Page 1

ENGINEERING TOMORROW
Programming Guide
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
vlt-drives.danfoss.com
Page 2

Page 3

Contents Programming Guide
Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 How to Read This Programming Guide
1.2 Denitions
1.3 Electrical Wiring - Control Cables
2 Safety
2.1 Safety Symbols
2.2 Qualied Personnel
2.3 Safety Precautions
3 Programming
3.1 Local Control Panel Operations
3.2 Basic Programming
4 Parameter Descriptions
4.1 Parameters: 0-** Operation and Display
4.2 Parameters: 1-** Load and Motor
4.3 Parameters: 2-** Brakes
3
3
4
7
11
11
11
11
13
13
21
24
24
33
45
4.4 Parameters: 3-** Reference/Ramps
4.5 Parameters: 4-** Limits/Warnings
4.6 Parameters: 5-** Digital In/Out
4.7 Parameters: 6-** Analog In/Out
4.8 Parameters: 7-** Controllers
4.9 Parameters: 8-** Communications and Options
4.10 Parameters: 9-** PROFIdrive
4.11 Parameters: 12-** Ethernet
4.12 Parameters: 13-** Smart Logic Control
4.13 Parameters: 14-** Special Functions
4.14 Parameters: 15-** Drive Information
4.15 Parameters: 16-** Data Readouts
4.16 Parameters: 17-** Feedback Options
4.17 Parameters: 18-** Data Readouts 2
4.18 Parameters: 21-** Ext. Closed Loop
4.19 Parameters: 22-** Application Functions
4.20 Parameters: 30-** Special Features
47
53
57
69
72
77
81
87
90
96
103
105
108
109
110
111
112
4.21 Parameters: 32-** Motion Control Basic Settings
4.22 Parameters: 33-** Motion Control Adv. Settings
4.23 Parameters: 34-** Motion Control Data Readouts
4.24 Parameters: 37-** Application Settings
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 1
113
113
114
115
Page 4

Contents
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
5 Parameter Lists
5.1 Introduction
5.2 Parameter Lists
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Warnings and Alarms
Index
121
121
124
143
143
152
2 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 5
Introduction Programming Guide
1 Introduction
1.1 How to Read This Programming Guide
1.1.1 Purpose of the Manual
This programming guide provides information about
controlling the frequency converter, parameter access,
programming, and troubleshooting.
The programming guide is intended for use by
personnel who are familiar with VLT® AutomationDrive FC
360.
Read the instructions before programming and follow the
procedures in this manual.
VLT® is a registered trademark.
1.1.2 Additional Resources
Additional resources include:
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360 Quick Guide provides
•
the necessary information for getting the
frequency converter up and running.
®
VLT
•
AutomationDrive FC 360 Design Guide
provides detailed technical information about the
frequency converter and customer design and
applications.
Contact the local Danfoss supplier or go to
www.danfoss.com/fc360 to download the documentation.
1.1.3 Document and Software Version
This manual is regularly reviewed and updated. All
suggestions for improvement are welcome. Table 1.1 shows
the document version and the corresponding software
version.
Edition Remarks
MG06C8
Table 1.1 Document and Software Version
Update due to new hardware and
software release.
qualied
Software
version
1.8x
°C
°F
AC Alternating current
AEO Automatic energy optimization
ACP Application control processor
AWG American wire gauge
AMA Automatic motor adaptation
DC Direct current
EEPROM
EMC Electromagnetic compatibility
EMI Electromagnetic interference
ESD Electrostatic discharge
ETR Electronic thermal relay
f
M,N
FC Frequency converter
IGBT Insulated-gate bipolar transistor
IP Ingress protection
I
LIM
I
INV
I
M,N
I
VLT,MAX
I
VLT,N
L
d
L
q
LCP Local control panel
LED Light-emitting diode
MCP Motor control processor
N.A. Not applicable
NEMA
P
M,N
PCB Printed circuit board
PE Protective earth
PELV Protective extra low voltage
PWM Pulse width modulation
R
s
Regen Regenerative terminals
RPM Revolutions per minute
RFI Radio frequency interference
SCR Silicon controlled rectier
SMPS Switch mode power supply
T
LIM
U
M,N
X
h
Degrees Celsius
Fahrenheit
Electrically erasable programmable
read-only memory
Nominal motor frequency
Current limit
Rated inverter output current
Nominal motor current
Maximum output current
Rated output current supplied by the
frequency converter
Motor d-axis inductance
Motor q-axis inductance
National Electrical Manufacturers
Association
Nominal motor power
Stator resistance
Torque limit
Nominal motor voltage
Motor main reactance
1 1
Table 1.2 Abbreviations
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 3
Page 6
175ZA078.10
Pull-out
RPM
Torque
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
11
1.1.4 Approvals and Certications
I
M,N
Nominal motor current (nameplate data).
n
M,N
Nominal motor speed (nameplate data).
n
s
Synchronous motor speed.
2 × Parameter 1−23 × 60s
1.2 Denitions
1.2.1 Frequency Converter
Coast
The motor shaft is in free mode. No torque on the motor.
I
VLT,MAX
Maximum output current.
I
VLT,N
Rated output current supplied by the frequency converter.
U
VLT,MAX
Maximum output voltage.
ns=
n
slip
Parameter 1−39
Motor slip.
P
M,N
Rated motor power (nameplate data in kW or hp).
T
M,N
Rated torque (motor).
U
M
Instantaneous motor voltage.
U
M,N
Rated motor voltage (nameplate data).
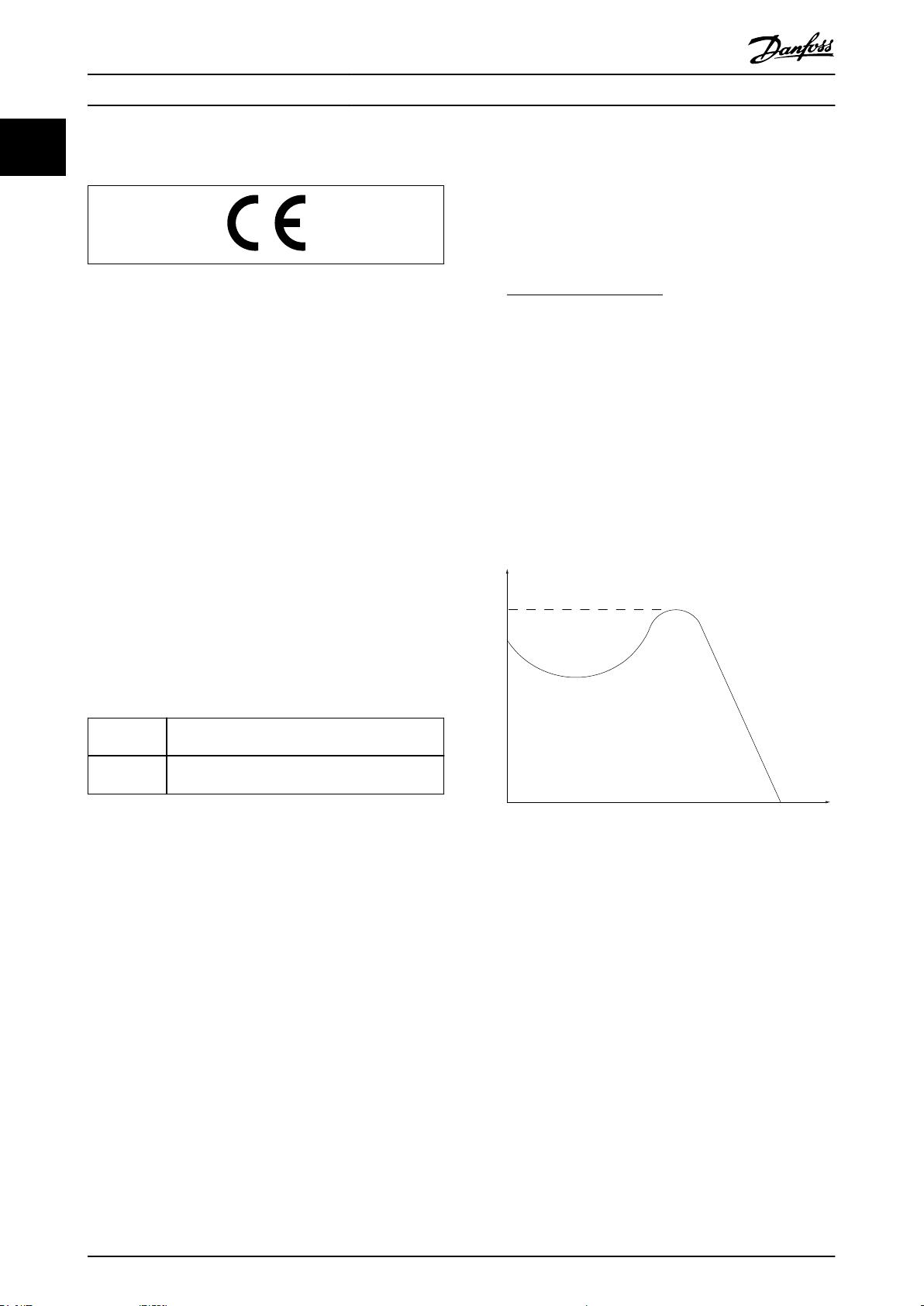
Break-away torque
1.2.2 Input
Control commands
Start and stop the connected motor with the LCP and
digital inputs.
Functions are divided into 2 groups.
Functions in group 1 have higher priority than functions in
group 2.
Group 1 Coast stop, reset and coast stop, quick stop, DC
braking, stop, and [OFF].
Group 2 Start, latched start, start reversing, jog, freeze
output, and [Hand On].
Table 1.3 Function Groups
1.2.3 Motor
Motor running
Torque generated on the output shaft and speed from
0 RPM to maximum speed on the motor.
f
JOG
Motor frequency when the jog function is activated (via
digital terminals or bus).
f
M
Motor frequency.
f
MAX
Maximum motor frequency.
f
MIN
Minimum motor frequency.
f
M,N
Rated motor frequency (nameplate data).
I
M
Motor current (actual).
Illustration 1.1 Break-away Torque
η
VLT
The eciency of the frequency converter is dened as the
ratio between the power output and the power input.
Start-disable command
A start-disable command belonging to the control
commands in group 1. See Table 1.3 for more details.
Stop command
A stop command belonging to the control commands in
group 1. See Table 1.3 for more details.
1.2.4 References
Analog reference
A signal transmitted to the analog inputs 53 or 54 can be
voltage or current.
Binary reference
A signal transmitted via the serial communication port.
4 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 7

Introduction Programming Guide
Preset reference
A dened preset reference to be set from -100% to +100%
of the reference range. Selection of 8 preset references via
the digital terminals. Selection of 4 preset references via
the bus.
Pulse reference
A pulse frequency signal transmitted to the digital inputs
(terminal 29 or 33).
Ref
MAX
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
100% full scale value (typically 10 V, 20 mA) and the
resulting reference. The maximum reference value is set in
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.
Ref
MIN
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
0% value (typically 0 V, 0 mA, 4 mA) and the resulting
reference. The minimum reference value is set in
parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference.
1.2.5 Miscellaneous
Analog inputs
The analog inputs are used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
There are 2 types of analog inputs:
Current input: 0–20 mA and 4–20 mA.
•
Voltage input: 0–10 V DC.
•
Analog outputs
The analog outputs can supply a signal of 0–20 mA, or 4–
20 mA.
Automatic motor adaptation, AMA
The AMA algorithm determines the electrical parameters
for the connected motor at standstill.
Brake resistor
The brake resistor is a module capable of absorbing the
brake power generated in regenerative braking. This
regenerative brake power increases the DC-link voltage
and a brake chopper ensures that the power is transmitted
to the brake resistor.
CT characteristics
Constant torque characteristics used for all applications
such as conveyor belts, displacement pumps, and cranes.
Digital inputs
The digital inputs can be used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
Digital outputs
The frequency converter features 2 solid-state outputs that
can supply a 24 V DC (maximum 40 mA) signal.
ETR
Electronic thermal relay is a thermal load calculation based
on present load and time. Its purpose is to estimate the
motor temperature.
FC standard bus
Includes RS485 bus with FC protocol or MC protocol. See
parameter 8-30 Protocol.
Initializing
If initializing is carried out (parameter 14-22 Operation Mode
or 2-nger reset), the frequency converter returns to the
default setting.
Intermittent duty cycle
An intermittent duty rating refers to a sequence of duty
cycles. Each cycle consists of an on-load and an o-load
period. The operation can be either periodic duty or nonperiodic duty.
LCP
The local control panel makes up a complete interface for
control and programming of the frequency converter. The
LCP is detachable. With the installation kit option, the LCP
can be installed up to 3 m (9.8 ft) from the frequency
converter in a front panel.
GLCP
The graphic local control panel (LCP 102) interface for
control and programming of the frequency converter. The
display is graphic and the panel is used to show process
values. The GLCP has storing and copy functions.
NLCP
The numerical local control panel (LCP 21) interface for
control and programming of the frequency converter. The
display is numerical and the panel is used to show process
values. The NLCP has storing and copy functions.
lsb
Least signicant bit.
msb
Most signicant bit.
MCM
Short for mille circular mil, an American measuring unit for
cable cross-section. 1 MCM = 0.5067 mm2.
On-line/o-line parameters
Changes to on-line parameters are activated immediately
after the data value is changed. To activate changes to o-
line parameters, press [OK].
Process PID
The PID control maintains speed, pressure, and
temperature by adjusting the output frequency to match
the varying load.
PCD
Process control data.
Power cycle
Switch o the mains until the display (LCP) is dark, then
turn power on again.
Power factor
The power factor is the relation between I1 and I
Power factor =
3xUxI1cosϕ1
3xUxI
RMS
RMS
.
1 1
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 5
Page 8

Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
11
For VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360 frequency converters,
cosϕ
1 = 1, therefore:
Power factor =
I1xcosϕ1
I
RMS
=
I
I
RMS
1
The power factor indicates to which extent the frequency
converter imposes a load on the mains supply.
The lower the power factor, the higher the I
RMS
for the
same kW performance.
I
RMS
= I
+ I
1
5
+ I
2
+ .. + I
7
2
n
2
2
In addition, a high power factor indicates that the dierent
harmonic currents are low.
The built-in DC coils produce a high power factor,
minimizing the imposed load on the mains supply.
STW
Status word.
THD
Total harmonic distortion states the total contribution of
harmonic distortion.
Thermistor
A temperature-dependent resistor placed where the
temperature is monitored (frequency converter or motor).
Trip
A state entered in fault situations, for example if the
frequency converter is subject to overvoltage or when it is
protecting the motor, process, or mechanism. Restart is
prevented until the cause of the fault has disappeared, and
the trip state is canceled by activating reset or, sometimes,
Pulse input/incremental encoder
An external, digital pulse transmitter used for feeding back
by being programmed to reset automatically. Do not use
trip for personal safety.
information on motor speed. The encoder is used in
applications where great accuracy in speed control is
required.
Trip lock
Trip lock is a state entered in fault situations when the
frequency converter is protecting itself and requiring
RCD
Residual current device.
Set-up
Save parameter settings in 2 set-ups. Change between the
2 parameter set-ups and edit 1 set-up while another set-up
is active.
SFAVM
Acronym describing the switching pattern stator uxoriented asynchronous vector modulation.
Slip compensation
The frequency converter compensates for the motor slip by
giving the frequency a supplement that follows the
measured motor load, keeping the motor speed almost
constant.
Smart logic control (SLC)
The SLC is a sequence of user-dened actions executed
when the smart logic controller evaluates the associated
user-dened events as true (parameter group 13-** Smart
physical intervention., An example causing a trip lock is the
frequency converter being subject to a short circuit on the
output. A locked trip can only be canceled by cutting o
mains, removing the cause of the fault, and reconnecting
the frequency converter. Restart is prevented until the trip
state is canceled by activating reset or, sometimes, by
being programmed to reset automatically. Do not use trip
lock for personal safety.
VT characteristics
Variable torque characteristics used for pumps and fans.
+
VVC
If compared with standard voltage/frequency ratio control,
voltage vector control (VVC+) improves the dynamics and
stability, both when the speed reference is changed and in
relation to the load torque.
60° AVM
°
Refers to the switching pattern 60
asynchronous vector
modulation.
Logic Control).
6 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 9
130BC438.19
3 phase
power
input
Switch mode
power supply
Motor
Interface
(PNP) = Source
(NPN) = Sink
ON=Terminated
OFF=Open
Brake
resistor
91 (L1)
92 (L2)
93 (L3)
PE
50 (+10 V OUT)
53 (A IN)
54 (A IN)
55 (COM A IN/OUT)
0/4-20 mA
12 (+24 V OUT)
33 (D IN)
18 (D IN)
20 (COM D IN)
10 V DC
15 mA 100 mA
+ - + -
(U) 96
(V) 97
(W) 98
(PE) 99
(P RS485) 68
(N RS485) 69
(COM RS485) 61
0V
5V
S801
RS485
RS485
03
+10 V DC
0/4-20 mA
0-10 V DC
24 V DC
02
01
05
04
250 V AC, 3 A
24 V (NPN)
0 V (PNP)
0 V (PNP)
24 V (NPN)
19 (D IN)
24 V (NPN)
0 V (PNP)
27 (D IN/OUT)
24 V
0 V
0 V (PNP)
24 V (NPN)
0 V
24 V
29 (D IN/OUT)
24 V (NPN)
0 V (PNP)
0 V (PNP)
24 V (NPN)
32 (D IN)
31 (D IN)
95
P 5-00
21
ON
(+UDC) 89
(BR) 81 5)
24 V (NPN)
0 V (PNP)
0-10 V DC
(-UDC) 88
RFI
3)
0 V
250 V AC, 3 A
Relay 1
1)
Relay 2 2)
4)
06
42 (A OUT)
45 (A OUT)
Analog
output
0/4-20 mA
Introduction Programming Guide
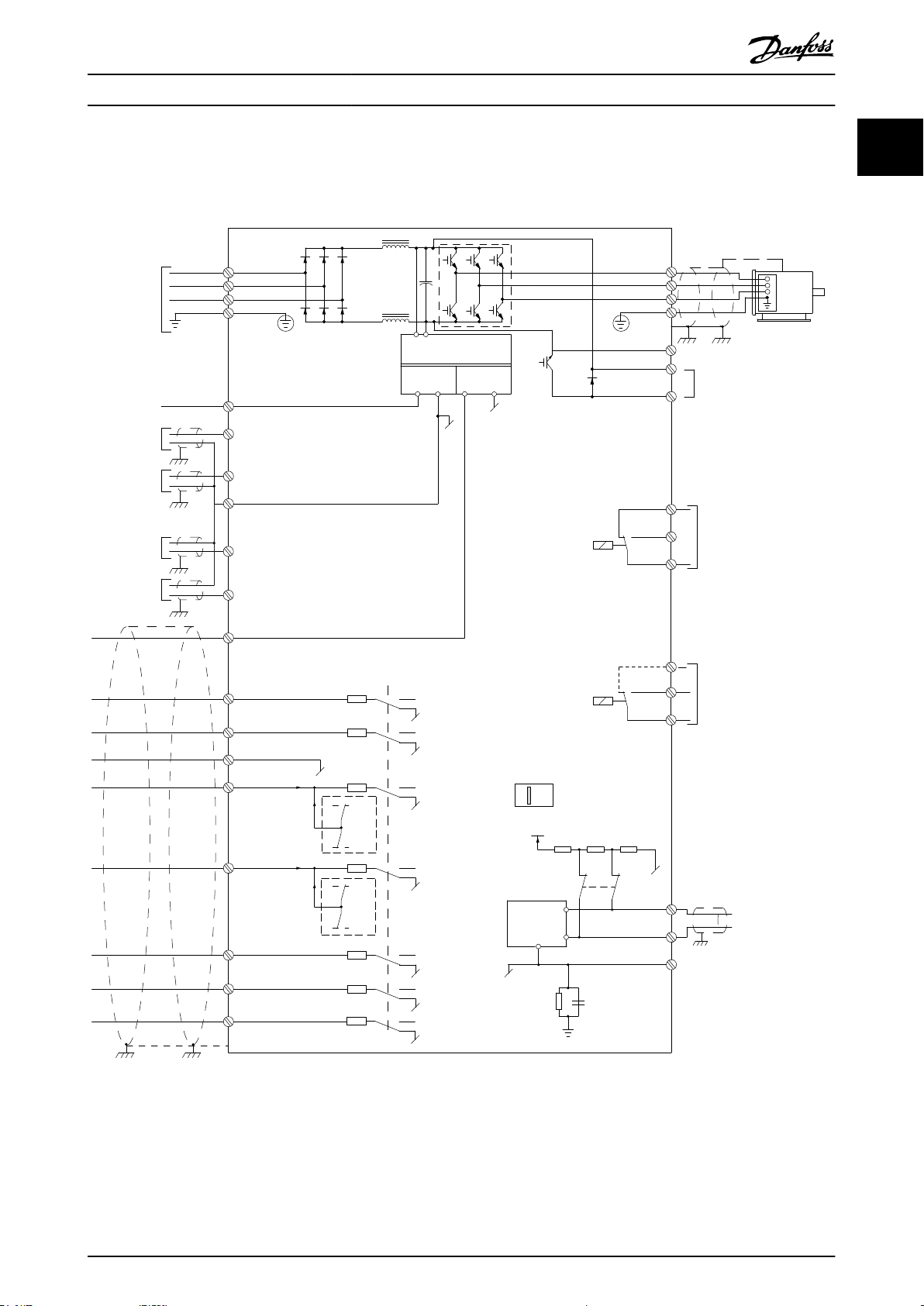
1.3 Electrical Wiring - Control Cables
1.3.1 Overview
1 1
Illustration 1.2 Basic Wiring Schematic Drawing
A = Analog, D = Digital
1) Built-in brake chopper available from J1–J5.
2) Relay 2 is 2-pole for J1–J3 and 3-pole for J4–J7. Relay 2 of J4–J7 with terminals 4, 5, and 6 has same NO/NC logic as relay 1.
Relays are pluggable in J1–J5 and xed in J6–J7.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 7
Page 10
130BD367.11
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 55
+24 VDC
0 VDC
PNP (Source)
Digital input wiring
NPN (Sink)
Digital input wiring
12 18 19 27 29 31 32 33 55
+24 VDC
0 VDC
130BD368.11
130BA681.10
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
11
3) Single DC choke in J1–J5; Dual DC choke in J6–J7.
4) Switch S801 (bus terminal) can be used to enable termination on the RS485 port (terminals 68 and 69).
5) No BR for J6–J7.
In rare cases, long control cables and analog signals could
result in 50/60 Hz ground loops due to noise from mains
supply cables. If this occurs, break the shield or insert a
100 nF capacitor between shield and chassis.
The digital and analog inputs and outputs must be
connected separately to the common inputs (terminal 20
and 55) of the frequency converter to avoid ground
currents from both groups to aect other groups. For
example, switching on the digital input could disturb the
analog input signal.
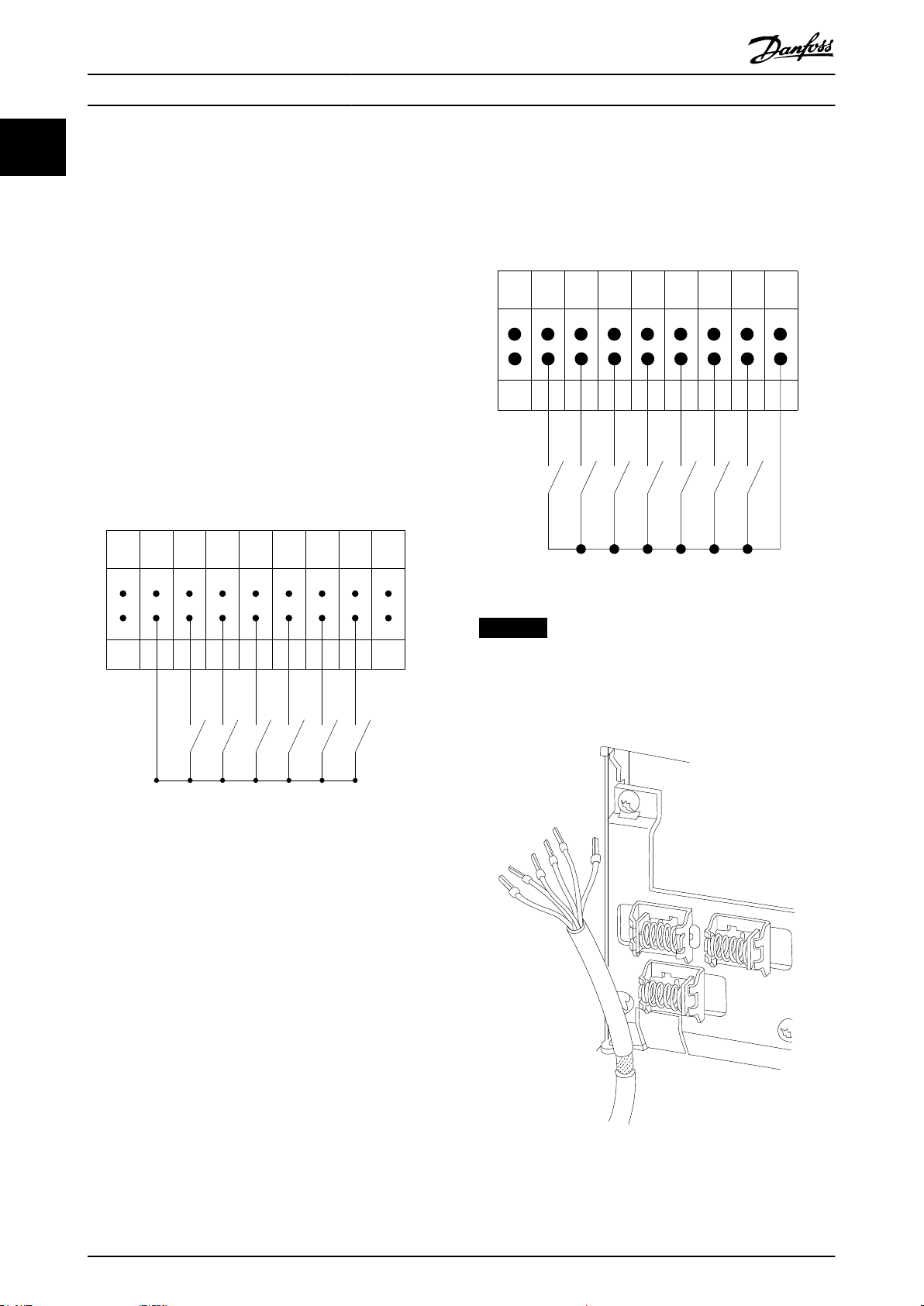
Input polarity of control terminals
Illustration 1.4 NPN (Sink)
Illustration 1.3 PNP (Source)
NOTICE
Control cables must be shielded/armored.
See the section Using Shielded Control Cables in the design
guide for the correct termination of control cables.
Illustration 1.5 Grounding of Shielded/Armored Control Cables
8 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 11
12 18 19
130BD369.11
322927 31 33 20
P 5-12 [0]
P 5-10 [8]
Start/Stop
+24V
Speed
Start
[18]
1312 18 19
130BD370.11
322927 33
P 5 - 12 [6]
P 5 - 10 [9]
+24 V
Speed
Latched start Stop inverse
Latched start (18)
Stop inverse (27)
Introduction Programming Guide
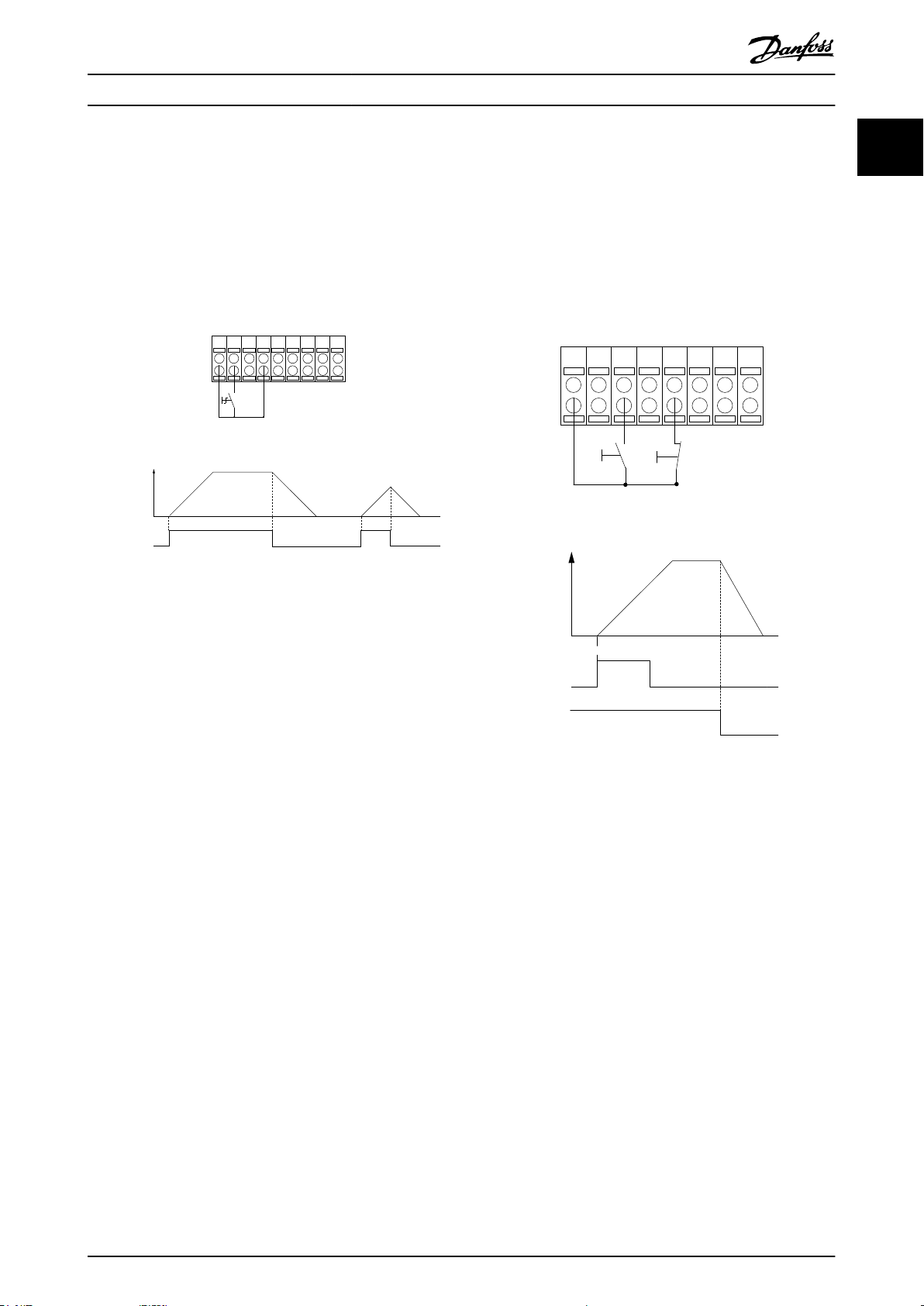
1.3.2 Start/Stop
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input [8]
Start.
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input [0]
No operation (Default coast inverse).
Illustration 1.6 Start/Stop
1.3.3 Latched Start/Stop Inverse
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input [9]
Latched start.
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input [6]
Stop inverse.
1 1
Illustration 1.7 Latched Start/Stop Inverse
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 9
Page 12
FC
+24 V
D IN
D IN
D IN
D IN
D IN
D IN
+10
V
A IN
A IN
COM
A OUT
12
31
18
19
27
29
32
33
50
53
54
55
42
130BF821.10
D IN
130BF873.10
5553 5450
Speed
P 6-15
1 kΩ
+10 V/30 mA
Ref. voltage
P 6-11 10V
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
11
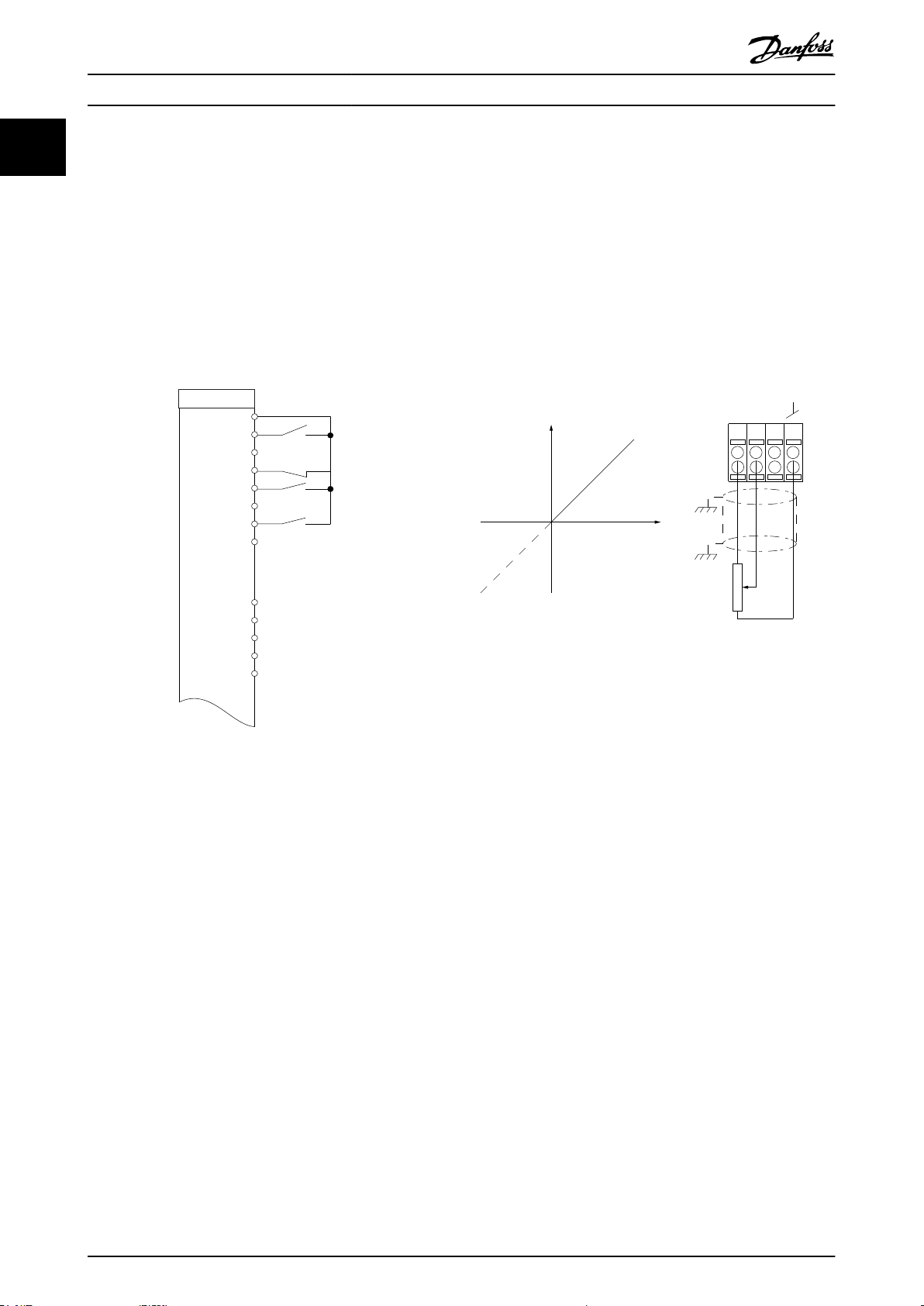
1.3.4 Speed Up/Down
Terminals 29/32=Speed up/down
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital
Input [8] Start (default).
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital
Input [19] Freeze reference.
Terminal 29 = Parameter 5-13 Terminal 29 Digital
Input [21] Speed up.
Terminal 32 = Parameter 5-14 Terminal 32 Digital
1.3.5 Potentiometer Reference
Voltage reference via a potentiometer
Reference source 1 = [1] Analog input 53 (default).
Terminal 53, low voltage = 0 V.
Terminal 53, high voltage = 10 V.
Terminal 53, low ref./feedback = 0.
Terminal 53, high ref./feedback = 50.
Parameter 6-19 Terminal 53 mode = [1] Voltage.
Input [22] Speed down.
Illustration 1.9 Potentiometer Reference
Illustration 1.8 Speed Up/Down
10 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 13
Safety Programming Guide
2 Safety
2.1 Safety Symbols
The following symbols are used in this guide:
WARNING
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that could
result in death or serious injury.
CAUTION
Indicates a potentially hazardous situation that could
result in minor or moderate injury. It can also be used to
alert against unsafe practices.
NOTICE
Indicates important information, including situations that
can result in damage to equipment or property.
2.2 Qualied Personnel
WARNING
UNINTENDED START
When the frequency converter is connected to AC mains,
DC supply, or load sharing, the motor may start at any
time. Unintended start during programming, service, or
repair work can result in death, serious injury, or
property damage. The motor can start via an external
switch, a serial bus command, an input reference signal
from the LCP, or after a cleared fault condition.
To prevent unintended motor start:
Disconnect the frequency converter from the
•
mains.
Press [O/Reset] on the LCP before
•
programming parameters.
Completely wire and assemble the frequency
•
converter, motor, and any driven equipment
before connecting the frequency converter to
AC mains, DC supply, or load sharing.
2 2
Correct and reliable transport, storage, installation,
operation, and maintenance are required for the troublefree and safe operation of the drive. Only qualied
personnel are allowed to install and operate this
equipment.
Qualied personnel are dened as trained sta, who are
authorized to install, commission, and maintain equipment,
systems, and circuits in accordance with pertinent laws and
regulations. Also, the qualied personnel must be familiar
with the instructions and safety measures described in this
manual.
Safety Precautions
2.3
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE
Drives contain high voltage when connected to AC mains
input, DC supply, or load sharing. Failure to perform
installation, start-up, and maintenance by qualied
personnel can result in death or serious injury.
Only qualied personnel must perform instal-
•
lation, start-up, and maintenance.
Before performing any service or repair work,
•
use an appropriate voltage measuring device to
make sure that there is no remaining voltage on
the drive.
WARNING
DISCHARGE TIME
The frequency converter contains DC-link capacitors,
which can remain charged even when the frequency
converter is not powered. High voltage can be present
even when the warning LED indicator lights are o.
Failure to wait the specied time after power has been
removed before performing service or repair work can
result in death or serious injury.
Stop the motor.
•
Disconnect AC mains and remote DC-link power
•
supplies, including battery back-ups, UPS, and
DC-link connections to other frequency
converters.
Disconnect or lock PM motor.
•
Wait for the capacitors to discharge fully. The
•
minimum waiting time is specied in Table 2.1
and is also visible on the product label on top
of the frequency converter.
Before performing any service or repair work,
•
use an appropriate voltage measuring device to
make sure that the capacitors are fully
discharged.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 11
Page 14

