
ENGINEERING TOMORROW
Programming Guide
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Software versions, control card MK II: 8.43, 48.40
vlt-drives.danfoss.com


Contents Programming Guide
Contents
1 Introduction
1.1 Software Version
1.2 Approvals
1.3 Denitions
1.3.1 Frequency Converter 4
1.3.2 Input 4
1.3.3 Motor 4
1.3.4 References 5
1.3.5 Miscellaneous 5
1.4 Safety
1.5 Electrical Wiring
1.6 Integrated Motion Controller
2 How to Program
2.1 Graphical and Numerical Local Control Panels
2.1.1 LCD Display 13
2.1.2 Quick Transfer of Parameter Settings between Multiple Frequency Converters 15
2.1.3 Display Mode 15
4
4
4
4
7
9
11
12
12
2.1.4 Display Mode - Selection of Readouts 15
2.1.5 Parameter Set-up 17
2.1.6 Quick Menu Key Functions 17
2.1.7 Initial Commissioning 18
2.1.8 Main Menu Mode 19
2.1.9 Parameter Selection 19
2.1.10 Changing Data 19
2.1.11 Changing a Text Value 19
2.1.12 Changing a Data Value 20
2.1.13 Innitely Variable Change of Numeric Data Value 20
2.1.14 Value, Step by Step 20
2.1.15 Readout and Programming of Indexed Parameters 20
2.1.16 How to Program on the Numerical Local Control Panel 20
2.1.17 LCP Keys 22
3 Parameter Descriptions
3.1 Parameters: 0-** Operation and Display
3.2 Parameters: 1-** Load and Motor
24
24
48
3.3 Parameters: 2-** Brakes
3.4 Parameters: 3-** Reference/Ramps
3.5 Parameters: 4-** Limits/Warnings
3.6 Parameters: 5-** Digital In/Out
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 1
79
86
102
114

Contents
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3.7 Parameters: 6-** Analog In/Out
3.8 Parameters: 7-** Controllers
3.9 Parameters: 8-** Communications and Options
3.10 Parameters: 9-** PROFIBUS
3.11 Parameters: 10-** DeviceNet CAN Fieldbus
3.12 Parameters: 12-** Ethernet
3.13 Parameters: 13-** Smart Logic Control
3.14 Parameters: 14-** Special Functions
3.15 Parameters: 15-** Drive Information
3.16 Parameters: 16-** Data Readouts
3.17 Parameters: 17-** Feedback
3.18 Parameters: 18-** Data Readouts 2
3.19 Parameters: 19-** Application Parameters
3.20 Parameters: 22-** Appl. Functions
3.21 Parameters: 23-** Time-based Functions
3.22 Parameters: 30-** Special Features
3.23 Parameters: 31-** Bypass Option
162
172
183
200
200
200
201
228
242
250
259
269
271
271
271
278
283
3.24 Parameters: 32-** MCO Basic Settings
3.25 Parameters: 33-** MCO Advanced Settings
3.26 Parameters: 34-** MCO Data Readouts
3.27 Parameters: 35-** Sensor Input Option
3.28 Parameters: 36-** Programmable I/O Option
3.29 Parameters: 40-** Special Settings
3.30 Parameters: 42-** Safety Functions
3.31 Parameters: 43-** Unit Readouts
3.32 Parameters: 600-** PROFIsafe
3.33 Parameters: 601-** PROFIdrive 2
4 Integrated Motion Controller
4.1 Introduction
4.2 Positioning, Homing, and Synchronization
4.3 Control
5 Parameter Lists
5.1 Introduction
283
286
293
295
297
305
306
310
312
312
313
313
313
317
320
320
5.2 Parameter Lists and Options
6 Troubleshooting
6.1 Status Messages
7 Appendix
7.1 Symbols, Abbreviations, and Conventions
2 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
321
351
351
365
365

Contents Programming Guide
Index
366
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 3
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
11
1 Introduction
1.1 Software Version
Programming Guide
Software versions:
Control card MK II: 8.33, 48.40
The software version number can be read from
parameter 15-43 Software Version.
Group 1 Reset, coast stop, reset and coast stop, quick stop,
DC brake, stop, the [OFF] key.
Group 2 Start, pulse start, reversing, start reversing, jog,
freeze output.
Table 1.2 Function Groups
1.3.3 Motor
Table 1.1 Software Version
Motor running
1.1.1 Control Card MK II
Software version 8.03/48.33 and later can only be installed
on control card MK II. Software version 7.62/48.22 and
earlier can only be installed on control card MK I. Identify
the control card version by the color of the USB port:
MK I: Black USB port.
MK II: White USB port.
1.2 Approvals
1.3 Denitions
1.3.1 Frequency Converter
I
VLT,MAX
Maximum output current.
I
VLT,N
Rated output current supplied by the frequency converter.
U
VLT,MAX
Maximum output voltage.
1.3.2 Input
Control command
Start and stop the connected motor with LCP and digital
inputs.
Functions are divided into 2 groups.
Functions in group 1 have higher priority than functions in
group 2.
Torque generated on output shaft and speed from 0 RPM
to maximum speed on motor.
f
JOG
Motor frequency when the jog function is activated (via
digital terminals).
f
M
Motor frequency.
f
MAX
Maximum motor frequency.
f
MIN
Minimum motor frequency.
f
M,N
Rated motor frequency (nameplate data).
I
M
Motor current (actual).
I
M,N
Rated motor current (nameplate data).
n
M,N
Nominal motor speed (nameplate data).
n
s
Synchronous motor speed.
2 × par . 1 − 23 × 60s
ns=
n
slip
par . 1 − 39
Motor slip.
P
M,N
Rated motor power (nameplate data in kW or hp).
T
M,N
Rated torque (motor).
U
M
Instant motor voltage.
U
M,N
Rated motor voltage (nameplate data).
4 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
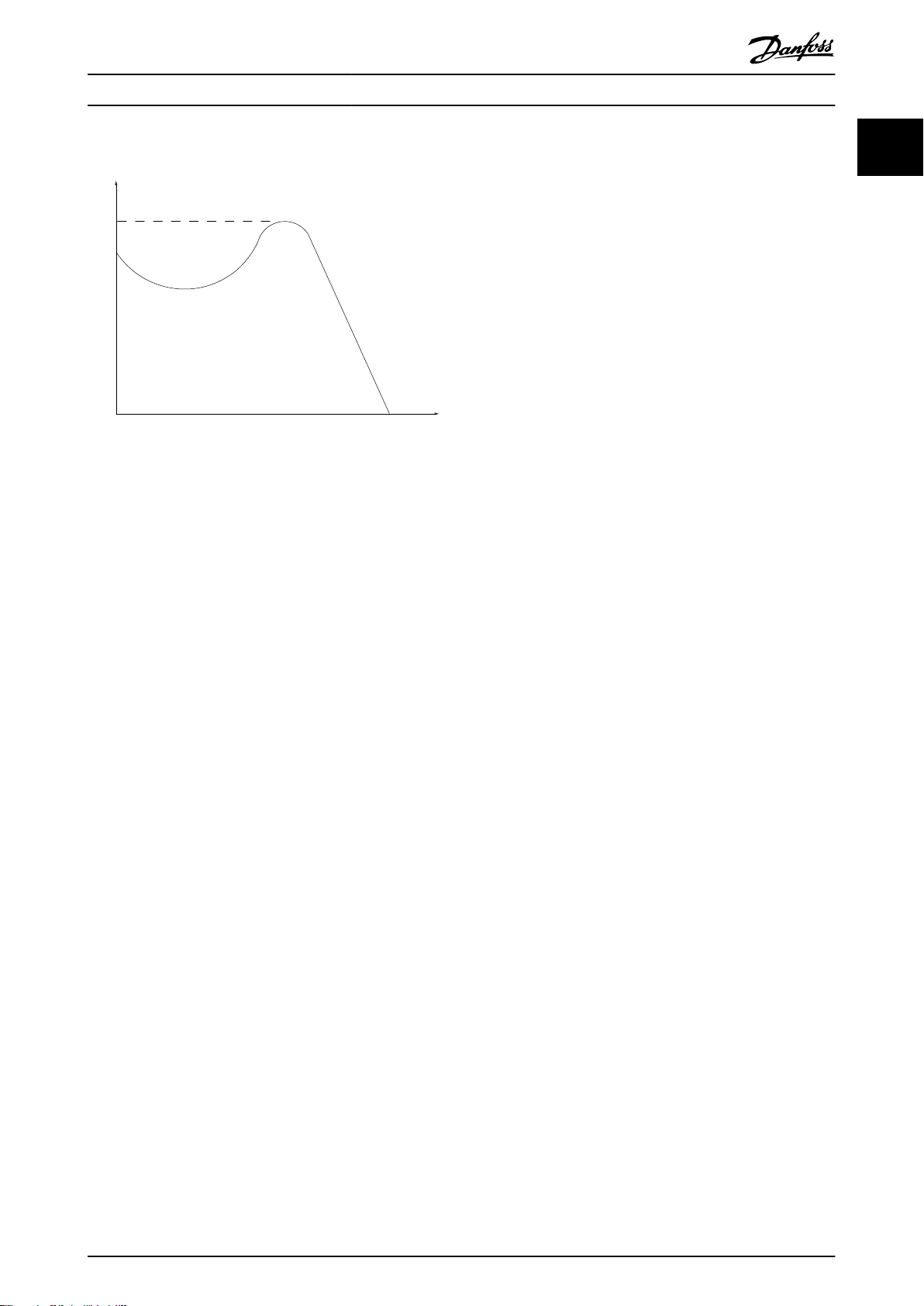
175ZA078.10
Pull-out
RPM
Torque
Introduction Programming Guide
Break-away torque
Illustration 1.1 Break-away Torque
η
VLT
The eciency of the frequency converter is dened as the
ratio between the power output and the power input.
Start-disable command
A stop command belonging to Group 1 control commands
- see Table 1.2.
Stop command
A stop command belonging to Group 1 control commands
- see Table 1.2.
1.3.4 References
Analog reference
A signal transmitted to the analog inputs 53 or 54 (voltage
or current).
Binary reference
A signal transmitted to the serial communication port.
Preset reference
A dened preset reference to be set from -100% to +100%
of the reference range. Selection of 8 preset references via
the digital terminals.
Pulse reference
A pulse frequency signal transmitted to the digital inputs
(terminal 29 or 33).
Ref
MAX
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
100% full scale value (typically 10 V, 20 mA) and the
resulting reference. The maximum reference value is set in
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.
Ref
MIN
Determines the relationship between the reference input at
0% value (typically 0 V, 0 mA, 4 mA) and the resulting
reference. The minimum reference value is set in
parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference.
1.3.5 Miscellaneous
Analog inputs
The analog inputs are used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
There are 2 types of analog inputs:
Current input, 0–20 mA, and 4–20 mA
Voltage input, -10 V DC to +10 V DC.
Analog outputs
The analog outputs can supply a signal of 0–20 mA and 4–
20 mA.
Automatic motor adaptation, AMA
The AMA algorithm determines the electrical parameters
for the connected motor at standstill.
Brake resistor
The brake resistor is a module capable of absorbing the
brake power generated in regenerative braking. This
regenerative brake power increases the DC-link voltage
and a brake chopper ensures that the power is transmitted
to the brake resistor.
CT characteristics
Constant torque characteristics used for all applications
such as conveyor belts, displacement pumps, and cranes.
Digital inputs
The digital inputs can be used for controlling various
functions of the frequency converter.
Digital outputs
The frequency converter features 2 solid-state outputs that
can supply a 24 V DC (maximum 40 mA) signal.
DSP
Digital signal processor.
ETR
Electronic thermal relay is a thermal load calculation based
on present load and time. Its purpose is to estimate the
motor temperature.
HIPERFACE
HIPERFACE® is a registered trademark by Stegmann.
Initializing
If initializing is carried out (parameter 14-22 Operation
Mode), the frequency converter returns to the default
setting.
Intermittent duty cycle
An intermittent duty rating refers to a sequence of duty
cycles. Each cycle consists of an on-load and an
period. The operation can be either periodic duty or nonperiodic duty.
IGBT
An insulated-gate bipolar transistor is a power semiconductor electronic module which combines high eciency
and fast switching. In frequency converters, it synthesizes
the sinusoidal current output with pulse-width modulation.
Some IGBT modules additionally control a brake resistor.
®
o-load
1 1
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 5

Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
11
LCP
The local control panel makes up a complete interface for
control and programming of the frequency converter. The
control panel is detachable and can be installed up to 3 m
(10 ft) from the frequency converter, that is, in a front
panel with the installation kit option.
NLCP
Numerical local control panel interface for control and
programming of the frequency converter. The display is
numerical and the panel is used to show process values.
The NLCP has no storage and copy functions.
lsb
Least signicant bit.
msb
Most signicant bit.
MCM
Short for mille circular mil, an American measuring unit for
cable cross-section. 1 MCM=0.5067 mm2.
Online/oine parameters
Changes to online parameters are activated immediately
after the data value is changed. Press [OK] to activate
changes to o-line parameters.
Process PID
The PID control maintains the required speed, pressure,
temperature, and so on, by adjusting the output frequency
to match the varying load.
PCD
Process control data.
Power cycle
Switch o the mains until the display (LCP) is dark, then
turn power on again.
Pulse input/incremental encoder
An external, digital pulse transmitter used for feeding back
information on motor speed. The encoder is used in
applications where great accuracy in speed control is
required.
RCD
Residual current device.
Set-up
Save parameter settings in 4 set-ups. Change between the
4 parameter set-ups and edit 1 set-up, while another setup is active.
SFAVM
Switching pattern called stator ux-oriented asynchronous
vector modulation (parameter 14-00 Switching Pattern).
Slip compensation
The frequency converter compensates for the motor slip by
giving the frequency a supplement that follows the
measured motor load keeping the motor speed almost
constant.
SLC
The SLC (smart logic control) is a sequence of user-dened
actions executed when the associated user-dened events
are evaluated as true by the SLC. (See
chapter 3.13 Parameters: 13-** Smart Logic Control).
STW
Status word.
FC standard bus
Includes RS485 bus with FC protocol or MC protocol. See
parameter 8-30 Protocol.
THD
Total harmonic distortion states the total contribution of
harmonics.
Thermistor
A temperature-dependent resistor placed on the frequency
converter or the motor.
Trip
A state entered in fault situations, for example if the
frequency converter is subject to an overtemperature or
when the frequency converter is protecting the motor,
process, or mechanism. The frequency converter prevents a
restart until the cause of the fault has disappeared. To
cancel the trip state, restart the frequency converter. Do
not use the trip state for personal safety.
Trip lock
The frequency converter enters this state in fault situations
to protect itself. The frequency converter requires physical
intervention, for example when there is a short circuit on
the output. A trip lock can only be canceled by disconnecting mains, removing the cause of the fault, and
reconnecting the frequency converter. Restart is prevented
until the trip state is canceled by activating reset or,
sometimes, by being programmed to reset automatically.
Do not use the trip lock state for personal safety.
VT characteristics
Variable torque characteristics used for pumps and fans.
+
VVC
If compared with standard voltage/frequency ratio control,
voltage vector control (VVC+) improves the dynamics and
the stability, both when the speed reference is changed
and in relation to the load torque.
60° AVM
60° asynchronous vector modulation
(parameter 14-00 Switching Pattern).
Power factor
The power factor is the relation between I1 and I
Power factor =
3xUxI1cosϕ
3xUxI
RMS
RMS
.
The power factor for 3-phase control:
Power factor =
I1xcosϕ1
I
RMS
=
I
1
sincecosϕ1 = 1
I
RMS
The power factor indicates to which extent the frequency
converter imposes a load on the mains supply.
6 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Introduction Programming Guide
The lower the power factor, the higher the I
same kW performance.
2
2
I
= I
RMS
In addition, a high power factor indicates that the dierent
harmonic currents are low.
The DC coils in the frequency converters produce a high
power factor, which minimizes the imposed load on the
mains supply.
Target position
The nal target position specied by positioning
commands. The prole generator uses this position to
calculate the speed prole.
Commanded position
The actual position reference calculated by the prole
generator. The frequency converter uses the commanded
position as setpoint for position PI.
Actual position
The actual position from an encoder, or a value that the
motor control calculates in open loop. The frequency
converter uses the actual position as feedback for position
PI.
Position error
Position error is the dierence between the actual position
and the commanded position. The position error is the
input for the position PI controller.
Position unit
The physical unit for position values.
1.4
+ I
1
Safety
5
+ I
2
+ .. + I
7
2
n
RMS
for the
WARNING
HIGH VOLTAGE
Drives contain high voltage when connected to AC mains
input, DC supply, or load sharing. Failure to perform
installation, start-up, and maintenance by qualied
personnel can result in death or serious injury.
Only qualied personnel must perform instal-
•
lation, start-up, and maintenance.
Before performing any service or repair work,
•
use an appropriate voltage measuring device to
make sure that there is no remaining voltage on
the drive.
Ground the equipment properly, protect the user
•
against supply voltage, and protect the motor
against overload in accordance with applicable
national and local regulations.
The ground leakage current exceeds 3.5 mA.
•
Ensure correct grounding of the equipment by a
certied electrical installer.
Do not remove the plugs for the motor and
•
mains supply while the frequency converter is
connected to mains. Check that the mains supply
has been disconnected and that the necessary
time has elapsed before removing motor and
mains plugs.
The frequency converter has more voltage
•
sources than L1, L2, and L3, when load sharing
(linking of DC intermediate circuit) or external
24 V DC is installed. Check that all voltage
sources have been disconnected and that the
necessary time has elapsed before commencing
repair work. For information about the discharge
time, see Table 1.3.
WARNING
UNINTENDED START
When the drive is connected to AC mains, DC supply, or
load sharing, the motor may start at any time.
Unintended start during programming, service, or repair
work can result in death, serious injury, or property
damage. The motor can start via an external switch, a
eldbus command, an input reference signal from the
LCP, or after a cleared fault condition.
To prevent unintended motor start:
Disconnect the drive from the mains.
•
Press [O/Reset] on the LCP before
•
programming parameters.
Completely wire and assemble the drive, motor,
•
and any driven equipment before connecting
the drive to AC mains, DC supply, or load
sharing.
1 1
Safety regulations
Disconnect mains supply to the frequency
•
converter whenever repair work is to be carried
out. Check that the mains supply has been
disconnected and that the necessary time has
elapsed before removing motor and mains supply
plugs. For information about the discharge time,
see Table 1.3.
[O] does not disconnect the mains supply and
•
must not be used as a safety switch.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 7
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
11
WARNING
DISCHARGE TIME
The frequency converter contains DC-link capacitors,
which can remain charged even when the frequency
converter is not powered. High voltage can be present
even when the warning LED indicator lights are o.
Failure to wait the specied time after power has been
removed before performing service or repair work can
result in death or serious injury.
Stop the motor.
•
Disconnect AC mains and remote DC-link power
•
supplies, including battery back-ups, UPS, and
DC-link connections to other frequency
converters.
Disconnect or lock PM motor.
•
Wait for the capacitors to discharge fully. The
•
minimum waiting time is specied in Table 1.3
and is also visible on the product label on top
of the frequency converter.
Before performing any service or repair work,
•
use an appropriate voltage measuring device to
make sure that the capacitors are fully
discharged.
Voltage [V] Minimum waiting time (minutes)
4 7 15
200–240 0.25–3.7 kW
(0.34–5 hp)
380–500 0.25–7.5 kW
(0.34–10 hp)
525–600 0.75–7.5 kW
(1–10 hp)
525–690 – 1.5–7.5 kW
– 5.5–37 kW
(7.5–50 hp)
– 11–75 kW
(15–100 hp)
– 11–75 kW
(15–100 hp)
(2–10 hp)
(15–100 hp)
11–75 kW
NOTICE
Hazardous situations must be identied by the machine
builder/integrator who is responsible for considering the
necessary preventive means. More monitoring and
protective devices may be included, always according to
valid national safety regulations, for example law on
mechanical tools and regulations for the prevention of
accidents.
Crane, lifts, and hoists
The controlling of external brakes must always have a
redundant system. The frequency converter can in no
circumstances be the primary safety circuit. Comply with
relevant standards, for example:
Hoists and cranes: IEC 60204-32.
Lifts: EN 81.
Protection mode
Once a hardware limit on motor current or DC-link voltage
is exceeded, the frequency converter enters protection
mode. Protection mode means a change of the PWM
modulation strategy and a low switching frequency to
minimize losses. This continues for 10 s after the last fault
and increases the reliability and the robustness of the
frequency converter while re-establishing full control of the
motor.
In hoist applications, protection mode is not usable
because the frequency converter is unable to leave this
mode again and therefore it extends the time before
activating the brake, which is not recommended.
Protection mode can be disabled by setting
parameter 14-26 Trip Delay at Inverter Fault to 0, which
means that the frequency converter trips immediately if 1
of the hardware limits is exceeded.
NOTICE
Disabling protection mode in hoisting applications
(parameter 14-26 Trip Delay at Inverter Fault = 0) is
recommended.
Table 1.3 Discharge Time
NOTICE
When using Safe Torque O, always follow the
instructions in VLT® Frequency Converters - Safe Torque
O Operating Instructions.
NOTICE
Control signals from, or internally within, the frequency
converter may in rare cases be activated in error, be
delayed, or fail to occur entirely. When used in situations
where safety is critical, for example when controlling the
electromagnetic brake function of a hoist application, do
not rely on these control signals exclusively.
8 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
3 Phase
power
input
DC bus
Switch Mode
Power Supply
Motor
Analog Output
Interface
relay 1
relay 2
ON=Terminated
OFF=Open
Brake
resistor
130BC931.12
91 (L1)
92 (L2)
93 (L3)
PE
88 (-)
89 (+)
50 (+10 V OUT)
53 (A IN)
54 (A IN)
55 (COM A IN)
0/4-20 mA
12 (+24 V OUT)
13 (+24 V OUT)
37 (D IN)
18 (D IN)
20 (COM D IN)
10 V DC
15 mA 130/200 mA
+ - + -
(U) 96
(V) 97
(W) 98
(PE) 99
(COM A OUT) 39
(A OUT) 42
(P RS485) 68
(N RS485) 69
(COM RS485) 61
0V
5V
S801
0/4-20 mA
RS485
RS485
03
+10 V DC
0/-10 V DC -
+10 V DC
+10 V DC
0/4-20 mA
0/-10 V DC -
240 V AC, 2 A
24 V DC
02
01
05
04
06
240 V AC, 2 A
24 V (PNP)
0 V (NPN)
0 V (NPN)
24 V (PNP)
19 (D IN)
24 V (PNP)
0 V (NPN)
27
24 V
0 V
(D IN/OUT)
0 V (NPN)
24 V (PNP)
(D IN/OUT)
0 V
24 V
29
24 V (PNP)
0 V (NPN)
0 V (NPN)
24 V (PNP)
33 (D IN)
32 (D IN)
1 2
ON
S201
ON
21
S202
ON=0/4-20 mA
OFF=0/-10 V DC +10 V DC
95
400 V AC, 2 A
Par. E-00
21
ON
S801
(R+) 82
(R-) 81
: Chassis
: Earth
1)
2)
1)
1)
Introduction Programming Guide
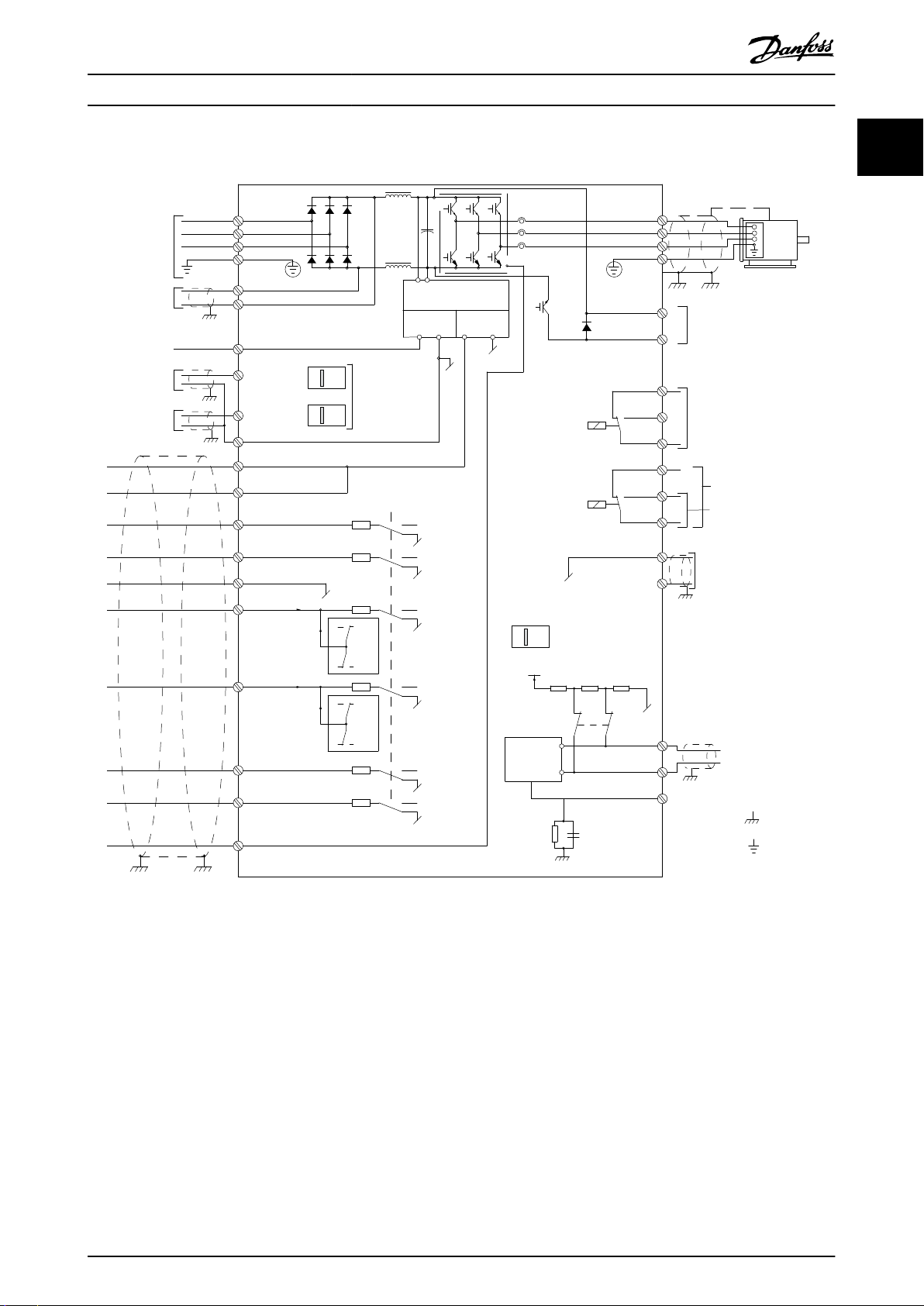
1.5 Electrical Wiring
1 1
Illustration 1.2 Basic Wiring Schematic Drawing
A=Analog, D=Digital
Terminal 37 is used for Safe Torque O. For Safe Torque O installation instructions, refer to the VLT® Frequency Converters -
Safe Torque O Operating Instructions.
1) Terminal 37 is not included in FC 301 (except enclosure type A1). Relay 2 and terminal 29 have no function in FC 301.
2) Do not connect cable shield.
Very long control cables and analog signals may in rare cases, and depending on installation, result in 50/60 Hz ground
loops due to noise from mains supply cables.
If 50/60 Hz ground loops occur, consider breaking the shield or insert a 100 nF capacitor between shield and enclosure.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 9
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 20 37
+24 VDC
0 VDC
130BT106.10
PNP (Source)
Digital input wiring
NPN (Sink)
Digital input wiring
12 13 18 19 27 29 32 33 20 37
+24 VDC
0 VDC
130BT107.11
130BA681.10
12 13 18 37
130BA155.12
322719 29 33 20
P 5-12 [0]
P 5-10 [8]
Start/Stop
+24V
Speed
Safe Stop
Start/Stop
[18]
Introduction
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
11
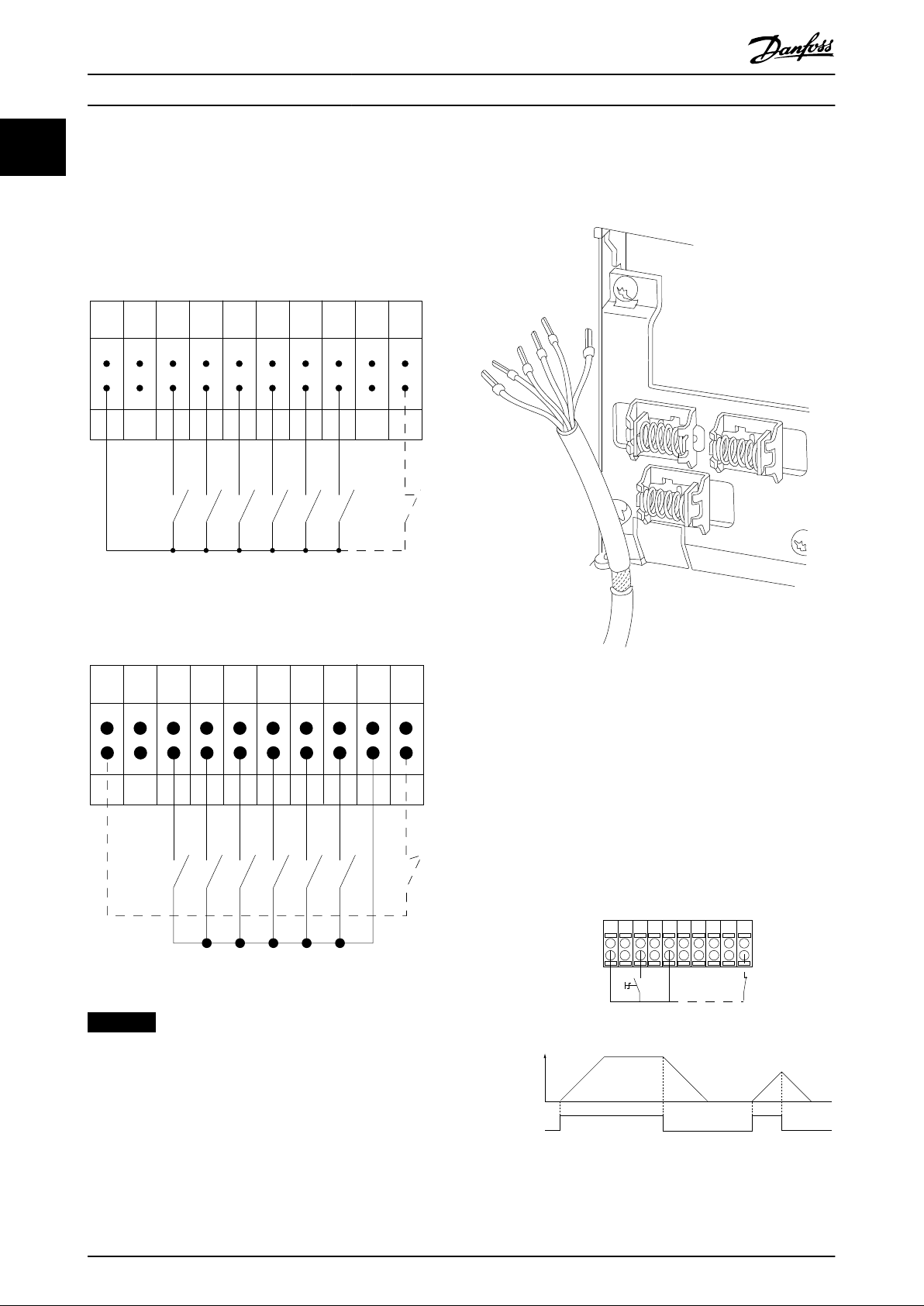
To avoid ground currents from both groups to aect other groups, connect the digital and analog inputs and outputs
separately to the common inputs (terminals 20, 55, and 39) of the frequency converter. For example, switching on the digital
input may disturb the analog input signal.
Input polarity of control terminals
Illustration 1.3 PNP (Source)
Illustration 1.4 NPN (Sink)
NOTICE
Control cables must be shielded/armored.
See the section Grounding of Shielded Control Cables in the
design guide for the correct termination of control cables.
Illustration 1.5 Grounding of Shielded/Armored Control Cables
1.5.1 Start/Stop
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input [8]
Start.
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input [0]
No operation (Default [2] Coast inverse).
Terminal 37 = Safe Torque O (where available).
10 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Illustration 1.6 Start/Stop
12 13 18 37
130BA156.12
322719 29 33 20
P 5 - 12 [6]
P 5 - 10[9]
+24V
Speed
Start Stop inverse Safe Stop
Start (18)
Start (27)
12
18
27
29
32
37
+24V
Par. 5-10
Par. 5-12
Par. 5-13
Par. 5-14
130BA021.12
130BA154.11
555039 42 53 54
Speed RPM
P 6-15
1 kΩ
+10V/30mA
Ref. voltage
P 6-11 10V
Introduction Programming Guide
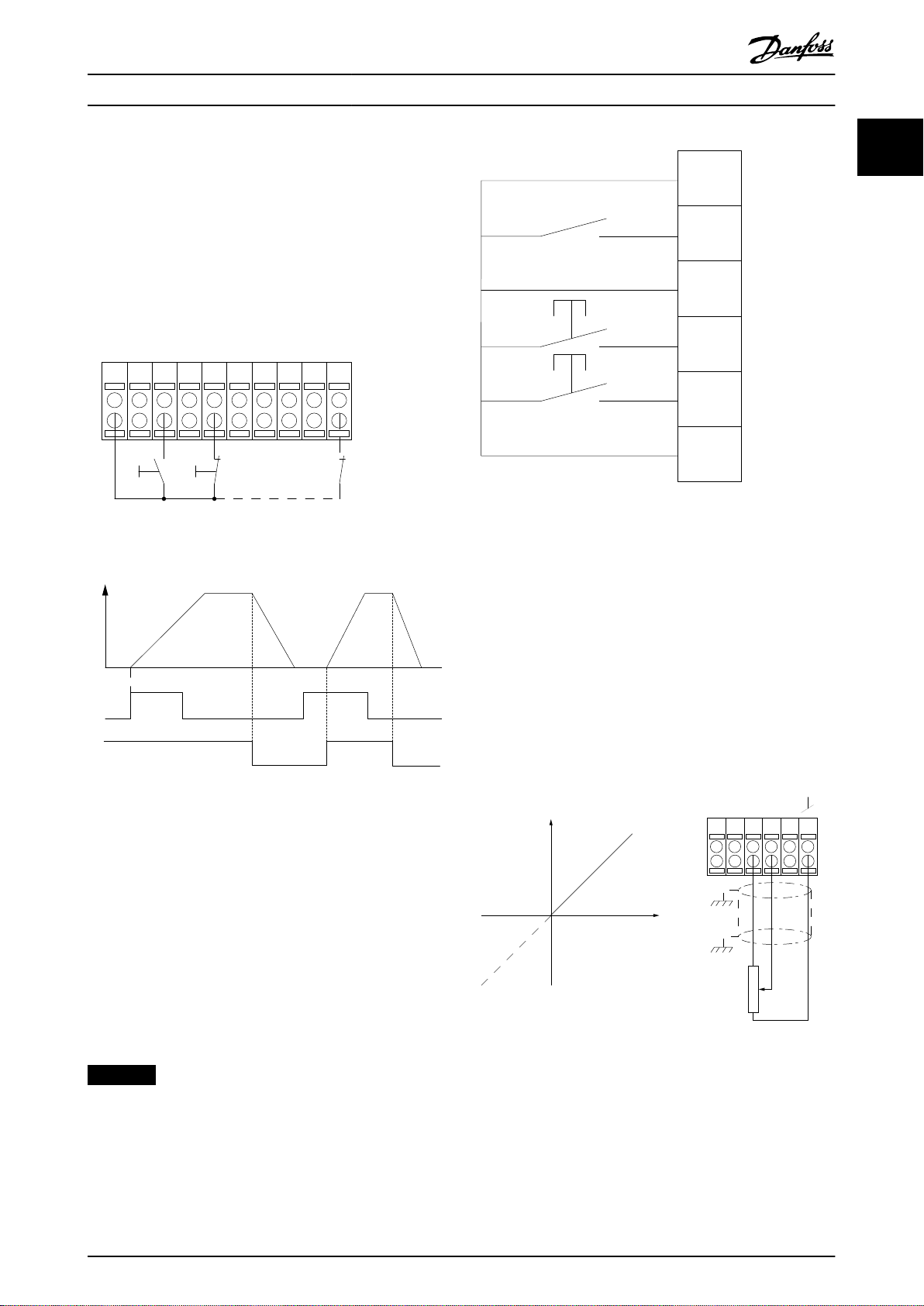
1.5.2 Pulse Start/Stop
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital Input, [9]
Latched start.
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input, [6]
Stop inverse.
Terminal 37 = Safe Torque O (where available).
1 1
Illustration 1.8 Speed up/Speed down
1.5.4 Potentiometer Reference
Voltage reference via a potentiometer
Reference source 1 = [1] Analog input 53 (default).
Terminal 53, low voltage = 0 V.
Terminal 53, high voltage = 10 V.
Terminal 53, low reference/feedback = 0 RPM.
Terminal 53, high reference/feedback = 1500 RPM.
Switch S201 = OFF (U)
Illustration 1.7 Pulse Start/Stop
1.5.3 Speed up/Speed Down
Terminals 29/32 = Speed up/Speed down
Terminal 18 = Parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital
Input [9] Start (default).
Terminal 27 = Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital
Input [19] Freeze reference.
Terminal 29 = Parameter 5-13 Terminal 29 Digital
Input [21] Speed up.
Terminal 32 = Parameter 5-14 Terminal 32 Digital
Input [22] Speed down.
NOTICE
Terminal 29 only in FC x02 (x=series type).
Illustration 1.9 Potentiometer Reference
1.6 Integrated Motion Controller
The integrated motion controller (IMC) enables position
control. For more information about IMC, see
chapter 4 Integrated Motion Controller.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 11
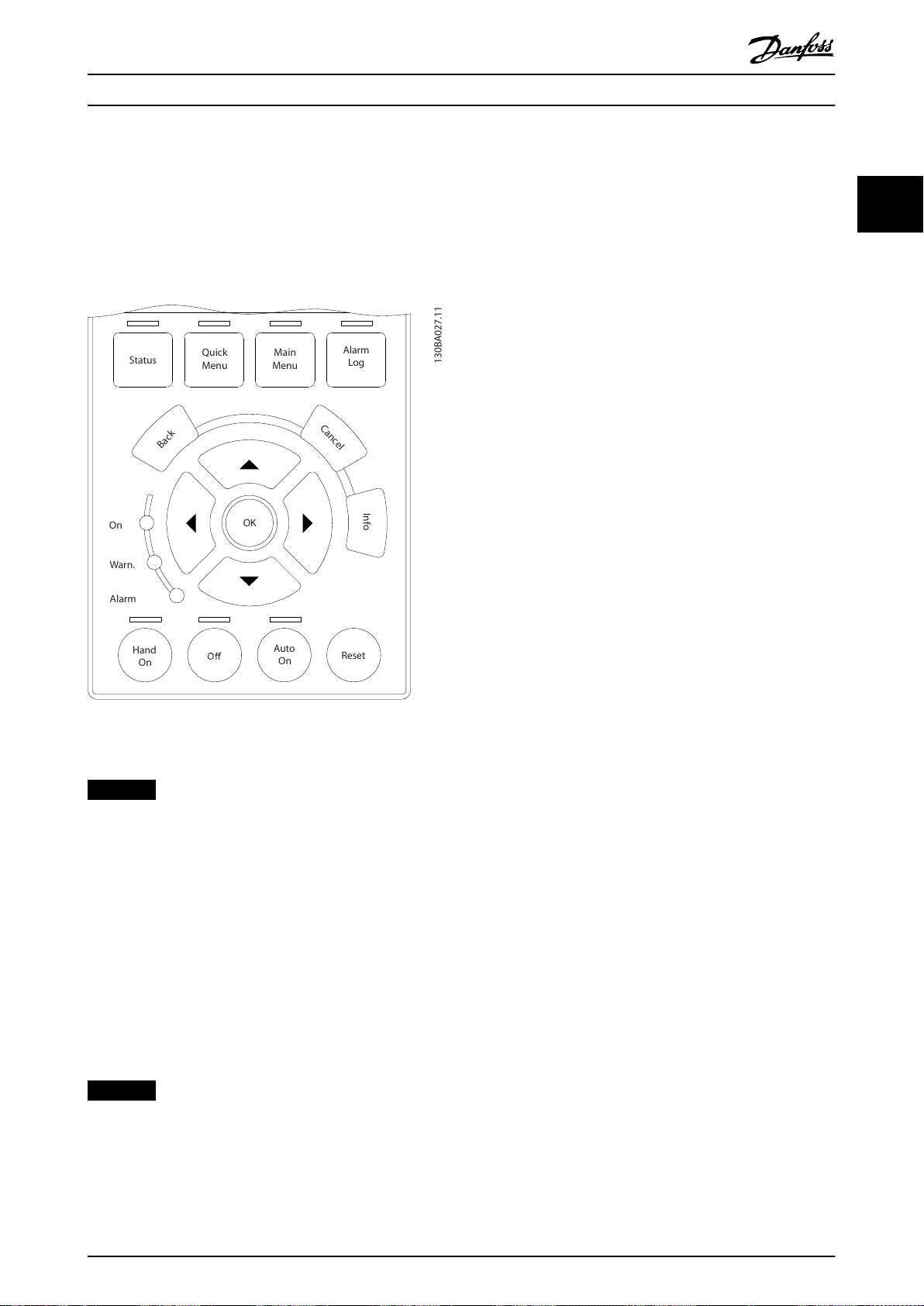
Auto
On
Reset
Hand
On
Off
Status
Quick
Menu
Main
Menu
Alarm
Log
Back
Cancel
Info
OK
Status
1(0)
1234rpm 10,4A 43,5Hz
Run OK
43,5Hz
On
Alarm
Warn.
e30ba018.14
1
2
3
4
b
a
c
How to Program
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
2 How to Program
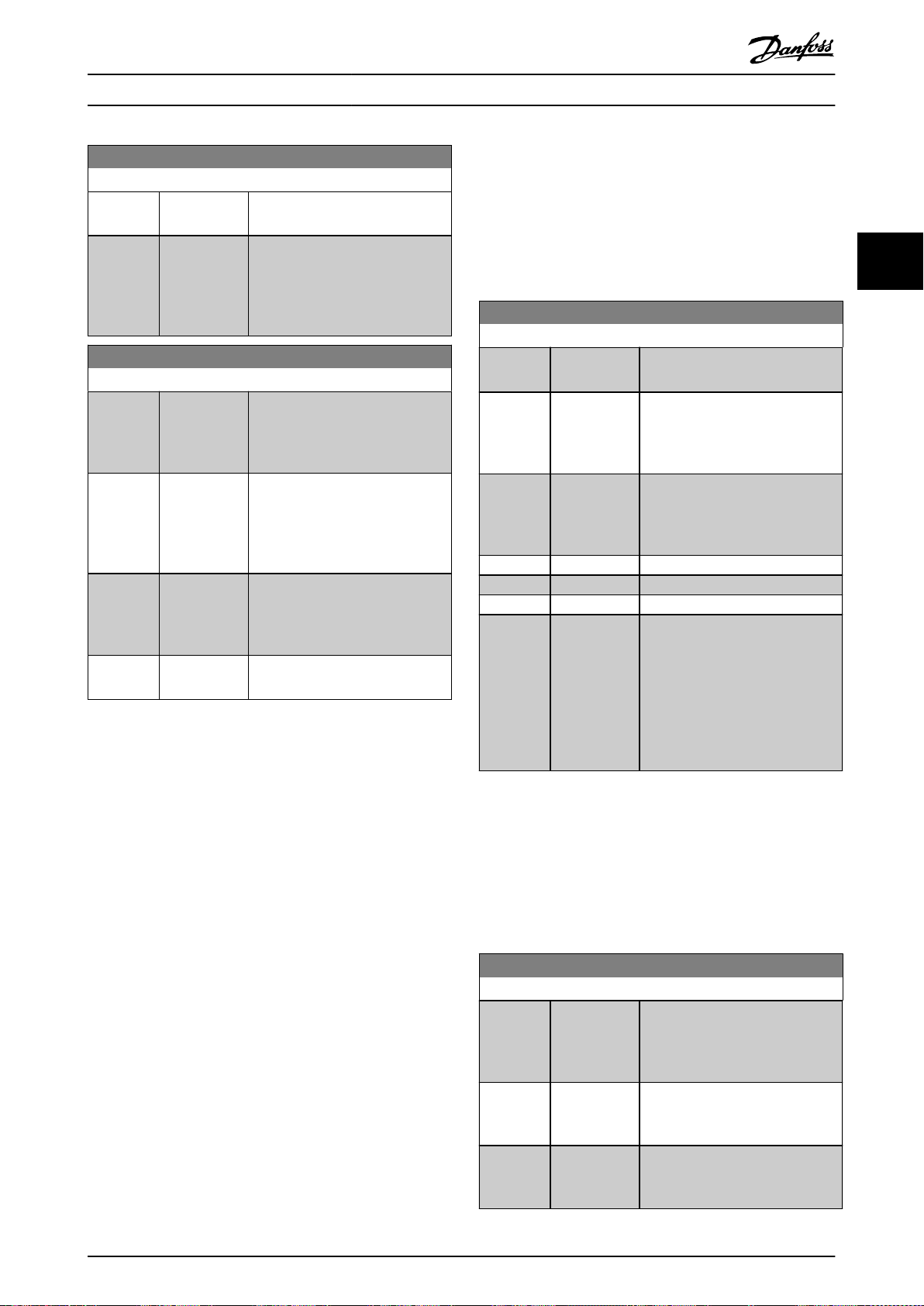
22
2.1 Graphical and Numerical Local Control
Panels
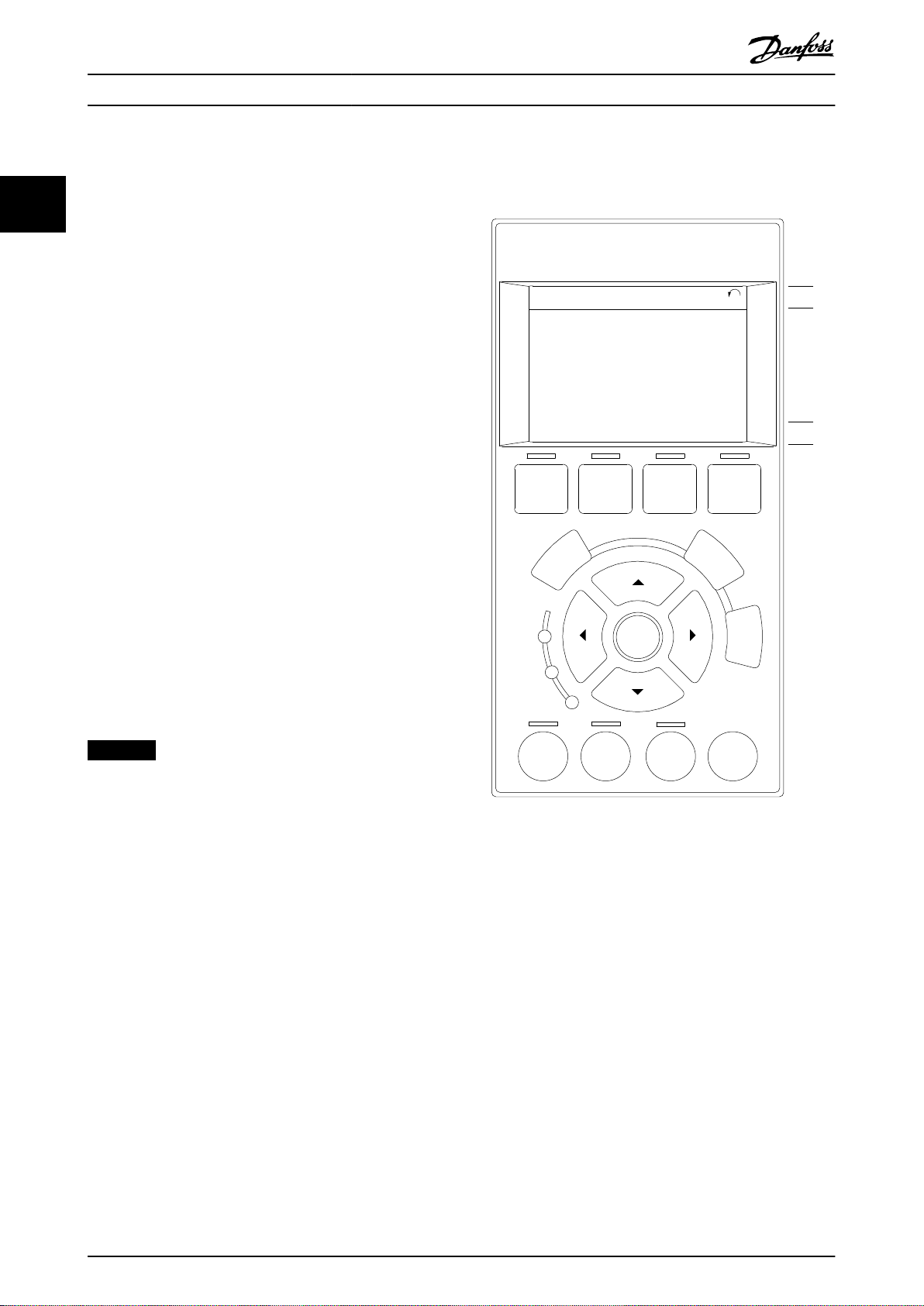
Easy programming of the frequency converter is done via
the graphical LCP (LCP 102). For information about using
the numerical local control panel (LCP 101), see
chapter 2.1.16 How to Program on the Numerical Local
Control Panel.
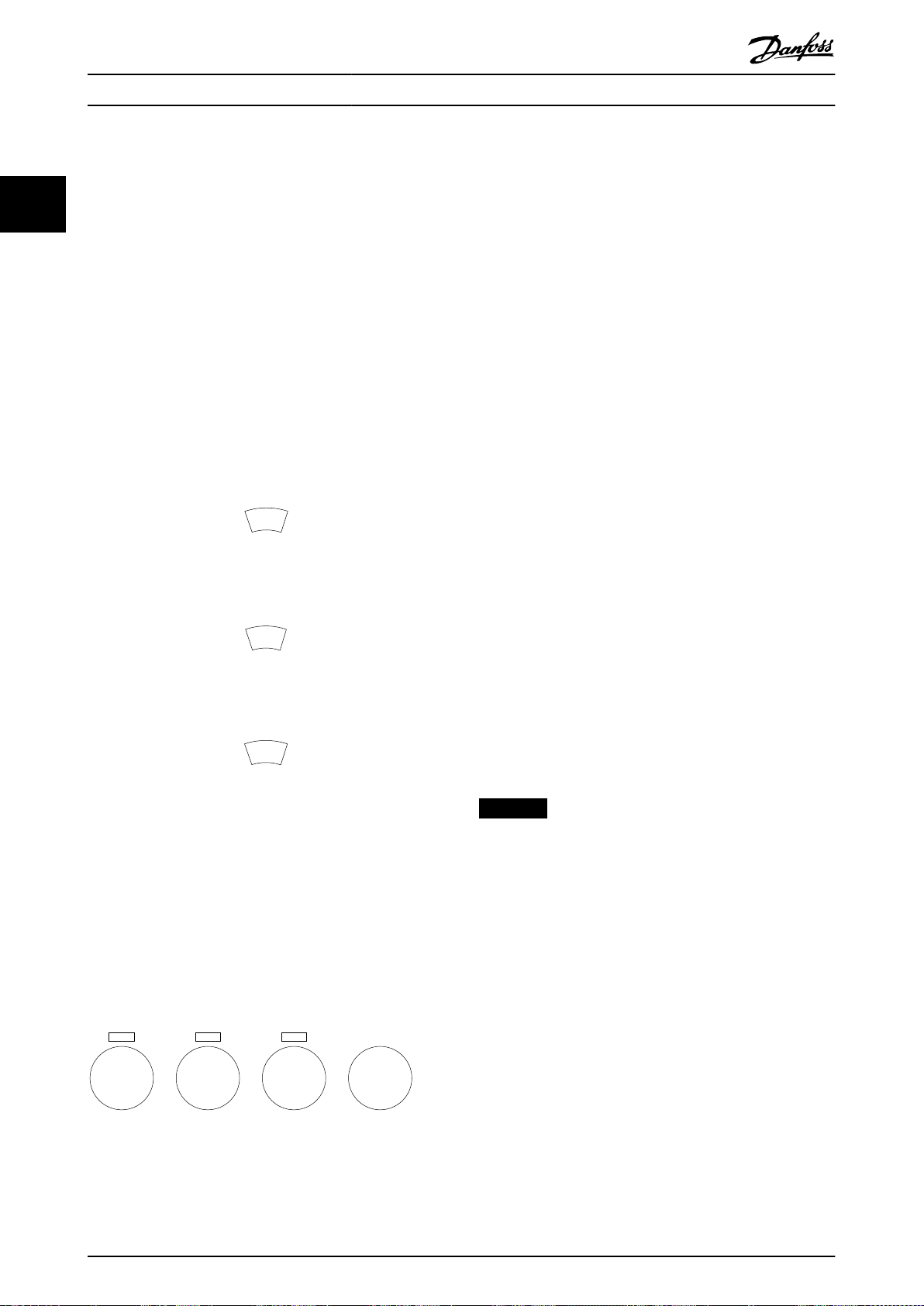
The LCP is divided into 4 functional groups:
1. Graphical display with status lines.
2. Menu keys and indicator lights - changing
parameters and switching between display
functions.
3. Navigation keys and indicator lights.
4. Operation keys and indicator lights.
The LCP display can show up to 5 items of operating data
while showing Status.
Display lines:
a. Status line: Status messages showing icons and
graphics.
b. Line 1–2: Operator data lines showing data
dened or selected. Add up to 1 extra line by
pressing [Status].
c. Status line: Status messages showing text.
NOTICE
If start-up is delayed, the LCP shows the INITIALIZING
message until it is ready. Adding or removing options
can delay the start-up.
Illustration 2.1 LCP
12 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Top section
Middle section
Bottom section
Status
43 RPM
1.4 Hz
Auto Remote Running
! Pwr.card temp (W29)
2.9%
5.44 A 25.3kW
1(1)
130BP074.10
!
On
Warn.
Alarm
130BP044.10
130BP045.10
Status
Quick
Menu
Main
Menu
Alarm
Log
How to Program Programming Guide
2.1.1 LCD Display
The display has backlight and a total of 6 alpha-numeric
lines. The display lines show the direction of rotation
(arrow), the selected set-up, and the programming set-up.
The display is divided into 3 sections.
Top section
The top section shows up to 2 measurements in normal
operating status.
Middle section
The top line shows up to 5 measurements with related
unit, regardless of status (except in the case of alarm/
warning).
Bottom section
The bottom section always shows the state of the
frequency converter in Status mode.
2 2
Illustration 2.3 Indicator Lights
LCP keys
The control keys are divided into functions. The keys below
the display and indicator lights are used for parameter setup, including option of display indication during normal
operation.
Illustration 2.4 LCP Keys
Illustration 2.2 Display
The active set-up (selected as the active set-up in
parameter 0-10 Active Set-up) is shown. When programming
another set-up than the active set-up, the number of the
programmed set-up appears to the right.
Display contrast adjustment
Press [Status] and [▲] for darker display.
Press [Status] and [▼] for brighter display.
Most parameter set-ups can be changed immediately via
the LCP, unless a password has been created via
parameter 0-60 Main Menu Password or via
parameter 0-65 Personal Menu Password.
Indicator lights
If certain threshold values are exceeded, the alarm and/or
warning indicator lights up. A status and alarm text appear
on the LCP.
The ON indicator light is activated when the frequency
converter receives mains voltage or via a DC bus terminal
or 24 V external supply. At the same time, the back
indicator light is on.
Green LED/On: Control section is working.
•
Yellow LED/Warn: Indicates a warning.
•
Flashing Red LED/Alarm: Indicates an alarm.
•
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 13
[Status]
Indicates the status of the frequency converter and/or the
motor. Select between 3 dierent readouts by pressing
[Status]: 5 line readouts, 4 line readouts, or smart logic
control.
Press [Status] for selecting the mode of display or for
changing back to display mode from either the quick
menu mode, the main menu mode, or the alarm mode.
Also use [Status] to toggle single or double readout mode.
[Quick Menu]
Allows quick access to dierent quick menus such as:
My personal menu.
•
Quick set-up.
•
Changes made.
•
Loggings.
•
Press [Quick Menu] to program the parameters belonging
to the Quick Menu. It is possible to switch directly
between quick menu mode and main menu mode.
[Main Menu]
Is used for programming all parameters.
It is possible to switch directly between main menu mode
and quick menu mode.
Parameter shortcut can be carried out by pressing down
[Main Menu] for 3 s. The parameter shortcut allows direct
access to any parameter.
B
a
c
k
C
a
n
c
e
l
I
n
f
o
e30bp046.12
Hand
On
Off
Auto
On
Reset
How to Program
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
[Alarm Log]
Shows an alarm list of the 5 latest alarms (numbered A1–
A5). To obtain extra details about an alarm, press the
22
navigation keys to maneuver to the alarm number and
press [OK]. Information is shown about the condition of
the frequency converter before it enters the alarm mode.
[Back]
Returns to the previous step or layer in the navigation
structure.
[Cancel]
Last change or command is canceled as long as the display
has not been changed.
[Info]
Supplies information about a command, parameter, or
function in any display window. [Info] provides detailed
information whenever help is needed.
Exit Info mode by pressing either [Info], [Back], or [Cancel].
Illustration 2.5 Back
[Hand On]
Enables control of the frequency converter via the LCP.
[Hand On] also starts the motor, and it is now possible to
enter the motor speed data with the navigation keys. The
key can be selected as [1] Enable or [0] Disable via
parameter 0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP.
External stop signals activated with control signals or a
eldbus override a start command via the LCP.
The following control signals are still active when [Hand
On] is activated:
[Hand On] - [O] - [Auto On].
•
Reset.
•
Coast stop inverse.
•
Reversing.
•
Set-up select bit 0 - Set-up select bit 1.
•
Stop command from serial communication.
•
Quick stop.
•
DC brake.
•
[O]
Stops the connected motor. The key can be selected as [1]
Enable or [0] Disable via parameter 0-41 [O] Key on LCP. If
no external stop function is selected and the [O] key is
inactive, the motor can be stopped by disconnecting the
voltage.
Illustration 2.6 Cancel
[Auto On]
Enables the frequency converter to be controlled via the
control terminals and/or serial communication. When a
start signal is applied on the control terminals and/or the
bus, the frequency converter starts. The key can be
selected as [1] Enable or [0] Disable via
Illustration 2.7 Info
parameter 0-42 [Auto on] Key on LCP.
NOTICE
An active HAND-OFF-AUTO signal via the digital inputs
Navigation keys
The 4 navigation keys are used to navigate between the
dierent options available in Quick Menu, Main Menu, and
Alarm Log. Press the keys to move the cursor.
[OK]
Press for selecting a parameter marked by the cursor and
for enabling the change of a parameter.
Local control keys
Local control keys are at the bottom of the LCP.
has higher priority than the control keys [Hand On] –
[Auto On].
[Reset]
Is used for resetting the frequency converter after an alarm
(trip). It can be selected as [1] Enable or [0] Disable via
parameter 0-43 [Reset] Key on LCP.
The parameter shortcut can be carried out by pressing
down the [Main Menu] key for 3 s. The parameter shortcut
provides direct access to any parameter.
Illustration 2.8 Local Control Keys
14 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Au t o
On R eset
Hand
On
S
ta
tus
Q
uick
M
enu
M
ain
M
enu
A
lar
m
Lo
g
Back
C
anc
el
I
n
fo
OK
On A lar m W
ar
n.
130BA027.11
How to Program Programming Guide
2.1.2 Quick Transfer of Parameter Settings
between Multiple Frequency
Converters
Once the set-up of a frequency converter is complete,
store the data in the LCP or on a PC via MCT 10 Set-up
Software.
3. Select [2] All from LCP.
4. Press the [OK] key.
The parameter settings stored in the LCP are now
transferred to the frequency converter indicated by the
progress bar. When 100% is reached, press [OK].
2.1.3 Display Mode
In normal operation, up to 5 dierent operating variables
can be indicated continuously in the middle section: 1.1,
1.2, and 1.3, as well as 2 and 3.
2.1.4 Display Mode - Selection of Readouts
It is possible to toggle between 3 status readout screens
by pressing [Status].
Operating variables with dierent formatting are shown in
each status view further in this section.
Table 2.1 shows the measurements that can be linked to
each of the operating variables. When options are
mounted, additional measurements are available.
2 2
Illustration 2.9 LCP
Data storage in LCP
NOTICE
Stop the motor before performing this operation.
To store the data in the LCP:
1. Go to parameter 0-50 LCP Copy.
2. Press the [OK] key.
3. Select [1] All to LCP.
4. Press the [OK] key.
All parameter settings are now stored in the LCP indicated
by the progress bar. When 100% is reached, press [OK].
Connect the LCP to another frequency converter and copy
the parameter settings to this frequency converter as well.
Dene the links via:
Parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
•
Parameter 0-21 Display Line 1.2 Small.
•
Parameter 0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small.
•
Parameter 0-23 Display Line 2 Large.
•
Parameter 0-24 Display Line 3 Large.
•
Each readout parameter selected in parameter 0-20 Display
Line 1.1 Small to parameter 0-24 Display Line 3 Large has its
own scale and digits after a possible decimal point. The
larger the numeric value of a parameter is, the fewer digits
are shown after the decimal point.
Example: Current readout 5.25 A, 15.2 A, 105 A.
Data transfer from LCP to frequency converter
NOTICE
Stop the motor before performing this operation.
To transfer the data from the LCP to the frequency
converter:
1. Go to parameter 0-50 LCP Copy.
2. Press the [OK] key.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 15
1.1
2
3
1.3
1.2
130BP041.10
799 RPM
Auto Remote Ramping
1 (1)
36.4 kw7.83 A
0.000
53.2 %
Status
1.1
1.2
2
1.3
130BP062.10
207RPM
Auto Remote Running
1 (1)
24.4 kW5.25A
6.9
Hz
Status
130BP063.10
778 RPM
Auto Remote Running
1 (1)
4.0 kW0.86 A
State: 0 o 0 (o)
When: Do: -
Status
How to Program
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Operating variable Unit
Parameter 16-00 Control Word hex
22
Parameter 16-01 Reference [Unit] [Unit]
Parameter 16-02 Reference [%] %
Parameter 16-03 Status Word hex
Parameter 16-05 Main Actual Value [%] %
Parameter 16-10 Power [kW] [kW]
Parameter 16-11 Power [hp] [hp]
Parameter 16-12 Motor Voltage [V ]
Parameter 16-13 Frequency [Hz]
Parameter 16-14 Motor current [A]
Parameter 16-16 Torque [Nm] Nm
Parameter 16-17 Speed [RPM] [RPM]
Parameter 16-18 Motor Thermal %
Parameter 16-20 Motor Angle
Parameter 16-30 DC Link Voltage V
Parameter 16-32 Brake Energy /s kW
Parameter 16-33 Brake Energy Average kW
Parameter 16-34 Heatsink Temp.
°C
Parameter 16-35 Inverter Thermal %
Parameter 16-36 Inv. Nom. Current A
Parameter 16-37 Inv. Max. Current A
Parameter 16-38 SL Controller State
Parameter 16-39 Control Card Temp.
°C
Parameter 16-40 Logging Buer Full
Parameter 16-50 External Reference
Parameter 16-51 Pulse Reference
Parameter 16-52 Feedback[Unit] [Unit]
Parameter 16-53 Digi Pot Reference
Parameter 16-60 Digital Input bin
Parameter 16-61 Terminal 53 Switch Setting V
Parameter 16-62 Analog Input 53
Parameter 16-63 Terminal 54 Switch Setting V
Parameter 16-64 Analog Input 54
Parameter 16-65 Analog Output 42 [mA] [mA]
Parameter 16-66 Digital Output [bin] [bin]
Parameter 16-67 Pulse Input #29 [Hz] [Hz]
Parameter 16-68 Freq. Input #33 [Hz] [Hz]
Parameter 16-69 Pulse Output #27 [Hz] [Hz]
Parameter 16-70 Pulse Output #29 [Hz] [Hz]
Parameter 16-71 Relay Output [bin]
Parameter 16-72 Counter A
Parameter 16-73 Counter B
Parameter 16-80 Fieldbus CTW 1 hex
Parameter 16-82 Fieldbus REF 1 hex
Parameter 16-84 Comm. Option STW hex
Parameter 16-85 FC Port CTW 1 hex
Parameter 16-86 FC Port REF 1 hex
Parameter 16-90 Alarm Word
Parameter 16-92 Warning Word
Parameter 16-94 Ext. Status Word
16 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Table 2.1 Units
This readout state is standard after start-up or initialization.
Press [Info] to obtain information about the units linked to
the shown operating variables (1.1, 1.2, 1.3, 2 and 3).
See the operating variables shown in Illustration 2.10.
Illustration 2.10 Status View I
Status view II
See the operating variables (1.1, 1.2, 1.3, and 2) shown in
Illustration 2.11.
In the example, speed, motor current, motor power, and
frequency are selected as variables in the 1st and 2nd lines.
Illustration 2.11 Status View II
Status view III
This state shows the event and action of the smart logic
control. For further information, see
chapter 3.13 Parameters: 13-** Smart Logic Control.
Illustration 2.12 Status View III
Status view I

