
User Guide
Integrated Motor / Generator
EM-PME375
www.danfoss.com

User Guide
EM-PME375
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
July 2021 Updated user guide 0201
2 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Contents
General information
Safety information
Product overview
Design principles
Transportation and storage
Installation
Operation
Maintenance
Intended use of the user guide................................................................................................................................................... 5
Product naming convention ....................................................................................................................................................... 5
Conformity according to standards...........................................................................................................................................6
Warranty.............................................................................................................................................................................................. 6
Terms and abbreviations...............................................................................................................................................................7
Responsibility of the manufacturer........................................................................................................................................... 7
General safety statement...............................................................................................................................................................8
Safety message signal words....................................................................................................................................................... 8
Safety symbols...................................................................................................................................................................................8
Personal protective equipment.................................................................................................................................................. 9
Security features............................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC).....................................................................................................................................10
Intended use of the electric machine.....................................................................................................................................12
Used technology............................................................................................................................................................................ 12
System introduction..................................................................................................................................................................... 13
Connections and interfaces........................................................................................................................................................14
Rating plate......................................................................................................................................................................................15
Tightening torques........................................................................................................................................................................17
System design.................................................................................................................................................................................18
Cooling and temperature measurement ........................................................................................................................18
Inverter......................................................................................................................................................................................... 18
Mounting structure....................................................................................................................................................................... 20
Supporting structure requirements...................................................................................................................................20
Shaft alignment and load...................................................................................................................................................... 21
Customer connection interface design instruction..................................................................................................... 22
Transportation................................................................................................................................................................................ 29
Receiving and unpacking............................................................................................................................................................29
Lifting................................................................................................................................................................................................. 29
Storage...............................................................................................................................................................................................31
Extended storage......................................................................................................................................................................31
Required tools.................................................................................................................................................................................33
Insulation resistance test.............................................................................................................................................................33
Mechanical installation................................................................................................................................................................33
Allowed mounting positions................................................................................................................................................33
Mounting the electric machine........................................................................................................................................... 34
Installation procedure.............................................................................................................................................................36
Cooling connections............................................................................................................................................................... 47
Electrical installation.....................................................................................................................................................................48
Power connections.................................................................................................................................................................. 48
High voltage connection..................................................................................................................................................48
Connection diagram.......................................................................................................................................................... 50
Low voltage connections.......................................................................................................................................................50
Grounding connections......................................................................................................................................................... 52
Operation conditions....................................................................................................................................................................56
Condition monitoring during operation...............................................................................................................................56
Recommended coolants............................................................................................................................................................. 56
Emergency operation...................................................................................................................................................................57
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 3

User Guide
EM-PME375
Contents
Regular maintenance................................................................................................................................................................... 58
Cleaning............................................................................................................................................................................................ 59
Cooling system maintenance....................................................................................................................................................59
Dismounting
Troubleshooting
Aftersales
Service policy...................................................................................................................................................................................62
Service parts.....................................................................................................................................................................................62
Disposal
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
4 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
General information
Intended use of the user guide
Product naming convention
This user guide is the installation, operation and maintenance user guide for the EM-PME375-T150 and
EM-PME375-T200 electric machines.
This user guide contains instructions necessary to safely and properly handle, install, operate and
maintain the electric machine. They should be brought to the attention of anyone who installs, operates
or maintains the machine or associated equipment.
All of the safety warnings and instructions in this user guide must be followed to prevent injury to
personnel or damage to property. Only qualified and authorized personnel, familiar with health and
safety requirements and national legislation, shall be permitted to handle, install, operate and maintain
the device.
This user guide must be kept for future reference during installation, operation and maintenance.
This user guide uses illustrations as examples only. Illustrations in this user guide may not necessarily
reflect all system features.
In this user guide, EM-PME family permanent magnet motors and generators are referred to as the
electric machine.
Frame model indicates dimensions and electrical characteristics of the electric machine. The following
naming convention is used to refer to the electric machine frame model:
EM-PME375-T150-XXXX+XX
•
EM-PME375-T200-XXXX+XX
•
The naming codes of the electric machine
Part of the name Meaning
EM Electric Machine
PMIXXX or PMEXXX Permanent Magnet Internal and a number relative to
the diameter of the electric machine, or Permanent
Magnet External and a number relative to diameter of the
electric machine
TXXXX Average continuous torque of the motor range, relative
to the lenght of the machine
XXXX Rated rotation speed
+XX Options, see option table below. Standard options are
indicated by a star (*).
The power input of the electrical machine requires a three phase power system.
The electric machine can include some of the options available. The options of the electric machine are
shown also in the rating plate, following the frame model code. Note! Only options that differ from the
standard delivery are indicated. Following options are used, see Table below. For detailed information of
the models, options and characteristics, see product data sheets.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 5
User Guide
EM-PME375
General information
EM-PME375-T150 and EM-PME375-T200 options
Variant Code Description Additional information
High voltage connector * High voltage plug-in
Rotation sensor * None No resolver
Conformity according to standards
The electric machine as partly completed machinery is in conformity with the following other directive(s),
harmonized standard(s) or other normative document(s), provided it/they are used in accordance with
our instructions. As partly completed machinery the product itself does not have declaration of
conformity but instead declaration of incorporation. This partly completed machinery must not be used
before the final machinery into which it is to be incorporated has been declared in conformity with the
Machinery Directive and other relevant directives.
One plug-in connector per phase for 50
connectors for 50 mm
cables
+HVC1 High voltage plug-in
connectors for 35 mm
cables
+RES1 Resolver In-built non contacting resolver, 5-pole
2
mm2 cable
One plug-in connector per phase for
2
35 mm2 cable
pair
Warranty
Applicable Directives and standards
Standard Explanation
Low Voltage Directive
2006/95/EC (until 19.4.2016)
and Low Voltage Directive
2014/35/EU (from 20.4.2016
onwards)
Machinery Directive
2006/42/EC
IEC 60034-1:2010 Rotating electrical machines - Part 1: Rating and performance
IEC 60034-5:2000/A1:2006 Rotating electrical machines - Part 5: Degrees of protection provided by the integral
IEC 60034-6:1991 Rotating electrical machines - Part 6: Methods of cooling
IEC 60034-7:1992/A1:2000 Rotating electrical machines - Part 7: Classification of types of construction,
IEC 60034-8:2007/A1:2014 Rotating electrical machines - Part 8: Terminal markings and direction of rotation
IEC 60034-14:2018 Amendment 1 - Rotating electrical machines - Part 14: Mechanical vibration of
Electrical equipment means any equipment designed for use with a voltage rating
of between 50 and 1000 V for alternating current. This electric machine is subject to
the Low Voltage Directive 2006/95/EC or 2014/35/EC.
This electric machine is partly subject to the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and it
is considered as partly completed machinery, as a part of the final machinery.
design of rotating electrical machines (IP code) - Classification
mounting arrangements and connection box position (IM Code)
certain machines with shaft heights 56 mm and higher - Measurement, evaluation
and limits of vibration severity.
Danfoss offers warranty against defects in workmanship and materials for its products for a period of
twelve (12) months from commissioning or eighteen months (18) from delivery (Incoterms-EXW),
whichever occurs first.
In order for the warranty to be valid, the customer must follow the requirements of this and all related
documents, especially those set out in the product installation and maintenance, as well as the applicable
standards and regulations in force in each country.
Defects arising from the improper or negligent use, operation, and/or installation of the equipment, nonexecution of regular preventive maintenance, as well as defects resulting from external factors or
equipment and components not supplied/recommended by Danfoss, will not be covered by the
warranty.
6 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
General information
Terms and abbreviations
The warranty will not apply if the customer at its own discretion makes repairs and/or modifications to
the equipment without prior written consent from Danfoss.
The symbols, terms and abbreviations in the Tables below are possibly used in this manual.
Symbols
Symbol Variable Unit
U Rated voltage (phase-to-phase AC) V
I Rated current (AC) A
P Rated Power (S1) kW
T Rated torque (S1) at rated speed Nm
T
max
n Rated speed rpm
Max n Maximum speed rpm
f Rated supply frequency at nominal speed Hz
PF Power factor (cosφ)
Q
c
T
c
T
amb
RES_COS Cosine signal received from the resolver deg
RES_SIN Sinusoidal signal received from the machine resolver deg
GND Ground in electrical connections
Ω (Ohm) Resistance Ω
Maximum torque Nm
Rated coolant liquid flow l/min
Rated coolant liquid input temperature °C
Rated ambient temperature °C
rms
rms
Term / abbreviation
Term/ Abbreviation Explanation
Resolver Rotation meter in electric machines, used for measuring degrees of rotation
AC Alternating current
DC Direct current
PMSM Permanent Magnet Synchronous Machine
SRPM Syncronous Reluctance assisted Permanent Magnet
S1 Duty type according to the IEC60034; Continuous running duty
S9 Duty type according to the IEC60034; Duty with non-periodic load and speed variations
Responsibility of the manufacturer
Danfoss is responsible for the safety, reliability and performance of the electric machine only if:
•
Handling, mounting, installation, operation and maintenance are done by qualified and authorized
personnel.
•
The installation of the system complies with the requirements of the appropriate regulations.
•
The electric machine is used in accordance with the instructions in this user guide.
•
The electric machine is installed, maintained and serviced in accordance with the instructions in this
user guide.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 7
User Guide
EM-PME375
Safety information
General safety statement
Safety message signal words
•
The electric machine is intended for use as a component for industrial and commercial installations.
The end product containing the electric machine must conform with all related regulations.
•
The use of the electric machine is prohibited in hazardous areas unless it is expressly designed for
such use.
•
The electric machine is intended for installation, use and maintenance by qualified personnel, familiar
with health and safety requirements and national legislation. Ignoring these instructions may
invalidate all applicable warranties.
•
These instructions must be followed to make sure of safe and correct installation, operation and
maintenance of the electric machine. They should be brought to the attention of anyone who installs,
operates or maintains the electric machine or associated equipment.
•
High voltage and rotating parts can cause serious or fatal injuries. For electric machine covered by
this user guide, it is important to observe safety precautions to protect personnel from possible
injury.
Safety message signal words indicate the severity of a potential hazard.
DANGER Indicates an imminently hazardous situation which, if not avoided, will result in death or serious
injury.
WARNING Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in death or
serious injury.
CAUTION Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, may result in minor or
moderate injury. CAUTION may also alert against unsafe practices.
NOTICE Indicates a potentially hazardous situation which, if not avoided, could result in property
damage.
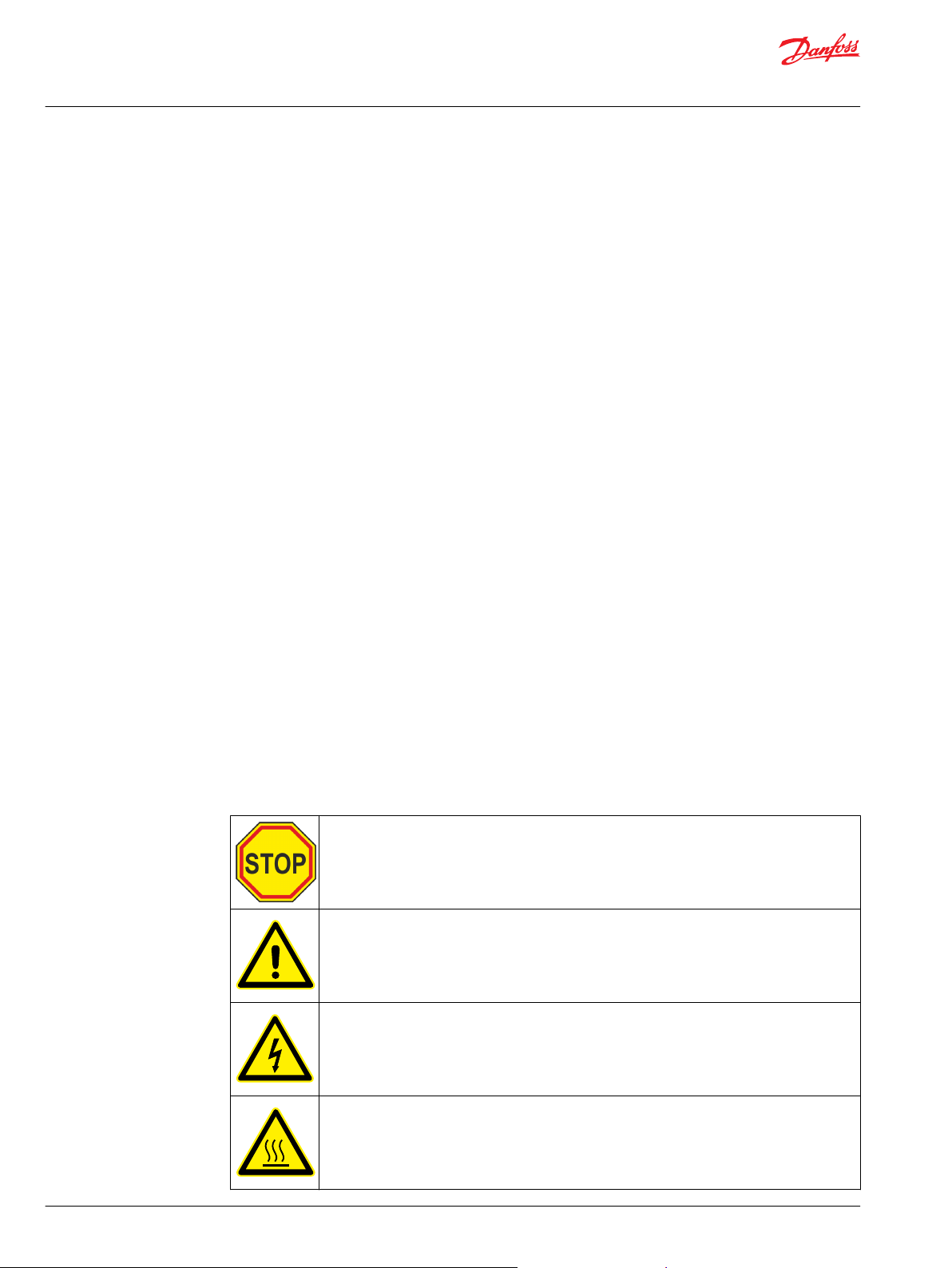
Safety symbols
The following safety and information related symbols appear in this user guide and on the electric
machine.
Danger
This symbol is identified by a yellow background, red octagonal band and a black STOP text.
It indicates a hazardous situation that causes severe injury or death. Action indicated by this
symbol may not be executed.
General warning
This symbol is identified by a yellow background, black triangular band, and a black
exclamation point symbol. It indicates a general potentially hazardous situation.
Electric shock warning
The symbol is identified by a yellow background, black triangular band, and a black
arrowhead symbol. It indicates dangerous electrical voltage that could cause an electric shock
to a person.
Burn warning
The symbol is identified by a yellow background, black triangular band, and a black wavy
lines symbol. It indicates a hot device that could cause burns to a person.
The symbol also indicates that the device should be placed and installed so that contact with
its potentially hot surface is not possible.
8 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Safety information
Magnet warning
The symbol is identified by a yellow background, black triangular band, and a black magnet
symbol. It indicates strong magnetic field that could cause harm to a person or property.
Rotating shaft warning
The symbol is identified by a yellow background, black triangular band, and a black rotating
shaft symbol. It indicates strong rotating shaft that could cause harm to a person or property.
General Information.
Read the instructions in the user guide.
Personal protective equipment
Personal protective equipment shall be used when necessary during handling, installation and
maintenance of the electric machine to avoid injury.
Use eye protective equipment like safety goggles or mask when you work with the electric
machine. Permanent damage to the eye could be caused if bearing grease, melted nitrile
rubber (radial lip seal), glycol or other fluids splash.
Use hearing protective equipment when you work on the electric machine. Hearing injuries
can be caused by too loud noise (noise in excess of 85 dBA).
Use head protective equipment like helmet when you lift the electric machine! Head injuries
can be caused by object impact.
Use cut resistant gloves when you handle and maintain the electric machine. There is a risk of
cut injuries.
Use protective footwear when you lift or move the electric machine! Foot injuries could be
caused if lifting system or lifting brackets fail.
Security features
The electric machines have at least three PT100 temperature sensors in the windings. The amount of the
sensors depend on the options chosen. The temperature signal(s) can be read out from the measurement
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 9

