Page 1

User Guide
Case/room controller (EEV)
Type AK-CC55 Compact
SW Ver. 2.0x
For refrigeration appliances and cold storage rooms.
Page 2

AK-CC55 Compact
Contents
Introduction 5
Portfolio overview 6
Function overview 6
Connectivity 7
Data communication 7
AK-CC55 Compact 7
External display 7
Controller functionality 9
Functions 9
Liquid injection by use of AKV 9
Thermostatic expansion valve control 10
Temperature control 11
Temperature monitoring 11
Thermostat bands 11
Night setback of thermostat value 11
Appliance cleaning 12
Appliance shutdown 12
Defrost 12
Start of defrost 13
Stop of defrost 13
Compressor run during hot gas defrost 13
Fans 13
Defrost sequence 13
Real-time clock 13
Coordinated defrost 14
Melt function 14
Control of two compressors (only with custom set-up) 14
Rail heat 15
Fan 16
Light function 17
Night blind 17
Heating function (only with custom set-up) 18
Digital inputs 18
Forced closing 19
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 2
Page 3

AK-CC55 Compact
Door contact 19
Display 19
Override 19
Applications 21
AK-CC55 Compact connections and application options 21
Application set-ups and IO connections 22
Product identication 25
AK-CC55 Compact connections 26
Data communication 26
AKV info 26
External solid state relay for rail heat 27
AKS 32R info 27
Coordinated defrost via cable connections 27
External display AK-UI55 28
Connections 28
Operation 30
Operation via data communication 30
Direct operation 30
Operation via AK-UI55 Set 30
Parameter groups when operating via display 32
Get a good start 32
AK-UI55 display menu (SW ver. 2.0x) 34
Thermostat 34
Alarm settings 34
Compressor 35
Defrost 35
Injection control 35
Fan control 35
Defrost schedule 36
Miscellaneous 36
Control 38
DO cong and manual 38
Service 39
Operation via AK-UI55 Bluetooth 41
AK-CC55 Connect menu (SW ver. 2.0x) 42
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 3
Page 4