Safety
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
Voltage
[V]
22
380–480
380–480
Table 2.1 Discharge Time
Power range
[kW (hp)]
0.37–7.5 kW
(0.5–10 hp)
11–75 kW
(15–100 hp)
Minimum waiting
time
(minutes)
4
15
WARNING
LEAKAGE CURRENT HAZARD
Leakage currents exceed 3.5 mA. Failure to ground the
drive properly can result in death or serious injury.
Ensure the correct grounding of the equipment
•
by a certied electrical installer.
WARNING
EQUIPMENT HAZARD
Contact with rotating shafts and electrical equipment
can result in death or serious injury.
Ensure that only trained and qualied personnel
•
perform installation, start-up, and maintenance.
Ensure that electrical work conforms to national
•
and local electrical codes.
Follow the procedures in this guide.
•
CAUTION
INTERNAL FAILURE HAZARD
An internal failure in the drive can result in serious injury
when the drive is not properly closed.
Ensure that all safety covers are in place and
•
securely fastened before applying power.
NOTICE
HIGH ALTITUDES
For installation at altitudes above 2000 m (6562 ft),
contact Danfoss regarding PELV.
NOTICE
USE ON ISOLATED MAINS
For details about the use of the frequency converter on
isolated mains, refer to the section RFI Switch in the
design guide.
Follow the recommendations regarding the installation
on IT mains. Use relevant monitoring devices for IT
mains to avoid damage.
12 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 15
130BC506.10
Setup 1
A
B
C
D
5
12
13 14 15
10
11
10
9
6
7
8
4
1
2
3
Menu
Status
Quick
Menu
Main
Menu
Hand
On
O
Reset
Auto
On
Back
OK
On
Warn
Alarm
130BD135.10
Setup 1234
INDEX
AHP
VkW
srpm
Hz%
n2n1
n3
p5 p4
p3 p2 p1
Programming Programming Guide
3 Programming
3.1 Local Control Panel Operations
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360 supports numerical local
control panel (NLCP) LCP 21, graphic local control panel
(GLCP) LCP 102, and blind cover. This chapter describes the
operations with LCP 21 and LCP 102.
NOTICE
The frequency converter can also be programmed from
the MCT-10 Set-up Software on PC via RS485 com-port.
This software can be ordered using code number
130B1000 or downloaded from the Danfoss website:
drives.danfoss.com/downloads/pctools/#/.
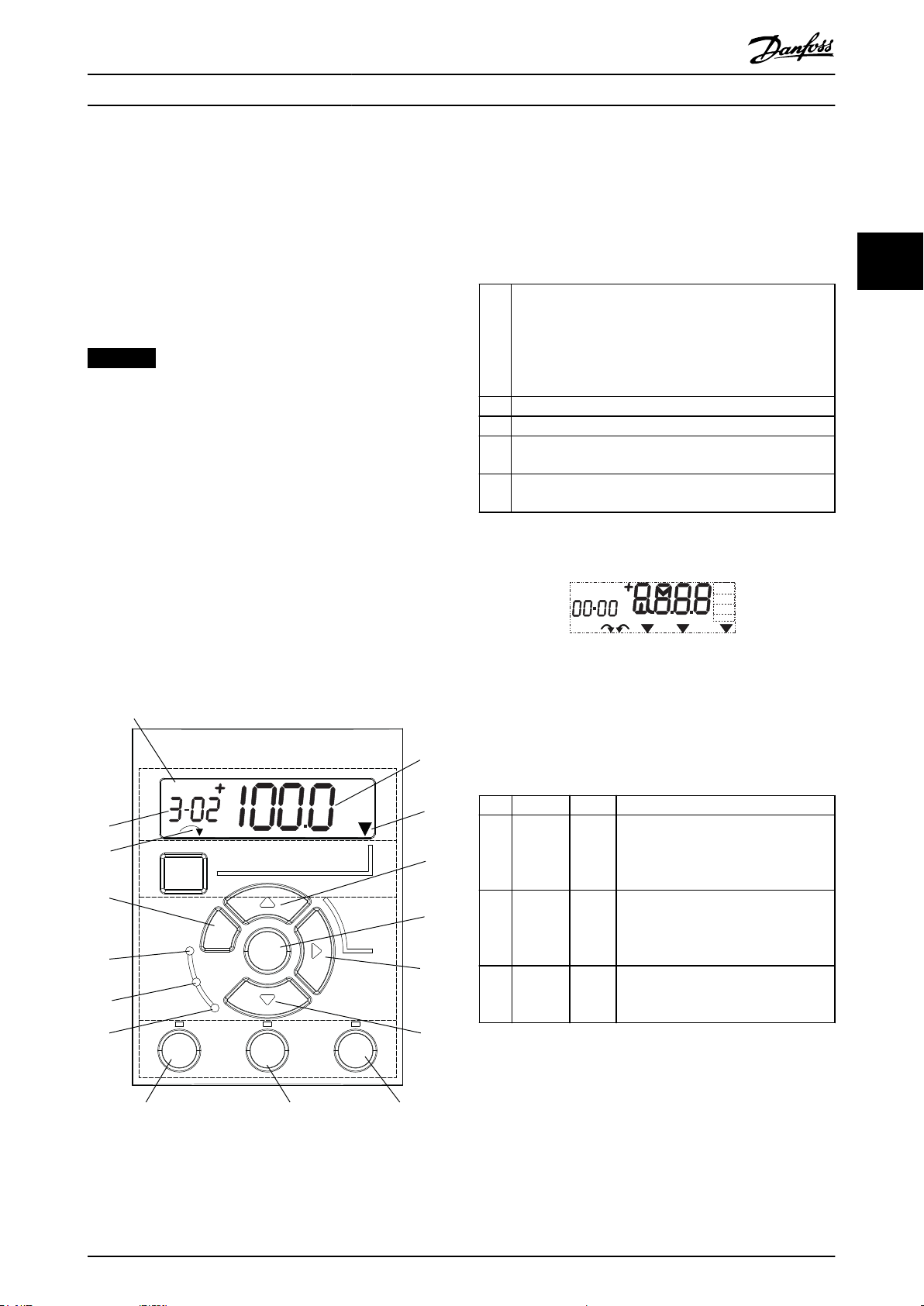
3.1.1 Numerical Local Control Panel
The numerical local control panel LCP 21 is divided into 4
functional sections.
A. Numeric display.
B. Menu key.
C. Navigation keys and indicator lights (LEDs).
D. Operation keys and indicator lights (LEDs).
A. Numeric display
The LCD display is backlit with 1 numeric line. All data is
shown in the LCP.
1 The set-up number shows the active set-up and the edit
set-up. If the same set-up acts as both active and edit setup, only that set-up number is shown (factory setting).
When active and edit set-ups dier, both numbers are
shown in the display (set-up 12). The number ashing
indicates the edit set-up.
2 Parameter number.
3 Parameter value.
4 Motor direction is shown at the bottom left of the display.
A small arrow indicates the direction.
5 The triangle indicates whether the LCP is in Status, Quick
Menu, or Main Menu.
Table 3.1 Legend to Illustration 3.1, Section A
Illustration 3.2 Display Information
3 3
B. Menu key
To select between Status, Quick Menu, or Main Menu,
press [Menu].
C. Indicator lights (LEDs) and navigation keys
Indicator Light Function
ON turns on when the frequency
6 On Green
Illustration 3.1 View of the LCP 21
7 Warn Yellow
8 Alarm Red
Table 3.2 Legend to Illustration 3.1, Indicator Lights (LEDs)
converter receives power from the
mains voltage, a DC bus terminal, or a
24 V external supply.
When warning conditions are met, the
yellow WARN LED turns on, and text
appears in the display area identifying
the problem.
A fault condition causes the red alarm
LED to ash and an alarm text is
shown.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 13
Page 16

130BC440.10
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Programming
Key Function
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
9 [Back]
33
10
11 [OK]
12
Table 3.3 Legend to Illustration 3.1, Navigation Keys
[▲] [▼]
[►]
For moving to the previous step or layer
in the navigation structure.
For switching between parameter groups,
parameters, and within parameters, or
increasing/decreasing parameter values.
Arrows can also be used for setting local
reference.
Press to access parameter groups or to
enable a selection.
Press to move from left to right within
the parameter value to change each digit
individually.
D. Operation keys and indicator lights (LEDs)
Key Function
Starts the frequency converter in local control.
An external stop signal by control input or
13 Hand On
14 O/Reset
15 Auto On
•
serial communication overrides the local
hand on.
Stops the motor but does not remove power
to the frequency converter, or resets the
frequency converter manually after a fault has
been cleared. If in alarm mode, the alarm is
reset if the alarm condition is removed.
Puts the system in remote operational mode.
Responds to an external start command by
•
control terminals or bus communication.
Illustration 3.3 Right-key Function
[►] can also be used for moving between parameter
groups. When in Main Menu, press [►] to move to the rst
parameter in the next parameter group (for example, move
from parameter 0-03 Regional Settings [0] International to
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode [0] Open loop).
Table 3.4 Legend to Illustration 3.1, Section D
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE
Touching the frequency converter after pressing the [O/
Reset] key is still dangerous, because the key does not
disconnect the frequency converter from the mains.
Disconnect the frequency converter from the
•
mains and wait for the frequency converter to
fully discharge. See the discharge time in
Table 2.1.
3.1.2 The Right-key Function on NLCP
Press [►] to edit any of the 4 digits on the display
individually. When pressing [►] once, the cursor moves to
the rst digit and the digit starts ashing as shown in
Illustration 3.3. Press the [▲] [▼] to change the value.
Pressing [►] does not change the value of the digits or
move the decimal point.
3.1.3 Quick Menu on NLCP
The Quick Menu gives easy access to the most frequently
used parameters.
1. To enter Quick Menu, press [Menu] until the
indicator in the display is placed above Quick
Menu.
2.
Press [▲] [▼] to select either QM1 or QM2, then
press [OK].
3.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameters in
Quick Menu.
4. Press [OK] to select a parameter.
5.
Press [▲] [▼] to change the value of a parameter
setting.
6. Press [OK] to accept the change.
7. To exit, press either [Back] twice (or 3 times if in
QM2 and QM3) to enter Status, or press [Menu]
once to enter Main Menu.
14 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 17
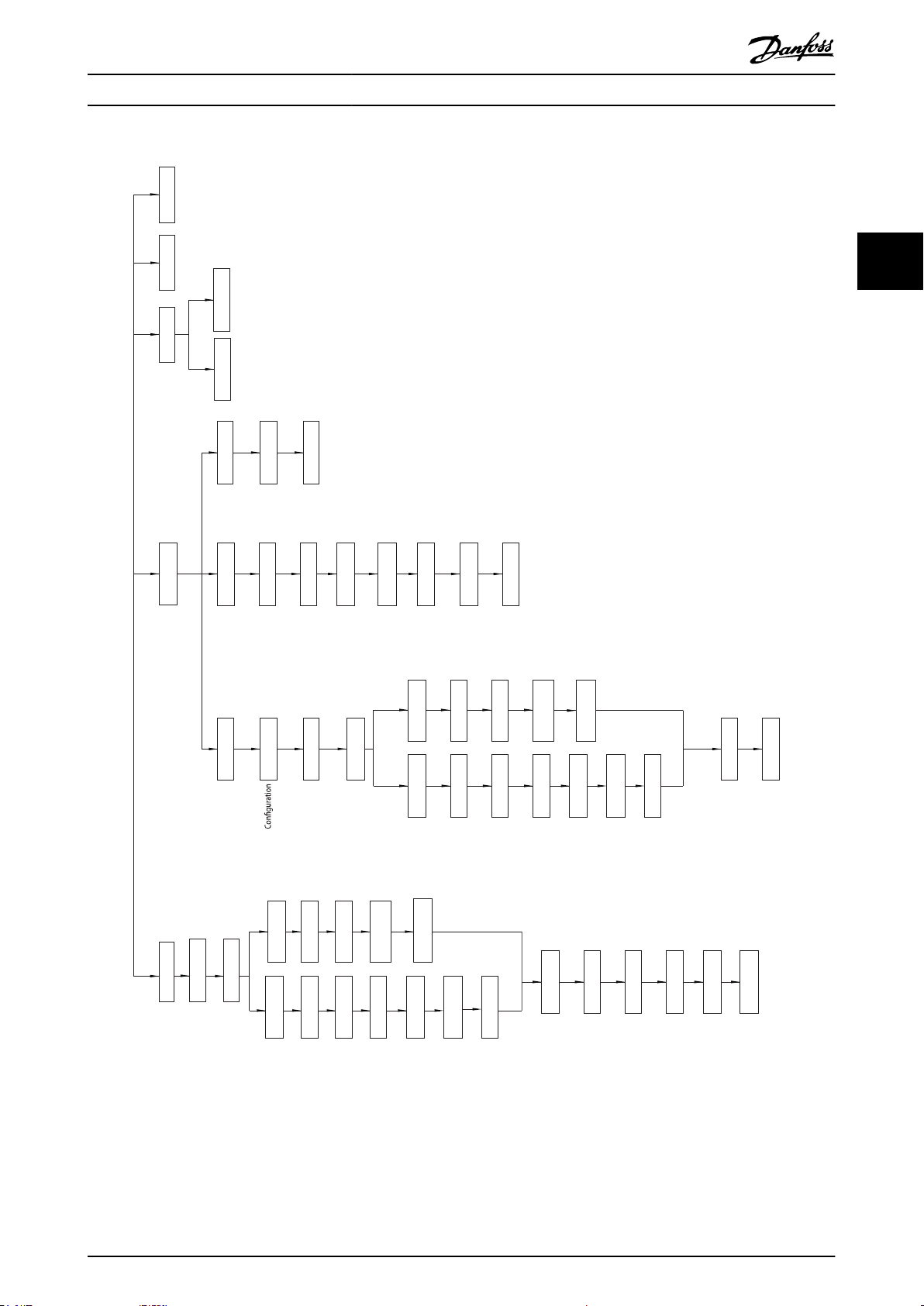
130BC445.13
1-22 XXXX V
Motor
nominal
speed
QM 1
0-01 [0]
1-10 [0]
1-24 XXXX A
Language
Motor Type
1-20 XXXX kW
Motor power
Motor voltage
1-26 XXXX 1-23 XXXX
Stator
Motor frequency
1-25 XXXX
1-30 XXXX
1-39 XXXX
1-40 XXXX
1-37 XXXX
1-25 XXXX
1-24 XXXX
A
3-02 XXXX
3-03 XXXX
3-41 XXXX S
3-42 XXXX S
5-12
[2]
1-29 [1]
AMA
Back EMF at
1000 RPM
d-axis
QM 2
BMS
AMS
ES
5-70 XXXX
5-71 [0]
1-30 XXXX
1-39 XXXX
1-90 [0]
2-10 [0]
4-16 XXXX %
4-17 XXXX %
4-18 XXXX %
1-00 [0]
1-01 [1]
1-10 [0]
1-24 XXXX A 1-20 XXXX kW
1-22 XXXX V
Motor
nominal
speed
Motor power
Motor voltage
1-26 XXXX 1-23 XXXX
Motor frequency
1-25 XXXX
1-30 XXXX
1-40 XXXX
1-37 XXXX
1-25 XXXX
1-24 XXXX
A
Back EMF at
1000 RPM
d-axis
1-39 XXXX
4-14 XXXX
4-19 XXXX
Stator
QM 3
QM 4 QM 5
L10C
SFS
TBD
Motor
nominal
speed
Motor
nominal
speed
Motor current
Motor cont.
rated torque
Resistance (Rs)
Motor poles
inductance (Ld)
Asynchronous motor
Motor current
Minimum reference
Maximum reference
Ramp 1 ramp-up time
Ramp 1 ramp-down time
Terminal 27 digital input
Basic motor set-up
mode
Motor control
principle
Motor type
PM motor
PM motor
Motor
current
Motor cont.
rated torque
Stator
Resistance (Rs)
Motor poles
inductance (Ld)
Motor speed high limit [Hz]
Maximum output frequency
Asynchronous motor
Motor current
RPM
RPM
RPM
Hz
RPM
Hz
Hz
Hz
Hz
Hz
Adv. motor set-up
Resistance (Rs)
Motor poles
Motor thermal
protection
Brake function
Torque limit motor mode
Torque limit generator mode
Current limit
Encoder set-up
Terminal 32/33
pulses per revolution
Terminal 32/33
encoder direction
Changes made
Last 10 changes Since factory setting
Alarm log
Programming Programming Guide
3 3
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 15
Illustration 3.4 Quick Menu Structure
Page 18

130BA466.10
Programming
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
3.1.4 Status Menu on NLCP
After power-up, Status Menu is active. Press [Menu] to
toggle between Status, Quick Menu, and Main Menu.
33
[▲] and [▼] toggle between the options in each menu.
The display indicates the status mode with a small arrow
above Status.
Illustration 3.5 Indicating Status Mode
The following 8 parameters can be accessed from the NLCP
status menu in auto-on mode:
Parameter 16-02 Reference [%].
•
Parameter 16-09 Custom Readout.
•
Parameter 16-10 Power [kW].
•
Parameter 16-13 Frequency.
•
Parameter 16-14 Motor current.
•
Parameter 16-16 Torque [Nm].
•
Parameter 16-30 DC Link Voltage.
•
Parameter 16-52 Feedback[Unit].
•
The following 6 parameters can be accessed from the NLCP
status menu in [Hand On] mode:
Parameter 16-09 Custom Readout.
•
Parameter 16-10 Power [kW].
•
Parameter 16-13 Frequency.
•
Parameter 16-14 Motor current.
•
Parameter 16-16 Torque [Nm].
•
Parameter 16-30 DC Link Voltage.
•
3.1.5 Main Menu on NLCP
The Main Menu gives access to all parameters.
1. To enter Main Menu, press [Menu] until the
indicator in the display is placed above Main
Menu.
2.
[▲] [▼]: Browse through the parameter groups.
3. Press [OK] to select a parameter group.
4.
[▲] [▼]: Browse through the parameters in the
specic group.
5. Press [OK] to select the parameter.
6.
[►] and [▲] [▼]: Set/change the parameter value.
7. Press [OK] to accept the value.
8. To exit, press either [Back] twice (or 3 times for
array parameters) to enter Main Menu, or press
[Menu] once to enter Status.
See Illustration 3.6, Illustration 3.7, and Illustration 3.8 for the
principles of changing the value of continuous,
enumerated, and array parameters, respectively. The
actions in the illustrations are described in Table 3.5,
Table 3.6, and Table 3.7.
16 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 19
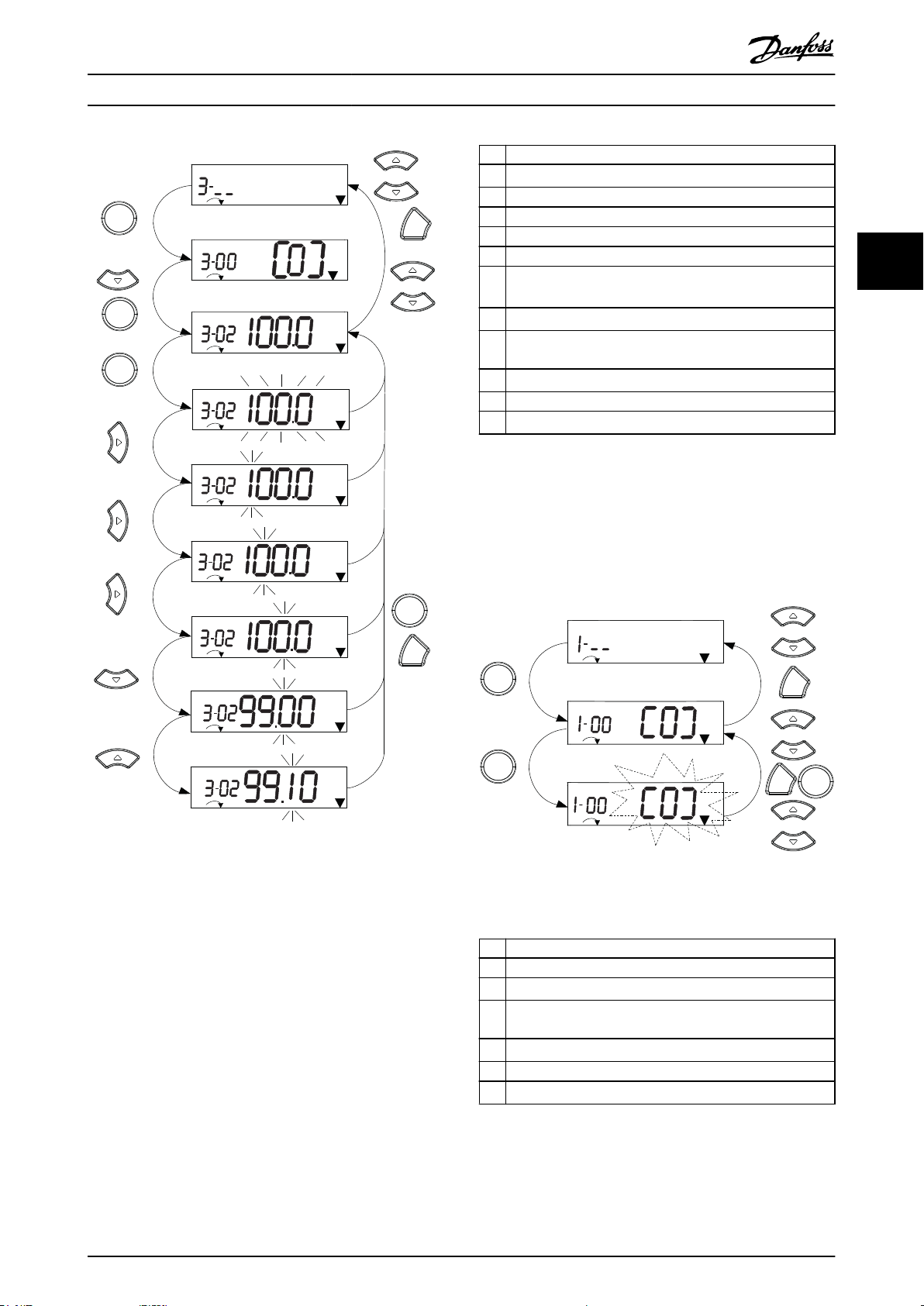
130BC446.10
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
10
11
12
OK
OK
Back
8
Back
Setup 1
2 x
+
OK
9
OK
130BC447.11
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
1
2
3
4
5
6
OK
OK
Back
7
OK
Back
Programming Programming Guide
1 [OK]: The rst parameter in the group is shown.
2
Press [▼] repeatedly to move down to the parameter.
3 Press [OK] to start editing.
4
[►]: First digit ashing (can be edited).
5
[►]: Second digit ashing (can be edited).
6
[►]: Third digit ashing (can be edited).
7
[▼]: Decreases the parameter value, the decimal point
changes automatically.
8
[▲]: Increases the parameter value.
9 [Back]: Cancel changes, return to 2.
[OK]: Accept changes, return to 2.
10
[▲][▼]: Select parameter within the group.
11 [Back]: Removes the value and shows the parameter group.
12
[▲][▼]: Select group.
Table 3.5 Changing Values in Continuous Parameters
For enumerated parameters, the interaction is similar, but
the parameter value is shown in brackets because of the
LCP 21 digits limitation (4 large digits), and the enum can
be greater than 99. When the enum value is greater than
99, the LCP 21 can only show the
rst part of the bracket.
3 3
Illustration 3.6 Main Menu Interactions - Continuous
Parameters
Illustration 3.7 Main Menu Interactions - Enumerated
Parameters
1 [OK]: The rst parameter in the group is shown.
2 Press [OK] to start editing.
3
[▲][▼]: Change parameter value (ashing).
4 Press [Back] to cancel changes or [OK] to accept changes
(return to screen 2).
5
[▲][▼]: Select a parameter within the group.
6 [Back]: Removes the value and shows the parameter group.
7
[▲][▼]: Select a group.
Table 3.6 Changing Values in Enumerated Parameters
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 17
Page 20
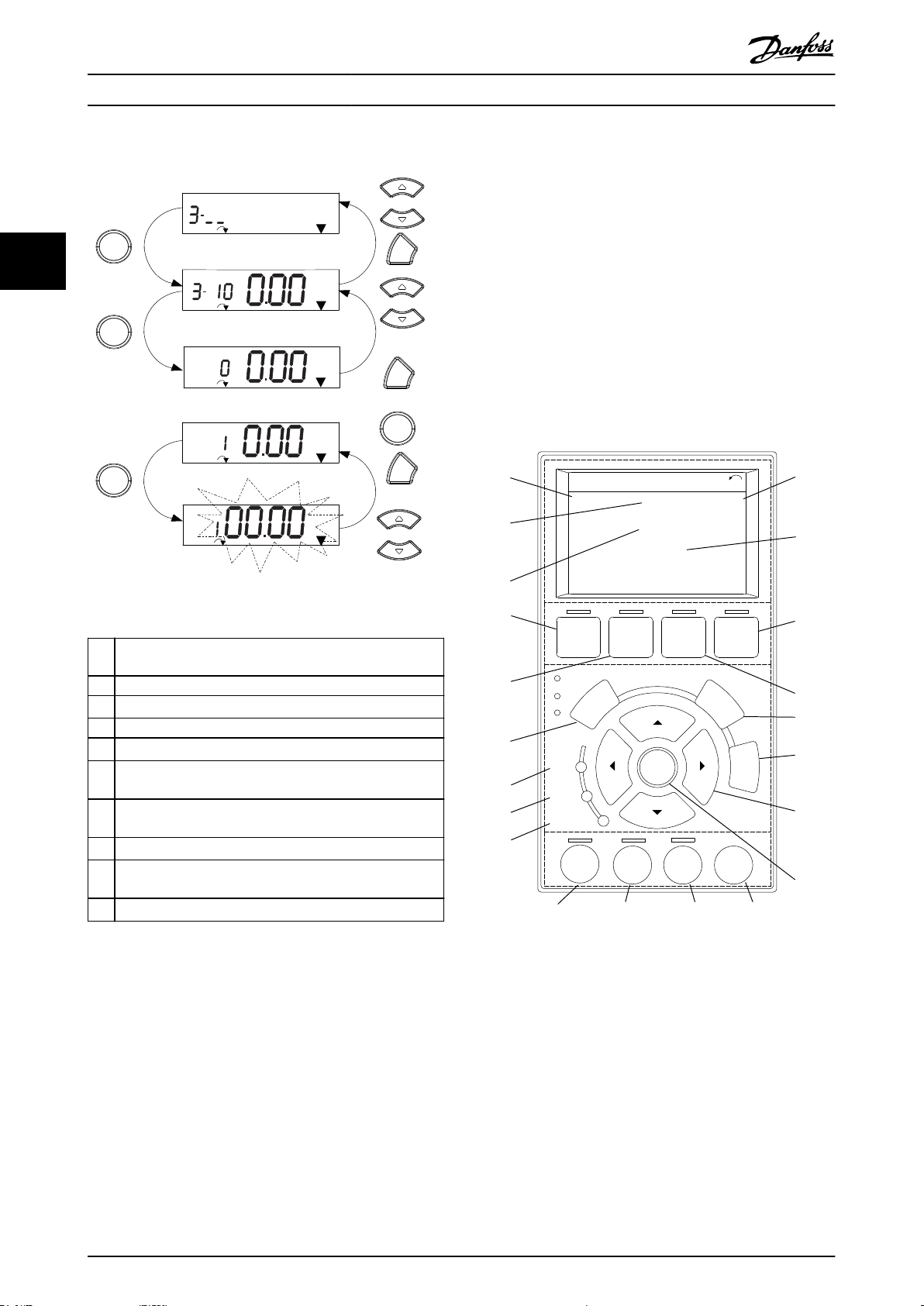
130BC448.10
1
2
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
OK
Back
Back
Back
5 x
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
Setup 1
%
INDEX
%
INDEX
%
INDEX
Setup 1
INDEX
%
OK
OK
OK
130BD598.10
Auto
On
Reset
Hand
On
O
Status
Quick
Menu
Main
Menu
Alarm
Log
Back
Cancel
Info
OK
Status
1(1)
36.4 kW
Auto Remote Ramping
0.000
On
Alarm
Warn.
A
7.83 A
799 RPM
B
C
D
53.2 %
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18 19 20 21
Programming
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
Array parameters function as follows:
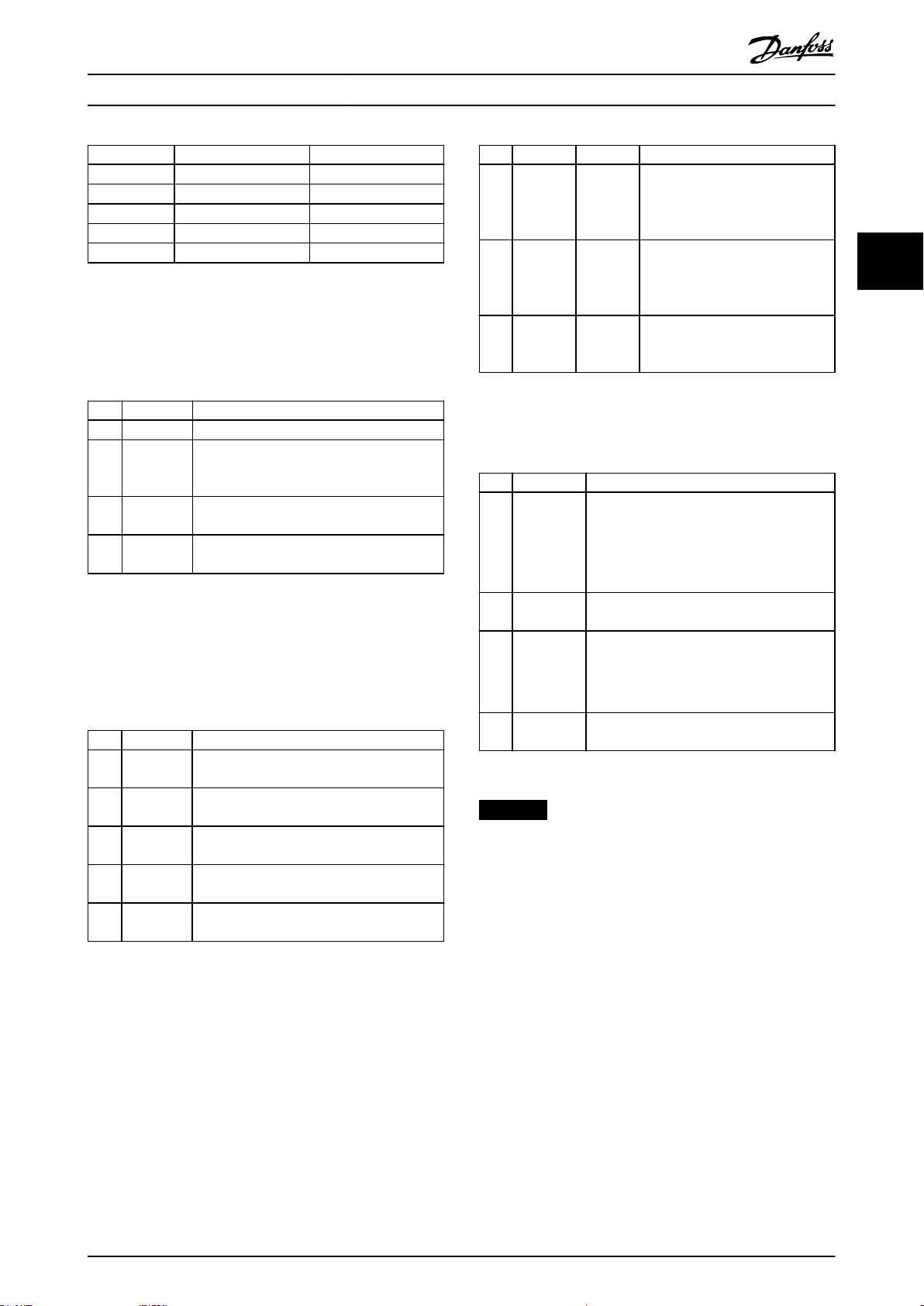
3.1.6 Graphical Local Control Panel
The graphical local control panel LCP 102 has a larger
display area, which shows more information than LCP 21.
LCP 102 supports English, Chinese, and Portuguese
displays.
33
The GLCP is divided into 4 functional groups (see
Illustration 3.9).
A. Display area.
B. Display menu keys.
C. Navigation keys and indicator lights (LEDs).
D. Operation keys and reset.
Illustration 3.8 Main Menu Interactions - Array Parameters
1 [OK]: Shows parameter numbers and the value in the rst
index.
2 [OK]: Index can be selected.
3
[▲][▼]: Select index.
4 [OK]: Value can be edited.
5
[▲][▼]: Change parameter value (ashing).
6 [Back]: Cancels changes.
[OK]: Accepts changes.
7 [Back]: Cancels editing index, a new parameter can be
selected.
8
[▲][▼]: Select parameter within the group.
9 [Back]: Removes parameter index value and shows the
10
Table 3.7 Changing Values in Array Parameters
18 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
parameter group.
[▲][▼]: Select group.
Illustration 3.9 Graphic Local Control Panel (GLCP)
A. Display area
The display area is activated when the frequency converter
receives power from the mains voltage or a DC bus
terminal.
The information shown on the LCP can be customized for
user applications. Select options in the Quick Menu Q3-13
Display Settings.
Page 21
Programming Programming Guide
Display Parameter number Default setting
1 0-20 [1602] Reference [%]
2 0-21 [1614] Motor Current
3 0-22 [1610] Power [kW]
4 0-23 [1613] Frequency
5 0-24 [1502] kWh Counter
Table 3.8 Legend to Illustration 3.9, Display Area
B. Display menu keys
Menu keys are used for menu access for parameter set-up,
toggling through status display modes during normal
operation, and viewing fault log data.
Key Function
6 Status Shows operational information.
Quick
7
Menu
8 Main Menu
9 Alarm Log
Table 3.9 Legend to Illustration 3.9, Display Menu Keys
Allows access to programming parameters
for initial set-up instructions and many
detailed application instructions.
Allows access to all programming
parameters.
Shows a list of current warnings, the last 10
alarms, and the maintenance log.
C. Navigation keys and indicator lights (LEDs)
Navigation keys are used for programming functions and
moving the display cursor. The navigation keys also
provide speed control in local operation. There are also 3
frequency converter status indicator lights in this area.
Key Function
10 Back
11 Cancel
12 Info
Navigation
13
14 OK
keys
Reverts to the previous step or list in the
menu structure.
Cancels the last change or command as long
as the display mode has not changed.
Press for a denition of the function being
shown.
To move between items in the menu, use the
4 navigation keys.
Press to access parameter groups or to
enable a selection.
Indicator Light Function
ON turns on when the frequency
15 On Green
16 Warn Yellow
17 Alarm Red
Table 3.11 Legend to Illustration 3.9, Indicator Lights (LEDs)
converter receives power from the
mains voltage or a DC bus
terminal.
When warning conditions are met,
the yellow WARN LED turns on,
and text appears in the display
area identifying the problem.
A fault condition causes the red
alarm LED to ash, and an alarm
text is shown.
D. Operation keys and reset
Operation keys are at the bottom of the LCP.
Key Function
Starts the frequency converter in hand-on
mode.
An external stop signal by control input
18 Hand On
19 O
20 Auto On
21 Reset
Table 3.12 Legend to Illustration 3.9, Operation Keys and Reset
•
or serial communication overrides the
local hand on.
Stops the motor but does not remove power
to the frequency converter.
Puts the system in remote operational mode.
Responds to an external start command
•
by control terminals or serial communication.
Resets the frequency converter manually
after a fault has been cleared.
NOTICE
To adjust the display contrast, press [Status] and the
[▲]/[▼] keys.
3 3
Table 3.10 Legend to Illustration 3.9, Navigation Keys
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 19
Page 22
130BD532.10
Programming
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
3.1.7 Changing Parameter Settings with
GLCP
Access and change parameter settings from the Quick
Menu or from the Main Menu. The Quick Menu only gives
access to a limited number of parameters.
33
1. Press [Quick Menu] or [Main Menu] on the LCP.
2.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameter
groups, press [OK] to select a parameter group.
3.
Press [▲] [▼] to browse through the parameters,
press [OK] to select a parameter.
4.
Press [▲] [▼] to change the value of a parameter
setting.
5.
Press [◄] [►] to shift digit when a decimal
parameter is in the editing state.
6. Press [OK] to accept the change.
7. Press either [Back] twice to enter Status, or press
[Main Menu] once to enter the Main Menu.
View changes
Quick Menu Q5 - Changes Made lists all parameters
changed from default settings.
The list only shows parameters which have been
•
changed in the current edit set-up.
Parameters which have been reset to default
•
values are not listed.
The message Empty indicates that no parameters
•
have been changed.
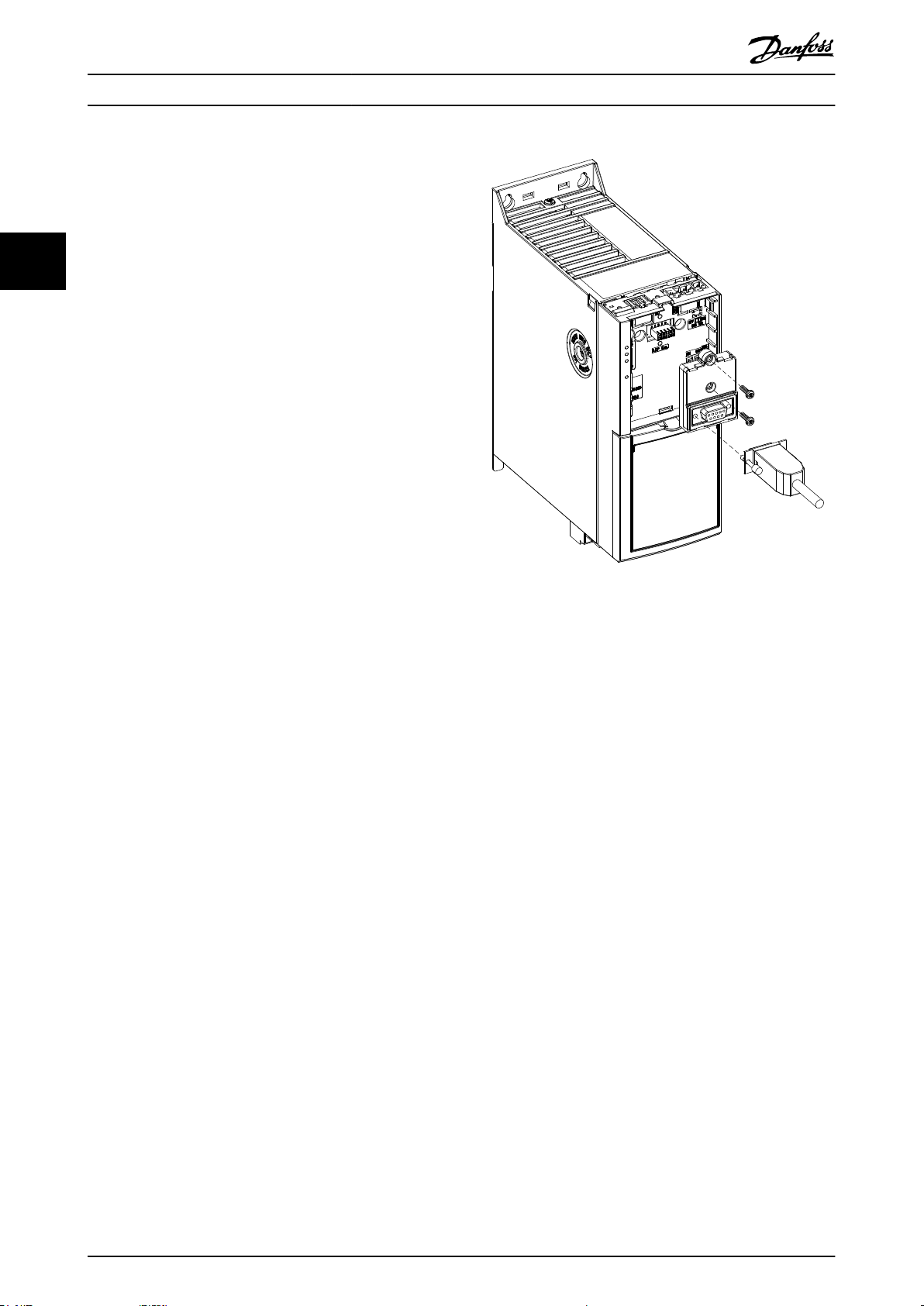
3.1.8 Mounting the GLCP
Use the GLCP adapter (ordering number: 132B0281) and a
cable to connect the LCP 102 to the frequency converter,
as shown in Illustration 3.10.
Illustration 3.10 GLCP Adapter and Connecting Cable
3.1.9 Backing Up/Downloading Parameters
with LCP
Establishing the correct programming for applications
often requires setting functions in several related
parameters. Parameter details are provided in
chapter 4 Parameter Descriptions.
Programming data is stored internally in the frequency
converter.
For back-up, upload data into the LCP memory.
•
To download data to another frequency
•
converter, connect the LCP to that unit and
download the stored settings.
Restoring factory default settings does not
•
change data stored in the LCP memory.
Back-up/download process
1. Press [O] on the GLCP or [O Reset] on the
NLCP to stop the motor before uploading or
downloading data.
2. Press [Main Menu] parameter 0-50 LCP Copy and
press [OK].
3. Select [1] All to LCP to upload data to the LCP, or
select [2] All from LCP to download data from the
LCP, or select [3] Size indep. from LCP to download
motor size independent parameters from LCP.
20 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 23

