 Reference Resource 3
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog input 60
[8] Pulse input 33
*[11] Local bus ref
[21] LCP Potentiometer
3-18 Relative Scaling Ref.
Resource
*[0] No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog input 60
[8] Pulse input 33
[11] Local bus ref
[21] LCP Potentiometer
3-4* Ramp 1
3-40 Ramp 1 Type
*[0] Linear
[2] Sine2 ramp
3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp up Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00 s (10.00 s1))
3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00s (10.00s1))
3-5* Ramp 2
3-50 Ramp 2 Type
*[0] Linear
[2] Sine2 ramp
3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp up Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00 s (10.00 s1))
3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp down Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00 s (10.00 s1))
3-8* Other Ramps
3-80 Jog Ramp Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00 s (10.00s1))
1) M4 and M5 only
3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time
0.05–3600 s *3.00 s (10.00s1))
4-** Limits/Warnings
4-1* Motor Limits 4-10 Motor
Speed Direction
*[0] Clockwise If Par. 1-00 is set
to close loop control
[1] CounterClockwise
*[2] Both if Par. 1-00 is set to
open loop control
4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit
[Hz]
0.0–400.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
4-14 Motor Speed High Limit
[Hz]
0.1–400.0 Hz *65.0 Hz
4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode
0–400% *150%
4-17 Torque Limit Generator
Mode
0–400% *100%
4-4* Adj. Warnings 2
4-40 Warning Frequency Low
0.00–Value of 4-41 Hz *0.0 Hz
4-41 Warning Frequency High
Value of 4-40–400.0 Hz *400.00
Hz
4-5* Adj. Warnings
4-50 Warning Current Low
0.00–100.00 A *0.00 A
4-51 Warning Current High
0.0–100.00 A *100.00 A
4-54 Warning Reference Low
-4999.000–Value of 4-55
* -4999.000
4-55 Warning Reference High
Value of 4-54–4999.000
*4999.000
4-56 Warning Feedback Low
-4999.000–Value of 4-57
* -4999.000
4-57 Warning Feedback High
Value of 4-56–4999.000 *4999.000
4-58 Missing Motor Phase
Function
[0] Off
*[1] On
4-6* Speed Bypass
4-61 Bypass Speed From [Hz]
0.0–400.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
4-63 Bypass Speed To [Hz]
0.0–400.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
5-1* Digital Inputs5-10 Terminal
18 Digital Input
[0] No function
[1] Reset
[2] Coast inverse
[3] Coast and reset inv.
[4] Quick stop inverse
[5] DC-brake inv.
[6] Stop inv
*[8] Start
[9] Latched start
[10] Reversing
[11] Start reversing
[12] Enable start forward
[13] Enable start reverse
[14] Jog
[16-18] Preset ref bit 0-2
[19] Freeze reference5-10
Terminal 18 Digital Input
[20] Freeze output
[21] Speed up
[22] Speed down
[23] Set-up select bit 0
[28] Catch up
[29] Slow down
[34] Ramp bit 0
[60] Counter A (up)
[61] Counter A (down)
[62] Reset counter A
[63] Counter B (up)
[64] Counter B (down)
[65] Reset counter B
5-11 Terminal 19 Digital Input
See par. 5-10. * [10] Reversing
5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input
See par. 5-10. * [1] Reset
5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input
See par. 5-10. * [14] Jog
5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input
See par. 5-10. * [16] Preset ref bit
0
[26] Precise Stop Inverse
[27] Start, Precise Stop
[32] Pulse Input
5-3* Digital Outputs
5-34 On Delay, Terminal 42
Digital Output
0.00–600.00 s * 0.01 s
5-35 Off Delay, Terminal 42
Digital Output
0.00–600.00 s * 0.01 s
5-4* Relays
5-40 Function Relay
[52] Remote ref. active
[53] No alarm
[54] Start cmd active
[55] Running reverse
[56] Drive in hand mode
[57] Drive in auto mode
[60-63] Comparator 0-3
[70-73] Logic rule 0-3
[81] SL digital output B
5-41 On Delay, Relay
0.00–600.00 s *0.01 s
5-42 Off Delay, Relay
0.00–600.00 s *0.01 s
5-5* Pulse Input
5-55 Terminal 33 Low
Frequency
20–4999 Hz *20 Hz
5-56 Terminal 33 High
Frequency
21–5000 Hz *5000 Hz
5-57 Term. 33 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value
-4999–4999 *0.000
5-58 Term. 33 High Ref./Feedb.
Value
-4999–4999 *50.000
6-** Analog In/Out
6-0* Analog I/O Mode
6-00 Live Zero Timeout Time
1-99 s *10 s
6-01 Live Zero TimeoutFunction
*[0] Off
[1] Freeze output
[2] Stop
[3] Jogging
[4] Max speed
[5] Stop and trip
6-1* Analog Input 1
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage
0.00–9.99 V *0.07 V
6-11 Terminal 53 High Voltage
0.01–10.00 V *10.00 V
6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current
0.00–19.99 mA *0.14 mA
6-13 Terminal 53 High Current
0.01–20.00 mA *20.00 mA
6-14 Term. 53 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value
-4999-4999 *0.000
6-15 Term. 53 High Ref./Feedb.
Value
-4999-4999 *50.000
6-16 Terminal 53 Filter Time
Constant
0.01–10.00 s *0.01 s
5 5
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 53
Page 56