User Guide
EM-PME375
Safety information
connector of the electric machine. You can connect the temperature signal to the temperature
surveillance pin in the inverter (EC-C) and make sure that the inverter has the temperature protection
feature of the electric machine activated.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
EMC stands for Electromagnetic compatibility. It is the ability of electric equipment to operate without
problems within an electromagnetic environment. Likewise, the equipment must not disturb or interfere
with any other product or system within its locality. This is a legal requirement for all equipment taken
into service within the European Economic Area (EEA).
Our products are designed with high standards of EMC in mind. Connect the power lines and groundings
along the instructions in this user guide to achieve the required level of EMI protection.
It is the responsibility of the installer to make sure that the equipment or system into which the product is
incorporated complies with the EMC legislation of the country of use. Within the European Union,
equipment into which this product is incorporated must comply with the EMC Directive 2014/30/EU.
When interfacing other equipment, connect only equipment that are specified as part of the
system and that are compatible.
Magnetic and electromagnetic fields generated near the current-carrying conductors and
permanent magnets in electric machines represent a health danger to persons with heart
pacemakers, metal implants and hearing aids. Persons with a heart pacemaker, metal
implants or hearing aids must consult a doctor before they enter the following areas:
•
Areas in which electric equipment and parts are operated
•
Areas in which electric equipment with permanent magnets are stored, mounted,
operated or repaired
If necessary, perform a special electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) test on the installation.
10 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
The electric machine is not a complete machine as such, but it must be integrated to another
system. This requires more work and planning than normal electric machine does.
For harsh conditions, like salty air in marine applications, it is recommended to check the
surface treatment possibilities with the factory.
The electric machines have been developed especially for heavy duty, marine and transportation
applications. They are more reliable, smaller, lighter and more efficient than conventional products on
the market.
Typical applications of the electric machines are:
Motor (electric propulsion) and generator for hybrid marine vessels or mobile work machine and bus
•
parallel hybrid applications.
Traction motor and generator for electrical or hybrid electrical mobile work machines or buses.
•
The electric machines feature Synchronous Reluctance assisted Permanent Magnet (SRPM) motor
technology, having several advanced features:
Extremely compact and robust structure.
•
High efficiency throughout the operation range.
•
Liquid cooling with water/glycol mixture.
•
Low coolant flow required.
•
High allowed coolant temperature.
•
Possibility for IP65 enclosure class to maximize reliability.
•
Multiple mounting possibilities.
•
Extended speed and torque capabilities compared to standard PM machines.
•
Machine structure designed to be able to produce high starting torques (instant torque to non-
•
moving wheel).
Optimized speed range to meet most common gear ratios used in heavy mobile machinery.
•
The electric machine
The integrated electric machines have several frame models (sizes) to be the optimal solutions for several
applications. These are T150 and T200 frames. The electric machines also have options for temperature
sensors.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 11