Programming Programming Guide
4. Press [OK]. A progress bar shows the uploading or
downloading progress.
5. Press [Hand On] or [Auto On] to return to normal
operation.
3.1.10 Restoring Default Settings with LCP
NOTICE
Risk of losing programming, motor data, localization, and
monitoring records by restoration of default settings. To
provide a back-up, upload data to the LCP before initialization.
Restoring the default parameter settings is done by initialization of the frequency converter. Initialization is carried
out through parameter 14-22 Operation Mode
(recommended) or manually. Initialization does not reset
the settings for parameter 1-06 Clockwise Direction and
parameter 0-03 Regional Settings.
Initialization using parameter 14-22 Operation
•
Mode does not reset frequency converter settings,
such as operating hours, serial communication
selections, fault log, alarm log, and other
monitoring functions.
Manual initialization erases all motor,
•
programming, localization, and monitoring data,
and restores factory default settings.
Recommended initialization procedure, via
parameter 14-22 Operation Mode
1. Select parameter 14-22 Operation Mode and press
[OK].
2. Select [2] Initialisation and press [OK].
3. Remove power to the unit and wait until the
display turns
4. Apply power to the unit.
Default parameter settings are restored during start-up.
This may take slightly longer than normal.
5. Alarm 80, Drive initialized to default value is shown.
6. Press [Reset] to return to operating mode.
Manual initialization procedure
1. Remove power to the unit and wait until the
display turns o.
2. Press and hold [Status], [Main Menu], and [OK] at
the same time on the GLCP, or press [Menu] and
[OK] at the same time on the NLCP while
applying power to the unit (approximately 5 s or
until a click is heard and the fan starts).
Factory default parameter settings are restored during
start-up. This may take slightly longer than normal.
o.
Manual initialization does not reset the following
frequency converter information:
Parameter 0-03 Regional Settings
•
Parameter 1-06 Clockwise Direction
•
Parameter 15-00 Operating hours
•
Parameter 15-03 Power Up's
•
Parameter 15-04 Over Temp's
•
Parameter 15-05 Over Volt's
•
Parameter 15-30 Alarm Log: Error Code
•
3.2 Basic Programming
3.2.1 Asynchronous Motor Set-up
Enter the following motor data in the listed order. Find the
information on the motor nameplate.
1. Parameter 1-20 Motor Power.
2. Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage.
3. Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency.
4. Parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
5. Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed.
For optimum performance in VVC+ mode, extra motor data
is required to set up the following parameters.
6. Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs).
7. Parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr).
8. Parameter 1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1).
9. Parameter 1-35 Main Reactance (Xh).
The data is found in the motor datasheet (this data is
typically not available on the motor nameplate). Run a
complete AMA using parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor
Adaption (AMA) [1] Enable Complete AMA or enter the
parameters manually.
Application-specic adjustment when running VVC
VVC+ is the most robust control mode. In most situations,
it provides optimum performance without further
adjustments. Run a complete AMA for best performance.
3.2.2
PM Motor Set-up in VVC
Initial programming steps
1. Set parameter 1-10 Motor Construction to the
following options to activate PM motor operation:
1a [1] PM, non salient SPM
1b [3] PM, salient IPM
2. Select [0] Open Loop in parameter 1-00 Congu-
ration Mode.
+
+
3 3
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 21
Page 24
Programming
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
NOTICE
Encoder feedback is not supported for PM motors.
Programming motor data
When the initial programming steps are completed, the PM
33
motor-related parameters in parameter groups 1-2* Motor
Data, 1-3* Adv. Motor Data, and 1-4* Adv. Motor Data II are
active.
The information is on the motor nameplate and in the
motor datasheet.
Program the following parameters in the listed order:
1. Parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
2. Parameter 1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque.
3. Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed.
4. Parameter 1-39 Motor Poles.
5. Parameter 1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM.
6. Parameter 1-42 Motor Cable Length.
Run a complete AMA using parameter 1-29 Automatic
Motor Adaption (AMA) and select [1] Enable Complete AMA.
If a complete AMA is not performed successfully, congure
the following parameters manually.
1. Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs).
Enter phase common stator winding resistance
(Rs). If only phase-to-phase data is available,
divide the phase-to-phase value by 2 to achieve
the phase value.
It is also possible to measure the value with an
ohmmeter, which also takes the resistance of the
cable into account. Divide the measured value by
2 and enter the result.
2. Parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld).
Enter direct axis inductance of the PM motor.
If only phase-to-phase data is available, divide the
phase-to-phase value by 2 to achieve the phase
value.
It is also possible to measure the value with an
inductance meter, which also takes the
inductance of the cable into account. Divide the
measured value by 2 and enter the result.
3. Parameter 1-38 q-axis Inductance (Lq).
This parameter is active only when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to [3] PM,
salient IPM.
Enter the quadrature axis inductance of the PM
motor. If only phase-to-phase data is available,
divide the phase-to-phase value by 2 to achieve
the phase value.
It is also possible to measure the value with an
inductance meter, which also takes the
inductance of the cable into account. Make 1
rotation of the motor’s rotor and nd the
Test motor operation
Rotor detection
This function is the recommended selection for
applications where the motor starts from standstill, for
example pumps or conveyors. For some motors, a sound is
heard when the frequency converter performs the rotor
detection. This sound does not harm the motor. Adjust the
value in parameter 1-46 Position Detection Gain for dierent
motors. If the frequency converter fails to start, or an
overcurrent alarm occurs when the frequency converter
starts, check if the rotor is blocked or not. If the rotor is
not blocked, set parameter 1-70 Start Mode to [1] Parking
and try again.
Parking
This function is the recommended option for applications
where the motor is rotating at low speed, for example
windmilling in fan applications. Parameter 2-06 Parking
Current and parameter 2-07 Parking Time are adjustable.
Increase the factory setting of these parameters for
applications with high inertia.
Start the motor at nominal speed. If the application does
not run well, check the VVC+ PM settings. Table 3.13 shows
recommendations in dierent applications.
maximum phase-to-phase inductance value.
Divide the value by 2 and enter the result.
4. Parameter 1-44 d-axis Inductance Sat. (LdSat).
This parameter is active only when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to [3] PM,
salient IPM.
This parameter corresponds to the saturation
inductance of d-axis. The default value is the
value set in parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld).
Do not change the default value in most cases. If
the motor supplier provides the saturation curve,
enter the d-axis inductance value, which is 100%
of the nominal current.
5. Parameter 1-45 q-axis Inductance Sat. (LqSat).
This parameter is active only when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to [3] PM,
salient IPM.
This parameter corresponds to the saturation
inductance of q-axis. The default value is the
value set in parameter 1-38 q-axis Inductance (Lq).
In most cases, do not change the default. If the
motor supplier provides the saturation curve,
enter the q-axis inductance value, which is 100%
of the nominal current.
1. Start the motor at low speed (100–200 RPM). If
the motor does not run, check installation,
general programming, and motor data.
2. Check if the start function in parameter 1-70 Start
Mode ts the application requirements.
22 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 25
Programming Programming Guide
Application Settings
Low inertia applications
1)
I
Load
Medium inertia
applications
50>I
High inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
High load at low speed
<30% (rated speed)
Table 3.13 Recommendations in Dierent Applications
1) I
2) I
2)
/I
<5
Motor
Load/IMotor
Load
Motor
>5
> 50
= The inertia of load.
= The inertia of motor.
Increase the value for
•
parameter 1-17 Voltage lter time
const. by factor 5 to 10.
Reduce the value for
•
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain.
Reduce the value (<100%) for
•
parameter 1-66 Min. Current at
Low Speed.
Keep calculated values.
Increase the values for
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain,
parameter 1-15 Low Speed Filter Time
Const., and parameter 1-16 High
Speed Filter Time Const.
Decrease parameter 1-17 Voltage
lter time const.
Decrease parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed (>100% for longer time
can overheat the motor).
To run AMA using the numeric LCP
1. By default parameter setting, connect terminals
12 and 27 before running AMA.
2. Enter the Main Menu.
3. Go to parameter group 1-** Load and Motor.
4. Press [OK].
5. Set motor parameters using nameplate data for
parameter group 1-2* Motor Data.
6. Set parameter 1-39 Motor Poles for IM and PM.
7. Set parameter 1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM for PM.
8. Set motor cable length in parameter 1-42 Motor
Cable Length.
9. Go to parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor Adaptation
(AMA).
10. Press [OK].
11. Select [1] Enable complete AMA.
12. Press [OK].
13. Press [Hand On] to activate AMA.
14. The test runs automatically and indicates when it
is complete.
Depending on the power size, the AMA takes 3–10
minutes to complete.
3 3
If the motor starts oscillating at a certain speed, increase
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain. Increase the value in small
steps.
Adjust the starting torque in parameter 1-66 Min. Current at
Low Speed. 100% provides nominal torque as starting
torque.
3.2.3 Automatic Motor Adaptation (AMA)
It is highly recommended to run AMA because it measures
the electrical characteristics of the motor to optimize
compatibility between the frequency converter and the
motor under VVC+ mode.
The frequency converter builds a mathematical
•
model of the motor for regulating output motor
current, thus enhancing motor performance.
Some motors are unable to run the complete
•
version of the test. In that case, select Enable
reduced AMA (not for PM).
If warnings or alarms occur, see
•
chapter 6.1.3 Warning/alarm Messages.
Run this procedure on a cold motor for best
•
results.
NOTICE
The AMA function does not cause the motor to run, and
it does not harm the motor.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 23
Page 26
Parameter Descriptions
4 Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.1 Parameters: 0-** Operation and Display
Parameters related to the basic functions of the frequency
converter, function of the LCP keys, and conguration of
the LCP display.
44
0-06 GridType
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Not all options are supported in
all power sizes.
4.1.1 0-0* Basic Settings
IT grid is a supply mains where the
0-01 Language
Option: Function:
[0] * English
[10] Chinese
[28] Portuguese
0-03 Regional Settings
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while
the motor is running.
[0] Interna-
tional
[1] US Activate parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW] for
0-04 Operating State at Power-up (Hand)
Option: Function:
[0] Resume Restart the frequency converter, maintaining
[1] * Forced stop,
ref=old
[2] Forced stop,
ref=0
Activate parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW] for
setting the motor power in kW and set the
default value of parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency
to 50 Hz.
setting the motor power in hp and set the default
value of parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency to 60 Hz.
Select the operating mode upon
reconnection of the frequency converter to
mains voltage after power-down in hand-on
mode.
the start/stop settings (applied by [Hand On/
O]) selected before power-down of the
frequency converter.
Restart the frequency converter with a saved
local reference after mains voltage reappears
and after pressing [Hand On].
Reset the local reference to 0 upon restarting
the frequency converter.
[10] 380-440V/50Hz/IT-
grid
[11] 380-440V/50Hz/
Delta
[12] 380-440V/50Hz
[20] 440-480V/50Hz/IT-
grid
[21] 440-480V/50Hz/
Delta
[22] 440-480V/50Hz
[110] 380-440V/60Hz/IT-
grid
[111] 380-440V/60Hz/
Delta
[112] 380-440V/60Hz
[120] 440-480V/60Hz/IT-
grid
[121] 440-480V/60Hz/
Delta
[122] 440-480V/60Hz
0-07 Auto DC Braking
Option: Function:
Protective function against overvoltage at coast in IT
grid environment. This parameter is active only when
[1] On is selected in this parameter.
[0] O This function is not active.
[1] * On This function is active.
neutral point of secondary side of the
transformer is not connected to
ground.
Delta is a supply mains where the
secondary part of the transformer is
delta-connected and 1 phase is
connected to ground.
0-06 GridType
Option: Function:
Select the grid type of the supply
voltage/frequency.
24 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 27
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.1.2 0-1* Set-up Operations
Dene and control the individual parameter set-ups.
The frequency converter has 2 parameter set-ups that can
be programmed independently of each other. This makes
the frequency converter exible and able to solve
advanced control functionality problems, often saving the
cost of external control equipment. For example, the 2 setups can be used to program the frequency converter to
operate according to 1 control scheme in 1 set-up (for
example, motor 1 for horizontal movement) and another
control scheme in another set-up (for example, motor 2 for
vertical movement). Alternatively, they can be used by an
OEM machine builder to program all their factory-tted
frequency converters for dierent machine types within a
range to have the same parameters and then during
production/commissioning simply select a specic set-up,
depending on which machine the frequency converter is
installed on.
The active set-up (that is, the set-up in which the
frequency converter is operating) can be selected in
parameter 0-10 Active Set-up and is shown in the LCP. By
selecting [9] Multi set-up, it is possible to switch between
set-ups with the frequency converter running or stopped,
via digital input or serial communication commands. If it is
necessary to change set-ups while running, ensure that
parameter 0-12 Link Setups is set as required. Use
parameter 0-11 Programming Set-up to edit parameters
within any of the set-ups while continuing the operation of
the frequency converter in its active set-up, which can be a
dierent set-up to that being edited. Use
parameter 0-51 Set-up Copy to copy parameter settings
between the set-ups to enable quicker commissioning if
similar parameter settings are required in dierent set-ups.
0-10 Active Set-up
Option: Function:
Select the set-up in which the frequency converter
is to operate. Select parameter 0-51 Set-up Copy to
copy a set-up to 1 or all set-ups. To avoid
conicting settings of the same parameter within
2 dierent set-ups, link the set-ups together in
parameter 0-12 Link Setups. Stop the frequency
converter before switching between set-ups where
the parameters marked Not changeable during
operation have dierent values. Parameters which
are Not changeable during operation are marked
FALSE in the parameter lists in chapter 5 Parameter
Lists.
[1] * Set-up1Set-up 1 is active.
[2] Set-up2Set-up 2 is active.
[9] Multi
Set-up
This option is used for remote set-up selections
via digital inputs and the serial communication
port. This set-up uses the settings from
parameter 0-12 Link Setups.
0-11 Programming Set-up
Option: Function:
Select the set-up to be programmed during
operation; either the active set-up or the
inactive set-up. The set-up number being
edited ashes in the LCP.
[1] Set-up 1 [1] Set-up 1 to [2] Set-up 2 can be edited freely
during operation, independently of the active
set-up.
[2] Set-up 2
[9] * Active
Set-up
The set-up in which the frequency converter is
operating can also be edited during operation.
0-12 Link Setups
Option: Function:
The link ensures synchronizing of the Not
changeable during operation parameter values
enabling shift from 1 set-up to another during
operation.
If the set-ups are not linked, a change between
them is not possible while the motor is running.
Thus the set-up change does not occur until the
motor is coasted.
[0] Not
linked
[20] * Linked Copy Not changeable during operation
Leave parameters unchanged in both set-ups.
These parameters cannot be changed while the
motor is running.
parameters from 1 set-up to the other, so they
are identical in both set-ups.
0-14 Readout: Edit Set-ups / Channel
Range: Function:
0* [-2147483647 -
2147483647 ]
View the setting of
parameter 0-11 Programming Set-up. Edit
set-up for each communication channel. A
means active set-up; F means factory;
numbers indicate set-up code. Communication channels from right to left are LCP,
FC-bus, USB, and HPFB1-5.
0-16 Application Selection
Option: Function:
Select integrated application
functions. When an application
is selected, a set of related
parameters are set automatically.
[0] * None
[1] Simple Process Close Loop
[2] Local/Remote
[3] Speed Open Loop
[4] Simple Speed Close Loop
[5] Multi Speed
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 25
Page 28
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
0-16 Application Selection
Option: Function:
[6] OGD LA10
[7] OGD V210
[8] Hoist
[9] Hoist Speed Close Loop
4.1.3 0-2* LCP Display
44
Use parameters in this group to dene the variables that
are shown in the GLCP. Parameter 16-17 Speed [RPM] is 1
option for each parameter in parameter group 0-2* LCP
Display.
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, left position.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[748] PCD Feed Forward
[953] Probus Warning Word
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] * Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW ]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom. Current
[1637] Inv. Max. Current
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, left position.
Option: Function:
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1890] Process PID Error
[1891] Process PID Output
[1892] Process PID Clamped Output
[1893] Process PID Gain Scaled Output
[2117] Ext. 1 Reference [Unit]
[2118] Ext. 1 Feedback [Unit]
[2119] Ext. 1 Output [%]
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
26 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 29

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, left position.
Option: Function:
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
0-21 Display Line 1.2 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, middle position.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[748] PCD Feed Forward
[953] Probus Warning Word
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] * Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom. Current
[1637] Inv. Max. Current
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
0-21 Display Line 1.2 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, middle position.
Option: Function:
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1890] Process PID Error
[1891] Process PID Output
[1892] Process PID Clamped Output
[1893] Process PID Gain Scaled Output
[2117] Ext. 1 Reference [Unit]
[2118] Ext. 1 Feedback [Unit]
[2119] Ext. 1 Output [%]
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 27
Page 30
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, right position.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[748] PCD Feed Forward
44
[953] Probus Warning Word
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] * Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom. Current
[1637] Inv. Max. Current
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable to be shown in line 1, right position.
Option: Function:
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1890] Process PID Error
[1891] Process PID Output
[1892] Process PID Clamped Output
[1893] Process PID Gain Scaled Output
[2117] Ext. 1 Reference [Unit]
[2118] Ext. 1 Feedback [Unit]
[2119] Ext. 1 Output [%]
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
28 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 31

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable to be shown in line 2.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[748] PCD Feed Forward
[953] Probus Warning Word
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW ]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] * Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom. Current
[1637] Inv. Max. Current
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable to be shown in line 2.
Option: Function:
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1890] Process PID Error
[1891] Process PID Output
[1892] Process PID Clamped Output
[1893] Process PID Gain Scaled Output
[2117] Ext. 1 Reference [Unit]
[2118] Ext. 1 Feedback [Unit]
[2119] Ext. 1 Output [%]
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 29
Page 32

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Select a variable to be shown in line 3.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[748] PCD Feed Forward
44
[953] Probus Warning Word
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] * kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW ]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom. Current
[1637] Inv. Max. Current
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Select a variable to be shown in line 3.
Option: Function:
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1890] Process PID Error
[1891] Process PID Output
[1892] Process PID Clamped Output
[1893] Process PID Gain Scaled Output
[2117] Ext. 1 Reference [Unit]
[2118] Ext. 1 Feedback [Unit]
[2119] Ext. 1 Output [%]
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
30 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 33

130BD380.10
0
Custom Readout (Value)
P 16-09
Custom Readout
Unit P 0-30
Max value
P 0-32
Min value
P 0-31
Motor Speed
Motor Speed
High limit
P 4-14 (Hz)
Linear Unit (e.g. Speed and flow)
Quadratic Unit (Pressure)
Cubic Unit (Power)
Liniar
units only
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.1.4 0-3* LCP Custom Readout
It is possible to customize the display elements in the LCP.
Custom readout
The calculated value to be shown is based on settings in
parameter 0-30 Custom Readout Unit,
parameter 0-31 Custom Readout Min Value (linear only),
parameter 0-32 Custom Readout Max Value,
parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz], and actual
speed.
Illustration 4.1 Custom Readout
The relation depends on the type of unit selected in
parameter 0-30 Custom Readout Unit:
Unit type Speed relation
Dimensionless
Speed
Flow, volume
Flow, mass
Velocity
Length
Temperature
Pressure Quadratic
Power Cubic
Table 4.1 Relation between Unit Type and Speed
Linear
0-30 Custom Readout Unit
Option: Function:
Set a value to be shown in the LCP. The value has
a linear, squared, or cubed relation to speed. This
relation depends on the unit selected. See
Table 4.1. The actual calculated value can be read
in parameter 16-09 Custom Readout.
[0] None
[1] * %
[5] PPM
[10] 1/min
[11] RPM
[12] Pulse/s
[20] l/s
[21] l/min
[22] l/h
[23] m³/s
[24] m³/min
[25] m³/h
[30] kg/s
[31] kg/min
[32] kg/h
[33] t/min
[34] t/h
[40] m/s
[41] m/min
[45] m
[60] °C
[70] mbar
[71] bar
[72] Pa
[73] kPa
[74] m WG
[80] kW
[120] GPM
[121] gal/s
[122] gal/min
[123] gal/h
[124] CFM
[127] ft³/h
[140] ft/s
[141] ft/min
[160] °F
[170] psi
[171] lb/in2
[172] in WG
[173] ft WG
[180] HP
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 31
Page 34

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
0-31 Custom Readout Min Value
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUnit*
44
[ 0 -
999999.99
CustomReadoutUnit]
This parameter sets the
minimum value of the custom
readout (occurs at 0 speed). It is
only possible to select a value
dierent from 0 when selecting a
linear unit in
parameter 0-30 Custom Readout
Unit. For quadratic and cubic
units, the minimum value is 0.
0-44 [O/Reset] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Select [0] Disabled to avoid accidental stop
or reset of the frequency converter from
LCP. Setting can be locked by
parameter 0-60 Main Menu Password.
[1] * Enabled
[7] Enable Reset
Only
4.1.6 0-5* Copy/Save
0-32 Custom Readout Max Value
Range: Function:
100 CustomReadoutUnit*
[ 0.0 -
999999.99
CustomReadoutUnit]
This parameter sets the
maximum value to be shown
when the motor speed has
reached the value set in
parameter 4-14 Motor Speed
High Limit [Hz].
0-37 Display Text 1
Range: Function:
[0 - 0 ] Free text, for example used for the device tag of
eldbus application.
0-38 Display Text 2
Range: Function:
[0 - 0 ] Free text, for example used for the location tag of
eldbus application.
0-39 Display Text 3
Range: Function:
[0 - 0 ] Free text, for example used for the help tag of
eldbus application.
4.1.5 0-4* LCP Keypad
Enable, disable, and password protect individual keys on
the LCP.
0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Avoid accidental start of the frequency converter
in hand-on mode.
[1] * Enabled [Hand On] is enabled.
0-42 [Auto on] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Avoid accidental start of the freqeuncy converter
from LCP.
[1] * Enabled [Hand On] is enabled.
Copy parameters from and to the NLCP and GLCP. Use
these parameters for saving and copying set-ups from 1
frequency converter to another.
0-50 LCP Copy
Option: Function:
[0] * No copy No function.
[1] All to LCP Copy all parameters in all set-ups from the
frequency converter memory to the LCP. For
service purposes, copy all parameters to the
LCP after commissioning.
[2] All from
LCP
[3] Size indep.
from LCP
Copy all parameters in all set-ups from the LCP
memory to the frequency converter memory.
Copy only the parameters that are
independent of the motor size. This selection
can be used to program several frequency
converters with the same function without
disturbing motor data that is already set.
0-51 Set-up Copy
Option: Function:
[0] * No copy No function.
[1] Copy from
setup 1
[2] Copy from
setup 2
[9] Copy from
Factory setup
Copy from set-up 1 to set-up 2.
Copy from set-up 2 to set-up 1.
Copy factory setting to programming setup (selected in parameter 0-11 Programming
Set-up).
4.1.7 0-6* Password
0-60 Main Menu Password
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 999 ] Dene the password for access to the Main Menu
via the [Main Menu] key. Setting values to 0
disables the password function.
32 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 35

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.2 Parameters: 1-** Load and Motor
4.2.1 1-0* General Settings
1-00 Conguration Mode
Option: Function:
Select the application control principle to be
used when a remote reference (that is, via
analog input or eldbus) is active.
[0]*Open Loop Enables speed control (without feedback signal
from motor) with automatic slip compensation
for almost constant speed at varying loads.
Compensations are active, but can be disabled
in parameter group 1-** Load and Motor.
[1] Speed
closed loop
[2] Torque
closed loop
[3] Process
Closed
Loop
[4] Torque
open loop
[6] Surface
Winder
[7] Extended
PID Speed
OL
Enables speed closed-loop control with
feedback. For increased speed accuracy,
provide a feedback signal and set the speed
PID control. The speed control parameters are
set in parameter group 7-0* Speed PID Control.
Enables torque closed-loop control with speed
feedback. Only possible when option [1] VVC
is selected in parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle.
Enables the use of process control in the
frequency converter. The process control
parameters are set in parameter group 7-2*
Process Ctrl. Feedback and parameter group 7-3*
Process PID Ctrl.
Enables the use of torque open loop in VVC+
mode (parameter 1-01 Motor Control Principle).
The torque PID parameters are set in parameter
group 7-1* Torque PI Control.
Enables the use of surface winder control.
Specic parameters in parameter group 7-2*
Process Ctrl. Feedb. and parameter group 7-3*
Process PID Ctrl.
Enables the use of extended PID speed OL.
Specic parameters in parameter group 7-2*
Process Ctrl. Feedb. to parameter group 7-5* Ext.
Process PID Ctrl.
1-01 Motor Control Principle
Option: Function:
[0] U/f
NOTICE
When running U/f, control slip and load
compensations are not included.
Used for parallel-connected motors and/or special
motor applications. Set the U/f settings in
[1] * VVC+
parameter 1-55 U/f Characteristic - U and
parameter 1-56 U/f Characteristic - F.
NOTICE
4 4
When parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is
set to PM-enabled options, only VVC+ option
is available.
Normal running mode, including slip and load
compensations.
1-03 Torque Characteristics
+
Option: Function:
Select the torque characteristic required. VT
and AEO are both energy-saving operations.
[0] * Constant
torque
[1] Variable
Torque
[2] Auto Energy
Optim. CT
Motor shaft output provides constant torque
under variable speed control.
Motor shaft output provides variable torque
under variable speed control. Set the variable
torque level in parameter 14-40 VT Level.
Automatically optimizes energy consumption
by minimizing magnetization and frequency
via parameter 14-41 AEO Minimum Magneti-
sation.
1-06 Clockwise Direction
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while
the motor is running.
This parameter denes the term clockwise
corresponding to the LCP direction arrow. Used for
easy change of direction of shaft rotation without
swapping motor wires.
[0] * Normal The motor shaft turns in clockwise direction when
frequency converter is connected U⇒U; V⇒V; and
W⇒W to motor.
[1] Inverse The motor shaft turns in counterclockwise
direction when frequency converter is connected
U⇒U; V⇒V; and W⇒W to motor.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 33
Page 36