130BC916.10
Q1 My Personal Menu
Q2 Quick Setup
Q4 Smart Setup
Q5 Changes Made
0RPM 0.00A 1(1)
Quick Menus
How to Program Programming Guide
2.1.5 Parameter Set-up
The frequency converter can be used for practically all
assignments and oers 2 programming mode options:
Main menu mode.
•
Quick menu mode.
•
Main menu provides access to all parameters. Quick menu
takes the user through a few parameters, making it
possible to start operating the frequency converter.
Change a parameter in either main menu mode or quick
menu mode.
2.1.6 Quick Menu Key Functions
Press [Quick Menu] to enter a list of dierent areas
contained in the Quick Menu.
Select Q1 My Personal Menu to show the selected personal
parameters. These parameters are selected in
parameter 0-25 My Personal Menu. Up to 50 dierent
parameters can be added in this menu.
Illustration 2.13 Quick Menus
Parameter Setting
Parameter 0-01 Language
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW] [kW]
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage [V ]
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency [Hz]
Parameter 1-24 Motor Current [A]
Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed [RPM]
Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital Input
Parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor
Adaptation (AMA)
Parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference [RPM]
Parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference [RPM]
Parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time [s]
Parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time [s]
Parameter 3-13 Reference Site
Table 2.2 Selection of Parameter
1) If terminal 27 is set to [0] No operation, no connection to +24 V
on terminal 27 is necessary.
[0] No function
[1] Enable complete
AMA
1)
Select Changes made to get information about:
The last 10 changes. Use the [▲] [▼] navigation
•
keys to scroll between the last 10 changed
parameters.
The changes made since default setting.
•
Select Loggings to get information about the show line
readouts. The information is shown as graphs.
Only parameters selected in parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small and parameter 0-24 Display Line 3 Large can be
viewed. It is possible to store up to 120 samples in the
memory for later reference.
2 2
Select Q2 Quick Setup to go through a selection of
parameters to get the motor running almost optimally. The
default settings for the other parameters consider the
required control functions and the conguration of signal
inputs/outputs (control terminals).
The parameter selection is eected with the navigation
keys. The parameters in Table 2.2 are accessible.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 17
Quick
Menu
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
OK
How to Program
2.1.7 Initial Commissioning
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
22
procedure using LCP 102 (read Table 2.3 from left to right). The example applies to open-loop applications.
Press
Q2 Quick Menu.
Parameter 0-01 Language
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW]
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency
Parameter 1-24 Motor Current
Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
Set language.
Set motor nameplate power.
Set nameplate voltage.
Set nameplate frequency.
Set nameplate current.
Set nameplate speed in RPM.
The easiest way of carrying out the initial commissioning is by pressing [Quick Menu] and following the quick set-up
Parameter 5-12 Terminal 27 Digital
Input
Parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor
Adaptation (AMA)
Parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference
Parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference
Parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time
Parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down
Time
Parameter 3-13 Reference Site
Table 2.3 Quick Set-up Procedure
If terminal default is [2] Coast
inverse, it is possible to change
this setting to [0] No function.
No connection to terminal 27 is
then needed for running AMA.
Set desired AMA function.
Enable complete AMA is
recommended.
Set the minimum speed of the
motor shaft.
Set the maximum speed of the
motor shaft.
Set the ramp-up time with
reference to synchronous motor
speed, ns.
Set the ramp-down time with
reference to synchronous motor
speed, ns.
Set the site from where the
reference must work.
18 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

e30bp066.14
0-** Operation/Display
1-** Load/Motor
2-** Brakes
1107 RPM 3.84 A
Main Menu
1(1)
3-** References/Ramps
130BP067.10
740RPM
0 -01 Language
[0] English
10.64A 1 [1]
0-0
*
Basic Settings
130BP068.10
740RPM
0 -01 Language
[0] English
10.64 A 1 [1]
0-0
*
Basic Settings
How to Program Programming Guide
Another easy way of commissioning the frequency
converter is by using the smart application set-up (SAS),
which can also be found by pressing [Quick Menu]. To set
up the applications listed, follow the instructions on the
successive screens.
The [Info] key can be used throughout the SAS to see help
information for various selections, settings, and messages.
The following 3 applications are included:
Mechanical brake.
•
Conveyor.
•
Pump/fan.
•
The following 4 eldbusses can be selected:
PROFIBUS.
•
PROFINET.
•
DeviceNet.
•
EtherNet/IP.
•
NOTICE
The frequency converter ignores the start conditions
when SAS is active.
All parameters can be changed in the Main Menu.
However, depending on the conguration
(parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode), some parameters can
be hidden. For example, open loop hides all the PID
parameters, and other enabled options make more
parameter groups visible.
2.1.9 Parameter Selection
In the main menu mode, the parameters are divided into
groups. Select a parameter group with the navigation keys.
After selecting a parameter group, select a parameter with
the navigation keys.
The middle section on the display shows the parameter
number and name, and the selected parameter value.
2 2
NOTICE
The smart set-up runs automatically on the rst powerup of the frequency converter or after a reset to factory
settings. If no action is taken, the SAS screen automatically disappears after 10 minutes.
2.1.8 Main Menu Mode
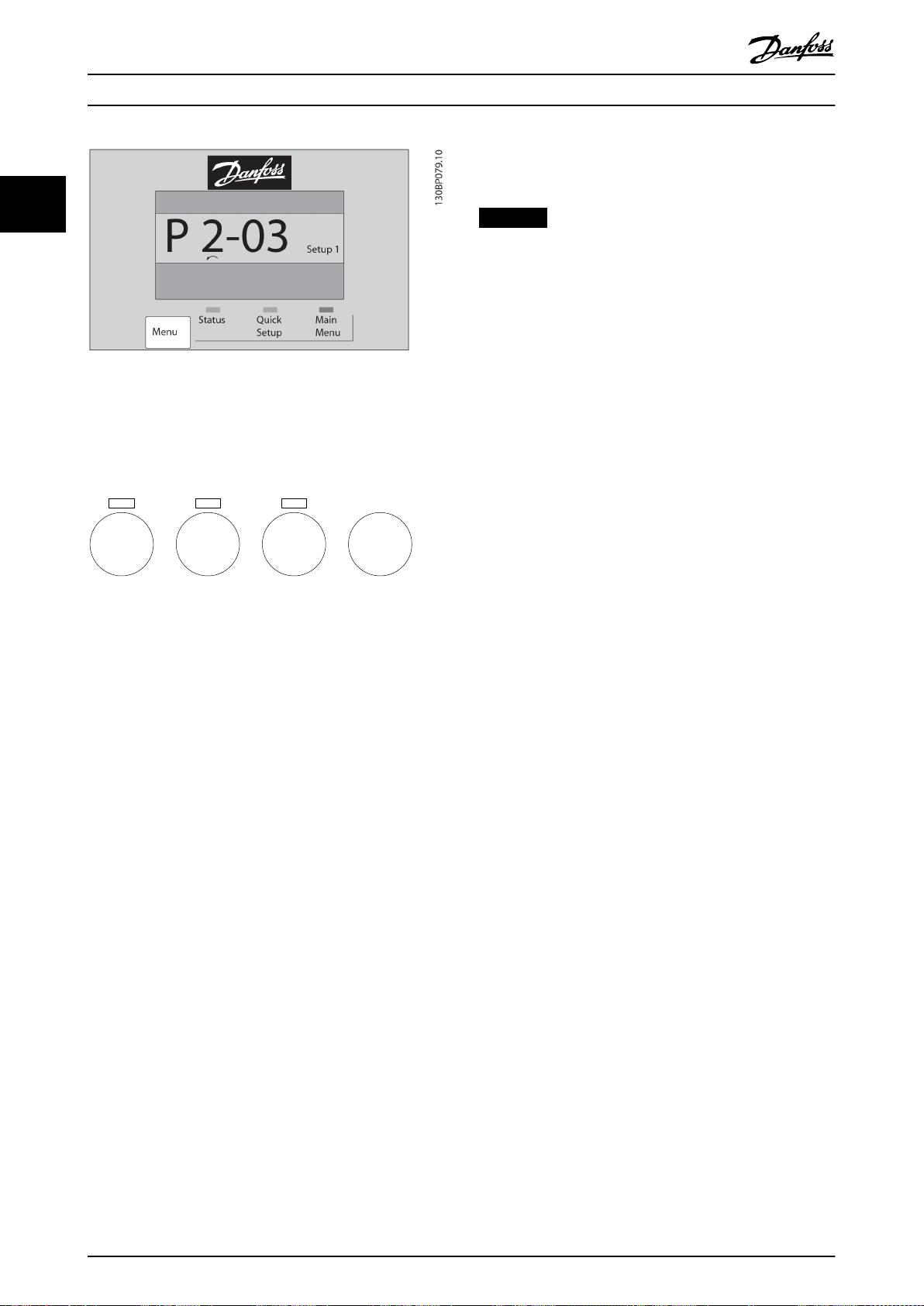
Press [Main Menu] to enter the main menu mode. The
readout in Illustration 2.14 appears on the display.
The middle and bottom sections in the display show a list
of parameter groups, which can be selected by toggling
the [▲] and [▼] keys.
Illustration 2.14 Main Menu Mode
Illustration 2.15 Parameter Selection
2.1.10 Changing Data
The procedure for changing data is the same in the quick
menu mode and the main menu mode. Press [OK] to
change the selected parameter.
The procedure for changing data depends on whether the
selected parameter represents a numeric data value or a
text value.
2.1.11 Changing a Text Value
If the selected parameter is a text value, change the text
value with the [▲] [▼] keys.
Place the cursor on the value to save and press [OK].
Each parameter has a name and number, which remain the
same regardless of the programming mode. In the main
menu mode, the parameters are divided into groups. The
rst digit of the parameter number (from the left) indicates
the parameter group number.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 19
Illustration 2.16 Changing a Text Value

130BP069.10
1- 6*
113 RPM 1.78 A 1(1)
Load depen. setting
1 - 60 Low speed load
compensation
100%
130BP070.10
1 - 60 Low speed load
compensation
1 0%
Load depen. setting 1- 6*
729RPM 6.21A 1(1)
6
130BP073.10
635 RPM
1 - 71 Start Delay
00.0s
0.44 A 1 (1)
1- 7*
Start Adjustments
130BP072.10
957RPM
1-71 High starting torque time
0. s
11.58A 1 (1)
1-7*Start Adjustments
4
How to Program
2.1.12 Changing a Data Value
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
22
change the selected data value with the [◀] [▶] navigation
keys and the [▲] [▼] navigation keys. Press [◀] [▶] keys to
move the cursor horizontally.
If the selected parameter shows a numeric data value,
Illustration 2.20 Saving
2.1.14 Value, Step by Step
Certain parameters can be changed step by step. This
applies to:
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW].
•
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage.
Illustration 2.17 Changing a Data Value
Press the [
] [▼] keys to change the data value. [▲]
▲
increases the data value, and [▼] decreases the data value.
•
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency.
•
The parameters are changed both as a group of numeric
data values and as numeric data values that are innitely
varying.
Place the cursor on the value to save and press [OK].
2.1.15 Readout and Programming of
Indexed Parameters
Parameters are indexed when placed in a rolling stack.
Parameter 15-30 Fault Log: Error Code to
parameter 15-32 Alarm Log: Time contain a fault log, which
can be read out. Select a parameter, press [OK], and press
Illustration 2.18 Saving a Data Value
the [▲] [▼] keys to scroll through the value log.
For example, parameter 3-10 Preset Reference is changed as
2.1.13 Innitely Variable Change of
Numeric Data Value
follows:
1.
Select the parameter, press [OK], and press [▲] [▼]
to scroll through the indexed values.
If the selected parameter shows a numeric data value,
select a digit with [◀] [▶].
2. To change the parameter value, select the
indexed value and press [OK].
3.
Change the value by pressing [▲] [▼].
4. Press [OK] to accept the new setting.
5. Press [Cancel] to abort. Press [Back] to leave the
parameter.
2.1.16 How to Program on the Numerical
Local Control Panel
Illustration 2.19 Selecting a Digit
The following instructions are valid for the numerical LCP
(LCP 101).
Change the selected digit innitely variably with [▲] [▼].
The cursor indicates the selected digit. Place the cursor on
the digit to save and press [OK].
20 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
The control panel is divided into 4 functional groups:
Numerical display.
•
Menu keys and indicator lights - changing
•
parameters and switching between display
functions.
Navigation keys and indicator lights.
•
Operation keys and indicator lights.
•
e30ba191.11
1
Auto
On
Reset
Hand
On
Off
Menu
Status
Quick
Setup
Main
Menu
Back
2
3
4
OK
On
Alarm
Warn.
Setup
130BP077.10
22.8
rpm
Setup 1
Setup 1
130BP078.10
A 17
How to Program Programming Guide
Display line
Status messages showing icons and numeric value.
Indicator lights
Green LED/On: Indicates if control section is on.
•
Yellow LED/Wrn: Indicates a warning.
•
Flashing red LED/Alarm: Indicates an alarm.
•
LCP keys
[Menu]
Select 1 of the following modes:
Status.
•
Quick set-up.
•
Main menu.
•
Status mode
Status mode shows the status of the frequency converter
or the motor.
If an alarm occurs, the NLCP automatically switches to
status mode.
Several alarms can be shown.
NOTICE
Parameter copy is not possible with LCP 101 numerical
local control panel.
Illustration 2.22 Status Mode
Illustration 2.23 Alarm
2 2
Main Menu/Quick Set-up
Used for programming all parameters or only the
parameters in the Quick Menu (see also description of the
LCP 102 in chapter 2.1 Graphical and Numerical Local
Control Panels).
When the value ashes, press [▲] or [▼] to change
parameter values.
Illustration 2.21 LCP Keys
1. Press [Main Menu] to select main menu.
2. Select the parameter group [xx-__] and press
[OK].
3. Select the parameter [__-xx] and press [OK].
4. If the parameter is an array parameter, select the
array number and press [OK].
5. Select the required data value and press [OK].
Parameters with functional options show values such as
[1], [2], and so on. For a description of the dierent
options, see the individual parameter descriptions in
chapter 3 Parameter Descriptions.
[Back]
Used for stepping backwards.
[▲] [▼] are used for maneuvering between commands and
within parameters.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 21
e30bp046.12
Hand
On
Off
Auto
On
Reset
How to Program
22
Illustration 2.24 Main Menu/Quick Set-up
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
frequency converter starts. The key can be selected as [1]
Enable or [0] Disable via parameter 0-42 [Auto on] Key on
LCP.
NOTICE
An active HAND-OFF-AUTO signal via the digital inputs
has higher priority than the control keys [Hand On] and
[Auto On].
[Reset]
Used for resetting the frequency converter after an alarm
(trip). It can be selected as [1] Enable or [0] Disable via
parameter 0-43 [Reset] Key on LCP.
2.1.17 LCP Keys
Keys for local control are at the bottom of the LCP.
Illustration 2.25 LCP Keys
[Hand On]
Enables control of the frequency converter via the LCP.
[Hand On] also starts the motor and it is now possible to
enter the motor speed data with the navigation keys. The
key can be selected as [1] Enable or [0] Disable via
parameter 0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP.
External stop signals activated with control signals, or a
eldbus, override a start command via the LCP.
The following control signals are still active when [Hand
On] is activated:
[Hand On] - [O] - [Auto On].
•
Reset.
•
Coast stop inverse.
•
Reversing.
•
Set-up select lsb - Set-up select msb.
•
Stop command from serial communication.
•
Quick stop.
•
DC brake.
•
[O]
Stops the connected motor. The key can be selected as [1]
Enable or [0] Disable via parameter 0-41 [O] Key on LCP.
If no external stop function is selected and the [O] key is
inactive, stop the motor by disconnecting the voltage.
[Auto On]
Enables control of the frequency converter via the control
terminals and/or serial communication. When a start signal
is applied on the control terminals and/or the bus, the
2.1.18 Initialization to Default Settings
Initialize the frequency converter to default settings in 2
ways.
Recommended initialization (via
parameter 14-22 Operation Mode)
1. Select parameter 14-22 Operation Mode.
2. Press [OK].
3. Select [2] initialization.
4. Press [OK].
5. Disconnect the mains supply and wait until the
display turns o.
6. Reconnect the mains supply. The frequency
converter is now reset.
Parameter 14-22 Operation Mode initializes all except:
Parameter 14-50 RFI Filter.
•
Parameter 8-30 Protocol.
•
Parameter 8-31 Address.
•
Parameter 8-32 FC Port Baud Rate.
•
Parameter 8-35 Minimum Response Delay.
•
Parameter 8-36 Max Response Delay.
•
Parameter 8-37 Max Inter-Char Delay.
•
Parameter 15-00 Operating hours to
•
parameter 15-05 Over Volt's.
Parameter 15-20 Historic Log: Event to
•
parameter 15-22 Historic Log: Time.
Parameter 15-30 Fault Log: Error Code to
•
parameter 15-32 Alarm Log: Time.
22 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
How to Program Programming Guide
Manual initialization
1. Disconnect from mains and wait until the display
turns o.
2. 2a Press [Status] - [Main Menu] - [OK] at
the same time while powering up the
LCP 102, graphical display.
2b Press [Menu] - [OK] while powering up
the LCP 101, numerical display.
3. Release the keys after 5 s.
4. The frequency converter is now programmed
according to default settings.
This procedure initializes all except:
Parameter 15-00 Operating hours.
•
Parameter 15-03 Power Up's.
•
Parameter 15-04 Over Temp's.
•
Parameter 15-05 Over Volt's.
•
NOTICE
A manual initialization also resets serial communication,
RFI lter settings (parameter 14-50 RFI Filter), and fault
log settings.
2 2
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 23
0-01 Language
Option: Function:
Denes display language. The
frequency converter is delivered
with 4 dierent language packages.
English and German are included in
all packages. English cannot be
erased or manipulated.
[0] * English Part of language packages 1–4
[1] Deutsch Part of language packages 1–4
[2] Francais Part of language package 1
[3] Dansk Part of language package 1
[4] Spanish Part of language package 1
[5] Italiano Part of language package 1
[6] Svenska Part of language package 1
[7] Nederlands Part of language package 1
[10] Chinese Part of language package 2
[20] Suomi Part of language package 1
[22] English US Part of language package 4
[27] Greek Part of language package 4
[28] Bras.port Part of language package 4
[36] Slovenian Part of language package 3
[39] Korean Part of language package 2
[40] Japanese Part of language package 2
[41] Turkish Part of language package 4
[42] Trad.Chinese Part of language package 2
[43] Bulgarian Part of language package 3
[44] Srpski Part of language package 3
[45] Romanian Part of language package 3
[46] Magyar Part of language package 3
[47] Czech Part of language package 3
0-01 Language
Option: Function:
[48] Polski Part of language package 4
[49] Russian Part of language package 3
[50] Thai Part of language package 2
[51] Bahasa
Indonesia
Part of language package 2
0-02 Motor Speed Unit
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
The information shown in the
display depends on the settings in
parameter 0-02 Motor Speed Unit
and parameter 0-03 Regional
Settings. The default settings of
parameter 0-02 Motor Speed Unit
and parameter 0-03 Regional
Settings depend on to which region
of the world the frequency
converter is supplied.
NOTICE
Changing the motor speed
unit resets certain parameters
to their initial value. Select the
motor speed unit before
modifying other parameters.
[0] RPM Select to show motor speed
variables and parameters using
motor speed (RPM).
[1] Hz Select to show motor speed
variables and parameters using
output frequency (Hz).
0-03 Regional Settings
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
[0] International Activate parameter 1-20 Motor Power
[kW] for setting the motor power in
kW and set the default value of
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3 Parameter Descriptions
3.1 Parameters: 0-** Operation and Display
33
Parameters related to the basic functions of the frequency
converter, function of the LCP keys, and conguration of
the LCP display.
3.1.1 0-0* Basic Settings
24 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
0-03 Regional Settings
Option: Function:
parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency to
50 Hz.
[1] US Activate parameter 1-20 Motor Power
[kW] for setting the motor power in
hp and set the default value of
parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency to
60 Hz.
0-04 Operating State at Power-up (Hand)
Option: Function:
Select the operating mode upon
reconnection of the frequency
converter to mains voltage after
power-down in hand-on mode.
[0] Resume Restart the frequency converter,
maintaining the start/stop settings
(applied by [Hand On/O]) selected
before the power-down of the
frequency converter.
[1] * Forced stop,
ref=old
Restart the frequency converter
with a saved local reference after
mains voltage reappears and after
pressing [Hand On].
[2] Forced stop,
ref=0
Reset the local reference to 0 upon
restarting the frequency converter.
0-10 Active Set-up
Option: Function:
Select the set-up to control the
frequency converter functions.
[0] Factory setup Cannot be changed. It contains the
Danfoss data set and can be used
as a data source when returning
the other set-ups to a known state.
[1] * Set-up 1 [1] Set-up 1 to [4] Set-up 4 are the 4
separate parameter set-ups within
which all parameters can be
programmed.
[2] Set-up 2
[3] Set-up 3
[4] Set-up 4
[9] Multi Set-up Remote set-up selections using
digital inputs and the serial
communication port. This set-up
uses the settings from
parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked to.
Stop the frequency converter
before making changes to openloop and closed-loop functions.
0-11 Edit Set-up
Option: Function:
Select the set-up to be edited (that
is programmed) during operation;
either the active set-up or 1 of the
inactive set-ups.
[0] Factory setup Cannot be edited but it is useful as
a data source to return the other
set-ups to a known state.
[1] * Set-up 1 [1] Set-up 1 to [4] Set-up 4 can be
edited freely during operation,
independently of the active set-up.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
is programmed as required. By using parameter 0-11 Edit
Set-up, it is possible to edit parameters within any of the
set-ups while continuing the operation of the frequency
converter in its active set-up, which can be a dierent setup to the one being edited. By using parameter 0-51 Set-up
Copy, it is possible to copy parameter settings between the
set-ups to enable quicker commissioning if similar
parameter settings are required in dierent set-ups.
3 3
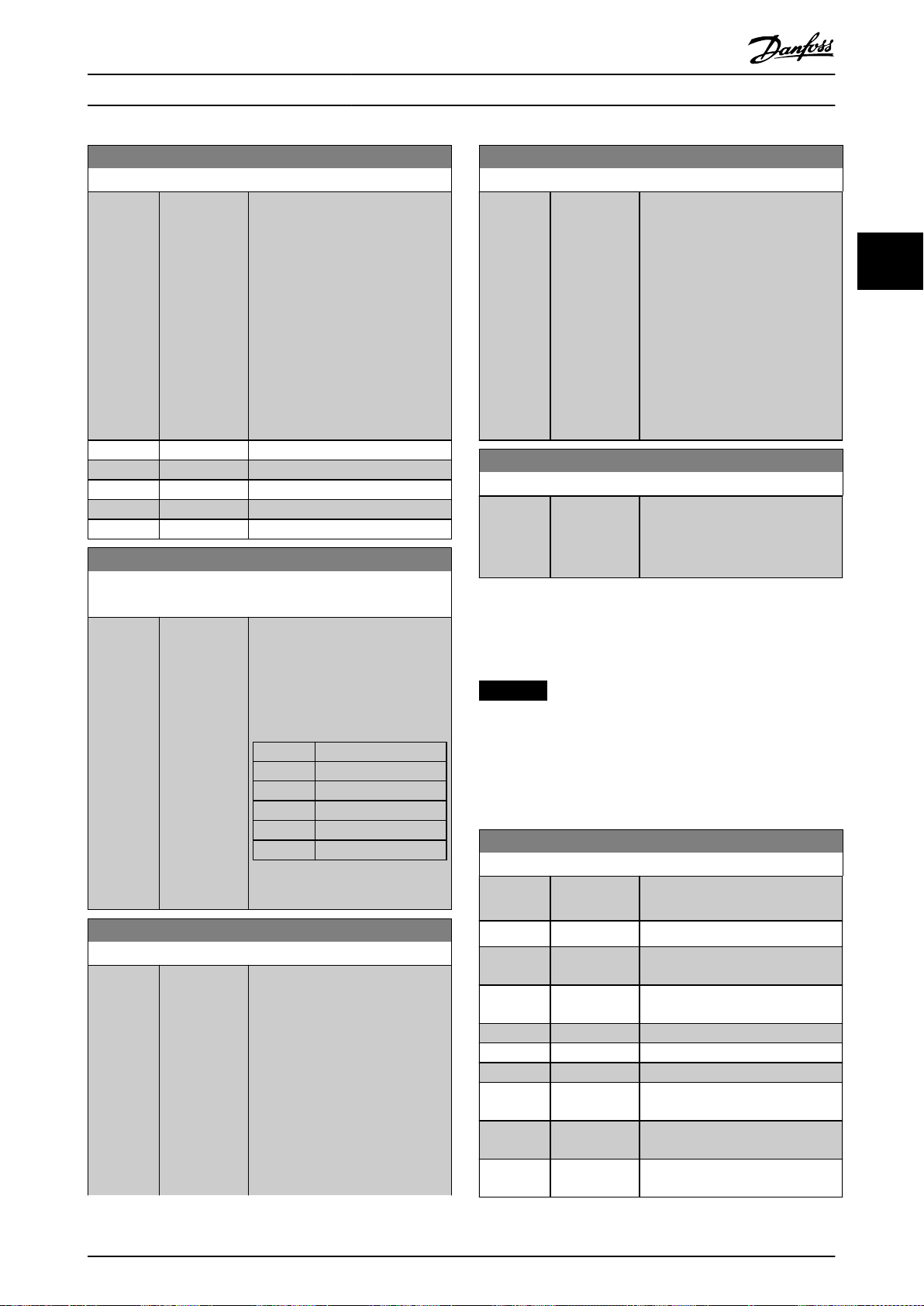
3.1.2 0-1* Set-up Operations
Dene and control the individual parameter set-ups.
The frequency converter has 4 parameter set-ups that can
be programmed independently of each other. This makes
the frequency converter very exible and able to solve
advanced control functionality problems, often saving the
cost of external control equipment. Parameter set-ups can
be used to program the frequency converter to operate
according to 1 control scheme in 1 set-up (for example
motor 1 for horizontal movement) and another control
scheme in another set-up (for example motor 2 for vertical
movement). Alternatively, parameter set-ups can be used
by an OEM machine builder to identically program all their
factory-tted frequency converters for dierent machine
types within a range to have the same parameters. During
production/commissioning, simply select a specic set-up
depending on which machine the frequency converter is
installed on.
The active set-up (that is the set-up in which the frequency
converter is currently operating) can be selected in
parameter 0-10 Active Set-up and is shown in the LCP. By
using multi set-up, it is possible to switch between set-ups
with the frequency converter running, or it can be stopped
via digital input or serial communication commands. If it is
necessary to change set-ups while the frequency converter
is running, ensure that parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked to
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 25
Use parameter 0-51 Set-up Copy to copy a set-up to 1 or all
other set-ups. Stop the frequency converter before
switching between set-ups where parameters marked not
changeable during operation have dierent values. To avoid
conicting settings of the same parameter within 2
dierent set-ups, link the set-ups together using
parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked to. Parameters which are
not changeable during operation are marked FALSE in the
parameter lists in chapter 5 Parameter Lists.
0-11 Edit Set-up
Option: Function:
[2] Set-up 2
[3] Set-up 3
[4] Set-up 4
[9] Active Set-up Can also be edited during
operation. Edit the selected set-up
from a range of sources: LCP, FC
RS485, FC USB, or up to 5 eldbus
sites.
130BA199.10
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
3
4
P 0-11
P 0-11
P 0-11
P 0-11
Set-up
Set-up
Set-up
Set-up
PLC Fieldbus
0-12 This Set-up Linked to
Option: Function:
To enable conict-free changes
from 1 set-up to another during
operation, link set-ups containing
parameters which are not
changeable during operation. The
link ensures synchronizing of the
not changeable during operationparameter values when moving
0-12 This Set-up Linked to
Option: Function:
from 1 set-up to another during
operation. Not changeable during
operation-parameters can be
identied by the label FALSE in the
parameter lists in
chapter 5 Parameter Lists.
Parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked to
is used by [9] Multi set-up in
parameter 0-10 Active Set-up. Multi
set-up is used to move from 1 setup to another during operation
(that is while the motor is running).
Example:
Use multi set-up to shift from setup 1 to set-up 2 while the motor is
running.Program in set-up 1 rst,
then ensure that set-up 1 and setup 2 are synchronized (or linked).
Synchronization can be performed
in 2 ways:
1. Select the following options:
•
[2] Set-up 2 in
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up.
•
parameter 0-12 This Set-up
Linked to to [1] Set-up 1.
This starts the linking (synchronizing) process.
130BP075.10
0-12 This Set-up Linked to
0 RPM
0.00A
1(1)
Set-up Handling 0-1*
[1]
Setup 1
Illustration 3.2 Set-up 1
OR
2. While still in set-up 1, copy setup 1 to set-up 2. Then set
parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked to
to [2] Set-up 2. This starts the
linking process.
130BP076.10
0-12 This Set-up Linked to
0 RPM
0.00A
1(1)
Set-up Handling
0-1*
[2]
Setup 2
Illustration 3.3 Set-up 2
Parameter Descriptions
33
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Illustration 3.1 Edit Set-up
26 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
0-12 This Set-up Linked to
Option: Function:
When completed,
parameter 0-13 Readout: Linked Setups reads {1,2} to indicate that all
not changeable during operation-
parameters are now the same in
set-up 1 and set-up 2. If there are
changes to a not changeable during
operation-parameter, for example
parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs),
in set-up 2, they are also changed
automatically in set-up 1. A switch
between set-up 1 and set-up 2
during operation is now possible.
[0] * Not linked
[1] Set-up 1
[2] Set-up 2
[3] Set-up 3
[4] Set-up 4
0-13 Readout: Linked Set-ups
Array [5]
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 255 ] View a list of all the set-ups linked
by parameter 0-12 This Set-up Linked
to. The parameter has 1 index for
each parameter set-up. The value
for each index shows which set-ups
are linked to that parameter set-up.
Index LCP value
0 {0}
1 {1,2}
2 {1,2}
3 {3}
4 {4}
Table 3.1 Set-up Link Example
0-14 Readout: Edit Set-ups / Channel
Range: Function:
0* [-2147483648
2147483647 ]
View the setting of
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up for each
of the 4 dierent communication
channels. When the number is
shown as a hex number, as it is in
the LCP, each number represents 1
channel.
Numbers 1–4 represent a set-up
number; F means factory setting;
and A means active set-up. The
channels are, from right to left: LCP,
FC bus, USB, HPFB1-5.
0-14 Readout: Edit Set-ups / Channel
Range: Function:
Example: The number AAAAAA21h
means the following:
•
The frequency converter
received the setting set-up
2 via a eldbus channel.
This selection is reected
in parameter 0-11 Edit Set-
up.
•
A user selected set-up 1
via the LCP.
•
All other channels are
using the active set-up.
0-15 Readout: actual setup
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 255 ] Makes it possible to read out the
active set-up, also when [9] Multi
set-up is selected in
parameter 0-10 Active Set-up.
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
Select a variable for display in line
1, left position.
[0] None No display value selected.
[9] Performance
Monitor
[15] Readout:
actual setup
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[89] Date and Time
Readout
[748] PCD Feed
Forward
[953] Probus
Warning Word
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 27
3.1.3 0-2* LCP Display
Dene the variables shown in the LCP.
NOTICE
For information on how to write display texts, refer to:
Parameter 0-37 Display Text 1.
•
Parameter 0-38 Display Text 2.
•
Parameter 0-39 Display Text 3.
•
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[1005] Readout
Transmit Error
Counter
[1006] Readout
Receive Error
Counter
[1007] Readout Bus
O Counter
[1013] Warning
Parameter
[1230] Warning
Parameter
[1397] Alert Alarm
Word
[1398] Alert Warning
Word
[1399] Alert Status
Word
[1472] Legacy Alarm
Word
[1473] Legacy
Warning Word
[1474] Leg. Ext.
Status Word
[1500] Operating
hours
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1580] Fan Running
Hours
[1600] Control Word Present control word.
[1601] Reference
[Unit]
Total reference (sum of digital/
analog/preset/bus/freeze reference/
catch up and slow down) in
selected unit.
[1602] Reference % Total reference (sum of digital/
analog/preset/bus/freeze reference./
catch up and slow down) in
percent.
[1603] Status Word Present status word.
[1605] Main Actual
Value [%]
Actual value as a percentage.
[1606] Actual Position Actual position in position units
selected in parameter 17-70 Position
Unit.
[1607] Target Position Active target position in position
units selected in
parameter 17-70 Position Unit.
[1608] Position Error Actual position PI error in position
units selected in
parameter 17-70 Position Unit.
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[1609] Custom
Readout
[1610] Power [kW] Actual power consumed by the
motor in kW.
[1611] Power [hp] Actual power consumed by the
motor in hp.
[1612] Motor Voltage Voltage supplied to the motor.
[1613] Frequency Motor frequency, that is the output
frequency from the frequency
converter in Hz.
[1614] Motor current Phase current of the motor
measured as eective value.
[1615] Frequency [%] Motor frequency, that is the output
frequency from the frequency
converter in percent.
[1616] Torque [Nm] Actual motor torque in Nm.
[1617] Speed [RPM] Speed in RPM (revolutions per
minute), that is the motor shaft
speed in closed loop.
[1618] Motor Thermal Thermal load on the motor,
calculated by the ETR function.
[1619] Thermistor
Sensor
Temperature
[1620] Motor Angle
[1621] Torque [%]
High Res.
[1622] Torque [%] Present motor load as a percentage
of the rated motor torque.
[1623] Motor Shaft
Power [kW ]
[1624] Calibrated
Stator
Resistance
[1625] Torque [Nm]
High
[1628] Angle Error
[1630] DC Link
Voltage
DC-link voltage in the frequency
converter.
[1631] System Temp.
[1632] Brake
Energy /s
Present brake power transferred to
an external brake resistor.
Stated as an instant value.
[1633] Brake Energy
Average
Brake power transferred to an
external brake resistor. The mean
power is calculated continuously for
the most recent 120 s.
[1634] Heatsink
Temp.
Present heat sink temperature of
the frequency converter. The cutout
Parameter Descriptions
33
28 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
limit is 95 ±5 °C (203 ±9 °F);
cutting back in occurs at 70 ±5 °C
(203 ±9 °F).
[1635] Inverter
Thermal
Percentage load of the inverters.
[1636] Inv. Nom.
Current
Nominal current of the frequency
converter.
[1637] Inv. Max.
Current
Maximum current of the frequency
converter.
[1638] SL Controller
State
State of the event executed by the
control.
[1639] Control Card
Temp.
Temperature of the control card.
[1642] Service Log
Counter
[1643] Timed Actions
Status
[1644] Speed Error
[RPM]
[1645] Motor Phase U
Current
[1646] Motor Phase V
Current
[1647] Motor Phase
W Current
[1648] Speed Ref.
After Ramp
[RPM]
[1650] External
Reference
Sum of the external reference as a
percentage, that is the sum of
analog/pulse/bus.
[1651] Pulse
Reference
Frequency in Hz connected to the
digital inputs (18, 19 or 32, 33).
[1652] Feedback[Unit] Reference value from programmed
digital inputs.
[1653] Digi Pot
Reference
[1657] Feedback
[RPM]
[1660] Digital Input Signal states from the 6 digital
terminals (18, 19, 27, 29, 32, and
33). There are 16 bits in total, but
only 6 of them are used. Input 18
corresponds to the far left of the
used bits. Signal low = 0; Signal
high = 1.
[1661] Terminal 53
Switch Setting
Setting of input terminal 54.
Current = 0; Voltage = 1.
[1662] Analog Input53Actual value at input 53 either as a
reference or protection value.
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[1663] Terminal 54
Switch Setting
Setting of input terminal 54.
Current = 0; Voltage = 1.
[1664] Analog Input54Actual value at input 54 either as
reference or protection value.
[1665] Analog Output
42 [mA]
Actual value at output 42 in mA.
Use parameter 6-50 Terminal 42
Output to select the value to be
shown.
[1666] Digital Output
[bin]
Binary value of all digital outputs.
[1667] Freq. Input
#29 [Hz]
Actual value of the frequency
applied at terminal 29 as an
impulse input.
[1668] Freq. Input
#33 [Hz]
Actual value of the frequency
applied at terminal 33 as an
impulse input.
[1669] Pulse Output
#27 [Hz]
Actual value of impulses applied to
terminal 27 in digital output mode.
[1670] Pulse Output
#29 [Hz]
Actual value of impulses applied to
terminal 29 in digital output mode.
[1671] Relay Output
[bin]
[1672] Counter A Application-dependent (for example
SLC control).
[1673] Counter B Application-dependent (for example
SLC control).
[1674] Prec. Stop
Counter
Shows the actual value of the
counter.
[1675] Analog In
X30/11
Actual value at input X30/11 either
as reference or protection value.
[1676] Analog In
X30/12
Actual value at input X30/12 either
as reference or protection value.
[1677] Analog Out
X30/8 [mA]
Actual value at output X30/8 in mA.
Use parameter 6-60 Terminal X30/8
Output to select the value to be
shown.
[1678] Analog Out
X45/1 [mA]
[1679] Analog Out
X45/3 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW1Control word (CTW ) received from
the bus master.
[1681] Fieldbus Sync.
REF
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1 Main reference value sent with
control word from the bus master.
[1683] Fieldbus Pos.
REF
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 29
3 3

