Page 1

MAKING MODERN LIVING POSSIBLE
Electronic Controls
Fitter’s Notes
www.danfoss.com
Page 2

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
2 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 3

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Contents
Measuring 4
Measuring a temperature 4
Temperature sensor type EKS 111 5
Temperature sensor type EKS 211 5
Positioning sensors 6
Evaporator positions 6
S1 and S2 sensors 7
How to mount S2 sensor on a vertical pipe 7
How to mount S2 sensor on a horizontal pipe 7
Measuring a pressure 8
Positioning sensors 11
Pressure transmitter in liquid line with pulse snubber 12
Electrical connections 13
Pulse width modulation electronically operated expansion valve type AKV 13
Stepper motor electronically operated expansion valve type ETS 13
Digital Input (DI) / Digital Output (DO) 14
No power 14
Split sensors and AKV 14
External Start/Stop of regulation 14
Controlling 15
Input and output 15
Op eratio n 15
Evaporator controls 16
Parameters 16
What is the controller doing...? 17
Quick start 17
What is wrong....? 18
Communication 19
Why...? 19
How…? 19
Cable selection / termination 20
Requirement to installation 20
Cable 21
Addressing 24
Trouble shooting 24
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 3
Page 4
Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
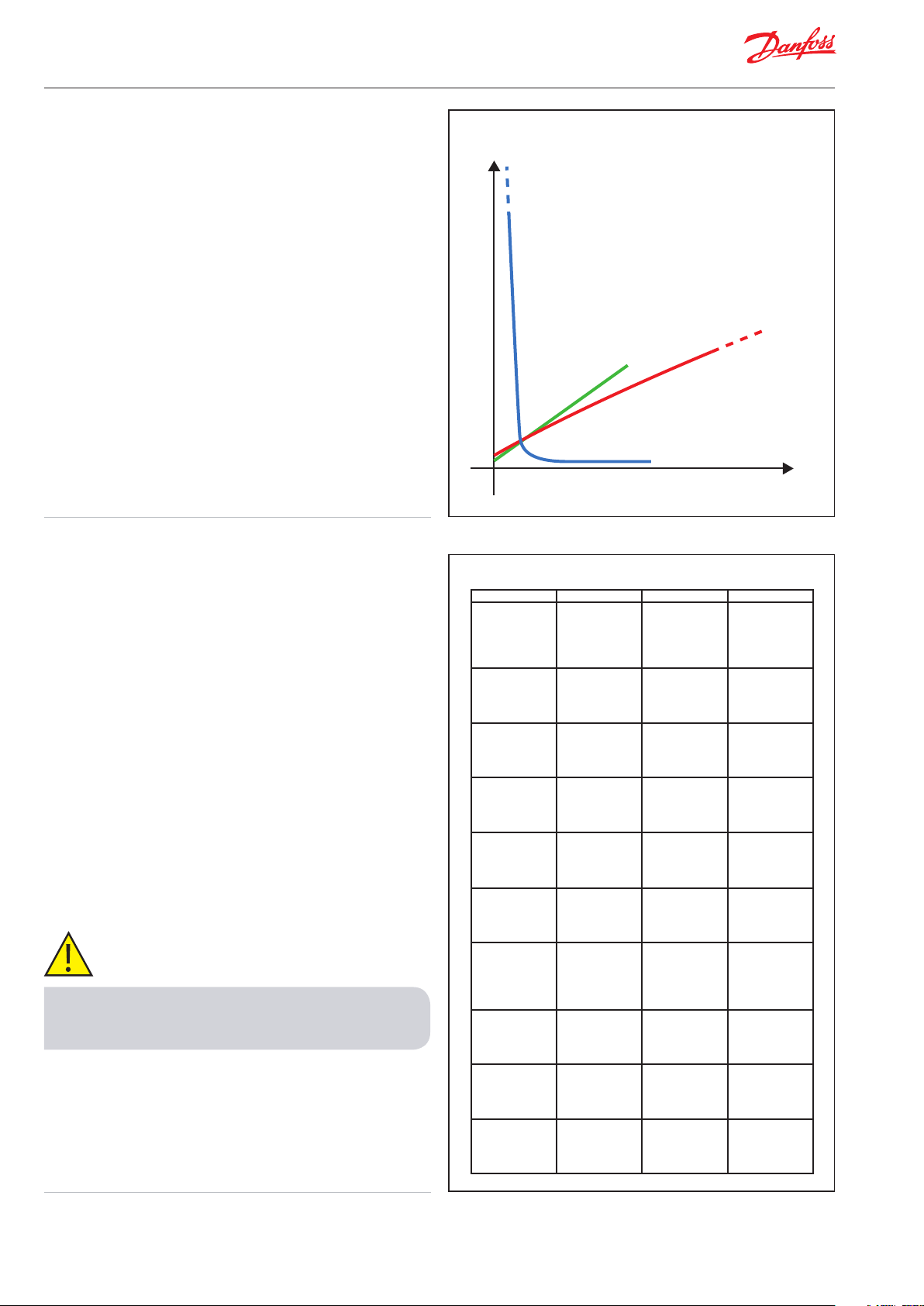
R
NTC
PTC
Pt
T
Measuring
Measuring a temperature
Pressure temperature inputs
With the use of electronic controllers such as
Danfoss ADAP-KOOL® products the installation requirements must
be followed to ensure the electrical connections, pressure and
temperature sensors and any communication network
connections are correct so that the unit operates as intended.
The following are some general guidelines:
y Pressure temperature inputs
It is very important that the correct type of temperature sensor
is used for the temperature range, sensing application, and the
temperature sensor signal is compatible with the electronic
refrigeration controller, (please see the technical manual for the
controller to ensure the correct temperature sensor is used).
y Sensor types
The product programme of temperature sensors for
refrigeration consists of two main families: AKS and EKS.
These sensor elements are based on the three technologies:
Pt, PTC and NTC.
Temperature sensor type:
AKS11, AKS12, AKS21, AK-HS 1000
Pt sensor
These sensors are also known as RTD´s, Resistance Temperature
Detectors. The sensing elements is made of platinum, example
PT1000, where the number describes the nominal resistance at
0°C, here 1.000Ω. The resistance increases 4Ω per 1°C. The sensor
characteristic is linear. In Danfoss these sensors are the type AKS.
The tolerance of a Pt1000 sensor is less than ± (0.3 + 0.005 T).
This translates into a temperature error of less than 0.5 degree for
refrigeration control.
The Pt1000 sensor must be used for food safety logs and
regulation of superheat as they conform to the tolerance
requirements of EN 60751 Class B and therefore satisfy the HACCP
requirements of EN 12830, EN 13485.
Extension of sensor cables
When extending a sensor cable, the new resistance value of the
longer cable may give rise to indication error. It is recommended
that the total cable resistance should not exceed 2Ω
corresponding to an indication error of 0.5°C (Pt1000Ω).
Note
Up to 50m use 0.75mm²
Up to 100m use 1.5mm²
Up to 150m use 2.5mm²
The typical resistance values for cables are:
y -2.4Ω/100m for core cross-sectional area of 0.75mm².
y -1.2Ω/100m for core cross-sectional area of 1.5mm².
y -0.7Ω/100m for core cross-sectional area of 2.5mm² .
AKS 11, AKS 12, AKS 21, AK-HS 1000
°C ohm °C ohma
0 1000.0 1000.0
1 1003.9 -1 996.1
2 1007.8 -2 992.2
3 1011.7 -3 988.3
4 1015.6 -4 984.4
5 1019.5 -5 980.4
6 1023.4 -6 976.5
7 1027.3 -7 972.6
8 1031.2 -8 968.7
9 10.35.1 -9 964.8
10 1039.0 -10 960.9
11 1042.9 -11 956.9
12 1046.8 -12 953.0
13 1050.7 -13 949.1
14 1054.6 -14 945.2
15 1058.5 -15 941.2
16 1062.4 -16 937.3
17 1066.3 -17 933.4
18 1070.2 -18 929.5
19 1074.0 -19 925.5
20 1077.9 -20 921.6
21 1081.8 -21 917.7
22 1085.7 -22 913.7
23 1089.6 -23 909.8
24 1093.5 -24 905.9
25 1097.3 -25 901.9
26 1101.2 -26 898.0
27 1105.1 -27 894.0
28 1109.0 -28 890.1
29 1112.8 -29 886.2
30 1116.7 -30 882.2
31 1120.6 -31 878.3
32 1124.5 -32 874.3
33 1128.3 -33 870.4
34 1132 -34 866.4
34 1132.2 -34 866.4
35 1136.1 -35 862.5
36 1139 -36 858.5
37 1143.8 -37 854.6
38 1147.7 -38 850.6
39 1151.5 -39 846.7
40 1155.4 -40 842.7
41 1159.3 -41 838.8
42 1163.1 -42 835.0
43 1167.0 -43 830.8
44 1170.8 -44 826.9
45 1174.7 -45 822.9
46 1178.5 -46 818.9
47 1182.4 -47 815.0
48 1186.3 -48 811.0
49 1190.1 -49 807.0
50 1194.0 -50 803.1
approx 3.9 ohm/K
4 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 5
Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Temperature sensor type EKS 111
PTC sensor
The PTC sensor got their name as the sensing element has a
positive temperature coecient.
The sensing element is a semi conductor, example PTC1000
where the number describes the nominal resistance at 25°C.
The sensor characteristic is almost linear but is not standardized,
the manufacturer can dene their own characteristics.
In Danfoss the EKS111 is a PTC1000 type.
The PTC temperature sensor type EKS111 must not be used for
food safety logs as they do not conform to the requirements
EN 12830, EN 13485 or regulation of superheat because they do
not have the needed accuracy of +/- 0.5K.
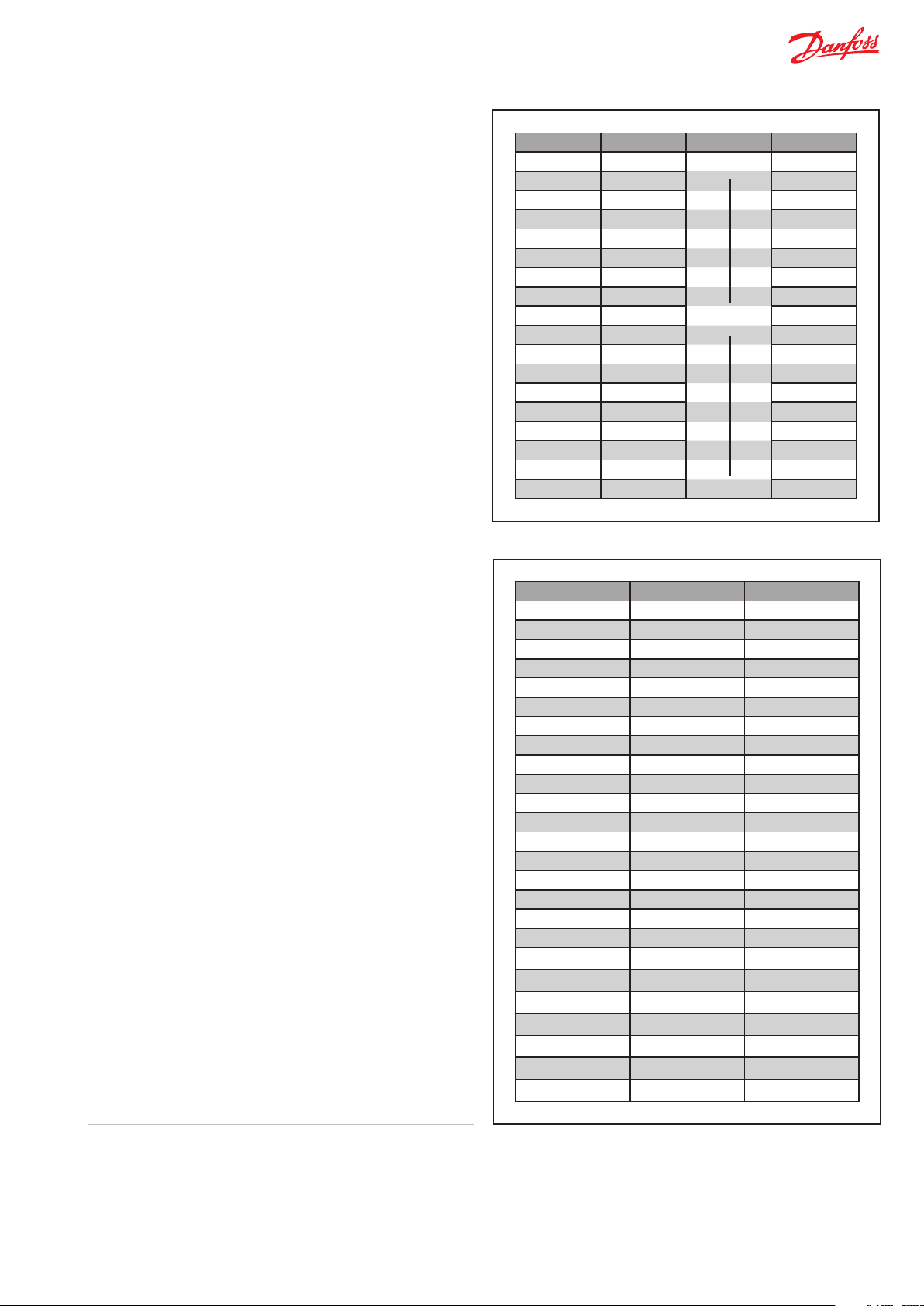
R (typ.) Ohm Tem p. °C Error K Te mp ° F
1679 100 +/-3.5 212
1575 90 194
1475 80 176
1378 70 15 8
128 6 60 14 0
119 6 50 12 2
1111 40 104
1029 30 86
990 25 +/-1.3 77
951 20 68
877 10 50
807 0 32
740 -10 14
677 -20 -4
617 -30 -2 2
562 -40 -40
510 -50 -58
485 -55 +/-3.0 - 67
Temperature sensor type EKS 211
NTC sensor
The sensing element in NTC´s is a thermistor having a
negative temperature coecient.
The sensor characteristic is described by a number, that as with
PTC´s, indicates the nominal resistance at 25°C, and by a β-value
which denes the curve characteristic.
Due to the variety of characteristics it is not possible to develop a
standard NTC sensor that can be used for all controller types.
Hence, when making service you must install an “original” NTC
