Page 1

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors
Including Fan Drive
www.danfoss.com
Page 2
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Revision history Table of revisions
Date Changed Rev
March 2021 Updated product code information for anti-cavitation / shock valve function; updated radial
and axial loading information
May 2020 Updated table in Dimension drawings section: Standard motor 0103
December 2019 Dimensions for standard motor change. 0102
October 2019 First edition 0101
0105
2 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 3

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Contents
General information
Overview..............................................................................................................................................................................................5
Features and Benefits................................................................................................................................................................ 5
Fan drive motors......................................................................................................................................................................... 5
Features................................................................................................................................................................................................6
Benefits.................................................................................................................................................................................................6
System schematics...........................................................................................................................................................................7
Product features................................................................................................................................................................................8
Technical specifications................................................................................................................................................................. 9
Fluid specifications.......................................................................................................................................................................... 9
Sizing equations.............................................................................................................................................................................10
Operating Parameters
Overview........................................................................................................................................................................................... 11
Pressure............................................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Peak pressure.............................................................................................................................................................................11
Rated pressure...........................................................................................................................................................................11
System pressure........................................................................................................................................................................11
Back pressure............................................................................................................................................................................. 11
Case drain pressure..................................................................................................................................................................11
Temperature and viscosity......................................................................................................................................................... 12
Temperature...............................................................................................................................................................................12
Viscosity........................................................................................................................................................................................12
Speed............................................................................................................................................................................................ 12
Hydraulic fluid.................................................................................................................................................................................12
Filtration............................................................................................................................................................................................ 13
Filters.............................................................................................................................................................................................13
Selecting a filter.........................................................................................................................................................................13
Reservoir............................................................................................................................................................................................13
Line sizing......................................................................................................................................................................................... 14
Motor life...........................................................................................................................................................................................14
Motor shaft connection............................................................................................................................................................... 14
Radial and axial loading...............................................................................................................................................................15
Product code
Model code.......................................................................................................................................................................................16
Fan drive motor code example.................................................................................................................................................16
A - Sense of rotation................................................................................................................................................................ 16
B1 - Displacement.....................................................................................................................................................................16
B2 - Input shaft...........................................................................................................................................................................16
C - Mounting flange.................................................................................................................................................................17
D1 - Cover....................................................................................................................................................................................17
D2 - Rear cover port option...................................................................................................................................................18
D - Rear cover availability.......................................................................................................................................................18
E - Relief valve availability......................................................................................................................................................19
F - Anti-cavitation/shock valve function.......................................................................................................................... 20
G - Integrated reversing modulating function...............................................................................................................20
J - Name plate............................................................................................................................................................................ 21
K - Name plate............................................................................................................................................................................21
Dimension drawings
Mounting flanges...........................................................................................................................................................................23
Shaft options....................................................................................................................................................................................24
Port options......................................................................................................................................................................................27
Selecting port options..................................................................................................................................................................28
Integrated reversing motor with proportional relief and shock/anti-cavitation valves...................................... 29
Features and benefits..............................................................................................................................................................29
Technical data............................................................................................................................................................................29
Integrated reversing function..............................................................................................................................................30
Options
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 3
Page 4

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Contents
Standard relief valve..................................................................................................................................................................... 31
Anti-cavitation check valve........................................................................................................................................................ 32
Proportional relief valve with anti-cavitation valve...........................................................................................................33
Valve settings.............................................................................................................................................................................34
Performance graphs................................................................................................................................................................ 35
Valve settings.............................................................................................................................................................................36
Performance graphs................................................................................................................................................................ 36
Hall effect speed sensor...............................................................................................................................................................37
Dimension drawings
Fan drive motor.............................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Standard motor.............................................................................................................................................................................. 39
Standard motor with split flange ports..................................................................................................................................40
Integrated reversing motor with proportional relief and shock/anti-cavitation valves...................................... 42
Performance data
Motor performance graphs........................................................................................................................................................44
4 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 5
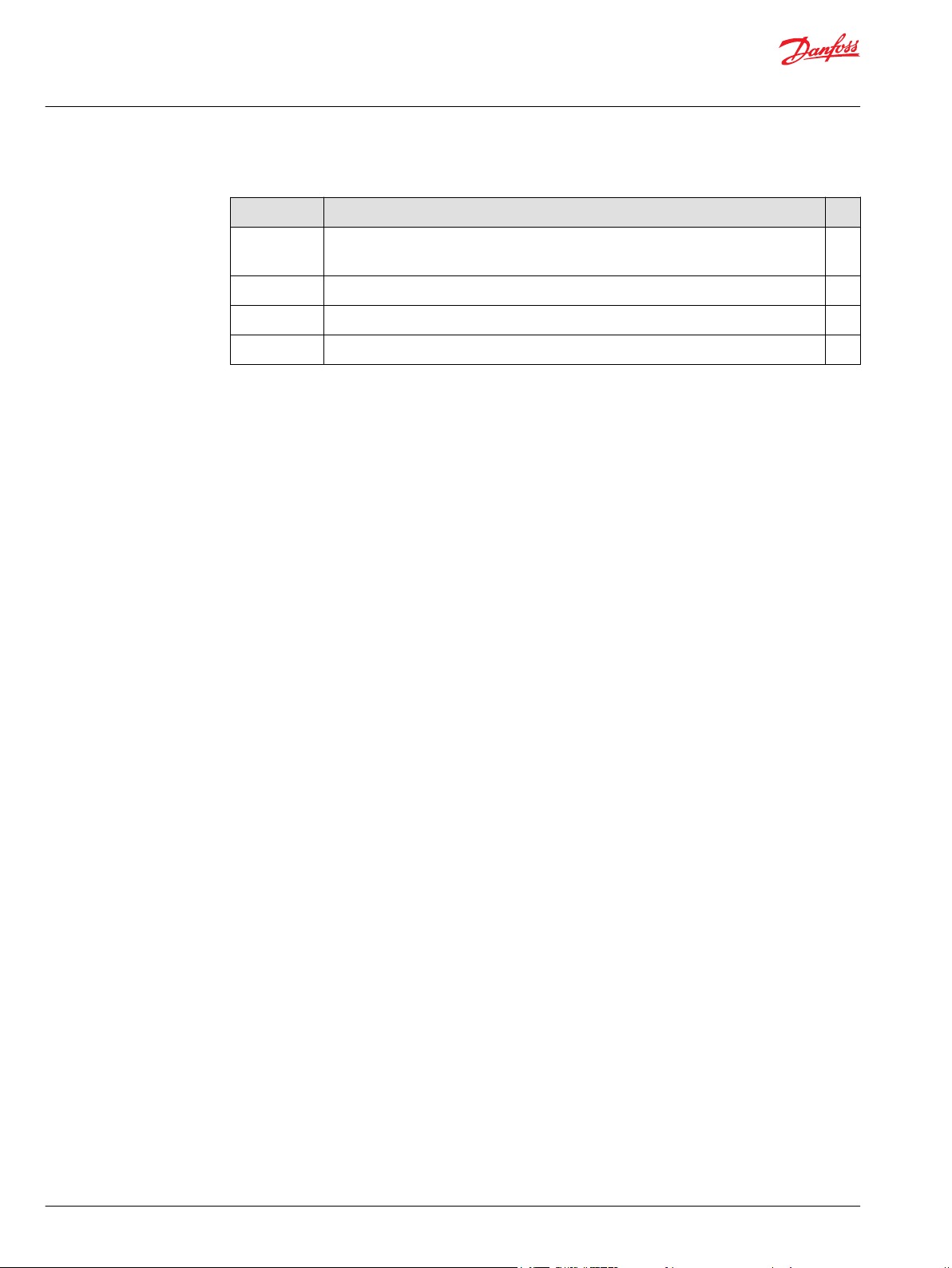
300
250
200
150
100
50
0
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50
Displacement
cm3/rev
P
ressure
psi
P107 949E
400
350
SGM3Y Aluminum
Gear Motor
SGM2Y Aluminum
Gear Motor
D SERIES Cast Iron Gear Motor
SERIES 40 Piston Motor
Bar
in3/rev
5000
4000
3000
2000
1000
0
0.5
0
1.0
1.5
2.0 2.5
3.0
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
Overview
The Danfoss D Series fixed displacement gear motor has been specifically designed for demanding
mobile equipment applications where maximum performance is required at peak power levels and
operating temperatures.
The D Series motor is available in displacements of 17.6cm³ to 48,3cm³ [1.08 in3 to 2.95 in3]. This motor
delivers consistent efficiency across the entire operating range of pressure, speed, and temperature; all in
an industry-leading package size that maximizes power density.
Features and Benefits
•
High strength cast iron construction allows consistently efficient performance in continuous
operation at 276 bar (4000 psi) and 110°C (230°F).
•
Custom engineered shaft bearings and dual pressure-balanced thrust plates optimize internal
bearing lubrication, allowing for high starting torque and long life with fluid viscosities as low as 8
mm²/sec (cSt) [52 SUS].
•
Compact three-piece design with bearings located in the front flange and rear cover minimizes the
overall package length and increases radial load carrying capability, eliminating the need for
outrigger bearings on most applications.
•
Variety of integrated valve options make the D Series motor ideally suited for high performance fan
drive applications.
Fan drive motors
D Series cast iron motors complement the Danfoss portfolio of fan drive products. Including aluminum
and cast iron pumps and motors, piston pumps and motors, valves and microcontrollers, you can apply
the Danfoss range in various combinations to create high-performance fan drive systems. D series motors
with integrated reversing and proportional relief valves are PLUS+1® Compliant for easy plug-andperform™ installations and offer precise control of fan speed to optimize engine cooling performance.
Quick reference chart: Fan drive motors
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 5
Page 6