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
1-08 Motor Control Bandwidth
Option: Function:
[0] High Suitable for high dynamic response.
[1] * Medium Suitable for smooth steady-state operation.
[2] Low Suitable for smooth steady-state operation with
lowest dynamic response.
1-08 Motor Control Bandwidth
Option: Function:
[3] Adaptive 1 Optimized for smooth steady-state operation,
with extra active damping.
[4] Adaptive 2 Focus on low-inductance PM motors. This
option is an alternative to [3] Adaptive 1.
4.2.2 1-1* Motor Selection
44
Parameter group for setting general motor data. The parameters cannot be adjusted while the motor is running.
The active parameters are shown in Table 4.2. x indicates that a particular parameter is active when the option is selected.
Parameter 1-10 Motor Construction [0] Asynchron [1] PM, non salient SPM [3] PM, salient IPM
Parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode x x x
Parameter 1-03 Torque Characteristics x
Parameter 1-06 Clockwise Direction x x x
Parameter 1-08 Motor Control Bandwidth x x x
Parameter 1-14 Damping Gain x x
Parameter 1-15 Low Speed Filter Time Const. x x
Parameter 1-16 High Speed Filter Time Const. x x
Parameter 1-17 Voltage lter time const. x x
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW] x
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage x
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency x
Parameter 1-24 Motor Current x x x
Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed x x x
Parameter 1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque x x
Parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor Adaption (AMA) x x x
Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs) x x x
Parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr) x
Parameter 1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1) x
Parameter 1-35 Main Reactance (Xh) x
Parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld) x x
Parameter 1-38 q-axis Inductance (Lq) x
Parameter 1-39 Motor Poles x x x
Parameter 1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM x x
Parameter 1-42 Motor Cable Length x x x
Parameter 1-43 Motor Cable Length Feet x x x
Parameter 1-44 d-axis Inductance Sat. (LdSat) x
Parameter 1-45 q-axis Inductance Sat. (LqSat) x
Parameter 1-46 Position Detection Gain x x
Parameter 1-48 Current at Min Inductance for d-axis x
Parameter 1-49 Current at Min Inductance for q-axis x
Parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation at Zero Speed x
Parameter 1-52 Min Speed Normal Magnetising [Hz] x
Parameter 1-55 U/f Characteristic - U x
Parameter 1-56 U/f Characteristic - F x
Parameter 1-60 Low Speed Load Compensation x
Parameter 1-61 High Speed Load Compensation x
Parameter 1-62 Slip Compensation x
Parameter 1-63 Slip Compensation Time Constant x
Parameter 1-64 Resonance Dampening x
Parameter 1-65 Resonance Dampening Time Constant x
34 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 37

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
Parameter 1-10 Motor Construction [0] Asynchron [1] PM, non salient SPM [3] PM, salient IPM
Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low Speed x x
Parameter 1-70 Start Mode x x
Parameter 1-71 Start Delay x x x
Parameter 1-72 Start Function x x x
Parameter 1-73 Flying Start x x x
Parameter 1-80 Function at Stop x x x
Parameter 1-88 AC Brake Gain x
Parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection x x x
Parameter 2-00 DC Hold Current x x x
Parameter 2-01 DC Brake Current x x x
Parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time x x x
Parameter 2-04 DC Brake Cut In Speed [Hz] x x x
Parameter 2-06 Parking Current x x
Parameter 2-07 Parking Time x x
Parameter 2-10 Brake Function x x x
Parameter 2-16 AC brake Max. Current x
Parameter 2-17 Over-voltage Control x x x
Parameter 4-10 Motor Speed Direction x x x
Parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz] x x x
Parameter 4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode x
Parameter 4-17 Torque Limit Generator Mode x
Parameter 4-18 Current Limit x x x
Parameter 4-19 Max Output Frequency x x x
Parameter 4-58 Missing Motor Phase Function x x x
Parameter 14-01 Switching Frequency x x x
Parameter 14-03 Overmodulation x x x
Parameter 14-07 Dead Time Compensation Level x x x
Parameter 14-08 Damping Gain Factor x x x
Parameter 14-09 Dead Time Bias Current Level x x x
Parameter 14-10 Mains Failure x
Parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level x
Parameter 14-12 Response to Mains Imbalance x x x
Parameter 14-27 Action At Inverter Fault x x x
Parameter 14-40 VT Level x
Parameter 14-41 AEO Minimum Magnetisation x
Parameter 14-50 RFI Filter x x x
Parameter 14-51 DC-Link Voltage Compensation x x x
Parameter 14-55 Output Filter x x x
Parameter 14-64 Dead Time Compensation Zero Current Level x x x
Parameter 14-65 Speed Derate Dead Time Compensation x x x
Parameter 30-22 Locked Rotor Protection x x
Parameter 30-23 Locked Rotor Detection Time [s] x x
4 4
Table 4.2 Active Parameters
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 35
Page 38

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
1-10 Motor Construction
4.2.3 1-2* Motor Data
Option: Function:
[0] * Asynchron For asynchronous motors.
[1] PM, non
salient SPM
44
[3] PM, salient
IPM
For permanent magnet (PM) motors with
surface-mounted (non-salient) magnets.
Refer to parameter 1-14 Damping Gain to
parameter 1-17 Voltage lter time const. for
details about optimizing the motor
operation.
For permanent magnet (PM) motors with
interior (salient) magnets.
1-14 Damping Gain
Range: Function:
120%* [ 0 -
250 %]
The damping gain stabilizes the PM machine.
The value of damping gain controls the dynamic
performance of the PM machine. High damping
gain gives high dynamic performance, and low
damping gain gives low dynamic performance.
The dynamic performance is related to the
machine data and load type. If the damping gain
is too high or low, the control becomes unstable.
1-15 Low Speed Filter Time Const.
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0.01 - 20s]This time constant is used below
10% rated speed. Obtain quick
control through a short damping
time constant. However, if this value
is too short, the control becomes
unstable.
1-16 High Speed Filter Time Const.
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0.01 - 20s]This time constant is used above
10% rated speed. Obtain quick
control through a short damping
time constant. However, if this value
is too short, the control becomes
unstable.
1-17 Voltage lter time const.
This parameter group comprises input data from the
nameplate on the connected motor.
NOTICE
Changing the value of these parameters aects the
setting of other parameters.
1-20 Motor Power
Option: Function:
[2] 0.12 kW - 0.16 hp
[3] 0.18 kW - 0.25 hp
[4] 0.25 kW - 0.33 hp
[5] 0.37 kW - 0.5 hp
[6] 0.55 kW - 0.75 hp
[7] 0.75 kW - 1 hp
[8] 1.1 kW - 1.5 hp
[9] 1.5 kW - 2 hp
[10] 2.2 kW - 3 hp
[11] 3 kW - 4 hp
[12] 3.7 kW - 5 hp
[13] 4 kW - 5.4 hp
[14] 5.5 kW - 7.5 hp
[15] 7.5 kW - 10 hp
[16] 11 kW - 15 hp
[17] 15 kW - 20 hp
[18] 18.5 kW - 25 hp
[19] 22 kW - 30 hp
[20] 30 kW - 40 hp
[21] 37 kW - 50 hp
[22] 45 kW - 60 hp
[23] 55 kW - 75 hp
[24] 75 kW - 100 hp
[25] 90 kW - 120 hp
1-22 Motor Voltage
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[50 - 1000V]Enter the nominal motor voltage
according to the motor nameplate
data. The default value corresponds to
the nominal rated output of the unit.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.001 - 1s]Reduces the inuence of high
frequency ripple and system
resonance in the calculation of supply
voltage. Without this lter, the ripples
in the currents can distort the
calculated voltage and aect the
stability of the system.
36 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 39

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-23 Motor Frequency
Range: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while the motor is running.
Size
related*
[ 20 -
Select the motor frequency value from the
500
motor nameplate. For 87 Hz operation with
Hz]
230/440 V motors, set the value according to
the nameplate data for 230 V/50 Hz. Adapt
parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz] and
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference to the 87
Hz application.
1-24 Motor Current
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 -
1000.00 A]
Enter the nominal motor current
value from the motor nameplate
data. This data is used for calculating
motor torque, motor thermal
protection, and so on.
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
Range: Function:
Size related* [50 - 60000
RPM]
Enter the nominal motor speed
value from the motor nameplate
data. This data is used for
calculating automatic motor
compensations.
1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.1 -
10000.0
Nm]
Enter the value from the motor
nameplate data. The default value
corresponds to the nominal rated output.
This parameter is available when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set
to [1] PM, non salient SPM or [3] PM,
salient IPM, that is, the parameter is valid
for PM, non-salient SPM and PM, salient
IPM motors only.
1-29 Automatic Motor Adaption (AMA)
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while
the motor is running.
1-29 Automatic Motor Adaption (AMA)
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Terminal 27 digital input
(parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input)
has coast inverse as the default setting.
This setting means that AMA cannot be
performed if terminal 27 is switched o.
The AMA function optimizes dynamic motor
performance by automatically optimizing the
advanced motor parameters.
[0]*O No function.
[1] Enable
Complete
AMA
[2] Enable
Reduced
AMA
Depending on the option selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction, the AMA is
performed on dierent parameters.
If [0] Asynchron is selected, the AMA is
•
performed on:
- Parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs).
- Parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance
(Rr).
- Parameter 1-33 Stator Leakage
Reactance (X1).
- Parameter 1-35 Main Reactance
(Xh).
If [1] PM, non-salient SPM is selected,
•
the AMA is performed on:
- Parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs).
- Parameter 1-37 d-axis
Inductance (Ld).
If [3] PM, salient IPM is selected, the
•
AMA is performed on:
- Parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs).
- Parameter 1-37 d-axis
Inductance (Ld).
- Parameter 1-38 q-axis
Inductance (Lq).
- Parameter 1-44 d-axis
Inductance Sat. (LdSat).
- Parameter 1-45 q-axis
Inductance Sat. (LqSat).
Perform a reduced AMA of the stator resistance
Rs (parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)) in the
system only. If an LC lter is used between the
frequency converter and the motor, select this
option. (This option is only for asynchronous
motors.)
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 37
Page 40

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
When parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to options
that enable permanent motor mode, the only option
available is [1] Enable Complete AMA.
Activate the AMA function by pressing [Hand On] after
selecting [1] Enable Complete AMA or [2] Enable Reduced
AMA. After a normal sequence, the display reads: Press [OK]
to nish AMA. After pressing [OK], the frequency converter
is ready for operation.
44
NOTICE
For the best adaptation of the frequency
•
converter, run AMA on a cold motor.
AMA cannot be performed while the motor is
•
running.
NOTICE
Avoid generating external torque during AMA.
If an LC lter is used, set the frequency converter to run in
U/f control mode (recommended), or perform reduced
AMA in VVC+ mode. If an LC lter is not used, perform
complete AMA.
1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr)
Range: Function:
motor. The default setting is calculated
by the frequency converter from the
motor nameplate data.
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
1-35 Main Reactance (Xh)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0 -
9999.000
Ohm]
[ 0.0 -
9999.00
Ohm]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Set the stator leakage reactance
value. Obtain the value from a motor
datasheet or perform an AMA on a
cold motor. The default setting is
calculated by the frequency converter
from the motor nameplate data.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while the motor is running.
4.2.4 1-3* Adv. Motor Data I
Set parameters for advanced motor data. The motor data
in parameters 1-30 to 1-39 must match the motor for
optimal performance. If the motor data is not known,
running an AMA is recommended.
1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0 -
9999.000
Ohm]
[ 0 -
9999.000
Ohm]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Set the stator resistance value. Enter
the value from a motor datasheet
or perform an AMA on a cold
motor.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Enter the rotor resistance value. Obtain
the value from a motor datasheet or
by performing an AMA on a cold
Set the main reactance of the motor using
1 of these methods:
Run an AMA on a cold motor.
•
The frequency converter
measures the value from the
motor.
Enter the Xh value manually.
•
Obtain the value from the motor
supplier.
Use the Xh default setting. The
•
frequency converter establishes
the setting based on the motor
nameplate data.
1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 65535
mH]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Enter the value of the d-axis
inductance. Obtain the value from the
permanent magnet motor datasheet
or perform an AMA on a cold motor.
38 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 41

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-38 q-axis Inductance (Lq)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.000 65535 mH]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Set the value of the q-axis
inductance. Find the value in the
motor datasheet or perform an AMA
on a cold motor.
1-39 Motor Poles
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[2 100 ]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while the motor is running.
Enter the number of motor poles.
The motor pole value is always an even
number, because it refers to the total pole
numbers, not pairs of poles.
1-42 Motor Cable Length
Range: Function:
50 m* [0 - 100 m] Set the motor cable length in meters.
1-43 Motor Cable Length Feet
Range: Function:
164 ft* [0 - 328 ft] Set the motor cable length. The length unit
is foot.
1-44 d-axis Inductance Sat. (LdSat)
Range: Function:
Size
related
[ 0 65535
mH]
This parameter is active only when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to
[3] PM, salient IPM.
This parameter corresponds to the saturation
inductance of d-axis. The default value is the
value set in parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance
(Ld). In most cases, do not change the
default value. If the motor supplier provides
the saturation curve, enter the d-axis
inductance value, which is under 100% of
the nominal current or perform an AMA on a
cold motor.
4 4
4.2.5 1-4* Adv. Motor Data II
Set parameters for advanced motor data.
1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 1 9000 V]
Set the nominal back EMF for the motor
when running at 1000 RPM.
Back EMF is the voltage generated by a PM
motor when no frequency converter is
connected and the shaft is turned
externally. Back EMF is normally specied
for nominal motor speed or for 1000 RPM
measured between 2 lines. If the value is
not available for a motor speed of 1000
RPM, calculate the correct value as follows:
If back EMF is, for example, 320 V at 1800
RPM, it can be calculated at 1000 RPM:
Example
Back EMF 320 V at 1800 RPM. Back EMF =
(Voltage/RPM)*1000 = (320/1800)*1000 =
178.
This parameter is only active when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to
options that enable PM (permanent
magnet) motors.
NOTICE
When using PM motors, it is
recommended to use brake resistors.
1-45 q-axis Inductance Sat. (LqSat)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 65535
mH]
This parameter is active only when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to
[3] PM, salient IPM.
This parameter corresponds to the q-axis
saturation inductance. The default value is
the value set in parameter 1-38 q-axis
Inductance (Lq). In most cases, do not
change the default value. If the motor
supplier provides the saturation curve, enter
the q-axis inductance value, which is under
100% of the nominal current or perform an
AMA on a cold motor.
1-46 Position Detection Gain
Range: Function:
100 %* [ 20 -
200 %]
Adjust the amplitude of the test pulse
during position detection at start. Adjust
this parameter to improve the position
measurement.
1-48 Current at Min Inductance for d-axis
Range: Function:
100 % [ 20 - 200 %] Use this parameter to set the inductance
saturation point.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 39
Page 42

Magn. current
130BB780.10
Hz
Par.1-50
90%
Par.1-52
Motor Voltage
Par 1-55 [x]
Output Frequency
Par 1-56 [x]
1-55[5]
1-55[4]
1-55[3]
1-55[2]
1-55[1]
1-55[0]
1-56
[0]
1-56
[1]
1-56
[2]
1-56
[3]
1-56
[4]
1-56
[5]
130BA166.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
1-49 Current at Min Inductance for q-axis
Range: Function:
100 % [ 20 -
200 %]
44
This parameter species the saturation curve of
the q-inductance values. From 20–100% of this
parameter, the inductance is linearly
approximated due to parameter 1-38 q-axis
Inductance (Lq) and parameter 1-45 q-axis
Inductance Sat. (LqSat). These parameters are
related to the motor nameplate load compensations, the application load type, and the
1-56 U/f Characteristic - F
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 -
500.0
Hz]
Enter frequency points to form a U/f characteristic which matches the motor. Voltage at
each point is dened in parameter 1-55 U/f
Characteristic - U.
Make a U/f characteristic based on 6
denable voltages and frequencies, see
Illustration 4.3.
electronic brake function for quick stop/hold of
the motor.
4.2.6 1-5* Load Indep. Setting
Parameters for load-independent motor settings.
1-50 Motor Magnetisation at Zero Speed
Range: Function:
100%* [0 -
Use this parameter along with parameter 1-52 Min
300 %
Speed Normal Magnetising [Hz] to obtain a
]
dierent thermal load on the motor when running
at low speed.
Enter a value that is a percentage of the rated
magnetizing current. If the setting is too low, the
torque on the motor shaft may be reduced.
4.2.7 1-6* Load Depen. Setting
Parameters for adjusting the load-dependent motor
settings.
Illustration 4.3 Example of U/f Charac-
teristic
Illustration 4.2 Motor Magnetization
1-52 Min Speed Normal Magnetising [Hz]
Range: Function:
1 Hz* [ 0.1 - 10.0
Hz]
Set the required frequency for normal
magnetizing current. Use this parameter
along with parameter 1-50 Motor Magneti-
sation at Zero Speed, also see Illustration 4.2.
1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 1000V]Enter voltage at each frequency point
to manually form a U/f characteristic
which matches the motor. Frequency
points are dened in
parameter 1-56 U/f Characteristic - F.
1-60 Low Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
300 %]
Enter the low-speed voltage compensation
value in percent. This parameter is used for
optimizing the low-speed load performance.
This parameter is only active if
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction = [0]
Asynchron.
1-61 High Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
300 %]
Enter the high-speed load voltage compensation value in percent. This parameter is
used for optimizing the high-speed load
performance. This parameter is only active if
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction = [0]
Asynchron.
1-62 Slip Compensation
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ -400 -
400.0 %]
Enter the % value for slip compensation
to compensate for tolerance in the
value of n
. Slip compensation is
M,N
calculated automatically, that is, based
on the nominal motor speed n
M,N
.
40 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 43

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-63 Slip Compensation Time Constant
Range: Function:
0.1 s* [0.05 - 5 s] Enter the slip compensation reaction speed.
A high value results in slow reaction, and a
low value results in quick reaction. If lowfrequency resonance problems occur, use a
longer time setting.
1-64 Resonance Dampening
Range: Function:
100%* [0 -
500 %]
Enter the resonance dampening value. Set
parameter 1-64 Resonance Dampening and
parameter 1-65 Resonance Dampening Time
Constant to help eliminate high-frequency
resonance problems. To reduce resonance
oscillation, increase the value of
parameter 1-64 Resonance Dampening.
1-65 Resonance Dampening Time Constant
Range: Function:
0.005 s* [ 0.001 -
0.05 s]
Set parameter 1-64 Resonance Dampening
and parameter 1-65 Resonance Dampening
Time Constant to help eliminate highfrequency resonance problems. Enter the
time constant that provides the best
dampening.
1-66 Min. Current at Low Speed
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 0 -
120 %]
Enter the minimum motor current at low
speed. Increasing this current improves
motor torque at low speed.
Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low Speed is
enabled only for PM motor.
4.2.8 1-7* Start Adjustments
Parameters for adjusting the motor start settings.
1-70 Start Mode
Select the PM motor start-up mode. To initialize the VVC+ control
core for previously free-running PM motor. Active for PM motors
in VVC+ only if the motor is stopped (or running at low speed).
Option: Function:
[0] * Rotor
Detection
[1] Parking The parking function applies DC current
[3] Rotor Last
Position
Estimates the electrical angle of the rotor
and uses this angle as a starting point.
This option is the standard selection for
industrial applications. If ystart detects
that the motor runs at low speed or has
stopped, the frequency converter detects
the rotor position (the angle) and starts
the motor from that position.
across the stator winding and rotates the
rotor to electrical 0 position. This option is
typically for pump and fan applications. If
ystart detects that the motor runs at low
speed or has stopped, the frequency
converter sends out a DC current to make
the motor park at an angle and then starts
the motor from that position.
This option takes the advantage of the last
position of rotor at stop and gives a quick
start. It is only used in the situation of
controlled stop, the frequency converter
records the last position of rotor at stop
and starts the motor directly without rotor
detection and angle calculation. When in
the situation of non-controlled stop and
power cycle, the frequency converter
needs to detect the rotor position.
This option can be used for fast restart
application. Start may fail if the rotor
position has been changed.
4 4
1-71 Start Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0.0 -
10.0 s]
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 41
This parameter enables a delay of the starting
time. The frequency converter begins with the
start function selected in parameter 1-72 Start
Function. Set the start delay time until
acceleration is to begin.
Page 44

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
1-72 Start Function
Option: Function:
Select the start function during start delay.
This parameter is linked to parameter 1-71 Start
Delay.
[0] DC Hold/
delay time
44
[2]*Coast/delay
time
[3] Start speed
cw
[4] Horizontal
operation
[5] VVC+
clockwise
Energizes motor with a DC hold current
(parameter 2-00 DC Hold/Motor Preheat Current)
during the start delay time.
Motor coasted during the start delay time
(inverter o).
Only possible with VVC+. Regardless of the
value applied by the reference signal, the
output speed applies the setting of the start
speed in parameter 1-75 Star t Speed [Hz] and
the output current corresponds to the setting
of the start current in parameter 1-76 Start
Current. This function is typically used in
hoisting applications without counterweight
and especially in applications with a Conemotor, where the start is clockwise, followed
by rotation in the reference direction.
Only possible with VVC+.
For obtaining the function described in
parameter 1-75 Start Speed [Hz] and
parameter 1-76 Start Current during the start
delay time. The motor rotates in the reference
direction. If the reference signal equals zero (0),
parameter 1-75 Start Speed [Hz] is ignored and
the output speed equals zero (0). The output
current corresponds to the setting of the start
current in parameter 1-76 Start Current.
The start speed is calculated automatically. This
function uses the start speed in the start delay
time only.
1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
NOTICE
To obtain the best ying start
performance, the advanced motor data,
parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs) to
parameter 1-35 Main Reactance (Xh),
must be correct.
Catch a motor which is spinning freely due to
a mains dropout.
[0]*Disabled No function.
1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
[2] Enabled
Always
[3] Enabled
Ref. Dir.
[4] Enab.
Always Ref.
Dir.
Enable ying start at every start command.
Enable the frequency converter to catch and
control a spinning motor. The search is
performed only in the reference direction.
Enable ying start at every start command. The
search is performed only in the reference
direction.
1-75 Start Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 -
500.0
Hz]
This parameter can be used for hoist
applications (cone rotor). Set a motor start
speed. After the start signal, the output
speed leaps to the set value. Set the start
function in parameter 1-72 Start Function to
[3] Start speed cw, [4] Horizontal operation, or
[5] VVC+ clockwise, and set a start delay time
in parameter 1-71 Start Delay.
1-76 Start Current
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 1000 A]
Some motors, for example cone rotor
motors, need extra current/starting speed to
disengage the rotor. To obtain this boost, set
the required current in this parameter. Set
parameter 1-72 Start Function to [3] Start
speed cw or [4] Horizontal operation, and set
a start delay time in parameter 1-71 Start
Delay.
1-78 Compressor Start Max Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [ 0 -
500 Hz]
This parameter enables high starting torque. This
function ignores current limit and torque limit
during start of the motor. The time from the start
signal is given until the speed exceeds the speed
set in this parameter becomes a start zone. In
the start zone, the current limit and motoric
torque limit are set to the maximum possible
value for the frequency converter/motor
combination. The time without protection from
the current limit and torque limit must not
exceed the value set in
parameter 1-79 Compressor Start Max Time to Trip.
Otherwise, the frequency converter trips with
alarm 18, Start Failed.
[1] Enabled Enable the frequency converter to catch and
control a spinning motor. When
parameter 1-73 Flying Start is enabled,
parameter 1-71 Start Delay, and
parameter 1-72 Start Function have no function.
42 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
1-79 Compressor Start Max Time to Trip
Range: Function:
5 s* [0 -
10 s]
The time from the start signal is given until the
speed exceeds the speed set in
parameter 1-78 Compressor Start Max Speed [Hz]
Page 45

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-79 Compressor Start Max Time to Trip
Range: Function:
must not exceed the time set in this parameter.
Otherwise, the frequency converter trips with alarm
18, Start Failed. Any time set in parameter 1-71 Start
Delay for use of a start function must be executed
within the time limit.
4.2.9 1-8* Stop Adjustments
Parameters for adjusting motor stop settings.
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
Select the frequency converter function after
a stop command or after the speed is ramped
down to the settings in parameter 1-82 Min
Speed for Function at Stop [Hz].
Available selections depend on the setting in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
[0] Asynchron.
•
- [0] Coast.
- [1] DC hold / Motor Preheat.
- [3] Pre-magnetizing.
[1] PM, non salient SPM.
•
[3] PM, salient IPM.
•
- [0] Coast.
- [1] DC hold / Motor Preheat.
[0]*Coast Leaves the motor in free mode.
[1] DC hold /
Motor
Preheat
[3] Pre-
magnetizing
Energizes the motor with a DC hold current
(see parameter 2-00 DC Hold/Motor Preheat
Current.
Builds up a magnetic eld while the motor is
stopped. This allows the motor to produce
torque quickly at commands (asynchronous
motors only). This premagnetizing function
does not help the very rst start command.
Two dierent solutions are available to premagnetize the machine for the rst start
command:
Solution 1:
1. Start the frequency converter with a
0 RPM reference.
2. Wait 2 to 4 rotor time constants (see
the equation below) before
increasing the speed reference.
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
Solution 2:
1. Set parameter 1-71 Start Delay to the
premagnetize time (2–4 rotor time
constants).
2. Set parameter 1-72 Start Function to
[0] DC hold.
3. Set the DC-hold current magnitude
(parameter 2-00 DC Hold/Motor
Preheat Current to be equal to I
= U
/(1.73 x Xh).
nom
Sample rotor time constants =
(Xh+X2)/(6.3*Freq_nom*Rr)
1 kW = 0.2 s
10 kW = 0.5 s
100 kW = 1.7 s
1-82 Min Speed for Function at Stop [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [0 - 20 Hz] Set the output frequency at which to
activate parameter 1-80 Function at Stop.
1-88 AC Brake Gain
Range: Function:
1.4* [1.0 -
2.0 ]
This parameter is used to set AC brake power
capability (set ramp-down time when inertia is
constant). In cases where the DC-link voltage is
not higher than DC-link voltage trip value, the
generator torque can be adjusted with this
parameter. The higher AC brake gain is, the
stronger the brake capability is. Select 1.0 means
that there is no AC brake capability.
NOTICE
If there is continuous generator torque,
higher generator torque causes higher
motor current, and the motor becomes hot.
In this condition, parameter 2-16 AC Brake,
Max current can be used to protect the
motor from overheating.
4.2.10 1-9* Motor Temperature
Parameters for adjusting temperature protection settings
for the motor.
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
[0] * No
protection
Continuously overloaded motor, when no
warning or trip of the frequency converter is
required.
4 4
pre-mag
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 43
Page 46

1330
550
250
-20 °C
175HA183.11
4000
3000
R
(Ω)
nominal
nominal -5 °C nominal +5 °C
[°C]
PTC / Thermistor
R
OFF
ON
<800 Ω
+10 V
130BF960.10
>2.9 kΩ
12 13 1837 322719 29 3338
5550
42
53 54
31
PTC / Thermistor
R
OFF
ON
<800 Ω
+10 V
130BF694.10
>2.9 kΩ
5550
42
53 54
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
[1] Thermistor
warning
[2] Thermistor
trip
44
[3] ETR warning1Calculates the load and activates a warning in
[4] ETR trip 1 Calculates the load and stops (trips) the
[22] ETR Trip -
Extended
Detection
Activates a warning when the connected
thermistor in the motor reacts to a motor
overtemperature.
Stops (trips) the frequency converter when
the connected thermistor in the motor reacts
to a motor overtemperature.
The thermistor cutout value must be >3 kΩ.
Integrate a thermistor (PTC sensor) in the
motor for winding protection.
the display when the motor is overloaded.
Program a warning signal via 1 of the digital
outputs.
frequency converter when the motor is
overloaded. Program a warning signal via 1 of
the digital outputs. The signal appears in the
event of a warning and if the frequency
converter trips (thermal warning). Once the
MOTOR ETR OVER alarm is reported, it can
reset immediately.
Calculates the load and stops (trips) the
frequency converter when the motor is
overloaded. Program a warning signal via 1 of
the digital outputs. The signal appears in the
event of a warning and if the frequency
converter trips (thermal warning). Once the
MOTOR ETR OVER alarm is reported, it can
only reset after parameter 16-18 Motor
Thermal decreases to 0.
Using a digital input and 10 V as supply:
Example: The frequency converter trips when the motor
temperature is too high.
Parameter set-up:
Set parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection to [2]
•
Thermistor Trip.
Set parameter 1-93 Thermistor Source to [6] Digital
•
Input 33.
Illustration 4.5 PTC Thermistor Connection - Digital Input
Using an analog input and 10 V as supply:
Example: The frequency converter trips when the motor
temperature is too high.
Parameter set-up:
Set parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection to [2]
•
Thermistor Trip.
Set parameter 1-93 Thermistor Source to [2] Analog
•
Input 54.
Illustration 4.6 PTC Thermistor Connection - Analog Input
Illustration 4.4 PTC Prole
44 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Input
digital/analog
Digital 10 V
Analog 10 V
Table 4.3 Threshold Cutout Values
Supply voltage Threshold
cutout values
<800 Ω - 2.9 kΩ
<800 Ω - 2.9 kΩ
NOTICE
Check that the selected supply voltage follows the
specication of the used thermistor element.
Page 47

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
1-93 Thermistor Source
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be changed
while the motor is running.
NOTICE
Digital input should be set to [0] PNP
- Active at 24 V in
parameter 5-00 Digital Input Mode.
Select the input to which the thermistor
(PTC sensor) should be connected. If an
analog input in this parameter is set as a
source, it cannot be used for an other
purpose, for example, reference, feedback.
[0] * None
[1] Analog Input
53
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] Digital input
18
[4] Digital input
19
[5] Digital input
32
[6] Digital input
33
[7] Digital input
31
2-01 DC Brake Current
Range: Function:
50%* [0 -
NOTICE
150 %
MOTOR OVERHEATING
]
The maximum value depends on the rated
motor current.
To avoid motor damage caused by
overheating, do not run at 100% for too
long.
Set current as % of rated motor current,
parameter 1-24 Motor Current. When speed is
below the limit set in parameter 2-04 DC Brake Cut
In Speed, or when the DC-brake inverse function is
active (in parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs set to
[5] DC-brake inverse; or via the serial port), a DCbrake current is applied on a stop command. See
parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time for duration.
2-02 DC Braking Time
Range: Function:
10 s* [0 - 60 s] Set the duration of the DC brake current set in
parameter 2-01 DC Brake Current, once
activated.
2-04 DC Brake Cut In Speed
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [ 0 - 500
Hz]
This parameter is for setting the DC brake
cut-in speed at which the DC brake current
parameter 2-01 DC Brake Current is to be
active, with a stop command.
4 4
4.3 Parameters: 2-** Brakes
4.3.1 2-0* DC Brake
Use this parameter group to congure DC brake and DC
hold functions.
2-00 DC Hold/Motor Preheat Current
Range: Function:
50 %* [0 -
160 %]
Set the holding current as a percentage of the
rated motor current I
Current. This parameter holds the motor function
(holding torque) or pre-heats the motor. This
parameter is active if [0] DC hold is selected in
parameter 1-72 Start Function, or if [1] DC hold/preheat is selected in parameter 1-80 Function at
Stop.
parameter 1-24 Motor
M,N
NOTICE
The maximum value depends on the rated
motor current. Avoid 100% current for too
long. It may damage the motor.
2-06 Parking Current
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 150 %] Set current as percentage of rated motor
current, parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
2-07 Parking Time
Range: Function:
3 s* [0.1 - 60 s] Set the duration of the parking current set in
parameter 2-06 Parking Current, once activated.
4.3.2 2-1* Brake Energy Funct.
Parameter group for selecting dynamic braking parameters.
Only valid for frequency converters with brake chopper.
2-10 Brake Function
Option: Function:
[0]*O No brake resistor is installed.
[1] Resistor
brake
A brake resistor is incorporated in the system for
dissipating surplus brake energy as heat.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 45
Page 48

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
2-10 Brake Function
Option: Function:
Connecting a brake resistor allows a higher DClink voltage during braking (generating
operation). The brake resistor function is only
active in frequency converters with an integral
dynamic brake.
[2] AC brake Improve braking without using a brake resistor.
44
This parameter controls an overmagnetization of
the motor when running with a generatoric load.
This function can improve the OVC function.
Increasing the electrical losses in the motor
allows the OVC function to increase braking
torque without exceeding the voltage limit.
NOTICE
The AC brake is not as ecient as
dynamic braking with resistor.
AC brake is for VVC+ mode in both open
and closed loop.
2-11 Brake Resistor (ohm)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
2-12 Brake Power Limit (kW)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 6200
Ohm]
[0.001 2000
kW]
Set the brake resistor value in Ω. This
value is used for monitoring the power to
the brake resistor. Parameter 2-11 Brake
Resistor (ohm) is only active in frequency
converters with an integral dynamic brake.
Use this parameter for values without
decimals.
Parameter 2-12 Brake Power Limit (kW) is the
expected average power dissipated in the
brake resistor over a period of 120 s. It is
used as the monitoring limit for
parameter 16-33 Brake Energy Average and
species when a warning/alarm is given.
To calculate parameter 2-12 Brake Power
Limit (kW), the following formula can be
used.
P
br, avg
P
br,avg
the brake resistor. Rbr is the resistance of
the brake resistor. tbr is the active breaking
time within the 120 s period Tbr.
Ubr is the DC voltage where the brake
resistor is active. For T4 units, the DC
voltage is 770 V, which can be reduced by
parameter 2-14 Brake voltage reduce.
2
U
V × tbrs
br
W =
RbrΩ × Tbrs
is the average power dissipated in
2-12 Brake Power Limit (kW)
Range: Function:
NOTICE
If Rbr is not known or if Tbr is dierent
from 120 s, the practical approach is
to run the brake application, read out
parameter 16-33 Brake Energy Average,
and then enter this value + 20% in
parameter 2-12 Brake Power Limit
(kW).
2-14 Brake voltage reduce
Range: Function:
0 V* [ 0 - 71 V] Setting this parameter may change the brake
resistor (parameter 2-11 Brake Resistor (ohm)).
2-16 AC Brake, Max current
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
160 %]
Enter the maximum allowed current when
using AC brake to avoid overheating of
motor windings.
NOTICE
Parameter 2-16 AC Brake, Max current
is only available for asynchronous
motors.
2-17 Over-voltage Control
Option: Function:
Overvoltage control (OVC) reduces the risk of
the frequency converter tripping due to an
overvoltage on the DC link caused by
generative power from the load.
[0] * Disabled No OVC required.
[1] Enabled
(not at
stop)
[2] Enabled Activate OVC.
Activate OVC except when using a stop signal
to stop the frequency converter.
CAUTION
PERSONAL INJURY AND
EQUIPMENT DAMAGE
Enabling OVC in hoisting applications
may lead to personal injuries and
equipment damage.
DO NOT enable OVC in hoisting
•
applications.
2-19 Over-voltage Gain
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 200 %] Select overvoltage gain.
46 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 49

