Page 1

Controller for operation of
evaporator on water chiller
EKC 316A
Manual
Page 2
2 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Contents
Introduction ....................................................................................................... 2
Operation ............................................................................................................ 3
Survey of functions .......................................................................................... 4
Operation ............................................................................................................ 8
Introduction
Application
The controller and valve can be used where there are requirements to accurate control of superheat and temperature in connection with refrigeration.
E.g.:
• Processing plant (water chillers)
• Cold store (air coolers)
• A/C plant
Advantages
• The evaporator is charged optimally – even when there are great
variations of load and suction pressure.
• Energy savings – the adaptive regulation of the refrigerant injection ensures optimum utilisation of the evaporator and hence a
high suction pressure.
• The superheating is regulated to the lowest possible value at
the same time as the media temperature is controlled by the
thermostat function.
Menu survey ....................................................................................................... 8
Data .....................................................................................................................10
Connections .....................................................................................................10
Ordering ............................................................................................................10
Functions
• Regulation of superheat
• Temperature control
• MOP function
• ON/OFF input for start/stop of regulation
• Input signal that can displace the superheat reference or the
temperature reference
• Alarm if the set alarm limits are exceeded
• Relay output for solenoid valve
• PID regulation
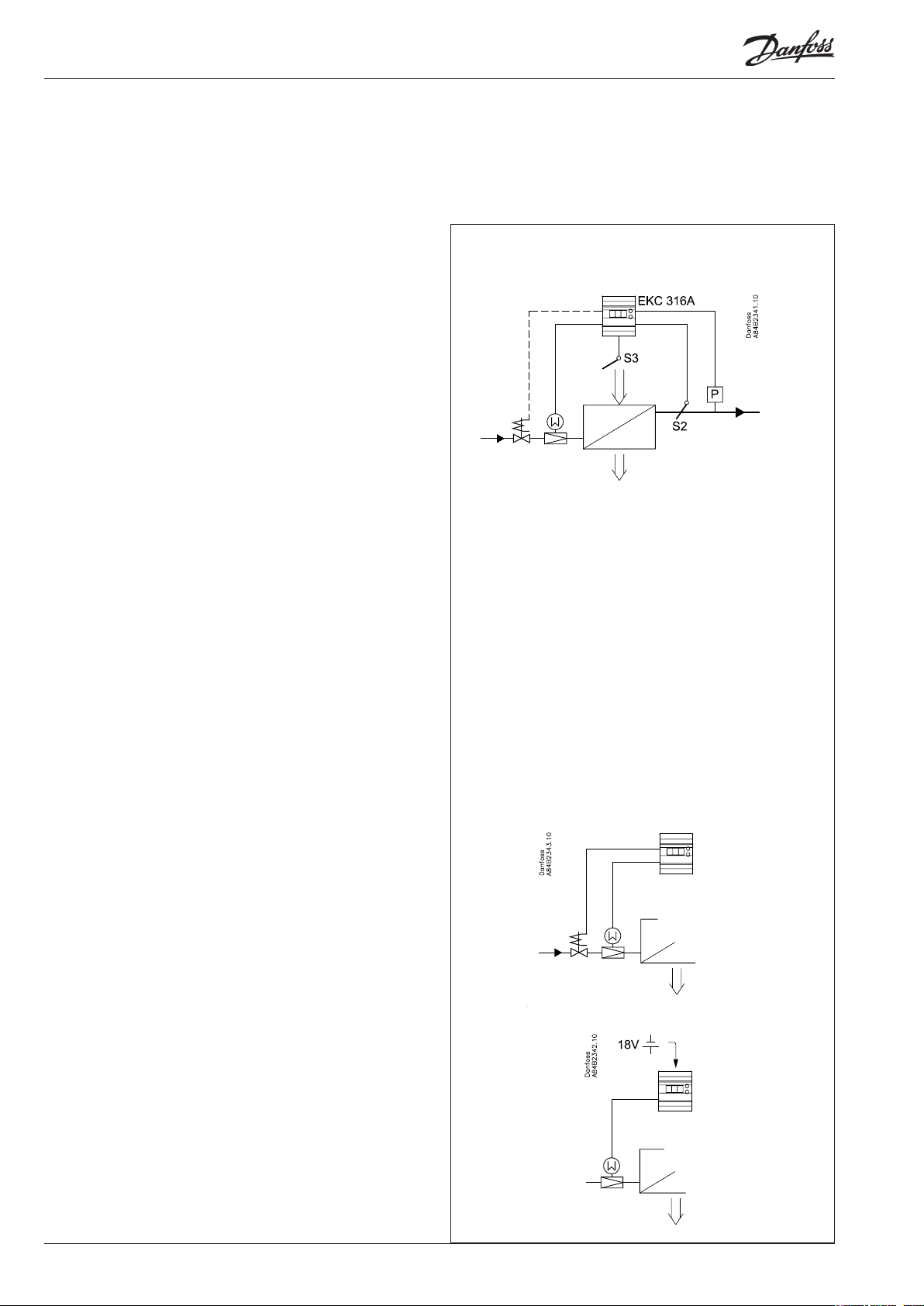
System
The superheat in the evaporator is controlled by one pressure
transmitter P and one temperature sensor S2.
The expansion valve is with step motor of the type ETS.
If temperature control is required, this can be accomplished via
a signal from temperature sensor S3 placed in the air flow before
the evaporator. The temperature control is an ON/OFF thermostat
that opens for the liquid ow when refrigeration is required – the
ETS valve opens and the thermostat relay cuts in.