sensor to ensure the controller to work properly.
Temperature sensor type EKS 211
NTC characteristic matches controllers type EKC and AK-CC.
The NTC temperature sensor type EKS211 must not be used for
food safety logs as they do not conform to the requirements
EN 12830, EN 13485 or regulation of superheat because they do
not have the needed accuracy of +/- 0.5K.
R_nom Ohm Tem p. °C Temp °F
631.0 80 176
743.2 75 167
878.9 70 158
104 4 65 149
1247 60 14 0
1495 55 131
1803 50 12 2
2186 45 113
2665 40 104
3266 35 95
4029 30 86
5000 25 77
6246 20 68
7855 15 59
9951 10 50
12696 5 41
16330 0 32
21166 -5 23
27681 -10 14
36503 -15 5
48 614 -20 -4
65333 -25 -13
88766 -30 -22
12179 5 -35 - 31
16915 7 -40 -40
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 5
Page 6
Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
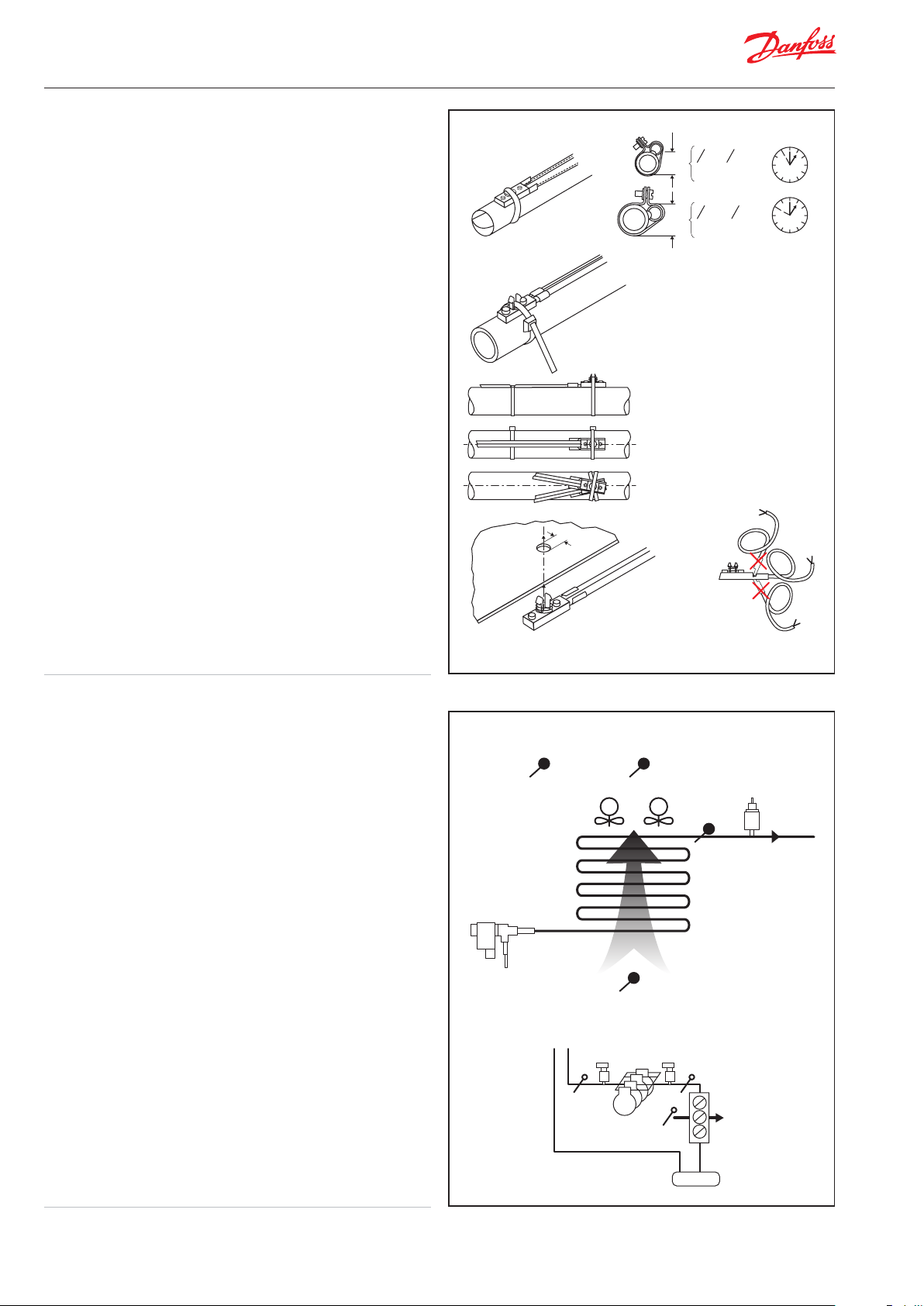
Positioning sensors
It is very important that during the installation process and also
during maintenance schedules the correct position and mounting
of all temperature sensors is in line with the recommendations.
Incorrect mounting can cause faulty temperature signals to be
used by the controller which will result in, in-correct operation of
the refrigeration application.
Ø=
Ø=
125
in.
8
12 - 16mm
341
1
8
18 - 26mm
in.
12
1
2
3
4
12
1
2
3
4
Evaporator positions
Nomenclature of temperature tensors & pressure
transmitters in Danfoss controllers
y S1: Temperature sensor measuring evaporating temperature
(Can be used as a less accurate measurement of
evaporating temperature without the need for a pressure
transmitter)
y Pe: Pressure transmitter measuring true evaporating pressure
(preferred method)
y S2: Suction temperature outlet of the evaporator
y S3: Air entering the evaporator
y S4: Air leaving the evaporator
y S5: Defrost termination temperature sensor when defrost is
being used
y S6: Is used as a product sensor (type AK-HS1000,HACCP
compliance for food safety)
Pack positions
y Po: Pressure transmitter - Suction pressure
y Pc: Pressure transmitter - Discharge pressure
y Ss: Temperature sensor - Suction temperature to work out
suction superheat in connection with suction pressure Po
y Sd: Temperature sensor - Discharge temperature
y Sc3: Temperature sensor - Ambient temperature of the air
entering the condenser
Ø=6.5
S6 S4
M M
S3
Po Pc
S
S
NB!
Pe
S2
S5
Sd
S
CS
6 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 7
Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
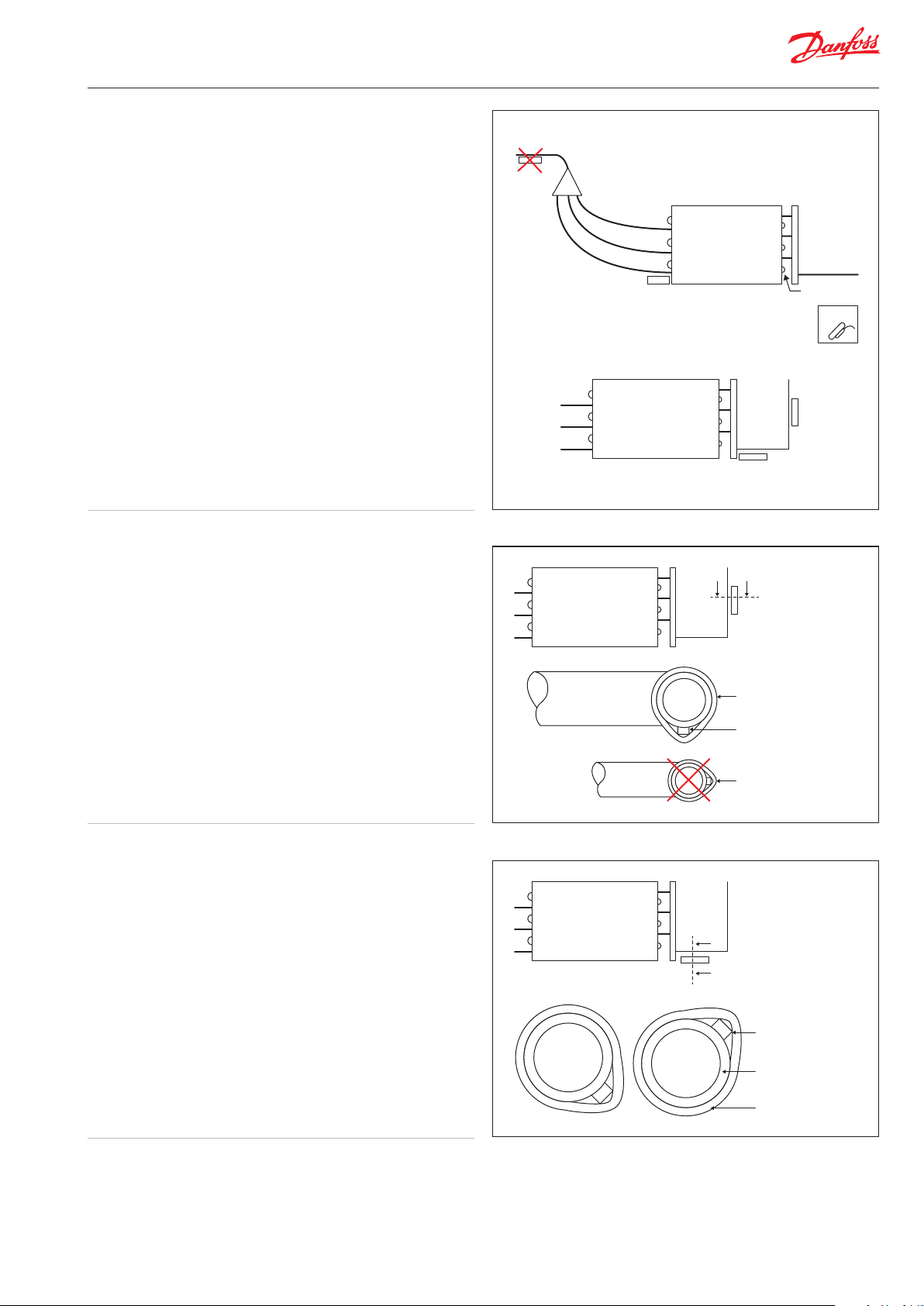
S1 and S2 sensors
S1 and S2 sensors measuring saturation temperature and
temperature of superheat gasses.
y S1: This sensor is measuring the evaporating temperature of
the evaporator and therefore must be mounted on the
coldest point on the evaporator, normally the rst return
bend.
The reading should be checked against the suction gauge
pressure to conrm that the pressure and temperature
relationship is correct otherwise the control of superheat
will be incorrect.
Where and how to mount the S1 sensor
S1
S1S1A
S1
B
B
y S2: Sensor function is to measure the temperature of the
refrigerant exiting at the evaporator’s pipe outlet and, has
thus, the same goal as a thermostatic expansion valve’s
bulb and should be placed exactly according to the same
rules.
Only a Pt1000 AKS11 type sensor must be used, as it is the
only type providing the necessary accuracy needed for
this purpose.
How to mount S2 sensor on a vertical pipe
Steel pipes
If steel pipes are used on the evaporator outlet the superheat
signal it must be measured using a pocket sensor “S2” to get a
correct signal. This is absolutely necessary to get a good injection
control.
Copper pipes (exceeding 50mm)
When pipe dimensions go up so does the material thickness.
Bigger thickness also means greater temperature dierence
between inner and outer temperatures. You should use
immersion pocket sensors here also.
Where and how to mount the S2 sensor
Mount on vertical pipe if possible not too close to bend
and not to far from evaporator outlet
AA
Cut A-A
Cut A-A
A
S2
S2 B
The sensor should be
mounted rmly on the
pipe using heat-conducting
paste and the sensor
should be insulated
S2
Pipe isolation
S2 sensor
Oil splash can disturb the signal
How to mount S2 sensor on a horizontal pipe
The sensor should be
When mounted on horizontal pipe the position depends on the
size of the pipe.
y Mount at 1 o’clock when diameter is between 1/2 and 5/8inch
(12-16mm).
y Mount at 2 o’clock when diameter is between 3/4 and
1- 1/8inch (18-26mm).
y Mount at 4 o’clock when diameter is over 1- 1/2inch (38mm).
y Use immerse pocket sensor if you want to measure on steel
pipe.
B
B
Cut B-B
mounted rmly on the
pipe using heat-conducting
paste and the sensor
should be insulated
S2
S2 sensor
Pipe
Isolation
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 7
Page 8
Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Measuring a pressure
It is very important that the correct type of pressure transmitter is
used for the pressure range, sensing application, and the pressure
transmitter signal is compatible with the electronic refrigeration
controller, (please see the technical manual for the controller to
ensure correct pressure transmitter is used).
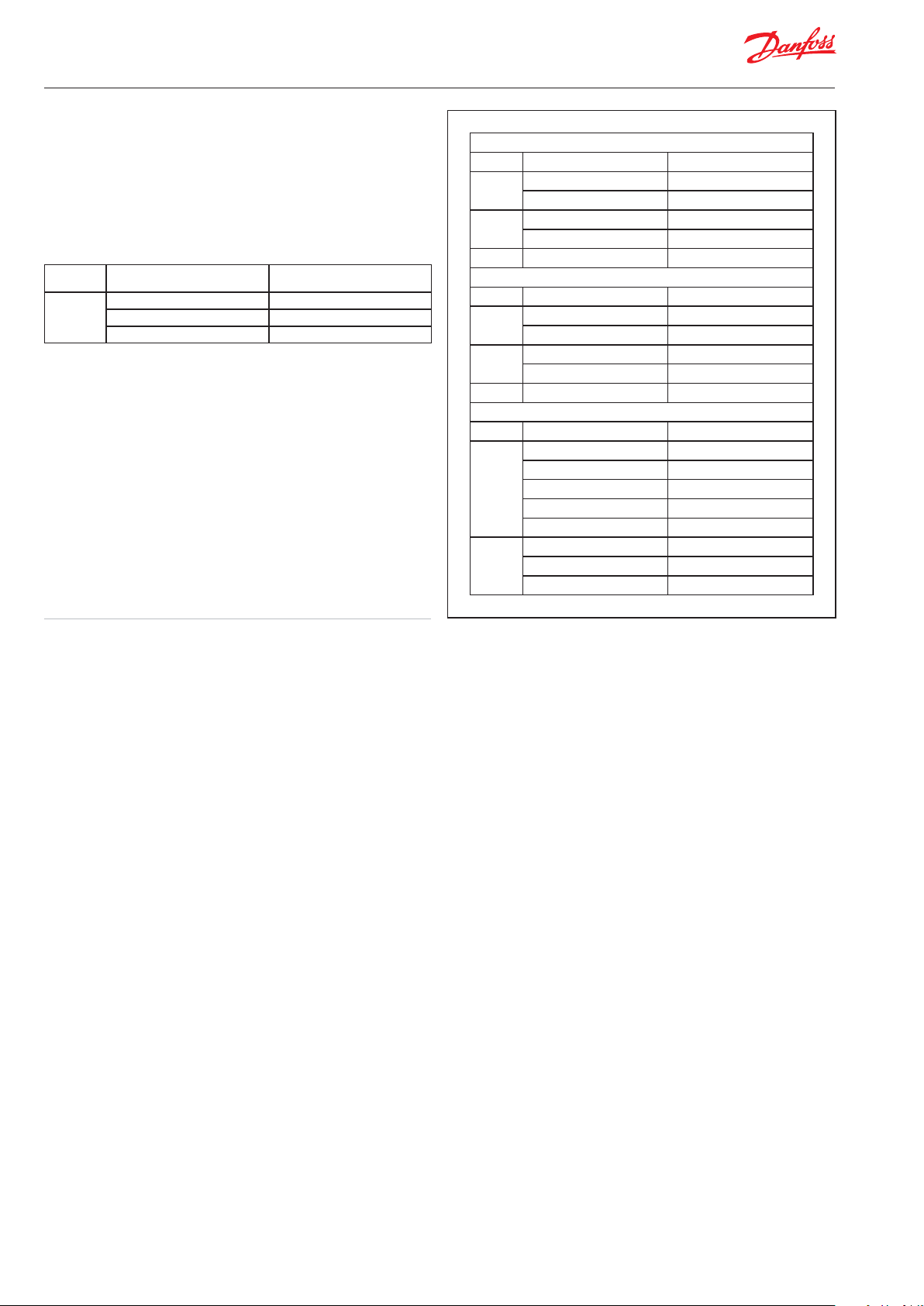
AKS ratiometric
Typ e Operating range [bar] Permissible working pressure
AKS 2050 -1 to 59 100
-1 to 99 150
-1 to 159 250
PB [b ar]
AKS 32, ver sion 1-5V
Operating range Max working pressure PB
LP
HP
AKS 32, ver sion 0-10V
LP
HP
AKS 33, version 4-20mA
LP
HP
-1 --> 6 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 12 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 20 [bar] 40 [bar]
-1 --> 34 [bar] 55 [bar]
Operating range Max working pressure PB
-1 --> 5 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 9 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 21 [bar] 10 [b ar]
-1 --> 39 [bar] 60 [bar]
Operating range Max working pressure PB
-1 --> 5 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 6 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 9 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 12 [bar] 33 [bar]
-1 --> 20 [bar] 40 [bar]
-1 --> 34 [bar] 55 [bar]
0 --> 16 [bar] 40 [bar]
0 --> 25 [bar] 4 0 [bar]
8 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 9

