Page 1

Data sheet
Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection
Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Solenoid valve range for water leak detection in
residential and industrial buildings:
• Houses and apartments
- Kitchen and bathrooms
• Commercial buildings
• Industrial buildings
Solenoid valves used for shut-off water supply to
prevent water damages from leaking systems.
Features and versions
y Clip-on coil
y Flow range for water in Kv: 0.7 - 40 m³ / h
y Differential pressure: 0.3 – 16 bar
y Media temperature from 0 – 120 °C
y Ambient temperature: up to 80 °C
y Coil enclosure: IP65
y Thread connections: From G 3/8 – G 2
y DN 6 – 50
y Water hammer damped
y Built-in filter
y Adjustable closing time available
y EV220T 14-18, NC, polymer
y EV220W 10-22, NC, brass
y EV220B 6 -12, NO, brass and DZR brass
y EV220B 6 -12, NC, brass
y EV220B 15-50, NO, brass and DZR brass
y EV220B 15-50, NC, brass
y EV228B 15-25, UN (Latching), DZR Brass
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201| 1
Page 2
24h
ON
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
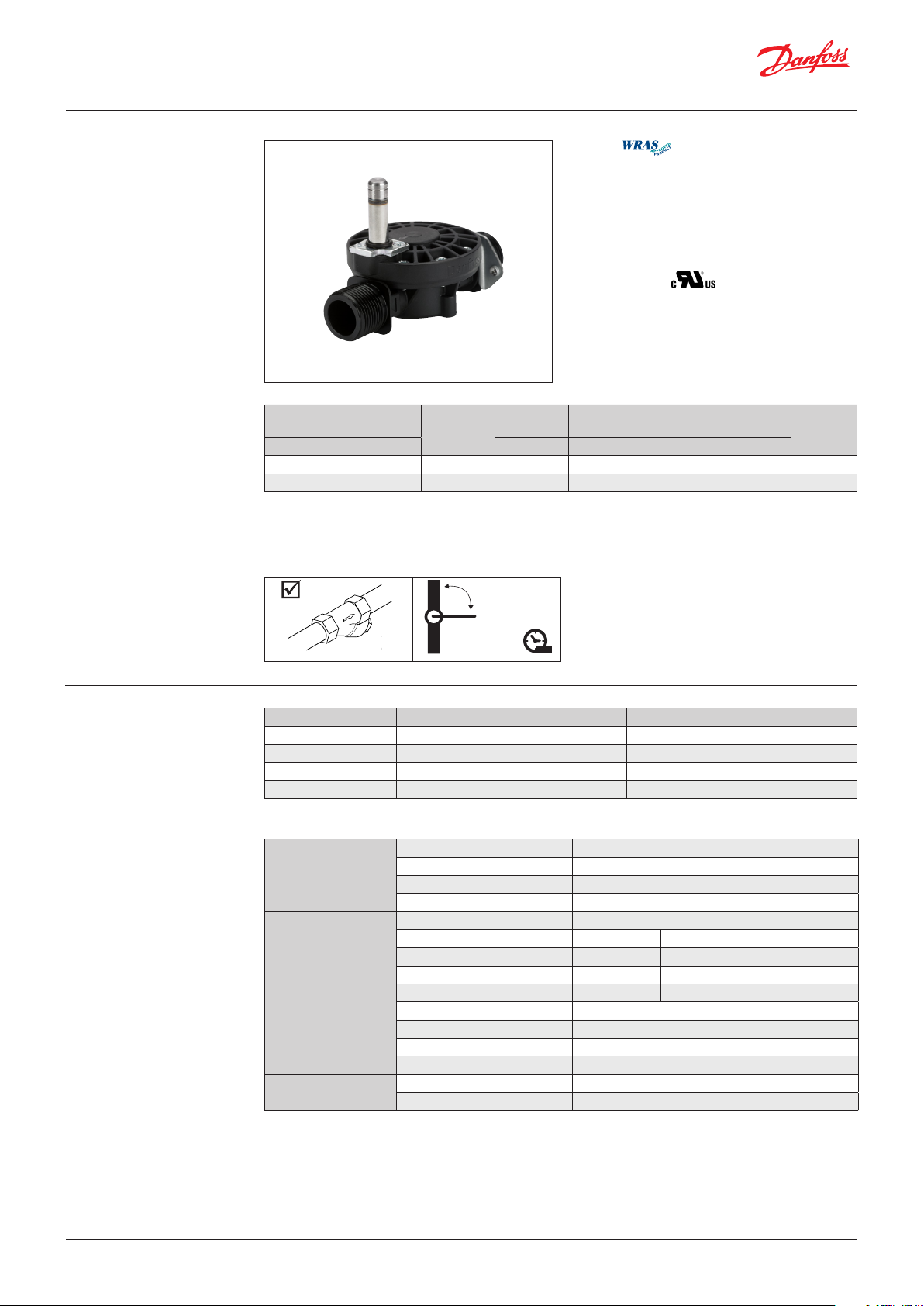
EV220T
Polymer valve body, NC
y WRAS
y RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
y - Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
(Notified body by Semko)
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO 228-1 connection
Inlet Outlet [mm] [m³ / h] [°C] [bar]
Seal
material
Orifice
size
G ¾ ext. G ¾ ext. EPDM 14 4 0 – 85 0.3 – 10 042U 8125
G ¾ ext. G ¾ ext. EPDM 18 6 0 – 85 0.3 – 10 042U8175
See separate table for AS/AZ coils.
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
OFF
Typ e EV22 0T 14 EV220T 18
Time to open [ms] 3 100 200
Time to close [ms] 3 400 500
Capacity, Kv [m3/h] 4 6
Capacity Cv [gal/min] 4.7 7
3
Times are indicative and apply to water. Exact times will depend on pressure conditions
Max. working pressure (MWP) 10 bar
Valve
Max. test pressure 15 bar
Ambient temperature Max. 50 °C / 122 °F
Media viscosity 50 cSt
Body EMS Grivory HT (Glass-fiber reinforced)
Armature Stainless steel W no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature stop Stainless steel W. no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W. no. 1.4303 / AISI 305
