Page 1

Data sheet
Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters
Type CTI 15
Circuit breakers/Manual motor starters CTI 15
cover the power ranges 0.09 – 7.5 kW
This product range is modular, flexible, and offers
a large selection of clip-on auxiliary functions
and accessories: auxiliary contact blocks, shunt
releases, connection terminal, bus bars and
enclosures.
Features • Short-circuit protection:
An advanced and fast reacting contact system
with arc-control devices give CTI high
short-circuit break capability which makes
them very suitable for the protection of
electrical panels.
• Indicating functions:
– condition (ON or OFF)
• Supply isolation:
– operation switch (manual motor starter)
– isolation switch (with locking device)
– emergency stop switch
(with undervoltage trip)
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 1
Page 2
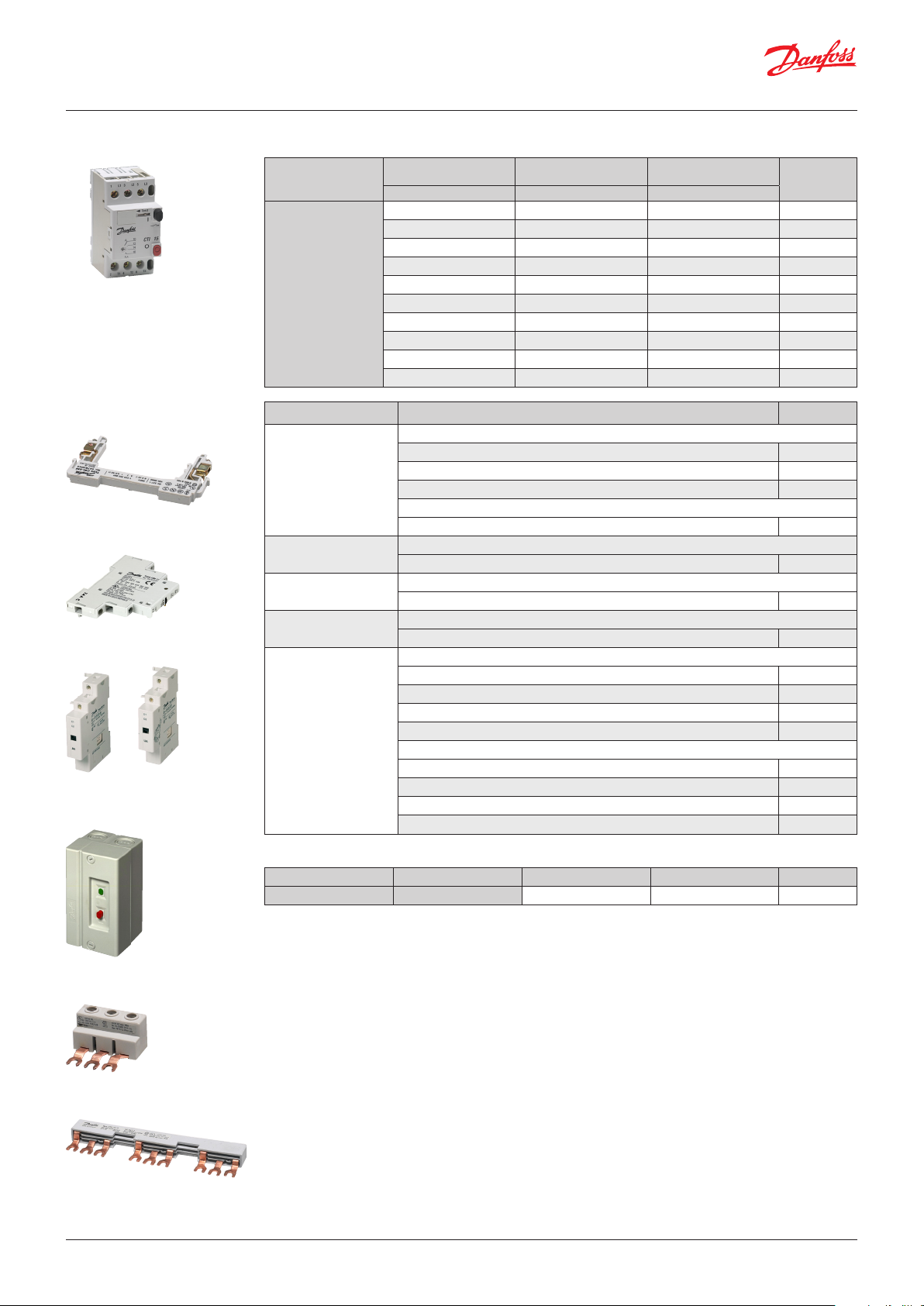
Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Ordering
CBI-NO / CBI-NC
Auxiliary contact block
CBI-11
Auxiliary contact block
CBI-UA / CBI-AA
Undervoltage trip/ Shunt trip
Enclosure BXI
For CTI 15
Circuit breakers/Manual motor starters CTI 15
Type
AC-3 load U
380 – 415 V
e
[kW] [A] [A]
Range
Motor starter
Electromagnetic
trip current
Code no.