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Pressure transmitter
Range and types of signals
A pressure transmitter will measure the pressure and this
measurement will be conditioned in the form of a dened
electrical signal that will allow it to be “transmitted” on a further
distance.
A pressure transmitter needs a power supply, most of the time this
is going to be provided from the controller it is connected to.
Don’t forget that sensors, in general, are the “eyes” of a controller.
The better they are selected and positioned, the better the controller is
able to do its job!
Two main data will be needed to dene a pressure transmitter:
1. The pressure range, depending on the application where the
pressure transmitter is needed.
In traditional refrigeration system, mostly two dierent ranges
of pressures will be found, the evaporating pressure (LP) and
the condensing pressure (HP).
This is happening at rather dierent pressure levels so the
pressure range of the pressure transmitter for the low pressure
side will be dierent than the one for the high pressure side.
Typically, a range from -1 to 12bar is used for the low pressure
side and a range of -1 to 34bar is used on the high pressure
side. It is important, for the accuracy of the signal, that the
range is properly selected according to the application.
Example:
If you need to measure a pressure of 5bar, a pressure
transmitter of -1 to 12bar will give you a much better accuracy
than one of -1 to 34bar.
2. The type of electrical signal, can be either in current [mA] or
voltage [V]. The two rst types mentioned, the electrical signal
issued is directly proportional to the pressure only.
How to nd the value of the expected signal for a known
pressure?
Example:
A pressure transmitter with a range -1 to 12bar is used.
The pressure in the system is 5bar. The total pressure range is
thus from -1 to 12bar making a total of 13bar (+12-(-1)).
For a 4-20mA transmitter, a signal of 4mA will be issued for a
pressure of -1bar and 20mA will be for 12bar.
The current output range is from 4 to 20mA making a total
range of 16mA (20-4). We divide the 16mA by 13bar, and this
will give us 1,23mA/bar. We multiply now by the number of bar
starting from -1bar, thus 1+5 = 6bar by 1,23. Results = 7.38mA
and we nally add the starting point of 4mA (not “0” !!) to give
us the nal answer of 11,38mA for a pressure of 5bar.
This value can be easily controlled by using a ammeter in series
with the sensor’s wires.
For a 0-10V transmitter, a signal of 0V will be issued for a
pressure of -1bar and 10V will be for 12bar. The total pressure
range is thus from -1 to 12bar making a total of 13bar (+12-(-1)).
The voltage output range is from 0 to 10V making a total range
of 10V.
We divide the 10V by 13bar, and this will give us 0.77V/bar.
We multiply now by the number of bar starting from -1bar, thus
1+5 = 6bar by 0.77. Results = 4.62V for a pressure of 5bar.
This value can be easily controlled by using a voltmeter on the
sensor’s wires.
1
3
R
2
L
4-20mA output, 2 wires (+,-)
1
3
R
2
L
0-10V or 1-5V output, 3 wires (+, s, -)
U
B
U
B
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 9
Page 10