Materials
Spring Stainless steel W. no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-ring EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Screws Steel zinc plated delta PT
Features
Mounting Metal bracket (see dimension drawing on page 4)
Media Built-in filter mesh width 0.45 mm
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 2
Page 3
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
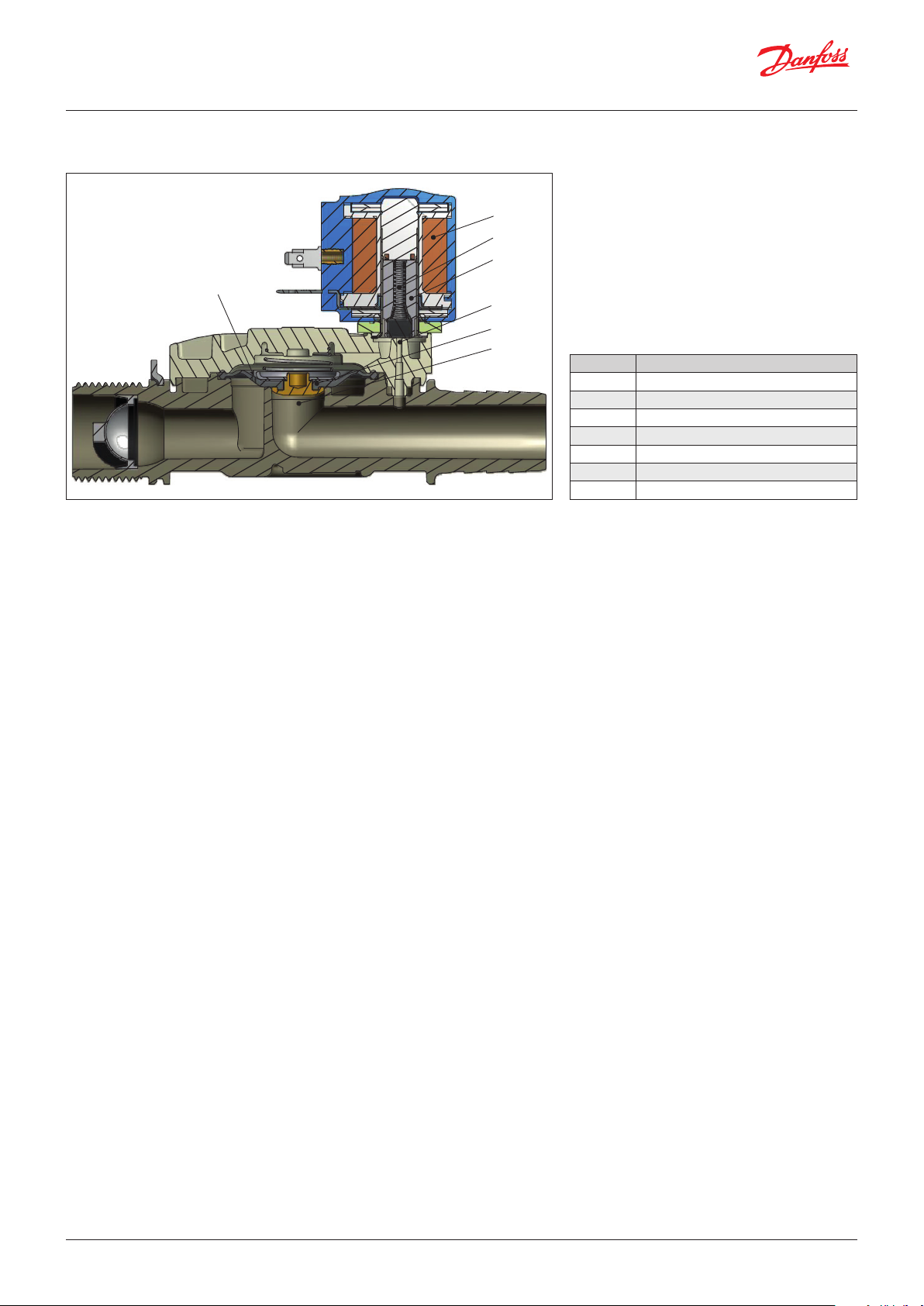
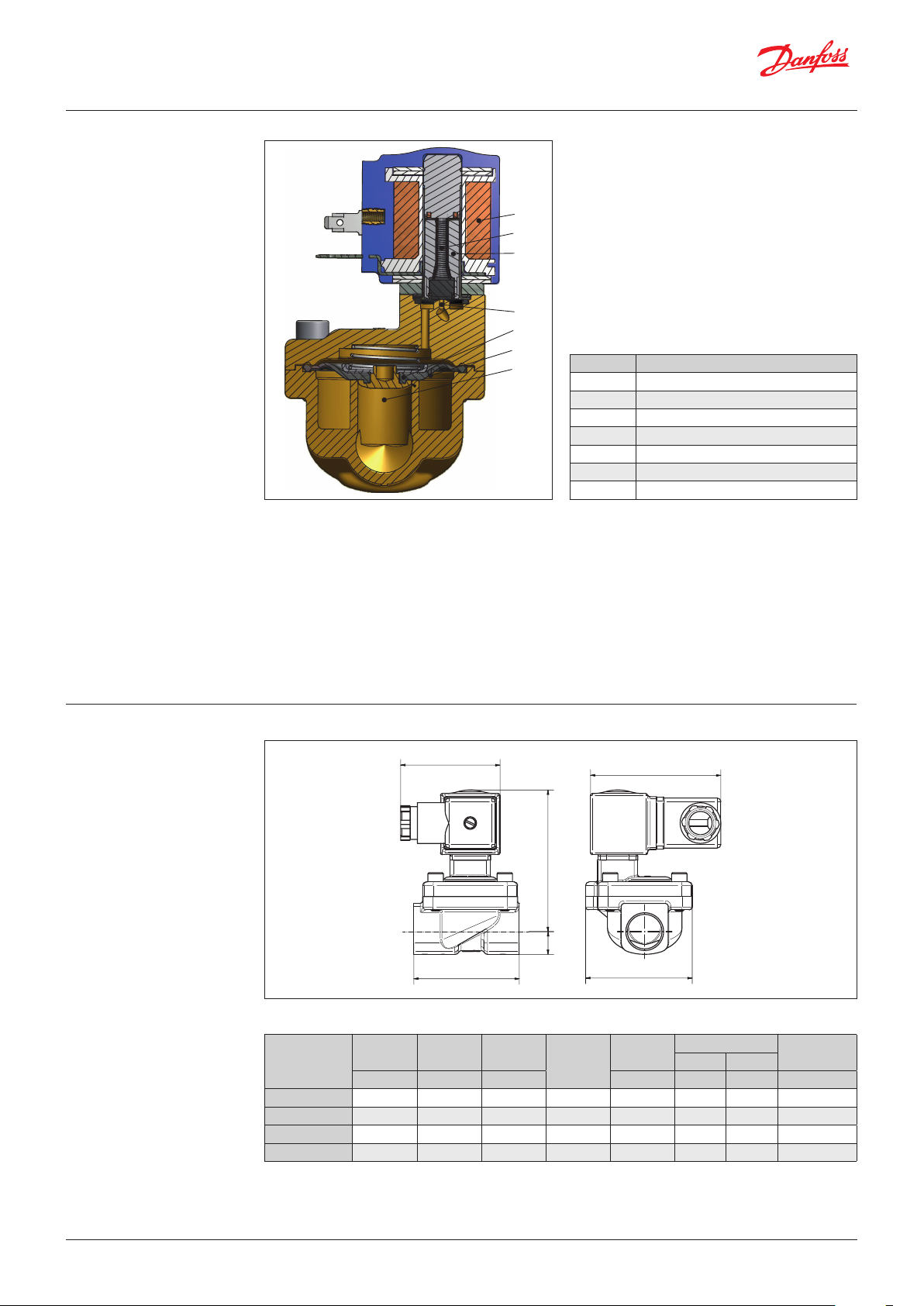
Function, NC
1
2
3
6
4
5
7
Pos. no. Description
1 Coil
2 Armature spring
3 Armature
4 Pilot orifice
5 Diaphragm
6 Equalizing orifice
7 Main orifice
Coil voltage disconnected (Closed)
When voltage is disconnected, the armature
spring (2) presses the armature (3) down against
the pilot orifice (4). Pressure builds up over the
diaphragm (5) via the equalizing orifice (6). The
diaphragm closes the main orifice (7) as soon as
the pressure over the diaphragm equals the inlet
pressure. The valve stays closed for as long as
voltage remains disconnected.
Coil voltage connected (open)
When voltage is applied to the coil (1), the pilot
orifice (4) is opened. Since the pilot orifice is
larger than the equalizing orifice (6), pressure
over the diaphragm (5) falls and the diaphragm
is lifted clear of the main orifice (7). The valve
stays open for as long as the required minimum
differential pressure is present and voltage is
applied to the coil.
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 3
Page 4
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
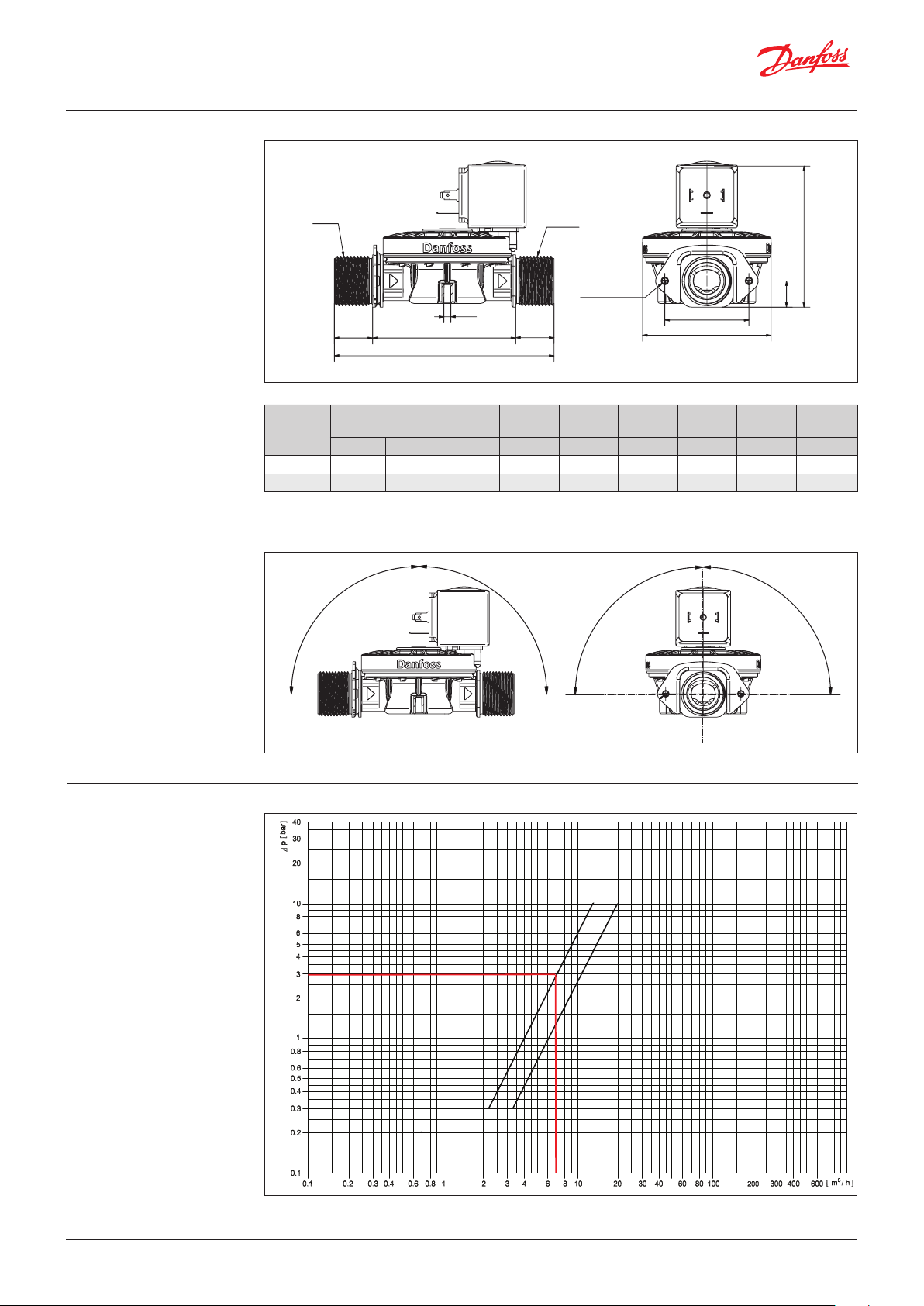
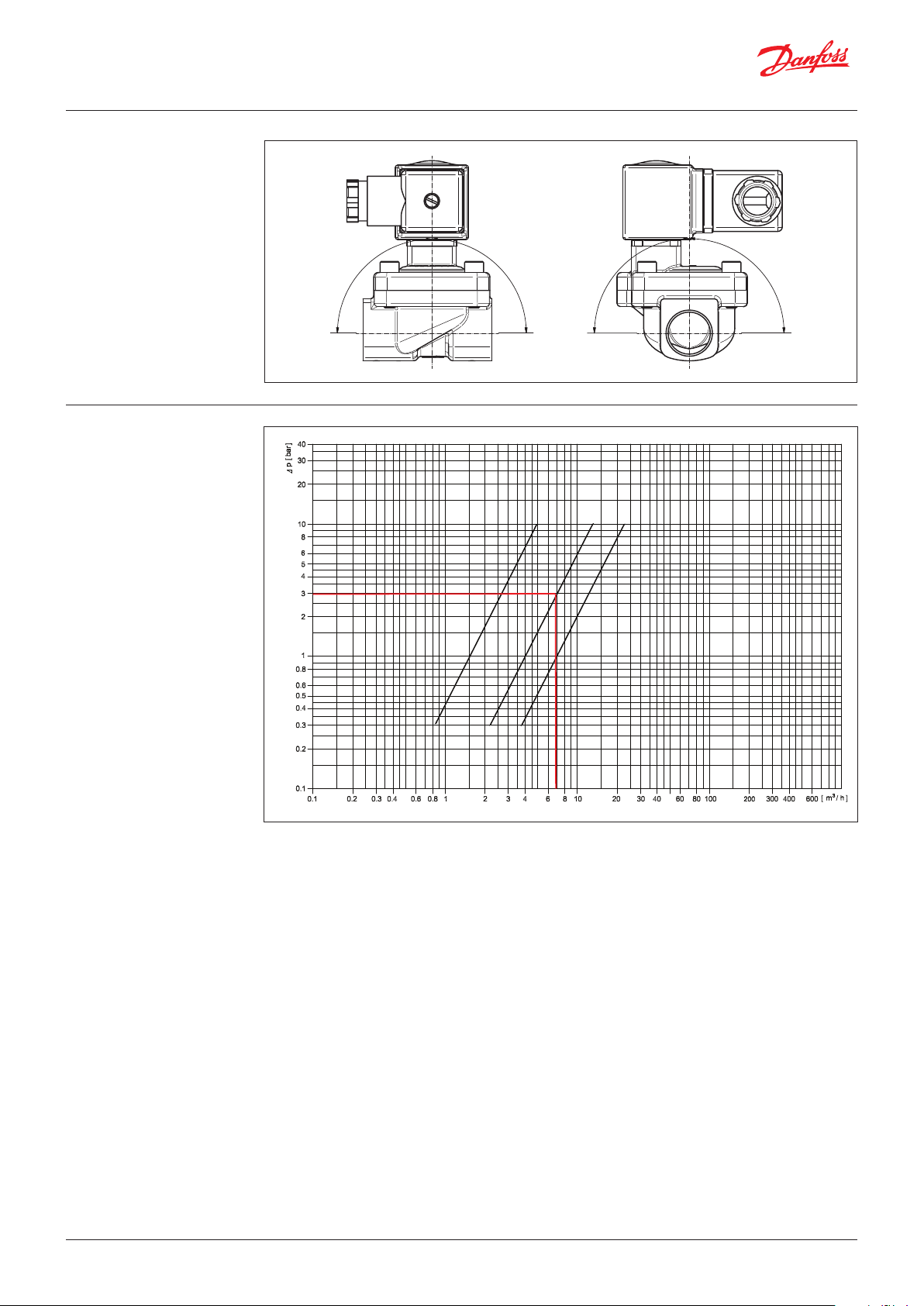
Dimensions and weight
Mounting angle
Inlet
3,7Ø
L2L1
L
ISO 228-1
Orifice
DN 14 G ¾ ext. G ¾ ext. 127.5 20.5 76.5 68.8 45.0 77.7 14.0
DN 18 G ¾ ext. G ¾ ext. 127. 5 20.5 76.5 68.8 45.0 79.9 14.0
connection
Inlet Outlet [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm]
90°
L L1 L2 B B1 H H1
M
a
Max.
Outlet
H
M4x0.7 - 6H
B1
L1
x
.
90
°
90°
Max.
B
M
H1
a
x
.
90
°
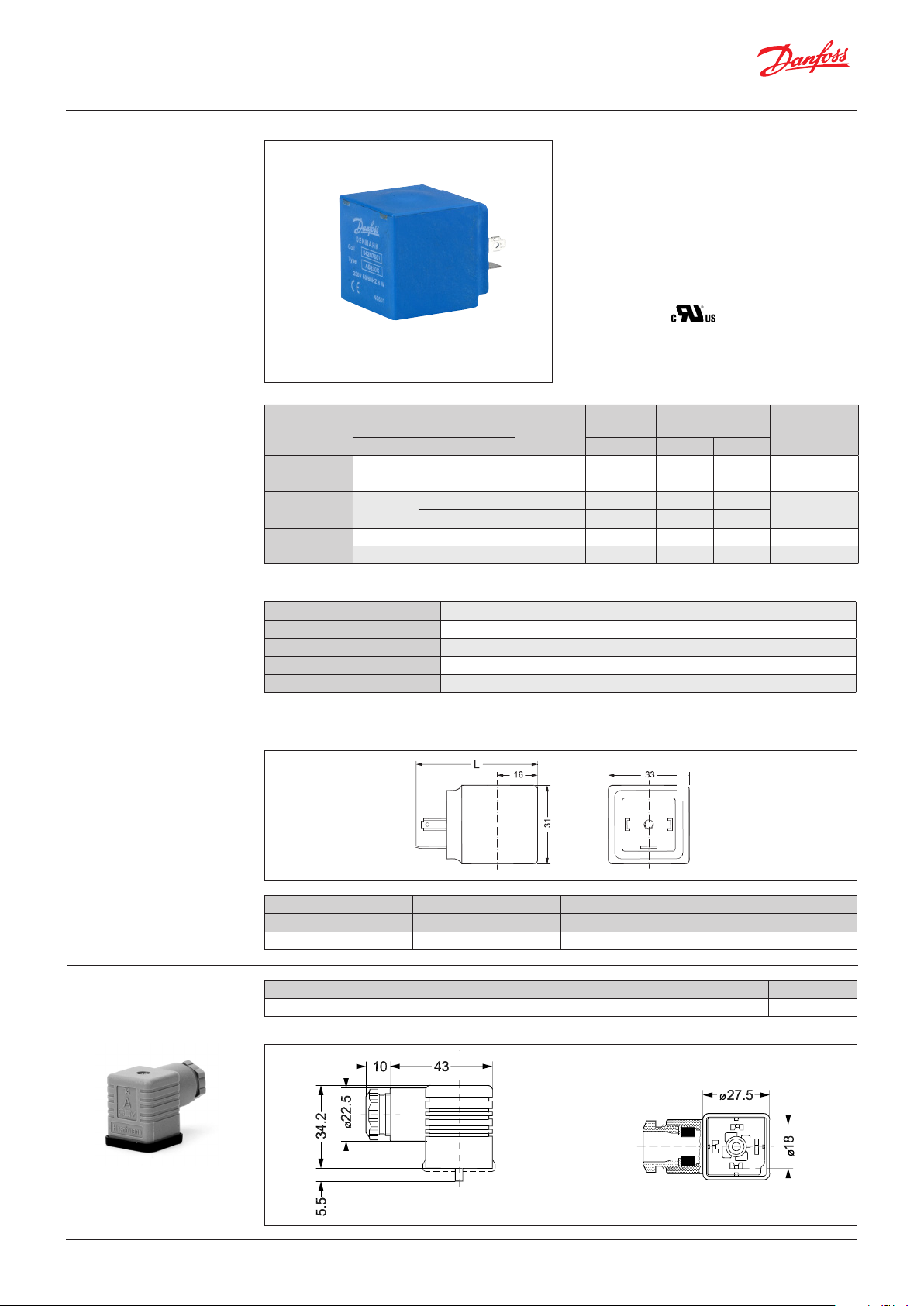
Capacity diagram
Example for water:
Capacity for EV220T at a
differential pressure of 3 bar:
Approx. 7 m3 / h
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
EV220W 14