0.09 0.25 – 0.4 4.4 047B3051
0.12 0.4 – 0.63 6.9 047B3052
0.37 0.63 – 1.0 11 047B3053
0.55 1.0 – 1.6 18 047B3054
CTI 15
0.75 1.6 – 2.5 28 047B3055
1.5 2.5 – 4.0 44 047B3056
2.5 4.0 – 6.3 69 047B3057
5.5 6.3 – 10 110 047B3058
7.5 10 – 16 176 047B3059
12.5 20 – 25 275 047B3060
Description Comments Code no.
Auxiliary contact blocks for building in
CBI-NO (make) terminal 13 – 14 047B3040
Auxiliary contact blocks
for CTI 15
CBI-NO (make) terminal 23 – 24 047B3041
CBI-NC (break) terminal 11 – 12 047B3042
Auxiliary contact blocks for lefthand mounting
CBI-11 (1 make + 1 break), terminal 13 – 14, 21 – 22 047B3049
Undervoltage
for CTI 15
Shunt trip
for CTI 15
Terminal block for CTI 15
Undervoltage trip for righthand mounting
CBI-UA 220 – 230 V, 50 Hz – 254 V, 60 Hz, D1 – D2 047B3061
Shunt trip for righthand mounting
CBI-AA 220 – 230 V, 50 Hz – 254 V, 60 Hz, C1 – C2 047B3067
For mounting direct on
CTI 15, max. 16 mm², CTT 25 047B3076
For parallel connection fo CTI 15 in panel
CTS 45-2 (2 x 45 mm) 047B3084
CTS 45-3 (2 x 45 mm) 047B3096
CTS 45-4 (2 x 45 mm) 047B3085
Bus bars
for CTI 15
CTS 45-5 (2 x 45 mm) 047B3086
For CTI 15 with auxiliary contact mounted on side
CTS 54-2 (2 x 54 mm) 047B3087
CTS 54-3 (3 x 54 mm) 047B3097
CTS 54-4 (4 x 54 mm) 047B3088
CTS 54-5 (5 x 54 mm) 047B3089
CTT 25
Terminal block
CTS 54-
Bus bar
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
Plastic enclosures for circuit breakers/manual motor starters CTI 15 (IP55)
Type 1) 2) Application Pushbuttons Knockouts Code no.