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
For ratiometric transmitter, the ratio metric transmitter, the
output signal is not only proportional to the pressure but is also
directly depending of the voltage on the power supply.
This is the type that is commonly used on most of the
controllers. The output signal of the transmitter will be
presented as a percentage of the voltage of the power supply
Example: 10….90% of [V] supply.
For a ratiometric transmitter, let’s take an example:
a pressure transmitter with a range -1 to 12bar is used.
The pressure in the system is 5bar and the power supply is of
5VDC. The lowest signal will be for -1bar and will correspond to
10% of the power supply, thus 0.5V.
The highest signal will be for 12bar and will correspond to 90%
of the power supply, thus 4.5V.
A signal of 0.5V will be issued for a pressure of -1bar and 4.5V
will be for 12bar. The total pressure range is thus from -1 to
12bar making a total of 13bar (+12-(-1)). The voltage output
range is from 0.5V to 4.5V making a total range of 4V (4.5-0.5).
We divide the 4V by 13 (bar), and this will give us 0.3V/bar.
We multiply now by the number of bar starting from
-1 bar, thus 1+5 = 6bar by 0.3. Results = 1.8V and we nally add
the starting point of 0.5V (not “0” !!) to give us the nal answer
of 2.3V for a pressure of 5bar.
This value can be easily controlled by using a voltmeter on the
sensor’s wires but you need to measure not only the signal but
also the value of the power supply to ensure a correct answer
1
3
R
2
L
Ratio metric [V] output, 3 wires (+, s, -)
U
B
10 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 11

