Page 1

Fact Sheet
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302 with integrated motion controller
– for positioning and synchronization applications
hardware. With sensorless control (no
motor feedback) best performance is
achieved with a PM motor. The performance of sensorless control of induction motors is however sufficient for
less-demanding applications.
With IMC you save time and cost:
No advanced programming and
fewer components means fewer
hours needed for engineering,
installation and commissioning
Save further cost for a feedback
Discover precision positioning and
synchronization control in modern dance
Perform high-precision positioning
and synchronization, simply using an
AC drive. With the Integrated Motion
Controller (IMC) functionality, the
VLT® AutomationDrive FC 302
replaces more complex positioning
and synchronization controllers, to save
time and cost.
Positioning and synchronization
operations are typically performed
using a servo drive or a motion
controller. However, many of these
applications do not actually require
the dynamic performance available
from a servo drive.
Encoderfree
to save costs and
reduce complexity
Therefore the FC 302 with IMC is a costeffective, high-performance alternative
to servo in single-axis positioning and
synchronizing applications.
Use IMC for many applications that
have been solved with servo drives
until now, such as:
Rotary tables
Cutting machines
Packaging machines
Use FC 302 to run an induction or PM
motor with or without motor feed-
back – with no need for additional
Feature Benefit
Motion control functionality
integrated into the AC drive
No encoder and no encoder wiring required
No servo drive required
Configuration via parameters
Home synchronizing
– Renewal of calibration on every cycle
Homing on torque limit
– No sensor required
device, cabling and installation by
using sensorless control
To save cost for a home sensor and
cabling, use the “homing on torque
limit” function
The IMC solution provides
easy and safe set-up:
Configuration via parameters, with
no advanced programming required.
Reduced complexity will minimize
the risk of errors
To add more functionality, use the
Smart Logic Controller (SLC), which
is fully compatible with IMC
To realign the home position
during operation, use the “home
synchronizing” function
– Save cost and time for extra components
– Lower purchase cost due to fewer components
– More robust installation
– Reduced electrical and mechanical
installation time
– Easier and faster set-up
– No advanced programming required
– Lower purchase cost
– Achieve a safe result
– Save time
– Avoid complexity
– Minimize risk of errors associated
with advanced programming
High level of accuracy maintained continuously