0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[1684] Comm. Option
STW
Extended eldbus communication
option status word.
[1685] FC Port CTW 1 Control word (CTW) received from
the bus master.
[1686] FC Port REF 1 Status word (STW) sent to the bus
master.
[1687] Bus Readout
Alarm/Warning
[1689] Congurable
Alarm/Warning
Word
[1690] Alarm Word 1 or more alarms in a hex code.
[1691] Alarm Word 2 1 or more alarms in a hex code.
[1692] Warning Word 1 or more warnings in a hex code.
[1693] Warning Word21 or more warnings in a hex code.
[1694] Ext. Status
Word
1 or more status conditions in a
hex code.
[1695] Ext. Status
Word 2
1 or more status conditions in a
hex code.
[1696] Maintenance
Word
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1698] Warning Word
3
[1804] Mech Brake
Count
[1820] Commanded
Position
[1821] Master
Position
[1823] Virtual Master
Pos.
[1827] Safe Opt. Est.
Speed
[1828] Safe Opt.
Meas. Speed
[1829] Safe Opt.
Speed Error
[1836] Analog Input
X48/2 [mA]
[1837] Temp. Input
X48/4
[1838] Temp. Input
X48/7
[1839] Temp. Input
X48/10
[1840] Analog Input
X49/1
[1841] Analog Input
X49/3
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[1842] Analog Input
X49/5
[1843] Analog Out
X49/7
[1844] Analog Out
X49/9
[1845] Analog Out
X49/11
[1846] X49 Digital
Output [bin]
[1860] Digital Input 2
[1870] Mains Voltage
[1871] Mains
Frequency
[1872] Mains
Imbalance
[1875] Rectier DC
Volt.
[1890] Process PID
Error
[1891] Process PID
Output
[1892] Process PID
Clamped
Output
[1893] Process PID
Gain Scaled
Output
[2316] Maintenance
Text
[3019] Wobble Delta
Freq. Scaled
[3110] Bypass Status
Word
[3111] Bypass
Running Hours
[3401] PCD 1 Write
to MCO
[3402] PCD 2 Write
to MCO
[3403] PCD 3 Write
to MCO
[3404] PCD 4 Write
to MCO
[3405] PCD 5 Write
to MCO
[3406] PCD 6 Write
to MCO
[3407] PCD 7 Write
to MCO
[3408] PCD 8 Write
to MCO
[3409] PCD 9 Write
to MCO
Parameter Descriptions
33
30 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[3410] PCD 10 Write
to MCO
[3421] PCD 1 Read
from MCO
[3422] PCD 2 Read
from MCO
[3423] PCD 3 Read
from MCO
[3424] PCD 4 Read
from MCO
[3425] PCD 5 Read
from MCO
[3426] PCD 6 Read
from MCO
[3427] PCD 7 Read
from MCO
[3428] PCD 8 Read
from MCO
[3429] PCD 9 Read
from MCO
[3430] PCD 10 Read
from MCO
[3440] Digital Inputs
[3441] Digital
Outputs
[3450] Actual Position
[3451] Commanded
Position
[3452] Actual Master
Position
[3453] Slave Index
Position
[3454] Master Index
Position
[3455] Curve Position
[3456] Track Error
[3457] Synchronizing
Error
[3458] Actual Velocity
[3459] Actual Master
Velocity
[3460] Synchronizing
Status
[3461] Axis Status
[3462] Program
Status
[3464] MCO 302
Status
[3465] MCO 302
Control
[3466] SPI Error
Counter
0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small
Option: Function:
[3470] MCO Alarm
Word 1
[3471] MCO Alarm
Word 2
[4029] B-EMF
Protection Log
Readout
[4235] S-CRC Value
[4282] Safe Control
Word
[4283] Safe Status
Word
[4285] Active Safe
Func.
[4286] Safe Option
Info
[9913] Idle time
[9914] Paramdb
requests in
queue
[9917] tCon1 time
[9918] tCon2 time
[9919] Time Optimize
Measure
[9920] Fan Ctrl deltaT
[9921] Fan Ctrl
Tmean
[9922] Fan Ctrl NTC
Cmd
[9923] Fan Ctrl i-term
[9924] Rectier
Current
[9952] PC Debug 0
[9953] PC Debug 1
[9954] PC Debug 2
[9961] FPC Debug 0
[9962] FPC Debug 1
[9963] FPC Debug 2
[9964] FPC Debug 3
[9965] FPC Debug 4
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[9] Performance
Monitor
[15] Readout:
actual setup
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 31
3 3

0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[39] Display Text 3
[89] Date and Time
Readout
[748] PCD Feed
Forward
[953] Probus
Warning Word
[1005] Readout
Transmit Error
Counter
[1006] Readout
Receive Error
Counter
[1007] Readout Bus
O Counter
[1013] Warning
Parameter
[1230] Warning
Parameter
[1397] Alert Alarm
Word
[1398] Alert Warning
Word
[1399] Alert Status
Word
[1472] Legacy Alarm
Word
[1473] Legacy
Warning Word
[1474] Leg. Ext.
Status Word
[1500] Operating
hours
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1580] Fan Running
Hours
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference
[Unit]
[1602] Reference %
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual
Value [%]
[1606] Actual Position
[1607] Target Position
[1608] Position Error
[1609] Custom
Readout
[1610] * Power [kW]
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1619] Thermistor
Sensor
Temperature
[1620] Motor Angle
[1621] Torque [%]
High Res.
[1622] Torque [%]
[1623] Motor Shaft
Power [kW ]
[1624] Calibrated
Stator
Resistance
[1625] Torque [Nm]
High
[1628] Angle Error
[1630] DC Link
Voltage
[1631] System Temp.
[1632] Brake
Energy /s
[1633] Brake Energy
Average
[1634] Heatsink
Temp.
[1635] Inverter
Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom.
Current
[1637] Inv. Max.
Current
[1638] SL Controller
State
[1639] Control Card
Temp.
[1642] Service Log
Counter
[1643] Timed Actions
Status
[1644] Speed Error
[RPM]
[1645] Motor Phase U
Current
Parameter Descriptions
33
32 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[1646] Motor Phase V
Current
[1647] Motor Phase
W Current
[1648] Speed Ref.
After Ramp
[RPM]
[1650] External
Reference
[1651] Pulse
Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot
Reference
[1657] Feedback
[RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53
Switch Setting
[1662] Analog Input
53
[1663] Terminal 54
Switch Setting
[1664] Analog Input
54
[1665] Analog Output
42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[bin]
[1667] Freq. Input
#29 [Hz]
[1668] Freq. Input
#33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse Output
#27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse Output
#29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay Output
[bin]
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1674] Prec. Stop
Counter
[1675] Analog In
X30/11
[1676] Analog In
X30/12
[1677] Analog Out
X30/8 [mA]
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[1678] Analog Out
X45/1 [mA]
[1679] Analog Out
X45/3 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW
1
[1681] Fieldbus Sync.
REF
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1683] Fieldbus Pos.
REF
[1684] Comm. Option
STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1687] Bus Readout
Alarm/Warning
[1689] Congurable
Alarm/Warning
Word
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word
2
[1694] Ext. Status
Word
[1695] Ext. Status
Word 2
[1696] Maintenance
Word
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1698] Warning Word
3
[1804] Mech Brake
Count
[1820] Commanded
Position
[1821] Master
Position
[1823] Virtual Master
Pos.
[1827] Safe Opt. Est.
Speed
[1828] Safe Opt.
Meas. Speed
[1829] Safe Opt.
Speed Error
[1836] Analog Input
X48/2 [mA]
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 33
3 3

0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[1837] Temp. Input
X48/4
[1838] Temp. Input
X48/7
[1839] Temp. Input
X48/10
[1840] Analog Input
X49/1
[1841] Analog Input
X49/3
[1842] Analog Input
X49/5
[1843] Analog Out
X49/7
[1844] Analog Out
X49/9
[1845] Analog Out
X49/11
[1846] X49 Digital
Output [bin]
[1860] Digital Input 2
[1870] Mains Voltage
[1871] Mains
Frequency
[1872] Mains
Imbalance
[1875] Rectier DC
Volt.
[1890] Process PID
Error
[1891] Process PID
Output
[1892] Process PID
Clamped
Output
[1893] Process PID
Gain Scaled
Output
[2316] Maintenance
Text
[3019] Wobble Delta
Freq. Scaled
[3110] Bypass Status
Word
[3111] Bypass
Running Hours
[3401] PCD 1 Write
to MCO
[3402] PCD 2 Write
to MCO
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[3403] PCD 3 Write
to MCO
[3404] PCD 4 Write
to MCO
[3405] PCD 5 Write
to MCO
[3406] PCD 6 Write
to MCO
[3407] PCD 7 Write
to MCO
[3408] PCD 8 Write
to MCO
[3409] PCD 9 Write
to MCO
[3410] PCD 10 Write
to MCO
[3421] PCD 1 Read
from MCO
[3422] PCD 2 Read
from MCO
[3423] PCD 3 Read
from MCO
[3424] PCD 4 Read
from MCO
[3425] PCD 5 Read
from MCO
[3426] PCD 6 Read
from MCO
[3427] PCD 7 Read
from MCO
[3428] PCD 8 Read
from MCO
[3429] PCD 9 Read
from MCO
[3430] PCD 10 Read
from MCO
[3440] Digital Inputs
[3441] Digital
Outputs
[3450] Actual Position
[3451] Commanded
Position
[3452] Actual Master
Position
[3453] Slave Index
Position
[3454] Master Index
Position
[3455] Curve Position
[3456] Track Error
Parameter Descriptions
33
34 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[3457] Synchronizing
Error
[3458] Actual Velocity
[3459] Actual Master
Velocity
[3460] Synchronizing
Status
[3461] Axis Status
[3462] Program
Status
[3464] MCO 302
Status
[3465] MCO 302
Control
[3466] SPI Error
Counter
[3470] MCO Alarm
Word 1
[3471] MCO Alarm
Word 2
[4029] B-EMF
Protection Log
Readout
[4235] S-CRC Value
[4282] Safe Control
Word
[4283] Safe Status
Word
[4285] Active Safe
Func.
[4286] Safe Option
Info
[9913] Idle time
[9914] Paramdb
requests in
queue
[9917] tCon1 time
[9918] tCon2 time
[9919] Time Optimize
Measure
[9920] Fan Ctrl deltaT
[9921] Fan Ctrl
Tmean
[9922] Fan Ctrl NTC
Cmd
[9923] Fan Ctrl i-term
[9924] Rectier
Current
[9952] PC Debug 0
[9953] PC Debug 1
0-22 Display Line 1.3 Small
Select a variable for display in line 1, right position. The options
are the same as those listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small.
Option: Function:
[9954] PC Debug 2
[9961] FPC Debug 0
[9962] FPC Debug 1
[9963] FPC Debug 2
[9964] FPC Debug 3
[9965] FPC Debug 4
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[0] None
[9] Performance
Monitor
[15] Readout:
actual setup
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[89] Date and Time
Readout
[748] PCD Feed
Forward
[953] Probus
Warning Word
[1005] Readout
Transmit Error
Counter
[1006] Readout
Receive Error
Counter
[1007] Readout Bus
O Counter
[1013] Warning
Parameter
[1230] Warning
Parameter
[1397] Alert Alarm
Word
[1398] Alert Warning
Word
[1399] Alert Status
Word
[1472] Legacy Alarm
Word
[1473] Legacy
Warning Word
[1474] Leg. Ext.
Status Word
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 35
3 3

0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[1500] Operating
hours
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1580] Fan Running
Hours
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference
[Unit]
[1602] Reference %
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual
Value [%]
[1606] Actual Position
[1607] Target Position
[1608] Position Error
[1609] Custom
Readout
[1610] Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] * Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1619] Thermistor
Sensor
Temperature
[1620] Motor Angle
[1621] Torque [%]
High Res.
[1622] Torque [%]
[1623] Motor Shaft
Power [kW ]
[1624] Calibrated
Stator
Resistance
[1625] Torque [Nm]
High
[1628] Angle Error
[1630] DC Link
Voltage
[1631] System Temp.
[1632] Brake
Energy /s
[1633] Brake Energy
Average
[1634] Heatsink
Temp.
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[1635] Inverter
Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom.
Current
[1637] Inv. Max.
Current
[1638] SL Controller
State
[1639] Control Card
Temp.
[1642] Service Log
Counter
[1643] Timed Actions
Status
[1644] Speed Error
[RPM]
[1645] Motor Phase U
Current
[1646] Motor Phase V
Current
[1647] Motor Phase
W Current
[1648] Speed Ref.
After Ramp
[RPM]
[1650] External
Reference
[1651] Pulse
Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot
Reference
[1657] Feedback
[RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53
Switch Setting
[1662] Analog Input
53
[1663] Terminal 54
Switch Setting
[1664] Analog Input
54
[1665] Analog Output
42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[bin]
[1667] Freq. Input
#29 [Hz]
[1668] Freq. Input
#33 [Hz]
Parameter Descriptions
33
36 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[1669] Pulse Output
#27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse Output
#29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay Output
[bin]
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1674] Prec. Stop
Counter
[1675] Analog In
X30/11
[1676] Analog In
X30/12
[1677] Analog Out
X30/8 [mA]
[1678] Analog Out
X45/1 [mA]
[1679] Analog Out
X45/3 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW
1
[1681] Fieldbus Sync.
REF
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1683] Fieldbus Pos.
REF
[1684] Comm. Option
STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1687] Bus Readout
Alarm/Warning
[1689] Congurable
Alarm/Warning
Word
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word
2
[1694] Ext. Status
Word
[1695] Ext. Status
Word 2
[1696] Maintenance
Word
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1698] Warning Word
3
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[1804] Mech Brake
Count
[1820] Commanded
Position
[1821] Master
Position
[1823] Virtual Master
Pos.
[1827] Safe Opt. Est.
Speed
[1828] Safe Opt.
Meas. Speed
[1829] Safe Opt.
Speed Error
[1836] Analog Input
X48/2 [mA]
[1837] Temp. Input
X48/4
[1838] Temp. Input
X48/7
[1839] Temp. Input
X48/10
[1840] Analog Input
X49/1
[1841] Analog Input
X49/3
[1842] Analog Input
X49/5
[1843] Analog Out
X49/7
[1844] Analog Out
X49/9
[1845] Analog Out
X49/11
[1846] X49 Digital
Output [bin]
[1860] Digital Input 2
[1870] Mains Voltage
[1871] Mains
Frequency
[1872] Mains
Imbalance
[1875] Rectier DC
Volt.
[1890] Process PID
Error
[1891] Process PID
Output
[1892] Process PID
Clamped
Output
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 37
3 3

0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[1893] Process PID
Gain Scaled
Output
[2316] Maintenance
Text
[3019] Wobble Delta
Freq. Scaled
[3110] Bypass Status
Word
[3111] Bypass
Running Hours
[3401] PCD 1 Write
to MCO
[3402] PCD 2 Write
to MCO
[3403] PCD 3 Write
to MCO
[3404] PCD 4 Write
to MCO
[3405] PCD 5 Write
to MCO
[3406] PCD 6 Write
to MCO
[3407] PCD 7 Write
to MCO
[3408] PCD 8 Write
to MCO
[3409] PCD 9 Write
to MCO
[3410] PCD 10 Write
to MCO
[3421] PCD 1 Read
from MCO
[3422] PCD 2 Read
from MCO
[3423] PCD 3 Read
from MCO
[3424] PCD 4 Read
from MCO
[3425] PCD 5 Read
from MCO
[3426] PCD 6 Read
from MCO
[3427] PCD 7 Read
from MCO
[3428] PCD 8 Read
from MCO
[3429] PCD 9 Read
from MCO
[3430] PCD 10 Read
from MCO
0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[3440] Digital Inputs
[3441] Digital
Outputs
[3450] Actual Position
[3451] Commanded
Position
[3452] Actual Master
Position
[3453] Slave Index
Position
[3454] Master Index
Position
[3455] Curve Position
[3456] Track Error
[3457] Synchronizing
Error
[3458] Actual Velocity
[3459] Actual Master
Velocity
[3460] Synchronizing
Status
[3461] Axis Status
[3462] Program
Status
[3464] MCO 302
Status
[3465] MCO 302
Control
[3466] SPI Error
Counter
[3470] MCO Alarm
Word 1
[3471] MCO Alarm
Word 2
[4029] B-EMF
Protection Log
Readout
[4235] S-CRC Value
[4282] Safe Control
Word
[4283] Safe Status
Word
[4285] Active Safe
Func.
[4286] Safe Option
Info
[9913] Idle time
[9914] Paramdb
requests in
queue
[9917] tCon1 time
Parameter Descriptions
33
38 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-23 Display Line 2 Large
Select a variable for display in line 2. The options are the same
as listed for parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1 Small.
Option: Function:
[9918] tCon2 time
[9919] Time Optimize
Measure
[9920] Fan Ctrl deltaT
[9921] Fan Ctrl
Tmean
[9922] Fan Ctrl NTC
Cmd
[9923] Fan Ctrl i-term
[9924] Rectier
Current
[9952] PC Debug 0
[9953] PC Debug 1
[9954] PC Debug 2
[9961] FPC Debug 0
[9962] FPC Debug 1
[9963] FPC Debug 2
[9964] FPC Debug 3
[9965] FPC Debug 4
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[0] None
[9] Performance
Monitor
[15] Readout:
actual setup
[37] Display Text 1
[38] Display Text 2
[39] Display Text 3
[89] Date and Time
Readout
[748] PCD Feed
Forward
[953] Probus
Warning Word
[1005] Readout
Transmit Error
Counter
[1006] Readout
Receive Error
Counter
[1007] Readout Bus
O Counter
[1013] Warning
Parameter
[1230] Warning
Parameter
[1397] Alert Alarm
Word
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[1398] Alert Warning
Word
[1399] Alert Status
Word
[1472] Legacy Alarm
Word
[1473] Legacy
Warning Word
[1474] Leg. Ext.
Status Word
[1500] Operating
hours
[1501] Running Hours
[1502] kWh Counter
[1580] Fan Running
Hours
[1600] Control Word
[1601] Reference
[Unit]
[1602] * Reference %
[1603] Status Word
[1605] Main Actual
Value [%]
[1606] Actual Position
[1607] Target Position
[1608] Position Error
[1609] Custom
Readout
[1610] Power [kW]
[1611] Power [hp]
[1612] Motor Voltage
[1613] Frequency
[1614] Motor current
[1615] Frequency [%]
[1616] Torque [Nm]
[1617] Speed [RPM]
[1618] Motor Thermal
[1619] Thermistor
Sensor
Temperature
[1620] Motor Angle
[1621] Torque [%]
High Res.
[1622] Torque [%]
[1623] Motor Shaft
Power [kW ]
[1624] Calibrated
Stator
Resistance
[1625] Torque [Nm]
High
[1628] Angle Error
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 39
3 3

0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[1630] DC Link
Voltage
[1631] System Temp.
[1632] Brake
Energy /s
[1633] Brake Energy
Average
[1634] Heatsink
Temp.
[1635] Inverter
Thermal
[1636] Inv. Nom.
Current
[1637] Inv. Max.
Current
[1638] SL Controller
State
[1639] Control Card
Temp.
[1642] Service Log
Counter
[1643] Timed Actions
Status
[1644] Speed Error
[RPM]
[1645] Motor Phase U
Current
[1646] Motor Phase V
Current
[1647] Motor Phase
W Current
[1648] Speed Ref.
After Ramp
[RPM]
[1650] External
Reference
[1651] Pulse
Reference
[1652] Feedback[Unit]
[1653] Digi Pot
Reference
[1657] Feedback
[RPM]
[1660] Digital Input
[1661] Terminal 53
Switch Setting
[1662] Analog Input
53
[1663] Terminal 54
Switch Setting
[1664] Analog Input
54
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[1665] Analog Output
42 [mA]
[1666] Digital Output
[bin]
[1667] Freq. Input
#29 [Hz]
[1668] Freq. Input
#33 [Hz]
[1669] Pulse Output
#27 [Hz]
[1670] Pulse Output
#29 [Hz]
[1671] Relay Output
[bin]
[1672] Counter A
[1673] Counter B
[1674] Prec. Stop
Counter
[1675] Analog In
X30/11
[1676] Analog In
X30/12
[1677] Analog Out
X30/8 [mA]
[1678] Analog Out
X45/1 [mA]
[1679] Analog Out
X45/3 [mA]
[1680] Fieldbus CTW
1
[1681] Fieldbus Sync.
REF
[1682] Fieldbus REF 1
[1683] Fieldbus Pos.
REF
[1684] Comm. Option
STW
[1685] FC Port CTW 1
[1686] FC Port REF 1
[1687] Bus Readout
Alarm/Warning
[1689] Congurable
Alarm/Warning
Word
[1690] Alarm Word
[1691] Alarm Word 2
[1692] Warning Word
[1693] Warning Word
2
[1694] Ext. Status
Word
[1695] Ext. Status
Word 2
Parameter Descriptions
33
40 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[1696] Maintenance
Word
[1697] Alarm Word 3
[1698] Warning Word
3
[1804] Mech Brake
Count
[1820] Commanded
Position
[1821] Master
Position
[1823] Virtual Master
Pos.
[1827] Safe Opt. Est.
Speed
[1828] Safe Opt.
Meas. Speed
[1829] Safe Opt.
Speed Error
[1836] Analog Input
X48/2 [mA]
[1837] Temp. Input
X48/4
[1838] Temp. Input
X48/7
[1839] Temp. Input
X48/10
[1840] Analog Input
X49/1
[1841] Analog Input
X49/3
[1842] Analog Input
X49/5
[1843] Analog Out
X49/7
[1844] Analog Out
X49/9
[1845] Analog Out
X49/11
[1846] X49 Digital
Output [bin]
[1860] Digital Input 2
[1870] Mains Voltage
[1871] Mains
Frequency
[1872] Mains
Imbalance
[1875] Rectier DC
Volt.
[1890] Process PID
Error
[1891] Process PID
Output
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[1892] Process PID
Clamped
Output
[1893] Process PID
Gain Scaled
Output
[2316] Maintenance
Text
[3019] Wobble Delta
Freq. Scaled
[3110] Bypass Status
Word
[3111] Bypass
Running Hours
[3401] PCD 1 Write
to MCO
[3402] PCD 2 Write
to MCO
[3403] PCD 3 Write
to MCO
[3404] PCD 4 Write
to MCO
[3405] PCD 5 Write
to MCO
[3406] PCD 6 Write
to MCO
[3407] PCD 7 Write
to MCO
[3408] PCD 8 Write
to MCO
[3409] PCD 9 Write
to MCO
[3410] PCD 10 Write
to MCO
[3421] PCD 1 Read
from MCO
[3422] PCD 2 Read
from MCO
[3423] PCD 3 Read
from MCO
[3424] PCD 4 Read
from MCO
[3425] PCD 5 Read
from MCO
[3426] PCD 6 Read
from MCO
[3427] PCD 7 Read
from MCO
[3428] PCD 8 Read
from MCO
[3429] PCD 9 Read
from MCO
[3430] PCD 10 Read
from MCO
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 41
3 3

0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[3440] Digital Inputs
[3441] Digital
Outputs
[3450] Actual Position
[3451] Commanded
Position
[3452] Actual Master
Position
[3453] Slave Index
Position
[3454] Master Index
Position
[3455] Curve Position
[3456] Track Error
[3457] Synchronizing
Error
[3458] Actual Velocity
[3459] Actual Master
Velocity
[3460] Synchronizing
Status
[3461] Axis Status
[3462] Program
Status
[3464] MCO 302
Status
[3465] MCO 302
Control
[3466] SPI Error
Counter
[3470] MCO Alarm
Word 1
[3471] MCO Alarm
Word 2
[4029] B-EMF
Protection Log
Readout
[4235] S-CRC Value
[4282] Safe Control
Word
[4283] Safe Status
Word
[4285] Active Safe
Func.
[4286] Safe Option
Info
[9913] Idle time
[9914] Paramdb
requests in
queue
[9917] tCon1 time
[9918] tCon2 time
0-24 Display Line 3 Large
Option: Function:
[9919] Time Optimize
Measure
[9920] Fan Ctrl deltaT
[9921] Fan Ctrl
Tmean
[9922] Fan Ctrl NTC
Cmd
[9923] Fan Ctrl i-term
[9924] Rectier
Current
[9952] PC Debug 0
[9953] PC Debug 1
[9954] PC Debug 2
[9961] FPC Debug 0
[9962] FPC Debug 1
[9963] FPC Debug 2
[9964] FPC Debug 3
[9965] FPC Debug 4
0-25 My Personal Menu
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 9999 ] Dene up to 50 parameters to
appear in the Q1 Personal Menu,
accessible via the [Quick Menu] key
on the LCP. The parameters are
shown in the Q1 Personal Menu in
the order they are programmed
into this array parameter. Delete
parameters by setting the value to
0000.
For example, this can be used to
provide quick, simple access to just
1 or up to 50 parameters, which
require changing on a regular basis
(for example, for plant maintenance
reasons) or by an OEM to enable
simple commissioning of their
equipment.
Parameter Descriptions
33
42 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3.1.4 0-3* LCP Custom Readout
It is possible to customize the display elements for various
purposes:
Custom readout. Value proportional to speed
•
(linear, squared, or cubed depending on unit
selected in parameter 0-30 Custom Readout Unit).
Display text. Text string stored in a parameter.
•
Custom readout

Custom Readout (Value)
P 16-09
Custom Readout
Unit P 0-30
Max value
P 0-32
Min value
P 0-31
Linear
units only
Quadratic Unit (Pressure)
Cubic Unit (Power)
Motor Speed
Motor Speed
High limit
P 4-13 (RPM)
P 4-14 (Hz)
0
130BT105.12
Linear Unit (e.g. speed and ow)
0-30 Unit for User-dened Readout
Option: Function:
It is possible to program a value to
be shown in the display of the LCP.
The value has a linear, squared, or
cubed relation to speed. This
relation depends on the unit
selected (see Table 3.2). The actual
calculated value can be read in
parameter 16-09 Custom Readout,
and/or shown in the display by
0-30 Unit for User-dened Readout
Option: Function:
selecting [16-09] Custom Readout in
parameter 0-20 Display Line 1.1
Small to parameter 0-24 Display Line
3 Large.
[0] * None
[1] %
[5] PPM
[10] 1/min
[11] rpm
[12] Pulse/s
[20] l/s
[21] l/min
[22] l/h
[23] m³/s
[24] m³/min
[25] m³/h
[30] kg/s
[31] kg/min
[32] kg/h
[33] t/min
[34] t/h
[40] m/s
[41] m/min
[45] m
[60] °C
[70] mbar
[71] bar
[72] Pa
[73] kPa
[74] m WG
[80] kW
[120] GPM
[121] gal/s
[122] gal/min
[123] gal/h
[124] CFM
[125] ft³/s
[126] ft³/min
[127] ft³/h
[130] lb/s
[131] lb/min
[132] lb/h
[140] ft/s
[141] ft/min
[145] ft
[160] °F
[170] psi
[171] lb/in²
[172] in WG
[173] ft WG
[176] kpsi
[177] MPa
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
The calculated value to be shown is based on the settings
in:
Parameter 0-30 Custom Readout Unit.
•
Parameter 0-31 Custom Readout Min Value (linear
•
Illustration 3.4 Custom Readout
The relation depends on the type of unit selected in
parameter 0-30 Custom Readout Unit:
Unit type Speed relation
Dimensionless
Speed
Flow, volume
Flow, mass
Velocity
Length
Temperature
Pressure Quadratic
Power Cubic
Table 3.2 Speed Relations for Dierent Unit Types
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 43
only).
Parameter 0-32 Custom Readout Max Value.
•
Parameter 4-13 Motor Speed High Limit [RPM].
•
•
•
Parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High Limit [Hz].
Actual speed.
Linear
3 3

0-30 Unit for User-dened Readout
Option: Function:
[178] kBar
[180] HP
0-31 Min Value of User-dened Readout
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t*
[ -999999.99 -
par. 0-32
CustomRea-
doutUnit]
This parameter sets the minimum
value of the custom-dened
readout (occurs at 0 speed). Only
possible to set dierent from 0
when selecting a linear unit in
parameter 0-30 Unit for User-dened
Readout. For quadratic and cubic
units, the minimum value is 0.
0-32 Max Value of User-dened Readout
Range: Function:
100
CustomReadoutUni
t*
[ par. 0-31 -
999999.99
CustomRea-
doutUnit]
This parameter sets the maximum
value to be shown when the speed
of the motor has reached the set
value for parameter 4-13 Motor
Speed High Limit [RPM] or
parameter 4-14 Motor Speed High
Limit [Hz] (depends on setting in
parameter 0-02 Motor Speed Unit).
0-33 Source for User-dened Readout
Option: Function:
Enter the source of the user-dened
readout.
[105] Torq relate to
rated
[143] PID Clamped
Output
4-20mA
[240] * Default Source
0-37 Display Text 1
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 25 ] Enter a text which can be viewed in
the graphical display by selecting
[37] Display Text 1 in
•
Parameter 0-20 Display Line
1.1 Small,
•
Parameter 0-21 Display Line
1.2 Small,
•
Parameter 0-22 Display Line
1.3 Small,
•
Parameter 0-23 Display Line
2 Large, or
•
Parameter 0-24 Display Line
3 Large.
0-38 Display Text 2
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 25 ] Enter a text which can be viewed in
the graphical display by selecting
[38] Display Text 2 in
•
Parameter 0-20 Display Line
1.1 Small,
•
Parameter 0-21 Display Line
1.2 Small,
•
Parameter 0-22 Display Line
1.3 Small,
•
Parameter 0-23 Display Line
2 Large, or
•
Parameter 0-24 Display Line
3 Large.
0-39 Display Text 3
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 25 ] Enter a text which can be viewed in
the graphical display by selecting
[39] Display Text 3 in
•
Parameter 0-20 Display Line
1.1 Small,
•
Parameter 0-21 Display Line
1.2 Small,
•
Parameter 0-22 Display Line
1.3 Small,
•
Parameter 0-23 Display Line
2 Large, or
•
Parameter 0-24 Display Line
3 Large.
0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled No eect when [Hand On] is
pressed. Select [0] Disabled to avoid
accidental start of the frequency
converter in hand-on mode.
[1] Enabled The LCP switches to hand-on mode
directly when [Hand On] is pressed.
[2] Password After pressing [Hand On] a
password is required. If
parameter 0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP
is included in My Personal Menu,
dene the password in
parameter 0-65 Personal Menu
Password. Otherwise dene the
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
44 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
3.1.5 0-4* LCP Keypad
Enable, disable, and password protect individual keys on
the LCP.

0-40 [Hand on] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
password in parameter 0-60 Main
Menu Password.
[3] Hand O/On When [Hand On] is pressed once,
the LCP switches to O mode.
When pressed again, the LCP
switches to hand-on mode.
[4] Hand O/On
w. Passw.
Same as option [3] Hand O/On but
a password is required (see option
[2] Password).
[9] Enabled, ref =
0
0-41 [O] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Avoids accidental stop of the
frequency converter.
[1] Enabled
[2] Password Avoids unauthorized stop. If
parameter 0-41 [O] Key on LCP is
included in the Quick Menu, then
dene the password in
parameter 0-65 Personal Menu
Password.
0-42 [Auto on] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Avoids accidental start of the
frequency converter in auto-on
mode.
[1] Enabled
[2] Password Avoids unauthorized start in auto-
on mode. If parameter 0-42 [Auto
on] Key on LCP is included in the
Quick Menu, then dene the
password in parameter 0-65 Personal
Menu Password.
0-43 [Reset] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled No eect when [Reset] is pressed.
Avoids accidental alarm reset.
[1] Enabled
[2] Password Avoids unauthorized resetting. If
parameter 0-43 [Reset] Key on LCP is
included in the Quick Menu, then
dene the password in
parameter 0-65 Personal Menu
Password.
[7] Enabled
without OFF
Resets the frequency converter
without setting it in O mode.
0-43 [Reset] Key on LCP
Option: Function:
[8] Password
without OFF
Resets the frequency converter
without setting it in O mode. A
password is required when pressing
[Reset] (see option [2] Password).
0-44 [O/Reset] Key on LCP
Enable or disable the [O/Reset] key.
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled
[1] * Enabled
[2] Password
0-45 [Drive Bypass] Key on LCP
Press [O] and select [0] Disabled to avoid unintended stop of
the frequency converter. Press [O] and select [2] Password to
avoid unauthorized bypass of the frequency converter. If
parameter 0-45 [Drive Bypass] Key on LCP is included in the Quick
Menu, dene the password in parameter 0-65 Personal Menu
Password.
Option: Function:
[0] Disabled Select to disable the key.
[1] * Enabled
[2] Password
0-50 LCP Copy
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
[0] * No copy
[1] All to LCP Copies all parameters in all set-ups
from the frequency converter
memory to the LCP memory.
[2] All from LCP Copies all parameters in all set-ups
from the LCP memory to the
frequency converter memory.
[3] Size indep.
from LCP
Copy only the parameters that are
independent of the motor size. The
latter selection can be used to
program several frequency
converters with the same function
without disturbing motor data.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 45
3.1.6 0-5* Copy/Save
Copy parameters from and to the LCP. Use these
parameters for saving and copying set-ups from 1
frequency converter to another.