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Positioning sensors
Sensor mounting
It is very important that during the installation process and also
during maintenance schedules the correct position and mounting
of all pressure transmitters is in line with the recommendations.
Incorrect mounting can cause faulty pressure signals to be used
by the controller which will result in, in-correct operation of the
refrigeration application.
Cable version
The pressure transmitter must be mounted before the cable is
fastened to avoid twisting the cable.
Orientation
Can be mounted horizontal or vertical but with the pressure
connection facing downwards, example not on the bottom of the
pipe to avoid oil or dirt contamination. Plug cable facing
downwards prevents water collection in the cable entry.
Hot gas pipe
Use a distance sleeve to reduce the temperature inuence on hot
gas lines to avoid overheating the pressure transmitter.
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 11
Page 12

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Pressure transmitter in liquid line with pulse
snubber
y Cavitation, liquid hammer and pressure peaks may occur in
liquid lled systems with changes in ow velocity, example fast
closing of a valve or pump starts and stops. The problem may
occur on the inlet and outlet side, even at rather low operating
pressures.
y Pressure pulsations do not normally limit the pressure sensor
lifetime, however for the sake of the controller or the pressure
display equipment it may be expedient to dampen or lter the
signal from the pressure sensor.
y Dampening can be performed by electronics in the controller
equipment, or by means of connecting the sensor to the plant
through normal damping coils (capillary tubes).
y It is also possible to order specic pressure transmitters which
have a damping orice tted.
If a control valve is mounted on an evaporator, a separate pressure
measurement will have to be made for the other controllers on
the common suction if the evaporator controllers are of course
using a pressure transmitter to measure the evaporating
temperature.
Damping orice
AKS 32R
AKS 32R
AKS 32R
12 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 13