EV220W 18
AI256649466639en-000201 | 4
Page 5
24h
ON
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
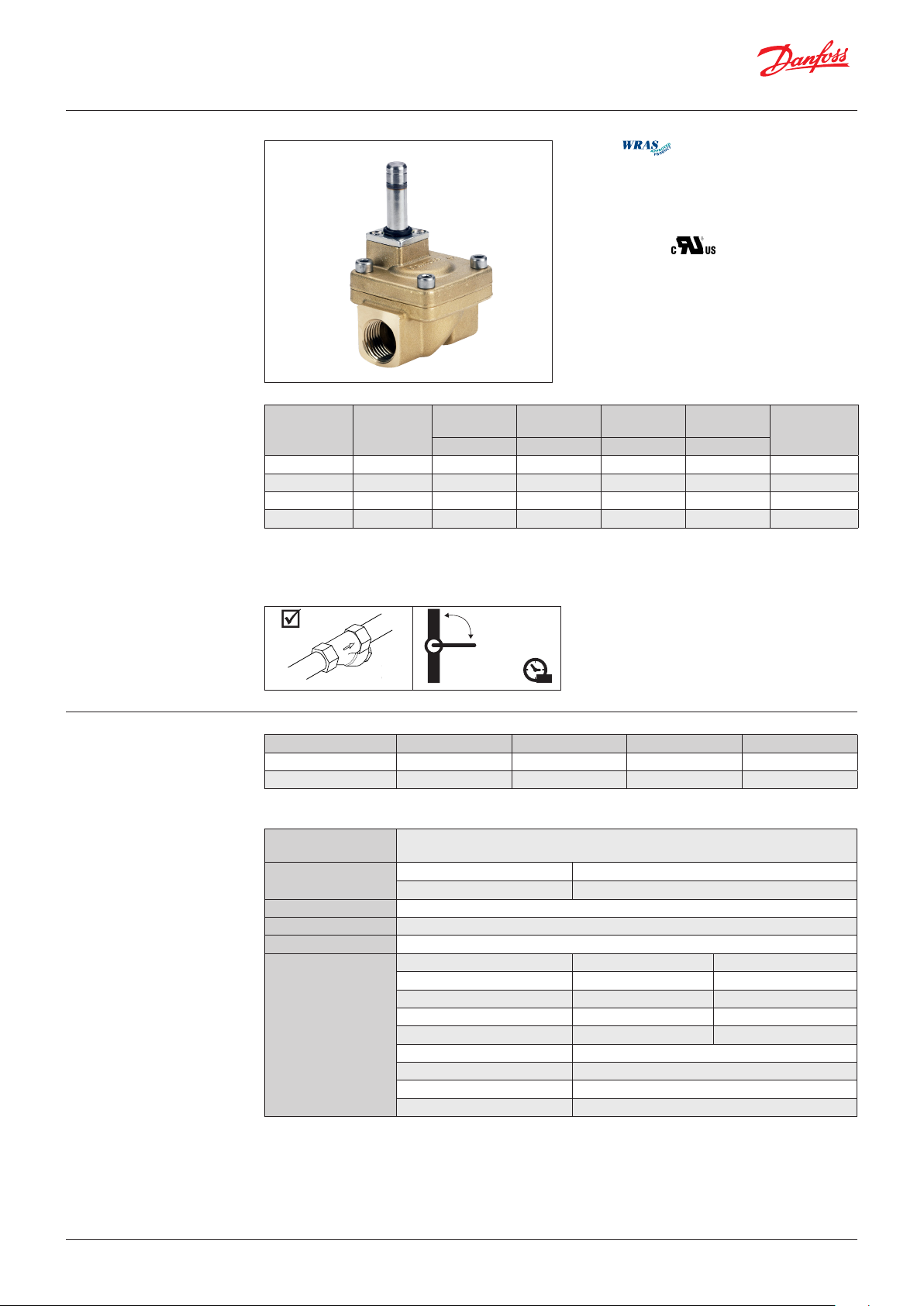
EV220W
Brass valve body, NC
y WRAS
y RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
y - Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G 3/8 EPDM 10 1.6 0 – 100 0.3 – 10 042U4410
G 1/2 EPDM 14 4 0 – 100 0.3 – 10 042U4 414
G 3/4 EPDM 18 7 0 – 100 0.3 – 10 042U 4418
G 1 EPDM 22 7 0 – 100 0.3 – 10 042U4422
See separate table for AC/AZ coils
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Kv-
value
Media temp.
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
OFF
Type EV220W 10 EV220W 14 EV220W 18 EV220W 22
Time to open [ms] 3 50 100 200 200
Time to close [ms] 3 300 400 500 500
3
Times are indicative and apply to water. Exact times will depend on pressure conditions.
Max. working
pressure (MWP)
Max. test pressure
10 bar
EV220W 10 50 bar
EV220W 14 - EV220W 22 25 bar
Ambient temperature -40 – 50 °C
Media temperature -10 – 100
Media viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body Brass W. no. 2.0401
Armature Stainless steel W. no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature stop Stainless steel W. no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W. no. 1.4303 / AISI 305
Materials
Spring Stainless steel W. no. 14310 / AISI 301
O-ring EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Diaphragm valve cone Brass CW614N, W.no. 2.0401
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 5
Page 6
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function, NC
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
Pos. no. Description
1
Coil
2
Armature spring
3
Armature
4
Pilot orifice
5
Diaphragm
6
Equalizing orifice
7
Main orifice
Dimensions and weight
Coil voltage disconnected (Closed)
When voltage is disconnected, the armature
spring (2) presses the armature (3) down against
the pilot orifice (4). Pressure builds up over the
diaphragm (5) via the equalizing orifice (6). The
diaphragm closes the main orifice (7) as soon as
the pressure over the diaphragm equals the inlet
pressure. The valve stays closed for as long as
voltage remains disconnected.
L1
L
Coil voltage connected (open)