Parameter Lists
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
6-19 Terminal 53 mode
*[0] Voltage mode
[1] Current mode 4
6-2* Analog Input 2
6-22 Terminal 60 Low Current
0.00–19.99 mA *0.14 mA
6-23 Terminal 60 High Current
0.01–20.00 mA *20.00 mA
6-24 Term. 60 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value
-4999-4999 *0.000
6-25 Term. 60 High Ref./Feedb.
55
Value
-4999–4999 *50.00
6-26 Terminal 60 Filter Time
Constant
0.01–10.00 s *0.01 s
6-8* LCP Potentiometer
6-80 LCP Potmeter Enable
[0] Disabled
*[1] Enable
6-81 LCP potm. Low Reference
-4999–4999 *0.000
6-82 LCP potm. High Reference
-4999–4999 *50.00
6-9* Analog Output xx
6-90 Terminal 42 Mode
*[0] 0-20 mA
[1] 4-20 mA
[2] Digital Output
6-91 Terminal 42 Analog Output
*[0] No operation
[10] Output Frequency
[11] Reference
[12] Feedback
[13] Motor Current
[16] Power
[19] DC Link Voltage
[20] Bus Reference
6-92 Terminal 42 Digital Output
See parameter 5-40
*[0] No Operation
[80] SL Digital Output A
6-93 Terminal 42 Output Min
Scale
0.00-200.0% *0.00%
6-94 Terminal 42 Output Max
Scale
0.00-200.0% *100.0%
7-** Controllers
7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedb
7-20 Process CL Feedback 1
Resource
*[0] NoFunction
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog input 60
[8] PulseInput33
[11] LocalBusRef
7-3* Process PI
Ctrl. 7-30 Process PI Normal/
Inverse Ctrl
*[0] Normal
[1] Inverse
7-31 Process PI Anti Windup
[0] Disable
*[1] Enable
7-32 Process PI Start Speed
0.0–200.0 Hz *0.0 Hz
7-33 Process PI Proportional
Gain
0.00–10.00 *0.01
7-34 Process PI Integral Time
0.10–9999 s *9999 s
7-38 Process PI Feed Forward
Factor
0–400% *0%
7-39 On Reference Bandwidth
0–200% *5%
8-** Comm. and Options
8-0* General Settings
8-01 Control Site
*[0] Digital and ControlWord
[1] Digital only
[2] ControlWord only
8-02 Control Word Source
[0] None
*[1] FC RS485
8-03 Control Word Timeout
Time
0.1–6500 s *1.0 s
8-04 Control Word Timeout
Function
*[0] Off
[1] Freeze Output
[2] Stop
[3] Jogging
[4] Max. Speed
[5] Stop and trip
8-06 Reset Control Word
Timeout
*[0] No Function
[1] Do reset
8-3* FC Port Settings
8-30 Protocol
*[0] FC
[2] Modbus
8-31 Address
1-247 *1
8-32 FC Port Baud Rate
[0] 2400 Baud
[1] 4800 Baud
*[2] 9600 Baud For choose FC
Bus in 8-30
*[3] 19200 Baud For choose
Modbus in 8-30
[4] 38400 Baud
8-33 FC Port Parity
*[0] Even Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[1] Odd Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[2] No Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[3] No Parity, 2 Stop Bits
8-35 Minimum Response Delay
0.001–0.5 *0.010 s
8-36 Max Response Delay
0.100–10.00 s *5.000 s
8-4* FC MC protocol set
8-43 FC Port PCD Read Configuration
*[0] None Expressionlimit
[1] [1500] Operation Hours
[2] [1501] Running Hours
[3] [1502] kWh Counter
[4] [1600] Control Word
[5] [1601] Reference [Unit]
[6] [1602] Reference %
[7] [1603] Status Word
[8] [1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[9] [1609] Custom Readout
[10] [1610] Power [kW]
[11] [1611] Power [hp]
[12] [1612] Motor Voltage
[13] [1613] Frequency
[14] [1614] Motor Current
[15] [1615] Frequency [%]
[16] [1618] Motor Thermal
[17] [1630] DC Link Voltage
[18] [1634] Heatsink Temp.
[19] [1635] Inverter Thermal
[20] [1638] SL Controller State
[21] [1650] External Reference
[22] [1651] Pulse Reference
[23] [1652] Feedback [Unit]
[24] [1660] Digital Input
18,19,27,33
[25] [1661] Digtial Input 29
[26] [1662] Analog Input 53 (V)
[27] [1663] Analog Input 53 (mA)
[28] [1664] Analog Input 60
[29] [1665] Analog Output 42
[mA]
[30] [1668] Freq. Input 33 [Hz]
[31] [1671] Relay Output [bin]
[32] [1672] Counter A
[33] [1673] Counter B
[34] [1690] Alarm Word
[35] [1692] Warning Word
[36] [1694] Ext. Status Word
8-5* Digital/Bus
8-50 Coasting Select
[0] DigitalInput
[1] Bus
[2] LogicAnd
*[3] LogicOr
8-51 Quick Stop Select
See par. 8-50 * [3] LogicOr
8-52 DC Brake Select
See par. 8-50 *[3] LogicOr
8-53 Start Select
See par. 8-50 *[3] LogicOr
8-54 Reversing Select
See par. 8-50 *[3] LogicOr
8-55 Set-up Select
See par. 8-50 *[3] LogicOr
8-56 Preset Reference Select
See parameter 8-50 * [3] LogicOr
8-8* Bus communication
Diagnostics
8-80 Bus Message Count
0-0 N/A *0 N/A
8-81 Bus Error Count
0-0 N/A *0 N/A
8-82 Slave Messages Rcvd
0-0 N/A *0 N/A
8-83 Slave Error Count
0-0 N/A *0 N/A
8-9* Bus Jog / Feedback
8-94 Bus feedback 1
0x8000-0x7FFF *0
13-** Smart Logic
13-0* SLC Settings
13-00 SL Controller Mode
*[0] Off
[1] On
13-01 Start Event
[0] False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] InRange
[4] OnReference
[7] OutOfCurrentRange
[8] BelowILow
[9] AboveIHigh
[16] ThermalWarning
[17] MainOutOfRange
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm_Trip
[21] Alarm_TripLock
[22-25] Comparator 0-3
[26-29] LogicRule0-3
[33] DigitalInput_18
[34] DigitalInput_19
[35] DigitalInput_27
[36] DigitalInput_29
[38] DigitalInput_33
*[39] StartCommand
[40] DriveStopped
13-02 Stop Event
See parameter 13-01 * [40]
DriveStopped
13-03 Reset SLC
*[0] Do not reset
[1] Reset SLC
54 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 57