–
in systems with slip
– Save purchase, installation and maintenance
cost of extra equipment
www.danfoss.com/imc
Page 2
Positioning
In positioning mode, the drive controls
movement over a specific distance
(relative positioning) or to a specific
target (absolute positioning). The drive
calculates the motion profile based on
target position, speed reference and
ramp settings (see the examples in Fig. 1
and Fig. 2 on the right).
There are 3 positioning types using different references for defining the target
position:
Absolute positioning
Target position is relative to the
defined zero point of the machine.
Relative positioning
Target position is relative to
the actual position of the machine.
Touch probe positioning
Target position is relative to a signal
on a digital input
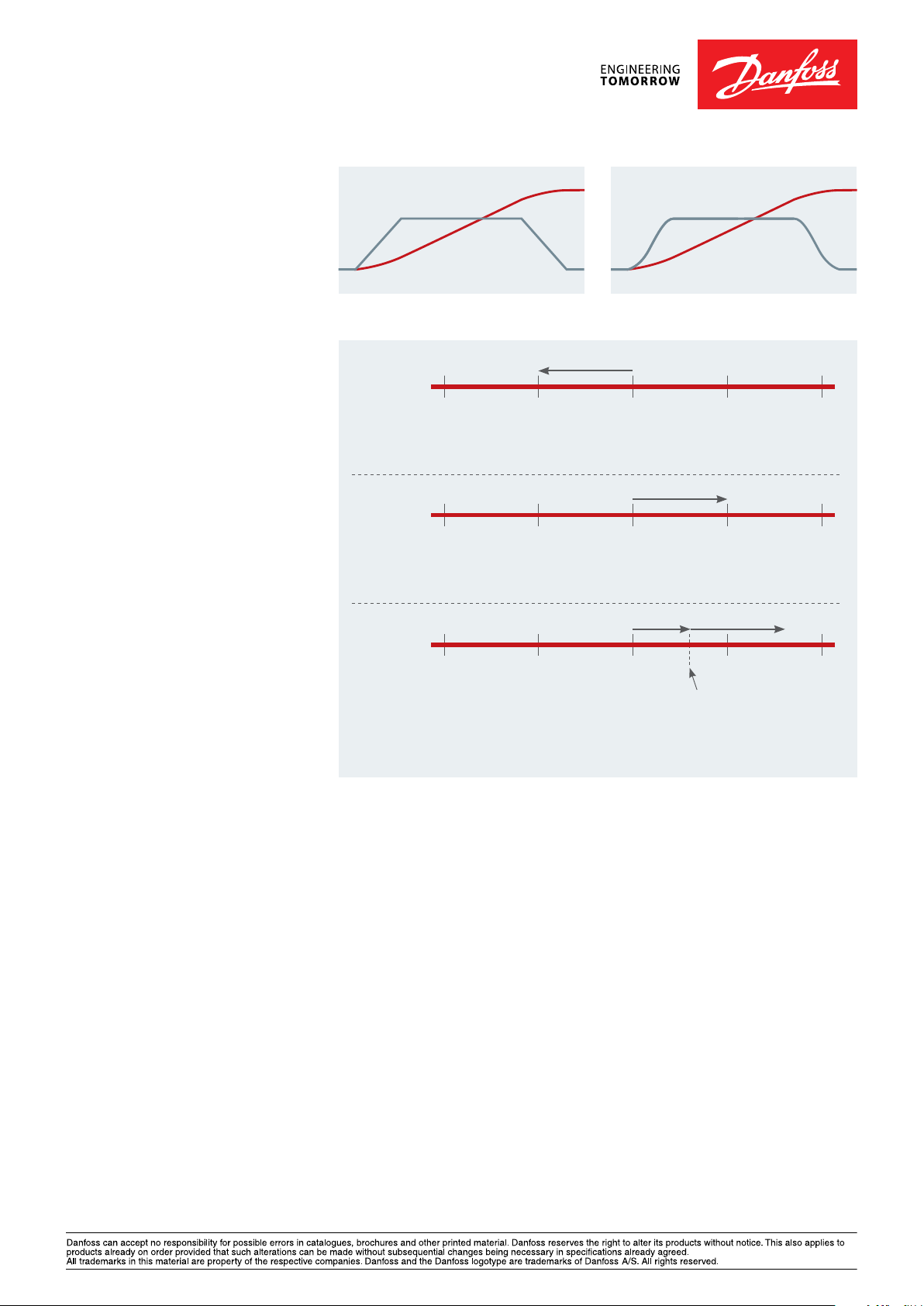
This illustration (Fig. 3) shows the
different resulting target with a set
target position (reference) of 1000 and
starting position of 2000 for each of the
positioning types.
Synchronizing
In synchronizing mode the drive follows the position of a master, multiple
drives can follow the same master. The
master signal can be an external signal
e.g. from an encoder, a virtual master
signal generated by a drive or master
positions transferred by fieldbus. Gear
ratio and position offset is adjustable by
parameter.
Homing
With sensorless control and closed
loop control with an incremental
encoder homing is required to create
a reference for the physical position of
PositionPosition
Speed Speed
Fig. 1. Motion profile with linear ramps Fig. 2. Motion profile with S-ramps
Absolute
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
With absolute positioning, the drive moves backwards from the starting position
of 2000 to the absolute position of 1000 related to 0.
Relative
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
With relative positioning, the drive moves a distance of 1000 forward from
the starting position of 2000 ending at position 3000.
Touch probe
0 1000 2000 3000 4000
Touch probe sensor
With touch probe positioning, the drive starts moving forward from the starting
position of 2000, detects the touch probe sensor and moves a distance of 1000
forward from the position of the touch probe sensor.
Fig. 3. IMC supports 3 positioning modes
the machine after power up. There are
several home functions with and without sensor to choose from. The home
synchronizing function can be used to
continuously realign the home position
during operation when there is some
sort of slip in the system. For example
in case of sensorless control with an
induction motor or in case of slip in the
mechanical transmission.
DKDD.PFF.300.A5.02 © Copyright Danfoss Drives | 2020.09
 Loading...
Loading...