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Electrical connections
Pulse width modulation electronically
operated expansion valve type AKV
Using AC coil (alternating current)
On present controllers (AK-CC) you nd the electronic contact
which switches the power to the AC coil.
Note
Do not use a switch between the output and AKV coil.
Using DC coil (direct current)
In previous controllers (AKC or EKC) the supply came directly from
the controller to the DC coil.
56
~
230V a.c.
~
230V a.c. coil
15
230V d.c.
14
Stepper motor electronically operated
expansion valve type ETS
On some controllers the length between the controller and the
valve ETS have to be max 5m.
If the cable distance is greater than 5m a lter need to be used on
some controllers to extend the cabling up to 50m.
Find more information in the Instruction or Manual of the specic
controller.
Filter
The lter has to placed beside the controller.
L < 5m
ETS
L
5m < L < 50m
ETSAKA 211
L
ETS
AKA 211
4x10mH
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 13
Page 14

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Digital Input (DI) / Digital Output (DO)
Digital Output NC/NO
You must be aware, which type of contact do you have.
3132 33 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50
25 16 17 18 19
Digital Input powerless contacts
No power
Generally
The drawings ( especially the digital outputs ) of the electrical
connections are always shown without connected power supply.
~ ~
1
V/Ω
Ω
SIG GND
1
Relay or
AKV coil
110/230V
C24NO NC
1 2 3
DI1 DI2
24 25
24 25
Split sensors and AKV
Temperature sensor
Each controller needs its own temperature sensor input.
Pressure transmitter
The signal from one ratiometric pressure transmitter can be
received by up to 10 controllers. But only if there are no signicant
pressure dierence between the evaporators to be controlled.
AKV
Use only one AKV coil for one solid state output.
(“Pulse width modulation electronically operated
expansion valve type AKV“) on page 13.
External Start/Stop of regulation
Some controllers can be started and stopped externally via a
contact function connected to input terminals.
The function must be used when the compressor is stopped.
The controller then closes the solenoid valve so that the
evaporator is not charged with refrigerant.
AKS 32R info
AKS 32R info
+ - out
1 2 3
blue
black
30 31 32
+ s
The signal from one pressure transmitter
can be received by up to ten controllers
Solid State Output DO1 (for AKV co il) Max 240V a.c.
brown
30 31 32
+ s
MAx 0.5 A
Leak < 1mA
Max 1 pcs . AKV
Start/Stop
14 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 15

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Controlling
Input and output
Electronic controllers will have a number of inputs and outputs
that will allow the measurement and control of several tasks
related to refrigeration, mostly for evaporators and packs.
Inputs can roughly be divided in 2 types:
y Analog inputs that are typical for either temperature or
pressure sensors, readings being °C/°F or bar/psi,
(see MEASURING).
y Digital inputs that are typical for contact or voltage detection,
readings being an ON/OFF results, (see CONNECTION).
Outputs can be divided in several types like:
y Digital outputs that are typically electromechanical relays.
y Electronics outputs generating pulses signals typically for
controls of electronic expansion valves like AKV
(pulse width modulation) or ETS (stepper motor).
y Analog outputs generating mostly a 0 to 10VDC signal
available either as information or additional controls.
See the example beside
Operation
1
S2
S3
18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26
S2 S3
ETS
white
black
red
green
Display
The values will be shown with three digits, and with a setting you
can determine whether the temperature is to be shown in °C or
in ° F.
Light-Emitting Diodes (LED) on front panel
The LED’s on the front panel will light up when the relevant relay
is activated.
The light-emitting diodes will ash when there is an alarm.
In this situation you can download the error code to the display
and cancel/sign for the alarm by giving the top button a brief
push.
The buttons
When you want to change a setting, the upper and the lower
buttons will give you a higher or lower value depending on the
button you are pushing. But before you change the value, you
must have access to the menu. You obtain this by pushing the
upper button for a couple of seconds, you will then enter the
column with parameter codes. Find the parameter code you want
to change and push the middle buttons until value for the
parameter is shown. When you have changed the value, save the
new value by once more pushing the middle button.
Examples:
Set menu
1. Push the upper button until a parameter r01 is shown
2. Push the upper or the lower button and nd that parameter you
want to change
3. Push the middle button until the parameter value is shown
4. Push the upper or the lower button and select the new value
5. Push the middle button againt to freeze the value
Refrigeration
Defrost
Fan running
Cutout alarm relay/receipt alarm/see alarm code
y A short press of the upper button If there are several alarm codes
they are found in a rolling stack. Push the uppermost or lowermost
button to scan the rolling stack.
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 15
Page 16

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Set temperature
1. Push the middle button until the temperature value is shown
2. Push the upper or the lower button and select the new value
3. Push the middle button again to conclude the setting
Reading the temperature at defrost sensor
(Or product sensor, if selected in “o92”)
y A short press of the lower button
Manuel start or stop of a defrost
(Or product sensor, if selected in “o92”)
y Push the lower button for four seconds
Evaporator controls
Controllers for evaporators have built in functionalities that allow
them to perform the necessary tasks for the control of the
application including evaporators like cold rooms, cases, etc.
Being electronic, allow them a large choice in the available
functionalities under a very compact format, this is giving a lot of
exibility in their use.
Access to the functionalities is easily made through the use of a
display and keys, allowing access to a list containing the dierent
parameters. Basically, no “programming” is necessary, just setting
of parameters values. An explanation on how to access
parameters via display and keys is shown beside.
Parameters
Parameters are placed in “groups” related to their functions.
Example:
Thermostat related functions are all placed in the group of
parameters starting with letter “r” followed by a number.
Access to the thermostat dierential is done via parameter “r01”
and the value is expressed in degree Kelvin (to show it’s a
dierence). In all available controllers, “r01” will be referring to the
dierential therefore making the use of dierent controllers much
easier. And so on for the others parameters.
y Group “r..” refers to thermostat related functions.
y Group “A..” refers to Alarms setting and functions.
y Group “C..” refers to Compressor management.
y Group “D..” refers to Defrost functions.
y Group “F..” refers to Fan functions.
y Group “h..” refers to HACCP temperature.
y Group “n..” refers to setting linked with the use of electronic
expansion valves.
y Group “t” refers to the real-time clock.
y Group “o..” refers to miscellaneous functions like addressing,
door functions, refrigerant, etc.
Beside parameters, readings are available in the “u..” group
allowing to access sensors readings and Input/output status
like opening degree of an electronic expansion valve or
superheat value. These are usefully indications for the service
technician, allowing him to see what the controller “sees” and
helping drawn a fast diagnostic in case of problems.
Continued Code 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10
Service
Temperatur e measured with S5 se nsor u09 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Status on DI1 inp ut. on/1=closed u10 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Actual defrost time (minutes)
Temperatur e measured with S3 se nsor u12 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Status on ni ght operation
(on or o) 1= on
Temperatur e measured with S4 s ensor u1 6 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Thermostat temperature u17 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Run time of t hermostat (cooli ng time)
in minutes
Temperatur e of evaporator ou tlet
temp.
Superheat across evaporator u 21 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Reference of superheat control u22 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Openin g degree of AKV va lve ** u23 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Evaporating pressure Po (relative) u25 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Evapor ator temperature To
(Calculated)
Temperatur e measured with S6 s ensor
(product temperature)
Status on DI2 o utput. on/1=clos ed u37 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Air tempe rature . Weighted S3 an d S4 u56 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Measured temperature for alarm
thermostat
Status on re lay for cooling ** u58 1 1 1 1
Status on re lay for fan ** u59 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Status on re lay for defrost ** u 60 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Status on re lay for rail heat ** u61 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
Status on relay for alarm
Status on re lay for light
Status on re lay for valve in suct ion line
u11
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u13 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u18 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u20 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u26 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u36 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
u57 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
** u62
1 1 1 1 1
** u63
1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1
** u64
1
16 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 17