For safety reasons the liquid ow to the evaporator must be cut
off if there is power failure for the controller. As the ETS valve is
provided with step motor, it will remain open in such a situation.
There are two ways of coping with this situation:
- Mounting of a solenoid valve in the liquid line
- Mounting of battery backup for the valve
Superheat regulation
Shown on page 12 are the different forms of regulation
algorithms which the controller can be set for.
Page 3
EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 3
Operation
Superheat function
You may choose between two kinds of superheat, either:
• Adaptive superheat or
• Load-dened superheat
MOP
The MOP function limits the valve’s opening degree as long as the
evaporating pressure is higher than the set MOP value.
Override function
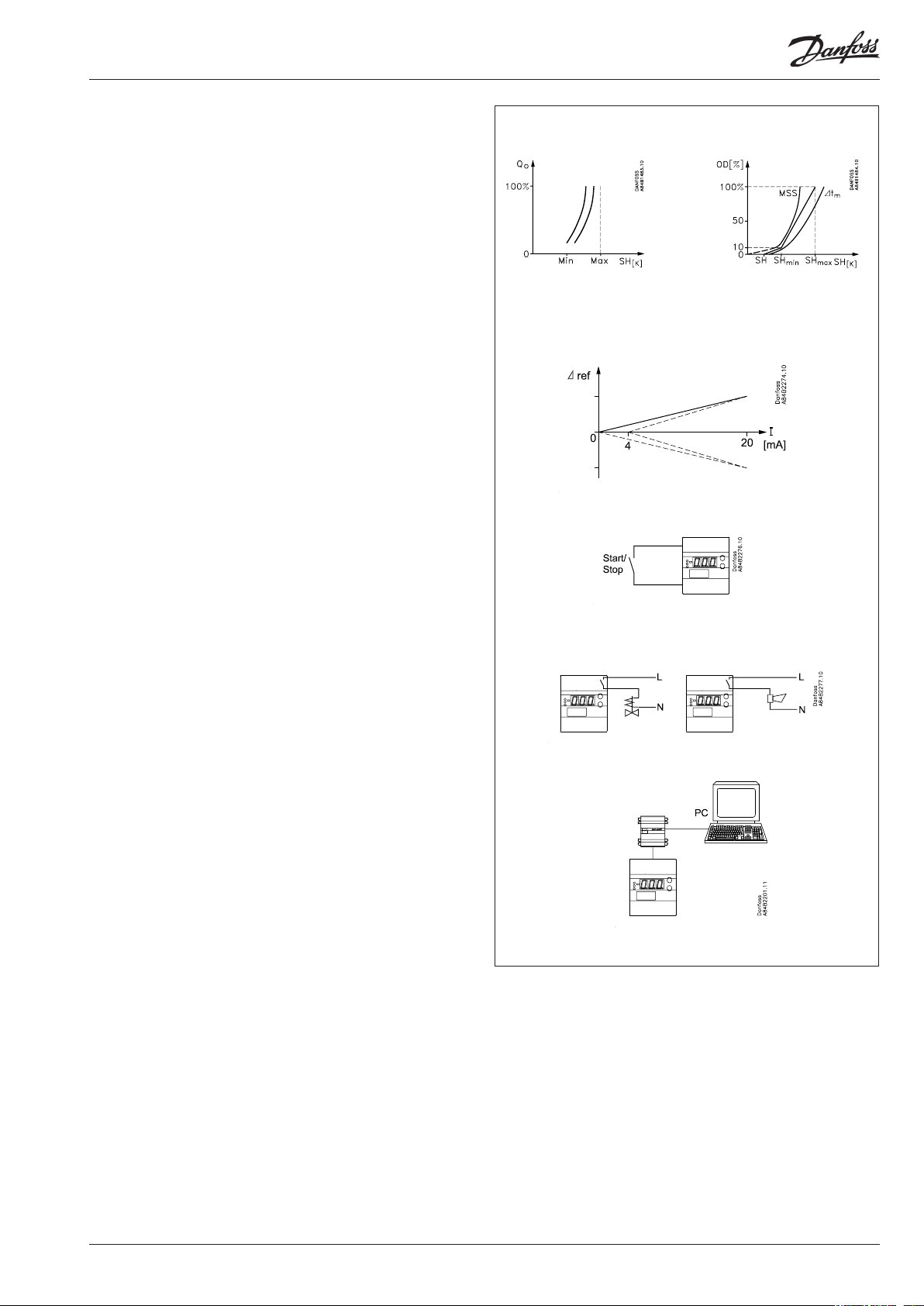
Via the analog input a displacement can be made of the temperature reference or of the superheat reference. The signal can either
be a 0-20 mA signal or a 4-20 mA signal. The reference can be
dsplaced in positive or negative direction.
The signal can be used to override the valve's opening degree.
External start/stop of regulation
The controller can be started and stopped externally via a contact
function connected to input terminals 1 and 2. Regulation is
stopped when the connection is interrupted. The function must
be used when the compressor is stopped. The controller then
closes the solenoid valve so that the evaporator is not charged
with refrigerant.
Relays
The relay for the solenoid valve will operate when refrigeration is
required. The relay for the alarm function works in such a way that
the contact is cut in in alarm situations and when the controller is
de-energised.
PC operation
The controller can be provided with data communication so that it
can be connected to other products in the range of ADAP-KOOL®
refrigeration controls. In this way operation, monitoring and data
collection can be performed from one PC – either on the spot or in
a service company.