When voltage is applied to the coil (1), the pilot
orifice (4) is opened. Since the pilot orifice is
larger than the equalizing orifice (6), pressure
over the diaphragm (5) falls and the diaphragm
is lifted clear of the main orifice (7). The valve
stays open for as long as the required minimum
differential pressure is present and voltage is
applied to the coil.
B1
H
1
H
B
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
Type
EV220W 10 51 50 50 70 13 77 81 0.56
EV220W 14 58 50 58 70 13 78 82 0.62
EV220W 18 90 50 58 70 18 79 83 0.84
EV220W 22 90 50 58 70 22 84 84 1.12
L L1 B
[mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [mm] [kg]
B1
Coil AS
H1
H
NC NO
Weight with
AS coil
AI256649466639en-000201 | 6
Page 7
90°
Max.
90
°
M
a
x
.
90°Ma
x
.
9
0
°
M
a
x.
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Mounting angle
Capacity diagram
Example for water:
Capacity for EV220W at a
differential pressure of 3 bar:
Approx. 7 m3 / h
EV220W 10
EV220W 14
EV220W 18 - EV220W 22
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 7
Page 8
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
AS/AZ,
Compact UL recognised,
clip-on coils
y Enclosure:
Up to IP65 / NEMA 4
y Used with EV220T and EV220W
y For UL recognised valves
y In accordance with:
- RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
y UL recognized
Type
AS024CS -40 – 50
AS230CS -40 – 50
AZ012DS -40 – 50 12 -10%, +6% DC 6.0 – 042N7616
AZ024DS -40 – 50 24 -10%, +6% DC 6.5 – 042N7617
Tambient Supply voltage
[°C] [V] [Hz] [W] [VA]
24 -10%, +6% 50 9.5 18
24 -10%, +6% 60 7.0 14
230 -10%, +6% 50 8.0 16
208 - 240 ±6% 60 7.0 14
Voltage
variation
Frequency
Power
consumption
Code no.
042N7608
042N7601
Technical data
Dimensions and weight
Accessories:
Cable plug
Design In accordance with UL 429
Insulation of coil windings Class H according to IEC 85
Connection Spade connector in accordance with DIN 43650 form A
Enclosure, IEC 529 IP00 with DIN spade connector, IP65 with cable plug
Plug type Cable plug (042N0156)
L without cable plug L with cable plug L with protective cap Weight
[mm] [mm] [mm] [kg]
48 72 64 0.10
Type, Form A Code no.
GDM 2011 (grey) cable plug according to DIN 43650-A PG11 042N 0156
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 8
Page 9