User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
Intended use of the electric machine
This electric machine is intended to be used as a motor or generator and as a part of a machinery, for
example in:
Power train of a marine vessel, transportation vehicle or a heavy duty work machine.
•
Power generation equipment.
•
In a power generation equipment the electric machines are intended to be powered by a prime mover,
for example, an internal combustion engine and controlled by the above mentioned electric power
inverter.
The electric machine is solely intended for professional use, and may be operated only by trained
professionals. The maintenance of the electric machine may be done only by trained professionals.
Forbidden use of the electric machine
It is forbidden to use, handle and maintain the machine in following ways (including but not limited to):
•
Using the electric machine for other purposes than defined in this user guide.
•
Disregarding the obligation to comply with the user guide, safety signs and rating plate of the electric
machine.
•
Using the electric machine, making adjustments and maintenance without first reading this user
guide.
•
Exceeding the designed limits during the electric machine operation.
•
Using non-original service parts of wrong material causing corrosion problems and mechanical
failures in time.
•
Operating and performing maintenance for the electric machine without appropriate personal
protective equipment.
•
Using electric machine parts like frame, shaft end or terminal box for climbing or for support for other
structures.
•
Causing any kind of impact forces to the electric machine (for example hitting or hammering or
dropping objects).
•
Operating the electric machine with electric connections other than defined in the user guide and/or
other documents.
•
Operating the electric machine with insufficiently tightened connections or cable glands.
•
Operating the electric machine with power cables routed against the instructions.
•
Operating the electric machine without properly dimensioned and operating cooling system.
•
Operating the electric machine without following the bearing lubrication instructions.
•
Touching the connection terminal of the electric machine or doing maintenance or adjustment
operations on the electric machine with the electricity connected.
•
Touching the connection terminal if the rotor can be turned by an external prime mover.
•
Lifting the electric machine from wrong lifting points and without correct lifting equipment.
•
Lifting additional load with the machine.
•
Storing the electric machine outdoors in wet or dusty conditions.
•
Storing the electric machine without correct support to prevent rolling or falling of the machines.
•
Using the electric machine in potentially explosive environment.
•
Allowing dirt or liquid to enter into the electric machine or connection box.
•
Using cables that cannot withstand the maximum currents of the electric machine.
Used technology
This electric machine is a Synchronous Reluctance assisted Permanent Magnet (SRPM) machine. This
technology has several benefits compared to standard permanent magnet (PM) technology and
traditional induction machine (IM) technology. The SRPM technology combines the benefits of PM and
Synchronous Reluctance technology, having increased torque capability over wide speed range and
ability to produce torque to higher speeds. The machine efficiency at lower speeds is also good.
12 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
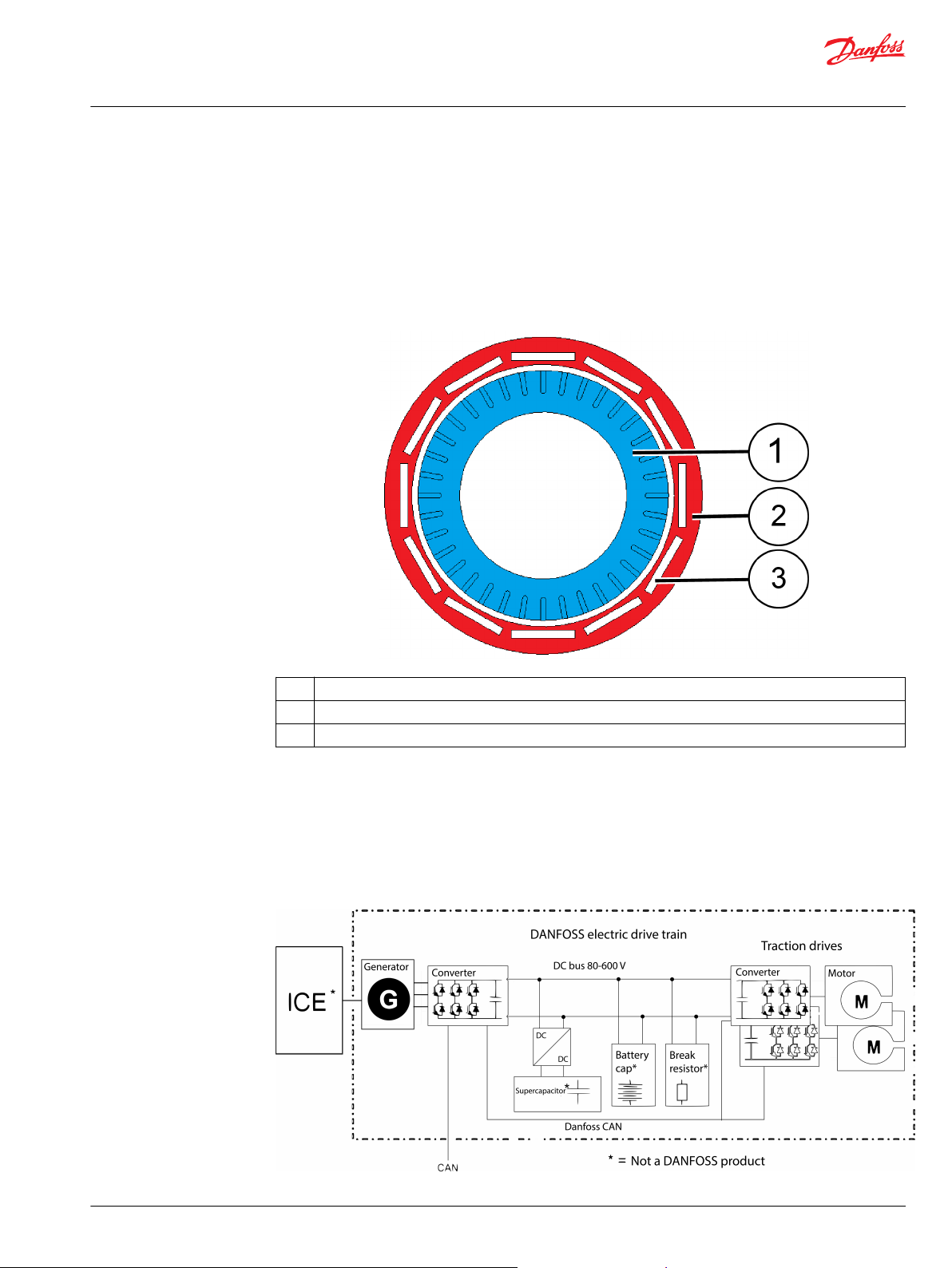
The supply current to the stator windings create rotating magnetic field, which in turn rotates the rotor
containing permanent magnets. In the synchronous permanent magnet machine, the rotation of the
rotor (shaft) is synchronized with the frequency of the power supply current. The reluctance technology
maximizes the pull-out torque of the machine.
The permanent magnets of the rotor are of salient-pole design, having embedded permanent magnets in
the rotor structure. This structure makes the machine mechanically more stable and capable of higher
speed operations. See Figure below illustrating the magnet topology of the electric machine. The Figure
shows the principle only, and is not an exact illustration of the structure.
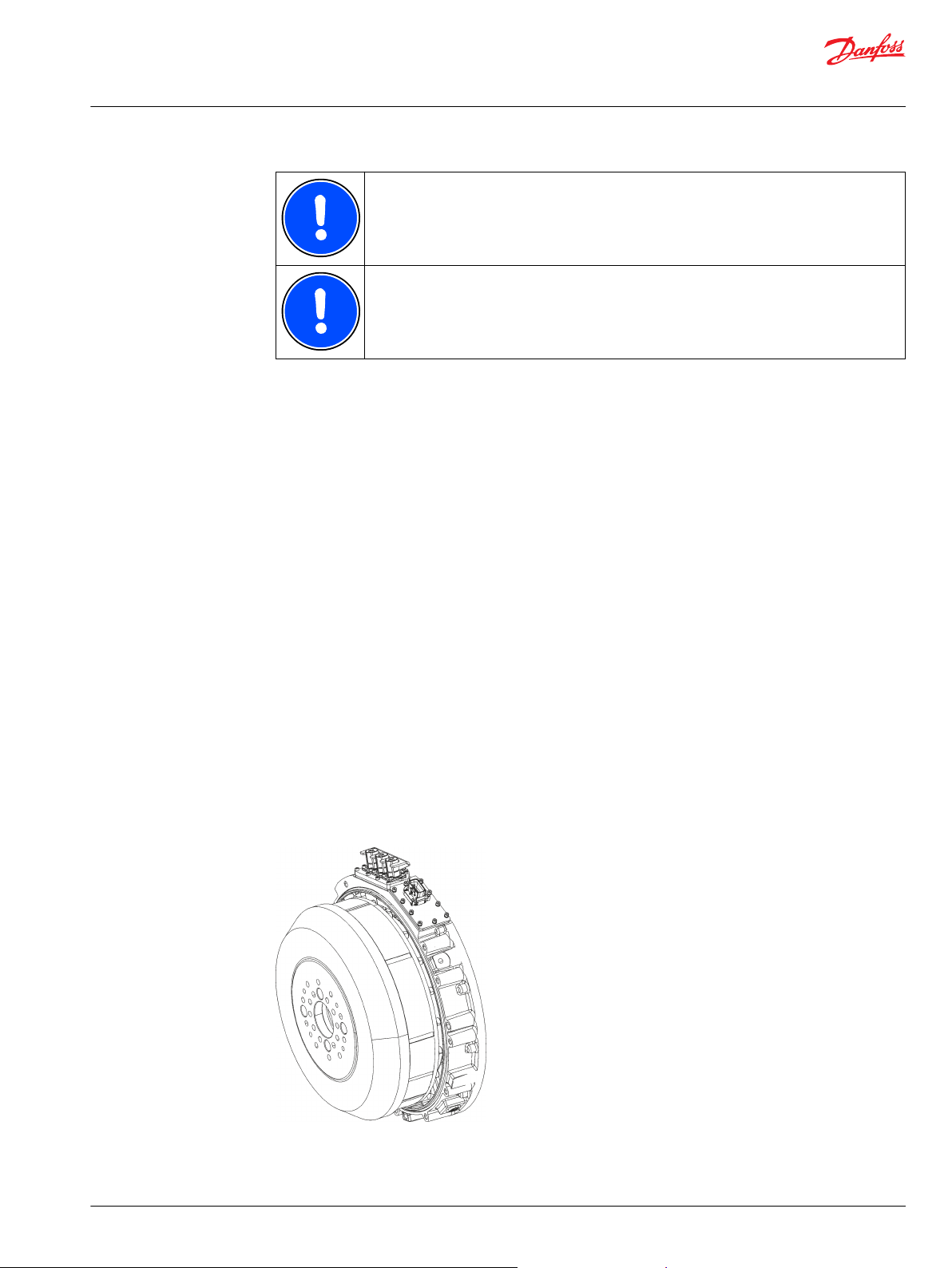
System introduction
Machine topology
1 Electric machine stator and stator windings
2 Electric machine rotor
3 Permanent magnets in the rotor
Danfoss provides electric drive trains for applications in heavy mobile work machines, marine vessels and
buses. The drive trains include all essential components from converting from traditional to hybrid
electric (HEV) or electric vehicle (EV) solutions. Danfoss technology saves fuel and lowers emission and
noise levels.
Overview of the Danfoss drive train system
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 13
User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
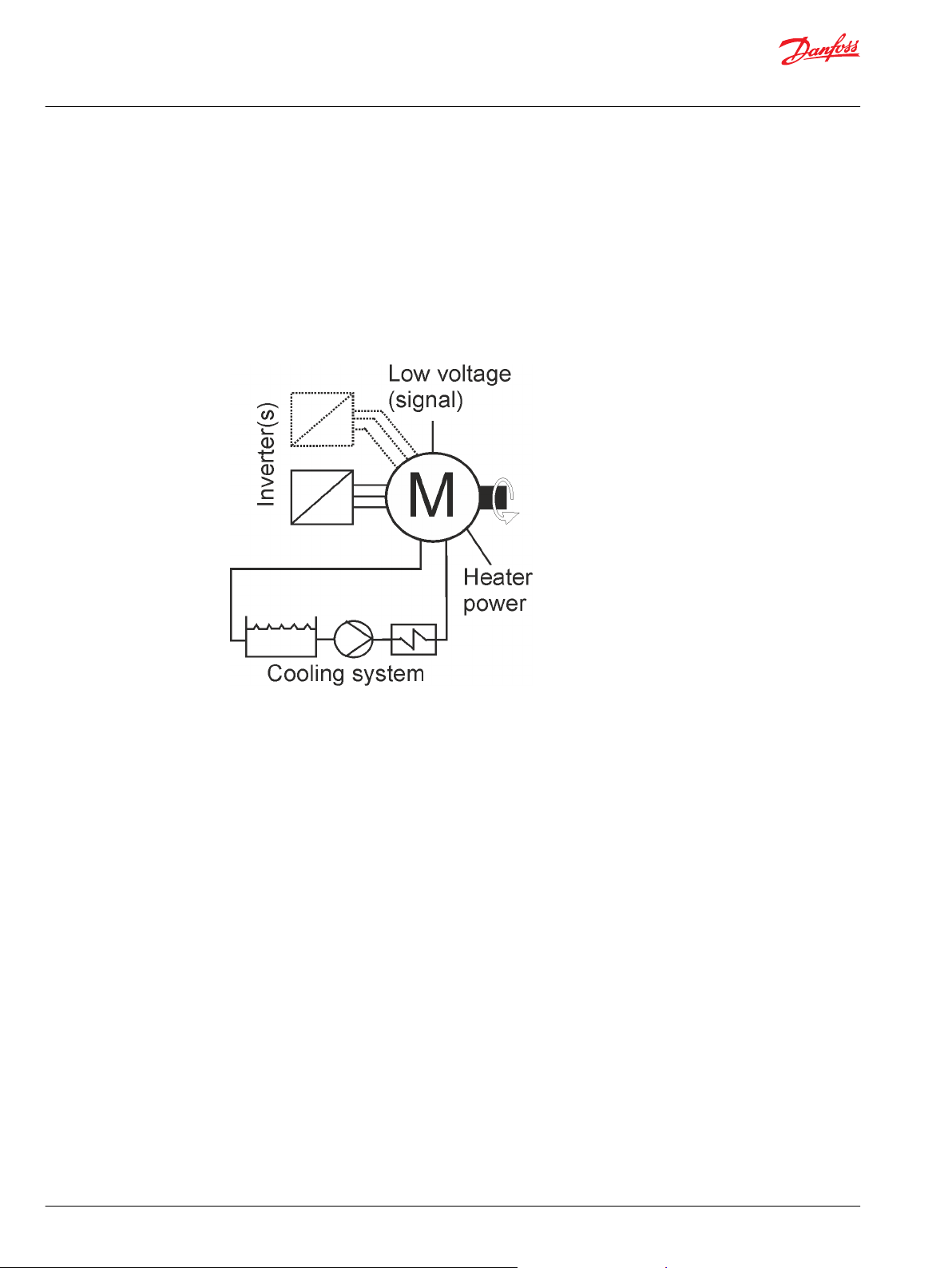
The electric machines are liquid cooled with water/glycol mixture. For more information, see
Chapter Cooling connections.
A low voltage measurement signal connector is attached to the electric machines. Different temperature
and resolver signals can be read, depending on the machine options chosen. For more information about
the connection, see Chapter Low voltage connections.
The electric machines (some models) can be equipped with one or two anti-condensations heater(s),
depending on the machine type and the option chosen. The heater is used to prevent any water
condensing inside the machine enclosure.
Overview of electric machine system
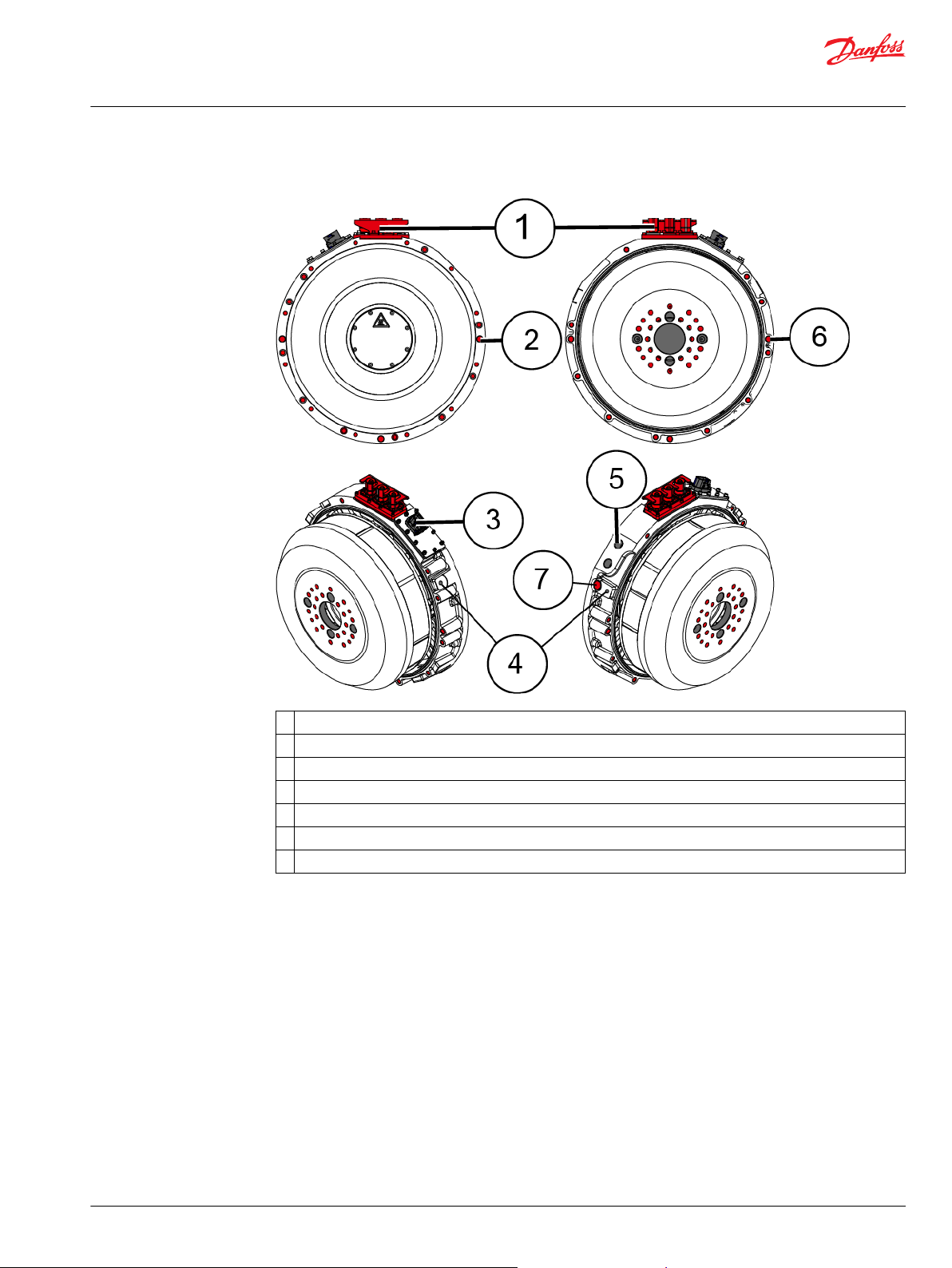
Connections and interfaces
The electric machines are connected mechanically and electrically as a part of a machinery or as a part of
a power generation equipment.
Mechanical interfaces:
Lifting points.
•
Flange mounting (D-end and N-end).
•
Cooling system connections (bores).
•
Air ventilation plug.
•
Electrical interfaces:
Power connections.
•
Measurement connections.
•
Low voltage (measurement signal) grounding connection.
•
Power grounding connection.
•
14 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
Connections and interfaces
Rating plate
1 Power connections
2 N-end flange mounting
3 Low voltage connector (measurement connector), including low voltage grounding connector
4 Lifting points
5 Cooling system connections (bores)
6 D-end flange mounting
7 Air ventilation plug
Each electric machine has a rating plate which can be found on the machine frame. The rating plate
contains machine rating and identification. The rating values in the Figure below are not correct for this
machine. See the rating plate on the machine and data sheets for the correct values.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 15