See also page 14.
Page 4
4 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Survey of functions
Function Para-
meter
Normal display
Normally the superheat is shown (but the valve’s opening degree or air temperature
may also be selected. See o17).
Reference Thermostat control
Set point (set only if r14=1)
Regulation is performed based on the set value provided that there is no external
contribution (o10).
(Push both buttons simultaneously to set the setpoint).
Differential
When the temperature is higher than the reference plus the set dierential, the solenoid valve’s relay will be activated. It will become deactivated when the temperature
drops below the set reference.
Ref. Diff.
Unit
Here you select whether the controller is to indicate the temperature values in °C or
in °F.
And pressure values in bar or psig.
If indication in °F is selected, other temperature settings will also change over to
Fahrenheit, either as absolute values or as delta values
The combination of temperature unit and pressure unit is depicted to the right.
External contribution to the reference
This setting determines how large a contribution is to be added to the set setpoint
when the input signal is max. (20 mA). See o10.
Correction of signal from S2
(Compensation possibility through long sensor cable).
Correction of signal from S3
(Compensation possibility through long sensor cable).
Start/stop of refrigeration
With this setting refrigeration can be started and stopped. Start/stop of refrigeration
can also be accomplished with the external switch function. See also appendix 1.
Parameter by operation via
data communication
SH / OD% / S3 temp
- * TempSetpoint.
r01 * Differential
r05 Units (Menu = Misc.)
0: °C + bar
1: °F + psig
(in AKM only °C + bar – is displayed
– whatever the setting).
r06 ExtRefOset
r09 Adjust S2 (Menu = Misc.)
r10 Adjust S3 (Menu = Misc.)
r12 Main Switch
Define thermostat function
0: No thermostat function. Only the superheat is regulated
1: Thermostat function as well as regulation of superheat.
Alarm Alarm setting
The controller can give alarm in different situations. When there is an alarm all the
light-emitting diodes (LED) will ash on the controller front panel, and the alarm relay
will cut in.
Alarm for upper deviation
The alarm for too high S3 temperature is set here. The value is set in Kelvin. The alarm
becomes active when the S3 temperature exceeds the actual reference plus A01. (The
actual reference can be seen in u28).
Alarm for lower deviation
The alarm for too low S3 temperature is set here. The value is set in Kelvin. The alarm
becomes active when the S3 temperature drops below the actual reference minus
A02.
Alarm delay
If one of the two limit values is exceeded, a timer function will commence. The alarm
will not become active until the set time delay has been passed. The time delay is set
in minutes.
Battery alarm
Here it is dened whether the controller is to monitor the voltage from the battery
backup. If there is low voltage or no voltage alarm will be given.
*) Only used if thermostat function (r14 = 1) is also to be selected.
r14 Therm. Mode
A01 * Upp.TempAlrm
A02 * Low.TempAlrm
A03 * TempAlrmDel
A34 Batt. alarm
Page 5
EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 5
With data communication the importance of the individual alarms can be
dened. Setting is carried out in the
“Alarm destinations” menu. See also
page 14
Control parameters Injection control
P: Amplification factor Kp
If the Kp value is reduced the regulation becomes slower.
I: Integration time Tn
If the Tn value is increased the regulation becomes slower.
D: Differentiation time Td
The D-setting can be cancelled by setting the value to min. (0).
Max. value for the superheat reference n09 Max SH
Min. value for the superheat reference
Warning! Due to the risk of liquid ow the setting should not be lower than approx.
2-4 K.
MOP
If no MOP function is required, select pos. O.
Start-up time for safety signal
If the controller does not obtain a reliable signal within this period of time the controller will in other ways try to establish a stable signal. (A too high value may result in
a ooded evaporator).
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Signal safety during start-up
The control function uses the value as start value for the valve’s opening degree at
each thermostat cutin. By adaptive control the controller continuously calculates a
new value.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Stability factor for regulation of superheat
With a higher value the control function will allow a greater fluctuation of the super-
heat before the reference is changed. The value should only be changed by specially
trained staff.
Damping of amplification near reference value
This setting damps the normal amplication Kp, but only just around the reference
value. A setting of 0.5 will reduce the KP value by half.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Amplification factor for the superheat
This setting determines the valve’s opening degree as a function of the change in
evaporating pressure. An increase of the evaporating pressure will result in a reduced
opening degree. When there is a drop-out on the low-pressure thermostat during
start-up the value must be raised a bit. If there is pendling during start-up the value
must be reduced a little.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Definition of superheat regulation (Ref. appendix 3)
1: Lowest permissible superheat (MSS). Adaptive regulation.
2: Load-dened superheat. The reference is established based on the line formed by
the three points: n09, n10 and n22.
Value of min. superheat reference for loads under 10%
(The value must be smaller than ”n10”).
Max. opening degree (AKV only)
The valve’s opening degree can be limited. The value is set in %
The parameters ”n37” to ”n42” are settings for step motor ETS 50. The settings in
n37 must be changed when another valve is used. The other settings should not
be changed.