24h
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 6 - EV220B 12
Brass valve body, NO
y WRAS
y ACS
y PZH
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar] [Bar]
G 3/8 EPDM 6 0.7 0 – 100 20 0.1 – 10 032U1238
G 1/2 EPDM 12 2.1 0 – 100 10 0.3 – 10 032U1250
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
ON
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Max working
pressure
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
OFF
Type EV220B 6 EV220B 12
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water. The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
40 60
250 600
Installation Vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. test pressure
EV220B 6 30 bar
EV220B 12 15 bar
BB DC Up to 50 °C
Ambient temperature
BB AC Up to 80 °C
EEC BE 240 CS Up to 55 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body Brass W.no. 2.0402
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304L
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Materials
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Diaphragm valve cone Brass CW614N, W.no. 2.0401
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 9
Page 10

24h
ON
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 6 - EV220B 12
DZR Brass valve body, NO
y WRAS
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar] [Bar]
G 3/8 EPDM 6 0.7 0 – 100 20 0.1 – 10 032U5818
G 1/2 EPDM 12 2.1 0 – 100 10 0.3 – 10 032U5821
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Max working
pressure
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
OFF
Type
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water. The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
EV220B 6 EV220B 12
40 60
250 600
Installation Vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. test pressure
EV220B 6 30 bar
EV220B 12 15 bar
BB DC Up to 50 °C
Ambient temperature
BB AC Up to 80 °C
EEC BE 240 CS Up to 55 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body DZR Brass W.no. CuZn36Pb2As/CZ132
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304L
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Materials
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Diaphragm valve cone Stainless steel W.no. 1.4404
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 10
Page 11