One piece steel gears
with 12 tooth profile
Flexible configuration
of shaft, flange
and ports
Heavy duty, low friction
hydrodynamic journal bearings
High strength
ductile iron
body and covers
P107 920E
Pressure balanced
bronze-on-steel
thrust plates
High performance
integrated
PLUS+1
High temperature
Viton ® seals
Dust protector
Radial
case drain
compliant
TM
valves
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
Features
Quality components and construction
Benefits
•
Pressure-balanced thrust plates for improved efficiency at extreme pressures and temperatures
•
High-temperature Viton® seals for today’s hotter running machines
•
Three-piece ductile iron construction for increased durability, increased power density, with reduced
adverse efficiency effects at high temperatures
•
High quality steel backed bronze bearings for maximum pressure handling capacity, located in the
front flange, allowing extended radial loading capacity without an external roller bearing
•
Output shaft external dust protector to protect the oil seal from contamination damage
•
Available side or rear ports, SAE A or B flange, with a variety of shafts for versatility
•
Integrated, normally-closed electrohydraulic proportional relief valve option for today’s highperforming fan systems
6 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 7
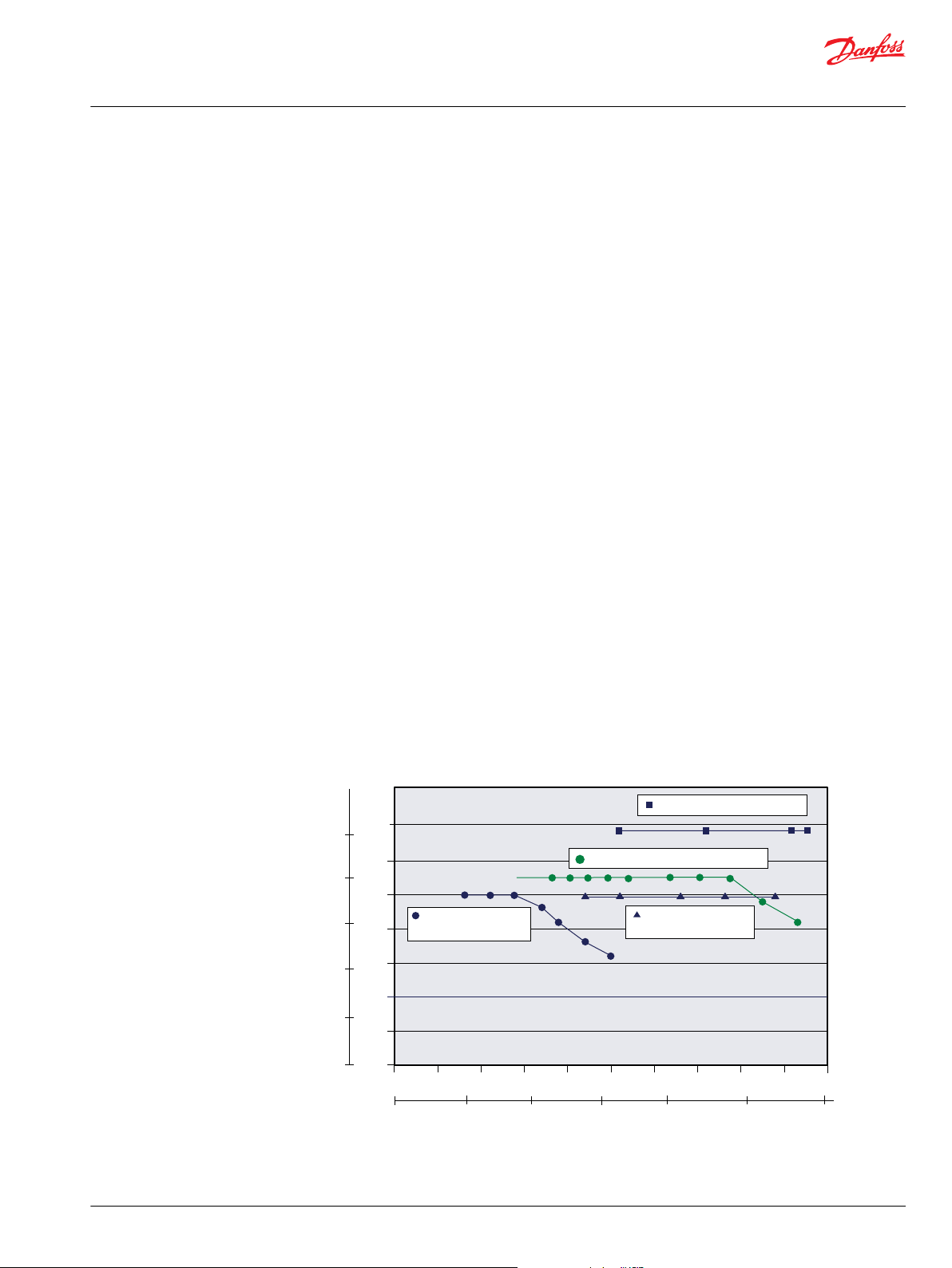
PLUS+1
TM
Microcontroller
Filter
T3
T2
T1
Temperature
sensors
D Series
gear pump
D Series
gear motor
RESERVOIR
DIESEL ENGINE
P107 929E
Case drain
CAN bus
T3
T2
T1
Temperature
sensors
RESERVOIR
D Series
gear motor
Microcontroller
(PLUS+1TM)
Filter
DIESEL ENGINE
Series 45
variable pump
P107 931E
Case drain
CAN bus
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
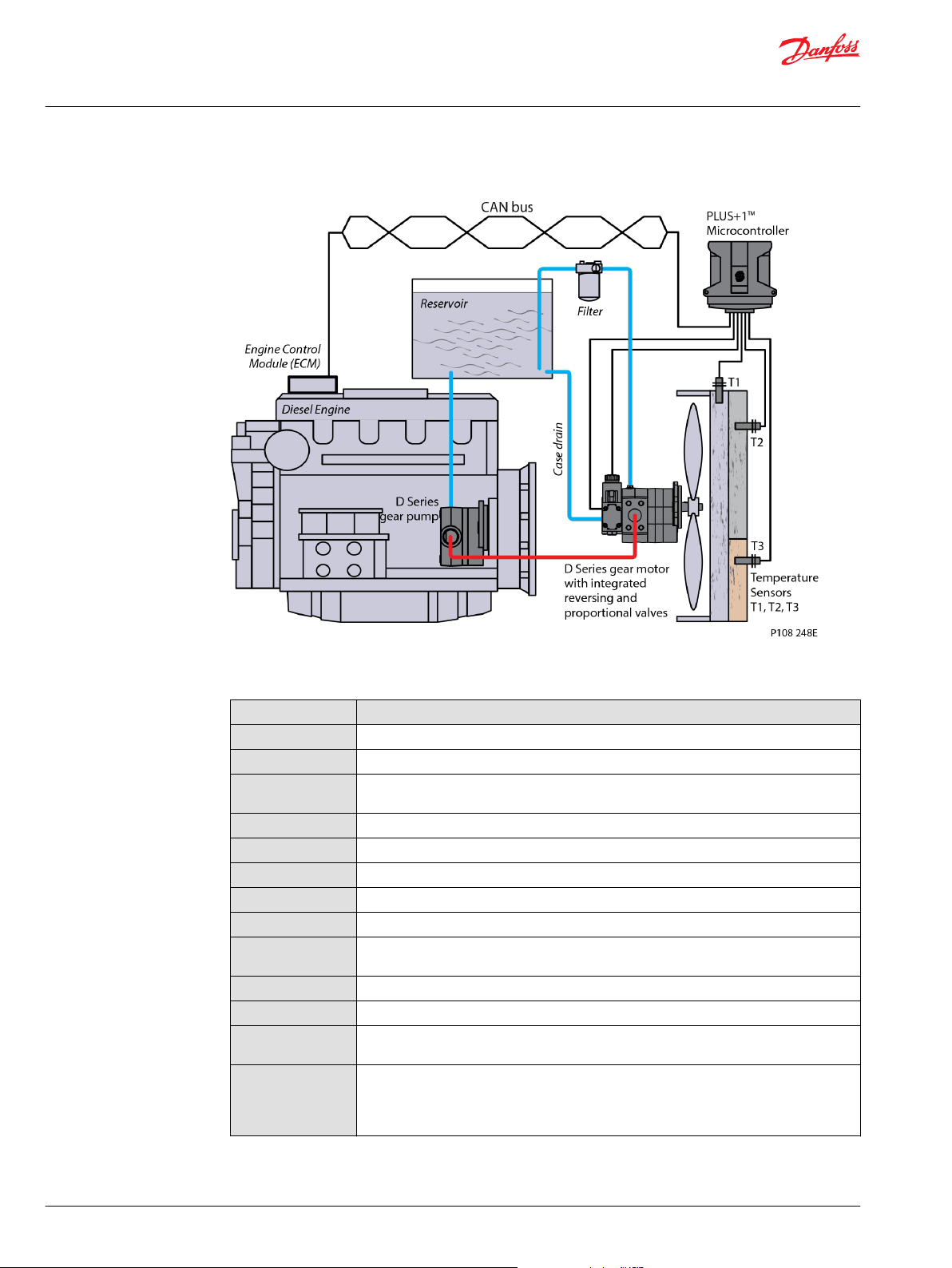
System schematics
Gear pump/gear motor system with electronic control
Piston pump/gear motor system with electronic control
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 7
Page 8
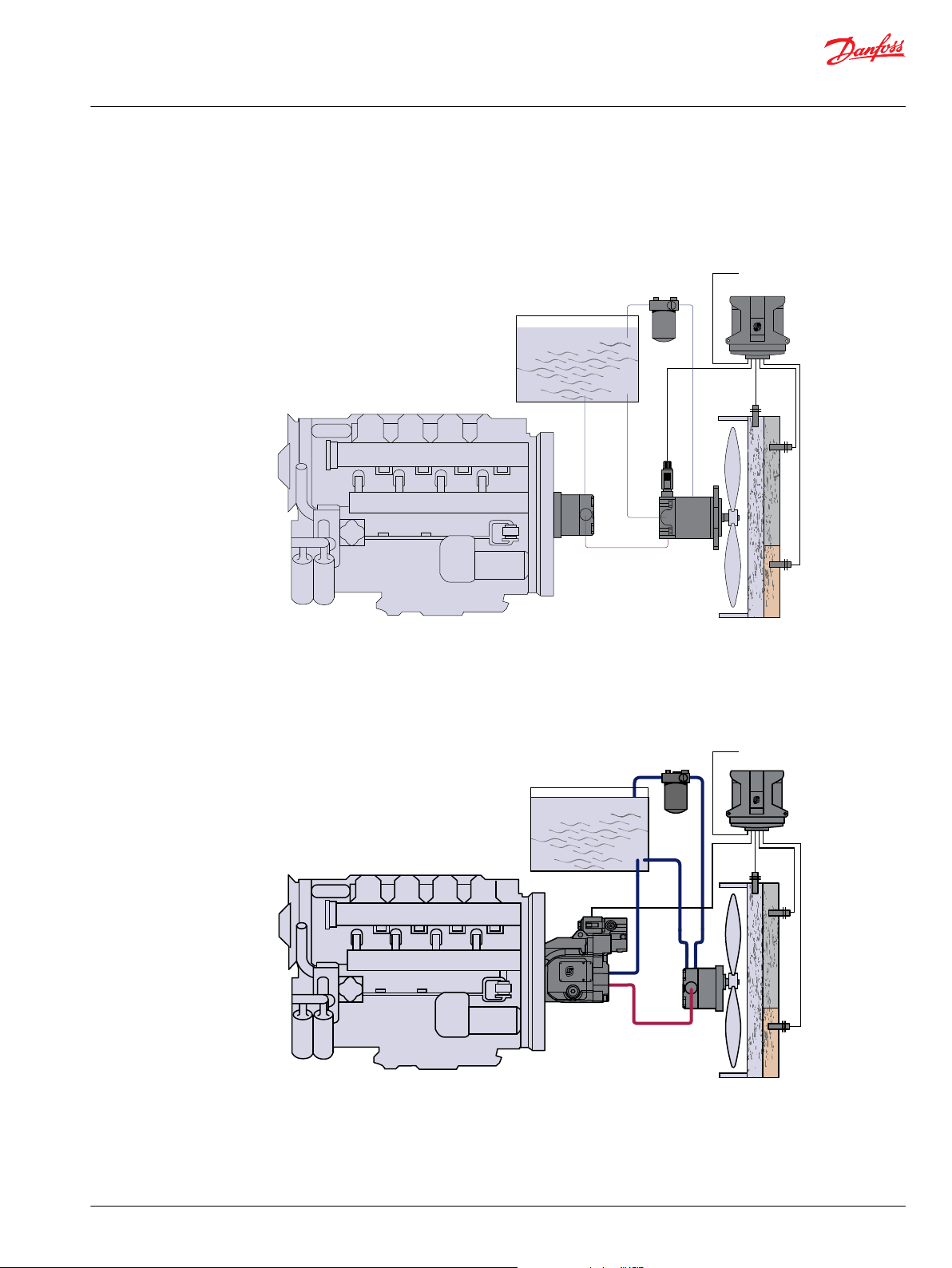
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
Gear pump/gear motor system with integrated reversing valve
Product features
Features Descriptions
Construction
Displacements
Continuous
Pressure
Peak Pressure
Speed
Mounting
Shaft (types)
Fluid viscosity
Filtration
requirement
Inlet options
Fluids
Operating
temperature
Integrated valve
options
Heavy duty ductile iron 3-piece construction
17.6 to 48.3 cm³ [1.08 to 2.95 in3/rev]
276 bar [4000 psi] to 40.9 cm³ [2.50 in3]
303 bar [4400 psi] to 40.9 cm³ [2.50 in3]
600 to 3400 min-1 (rpm) - up to 40.9 cm³ [2.50 in3]
SAE A two bolt, SAE B two bolt
SAE straight keyed, 1:8 tapered keyed, splined
8 mm²/sec (cSt) [52 SUS] minimum, 1600 mm²/sec (cSt) [7500 SUS] maximum
22/18/13 ISO 4406 at motor inlet
SAE O-ring boss, SAE split flange
Petroleum/mineral based
-40°C [-40°F] minimum for cold start
110°C [230°F] normal operating conditions 115°C [239°F] peak intermittent
Proportional relief valve, normally closed, 12 Vdc and 24 Vdc
Two position directional control valve, 12 Vdc and 24 Vdc
Relief valve
Anti-cavitation check valve
8 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 9
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
Technical specifications
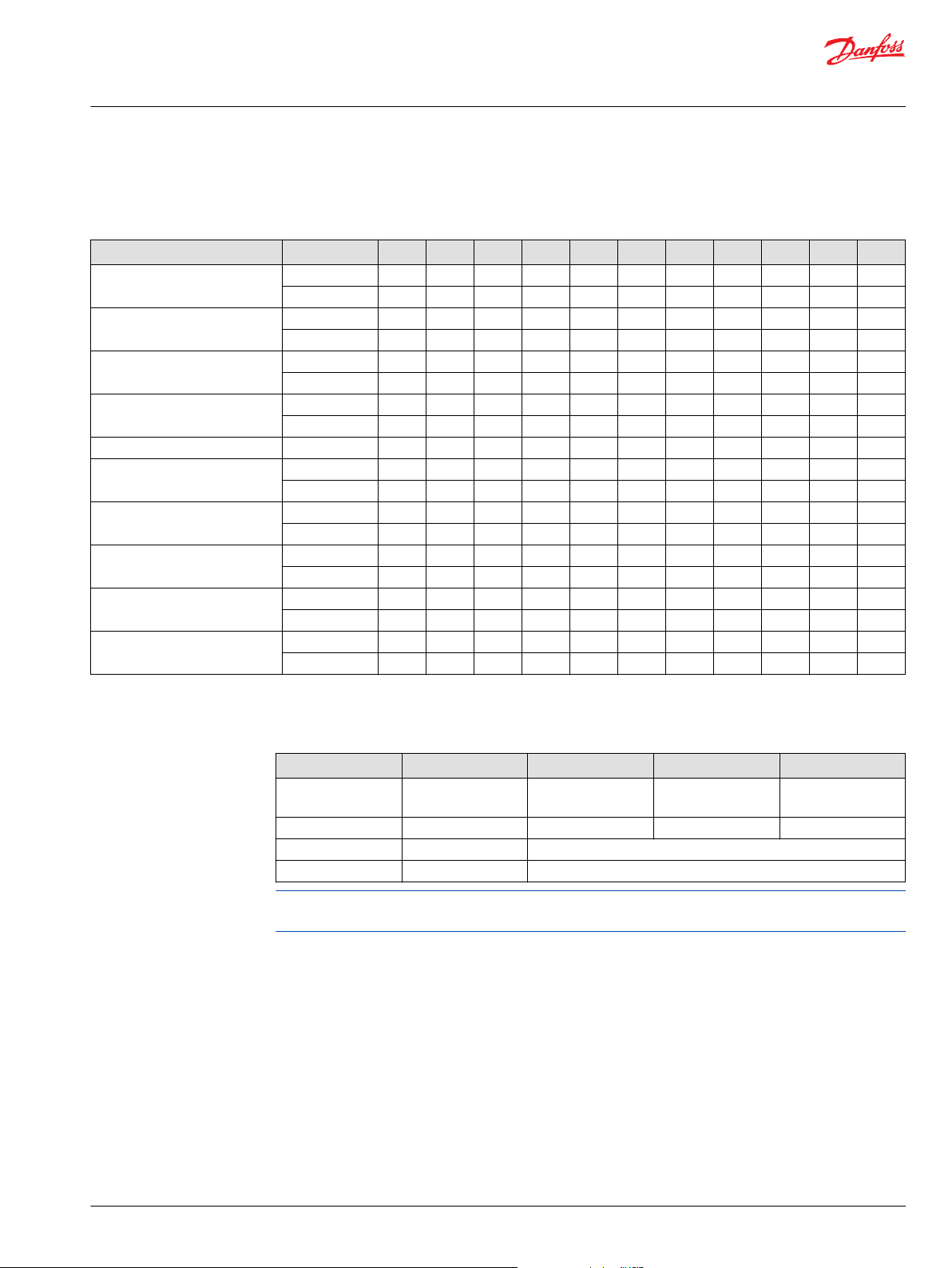
Technical data for D Motors
Ratings Units 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
Displacement cm3/rev 17.6 19.9 22.4 23.2 26.2 30.6 34.4 38.6 40.9 42.9 48.3
in3/rev 1.08 1.22 1.37 1.42 1.6 1.87 2.1 2.36 2.5 2.62 2.95
Rated pressure bar 276 276 276 276 276 276 276 276 276 241 210
psi 4000 4000 4000 4000 4000 4000 4000 4000 4000 3495 3045
Peak pressure bar 303 303 303 303 303 303 303 303 303 265 231
psi 4400 4400 4400 4400 4400 4400 4400 4400 4400 3843 3350
Speed at rated pressure maximum 3400 3400 3400 3400 3400 3400 3400 3400 3400 3000 3000
minimum
Start speed at 1000 PSI rpm 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 400 400
Standard Weight kg 8.53 8.66 8.80 8.94 9.07 9.38 9.53 9.84 9.93 10.16 10.43
lb 18.8 19.1 19.4 19.7 20.0 20.7 21.0 21.7 21.9 22.4 23.0
Mass moment of inertia of
internal rotating components
Theoretical torque at rated
pressure
Theoretical power at rated
speed
Case drain pressure bar 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0 5.0
*
minimum speed at maximum pressure
x10-6 kg•m² 127 138 146 156 172 191 206 228 239 255 276
x10-6slug•ft² 94 102 107 115 127 141 152 168 176 188 204
N•m 65.7 73.4 79.2 87.0 98.2 112.1 122.9 139.6 146.9 138.4 132.4
lbf•ft 48.5 54.2 58.4 64.2 72.4 82.7 90.7 102.9 108.3 102.1 97.6
kW 23.4 26.1 28.2 31.0 35.0 39.9 43.8 49.7 46.1 43.5 41.6
hp 31.2 34.9 37.6 41.3 46.6 53.2 58.4 66.3 61.1 58.0 55.5
psi 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5 72.5
*
1000 600 600 600 600 600 600 600 600 600 600
Fluid specifications
Parameter Unit Minimum Continuous Maximum
Viscosity
Temperature °C [°F] -40 [-40] 110 [230] 115 [239]
Cleanliness n/a ISO 4406 Class 22/18/13 or better
Filtration efficiency charge filtration β
mm²/sec (cSt)
[SUS]
8
[52]
10 - 100
[59 - 456]
=75(β10≥10)
15-20
1600
[7500]
Ratings are based on operation with premium petroleum-based hydraulic fluids containing oxidation,
rust, and foam inhibitors.
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 9
Page 10