0-50 LCP Copy
Option: Function:
[4] File from MCO
to LCP
[5] File from LCP
to MCO
[6] Data from
DYN to LCP
[7] Data from LCP
to DYN
[9] Safety Par.
from LCP
[10] Delete LCP
copy data
Use to delete the copy after the
transfer is complete.
0-51 Set-up Copy
Option: Function:
[0] * No copy No function.
[1] Copy to set-up1Copies all parameters in the present
programming set-up (dened in
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up) to set-up
1.
[2] Copy to set-up2Copies all parameters in the present
programming set-up (dened in
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up) to set-up
2.
[3] Copy to set-up3Copies all parameters in the present
programming set-up (dened in
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up) to set-up
3.
[4] Copy to set-up4Copies all parameters in the present
programming set-up (dened in
parameter 0-11 Edit Set-up) to set-up
4.
[9] Copy to all Copies the parameters in the
present set-up to each of the setups 1 to 4.
0-60 Main Menu Password
Range: Function:
100* [-9999 -
9999 ]
Dene the password for access to
the Main Menu via the [Main Menu]
key. If parameter 0-61 Access to Main
Menu w/o Password is set to [0] Full
access, this parameter is ignored.
0-61 Access to Main Menu w/o Password
Option: Function:
[0] * Full access Disables password dened in
parameter 0-60 Main Menu
Password.
[1] LCP: Read only Prevent unauthorized editing of
Main Menu parameters.
[2] LCP: No access Prevent unauthorized viewing and
editing of Main Menu parameters.
[3] Bus: Read only Read-only functions for parameters
on eldbus and/or FC standard bus.
[4] Bus: No access No access to parameters is allowed
via eldbus and/or FC standard bus.
[5] All: Read only Read-only function for parameters
on LCP, eldbus, or FC standard
bus.
[6] All: No access No access from LCP, eldbus, or FC
standard bus is allowed.
0-65 Personal Menu Password
Range: Function:
200* [-9999 -
9999 ]
Dene the password for access to
the Quick Menu via the [Quick
Menu] key. If parameter 0-66 Access
to Personal Menu w/o Password is
set to [0] Full access, this parameter
is ignored.
0-66 Access to Personal Menu w/o Password
If parameter 0-61 Access to Main Menu w/o Password is set to [0]
Full access, then this parameter is ignored.
Option: Function:
[0] * Full access Disables the password dened in
parameter 0-65 Personal Menu
Password.
[1] LCP: Read only Prevents unauthorized editing of
Quick Menu parameters.
[3] Bus: Read only Read-only functions for Quick Menu
parameters on eldbus and/or FC
standard bus.
[5] All: Read only Read-only function for Quick Menu
parameters on LCP, eldbus, or
frequency converter standard bus.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
3.1.7 0-6* Password
46 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
If [0] Full access is selected, parameter 0-60 Main Menu
Password, parameter 0-65 Personal Menu Password, and
parameter 0-66 Access to Personal Menu w/o Password are
ignored.
NOTICE
A more complex password protection is available for
OEMs upon request.

0-67 Bus Password Access
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 9999 ] Use this parameter to unlock the
frequency converter via eldbus or
MCT 10 Set-up Software.
0-68 Safety Parameters Password
Range: Function:
300* [0 - 9999 ] Enter the password for the safety
parameters access. If
parameter 0-69 Password Protection
of Safety Parameters is set to [0]
Disabled, this parameter is ignored.
0-69 Password Protection of Safety Parameters
Option: Function:
[0] * Disabled
[1] Enabled
0-70 Date and Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 0 ] Sets the date and time of the
internal clock. The format to be
used is set in parameter 0-71 Date
Format and parameter 0-72 Time
Format.
When using the VLT® Real-time
Clock MCB 117 option, the time is
synchronized at 15:00 every day.
0-71 Date Format
Option: Function:
[0] YYYY-MM-DD
[1] DD-MM-YYYY
[2] MM/DD/YYYY
0-72 Time Format
Option: Function:
[0] 24 h
[1] 12 h
0-73 Time Zone Oset
Range: Function:
0 min* [-780 - 780
min]
Enter the time zone oset relative
to UTC. This parameter is required
for the automatic daylight saving
time adjustment.
0-74 DST/Summertime
Option: Function:
Select how to handle daylight
saving time/summer time. For
manual setting of DST/summer
time, enter the start date and end
date in parameter 0-76 DST/
0-74 DST/Summertime
Option: Function:
Summertime Start and
parameter 0-77 DST/Summertime
End.
[0] * O
[2] Manual
0-76 DST/Summertime Start
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 0 ] Sets the date and time when DST/
summer time starts. The date is
programmed in the format selected
in parameter 0-71 Date Format.
0-77 DST/Summertime End
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 0 ] Sets the date and time when DST/
summer time ends. The date is
programmed in the format selected
in parameter 0-71 Date Format.
0-79 Clock Fault
Option: Function:
Enables or disables the clock
warning when the clock has not
been set, or has been reset due to
a power-down and no back-up is
installed. If VLT® Analog I/O Option
MCB 109 is installed, [1] Enabled is
default.
[0] Disabled
[1] Enabled
0-81 Working Days
Array [7]
Array with 7 elements [0]–[6] shown below the parameter
number in the display. Press [OK] and step between elements
with [▲] and [▼].
Option: Function:
Set for each weekday if it is a
working day or a non-working day.
First element of the array is
Monday. The working days are used
for timed actions.
[0] No
[1] Yes
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 47

0-82 Additional Working Days
Array [5]
Array with 5 elements [0]–[4] shown below the parameter
number in the display. Press [OK] and step between elements
with [▲] and [▼].
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 0 ] Denes dates for additional working
days that would normally be nonworking days according to
parameter 0-81 Working Days.
0-83 Additional Non-Working Days
Array [15]
Array with 15 elements [0]–[14] shown below the parameter
number in the display. Press [OK] and step between elements
with [▲] and [▼].
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 0 ] Denes dates for additional non-
working days that would normally
be working days according to
parameter 0-81 Working Days.
0-84 Time for Fieldbus
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
Shows the time for eldbus.
0-85 Summer Time Start for Fieldbus
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
Shows the summer time start for
eldbus.
0-86 Summer Time End for Fieldbus
Range: Function:
0* [0 -
4294967295 ]
Shows the summer time end for
eldbus.
0-89 Date and Time Readout
Range: Function:
0* [0 - 25 ] Shows the current date and time.
The date and time is updated
continuously.
The clock does not begin counting
until a setting dierent from default
has been made in
parameter 0-70 Date and Time.
1-00 Conguration Mode
Option: Function:
Select the application control
principle to be used when a remote
reference (that is via analog input
or eldbus) is active. A remote
reference can only be active when
parameter 3-13 Reference Site is set
to [0] Linked to Hand/Auto or [1]
Remote.
[0] Speed open
loop
Enables speed control (without
feedback signal from motor) with
automatic slip compensation for
almost constant speed at varying
loads.
Compensations are active, but can
be disabled in parameter group 1-0*
Load/Motor. Set the speed control
parameters in parameter group 7-0*
Speed PID Ctrl.
[1] Speed closed
loop
Enables speed closed-loop control
with feedback. Obtain full holding
torque at 0 RPM.
For increased speed accuracy,
provide a feedback signal and set
the speed PID control. Set the
speed control parameters in
parameter group 7-0* Speed PID Ctrl.
[2] Torque Enables torque closed-loop control
with feedback. Only possible with
Flux with motor feedback option,
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle.
NOTICE
This is valid for FC 302 only.
[3] Process Enables the use of process control
in the frequency converter. Set the
process control parameters in
parameter groups 7-2* Process Ctrl.
Feedb. and 7-3* Process PID Ctrl.
[4] Torque open
loop
Enables the use of torque open
loop. mode (parameter 1-01 Motor
Control Principle). Set the torque PID
parameters in parameter group 7-1*
Torque PI Control.
[5] Wobble Enables the wobble functionality in
parameter 30-00 Wobble Mode to
parameter 30-19 Wobble Delta Freq.
Scaled.
[6] Surface
Winder
Enables the surface winder control
specic parameters in parameter
Parameter Descriptions
33
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3.2 Parameters: 1-** Load and Motor
3.2.1 1-0* General Settings
Dene whether the frequency converter operates in speed
mode or torque mode, and whether the internal PID
control should be active or not.
48 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-00 Conguration Mode
Option: Function:
groups 7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedb. and
7-3* Process PID Ctrl.
[7] Extended PID
Speed OL
Specic parameters in parameter
groups 7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedb. to
7-5* Ext. Process PID Ctrl.
[8] Extended PID
Speed CL
Specic parameters in parameter
groups 7-2* Process Ctrl. Feedb. to
7-5* Ext. Process PID Ctrl.
[9] Positioning
NOTICE
This option is available only
with software version 48.XX.
Activates the positioning mode.
[10] Synchroni-
zation
NOTICE
This option is available only
with software version 48.XX.
Activates the synchronization mode.
1-01 Motor Control Principle
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Select which motor control
principle to employ.
[0] U/f Special motor mode, for parallel-
connected motors in special motor
applications. When U/f is selected,
the characteristic of the control
principle can be edited in
parameter 1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
and parameter 1-56 U/f Characteristic - F.
[1] VVC+ Voltage vector control principle is
suitable for most applications. The
main benet of VVC+ operation is
that it uses a robust motor model.
[2] Flux sensorless Flux vector control without encoder
feedback, for simple installation and
robustness against sudden load
changes.
NOTICE
This is valid for FC 302 only.
1-01 Motor Control Principle
Option: Function:
[3] Flux w/ motor
feedb
High accuracy speed and torque
control, suitable for the most
demanding applications.
NOTICE
This is valid for FC 302 only.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 49
The best shaft performance is normally achieved using
either of the 2 ux vector control modes [2] Flux sensorless
and [3] Flux with encoder feedback.
1-02 Flux Motor Feedback Source
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be adjusted while
the motor is running.
The options 12 and 13 are only available
for software version 48.XX.
Select the source of the feedback for ux
closed loop motor control. Set
parameter 1-01 Motor Control Principle to [3]
Flux with motor feedback option.
The feedback device is typically mounted
directly on the motor shaft. The feedback
device can also be mounted in the application
provided the gear ratio between motor and
encoder is xed and accurate.
Congure the gear ratio between motor and
encoder in parameter 7-94 Position PI Feedback
Scale Numerator and parameter 7-95 Position PI
Feebback Scale Denominator without any
rounding error.
[1] * 24V
encoder
32/33
[2] MCB 102
[3] MCB 103
[4] MCO
Encoder 1
X56
Single signal generated from 24 V High
Threshold Logic (HTL) encoder connected to
terminals 32 and 33. Congure the 24 V
encoder interface in parameter group 5.7* 24 V
Encoder Input.
Program terminals 32/33 to [0] No operation.
The option is named as 24 V encoder in
software version 8.XX.
This option is only available for VLT® Encoder
Option MCB 102. Congure the encoder
interface in parameter groups 17-0*, 17-1* and
17-2*.
This option is only available for VLT® Resolver
Option MCB 103. Congure the resolver
interface in parameter groups 17-5* Resolver
Interface.
The MCO encoder 1 X56 is only available with
motion control options MCO 305, MCO 350,
and MCO 351.
Congure the encoder interface in Parameter
group 32-3* Encoder 1.
3 3

1-03 Torque Characteristics
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Select the torque characteristic
required.
VT and AEO are both energy-saving
operations.
[0] * Constant
torque
Motor shaft output provides
constant torque under variable
speed control.
[1] Variable
torque
Motor shaft output provides
variable torque under variable
speed control. Set the variable
torque level in parameter 14-40 VT
Level.
[2] Auto Energy
Optim.
Automatically optimizes energy
consumption by minimizing
magnetization and frequency via
parameter 14-41 AEO Minimum
Magnetisation and
parameter 14-42 Minimum AEO
Frequency.
[5] Constant
Power
The function provides a constant
power in the eld weakening area.
The torque shape of motor mode is
used as a limit in the generator
mode. This is done to limit the
power in generator mode that
otherwise becomes considerably
larger than in motor mode, due to
the high DC-link voltage available
in generator mode.
P
shaft
W = ω
mech
rad/s × T Nm
1-03 Torque Characteristics
Option: Function:
This relationship with the constant
power is shown in Illustration 3.5:
ω
nom2ωnom
ω [rad/S]
P[W]
130BB655.10
T[Nm]
P
T
P
nom
T
nom
Illustration 3.5 Constant Power
1-04 Overload Mode
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Use this parameter to congure the
frequency converter for either high
or normal overload. When selecting
the frequency converter size, always
review the technical data in the
operating guide or the design guide
to know the available output
current.
[0] * High torque Allows up to 160% over torque.
[1] Normal torque For oversized motor - allows up to
110% over torque.
1-05 Local Mode Conguration
Option: Function:
Select which application conguration mode
(parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode),
that is application control principle,
to use when a local (LCP) reference
is active. A local reference can be
active only when
parameter 3-13 Reference Site is set
to [0] Linked to Hand/Auto or [2]
Local. By default the local reference
is active in hand-on mode only.
[0] Speed open
loop
[1] Speed Closed
Loop
[2] * As mode par
1-00
[4] Positioning
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
1-02 Flux Motor Feedback Source
Option: Function:
[5] MCO
Encoder 2
X55
33
[12] MCB 102
Absolute
[13] 24V
encoder
27/29
The MCO encoder 1 X56 is only available with
motion control options MCO 305, MCO 350,
and MCO 351.
Congure the encoder interface in Parameter
group 32-0* Encoder 2.
The option is only available for VLT® Encoder
Option MCB 102 with version 4.00 and higher
and when parameter 17-00 Encoders Connected
is set to [1] Two Encoders.
Single-signal HTL encoder connected to digital
inputs 27 and 29. 24 V encoder is congured in
parameter group 5.7* 24V Encoder Input.
Program terminals 27/29 to [0] No operation.
50 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-06 Clockwise Direction
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
This parameter denes the term
clockwise corresponding to the LCP
direction arrow. Used for easy
change of direction of shaft
rotation without swapping motor
wires.
[0] * Normal The motor shaft turns in clockwise
direction when the frequency
converter is connected U⇒U, V⇒V,
and W⇒W to the motor.
[1] Inverse Motor shaft turns in counter-
clockwise direction when the
frequency converter is connected
U⇒U, V⇒V, and W⇒W to the motor.
[2] Inverse All
1-07 Motor Angle Oset Adjust
Range: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter is only valid for
FC 302 and only in
combination with a PM motor
with feedback.
0* [Manual] The functionality of this option
depends on the type of the
feedback device. This option sets
the frequency converter to use the
motor angle oset entered in
parameter 1-41 Motor Angle Oset, if
an absolute feedback device is
used.
If an incremental feedback device is
selected, the frequency converter
automatically adjusts the motor
angle oset on the 1st start after
power-up, or when the motor data
is changed.
[1] Auto The frequency converter adjusts the
motor angle oset automatically on
the 1st start after power-up, or
when the motor data is changed
no matter what feedback device is
selected. This means that options
Manual and Auto are identical for
the incremental encoder.
1-07 Motor Angle Oset Adjust
Range: Function:
[2] Auto Every
Start
The frequency converter adjusts the
motor angle oset automatically on
every start, or when the motor data
is changed.
[3] O Selecting this option turns the
automatic oset adjustment o.
[4] Once with
Store
This option updates
parameter 1-41 Motor Angle Oset
automatically when the angle value
is 0. This option is valid only for
absolute feedback devices. The
function uses rotor detection and
then applies DC hold to make the
oset adjustment more accurate.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
3.2.2 1-1* Special Settings
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 51
NOTICE
The parameters within this parameter group cannot be
adjusted while the motor is running.
3.2.3 Asynchronous Motor Set-up
Enter the following motor data. Find the information on
the motor nameplate.
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW] or
•
parameter 1-21 Motor Power [HP].
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage.
•
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency.
•
Parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
•
Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed.
•
When running in ux control principle, or for optimum
performance in VVC+ mode, extra motor data is required to
set up the following parameters. Find the data in the
motor datasheet (this data is typically not available on the
motor nameplate). Run a complete automatic motor
adaptation (AMA) using parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor
Adaptation (AMA) [1] Enable Complete AMA or enter the
parameters manually. Parameter 1-36 Iron Loss Resistance
(Rfe) is always entered manually.
Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs).
•
Parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr).
•
Parameter 1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1).
•
Parameter 1-34 Rotor Leakage Reactance (X2).
•
Parameter 1-35 Main Reactance (Xh).
•
Parameter 1-36 Iron Loss Resistance (Rfe).
•

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Application-specic adjustment when running VVC
+
3.2.4 PM Motor Set-up
VVC+ is the most robust control mode. In most situations,
it provides optimum performance without further
adjustments. Run a complete AMA for best performance.
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Application-specic adjustment when running ux
33
Flux control principle is the preferred control principle for
optimum shaft performance in dynamic applications.
Perform an AMA since this control mode requires precise
motor data. Depending on the application, further
adjustments may be required.
See Table 3.3 for application-related recommendations.
Application Settings
Low-inertia applications Keep calculated values.
High-inertia applications Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed.
Increase current to a value between
default and maximum depending on
the application.
Set ramp times matching the
application. Too fast ramp-up causes
an overcurrent or overtorque. Too
fast ramp-down causes an
overvoltage trip.
High load at low speed Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed.
Increase current to a value between
default and maximum depending on
the application.
No-load application Adjust parameter 1-18 Min. Current at
No Load to achieve smoother motor
operation by reducing torque ripple
and vibration.
Flux sensorless control
principle only
Table 3.3 Recommendations for Flux Applications
Adjust parameter 1-53 Model Shift
Frequency.
Example 1: If the motor oscillates at
5 Hz, and dynamics performance is
required at 15 Hz, set
parameter 1-53 Model Shift Frequency
to 10 Hz.
Example 2: If the application
involves dynamic load changes at
low speed, reduce
parameter 1-53 Model Shift Frequency.
Observe the motor behavior to
make sure that the model shift
frequency is not reduced too much.
Symptoms of inappropriate model
shift frequency are motor oscillations
or frequency converter tripping.
This section describes how to set up a PM motor.
Initial programming steps
To activate PM motor operation, select [1] PM, non-salient
SPM in parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
Programming motor data
After selecting a PM motor, the PM motor-related
parameters in parameter groups 1-2* Motor Data, 1-3* Adv.
Motor Data, and 1-4* Adv. Motor Data II are active.
The necessary data is on the motor nameplate and on the
motor datasheet.
Run a complete AMA using parameter 1-29 Automatic
Motor Adaptation (AMA) [1] Enable Complete AMA.
If a complete AMA is not performed, congure the
following parameters manually:
1. Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
Enter the line-to-common stator winding
resistance (Rs). If only line-line data is available,
divide the line-line value by 2 to get the linecommon value.
2. Parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld)
Enter the line-to-common direct axis inductance
of the PM motor.
If only line-line data is available, divide the lineline value by 2 to get the line-common value.
3. Parameter 1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM
Enter the line-to-line back EMF of the PM motor
at 1000 RPM (RMS value). Back EMF is the voltage
generated by a PM motor when no frequency
converter is connected and the shaft is turned
externally. It is normally specied for nominal
motor speed or for 1000 RPM measured between
2 lines. If the value is not available for a motor
speed of 1000 RPM, calculate the correct value as
follows:
If back EMF is, for example, 320 V at 1800 RPM, it
can be calculated at 1000 RPM as follows:
Back EMF = (Voltage/RPM)x1000 =
(320/1800)x1000 = 178.
Test motor operation
1. Start the motor at low speed (100–200 RPM). If
the motor does not turn, check the installation,
general programming, and motor data.
2. Check if the start function in parameter 1-70 Start
Mode ts the application requirements.
Rotor detection
This function is the recommended selection for
applications where the motor starts from standstill, for
example pumps or conveyors. On some motors, a sound is
52 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
heard when the frequency converter performs the rotor
detection. This does not harm the motor.
Parking
This function is the recommended selection for
applications where the motor is rotating at slow speed, for
example windmilling in fan applications.
Parameter 2-06 Parking Current and parameter 2-07 Parking
Time can be adjusted. Increase the factory setting of these
parameters for applications with high inertia.
Application-specic adjustment when running VVC
+
VVC+ is the most robust control mode. In most situations,
it provides optimum performance without further
adjustments. Run a complete AMA for best performance.
Start the motor at nominal speed. If the application does
not run well, check the VVC+ PM settings. Table 3.4
contains recommendations for various applications.
Application Settings
Low-inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
Low-inertia applications
50>I
High-inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
High load at low speed
<30% (rated speed)
<5
>5
Load/IMotor
>50
Table 3.4 Recommendations for Various Applications
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const. by factor 5–10.
Reduce parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain.
Reduce parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed (<100%).
Keep the default values.
Increase parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain, parameter 1-15 Low Speed Filter
Time Const., and parameter 1-16 High
Speed Filter Time Const.
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const.
Increase parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed to adjust the starting
torque. 100% current provides
nominal torque as starting torque.
This parameter is independent of
parameter 30-20 High Starting Torque
Time [s] and parameter 30-21 High
Starting Torque Current [%]). Working
at a current level higher than 100%
for a prolonged time can cause the
motor to overheat.
If the motor starts oscillating at a certain speed, increase
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain. Increase the value in small
steps. Depending on the motor, this parameter can be set
to 10–100% higher than the default value.
Application-specic adjustment when running ux
Flux control principle is the preferred control principle for
optimum shaft performance in dynamic applications.
Perform an AMA because this control mode requires
precise motor data. Depending on the application, further
adjustments may be required.
See chapter 3.2.3 Asynchronous Motor Set-up for application-
specic recommendations.
3.2.5
SynRM Motor Set-up with VVC
+
This section describes how to set up a SynRM motor with
VVC+.
NOTICE
The SmartStart wizard covers the basic conguration of
SynRM motors.
Initial programming steps
To activate SynRM motor operation, select [5] Sync.
Reluctance in parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
Programming motor data
After performing the initial programming steps, the SynRM
motor-related parameters in parameter groups 1-2* Motor
Data, 1-3* Adv. Motor Data, and 1-4* Adv. Motor Data II are
active.
Use the motor nameplate data and the motor datasheet to
program the following parameters in the order listed:
1. Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency.
2. Parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
3. Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed.
4. Parameter 1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque.
Run a complete AMA using parameter 1-29 Automatic
Motor Adaptation (AMA) [1] Enable Complete AMA or enter
the following parameters manually:
1. Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs).
2. Parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld).
3. Parameter 1-44 d-axis Inductance Sat. (LdSat).
4. Parameter 1-45 q-axis Inductance Sat. (LqSat).
5. Parameter 1-48 Inductance Sat. Point.
Application-specic adjustments
Start the motor at nominal speed. If the application does
not run well, check the VVC+ SynRM settings. Table 3.5
provides application-specic recommendations:
Application Settings
Low-inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
Low-inertia applications
50>I
<5
Load/IMotor
>5
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const. by factor 5–10.
Reduce parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain.
Reduce parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed (<100%).
Keep the default values.
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 53

1-10 Motor Construction
Option: Function:
Select the motor design type.
NOTICE
FC 301 allows only selection of
asynchronous motors.
[0] * Asynchron Use for ASM/IM motors.
[1] PM, non
salient SPM
Use for SPM motors, surface
mounted magnet.
PM motors are divided into 2
groups, with either surfacemounted (SPM)/non-salient
magnets or interior-mounted (IPM)/
salient magnets.
1-10 Motor Construction
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This option is valid for FC 302
only.
[2] PM, salient
IPM
Use for IPM motors, interiormounted magnet.
PM motors are divided into 2
groups, with either surfacemounted (SPM)/non-salient
magnets or interior-mounted (IPM)/
salient magnets.
NOTICE
This option is valid for FC 302
only.
[5] SynRM Use for SynRM, synchronous
reluctance motors.
[6] PMaSynRM Use for PMaSynRM, Permanent
Magnet assisted synchronous
reluctance motors.
1-11 Motor Model
Option: Function:
Automatically sets the factory
values for the selected motor. If the
default value Std. Asynchron is used,
determine settings manually
according to the selection
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
[1] Std. Asynchron Default motor model when [0]
Asynchron is selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
[2] Std. PM, non
salient
Selectable when [1] PM, non-salient
SPM is selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
[3] Std. PM salient
[10] Danfoss OGD
LA10
Selectable when [1] PM, non-salient
SPM is selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
Only available for T4, T5 in 1.5–
3 kW. Settings are loaded automatically for this specic motor.
[11] Danfoss OGD
V210
Selectable when [1] PM, non-salient
SPM is selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction.
Only available for T4, T5 in 0.75–
3 kW. Settings are loaded automatically for this specic motor.
Parameter Descriptions
Application Settings
High-inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
High-load at low speed
33
<30% (rated speed)
Dynamic applications Increase parameter 14-41 AEO
Motor sizes less than
18 kW (24 hp)
>50
Increase parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain, parameter 1-15 Low Speed Filter
Time Const., and parameter 1-16 High
Speed Filter Time Const.
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const.
Increase parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed to adjust the starting
torque. 100% current provides
nominal torque as starting torque.
This parameter is independent of
parameter 30-20 High Starting Torque
Time [s] and parameter 30-21 High
Starting Torque Current [%]). Working
at a current level higher than 100%
for a prolonged time can cause the
motor to overheat.
Minimum Magnetisation for highly
dynamic applications. Adjusting
parameter 14-41 AEO Minimum
Magnetisation ensures a good
balance between energy eciency
and dynamics. Adjust
parameter 14-42 Minimum AEO
Frequency to specify the minimum
frequency at which the frequency
converter should use minimum
magnetization.
Avoid short ramp-down times.
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Table 3.5 Recommendations for Various Applications
If the motor starts oscillating at a certain speed, increase
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain. Increase the damping gain
value in small steps. Depending on the motor, this
parameter can be set to 10–100% higher than the default
value.
54 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-14 Damping Gain
Range: Function:
140 %* [0 - 250 %] The damping gain stabilizes the PM
machine to run smoothly and with
stability. The value of damping gain
controls the dynamic performance
of the PM machine. High damping
gain gives high dynamic
performance and low damping gain
gives low dynamic performance.
The dynamic performance is related
to the machine data and load type.
If the damping gain is too high or
low, the control becomes unstable.
1-15 Low Speed Filter Time Const.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01 - 20 s] This time constant is used below
10% rated speed. Obtain quick
control through a short damping
time constant. However, if this value
is too short, the control becomes
unstable.
1-16 High Speed Filter Time Const.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.01 - 20 s] This time constant is used above
10% rated speed. Obtain quick
control through a short damping
time constant. However, if this value
is too short, the control becomes
unstable.
1-17 Voltage lter time const.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.001 - 2 s] Reduces the inuence of high
frequency ripple and system
resonance in the calculation of
supply voltage. Without this lter,
the ripples in the currents can
distort the calculated voltage and
aect the stability of the system.
1-18 Min. Current at No Load
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 - 50 %] Adjust this parameter to achieve a
smoother motor operation.
1-20 Motor Power [kW]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.09 -
3000.00 kW]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Enter the nominal motor power in
kW according to the motor
nameplate data. The default value
corresponds to the nominal rated
output of the frequency converter.
This parameter is visible in the LCP
if parameter 0-03 Regional Settings is
set to [0] International.
1-21 Motor Power [HP]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.09 -
3000.00 hp]
Enter the nominal motor power in
hp according to the motor
nameplate data. The default value
corresponds to the nominal rated
output of the unit. This parameter
is visible in the LCP if
parameter 0-03 Regional Settings is
[1] US.
1-22 Motor Voltage
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 10 - 1000V]Enter the nominal motor voltage
according to the motor nameplate
data. The default value corresponds
to the nominal rated output of the
unit.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.2.6 1-2* Motor Data
This parameter group contains input data from the
nameplate on the connected motor.
NOTICE
Changing the value of these parameters aects the
setting of other parameters.
NOTICE
The following parameters have no eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is set to [1] PM, nonsalient SPM, [2] PM, salient IPM, [5] Sync. Reluctance:
Parameter 1-20 Motor Power [kW].
•
Parameter 1-21 Motor Power [HP].
•
Parameter 1-22 Motor Voltage.
•
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency.
•
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 55

1-23 Motor Frequency
Range: Function:
50 Hz* [20 - 1000
Hz]
NOTICE
From software version 6.72
onwards, the output frequency
of the frequency converter is
limited to 590 Hz.
Select the motor frequency value
from the motor nameplate data. If a
value other than 50 Hz or 60 Hz is
selected, adapt the loadindependent settings in
parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation
at Zero Speed to
parameter 1-53 Model Shift
Frequency. For 87 Hz operation with
230/400 V motors, set the
nameplate data for 230 V/50 Hz. To
run at 87 Hz, adapt
parameter 4-13 Motor Speed High
Limit [RPM] and
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.
1-24 Motor Current
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.10 -
10000.00 A]
Enter the nominal motor current
value from the motor nameplate
data. The data is used for
calculating torque, motor overload
protection, and so on.
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[10 - 60000
RPM]
Enter the nominal motor speed
value from the motor nameplate
data. The data is used for
1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
Range: Function:
calculating motor compensations.
n
m,n
= ns - n
slip
.
1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.1 -
100000.0 Nm]
Enter the value from the motor
nameplate data. The default value
corresponds to the nominal rated
output. This parameter is available
when parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction is set to [1] PM, nonsalient SPM, that is the parameter is
valid for PM and non-salient SPM
motors only.
1-29 Automatic Motor Adaptation (AMA)
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
The AMA function optimizes
dynamic motor performance by
automatically optimizing the
advanced motor parameters
(parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance
(Rs) to parameter 1-35 Main
Reactance (Xh)) at motor standstill.
Activate the AMA function by
pressing [Hand On] after selecting
Enable Complete AMA or [2] Enable
Reduced AMA. See also the section
Automatic Motor Adaptation in the
design guide. After a normal
sequence, the display reads: Press
[OK] to nish AMA. After pressing
[OK], the frequency converter is
ready for operation.
NOTICE
Ensure that a value is set in
parameter 14-43 Motor Cosphi
before running AMA II.
[0] * O
[1] Enable
Complete
AMA
Performs
•
AMA of the stator
resistance RS,
•
The rotor resistance Rr,
•
The stator leakage
reactance X1,
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
1-23 Motor Frequency
Range: Function:
50* [20 -
56 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
NOTICE
1000
Hz]
The default range for the parameter is only
available for software version 8.23.
From software version 6.72 onwards, the
output frequency of the frequency
converter is limited to 590 Hz.
Select the motor frequency value from the motor
nameplate data. If a value other than 50 Hz or
60 Hz is selected, adapt the load-independent
settings in parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation at
Zero Speed to parameter 1-53 Model Shift Frequency.
For 87 Hz operation with 230/400 V motors, set the
nameplate data for 230 V/50 Hz. To run at 87 Hz,
adapt parameter 4-13 Motor Speed High Limit [RPM]
and parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference.