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function, NO
1
2
8
3
4
6
7
5
Coil voltage disconnected (open):
When the voltage to the coil (8) is disconnected,
the pilot orifice (6) is open. As the pilot orifice is
larger than the equalizing orifice (4), the pressure
across the diaphragm (7) drops and therefore it
is lifted clear of the main orifice (5). The valve will
be open for as long as the minimum differential
pressure across the valve is maintained, and for
as long as the voltage to the coil is disconnected.
Pos. no. Description
1 Armature
2 Opening spring
3 Valve plate
4 Equalizing orifice
5 Main orifice
6 Pilot orifice
7 Diaphragm
8 Coil
Coil voltage connected (closed):
When voltage is applied to the coil, the valve
plate (3) is pressed down against the pilot orifice
(6). The pressure across the diaphragm (7) is built
up via the equalizing orifice (4). The diaphragm
closes the main orifice (5) as soon as the pressure
across the diaphragm is equivalent to the inlet
pressure. The valve will be closed for as long as
there is voltage to the coil.
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 11
Page 12

24h
OFF
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 6 - EV220B 12
Brass valve body, NC
y WRAS
y ACS
y PZH
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G 3/8 EPDM 6 0.7 0 – 100 0.1 – 10 032U1241
G 1/2 EPDM 12 2.5 0 – 100 0.3 – 10 032U1255
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
ON
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
Type
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water. The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
EV220B 6 EV220B 12
40 60
250 300
Installation Vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. working
pressure (MWP)
Max. test pressure
DN 6 20 bar
DN 12 10 bar
EV220B 6 30 bar
EV220B 12 15 bar
BB DC Up to 50 °C
Ambient temperature
BB AC Up to 80 °C
EEC BE 240 CS Up to 55 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body Brass W.no. 2.0402
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304L
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430FR
Materials
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Diaphragm valve cone Stainless steel W.no. 1.4404
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 12
Page 13