Number of steps from 0% to 100% open n37 Max. steps (0 - 5000 step)
Spindle stroke speed (number of steps per second) n38 Steps / sec (10 - 300 step/sec)
Compensation value for spindle play at valve’s closing point (number of steps) n39 Start bcklsh (Menu=Danfoss only)
Compensation value for spindle play during operation (number of steps) n40 Backlash (Menu=Danfoss only)
Valve denition
1=Valve must open when more capacity is required (NC function)
2=Valve must close when more capacity is required (NO function)
Compensation direction
1=Compensation takes place when the valve opens (normal setting)
2=Compensation takes place when the valve closes
Attenuation factor for the inner loop gain
Used only when o56 = 2 or 3.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
n04 Kp factor
n05 Tn sec.
n06 Td sec.
n10 Min SH
n11 MOP (bar)
(A value on max (60) corresponds to
O)
n15 StartUp time
n17 Start OD%
n18 Stability
n19 Kp Min
n20 Kp T0
n21 SH mode
n22 SH Close
n32 ETS OD% Max (Menu=Danfoss only)
n41 Valve type (Menu=Danfoss only)
n42 Comp.dir. (Menu=Danfoss only)
n43 Atten. factor
Page 6

6 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Integration time for the inner loop gain
Used only when o56 = 2 or 3.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Safety value for the lower temperature reference
Used only when o56 = 3.
The value should only be changed by specially trained sta.
Miscellaneous Miscellaneous
Address
If the controller is built into a network with data communication, it must have an
address, and the master gateway of the data communication must then know this
address.
These settings can only be made when a data communication module has been
mounted in the controller and the installation of the data communication cable has
been completed.
This installation is mentioned in a separate document “RC8AC”
The address is set between 0 and 119 o03 -
n44 TnT0 sec
n45 Min.Lim.Ref.
Following installation of a data communication module, the controller can
be operated on a par with the other
controllers in ADAP-KOOL® refrigeration controls.
The address is sent to the gateway when the menu is set in pos. ON
(The setting will automatically change back to O after a few seconds.)
Input signal for reference displacement
Denition of function and signal range.
0: No signal
1: Displacement of temperature reference with 0-20 mA
2: Displacement of temperature reference with 4-20 mA
3: Displacement of superheat reference with 0-20 mA
4: Displacement of superheat reference with 4-20 mA
(1-4 or 0 mA will not give a displacement. 20 mA will displace the reference by the
value set in menu r06)
5: Forced control of valves max. opening degree with 0-20 mA
6: Forced control of valves max. opening degree with 4-20 mA
(5-6: 4 or 0 mA will force close the valve. 20 mA will allow 100% opening degree. With
a current signal which is less than the 20 mA the opening degree will be limited so
the PI regulations opening degree not will exceed this value.)
Frequency
Set the net frequency.
Select signal for showing display
Here you can select the signal to be shown in the normal display.
1: Superheat
2: Valve’s opening degree
3: Air temperature
(If you during operation give the lower button a brief push, you can see the following: The S3 temperature, if 1 has been selected. The superheat reference, if 2 has been
selected. Temperature reference if 3 has been selected)
Manual control of outputs
For service purposes the individual relay outputs and the ETS-output can be forced
However only when regulation has been stopped.
OFF: No override
1: Relay to the solenoid valve is ON.
2: Relay to the solenoid valve is OFF
3: Alarm relay is activated (connection established between terminals 12 and 13).
4: Forced control of valve opening degree with 0-20 mA signal (0=closed, 20 open)
5: Forced control of valve opening degree with 4-20 mA signal (4=closed, 20 open)
At "4" and "5" relays for solenoid valve and alarm relays are o.
In settings 1-3, ”o45” will become active and the ETS output can be set manually.
Manual control of the ETS valve
When ”o18” is activated (1-3) the valve’s opening degre can be determined from this
menu.
Working range for pressure transmitter
Depending on the application a pressure transmitter with a given working range
is used. This working range (say, -1 to 12 bar) must be set in the controller. The min.
value is set.
The max. value is set o21 MaxTransPres.
Selection of control mode
Depending on the application control can be carried out based on different parameters.
The three possibilities are shown in appendix 4.
1=normal control
2=with inner loop regulation and T0
3=with inner loop regulation and S4 temperature less T0
o04 -
o10 AI A type
o12 50 / 60 Hz
(50=0, 60=1)
o17 Display mode
o18 Manual ctrl
o45 Manual ETS OD%
o20 MinTransPres.
o56 Reg. type
Page 7

EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 7
Refrigerant setting
Before refrigeration can be started, the refrigerant must be dened. You can select the
following refrigerants:
1=R12. 2=R22. 3=R134a. 4=R502. 5=R717. 6=R13. 7=R13b1. 8=R23. 9=R500.
10=R503. 11=R114. 12=R142b. 13=User dened. 14=R32. 15=R227. 16=R401A.
17=R507. 18=R402A. 19=R404A. 20=R407C. 21=R407A. 22=R407B. 23=R410A.
24=R170. 25=R290. 26=R600. 27=R600a. 28=R744. 29=R1270.
(Warning: Wrong selection of refrigerant may cause damage to the compressor).
Service Service
A number of controller values can be printed for use in a service situation
Read value of external current signal (AIA) u06 AI A mA
Read status of input DI (start/stop input) u10 DI
Read the ongoing cutin time for the thermostat or the duration of the last completed
cutin
Read the temperature at the S2 sensor u20 S2 temp.
Read superheat u21 SH
Read the control’s actual superheat reference u22 SH ref.