BXI 55 CTI 15 Start-Stop/reset 4 Pg 16 / 4 Pg 21 047B3091
1
) With neutral and earth terminals
2
) The enclosure also leaves space for a shunt release or an undervoltage release
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 2
Page 3
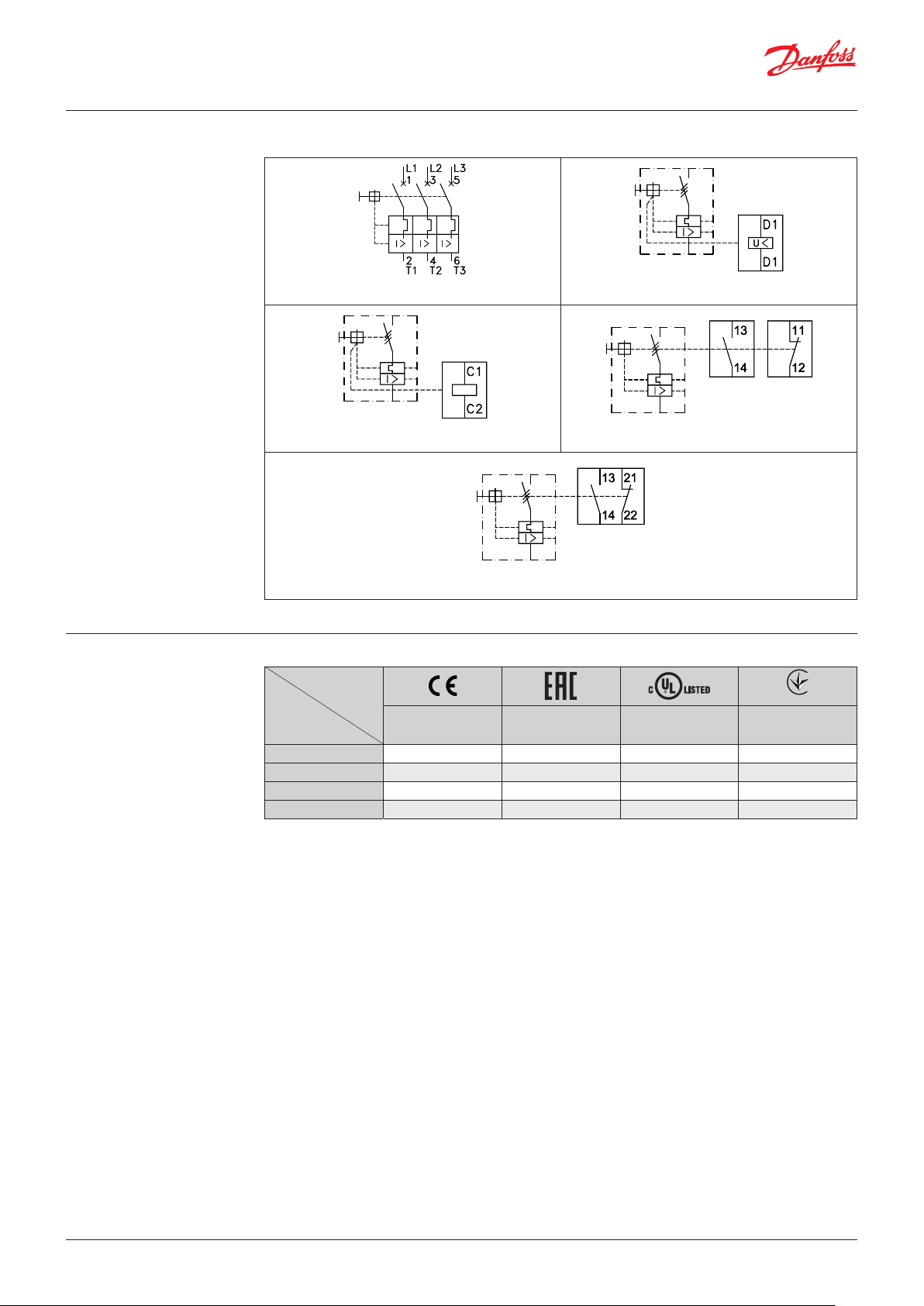
Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
089
Contact symbols and
terminal markings
Circuit breakers
Circuit breakers CTI 15 Under voltage trip for CTI 15 CBI-UA
Shunt trip for CTI 15 CBI-AA Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 CBI-NO, CBI-NC
Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 CBI-11
Approvals
Product type
CTI 15
CTS-
CTT 25
CBI-
• Approved
Approval
authority
EN 60947
EAC
USA
UL-listed
LLC
CDC
TYSK
–
–
–
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 3
Page 4
Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
General data
Parameters
Isolation voltage IEC, cULus 690 V
Pulse voltage 6 kV
Rated frequency range 40 – 60 Hz
Ambient temperature
Temperature compensated -20 °C – 60 °C
Weather resistance
Vibration (IEC 68) (all directions) >7,5 g, 10 – 150 Hz
Shock (IEC 68-2-27) 30 g, 20 ms
Degree of protection IP20
Installation orientation Any direction
Rated current 0.25 – 16 A
Release range 9
Differential release no
Magnetic trip (IeF max. = setting range max. value) 11 x IeFmax
No. of operations per hour 30
Mechanical life (operations) 100.000
Electrical life (operations) 50.000
Release time on short-circuiting 2 ms
Power loss, typical 7 W
Storage/transport -25 °C – 80 °C
Operation -25 °C – 60 °C
(IEC 68) Temp. / rel. humidity
Temperate climate
Type
CTI 15
40 °C, 92% RH: 56 days
23 °C, 83% RH/40 °C, 93% RH
Mounting direction
Max. motor load
AC-2 and AC-3 operation
The table contains kW values of
rated motor sizes according to
IEC 60072 which fits to the current
range of the circuit breaker.