User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
Rating plate
Rating plate fields
Field Explanation Unit
1 Electric machine product family: EM-PMI or EM-PME
2 Electric machine type code and options
Serial No. Serial number
U Rated voltage V
I Rated current (AC) I
n Rated speed rpm
PF Power factor
f Rated supply frequency at nominal speed Hz
Q
c
Pole pairs Number of magnetic pole pairs of the machine
T
c
Mounting Allowed mounting position according to IEC60034-7
Mass Mass of the electric machine kg
Duty Defined rotating electric machine duty cycles by IEC60034-1 standard
T
amb
IP rating Enclosure class according to IEC60034-5
Cooling Cooling method according to IEC60034-6
Rotation Direction of rotor rotation with default phase order. Observed facing the D-end.
Max n Maximum rotation speed rpm
Insul. class Temperature rating (class) of insulation of the electric machine according to IEC60034-1
Temp. class Temperature rating (class) of individual insulation materials of the insulation according to
Rated coolant liquid flow l/min
Rated coolant liquid input temperature °C
Rated ambient temperature °C
IEC60034-1
rms
rms
16 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
Product overview
Tightening torques
Rating plate fields (continued)
Bear. / D-end Bearing type (types) in the D-end of the electric machine
Bear. / N-end Bearing type in the N-end of the electric machine
Max. pressure Cooling liquid max pressure
CE Depending on the details of the delivery, the rating plate might not have CE-marking
Tightening torque tolerance is +/- 5% of the specified tightening torque.
Use threadlocking adhesive for RST bolts.
Do not install dry screws or other fastening equipment.
Add suitable lubrication, for example Wuerth HSP 1400, to prevent excess friction.
Tightening torques to use unless otherwise noted
8.8 10.9 12.9
Thread Nm Nm Nm
M5 7 10 11
M6 11 17 19
M8 27 40 47
M10 54 79 93
M12 93 137 160
M14 148 218 255
M16 230 338 395
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 17