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
What is the controller doing...?
Through status codes, the controller keeps you informed about his present behavior.
Example:
“S11” indicate that refrigeration has stopped after reaching thermostat cutout.
“S14” would indicate that a defrost is in progress.
S0 Normal regulation S23 Adaptive control S46
S1 Waiting for the end of the coord def. S24 Start up phase: signal reliability S47
S2 Comp. must run for at least x min S25 Manual control of outputs S48
S3 Comp. must remain stop for x min S26 No refrigerant selected S49
S4 Evaporator drips OFF S27 Forced cooling S50
S5 Renewed cuting of relay wait x min S28 Stopped regulation S51
S6 Day operation (Sout control) S29 Case cleanig procedure S52
S7 Night operation (sin control) S30 Forced cooling S53
S8 Next relay must not cutin until x min S31 Door is oper (DI open) S54
S9 Nerxt relay must not cutout until x min S32 Delay on outputs during start up S55
S10 Stopped by mainswitch “r12 ” or DI S33 Heat func tion “r36” is active S56
S11 Refrig. stopped by thermostat S34 Safety cutout S57
S12 Refrig. stopped due to low sair S35 Cooling ON section B S58
S13 Defrost KVQ valve is closing S36 Cooling OFF sec tion B S59
S14 Defrost in progress S37 Cooling ON section C S60
S15 Defrost sequence: fan delay S38 Cooling OFF section C S 61
S16 Refrig. stopped by ON input S39 Cooling ON section D S62
S17 Door is open. DI input is open S40 Cooling OFF section D S63
S18 Melt function S41 S64
S19 Modulating thermostat control S42 S65
S20 Emergency cool sensor error S43 S66
S21 Injection problems S44 S67
S22 Start up: evaporator beign charged S45 S68
Quick start
Before allowing the controller to start the regulation, it is
important to check if the controller readings are showing the right
measurements.
(“u”, see chapter “Parameters” at page 16).
Accessing the “u” readings in the service group, allow you to
check this.
Use the instruction sheet of the specic controller to locate the “u”
readings corresponding to the connected sensors and contacts.
y Begin with checking that parameter “r12 ” (main switch) is set to
OFF(0), that will stop the regulation.
y When done, ensure that the proper selection of the electrical
diagram for the outputs has be done via the parameter “o 61”.
y An easy way would then be to use preselected settings for your
application room/case/cooling/freezing via the parameter
“o62”.
y Setting parameter “r12 ” to ON(1) will then start the regulation
with immediate eect.
100% tight
The buttons and the seal are imbedded in the front.
A special moulding technique unites the hard front plastic, the
softer buttons and the seal, so that they become an integral
part of the front panel.
There are no openings that can receive moisture or dirt.
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 17
Page 18

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
What is wrong....?
In case of a default, Error and Alarm codes will be shown pointing directly to the problem.
Example:
“A1” will tell you that the alarm temperature has been reached.
“E8” shows that the “S4” temperature sensor wiring is short-circuited.
A1 High temperature alarm A24 Compressor 6 fault A47 Fan 6 fault
A2 Low temperature/P0 alarm A25 Compressor 7 fault A48 Fan 7 fault
A3 Alarm level limit reached A26 Compressor 8 fault A49 Fan 8 fault
A4 Door alarm A27 Housing temperature A50 Saux1 temperature
A5 Max hold time/Slv def time-out A28 Digital input 1 alarm A51 DO1 fault
A6 “S4” out high temperature A29 Digital input 2 alarm A52 DO2 fault
A7 “S4” out low temperature A30 Digital input 3 alarm A53 DO3 fault
A8 “S3 ” in high temperature A31 Digital input 4 alarm A54 DO4 fault
A9 “S3 ” in low temperature A32 Digital input 5 alarm A55 DO5 fault
A10 Injection problem A33 Conguration change A56 DO6 fault
A11 No refrigerant selected A34 Fan 1 fault A57 DO7 fault
A12 Digital input alarm A35 Fan 2 fault A58 DO8 fault
A13 High temperature “S6” A36 Fan 3 fault A59 Case cleaning (DI input)
A14 Low temperature “S6” A367 Fan 4 fault A60 HACCP alarm
A15 Digital input 1 alarm A38 Fan 5 fault A61 Condenser alarm
A16 Digital input 2 alarm A39 Fan 6 fault A62 High T1 alarm
A17 Pc high alarm A4 0 Fan 7 fault A63 Low T1 alarm
A18 Pc low alarm A41 Fan 8 fault A64 High T2 alarm
A19 Compressor 1 fault A42 Amb. mode A65 Low T2 alarm
A20 Compressor 2 fault A43 Stepper motor alarm A66 High T3 alarm
A21 Compressor 3 fault A44 Battery alarm A67 Low T3 alarm
A22 Compressor 4 fault A45 Standby mode (“r12 ” or DI) A68 High temperature B
A23 Compressor 5 fault A46 Fan 5 fault A69 Low temperature
A70 High temperature C E1 Faults in the controller E24 Sensor “S2” error
A71 Low temperature C E2 Air sensor open circuit E25 Sensor “S3” error
A72 High temperature D E3 Air sensor short circuit E26 Sensor “S4” error
A73 Low temperature D E4 Defrost sensor open circuit E27 Defrost sensor “S5” error
A74 Adaptive defrost fault E5 Defrost sensor short circuit E28 Product sensor “S6” error
A75 Adaptive defrost evaporator iced E6 Realtime clock error (battery) E29 Sensor Sair error
A76 Adaptive Defrost not defrosted E7 “S4” out sensor open circuit E30 Sensor Saux error
A77 Pump 1 fault E8 “S4” out sensor short circuit E31 T1 error
A78 Pump 2 fault E9 “S3” in sensor open circuit E32 T2 error
A79 Pump 1 & 2 fault E10 “S3” in sensor short circuit E33 T3 error
A80 Condensor blocked E11 Q-actuator error E34 Sensor “S3 ” error B
A81 “S3 ” in “S4” out switched E12 AI input signal outside range E35 Sensor “S3” error C
A82 E13 “S1” sensor open circuit E36 Sensor “S3” error D
A83 E14 “S1” sensor short circuit E37 Sensor “S5” error B
A84 E15 “S2” sensor open circuit E38 Sensor “S6” error B
A85 E16 “S2 ” sensor short circuit E39
A86 E17 “S3” sensor open circuit E40
A87 E18 “S3 ” sensor short circuit E41
A88 E19 Analog input error E42
A89 E20 Po pressure input error E43
A90 E21 Level signal outside the range E44
A91 E22 Signal AK S45 outside range E45
A92 E23 Sensor “S1” error E46
18 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 19