1-29 Automatic Motor Adaptation (AMA)
Option: Function:
•
The rotor leakage
reactance X2, and
•
The main reactance Xh.
Do not select this option if an LC
lter is used between the frequency
converter and the motor.
FC 301: The complete AMA does
not include Xh measurement for FC
301. Instead, the Xh value is
determined from the motor
database. RS is the best adjustment
method (see parameter group 1-3*
Adv. Motor Data).
For best performance, it is
recommended to obtain the
advanced motor data from the
motor manufacturer to enter into
parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr)
through parameter 1-36 Iron Loss
Resistance (Rfe).
Complete AMA cannot be
performed on permanent magnet
motors.
[2] Enable
Reduced AMA
Performs a reduced AMA of the
stator resistance Rs in the system
only. This option is available for
standard asynchronous motors and
non-salient PM motors.
[3] Enable
Complete
AMA II
Performs AMA of the stator
resistance Rs, the rotor resistance
Rr, the stator leakage reactance X1,
the rotor leakage reactance X21, and
the main reactance Xh.
[4] Enable
Reduced AMA
II
Performs a reduced AMA of the
stator resistance Rs in the system
only. Select this option if an LC
lter is used between the frequency
converter and the motor.
The AMA II is a variant of AMA,
based on the principles of the
torque calibration. It is
recommended for special motors
(for example S3) and high power
motors.
[5] Enable
Rotating AMA
II
Performs rotation with 60% of
nominal speed in Flux Sensorless
with soft PID independent of
selection in parameter 1-01 Motor
Control Principle.
Measures Back EMF on PM motors
and re-measures main reactance
(Xh) on induction motors.
1-29 Automatic Motor Adaptation (AMA)
Option: Function:
Ensure that the motor poles
specied in parameter 1-39 Motor
Poles are correct for accurate back
EMF measurement.
[6] Enable 360°
Turn OL
Sensorless: Performs a 360 degree
test run in sensorless mode to
verify the number of motor poles
specied in parameter 1-39 Motor
Poles.
Closed loop: Performs a 360 degree
test run in sensorless mode to test
the encoder before running in
closed loop. The speed is set in
parameter 3-19 Jog Speed [RPM].
During the test run, the direction of
rotation is veried and the number
of pulses per revolution is veried
to match the conguration in
parameter group 17-** Motor Feedb.
Option or parameter group 5-**
Digital In/Out based on the selected
encoder.
After completing the 360 degree
test run, either of the following
messages are shown:
•
Encoder/Resolver OK
•
Encoder/Resolver Fail
•
Encoder/Resolver Inverted
•
Encoder/Resolver
resolution/poles low
•
Encoder/Resolver
resolution/poles high
The parameter 1-41 Motor Angle
Oset is automatically set when
using PM motor and absolute
encoder or resolver.
[7] Enable Inertia
Run
Use this option to ramp up in the
mode as specied in
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle. Measured inertia is set in
parameter 1-69 System Inertia and
parameter 7-08 Speed PID Feed
Forward Factor is set to 90%.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 57
3 3

130BA065.12
P 1-30
R
Fe
X
h
R'
r
R
s
U
1
I
1
P 1-33
P 1-34
P 1-31P 1-35P 1-36
X'
2δ
X
1δ
1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0140 -
140.0000
Ohm]
Set the line-to-common stator
resistance value. Enter the value
from a motor datasheet or perform
an AMA on a cold motor.
NOTICE
For salient PM motors:
AMA is not available.
If only line-line data is
available, divide the line-line
value by 2 to achieve the lineto-common (star point) value.
Alternatively, measure the
value with an ohmmeter. This
also takes the resistance of the
cable into account. Divide the
measured value by 2 and enter
the result.
NOTICE
The parameter value is
updated after each torque
calibration if option [3] 1st
start with store or option [4]
Every start with store is
selected in
parameter 1-47 Torque
Calibration.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
NOTICE
For the best adaptation of the frequency
•
converter, run AMA on a cold motor.
AMA cannot be performed while the motor is
•
running.
33
AMA cannot run with a sine-wave lter
•
NOTICE
A simple check of the X1 + Xh sum value is to divide the
line-to-line motor voltage by the sqrt(3) and divide this
value by the motor no load current. [VL-L/sqrt(3)]/INL =
X1 + Xh, see Illustration 3.6. These values are important
to magnetize the motor properly. For high-pole motors,
it is highly recommended to perform this check.
connected.
NOTICE
It is important to set motor parameter group 1-2* Motor
Data correctly, since these form part of the AMA
algorithm. Perform an AMA to achieve optimum dynamic
motor performance. It may take up to 10 minutes,
depending on the power rating of the motor.
NOTICE
Avoid generating external torque during AMA.
Illustration 3.6 Motor Equivalent Diagram of an Asynchronous
Motor
NOTICE
If 1 of the settings in parameter group 1-2* Motor Data is
changed, parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs) to
parameter 1-39 Motor Poles, the advanced motor
parameters, return to default setting.
NOTICE
AMA works problem-free on 1 motor size down, typically
works on 2 motor sizes down, rarely works on 3 sizes
down, and never works on 4 sizes down. Keep in mind
that the accuracy of the measured motor data is poorer
when operating on motors smaller than the nominal
frequency converter size.
3.2.7 1-3* Adv. Motor Data
Parameters for advanced motor data. Ensure that the
motor data in parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs) to
parameter 1-39 Motor Poles matches the motor. The default
settings are based on standard motor values. If the motor
parameters are not set correctly, a malfunction of the
frequency converter system may occur. If the motor data is
unknown, running an AMA (automatic motor adaptation) is
recommended. See parameter 1-29 Automatic Motor
Adaptation (AMA).
Parameter groups 1-3* Adv. Motor Data and 1-4* Adv. Motor
Data II cannot be adjusted while the motor is running.
58 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0100 -
100.0000
Ohm]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance
(Rr) has no eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction is set to [1] PM,
non-salient SPM, [5] Sync.
Reluctance.
Set the rotor resistance value Rr to
improve shaft performance using 1
of these methods:
•
Run an AMA on a cold
motor. The frequency
converter measures the
value from the motor. All
compensations are reset
to 100%.
•
Enter the Rr value
manually. Obtain the value
from the motor supplier.
•
Use the Rr default setting.
The frequency converter
establishes the setting
based on the motor
nameplate data.
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0400 -
400.0000
Ohm]
NOTICE
This parameter is only relevant
for asynchronous motors.
Set the stator leakage reactance of
the motor using 1 of these
methods:
•
Run an AMA on a cold
motor. The frequency
converter measures the
value from the motor.
•
Enter the X1 value
manually. Obtain the value
from the motor supplier.
•
Use the X1 default setting.
The frequency converter
establishes the setting
based on the motor
nameplate data.
See Illustration 3.6.
1-33 Stator Leakage Reactance (X1)
Range: Function:
NOTICE
The parameter value is
updated after each torque
calibration if option [3] 1st
start with store or option [4]
Every start with store is
selected in
parameter 1-47 Torque
Calibration.
1-34 Rotor Leakage Reactance (X2)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.0400 -
400.0000
Ohm]
NOTICE
This parameter is only relevant
for asynchronous motors.
Set the rotor leakage reactance of
the motor using 1 of these
methods:
•
Run an AMA on a cold
motor. The frequency
converter measures the
value from the motor.
•
Enter the X2 value
manually. Obtain the value
from the motor supplier.
•
Use the X2 default setting.
The frequency converter
establishes the setting
based on the motor
nameplate data.
See Illustration 3.6.
NOTICE
The parameter value is
updated after each torque
calibration if option [3] 1st
start with store or option [4]
Every start with store is
selected in
parameter 1-47 Torque
Calibration.
1-35 Main Reactance (Xh)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 1.0000 -
10000.0000
Ohm]
Set the main reactance of the
motor using 1 of these methods:
1. Run an AMA on a cold
motor. The frequency
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 59

1-35 Main Reactance (Xh)
Range: Function:
converter measures the
value from the motor.
2. Enter the Xh value
manually. Obtain the value
from the motor supplier.
3. Use the Xh default setting.
The frequency converter
establishes the setting
based on the motor
nameplate data.
1-36 Iron Loss Resistance (Rfe)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 -
10000.000
Ohm]
Enter the equivalent iron loss
resistance (RFe) value to compensate
for iron loss in the motor.
The RFe value cannot be found by
performing an AMA.
The RFe value is especially
important in torque control
applications. If RFe is unknown,
leave parameter 1-36 Iron Loss
Resistance (Rfe) on default setting.
1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld)
Range: Function:
0.0 mH* [0.0 - 1000.0
mH]
Enter line-to-common direct axis
inductance of the PM motor. Obtain
the value from the permanent
magnet motor datasheet.
If only line-line data is available,
divide the line-line value by 2 to
achieve the line-common (star
point) value. Alternatively, measure
the value with an inductance meter.
This also takes the inductance of
the cable into account. Divide the
measured value by 2 and enter the
result.
This parameter is only active when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction is
set to [1] PM, non-salient SPM
(Permanent Magnet Motor) or [5]
Sync. Reluctance.
For a selection with 1 decimal, use
this parameter. For a selection with
3 decimals, use parameter 30-80 d-
axis Inductance (Ld).
FC 302 only.
1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld)
Range: Function:
NOTICE
The parameter value is
updated after each torque
calibration if option [3] 1st
start with store or option [4]
Every start with store is
selected in
parameter 1-47 Torque
Calibration.
1-38 q-axis Inductance (Lq)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.000 - 1000
mH]
Set the value of the q-axis
inductance. See the motor
datasheet.
1-39 Motor Poles
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[2 - 132 ] Enter the number of motor poles.
Make sure not to enter pairs of
motor poles.
1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[1 - 9000 V ]
NOTICE
This parameter is only active
when parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction is set to options
that enable PM (permanent
magnet) motors.
Set the nominal back EMF for the
motor when running at 1000 RPM.
Back EMF is the voltage generated
by a PM motor when no frequency
converter is connected and the
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
60 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Poles ~nn@ 50 Hz ~nn@ 60 Hz
2 2700–2880 3250–3460
4 1350–1450 1625–1730
6 700–960 840–1153
Table 3.6 Pole Number for Normal Speed Ranges
Table 3.6 shows the pole number for normal speed ranges
of various motor types.
Dene motors designed for other
frequencies separately. The motor pole value is always an
even number because it refers to the total pole number,
not pairs of poles. The frequency converter creates the
initial setting of parameter 1-39 Motor Poles based on
parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency and parameter 1-25 Motor
Nominal Speed.

1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM
Range: Function:
shaft is turned externally. Back EMF
is normally specied for nominal
motor speed or for 1000 RPM
measured between 2 lines. If the
value is not available for a motor
speed of 1000 RPM, calculate the
correct value as follows. If back EMF
is for example 320 V at 1800 RPM,
it can be calculated at 1000 RPM:
Example
Back EMF 320 V at 1800 RPM. Back
EMF=(Voltage/
RPM)*1000=(320/1800)*1000=178.
NOTICE
When using PM motors, it is
recommended to use brake
resistors.
1-41 Motor Angle Oset
Range: Function:
0* [-32768 -
32767 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is only active
when parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction is set to [1] PM,
non-salient SPM (Permanent
Magnet Motor).
Enter the correct oset angle
between the PM motor and the
index position (single-turn) of the
attached encoder or resolver. The
value range of 0–32768
corresponds to 0–2 x pi (radians).
To obtain the oset angle value:
After frequency converter start-up,
apply DC hold and enter the value
of parameter 16-20 Motor Angle into
this parameter.
1-44 d-axis Inductance Sat. (LdSat)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 1000
mH]
This parameter corresponds to the
inductance saturation of Ld. Ideally,
this parameter has the same value
as parameter 1-37 d- axis Inductance
(Ld). If the motor supplier provides
an induction curve, enter the
induction value at 200% of the
nominal value.
1-45 q-axis Inductance Sat. (LqSat)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 1000
mH]
This parameter corresponds to the
inductance saturation of Lq. Ideally,
this parameter has the same value
as parameter 1-38 q- axis Inductance
(Lq). If the motor supplier provides
an induction curve, enter the
induction value at 200% of the
nominal value.
1-46 Position Detection Gain
Range: Function:
120 %* [20 - 200 %] Adjusts the amplitude of the test
pulse during position detection at
start. Adjust this parameter to
improve the position measurement.
1-47 Torque Calibration
Option: Function:
Use this parameter to optimize the
torque estimate in the full speed
range. The estimated torque is
based on the shaft power, P
shaft
=
Pm - Rs x I2. Make sure that the R
s
value is correct. The Rs value in this
formula is equal to the power loss
in the motor, the cable, and the
frequency converter. When this
parameter is active, the frequency
converter calculates the Rs value
during power-up, ensuring the
optimal torque estimate and
optimal performance. Use this
feature in cases when it is not
possible to adjust
parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs)
on each frequency converter to
compensate for the cable length,
frequency converter losses, and the
temperature deviation on the
motor.
[0] O
[1] 1st start after
pwr-up
Calibrates at the 1st start-up after
power-up and keeps this value until
reset by a power cycle.
[2] Every start Calibrates at every start-up,
compensating for a possible change
in motor temperature since last
start-up. The value is reset after a
power cycle.
[3] 1st start with
store
The frequency converter calibrates
the torque at the 1st start-up after
power-up. This option is used to
update motor parameters:
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 61

1-47 Torque Calibration
Option: Function:
•
Parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs).
•
Parameter 1-33 Stator
Leakage Reactance (X1).
•
Parameter 1-34 Rotor
Leakage Reactance (X2).
•
Parameter 1-37 d-axis
Inductance (Ld).
[4] Every start
with store
The frequency converter calibrates
the torque at every start-up,
compensating for a possible change
in motor temperature since last
start-up. This option is used to
update motor parameters:
•
Parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs).
•
Parameter 1-33 Stator
Leakage Reactance (X1).
•
Parameter 1-34 Rotor
Leakage Reactance (X2).
•
Parameter 1-37 d-axis
Inductance (Ld).
1-48 d-axis Inductance Sat. Point
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[1 - 500 %]
NOTICE
Run an AMA to set the value
of this parameter. Edit the
value manually only when the
application requires a value
other than determined by
AMA.
Select the d-axis inductance
saturation point. The frequency
converter uses this value to
optimize the performance of SynRM
motors.
Select the value that matches the
point where the inductance equals
the mean value of
parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance
(Ld) and parameter 1-44 d-axis
Inductance Sat. (LdSat), as
percentage of nominal current.
1-49 q-axis Inductance Sat. Point
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 200 %]
NOTICE
Run an AMA to set the value
of this parameter. Edit the
value manually only when the
application requires a value
other than determined by
AMA.
Enter the q-axis inductance
saturation point. The frequency
converter uses this value to
optimize the performance of IPM
motors.
Select the value that matches the
point where the inductance equals
the average value of
parameter 1-38 q-axis Inductance
(Lq) and parameter 1-45 q-axis
Inductance Sat. (LqSat), as
percentage of nominal current.
1-50 Motor Magnetisation at Zero Speed
This parameter is not visible on the LCP.
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 300 %]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation at Zero Speed has no
eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction = [1] PM, nonsalient SPM.
Use this parameter along with
parameter 1-51 Min Speed Normal
Magnetising [RPM] to obtain a
dierent thermal load on the motor
when running at low speed.
Enter a value which is a percentage
of the rated magnetizing current. If
the setting is too low, the torque
on the motor shaft may be
reduced.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
62 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
3.2.8 1-5* Load Indep. Setting

1-50 Motor Magnetisation at Zero Speed
This parameter is not visible on the LCP.
Range: Function:
Magn. current
130BA045.11
Hz
Par.1-50
Par.1-51
100%
Par.1-52 RPM
Illustration 3.7 Motor Magneti-
zation
1-51 Min Speed Normal Magnetising [RPM]
This parameter is not visible on the LCP.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[10 - 600
RPM]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-51 Min Speed
Normal Magnetising [RPM] has
no eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction= [1] PM, nonsalient SPM.
Set the required speed for normal
magnetizing current. If the speed is
set lower than the motor slip
speed, parameter 1-50 Motor
Magnetisation at Zero Speed and
parameter 1-51 Min Speed Normal
Magnetising [RPM] are of no signif-
icance.
Use this parameter along with
parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation
at Zero Speed. See Table 3.6.
1-52 Min Speed Normal Magnetising [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 250.0
Hz]
Set the required frequency for
normal magnetizing current. If the
frequency is set lower than the
motor slip frequency,
parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation
at Zero Speed is inactive.
Use this parameter along with
parameter 1-50 Motor Magnetisation
at Zero Speed. See Illustration 3.7.
1-53 Model Shift Frequency
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 4 - 18.0 Hz]
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Flux model shift
Enter the frequency value for shift
between 2 models for determining
motor speed. Select the value
based on settings in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
and parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle.
There are the following options:
•
Shift between ux model
1 and ux model 2.
•
Shift between variable
current mode and ux
model 2.
•
No shift between models
at low speed if
parameter 40-50 Flux
Sensorless Model Shift is
set to option [0] O.
NOTICE
This is valid for FC 302 only.
Flux model 1 – ux model 2
This model is used when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [1] Speed closed loop or [2]
Torque, and parameter 1-01 Motor
Control Principle is set to [3] Flux w/
motor feedback. With this
parameter, it is possible to make an
adjustment of the shifting point
where the frequency converter
changes between ux model 1 and
ux model 2, which is useful in
some sensitive speed and torque
control applications.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 63

1-53 Model Shift Frequency
Range: Function:
P 1-53
130BA146.11
f
out
f
N,M
x 0.125 f
N,M
x 0.1
Flux model 2Flux model 1
Illustration 3.8 Parameter 1-00 Co
nguration Mode = [1] Speed
closed loop or [2] Torque and
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle = [3] Flux w/motor
feedback
Variable current - ux model -
sensorless
This model is used when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [0] Speed open loop and
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [2] Flux sensorless.
In speed open loop in ux mode,
the speed is determined from the
current measurement.
Below f
norm
x 0.1, the frequency
converter runs on a variable current
model. Above f
norm
x 0.125 the
frequency converter runs on a ux
model.
P 1-53
130BA147.10
x 0.1
Variable
current
model
Flux model 2
f
out
f
N,M
f
N,M
x 0.125
Illustration 3.9
Parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode = [0] Speed open loop,
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle = [2] Flux sensorless
1-54 Voltage reduction in eldweakening
Range: Function:
0 V* [-50 - 100 V] The value of this parameter reduces
the maximum voltage available for
the ux of the motor in eld
weakening, providing more voltage
for torque. Increasing the value
increases the risk of stalling at high
speed.
1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
Array [6]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 1000 V ] Enter the voltage at each frequency
point to manually form a U/f
characteristic matching the motor.
The frequency points are dened in
parameter 1-56 U/f Characteristic - F.
This parameter is an array
parameter [0-5] and is only
accessible when
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [0] U/f.
1-56 U/f Characteristic - F
Array [6]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 1000.0
Hz]
Enter the frequency points to form
a U/f characteristic manually
matching the motor.
The voltage at each point is dened
in parameter 1-55 U/f Characteristic -
U.
This parameter is an array
parameter [0–5] and is only
accessible when
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [0] U/f.
Motor Voltage
Par 1-55 [x]
Output Frequency
Par 1-56 [x]
1-55[5]
1-55[4]
1-55[3]
1-55[2]
1-55[1]
1-55[0]
1-56
[0]
1-56
[1]
1-56
[2]
1-56
[3]
1-56
[4]
1-56
[5]
130BA166.10
1-57 Torque Estimation Time Constant
Range: Function:
150 ms* [50 - 1000
ms]
NOTICE
This parameter is only valid
with software version 48.XX.
Enter the time constant for the
torque estimation below model
Parameter Descriptions
33
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
64 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Illustration 3.10 U/f Characteristic

1-57 Torque Estimation Time Constant
Range: Function:
change point in ux sensorless
control principle.
1-58 Flying Start Test Pulses Current
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 200 %]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available in VVC+.
NOTICE
This parameter has eect on
PM motors only.
Sets the current level for the ying
start test pulses that are used to
detect the motor direction. 100%
means I
m,n
. Adjust the value to be
high enough to avoid noise
inuence, but low enough to avoid
aecting the accuracy (current must
be able to drop to 0 before the
next pulse). Reduce the value to
reduce the generated torque.
Default is 30% for asynchronous
motors, but may vary for PM
motors. For adjusting PM motors,
the value tunes for back EMF and
d-axis inductance of the motor.
1-59 Flying Start Test Pulses Frequency
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 500 %] Asynchronous motor: Set the
frequency of the ying start test
pulses that are used to detect the
motor direction. For asynchronous
motors, the value 100% means that
the slip is doubled. Increase this
value to reduce the generated
torque.
For synchronous motors, this value
is the percentage n
m,n
of the freerunning motor. Above this value,
ying start is always performed.
Below this value, the start mode is
selected in parameter 1-70 Start
Mode
1-60 Low Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 300 %] Enter the % value to compensate
voltage in relation to load when the
motor is running at low speed and
obtain the optimum U/f characteristic. The motor size determines
the frequency range within which
this parameter is active.
130BA046.11
60%
0%
100%
U
m
Changeover
f
out
Par.1-60 Par.1-61
1-61 High Speed Load Compensation
Range: Function:
100 %* [0 - 300 %] Enter the % value to compensate
voltage in relation to load when the
motor is running at high speed and
obtain the optimum U/f characteristic. The motor size determines
the frequency range within which
this parameter is active.
1-62 Slip Compensation
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[-500 500 %]
Enter the % value for slip compensation to compensate for tolerances
in the value of n
M,N
. Slip compensation is calculated automatically,
that is on the basis of the nominal
motor speed n
M,N
.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.2.9 1-6* Load Depend. Setting
3 3
Motor size Changeover
0.25–7.5 kW <10 Hz
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 65
Illustration 3.11 Changeover
Motor size Changeover
0.25–7.5 kW >10 Hz
Table 3.7 Changeover Frequency

1-62 Slip Compensation
Range: Function:
This function is not active when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [1] Speed closed loop or [2]
Torque torque control with speed
feedback or when
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [0] U/f special
motor mode.
1-63 Slip Compensation Time Constant
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0.05 - 5 s]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-63 Slip Compensation Time Constant has no
eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction = [1] PM, nonsalient SPM.
Enter the slip compensation
reaction speed. A high value results
in slow reaction, and a low value
results in quick reaction. If lowfrequency resonance problems
arise, use a longer time setting.
1-64 Resonance Damping
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 1000 %]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-64 Resonance
Damping has no eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction= [1] PM, non-
salient SPM.
Enter the resonance damping value.
Set parameter 1-64 Resonance
Damping and
parameter 1-65 Resonance Damping
Time Constant to help eliminate
high frequency resonance
problems. To reduce resonance
oscillation, increase the value of
parameter 1-64 Resonance Damping.
1-65 Resonance Damping Time Constant
Range: Function:
5 ms* [1 - 50 ms]
NOTICE
Parameter 1-65 Resonance
Damping Time Constant has no
eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction = [1] PM, nonsalient SPM.
Set parameter 1-64 Resonance
Damping and
parameter 1-65 Resonance Damping
Time Constant to help eliminate
high-frequency resonance problems.
Enter the time constant that
provides the best dampening.
1-66 Min. Current at Low Speed
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 1 - 200 %]
NOTICE
If parameter 40-50 Flux
Sensorless Model Shift is set to
[0] O, this parameter is
ignored.
Enter the minimum motor current
at low speed, see
parameter 1-53 Model Shift
Frequency. Increasing this current
improves motor torque at low
speed.
Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed is enabled when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [0] Speed open loop only.
The frequency converter runs with
constant current through motor for
speeds below 10 Hz.
For speeds above 10 Hz, the motor
ux model in the frequency
converter controls the motor.
Parameter 4-16 Torque Limit Motor
Mode and/or parameter 4-17 Torque
Limit Generator Mode automatically
adjust parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed. The parameter with
the highest value adjusts
parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed. The current setting in
parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed is composed of the torque
generating current and the
magnetizing current.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
66 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-66 Min. Current at Low Speed
Range: Function:
Example: Set parameter 4-16 Torque
Limit Motor Mode to 100% and set
parameter 4-17 Torque Limit
Generator Mode to 60%.
Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed automatically adjusts to
about 127%, depending on the
motor size.
1-67 Load Type
This parameter is valid for FC 302 only.
Option: Function:
[0] * Passive load For conveyors, fan, and pump
applications.
[1] Active load For hoisting applications. This
option allows the frequency
converter to ramp up at 0 RPM.
When [1] Active Load is selected, set
parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed to a level which corresponds
to maximum torque.
1-68 Motor Inertia
Range: Function:
0 kgm²* [0.0000 -
10000.0000
kgm²]
Enter the motor inertia to obtain an
improved torque readout and
therefore a better estimate of the
mechanical torque on the shaft.
Available in ux control principle
only.
1-69 System Inertia
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0000 -
10000.0000
kgm²]
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while motor is
running.
The system inertia and
parameter 7-08 Speed PID Feed
Forward Factor is used to calculate
acceleration feed forward for the
speed PID controller.
NOTICE
Valid for software version
48.3X only.
Automatic measurement of system
inertia and setting of this parameter
is activated by setting the
parameter to 0. System inertia is
1-69 System Inertia
Range: Function:
calculated after 1st running cycle
with sucient data and the
parameter is automatically set after
stop.
The function is only active when
parameter 1-01 Motor Control
Principle is set to [2] Flux Sensorless
or [3] Flux w/motor feedb.
Acceleration to at least model shift
frequency (parameter 1-53 Model
Shift Frequency) + 10 Hz and
decelerate to produce a result.
Measurement is possible in both
speed, position, or synchronization
mode.
1-70 Start Mode
Select the start-up mode. This is done to initialize the VVC
+
control core for previously free-running motor. Both selections
estimate the speed and angle. Active for PM and SynRM motors
in VVC+ only.
Option: Function:
[0] * Rotor
Detection
Estimates the electrical angle of the
rotor and uses this as a starting
point. Standard selection for VLT
®
AutomationDrive applications.
[1] Parking The parking function applies DC
current across the stator winding
and rotates the rotor to electrical 0
position (typically selected for HVAC
applications). Parking current and
time are congured in
parameter 2-06 Parking Current and
parameter 2-07 Parking Time.
[2] Rotor Det. w/
Parking
1-71 Start Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 25.5 s] This parameter refers to the start
function selected in
parameter 1-72 Start Function.
Enter the time delay required
before commencing acceleration.
1-72 Start Function
Option: Function:
Select the start function during
start delay. This parameter is linked
to parameter 1-71 Star t Delay.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
3.2.10 1-7* Start Adjustments
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 67

1-72 Start Function
Option: Function:
[0] DC Hold/delay
time
Energize the motor with a DC hold
current (parameter 2-00 DC Hold
Current) during the start delay time.
[1] DC Brake/
delay time
Energize the motor with a DC brake
current (parameter 2-01 DC Brake
Current) during the start delay time.
[2] * Coast/delay
time
Motor coasted during the start
delay time (inverter o).
[3] Start speed
cw
Only possible with VVC+.
Connect the function described in
parameter 1-74 Start Speed [RPM]
and parameter 1-76 Star t Current in
the start delay time.
Regardless of the value applied by
the reference signal, the output
speed applies the setting of the
start speed in parameter 1-74 Start
Speed [RPM] or parameter 1-75 Start
Speed [Hz], and the output current
corresponds to the setting of the
start current in parameter 1-76 Start
Current. This function is typically
used in hoisting applications
without counterweight and
especially in applications with a
cone-motor where the start is
clockwise, followed by rotation in
the reference direction.
[4] Horizontal
operation
Only possible with VVC+.
For obtaining the function
described in parameter 1-74 Start
Speed [RPM] and
parameter 1-76 Start Current during
the start delay time. The motor
rotates in the reference direction. If
the reference signal equals 0,
parameter 1-74 Start Speed [RPM] is
ignored and the output speed
equals 0. The output current
corresponds to the setting of the
start current in parameter 1-76 Start
Current.
[5] VVC+/Flux
clockwise
For the function described in
parameter 1-74 Start Speed [RPM]
only. The start current is calculated
automatically. This function uses
the start speed in the start delay
time only. Regardless of the value
set by the reference signal, the
output speed equals the setting of
the start speed in
parameter 1-74 Start Speed [RPM]. [3]
Start speed/current clockwise and [5]
1-72 Start Function
Option: Function:
VVC+/Flux clockwise are typically
used in hoisting applications. [4]
Start speed/current in reference
direction is particularly used in
applications with counterweight
and horizontal movement.
[6] Hoist Mech.
Brake Rel
For utilizing mechanical brake
control functions
(parameter 2-24 Stop Delay to
parameter 2-28 Gain Boost Factor).
This parameter is only active in ux
control principle, in a mode with
motor feedback or sensorless mode.
[7] VVC+/Flux
counter-cw
1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running. This block is available
only with software version
48.XX
This function makes it possible to
catch a freely spinning motor, for
example coasted because of mains
dropout.
When ying start is enabled,
parameter 1-71 Start Delay and
parameter 1-72 Start Function have
no function.
When options [1] and [2] are
enabled, parameter 1-58 Flying Start
Test Pulses Current and
parameter 1-59 Flying Start Test
Pulses Frequency are used to specify
conditions for ying start.
Options [3] and [4] are set to search
for the motor in the reference
direction only, which allows a faster
execution of the motor catch.
[0] Disabled No function.
[1] Enabled Enable after coast.
[2] Enabled
Always
Enable at every start.
[3] Enabled Ref.
Dir.
Enable after coast, search in
reference direction only.
[4] Enab. Always
Ref. Dir.
Enable at every start, search in
reference direction only.
Parameter Descriptions
33
68 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This block is available only
with software version 8.XX.
This function makes it possible to
catch a freely spinning motor, for
example coasted because of mains
dropout.
When
ying start is enabled,
parameter 1-71 Start Delay and
parameter 1-72 Start Function have
no function.
When options [1] and [2] are
enabled, parameter 1-58 Flying Start
Test Pulses Current and
parameter 1-59 Flying Start Test
Pulses Frequency are used to specify
conditions for ying start.
For ying start version 1, options [3]
and [4] are set to search for the
motor in the reference direction
only, which allows a faster
execution of the motor catch.
For ying start version 2, Options
[11] to [14] is specic to
asynchronous motor (induction
motor) in VVC+ upto 132 Hz output
frequency. These options provides a
more fast, reliable, and robust ying
start, especially for high power
motors (>250 kW).
[0] Disabled No function
[1] Enabled Enables frequency converter to
catch and control a spinning motor.
[2] Enabled
Always
[3] Enabled Ref.
Dir.
1-73 Flying Start
Option: Function:
[4] Enab. Always
Ref. Dir.
[11] v2 Enabled Enable ying start version 2, after
coast.
[12] v2 Enabled
Always
Enable ying start version 2, at
every start.
[13] v2 Enabled
Ref. Dir.
Enable ying start version 2, after
coast, search in reference direction
only.
[14] v2 Enab. Alw.
Ref. Dir.
Enable ying start version 2, ok at
every start, search in reference
direction only.
1-74 Start Speed [RPM]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 600
RPM]
Set a motor start speed. After the
start signal, the output speed leaps
to set value. Set the start function
in parameter 1-72 Star t Function to
[3] Start speed cw, [4] Horizontal
operation, or [5] VVC+ /Flux
clockwise, and set a start delay time
in parameter 1-71 Star t Delay.
1-75 Start Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 500.0
Hz]
This parameter can be used for
hoist applications (cone rotor). Set a
motor start speed. After the start
signal, the output speed leaps to
the set value. Set the start function
in parameter 1-72 Star t Function to
[3] Start speed cw, [4] Horizontal
operation, or [5] VVC+/Flux clockwise,
and set a start delay time in
parameter 1-71 Start Delay.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
NOTICE
This function is not recommended for hoisting
applications.
For power levels above 55 kW, ux mode must be used
to achieve the best performance.
NOTICE
To obtain the best ying start performance, the
advanced motor data, parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance
(Rs) to parameter 1-35 Main Reactance (Xh), must be
correct.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 69
When parameter 1-73 Flying Start is enabled,
parameter 1-71 Start Delay has no function.
Search direction for ying start is linked to the setting in
parameter 4-10 Motor Speed Direction.
[0] Clockwise: Flying start search in clockwise direction. If
not successful, a DC brake is carried out.
[2] Both Directions: The
ying start rst searches in the
direction determined by the last reference (direction). If
not nding the spee, it searches in the other direction. If
not successful, a DC brake activates in the time set in
parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time. Start then takes place
from 0 Hz.
3 3

1-76 Start Current
Range: Function:
0 A* [ 0 - par. 1-24A]Some motors, for example cone
rotor motors, need extra current/
starting speed to disengage the
rotor. To obtain this boost, set the
required current in
parameter 1-76 Start Current. Set
parameter 1-74 Start Speed [RPM].
Set parameter 1-72 Start Function to
[3] Start speed cw or [4] Horizontal
operation, and set a start delay time
in parameter 1-71 Star t Delay.
This parameter can be used for
hoist applications (cone rotor).
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
Select the frequency converter
function after a stop command or
after the speed is ramped down to
the settings in parameter 1-81 Min
Speed for Function at Stop [RPM].
[0] * Coast Leaves motor in free mode. The
motor is disconnected from the
frequency converter.
[1] DC hold Energizes the motor with a DC hold
current (see parameter 2-00 DC Hold
Current).
[2] Motor check Checks if a motor has been
connected. The interval for
checking the motor can be dened
in parameter 4-49 Motor Check Time
Interval.
[3] Pre-
magnetizing
Builds up a magnetic eld while the
motor is stopped. This allows the
motor to produce torque quickly at
subsequent start commands
(asynchronous motors only). This
premagnetizing function does not
help the very 1st start command.
Two dierent solutions are available
to premagnetize the machine for
the 1st start command:
•
Start the frequency
converter with a 0 RPM
reference and wait 2-4
rotor time constants
1-80 Function at Stop
Option: Function:
before increasing the
speed reference.
•
Use the start delay with
DC hold:
Set parameter 1-71 Start Delay to
the required premagnetizing time
(2–4 rotor time constants. See the
time constants description further
in this section.
Set parameter 1-72 Start Function to
either [0] DC hold or [1] DC Brake
Set the DC hold or DC brake
current magnitude
(parameter 2-00 DC Hold Current or
parameter 2-01 DC Brake Current) to
be equal to I_pre-mag = Unom/
(1.73 x Xh)
Sample rotor time constants =
(Xh+X2)/(6.3*Freq_nom*Rr)
1 kW = 0.2 s
10 kW = 0.5 s
100 kW = 1.7 s
1000 kW = 2.5 s
[4] DC Voltage U0 When the motor is stopped, the
parameter 1-55 U/f Characteristic - U
[0] denes the voltage at 0 Hz.
[5] Coast at low
reference
When the reference is below
parameter 1-81 Min Speed for
Function at Stop [RPM], the motor is
disconnected from the frequency
converter.
[6] Motor check,
alarm
[8] Torque ramp
to zero
1-81 Min Speed for Function at Stop [RPM]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 600
RPM]
Set the speed at which to activate
parameter 1-80 Function at Stop.
1-82 Min Speed for Function at Stop [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 500.0
Hz]
Set the output frequency at which
to activate parameter 1-80 Function
at Stop.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
3.2.11 1-8* Stop Adjustments
70 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