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.3.3 2-2* Mechanical Brake
2-20 Release Brake Current
Range: Function:
0 A* [0 - 100A]Set the motor current for release of the
mechanical brake when a start condition is
present. The upper limit is specied in
parameter 16-37 Inv. Max. Current.
NOTICE
When mechanical brake control output is
selected, but no mechanical brake is
connected, the function does not work by
default setting due to too low motor
current.
2-22 Activate Brake Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [0 - 400 Hz] Set the motor frequency for activation of
the mechanical brake when a stop
condition is present.
2-23 Activate Brake Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] Enter the brake delay time of the coast after
ramp-down time. The shaft is held at 0 speed
with full holding torque. Ensure that the
mechanical brake has locked the load before the
motor enters coast mode.
2-33 Speed PID Start Lowpass Filter Time
Range: Function:
10.0 ms* [0.1 - 100.0
ms]
It is the speed control low-pass lter
during the time set in
parameter 2-25 Brake Release Time.
2-39 Mech. Brake w/ dir. Change
Enable or disable the mechanical brake function when the shaft
changes direction.
Option: Function:
[0] * OFF
[1] ON
[2] ON with start delay The start delay time is set in
parameter 1-71 Start Delay.
4.4 Parameters: 3-** Reference/Ramps
4.4.1 3-0* Reference Limits
Parameters for setting the reference unit, limits, and
ranges.
3-00 Reference Range
Option: Function:
[0] * Min - Max Select the range of the reference signal and
the feedback signal. Signal values can be
positive only, or positive and negative.
[1] -Max -
+Max
For both positive and negative values (both
directions), relative to parameter 4-10 Motor
Speed Direction.
4 4
2-24 Stop Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] It is used to dene a time, during which the
speed close loop controls the motor to run at 0
RPM, after that the brake is activated.
2-25 Brake Release Time
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] It reserves a time before ramping up after
opening the brake, and the speed close loop
control controls the speed at 0 RPM.
2-31 Speed PID Start Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.015* [0.000 -
1.000 ]
It is the speed controller proportional
gain during the time set in
parameter 2-25 Brake Release Time.
2-32 Speed PID Start Integral Time
Range: Function:
200.0 ms* [1.0 - 20000.0
ms]
It is the speed controller integral
time during the time set in
parameter 2-25 Brake Release Time.
3-01 Reference/Feedback Unit
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] %
[2] RPM
[3] Hz
[4] Nm
[5] PPM
[10] 1/min
[12] Pulse/s
[20] l/s
[21] l/min
[22] l/h
[23] m³/s
[24] m³/min
[25] m³/h
[30] kg/s
[31] kg/min
[32] kg/h
[33] t/min
[34] t/h
[40] m/s
[41] m/min
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 47
Page 50

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
3-01 Reference/Feedback Unit
Option: Function:
[45] m
[60] °C
[70] mbar
[71] bar
[72] Pa
[73] kPa
44
[74] m WG
[80] kW
[120] GPM
[121] gal/s
[122] gal/min
[123] gal/h
[124] CFM
[125] ft³/s
[126] ft³/min
[127] ft³/h
[130] lb/s
[131] lb/min
[132] lb/h
[140] ft/s
[141] ft/min
[145] ft
[150] lb ft
[160] °F
[170] psi
[171] lb/in2
[172] in WG
[173] ft WG
[180] HP
3-02 Minimum Reference
Range: Function:
0 ReferenceFeedbackUnit*
[ -4999.0 4999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
Enter the minimum reference. The
minimum reference is the lowest
value obtainable by summing all
references.
The minimum reference is active
only when
parameter 3-00 Reference Range is
set to [0] Min.–Max.
The minimum reference unit
matches:
The option in
•
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode.
The unit selected in
•
parameter 3-01 Reference/
Feedback Unit.
3-03 Maximum Reference
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[-4999.0 - 4999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
Enter the maximum reference. The
maximum reference is the highest
value obtainable by summing all
references.
The maximum reference unit
matches:
The option selected in
•
parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode.
The unit selected in
•
parameter 3-00 Reference
Range.
3-04 Reference Function
Option: Function:
[0] * Sum Sum both external and preset reference
sources.
[1] External/
Preset
Use either the preset or the external
reference source. Shift between external and
preset via a command or a digital input.
4.4.2 3-1* References
3-10 Preset Reference
Range: Function:
0 %* [-100 -
100 %]
3-11 Jog Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
5 Hz* [ 0 -
500.0 Hz]
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
100 %]
Enter up to 8 dierent preset references (0–7)
in this parameter, using array programming. For
selecting dedicated references, select preset
reference bit 0/1/2 [16], [17], or [18] for the
corresponding digital inputs in parameter group
5-1* Digital Inputs.
The jog speed is a xed output speed at which
the frequency converter runs when the jog
function is activated. See also
parameter 3-80 Jog Ramp Time.
The jog speed must not exceed the setting in
parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz].
Enter a percentage value to be either added to or
deducted from the actual reference for catching
up or slowing down respectively. If [28] Catch up is
selected via 1 of the digital inputs
(parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input to
parameter 5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input), the
percentage value is added to the total reference. If
[29] Slow down is selected via 1 of the digital
48 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 51

Relative
Z=X+X*Y/100
Resulting
actual
reference
Y
X
130BA059.12
Z
X
100
%
0-100
Z
Y
X+X*Y/100
P 3-14
130BA278.10
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value
Range: Function:
inputs (parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input to
parameter 5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input), the
percentage value is deducted from the total
reference.
3-13 Reference Site
Select which reference site to activate.
Option: Function:
[0] * Linked to Hand /
Auto
[1] Remote Use the reference in hand mode.
[2] Local Use the reference in auto mode.
Use the local reference in hand mode
or the remote reference in auto mode.
3-14 Preset Relative Reference
Range: Function:
0 %* [-100 -
100 %]
Illustration 4.7 Preset Relative Reference
The actual reference, X, is increased or decreased
with the percentage Y, set in
parameter 3-14 Preset Relative Reference. This
results in the actual reference Z. Actual reference
(X) is the sum of the inputs selected in
parameter 3-15 Reference 1 Source,
parameter 3-16 Reference 2 Source,
parameter 3-17 Reference 3 Source, and
parameter 8-02 Control Source.
3-15 Reference 1 Source
Option: Function:
up to 3 dierent reference signals. The
sum of these reference signals denes
the actual reference.
[0] No function
[1] * Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[7] Frequency input
29
[8] Frequency input
33
[11] Local bus
reference
[20] Digital pot.meter
[32] Bus PCD
3-16 Reference 2 Source
Option: Function:
Select the reference input to be used
for the second reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference 1 Source,
parameter 3-16 Reference 2 Source, and
parameter 3-17 Reference 3 Source dene
up to 3 dierent reference signals. The
sum of these reference signals denes
the actual reference.
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] * Analog Input 54
[7] Frequency input
29
[8] Frequency input
33
[11] Local bus
reference
[20] Digital pot.meter
[32] Bus PCD
4 4
3-17 Reference 3 Source
Option: Function:
Select the reference input to be used
for the third reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference 1 Source,
Illustration 4.8 Actual Reference
3-15 Reference 1 Source
Option: Function:
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 49
Select the reference input to be used
for the rst reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference 1 Source,
parameter 3-16 Reference 2 Source, and
parameter 3-17 Reference 3 Source dene
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[7] Frequency input
29
parameter 3-16 Reference 2 Source, and
parameter 3-17 Reference 3 Source
dene up to 3 dierent reference
signals. The sum of these reference
signals denes the actual reference.
Page 52

Relative
Z=X+X*Y/100
Resulting
actual
reference
Y
X
130BA059.12
Z
t
acc
t
dec
130BD379.10
P 3-*2
Ramp (X)
Down
Time (Dec)
P 4-14
High-limit
Hz
Reference
P 1-23
Motor
frequency
P 4-12
Low limit
Time
P 3-*1
Ramp (X)Up
Time (Acc)
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
44
3-17 Reference 3 Source
Option: Function:
[8] Frequency input
33
[11] * Local bus
reference
[20] Digital pot.meter
[32] Bus PCD
3-18 Relative Scaling Reference Resource
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while the motor is running.
Select a variable value to be added to the
xed value (dened in
parameter 3-14 Preset Relative Reference).
The sum of the xed and variable values
(labeled Y in Illustration 4.9) is multiplied
by the actual reference (labeled X in
Illustration 4.9). This product is then
added to the actual reference (X+X*Y/100)
to give the resulting actual reference.
Illustration 4.9 Resulting Actual
Reference
[0] * No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[7] Frequency input
29
[8] Frequency input
33
[11] Local bus
reference
4.4.3 3-4* Ramp 1
Congure the ramp parameter, ramping times, for each of
the 4 ramps (parameter group 3-4* Ramp 1, parameter
group 3-5* Ramp 2, parameter group 3-6* Ramp 3, and
parameter group 3-7* Ramp 4).
Illustration 4.10 Example of Ramp 1
3-40 Ramp 1 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/deceleration. A
linear ramp gives constant acceleration during
ramping. A sine 2 ramp gives non-linear
acceleration.
[0] * Linear
[2] Sine 2
Ramp
3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
(Only to be used with speed control mode.) Sramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time and
parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time.
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-up time, that is the
acceleration time from 0 Hz to the
synchronous motor speed nS
parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency or from 0
NM to the nominal torque if torque congu-
ration modes are selected. It is applicable
for Ramp 1 to Ramp 4. Select a ramp-up
time such that the output current does not
exceed the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during ramping.
See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time.
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 41 =
acc
ref Hz
50 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 53

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-down time, that is the
deceleration time from the synchronous
motor speed ns to 0 Hz or from the
nominal torque to 0 NM if the torque
conguration modes are selected. Select a
ramp-down time such that no overvoltage
occurs in the inverter due to regenerative
operation of the motor, and such that the
generated current does not exceed the
current limit set in parameter 4-18 Current
Limit. See ramp-up time in
parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time.
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 42 =
dec
ref Hz
4.4.4 3-5* Ramp 2
This parameter group congures ramp 2 parameters.
3-50 Ramp 2 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/deceleration. A
linear ramp gives constant acceleration during
ramping. A sine 2 ramp gives non-linear
acceleration.
[0] * Linear
[2] Sine 2
Ramp
3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time and
parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time.
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-up time, which is the
acceleration time from 0 Hz to the rated
motor speed ns. Select a ramp-up time
such that the output current does not
exceed the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time.
t
s xns Hz
acc
ref Hz
[0.01 3600 s]
Par . 3 − 51 =
Enter the ramp-down time, that is the
deceleration time from the rated motor
speed ns to 0 Hz or from the nominal
torque to 0 NM if the torque conguration
modes are selected. Select a ramp-down
time such that no overvoltage arises in the
frequency converter due to regenerative
operation of the motor, and such that the
3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
generated current does not exceed the
current limit set in parameter 4-18 Current
Limit. See ramp-up time in
parameter 3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time.
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 52 =
dec
ref Hz
4.4.5 3-6* Ramp 3
This parameter group congures ramp 3 parameters.
3-60 Ramp 3 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/deceleration. A
linear ramp gives constant acceleration during
ramping. An S-ramp gives non-linear
acceleration.
[0] * Linear
[2] Sine 2
Ramp
3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up Time and
parameter 3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time.
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-up time, which is the
acceleration time from 0 Hz to the rated
motor speed ns. Select a ramp-up time
such that the output current does not
exceed the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time.
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-down time, which is the
deceleration time from the rated motor
speed ns to 0 Hz. Select a ramp-down time
such that no overvoltage arises in the
inverter due to regenerative operation of the
motor, and such that the generated current
does not exceed the current limit set in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit. See ramp-up
time in parameter 3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up
Time.
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 62 =
dec
ref Hz
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 51
Page 54

130BD375.11
Time
P 3-80
Hz
P 4-14 Hz
High limit
Jog speed
P 3-19
P 3-80
Ramp up
(acc)
Ramp down
(dec)
t jog t jog
P 4-12 Hz
Low limit
P 1-23
Motor frequency
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.4.6 3-7* Ramp 4
This parameter group congures ramp 4 parameters.
3-70 Ramp 4 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/deceleration. A
linear ramp gives constant acceleration during
44
[0] * Linear
[2] Sine 2
Ramp
ramping. An S-ramp gives non-linear
acceleration.
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-71 Ramp 4 Ramp up Time and
parameter 3-72 Ramp 4 Ramp Down Time.
4.4.7 3-8* Other Ramps
3-80 Jog Ramp Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01
- 3600
s]
Enter the jog ramp time, which is the
acceleration/deceleration time between 0 Hz
and the rated motor frequency ns. Ensure that
the resulting output current required for the
given jog ramp time does not exceed the
current limit in parameter 4-18 Current Limit.
The jog ramp time starts when activating a
jog signal via the LCP, a selected digital
output, or the serial communication port.
When jog state is disabled, the normal
ramping times are valid.
3-71 Ramp 4 Ramp up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-up time, which is the
acceleration time from 0 Hz to the rated
motor speed ns. Select a ramp-up time
such that the output current does not
exceed the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-72 Ramp 4 Ramp Down Time.
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 71 =
acc
ref Hz
3-72 Ramp 4 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
52 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the ramp-down time, which is the
deceleration time from the rated motor
speed ns to 0 Hz. Select a ramp-down time
such that no overvoltage arises in the
inverter due to regenerative operation of the
motor, and such that the generated current
does not exceed the current limit set in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit. See ramp-up
time in parameter 3-71 Ramp 4 Ramp up
Time.
Par . 3 − 72 =
t
s xns Hz
dec
ref Hz
Illustration 4.11 Jog Ramp Time
t
s xns Hz
Par . 3 − 80 =
jog
Δ jogspeed par . 3 − 19 Hz
3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01 3600 s]
Enter the quick-stop ramp-down time,
which is the deceleration time from the
synchronous motor speed to 0 Hz. Ensure
that no resulting overvoltage occurs in the
inverter due to regenerative operation of
the motor required to achieve the given
ramp-down time. Ensure also that the
generated current required to achieve the
given ramp-down time does not exceed
the current limit (set in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit). Activate quick
stop with a signal on a selected digital
input, or via the serial communication port.
Page 55

130BD376.11
Time
Hz
P 4-14 Hz
high limit
Reference
P 1-23
Motor frequency
low limit
P 4-12 Hz
P 3-81
Qramp
Qstop
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3-95 Ramp Delay
Range: Function:
1000
ms*
[0 3600000 ms]
Enter the delay required from activation
of the digital potentiometer function
until the frequency converter starts to
ramp the reference. With a delay of 0 ms,
the reference starts to ramp as soon as
increase/decrease is activated.
Illustration 4.12 Quick Stop Ramp Time
4.4.8 3-9* Digital Potentiometer
The digital potentiometer enables increase or decrease of
the actual reference by adjusting the set-up of the digital
inputs using the functions Increase, Decrease or Clear. To
activate the function, at least 1 digital input must be set to
Increase or Decrease.
3-90 Step Size
Range: Function:
0.10 %* [0.01 -
200 %]
Enter the increment size required for
increase/decrease as a percentage of the
synchronous motor speed, ns. If increase/
decrease is activated, the resulting reference
is increased/decreased by the amount set in
this parameter.
4.5 Parameters: 4-** Limits/Warnings
4.5.1 4-1* Motor Limits
Dene torque, current, and speed limits for the motor, and
the reaction of the frequency converter when the limits are
exceeded.
A limit may generate a message in the display. A warning
always generates a message in the display or on the
eldbus. A monitoring function may initiate a warning or a
trip, after which the frequency converter stops and
generates an alarm message.
4-10 Motor Speed Direction
Option: Function:
[0] Clockwise
[2] * Both
directions
NOTICE
The setting in parameter 4-10 Motor
Speed Direction has impact on
parameter 1-73 Flying Start.
Only operation in clockwise direction is
allowed.
Operation in both clockwise and counterclockwise directions is allowed.
4 4
3-92 Power Restore
Option: Function:
[0] * O Reset the digital potentiometer reference to 0% after
power-up.
[1] On Restore the most recent digital potentiometer
reference at power-up.
3-93 Maximum Limit
4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [ 0 -
400.0 Hz]
Enter the minimum limit for motor speed. The
motor speed low limit can be set to
correspond to the minimum output frequency
of the motor shaft.
The motor speed low limit must not exceed
the setting in parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High
Limit [Hz].
Range: Function:
100 %* [-200 -
200 %]
3-94 Minimum Limit
Range: Function:
-100 % [-200 -
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 53
200 %]
Set the maximum permissible value for the
resulting reference. This is recommended if
the digital potentiometer is used for ne-
tuning of the resulting reference.
Set the minimum permissible value for the
resulting reference. This is recommended if
the digital potentiometer is used for ne-
tuning of the resulting reference.
4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz]
Range: Function:
65
Hz*
[ 0.1 500
Hz]
NOTICE
Maximum output frequency cannot exceed
10% of the inverter switching frequency
(parameter 14-01 Switching Frequency).
Enter the maximum limit for motor speed. The
motor speed high limit can be set to correspond
to the manufacturer’s recommended maximum of
the motor shaft.
Page 56

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz]
4.5.2 4-2* Limit Factors
Range: Function:
The motor speed high limit must exceed the
value in parameter 4-12 Motor Speed Low Limit
[Hz], and must not exceed the value in
parameter 4-19 Max Output Frequency.
4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode
44
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0 - 1000 %] This function limits the torque on
the shaft to protect the mechanical
installation.
4-17 Torque Limit Generator Mode
Range: Function:
100 %* [ 0 - 1000 %] This function limits the torque on the
shaft to protect the mechanical installation.
4-18 Current Limit
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 1000 %]
This is a true current limit function that
continues in the oversynchronous range.
However, due to eld weakening, the
motor torque at current limit drops
accordingly when the voltage increase
stops above the synchronized motor
speed.
4-19 Max Output Frequency
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 -
NOTICE
500
This parameter cannot be adjusted
Hz]
while the motor is running.
4-20 Torque Limit Factor Source
Select an analog input for scaling the settings in
parameter 4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode and
parameter 4-17 Torque Limit Generator Mode 0–100% (or inverse).
The signal levels corresponding to 0% and 100% are dened in
the analog input scaling, for example parameter group 6-1*
Analog Input 1. This parameter is only active when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode is set to [0] Open Loop or [1]
Speed Closed Loop.
Option: Function:
[0] * No function
[2] Analog in 53
[4] Analog in 53 inv
[6] Analog in 54
[8] Analog in 54 inv
[18] Bus Control
4-21 Speed Limit Factor Source
Select an analog input for scaling the settings in
parameter 4-19 Max Output Frequency 0–100% (or inverse). The
signal levels corresponding to 0% and 100% are dened in the
analog input scaling, for example parameter group 6-1* Analog
Input 1. This parameter is only active when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode is in torque mode.
Option: Function:
[0] * No function
[2] Analog in 53
[4] Analog in 53 inv
[6] Analog in 54
[8] Analog in 54 inv
[18] Bus Control
4-22 Break Away Boost
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Maximum output frequency cannot
exceed 10% of the inverter switching
frequency (parameter 14-01 Switching
[0] * O
[1] On The frequency converter provides higher current than
normal current levels to enhance breakaway-torque
capacity.
Frequency).
4-27 Torque Limit Bus Control
Provide a nal limit on the output frequency
for improved safety in applications at risk of
overspeeding. This limit is nal in all congu-
rations (independent of the setting in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode).
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
16384 ]
This parameter is used to specify the bus factor
to control the torque limit. It only works when
parameter 4-20 Torque Limit Factor Source is set
to [18] Bus Control. This parameter is N2 format.
4-28 Speed Limit Bus Control
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
16384 ]
54 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
This parameter is used to specify the bus factor
to control the speed limit. It only works when
parameter 4-21 Speed Limit Factor Source is set
to [18] Bus Control. This parameter is N2 format.
Page 57

Time
[sec]
Speed
[rpm]
n
calc
n
actual
P 4-32
130BA221.10
P 4-31
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.5.3 4-3* Motor Feedback Monitoring
NOTICE
Warning 61, Feedback error is active as soon as the value
in parameter 4-31 Motor Feedback Speed Error is
exceeded, regardless of the setting in
parameter 4-32 Motor Feedback Loss Timeout. Alarm 61,
Feedback error is related to the motor feedback loss
function.
4-30 Motor Feedback Loss Function
Option: Function:
This function is used to monitor consistency
in the feedback signal, that is if the feedback
signal is available. Select the action of the
frequency converter if a feedback fault is
detected. The selected action takes place
when the feedback signal diers from the
output speed by the value set in
parameter 4-31 Motor Feedback Speed Error
for longer than the value set in
parameter 4-32 Motor Feedback Loss Timeout.
[0] Disabled
[1] Warning
[2] * Trip
[3] Jog
[4] Freeze
Output
[5] Max Speed
[6] Switch to
Open Loop
4-31 Motor Feedback Speed Error
Range: Function:
20 Hz* [0 - 50 Hz] Select the maximum allowed error in speed
(output speed versus feedback).
Illustration 4.13 Motor Feedback Speed Error
4-32 Motor Feedback Loss Timeout
Range: Function:
0.05 s* [0 - 60s]Set the timeout value allowing the speed
error set in parameter 4-31 Motor Feedback
Speed Error to be exceeded before enabling
the function selected in parameter 4-30 Motor
Feedback Loss Function.
4.5.4 4-4* Adjustable Warnings 2
4-40 Warning Freq. Low
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 -
Use this parameter for setting a lower limit for
500
the frequency range. When the motor speed
Hz]
drops below this limit, the display reads Speed
low. Warning bit 10 is set in
parameter 16-94 Ext. Status Word. Output relay
can be congured to indicate this warning.
LCP warning light is not lit when the limit set
is reached.
The value must not exceed the setting in
parameter 4-41 Warning Freq. High.
4 4
4-41 Warning Freq. High
Range: Function:
Size
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 55
related*
[ 0 -
Use this parameter for setting a higher limit
500
for the frequency range. When the motor
Hz]
speed exceeds this limit, the display reads
Speed high. Warning bit 9 is set in
parameter 16-94 Ext. Status Word. Output relay
can be congured to indicate this warning.
LCP warning light is not lit when the limit set
is reached.
The value must exceed the value in
parameter 4-40 Warning Freq. Low, and must
Page 58

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4-41 Warning Freq. High
Range: Function:
not exceed the value in parameter 4-14 Motor
Speed High Limit [Hz].
4-42 Adjustable Temperature Warning
Range: Function:
0* [ 0 - 200 ] Use this parameter to set the motor temperature
44
limit.
4.5.5 4-5* Adjustable Warnings
Use these parameters to adjust warning limits for current,
speed, reference, and feedback.
4-50 Warning Current Low
Range: Function:
0 A* [ 0 - 500A]Enter the I
drops below this limit, a bit in the status word
is set. This value can also be programmed to
produce a signal on the digital output or the
relay output.
4-51 Warning Current High
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0 -
500.00 A]
value. When the motor current
LOW
Enter the I
current exceeds this limit, a bit in the
status word is set. This value can also
be programmed to produce a signal on
the digital output or the relay output.
value. When the motor
HIGH
4-56 Warning Feedback Low
Range: Function:
-4999
ProcessCtrlUnit*
[-4999 - 4999
ProcessCtrlUnit]
Use this parameter to set a
low limit for the feedback
range. When the feedback
drops below this limit, the
display shows Feedb Low. Bit
6 is set in
parameter 16-94 Ext. Status
Word. The output relay or the
digital output can be
congured to indicate this
warning. The LCP warning
light is not turned on when
this parameter set limit is
reached.
4-57 Warning Feedback High
Range: Function:
4999
ProcessCtrlUnit*
[-4999 - 4999
ProcessCtrlUnit]
Use this parameter to set a
high limit for the feedback
range. When the feedback
exceeds this limit, the display
reads Feedb High. Bit 5 is set
in parameter 16-94 Ext. Status
Word. The output relay or the
digital output can be
congured to indicate this
warning. The LCP warning
light is not turned on when
this parameter set limit is
reached.
4-54 Warning Reference Low
Range: Function:
-4999* [-4999 4999 ]
Enter the low reference limit. When the actual
reference drops below this limit, the display
shows Ref
parameter 16-94 Ext. Status Word. The output
relay or the digital output can be congured
to indicate this warning. The LCP warning
light is not turned on when this parameter set
limit is reached.
LOW
4-55 Warning Reference High
Range: Function:
4999* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Use this parameter to set a high limit for the
reference range. When the actual reference
exceeds this limit, the display shows Ref
19 is set in parameter 16-94 Ext. Status Word.
The output relay or the digital output can be
congured to indicate this warning. The LCP
warning light is not turned on when this
parameter set limit is reached.
. Bit 20 is set in
HIGH
. Bit
4-58 Missing Motor Phase Function
Option: Function:
[0] O No alarm is shown if a missing motor phase occurs.
[1] * On An alarm is shown if a missing motor phase occurs.
4.5.6 4-6* Speed Bypass
4-61 Bypass Speed From [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [ 0 -
500 Hz]
Some systems call for avoiding certain output
speeds due to resonance problems in the
system. Enter the lower limits of the speeds to
be avoided.
The bypass speed from must not exceed the
setting in parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit
[Hz].
56 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 59

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4-63 Bypass Speed To [Hz]
Range: Function:
0 Hz* [ 0 -
500 Hz]
Some systems call for avoiding certain output
speeds due to resonance problems in the
system. Enter the upper limits of the speeds to
be avoided.
The bypass speed to must not exceed the
setting in parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit
[Hz].
4.6 Parameters: 5-** Digital In/Out
4.6.1 5-0* Digital I/O Mode
Parameters for conguring the input and output using
NPN and PNP.
5-00 Digital Input Mode
Option: Function:
Set NPN or PNP mode for digital inputs.
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while the
motor is running.
[0] * PNP Action on positive directional pulses (0). PNP systems
are pulled down to ground (GND).
[1] NPN Action on negative directional pulses (1). NPN
systems are pulled up to +24 V, internally in the
frequency converter.
5-01 Terminal 27 Mode
Option: Function:
[0] * Input Denes terminal 27 as a digital input.
[1] Output Denes terminal 27 as a digital output.
5-02 Terminal 29 Mode
Option: Function:
[0] * Input Denes terminal 29 as a digital input.
[1] Output Denes terminal 29 as a digital output.
The digital inputs are used for selecting various functions
in the frequency converter.
5-10 to 5-16 Digital Inputs
[0] No
operation
[1] Reset Resets frequency converter after a TRIP/ALARM.
[2] Coast
inverse
[3] Coast and
reset
inverse
No reaction to signals transmitted to the
terminal.
Not all alarms can be reset.
Coasting stop, inverted input (NC). The
frequency converter leaves the motor in free
mode.
Logic 0⇒ coasting stop.
Reset and coasting stop inverted input (NC).
Leaves motor in free mode and resets
frequency converter.
Logic 0⇒coasting stop.
Logic 1 to Logic 0⇒reset.
[4] Quick stop
inverse
[5] DC-brake
inverse
[6] Stop
inverse
Inverted input (NC). Generates a stop in
accordance with the quick stop ramp time set
in parameter 3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time. When
the motor stops, the shaft is in free mode.
Logic 0⇒ Quick-stop.
Inverted input for DC braking (NC). Stops the
motor by energizing it with a DC current for a
certain time period. See parameter 2-01 DC
Brake Current to parameter 2-04 DC Brake Cut In
Speed [Hz]. The function is only active when
the value in parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time is
dierent from 0. Logic 0=>DC braking.
NOTICE
When the frequency converter is at the
torque limit and has received a stop
command, it may not stop by itself. To
ensure that the frequency converter
stops, congure a digital output to [27]
Torque limit and stop and connect this
digital output to a digital input that is
congured as coast.
Stop inverted function. Generates a stop
function when the selected terminal goes from
logic 1 to logic 0. The stop is performed
according to the selected ramp time
(parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time,
parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time,
parameter 3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time,
parameter 3-72 Ramp 4 Ramp Down Time).
[8] Start Select start for a start/stop command. Logic 1
= start, logic 0 = stop.
[9] Latched
start
[10] Reversing Change the direction of motor shaft rotation.
[11] Start
reversing
[12] Enable
start
forward
[13] Enable
start
reverse
[14] Jog Use to activate jog speed. See
The motor starts when a pulse is applied for
minimum 4 ms. The motor stops when stop
commands are given.
Select logic 1 to reverse. The reversing signal
only changes the direction of rotation. It does
not activate the start function. Select both
directions in parameter 4-10 Motor Speed
Direction. The function is not active in process
closed loop.
Used for start/stop and for reversing on the
same wire. Signals on start are not allowed at
the same time.
Disengages the counterclockwise movement
and allows for the clockwise direction.
Disengages the clockwise movement and
allows for the counterclockwise direction.
parameter 3-11 Jog Speed [Hz].
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 57
Page 60

Speed [rpm] Spee d [rpm]
Time[sec] Time[sec]a b
130BB462.10
Read Timer:
20 timer tides
Read Timer:
20 timer tides
Time Start
Time counter
Sample time
Timer
Pulse
130BB464.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
[15] Preset
reference
on
[16] Preset ref
bit 0
Shifts between external reference and preset
reference. It is assumed that [1] External/preset
has been selected in parameter 3-04 Reference
Function. Logic 0 = external reference active;
logic 1 = 1 of the 8 preset references is active.
Preset ref. bits 0, 1, and 2 enable the selection
of 1 of the 8 preset references according to
Unchanged speed 0 0
Reduced by %-value 1 0
Increased by %-value 0 1
Reduced by %-value 1 1
Table 4.5 Shut Down/Catch Up
Shut down Catch up
Table 4.4.
[17] Preset ref
44
bit 1
[18] Preset ref
Same as [16] Preset ref bit 0.
Same as [16] Preset ref bit 0.
bit 2
[22] Speed
down
[23] Set-up
select
bit 0
Preset ref. bit 2 1 0
[28] CatchupIncreases reference value by percentage (relative)
Preset ref. 0 0 0 0
Preset ref. 1 0 0 1
Preset ref. 2 0 1 0
Preset ref. 3 0 1 1
Preset ref. 4 1 0 0
[29] Slow
down
[32] Pulse
input
Preset ref. 5 1 0 1
Preset ref. 6 1 1 0
Preset ref. 7 1 1 1
Same as [21] Speed up.
Select [23] Set-up select bit 0 to select 1 of the 2
set-ups. Set parameter 0-10 Active Set-up to [9]
Multi Set-up.
set in parameter 3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value.
Reduces reference value by percentage (relative)
set in parameter 3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value.
(Terminal 29 or 33 only) Measures the duration
between pulse anks. This parameter has a higher
resolution at lower frequencies, but is not as
precise at higher frequencies. This principle has a
cut-o frequency, which makes it unsuited for
encoders with low resolutions (for example 30
Table 4.4 Preset Ref. Bit
PPR) at low speeds.
[19] Freeze
ref
Freezes the actual reference, which is now the
point of enable/condition for [21] Speed up and [22]
Speed down to be used. If [21] Speed up or [22]
Speed down is used, the speed change always
follows ramp 2 (parameter 3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up
Time and parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time)
in the range 0–parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.
[20] Freeze
output
NOTICE
When [20] Freeze output is active, the
frequency converter cannot be stopped by
setting the signal on [8] Start to low. Stop
the frequency converter via a terminal
programmed for [2] Coasting inverse or [3]
Coast and reset, inverse.
Freezes the actual motor frequency (Hz), which is
now the point of enable/condition for [21] Speed
up and [22] Speed down to be used. If [21] Speed up
or [22] Speed down is used, the speed change
always follows ramp 2 (parameter 3-51 Ramp 2
Ramp Up Time and parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp
Down Time) in the range 0–parameter 1-23 Motor
Frequency.
[21] SpeedupSelect [21] Speed up and [22] Speed down if digital
control of the up/down speed is needed (motor
potentiometer). Activate this function by selecting
either [19] Freeze reference or [20] Freeze output.
When speed up/down is activated for less than 400
ms, the resulting reference is increased/decreased
by 0.1%. If speed up/down is activated for more
than 400 ms, the resulting reference follows the
setting in ramping up/down parameter 3-51/3-52.
a: Low encoder
resolution
b: Standard encoder
resolution
Illustration 4.14 Duration Between Pulse Flanks
[34] Ramp
bit 0
[35] Ramp
Enables a selection from the 4 ramps available,
according to Table 4.6.
Same as ramp bit 0.
bit 1
Preset ramp bit 1 0
Ramp 1 0 0
Ramp 2 0 1
Ramp 3 1 0
Ramp 4 1 1
Table 4.6 Preset Ramp Bits
[45] Latched
start
reverse
[51] External
interlock
The motor starts to run reverse when a pulse
is applied for minimum 4 ms. The motor stops
when stop commands are given.
This function makes it possible to give an
external fault to the frequency converter. This
58 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 61