Parameter Lists
Programming Guide
13-1* Comparators
13-10 Comparator Operand
*[0] Disabled
[1] Reference
[2] Feedback
[3] MotorSpeed
[4] MotorCurrent
[6] MotorPower
[7] MotorVoltage
[8] DCLinkVoltage
[12] AnalogInput53
[13] AnalogInput60
[18] PulseInput33
[20] AlarmNumber
[30] CounterA
[31] CounterB
13-11 Comparator Operator
[0] Less Than
*[1] Approximately equals
[2] Greater Than
13-12 Comparator Value
-9999–9999 *0.0
13-2* Timers
13-20 SL Controller Timer
0.0–3600 s *0.0 s
13-4* Logic Rules
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1
See par. 13-01 *[0] False
[30] - [32] SL Time-out 0-2
13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1
*[0] Disabled
[1] And
[2] Or
[3] And not
[4] Or not
[5] Not and
[6] Not or
[7] Not and not
[8] Not or not
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2
See par. 13-40 * [0] False
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
See par. 13-41 *[0] Disabled
13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3
See par. 13-40 * [0] False
13-5* States
13-51 SL Controller Event
See par. 13-40 *[0] False
13-52 SL Controller Action
*[0] Disabled
[1] NoAction
[2] SelectSetup1
[3] SelectSetup2
[10-17] SelectPresetRef0-7
[18] SelectRamp1
[19] SelectRamp2
[22] Run
[23] RunReverse
[24] Stop
[25] Qstop
[26] DCstop
[27] Coast
[28] FreezeOutput
[29] StartTimer0
[30] StartTimer1
[31] StartTimer2
[32] Set Digital Output A Low
[33] Set Digital Output B Low
[38] Set Digital Output A High
[39] Set Digital Output B High
[60] ResetCounterA
[61] ResetCounterB
14-** Special Functions
14-0* Inverter Switching
14-01 Switching Frequency
[0] 2 kHz
*[1] 4 kHz
[2] 8 kHz
[4] 16 kHz not available for M5
14-03 Overmodulation
[0] Off
*[1] On
14-1* Mains monitoring
14-12 Function at mains
imbalance
*[0] Trip
[1] Warning
[2] Disabled
14-2* Trip Reset
14-20 Reset Mode
*[0] Manual reset
[1-9] AutoReset 1-9
[10] AutoReset 10
[11] AutoReset 15
[12] AutoReset 20
[13] Infinite auto reset
[14] Reset at power up
14-21 Automatic Restart Time
0–600s * 10s
14-22 Operation Mode
*[0] Normal Operation
[2] Initialisation 14-26 Action At
Inverter Fault
*[0] Trip
[1] Warning 14-4* Energy
Optimising
14-41 AEO Minimum Magnetisation
40–75 %*66 %
14-9* Fault Settings
14-90 Fault level[3] Trip Lock
[4] Trip with delayed reset
15-** Drive Information
15-0* Operating Data
15-00 Operating Days
15-01 Running Hours
15-02 kWh Counter
15-03 Power Ups
15-04 Over Temps
15-05 Over Volts
15-06 Reset kWh Counter
*[0] Do not reset
[1] Reset counter
15-07 Reset Running Hours
Counter
*[0] Do not reset
[1] Reset counter
15-3* Fault Log
15-30 Fault Log: Error Code
15-4* Drive Identification
15-40 FC Type
15-41 Power Section
15-42 Voltage
15-43 Software Version
15-46 Frequency Converter
Order. No
15-48 LCP Id No
15-51 Frequency Converter
Serial No
16-** Data Readouts 16-0*
General Status
16-00 Control Word
0-0XFFFF
16-01 Reference [Unit]
-4999–4999 *0.000
16-02 Reference %
-200.0–200.0% *0.0%
16-03 Status Word
0–0XFFFF
16-05 Main Actual Value [%]
-200.0–200.0% *0.0%
16-09 Custom Readout
Dep. on par. 0-31, 0-32
16-1* Motor Status
16-10 Power [kW]
16-11 Power [hp]
16-12 Motor Voltage [V]
16-13 Frequency [Hz]
16-14 Motor Current [A]
16-15 Frequency [%]
16-18 Motor Thermal [%]
16-3* Drive Status
16-30 DC Link Voltage
16-34 Heat sink Temp.
16-35 Inverter Thermal
16-36 Inv.Nom. Current
16-37 Inv. Max. Current
16-38 SL Controller State
16-5* Ref./Feedb.
16-50 External Reference
16-51 Pulse Reference
16-52 Feedback [Unit]
16-6* Inputs/Outputs
16-60 Digital Input 18,19,27,33
0-1111
16-61 Digital Input 29
0-1
16-62 Analog Input 53 (volt)
16-63 Analog Input 53 (current)
16-64 Analog Input 60
16-65 Analog Output 42 [mA]
16-68 Pulse Input [Hz]
16-71 Relay Output [bin]
16-72 Counter A
16-73 Counter B
16-8* Fieldbus/FC Port
16-86 FC Port REF 1
0x8000-0x7FFFF
16-9* Diagnosis Readouts
16-90 Alarm Word
0-0XFFFFFFFF
16-92 Warning Word
0-0XFFFFFFFF
16-94 Ext. Status Word
0-0XFFFFFFFF
18-** Extended Motor Data
18-8* Motor Resistors
18-80 Stator Resistance (High
resolution)
0.000–99.990 ohm *0.000 ohm
18-81 Stator Leakage
Reactance(High resolution)
0.000–99.990 ohm *0.000 ohm
5 5
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 55
Page 58

Parameter Lists
5.2 Parameter Lists
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
5.2.4
Type
5.2.1 Conversion Index
The various attributes of each parameter are displayed in
the section Factory Settings. Parameter values are
transferred as whole numbers only. Conversion factors are
therefore used to transfer decimals according to Table 5.1.
Example:
1-24 Motor Current has a conversion index of -2 (i.e.
conversion factor of 0.01 according to Table 5.1). To set the
55
parameter to 2.25 A, transfer the value 225 via Modbus.
The Conversion Factor of 0.01 means that the value
transferred is multiplied by 0.01 in the frequency converter.
The vale 225 transferred on the bus is thus perceived as
2.25 A in the frequency converter.
Conversion index Conversion factor
2 10
1 100
0 1
-1 0.1
-2 0.01
-3 0.001
-4 0.0001
-5 0.00001
Data type Description Type
2 Integer 8 Int8
3 Integer 16 Int16
4 Integer 32 Int32
5 Unsigned 8 Uint8
6 Unsigned 16 Uint16
7 Unsigned 32 Uint32
9 Visible string VisibleString
Table 5.2 Type
Table 5.1 Conversion Table
Change During Operation
5.2.2
TRUE means that the parameter can be changed while the
frequency converter is in operation and FALSE means that
the frequency converter must be stopped before a change
can be made.
2-Set-up
5.2.3
All set-up: The parameter can be set individually in each of
the two set-ups, i.e. one single parameter can have two
different data values.
1 set-up: Data value will be the same in both set-ups.
56 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 59