Read the valve’s opening degree u24 OD%
Read evaporating pressure u25 Evap. pres. Pe
Read evaporating temperature u26 Evap.Press.Te
Read the temperature at the S3 sensor u27 S3 temp.
o30
Refrigerant
u18 Ther. RunTime
Read control reference
(Set setpoint + any contribution from external signal)
Read value of current signal from pressure transmitter (AIB) u29 AI B mA
Operating status
The controller’s operating status can be called forth by a brief (1s) activation of the
upper button. If a status code exists it will be shown. (Status codes have lower priority
than alarm codes. This means that status codes cannot be seen if there is an active
alarm code.
The individual status codes have the following meanings:
S10: Refrigeration stopped by the internal or external start/ stop. 10
S11: Thermostat is cutout 11
Conguration settings (n37, n38, o56 and o30) only available when regulation is stopped (r12 = o).
u28 Temp ref.
-- DO1 Alarm
Read status of alarm relay
-- DO2 Liq. Valv
Read status of relay for solenoid valve
EKC State
(0 = regulation)
Page 8

8 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Operation Menu survey
Display
The values will be shown with three digits, and with a setting you
can determine whether the temperature are to be shown in °C or
in °F. (Pressure in bar or psig.)
Light-emitting diodes (LED) on front panel
There are LED’s on the front panel which will light up when the
belonging relay is activated.
The uppermost LED will indicate when the valve is moving
towards a greater opening degree.
The next LED will indicate when the valve is moving towards a
smaller opening degree.
The third one will indicate when the thermostat demands
refrigeration.
All light-emitting diodes will flash when there is an error in the
regulation.
In this situation you can upload the error code on the display and
cancel the alarm by giving the uppermost button a brief push.
The buttons
When you want to change a setting, the two buttons will give you
a higher or lower value depending on the button you are pushing. But before you change the value, you must have access to the
menu. You obtain this by pushing the upper button for a couple
of seconds - you will then enter the column with parameter codes.
Find the parameter code you want to change and push the two
buttons simultaneously. When you have changed the value, save
the new value by once more pushing the two buttons simultaneously.
Gives access to the menu
Gives access to changes
Saves a change
(or cutout an alarm)
Examples of operations
Set set-point for the thermostat
1. Push the two buttons simultaneously
2. Push one of the buttons and select the new value
3. Push both buttons again to conclude the setting
Set one of the other menus
1. Push the upper button until a parameter is shown
2. Push one of the buttons and nd the parameter you want to
change
3. Push both buttons simultaneously until the parameter value is
shown
4. Push one of the buttons and select the new value
5. Push both buttons again to conclude the setting
Function
Normal display
Shows the actual superheat/ valve's opening
degree/ temperature
Dene view in o17
If you wish to see the expansion valve’s actual
opening degree, give the lower button a brief
push (1s). Dene view in o17
Reference
Set the required set point for the thermostat - * -60°C 50°C 3.0
Differential r01 * 0.1 K 20.0 K 2.0
Units (0=°C+bar /1=°F+psig) r05 0 1 0
External contribution to the reference r06 -50 K 50 K 0..0
Correction of signal from S2 r09 -10.0 K 10.0 K 0.0
Correction of signal from S3 r10 -10.0 K 10.0 K 0.0
Start / stop of refrigeration r12 OFF On On
Dene thermostat function
(0= no thermostat function, 1=On/o thermostat)
Alarm
Upper deviation (above the temperature setting) A01 * 3 K 20 K 5
Lower deviation (below the temperature setting) A02 * 1 K 10 K 3
Alarm’s time delay A03 * 0 min. 90 min. 30
Battery monitoring A34 O On O
Regulating parameters
P: Amplication factor Kp n04 0.5 20 3.0
I: Integration time T n05 30 s 600 s 120
D: Dierentiation time Td (0 = o ) n06 0 s 90 s 0
Max. value of superheat reference n09 2 K 30 K 10
Min. value of superheat reference n10 1 K 12 K 4
MOP (max = o) n11 0.0 bar 60 bar 20
Signal reliability during start-up. Safety time
period.
Should only be changed by trained sta
Signal reliability during start-up – Opening
degree’s start value. Should only be changed by
trained staff.
Stability factor for superheat control.
Changes should only be made by trained sta
Damping of amplication around reference
value
Changes should only be made by trained sta
Amplication factor for superheat
Changes should only be made by trained sta
Denition of superheat control
1=MSS, 2=LOADAP
Value of min. superheat reference for loads
under 10%
Max. opening degree
Changes should only be made by trained sta
”n37” to ”n42” are adapted to valve type ETS 50
and should only be changed through the use of
another valve.
Number of steps from 0-100% opening degree
(x10)
(ETS 50 = 263. ETS 100 = 353)
Number of steps per second n38
Compensation of spindle play at the valve’s
closing point
SW =1.2x
Param-
Min. Max.
eter
- K
- %
r14 0 1 0
n15 0 s 90 s 0
n17 0 100 0
n18 0 10 5
n19 0.2 1.0 0.3
n20 0.0 10.0 0.4
n21 1 2 1
n22 1 K 15 K 2
n32 0 % 100 % 100
000
n37
stp**
10
stp/s
n39 0 stp 100 stp 50
5000
stp **
300
stp/s
Fac.
sett.
263
250
*) Used only when thermostat function (r14 = 1) is selected.
**) The display on the controller can show 3 digits only, but the setting value has 4
digits. Only the 3 most important will be shown. It means fx. 250 will give a setting
of 2500.