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
fault is treated in the same way as an
internally generated alarm.
[55] DigiPot
increase
[56] DigiPot
decrease
[57] DigiPot
clear
[60] Counter A
(up)
[61] Counter A
(down)
[62] Reset
Counter A
[63] Counter B
(up)
[64] Counter B
(down)
[65] Reset
Counter B
[72] PID error
inverse
[73] PID reset I-
part
[74] PID enable This option enables the extended process PID
[150] Go To
Home
[151] Home Ref.
Switch
[155] HW Limit
Positive
[156] HW Limit
Negative
[157] Pos. Quick
Stop Inv
[160] Go To
Target Pos.
Increase signal to the digital potentiometer
function described in parameter group 3-9*
Digital Pot. Meter.
Decrease signal to the digital potentiometer
function described in parameter group 3-9*
Digital Pot. Meter.
Clear the digital potentiometer reference
described in parameter group 3-9* Digital Pot.
Meter.
Input for increment counting in the SLC
counter.
Input for decrement counting in the SLC
counter.
Input for reset of counter A.
Input for increment counting in the SLC
counter.
Input for decrement counting in the SLC
counter.
Input for reset of counter B.
Inverts the resulting error from the process
PID controller. Available only if
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode is set to [6]
Surface Winder or [7] Extended PID Speed OL.
Resets the I-part of the process PID controller.
Equivalent to parameter 7-40 Process PID I-part
Reset. Available only when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode is set to [6]
Surface Winder or [7] Extended PID Speed OL.
controller. Equivalent to
parameter 7-50 Process PID Extended PID.
Available only if parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode is set to [7] Extended PID Speed OL.
The frequency converter moves to the home
position.
Indicates the status of the home referenced
switch. On means that the home position is
reached, o means that the home position is
not reached.
The positive hardware position limit is
exceeded. This option is active on the falling
edge.
The negative hardware position limit is
exceeded. This option is active on the falling
edge.
Stops the frequency converter during
positioning with the ramp time that is set in
parameter 32-81 Motion Ctrl Quick Stop Ramp.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [2]
Position Control.
The frequency converter moves to the target
position. This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [2]
Position Control.
[162] Pos. Idx
Bit0
[163] Pos. Idx
Bit1
[164] Pos. Idx
Bit2
[165] Core
diameter
source
[166] New
diameter
select
[167] Reset
diameter
[168] Winder jog
forward
[169] Winder jog
reverse
[170] Tension on Enables tension PID control. This option is
Position index bit 0. This option is only
eective when parameter 37-00 Application
Mode is set to [2] Position Control.
Position index bit 1. This option is only
eective when parameter 37-00 Application
Mode is set to [2] Position Control.
Position index bit 2. This option is only
eective when parameter 37-00 Application
Mode is set to [2] Position Control.
The core diameter source. O means core 1 is
selected, and on means that core 2 is
selected. This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [1]
Center winder.
Congures whether to select partial roll
diameter (o) or core diameter (on). This
option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [1]
Center winder.
Resets the diameter. This option is only
eective when parameter 37-00 Application
Mode is set to [1] Center winder.
Enables jog forward during center winding.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [1]
Center winder.
Enables jog reverse during center winding.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [1]
Center winder.
only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to [1]
Center winder.
5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[8] * Start Functions are described in parameter group 5-1*
Digital Inputs.
5-11 Terminal 19 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[10] * Reversing Functions are described in parameter group 5-1*
Digital Inputs.
5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[2] * Coast inverse Functions are described in parameter group
5-1* Digital Inputs.
5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[14] * Jog Functions are described in parameter group
5-1* Digital Inputs.
[32] Pulse input
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 59
Page 62

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
5-14 Terminal 32 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation Functions are described in parameter
group 5-1* Digital Inputs.
[82] Encoder input B
5-15 Terminal 33 Digital Input
[8] Run on
reference / no
warning
[9] Alarm An alarm activates the output.
[10] Alarm or
warning
[11] At torque limit The torque limit set in
Option: Function:
44
[0] No operation Functions are described in parameter
group 5-1* Digital Inputs.
[16] * Preset ref bit 0
[32] Pulse input
[81] Enocder input A
5-16 Terminal 31 Digital Input
Option: Function:
[0] No operation Functions are described in parameter group
5-1* Digital Inputs.
4.6.2 5-3* Digital Outputs
The 2 solid-state digital outputs are common for terminals
27 and 29. Set the I/O function for terminal 27 in
[12] Out of current
range
[13] Below current,
low
[14] Above current,
high
[15] Out of
frequency
range
[16] Below
frequency, low
[17] Above
frequency, high
parameter 5-01 Terminal 27 Mode, and set the I/O function
for terminal 29 in parameter 5-02 Terminal 29 Mode.
[18] Out of
feedback range
Terminals 42 and 45 can also be congured as digital
outputs.
NOTICE
These parameters cannot be adjusted while the motor is
running.
[19] Below
feedback low
[20] Above
feedback high
[21] Thermal
warning
5-30 to 5-31 Digital Outputs
[0] No operation Default for all digital outputs and relay
outputs.
[1] Control ready The control card is ready.
[2] Drive ready The frequency converter is ready for
operation and applies a supply signal on
the control board.
[3] Drive ready /
remote control
[4] Enable / no
warning
[5] Running The motor is running and shaft torque is
[6] Running / no
warning
[7] Run in range /
no warning
The frequency converter is ready for
operation and is in auto-on mode.
Ready for operation. No start or stop
command is given (start/disable). No
warnings are active.
present.
The motor is running and there are no
warnings.
The motor is running within the
programmed current and speed ranges
set in parameter 4-50 Warning Current Low
to parameter 4-51 Warning Current High.
There are no warnings.
[22] Ready, no
thermal
warning
[23] Remote, ready,
no thermal
warning
[24] Ready, no
overvoltage/
undervoltage
[25] Reverse The motor runs (or is ready to run)
[26] Bus OK Active communication (no timeout) via
[27] Torque limit
and stop
The motor runs at reference speed. No
warnings.
An alarm or a warning activates the
output.
parameter 4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode
or parameter 4-17 Torque Limit Generator
Mode has been exceeded.
The motor current is outside the range
set in parameter 4-18 Current Limit.
The motor current is lower than set in
parameter 4-50 Warning Current Low.
The motor current is higher than set in
parameter 4-51 Warning Current High.
Output frequency is outside the
frequency range.
The output speed is lower than the
setting in parameter 4-40 Warning Freq.
Low.
The output speed is higher than the
setting in parameter 4-41 Warning Freq.
High.
The feedback is outside the range set in
parameter 4-56 Warning Feedback Low and
parameter 4-57 Warning Feedback High.
The feedback is below the limit set in
parameter 4-56 Warning Feedback Low.
The feedback is above the limit set in
parameter 4-57 Warning Feedback High.
The thermal warning turns on when the
temperature exceeds the limit in the
motor, the frequency converter, the brake
resistor, or the thermistor.
The frequency converter is ready for
operation, and there is no overtemperature warning.
The frequency converter is ready for
operation and is in auto-on mode. There
is no overtemperature warning.
The frequency converter is ready for
operation and the mains voltage is within
the specied voltage range (see General
Specications section in the design guide).
clockwise when logic = 0 and counterclockwise when logic = 1. The output
changes as soon as the reversing signal is
applied.
the serial communication port.
Use in performing a coast stop and in
torque limit condition. If the frequency
60 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 63

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
converter has received a stop signal and
is at the torque limit, the signal is logic 0.
[28] Brake, no brake
warning
[29] Brake ready, no
fault
[30] Brake fault
(IGBT)
[31] Relay 123 The relay is activated when [0] Control
[32] Mechanical
brake control
[36] Control word
bit 11
[37] Control word
bit 12
[40] Out of ref
range
[41] Below
reference low
[42] Above
reference high
[45] Bus Ctrl Controls output via eldbus. The state of
[46] Bus Ctrl On at
timeout
[47] Bus Ctrl O at
timeout
[55] Pulse output
[56] Heat sink
cleaning
warning, high
[60] Comparator 0 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
[61] Comparator 1 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
[62] Comparator 2 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
The brake is active and there are no
warnings.
The brake is ready for operation and
there are no faults.
The output is logic 1 when the brake
IGBT is short-circuited. Use this function
to protect the frequency converter if
there is a fault on the brake modules. Use
the output/relay to cut out the mains
voltage from the frequency converter.
Word is selected in parameter group 8-**
Communications and Options.
Enables control of an external mechanical
brake. See parameter group 2-2*
Mechanical Brake for more details.
This option is active when the actual
speed is outside the settings in
parameter 4-54 Warning Reference Low to
parameter 4-55 Warning Reference High.
This option is active when the actual
speed is below the speed reference
setting.
This option is active when the actual
speed is above the speed reference
setting.
the output is set in parameter 5-90 Digital
& Relay Bus Control. The output state is
retained in the event of eldbus timeout.
Controls output via eldbus. The state of
the output is set in parameter 5-90 Digital
& Relay Bus Control. When bus timeout
occurs, the output state is set high (On).
comparator 0 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
comparator 1 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
comparator 2 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[63] Comparator 3 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
comparator 3 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[64] Comparator 4 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
comparator 4 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[65] Comparator 5 See parameter group 13-1* Comparators. If
comparator 5 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[70] Logic Rule 0 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 0 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[71] Logic Rule 1 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 1 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[72] Logic Rule 2 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 2 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[73] Logic Rule 3 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 3 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[74] Logic Rule 4 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 4 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[75] Logic Rule 5 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules. If
logic rule 5 is evaluated as TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it is low.
[80] SL Digital
Output A
[81] SL Digital
Output B
[82] SL Digital
Output C
[83] SL Digital
Output D
[160] No alarm The output is high when no alarm is
[161] Running
reverse
See parameter 13-52 SL Controller Action.
The output goes high whenever the
smart logic action [38] Set dig. out. A high
is executed. The output goes low
whenever the smart logic action [32] Set
dig. out. A low is executed.
See parameter 13-52 SL Controller Action.
The input goes high whenever the smart
logic action [39] Set dig. out. B high is
executed. The input goes low whenever
the smart logic action [33] Set dig. out. B
low is executed.
See parameter 13-52 SL Controller Action.
The input goes high whenever the smart
logic action [40] Set dig. out. C high is
executed. The input goes low whenever
the smart logic action [34] Set dig. out. C
low is executed.
See parameter 13-52 SL Controller Action.
The input goes high whenever the smart
logic action [41] Set dig. out. D high is
executed. The input goes low whenever
the smart logic action [35] Set dig. out. D
low is executed.
present.
The output is high when the frequency
converter is running counterclockwise
(the logical product of the status bits
Running AND Reverse).
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 61
Page 64

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
[165] Local reference
active
[166] Remote ref
active
[167] Start command
active
[168] Drive in hand
mode
44
[169] Drive in auto
mode
[170] Homing
Completed
[171] Target Position
Reached
[172] Position
Control Fault
[173] Position Mech
Brake
[174] TLD indicator Indicates whether the tension is out of
[175] Running on
tension
[176] Ready to run The center winder control is ready to run.
[177] End of roll The diameter limit is reached. This option
[193] Sleep mode The frequency converter/system has
[194] Broken belt A broken belt condition has been
The output is high when there is an
active start command, and no stop
command is active.
The output is high when the frequency
converter is in hand-on mode.
The output is high when the frequency
converter is in auto-on mode.
The homing operation is completed. This
option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[2] Position Control.
The target position is reached. This option
is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[2] Position Control.
A fault occurred in the positioning
process. Refer to parameter 37-18 Pos. Ctrl
Fault Reason for details about the fault.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[2] Position Control.
Selects mechanical control for positioning.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[2] Position Control.
limit (on) during center winding. This
option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[1] Center winder.
Indicates whether tension PID control is
active (on) or inactive (o). This option is
only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[1] Center winder.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[1] Center winder.
is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set to
[1] Center winder.
entered sleep mode. See parameter group
22-4* Sleep Mode.
detected. See parameter group 22-4* Sleep
Mode.
5-30 Terminal 27 Digital Output
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation Functions are described in parameter group
5-3* Digital Outputs.
5-31 Terminal 29 Digital Output
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation Functions are described in parameter group
5-3* Digital Outputs.
5-34 On Delay, Digital Output
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s]
5-35 O Delay, Digital Output
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s]
4.6.3 5-4* Relays
Parameters for conguring the timing and the output
functions for the relays.
The parameter is an array parameter representing 2 relays:
Array [2] (Relay 1 [0], Relay 2 [1]).
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[0] No operation Default setting for all digital and relay
outputs.
[1] Control Ready The control card is ready.
[2] Drive ready The frequency converter is ready to
operate. Mains and control supplies are
OK.
[3] Drive rdy/rem ctrl The frequency converter is ready for
operation and is in auto-on mode.
[4] Stand-by / no
warning
[5] Running The motor is running and a shaft
[6] Running / no
warning
[7] Run in range/no
warn
[8] Run on ref/no
warn
[9] Alarm An alarm activates the output.
[10] Alarm or warning An alarm or warning activates the
Ready for operation. No start or stop
commands have been applied. No
warnings are active.
torque is present.
The motor is running and no warnings
are present.
The motor is running within the
programmed current ranges set in
parameter 4-50 Warning Current Low.
The motor runs at reference speed. No
warnings.
output.
62 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 65

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[11] At torque limit The torque limit set in
parameter 4-16 Torque Limit Motor Mode
or parameter 4-17 Torque Limit
Generator Mode has been exceeded.
[12] Out of current
range
[13] Below current,
low
[14] Above current,
high
[15] Out of frequency
range
[16] Below frequency,
low
[17] Above frequency,
high
[18] Out of feedb.
range
[19] Below feedback,
low
[20] Above feedback,
high
[21] Thermal warning Thermal warning turns on when the
[22] Ready, no thermal
warning
[23] Remote,ready,noTWThe frequency converter is ready for
[24] Ready, no over-/
under voltage
[25] Reverse The motor runs (or is ready to run)
[26] Bus OK Active communication (no timeout) via
The motor current is outside the range
set in parameter 4-18 Current Limit.
The motor current is lower than set in
parameter 4-50 Warning Current Low.
The motor current is higher than set in
parameter 4-51 Warning Current High.
The output speed/frequency exceeds
the limit that is set in
parameter 4-40 Warning Freq. Low and
parameter 4-41 Warning Freq. High.
The output frequency is lower than the
setting in parameter 4-40 Warning Freq.
Low.
The frequency is higher than the
setting in parameter 4-41 Warning Freq.
High.
The feedback is outside the range set
in parameter 4-56 Warning Feedback
Low and parameter 4-57 Warning
Feedback High.
The feedback is below the limit set in
parameter 4-56 Warning Feedback Low.
The feedback is above the limit set in
parameter 4-57 Warning Feedback High.
temperature exceeds the limit within
the motor, frequency converter, brake
resistor, or connected resistor.
The frequency converter is ready for
operation and there is no overtemperature warning.
operation and is in auto-on mode.
There is no overtemperature warning.
The frequency converter is ready for
operation, and the mains voltage is
within the specied voltage range.
clockwise when logic = 0 and counterclockwise when logic = 1. The output
changes as soon as the reversing signal
is applied.
the serial communication port.
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[27] Torque limit &
stop
[28] Brake, no brake
warning
[29] Brake ready, no
fault
[30] Brake fault (IGBT) The output is logic = 1 when the brake
[31] Relay 123 Digital output/relay is activated when
[32] Mech brake ctrl Selection of mechanical brake control.
[36] Control word bit11Activate relay 1 by a control word from
[37] Control word bit12Activate relay 2 by a control word from
[40] Out of ref range Active when the actual speed is
[41] Below reference,
low
Use for performing a coasted stop for
frequency converter in torque limit
condition. If the frequency converter
has received a stop signal and is in
torque limit, the signal is logic = 0.
The brake is active and there are no
warnings.
The brake is ready for operation and
there are no faults.
IGBT is short-circuited. Use this
function to protect the frequency
converter if there is a fault on the
brake module. Use the digital output/
relay to cut out the mains voltage from
the frequency converter.
[0] Control word is selected in
parameter group 8-** Comm. and
Options.
When selected parameters in parameter
group 2-2* Mechanical Brake are active,
the output must be reinforced to carry
the current for the coil in the brake.
This issue is solved by connecting an
external relay to the selected digital
output.
the eldbus. No other functional
impact on the frequency converter.
Typical application: Controlling an
auxiliary device from a eldbus. The
function is valid when [0] FC Prole is
selected in parameter 8-10 Control Word
Prole.
the eldbus. No other functional
impact on the frequency converter.
Typical application: Controlling an
auxiliary device from a eldbus. The
function is valid when [0] FC Prole is
selected in parameter 8-10 Control Word
Prole.
outside the settings in
parameter 4-54 Warning Reference Low
and parameter 4-55 Warning Reference
High.
Active when the actual speed is below
the speed reference setting.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 63
Page 66

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[42] Above ref, high Active when the actual speed is above
the speed reference setting.
[45] Bus ctrl. Controls the digital output/relay via
bus. The state of the output is set in
parameter 5-90 Digital & Relay Bus
Control. The output state is retained in
44
[46] Bus control,
timeout: On
[47] Bus control,
timeout: O
[56] Heat sink
cleaning warning,
high
[60] Comparator 0 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[61] Comparator 1 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[62] Comparator 2 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[63] Comparator 3 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[64] Comparator 4 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[65] Comparator 5 See parameter group 13-1* Smar t Logic
[70] Logic rule 0 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
[71] Logic rule 1 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
the event of a bus timeout.
Controls output via bus. The state of
the output is set in
parameter 5-90 Digital & Relay Bus
Control. When a bus timeout occurs,
the output state is set high (on).
Controls output via bus. The state of
the output is set in
parameter 5-90 Digital & Relay Bus
Control. When a bus timeout occurs,
the output state is set low (o).
Control. If comparator 0 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
Control. If comparator 1 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
Control. If comparator 2 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
Control. If comparator 3 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
Control. If comparator 4 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
Control. If comparator 5 in SLC is TRUE,
the output goes high. Otherwise, it
goes low.
If logic rule 0 in SLC is TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
If logic rule 1 in SLC is TRUE, the
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
[72] Logic rule 2 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
If logic rule 2 in SLC is TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
[73] Logic rule 3 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
If logic rule 3 in SLC is TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
[74] Logic rule 4 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
If logic rule 4 in SLC is TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
[75] Logic rule 5 See parameter group 13-4* Logic Rules.
If logic rule 5 in SLC is TRUE, the
output goes high. Otherwise, it goes
low.
[80] SL digital outputASee parameter 13-52 SL Controller
Action. Output A is low on [32] Smart
Logic Action. Output A is high on [38]
Smart Logic Action.
[81] SL digital outputBSee parameter 13-52 SL Controller
Action. Output B is low on [32] Smart
Logic Action. Output B is high on [38]
Smart Logic Action.
[82] SL digital outputCSee parameter 13-52 SL Controller
Action. Output C is low on [32] Smart
Logic Action. Output C is high on [38]
Smart Logic Action.
[83] SL digital outputDSee parameter 13-52 SL Controller
Action. Output D is low on [32] Smart
Logic Action. Output D is high on [38]
Smart Logic Action.
[160] No alarm The output is high when no alarm is
present.
[161] Running reverse The output is high when the frequency
converter is running counterclockwise
(the logical product of the status bits
Running AND Reverse).
[165] Local ref active
[166] Remote ref active
[167] Start command
activ
[168] Drive in hand
mode
[169] Drive in auto
mode
The output is high when there is an
active start command, and no stop
command is active.
The output is high when the frequency
converter is in hand-on mode.
The output is high when the frequency
converter is in auto-on mode.
64 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 67

Selected
Event
Relay
output
Selected
Event
Relay
output
On Delay
P 5-41
On Delay
P 5-41
O Delay
P 5-42
130BA171.10
Selected
Event
Relay
output
On Delay
P 5-41
O Delay
P 5-42
130BA172.10
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
5-40 Function Relay
Option: Function:
[170] Homing
Completed
[171] Target Position
Reached
[172] Position Control
Fault
[173] Position Mech
Brake
[175] Running on
tension
[176] Ready to run The center winder control is ready to
[193] Sleep Mode The frequency converter/system has
[194] Broken Belt
Function
The homing operation is completed.
This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [2] Position Control.
The target position is reached. This
option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [2] Position Control.
A fault occurred in the positioning
process. Refer to parameter 37-18 Pos.
Ctrl Fault Reason for details about the
fault. This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [2] Position Control.
Selects mechanical control for
positioning. This option is only
eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [2] Position Control.
Indicates whether tension PID control
is active (on) or inactive (o). This
option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [1] Center winder.
run. This option is only eective when
parameter 37-00 Application Mode is set
to [1] Center winder.
entered sleep mode. See parameter
group 22-4* Sleep Mode.
A broken belt condition has been
detected. See parameter group 22-4*
Sleep Mode.
4 4
Illustration 4.15 On Delay, Relay
5-42 O Delay, Relay
Array[2]: Relay1[0], Relay2[1]
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s] Enter the delay of the relay cutout time.
Illustration 4.16 O Delay, Relay
If the selected event condition changes before the on- or
o delay timer expires, the relay output is unaected.
5-41 On Delay, Relay
Array [2] (Relay 1 [0], Relay 2 [1])
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0 - 600 s] Enter the delay of the relay cut-in time. The
relay only cuts in if the condition in
parameter 5-40 Function Relay is uninterrupted during the specied time.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 65
Page 68

130BD377.10
Ref.
Low freq.
P 5-50/
P 5-55
Input
(Hz)
High
ref.
value
P 5-53/
p 5-58
High freq.
P 5-51/
P 5-56
Low
ref.
value
P 5-52/
p 5-57
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.6.4 5-5* Pulse Input
5-53 Term. 29 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
The pulse input parameters are used to dene an
appropriate window for the impulse reference area by
conguring the scaling and lter settings for the pulse
inputs. Input terminals 29 or 33 act as frequency reference
inputs. Set terminal 29 (parameter 5-13 Terminal 29 Digital
Input) or terminal 33 (parameter 5-15 Terminal 33 Digital
Input) to [32] Pulse input. If terminal 29 is used as an input,
44
then set parameter 5-02 Terminal 29 Mode to [0] Input.
Size
related*
[-4999 4999 ]
Enter the high reference value [Hz] for the
motor shaft speed, and the high feedback
value. See also parameter 5-58 Term. 33
High Ref./Feedb. Value. Select terminal 29
as a digital input (parameter 5-02 Terminal
29 Mode = [0] Input (default) and
parameter 5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input =
applicable value).
5-55 Term. 33 Low Frequency
Range: Function:
4 Hz* [4 - 31999
Hz]
Enter the low frequency corresponding to
the low motor shaft speed (which is low
reference value) in parameter 5-57 Term. 33
Low Ref./Feedb. Value.
5-56 Term. 33 High Frequency
Range: Function:
32000
Hz*
Illustration 4.17 Pulse Input
[5 - 32000
Hz]
Enter the high frequency corresponding
to the high motor shaft speed (that is
high reference value) in
parameter 5-58 Term. 33 High Ref./Feedb.
Value.
5-50 Term. 29 Low Frequency
Range: Function:
4 Hz* [4 - 31999
Hz]
Enter the low frequency limit corresponding
to the low motor shaft speed (that is low
reference value) in parameter 5-52 Term. 29
Low Ref./Feedb. Value. Refer to
Illustration 4.17.
5-51 Term. 29 High Frequency
Range: Function:
32000
Hz*
[5 - 32000
Hz]
Enter the high frequency limit
corresponding to the high motor shaft
speed (which is high reference value) in
parameter 5-53 Term. 29 High Ref./Feedb.
Value.
5-52 Term. 29 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
0* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Enter the low reference value limit for the motor
shaft speed [Hz]. This value is also the lowest
feedback value. See also parameter 5-57 Term. 33
Low Ref./Feedb. Value. Set terminal 29 to digital
input (parameter 5-02 Terminal 29 Mode = [0]
Input and parameter 5-13 Terminal 29 Digital Input
= applicable value).
5-57 Term. 33 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
0* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Enter the low reference value [Hz] for the
motor shaft speed. This value is also the low
feedback value. See also parameter 5-52 Term.
29 Low Ref./Feedb. Value.
5-58 Term. 33 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
Size related* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Enter the high reference value [Hz]
for the motor shaft speed. See also
parameter 5-53 Term. 29 High Ref./
Feedb. Value.
66 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 69

Output value
Output
(Hz)
High output
value
P 5-60(term27)
P 5-63(term29)
High freq.
P 5-62(term27)
P 5-65(term29)
130BA089.11
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.6.5 5-6* Pulse Outputs
NOTICE
These parameters cannot be adjusted while the motor is
running.
Use these parameters to congure pulse outputs with their
functions and scaling. Terminal 27 and 29 are allocated to
pulse output via parameter 5-01 Terminal 27 Mode and
parameter 5-02 Terminal 29 Mode.
5-63 Terminal 29 Pulse Output Variable
Option: Function:
[45] Bus ctrl.
[48] Bus ctrl., timeout
[100] Output frequency
[101] Reference
[102] Process Feedback
[103] Motor Current
[104] Torque rel to limit
[105] Torq relate to rated
[106] Power
[107] Speed
[109] Max Out Freq
[113] PID Clamped Output
5-65 Pulse Output Max Freq 29
Range: Function:
5000 Hz* [4 - 32000
Hz]
Set the maximum frequency for terminal
29 corresponding to the output variable
set in parameter 5-63 Terminal 29 Pulse
Output Variable.
4.6.6 5-7* 24 V Encoder Input
4 4
Illustration 4.18 Conguration of Pulse Outputs
5-60 Terminal 27 Pulse Output Variable
Select the desired output on terminal 27.
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation
[45] Bus ctrl.
[48] Bus ctrl., timeout
[100] Output frequency
[101] Reference
[102] Process Feedback
[103] Motor Current
[104] Torque rel to limit
[105] Torq relate to rated
[106] Power
[107] Speed
[109] Max Out Freq
[113] PID Clamped Output
5-62 Pulse Output Max Freq 27
Range: Function:
5000 Hz* [4 - 32000
Hz]
Set the maximum frequency for terminal
27, corresponding to the output variable
selected in parameter 5-60 Terminal 27
Pulse Output Variable.
5-63 Terminal 29 Pulse Output Variable
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation
Connect the 24 V encoder to terminal 12 (24 V DC supply),
terminal 32 (channel A), terminal 33 (channel B), and
terminal 20 (GND). The digital inputs 32/33 are active for
encoder inputs when [1] 24 V encoder is selected in
parameter 7-00 Speed PID Feedback Source. The encoder is a
dual channel (A and B) 24 V type. Maximum input
frequency: 32 kHz.
Encoder connection to the frequency converter
24 V incremental encoder. Maximum cable length is 5 m
(16.4 ft).
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 67
Page 70

130BD366.12
+24 V DC
A
B
GND
12 18 322719 29 33 20
B
A
B
A
130BA646.10
CW
CCW
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
5-71 Term 32/33 Encoder Direction
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted
while the motor is running.
Change the detected encoder rotation
direction without changing the wiring to the
44
[0] * Clockwise
[1] Counter
clockwise
4.6.7 5-9* Bus Controlled
This parameter group selects digital and relay outputs via a
eldbus setting.
encoder.
Set channel A 90° (electrical degrees) behind
channel B after clockwise rotation of the
encoder shaft.
Set channel A 90° (electrical degrees) ahead
of channel B after clockwise rotation of the
encoder shaft.
5-90 Digital & Relay Bus Control
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 0xFFFFFFFF ] This parameter holds the state of the bus-
Illustration 4.19 24 V or 10–30 V Encoder Connection
Bit 0 Digital output terminal 27
Bit 1 Digital output terminal 29
Bit 2–3 Reserved
Bit 4 Relay 1 output terminal
Bit 6–23 Reserved
Bit 24 Terminal 42 digital output
Bit 26–31 Reserved
Table 4.7 Bit Functions
controlled digital outputs and relays.
A logical 1 indicates that the output is
high or active.
A logical 0 indicates that the output is
low or inactive.
5-93 Pulse Out 27 Bus Control
Range: Function:
Illustration 4.20 Encoder Rotation Direction
5-70 Term 32/33 Pulses Per Revolution
Range: Function:
1024* [1 - 4096 ] Set the encoder pulses per revolution on the
motor shaft. Read the correct value from the
encoder.
0 %* [0 -
100 %]
5-94 Pulse Out 27 Timeout Preset
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
100 %]
Set the output frequency transferred to the
output terminal 27 when the terminal is
congured as [45] Bus Controlled in
parameter 5-60 Terminal 27 Pulse Output
Variable.
Set the output frequency transferred to the
output terminal 27 when the terminal is
congured as [48] Bus Ctrl Timeout in
68 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 71

Ref./Feedback
Analog input
High Ref./
Feedb. Value'
Low Ref./
Feedb. Value'
'Low Voltage'or
'Low Current'
'High Voltage'or
'High Current'
1 V 5 V 10 V
10
20
30
40
50
[V]
5
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
Par 6-xx
130BD378.11
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
5-94 Pulse Out 27 Timeout Preset
Range: Function:
parameter 5-60 Terminal 27 Pulse Output Variable
and a timeout is detected.
5-95 Pulse Out 29 Bus Control
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
100 %]
Set the output frequency transferred to the
output terminal 29 when the terminal is
congured as [45] Bus Controlled in
parameter 5-63 Terminal 29 Pulse Output
Variable.
5-96 Pulse Out 29 Timeout Preset
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
100 %]
Set the output frequency transferred to the
output terminal 29 when the terminal is
congured as [48] Bus Ctrl Timeout in
parameter 5-63 Terminal 29 Pulse Output
Variable, and a timeout is detected.
4.7 Parameters: 6-** Analog In/Out
Parameter group for setting up the analog I/O congu-
ration and the digital output.
6-01 Live Zero Timeout Function
Option: Function:
[3] Jogging
[4] Max. speed
[5] Stop and
trip
4 4
Illustration 4.21 Timeout Function
The frequency converter provides 2 analog inputs:
Terminal 53.
•
Terminal 54.
•
The analog inputs can be freely allocated to either voltage
(0–10 V) or current input (0/4–20 mA).
4.7.1 6-0* Analog I/O Mode
6-00 Live Zero Timeout Time
Range: Function:
10 s* [1 - 99 s] Enter the timeout time.
4.7.2 6-1* Analog Input 53
Parameters for conguring the scaling and limits for analog
input 53 (terminal 53).
6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage
Range: Function:
0.07 V* [0 - 10V]Enter the voltage (V) that corresponds to
parameter 6-14 Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value. To activate parameter 6-01 Live Zero
Timeout Function, set the value to >1 V.
6-11 Terminal 53 High Voltage
6-01 Live Zero Timeout Function
Option: Function:
Select the timeout function. The function set
in parameter 6-01 Live Zero Timeout Function is
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 69
[0] * O
[1] Freeze
[2] Stop
output
activated if the input signal on terminal 53 or
54 is below 50% of the value in
parameter 6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage,
parameter 6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current,
parameter 6-20 Terminal 54 Low Voltage, or
parameter 6-22 Terminal 54 Low Current for a
time period dened in parameter 6-00 Live
Zero Timeout Time.
Range: Function:
10 V* [0 - 10 V] Enter the voltage (V) that corresponds to the
high reference value (set in
parameter 6-15 Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb.
Value).
6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current
Range: Function:
4 mA* [0 - 20
mA]
Enter the low current value. This reference
signal corresponds to the low reference/
feedback value that is set in
parameter 6-14 Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value. To activate parameter 6-01 Live Zero
Timeout Function, set the value to >2 mA.
Page 72

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
6-13 Terminal 53 High Current
Range: Function:
20 mA* [0 - 20
mA]
Enter the high current value corresponding
to the high reference/feedback set in
parameter 6-15 Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb.
Value.
6-14 Terminal 53 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
44
Range: Function:
0* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Enter the reference or feedback value that
corresponds to the voltage or current set in
parameter 6-10 Terminal 53 Low Voltage to
parameter 6-12 Terminal 53 Low Current.
6-15 Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb. Value
6-21 Terminal 54 High Voltage
Range: Function:
10 V* [0 - 10 V] Enter the voltage (V) that corresponds to the
high reference value (set in
parameter 6-25 Terminal 54 High Ref./Feedb.
Value).
6-22 Terminal 54 Low Current
Range: Function:
4 mA* [0 - 20
mA]
Enter the low current value. This reference
signal corresponds to the low reference/
feedback value set in parameter 6-24 Terminal
54 Low Ref./Feedb. Value. To activate the live
zero timeout function in parameter 6-01 Live
Zero Timeout Function, set the value to >2 mA.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[-4999 4999 ]
Enter the reference or feedback value
that corresponds to the voltage or
current set in parameter 6-11 Terminal
53 High Voltage to
parameter 6-13 Terminal 53 High
Current.
6-16 Terminal 53 Filter Time Constant
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0.01 - 10s]Enter the time constant. This constant is a
rst-order digital low-pass lter time
constant for suppressing electrical noise in
terminal 53. A high time constant value
improves dampening, but also increases the
time delay through the lter.
6-23 Terminal 54 High Current
Range: Function:
20 mA* [0 - 20
mA]
Enter the high current value corresponding
to the high reference/feedback value set in
parameter 6-25 Terminal 54 High Ref./Feedb.
Value.
6-24 Terminal 54 Low Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
0* [-4999 -
4999 ]
Enter the reference or feedback value that
corresponds to the voltage or current set in
parameter 6-21 Terminal 54 High Voltage/
parameter 6-22 Terminal 54 Low Current.
6-25 Terminal 54 High Ref./Feedb. Value
Range: Function:
6-19 Terminal 53 mode
Select whether terminal 53 is used for current or voltage input.
Option: Function:
[0] Current mode
[1] * Voltage mode
Size
related*
[-4999 4999 ]
Enter the reference or feedback value
that corresponds to the voltage or
current set in parameter 6-21 Terminal
54 High Voltage/
parameter 6-23 Terminal 54 High
Current.
4.7.3 6-2* Analog Input 54
Parameters for conguring the scaling and limits for analog
input 54 (terminal 54).
6-20 Terminal 54 Low Voltage
Range: Function:
0.07 V* [0 - 10V]Enter the voltage (V) that corresponds to the
low reference value (set in
parameter 6-24 Terminal 54 Low Ref./Feedb.
Value). To activate parameter 6-01 Live Zero
Timeout Function, set the value to >1 V.
70 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
6-26 Terminal 54 Filter Time Constant
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0.01 - 10s]Enter the time constant, which is a rstorder digital low-pass lter time constant
for suppressing electrical noise in terminal
54. A high time constant value improves
dampening, but also increases the time
delay through the lter.
6-29 Terminal 54 mode
Option: Function:
Select if terminal 54 is used for current
input or voltage input.
[0] Current mode
[1] * Voltage mode
Page 73

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.7.4 6-7* Analog/Digital Output 45
Parameters for conguring the scaling and limits for
analog/digital output terminal 45. Analog outputs are
current outputs: 0/4–20 mA. Resolution on analog output
is 12 bit. Analog output terminals can also be set up as
digital output.
6-70 Terminal 45 Mode
Set terminal 45 to act as analog output or as digital output.
Option: Function:
[0] * 0-20 mA
[1] 4-20 mA
[2] Digital Output
6-71 Terminal 45 Analog Output
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation
[100] Output frequency 0–100 Hz
[101] Reference Min
[102] Process Feedback MinFB–Max
[103] Motor Current 0–I
[104] Torque rel to limit
[105] Torq relate to rated
[106] Power 0–P
[107] Speed
[111] Speed Feedback
[113] PID Clamped Output
[139] Bus Control 0–100%
[143] Ext. CL 1
[162] Tapered tension set point
[254] DC Link Voltage
6-72 Terminal 45 Digital Output
Option: Function:
Select the function of terminal 45 as a
digital current output. See also
parameter 6-70 Terminal 45 Mode. See
chapter 4.6.2 5-3* Digital Outputs for each
option and description.
[0] * No operation
[198] Drive Bypass
6-73 Terminal 45 Output Min Scale
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
200 %]
Scale for the minimum output (0 or 4 mA) of
the analog signal at terminal 45. Set the value
to be the percentage of the full range of the
variable selected in parameter 6-71 Terminal 45
Analog Output.
max
Ref
nom
–Max
Ref
FB
6-74 Terminal 45 Output Max Scale
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
200 %]
Scale for the maximum output (20 mA) of the
analog signal at terminal 45. Set the value to
be the percentage of the full range of the
variable selected in parameter 6-71 Terminal 45
Analog Output.
6-76 Terminal 45 Output Bus Control
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 16384 ] Holds the level of analog output if controlled
by bus. This parameter is N2 format.
4.7.5 6-9* Analog/Digital Output 42
Parameters for conguring the limits for analog/digital
output terminal 42. Analog outputs are current outputs:
0/4–20 mA. Resolution on analog outputs is 12 bit. Analog
output terminals can also be set up as digital output.
6-90 Terminal 42 Mode
Set terminal 42 to act as analog output or as digital output.
Option: Function:
[0] * 0-20 mA
[1] 4-20 mA
[2] Digital Output
6-91 Terminal 42 Analog Output
Option: Function:
[0] * No operation
[100] Output frequency
[101] Reference
[102] Process Feedback
[103] Motor Current
[104] Torque rel to limit
[105] Torq relate to rated
[106] Power
[107] Speed
[111] Speed Feedback
[113] PID Clamped Output
[139] Bus Control
[143] Ext. CL 1
[162] Tapered tension set point
[254] DC Link Voltage
6-92 Terminal 42 Digital Output
Option: Function:
See chapter 4.6.2 5-3* Digital Outputs for
each option and description.
[0] * No operation
[198] Drive Bypass
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 71
Page 74