1-83 Precise Stop Function
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
Valid for FC 302 only.
[0] * Precise ramp
stop
Only optimal when the operational
speed, for example the operational
speed of a conveyor belt, is
constant. This is an open-loop
control. Achieves high repetitive
precision at the stop point.
[1] Cnt stop with
reset
Counts the number of pulses,
typically from an encoder, and
generates a stop signal after a preprogrammed number of pulses,
dened in parameter 1-84 Precise
Stop Counter Value, has been
received at terminal 29 or terminal
33.
This is direct feedback with oneway closed-loop control.
The counter function is activated
(starts timing) at the edge of the
start signal (when it changes from
stop to start). After each precise
stop, the number of pulses counted
during ramp-down to 0 RPM are
reset.
[2] Cnt stop w/o
reset
Same as [2] Cnt stop with reset but
the number of pulses counted
during ramp-down to 0 RPM are
deducted from the counter value
entered in parameter 1-84 Precise
Stop Counter Value.
This reset function can be used to
compensate for the extra distance
done during ramping down and to
reduce the impacts of gradual wear
of mechanical parts.
[3] Speed comp
stop
Stops at precisely the same point,
regardless of the present speed.
The stop signal is delayed internally
when the present speed is lower
than the maximum speed (set in
parameter 4-19 Max Output
Frequency).
The delay is calculated on the basis
of the reference speed of the
frequency converter and not on the
basis of the actual speed. Make
sure that the frequency converter
1-83 Precise Stop Function
Option: Function:
has ramped up before activating
the speed–compensated stop.
[4] Com cnt stop
w/rst
Same as Speed comp stop but after
each precise stop, the number of
pulses counted during ramp-down
to 0 RPM are reset.
[5] Comp cnt stop
w/o r
Same as Speed comp stop but the
number of pulses counted during
ramp-down to 0 RPM is deducted
from the counter value entered in
parameter 1-84 Precise Stop Counter
Value.
This reset function can be used to
compensate for the extra distance
done during ramping down and to
reduce the impacts of gradual wear
of mechanical parts.
1-84 Precise Stop Counter Value
Range: Function:
100000* [0 -
999999999 ]
Enter the counter value to be used
in the integrated precise stop
function, parameter 1-83 Precise Stop
Function.
The maximum permissible
frequency at terminal 29 or 33 is
110 kHz.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 71
The precise stop functions are advantageous in
applications where high precision is required.
If using a standard stop command, the accuracy is
determined by the internal task time. That is not the case
when using the precise stop function. It eliminates the task
time dependence and increases the accuracy substantially.
The frequency converter tolerance is normally given by its
task time. However, by using its special precise stop
function, the tolerance is independent of the task time
because the stop signal immediately interrupts the
execution of the frequency converter program. The precise
stop function gives a highly reproducible delay from the
stop signal is given until the ramping down starts. Run a
test to nd this delay as it is a sum of sensor, PLC,
frequency converter, and mechanical parts.
To ensure optimum accuracy, there should be at least 10
cycles during ramping down, see:
Parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time.
•
Parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time.
•
Parameter 3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time.
•
Parameter 3-72 Ramp 4 Ramp Down Time.
•
The precise stop function is set up here and enabled from
DI at terminal 29 or terminal 33.
3 3

1-84 Precise Stop Counter Value
Range: Function:
NOTICE
Not used for selections [0]
Precise ramp stop and [3] Speed
comp stop in
parameter 1-83 Precise Stop
Function.
1-85 Precise Stop Speed Compensation Delay
Range: Function:
10 ms* [0 - 100 ms] Enter the delay time for sensors,
PLCs, and so on for use in
parameter 1-83 Precise Stop Function.
In speed–compensated stop mode,
the delay time at dierent
frequencies has a major inuence
on the stop function.
NOTICE
Not used for selections [0]
Precise ramp stop, [1] Cnt stop
with reset, and [2] Cnt stop w/o
reset in parameter 1-83 Precise
Stop Function.
1-89 Stop Func Torque Ramp Time
Range: Function:
0.01 s* [0.01 -
3600.00 s]
Congure the time in seconds
during which the torque is ramped
to 0, after the motor speed is
ramped down to the minimum
speed as specied in
parameter 1-81 Min Speed for
Function at Stop [RPM].
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
Motor thermal protection can be
implemented using a range of
techniques:
•
Via a PTC sensor in the
motor windings connected
to 1 of the analog or
digital inputs
(parameter 1-93 Thermistor
Resource). See
1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
chapter 3.2.13 PTC
Thermistor Connection.
•
Via a KTY sensor in the
motor winding connected
to an analog input
(parameter 1-96 Thermistor
Sensor Resource). See
chapter 3.2.14 KTY Sensor
Connection.
•
Via calculation (ETR =
Electronic Thermal Relay)
of the thermal load, based
on the actual load and
time. The calculated
thermal load is compared
with the rated motor
current I
M,N
and the rated
motor frequency f
M,N
. See
chapter 3.2.15 ETR and
chapter 3.2.16 ATEX ETR.
•
Via a mechanical thermal
switch (Klixon type). See
chapter 3.2.17 Klixon.
For the North American market: The
ETR functions provide class 20
motor overload protection in
accordance with NEC.
[0] No protection Continuously overloaded motor
when no warning or trip of the
frequency converter is required.
[1] Thermistor
warning
Activates a warning when the
connected thermistor or KTY sensor
in the motor reacts in the event of
motor overtemperature.
[2] Thermistor trip Stops (trips) the frequency
converter when connected
thermistor or KTY sensor in the
motor reacts in the event of motor
overtemperature.
The thermistor cutout value must
be more than 3 kΩ.
Integrate a thermistor (PTC sensor)
in the motor for winding
protection.
[3] ETR warning 1 Calculates the load when set-up 1
is active and activates a warning on
the display when the motor is
overloaded. Program a warning
signal via 1 of the digital outputs.
[4] ETR trip 1 Calculates the load when set-up 1
is active and stops (trips) the
Parameter Descriptions
33
3.2.12 1-9* Motor Temperature
72 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

1-90 Motor Thermal Protection
Option: Function:
frequency converter when the
motor is overloaded. Program a
warning signal via 1 of the digital
outputs. The signal appears in the
event of a warning and if the
frequency converter trips (thermal
warning).
[5] ETR warning 2
[6] ETR trip 2
[7] ETR warning 3
[8] ETR trip 3
[9] ETR warning 4
[10] ETR trip 4
[20] ATEX ETR Activates the thermal monitoring
function for Ex-e motors for ATEX.
Enables parameter 1-94 ATEX ETR
cur.lim. speed reduction,
parameter 1-98 ATEX ETR interpol.
points freq., and
parameter 1-99 ATEX ETR interpol
points current.
[21] Advanced ETR
1330
550
250
-20 °C
175HA183.11
4000
3000
R
(Ω)
nominal
nominal -5 °C nominal +5 °C
[°C]
PTC / Thermistor
R
OFF
ON
<800 Ω
+10V
130BA152.10
>2.7 kΩ
12 13 18 37322719 29 33 20
5550
39 42 53 54
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.2.13 PTC Thermistor Connection
3 3
NOTICE
If [20] ATEX ETR is selected, follow the instructions in the
dedicated chapter of the design guide and the
instructions provided by the motor manufacturer.
NOTICE
If [20] ATEX ETR is selected, set parameter 4-18 Current
Limit to 150%.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 73
Illustration 3.12 PTC Prole
Using a digital input and 10 V as supply:
Example: The frequency converter trips when the motor
temperature is too high.
Parameter set-up:
Set parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection to [2]
•
Thermistor Trip.
Set parameter 1-93 Thermistor Source to [6] Digital
•
Input.
Illustration 3.13 PTC Thermistor Connection - Digital Input
Using an analog input and 10 V as supply:
Example: The frequency converter trips when the motor
temperature is too high.
Parameter set-up:
Set parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection to [2]
•
Thermistor Trip.
Set parameter 1-93 Thermistor Source to [2] Analog
•
Input 54.

555039 42 53 54
R
<3.0 k Ω
>3.0 k Ω
+10V
130BA153.11
PTC / Thermistor
OFF
ON
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
-25 0 25 50 75 100 125 150
Temperature [°C]
Resistance [Ohm]
KTY type 1 KTY type 2 KTY type 3
130BB917.10
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
Illustration 3.14 PTC Thermistor Connection - Analog Input
Input
digital/analog
Digital 10 V
Analog 10 V
Table 3.8 Threshold Cutout Values
Supply voltage Threshold
cutout values
<800 Ω⇒2.7 kΩ
<3.0 kΩ⇒3.0 kΩ
NOTICE
Check that the selected supply voltage follows the
specication of the used thermistor element.
3.2.14 KTY Sensor Connection
NOTICE
This is valid for FC 302 only.
KTY sensors are used especially in permanent magnet
servo motors (PM motors) for dynamic adjusting of motor
parameters as stator resistance (parameter 1-30 Stator
Resistance (Rs)) for PM motors and also rotor resistance
(parameter 1-31 Rotor Resistance (Rr)) for asynchronous
motors, depending on winding temperature. The
calculation is:
Illustration 3.15 KTY Type Selection
KTY Sensor 1: 1 kΩ at 100 °C (212 °F) (for example Philips
KTY 84-1).
KTY Sensor 2: 1 kΩ at 25 °C (77 °F) (for example Philips
KTY 83-1).
KTY Sensor 3: 2 kΩ at 25 °C (77 °F) (for example
Inneon
KTY-10).
NOTICE
If the temperature of the motor is utilized through a
thermistor or KTY sensor, the PELV is not complied with
if there are short circuits between motor windings and
the sensor. Put extra isolation on the sensor to comply
with PELV.
Rs
= Rs
x(1 + αcuxΔT)
20°C
KTY sensors can be used for motor protecting
(parameter 1-97 Thermistor Threshold level).
FC 302 can handle 3 types of KTY sensors, dened in
parameter 1-95 Thermistor Sensor Type. The actual sensor
temperature can be read out from
parameter 16-19 Thermistor Sensor Temperature.
74 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Ω where
α
= 0 . 00393
cu

1.21.0 1.4
30
10
20
100
60
40
50
1.81.6 2.0
2000
500
200
400
300
1000
600
t [s]
175ZA052.12
f
OUT
= 2 x f
M,N
f
OUT
= 0.2 x f
M,N
f
OUT
= 1 x f
M,N
(par. 1-23)
IMN(par. 1-24)
I
M
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.2.15 ETR
The calculations estimate the need for a lower load at
lower speed due to less cooling from the fan incorporated
in the motor.
Illustration 3.16 ETR Prole
3.2.16 ATEX ETR
The VLT® PTC Thermistor Card MCB 112 oers ATEXapproved monitoring of motor temperature. Alternatively,
an external ATEX-approved PTC protection device can be
used.
Function Setting
Parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal
Protection
Parameter 1-94 ATEX ETR cur.lim.
speed reduction
Parameter 1-98 ATEX ETR
interpol. points freq.
Parameter 1-99 ATEX ETR interpol
points current
Parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency Enter the same value as for
Parameter 4-19 Max Output
Frequency
Parameter 4-18 Current Limit Forced to 150% by 1-90 Motor
Parameter 5-15 Terminal 33
Digital Input
Parameter 5-19 Terminal 37 Safe
Stop
Parameter 14-01 Switching
Frequency
Parameter 14-26 Trip Delay at
Inverter Fault
Table 3.9 Parameters
[20] ATEX ETR
20%
Motor nameplate.
parameter 4-19 Max Output
Frequency.
Motor nameplate, possibly
reduced for long motor cables,
sine-wave lter, or reduced
supply voltage.
Thermal Protection option [20]
[80] PTC Card 1
[4] PTC 1 Alarm
Check that the default value
fullls the requirement from
the motor nameplate. If not,
use a sine-wave lter.
0
3 3
NOTICE
Only use ATEX Ex-e-approved motors for this function.
See the motor nameplate, approval certicate, datasheet,
or contact motor supplier.
When controlling an Ex-e motor with increased safety, it is
important to ensure certain limitations. The parameters
that must be programmed are presented in Table 3.9.
NOTICE
Compare the minimum switching frequency requirement
stated by the motor manufacturer to the minimum
switching frequency of the frequency converter, the
default value in parameter 14-01 Switching Frequency. If
the frequency converter does not meet this requirement,
use a sine-wave lter.
More information about ATEX ETR thermal monitoring can
be found in Application Note for FC 300 ATEX ETR Thermal
Monitoring Function.
3.2.17 Klixon
The Klixon type thermal circuit breaker uses a KLIXON
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 75
metal dish. At a predetermined overload, the heat caused
by the current through the disc causes a trip.
Using a digital input and 24 V as supply:
Example: The frequency converter trips when the motor
temperature is too high.
Parameter set-up:
®

PTC / Thermistor
OFF
ON
+24V
12 13 18 3732
A
2719 29 33B20
GND
R<6.6 k Ω >10.8 k Ω
130BA151.11
1-91 Motor External Fan
Option: Function:
[0] No No external fan is required, that is
the motor is derated at low speed.
[1] Yes Applies an external motor fan
(external ventilation), so no
derating of the motor is required at
low speed. The upper curve in
Illustration 3.16 (f
out
= 1 x f
M,N
) is
followed if the motor current is
lower than nominal motor current
(see parameter 1-24 Motor Current).
If the motor current exceeds
nominal current, the operation time
still decreases as if no fan was
installed.
1-93 Thermistor Resource
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
NOTICE
Set digital input to [0] PNP Active at 24 V in
parameter 5-00 Digital I/O
Mode.
Select the input to which the
thermistor (PTC sensor) should be
connected. An analog input option
[1] Analog Input 53 or [2] Analog
Input 54 cannot be selected if the
analog input is already in use as a
reference source (selected in
parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1,
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2,
1-93 Thermistor Resource
Option: Function:
or parameter 3-17 Reference Resource
3).
When using VLT® PTC Thermistor
Card MCB 112, always select [0]
None.
[0] * None
[1] Analog Input
53
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] Digital input
18
[4] Digital input
19
[5] Digital input
32
[6] Digital input
33
1-94 ATEX ETR cur.lim. speed reduction
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 - 100 %]
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Only visible if parameter 1-90 Motor
Thermal Protection is set to [20]
ATEX ETR.
1-95 Thermistor Sensor Type
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Select the used type of thermistor
sensor.
[0] * KTY Sensor 1
1 kΩ at 100 °C (212 °F).
[1] KTY Sensor 2
1 kΩ at 25 °C (77 °F).
[2] KTY Sensor 3
2 kΩ at 25 °C (77 °F).
[3] Pt1000
Parameter Descriptions
Set parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection to [2]
•
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
Thermistor Trip.
Set parameter 1-93 Thermistor Source to [6] Digital
•
Input.
33
Illustration 3.17 Thermistor Connection
76 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
Congure the reaction for operating in Ex-e current limit.
0%: The frequency converter does not change anything
besides issuing warning 163, ATEX ETR cur.lim.warning.
>0%: The frequency converter issues warning 163, ATEX ETR
cur.lim.warning and reduces motor speed following ramp 2
(parameter group 3-5* Ramp 2).
Example:
Actual reference = 50 RPM
Parameter 1-94 ATEX ETR cur.lim. speed reduction = 20%
Resulting reference = 40 RPM

1-95 Thermistor Sensor Type
Option: Function:
[4] Ni1000 (6178
ppm/K)
[5] Ni1000-LG
(TC5)
Examples:
•
Siemens LG-Ni1000
•
Tasseron RTD Ni1000-TC5
1000 Ohm
1-96 Thermistor Sensor Resource
Option: Function:
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Selecting analog input terminal 54
to be used as thermistor sensor
input. Terminal 54 cannot be
selected as thermistor source if
otherwise used as reference (see
parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1
to parameter 3-17 Reference Resource
3).
NOTICE
Connection of thermistor
sensor between terminals 54
and 55 (GND). See
Illustration 3.15.
[0] * None
[2] Analog Input
54
1-97 Thermistor Threshold level
Range: Function:
80 °C* [ -40 -
220 °C]
Select the thermistor sensor
threshold level for motor thermal
protection.
1-98 ATEX ETR interpol. points freq.
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 1000.0
Hz]
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Only visible if parameter 1-90 Motor
Thermal Protection is set to [20].
1 0 0 %
8 0 %
4 0 %
5 Hz 15 Hz 25 Hz 50 Hz
130BB909.10
1-99 ATEX ETR interpol points current
Only visible if parameter 1-90 Motor Thermal Protection is set to
[20] or [21].
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 - 100 %]
NOTICE
Valid for FC 302 only.
Denition of thermal limitation
curve. For example, see
parameter 1-98 ATEX ETR interpol.
points freq.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
Illustration 3.18 Example of ATEX ETR Thermal Limitation
Curve
x-axis: fm [Hz]
y-axis: Im/I
x 100 [%]
m,n
3 3
Parameter 1-98 ATEX ETR interpol.
points freq.
[0]=5 Hz [0]=40%
[1]=15 Hz [1]=80%
[2]=25 Hz [2]=100%
[3]=50 Hz [3]=100%
Table 3.10 Interpolation Points
Parameter 1-99 ATEX ETR
interpol points current
All operating points underneath the curve are allowed
continuously. Above the line, however, these are only
allowed for a limited time calculated as a function of the
overload. When machine current is greater than 1.5 times
the rated current, shutdown is immediate.
Enter the 4 frequency points [Hz] from the motor
nameplate into this array. Table 3.10 shows the example of
frequency/current points.
NOTICE
All frequency/current limit points from the motor
nameplate or motor datasheet must be programmed.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 77
Use the 4 current points [A] from the motor nameplate.
Calculate the values as percentage of nominal motor
current, Im/I
x 100 [%], and enter into this array.
m,n
Together with parameter 1-98 ATEX ETR interpol. points freq.,
these constitute a table (f [Hz],I [%]).

Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
NOTICE
All frequency/current limit points from the motor
nameplate or motor data sheet must be programmed.
3.2.18 PM Settings
33
If [2] Std. PM, non-salient is selected in
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction, enter the motor
parameters manually in the following order:
1. Parameter 1-24 Motor Current.
2. Parameter 1-26 Motor Cont. Rated Torque.
3. Parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed.
4. Parameter 1-39 Motor Poles.
5. Parameter 1-30 Stator Resistance (Rs).
6. Parameter 1-37 d-axis Inductance (Ld).
7. Parameter 1-40 Back EMF at 1000 RPM.
Application Settings
Low–inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
Low– inertia applications
50>I
High–inertia applications
I
Load/IMotor
High load at low speed
<30% (rated speed)
<5
Load/IMotor
> 50
>5
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const. by factor 5–10.
Reduce parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain.
Reduce parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed (<100%).
Keep calculated values.
Increase parameter 1-14 Damping
Gain, parameter 1-15 Low Speed Filter
Time Const., and parameter 1-16 High
Speed Filter Time Const.
Increase parameter 1-17 Voltage lter
time const.
Increase parameter 1-66 Min. Current
at Low Speed (>100% for a longer
period of time can overheat the
motor).
The following parameters have been added for PM motors.
1. Parameter 1-41 Motor Angle Oset.
2. Parameter 1-07 Motor Angle Oset Adjust.
3. Parameter 1-14 Damping Gain.
4. Parameter 1-47 Torque Calibration.
5. Parameter 1-58 Flying Start Test Pulses Current.
Table 3.11 Recommendations for VVC+ Applications
If the motor starts oscillating at a certain speed, increase
parameter 1-14 Damping Gain. Increase the value in small
steps. Depending on the motor, a good value for this
parameter can be 10% or 100% higher than the default
value.
6. Parameter 1-59 Flying Start Test Pulses Frequency.
7. Parameter 1-70 Start Mode.
Adjust starting torque in parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed. 100% provides nominal torque as starting torque.
8. Parameter 30-20 High Starting Torque Time [s].
9. Parameter 30-21 High Starting Torque Current [%].
NOTICE
Standard parameters still need conguration (for
example parameter 4-19 Max Output Frequency).
Application Settings
Low inertia applications Keep calculated values.
High inertia applications Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed.
Increase speed to a value between
default and maximum depending on
application.
Set ramp times matching the
application. Too fast ramp-up causes
an overcurrent/overtorque. Too fast
ramp-down causes an overvoltage
trip.
High load at low speed Parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed.
Increase speed to a value between
default and maximum depending on
application.
Table 3.12 Recommendations for Flux Applications
Adjust starting torque in parameter 1-66 Min. Current at Low
Speed. 100% provides nominal torque as starting torque.
78 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

2-00 DC Hold Current
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 0 - 160 %]
NOTICE
The maximum value depends
on the rated motor current.
Avoid 100% current for too
long. It may damage the
motor.
In VVC+ control core, low
values (<20%) of DC hold may
result in wrong currents with
larger motor sizes (>90 kW)
and should be avoided. In
cases when low DC hold
currents with larger motors is
required, select Flux control
core to ensure the right
currents.
Enter a value for holding current as
a percentage of the rated motor
current I
M,N
set in
parameter 1-24 Motor Current. 100%
DC hold current corresponds to I
M,N
.
This parameter holds the motor
function (holding torque) or
preheats the motor.
This parameter is active if DC hold
is selected in parameter 1-72 Start
Function [0] or
parameter 1-80 Function at Stop [1].
2-01 DC Brake Current
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 0 - 1000 %]
NOTICE
The maximum value depends
on the rated motor current.
Avoid 100% current for too
long. It may damage the
motor.
Enter a value for current as a
percentage of the rated motor
current I
M,N
, see
parameter 1-24 Motor Current. 100%
DC brake current corresponds to
I
M,N
.
DC brake current is applied on a
stop command, when the speed is
2-01 DC Brake Current
Range: Function:
lower than the limit set in
parameter 2-03 DC Brake Cut In
Speed [RPM]; when the DC Brake
Inverse function is active, or via the
serial communication port. The
braking current is active during the
time period set in
parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time.
2-02 DC Braking Time
Range: Function:
10 s* [0 - 60 s] Set the duration of the DC brake
current set in parameter 2-01 DC
Brake Current, once activated.
2-03 DC Brake Cut In Speed [RPM]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par. 4-13
RPM]
Set the DC brake cut-in speed for
activation of the DC brake current
set in parameter 2-01 DC Brake
Current, upon a stop command.
2-04 DC Brake Cut In Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par. 4-14
Hz]
NOTICE
Parameter 2-04 DC Brake Cut In
Speed [Hz] is not eective
when parameter 1-10 Motor
Construction = [1] PM, nonsalient SPM.
Set the DC brake cut-in speed for
activation of the DC brake current
set in parameter 2-01 DC Brake
Current after a stop command.
2-05 Maximum Reference
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ par. 3-02 -
999999.999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
This is an access parameter to
parameter 3-03 Maximum Reference
for legacy products. The maximum
reference is the highest value
obtainable by summing all
references. The maximum reference
unit matches the option selected in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
and the unit in
parameter 3-01 Reference/Feedback
Unit.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.3 Parameters: 2-** Brakes
3.3.1 2-0* DC brakes
Parameter group for conguring the DC brake and DC hold
functions.
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 79

2-06 Parking Current
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 0 - 1000 %] Set current as percentage of rated
motor current, parameter 1-24 Motor
Current. Is used when enabled in
parameter 1-70 Start Mode.
2-07 Parking Time
Range: Function:
3 s* [0.1 - 60 s] Set the duration of the parking
current set in
parameter 2-06 Parking Current, once
activated.
2-10 Brake Function
Option: Function:
[0] O No brake resistor is installed.
[1] Resistor brake A brake resistor is incorporated in
the system for dissipation of surplus
brake energy as heat. Connecting a
brake resistor allows a higher DClink voltage during braking
(generating operation). The resistor
brake function is only active in
frequency converters with an
integral dynamic brake.
[2] AC brake Improves braking without using a
brake resistor. This parameter
controls an overmagnetization of
the motor when running with a
generatoric load. This function can
improve the OVC function.
Increasing the electrical losses in
the motor allows the OVC function
to increase the braking torque
without exceeding the overvoltage
limit.
NOTICE
The AC brake is not as ecient
as dynamic braking with
resistor.
AC brake is for VVC+ mode in
both open and closed loop.
2-11 Brake Resistor (ohm)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 65535
Ohm]
Set the brake resistor value in Ω.
This value is used for monitoring
2-11 Brake Resistor (ohm)
Range: Function:
the power to the brake resistor in
parameter 2-13 Brake Power
Monitoring. This parameter is only
active in frequency converters with
an integral dynamic brake.
Use this parameter for values
without decimals. For a selection
with 2 decimals, use
parameter 30-81 Brake Resistor
(ohm).
2-12 Brake Power Limit (kW)
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.001 -
2000.000 kW]
Parameter 2-12 Brake Power Limit
(kW) is the expected average power
dissipated in the brake resistor over
a period of 120 s. It is used as the
monitoring limit for
parameter 16-33 Brake Energy
Average and thereby species when
a warning/alarm is to be given.
To calculate parameter 2-12 Brake
Power Limit (kW), the following
formula can be used.
P
br, avg
W =
U
br
2
V × tbrs
RbrΩ × Tbrs
P
br,avg
is the average power
dissipated in the brake resistor, R
br
is the resistance of the brake
resistor. tbr is the active breaking
time within the 120 s period, Tbr.
Ubr is the DC voltage where the
brake resistor is active. This
depends on the unit as follows:
T2 units: 390 V
T4 units: 810 V
T5 units: 810 V
T6 units: 943 V/1099 V for D – F
frames
T7 units: 1099 V
NOTICE
If Rbr is not known, or if Tbr is
dierent from 120 s, the
practical approach is to run
the brake application, read
parameter 16-33 Brake Energy
Average and then enter this
+ 20% in parameter 2-12 Brake
Power Limit (kW).
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
3.3.2 2-1* Brake Energy Funct.
Parameter group for selecting dynamic brake parameters.
Only valid for frequency converters with brake chopper.
80 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

2-13 Brake Power Monitoring
Option: Function:
This parameter is only active in
frequency converters with a brake.
This parameter enables monitoring
of the power to the brake resistor.
The power is calculated based on
the resistance (parameter 2-11 Brake
Resistor (ohm)), the DC-link voltage,
and the resistor duty time.
[0] * O No brake power monitoring
required.
[1] Warning 120s Activates a warning on the display
when the power transmitted during
the duty time exceeds 100% of the
monitoring limit
(parameter 2-12 Brake Power Limit
(kW).
The warning disappears when the
transmitted power drops below
80% of the monitoring limit.
[2] Trip 120s Trips the frequency converter and
shows an alarm when the
calculated power exceeds 100% of
the monitoring limit.
[3] Warning & trip
120s
Activates both of the above,
including warning, trip, and alarm.
[4] Warning 30s
[5] Trip 30s
[6] Warning & trip
30s
[7] Warning 60s
[8] Trip 60s
[9] Warning & trip
60s
[10] Warning 300s
[11] Trip 300s
[12] Warning & trip
300s
[13] Warning 600s
[14] Trip 600s
[15] Warning & trip
600s
2-15 Brake Check
Option: Function:
Parameter 2-15 Brake Check is only
active in frequency converters with
an integral dynamic brake.
Select type of test and monitoring
function to check the connection to
the brake resistor, or whether a
brake resistor is present, and then
show a warning or an alarm in the
event of a fault.
NOTICE
The brake resistor disconnection function is tested
during power-up. However, the
brake IGBT test is performed
when there is no braking. A
warning or trip disconnects
the brake function.
The testing sequence is as follows:
1. The DC-link ripple
amplitude is measured for
300 ms without braking.
2. The DC-link ripple
amplitude is measured for
300 ms with the brake
turned on.
3. If the DC-link ripple
amplitude while braking is
lower than the DC-link
ripple amplitude before
braking + 1%: Brake check
has failed by returning a
warning or alarm.
4. If the DC-link ripple
amplitude while braking is
higher than the DC-link
ripple amplitude before
braking + 1%: Brake check
is OK.
[0] * O Monitors brake resistor and brake
IGBT for a short circuit during
operation. If a short circuit occurs,
Warning 25 Brake resistor shortcircuited appears.
[1] Warning Monitors brake resistor and brake
IGBT for a short circuit and runs a
test for brake resistor disconnection
during power-up.
[2] Trip Monitors for a short circuit or
disconnection of the brake resistor,
or a short circuit of the brake IGBT.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
If power monitoring is set to [0] O or [1] Warning, the
brake function remains active, even if the monitoring limit
is exceeded. This may lead to thermal overload of the
resistor. It is also possible to generate a warning via a
relay/digital output. The measuring accuracy of the power
monitoring depends on the accuracy of the resistance of
the resistor (better than ±20%).
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 81
3 3

2-15 Brake Check
Option: Function:
If a fault occurs, the frequency
converter cuts out while showing
an alarm (trip lock).
[3] Stop and trip Monitors for a short circuit or
disconnection of the brake resistor,
or a short circuit of the brake IGBT.
If a fault occurs, the frequency
converter ramps down to coast and
then trips. A trip lock alarm is
shown (for example, warnings 25,
27, or 28).
[4] AC brake Monitors for a short circuit or
disconnection of the brake resistor,
or a short circuit of the brake IGBT.
If a fault occurs, the frequency
converter performs a controlled
ramp-down. This option is available
for FC 302 only.
[5] Trip Lock
2-16 AC brake Max. Current
Range: Function:
100 %* [ 0 -
1000.0 %]
Enter the maximum allowed current
when using AC braking to avoid
overheating of motor windings.
2-17 Over-voltage Control
Option: Function:
Overvoltage control (OVC) reduces
the risk of the frequency converter
tripping due to an overvoltage on
the DC-link caused by generative
power from the load.
[0] * Disabled No OVC required.
[1] Enabled (not
at stop)
Activates OVC except when using a
stop signal to stop the frequency
converter.
2-17 Over-voltage Control
Option: Function:
[2] Enabled Activates OVC.
2-18 Brake Check Condition
Range: Function:
[0] * At Power Up Brake check is performed at power-
up.
[1] After Coast
Situations
Brake check is performed after
coast situations.
2-19 Over-voltage Gain
Range: Function:
100 %* [10 - 200 %] Select overvoltage gain.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
NOTICE
33
Do not enable OVC in hoisting applications.
NOTICE
Remove a warning arising with [0] O or [1] Warning by
cycling the mains supply. The fault must be corrected
rst. For [0] O or [1] Warning, the frequency converter
keeps running even if a fault is located.
NOTICE
Parameter 2-16 AC brake Max. Current has no eect when
parameter 1-10 Motor Construction=[1] PM, non salient
SPM.
82 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
3.3.3 2-2* Mechanical Brake
Parameters for controlling operation of an electro-magnetic
(mechanical) brake, typically required in hoisting
applications.
To control a mechanical braking, a relay output (relay 01 or
relay 02) or a programmed digital output (terminal 27 or
29) is required. Normally, this output must be closed
during periods when the frequency converter is unable to
hold the motor, for example due to an excessive load.
Select [32] Mechanical Brake Control for applications with
an electro-magnetic brake in parameter 5-40 Function Relay,
parameter 5-30 Terminal 27 Digital Output, or
parameter 5-31 Terminal 29 Digital Output. When selecting
[32] Mechanical brake control, the mechanical brake is
closed from start-up until the output current is above the
level selected in parameter 2-20 Release Brake Current.
During stop, the mechanical braking activates when the
speed drops below the level specied in
parameter 2-21 Activate Brake Speed [RPM]. If the frequency
converter enters an alarm condition, an overcurrent, or
overvoltage situation, the mechanical braking immediately
cuts in. This is also the case during Safe Torque O.
NOTICE
Protection mode and trip delay features
(parameter 14-25 Trip Delay at Torque Limit and
parameter 14-26 Trip Delay at Inverter Fault) may delay
the activation of the mechanical braking in an alarm
condition. These features must be disabled in hoisting
applications.