Sometimes more than one rated
current fits to the range. In such
cases both values are given and
they are valid for AC-2 as well as
for AC-3.
CTI 15
Type
CTI 15
Setting range
[A] [kW] [kW] [kW] [kW]
0.25 – 0.4 – 0.09 0.12 – –
0.4 – 0.63 0.06 0.09 0.12 0.18 0.18 0.25 0.25 0.37
0.63 – 1.0 0.12 0.18 0.18 0.25 0.25 0.37 0.37 0.55
1.0 – 1.6 0.18 0.25 0.37 0.55 0.55 0.75 0.75 1.1
1.6 – 2.5 0.37 0.55 0.75 1.1 1.1 1.5 1.8
2.5 – 4.0 0.55 0.75 1.1 1.8 1.5 2.2 2.2 3.0
4.0 – 6.3 1.1 1.5 1.8 3.0 3.0 3.7 3.7 4.0
6.3 – 10 1.8 2.2 3.0 4.0 3.7 6.3 5.5 7.5
10 – 16 3.0 4.0 5.5 7.5 6.3 10 10 13
230 – 240 V 400 – 415 V 500 V 690 V
Motor on operating voltage - Rated output in kW
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
Accessories for circuit breaker CTI 15
Max. load on supply block, current limiter, connection terminal and bus bar.
Type Application Description
CTT 25
CTS- Bus bars 63 690
CTI 15
Connection terminal 63 690
Thermal current I
[A] [V]
th
Voltage supply
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 4
Page 5

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Accessories for circuit breakers
Loads on auxiliary contact blocks
Load [A]
Type Application Description
CBI-NO/NC
CBI-11
CTI 15
Auxiliary contact for building in 6 4 2 1 0.8 0.5 2 0.6 0.2 0.1
Auxiliary contact for building on
(force-actuated PLC-compatible H contact)
I
th
40 °C 60 °C
220 –
240 V
AC-15 DC-13
380 –
500 V 690 V 24 V 48 V 110 V 220 V
415 V
10 6 2 1 0.8 0.5 2 0.6 0.2 0.1
Power consumption, undervoltage and shunt trip
Type Application Description
Rated control voltage U
CBI-UA
CTI 15
Undervoltage trip for building on
Function voltage
CBI-AA Shunt trip for building on Coil consumption
s
Make 0.8 – 1,1 x Us
Break
Make 5 VA, 6 W
Holding 3 VA, 1.2 W
24 – 380 V / 50 Hz, 28 – 440 V / 60 Hz
0.35 – 0.7 x Us
100% make, max. 1.2 Us
Terminations
Single and
multi core
[mm2] [mm2] [Nm]
1 – 6 1 – 4 2.5
Type Application Comments
CTI 15
Circuit breaker 16 A
Terminals
1-3-5 2-4-6
CBI-NO/NC Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 – – 0.75 – 4 0.75 – 2.5 2.5
CBI-11 Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 – – 0.75 – 4 0.75 – 2.5 2.5
CBI-AA Shunt release for CTI 15 – – 0.75 – 4 0.75 – 2.5 2.5
CTI 15
CBI-UA Undervoltage release for CTI 15 – – 0.75 – 4 0.75 – 2.5 2.5
CTT 25 Connection block for CTI 15
6 – 25 4 – 16 4
High
capacity
Tightening
torque
UL/CSA-approved loads
Motor load in hp (AC-3)
Type
Setting range
1-phase operation 3-phase operation
[A] 115 V 230 V 200 V 230 V 460 V 575 V
0.63 – 1.0 – – – – 1/2 3/4
1.0 – 1.6 – 1/10 1/10 – 1 1
1.6 – 2.5 1/10 1/6 1/6 3/4 1.5 2
CTI 15
2.5 – 4 1/8 1/3 1/3 1 3 3
4 – 6.3 1/4 3/4 3/4 2 5 5
6.3 – 10 1/2 1,5 1,5 3 7.5 10
10 – 16 1 3 3 5 10 15
Terminations UL/CSA
Single and
multi core
Type Application Comments
Terminals
1-3-5 2-4-6 [AWG ] [lb-in]
CTI 15
Circuit breaker 16 A
16 – 12 20 – 26
CBI-NO/NC Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 – – 18 – 14 20 – 26
CBI-11 Auxiliary contacts for CTI 15 – – 18 – 14 20 – 26
CBI-AA Shunt release for CTI 15 – – 18 – 14 20 – 26
CBI-UA