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function, NC
1
2
8
3
4
6
7
5
Coil voltage disconnected (closed):
When the supply voltage to the coil (8) is disconnected, the valve plate (3) is pressed down
against the pilot orifice (6) by the armature spring
(1). The pressure across the diaphragm (7) is built
up via the equalizing orifice (4). The diaphragm
closes the main orifice (5) as soon as the pressure
across the diaphragm is equivalent to the inlet
pressure. The valve will be closed for as long as
the voltage to the coil is disconnected.
Pos. no. Description
1 Armature spring
2 Armature
3 Valve plate
4 Equalizing orifice
5 Main orifice
6 Pilot orifice
7 Diaphragm
8 Coil
Coil voltage connected (open):
When voltage is applied to the coil, the pilot
orifice (6) is opened. As the pilot orifice is larger
than the equalizing orifice (4), the pressure across
the diaphragm (7) drops and therefore it is lifted
clear of the main orifice (5). The valve is now open
and will be open for as long as the minimum
differential pressure across the valve is
maintained, and for as long as there is voltage to
the coil.
Dimensions and weight
Type
EV220B 6B 45.5 43.5 32 46 68 78 13 0.22
EV220B 12B 58.0 54.0 32 46 68 81 13 0.35
L B B1 [mm] / Coil type H H
[mm] [mm] BA BB / BE BG [mm] [mm] [kg]
Weight gross valve
1
body without coil
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 13
Page 14

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Mounting angle
Capacity diagram:
Example, water: EV220B 6
NC, at 1 bar diff. pressure:
Approx: 0.7 m3 / h
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 14
Page 15

24h
ON
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 15 - EV220B 50
Brass valve body, NO
y WRAS
y ACS
y PZH
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G ½ EPDM 15 4 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7117
G ¾ EPDM 20 8 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7122
G 1 EPDM 25 11 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7127
G 1 ¼ EPDM 32 18 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7134
G 1 ½ EPDM 40 24 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7142
G 2 EPDM 50 40 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7152
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Approval
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
OFF
Main type
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water.
EV220B
15B
40 40 300 1000 1500 5000
350 1000 1000 2500 4000 10000
EV220B
20B
EV220B
25B
EV220B
32B
EV220B
40B
EV220B
50B
The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
Closing times can be changed by replacement of the equalizing orifice.
Installation Optional, but vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. working
pressure (MWP)
10 bar
Max. test pressure 20 bar
BB DC
Ambient temperature
BB AC
EEC BE240CS
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body/cover Brass W.no. 2.0402
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304 L
Materials
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 15
Page 16

24h
ON
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 15 - EV220B 25
DZR Brass valve body, NO
y WRAS
y PZH
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G 1/2 EPDM 15 4 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U5817
G 3/4 EPDM 20 8 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U7162
G 1 EPDM 25 11 0 – 120 0.3 – 10 032U5826
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
OFF
Main type EV220B 15B EV220B 20B EV220B 25B
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water.
40 40 300
1000 1000 1000
The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
Closing times can be changed by replacement of the equalizing orifice.
Installation Optional, but vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. working
pressure (MWP)
10 bar
Max. test pressure 20 bar
BB DC Up to 50 °C
Ambient temperature
BB AC Up to 80 °C
EEC BE240CS Up to 55 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body/cover DZR Brass W.no. CuZn36Pb2As/CZ132
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304 L
Materials
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 16
Page 17

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function, NO
7
Pos. no. Description
1 Coil
2 Armature spring
3 Valve plate
4 Pilot orifice
5 Diaphragm
6 Main orifice
7 Equalizing orifice
Coil voltage disconnected (open):
When the voltage to the coil (1) is disconnected,
the pilot orifice (4) is open. As the pilot orifice is
larger than the equalizing orifice (7), the pressure
across the diaphragm (5) drops and therefore it
is lifted clear of the main orifice (6). The valve will
be open for as long as the minimum differential
pressure across the valve is maintained, and for as
long as the voltage to the coil is disconnected.
Coil voltage connected (closed):
When voltage is applied to the coil (1), the valve
plate (3) is pressed down against the pilot orifice
(4). The pressure across the diaphragm (5) is built
up via the equalizing orifice (7). The diaphragm
closes the main orifice (6) as soon as the pressure
across the diaphragm is equivalent to the inlet
pressure. The valve will be closed for as long as
there is voltage to the coil.
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 17
Page 18

24h
ON
OFF
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV220B 15 - EV220B 50
Brass valve body, NC
y WRAS
y ACS
y PZH
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
y UL recognized
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G ½ EPDM 15 4 0 – 100 0.3 – 16 032U7115
G ¾ EPDM 20 8 0 – 100 0.3 – 16 032U7120
G 1 EPDM 25 11 0 – 100 0.3 – 16 032U7125
G 1 ¼ EPDM 32 18 0 – 100 0.3 – 12 032U7132
G 1 ½ EPDM 40 24 0 – 100 0.3 – 12 032U7140
G 2 EPDM 50 40 0 – 100 0.3 – 12 032U7150
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Approval
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Main type
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water.
EV220B
15B
40 40 300 1000 1500 5000
350 1000 1000 2500 4000 10000
EV220B
20B
EV220B
25B
EV220B
32B
EV220B
40B
EV220B
50B
The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
Closing times can be changed by replacement of the equalizing orifice.
Installation Optional, but vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. test pressure 20 bar
BB DC Up to 50 °C
Ambient temperature
BB AC Up to 80 °C
EEC BE240CS Up to 55 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body/cover Brass W.no. 2.0402
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304 L
Materials
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 18
Page 19

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function, NC
7
Pos. no. Description
1 Coil
2 Armature spring
3 Valve plate
4 Pilot orifice
5 Diaphragm
6 Main orifice
7 Equalizing orifice
Coil voltage disconnected (closed):
When the voltage is disconnected, the valve plate
(3) is pressed down against the pilot orifice (4) by
the armature spring (2). The pressure across the
diaphragm (5) is built up via the equalizing orifice
(7). The diaphragm closes the main orifice (6)
as soon as the pressure across the diaphragm is
equivalent to the inlet pressure. The valve will
be closed for as long as the voltage to the coil is
disconnected.
Coil voltage connected (open):
When voltage is applied to the coil (1), the pilot
orifice (4) is opened. As the pilot orifice is larger
than the equalizing orifice (7), the pressure across
the diaphragm (5) drops and therefore it is lifted
clear of the main orifice (6). The valve is now
open for unimpeded flow and will be open for as
long as the minimum differential pressure across
the valve is maintained, and for as long as there is
voltage to the coil.
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 19
Page 20