(mA)
0%
20
0/4
100%
Current
Analog
output
Min Scale
par. 6-93
Variable
for
output
example:
Power
Analog
Output
Max Scale
par. 6-94
130BB772.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
6-93 Terminal 42 Output Min Scale
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
200 %]
44
6-94 Terminal 42 Output Max Scale
Scale for the minimum output (0 mA or 4 mA)
of the analog signal at terminal 42. Set the
value to be the percentage of the full range of
the variable selected in parameter 6-91 Terminal
42 Analog Output.
Range: Function:
100%* [0 -
Scale for maximum output (20 mA) of the scaling
200 %]
at terminal 42. Set the value to be the
percentage of the full range of the variable
selected in parameter 6-91 Terminal 42 Analog
Output.
7-00 Speed PID Feedback Source
Option: Function:
[20] * None
7-02 Speed PID Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.015* [0 -
Enter the speed controller proportional gain. The
1 ]
proportional gain amplies the error (that is the
deviation between the feedback signal and the
setpoint). This parameter is used with
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode [1] Speed closed
loop control. Quick control is obtained at high
amplication. However, if the amplication is too
high, the process may become unstable.
7-03 Speed PID Integral Time
Range: Function:
8
Illustration 4.22 Output Scale versus Current
6-96 Terminal 42 Output Bus Control
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 16384 ] Hold the analog output at terminal 42 if
controlled by bus. This parameter is N2 format.
ms*
[2 20000
ms]
Enter the speed controller integral time, which
determines the time the internal PID control
takes to correct errors. The greater the error,
the more quickly the gain increases. The
integral time causes a delay of the signal, and
therefore a dampening eect, and can be used
to eliminate steady-state speed error. Obtain
quick control through a short integral time,
though if the integral time is too short, the
process becomes unstable. An excessively long
integral time disables the integral action,
leading to major deviations from the required
reference, since the process regulator takes too
long to regulate errors. This parameter is used
with [1] Speed closed loop control set in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode.
7-04 Speed PID Dierentiation Time
4.8 Parameters: 7-** Controllers
4.8.1 7-0* Speed PID Ctrl.
7-00 Speed PID Feedback Source
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
changed while the motor is
running.
Range: Function:
30
ms*
[0 200 ms]
Enter the speed controller dierentiation time.
The dierentiator does not react to constant
error. It provides gain proportional to the rate
of change of the speed feedback. The quicker
the error changes, the stronger the gain from
the dierentiator. The gain is proportional with
the speed at which errors change. Setting this
parameter to 0 disables the dierentiator. This
parameter is used with parameter 1-00 Congu-
ration Mode [1] Speed closed loop control.
Select feedback source for Speed CL
Control.
[1] 24V encoder
[2] MCB 102
[3] MCB 103
[6] Analog Input 53
[7] Analog Input 54
[8] Frequency input 29
[9] Frequency input 33
72 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
7-05 Speed PID Di. Gain Limit
Range: Function:
5* [1 -
20 ]
Set a limit for the gain provided by the dieren-
tiator. Since the dierential gain increases at higher
frequencies, limiting the gain may be useful. For
example, set up a pure D-link at low frequencies
and a constant D-link at higher frequencies. This
parameter is used with parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode [1] Speed closed loop control.
Page 75

0.6
0.6
f
g
= 10 Hz
175ZA293.11
Feedback
Disturbed feedback signal
t (Sec.)
t (Sec.)
Filtered feedback signal
Lowpass lter
Feedback
Par 7-07=1.00 Par 7-07=n1/n2
130BA871.10
Motor
n1 n2
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
7-06 Speed PID Lowpass Filter Time
Range: Function:
10
ms*
[1 6000
ms]
NOTICE
Severe ltering can be detrimental to
dynamic performance.
Set a time constant for the speed control low-
lter. The low-pass lter improves steady-
pass
state performance and dampens oscillations on
the feedback signal. This parameter is used
with parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode [1]
Speed closed loop or [2] Torque closed loop. This
parameter is useful if there is a great amount
of noise in the system, see Illustration 4.23. For
example, if a time constant (τ) of 100 ms is
programmed, the cuto frequency for the lowpass lter is 1/0.1 = 10 RAD/s., corresponding
to (10/2 x π) = 1.6 Hz. The PID regulator only
regulates a feedback signal that varies by a
frequency of less than 1.6 Hz. If the feedback
signal varies by a higher frequency than 1.6 Hz,
the PID regulator does not react.
Practical settings of parameter 7-06 Speed PID
Lowpass Filter Time taken from the number of
pulses per revolutions from encoder:
7-06 Speed PID Lowpass Filter Time
Range: Function:
4 4
Illustration 4.23 Feedback Signal
Encoder PPR Parameter 7-06 Speed
PID Lowpass Filter
Time
512 10 ms
7-07 Speed PID Feedback Gear Ratio
Range: Function:
1* [0.0001 - 32 ]
1024 5 ms
2048 2 ms
4096 1 ms
Illustration 4.24 Speed PID Feedback Gear
Ratio
7-08 Speed PID Feed Forward Factor
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 - 500 %] The reference signal bypasses the speed
controller by the amount specied. This
feature increases the dynamic performance
of the speed control loop.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 73
Page 76

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.8.2 7-1* Torque PI Control
7-22 Process CL Feedback 2 Resource
Option: Function:
Parameters for conguring the torque PI control.
7-12 Torque PID Proportional Gain
[4] Frequency input
33
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 500 %] Enter the proportional gain value for the
torque controller. Selection of a high value
makes the controller react faster. Too high
44
a setting leads to controller instability.
7-13 Torque PID Integration Time
Range: Function:
0.020 s* [0.002 - 2 s] Enter the integration time for the torque
controller. The lower the integration time,
the faster the controller reacts. However,
too low a setting leads to controller
instability.
4.8.4 7-3* Process PID Ctrl.
7-30 Process PID Normal/ Inverse Control
Option: Function:
Normal and inverse controls are implemented by
introducing a dierence between the reference
signal and the feedback signal.
[0] * Normal Set process control to increase the output
frequency.
[1] Inverse Set process control to decrease the output
frequency.
7-31 Process PID Anti Windup
4.8.3 7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedb.
Select the feedback sources for the process PID control,
and how this feedback should be handled.
7-20 Process CL Feedback 1 Resource
Option: Function:
[0] O Continue regulation of an error even when the output
frequency cannot be increased or decreased.
[1] * On Cease regulation of an error when the output
frequency can no longer be adjusted.
Option: Function:
The eective feedback signal is made up
of the sum of up to 2 dierent input
signals. Select which input is treated as
the source of the 1st of these signals. The
2nd input signal is dened in
parameter 7-22 Process CL Feedback 2
Resource.
[0] * No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[3] Frequency input
29
[4] Frequency input
33
7-22 Process CL Feedback 2 Resource
7-32 Process PID Start Speed
Range: Function:
0 RPM* [0 -
6000
RPM]
Enter the motor speed to be attained as a
start signal for commencement of PID
control. When the power is switched on, the
frequency converter starts to ramp and then
operates under speed open-loop control.
When the process PID start speed is reached,
the frequency converter changes to process
PID control.
7-33 Process PID Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.01* [0 - 10 ] Enter the PID proportional gain. The proportional gain multiplies the error between the
setpoint and the feedback signal.
Option: Function:
The eective feedback signal is made up
of the sum of up to 2 dierent input
signals. Select which input is treated as
the source of the 2nd of these signals.
The 1st input signal is dened in
parameter 7-20 Process CL Feedback 1
Resource.
[0] * No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[3] Frequency input
29
7-34 Process PID Integral Time
Range: Function:
9999 s* [0.10 -
9999 s]
Enter the PID integral time. The integrator
provides an increasing gain at a constant
error between the setpoint and the
feedback signal. The integral time is the
time needed by the integrator to reach the
same gain as the proportional gain.
74 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 77

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
7-35 Process PID Dierentiation Time
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 20 s] Enter the PID dierentiation time. The dieren-
tiator does not react to a constant error, but
provides a gain only when the error changes.
The shorter the PID dierentiation time, the
stronger the gain from the dierentiator.
7-36 Process PID Di. Gain Limit
Range: Function:
5* [1 - 50 ] Enter a limit for the dierentiator gain. If there is
no limit, the dierentiator gain increases when
there are fast changes. To obtain a pure dieren-
tiator gain at slow changes and a constant
dierentiator gain where fast changes occur, limit
the dierentiator gain.
7-38 Process PID Feed Forward Factor
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 -
200 %]
Enter the PID feed forward (FF) factor. The FF
factor sends a constant fraction of the reference
signal to bypass the PID control, so the PID
control only aects the remaining fraction of the
control signal. Any change to this parameter
aects the motor speed. When the FF factor is
activated, it provides less overshoot, and high
dynamics when changing the setpoint.
Parameter 7-38 Process PID Feed Forward Factor is
active when parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [3] Process.
7-39 On Reference Bandwidth
Range: Function:
5 %* [0 -
200 %]
Enter the on-reference bandwidth. When the
PID control error (the dierence between the
reference and the feedback) is less than the
value of this parameter, the on-reference
status bit is 1.
4.8.5 7-4* Advanced Process PID Ctrl.
This parameter group is only used if parameter 1-00 Cong-
uration Mode is set to [7] Extended PID speed CL.
7-40 Process PID I-part Reset
Option: Function:
[0] * No
[1] Yes Select [1] Yes to reset the I-part of the process PID
controller. The selection automatically returns to [0]
No. Resetting the I-part makes it possible to start from
a well-dened point after changing something in the
process, for example changing a textile roll.
7-41 Process PID Output Neg. Clamp
Range: Function:
-100 %* [ -100 - 100 %] Enter a negative limit for the process
PID controller output.
7-42 Process PID Output Pos. Clamp
Range: Function:
100 %* [ -100 - 100 %] Enter a positive limit for the process
PID controller output.
7-43 Process PID Gain Scale at Min. Ref.
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
100 %]
Enter a scaling percentage to apply to the
process PID output when operating at the
minimum reference. The scaling percentage is
adjusted linearly between the scale at
minimum reference (parameter 7-43 Process PID
Gain Scale at Min. Ref.) and the scale at
maximum reference (parameter 7-44 Process
PID Gain Scale at Max. Ref.).
7-44 Process PID Gain Scale at Max. Ref.
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 -
100 %]
Enter a scaling percentage to apply to the
process PID output when operating at the
maximum reference. The scaling percentage is
adjusted linearly between the scale at
minimum reference (parameter 7-43 Process PID
Gain Scale at Min. Ref.) and the scale at
maximum reference (parameter 7-44 Process
PID Gain Scale at Max. Ref.).
7-45 Process PID Feed Fwd Resource
Option: Function:
Select which frequency converter input
is used as the feed-forward factor. The
FF factor is added directly to the
output of the PID controller. This
parameter can increase dynamic
performance.
The feed-forward set from bus should
be in N2 format.
[0] * No function
[1] Analog Input 53
[2] Analog Input 54
[7] Frequency input 29
[8] Frequency input 33
[11] Local bus reference
[32] Bus PCD
7-46 Process PID Feed Fwd Normal/ Inv. Ctrl.
Option: Function:
[0] * Normal Select [0] Normal to set the feed-forward factor to
treat the FF resource as a positive value.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 75
Page 78

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
7-46 Process PID Feed Fwd Normal/ Inv. Ctrl.
Option: Function:
[1] Inverse Select [1] Inverse to treat the feed-forward resource
as a negative value.
7-48 PCD Feed Forward
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] Readout parameter where the bus
44
parameter 7-45 Process PID Feed Fwd Resource
[32] can be read.
The feed forward set from bus should be in N2
format.
7-49 Process PID Output Normal/ Inv. Ctrl.
7-53 Process PID Feed Fwd Ramp down
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0.01 - 100 s] Control the dynamics of the feed-forward
signal when ramping down.
7-56 Process PID Ref. Filter Time
Range: Function:
0.001 s* [0.001 - 1s]Set a time constant for the reference rst-
order low-pass lter. The low-pass lter
improves steady-state performance and
dampens oscillations on the reference/
feedback signals. However, severe ltering
can be detrimental to dynamic
performance.
Option: Function:
[0] * Normal Select [0] Normal to use the resulting output from
the process PID controller as is.
[1] Inverse Select [1] Inverse to invert the resulting output
from the process PID controller. This operation is
performed after the feed-forward factor is applied.
4.8.6 7-5* Ext. Process PID Ctrl.
7-57 Process PID Fb. Filter Time
Range: Function:
0.001 s* [0.001 - 1s]Set a time constant for the feedback rst-
order low-pass lter. The low-pass lter
improves steady-state performance and
dampens oscillations on the reference/
feedback signals. However, severe ltering
can be detrimental to dynamic
performance.
This parameter group is only used if parameter 1-00 Cong-
uration Mode is set to [7] Extended PID speed CL.
4.8.7 7-6* Feedback Conversion
7-50 Process PID Extended PID
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Disable the extended parts of the process PID
controller.
[1] * Enabled Enable the extended parts of the PID controller.
7-51 Process PID Feed Fwd Gain
Range: Function:
1* [0 -
100 ]
The feed forward is used to obtain the gain, based
on a well-known signal available. The PID controller
then only takes care of the smaller part of the
control, necessary because of unknown characters.
The standard feed-forward factor in
parameter 7-38 Process PID Feed Forward Factor is
always related to the reference whereas
parameter 7-51 Process PID Feed Fwd Gain has more
options. In winder applications, the feed-forward
factor is typically the line speed of the system.
Use the parameter group to congure conversions for
feedback signals.
7-60 Feedback 1 Conversion
Select a conversion for the feedback 1 signal. Select [0] Linear to
leave the feedback signal unchanged.
Option: Function:
[0] * Linear
[1] Square root
7-62 Feedback 2 Conversion
Select a conversion for the feedback 2 signal. Select [0] Linear to
leave the feedback signal unchanged.
Option: Function:
[0] * Linear
[1] Square root
7-52 Process PID Feed Fwd Ramp up
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0.01 - 100 s] Control dynamics of the feed-forward
signal when ramping up.
76 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 79

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.9 Parameters: 8-** Communications and
Options
4.9.1 8-0* General Settings
8-00 Option A warning control
This parameter is used to enable or disable installed options.
Option: Function:
[0] * None
[1] Disable Warning
8-01 Control Site
Option: Function:
The setting in this parameter overrides
the settings in parameter 8-50 Coasting
Select to parameter 8-56 Preset Reference
Select.
[0] * Digital and
ctrl.word
[1] Digital only Control by using digital inputs only.
[2] Controlword
only
8-02 Control Source
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] FC Port
[3] Option A PROFIBUS and PROFINET.
8-03 Control Timeout Time
Range: Function:
1 s* [0.1 -
6000 s]
8-04 Control Timeout Function
Select the timeout function. The timeout function activates when
the control word fails to be updated within the time period
specied in parameter 8-03 Control Word Timeout Time.
Option: Function:
[0] * O Resume control via eldbus (eldbus or
[1] Freeze output Freeze output frequency until communi-
[2] Stop Stop with auto restart until communication
Control by using both digital input and
control word.
Control by using control word only.
Select the source of the control word.
Enter the maximum time expected to pass
between the reception of 2 consecutive
telegrams. If this time is exceeded, it indicates
that the serial communication has stopped. The
function that is selected in
parameter 8-04 Control Timeout Function is then
carried out.
standard), using the most recent control
word.
cation resumes.
resumes.
8-04 Control Timeout Function
Select the timeout function. The timeout function activates when
the control word fails to be updated within the time period
specied in parameter 8-03 Control Word Timeout Time.
Option: Function:
[3] Jogging Run the motor at jog frequency until
communication resumes.
[4] Max. speed Run the motor at maximum frequency until
communication resumes.
[5] Stop and trip Stop the motor and trip, then reset the
frequency converter to restart:
Via the eldbus.
•
Via [Reset].
•
Via a digital input.
•
8-07 Diagnosis Trigger
Option: Function:
[0] * Disable Send no extended diagnosis data (EDD).
[1] Trigger on
alarms
[2] Trigger
alarm/warn.
Send EDD upon alarms.
Send EDD upon alarms or warnings in
parameter 16-90 Alarm Word,
parameter 9-53 Probus Warning Word, or
parameter 16-92 Warning Word.
4.9.2 8-1* Ctrl. Word Settings
8-10 Control Word Prole
Select the interpretation of the control and status words
corresponding to the installed eldbus. Only the selections valid
for the installed eldbus are visible in the LCP display.
Option: Function:
[0] * FC prole
[1] PROFIdrive prole
8-14 Congurable Control Word CTW
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] * Prole default
[2] CTW Valid, active low
[4] PID error inverse
[5] PID reset I part
[6] PID enable
8-19 Product Code
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 2147483647 ]
Select 0 to read out the actual
eldbus product code according
to the mounted eldbus option.
Select 1 to read out the actual
vendor ID.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 77
Page 80

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.9.3 8-3* FC Port Settings
8-30 Protocol
Option: Function:
Select the protocol for the integrated RS485
port.
[0] * FC Communication according to the FC protocol.
44
[2] Modbus RTU Communication according to the Modbus
RTU protocol.
8-31 Address
Range: Function:
1* [ 0 - 247 ] Enter the address for the RS485 port. Valid range:
1–126 for FC-bus, or 1–247 for Modbus.
8-32 Baud Rate
Option: Function:
Select the baud rate for the RS485 port.
[0] 2400 Baud
[1] 4800 Baud
[2] 9600 Baud
[3] 19200 Baud
[4] 38400 Baud
[5] 57600 Baud
[6] 76800 Baud
[7] 115200 Baud
8-33 Parity / Stop Bits
Option: Function:
[0] * Even Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[1] Odd Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[2] No Parity, 1 Stop Bit
[3] No Parity, 2 Stop Bits
8-35 Minimum Response Delay
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [ 0.0010 - 0.5s]Specify the minimum delay time
between receiving a request and
transmitting a response. This is used for
overcoming modem turn-around
delays.
8-36 Maximum Response Delay
4.9.4 8-4* FC MC Protocol Set
8-42 PCD Write Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to the PCD's telegrams. The
number of available PCDs depends on the telegram type. The
values in the PCDs are then written to the selected parameters
as data values.
Enter up to 16 dierent preset mapping 0–15 in this parameter,
using array programming. If this parameter is active, addresses
2810–2825 represent values of the 16 parameters. If this
parameter is not active, addresses 2810 and 2811 are used as
input-data-drive control word and bus reference. Addresses
2812–2825 are reserved.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] [302] Minimum Reference
[2] [303] Maximum Reference
[3] [341] Ramp 1 Ramp up
time
[4] [342] Ramp 1 Ramp down
time
[5] [351] Ramp 2 Ramp up
time
[6] [352] Ramp 2 Ramp down
time
[7] [380] Jog Ramp Time
[8] [381] Quick Stop Time
[9] [412] Motor Speed Low
Limit [Hz]
[10] [414] Motor Speed High
Limit [Hz]
[11] [590] Digital & Relay Bus
Control
[12] [676] Terminal 45 Output
Bus Control
[13] [696] Terminal 42 Output
Bus Control
[15] FC Port CTW
[16] FC Port REF
[18] [311] Jog Speed [Hz]
[19] [427] Torque limit bus
control
[20] [428] Speed limit bus
control
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0.1 - 10.0s]Specify the maximum allowed delay
time between receiving a request and
transmitting the response. If this time
is exceeded, no response is returned.
78 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 81

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
8-43 PCD Read Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to the PCDs of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. PCDs contain the actual data values of the
selected parameters.
Enter up to 16 dierent preset mapping 0-15 in this parameter,
using array programming. If this parameter is active, addresses
2910–2925 represent values of the 16 parameters. If this
parameter is not active, addresses 2910 and 2911 are used as
status word register and main actual value. Addresses 2912–2925
are reserved.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1] [1500] Operation Hours
[2] [1501] Running Hours
[3] [1502] kWh Counter
[4] [1600] Control Word
[5] [1601] Reference [Unit]
[6] [1602] Reference %
[7] [1603] Status Word
[8] [1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[9] [1609] Custom Readout
[10] [1610] Power [kW]
[11] [1611] Power [hp]
[12] [1612] Motor Voltage
[13] [1613] Frequency
[14] [1614] Motor Current
[15] [1615] Frequency [%]
[16] [1616] Torque [Nm]
[17] [1618] Motor Thermal
[18] [1630] DC Link Voltage
[19] [1634] Heatsink Temp.
[20] [1635] Inverter Thermal
[21] [1638] SL Controller State
[22] [1650] External Reference
[23] [1652] Feedback [Unit]
[24] [1660] Digital Input
18,19,27,33
[25] [1661] Terminal 53 Switch
Setting
[26] [1662] Analog input 53
[27] [1663] Terminal 54 Switch
Setting
[28] [1664] Analog input 54
[29] [1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[30] [1671] Relay output
[31] [1672] Counter A
[32] [1673] Counter B
[33] [1690] Alarm Word
[34] [1692] Warning Word
[35] [1694] Ext. Status Word
[38] [1622] Torque [%]
[41] [1657] Feedback [RPM]
[42] [1679] Analog Output 45
[mA]
8-43 PCD Read Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to the PCDs of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. PCDs contain the actual data values of the
selected parameters.
Enter up to 16 dierent preset mapping 0-15 in this parameter,
using array programming. If this parameter is active, addresses
2910–2925 represent values of the 16 parameters. If this
parameter is not active, addresses 2910 and 2911 are used as
status word register and main actual value. Addresses 2912–2925
are reserved.
Option: Function:
[43] [1617] Speed [RPM]
[44] [1666] Digital Output
4.9.5 8-5* Digital/Bus
Parameters for conguring the control word merging.
NOTICE
These parameters are active only when
parameter 8-01 Control Site is set to [0] Digital and control
word.
8-50 Coasting Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the coasting function via the
terminals (digital input) and/or via the bus.
[0] Digital
input
[1] Bus Activate coasting command via the serial
[2] Logic AND Activate coasting command via the eldbus/
[3] * Logic OR Activate coasting command via the eldbus/
8-51 Quick Stop Select
Option: Function:
[0] Digital
input
[1] Bus Activate quick stop command via the serial
[2] Logic AND Activate quick stop command via the eldbus/
[3] * Logic OR Activate quick stop command via the eldbus/
Activate coasting command via a digital input.
communication port or eldbus option.
serial communication port and 1 extra digital
input.
serial communication port or via 1 of the
digital inputs.
Activate quick stop command via a digital
input.
communication port or eldbus option.
serial communication port and additionally via
1 of the digital inputs.
serial communication port or via 1 of the
digital inputs.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 79
Page 82

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
8-52 DC Brake Select
Option: Function:
Select control of the DC brake via the terminals
(digital input) and/or via the eldbus.
NOTICE
When parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is
set to [1] PM non-salient SPM, only
8-55 Set-up Select
Select the trigger for the set-up selection.
Option: Function:
[2] Logic AND The eldbus/serial communication port and a
digital input trigger the set-up selection.
[3] * Logic OR The eldbus/serial communication port or a
digital input triggers the set-up selection.
selection [0] Digital input is available.
44
[0] Digital
input
[1] Bus Activate DC brake command via the serial
[2] Logic
AND
[3] * Logic OR Activate DC brake command via the eldbus/
8-53 Start Select
Select the trigger for the start function.
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input A digital input triggers the start function.
[1] Bus A serial communication port or the eldbus
[2] Logic AND The eldbus/serial communication port and a
[3] * Logic OR The eldbus/serial communication port or a
8-54 Reversing Select
Option: Function:
[0] Digital
input
[1] Bus A serial communication port or the eldbus
[2] Logic AND The eldbus/serial communication port and a
[3] * Logic OR The eldbus/serial communication port or a
8-55 Set-up Select
Select the trigger for the set-up selection.
Activate DC brake command via a digital input.
communication port or eldbus option.
Activate DC brake command via the eldbus/
serial communication port and additionally via 1
of the digital inputs.
serial communication port or via 1 of the digital
inputs.
triggers the start function.
digital input trigger the start function.
digital input triggers the start function.
Select the trigger for the reversing function.
A digital input triggers the reversing function.
triggers the reversing function.
digital input trigger the reversing function.
digital input triggers the reversing function.
8-56 Preset Reference Select
Option: Function:
Select the trigger for the preset reference
selection.
[0] Digital
input
[1] Bus A serial communication port or the eldbus
[2] Logic AND The eldbus/serial communication port and a
[3] * Logic OR The eldbus/serial communication port or a
A digital input triggers the preset reference
selection.
triggers the preset reference selection.
digital input trigger the preset reference
selection.
digital input triggers the preset reference
selection.
8-57 Prodrive OFF2 Select
Select control of the frequency converter OFF2 selection via the
terminals (digital input) and/or via the eldbus. This parameter is
active only when parameter 8-01 Control Site is set to [0] Digital
and ctrl. word and parameter 8-10 Control Word Prole is set to [1]
PROFIdrive prole.
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input
[1] Bus
[2] Logic AND
[3] * Logic OR
8-58 Prodrive OFF3 Select
Select control of the frequency converter OFF3 selection via the
terminals (digital input) and/or via the eldbus. This parameter is
active only when parameter 8-01 Control Site is set to [0] Digital
and ctrl. word, and parameter 8-10 Control Word Prole is set to [1]
PROFIdrive prole.
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input
[1] Bus
[2] Logic AND
[3] * Logic OR
Option: Function:
[0] Digital input A digital input triggers the set-up selection.
[1] Bus A serial communication port or the eldbus
triggers the set-up selection.
80 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 83

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
4.9.6 8-7* Protocol SW Version
8-79 Protocol Firmware version
Range: Function:
Size related* [0 - 655 ] Firmware revision: FC is in index 0;
Modbus is in index 1; indexes 2–4 are
reserved.
4.9.7 8-8* FC Port Diagnostics
These parameters are used for monitoring the bus
communication via the frequency converter port.
8-80 Bus Message Count
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
valid telegrams detected on the bus.
8-81 Bus Error Count
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
telegrams with faults (for example CRC
faults) detected on the bus.
8-82 Slave Messages Rcvd
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
valid telegrams sent by the frequency
converter to the slave.
8-83 Slave Error Count
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
error telegrams, which could not be
executed by the frequency converter.
8-84 Slave Messages Sent
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
messages sent from the slave.
8-85 Slave Timeout Errors
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] This parameter shows the number of
slave timeout errors.
8-88 Reset FC port Diagnostics
Option: Function:
[0] * Do not reset Do not reset all FC port diagnostic counters.
[1] Reset counter Reset all FC port diagnostic counters.
4.9.8 8-9* Bus Feedback
Use the parameter group to congure the bus feedback.
8-90 Bus Jog 1 Speed
Range: Function:
100 RPM* [ 0 - 1500
RPM]
Enter the jog speed. This is a xed
jog speed activated via the serial
port or eldbus option.
8-91 Bus Jog 2 Speed
Range: Function:
200 RPM* [ 0 - 1500
RPM]
Enter the jog speed. This value is a
xed jog speed activated via the
serial port or eldbus option.
4.10 Parameters: 9-** PROFIdrive
For more information about PROFIBUS parameter
®
descriptions, see the VLT
PROFIBUS DP Programming Guide.
For more information about PROFINET parameter
descriptions, see the VLT
PROFINET Programming Guide.
9-00 Setpoint
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
65535 ]
This parameter receives cyclic reference from a
master class 2. If the control priority is set to
master class 2, the reference for the frequency
converter is taken from this parameter, whereas
the cyclic reference is ignored.
9-07 Actual Value
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] This parameter delivers the MAV for a master
class 2. The parameter is valid if the control
priority is set to master class 2.
9-15 PCD Write Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to PCD 3–10 of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. Values in PCD 3–10 are written to the selected
parameters as data. For standard PROFIBUS telegrams, see
parameter 9-22 Telegram Selection.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[302] Minimum Reference
[303] Maximum Reference
[311] Jog Speed [Hz]
[312] Catch up/slow Down Value
[341] Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time
[342] Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time
[351] Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time
[352] Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time
AutomationDrive FC 360
®
AutomationDrive FC 360
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 81
Page 84

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
9-15 PCD Write Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to PCD 3–10 of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. Values in PCD 3–10 are written to the selected
parameters as data. For standard PROFIBUS telegrams, see
parameter 9-22 Telegram Selection.
Option: Function:
[380] Jog Ramp Time
44
[381] Quick Stop Ramp Time
[412] Motor Speed Low Limit [Hz]
[414] Motor Speed High Limit [Hz]
[416] Torque Limit Motor Mode
[417] Torque Limit Generator Mode
[427] Torque Limit Bus Control
[428] Speed Limit Bus Control
[553] Term. 29 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[558] Term. 33 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[590] Digital & Relay Bus Control
[593] Pulse Out 27 Bus Control
[595] Pulse Out 29 Bus Control
[615] Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb.
Value
[625] Terminal 54 High Ref./Feedb.
Value
[676] Terminal 45 Output Bus Control
[696] Terminal 42 Output Bus Control
[733] Process PID Proportional Gain
[734] Process PID Integral Time
[735] Process PID Dierentiation Time
[748] PCD Feed Forward
[890] Bus Jog 1 Speed
[891] Bus Jog 2 Speed
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
9-16 PCD Read Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to PCD 3–10 of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. Values in PCD 3–10 contain the actual data values
of the selected parameters.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[1500] Operating hours
[1501] Running Hours
9-16 PCD Read Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to PCD 3–10 of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. Values in PCD 3–10 contain the actual data values
of the selected parameters.
Option: Function:
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
82 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 85

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
9-16 PCD Read Conguration
Select the parameters to be assigned to PCD 3–10 of the
telegrams. The number of available PCDs depends on the
telegram type. Values in PCD 3–10 contain the actual data values
of the selected parameters.
Option: Function:
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
9-18 Node Address
Range: Function:
126* [ 1 -
126 ]
Enter the station address in this parameter or,
alternatively, in the hardware switch. To adjust the
station address in parameter 9-18 Node Address,
set the hardware switch to 126 or 127 (that is all
switches set to on). Otherwise, this parameter
shows the actual setting of the switch.
9-19 Drive Unit System Number
Range: Function:
1037* [0 - 65535 ] Manufacturer specic system ID.
9-22 Telegram Selection
Select a standard PROFIBUS telegram conguration for the
frequency converter as an alternative to the freely congurable
telegrams in parameter 9-15 PCD Write Conguration and
parameter 9-16 PCD Read Conguration.
Option: Function:
[1] Standard telegram 1
[100] * None
[101] PPO 1
[102] PPO 2
[103] PPO 3
[104] PPO 4
[105] PPO 5
[106] PPO 6
[107] PPO 7
[108] PPO 8
[200] Custom telegram 1
9-23 Parameters for Signals
Option: Function:
[0] * None
[302] Minimum Reference
[303] Maximum Reference
[311] Jog Speed [Hz]
[312] Catch up/slow Down Value
[341] Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time
[342] Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time
[351] Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time
[352] Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time
[380] Jog Ramp Time
[381] Quick Stop Ramp Time
[412] Motor Speed Low Limit [Hz]
[414] Motor Speed High Limit [Hz]
[416] Torque Limit Motor Mode
[417] Torque Limit Generator Mode
[427] Torque Limit Bus Control
[428] Speed Limit Bus Control
[553] Term. 29 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[558] Term. 33 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[590] Digital & Relay Bus Control
[593] Pulse Out 27 Bus Control
[595] Pulse Out 29 Bus Control
[615] Terminal 53 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[625] Terminal 54 High Ref./Feedb. Value
[676] Terminal 45 Output Bus Control
[696] Terminal 42 Output Bus Control
[733] Process PID Proportional Gain
[734] Process PID Integral Time
[735] Process PID Dierentiation Time
[748] PCD Feed Forward
[890] Bus Jog 1 Speed
[891] Bus Jog 2 Speed
[1500] Operating hours
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference [Unit]
[1602] Reference [%]
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual Value [%]
[1609] Custom Readout
[1610] Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1622] Torque [%]
[1630] DC Link Voltage
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 83
Page 86

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
9-23 Parameters for Signals
Option: Function:
[1633] Brake Energy /2 min
[1634] Heatsink Temp.
[1635] Inverter Thermal
[1638] SL Controller State
[1639] Control Card Temp.
[1650] External Reference
44
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot Reference
[1657] Feedback [RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53 Setting
[1662] Analog input 53
[1663] Terminal 54 Setting
[1664] Analog input 54
[1665] Analog output 42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[1667] Pulse input 29 [Hz]
[1668] Pulse input 33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse output 27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse output 29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay output
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1679] Analog output 45 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW 1
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1684] Comm. Option STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word 2
[1694] Ext. Status Word
[1695] Ext. Status Word 2
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[3401] PCD 1 Write For Application
[3402] PCD 2 Write For Application
[3403] PCD 3 Write For Application
[3404] PCD 4 Write For Application
[3405] PCD 5 Write For Application
[3406] PCD 6 Write For Application
[3407] PCD 7 Write For Application
[3408] PCD 8 Write For Application
[3409] PCD 9 Write For Application
[3410] PCD 10 Write For Application
[3421] PCD 1 Read For Application
[3422] PCD 2 Read For Application
[3423] PCD 3 Read For Application
[3424] PCD 4 Read For Application
[3425] PCD 5 Read For Application
[3426] PCD 6 Read For Application
[3427] PCD 7 Read For Application
9-23 Parameters for Signals
Option: Function:
[3428] PCD 8 Read For Application
[3429] PCD 9 Read For Application
[3430] PCD 10 Read For Application
[3450] Actual Position
[3456] Track Error
9-27 Parameter Edit
Option: Function:
Parameters can be edited via PROFIBUS, the
standard RS485 interface, or the LCP.
[0] Disabled Disable editing via PROFIBUS.
[1] * Enabled Enable editing via PROFIBUS.
9-28 Process Control
Option: Function:
Process control (setting of control word, speed
reference, and process data) is possible via either
PROFIBUS or standard eldbus, but not both
simultaneously. Local control is always possible via
the LCP. Control via process control is possible via
either terminals or eldbus depending on the
settings in parameter 8-50 Coasting Select to
parameter 8-56 Preset Reference Select.
[0] Disable Disables process control via PROFIBUS master
class 1 and enables process control via standard
eldbus or PROFIBUS master class 2.
[1]*Enable
cyclic
master
Enables process control via PROFIBUS master class
1 and disables process control via standard
eldbus or PROFIBUS master class 2.
9-44 Fault Message Counter
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
65535 ]
Indicates the number of fault events presently
stored in parameter 9-45 Fault Code. The buer
capacity is maximum 8 error events. The buer
and counter are set to 0 by reset or power-up.
9-45 Fault Code
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 0 ] This buer contains the alarm word for all alarms
and warnings that have occurred since last reset or
power-up. The buer capacity is maximum 8 error
events.
9-47 Fault Number
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 0 ] This buer contains the alarm word for all alarms
and warnings that have occurred since last reset or
power-up. The buer capacity is maximum 8 error
events.
84 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 87