Based on SI units
Input flow Q = (l/min)
Output torque M = (N•m)
Output power P = (kW)
Motor speed n = (min
-1
(rpm))
Based on US units
Input f low Q = (US gal/min)
Output torque M = (lbf•in)
Output power P = (hp)
Motor speed n = (min
-1
(rpm))
SI units [US units]
Vg= Displacement per revolution cm3/rev [in3/rev]
pO= Outlet pressure bar [psi]
pi= Inlet pressure bar [psi]
∆p = pO– pi(system pressure) bar [psi]
n = Speed min-1(rpm)
ηv= Volumetric eff ciency
ηm= Mechanical eff ciency
ηt= Overall eff ciency (ηv• ηm)
Variables
Vg• n
1000 • η
v
Q • 1000 • η
v
V
g
Vg• n
231 • η
v
Vg• ∆p • η
m
20 • π
Q • ∆p • η
t
600
Vg• ∆p • η
m
2 • π
Q • ∆p • η
t
1714
Q • 231• η
v
V
g
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
General information
Sizing equations
Use these formulas to determine the nominal motor size for a specific application.
10 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 11
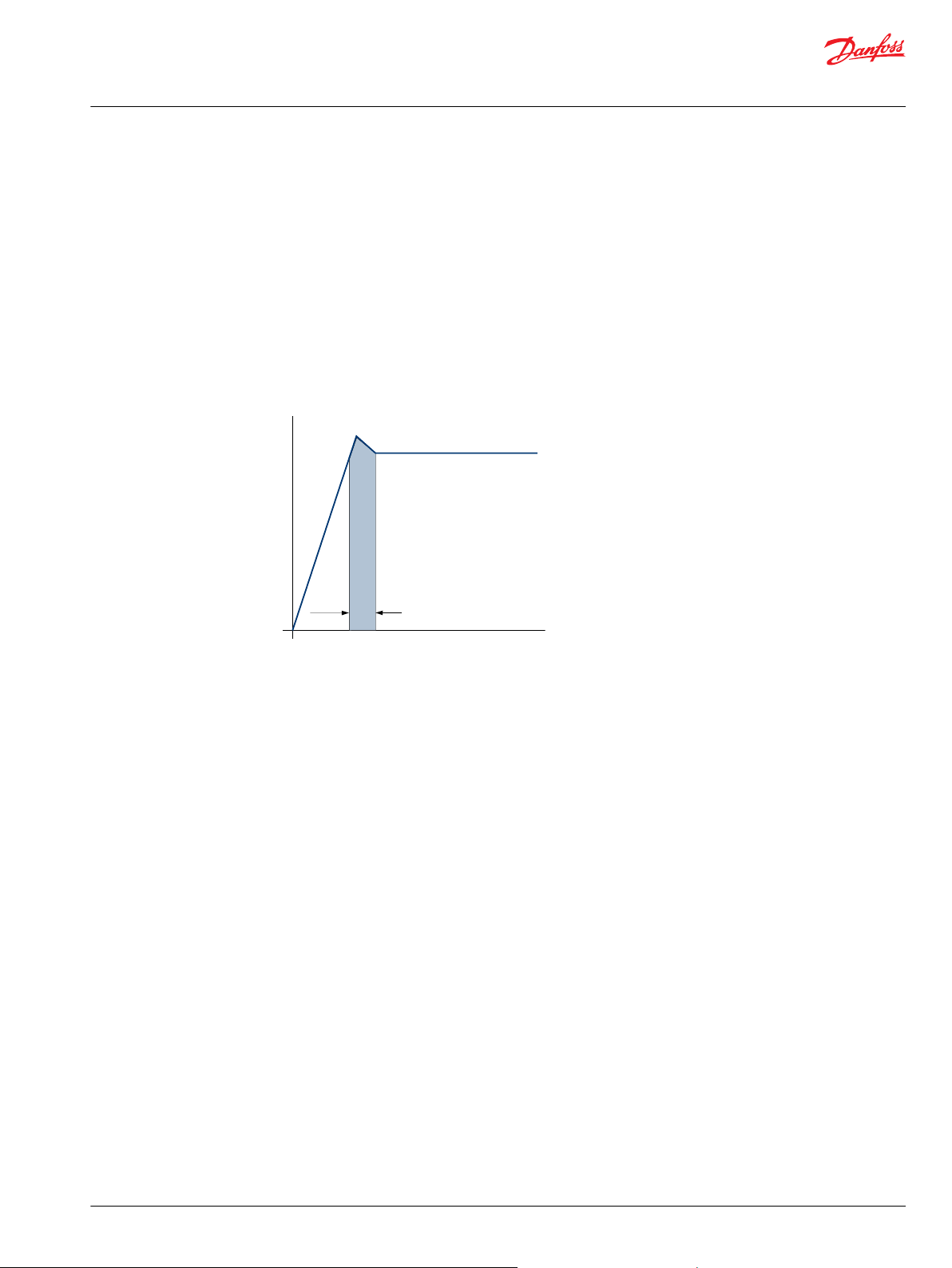
Peak pressure
Rated pressure
Reaction time (100 ms max)
Time
Pressure
P107 861E
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Operating Parameters
Overview
Definitions of the D Series operating parameters appear here. Consult your Danfoss representative for
applications running outside of these parameters.
Pressure
Peak pressure
Peak pressure is the highest intermittent pressure allowed.
The relief valve overshoot (reaction time) determines peak pressure. It is assumed to occur for less than
100 ms. The accompanying illustration shows peak pressure in relation to rated pressure and reaction
time (100 ms maximum).
Rated pressure
Rated pressure is the average, regularly occurring operating inlet pressure that should yield satisfactory
product life. The maximum machine load at the motor shaft determines rated pressure.
System pressure
System pressure is the differential between the inlet and outlet ports.
It is a dominant operating variable affecting hydraulic unit life. High system pressure, resulting from high
load at the motor shaft, reduces expected life. System pressure must remain at, or below, rated pressure
during normal operation to achieve expected life.
Back pressure
The hydraulic load downstream of the motor determines the back pressure. The D Series motor can work
with back pressure up to 100% of the maximum rated inlet pressure.
Case drain pressure
Case drain pressure is the pressure in the case drain line. Route case drain plumbing directly to the
reservoir to keep the case drain pressure as low as possible. Maximum continuous case drain pressure
allowed is 5 bar [72.5 psi].
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 11
Page 12
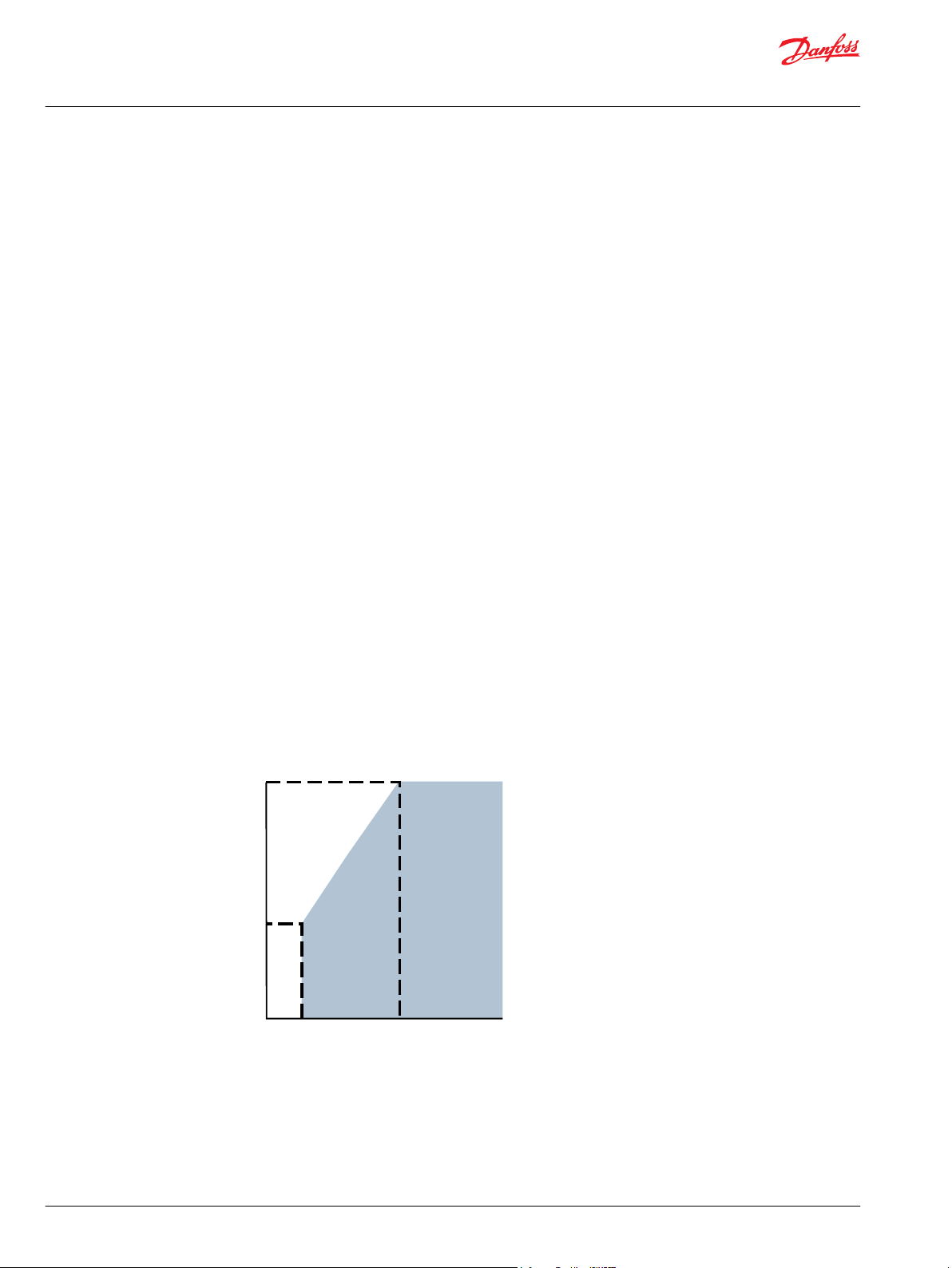
Rated
69
[1000]
Pressure - bar [psi]
0
400
P107 960E
Speed - min¯¹ (rpm)
Operating
envelope
Rated
600
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Operating Parameters
Temperature and viscosity
Temperature and viscosity requirements must be concurrently satisfied.
Temperature
High temperature limits apply at the inlet port of the motor. Ensure the motor runs at or below the
maximum continuous temperature.
Cold oil, generally, does not affect the durability of motor components. It may affect the ability of oil to
flow and transmit power. For this reason, keep the temperature at 16°C [61 °F] above the pour point of
the hydraulic fluid.
Minimum (cold start) temperature relates to the physical properties of component materials.
Continuous temperature is the temperature at or below which you may expect normal motor life.
Maximum temperature is the highest temperature that is tolerable by the machine for a transient/
limited time. (Duty cycle 1% or less)
Viscosity
Minimum viscosity occurs only during brief occasions of maximum fluid temperature and severe duty
cycle operation. It’s the minimum acceptable viscosity to guarantee the motor life. (Duty cycle 1% or less)
Maximum viscosity occurs only during cold start at very low temperatures. It is the upper limit of
viscosity that allows the motor to start.
Continuous viscosity is the viscosity range at which you may expect normal motor.
Hydraulic fluid
Speed
Maximum speed is the limit for a particular gear motor when operating at rated pressure. It is the
highest speed at which you may expect normal life.
The lower limit of operating speed is the minimum speed.
Minimum speed increases as operating system pressure increases. When operating under higher
pressures, a higher minimum speed must be maintained, as shown.
Ratings and data for gear motors are based on operation with premium hydraulic fluids containing
oxidation, rust, and foam inhibitors. These fluids must possess good thermal and hydrolytic stability to
prevent wear, and corrosion of internal components. Use petroleum/mineral-based fluids. Ensure only
clean fluid enters the hydraulic system.
12 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 13
C
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Operating Parameters
Caution
Never mix hydraulic fluids.
Filtration
Filters
Use a filter that conforms to Class 22/18/13 of ISO 4406 (or better). It may be on the motor outlet
(discharge filtration) or inlet (pressure filtration).
Selecting a filter
When selecting a filter, please consider:
•
Contaminant ingression rate (determined by factors such as the number of actuators used in the
system)
•
Generation of contaminants in the system
•
Required fluid cleanliness
•
Desired maintenance interval
•
Filtration requirements of other system components
Reservoir
Measure filter efficiency with a Beta ratio (βX). βx ratio is a measure of filter efficiency defined by ISO 4572.
It is the ratio of the number of particles greater than a given diameter (in microns) upstream of the filter
to the number of these particles downstream of the filter.
•
For discharge filtration with controlled reservoir ingression, use a β
•
For pressure filtration, use a filtration with an efficiency of β10 = 75
The filtration requirements for each system are unique. Evaluate filtration system capacity by monitoring
and testing prototypes.
Fluid cleanliness level and βX ratio
Fluid cleanliness level (per ISO 4406)
βX ratio (discharge filtration)
βX ratio (pressure or return filtration)
Recommended inlet screen size
The reservoir provides clean fluid, dissipates heat, removes entrained air, and allows fluid volume
changes associated with fluid expansion and cylinder differential volumes. A correctly sized reservoir
accommodates maximum volume changes during all system operating modes. It promotes de-aeration
of the fluid as it passes through, and accommodates a fluid dwell-time between 60 and 180 seconds,
allowing entrained air to escape.
Minimum reservoir capacity depends on the volume required to cool and hold the oil from all retracted
cylinders, allowing for expansion due to temperature changes. A fluid volume of 1 to 3 times the pump
output flow (per minute) is satisfactory. The minimum reservoir capacity is 125% of the fluid volume.
Install the suction line above the bottom of the reservoir to take advantage of gravity separation and
prevent large foreign particles from entering the line. Cover the line with a 100-125 micron screen. The
pump should be below the lowest expected fluid level.
Put the return-line below the lowest expected fluid level to allow discharge into the reservoir for
maximum dwell and efficient deaeration. A baffle (or baffles) between the return and suction lines
promotes deaeration and reduces fluid surges.
Class 22/18/13 or better
β
= 75 and β10 = 2
35-45
β10 = 75
100 – 125 μm [0.004 – 0.005 in]
35-45
= 75 filter
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 13
Page 14
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Operating Parameters
Line sizing
Choose pipe sizes that accommodate minimum fluid viscosity to reduce system noise, pressure drops
and overheating in order to maximize system life and performance. Line velocity should not exceed 6.0
m/s [20.0 ft/s]. Route case drain line direct to tank.
Most systems use hydraulic oil containing 10% dissolved air by volume. Over-aeration, or entrained air is
the result of flow line restrictions, where the dissolved air comes out of solution, or when air is allowed to
leak into the hydraulic circuit. These include inadequate pipe sizes, sharp bends, or elbow fittings,
causing reduction of flow-line cross-sectional area. This problem will not occur if these circuit
recommendations are followed, rated speed requirements are maintained, and reservoir size and
location are adequate.
Motor life
Motor life is a function of speed, system pressure, and other system parameters (such as fluid quality and
cleanliness).
All Danfoss gear motors use hydrodynamic journal bearings that rely on an oil film between the gear
shaft and bearing surfaces at all times. You can expect long life when this film is sustained through
proper system maintenance and operating within recommended limits.
A B10 bearing life expectancy number is generally associated with rolling element bearings. It does not
exist for hydrodynamic bearings.
High pressure impacts motor life. When submitting an application for review, provide machine duty cycle
data that includes percentages of time at various loads and speeds. We strongly recommend a prototype
testing program to verify operating parameters and their impact on life expectancy before finalizing any
system design.
Motor shaft connection
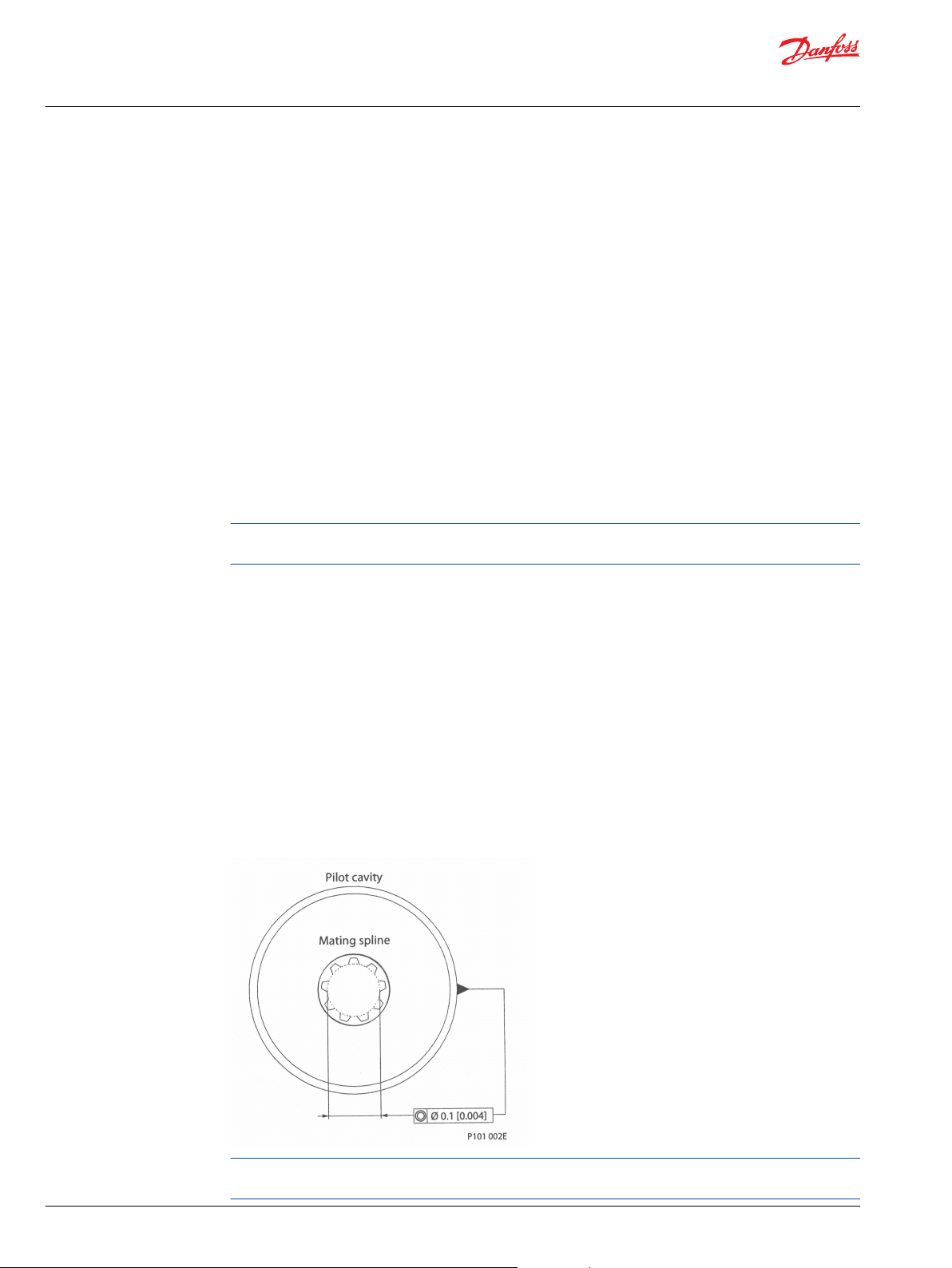
Shaft options for gear motors include tapered, splined, and parallel shafts.
Plug-in drives, with a splined shaft, can impose severe radial loads when the mating spline is rigidly
supported. Increasing spline clearance does not alleviate this condition.
Use plug-in drives only if the concentricity between the mating spline and pilot diameter is within 0.1
mm [0.004 in]. Lubricate the drive by flooding with oil. A three-piece coupling minimizes radial or thrust
shaft loads.
Motor shaft connection
To avoid spline shaft damage, use carburized and hardened steel couplings with 80-82 HRA surface
hardness.
14 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 15
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Operating Parameters
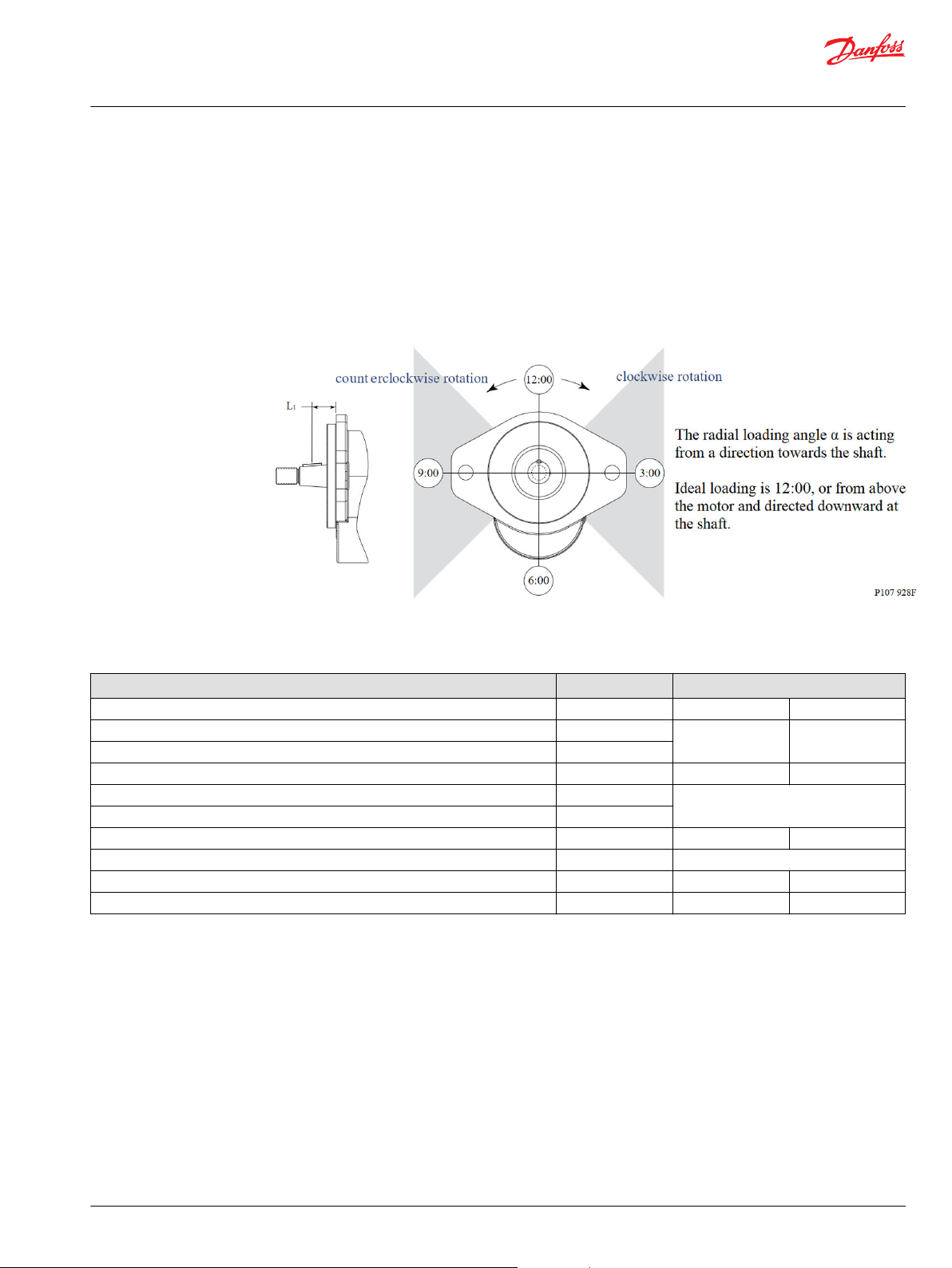
Radial and axial loading
External shaft loads may have an effect on bearing life, and may affect motor performance depending on
several factors such as load position and orientation, operating pressure, oil viscosity and motor speed.
D-motors are capable of carrying most plastic fans up to 11.75 kg (26 lbm) at rated pressure and speed.
For any other application where radial and/or axial shaft loads are present, pleas fill in the Motor shaft
load data form and contact your Danfoss representative for technical assistance.
Shaft loading
Motor shaft load data form
Item Value Based on SI or US units
Motor displacement □ cm3/rev □ in3/rev
Rated system pressure □bar □PSI
Peak pressure
Motor shaft rotation □left □right
Motor minimum speed min-1 (RPM)
Motor maximum speed
Radial load □N □lbf
Angular orientation from 12:00 (α) 12:00 - 11:59
Axial load □N □lbf
Distance from flange (L1) □mm □in
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 15
Page 16