CTT 25 Connection block for CTI 15
CTI 15
Undervoltage release for CTI 15
– – 18 – 14 20 – 26
– 14 – 6 36
Tightening
torque
UL/CSA approved loads
Type Application Description
CBI-NO/NC
CBI-11 Auxiliary contact for building in
CTI 15
Auxiliary contact for building in
AC DC
Standard pilot
duty B600
Load
Light pilot
duty R300
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 5
Page 6

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Short circuit protection
Short circuit coordination is the connection between
the specifications of the protection devices, such as
fuses, circuit breakers, MCCB and its ability to resist
short circuit.
Short circuit coordination type 1
Test demand
O-t-CO
O = Breaking a short circuiting
CO = Making and breaking a short circuiting
t = Defined pause (3 min)
No damage to equipment or personal injury may occur
in the event of short circuit. However, contactors and
thermal overload relays are not required to remain
functional after short circuit.
Terms Remarks
Prospective short circuit current (Icc)
Rated service short circuit breaking capacity (Icu)
Rated service short circuit breaking capacity (Ics)
“r”-current
Iq current
gI fuse
gL fuse Indicates full shoert circuit protection of wires.
gG fuse
T fuse Description of an English standard fuse.
BS 88 British Standard for smeltesikringer
Typically the maximum short circuit breaking capacity
Icu is in use when a plant is dimensioned according to
coordination type 1.
Short circuit coordination type 2
Test demand
O-t-CO-t-CO
O = Breaking a short circuiting
CO = Making and breaking a short circuiting
t = Defined pause (3 min)
t = Defined pause (3 min)
No damage to equipment or personal injury may occur
in the event of short circuit. However, light contact
welding is permissible, provided that contacts can be
separated without deformation, using a screwdriver for
example. Contactors and thermal overload relays must
remain completely functional after short circuit.
Typically the short circuit breaking capacity during
operation Ics is in use when a plant is dimensioned
according to coordination type 2.
The prospective short circuit current is the current that
flows during a bolt short circuiting without any short circuit
protection device mounted.
The ultimate short circuit breaking capacity is the maximum
short circuit current specified by the manufacturer that
a circuit breaker can handle under circumstances specified in
IEC 947-2 and in EN 60947-2
The rated service short circuit breaking capacity is
the maximum short circuit current specified by the
manufacturer that a circuit breaker can handle under
circumstances specified in IEC 947-2 and in EN 60947-2
The “r”-current is a short circuit test current. The size of
the “r”-current is determent by the nominal current of the
product. (See below)
Iq –current is the maximum prospective short circuiting
current stated by the manufacturer and often at the value
50 kA.
Indicates full short circuit protection at voltages 250 V, 400 V,
500 V and 690 V.
Indicates full short circuit protection at general applications.