Page 9

EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 9
Compensation of spindle play in the control
range
Valve status when power supply interrupted:
1 = NC, 2 = NO (special application)
Compensation of spindle play at the closing
point must take place: 1=when the valve opens,
2=when the valve closes
Attenuation factor for inner loop n43 0,1 1 0.4
Integration time for inner loop (TnT0) n44 10 s 120 s 30
Safety value for lower temperature dierence
for inner loop
Miscellaneous
Controller’s address
ON/OFF switch (service-pin message)
Dene input signal on the analoge input AIA:
0: no signal,
1: Temperature setpoint. 0-20 mA
2: Temperature setpoint. 4-20 mA
3: Displacement of superheat reference. 0-20
mA
4: Displacement of superheat reference. 4-20
mA
5: Forced control of valve's max. opening degree.
0-20 mA
6: Forced control of valve´s max. opening degree
4-20 mA
Set supply voltage frequency o12 50 Hz 60 Hz 50
Select display for ”normal picture”
1: Superheat
2: Valve’s opening degree
3: Air temperature
Manual control of outputs:
OFF: no manual control
1: Relay for solenoid valve: select ON
2: Relay for solenoid valve: select OFF
3: Alarm relay activated (cut out)
4: Forced control of valve's opening degree.
0-20 mA
5: Forced control of valve´s opening degree
4-20 mA
At settings 1-3, ”o45” will be active
Working range for pressure transmitter – min.
value
Working range for pressure transmitter – max.
value
Refrigerant setting
1=R12. 2=R22. 3=R134a. 4=R502. 5=R717.
6=R13. 7=R13b1. 8=R23. 9=R500. 10=R503.
11=R114. 12=R142b. 13=User dened. 14=R32.
15=R227. 16=R401A. 17=R507. 18=R402A.
19=R404A. 20=R407C. 21=R407A. 22=R407B.
23=R410A. 24=R170. 25=R290. 26=R600.
27=R600a. 28=R744. 29=R1270.
Manual control of the valve’s opening degree.
The function can only be operated if ”o18” has
been set.
Selection of control mode:
1=Normal
2 = With inner loop (T0)
3 = With inner loop (S media temperature less
T0)
n40 0 stp 100 stp 100
n41 1 2 1
n42 1 2 stp 1
n45 1 K 20 K 3.0
0 119 0
o03***
- - -
o04***
o10 0 6 0
o17 1 3 1
o18 off 5 0
o20 -1 bar 60 bar -1.0
o21 -1 bar 60 bar 12.0
o30 0 29 0
o45 0 % 100 % 0
o56 1 3 1
Service
Analog input AIA (16-17) u06 mA
Read status of input DI u10 on/o
Thermostat cut-in time u18 min.
Temperature at S2 sensor u20 °C
Superheat u21 K
Superheat reference u22 K
Read AKV valve’s opening degree u24 %
Read evaporating pressure u25 bar
Read evaporating temperature u26 °C
Temperature at S3 sensor u27 °C
Temperature reference u28 °C
Read signal at pressure transmitter input u29 mA
***) This setting will only be possible if a data communication module has been
installed in the controller.
Conguration settings available only when regulation is stopped.
The controller can give the following messages:
E1
E15 Cut-out S2 sensor
E16 Shortcircuited S2 sensor
E17 Cut-out S3 sensor
Error message
E18 Shortcircuited S3 sensor
E19
E20
A1
A2 Low-temperature alarm
Alarm message
A11 No refrigerant has been selected
A43 Check the supply voltage to the step motor
A44 Battery alarm (no voltage or too low voltage)
Fault in controller
The input signal on terminals 16-17 is outside
the range.
The input signal on terminals 14-15 is outside
the range (P0 signal)
High-temperature alarm
Factory setting
If you need to return to the factory-set values, it can be done in this way:
- Cut out the supply voltage to the controller
- Keep both buttons depressed at the same time as you recon nect the supply voltage
Page 10

10 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Data
Supply voltage
Power consumption
Input signal
Sensor input 2 pcs. Pt 1000 ohm
Thermostat relay 1 pcs. SPST
Alarm relay 1 pcs. SPST
Step motor output Pulsating 100 mA
Data communication
Environments
Enclosure IP 20
Weight 300 g
Mounting DIN rail
Display LED, 3 digits
Approvals
24 V a.c. +/-15% 50/60 Hz, 10 VA
(the supply voltage is galvanically separated
from the input and output signals)
Controller
ETS step motor
Current signal 4-20 mA or 0-20 mA
Pressure transmitter 4-20 mA from AKS 33
Digital input from external contact function
Possible to connect a data communication
module
0 to +55°C, during operations
-40 to +70°C, during transport
20 - 80% Rh, not condensed
No shock inuence / vibrations
EU Low Voltage Directive and EMC demands re
CE-marking complied with.
LVD-tested acc. to EN 60730-1 and EN 60730-
2-9
EMC-tested acc. to EN50081-1 and EN 50082-2
If battery backup is used:
Battery requirements:
18V d.c. min. 100 mAh
5 VA
1,3 VA
AC-1: 4 A (ohmic)
AC-15: 3 A (inductive)
Ordering
Type Function Code no.
EKC 316A Superheat controller 084B7088
EKA 173
EKA 175
EKA 174
Temperature sensor Pt 1000 ohm / Pressure transmitter type AKS 33:
Kindly refer to catalogue RK0YG
ETS valves: Kindly refer to data sheet DKRCC.PD-VD1.A1.--
Data communication module (ac-
cessories), (FTT 10 module)
Data communication module (ac-
cessories), (RS 485 module)
Data communication module (ac-
cessories), (RS 485 module)
with galvanic separation
084B7092
084B7093
084B7124
Connections
Necessary connections
Terminals:
25-26 Supply voltage 24 V a.c.