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
System design
This Chapter describes design principles that must be taken into account when designing the system
using the electric machine.
Cooling and temperature measurement
Do not operate the electric machine without correctly dimensioned and operating cooling
system.
Mount the electric machine in correct position, see Chapter Allowed mounting position.
When you connect the cooling system make sure that the cooling medium flows freely in and
out from the electric machine with the cooling medium flow equal or higher than rated.
The cooling medium temperature at the inlet of the electric machine must be lower or equal
to the rated temperature.
See more detailed information about coolant connection bore specifications, required coolant liquid flow
and other specifications in the product data sheet. Rated values can be found from the electric machine
rating plate.
The electric machine has at least one PT100 temperature sensor in the windings. The amount of the
sensors depend on the options chosen. The temperature signal(s) can be read out from the measurement
connector of the machine.
You can connect one temperature signal to the temperature surveillance pin in the inverter (EC-C1200)
and make sure that the inverter has the machine temperature protection feature activated.
The maximum allowed winding temperature of the electric machine is shown in the rating plate and in
the data sheet.
The PT100 temperature sensor characteristics are: resistance 100 Ω at 0 ºC temperature, and the
resistance increases 0.385 Ω per each 1 ºC increase of temperature.
Inverter
The electric machine is intended to be powered and controlled with an inverter capable of supplying
three-phase alternating current and that is capable of controlling the electric machine. The electric
machine is not suitable for direct online use.
If the electric machine is driven with an inverter from a supplier other than Danfoss Editron, the electric
machine performance may differ from rated values. The optimum performance of the electric machine is
obtained with Danfoss Editron inverters. These inverters are:
18 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
•
Compact and light.
•
Liquid cooled.
•
Tolerant to high mechanical vibration (10 G) and shock (50 G).
•
Efficient, efficiency > 98 %.
•
Reliable, no moving components.
Do not exceed the maximum rotation speed of the electric machine.
EC-C1200
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 19
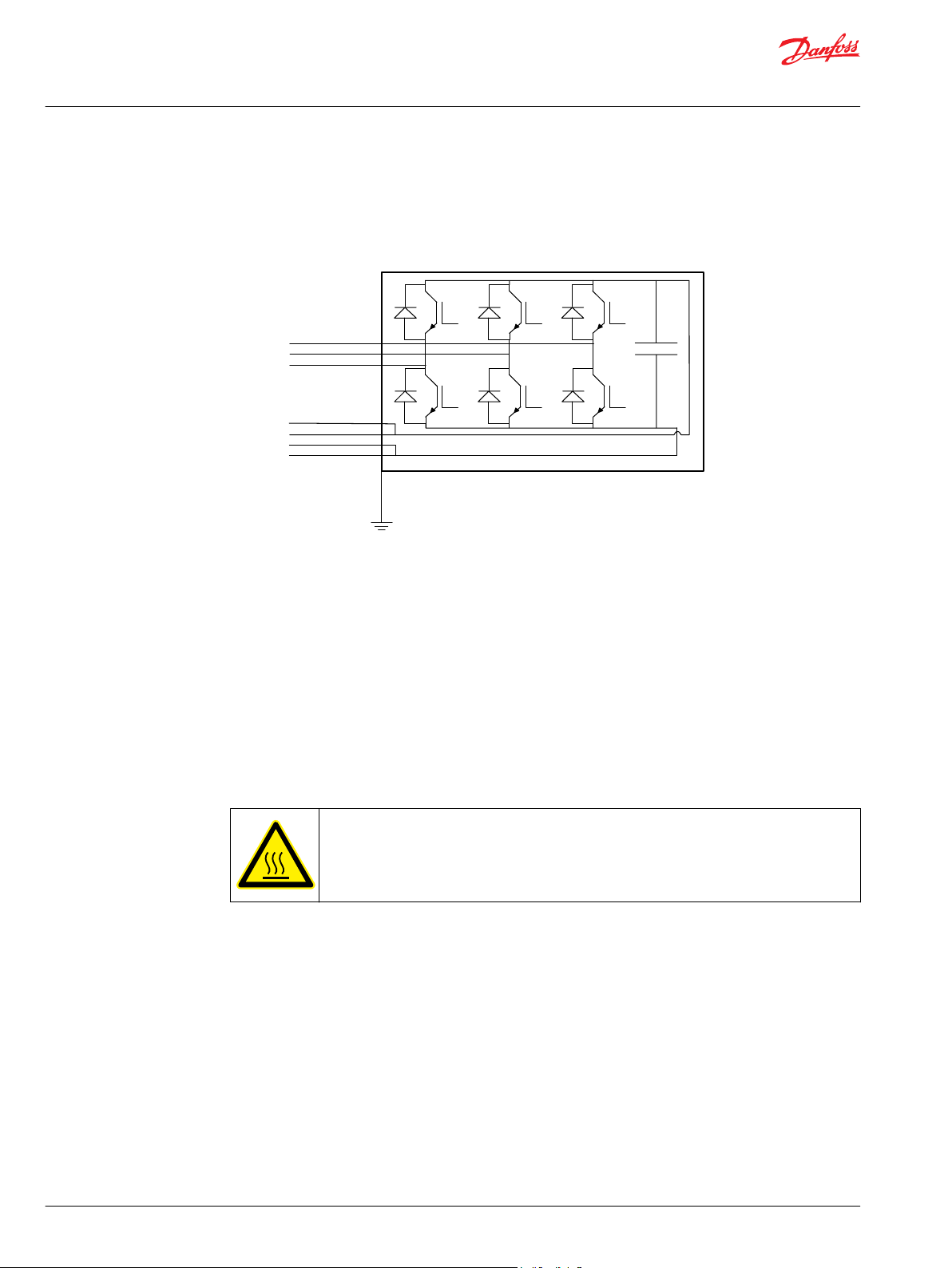
L1
L2
U
V
W
-
-
L3
DC +
+
+
DC -
AUX DC +
AUX DC -
User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Schematic of the inverter powerstage
Mounting structure
The main machine power driving parameters are shown in the machine rating plate. For more
information, contact Danfoss representative.
You can connect one of the temperature signals (from the low voltage connector) to the temperature
surveillance pin in the inverter and make sure that the inverter has the machine temperature protection
feature activated.
Supporting structure requirements
Do not install the electric machine near or in direct contact with easily flammable materials.
The surface of the electric machine can be hot.
The mating housing arrangement of the electric machine must be secure and sufficiently rigid to prevent
vibrations and mechanical failures. Necessary actions should be taken to avoid corrosion on the mating
housing arrangement.
The supporting structure for the electric machine must be such that the electric machine can be
mounted using its allowed mounting positions, see Chapter Allowed mounting positions.
The mounting space must be adequate for the electric machine mounting and possible auxiliary
components. See the length and the diameter data of the electric machine from the product drawing.
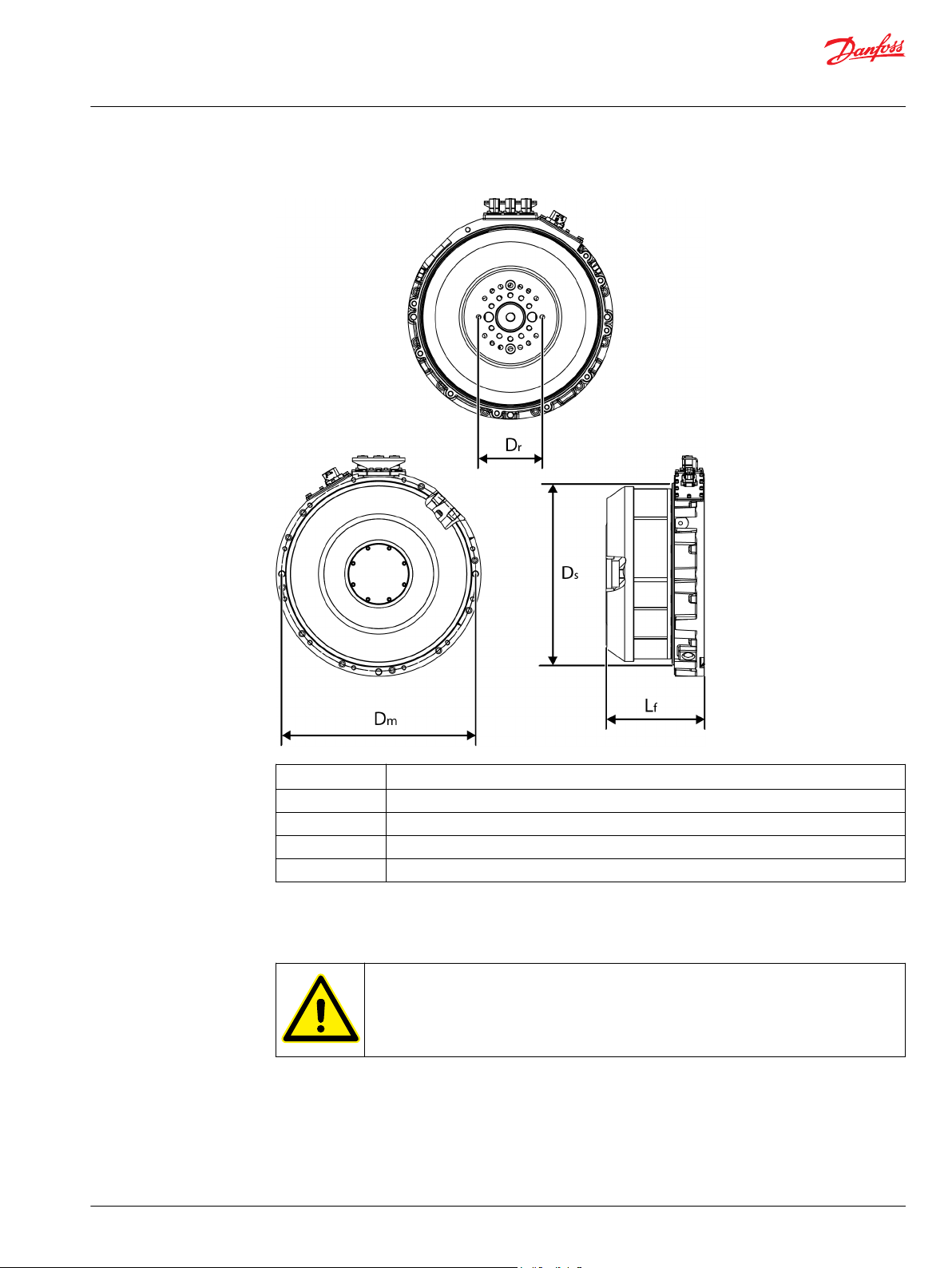
Main dimensions of the electric machine are shown in the Figure below (the illustration may differ from
the actual electric machine).
The electric machine has a SAE 3 flywheel housing in N-end. The D-end has a circle of bolt holes for
fastening. See specific installation instructions.
20 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Main dimensions of the electric machine
Symbol Explanation
L
F
D
M
D
S
D
R
Length of the electric machine frame.
Diameter of the flange mounting bore circle.
Diameter of the mounting shoulder.
Diameter of the rotor connection interface.
For all dimensions of the electric machine, see the product drawings.
Shaft alignment and load
Improper alignment (misalignment) may result in bearing overloads, premature bearing
failures, vibrations and shaft failures. Flexible coupling does not compensate for excessive
misalignment.
Alignment between the shaft and mating structure must be accurate.
The misalignment can be parallel or angular misalignment, or combination of those. With parallel
misalignment, the center lines of both shafts are parallel but they are offset. With angular misalignment,
the shafts are at an angle to each other. Figures below illustrate the parallel and angular misalignment.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 21

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Parallel alignment of the shaft and mating structure
Angular alignment of the shaft and mating structure
Customer connection interface design instruction
This Chapter describes the necessary design loads and tolerances for designing connection interface for
Danfoss integrated electric machines (EM-PME375-T150 and EM-PME375-T200).
Design loads for EM-PME375-T150 and EM-PME375-T200 rotor
F
= Magnetic force between rotor and frame
mgn
G = Gravitational force of rotor
22 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Design loads for EM-PME375-T150 rotor
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 23

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Design loads for EM-PME375-T200 rotor
Allowed axial tolerances of connection interfaces:
Electric machine type EM-PME375-T150: Dimension X = 129,6mm ± 0,5mm
Electric machine type EM-PME375-T200: Dimension X = 150,0mm ± 0,5mm
24 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Allowed axial tolerances
1 Connection face to electric machine rotor
2 Connection face to electric machine frame
Allowed concentricity tolerances of connection interfaces
1 Centerline of electric machine frame connection interface
2 Centerline of electric machine rotor connection interface
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 25

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Allowed angular displacement tolerances of connection interfaces
1 Connection face to electric machine frame
2 Centerline of electric machine frame connection interface
3 Centerline of electric machine rotor connection interface
Required radial stiffness of connection interface
When resultant force F
tot
(F
+ G, see the Figures at the beginning of the Chapter) is applied to the
mgn
system, the maximum allowed radial deformation of the rotor connection interface is 0,09mm in point P.
See the Figure below.
It should be noted that some components, for example bearings and gears, can cause additional
flexibility to rotor interface and it should be taken into account.
Required radial stiffness
The Figure below describes how to connect the electric machine frame to the interface.
26 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
Frame connection
The Figure below describes how to connect the electric machine rotor to the interface.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 27

User Guide
EM-PME375
Design principles
28 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Transportation and storage
Transportation
Receiving and unpacking
Heavy equipment. Handle with care during transportation.
Electric machine is shipped in first class condition. It has been inspected and packed correctly to prevent
damage from ordinary handling during shipment. During transportation, shocks, fails and humidity
should be avoided. Protect the cooling holes for transportation.
The weight of the electric machine can be found on the machine rating plate, and in the product data
sheet.
Do not touch the electric machine during the insulation resistance check. Discharge the
electric machine afterwards.
Lifting
Check upon arrival and unpacking
•
The electric machine and the package must be inspected immediately upon arrival. Make sure that
the rating plate data in the cover letter complies with the purchase order. Any external damage (in
rotor, flanges, electrical interfaces and paint) must be photographed and reported immediately.
•
It is recommended to measure the insulation resistance of the electric machine upon arrival, or before
installing the electric machine. Reference value of 150 MΩ shall be exceeded in room temperature,
otherwise contact Danfoss representative. Refer to Chapter Insulation resistance test on page 33.
Use correct, adequately dimensioned lifting devices and inspect them before lifting.
Do not lift from the shaft of the electric machine!
Do not apply any excess weight on the electric machine when lifting.
Use correct lifting slings. Use correct position and angle of lifting.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 29

User Guide
EM-PME375
Transportation and storage
See the electric machine rating plate for weight information.
Lift the electric machine using the correct lifting lugs/eyes only.
Do not go under a lifted load.
Lifting slings cannot touch the electric machine during the lifting.
Lifting lugs/eyes/points for lifting slings and lifting position of the electric machine
Lifting eye type: ANSI B18.15.1M M10x16 is recommended in M10 bores. Not included in the delivery
30 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Transportation and storage
Storage
Not allowed lifting procedures
Store the electric machine always indoors with the storage temperature above -20 ºC and the relative
•
humidity less than 60 %.
The storage should be dry, dust free and vibration free.
•
Treat the unprotected electric machine surfaces such as the shaft-end and flanges against corrosion.
•
Seal the cable exit holes and cooling bores for storage.
The electric machine must not be subject to any external vibrations during storage to avoid damage
•
to the bearings.
Use anti-condensation heaters, if fitted, or direct winding heating to avoid water condensing in the
•
electric machine.
Rotate the shaft of the electric machine by hand monthly at least ten revolutions to prevent grease
•
migration. If necessary, use a tool, for example a spanner. Do not damage the shaft in any case.
Do not keep the stator on its winding side down.
•
Storing stator
Extended storage
It is recommended to inspect the electric machine in storage at periodic intervals. Use attached storage
checklist.
Rotate the shaft of the electric machine once a month.
Keep the electric machine in its installation position while in storage. For example, vertically installed
electric machines should be stored in vertical position.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 31