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
Model code
Fan drive motor code example
DEMR-17TY-AA-B107-P1AB-A000-N000-AN-NNN
A Right hand rotation, B 17 cm³, SAE 1:8 taper shaft, C SAE A two bolt mounting, D 7/8-14 ports, idler side
drain, E 12 Vdc proportional relief valve, 25 US gal/min or less at 172 bar curve, F anti-cavitation valve.
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M
A - Sense of rotation
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ●
Sense of rotation
Code Description
Bidirectional rotation (reversing valve)
B
Left hand rotation (CCW)
L
Right hand rotation (CW)
R
B1 - Displacement
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ●
Displacement
Code Description
17.6 cm³/rev [1.07 in³/rev]
17
19.9 cm³/rev [1.21 in³/rev]
19
22.4 cm³/rev [1.37 in³/rev]
21
23.2 cm³/rev [1.42 in³/rev]
23
26.2 cm³/rev [1.60 in³/rev]
25
30.6 cm³/rev [1.87 in³/rev]
29
34.4 cm³/rev [2.10 in³/rev]
32
38.6 cm³/rev [2.36 in³/rev]
36
40.9 cm³/rev [2.50 in³/rev]
38
42.9 cm³/rev [2.62 in³/rev]
41
48.3 cm³/rev [2.95 in³/rev]
45
B2 - Input shaft
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ●
16 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 17