21-24 Supply to step motor
18-19 Pt 1000 sensor at evaporator outlet (S2)
14-15 Pressure transmitter type AKS 33
1-2 Switch function for start/stop of regulation. If a switch is
not connected, terminals 1 and 2 must be shortcircuited.
5-6 Battery (the voltage will close the ETS valve if the control-
ler loses its supply voltage. The battery connection may
however be replaced by installation of a solenoid valve in
the liquid line. This will then be connected to terminals 8-9.
IMPORTANT
The 24 Volts a.c. supply to the EKC 316A at terminals 25
and 26 should be completely isolated from the battery
supply at terminals 5 and 6, and under no circumstances
should these two supplies have common earth.
Application dependent connections
Terminal:
18-20 Pt 1000 sensor for measuring air temperature (S3)
8-9 Thermostat relay
12-13 Alarm relay
There is connection between 12 and 13 in alarm situa tions
and when the controller is dead
16-17 Current signal from other regulation (Ext.Ref.)
3-4 Data communication
Mount only, if a data communication module has been
mounted.
It is important that the installation of the data communi-
cation cable be done correctly. Cf. separate literature No.
RC8AC...
Data communication
< --------------- max. 5 m --------------->
L > 5 m, see page 14
Page 11
EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 11
Installation considerations
Accidental damage, poor installation, or site conditions, can give
rise to malfunctions of the control system, and ultimately lead to a
plant breakdown.
Every possible safeguard is incorporated into our products to
prevent this. However, a wrong installation, for example, could still
present problems. Electronic controls are no substitute for normal,
good engineering practice.
Danfoss wil not be responsible for any goods, or plant components, damaged as a result of the above defects. It is the installer's
responsibility to check the installation thoroughly, and to t the
necessary safety devices.
Particular attention is drawn to the need for a “force closing” signal
to controllers in the event of compressor stoppage, and to the
requirement for suction line accumulators.
Your local Danfoss agent will be pleased to assist with further
advice, etc.
Appendix 1
Interaction between internal and external start/stop functions
and active functions.
Internal Start/stop O O On On
External Start/stop (DI) O On O On
Refrigeration (DO2) O On
Temperature monitoring No Yes
Sensor monitoring Yes Yes
Set congurations Yes No
Appendix 3
The two types of regulation for superheat are, as follows:
Appendix 2
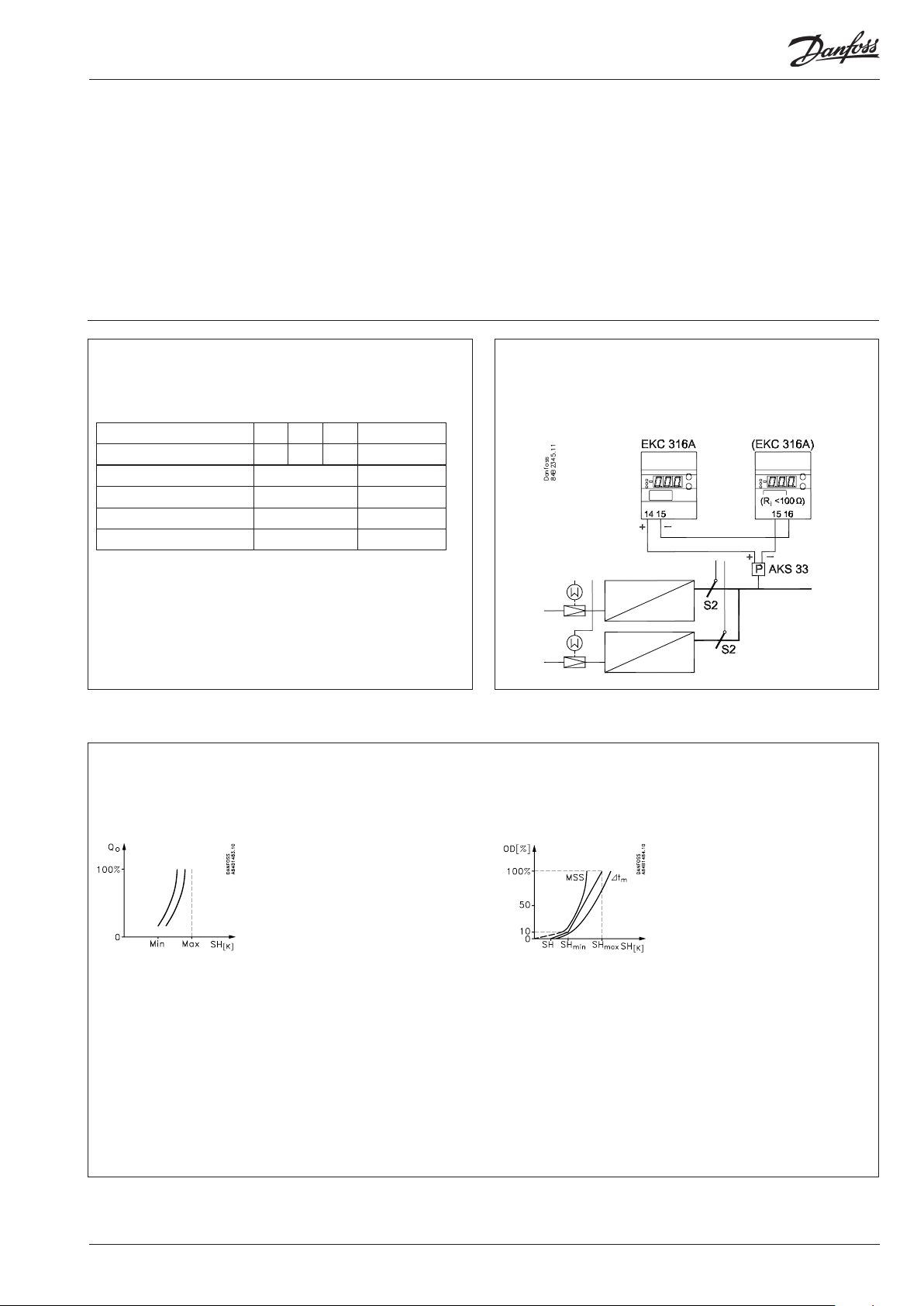
If there are two evaporators sharing the same suction line,
the signal from the pressure transmitter can be used by two
controllers.