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
9-52 Fault Situation Counter
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 1000 ] Indicates the number of fault events that have
occurred since last reset or power-up.
9-53 Probus Warning Word
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
65535 ]
This parameter shows PROFIBUS communication
warnings.
Bit Description
0 Connection with DP master is lost.
1 Not used.
2 FDL (eldbus data link layer) is not
OK.
3 Clear data command received.
4 Actual value is not updated.
5 Baud rate search.
6 PROFIBUS ASIC is not transmitting.
7 Initializing of PROFIBUS is not OK.
8 Frequency converter is tripped.
9 Internal CAN error.
10 Wrong conguration data from PLC.
11 Wrong ID sent by PLC.
12 Internal fault occurred.
13 Not congured.
14 Timeout active.
15 Warning 34 active.
9-64 Device Identication
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
NOTICE
0 ]
This parameter is not visible via LCP.
The device identication parameter. The data type is
array [n] of unsigned16. The assignment of the 1
subindexes is dened and shown in Table 4.9.
Index Content Value
0 Manufacturer 128
1 Device type 1
2 Version xxyy
3 Firmware date year yyyy
4 Firmware date
month
5 No. of axes Variable
6 Vendor specic: PB
Version
7 Vendor specic:
Database Version
8 Vendor specic:
AOC Version
9 Vendor specic:
MOC Version
Table 4.9 Device Identication 1st Subindex
Assignment
st
4 4
ddmm
xxyy
xxyy
xxyy
xxyy
Table 4.8 Bit Denition
9-63 Actual Baud Rate
Option: Function:
This parameter shows the actual
PROFIBUS baud rate. The PROFIBUS
master automatically sets the baud
rate.
[0] 9,6 kbit/s
[1] 19,2 kbit/s
[2] 93,75 kbit/s
[3] 187,5 kbit/s
[4] 500 kbit/s
[6] 1500 kbit/s
[7] 3000 kbit/s
[8] 6000 kbit/s
[9] 12000 kbit/s
[10] 31,25 kbit/s
[11] 45,45 kbit/s
[255] * No baudrate found
9-65 Prole Number
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 0 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is not visible via LCP.
This parameter contains the prole identication.
Byte 1 contains the prole number and byte 2 the
version number of the prole.
9-67 Control Word 1
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] This parameter accepts the control word from a
master class 2 in the same format as PCD 1.
9-68 Status Word 1
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] This parameter delivers the status word for a
master class 2 in the same format as PCD 2.
9-70 Edit Set-up
Option: Function:
Select the set-up in which programming
(change of data) is performed during operation.
It is possible to program the 2 set-ups
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 85
Page 88

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
9-70 Edit Set-up
Option: Function:
independently of the set-up selected as active
set-up. Parameter access from each master is
directed to the set-up selected by the
individual master (cyclic, acyclic MCL1, 1
acyclic MCL2, 2nd acyclic MCL2, 3rd acyclic
MCL2).
44
[1] Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[9] * Active Set-
up
st
9-71 Probus Save Data Values
9-81 Dened Parameters (2)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
9-82 Dened Parameters (3)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
9-83 Dened Parameters (4)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
Option: Function:
Parameter values changed via RS485 are not
automatically stored in a non-volatile memory.
Use this parameter to activate a function that
stores parameter values in the EEPROM nonvolatile memory, so changed parameter values
are retained at power-down.
[0] * O Deactivates the non-volatile storage function.
[1] Store all
setups
Stores all parameter values in the set-up selected
in parameter 9-70 Edit Set-up in the non-volatile
memory. The selection returns to [0] O when all
values are stored.
9-84 Dened Parameters (5)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
9-85 Dened Parameters (6)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
9-90 Changed Parameters (1)
Range: Function:
9-72 ProbusDriveReset
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Resets the VLT® PROFIBUS DP MCA
101 option only.
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the frequency
converter parameters deviating from default
setting.
9-91 Changed Parameters (2)
Range: Function:
[0] * No action
[1] Power-on reset Resets the frequency converter after
power-up, as for power cycle.
[2] Power-on reset
prep
[3] Comm option
reset
When reset, the frequency converter
disappears from the eldbus, which may
cause a communication error from the
master.
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the frequency
converter parameters deviating from default
setting.
9-92 Changed Parameters (3)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the frequency
converter parameters deviating from default
setting.
9-75 DO Identication
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] Provides information about the DO (drive
object). This parameter is for PROFINET only.
9-93 Changed Parameters (4)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the frequency
converter parameters deviating from default
setting.
9-80 Dened Parameters (1)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the dened
frequency converter parameters.
86 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 89

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
9-94 Changed Parameters (5)
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] This parameter shows a list of all the frequency
converter parameters deviating from default
setting.
9-99 Probus Revision Counter
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 65535 ] Readout of revision count.
4.11 Parameters: 12-** Ethernet
For more information about Ethernet parameter
descriptions, see the VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
PROFINET Programming Guide.
4.11.1 12-0* IP Settings
12-00 IP Address Assignment
Option: Function:
Select the IP address assignment method.
[0] MANUAL IP address can be set in parameter 12-01 IP
Address.
[1] DHCP IP address is assigned via DHCP server.
[2] BOOTP IP address is assigned via BOOTP server.
[10] * DCP DCP is assigned via the DCP protocol.
12-01 IP Address
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
12-02 Subnet Mask
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
12-03 Default Gateway
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
12-04 DHCP Server
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 2147483647 ]
Congure the IP address of the option.
Read-only if parameter 12-00 IP Address
Assignment is set to [1] DHCP, [2] BOOTP,
or via DIP switches.
Congure the IP subnet mask of the
option. Read-only if parameter 12-00 IP
Address Assignment is set to [1] DHCP or
[2] BOOTP.
Congure the IP default gateway of the
option. Read-only if parameter 12-00 IP
Address Assignment set to [1] DHCP or [2]
BOOTP.
NOTICE
A power cycle is necessary after
setting the IP parameters manually.
12-04 DHCP Server
Range: Function:
Read-only. Shows the IP address of the
found DHCP or BOOTP server.
12-05 Lease Expires
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] Read-only. Shows the lease time left for
the current DHCP-assigned IP address.
12-06 Name Servers
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] IP addresses of domain name servers.
Can be automatically assigned when
using DHCP.
12-07 Domain Name
Range: Function:
0* [1 - 48 ] Domain name of the attached network. Can be
automatically assigned when using DHCP network.
12-08 Host Name
Range: Function:
0* [1 - 48 ] Logical (given) name of option.
12-09 Physical Address
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 17 ] Read-only. Shows the physical (MAC) address of
the option.
4.11.2 12-1* Ethernet Link Parameters
12-10 Link Status
Option: Function:
[0] * No Link
[1] Link Shows the link status of the Ethernet ports.
12-11 Link Duration
Range: Function:
Size related* [ 0 - 0 ] Shows the duration of the present link
on each port in dd:hh:mm:ss.
12-12 Auto Negotiation
Option: Function:
Congures auto negotiation of Ethernet link
parameters, for each port: ON or OFF.
[0] O Link speed and link duplex can be congured in
parameter 12-13 Link Speed and parameter 12-14 Link
Duplex.
[1] * On
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 87
Page 90

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
12-13 Link Speed
Option: Function:
Forces the link speed for each port in 10 Mbps
or 100 Mbps. If parameter 12-12 Auto Negotiation
is set to [1] On, this parameter is read-only and
shows the actual link speed. If no link is present,
None is shown.
[0] * None
44
[1] 10 Mbps
[2] 100
Mbps
12-14 Link Duplex
Option: Function:
Forces the duplex for each port to full or half
duplex. If parameter 12-12 Auto Negotiation is
set to [1] On, this parameter is read-only.
[0] Half Duplex
[1] * Full Duplex
4.11.3 12-8* Other Ethernet Services
12-80 FTP Server
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled
[1] Enabled
12-81 HTTP Server
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled
[1] Enabled
12-82 SMTP Service
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled
[1] Enabled
12-89 Transparent Socket Channel Port
Range: Function:
4000* [0 - 65535 ] Congures the TCP port number for the
transient socket channel. This enables FC
telegrams to be sent transiently on Ethernet
via TCP. Default value is 4000. 0 indicates
disabled.
4.11.4 12-9* Advanced Ethernet Services
12-90 Cable Diagnostic
Option: Function:
Enables/disables advanced cable diagnosis
function. If enabled, the distance to cable errors
can be read out in parameter 12-93 Cable Error
Length. The parameter resumes to the default
12-90 Cable Diagnostic
Option: Function:
setting [0] Disable after the diagnostics have
nished.
NOTICE
The cable diagnostics function is only
issued on ports where there is no link (see
parameter 12-10 Link Status).
[0] * Disabled
[1] Enabled
12-91 Auto Cross Over
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Disabling of the auto-crossover function
requires crossed Ethernet cables for daisychaining the options.
[0] Disabled Disables the auto-crossover function.
[1] * Enabled Enables the auto-crossover function.
12-92 IGMP Snooping
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled
[1] * Enabled
12-93 Cable Error Length
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
65535 ]
12-94 Broadcast Storm Protection
Range: Function:
-1 %* [-1 -
If cable diagnostics is enabled in
parameter 12-90 Cable Diagnostic, the built-in
switch is possible via time domain reectometry
(TDR). This is a measurement technique which
detects common cabling problems such as open
circuits, short circuits, and impedance mismatches
or breaks in transmission cables. The distance from
the option to the error is shown in meters with an
accuracy of ±2 m (6.6 ft). The value 0 means no
errors detected.
The built-in switch is capable of protecting the
20 %]
switch system from receiving too many broadcast
packages, which can use up network resources. The
value indicates a percentage of the total
bandwidth that is allowed for broadcast messages.
Example:
OFF means that the lter is disabled - all broadcast
messages are passed through. The value 0% means
that no broadcast messages are passed through. A
value of 10% means that 10% of the total
bandwidth is allowed for broadcast messages. If
88 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 91

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
12-94 Broadcast Storm Protection
Range: Function:
the amount of broadcast messages exceeds the
10% threshold, they are blocked.
12-95 Broadcast Storm Filter
Applies to parameter 12-94 Broadcast Storm Protection, if the
broadcast storm protection also includes multicast telegrams.
Option: Function:
[0] * Broadcast only
[1] Broadcast & Multicast
12-96 Port Cong
Option: Function:
[0] * Normal
[1] Mirror Port 1 to 2
[2] Mirror Port 2 to 1
[10] Port 1 disabled
[11] Port 2 disabled
[254] Mirror Int. Port to 1
[255] Mirror Int. Port to 2
4 4
12-98 Interface Counters
Range: Function:
4000* [0 -
4294967295 ]
Read-only.
Advanced interface counters from a
built-in switch can be used for lowlevel troubleshooting. The parameter
shows a sum of port 1 + port 2.
12-99 Media Counters
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 4294967295 ] Read-only.
Advanced interface counters from a builtin switch can be used for low-level
troubleshooting. The parameter shows a
sum of port 1 + port 2.
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 89
Page 92

. . .
. . .
Par. 13-11
Comparator Operator
Par. 13-43
Logic Rule Operator 2
Par. 13-51
SL Controller Event
Par. 13-52
SL Controller Action
130BB671.13
Coast
Start timer
Set Do X low
Select set-up 2
. . .
Running
Warning
Torque limit
Digital input X 30/2
. . .
=
TRUE longer than..
. . .
. . .
130BA062.14
State 1
13-51.0
13-52.0
State 2
13-51.1
13-52.1
Start
event P13-01
State 3
13-51.2
13-52.2
State 4
13-51.3
13-52.3
Stop
event P13-02
Stop
event P13-02
Stop
event P13-02
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
4.12 Parameters: 13-** Smart Logic Control
Smart logic control (SLC) is a sequence of user-dened
actions (see parameter 13-52 SL Controller Action) executed
by the SLC when the associated user-dened event (see
parameter 13-51 SL Controller Event) is evaluated as true by
the SLC.
The condition for an event can be a particular status, or
that the output from a logic rule or a comparator operand
44
becomes true. That leads to an associated action as
illustrated:
Illustration 4.26 Events and Actions
Starting and stopping the SLC
Start and stop the SLC by selecting [1] On or [0]
O in
parameter 13-00 SL Controller Mode. The SLC always starts
in state 0 (where it evaluates event [0]). The SLC starts
when the Start Event (dened in parameter 13-01 Start
Event) is evaluated as true (provided that [1] On is selected
in parameter 13-00 SL Controller Mode). The SLC stops when
the stop event (parameter 13-02 Stop Event) is true.
Parameter 13-03 Reset SLC resets all SLC parameters and
starts programming from scratch.
NOTICE
SLC is only active in auto-on mode, not hand-on mode.
4.12.1 13-0* SLC Settings
Illustration 4.25 Smart Logic Control (SLC)
Events and actions are each numbered and linked in pairs
(states). This means that when the 1st event is fullled
(becomes true), the 1st action is executed. After this, the
conditions of the 2nd event are evaluated and if evaluated
true, the 2nd action is executed, and so on. Only 1 event is
evaluated at any time. If an event is evaluated as false,
nothing happens (in the SLC) during the current scan
interval and no other events are evaluated. This means
that when the SLC starts, it evaluates the 1st event (and
only the 1st event) in each scan interval. Only when the 1
st
event is evaluated true, the SLC executes the 1st action and
starts evaluating the 2nd event. It is possible to program 1–
20 events and actions.
When the last event/action has been executed, the
sequence starts over again from the 1st event/action.
Illustration 4.26 shows an example with 3 events/actions:
90 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Use the SLC settings to activate, deactivate, and reset the
smart logic control sequence. The logic functions and
comparators are always running in the background, which
opens for separate control of digital inputs and outputs.
13-00 SL Controller Mode
Option: Function:
[0] * O Disable the smart logic controller.
[1] On Enable the smart logic controller.
13-01 Start Event
Option: Function:
[0] False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
Page 93

Par. 13-11
Comparator Operator
=
TRUE longer than.
. . .
. . .
Par. 13-10
Comparator Operand
Par. 13-12
Comparator Value
130BB672.10
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
13-01 Start Event
Option: Function:
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[33] Digital input DI18
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] * Start command
[40] Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
[83] Broken Belt
13-02 Stop Event
Option: Function:
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] Start command
[40] * Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
[70] SL Time-out 3
[71] SL Time-out 4
[72] SL Time-out 5
[73] SL Time-out 6
[74] SL Time-out 7
[83] Broken Belt
13-03 Reset SLC
Option: Function:
[0] * Do not reset
SLC
[1] Reset SLC Reset all parameters in parameter group 13-
Retain programmed settings in parameter
group 13-** Smart Logic.
** Smart Logic to default settings.
4 4
[0] False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[30] SL Time-out 0
[31] SL Time-out 1
[32] SL Time-out 2
[33] Digital input DI18
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 91
13-02 Stop Event
Option: Function:
4.12.2 13-1* Comparators
Comparators are used for comparing continuous variables
(that is output frequency, output current, analog input, and
so on.) to xed preset values.
Illustration 4.27 Comparators
There are digital values that are compared to xed time
values. See explanation in parameter 13-10 Comparator
Operand. Comparators are evaluated once in each scan
interval. Use the result (true or false) directly. All
parameters in this parameter group are array parameters
with index 0 to 5. Select index 0 to program comparator 0,
select index 1 to program comparator 1, and so on.
13-10 Comparator Operand
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled
[1] Reference %
Page 94

. . .
. . .
. . .
. . .
Par. 13-43
Logic Rule Operator 2
Par. 13-41
Logic Rule Operator 1
Par. 13-40
Logic Rule Boolean 1
Par. 13-42
Logic Rule Boolean 2
Par. 13-44
Logic Rule Boolean 3
130BB673.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
44
13-10 Comparator Operand
Option: Function:
[2] Feedback %
[3] Motor speed
[4] Motor Current
[6] Motor power
[7] Motor voltage
[8] DC-link voltage
[12] Analog input AI53
[13] Analog input AI54
[18] Pulse input FI29
[19] Pulse input FI33
[20] Alarm number
[30] Counter A
[31] Counter B
13-11 Comparator Operator
Option: Function:
Select the operator to be used in the
comparison. This is an array parameter
containing comparator operators 0–5.
[0] Less Than (<) The result of the evaluation is true when the
variable selected in
parameter 13-10 Comparator Operand is
smaller than the xed value in
parameter 13-12 Comparator Value. The result
is false if the variable selected in
parameter 13-10 Comparator Operand is
greater than the xed value in
parameter 13-12 Comparator Value.
[1]*Approx.Equal
(~)
[2] Greater Than
(>)
The result of the evaluation is true when the
variable speed selected in
parameter 13-10 Comparator Operand is
approximately equal to the xed value in
parameter 13-12 Comparator Value.
Inverse logic of [0] Less Than (<).
13-12 Comparator Value
Range: Function:
0* [-9999 -
9999 ]
Enter the trigger level for the variable that is
monitored by this comparator. This is an
array parameter containing comparator
values 0–5.
until the timer value entered in this parameter has elapsed.
Then it becomes true again.
All parameters in this parameter group are array
parameters with index 0 to 2. Select index 0 to program
timer 0, select index 1 to program timer 1, and so on.
13-20 SL Controller Timer
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 3600s]Enter the value to dene the duration of the
false output from the programmed timer. A
timer is only false if it is started by an action
(for example [29] Start timer 1) and until the
given timer value has elapsed.
4.12.4 13-4* Logic Rules
Combine up to 3 boolean inputs (true/false inputs) from
timers, comparators, digital inputs, status bits, and events
using the logical operators AND, OR, and NOT. Select
boolean inputs for the calculation in parameter 13-40 Logic
Rule Boolean 1, parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2, and
parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3. Dene the operators
used to logically combine the selected inputs in
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1 and
parameter 13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2.
Illustration 4.28 Logic Rules
Priority of calculation
The results of parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1,
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1, and
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 are calculated rst.
The outcome (true/false) of this calculation is combined
with the settings of parameter 13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
and parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3, yielding the nal
result (true/false) of the logic rule.
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1
4.12.3 13-2* Timers
Use the result (true or false) from timers directly to dene
an event (see parameter 13-51 SL Controller Event), or as
boolean input in a logic rule (see parameter 13-40 Logic
Rule Boolean 1, parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2, or
parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3). A timer is only false
when started by an action (for example [29] Start timer 1)
92 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Option: Function:
Select the 1st boolean (true or false)
input for the selected logic rule. See
parameter 13-01 Start Event ([0]–[61])
and parameter 13-02 Stop Event ([70]–
[74]) for further description.
[0] * False
[1] True
[2] Running
Page 95

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1
Option: Function:
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[30] SL Time-out 0
[31] SL Time-out 1
[32] SL Time-out 2
[33] Digital input DI18
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] Start command
[40] Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
[70] SL Time-out 3
[71] SL Time-out 4
[72] SL Time-out 5
[73] SL Time-out 6
[74] SL Time-out 7
[83] Broken Belt
13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1
Option: Function:
Select the 1st logical operator to use on the
boolean inputs from parameter 13-40 Logic
Rule Boolean 1 and parameter 13-42 Logic Rule
Boolean 2.
[0] * Disabled Ignore parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2,
parameter 13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2, and
parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3.
[1] AND Evaluate the expression [13-40] AND [13-42].
[2] OR Evaluate the expression [13-40] OR [13-42].
13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1
Option: Function:
[3] AND NOT Evaluate the expression [13-40] AND NOT
[13-42].
[4] OR NOT Evaluate the expression [13-40] OR NOT
[13-42].
[5] NOT AND Evaluate the expression NOT [13-40] AND
[13-42].
[6] NOT OR Evaluate the expression NOT [13-40] OR
[13-42].
[7] NOT AND
NOT
[8] NOT OR
NOT
Evaluate the expression NOT [13-40] AND
NOT [13-42].
Evaluate the expression NOT [13-40] OR NOT
[13-42].
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2
Option: Function:
Select the 2nd boolean (true or false)
input for the selected logic rule. See
parameter 13-01 Start Event ([0]–[61]),
and parameter 13-02 Stop Event ([70]–
[74]) for further description.
[0] * False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[30] SL Time-out 0
[31] SL Time-out 1
[32] SL Time-out 2
[33] Digital input DI18
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] Start command
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 93
Page 96

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2
Option: Function:
[40] Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
44
[70] SL Time-out 3
[71] SL Time-out 4
[72] SL Time-out 5
[73] SL Time-out 6
[74] SL Time-out 7
[83] Broken Belt
13-43 Logic Rule Operator 2
Option: Function:
Select the 2nd logical operator to be used on
the boolean input calculated in
parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1,
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1, and
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2, and
the boolean input coming from
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2.
Parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2
signies the boolean input of
parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3.
Parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1, and
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2 signify
the boolean input calculated in
parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1,
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1, and
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2.
[0] * Disabled Ignore parameter 13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3.
[1] AND
[2] OR
[3] AND NOT
[4] OR NOT
[5] NOT AND
[6] NOT OR
[7] NOT AND
NOT
[8] NOT OR NOT
13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3
13-44 Logic Rule Boolean 3
Option: Function:
[0] * False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[30] SL Time-out 0
[31] SL Time-out 1
[32] SL Time-out 2
[33] Digital input DI18
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] Start command
[40] Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
[70] SL Time-out 3
[71] SL Time-out 4
[72] SL Time-out 5
[73] SL Time-out 6
[74] SL Time-out 7
[83] Broken Belt
Option: Function:
Select the 3rd boolean (true or false)
input for the selected logic rule. See
parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1,
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1,
and parameter 13-42 Logic Rule
Boolean 2, and the boolean input.
See parameter 13-01 Start Event ([0]–
[61]), and parameter 13-02 Stop Event
([70]–[74]) for further description.
4.12.5 13-5* States
13-51 SL Controller Event
Option: Function:
Select the 3rd boolean (true or false)
input for the selected logic rule. See
parameter 13-40 Logic Rule Boolean 1,
parameter 13-41 Logic Rule Operator 1,
94 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 97

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
13-51 SL Controller Event
Option: Function:
parameter 13-42 Logic Rule Boolean 2,
and the boolean input. See
parameter 13-01 Start Event ([0]–[61])
and parameter 13-02 Stop Event ([70]–
[74]) for further description.
[0] * False
[1] True
[2] Running
[3] In range
[4] On reference
[7] Out of current range
[8] Below I low
[9] Above I high
[16] Thermal warning
[17] Mains out of range
[18] Reversing
[19] Warning
[20] Alarm (trip)
[21] Alarm (trip lock)
[22] Comparator 0
[23] Comparator 1
[24] Comparator 2
[25] Comparator 3
[26] Logic rule 0
[27] Logic rule 1
[28] Logic rule 2
[29] Logic rule 3
[30] SL Time-out 0
[31] SL Time-out 1
[32] SL Time-out 2
[33] Digital input DI18
[34] Digital input DI19
[35] Digital input DI27
[36] Digital input DI29
[39] Start command
[40] Drive stopped
[42] Auto Reset Trip
[50] Comparator 4
[51] Comparator 5
[60] Logic rule 4
[61] Logic rule 5
[70] SL Time-out 3
[71] SL Time-out 4
[72] SL Time-out 5
[73] SL Time-out 6
[74] SL Time-out 7
[83] Broken Belt
13-52 SL Controller Action
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled Select the action corresponding to the SLC
event. Actions are executed when the
corresponding event (dened in
parameter 13-51 SL Controller Event) is
evaluated as true.
[1] No action
[2] Select set-up1Changes the active set-up
(parameter 0-10 Active Set-up) to 1. If the setup is changed, it merges with other set-up
commands coming from either the digital
inputs, or via a eldbus.
[3] Select set-up2Changes the active set-up
(parameter 0-10 Active Set-up) to 2. If the setup is changed, it merges with other set-up
commands coming from either the digital
inputs, or via a eldbus.
[10] Select preset
ref 0
[11] Select preset
ref 1
[12] Select preset
ref 2
[13] Select preset
ref 3
[14] Select preset
ref 4
[15] Select preset
ref 5
[16] Select preset
ref 6
Select preset reference 0. If the active preset
reference is changed, it merges with other
preset reference commands coming from
either the digital inputs or via a eldbus.
Selects preset reference 1. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
Selects preset reference 2. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
Selects preset reference 3. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
Selects preset reference 4. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
Selects preset reference 5. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
Selects preset reference 6. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 95
Page 98

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
13-52 SL Controller Action
Option: Function:
[17] Select preset
ref 7
[18] Select ramp 1 Selects ramp 1.
44
[19] Select ramp 2 Selects ramp 2.
[22] Run Issues a start command to the frequency
[23] Run reverse Issues a start reverse command to the
[24] Stop Issues a stop command to the frequency
[25] Qstop Issues a quick stop command to the
[26] DC Brake Issues a DC-brake command to the
[27] Coast The frequency converter coasts immediately.
[28] Freeze output Freezes the output of the frequency
[29] Start timer 0 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
[30] Start timer 1 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
[31] Start timer 2 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
[32] Set digital
out A low
[33] Set digital
out B low
[34] Set digital
out C low
[35] Set digital
out D low
[38] Set digital
out A high
[39] Set digital
out B high
[40] Set digital
out C high
[41] Set digital
out D high
[60] Reset
Counter A
[61] Reset
Counter B
Selects preset reference 7. If the active
preset reference is changed, it merges with
other preset reference commands coming
from either the digital inputs, or via a
eldbus.
converter.
frequency converter.
converter.
frequency converter.
frequency converter.
All stop commands including the coast
command stop the SLC.
converter.
further description.
further description.
further description.
Any output with SL output A is low.
Any output with SL output B is low.
Any output with SL output C is low.
Any output with SL output D is low.
Any output with SL output A is high.
Any output with SL output B is high.
Any output with SL output C is high.
Any output with SL output D is high.
Resets Counter A to zero.
Resets Counter B to zero.
13-52 SL Controller Action
Option: Function:
[70] Start Timer 3 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
further description.
[71] Start Timer 4 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
further description.
[72] Start Timer 5 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
further description.
[73] Start Timer 6 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
further description.
[74] Start Timer 7 See parameter 13-20 SL Controller Timer for
further description.
4.13 Parameters: 14-** Special Functions
14-01 Switching Frequency
Option: Function:
Select the inverter switching frequency. Changing
the switching frequency helps to reduce acoustic
noise from the motor.
[0] Ran3 3 kHz true random PWM (white noise
modulation).
[1] Ran5 5 kHz true random PWM (white noise
modulation).
[2] 2.0 kHz
[3] 3.0 kHz
[4] 4.0 kHz
[5] 5.0 kHz
[6] 6.0 kHz
[7] 8.0 kHz
[8] 10.0 kHz
[9] 12.0 kHz
[10] 16.0 kHz
14-03 Overmodulation
Option: Function:
[0] O To avoid torque ripple on the motor shaft, select [0]
O for no overmodulation of the output voltage. This
feature may be useful for applications such as grinding
machines.
[1] * On Select [1] On to enable the overmodulation function
for the output voltage. Select this setting when it is
required that the output voltage is >95% of the input
voltage (typical when running oversynchronously). The
output voltage is increased according to the degree of
overmodulation.
NOTICE
Overmodulation leads to increased torque
ripple as harmonics are increased.
96 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
Page 99

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
14-07 Dead Time Compensation Level
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 100 ]
Level of applied deadtime compensation
in percentage. A high level (>90%)
optimizes the dynamic motor response; a
level 50–90% is good for both motortorque-ripple minimization and the
motor dynamics. A 0-level turns the
deadtime compensation o.
14-08 Damping Gain Factor
Range: Function:
Size related* [0 - 100 %] Damping factor for DC-link voltage
compensation.
14-09 Dead Time Bias Current Level
Range: Function:
Size related* [0 - 100 %] Set a bias signal (in [%]) to add to
the current-sense signal for deadtime
compensation.
4.13.1 14-1* Mains On/O
Parameters for conguring mains failure monitoring and
handling. If a mains failure appears, the frequency
converter tries to continue in a controlled way until the
power in the DC link is exhausted.
14-10 Mains Failure
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Parameter 14-10 Mains Failure cannot be
changed while the motor is running.
Parameter 14-10 Mains Failure is typically used
where short mains interruptions (voltage dips) are
present. At 100% load and a short voltage
interruption, the DC voltage on the main
capacitors drops quickly. For larger frequency
converters, it only takes a few milliseconds before
the DC level is down to about 373 V DC and the
IGBTs cut
mains is restored, and the IGBTs start again, the
output frequency and voltage vector do not
correspond to the speed/frequency of the motor,
and the result is normally an overvoltage or
overcurrent, mostly resulting in a trip lock.
Parameter 14-10 Mains Failure can be programmed
to avoid this situation.
Select the function to which the frequency
converter must act when the threshold in
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level has been
reached.
o and lose control of the motor. When
14-10 Mains Failure
Option: Function:
[0]*No
function
[1] Ctrl.
rampdown
[2] Ctrl.
rampdown,
trip
[3] Coasting Centrifuges can run for an hour without power
[4] Kinetic
back-up
The frequency converter does not compensate for
a mains interruption. The voltage on the DC-link
drops quickly, and the motor is lost within
milliseconds to seconds. Trip lock is the result.
The frequency converter retains control of the
motor and does a controlled ramp down from
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level level. If
parameter 2-10 Brake Function is [0] O or [2] AC
brake, the ramp follows the overvoltage ramping.
If parameter 2-10 Brake Function is [1] Resistor
Brake, the ramp follows the setting in
parameter 3-81 Quick Stop Ramp Time. This
selection is useful in pump applications, where the
inertia is low and the friction is high. When mains
is restored, the output frequency ramps the motor
up to the reference speed (if the mains
interruption is prolonged, the controlled ramp
down might take down the output frequency to 0
RPM, and when the mains is restored, the
application is ramped up from 0 RPM to the
previous reference speed via the normal ramp up).
If the energy in the DC-link disappears before the
motor is ramped to 0, the motor is coasted.
This selection is similar to selection [1] Ctrl. ramp-
down, except that in [2] Ctrl. ramp-down, trip a
reset is necessary for starting up after power-up.
supply. In those situations, it is possible to select a
coast function at mains interruption, together with
a ying start, which occurs when the mains is
restored.
Kinetic back-up ensures that the frequency
converter keeps running as long as there is energy
in the system due to the inertia from motor and
load. This is done by converting the mechanical
energy to the DC-link and thereby maintaining
control of the frequency converter and motor. This
can extend the controlled operation, depending
on the inertia in the system. For fans, it is typically
several seconds, for pumps up to 2 s and for
compressors only for a fraction of a second. Many
industry applications can extend controlled
operation for many seconds, which is often
enough time for the mains to return.
4 4
MG06C802 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. 97
Page 100

130BC918.10
U
14-11*1.35
Ref
n [RPM]
t [S]
A B CDE A
DC
U
DC
[V]
t [S]
14-11*1.35
Ref
790 V
0
A B C D
130BC920.10
U
n [RPM]
t [S]
DC
U
DC
[V]
t [S]
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 360
14-10 Mains Failure
Option: Function:
44
[5] Kinetic
back-up,
trip
98 Danfoss A/S © 12/2018 All rights reserved. MG06C802
A Normal operation
B Mains failure
C Kinetic back-up
D Mains return
E Normal operation: Ramping
Illustration 4.29 Kinetic Back-up
The DC-level during [4] Kinetic back-up is
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level x 1.35.
If the mains does not return, UDC is maintained as
long as possible by ramping the speed down
towards 0 RPM. Finally, the frequency converter
coasts.
If mains returns while in kinetic back-up, U
increases above parameter 14-11 Mains Fault
Voltage Level x 1.35. This is detected in 1 of the
following ways:
If UDC >parameter 14-11 Mains Fault
•
Voltage Level x 1.35 x 1.05
If the speed is above the reference. This
•
is relevant if mains comes back at a
lower level than before, for example,
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level
x 1.35 x 1.02. This does not fulll the
criterion above, and the frequency
converter tries to reduce UDC to
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level
x 1.35 by increasing the speed. This does
not succeed as mains cannot be lowered.
If running motoric. The same mechanism
•
as in the previous point, but where the
inertia prevents the speed from going
above the reference speed. This leads to
the motor running motoric until the
speed is above the reference speed, and
the above situation occurs. Instead of
waiting for that, the present criterion is
introduced.
The dierence between kinetic back-up with and
without trip is that the latter always ramps down
to 0 RPM and trips, regardless of whether mains
return or not.
14-10 Mains Failure
Option: Function:
The function is made so that it does not even
detect if mains return. This is the reason for the
relatively high level on the DC-link during ramp
down.
A Normal operation
B Mains failure
C Kinetic back-up
D Trip
Illustration 4.30 Kinetic Back-up Trip
[6] Alarm
[7] Kin.
DC
back-up,
trip w
recovery
Kinetic back-up with recovery combines the
features of kinetic back-up and kinetic back-up
with trip. This feature makes it possible to select
between kinetic back-up and kinetic back-up with
trip based on a recovery speed, which is cong-
urable in parameter 14-15 Kin. Back-up Trip
Recovery Level to enable detection of mains
returning. If the mains do not return, the
frequency converter ramps down to 0 RPM and
trips. If mains return while kinetic back-up is at a
speed above the value set in parameter 14-15 Kin.
Back-up Trip Recovery Level, normal operation is
resumed. This is equal to [4] Kinetic Back-up. The
DC level during [7] Kinetic back-up is
parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level x 1.35. If
mains return while kinetic back-up is at a speed
below parameter 14-15 Kin. Back-up Trip Recovery
Level, the frequency converter ramps down to 0
RPM using the ramp and then trips.
14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level
Range: Function:
342V* [100 -
800 V]
This parameter denes the threshold voltage at
which the selected function in
parameter 14-10 Mains Failure is activated. Based
on the supply quality, consider to select 90% of
the nominal mains as the detection level. For a
supply of 380 V, parameter 14-11 Mains Fault
Voltage Level should be set to 342 V. This results
in a DC detection level of 462 V
(parameter 14-11 Mains Fault Voltage Level x
1.35).
 Loading...
Loading...