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
Input shaft
Code Description
SAE 22mm [7/8in] dia. X 41mm [1.62in] Extension, 1/4in key , with key
PB
SAE 22mm [7/8in] dia. X 51mm [2in] Extension, 1/4in key , with key
PW
SAE 1:8 taper, 22mm [7/8in] dia. x 59mm [2.34in] Extension, 5/8-18x21mm [.81in] external thread with #8
TY
Woodruff key
SAE 1:8 taper , 22mm [7/8in] dia. x 35mm [1.38in] Extension, 3/8-24x19mm [.75in] internal thread
TK
11 tooth, 48mm [1.89in] extension, (modified length) 30mm [1.20in] effective spline
SM
13 tooth, 41mm [1.62in] length
SH
SAE 22mm [7/8in] dia. X 41mm [1.62in] Extension, 1/4in keyway and key, with speed sensor
HB
SAE 22mm [7/8in] dia. X 51mm [2.00in] Extension, 1/4in keyway and key, with speed sensor
HW
SAE 11 tooth spline, 48mm [1.89in] extension (modified length), with speed sensor
HM
SAE 13 tooth spline, 41mm [1.62in] length, with speed sensor
HH
SAE1:8 taper , 22mm [7/8in] dia. x 35mm [1.38in] extension and internal thread, with speed sensor
HK
SAE1:8 taper, 22mm [7/8in] dia. x 59mm [2.34in] extension and external thread and/key, with
HY
speedsensor
C - Mounting flange
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ●
Mounting flange
Code Description
SAE A, 2 bolt
AA
SAE B, 2 Bolt
BB
SAE A, 2 bolt with speed sensor
AZ
SAE B, 2 bolt with speed sensor
BZ
D1 - Cover
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ●
Cover
Code Description
No valves, standard cover
N
Cover with anti-cavitation check valve
A
Cover for use with low flow relief valve (P1, P3 or F) and anti-cavitation check valve
B
Cover for use with high flow relief valve (P2, P4 or G) and anti-cavitation check valve
C
Cover with empty SAE 12-2 cavity and anti-cavity (customer supplied) relief valve
P
Cover with empty SAE 10-2 cavity and anti-cavity (customer supplied) relief valve
S
Cover for reversing function with proportional relief, primary CW rotation
R
Cover for reversing function with proportional relief, primary CCW rotation
L
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 17
Page 18

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
D2 - Rear cover port option
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ●
Rear cover port option
Code Description
Radial
105
106*
107
108
109
110
111
112
330
331
332
333
*
Port Sizes available for 17cc displacement motors only
**
See dimension drawings for explanation of drive and idler side.
Axial Inlet/Outlet Drain port
*
505* 3/4-16 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
506* 3/4-16 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
507 7/8-14 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
508 7/8-14 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
509 1 1/16-12 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
510 1 1/16-12 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
N/A 1 5/16-12 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
N/A 1 5/16-12 SAE O-ring boss Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
N/A 1 inch SAE Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
N/A 1 inch SAE Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
N/A 1-1/4 SAE Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (idler side**)
N/A 1-1/4 SAE Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (drive side**)
D - Rear cover availability
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ● ●
Rear cover availability matrix
Code D1 Rear cover/valve option
D2 Port options N B C A P S R L
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
330/331
332/333
505
506
●
● - - ● - - - -
●
●
●
●
●
●
● - - ● - -
● - - ● - -
● - - ● - - - -
● - - ● - - - -
- - ● - - - -
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
● ●
●
●
●
●
●
●
‡§
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ● ● ●
● ●
● ●
18 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 19