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Communication
Why...?
Although controllers have their own independent control,
communication between controllers and systems open up new
possibilities in terms of service, commissioning, monitoring,
alarming and optimization of energy on installations.
Some tasks can then be centralized in the system, allowing for
example scheduled defrosts, coordinated defrosts between
controllers, lighting control, scheduled stop of refrigeration and
optimization of the suction pressure for energy savings.
Access to any controller connected to the system can now be
done from a central point making set point and setting
adaptation faster and easier.
How…?
The interconnection between the controllers (and system) is done
by the mean of “bus”.
A ”bus” is physically a specic electrical cable containing twisted
wires in the form of a pair, with a shield.
The shield is protecting the signal transmitted on the pair from
external disturbances, it must only be connected to the proper
connection for shielding that is present on each controller.
Connection of the shied must never be done directly to the earth,
thus bypassing internal lters presents.
This can cause serious communication problems.
Communication occurs by sending high frequency digital signals
on the cable. Twisted pair is then a must to carry this signal
without deforming it. Every cable has a capacitance and the eect
of a capacitance is to act as a short circuit at high frequency.
So if capacitance increase, so do the losses.
The capacitance of the cable is counter balanced by the coil eect
created by the twisted pair, ensuring the signal is kept in form
properly across the cable. Recommended cross section of the
wiring must be respected to avoid increasing the capacitance of
the cable by increasing is cross section.
The bigger doesn’t mean the better in this case.
The electrical signals sent over the cable can have an analogy in
the following form:
A length of pipe is lled with water and the pipe is closed at both
ends. If an hammer is used on one of the ends, a pressure wave
(signal) will travel through the pipe and bounce at the other end,
going back to where it came from and thus mixing with the
incoming wave. This deforms the signal. To avoid that, we should
put a damper on both ends. This is called termination of the bus,
and it’s done by means of connecting resistors of 120Ω on both
ends of the cable.
The resistors are supplied with the system.
=
Not OK
!
OK
Termination of the bus: 120Ω
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 19
Page 20

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Cables selection / termination
When all cables have been mounted on the dierent units, the
cable must be terminated.
A section must be terminated at both ends.
The section must be terminated using a resistor.
A repeater will normally terminate two cable sections.
The termination should be made with 120Ω resistor
(the resistor can be in the range 100 to 130Ω).
Bus standards in use with the controllers are called:
LONbus RS-485, MODbus RS-485.
System
R
AB
R= 120Ω
Repeater
Requiements to installation
Cable type
Cables twisted in pairs must be used, and they may be provided
with a screen. Some types of communication require a cable with
a screen to be used.
The conductor’s cross section must be at least 0.60mm.
Examples of cable types:
y Belden 7703NH, single-thread 1 x 2 x 0.65mm, with screen.
y Belden 7704NH, single-thread 2 x 2 x 0.65mm, with screen.
y LAPP UNITRONIC Li2YCY (TP), multi-thread 2 x 2 x 0.65mm, with
screen.
y Dätwyler Uninet 3002 4P, single-thread 4 x 2 x 0.6mm, with screen.
Conductors
The wires in the cable that is connected to the controller must be
correct. Although there are four wires in the cable inside the
screen, you cannot simply choose colours freely. The wires are
twisted in pairs, example 2 and 2, and you must use a pair that is
twisted around each other.
If there are several “vacant” pairs in the cable, they must be used
for nothing else than data communication.
R
AB
R= 120Ω
Cable length
A cable length must not exceed 1200m (500m for Lon-FTT10.)
A repeater must be used for longer lengths.
See the additional requirements for the respective communication
forms.
20 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 21

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Cables
Note
Our experience indicates that problems can occur with
communication due to the following weaknesses:
Long wire ends
Do not strip more of the cable insulation than strictly necessary.
Max. 3-4cm. Continue the twisting of the cables right up to the
terminals.
Stubs
Avoid stubs on the cable. Feed the cable right to the end and then
back again.
Noise sources
Keep the cable away from electrical noise sources and power
cables (relays, contactors and especially electronic ballast for strip
lights are strong noise sources).
A distance of at least 10-15cm will be sucient.
Cable length extremities
Each section of data communication must be terminated
correctly.
Screen
See the respective communication forms. There should be a
continuity of the screening cable up to the last controller.
Cable tray
When the cable is ducted with other cables, there is a strong risk
that electrical noise will be transferred.
Keep away from live cables.
When the cable is ducted in a cable tray, the cable must be fed out
and right up to the controller. The fast solution where only wires
are fed out will cause problems.
Min 10-15cm
Max 10-15cm
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 21
Page 22

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Cabinet mounting
When controllers are installed in a cabinet, internal cable ducting
must also comply with the relevant requirements.
Use this cable ducting when one or more controllers are installed
in a cabinet.
The short connections between controllers must also be of the
correct cable types.
Keep a distance to relays, their cables and other things emitting
electric noises.
Bus standards
in use with the controllers are called:
LONbus RS-485, MODbus RS-485.
Standards dene the kind of electrical signals and “language”
used on the bus.
Signals are at a voltage level of 5V and at a speed of several
thousand bits per second, but this cannot be measured by
common voltmeters.
An oscilloscope is needed to visualize the presence of the signal.
Min
10-15cm
Lon RS-485 bus & wiring
The cable must be with screen.
The cable is connected from controller to controller, and no
branches are allowed on the cable.
If the cable length exceeds 1.200m a repeater AKA223 must be
inserted.
If the data communication cable runs through an electrically noisy
environment which impairs the data signal, one ore more
repeaters must be added to stabilize the signal.
Every 60 controllers a repeater AKA223 needs to be placed.
Conductors
The two wires are looped from device. There are no polarisation
requirements.
On some controllers, the clamps are designated A and B.
On others there is no designation.
Otherwise the connections are identical.
If the screen used, it must be connected to the system device and
any repeaters.
A screen must always be looped from device to device.
The screen must not be connected to anything else.
Lon RS-485 bus
RS-485
System
Wiring
max 1.200m
Lon RS-485
OK
OK
OK
22 DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
Page 23

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
MOD-bus
This data communication can be used in the series:
y EKC...
The system device must be:
y System manager type AK2-SM.
y Monitoring unit type AK2-AM.
Wiring
The cable must be with screen.
The cable is connected from controller to controller, and no
branches are allowed on the cable.
If the cable length exceeds 1.200m a repeater type AKA222 must
be inserted.
Every 32 controllers a repeater AKA222 is to be placed.
If the data communication cable runs through an electrically noisy
environment which impairs the data signal, one or more repeaters
must be added to stabilise the signal.
AK-SM
MOD
max 1.200m
32
32
Conductors
The wires are looked from device to device:
y A is connected to A.
y B is connected to B.
The screen must be connected to the system device, all
controllers and any repeaters.
A screen must always be looked from device to device.
The screen must not be connected to anything else.
The screen is earthed inside the system device and must not be
earthed in any other way.
MOD
A+ B- A+ B- A+ B-
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626 23
Page 24

Fitter notes – Electronic Controls
Addressing
Each controller need to have an unique address in the range of
1 to 120. This address can be set via parameter “o03” or by means
of rotary switch, depending of the type of controller.
If parameter “o03” and “o04” are not visible, it means that the
communication card is not seen as present by the controller.
Always power o the controller before inserting/extracting a
communication card.
A scan can be perform by the system to discover the connected
addresses. It is important that no address is used more than once!
Display EKA 163/164
L<15m
Max 15m
Displays communication
Some controllers allow remote placement of display, this can be
done in two ways:
y On short distances, less than 15m, connector type display can
be used.
y On long distance, up to 1.000m, Modbus display must be used
with communication cable.
Then, to activate the communication between the remote display
and the controller, an address must be set in parameter “o03”.
Trouble shooting
Trouble shooting communication without an oscilloscope can
prove dicult but there is some basic verication that can be
done:
y Are all controllers and systems properly earthed?
y Is the termination resistors in place, are they of the correct
value of 120Ohm?
y Is the shield not in contact with the earth somewhere?
That can be check with an ohmmeter, disconnect from the
system before measuring between the shield and the Earth.
y Is the used communication cards of the proper type?
y If Modbus is in use, is the polarity respected everywhere?
L>15m
EKA 163A/164A
12V
A
Max 1000m
Data com
B
RS MOD
54 55 56 57
A+
B-
58
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products already on order
provided that such alternations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
DKRCC.PF.000.G2.02 / 520H8626
© Danfoss A/S (EL-MSSM/AZ), 2014-March
 Loading...
Loading...