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
The following safety and information related symbols appear in this user guide and on the electric
machine.
Risk of electric shock when the connection box is open. When you work with power
connections make sure that electricity is disconnected and rotor rotation is prevented.
Magnetic and electromagnetic fields generated near the current-carrying conductors and
permanent magnets in electric machines represent a health danger to persons with heart
pacemakers, metal implants and hearing aids. Persons with a heart pacemaker, metal
implants or hearing aids must consult a doctor before they enter the following areas:
•
Areas in which electric equipment and parts are operated.
•
Areas in which electric equipment with permanent magnets are stored, mounted, operated
or repaired.
Risk of electric shock when working with the electric machine. Use isolated electric tools.
Only trained and qualified personnel familiar with the relevant safety requirements can work
with the electric machine.
Use correct personal protective equipment when you are near the electric machine.
Read the instructions in this user guide before you install the electric machine.
32 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Required tools
Insulation resistance test
Following tools are required to install the electric machine:
•
Ratchet torque wrench.
•
Hex head wrench kit with different metric sizes.
•
Socket wrench kit with different metric sizes.
•
Lifting slings with lifting eyes (with sufficient rated capacity) . Size according to machine type. See
Chapter Lifting on page 29
Do not touch the electric machine during the insulation resistance check. Discharge the
electric machine afterwards.
Measure the insulation resistance of the electric machine before and after the installation of
the electric machine.
Mechanical installation
Use a voltage of 500 V in the insulation resistance test.
Measure the insulation resistance of the electric machine before and after the installation of the electric
machine. Because of the structure of the electric machine, it is possible that the stator is damaged during
the installation.
If the electric machine is in continuous use, it is recommended to do the insulation resistance test three
or four times a year.
The reference value of 150 MΩ must be exceeded in room temperature. Contact Danfoss representative if
the reference value is not exceeded. Reference value of 150 MΩ should not be exceeded at reference
ambient temperature 25°C (measured with 500 VDC / 1 min Megger).
Allowed mounting positions
Allowed mounting position
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 33

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Mounting the electric machine
Refer to Chapter Allowed mounting positions for the correct mounting positions of the electric
machine.
Mount the electric machine on a correct supporting structure as discussed in Chapter Supporting structure
requirements.
Machine assembly
The rotor has a powerful magnetic field that can cause injuries or even death. Obey these
instructions when you are near the rotor.
•
Don´t put any electric devices near the rotor.
•
Don´t put any steel parts near the outer or inner surfaces of the rotor.
•
Handle the rotor carefully.
•
Use non-magnetic tools.
•
Persons with metallic, electronic or magnetic implants or devices in their body
cannot go near the rotor.
Do not put the frame near the rotor before it is connected to the hydraulic cylinder. Magnetic
force can pull the frame against the flywheel housing adapter.
Finger crushing hazard. When you work with the rotor, be careful with its strong magnetic
field: do not put your fingers in between rotor and other components during the installation.
Use correct screw preload. See the preload values below.
Threadlocker is not included in the delivery.
Mount the electric machine on a correct supporting structure that is discussed in Chapter Customer
connection interface design instruction on page 22.
Assembly procedure
1. Install flywheel adapter (2) to flywheel (1) with suitable screws (3) (not included in delivery). Use
strong threadlocker (for example Loctite 278, not included in delivery). Use sufficient screw
preload. Check preload from flywheel manufacturer.
2. Install flywheel housing adapter (4) to flywheel housing (1) with suitable screws (5) (not
included in the delivery). Use strong threadlocker (for example Loctite 278, not included in
delivery).
34 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
3. Assemble Enerpac BAD142 flange mount (6) with retainer nut (7) to Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic
cylinder (8).
4. Assemble hydraulic cylinder with flange mount to assembly tool cylinder holder (9) with
M10X25 DIN 912 screws (10), 4 pcs.
5. Connect hydraulic cylinder to hydraulic hand pump with hydraulic hoses, see Enerpac
instructions.
6. Assemble rotor bracket (12) to electric machine rotor (11) with M10X25 DIN 912 A4 stainless
screws (13), 2 pcs.
7. Install 2 pcs. of alignment pins (14) in the electric machine rotor (11).
8. Assemble the assembly tool with Enerpac cylinder to (15) flywheel housing adapter with
M10X25 DIN 912 screws (16), 4 pcs.
9. Lift the rotor carefully with lifting sling (not included in delivery) between the assembly tool
(15) and the flywheel housing adapter.
10. Push the rotor carefully inside to flywheel housing adapter to correct position using the
hydraulic cylinder.
11. Attach the rotor to the flywheel adapter with rotor connection screws (18), 10 pcs. and NordLock
locking washer. (17), 10 pcs. Make sure that rotor aligns correctly to flywheel adapter and rotor can be
rotated freely.
12. Remove the rotor bracket from the rotor and assembly tool with the Enerpac cylinder.
13. Install frame assemble pins (19), 3pcs. to flywheel housing adapter.
14. Assemble frame bracket (20) to frame (21) in correct position with M8x25 DIN 912 screws (22),
4 pcs.
15. Install O-ring (23) in frame (21).
16. Lift the frame using frame lifting points with suitable lifting eyes (not included in delivery) and
slide frame on to frame assembly pins.
17. Assemble the assembly tool with Enerpac cylinder to flywheel housing adapter with M10X25
DIN 912 screws (24), 4 pcs.
18. Connect hydraulic cylinder piston to frame bracket. Make sure that the hydraulic cylinder is
retracted fully inside. Make sure that hydraulic cylinder is not pressurized.
19. Push the frame carefully inside the rotor to correct position using the hydraulic cylinder, until
the frame is tightly against flywheel housing adapter. Make sure that O-ring stays in place
during assembly.
20. Connect the frame to flywheel housing adapter with M8x80 DIN 7991 screws (25), 10 pcs. Use
strong threadlocker (for example, Loctite 278, not included in delivery).
21. Remove:
1. Assembly tool with the Enerpac cylinder.
2. Frame bracket with connection screws.
3. Frame assembly pins.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 35

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Installation procedure
The rotor has powerful magnets. Persons with pacemakers cannot go near the rotor. Keep
electronic devices and credit cards clear of the rotor.
Do not put your fingers between components, as they might get crushed by sudden
movement of the components caused by magnetic or other forces.
Refer to flywheel manufacturer instructions for the screw preload. Flywheel attachment
screws are not included in the delivery.
Use strong threadlocker, for example Loctite 278. (Not included in the delivery)
Connection interface screws are not included in the delivery.
Brackets and installation tools not included in a standard delivery.
36 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Installation overview
Installation overview
1 Frame / Stator connection interface (for example diesel engine flywheel housing and flywheel
2 Rotor connection interface (for example diesel engine flywheel adapter)
3 Rotor of the electric machine
4 Frame of the electric machine
5 Stator attachment screws
6 Rotor attachment screws (Nord-Lock locking washers recommended)
7 Rotor bracket
8 Assembly tool
17 Frame bracket
18 Tool 30671, bearing installation tool
19 Tool 30867, locknut installation tool
housing adapter)
Flywheel and rotor installation
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 37

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
1. Install flywheel adapter (2) to flywheel housing (1) with suitable screws (6) (not included in delivery).
Use strong threadlocker (for example Loctite 278, not included in delivery). Use sufficient screw
preload (check preload from flywheel manufacturer).
2. Install flywheel housing adapter to flywheel housing (1) with suitable screws (not included in the
delivery). Use strong threadlocker (for example Loctite 278, not included in delivery).
Rotor and flywheel installation procedure principle
Rotor assembly tool assembly
1. Install the rotor bracket (7) on the rotor. Attach it with screws (9).
2. Install the rotor alignment pins (10) on the rotor if necessary.
See Figure below.
38 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Rotor bracket and rotor alignment pin installation
7 Rotor bracket
9 M10X25 DIN 912 A4 screws, 2 pcs. Use stainless steel screws.
10 Rotor alignment pin, 2 pcs. Optional.
3. Assemble the rotor assembly tool (8). See Figure below.
Rotor assembly tool (8) assembly
11 Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic cylinder
12 M10X25 DIN 912 screws, 4 pcs
13 Enerpac retainer nut
14 Enerpac BSS5904D flange mount
15 Assembly tool cylinder holder
4. Install the rotor assembly tool (8) on the rotor (3).
5. Lift the rotor next to the frame / stator connection interface (1) with the rotor connection interface (2).
6. Attach the assembly tool on the frame / stator connection interface with screws (21).
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 39

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
7. Connect a hydraulic hand pump to the Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic cylinder (11) of the rotor assembly
tool.
8. Pump pressure in Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic cylinder with the hydraulic hand pump until the rotor,
frame / stator connection interface and the rotor connection interface are firmly together.
9. Fasten the rotor on the rotor connection interface with screws (6).
10. Remove the rotor assembly tool (8) and the rotor bracket when most screws are in place.
11. Install the rest of the screws as the rotor bracket prevents some of them being installed.
Rotor installation with rotor assembly tool
21 M10X25 DIN 912 screws, 4 pcs
40 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Preparations for the frame installation
1. Install the shaft (20) in the stator. Fasten it with bolts (21). Note: Shaft is an optional part, and some
electric machines do not have it.
2. Install the frame assembly pins (16) in the frame / stator connection interface.
Installing frame assembly pins and shaft
16 Frame assembly pin, 3 pcs
20 Shaft 18364, optional
22 Fastening bolts 15999
3. Install the frame bracket (17) on the frame of the electric machine. Fasten it with screws (18).
4. Install the o-ring (19).
See Figure below.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 41

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Frame bracket installation
17 Frame bracket
18 M8x25 DIN 912 screw
19 O-ring, D400x3
Frame installation
Do not push the frame too close to the rotor before the assembly tool is installed and the
hydraulic cylinder is pressurized. Magnetic force can pull the frame in forcefully and damage
it.
Lift the frame next to the rotor and put in the position shown in the figure below. Make sure that
the frame assembly pins go into the correct holes of the frame.
42 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Frame lifting
Frame position before installation
This step of the installation is very dangerous for the fingers as they can be cut off by the
components moved by the magnetic forces. Do not put your fingers between the stator and
rotor.
Install the assembly tool on the frame / stator connection interface and fasten it with screws. See Figure
below.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 43

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Assembly tool installation
21 M10X25 DIN 912 screws, 4 pcs
1. Connect a hydraulic hand pump to the Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic cylinder (11) of the rotor assembly
tool.
2. Pump pressure in Enerpac BRD-46 hydraulic cylinder with the hydraulic hand pump until the frame
and the frame / stator connection interface are firmly together.
3. Fasten the frame on the frame / stator connection interface with screws (20).
4. Remove the assembly tool and the frame bracket.
Frame fastening
5 M8 DIN 912 screw, 10 pcs (client determines the length)
44 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Assembled electric machine
Bearing installation
This procedure applies only if the electric machine has bearings.
Assembled electric machine before bearing or resolver installation
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 45