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
Code D1 Rear cover/valve option
D2 Port options N B C A P S R L
507
508
509
510
‡
● Standard
§
- Not available
● - - ● - - - -
● - -- ● - - - -
● - - ● - - - -
● - - ● - - - -
‡§
E - Relief valve availability
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ● ●
Relief Valve Availability
Code Description Pressure bar
N000
R000
F138
F172
F207
F241
F276
G138
G172
G207
G241
G276
P1AA
P1AB
P1AC
P1AD
P1AF
P2BA
P2BB
P2BC
P2BD
P2BF
No relief valve N/A ● - - ● ● ● - -
Reversing, with
proportional relief
F style - low flow, fixed
setting pressure
reliefvalve
(non-reversing)
G style - high flow,
fixed setting pressure
relief valve (non-
reversing)
P1 style - low flow,
proportional relief
valve 12 Vdc (non-
reversing)
P2 style - high flow,
proportional relief
valve 12 Vdc (non-
reversing)
[psi]
See module G - - - - - - ● ●
138 [2000] - ● - - - - - -
172 [2500] - ● - - - - - -
207 [3000] - ● - - - - - -
241 [3500] - ● - - - - - -
276 [4000] - ● - - - - - -
138 [2000] - - ● - - - - -
172 [2500] - - ● - - - - -
207 [3000] - - ● - - - - -
241 [3500] - - ● - - - - -
276 [4000] - - ● - - - - -
138 [2000] - ● - - - - - -
172 [2500] - ● - - - - - -
207 [3000] - ● - - -- - -- -
241 [3500] - ● - - - - - -
276 [4000] - ● - - - - - -
138 [2000] - - ● - - - - -
172 [2500] - - ● - - - - -
207 [3000] - - ● - - - - -
241 [3500] - - ● - - - - -
276 [4000] - - ● - - - - -
Compatible with D1 - Rear cover function
N B C A P S R L
‡§
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 19
Page 20

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
Code Description Pressure bar
P3AA
P3AB
P3AC
P3AD
P3AF
P4BA
P4BB
P4BC
P4BD
P4BF
‡
● Standard
§
- Not available
P3 style - low flow,
proportional relief
valve 24 Vdc (non-
reversing)
P4 style - high flow,
proportional relief
valve 24 Vdc (non-
reversing)
[psi]
138 [2000] - ● - - - - - -
172 [2500] - ● - - - - - -
207 [3000] - ● - - - - - -
241 [3500] - ● - - - - - -
276 [4000] - ● - - - - - -
138 [2000] - - ● - - - - -
172 [2500] - - ● - - - - -
207 [3000] - - ● - - - - -
241 [3500] - - ● - - - - -
276 [4000] - - ● - - - - -
Compatible with D1 - Rear cover function
N B C A P S R L
F - Anti-cavitation/shock valve function
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ● ●
‡§
Anti-cavitation/shock valve function
Compatible with D1 - Rear cover option
F A B C N P S R L
No valves
Anti-cavitation valve
Shock with Anti-cavitation
Shock with Anti-cavitation
‡
● Standard
§
- Not available
N000 - - - ● - - - -
A000 ● ● ● ● ● - -
S300 - - - - - - ● ●
S240 - - - - - - ● ●
Units with integrated reversing are bi-directional motors, however, valves are rotation specific. User must
specify DEMB rotation and R or L rear cover.
Integrated reversing also requires R000 relief and S300 anti-cavitation/shock valves.
G - Integrated reversing modulating function
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ● ●
‡§
20 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 21

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
G Integrated reversing modulating function
Code Description Pressure
N000
A1AA
A1AB
A1AC
A1AD
A1AF
A2AA
A2AB
A2AC
A2AD
A2AF
B1AA
B1AB
B1AC
B1AD
B1AF
B2AA
B2AB
B2AC
B2AD
B2AF
‡
● Standard
§
- Not available
No integrated reversing valve N/A ● ● ● ● ● ● - -
D03 Directional Valve
P1 Style - Proportional relief valve 12
VDC
D03 Directional Valve
P3 Style - Proportional relief valve 24
VDC
D05 Directional Valve
P2 Style - Proportional relief valve 12
VDC
D05 Directional Valve
P4 Style - Proportional relief valve 24
VDC
bar [psi]
A‡§B‡§C‡§N‡§P‡§S‡§R‡§L
138 [2000] - - - - - - ● ●
172 [2500] - - - - - - ● ●
207 [3000] - - - - - - ● ●
241 [3500] - - - - - - ● ●
276 [4000] - - - - - - ● ●
138 [2000] - - - - - - ● ●
172 [2500] - - - - - - ● ●
207 [3000] - - - - - - ● ●
241 [3500] - - - - - - ● ●
276 [4000] - - - - - - ● ●
138 [2000] - - - - - - ● ●
172 [2500] - - - - - - ● ●
207 [3000] - - - - - - ● ●
241 [3500] - - - - - - ● ●
276 [4000] - - - - - - ● ●
138 [2000] - - - - - - ● ●
172 [2500] - - - - - - ● ●
207 [3000] - - - - - - ● ●
241 [3500] - - - - - - ● ●
276 [4000] - - - - - - ● ●
‡§
J - Name plate
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ●
Name plate
Code Description
AN
Standard name plate
K - Name plate
A B1 B2 C D1 D2 E F G J K
D E M ● ● ●
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 21
Page 22

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Product code
Name plate
Code Description
NNN
No special features, standard black paint
22 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 23

106.38
[4.188]
P107 926E
11.7
[0.46]
53.19
[2.094]
12.4
[0.49]
10.4
[0.41]
6.35
5.84
[0.250]
[0.230]
82.55
82.50
[3.250]
[3.248]
Inlet Outlet
95.5
[3.76]
P108 260E
Shaft seal
Dust protector
(standard)
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Mounting flanges
SAE-A 2-bolt flange (AA)
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 23
Page 24

P107 927E
146.05
[5.750]
73.02
[2.875]
14.2
[0.56]
9.65
9.14
[0.380]
[0.360]
12.4
[0.49]
10.4
[0.41]
101.60
101.55
[4.000]
[3.998]
InletOutlet
120.6
[4.75]
48.0
[1.89]
30.5
[1.20]
effective
spline
length
18.5
[0.730]
SAE 11 -tooth
16/32 pitch flat
root side fit
(modified length)
P107 888E
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
SAE-B 2-bolt flange (BB)
Shaft options
SM shaft option
24 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 25

41.1
[1.62]
25.5
[1.00]
22.2
[0.85]
24.9
[0.98]
SAE 7/8 inch diameter shaft
straight keyed
1/4 inch key
P107 889E
59.5
[2.34]
SAE 1:8 taper
5/8-18 x 0.64 inch thread
with #8 woodruff key
7/8 inch diameter shaft
36.4
[1.43]
P107 885E
35.0
[1.38]
SAE 1:8 taper
3/8-24 x 0.64 inch internal thread
with 1/4 inch key
7/8 inch diameter shaft
P107 886E
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
PB shaft option
TY shaft option
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 25
TK shaft option
Page 26

SAE 13-tooth
16/32-pitch
flat root side fit
41.2mm [1.62in] length
P108 259E
Ø
21.9
[0.864]
Effective
spline
length
30.0 [1.18]
41.2
[1.62]
50.8
[2.00]
25.4
[1.00]
22.2
[0.85]
24.9
[0.98]
SAE 7/8 inch diameter shaft
straight keyed
1/4 inch key
P108 249E
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
SH shaft option
PW shaft option
Shaft torque limits
Code Type Diameter
mm [in]
SM
PB
Spline 19.1 [0.75] 38.1 [1.50]
Straight
22.2 [0.875] 41.2 [1.62]
key
Tapered 22.2 [0.875] 49.6 [1.95]
TY
TK
SH
PW
Tapered 22.2 [0.875] 49.3 [1.94]
Spline 21.9 [0.864] 41.2 [1.62]
Straight
22.2 [0.875] 50.8 [2.00]
key
26 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Length
mm [in]
Description Allowable shaft
SAE 11 tooth, 48mm [1.89in] extension,
(modified length) 30mm [1.20in] effective
spline
SAE 2mm [7/8in] Ø x 41mm [1.62in]
Extension, 1/4in key, with key
SAE 1:8 taper, 22mm [7/8in] Ø x 59mm
[2.34in]
Extension, 5/8-18 x 21mm [.81in] external
thread with #8 Woodruff key
SAE 1:8 taper, 22mm [7/8in] Ø x 35mm
[1.38in]
Extension, 3/8-24 x 19mm [.75in] Internal
thread
SAE 13 tooth,
41mm [1.62in] length
SAE 22mm [7/8in] Ø x 51mm [2in]
Extension, 1/4in key, with key
torque N•m
[lbf•in]
176.3 [1560]
248.6 [2200]
225.9 [2000]
225.9 [2000]
248.6 [2200]
248.6 [2200]
Page 27

P107 904E
External drain
9/16-18 SAE Straight thread
for 3/8 inch O.D. tube
(Note: Location can be on
opposite side of motor)
Inlet port and outlet port
SAE ORB ports sized identically
sizes are 3/4-16, 7/8-14, 1 1/16-12,
and 1 5/16-12
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Port options
SAE O-ring boss
Code SAE O-ring boss ports - No valves
Radial Axial Inlet Outlet Drain port
N105 N505 3/4-16 SAE 3/4-16 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N106 N506 3/4-16 SAE 3/4-16 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
N107 N507 7/8-14 SAE 7/8-14 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N108 N508 7/8-14 SAE 7/8-14 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
N109 N509 1 1/16-12 SAE 1 1/16-12 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N110 N510 1 1/16-12 SAE 1 1/16-12 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
N111 N/A 1 5/16-12 SAE 1 5/16-12 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N112 N/A 1 5/16-12 SAE 1 5/16-12 SAE Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
Port locations (SAE O-ring port shown)
SAE Split flange ports
Code SAE Split flange ports - No valves
Radial Inlet Outlet Drain port
N330 1 inch Split flange 1 inch Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N331 1 inch Split flange 1 inch Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
N332 1-1/4 inch Split flange 1-1/4 inch Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on idler side)
N333 1-1/4 inch Split flange 1-1/4 inch Split flange Radial 9/16-18 SAE (on drive side)
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 27
Page 28

P107 942E
Inlet port and
outlet port
sized identically
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Split flange ports
Selecting port options
Use the following tables for selecting port options. Recommendations assume maximum rated speed.
Applications running at lower speeds may use smaller port sizes. Contact your Danfoss representative.
Recommended port size by displacement
Displacement code Recommended port size
17 1-1/16 inch
19 1-1/16 inch
21 1 - 5/16 inch
23 1 - 5/16 inch
25 1 - 5/16 inch
29 1 - 5/16 inch
32 1 - 5/16 inch
36 1 - 5/16 inch
38 1 - 5/16 inch
41 1 - 5/16 inch
45 1 inch split flange
Maximum flow by port size
Port size Maximum flow l/min [US gal/min]
3/4 -16 SAE ORB 26 [7]
7/8-14 SAE ORB 41 [11]
1 1/16-12 SAE ORB 68 [18]
1 5/16-12 SAE ORB 132 [35]
1 inch Split flange 216 [57]
1 1/4 inch Split flange 288 [76]
28 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 29