Parameter Lists Programming Guide
5.2.5 0-** Operation/Display
Parameter
number
0-03 Regional Settings [0] International 1 set-up FALSE - Uint8
0-04
0-10 Active Set-up [1] Set-up 1 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
0-11 Edit Set-up [1] Set-up 1 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
0-12 Link Setups [20] Linked All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
0-31
0-32
0-40 [Hand On] Key on LCP [1] Enabled All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
0-41 [Off / Reset] Key on LCP [1] Enable All All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
0-42 [Auto on] Key on LCP [1] Enabled All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
0-50 LCP Copy [0] No copy 1 set-up FALSE - Uint8
0-51 Set-up Copy [0] No copy 1 set-up FALSE - Uint8
0-60 Main Menu Password 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
0-61
Parameter description Default value 2 Setup
Operating State at Powerup (Hand) [1] Forced stop ref=old All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Custom Readout Min
Scale 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Int32
Custom Readout Max
Scale 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Int32
Access to Main/Quick
menu w/o Password 0 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
Change during
operation
Conversion
index
Type
5.2.6 1-** Load/Motor
5 5
Parameter
Number
1-00 Configuration Mode [0] Speed open loop All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
1-01 Motor Control Principle [1] VVC+ All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
1-03 Torque Characteristics [0] Constant torque All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
1-05 Hand Mode Configuration
1-20 Motor Power All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
1-22 Motor Voltage All set-ups FALSE 0 Uint16
1-23 Motor Frequency All set-ups FALSE 0 Uint16
1-24 Motor Current All set-ups FALSE -2 Uint16
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed All set-ups FALSE 0 Uint16
1-29
1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs) All set-ups FALSE -2 Uint16
1-33
1-35 Main Reactance (Xh) All set-ups FALSE -2 Uint32
1-50
1-52
1-55 U/f Characteristic-U All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
1-56 U/f Characteristic-F All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
1-60
1-61
1-62 Slip Compensation 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Int16
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
[2] As mode 1-00 Configu-
ration Mode
Automatic Motor Tuning
(AMT) [0] Off 1 set-up FALSE - Uint8
Stator Leakage Reactance
(X1) All set-ups FALSE -2 Uint32
Motor Magnetisation at
Zero Speed 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
Min Speed Normal
Magnetising [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
Low Speed Load Compensation 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
High Speed Load
Compensation 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 57
Page 60

Parameter Lists
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Parameter
Number
1-63
1-71 Start Delay 0 s All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint8
1-72 Start Function [2] Coast/delay time All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
1-73 Flying Start [0] Disabled All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
1-80 Function at Stop [0] Coast All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
1-82
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection [0] No protection All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
1-93 Thermistor Resource [0] None All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Slip Compensation Time
Constant 0.1 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
Min Speed for Function at
Stop [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
55
5.2.7 2-** Brakes
Parameter
Number
2-00 DC Hold Current 50% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
2-01 DC Brake Current 50% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
2-02 DC Braking Time 10 s All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
2-04 DC Brake Cut In Speed 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
2-10 Brake Function [0] Off All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
2-11 Brake Resistor (Ω) All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
2-14 Brake Voltage Reduce 0 All set-ups FALSE 0 Uint8
2-16 AC Brake, Max current 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
2-17 Over-voltage Control [0] Disabled All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
2-20 Release Brake Current 0 A All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
2-22 Activate Brake Speed [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
5.2.8 3-** Reference/Ramps
Parameter
Number
3-00 Reference Range [0] Min to Max All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
3-02 Minimum Reference 0 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
3-03 Maximum Reference 50 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
3-10 Preset Reference 0% All set-ups TRUE -2 Int16
3-11 Jog Speed [Hz] 5 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value 0% All set-ups TRUE -2 Int16
3-14 Preset Relative Reference 0% All set-ups TRUE -2 Int16
3-15 Reference Resource 1 [1] Analog in 53 All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
3-16 Reference Resource 2 [2] Analog in 60 All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
3-17 Reference Resource 3
3-18
3-40 Ramp 1 Type [0] Linear All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp up Time 3 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time 3 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
3-50 Ramp 2 Type [0] Linear All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp up Time 3 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp down Time 3 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
[11] Local bus
reference All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Relative Scaling Reference
Resource [0] No function All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Change
During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
58 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 61

Parameter Lists Programming Guide
Parameter
Number
3-80 Jog Ramp Time 3 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time 3 s 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint32
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change
During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5.2.9 4-** Limits/Warnings
Parameter
Number
4-10 Motor Speed Direction [2] Both directions All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups FALSE -1 Uint16
4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz] 65 Hz All set-ups FALSE -1 Uint16
4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode 150% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
4-17 Torque Limit Generator Mode 100% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
4-40 Warning Frequency Low 0Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
4-41 Warning Frequency High 400Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
4-50 Warning Current Low 0 A All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
4-51 Warning Current High 26 A All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
4-54 Warning Reference Low -4999 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
4-55 Warning Reference High 4999 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
4-56 Warning Feedback Low -4999 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
4-57 Warning Feedback High 4999 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
4-58 Missing Motor Phase Function [1] On All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
4-61 Bypass Speed From [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
4-63 Bypass Speed To [Hz] 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change
During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5 5
5.2.10 5-** Digital In/Out
Parameter
Number
5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input [8] Start All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-11 Terminal 19 Digital Input [10] Reversing All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input [1] Reset All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input [14] Jog All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input [16] Preset ref bit 0 All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-34 On Delay, Terminal 42 Digital Output 0.01s All set-ups TRUE -2- Uint16
5-35 Off Delay, Terminal 42 Digital Output 0.01s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
5-40 Function Relay [0] No operation All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
5-41 On Delay, Relay 0.01s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
5-42 Off Delay, Relay 0.01s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
5-55 Terminal 33 Low Frequency 20 Hz All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
5-56 Terminal 33 High Frequency 5000 Hz All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
5-57 Terminal 33 Low Ref./Feedb. Value 0 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
5-58 Terminal 33 High Ref./Feedb. Value 50 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change
During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 59
Page 62