Start
term.18
1=on
0=o
Shaft speed
Start delay time
on
o
Brake delay time
Time
Output current
Relay 01
Pre-magnetizing
current or
DC hold current
Reaction time EMK brake
Par 2-20
Release brake current
Par 1-76 Start current/
Par 2-00 DC hold current
Par 1-74
Start speed
Par 2-21
Activate brake
speed
Mechanical brake
locked
Mechanical brake
free
Par 1-71
Par 2-23
130BA074.12
2-20 Release Brake Current
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par.
16-37 A]
Set the motor current for release of
the mechanical braking when a
start condition is present. The
default value is the maximum
current the inverter can provide for
the particular power size. The upper
limit is specied in
parameter 16-37 Inv. Max. Current.
NOTICE
When mechanical brake
control output is selected, but
no mechanical braking is
connected, the function does
not work by default setting
due to too low motor current.
2-21 Activate Brake Speed [RPM]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par. 4-53
RPM]
Set the motor speed for activation
of the mechanical braking, when a
stop condition is present. The
upper speed limit is specied in
parameter 4-53 Warning Speed High.
2-22 Activate Brake Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - 5000.0
Hz]
Set the motor frequency for
activation of the mechanical
braking when a stop condition is
present.
2-23 Activate Brake Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] Enter the brake delay time of the
coast after ramp-down time. The
shaft is held at 0 speed with full
holding torque. Ensure that the
mechanical braking has locked the
load before the motor enters coast
mode. See Mechanical Brake Control
section in the design guide.
To adjust transition of the load to
the mechanical braking, set
parameter 2-23 Activate Brake Delay
and parameter 2-24 Stop Delay.
Setting of brake delay parameters
does not aect the torque. The
frequency converter does not
register that mechanical braking is
holding the load.
After setting parameter 2-23 Activate
Brake Delay, the torque drops to 0
after a few minutes. The sudden
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
Illustration 3.19 Mechanical Braking
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 83

2-23 Activate Brake Delay
Range: Function:
torque change leads to movement
and noise.
2-24 Stop Delay
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] Set the time interval from the
moment when the motor is
stopped until the brake closes.
To adjust transition of the load to
the mechanical braking, set
parameter 2-23 Activate Brake Delay
and parameter 2-24 Stop Delay.
This parameter is a part of the stop
function.
2-25 Brake Release Time
Range: Function:
0.20 s* [0 - 5 s] This value denes the time it takes
for the mechanical brake to open.
This parameter must act as a
timeout when brake feedback is
activated.
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3.3.4 Hoist Mechanical Brake
The hoist mechanical brake control supports the following
functions:
2 channels for mechanical braking feedback to
•
33
oer further protection against unintended
behavior resulting from broken cable.
Monitoring of mechanical braking feedback
•
throughout the complete cycle. This helps protect
the mechanical brake, especially if more
frequency converters are connected to the same
shaft.
No ramp-up until feedback conrms that
•
mechanical brake is open.
Improved load control at stop. If the value of
•
parameter 2-23 Activate Brake Delay is too low,
Warning 22 Hoist mech. brake is activated and the
torque is not allowed to ramp down.
The transition when motor takes over the load
•
from the brake can be
Parameter 2-28 Gain Boost Factor can be increased
to minimize the movement. To achieve smooth
transition, change the setting from the speed
control to the position control during the
changeover.
- Set parameter 2-28 Gain Boost Factor to
0 to enable position control during
parameter 2-02 DC Braking Time. This
enables parameter 2-30 Position P Start
Proportional Gain to
parameter 2-33 Speed PID Start Lowpass
Filter Time, which are PID parameters for
the position control.
congured.
84 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

130BA642.12
A22
Active
W22
Active
W22
Active
A22
Active
High
Low
High
Low
Open
Closed
Motor
Speed
Torque
Ref.
Brake
Relay
Mech Brake
Feedback
Gain Boost or
Postion Control
Mech Brake
Position
Activate Brake
Delay
P. 2-23
Torque Ramp
Down Time
p. 2-29
Stop Delay
P. 2-24
Ramp 1 Down
P. 3-42
Ramp 1 Up
P. 3-41
Brake Release
Time
p. 2-25
Torque Ramp
Up Time
p. 2-27
Contact no.2
OPTIONAL
E.g. DI33 [71] Mech. Brake Feedback
Contact no.1
E.g. DI32 [70] Mech. Brake Feedback
Gain Boost. p. 2-28
Torque Ref. p. 2-26
2-26 Torque Ref
Range: Function:
0 %* [ -300 -
300 %]
The value denes the torque
applied against the closed
mechanical brake before release.
The torque/load on a crane is
positive and is 10–160%. To obtain
the best starting point, set
parameter 2-26 Torque Ref to
approximately 70%.
The torque/load on a lift can be
both positive and negative and
between -160% and +160%. To
obtain the best starting point, set
parameter 2-26 Torque Ref to 0%.
The higher the torque error is
(parameter 2-26 Torque Ref vs. actual
torque), the more movement
during load takeover.
2-27 Torque Ramp Up Time
Range: Function:
0.2 s* [0 - 5 s] The value denes the duration of
the torque ramp in clockwise
direction. Value 0 enables very fast
magnetization in ux control
principle.
2-28 Gain Boost Factor
Range: Function:
1* [0 - 4 ] Only active in ux closed loop. The
function ensures a smooth
transition from torque control mode
to speed control mode when the
motor takes over the load from the
brake.
Increase to minimize the
movement. Activate the advanced
mechanical braking (parameter
group 2-3* Adv. Mech Brake) by
setting parameter 2-28 Gain Boost
Factor to 0.
2-29 Torque Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
0 s* [0 - 5 s] Torque ramp-down time.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
Illustration 3.20 Brake Release Sequence for Hoist Mechanical Brake Control
Parameter 2-26 Torque Ref to parameter 2-33 Speed PID Start
Lowpass Filter Time are only available for the hoist
mechanical brake control (ux with motor feedback).
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 85

2-30 Position P Start Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.0500* [0.0000 -
1.0000 ]
2-31 Speed PID Start Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.0500* [0.0000 -
1.0000 ]
2-32 Speed PID Start Integral Time
Range: Function:
20.0 ms* [1.0 -
20000.0 ms]
2-33 Speed PID Start Lowpass Filter Time
Range: Function:
2.0 ms* [0.1 - 100.0
ms]
2-34 Zero Speed Position P Proportional Gain
Range: Function:
0.0000* [0.0000 -
1.0000 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is available
only with software version
48.XX.
Enter the proportional gain for
position control at standstill in
speed mode.
3-00 Reference Range
Option: Function:
Select the range of the reference
signal and the feedback signal.
3-00 Reference Range
Option: Function:
Signal values can be positive only,
or positive and negative. The
minimum limit may have a negative
value, unless [1] Speed closed loop
control or [3] Process is selected in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode.
[0] Min - Max Select the range of the reference
signal and the feedback signal.
Signal values can be positive only,
or positive and negative. The
minimum limit may have a negative
value, unless [1] Speed closed loop
control or [3] Process is selected in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode.
[1] -Max - +Max For both positive and negative
values (both directions, relative to
parameter 4-10 Motor Speed
Direction).
3-01 Reference/Feedback Unit
Option: Function:
Select the unit to be used in
process PID control references and
feedbacks. Parameter 1-00 Congu-
ration Mode must be either [3]
Process or [8] Extended PID Control.
[0] None
[1] %
[2] RPM
[3] Hz
[4] Nm
[5] PPM
[10] 1/min
[12] Pulse/s
[20] l/s
[21] l/min
[22] l/h
[23] m³/s
[24] m³/min
[25] m³/h
[30] kg/s
[31] kg/min
[32] kg/h
[33] t/min
[34] t/h
[40] m/s
[41] m/min
[45] m
[60] °C
[70] mbar
[71] bar
[72] Pa
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
3.3.5 2-3* Adv. Mech Brake
Parameter 2-30 Position P Start Proportional Gain to
parameter 2-33 Speed PID Start Lowpass Filter Time can be
set up for very smooth transition change from speed
33
control to position control during parameter 2-25 Brake
Release Time - the time when the load is transferred from
the mechanical brake to the frequency converter.
Parameter 2-30 Position P Start Proportional Gain to
parameter 2-33 Speed PID Start Lowpass Filter Time are
activated when parameter 2-28 Gain Boost Factor is set to 0.
See Illustration 3.20 for more information.
3.4 Parameters: 3-** Reference/Ramps
Parameters for handling of reference, denition of
limitations, and conguration of the reaction of the
frequency converter to changes.
3.4.1 3-0* Reference Limits
86 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

3-01 Reference/Feedback Unit
Option: Function:
[73] kPa
[74] m WG
[80] kW
[120] GPM
[121] gal/s
[122] gal/min
[123] gal/h
[124] CFM
[125] ft³/s
[126] ft³/min
[127] ft³/h
[130] lb/s
[131] lb/min
[132] lb/h
[140] ft/s
[141] ft/min
[145] ft
[150] lb ft
[160] °F
[170] psi
[171] lb/in²
[172] in WG
[173] ft WG
[180] HP
3-02 Minimum Reference
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ -999999.999
- 999999.999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
Enter the minimum reference. The
minimum reference is the lowest
value obtainable by summing all
references.
Minimum reference is active only
when parameter 3-00 Reference
Range is set to [0] Min.- Max.
The minimum reference unit
matches:
•
The conguration of
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode: for [1] Speed
closed loop, RPM; for [2]
Torque, Nm.
•
The unit selected in
parameter 3-01 Reference/
Feedback Unit.
If option [10] Synchronization is
selected in parameter 1-00 Congu-
ration Mode, this parameter denes
the maximum speed deviation
when performing the position
oset dened in
parameter 3-26 Master Oset.
3-02 Minimum Reference
Range: Function:
Also see parameter 3-28 Master
Oset Speed Ref.
3-03 Maximum Reference
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.000 -
999999.999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
Enter the maximum reference. The
maximum reference is the highest
value obtainable by summing all
references.
The maximum reference unit
matches:
•
The conguration selected
in parameter 1-00 Congu-
ration Mode: For [1] Speed
closed loop, RPM; for [2]
Torque, Nm.
•
The unit selected in
parameter 3-00 Reference
Range.
If [9] Positioning is selected in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode,
this parameter denes the default
speed for positioning.
3-04 Reference Function
Option: Function:
[0] * Sum Sums both external and preset
reference sources.
[1] External/Preset Use either the preset or the
external reference source.
Shift between external and preset
via a command or a digital input.
3-05 On Reference Window
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[0 -
999999.999
ReferenceFeedbackUnit]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the tolerance window for on
reference or on target status.
Depending on the option selected
in parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode, this parameter denes the
following:
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 87

3-05 On Reference Window
Range: Function:
•
Speed mode: Speed
window for on reference
status.
•
Torque mode: Torque
window for on reference
status.
•
Position mode: Speed
window for on target
status. See also
parameter 3-08 On Target
Window.
3-06 Minimum Position
Range: Function:
-100000
CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[-2147483648
- 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the minimum position. This
parameter denes the position
range in linear axis mode
(parameter 17-76 Position Axis Mode)
and in the position limit function
(parameter 4-73 Position Limit
Function).
3-07 Maximum Position
Range: Function:
100000
CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[-2147483648
- 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the maximum position. This
parameter denes the position
range in linear and axis modes
(parameter 17-76 Position Axis
Mode).
Position range limits:
•
Linear:
Parameter 3-06 Minimum
Position to
parameter 3-07 Maximum
Position.
•
Rotary: 0–
parameter 3-07 Maximum
Position.
The position limit function uses this
parameter (parameter 4-73 Position
Limit Function).
3-08 On Target Window
Range: Function:
5 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[0 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
The frequency converter considers
the positioning completed and
sends the on target signal when
the actual position is within
parameter 3-08 On Target Window
for the duration of
parameter 3-09 On Target Time and
the actual speed is less than
parameter 3-05 On Reference
Window.
3-09 On Target Time
Range: Function:
1 ms* [0 - 60000
ms]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the time for evaluating the on
target window, see also
parameter 3-08 On Target Window.
3-10 Preset Reference
Array [8]
Range: 0-7
Range: Function:
0 %* [-100 -
100 %]
Enter up to 8 dierent preset
references (0–7) in this parameter,
using array programming. The
preset reference is stated as a
percentage of the value Ref
MAX
(parameter 3-03 Maximum
Reference). If a Ref
MIN
dierent from
0 (parameter 3-02 Minimum
Reference) is programmed, the
preset reference is calculated as a
percentage of the full reference
range, that is on the basis of the
dierence between Ref
MAX
and
Ref
MIN
. Afterwards, the value is
added to Ref
MIN
. When using preset
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
88 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
3.4.2 3-1* References
Select the preset references. Select Preset ref. bit 0/1/2 [16],
[17], or [18] for the corresponding digital inputs in
parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs.

3-10 Preset Reference
Array [8]
Range: 0-7
Range: Function:
references, select preset reference
bit 0/1/2 [16], [17] or [18] for the
corresponding digital inputs in
parameter group 5-1* Digital Inputs.
[P 5-13=Preset ref. bit 0]
Preset
[P 5-14=Preset ref. bit 1]
[P 5-15=Preset ref. bit 2]
10101010
76543210
29
12
(+24V)
11001100
32
11110000
33
130BA149.10
3-11 Jog Speed [Hz]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par. 4-14
Hz]
The jog speed is a xed output
speed at which the frequency
converter is running when the jog
function is activated.
See also parameter 3-80 Jog/Homing
Ramp Time.
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value
Range: Function:
0 %* [0 - 100 %] Enter a percentage (relative) value
to be either added to or deducted
from the actual reference for catch
up or slow down. If catch up is
selected via 1 of the digital inputs
(parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital
Input to parameter 5-15 Terminal 33
Digital Input), the percentage
(relative) value is added to the total
reference. If slow down is selected
3-12 Catch up/slow Down Value
Range: Function:
via 1 of the digital inputs
(parameter 5-10 Terminal 18 Digital
Input to parameter 5-15 Terminal 33
Digital Input), the percentage
(relative) value is deducted from
the total reference. Obtain
extended functionality with the
DigiPot function. See parameter
group 3-9* Digital Potentiometer.
3-13 Reference Site
Option: Function:
Select which reference site to
activate.
[0] Linked to
Hand / Auto
Use local reference when in handon mode, or remote reference
when in auto-on mode.
[1] Remote Use remote reference in both hand-
on mode and auto-on mode.
[2] Local Use local reference in both hand-on
mode and auto-on mode.
NOTICE
When set to [2] Local, the
frequency converter starts with
this setting again after a
power-down.
[3] Linked to H/A
MCO
Select this option to enable the
FFACC factor in
parameter 32-66 Acceleration FeedForward. Enabling FFACC reduces
jitter and makes the transmission
from the motion controller to the
control card of the frequency
converter faster. This leads to faster
response times for dynamic
applications and position control.
For more information about FFACC,
see VLT® Motion Control MCO 305
Operating Instructions.
3-14 Preset Relative Reference
Range: Function:
0 %* [-200 -
200 %]
The actual reference, X, is increased
or decreased with the percentage Y,
set in parameter 3-14 Preset Relative
Reference.
This results in the actual reference
Z. Actual reference (X) is the sum of
the inputs selected in:
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
Illustration 3.21 Preset Reference
3 3
Preset ref. bit 2 1 0
Preset ref. 0 0 0 0
Preset ref. 1 0 0 1
Preset ref. 2 0 1 0
Preset ref. 3 0 1 1
Preset ref. 4 1 0 0
Preset ref. 5 1 0 1
Preset ref. 6 1 1 0
Preset ref. 7 1 1 1
Table 3.13 Preset Reference Bits
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 89

3-14 Preset Relative Reference
Range: Function:
•
Parameter 3-15 Reference
Resource 1.
•
Parameter 3-16 Reference
Resource 2.
•
Parameter 3-17 Reference
Resource 3.
•
Parameter 8-02 Control
Word Source.
Relative
Z=X+X*Y/100
Resulting
actual
reference
Y
X
130BA059.12
Z
X
100
%
0-100
Z
Y
X+X*Y/100
P 3-14
130BA278.10
3-15 Reference Resource 1
Option: Function:
Select the reference input to be
used for the rst reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1,
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2,
and parameter 3-17 Reference
Resource 3 dene up to 3 dierent
reference signals. The sum of these
reference signals denes the actual
reference.
Select the speed reference source
in parameter 3-15 when
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode
is set to [9] in positioning mode.
NOTICE
The options 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 13,
14 are only available with
software version 48.XX
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input
53
3-15 Reference Resource 1
Option: Function:
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] 24V encoder
32/33
[4] MCB 102
[5] MCB 103
[6] Virtual Master
[7] Frequency
input 29
[8] Frequency
input 33
[11] Local bus
reference
Reference from terminals 68 and 69.
[12] Preset
Reference
Select this option to set the speed
reference in parameter 3-10 Preset
Reference together with the preset
target in parameter 3-20 Preset
Target to calculate speed prole for
positioning.
[13] 24V encoder
27/29
[14] MCB 102
Absolute
[15] MCO Encoder
1 X56
[16] MCO Encoder
2 X55
[20] Digital
pot.meter
[21] Analog input
X30/11
VLT® General Purpose I/O MCB 101
[22] Analog input
X30/12
VLT® General Purpose I/O MCB 101
[29] Analog Input
X48/2
[37] Analog Input
X49/1
[38] Analog Input
X49/3
[39] Analog Input
X49/5
3-16 Reference Resource 2
Option: Function:
NOTICE
The options 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 13,
and 14 are only available for
software version 48.XX.
Select the reference input to be
used for the 2nd reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1,
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2,
Parameter Descriptions
33
Illustration 3.22 Preset Relative Reference
Illustration 3.23 Actual Reference
90 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

3-16 Reference Resource 2
Option: Function:
and parameter 3-17 Reference
Resource 3 dene up to 3 dierent
reference signals. The sum of these
reference signals denes the actual
reference.
When parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode is set to [10] for synchronizing mode, congure
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2
to select the source for master
position.
When parameter 1-00 Conguration
Mode is set to [9] for positioning
mode, congure
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2
to select the source for target
position.
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input
53
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] 24V encoder
32/33
Single signal generated from 24 V
High Threshold Logic (HTL) encoder
connected to terminals 32 and 33.
Congure the 24 V encoder
interface in Parameter group 5–7*
24 V Encoder Option.
Program terminals 32/33 to [0] No
operation.
[4] MCB 102
This is only available for VLT
®
Encoder Option MCB 102. Congure
the encoder interface in parameter
groups 17-0*, 17-1*, and 17-2*.
[5] MCB 103
This is only available for VLT
®
Resolver Option MCB 103.
Congure the resolver interface in
parameter group 17-5* Resolver
Interface.
[6] Virtual Master Master signal for the drive which
hosts the virtual master without an
external connection. This option is
only active when option [10]
Synchronization is selected in
parameter 1-00 Conguration Mode.
[7] Frequency
input 29
[8] Frequency
input 33
[11] Local bus
reference
Reference from terminals 68 and 69.
3-16 Reference Resource 2
Option: Function:
[12] Preset
Reference
[13] 24V encoder
27/29
Single signal generated from 24 V
High Threshold Logic (HTL) encoder
connected to terminals 27 and 29.
Congure the 24 V encoder
interface in parameter group 5.7*
24 V Encoder Input.
Program terminals 27/29 to [0] No
operation.
[14] MCB 102
Absolute
The option is only available for
VLT® Encoder Option MCB 102 with
version 4.00 and newer and when
parameter 17-00 Encoders Connected
is set to option [1] Two Encoders.
[15] MCO Encoder
1 X56
[16] MCO Encoder
2 X55
[20] Digital
pot.meter
[21] Analog input
X30/11
[22] Analog input
X30/12
[29] Analog Input
X48/2
[37] Analog Input
X49/1
[38] Analog Input
X49/3
[39] Analog Input
X49/5
3-17 Reference Resource 3
Option: Function:
Select the reference input to be
used for the 3rd reference signal.
Parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1,
parameter 3-16 Reference Resource 2,
and parameter 3-17 Reference
Resource 3 dene up to 3 dierent
reference signals. The sum of these
reference signals denes the actual
reference.
[0] No function
[1] Analog Input
53
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] 24V encoder
32/33
[4] MCB 102
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 91
3 3

3-17 Reference Resource 3
Option: Function:
[5] MCB 103
[6] Virtual Master
[7] Frequency
input 29
[8] Frequency
input 33
[11] Local bus
reference
Reference from terminals 68 and 69.
[12] Preset
Reference
[13] 24V encoder
27/29
[14] MCB 102
Absolute
[15] MCO Encoder
1 X56
[16] MCO Encoder
2 X55
[20] Digital
pot.meter
[21] Analog input
X30/11
[22] Analog input
X30/12
[29] Analog Input
X48/2
[37] Analog Input
X49/1
[38] Analog Input
X49/3
[39] Analog Input
X49/5
3-18 Relative Scaling Reference Resource
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter cannot be
adjusted while the motor is
running.
The options 3, 4, 5, 6, 12, 13,
and 14 are only available for
software version 48.XX.
Select a variable value to be added
to the xed value (dened in
parameter 3-14 Preset Relative
Reference). The sum of the xed
and variable values (labeled Y in
Illustration 3.24) is multiplied by the
actual reference (labeled X in
Illustration 3.24). This product is
then added to the actual reference
3-18 Relative Scaling Reference Resource
Option: Function:
(X+X*Y/100) to give the resulting
actual reference.
Relative
Z=X+X*Y/100
Resulting
actual
reference
Y
X
130BA059.12
Z
Illustration 3.24 Resulting Actual
Reference
[0] * No function
[1] Analog Input
53
[2] Analog Input
54
[3] 24V encoder
32/33
[4] MCB 102
[5] MCB 103
[6] Virtual Master
[7] Frequency
input 29
[8] Frequency
input 33
[11] Local bus
reference
Reference from terminals 68 and 69.
[12] Preset
Reference
[13] 24V encoder
27/29
[14] MCB 102
Absolute
[15] MCO Encoder
1 X56
[16] MCO Encoder
2 X55
[20] Digital
pot.meter
[21] Analog input
X30/11
[22] Analog input
X30/12
[29] Analog Input
X48/2
[37] Analog Input
X49/1
[38] Analog Input
X49/3
[39] Analog Input
X49/5
Parameter Descriptions
33
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
92 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

3-19 Jog Speed [RPM]
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0 - par. 4-13
RPM]
Enter a value for the jog speed
n
JOG
, which is a xed output speed.
The frequency converter runs at
this speed when the jog function is
activated. The maximum limit is
dened in parameter 4-13 Motor
Speed High Limit [RPM].
See also parameter 3-80 Jog/Homing
Ramp Time.
3-20 Preset Target
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[-2147483648
- 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Array [8]
Set up to 8 target positions. Select
from the 8 preset positions using
digital inputs or the eldbus control
word.
3-21 Touch Target
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[-2147483648
- 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the target position in touch
probe positioning mode. This
parameter denes the distance
from the detection event of the
touch probe sensor to the nal
target position in position units.
3-22 Master Scale Numerator
Range: Function:
1* [-2147483648
2147483647 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Parameter 3-22 Master Scale
Numerator and
parameter 3-23 Master Scale
Denominator dene the gear ratio
between the master and the slave
3-22 Master Scale Numerator
Range: Function:
in synchronization mode.
Masterrevolutions =
Par . 3 − 22
Par . 3 − 23
× Slaverevolutions
3-23 Master Scale Denominator
Range: Function:
1* [-2147483648
2147483647 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
See parameter 3-22 Master Scale
Numerator.
3-24 Master Lowpass Filter Time
Range: Function:
20 ms* [1 - 2000 ms]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the time constant for master
speed calculation in synchronizing
mode.
3-25 Master Bus Resolution
Range: Function:
65536* [128 -
2147483647 ]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the resolution of the eldbus
master signal (eldbus Sync Ref ) in
synchronization mode.
3-26 Master Oset
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[-2147483648
- 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the position oset between
the master and the slave in
synchronization mode. This value is
added to the follower position at
each activation of a digital input
with option [113] Enable Reference
or bit 5 of the eldbus control
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3.4.3 3-2* References II
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 93

3-26 Master Oset
Range: Function:
word. Parameter 3-02 Minimum
Reference denes the maximum
deviation from the actual master
speed during the execution of the
oset.
3-27 Virtual Master Max Ref
Range: Function:
50.0 Hz* [0.0 - 590.0
Hz]
NOTICE
This parameter is available
only with software version
48.XX.
Enter the maximum reference for
the virtual master. The actual
reference is set relative to this value
using the source selected in
parameter 3-15 Reference Resource 1
or eldbus reference 1. The rotation
direction is controlled by the
forward/reverse signal on a digital
input or eldbus. Use parameter
group 3-6* Ramp 3 to congure
acceleration and deceleration.
3-28 Master Oset Speed Ref
Range: Function:
1500 RPM* [0 - 65000
RPM]
NOTICE
This parameter is only
available with software version
48.XX.
Enter the speed reference for
changing the master oset in
synchronization mode. To ensure
compatibility with software versions
48.01 and 48.10, this parameter is
only active when
parameter 3-02 Minimum Reference
is set to 0.
3-32 Ramp Speed Ref
Range: Function:
0 RPM* [0 - 1000000
RPM]
Enter a value to specify the ramp
speed reference. When 0 is
specied, the ramp speed is
selected based on the settings in
parameter 1-23 Motor Frequency for
induction motors and
parameter 1-25 Motor Nominal Speed
for synchronous motors.
3-32 Ramp Speed Ref
Range: Function:
When a value greater than 0 is
specied, the ramp speed reference
is used to accelerate or decelerate
irrespective of motor type or data.
3-33 Sync. Mode & Start Behavior
Option: Function:
NOTICE
This parameter is only valid
with software version 48.XX.
Select the type of synchronization
and start mechanism for synchronization mode. Marker
synchronization is enabled when
options [10], [11], or [12] is selected.
[0] * Relative Sync. Follower position is locked to
master position at start when
Enable Reference is active.
[1] Relative Re-
Sync.
Position of the follower drive stays
locked to master drive’s position
when Enable Reference is active,
though the drive is stopped or
coasted. For example, when the
drive is restarted after an alarm, the
follower drive realigns with the
master drive.
[2] Absolute Sync. Position of the follower drive is
always locked to the position of
master drive.
[10] Marker
Shortest
Controls the behaviour of rst
marker synchronization. Marker
synchronization start up behaviour
depends on parameter 3-34 Marker
Distance:
•
When
parameter 3-34 Marker
Distance = 0 (OFF), the 1
st
follower marker is aligned
with the rst master
marker.
•
When
parameter 3-34 Marker
Distance > 0, the 1
st
follower marker is aligned
with the closest master
marker to accelerate or
decelerate to the correct
position by a maximum of
half the marker distance.
Parameter Descriptions
33
94 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302

3-33 Sync. Mode & Start Behavior
Option: Function:
[11] Marker CatchUpSelect this option to accelerate the
follower to reach the position of
the previous master marker during
marker synchronization.
[12] Marker Slow
Down
Select this option to decelerate the
follower to align with the
subsequent master marker during
marker synchronization.
[13] Mar. Dis. Meas.
Fo.
Select this option to measure
follower marker distance while
synchronizing without marker
correction, when the master is
running. The measured follower
marker distance is set in
parameter 3-34 Marker Distance.
[14] Mar. Dis. Meas.
Ma.
Select this option to measure
master marker distance while
synchronizing without marker
correction, when the master is
running. The measured master
marker distance is set in
parameter 3-34 Marker Distance.
3-34 Marker Distance
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[0 2147483647
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only valid
with software version 48.XX.
Enter the approximate distance
between 2 markers. To measure the
marker distance for follower or
master marker, select the
corresponding marker measuring
function in parameter 3-33 Sync.
Mode & Start Behavior.
Marker distance is in position units
as
dened in parameter group 17-7*
Position Scaling. The value is
converted to the position units of
the follower using the master scale
set in parameter 3-22 Master Scale
Numerator and
parameter 3-23 Master Scale
Denominator.
Congure the marker distance in
order to utilize the marker window
function.
3-35 Marker Window
Range: Function:
0 CustomReadoutUni
t2*
[ 0 - par. 3-34
CustomReadoutUnit2]
NOTICE
This parameter is only valid
with software version 48.XX.
Ensure to congure
parameter 3-34 Marker Distance. The
marker window function is only
active when the marker distance is
set.
Enter the window size around the
expected marker position where the
marker is accepted.
The marker window is used for
both master and follower marker
and the position units are as
dened in parameter group 17-7*
Position Scaling.
Master position value is converted
to follower position units using the
master scale set in
parameter 3-22 Master Scale
Numerator and
parameter 3-23 Master Scale
Denominator.
P 3-*2
R
amp (
X) D o wn
T
ime (D
ec)
P 4-13
H
igh-limit
R
PM
R
ef
er
enc
e
n
s
P 4-11
L o w limit
t
dec
T
ime
P 3-*1
R
amp (
X) Up
T
ime ( A c
c)
t
a
cc
130BA872.11
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
3 3
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 95
3.4.4 3-4* Ramp 1
For each of the 4 ramps (parameter groups 3-4* Ramp 1,
3-5* Ramp 2, 3-6* Ramp 3, and 3-7* Ramp 4) congure the
ramp parameters:
Ramp type,
•
Ramping times (duration of acceleration and
•
deceleration), and
Level of jerk compensation for S-ramps.
•
Start by setting the linear ramping times corresponding to
Illustration 3.25 and Illustration 3.26.
Illustration 3.25 Linear Ramping Times

130BA168.10
Ramp (X) S-Ramp
Ratio at Accel.End
Jerk compensated
Ramp (X)
Up Time
Ramp (X)
S-Ramp
Ratio at
Accel.End
Linear
Speed
Ramp (X)
Down Time
Ramp (X)
S-Ramp
Ratio at
Dec.End
Ramp (X) S-Ramp
Ratio at Dec.End
3-40 Ramp 1 Type
Option: Function:
NOTICE
If [1] S-ramp Const Jerk is
selected and the reference
during ramping is changed,
the ramp time may be
prolonged to realize a jerk-free
movement, which may result
in a longer start or stop time.
Extra adjustment of the Sramp ratios or switching
initiators may be necessary.
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/
deceleration.
A linear ramp gives constant
acceleration during ramping. An Sramp gives non-linear acceleration,
compensating for jerk in the
application.
[0] * Linear
[1] S-ramp Const
Jerk
Acceleration with lowest possible
jerk.
[2] S-ramp Const
Time
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up
Time and parameter 3-42 Ramp 1
Ramp Down Time.
3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-up time, that is the
acceleration time from 0 RPM to
the synchronous motor speed nS.
Select a ramp-up time which
prevents the output current from
exceeding the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. The value 0.00
corresponds to 0.01 s in speed
mode. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down
Time.
Par . 3 − 41 =
t
acc
s xns RPM
ref RPM
3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-down time, that is
the deceleration time from the
synchronous motor speed ns to 0
RPM. Select a ramp-down time such
that no overvoltage occurs in the
inverter due to regenerative
operation of the motor, and such
that the generated current does not
exceed the current limit set in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit. The
value 0.00 corresponds to 0.01 s in
speed mode. See ramp-up time in
parameter 3-41 Ramp 1 Ramp Up
Time.
Par . 3 − 42 =
t
dec
s xns RPM
ref RPM
3-45 Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. Start
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-up time (parameter 3-41 Ramp
1 Ramp Up Time) in which the
acceleration torque increases. The
larger the percentage value, the
greater the jerk compensation
achieved, and thus the lower the
torque jerks occurring in the
application.
3-46 Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. End
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-up time (parameter 3-41 Ramp
1 Ramp Up Time) in which the
acceleration torque decreases. The
larger the percentage value, the
greater the jerk compensation
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
If S-ramps are selected, set the level of non-linear jerk
compensation required. Set jerk compensation by dening
the proportion of ramp-up and ramp-down times where
acceleration and deceleration are variable (that is,
increasing or decreasing). The S-ramp acceleration and
deceleration settings are dened as a percentage of the
33
actual ramp time.
Illustration 3.26 Linear Ramping Times
96 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101

3-46 Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. End
Range: Function:
achieved, and thus the lower the
torque jerks in the application.
3-47 Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Decel. Start
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-down time
(parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down
Time) where the deceleration
torque increases. The larger the
percentage value, the greater the
jerk compensation achieved, and
thus the lower the torque jerks in
the application.
3-48 Ramp 1 S-ramp Ratio at Decel. End
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-down time
(parameter 3-42 Ramp 1 Ramp Down
Time) where the deceleration
torque decreases. The larger the
percentage value, the greater the
jerk compensation achieved, and
thus the lower the torque jerks in
the application.
3-50 Ramp 2 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration/
deceleration. A linear ramp gives
constant acceleration during
ramping. An S-ramp gives nonlinear acceleration, compensating
for jerk in the application.
[0] * Linear
[1] S-ramp Const
Jerk
Acceleration with lowest possible
jerk.
[2] S-ramp Const
Time
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up
Time and parameter 3-52 Ramp 2
Ramp Down Time.
3-51 Ramp 2 Ramp Up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-up time, that is the
acceleration time from 0 RPM to
the nominal motor speed ns. Select
a ramp-up time such that the
output current does not exceed the
current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. The value 0.00
corresponds to 0.01 s in speed
mode. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down
Time.
Par . 3 − 51 =
t
acc
s xns RPM
ref RPM
3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-down time, that is
the deceleration time from the
nominal motor speed ns to 0 RPM.
Select a ramp-down time such that
no overvoltage occurs in the
frequency converter due to
regenerative operation of the
motor, and such that the generated
current does not exceed the current
limit set in parameter 4-18 Current
Limit. The value 0.00 corresponds to
0.01 s in speed mode. See ramp-up
time in parameter 3-51 Ramp 2
Ramp Up Time.
Par . 3 − 52 =
t
dec
s xns RPM
ref RPM
3-55 Ramp 2 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. Start
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-up time (parameter 3-51 Ramp
2 Ramp Up Time) in which the
acceleration torque increases. The
larger the percentage value, the
greater the jerk compensation
achieved, and thus the lower the
torque jerks in the application.
Parameter Descriptions Programming Guide
NOTICE
If [1] S-ramp Const Jerk is selected and the reference
during ramping is changed, the ramp time may be
prolonged to realize a jerk-free movement, which may
result in a longer start or stop time.
Additional adjustment of the S-ramp ratios or switching
initiators may be necessary.
3 3
3.4.5 3-5* Ramp 2
To select ramp parameters, see parameter group 3-4* Ramp
1.
M0013101 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. 97

3-56 Ramp 2 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. End
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-up time (parameter 3-51 Ramp
2 Ramp Up Time) in which the
acceleration torque decreases. The
larger the percentage value, the
greater the jerk compensation
achieved, and thus the lower the
torque jerks in the application.
3-57 Ramp 2 S-ramp Ratio at Decel. Start
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-down time
(parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down
Time) where the deceleration
torque increases. The larger the
percentage value, the greater the
jerk compensation achieved, and
thus the lower the torque jerks in
the application.
3-58 Ramp 2 S-ramp Ratio at Decel. End
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-down time
(parameter 3-52 Ramp 2 Ramp Down
Time) where the deceleration
torque decreases. The larger the
percentage value, the greater the
jerk compensation achieved, and
thus the lower the torque jerks in
the application.
3-60 Ramp 3 Type
Option: Function:
Select the ramp type, depending on
requirements for acceleration and
deceleration. A linear ramp gives
constant acceleration during
ramping. An S-ramp gives nonlinear acceleration, compensating
for jerk in the application.
[0] * Linear
[1] S-ramp Const
Jerk
Accelerates with lowest possible
jerk.
[2] S-ramp Const
Time
S-ramp based on the values set in
parameter 3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up
3-60 Ramp 3 Type
Option: Function:
Time and parameter 3-62 Ramp 3
Ramp down Time.
3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-up time, which is
the acceleration time from 0 RPM
to the nominal motor speed ns.
Select a ramp-up time such that
the output current does not exceed
the current limit in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit during
ramping. The value 0.00
corresponds to 0.01 s in speed
mode. See ramp-down time in
parameter 3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down
Time.
3-62 Ramp 3 Ramp down Time
Range: Function:
Size
related*
[ 0.01 - 3600s]Enter the ramp-down time, which is
the deceleration time from the
nominal motor speed ns to 0 RPM.
Select a ramp-down time such that
no overvoltage occurs in the
inverter due to regenerative
operation of the motor, and such
that the generated current does not
exceed the current limit set in
parameter 4-18 Current Limit. The
value 0.00 corresponds to 0.01 s in
speed mode. See ramp-up time in
parameter 3-61 Ramp 3 Ramp up
Time.
Par . 3 − 62 =
t
dec
s xns RPM
ref RPM
3-65 Ramp 3 S-ramp Ratio at Accel. Start
Range: Function:
50 %* [ 1 - 99 %] Enter the proportion of the total
ramp-up time (parameter 3-61 Ramp
3 Ramp up Time) in which the
acceleration torque increases. The
larger the percentage value, the
greater the jerk compensation
Parameter Descriptions
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 301/302
33
NOTICE
If [1] S-ramp Const Jerk is selected and the reference
during ramping is changed, the ramp time may be
prolonged to realize a jerk-free movement, which may
result in a longer start or stop time.
Extra adjustment of the S-ramp ratios or switching
initiators may be necessary.
3.4.6 3-6* Ramp 3
Congure ramp parameters, see parameter group 3-4*
Ramp 1.
98 Danfoss A/S © 10/2019 All rights reserved. M0013101
 Loading...
Loading...