(Will replace gI- and gL –fuses)
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
Contactor size
Rated current at AC-3 load “r” in kA
0 < Ie < 16 1
16 < Ie < 63 3
63 < Ie < 125 5
125 < Ie < 315 10
315 < Ie < 630 18
630 < Ie < 1000 30
Prospective short circuit
test current
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 6
Page 7

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Fuses
Type
CTI 15
= Short-circuit-proof without fuse
Setting range Fuses gI, aM, gL, gG and BS 88 type T when lcc > lcu
[A] 220 – 240 V 380 – 415 V 500 V 690 V
0.25 – 0.4
0.4 – 0.63
0.63 – 1.0
1.0 – 1.6
1.6 – 2.5 25
2.5 – 4.0 35
4.0 – 6.3 63 –
6.3 – 10.0 63 50 –
10.0 – 16.0 50 50 50 –
Rated short-circuit breaking
capacity I
cn
Circuit breaker
Type
CTI 15
Thermal
overload
relay
Setting range
[A] [A] Icu I
Magnetic
Release
current
trip
Short-circuit category Icu and Ics to IEC 947-2/EN 60947-2
Breaking capacity Icn in kA
220 – 240 V 380 – 415 V 500 V 690 V
I
cs
I
cu
I
cs
I
cu
I
cs
cu
0.25 – 0.4 4.4 65 65 65 65 50 50 50 50
0.4 – 0.63 6.9 65 65 65 65 50 50 50 50
0.63 – 1.0 11 65 65 65 65 50 50 50 50
1.0 – 1.6 18 65 65 65 65 50 50 50 50
1.6 – 2.5 28 50 50 50 50 50 50 4.5 4.5
2.5 – 4.0 44 50 50 10 10 6 3 2 2
4.0 – 6.3 69 50 50 10 10 10 10 – –
6.3 – 10 110 50 50 10 10 4.5 4.5 – –
10 – 16 176 20 16 6 8 4.5 4.5 – –
I
cs
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 7
Page 8

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Let-through graphs for
circuit breaker CTI 15
Maximum let-through energy
Rated voltage 400 – 415 V
A: Max. let-through energy ∫ i2 × dt [103 × A2 × s]
B: Prospective short-circuit current ICC [kA]
The energy graph can be used to assess whether a lead
is correctly protected against the thermal effect of a
short-circuit current.
The graph can be read as follows:
If the expected short-circuit current at the point of
installation is set at 8 kA, and a CTI 15 – 10 A is required,
the let-through energy will be 40000 A2s.
Calculation example:
The following generally applies to leads subject to brief
overload:
2
k x S
t = (
Where t = duration of short-circuit current in seconds
S = cross-section of lead in mm
I = short-circuit current in Aeff
k = a constant which for PVC-insulated Cu wire
)
which gives I2 x t = k2 x S
I
= 115
2
2
Maximum let-through current
Rated voltage 400 – 415 V
A: Max. let-through current ID [kA]
B: Prospective short-circuit current ICC [kA]
The theoretical short-circuit current Icc (prospective
short-circuit current) is limited by CTI 15. Id is the
maximum let-through current (highest momentary
value of the limited short-circuit current). This value
is given in the graph as a function of the prospective
short-circuit current.
The graphs have been plotted for eight different CTI 15
ranges.
Thus, for a 1.5 mm2 PVC-insulated Cu wire,
I² x t = (115 x 1.5)² = 29756 A2s.
From the energy graph it can be seen that with
Icc = 8 kA a CTI 15 with max. range setting = 10 A only
allows about 20000 A2s through and therefore protects
the lead satisfactorily.
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 8
Page 9

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Short-circuit protection
of wiring
Overload protection of
motors
Type Max. setting
6 4 2.5 1.5 1 0.75
CTI 15
4.0
6.3
10.0
16.0
Protection of PVC-insulated wires against overload
and short-circuiting, in accordance with IEC 364 and
CENELEC harmonizing documents 384–3 and 384–4.