Parameter Lists
5.2.11 6-** Analog In/Out
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Parameter
Number
6-00 Live Zero Timeout Time 10 s All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint8
6-01 Live Zero TimeoutFunction [0] Off All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage 0.07 V All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-11 Terminal 53 High Voltage 10 V All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current 0.14 mA All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-13 Terminal 53 High Current 20 mA All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
55
6-14
6-15
6-16 Terminal 53 Filter Time Constant 0.01 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-19 Terminal 53 mode [0] Voltage mode 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
6-22 Terminal 60 Low Current 0.14 mA All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-23 Terminal 60 High Current 20 mA All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-24
6-25
6-26 Terminal 60 Filter Time Constant 0.01 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-80 LCP Potmeter Enable 1 1 set-up FALSE - Uint8
6-81 LCP potentiometer Low Ref. 0 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
6-82 LCP potentiometer High Ref. 50 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
6-90 Terminal 42 Mode [0] 0-20 mA All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
6-91 Terminal 42 Analog Output [0] No operation All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
6-92 Terminal 42 Digital Output [0] No operation All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
6-93 Terminal 42 Output Min Scale 0% All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
6-94 Terminal 42 Output Max Scale 100% All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value 0 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb.
Value 50 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
Terminal 60 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value 0 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
Terminal 60 High Ref./Feedb.
Value 50 All set-ups TRUE -3 Int32
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5.2.12 7-** Controllers
Parameter
Number
7-20 Process CL Feedback 1 Resource [0] No function All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
7-30
7-31 Process PI Anti Windup [1] Enabled All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
7-32 Process PI Start Speed 0 Hz All set-ups TRUE -1 Uint16
7-33 Process PI Proportional Gain 0.01 All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint16
7-34 Process PI Integral Time 9999 s All set-ups TRUE -2 Uint32
7-38 Process PI Feed Forward Factor 0% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
7-39 On Reference Bandwidth 5% All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint8
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Process PI Normal/ Inverse
Control [0] Normal All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Change
During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
60 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 63

Parameter Lists Programming Guide
5.2.13 8-** Comm. and Options
Parameter
Number
8-01 Control Site [0] Digital and ctrl.word All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-02 Control Word Source [1] FC RS485 All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-03 Control Word Timeout Time 1 s 1 set-up TRUE -1 Uint16
8-04 Control Word Timeout Function [0] Off 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-06 Reset Control Word Timeout [0] No function 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-30 Protocol [0] FC 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
8-31 Address 1 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
8-32 FC Port Baud Rate [2] 9600 Baud 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-33 FC Port Parity [0] Even Parity 1 Stop Bit 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-35 Minimum Response Delay 0.01 s 1 set-up TRUE -3 Uint16
8-36 Max Response Delay 5 s 1 set-up TRUE -3 Uint16
8-43 FC Port PCD Read Configuration 0 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
8-50 Coasting Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-51 Quick Stop Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-52 DC Brake Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-53 Start Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-54 Reversing Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-55 Set-up Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-56 Preset Reference Select [3] Logic OR All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
8-94 Bus feedback 1 0 All set-ups TRUE 0 Int16
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5 5
5.2.14 13-** Smart Logic
Parameter
Number
13-00 SL Controller Mode [0] Off 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-01 Start Event [39] Start command 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-02 Stop Event [40] Drive stopped 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-03 Reset SLC [0] Do not reset 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-10 Comparator Operand [0] Disabled 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-11 Comparator Operator [1] ApproxEqual 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-12 Comparator Value 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Int32
13-20 SL Controller Timer 0 s 1 set-up TRUE -1 Uint32
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1 [0] False 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1 [0] Disabled 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 [0] False 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2 [0] Disabled 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3 [0] False 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-51 SL Controller Event [0] False 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
13-52 SL Controller Action [0] Disabled 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5.2.15 14-** Special Functions
Parameter
Number
14-01 Switching Frequency [1] 4.0 kHz All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
14-03 Overmodulation [1] On All set-ups FALSE - Uint8
14-12 Function at Mains Imbalance [0] Trip All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
14-20 Reset Mode [0] Manual reset All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 61
Page 64

Parameter Lists
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Parameter
Number
14-21 Automatic Restart Time 10 s All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint16
14-22 Operation Mode [0] Normal operation 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
14-26 Action At Inverter Fault [0] Trip All set-ups TRUE - Uint8
14-41 AEO Minimum Magnetisation 66 % All set-ups TRUE 0 Uint8
14-90 Fault Level [3] Trip Lock 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5.2.16 15-** Drive Information
Parameter
55
number
15-00 Operating Time 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
15-01 Running Hours 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
15-02 kWh Counter 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
15-03 Power Up's 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
15-04 Over Temp's 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
15-05 Over Volt's 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
15-06 Reset kWh Counter [0] Do not reset 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
15-07 Reset Running Hours Counter [0] Do not reset 1 set-up TRUE - Uint8
15-30 Fault Log: Error Code 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
15-40 FC Type 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
15-41 Power Section 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
15-42 Voltage 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
15-43 SW ID Control Card 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
15-46
15-48 LCP Id No 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
15-51
Parameter description Default value 2 Setup
Frequency Converter Ordering
No 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
Frequency Converter Serial
Number 1 set-up FALSE 0 VisibleString
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
5.2.17 16-** Data Readouts
Parameter
number
16-00 Control Word 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-01 Reference [Unit] 0 1 set-up TRUE -3 Int32
16-02 Reference % 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Int16
16-03 Status Word 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-05 Main Actual Value [%] 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Int16
16-09 Custom Readout 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Int32
16-10 Power [kW] 0 1 set-up TRUE -3 Uint16
16-11 Power [hp] 0 1 set-up TRUE -3 Uint16
16-12 Motor Voltage 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-13 Frequency 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Uint16
16-14 Motor Current 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-15 Frequency [%] 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Uint16
16-18 Motor Thermal 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
16-30 DC Link Voltage 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-34 Heatsink Temp. 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
16-35 Inverter Thermal 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
16-36 Inv. Nom. Current 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-37 Inv. Max. Current 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-38 SL Controller State 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
Parameter description Default value 2 Setup
Change during
operation
Conversion
index
Type
62 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 65