P108 250E
P
T
P
T
B
A
D
1
2
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Integrated reversing motor with proportional relief and shock/anti-cavitation valves
The D Series Motor can be configured to include an integrated reversing option for high performance fan
drive systems requiring variable speed and reversal of fan direction to purge coolers and radiators.
Features and benefits
•
Solenoid reversing valve directs flow to either side of the motor to reverse fan rotation. The valve uses
an open transition spool to reduce the likelihood of pressure spikes during sudden reversals and is
available in two flow ranges to minimize losses.
•
Integrated proportional pressure control to modulate fan speed by modulating pressure across the
fan motor. The valve is available in two flow ranges and is normally closed to ensure full fan speed in
case of loss of electrical signal.
•
Dual shock valves limit pressure spikes in both forward and reverse rotation and eliminates damage
to the system during sudden fan reversals.
•
Dual anti-cavitation check valves bypass motor flow during fan deceleration.
•
The motor is PLUS+1TM compliant allowing the user to take advantage of automatic cleaning
sequences available on Danfoss microcontrollers.
•
Valves are qualified to 276 bar (4000 psi) and are contained in a steel body to ensure maximum
performance and long life at elevated temperatures and pressures.
•
Deutsch connectors, Viton® seals and shaft dust protector are standard for operation in severe
environments.
•
Integrated valve design provides short length and high power density in a compact package while
minimizing installation costs.
Technical data
The directional control valve uses an internal spring to bias spool position and direct flow to the motor.
As a result, the preferred motor rotation must be specified in the model code. A right hand motor would
be biased for clockwise rotation with counter-clockwise reversing, while a left hand motor would be
biased for counter-clockwise rotation with clockwise reversing.
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 29
Page 30

0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
0 10 20 3 0 40 50 60 70 80 90 100
Pressure loss
Flow
P108 251E
P-T Pressure Drop in Forward Direction for Motor/Valve Assembly
l/min
psi
Bar
0
10
20
30
40
50
A1, A2 (D03)
5
10
15
20
25
US gal/min
0
B1, B2 (D05)
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
The reversing valve function is available in two flow ratings. The D05 directional valve is standard with
the high flow proportional valve, while the D03 directional valve is standard with the low flow
proportional valve. Use the P-T pressure drop curves to minimize pressure drop at maximum flow
conditions.
Integrated reversing function
Select the size and voltage of the reversing valve option using the codes and P-T pressure drop curves
below. The pressure settings and performance curves for the proportional relief valve can be found on
the following pages.
Code Description
A1 D03 Directional valve with P1 (low flow) style proportional relief valve, 12VDC
A2 D03 Directional valve with P3 (low flow) style proportional relief valve, 24VDC
B1 D05 Directional valve with P2 (high flow) style proportional relief valve, 12VDC
B2 D05 Directional valve with P4 (high flow) style proportional relief valve, 24VDC
Pressure loss measured with Mobile DTE 24 at 105°F [41°C]
Includes pressure drop across D03/D05 in default position as well as losses across unloaded gear motor
30 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 31

P107 946E
P107 938E
Anti-cavitation check valve
Section A-A
A
A
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
Standard relief valve
The fixed-setting pressure relief valve limits maximum fan speed and protects the motor from overpressurization.
Mount the motor so the relief valve is below the reservoir oil level. Keep the relief valve in a horizontal
position. Be sure to bleed the system to remove entrained air.
Code Description
F Relief valve internally drained - applications with 95 l/min [26 US gal/min] or less flow
G Relief valve internally drained - applications with 96-190 l/min [26-50 US gal/min] flow
Any modification to the valve to change the factory setting will void product warranty.
The fixed-setting relief valve can only be used to limit fan speed in one rotational direction. As a result,
the preferred motor rotation must be specified in the model code - DEML or DEMR.
Schematic: Motor with standard relief valve with optional anti-cavitation valve
Standard relief valve
Relief pressure vs flow at Toil=51.7°C [125°F], viscosity = 30 mm²/sec (cSt) [141 SUS] set at 19 l/min [5 US
gal/min]
F Valve settings
Valve option Pressure setting bar [psi]
276 276 [4000]
241 241 [3500]
207 207 [3000]
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 31
Page 32

0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
0 5 10 15 20 25 30
By-pass flow
P107 918E
US gal/min
l/min
0
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
Pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
110
20
10
138
172
207
241
276
By-pass flow
P107 919E
US gal/min
l/min
0
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
140
150
130
0 5 10 15 20 25 30 35 40 45
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
Pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
5000
160
120
110
2010
138
172
207
241
276
P107 956E
Anti-cavitation check valve
Section A-A
A
A
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
F Valve settings (continued)
Valve option Pressure setting bar [psi]
172 172 [2500]
138 138 [2000]
Anti-cavitation check valve
G valve settings
D motors are available with an optional anti-cavitation check valve. The valve is integrated into the rear
cover. The anti-cavitation check valve protects the motor from cavitation in overrunning conditions.
Standard rear cover with anti-cavitation valve
32 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 33

P107 945E
P107 937E
Anti-cavitation check valve
Section A-A
A
A
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
Schematic: Motor with anti-cavitation check valve
Proportional relief valve with anti-cavitation valve
The D Series motor may be equipped with a normally closed proportional relief valve, which modulates
the fan speed for on demand cooling in fan drive applications. This valve can also trim maximum fan
speed at a pre-set pressure. Mount the motor so the relief valve is below the reservoir oil level. Keep the
relief valve in a horizontal position. Be sure to bleed the system to remove entrained air.
Relief valve cutaway
Technical data
Capacity 95 l/min [25 US gal/min] or 96-190 l/min [25-50 US gal/min]
Electrical connector DEUTSCH® DT-04-2P (protection rate IP 69K DIN 40050)
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 33
Page 34

2466
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
Technical data (continued)
Electrical supply 0 -1.1 A at 12 Vdc with Coil resistance of 6.4 Ohms at 20° C [68° F]
0 -0.55 A at 24 Vdc with Coil resistance of 26.2 Ohms at 20° C [68° F]
PWM frequency 100 - 250 Hz
The proportional relief valve can only be used to modulate fan speed in one rotational direction. As a
result, the preferred motor rotation must be specified in the model code - DEML or DEMR.
Schematic: Motor with proportional relief valve and anti-cavitation check valve
Minimum voltage 10.8 Vdc
Maximum voltage 13.2 Vdc
Minimum voltage 21.6 Vdc
Maximum voltage 26.4 Vdc
Valve settings
Code Description
P1 12 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained, low flow
P2 12 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained, high flow
P3 24 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained, low flow
P4 24 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained, high flow
Select proportional relief valve setting using the pressure vs. bypass flow graphs. Any modification to the
valve to change the factory setting will void product warranty.
P1 and P3 valve settings (low flow)
Valve option Pressure setting bar [psi]
AF 276 [4000]
AD 241 [3500]
AC 207 [3000]
AB 172 [2500]
AA 138 [2000]
34 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 35

0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
Bypass flow
Delta Pressure
P107 909E
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
US gal/min
l/min
10
0
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
psi
Bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
AA
AB
AC
AD
AF
P107 911E
0 5 10 15 20
25 30 35
40
45
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
5000
Bypass flow
Delta pressure
US gal/min
l/min
0
20
40
psi
Bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
80
100
120
140
60
160
- 0 Bar
+ 7 Bar
BA
BB
BC
BD
BF
5 10 15 20 25 30 35
By-pass flow
Pressure
P107 913E
US gal/min
l/min
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
psi
Bar
0
5
10
15
20
25
30
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
350
400
450
100 110 120 130
P1, P3
P2, P4
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
P2 and P4 valve settings (high flow)
Valve option Pressure setting bar [psi]
BF 276 [4000]
BD 241 [3500]
BC 207 [3000]
BB 172 [2500]
BA 138 [2000]
Performance graphs
Relief pressure vs flow at Toil=51.7°C [125°F], viscosity = 30 mm²/sec (cSt) [141 SUS] set at 19 l/min [5 US
gal/min] and zero current
Pressure drop with coil energized, valve only
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 35
Page 36

0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2
Current (A)
P107 914E
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
Delta pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
AD
AA
AB
AC
AF
0 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 1 1.2
Current (A)
P107 915E
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
Delta pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
BA
BB
BC
BD
BF
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Current (A)
P107 916E
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
Delta pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
AA
AB
AC
AD
AF
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
Valve settings
Code Description
P1 12 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained - with 95 l/min [25 US gal/min] or less flow
P2 12 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained - with 96-190 l/min[26-50 US gal/min] flow
P3 24 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained - with 95 l/min [25 US gal/min] or less flow
P4 24 Vdc Proportional relief valve internally drained - with 96-190 l/min[26-50 US gal/min] flow
Any modification to the valve to change the factory setting will void product warranty.
Performance graphs
Relief pressure vs flow at Toil=51.7°C [125°F], viscosity = 30 mm²/sec (cSt) [141 SUS] set at 19 l/min [5 US
gal/min] and zero current
P1, Relief pressure vs. current
P2, Relief pressure vs. current
P3, Relief pressure vs. current
36 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 37

P107 917E
0
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500
4000
4500
Delta pressure
psi
bar
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
0 0.1 0.2 0.3 0.4 0.5 0.6
Current (A)
BA
BB
BC
BD
BF
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
P4, Relief pressure vs. current
Hall effect speed sensor
Dimensions mm [in]
Connector
Output signal
Supply voltage
Frequency range
DEUTSCH® DTM04-3P 3-Pin, Female
0 - 5 V, NPN @ < 25mA Sink
5 - 30 VDC @ < 18mA
8 pulses per revolution
425 Hz at maximum motor speed (3400 rpm)
Protection level
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 37
IP67
Page 38

Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Options
38 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 39

P107 882E
CW motor shown. For CCW motor, valve is on the opposite side.
B
44.4
[1.75]
85.1
[3.35]
A
C
Motor is also
available with
cavities only
(no valve)
20.32
[0.8]
170.0
[6.69]
2 pin
Deutsch
connector
88.9
[3.50]
44.4
[1.75]
External drain - drive side
Inlet port (opposite) and outlet port
sized identically
External drain - idler side
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Fan drive motor
Fan drive motor example
Fan drive motor:
Right hand rotation, 17 cm³, 1:8 taper shaft, SAE A two bolt mounting, 7/8-14 ports, idler side drain, P1
style proportional relief valve at 172 bar, anti-cavitation valve.
D motor dimensions; SAE-B two bolt fan drive motor shown
Dimensions (maximum)
Dimension Units 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
A mm 88.9 90.9 92.5 94.2 97.3 100.8 103.6 107.7 109.7 112.8 117.1
in 3.50 3.58 3.64 3.71 3.83 3.97 4.08 4.24 4.32 4.44 4.61
B mm 91.7 93.8 95.3 97.0 100.1 103.6 106.4 110.7 112.5 115.6 119.9
in 3.61 3.69 3.75 3.82 3.94 4.08 4.19 4.36 4.43 4.55 4.72
C mm 154.4 156.5 158.0 160.0 162.8 166.4 169.2 173.5 175.5 178.6 182.6
in 6.08 6.18 6.22 6.30 6.41 6.55 6.66 6.83 6.91 7.03 7.19
Standard motor
Standard motor example
Bi-rotational, 17 cm³, 1:8 taper shaft, SAE B two bolt mounting, 7/8-14 ports, idler side drain, no relief
valve.
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 39
Page 40

P107 887E
B
A
C
85.2
[3.35]
44.6
[1.75]
20.70
19.94
[0.815]
[0.785]
88.9
[3.50]
44.4
[1.75]
20.32
[0.80]
21.59
[0.85]
Axial ported rear cover
Top view
21.59
[0.85]
Case drain
Port
External drain - drive side
Inlet port and outlet port
sized identically
Radial ported rear cover
External drain - idler side
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Standard D Series motor dimensions, SAE-B two bolt motor shown
Dimensions (maximum)
DimensionUnits 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
A mm 90.7 92.7 94.3 96.1 99.1 102.7 105.4 109.7 111.7 114.7 118.9
in 3.57 3.65 3.71 3.78 3.9 4.04 4.15 4.32 4.4 4.51 4.68
B mm 90.9 92.9 94.4 96.3 99.3 102.8 105.6 109.9 111.8 114.8 119.1
in 3.58 3.66 3.72 3.79 3.91 4.05 4.16 4.33 4.4 4.52 4.69
C mm 112.9 115.0 116.5 118.3 121.3 124.9 127.7 131.9 133.9 136.9 141.1
in 4.45 4.53 4.59 4.66 4.78 4.92 5.03 5.19 5.27 5.39 5.56
Standard motor with split flange ports
Standard motor with split flange ports example
Bi-rotational, 17 cm³, SAE 1:8 taper shaft, SAE B two bolt mounting, Split flange ports, drive side drain, No
valve.
40 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 41