Adaptive superheat
Regulation is here based on the evaporator’s load by means of
MSS search (MSS = lowest permissible superheat).
(The superheat reference is lowered to the exact point where
instability sets in).
The superheat is limited by the settings for min.and max.super-
heat.
Load-defined superheat
The reference follows a dened curve.This curve is dened by
three values: the closing value, the min. value and the max.
value. These three values must be selected in such a way that
the curve is situated between the MSS curve and the curve for
average temperature difference ∆Tm (temperature dierence
between media temperature and evaporating temperature.
Setting example = 4, 6 and 10 K).
Page 12

12 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
Appendix 4
Regulation algorithms for the superheat.
There are several algorithms to choose between.
They are set in ”o56”.
Reg.type = 1
This regulation algorithm is used for the classical method
and is recommended for known applications – e.g. for earlier
installations with a Danfoss controller. For a start the values for Kp,
Tn and Td can be set to values corresponding to the earlier ones.
The thermostat function can also be selected, if required.
Reg.type = 2
This regulation algorithm is recommended for new installations
where the thermostat function is also to be used. The regulation
operates with an inner loop which improves the regulation and
makes it easier to make optimum settings.
The combination of adaptive evaporator and temperature control
makes for great temperature accuracy for the refrigerant.
(The algorithm can also be used without thermostat function, if
setting ”3” with temperature sensor is opted out).
Reg.type = 3
This setting is recommended if only one regulation of the
superheat is required.
The regulation algorithm necessitates the mounting of a
temperature sensor in the refrigerant, and as there is only one
sensor input for the temperature of the refrigerant, the setting
cannot be used in combination with the thermostat function.
The temperature sensor is connected to input ”S3” and mounted
in the chilled medium after the evaporator. (Danfoss calls a sensor
S4 when it is mounted in the refrigerant after the evaporator).
This regulation gives the best superheat regulation of the three
mentioned.
The T0 temperature also forms part of an inner loop regulation
The S4 and T0 temperatures also form part of an inner loop regulation.
Page 13

EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 13
Start of controller
When the electric wires have been connected to the controller,
the following points have to be attended to before the regulation
starts:
1. Switch o the external ON/OFF switch that starts and stops the
regulation.
2. Follow the menu survey on page 8, and set the various parameters to the required values.
3. Switch on the external switch, and regulation will start.
4. Follow the actual room temperature or superheat on the
display.
If the superheating fluctuates
When the refrigerating system has been made to work steadily,
the controller’s factory-set control parameters should in most
cases provide a stable and relatively fast regulating system.
If the system however uctuates this may be due to the fact that
too low superheat parameters have been selected:
If adaptive superheat has been selected:
Adjust: n09, n10 and n18.
If load-defined superheat has been selected:
Adjust: n09, n10 and n22.
Alternatively it may be due to the fact that the set regulation
parameters are not optimal.
Check that the ETS valve closes when the
supply voltage to the controller is interrupted
This control is performed if the controller is connected to battery
backup.
The battery will make the step motor move to the end stop and
thus close the valve.
If the time of oscillation is longer than the integration time:
(Tp > Tn , (Tn is, say, 240 seconds))
1. Increase Tn to 1.2 times T
2. Wait until the system is in balance again
3. If there is still oscillation, reduce Kp by, say, 20%
4. Wait until the system is in balance
5. If it continues to oscillate, repeat 3 and 4
If the time of oscillation is shorter than the integration time:
(Tp < Tn , (Tn is, say, 240 seconds))
1. Reduce Kp by, say, 20% of the scale reading
2. Wait until the system is in balance
3. If it continues to oscillate, repeat 1 and 2.
p
The control may be omitted if a solenoid valve is mounted and
connected via terminals 9-10.
Page 14

14 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
ETS connection
If the distance between EKC 316A and the ETS valve exceeds 5 m a
lter must be mounted to obtain the correct valve function.
L < 5 m
5 m < L < 50 m
Connection
Dimensions
DIN-rail mounting
Ordering
Type Description Code no.
AKA 211 Filter
4 x 10 mH
084B2238
Page 15

EKC 316A Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 15
Page 16

List of literature
Instructions RI8HA (extract from this manual).
Here you can see how controllers are mounted and programmed.
Installation guide for extended operation RC8AC
Here you can see how a data communication connection to ADAP-KOOL® Refrigeration control systems can be estab-
lished.
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alternations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respecitve companies. Danfoss and Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
16 Manual RS8CX802 © Danfoss 04-2009 EKC 316A
DE-BD
 Loading...
Loading...