Parameter Lists Programming Guide
Parameter
number
16-50 External Reference 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Int16
16-51 Pulse Reference 0 1 set-up TRUE -1 Int16
16-52 Feedback [Unit] 0 1 set-up TRUE -3 Int32
16-60 Digital input 18,19,27,33 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-61 Digital input 29 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
16-62 Analog Input 53 (V) 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-63 Analog Input 53 (mA) 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-64 Analog Input 60 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-65 Analog Output 42 [mA] 0 1 set-up TRUE -2 Uint16
16-68 Pulse input 33 20 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint16
16-71 Relay Output [bin] 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint8
16-72 Counter A 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Int16
16-73 Counter B 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Int16
16-86 FC Port REF 1 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Int16
16-90 Alarm Word 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
16-91 Alarm Word2 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 UNIT32
16-92 Warning Word 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
16-94 Ext. Status Word 0 1 set-up TRUE 0 Uint32
Parameter description Default value 2 Setup
Change during
operation
Conversion
index
Type
5.2.18 18-** Extended Motor Data
5 5
Parameter
Number
18-80
16-01
Parameter Description Default Value 2 Setup
Stator Resistance (Rs in high
resolution) 0.000 All set-ups FALSE -3 Uint32
(18-81) Stator Leakage
Reactance (X1 in high
resolution) 0.000 All set-ups FALSE -3 Uint32
Change During
Operation
Conversion
Index
Type
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 63
Page 66

Troubleshooting
6 Troubleshooting
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
6.1 Warnings and Alarms
If an alarm cannot be reset, the reason may be that its
cause has not been rectified, or the alarm is trip-locked
A warning or an alarm is signalled by the relevant LED on
(see also Table 6.1).
the front of the frequency converter and indicated by a
code on the display.
Alarms that are trip-locked offer additional protection,
means that the mains supply must be switched off before
A warning remains active until its cause is no longer
present. Under certain circumstances operation of the
motor may still be continued. Warning messages may be
critical, but are not necessarily so.
the alarm can be reset. After being switched back on, the
frequency converter is no longer blocked and may be reset
as described above once the cause has been rectified.
Alarms that are not trip-locked can also be reset using the
automatic reset function in 14-20 Reset Mode (Warning:
66
In the event of an alarm, the frequency converter will have
tripped. Alarms must be reset to restart operation once
their cause has been rectified.
automatic wake-up is possible!)
If a warning and alarm is marked against a code in the
Table 6.1, this means that either a warning occurs before
an alarm, or it can be specified whether it is a warning or
This may be done in 4 ways:
1. By pressing [Reset].
2. Via a digital input with the “Reset” function.
3. Via serial communication.
NOTICE
an alarm that is to be displayed for a given fault.
This is possible, for instance, in 1-90 Motor Thermal
Protection. After an alarm or trip, the motor carries on
coasting, and the alarm and warning flash on the
frequency converter. Once the problem has been rectified,
only the alarm continues flashing.
After a manual reset press [Reset], [Auto On] or [Hand
On] to restart the motor.
No. Description Warning Alarm Trip Lock Error Parameter Reference
2 Live zero error (X) (X) 6-01
4 Mains phase loss (X) (X) (X) 14-12
7 DC over voltage X X
8 DC under voltage X X
9 Inverter overloaded X X
10 Motor ETR over temperature (X) (X) 1-90
11 Motor thermistor over temperature (X) (X) 1-90
12 Torque limit (X) 4-16, 4-17
13 Over Current X X X
14 Earth fault X X X
16 Short Circuit X X
17 Control word timeout (X) (X) 8-04
25 Brake resistor short-circuited X X
27 Brake chopper short-circuited X X
28 Brake Check X
29 Power board over temp X X X
30 Motor phase U missing (X) (X) 4-58
31 Motor phase V missing (X) (X) 4-58
32 Motor phase W missing (X) (X) 4-58
38 Internal fault X X
44 Earth fault 2 X X
47 Control Voltage Fault X X
51 AMT check U
52 AMT low I
53 AMT motor too big X
nom
nom
and I
nom
X
X
64 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 67

Troubleshooting Programming Guide
No. Description Warning Alarm Trip Lock Error Parameter Reference
54 AMT motor too small X
55 AMT Parameter out of range X
59 Current limit X
63 Mechanical Brake Low X
80 Drive Initialized to Default Value X
84 The connection between drive and LCP is
lost
85 Button disabled X
86 Copy fail X
87 LCP data invalid X
88 LCP data not compatible X
89 Parameter read only X
90 Parameter database busy X
91 Parameter value is not valid in this mode X
92 Parameter value exceeds the min/max limits X
Table 6.1 Alarm/Warning Code List
(X) Dependent on parameter
X
A trip is the action when an alarm has appeared. The trip
will coast the motor and can be reset by pressing [Reset]
or make a reset by a digital input (parameter group 5-1*
[1]). The original event that caused an alarm cannot
damage the frequency converter or cause dangerous
conditions. A trip lock is an action when an alarm occurs,
which may cause damage to frequency converter or
connected parts. A trip lock situation can only be reset by
a power cycling.
6 6
Warning yellow
Alarm flashing red
Table 6.2 LED Indication
The alarm words, warning words and extended status
words can be read out via serial bus or optional fieldbus
for diagnosis. See also 16-90 Alarm Word, 16-92 Warning
Word and 16-94 Ext. Status Word.
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 65
Page 68