P107 957E
B
A
C
85.2
[3.35]
44.6
[1.75]
20.70
19.94
[0.815]
[0.785]
88.9
[3.50]
44.4
[1.75]
Case drain
Port
External drain - drive side
73.41
[2.89]
146.81
[5.78]
External drain - idler side
Inlet port and
outlet port
sized identically
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Standard D Series motor dimensions, SAE-B two bolt motor shown with split flange ports
Dimensions (maximum)
DimensionUnits 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
A mm 96.8 98.8 100.3 102.1 105.2 108.7 111.5 115.8 117.6 120.6 125.0
in 3.81 3.89 3.95 4.02 4.14 4.28 4.39 4.56 4.63 4.75 4.92
B mm 91.7 93.8 95.3 97.0 100.1 103.6 106.4 110.7 112.5 115.6 119.9
in 3.61 3.69 3.75 3.82 3.94 4.08 4.19 4.36 4.43 4.55 4.72
C mm 128.8 130.8 132.3 134.4 137.2 140.7 143.5 147.8 149.9 152.9 157.0
in 5.07 5.15 5.21 5.29 5.40 5.54 5.65 5.82 5.90 6.02 6.18
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 41
Page 42

P108 246E
2 pin
Deutsch
connector
2 pin
Deutsch
connector
44.4
[1.75]
88.9
[3.50]
73.4
[2.89]
166.4
[6.55]
119.7
[4.71]
146.8
[5.78]
External drain - idler side
B
Outlet port
(Near side)
D
A
C
External drain - drive side
60.3
[2.38]
Inlet port
(Far side)
Case drain
Inlet port and outlet port
sized identically
(Split flange ports shown)
20.70
19.94
[0.815]
[0.785]
118.8
[4.68]
Counterclockwise rotation
For counterclockwise rotation,
valve dimensions are reversed
about centerline.
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Integrated reversing motor with proportional relief and shock/anti-cavitation valves
Reversing fan drive motor with D03 directions valve, clockwise rotation
Dimensions (maximum)
Dimensions Port Units 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
A All mm 95.0 97.1 98.6 100.4 103.4 107.0 109.8 114.0 116.0 119.0 123.2
B
C All mm 88.2 90.3 91.8 93.6 96.6 100.2 103.0 107.3 109.2 112.2 116.4
D All mm 174.4 176.5 178.0 179.8 182.8 186.4 189.2 193.4 195.4 198.4 202.6
107-
108
109 -
110
111 -
112
330 -
331
332 -
333
in 3.74 3.82 3.88 3.95 4.07 4.21 4.32 4.49 4.57 4.69 4.85
mm 103.3 105.3 106.9 108.7 111.7 115.3 118.0 122.3 124.3 127.3 131.5
in 4.07 4.15 4.21 4.28 4.40 4.54 4.65 4.82 4.89 5.01 5.18
mm 101.1 103.1 104.7 106.5 109.5 113.1 115.8 120.1 122.1 125.1 129.3
in 398 4.06 4.12 4.19 4.31 4.45 4.56 4.73 4.81 4.93 5.09
mm 97.7 99.8 101.3 103.1 106.1 109.7 112.5 116.8 118.7 121.7 125.9
in 3.85 3.93 3.99 4.06 4.18 4.32 4.43 4.60 4.67 4.79 4.96
mm 100.6 102.7 104.2 106.0 109.0 112.6 115.4 119.6 121.6 124.6 128.8
in 3.96 4.04 4.10 4.18 4.29 4.43 4.54 4.71 4.79 4.91 5.07
mm 100.0 102.1 103.6 105.4 108.4 112.0 114.8 119.0 121.0 124.0 128.2
in 3.94 4.02 4.08 4.15 4.27 4.41 4.52 4.69 4.76 4.88 5.05
in 3.47 3.55 3.61 3.69 3.80 3.95 4.05 4.22 4.30 4.42 4.58
in 6.87 6.95 7.01 7.08 7.20 7.34 7.45 7.62 7.69 7.81 7.98
42 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 43

P108 247E
2 pin
Deutsch
connector
44.4
[1.75]
88.9
[3.50]
76.1
[3.00]
171.0
[6.73]
120.0
[4.73]
152.2
[5.99]
External drain
idler side
B
Outlet port
(Near side)
D
A
C
External drain - drive side
139.3
[5.50]
Inlet port
(Far side)
Case drain
Inlet port and outlet port
sized identically
(SAE ORB ports shown)
20.70
19.94
[0.815]
[0.785]
89.3
[3.51]
2 pin
Deutsch
connector on
200mm leads
Clockwise rotation
Counterclockwise rotation
For counterclockwise rotation,
valve dimensions are reversed
about centerline.
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Dimension drawings
Reversing fan drive motor with D05 directional valve, clockwise rotation
Dimensions (maximum)
Dimensions Port Units 17 19 21 23 25 29 32 36 38 41 45
A All mm 95.0 97.1 98.6 100.4 103.4 107.0 109.8 114.0 116.0 119.0 123.2
in 3.74 3.82 3.88 3.95 4.07 4.21 4.32 4.49 4.57 4.69 4.85
B
109 -
111 -
330 -
332 -
107-
108
110
112
331
333
mm 103.3 105.3 106.9 108.7 111.7 115.3 118.0 122.3 124.3 127.3 131.5
in 4.07 4.15 4.21 4.28 4.40 4.54 4.65 4.82 4.89 5.01 5.18
mm 101.1 103.1 104.7 106.5 109.5 113.1 115.8 120.1 122.1 125.1 129.3
in 398 4.06 4.12 4.19 4.31 4.45 4.56 4.73 4.81 4.93 5.09
mm 97.7 99.8 101.3 103.1 106.1 109.7 112.5 116.8 118.7 121.7 125.9
in 3.85 3.93 3.99 4.06 4.18 4.32 4.43 4.60 4.67 4.79 4.96
mm 100.6 102.7 104.2 106.0 109.0 112.6 115.4 119.6 121.6 124.6 128.8
in 3.96 4.04 4.10 4.18 4.29 4.43 4.54 4.71 4.79 4.91 5.07
mm 100.0 102.1 103.6 105.4 108.4 112.0 114.8 119.0 121.0 124.0 128.2
in 3.94 4.02 4.08 4.15 4.27 4.41 4.52 4.69 4.76 4.88 5.05
C All mm 88.2 90.3 91.8 93.6 96.6 100.2 103.0 107.3 109.2 112.2 116.4
D All mm 199.8 201.9 203.4 205.2 208.2 211.8 214.6 218.8 220.8 223.8 228.0
in 3.47 3.55 3.61 3.69 3.80 3.95 4.05 4.22 4.30 4.42 4.58
in 7.87 7.95 8.01 8.08 8.20 8.34 8.45 8.62 8.69 8.81 8.98
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 43
Page 44

Speed (rpm)
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
500
1000
1500 2000 2500 3000
3500
4000
Flow
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
Torque
P107 893E
N•m
lbf•ft
l/min
US gal
/min
3
6
10
20
30
40
50
9
12
15
18
21
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
500
1000
1500
2000 2500 300 0 3500
4000
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
P107 894E
Speed (rpm)
Flow
N•m
l/min
Torque
lbf•ft
10
20
30
40
50
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Performance data
Motor performance graphs
The graphs show typical inlet flow and output power for the D series motors at various working pressures
as a function of speed. Data were taken using hydraulic fluid conforming to ISO VG46 at 50°C [120º F]
with viscosity at 28 mm²/sec (cSt) [132 SUS].
17.6 cm3 [1.07 in3]
19.9 cm3 [1.21 in3]
44 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 45

103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 400 0
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
P107 895E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
10
20
30
40
50
Flow
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
l/min
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
500
1000
1500
2000
2500 3000
3500
4000
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
P107 896E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
20
30
40
50
Flow
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
l/min
60
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
500
1000
1500
2000
2500
3000
3500 4000
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
P107 897E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
Flow
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
l/min
60
25
70
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Performance data
22.4 cm3 [1.37 in3]
23.2 cm3 [1.42 in3]
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 45
26.2 cm3 [1.60 in3]
Page 46
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
500 1000
1500
2000
2500 300 0 3500
4000
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
P107 898E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
Flow
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
l/min
60
25
70
27
80
30
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
10
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
500 1000 150 0 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
P107 899E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
l/min
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
60
20
70
80
Flow
US gal
/min
3
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
500 1000
1500
2000 2500
3000 3500
4000
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
P107 900E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
l/min
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
60
70
80
Flow
US gal
/min
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
90
100
33
36
39
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Performance data
30.6 cm3 [1.87 in3]
34.4 cm3 [2.10 in3]
38.6 cm3 [2.36 in3]
46 | © Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
Page 47

103 bar [1500 PSI]
276 bar [4000 PSI]
276 bar [4000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
500
1000 1500
2000
2500 3000
3500
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
160
P107 901E
Speed (rpm)
N•m
l/min
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
60
70
80
Flow
US gal
/min
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
90
100
33
36
39
110
103 bar [1500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
241 bar [3500 PSI]
241 bar [3500PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
20
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 350 0
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
P107 902E
Speed (rpm)
l/min
Flow
US gal
/min
6
9
12
15
18
21
24
27
30
33
36
39
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
103 bar [1500 PSI]
210 bar [3000 PSI]
210 bar [3000PSI]
172 bar [2500 PSI]
103 bar [1500 PSI]
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
140
150
160
170
500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500
40
50
60
70
80
90
100
110
120
130
P107 903E
Speed (rpm)
l/min
Flow
US gal
/min
15
18
21
24
27
30
33
36
39
N•m
Torque
lbf•ft
30
40
50
60
70
80
90
42
Technical Information
D–Series Cast Iron Gear Motors, Including Fan Drive
Performance data
40.9 cm3 [2.50 in3]
42.9 cm3 [2.62 in3]
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105 | 47
48.3 cm3 [2.95 in3]
Page 48

Danfoss
Power Solutions GmbH & Co. OHG
Krokamp 35
D-24539 Neumünster, Germany
Phone: +49 4321 871 0
Danfoss
Power Solutions ApS
Nordborgvej 81
DK-6430 Nordborg, Denmark
Phone: +45 7488 2222
Danfoss
Power Solutions (US) Company
2800 East 13th Street
Ames, IA 50010, USA
Phone: +1 515 239 6000
Danfoss
Power Solutions Trading
(Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
Building #22, No. 1000 Jin Hai Rd
Jin Qiao, Pudong New District
Shanghai, China 201206
Phone: +86 21 2080 6201
Products we offer:
Hydro-Gear
www.hydro-gear.com
Daikin-Sauer-Danfoss
www.daikin-sauer-danfoss.com
Cartridge valves
•
DCV directional control
•
valves
Electric converters
•
Electric machines
•
Electric motors
•
Gear motors
•
Gear pumps
•
Hydraulic integrated
•
circuits (HICs)
Hydrostatic motors
•
Hydrostatic pumps
•
Orbital motors
•
PLUS+1® controllers
•
PLUS+1® displays
•
PLUS+1® joysticks and
•
pedals
PLUS+1® operator
•
interfaces
PLUS+1® sensors
•
PLUS+1® software
•
PLUS+1® software services,
•
support and training
Position controls and
•
sensors
PVG proportional valves
•
Steering components and
•
systems
Telematics
•
Danfoss Power Solutions is a global manufacturer and supplier of high-quality hydraulic and
electric components. We specialize in providing state-of-the-art technology and solutions
that excel in the harsh operating conditions of the mobile off-highway market as well as the
marine sector. Building on our extensive applications expertise, we work closely with you to
ensure exceptional performance for a broad range of applications. We help you and other
customers around the world speed up system development, reduce costs and bring vehicles
and vessels to market faster.
Danfoss Power Solutions – your strongest partner in mobile hydraulics and mobile
electrification.
Go to www.danfoss.com for further product information.
We offer you expert worldwide support for ensuring the best possible solutions for
outstanding performance. And with an extensive network of Global Service Partners, we also
provide you with comprehensive global service for all of our components.
Local address:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequent changes being necessary in specifications already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
©
Danfoss | March 2021 BC319463833479en-000105
 Loading...
Loading...