Overload protection is given by the adjustable thermal
circuit breakers in CTI 15 motor starters. The highest
possible release current is therefore significantly lower
than with overload protection by fuses. The magnetic
trips with fixed setting that rapidly open the main
contacts take over protection in the event of shortcircuiting. The low total release time ensures that
heating generated in leads by short-circuiting is limited
to a minimum.
Further information is contained in national regulations.
Tripping characteristic of CTI 15
Protected min. cross-section [mm2]
at 380 / 415 V, 50 Hz
Setting in short-circuit protection application
In many cases, CTI 15 are used exclusively for
short-circuit protection - overload protection being
provided by thermal overload relays, e.g. in multi stage
motors or star-delta starters with heavy start, and/or
in reducing motor lead cross-section. Here, the current
value can be set 20% higher than the operating current
so that only the thermal overload relays release when
overload occurs.
1. Thermal tripping current
The adjustable, current-dependent, delayed bimetal
breakers guarantee motor overload protection.
The graph gives the average value at 20 °C ambient
temperature, from the cold condition. When the unit
has warmed up, the release time is less or equal to the
release time in the cold condition.
The accurate adjustment ensures motor protection
even in the event of phase failure.
Short-circuit protection
A. Tripping time (s)
B: Times the adjustable current I
eF
It has become more and more general to short-circuitprotect panels with circuit breakers rather than fuses.
The clear advantages of “fuse-free” installations are:
- Space saving
- Cut-out in all three phases in the event of shortcircuiting.
- No problems with non-convertible fuse types
when exporting electrical equipment.
2. Magnetic tripping current
The electromagnetic, instantaneous high-speed trips
react at a fixed response current. At the highest setting
value this corresponds to 11 times the set current for
CTI 15. At a lower setting it is correspondingly higher.
Danfoss circuit breakers CTI 15 conform to IEC 947-2
and are tested in accordance with EN 60947-2. Because
of their fast reaction times and reliability they are
particularly suitable for the short-circuit protection of
panels.
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 9
Page 10

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Fuseless coordination tables
Fuseless coordination tables
Circuit breakers and contactors
Prospective short circuit current: Iq = 10/ 50 kA
Voltage: 380 – 415 V/ 50 Hz
Overload and short circuit protection with circuit breaker type: CTI
Short circuit coordination: T1
Short circuit coordination type
T1
Contactor type
Test current
“r ” 1) and Iq = 50 kA
Maximum CTI - range
[A]
CI 5-2, CI 5-5, CI 5-9 16 2)
CI 6, CI 9 16 2)
CI 12, CI 15 16 2)
CI 16 16 2)
CI 20, CI 25 16 2)
1
) Short circuit test current according to EN 60947-4 (see table page 8)
2
) Fuses should be installed in the front of CTI 15 with higher ratings than 6.3 A
when rated service breaking capacity exceed values in tables page 9
Circuit breakers, contactors and thermal overload relays (several groups)
Prospective short circuit current: Iq = 50 kA
Voltage: 380 – 415 V / 50 Hz
Overload protection with thermal overload relay type: TI
Short circuit protection with circuit breaker type: CTI
Short circuit coordination: T1
Test current “r”1) and Iq = 50 kA
Maximum CTI - range
Contactor type
Thermal overload relay
Range
[A] [A]
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.13 – 0.20
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.19 – 0.29
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.27 – 0.42
CTI 15 – 16 A 2)
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.4 – 0.62
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.6 – 0.92
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 0.85 – 1.3
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 1.2 – 1.9
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 1.8 – 2.8
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 2.7 – 4.2
CTI 15 – 16 A 2)
CI 5-5, CI 6, CI 9 4 – 6.2
CI 5-9, CI 9 6 – 9.2
CI 12, CI 15 8 – 12
CI 15, CI 16
1
) Short circuit test current according to EN 60947-4 (see table page 8)
2
) Fuses should be installed in the front of CTI 15 with higher ratings than 6.3 A when rated service breaking capacity
exceed values in tables page 9.