Troubleshooting
Par. 16-90 Par. 16-91 Par. 16-92 Par. 16-94
Bit Hex Dec AlarmWord AlarmWord2 WarningWord ExtendedStatusWord
0 1 1 Brake check
1 2 2 Pwr.card temp Pwr.card temp AMT running
2 4 4 Earth Fault Start CW/CCW
3 8 8 Slow down
4 10 16 Ctrl.word TO Ctrl.word TO Catch up
5 20 32 Over Current Over Current Above Feedback High
6 40 64 Torque limit Below Feedback Low
7 80 128 Motor th over Motor th over Output current high
8 100 256 Motor ETR over Motor ETR over Output current low
9 200 512 Inverter overload Inverter overload Above Frequency High
10 400 1024 DC under volt DC under volt Below Frequency Low
66
11 800 2048 DC over volt DC over volt
12 1000 4096 Short Circuit
13 2000 8192 Braking
14 4000 16384 Mains ph. loss Mains ph. loss
15 8000 32768 AMT Not OK OVC active
16 10000 65536 Live zero error Live zero error AC brake
17 20000 131072 Internal fault
18 40000 262144
19 80000 524288 U phase loss Above Reference High
20 100000 1048576 V phase loss Below Reference Low
21 200000 2097152 W phase loss Local Ref./Remote Ref.
22 400000 4194304
23 800000 8388608 Protection Mode
24 1000000 16777216
25 2000000 33554432 Current limit
26 4000000 67108864 Brake resistor short-circuit
27 8000000 134217728 Brake IGBT short-circuit
28 10000000 268435456
29 20000000 536870912 Drive initialised
30 40000000 1073741824
31 80000000 2147483648 Mech. brake low DatabaseBusy
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Control Voltage
Fault Ramping
M4/M5: Earth Fault
(Desat) MotorPhaseMissing
Table 6.3 Alarm, Warning, and Extended Status Word
The alarm words, warning words and extended staus
words can be read out via serial bus for diagnose. See also
16-94 Ext. Status Word.
WARNING/ALARM 2, Live zero error
Signal on terminal 53 or 60 is less than 50% of value set in
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage, 6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current
and 6-22 Terminal 60 Low Current.
WARNING/ALARM 4, Mains phase loss
A phase is missing on the supply side, or the mains
voltage imbalance is too high. This message also appears
for a fault in the input rectifier on the frequency converter.
Troubleshooting
WARNING/ALARM 7, DC overvoltage
If the intermediate circuit voltage exceeds the limit, the
frequency converter trips after a time.
Troubleshooting
Connect a brake resistor
Extend the ramp time
Change the ramp type
Activate the functions in 2-10 Brake Function
Increase 14-26 Trip Delay at Inverter Fault
The fault may be caused by mains distortions. Installing
Danfoss Line Filter may rectify this problem.
Check the supply voltage and supply currents to the
frequency converter. The fault may be caused by mains
distortions. Installing Danfoss line filter may rectify this
problem.
66 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 69

Troubleshooting
Programming Guide
WARNING/ALARM 8, DC under voltage
If the DC link voltage drops below the undervoltage limit,
the frequency converter checks if a 24 V DC back-up
supply is connected. If no 24 V DC back-up supply is
connected, the frequency converter trips after a fixed time
delay. The time delay varies with unit size.
Troubleshooting
Check that the supply voltage matches the
•
frequency converter voltage.
Perform an input voltage test.
•
Perform a soft charge circuit test.
•
WARNING/ALARM 9, Inverter overload
The frequency converter has run with more than 100%
overload for too long and is about to cut out. The counter
for electronic thermal inverter protection issues a warning
at 98% and trips at 100%, while giving an alarm. The
frequency converter cannot be reset until the counter is
below 90%.
Troubleshooting
Compare the output current shown on the LCP
•
with the frequency converter rated current.
Compare the output current shown on the LCP
•
with the measured motor current.
Display the thermal drive load on the LCP and
•
monitor the value. When running above the
frequency converter continuous current rating,
the counter increases. When running below the
frequency converter continuous current rating,
the counter decreases.
WARNING/ALARM 10, Motor overload temperature
According to the electronic thermal protection (ETR), the
motor is too hot. Select whether the frequency converter
gives a warning or an alarm when the counter reaches
100% in 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection. The fault occurs
when the motor is overloaded by more than 100% for too
long.
Troubleshooting
Check for motor overheating.
Check if the motor is mechanically overloaded
Check that the motor current set in 1-24 Motor
Current is correct.
Ensure that motor data in parameters 1-20
through 1-25 are set correctly.
Running AMT in 1-29 Automatic Motor Tuning
(AMT). The inverter peak current limit (approx.
200% of the rated current) is exceeded. The
warning will last approx. 8-12 s, then the
frequency converter trips and issues an alarm.
Turn off the frequency converter and check if the
motor shaft can be turned and if the motor size
matches the frequency converter. If extended
mechanical brake control is selected, trip can be
reset externally. may tune the frequency
converter to the motor more accurately and
reduce thermal loading.
WARNING/ALARM 11, Motor thermistor overtemp
The thermistor might be disconnected. Select whether the
frequency converter gives a warning or an alarm in
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection.
Troubleshooting
Check for motor overheating.
Check if the motor is mechanically overloaded.
WARNING/ALARM 13, Over current
The inverter peak current limit (approx. 200% of the rated
current) is exceeded. The warning will last approx. 8-12 s,
then the frequency converter trips and issues an alarm.
Turn off the frequency converter and check if the motor
shaft can be turned and if the motor size matches the
frequency converter. If extended mechanical brake control
is selected, trip can be reset externally.
Troubleshooting
Remove power and check if the motor shaft can
be turned.
Check that the motor size matches the frequency
converter.
Check parameters 1-20 through 1-25. for correct
motor data.
ALARM 14, Earth (ground) fault
There is current from the output phase to ground, either in
the cable between the frequency converter and the motor
or in the motor itself.
Troubleshooting
Remove power to the frequency converter and
•
repair the ground fault.
Check for ground faults in the motor by
•
measuring the resistance to ground of the motor
cables and the motor with a megohmmeter.
ALARM 16, Short circuit
There is short-circuiting in the motor or motor wiring.
Troubleshooting
Remove the power to the frequency converter
•
and repair the short circuit.
WARNING/ALARM 17, Control word timeout
There is no communication to the frequency converter.
The warning is only active when 8-04 Control Word Timeout
Function is NOT set to [0] Off.
If 8-04 Control Word Timeout Function is set to [5] Stop and
Trip, a warning appears and the frequency converter ramps
down until it trips, while giving an alarm. 8-03 Control
Timeout Time could possibly be increased.
6 6
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 67
Page 70