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Bearing installation
1. Install the bearing (3) with the tool 30671.
2. Install the spacer (2).
3. Install the locknut (1). Tighten it with the tool 30867. Tighten the axial bolts of the locknut according
to the manufacturer Instructions. The locknut is of type Schaeffler AM-45.
Resolver installation
This procedure applies only if the electric machine has a resolver.
Resolver installation
46 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
1. Install the resolver adapter and rotor assembly (1) on the shaft. Note that the resolver stator (2) is
installed by Danfoss. Make a heatshrink joint to fasten the adapter on the shaft: heat to temperature
of 150°C and put heat resistant Loctite glue on the contact area. Push the adapter against the
shoulder of the shaft.
Cover installation
Cover installation
1. Install the seal 18412 on the cover (2).
2. Install the cover (2) and fasten it with bolts (1).
Cooling connections
Make sure that cooling liquid runs freely into and out from the electric machine.
To prevent damage to the cooling connectors, refer to the documentation of the
manufacturer for the correct tightening torque of the cooling liquid nipples.
When selecting cooling liquid nipples, choose nipples that can resist galvanic corrosion.
Cooling connectors have G1/2 bores, depth 18.
Connect the electric machine properly to the cooling circuit. Make sure that the coolant flow is equal or
higher than rated and the coolant temperature at the inlet of the machine cooling is lower or equal to the
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 47

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Electrical installation
rated temperature. For more information, see Chapter Recommended coolants and product data sheet.
Rated values can be found in the electric machine rating plate.
Use only suitable and high-class connection parts and seals to connect the electric machine to the water
circuit. Check for possible leaks after the piping and joints have been connected.
It is recommended to use coolant connector equipped with o-ring seal or to use sealing washer (for
example Usit or Bonded seals) in the connection. In addition, it is recommended to use thread sealant
(Loctite 577 or similar) at the coolant connections to prevent loosening. Loosening can be caused by
vibration or temperature variations.
The electric machines are equipped with at least three PT100 temperature sensors in the windings. The
amount of the sensors depend on the options chosen. The temperature signal(s) can be read out from
the measurement connector of the machine.
You can connect the temperature signal to the temperature monitoring pin in the inverter (EC-C) and
make sure that the inverter has the electric machine temperature protection feature activated.
Power connections
High voltage connection
Risk of electric shock. When you work with power connections make sure that electricity is
disconnected and that the rotation of the rotor is prevented.
Mating connectors of the high voltage cables are not part of a standard delivery.
The order of the phases is marked on the power terminal with stickers.
48 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
High voltage connection
1. Power terminal
Connector type: AMPHENOL HVBI005R10AMHARD
Mating connector: AMPHENOL HVBI-7-05R10-XFC-XXXX-FG/PC (straight plug)
AMPHENOL HVBI-9-05R10-XFC-XXXX-FG/PC (right angle plug)
Installing the high voltage cables
Remove the power terminal shield. See the Figure below.
1.
Install the high voltage cables. Refer to the instructions of the manufacturer of the mating
2.
connectors.
Install the power terminal shield back.
3.
Power terminal shield
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 49

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
1 Fasteners
2 Power terminal shield
Connection diagram
The electric machines are intended to be powered and controlled by three-phase alternating current,
supplied by an inverter or inverters. The electric machine is not suitable for direct online use.
The amount of inverters depends on the electric machine and converter current ratings.
Connection diagram
Low voltage connections
Low voltage connector details
The electric machine has a low voltage (measurement signal) connector which is used to read out inbuilt
temperature and rotation sensor (resolver) data from the electric machine. Optionally the connector is
replaced with a connection box (option +LVB1). The temperature data comes from PT100 sensors located
in the stator windings. Check from the rating plate which pin configuration is valid. Find the
configuration for temperature and resolver measurements option in rating plate type field. The electric
machine has three PT100 sensors in windings as a standard option.
The measurement connector has these components:
•
12 pin TE HDSCS for temperature surveillance
•
Connector type: TE 115645201
•
Pin type of connector: TE 9642703 (gold plated)
•
Mating female connector type: TE 117036391
•
Pin type for the mating connector: TE 12413813 (use gold plated pins)
50 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Pin configuration of the connector TE 115645201
Default pin configuration
Pin Description
1 2 3 4 Temperature, PT100, windings
5 Temperature, PT100, windings
6 Temperature, PT100, windings
7 8 9 10 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin4 PT100)
11 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin5 PT100)
12 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin6 PT100)
Pin configuration with resolver (RES1)
Pin Description
1 Resolver, RES_COSN
2 Resolver, RES_SINN
3 Resolver, EXCN
4 Temperature, PT100, windings
5 Temperature, PT100, windings
6 Temperature, PT100, windings
7 Resolver, RES_COSP
8 Resolver, RES_SINP
9 Resolver, EXCP
10 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin4 PT100)
11 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin5 PT100)
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 51

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
Pin Description
12 GND, Temperature, PT100, windings (corresponds to pin6 PT100)
The shielded measurement cable shield can be connected to a low voltage grounding connection point.
See Chapter Grounding connections on page 52 for more information.
Grounding connections
Ground the electric machine from its frame to make sure it functions correctly and safely.
Ground the cable shields of the power cables to make sure the electric machine functions
correctly and safely.
Ground the cable shields of the low voltage cables to make sure the electric machine
functions correctly and safely.
It is recommended to perform a ground bond test after installing the electric machine to make
sure the electric machine is correctly grounded.
The grounding points on the frame of the electric machine are for safety grounding, and
signal cables and power cable shields have their own grounding points.
52 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
The machine enclosure grounding point, safety grounding
1 Grounding point
Low voltage cable grounding points
1 The grounding pin of the low voltage connector.
2 Cable shield grounding point.
Testing the power cable shield grounding (earthing)
The power cable shields are grounded (earthed) through the connection terminal and further to the
electric machine enclosure. After the cable gland assembly and power cable installations, and any time
when needed, make sure that the grounding (earthing) connections are correct.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 53

User Guide
EM-PME375
Installation
1.
Connect one terminal of the measurement device to the cable shield of one power cable (in the
inverter end of the cable)
2.
Connect the other terminal of the measurement device to the cable shield of an other power cable.
You can also use the machine enclosure grounding point for the measurement.
3.
Measure the resistance between the two cable shields or between the cable shield and the enclosure
grounding point.
4.
Change the measurement device terminal(s) to the shield of different power cable and repeat the
measurement until all cables have been measured.
Testing the low voltage (measurement signal) cable shield grounding (earthing)
The low voltage (measurement signal) cable shield is connected to the grounding (earthing) point. After
cable installation, and any time when needed, make sure that the grounding (earthing) connection is
valid.
1.
Connect one terminal of the measurement device to the low voltage cable shield (in the nonmachine end of the cable).
2.
Connect the other terminal of the measurement device to the machine enclosure grounding point.
3.
Measure the resistance between the cable shield and the enclosure grounding point.
54 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Operation
Only trained and qualified personnel familiar with the relevant safety requirements are
allowed to operate the electric machine.
Do not use the electric machine without properly dimensioned and operating cooling system.
Maximum operation temperature, current and rotational speed of the electric machine must
not be exceeded to avoid permanent damage.
The surface of the electric machine might be hot. Do not touch the electric machine during
operation.
Entanglement hazard! Do not touch the electric machine during operation.
Use the anti-condensation heater, if fitted, when the electric machine is not in use. This
prevents condensation and possible damage to the electric machine.
Use sufficient personal protective equipment when you are near the electric machine.
Read the instructions in this user guide before you install the electric machine.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 55

User Guide
EM-PME375
Operation
Operation conditions
The electric machine should be used for its intended purpose only and within limits specified by the
manufacturer, concerning:
•
Loading.
•
Cooling.
•
Speed range.
•
Service interval.
•
Ambient condition such as temperature and moisture.
The electric machine is designed for the following conditions:
•
Ambient temperature limits: -40°C...+65°C.
•
Maximum altitude 1000 m above sea level.
•
Maximum coolant liquid temperature at the inlet of the coolant circuit, see product data sheet.
•
Coolant liquid must be water- glycol mixture with maximum of 50 % glycol content. See
Chapter Recommended coolants.
If electric machine operation limits are exceeded, please contact Danfoss representative.
Condition monitoring during operation
Recommended coolants
Supervise the electric machine during operation to make sure that the electric machine
operates correctly and has a designed lifetime.
If you notice any deviations from the normal operation, for example elevated temperatures,
noise or vibration, stop the electric machine. Find the reason for the deviation and repair the
electric machine. Refer to Chapter Troubleshooting on page 61.
The maximum allowed winding temperature of the electric machine is shown on the rating
plate and in the data sheet.
Ethylene glycol is a toxic compound. Avoid exposure to the coolant.
Copper ions concentration of more than approx. 0.06 ppm causes copper induced pitting
corrosion. Do not use copper components in the cooling system.
Hard piping made of metal is recommended for the coolant instead of soft piping as rubber
hoses.
56 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Operation
Emergency operation
Use correct personal protective equipment when you handle the coolant.
Glycol coolant options:
Ethylene glycol based Glysantin® G48® (includes also corrosion inhibitors).
•
Propylene glycol based coolants, like Splash® RV&Marine antifreeze.
•
The electric machine should be operated within the operation limits and in the conditions specified by
the manufacturer. However, it can be used with some limitations in the following fault/emergency
situations.
Cooling of the electric machine fails
The cooling system failure can be caused by dregs (sediment) accumulating to the cooling system tubes.
Try opening the possible blockage by changing the coolant flow direction. See also Chapter Cooling
system maintenance.
If the cooling of the electric machine fails, limited operation is still possible with no coolant flow. The
operation speed must be limited to half (1/2) of the rated speed and maximum 20 % of the nominal
torque may be used. In such case, the electric machine may be operated for maximum one hour. Repair
the cooling system as soon as possible. For further information, contact Danfoss representative.
The temperature measurement of the electric machine fails
Contact Danfoss service.
Danfoss service contact information
Contact Danfoss service at https://danfosseditron.zendesk.com/hc/en-gb or send email to
editron.service@danfoss.com.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 57