11 – 16
CTI 15 – 16 A
2
)
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 10
Page 11

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Coordination tables with fuses
Contactors
Prospective short circuit current: Iq = 10/ 50 kA
Voltage: 380 – 415 V/ 50 Hz
Overload and short circuit protection with fuse types: gI, gL, gG and ‘T’ (BS 88)
Short circuit coordination: T1
Short circuit coordination type
T1
Contactor type
Test Current
“r ” 1) and Iq = 50 kA
gI,gL,gG ‘T’
[A] [A]
CI 5-2, CI 5-5, CI 5-9 50 63
CI 6, CI 9, CI 12, CI 15 50 63
CI 16 80 80
CI 20, CI 25 80 80
CI 30 80 80
CI 32 125 125
CI 37, CI 45, CI 50 125 125
CI 61, CI 73 250
CI 141 315
CI 180 355
CI 210 EI, CI 250 EI 500
CI 300 EI, CI 420 EI 630
1
) Short circuit test current according to EN 60947-4 (see table page 7)
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 11
Page 12

Data sheet | Circuit breakers / Manual motor starters, Type CTI 15
Coordination tables with
fuses
Contactors
Prospective short circuit current: Iq = 10/ 50 kA
Voltage: 380 – 415 V/ 50 Hz
Overload and short circuit protection with fuse types: gI, gL, gG and ‘T’ (BS 88)
Short circuit coordination: T1
Short circuit coordination type
Thermal overload
Contactor type
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.13 – 0.20 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.19 – 0.29 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.27 – 0.42 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.42 – 0.60 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.60 – 0.92 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 0.85 – 1.3 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 1.2 – 1.9 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 1.8 – 2.8 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 2.7 – 4.2 25 32
CI 5-5, CI 5-9, CI 6, CI 9 4 – 6.2 35 40
CI 5-9, CI 9 6 – 9.2 0 50
CI 12, CI 15 8 – 12 63 63
CI 15, CI 16 11 – 16 80 80
CI 16, CI 20 15 – 20 80 80
CI 25 19 – 25 80 80
CI 30 24 – 32 80 80
CI 32 16 – 23 125 125
CI 32 22 – 32 125 125
CI 37, CI 45 30 – 45 125 125
CI 50 42 – 63 125 125
CI 61 42 – 63 100
CI 73 60 – 80 125
CI 86 74 – 85 125
CI 140 20 – 180 315
CI 180 20 – 180 355
CI 210 El 160 – 630 500
CI 300 El 160 – 630 630
1
) Short circuit test current according to EN 60947-4 (see table page 7)
relay
gI,gL,gG ‘T’
[A] [A] [A]
T1
Test Current
“r ” 1) and Iq = 50 kA
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 12
Page 13

Coordination tables with
fuses or circuit breakers/MCB
Auxiliary contacts
Prospective short circuit current: Iq = 1 kA
Coordination type: “weld-free”
Fuse types: gI, gL, gG and ‘T’ (BS 88)
Dimensions
Circuit breakers CTI
For unit type
Auxiliary contacts
Clip-on Build-in
Max. permissible fuse
gl, gL, gG ‘T’
Let-throug
energy
MCCB
Max.
CTI-range
[A] [A] [A2s] [A]
CI 6
10 16 400 2
CI 5-2, CI 5-5, CI 5-9 CBM- 10 16 400 2
16 20 900 4
CI 6, CI 9, CI 12, CI 15 S 6 10 130 1
CI 16, CI 20, CI 25, CI 30 CB- NO-NC 16 20 900 4
CI 32, CI 37, CI 45, CI 50 EM-LB 25 32 3000 25
CI 61, CI 73, CI 86 CBD - 10 16 400 2
CI 141, CI 180 CBC -
25 32 3000 25
16 20 900 4
CTI 15 CBI - 16 20 900 4
Circuit breaker CTI 15 Circuit breaker CTI 15 with
bus bars CTS 45 or CTS 54
© Danfoss | DCS (az) | 2018.02
1
) Possibility of fixing on DIN rail EN 50022-35
²) Circuit breaker CTI 15, incl. auxiliary contact block CBI for building in
³) Auxiliary contact block CBI for mounting
) Shunt release CBI-AA or undervoltage release CBI-UA
IC.PD.C00.C4.02 | 13
 Loading...
Loading...