Troubleshooting
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Troubleshooting
Check connections on the serial communication
•
cable.
Increase 8-03 Control Word Timeout Time.
•
Check the operation of the communication
•
equipment.
Verify a proper installation based on EMC
•
requirements.
ALARM 25, Brake resistor short circuit
The brake resistor is monitored during operation. If a short
circuit occurs, the brake function is disabled and the
warning appears. The frequency converter is still
operational but without the brake function. Remove power
66
from the frequency converter and replace the brake
resistor (see 2-15 Brake Check).
ALARM 27, Brake chopper fault
The brake transistor is monitored during operation, and if
a short circuit occurs, the brake function is disabled and a
warning is issued. The frequency converter is still
operational but, since the brake transistor has shortcircuited, substantial power is transmitted to the brake
resistor, even if it is inactive.
Troubleshooting
Remove power to the frequency converter and
•
remove the brake resistor.
ALARM 28, Brake check failed
The brake resistor is not connected or not working.
ALARM 29, Heat Sink temp
The maximum temperature of the heat sink has been
exceeded. The temperature fault does not reset until the
temperature drops below a defined heat sink temperature.
The trip and reset points are different based on the
frequency converter power size.
Troubleshooting
Check for the following conditions:
Ambient temperature too high.
•
Motor cables too long.
•
Incorrect airflow clearance above and below the
•
frequency converter.
Blocked airflow around the frequency converter.
•
Damaged heat sink fan.
•
Dirty heat sink.
•
ALARM 30, Motor phase U missing
Motor phase U between the frequency converter and the
motor is missing.
Troubleshooting
Remove the power from the frequency converter
•
and check motor phase U.
ALARM 31, Motor phase V missing
Motor phase V between the frequency converter and the
motor is missing.
Troubleshooting
Remove the power from the frequency converter
•
and check motor phase V.
ALARM 32, Motor phase W missing
Motor phase W between the frequency converter and the
motor is missing.
Troubleshooting
Remove the power from the frequency converter
•
and check motor phase W.
ALARM 38, Internal fault
Troubleshooting
Cycle power.
•
Check that the option is properly installed.
•
Check for loose or missing wiring.
•
It may be necessary to contact the local Danfoss supplier
or service department. Note the code number for further
troubleshooting directions.
ALARM 46, Gate drive voltage fault
The supply on the power card is out of range.
There are 3 power supplies generated by the switch mode
power supply (SMPS) on the power card: 24 V, 5 V, and
±18 V.
Troubleshooting
Check for a defective power card.
•
ALARM 51, AMT check U
The settings for motor voltage, motor current, and motor
power are wrong. Check the settings in parameters 1-20 to
1-25.
ALARM 55, AMA parameter out of range
The parameter values of the motor are outside of the
acceptable range. AMA does not run.
ALARM 63, Mechanical brake low
The actual motor current has not exceeded the release
brake current within the start delay time window.
ALARM 80, Drive initialised to default value
Parameter settings are initialised to default settings after a
manual reset. To clear the alarm, reset the unit.
ERROR 84,The connection between drive and LCP is lost
Try to reassemble the LCP gently.
ERROR 85, Button disabled
See parameter group 0-4* LCP
ERROR 86, Copy fail
An error occurred while copying from frequency converter
to LCP or vice versa.
ERROR 87, LCP data invalid
Occurs when copying from LCP if the LCP contains
erroneous data - or if no data was uploaded to the LCP.
ERROR 88,LCP data not compatible
Occurs when copying from LCP if data are moved between
frequency converters with major differences in software
versions.
nom
and I
nom
68 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 71

Troubleshooting Programming Guide
ERROR 89, Parameter read only
Occurs when trying to write to a read-only parameter.
ERROR 90, Parameter database busy
LCP and RS-485 connection are trying to update
parameters simultaneously.
ERROR 91, Parameter value is not valid in this mode
Occurs when trying to write an illegal value to a
parameter.
ERROR 92, Parameter value exceeds the min/max limits
Occurs when trying to set a value outside the range.
Parameter can only be changed when the motor is
stopped. Err. A wrong password was entered, occurs when
using a wrong password for changing a passwordprotected parameter.
6 6
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 69
Page 72

Index
VLT® Micro Drive FC 51
Index
A
Abbreviation............................................................................................. 5
Active set-up................................................................. 8, 11, 13, 52, 57
AEO............................................................................................................ 47
Automatic motor tuning (AMT)....................................................... 15
B
Brake function, 2-10............................................................................. 19
Brake resistor............................................................................ 19, 52, 58
C
Current rating........................................................................................ 67
D
DC brake.................................................................................................. 54
DC-brake.................................................................................................. 19
Display........................................................................................................ 8
Disposal instruction............................................................................... 5
E
Edit set-up............................................................................. 8, 11, 52, 57
Electronic waste...................................................................................... 5
EMC............................................................................................................ 68
H
High altitude............................................................................................. 7
High voltage............................................................................................. 6
L
LCP 11.......................................................................................................... 8
LCP 12.......................................................................................................... 8
Leakage current....................................................................................... 6
Load compensation............................................................... 14, 52, 57
Load sharing...................................................................................... 6, 46
Local mode...................................................................................... 54, 57
M
Maximum reference............................................................................ 21
Minimum reference............................................................................. 21
Motor
phase.................................................................................................... 54
temperature....................................................................................... 52
Motor current.................................................................................. 15, 68
Motor direction........................................................................................ 9
Motor frequency................................................................................... 15
Motor nominal speed......................................................................... 15
Motor phase.................................................................................... 49, 59
Motor power.......................................................................................... 68
Motor temperature....................................................................... 18, 19
Motor voltage........................................................................................ 15
N
Not changeable during operation................................................. 12
O
Operation key........................................................................................... 9
Output current...................................................................................... 67
Overvoltage control..................................................................... 52, 58
P
Parameter number................................................................................. 8
PELV............................................................................................................. 7
Q
Qualified personnel................................................................................ 6
Quick menu............................................................................................... 9
R
Ramp1 ramp-down time.................................................................... 23
Ramp1 ramp-up time.......................................................................... 23
Readout mode......................................................................................... 9
Reset................................................................................................... 67, 68
S
Safety........................................................................................................... 7
Serial communication........................................ 9, 24, 37, 39, 49, 50
Set-up number......................................................................................... 8
Short circuit............................................................................................ 67
Slip compensation........................................................................ 52, 57
Smart logic.............................................................................................. 61
Status menu.............................................................................................. 9
T
Thermal load.......................................................................................... 49
Thermistor........................................................................................ 18, 52
Thermistor resource............................................................................ 57
Trip Reset, 14-2*.................................................................................... 46
Type code string...................................................................................... 3
U
Unintended start.............................................................................. 6, 46
70 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. MG02C702
Page 73

Index Programming Guide
MG02C702 Danfoss A/S © 12/2014 All rights reserved. 71
Page 74

Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to
products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specifications already agreed. All trademarks in this material are property
of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
Danfoss A/S
Ulsnaes 1
DK-6300 Graasten
www.danfoss.com/drives
132R0001 MG02C702 12/2014
*MG02C702*
 Loading...
Loading...