24h
ON
OFF
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
EV228B 15 - EV228B 25
Latching DZR brass
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
- Pressure Equipment Directive 2014/68/EU
ISO228/1
connection
Seal
material
Orifice
size
[mm] [m³/h] [°C] [Bar]
G 1/2 EPDM 15 4 0 – 60 0.3 – 10 032U7468
G 3/4 EPDM 20 8 0 – 60 0.3 – 10 032U7469
G 1 EPDM 25 11 0 – 60 0.3 – 10 032U7470
1
) It is recommended to install a filter in front of the valve.
2
) In water applications, exercise the valves at least once every 24 hours, meaning change the state of the valve.
The valve exercise will minimize the risk of the valve sticking due to calcium carbonate, zinc or iron oxide build-up.
Kv-
value
Media
temperature
Differential
pressure
Code no.
Technical data
Main type EV228B 15B EV228B 20B EV228B 25B
Time to open [ms] 3
Time to close [ms] 3
3
The times are indicative and apply to water.
40 40 300
350 1000 1000
The exact times will depend on the pressure conditions.
Closing times can be changed by replacement of the equalizing orifice.
Installation Optional, but vertical solenoid system is recommended
Max. working
pressure (MWP)
10 bar
Max. test pressure 20 bar
Ambient temperature Up to 50 °C
Viscosity Max. 50 cSt
Valve body/cover DZR Brass W.no. CuZn36Pb2As/CZ132
Armature Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Armature tube Stainless steel W.no. 1.4306 / AISI 304 L
Materials
Armature stop Stainless steel W.no. 1.4105 / AISI 430 FR
Springs Stainless steel W.no. 1.4310 / AISI 301
O-rings EPDM
Valve plate EPDM
Diaphragm EPDM
Switch power (on/off)
018F7396 (12V DC)
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 20
Page 21

+
+
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Function
+
–
8
+
Fig. a
7
Pos. no. Description
1 Coil
2 Armature spring
3 Valve plate
4 Pilot orifice
5 Diaphragm
6 Main orifice
7 Equalizing orifice
8 Permanent magnet
When – (minus) is supplied to the right terminal
pin and + (plus) to the left (see fig. a), the valve
plate is pressed down against the pilot orifice (4)
by the armature spring (2).
The pressure across the diaphragm (5) is built
up via the equalizing orifice (7). The diaphragm
closes the main orifice (6) as soon as the
pressure across the diaphragm is equivalent to
the inlet pressure. The valve will stay closed, until
the poles are switched (see fig. b).
–
+
+
Fig. b
Switching poles
When + (plus) is supplied to the right terminal
pin and – (minus) to the left (see fig. b), the pilot
orifice (4) is opened. As the pilot orifice is larger
than the equalizing orifice (7), the pressure across
the diaphragm (5) drops and therefore it is lifted
clear of the main orifice (6). The valve is now
open for flow and will stay open as long as the
minimum differential pressure across the valve
is maintained, until the poles are switched back
(see fig. a).
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 21
Page 22

EV220B
EV220B
EV228B
EV228B
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Dimensions and weight
Danfoss
32U1783.10
Mounting angle
Type
EV220B 15 80.0 52.0 32 46 68 45 99 15.0 0.7
EV228B 15 80.0 52.0 32 46 68 45 99 15.0 0.7
EV220B 20 90.0 58.0 32 46 68 45 103 18.0 0.9
EV228B 20 90.0 58.0 32 46 68 45 103 18.0 0.9
EV220B 25 109.0 70.0 32 46 68 45 113 22.0 1.3
EV228B 25 109.0 70.0 32 46 68 45 113 22.0 1.3
EV220B 32 120.0 82.0 32 46 68 45 120 27.0 2.0
EV220B 40 130.0 95.0 32 46 68 45 129 32.0 3.0
EV220B 50 162.0 113.0 32 46 68 45 135 37.0 4.8
L B B1 [mm] / coil type H H
[mm] [mm] BA BB / BE BG / BO BP [mm] [mm] [kg]
1
Weight
without coil
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 22
Page 23

Danfoss
A32U1267.01
EV220/228BW 15 NC/NO/UN
EV220/228BW 20 NC/NO/UN
EV220/228BW 25 NC/NO/UN
EV220/228BW 32 NC/NO/UN
EV220/228BW 40 NC/NO/UN
EV220/228BW 50 NC/NO/UN
Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
Capacity diagrams:
Example, water:
Capacity for
EV220B / EV228B 15B at
differential pressure of 3 bar.
Approx. 7 m3 / h
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 23
Page 24

Data sheet | Solenoid valves for water shut off and leak detection, Types EV220T, EV220W, EV220B, and EV228B
BB high performance coils
y Enclosure:
- IP00 version with DIN 43650 A spade
connectors
- IP20 version with protective cap
- IP65 version with mounted cable plug
y In accordance with:
- RoHS Directive 2011/65/EU
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
- EN60730-2-8
Type
BB024AS -40 – 80 24 -15%, +10% 50 NO, NC 11 19 018F7358
BB230AS -40 – 80 220 - 230 -15%, +10% 50 NO, NC 11 19 018F7351
BB012DS -40 – 50 12 ±10% DC
BB024DS -40 – 50 24 ±10% DC
Tambient
[°C] [V] [Hz] [W] [VA]
Supply
voltage
Voltage
variation
Frequency
Control
NO, NC,
Latching
NO, NC,
Latching
Power
consumption
13 – 018F7396
16 – 018F7397
Code no.
Technical data
Dimensions and weight
Design In accordance with VDE 0580
Insulation of coil windings Class H according to IEC 85
Connection Spade connector in accordance with DIN 43650 form A
Enclosure, IEC 529 IP00 with spade connector, IP20 with protective cap, IP65 with cable plug
Duty rating Continuous
Plug type Cable plug (042N0156)
without cable plug
L
with protective cap
[mm] [mm] [mm] [kg]
62 77 85 0.24
L
L
with cable plug
Weight
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10
AI256649466639en-000201 | 24
Page 25

Accessories:
Cable plug
Type, Form A Code no.
GDM 2011 (grey) cable plug according to DIN 43650-A PG11 042N 0156
EEC Electronic coil controller
Type
BE240CS -25 – 55
Tambient
[°C] [V] [Hz] [W]
EEC electronic coil controller for solenoid valves,
type EV220B.
The EEC gives the coil a short over-boost, and
controls the armature speed:
y Low power consumption (holding power: 4 W)
y Reduced noise during operation
y Increased MOPD compared to standard coils
y Increased lifetime of the solenoid valve
y Enclosure:
- IP67 version
y In accordance with:
- Low Voltage Directive 2014/35/EU
- EN60730-1
Supply
voltage
208 – 240 ±10% 60 NC, NO 4
208 – 240 ±10% 50 NC, NO 4
Voltage
variation
Frequency
Control
Power
consumption
Code no.
018F6783
© Danfoss | DCS (sb) | 2020.10 AI256649466639en-000201 | 25
 Loading...
Loading...