User Guide
EM-PME375
Maintenance
This Chapter contains necessary information for the qualified and trained personnel to carry out regular
maintenance work.
Do not disassemble the electric machine. Only procedures described in this user guide may be
done.
Only trained and qualified personnel familiar with the relevant safety requirements are
allowed to do maintenance to the electric machine.
Risk of electric shock when the connection box is open.
Voltage may be connected to the anti-condensation heater.
Use correct personal protective equipment when you are near the electric machine.
Read the instructions in the user guide before you start to work with the electric machine. To
make sure that the operation of the electric machine is safe and reliable, obey the
maintenance instructions.
Regular maintenance
Inspect the electric machine at regular intervals. Use the Storage, installation and maintenance
checklists on page 64.
58 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Maintenance
Do not attempt to tighten bolts or screws that are not discussed in this user guide and that are
not needed for normal installation and maintenance procedures. The sealing of the bolts and
screws can break.
Correct supervision and maintenance of the electric machine makes sure that the electric machine has
reliable operation and designed lifetime.
Maintenance schedule
Object Check/Task Weekly Monthly Yearly
General construction Operation Noise, vibration. If clearly increased, contact Danfoss. X
Mounting Bolt tightness. Tighten to proper value if necessary. Applies to bolts and
screws that are discussed in this manual. See Chapter Tightening torques.
Enclosure and
connected parts
Shaft seals Check the wear. Replace if necessary. X
Electrical system Cables Wearing of the cables. Replace if necessary. X
Electrical connections Check connections. Make sure that sufficient tightening torque is applied
Groundings (earthings) Check groundings (earthings). Make sure that the connection resistance
Cooling system Operation Functioning. Cooling system functions as specified. X
Tubing and connection
tightness
Ventilation plug Cleanliness. Clean if necessary
Coolant flow Coolant flow direction. Change direction by changing the connections or
Coolant quality Coolant as specified. Proper glycol used, and water/glycol mixture
Check cleanliness. Clean if necessary. See Chapter Cleaning. X
to cable glands. See Chapter Tightening torques.
is valid. Re-connect if necessary.
No visible leakage. If leaking, tighten connections appropriately, or
replace parts.
See Chapter Cooling system maintenance.
flow direction from the pump.
See Chapter Cleaning.
appropriate. Refill if necessary. See Chapter Cooling system maintenance.
X
X
X
X
X
X
X
Cleaning
Risk of electric shock if the electric machine is cleaned against instructions allowing water to
go in to the electric machine.
Keep the electric machine clean. For cleaning, use non-abrasive and non-corrosive cleaning products.
Make sure that the detergent may be used for aluminum.
Cooling system maintenance
The electric machine cooling system requires certain regular maintenance activities.
It is recommended to change the direction of the coolant liquid flow yearly. This is done by changing the
order of the coolant connections, or changing the coolant pump direction. The reason for changing the
coolant flow direction is to prevent possible dregs (sediment) accumulating to the cooling system.
The quality of the coolant must be checked yearly. The mixture of water and glycol as well as the type of
the glycol used must be as specified. See Chapter Recommended coolants.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 59

User Guide
EM-PME375
Dismounting
Make sure that the mating structure is not damaged. Do not pluck any bores or use at headed
bolts or rods for pushing the electric machine out of the mating structure.
See Chapter Mounting the electric machine on page 34. Dismount the electric machine in reverse order.
60 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Troubleshooting
Some difficulties may occur while operating the electric machine. Possible causes and actions are given in
the Table below. If the situation occurs, it should be corrected as soon as possible. These instructions do
not cover all details or variations in the equipment nor provide information for every possible condition
to be met in connection with installation, operation or maintenance.
For more information, contact Danfoss service at https://danfosseditron.zendesk.com/hc/en-gb or send
email to editron.service@danfoss.com.
Troubleshooting chart
Symptom Possible cause Action
Excessive vibration, noise Imbalance at connected electric machine
or the powertrain components.
Attachment bolts are loose. Replace and tighten the bolts.
Imbalance at the electric machine. Contact Danfoss.
Particles inside the electric machine. Contact Danfoss.
Electric machine overheating Overload. Reduce load. Check the electric machine model description and rating
Cooling system failure. Check the cooling system integrity, flow and fluid temperature.
Leakage in the cooling system. Check the cooling system circuit and connections.
Rigid particles inside the electric
machine cooling channel.
Wrong electric machine parameters in
the inverter.
Winding short circuit. Replace the electric machine.
Electric machine does not work
properly or the performance is poor
Temperature measurement failure The PT100 sensor is faulty. Measure the resistance of the PT100 sensor, see Chapter Low
Wrong electric machine parameters in
the inverter.
Demagnetization of magnets due to
overheating.
Insulation fault. Measure the insulation resistance, refer to manufacturer limits. See
Check the balance and installation of the actuator and drivetrain
components.
plate, check the inverter limits.
Change the cooling flow direction to flush the cooling system from
sediment possibly accumulated. See also Chapter Emergency
operation.
Try pulsating coolant to open the channels. Contact Danfoss.
Check and correct the machine parameters from the inverter.
Check and correct the parameters from the inverter.
Measure the winding resistance, refer to manufacturer data. Replace
the electric machine if necessary.
Chapter Insulation resistance test. Replace the electric machine if
necessary.
voltage connections. If the sensor is faulty, read out the signal from an
other sensor. Contact Danfoss. See also Chapter Emergency operation.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 61

User Guide
EM-PME375
Aftersales
Service policy
Service parts
Maintenance and service of the electric machine is limited to the procedures described in this user guide.
If the electric machine has service parts available, you can find them in Chapter Service parts on page 62.
For further information, go to https://danfosseditron.zendesk.com/hc/en-gb or send email to
editron.service@danfoss.com.
The recommended service parts are listed in this Section. Quantity describes the number of components
in a single electric machine. Maintenance procedures not described in this user guide require special
tools and instructions. Contact Danfoss for more information and purchasing.
Service parts
Position Part Order number
1 HV connector (standard option). AMPHONEL ART. NO. HVBI005R10AMHARD 14977
HV connector (+HVC1 -option). AMPHENOL ART. NO. HVBI003R8AMHARD19127101 15687
2 Seal for HV connector plate. T=3 14965
3 LV connector. TE 1-1564520-1 12 PIN ASSEMBLY FOR 3mm PLATE 11033
4 Seal for LV connector plate. SEAL. GASKET. T=3 14956
62 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Disposal
Dispose of the electric machine and any of its parts by appropriate means in accordance with local laws
and regulations.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 63

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
Electric machine installation checklist
Date:
Electric machine and customer information
Customer: Electric machine type (from the rating plate):
Customer reference: Electric machine serial number:
Service reference: Date installed:
N.A = Procedure not applicable PASS = Procedure passed FAIL = Procedure failed
Installation checklist
Approval N.A PASS FAIL
General
Electric machine type is correct ☐ ☐ ☐
Electric machine is
undamaged
Insulation resistance check >150MΩ ☐ ☐ ☐
Environmental conditions as
specified (see data sheet)
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
Mechanical installation
Supporting structure as required ☐ ☐ ☐
Shaft alignment as specified (see chapter Shaft alignment
and load).
Cooling circuit connected and coolant flowing ☐ ☐ ☐
Used coolant:
Power connections
Cable connector assembly as specified with correct cable
diameter
The phase connections order is correct (U, V, W -> L1, L2,
L3)
Grounding
Electric machine enclosure grounding connected ☐ ☐ ☐
Low voltage cable shield grounding connected ☐ ☐ ☐
Power cable shield connection resistances to ground
(electric machine enclosure) measured and valid
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
64 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
Installation checklist (continued)
Approval N.A PASS FAIL
Low voltage cable shield grounding resistances measured
and valid
Notes:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Date:
Signature:
☐ ☐ ☐
Do not try to tighten bolts or screws that are not discussed in the product manual and that are not
needed for the normal installation procedures. Sealing of the screws may break.
Electric machine weekly maintenance checklist
Date:
Electric machine and customer information
Customer: Electric machine type (from the rating plate):
Customer reference: Electric machine serial number:
Service reference: Date installed:
N.A = Procedure not applicable PASS = Procedure passed FAIL = Procedure failed
Electric machine weekly maintenance checklist
N.A PASS FAIL
General construction
Noise or vibration during operation
in general
Cooling system
☐ ☐ ☐
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 65

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
Electric machine weekly maintenance checklist (continued)
N.A PASS FAIL
Functioning of the cooling system in
general
Notes:
☐ ☐ ☐
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Electric machine monthly maintenance checklist
Date:
Electric machine and customer information
Customer: Electric machine type (from the rating plate):
Customer reference: Electric machine serial number:
Service reference: Date installed:
N.A = Procedure not applicable PASS = Procedure passed FAIL = Procedure failed
Electric machine monthly maintenance checklist
N.A PASS FAIL
General construction
Noise or vibration during operation
in general
Cleanliness of the enclosure and
connected parts
Electrical system
Weariness of the cables ☐ ☐ ☐
Cooling system
Functioning of the cooling system in
general
Tightness of the ventilation plug ☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
☐ ☐ ☐
66 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
Electric machine monthly maintenance checklist (continued)
N.A PASS FAIL
Cleanliness of the ventilation plug ☐ ☐ ☐
Notes:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Electric machine yearly maintenance checklist
Date:
Electric machine and customer information
Customer: Electric machine type (from the rating plate):
Customer reference: Electric machine serial number:
Service reference: Date installed:
N.A = Procedure not applicable PASS = Procedure passed FAIL = Procedure failed
Electric machine yearly maintenance checklist
Acceptance N.A PASS FAIL
General construction
Noise or vibration during operation in general ☐ ☐ ☐
Cleanliness of the enclosure and connected parts ☐ ☐ ☐
Electrical system
Weariness of the cables ☐ ☐ ☐
Electrical connections in general ☐ ☐ ☐
Cooling system
Coolant flow direction changed and connection checked ☐ ☐ ☐
Coolant quality as specified ☐ ☐ ☐
Used coolant:
Functioning of the cooling system in general ☐ ☐ ☐
Tightness of the tubing and connections (no leakages) ☐ ☐ ☐
Cleanliness of the ventilation plug ☐ ☐ ☐
Grounding
Power cable shield connection resistances to ground
(electric machine enclosure) checked
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 67
☐ ☐ ☐

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
Electric machine yearly maintenance checklist (continued)
Acceptance N.A PASS FAIL
Low voltage cable shield grounding resistances checked ☐ ☐ ☐
Notes:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Do not try to tighten bolts or screws that are not discussed in the product manual and that are not
needed for the normal installation procedures. Sealing of the screws may break.
For cleaning instructions, refer to Chapter Cleaning on page 59.
Used service parts
Part description Part type Quantity Item (order) number
_
_
_
_
_
Notes:
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
•
Date:
Signature:
Electric machine storage checklist
Date:
Electric machine and customer information
Customer: Electric machine type (from the rating plate):
Customer reference: Electric machine serial number:
Service reference: Date installed:
68 | © Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201

User Guide
EM-PME375
Storage, installation and maintenance checklists
This storage checklist is used when storing the electric machine. Regular inpection is required. See
specifications for storage in this User Guide or in the Data Sheet.
Fill in the date of each inspection to the Table below.
Storage checklist
Procedure Date Date Date Date Date
Storage base as
specified (vibration
free)
Storage temperature
and humidity as
specified
Electric machine type
and serial number is
correct
Electric machine
supported correctly
Shaft rotated as
specified (10 rotations
monthly)
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201 | 69

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions (US) Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions Trading
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 2080 6201
Products we offer:
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
Cartridge valves
•
DCV directional control
•
valves
Electric converters
•
Electric machines
•
Electric motors
•
Gear motors
•
Gear pumps
•
Hydraulic integrated
•
circuits (HICs)
Hydrostatic motors
•
Hydrostatic pumps
•
Orbital motors
•
PLUS+1® controllers
•
PLUS+1® displays
•
PLUS+1® joysticks and
•
pedals
PLUS+1® operator
•
interfaces
PLUS+1® sensors
•
PLUS+1® software
•
PLUS+1® software services,
•
support and training
Position controls and
•
sensors
PVG proportional valves
•
Steering components and
•
systems
Telematics
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electric components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market as well as the
marine sector. Building on our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with you to
ensure exceptional performance for a broad range of applications. We help you and other
customers around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles
and vessels to market faster.
Danfoss Power Solutions – your strongest partner in mobile hydraulics and mobile
electrification.
Go to www.danfoss.com for further product information.
We offer you expert worldwide support for ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also
provide you with comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
©
Danfoss | July 2021 BC265857345808en-000201
 Loading...
Loading...