AK-CC55 Compact
Start / Stop 42
Conguration 42
Thermostat control 43
Alarm limits and delays 45
Injection control 46
Defrost control 46
Defrost schedules 48
Compressor 48
Fan control 49
Railheat control 49
Light/Blinds/Cleaning control 50
Display control 51
Alarm relay priorities 51
Miscellaneous 52
Advanced 52
Fault message 54
Operating status 55
Product specication 56
Technical data 56
Electrical specications 56
Sensor and measuring data 56
Input and output relay specications 56
Function data 57
Environmental conditions 57
Dimensions 57
Certicates, declarations, and approvals 58
Statements for the AK-UI55 Bluetooth display 59
Online support 60
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 4
Page 5
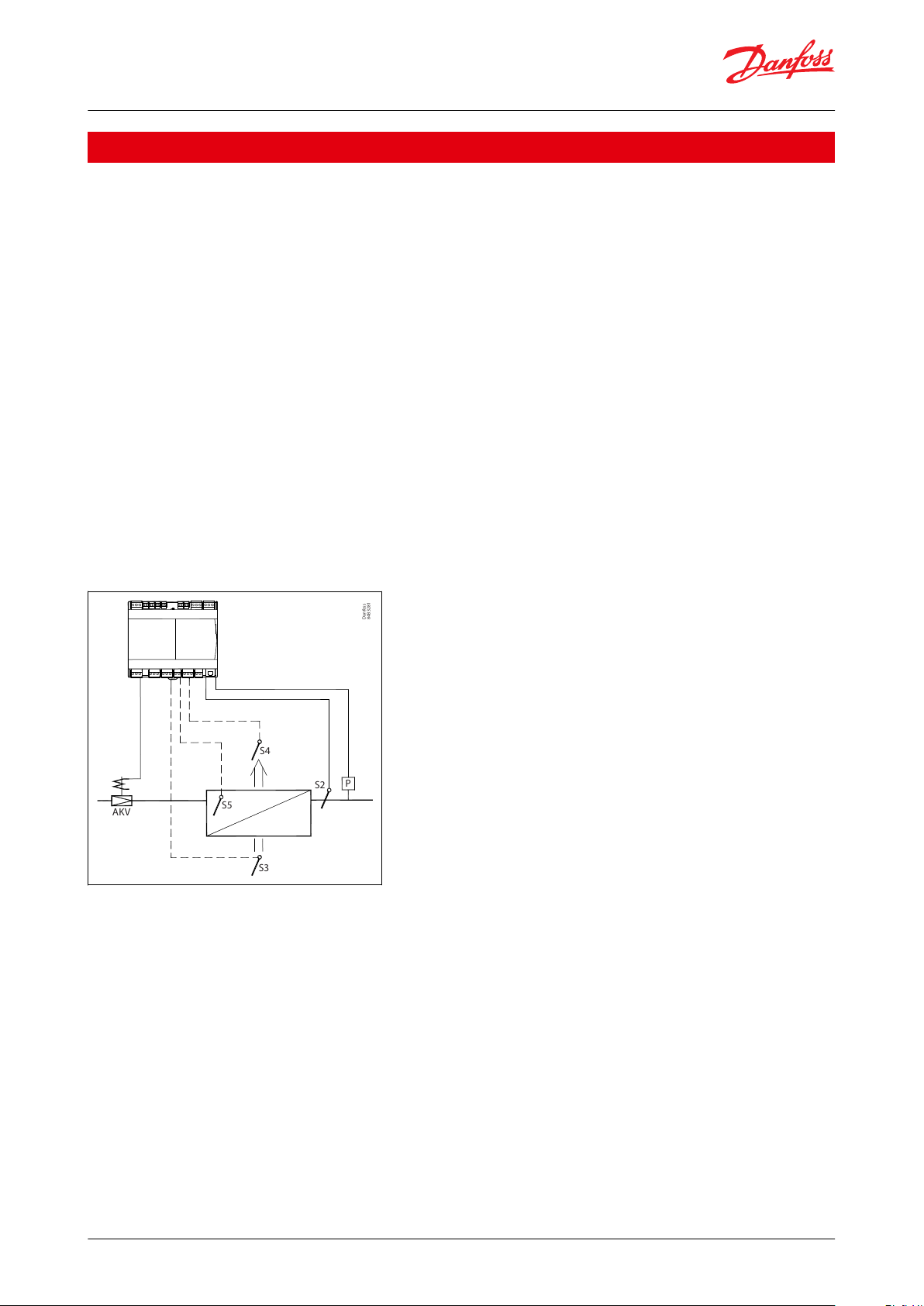
Danfoss
84B3281
S5
S3
S4
S2
P
AKV
AK-CC55 Compact
Introduction
Application
Refrigeration appliance control with great exibility to adapt to refrigeration appliances and cold storage rooms.
Advantages:
• Control of Thermostatic Expansion Valve (TEV) and Electronic Expansion valve(EEV) applications
• Quick set-up with predened settings
• Easy conguration and service using a mobile app with Bluetooth
• Adaptive Minimum Stable Superheat (MSS) control is performed with lowest possible superheat
• Allows the suction pressure to be raised several degrees
• Adaptive Liquid Control (ALC) can be performed with superheat down to 0 degrees on transcritical CO2 systems
with liquid ejectors
Principle
The temperature in the appliance is registered by one or two temperature sensors which are located in the air ow
before the evaporator (S3) or after the evaporator (S4) respectively. A setting for thermostat, alarm thermostat and
display reading determines the inuence the two sensor values should have for each individual function.
The temperature of the evaporator is registered with the S5 sensor which can be used as a defrosting sensor.
In addition to the output of the electronic AKV injection valve, the controller has relay outputs which are dened by
the application setting
Figure 1: AK-CC55 with evaporator, AKV valve and sensor positions
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 5
Page 6

AK-CC55 Compact
AK-CC55 Single Coil
AK-CC55 Single Coil UI
AK-CC55 Multi Coil
Product image
Valve
1 x TXV or AKV
1 x AKV
1 x AKV
3 x AKV
Digital Output3554
Digital input
1 (2)
3 (2)
3 (2)
3 (2)
Analogue Output1111
Analogue Input
5 (4)
6 (7)
6 (7)
6 (7)
Display
1 remote
2 remote
1 remote + 1 Integrated
2 remote
Comm. module
Modbus
Modbus
Modbus
Modbus
Optional comm. module
LON module
LON module
LON module
Application
AK-CC55 Compact
AK-CC55 Single Coil
AK-CC55 Single Coil UI
AK-CC55 Multi Coil
AKV - application (electrically operated expansion valve)
xxx
0 – 10 V to control external stepper driver
x
TXV - application (thermostatic expansion valve + solenoid valve or compressor)
x
Remote hot gas - application
x
One valve, one evaporator, one refrigeration section
xxx
One valve, one evaporator, two refrigeration sections
x
One valve and two evaporators, two refrigeration sections
x
Two valves and two evaporators (same refrigeration section)
x
Three valves and three evaporators (same refrigeration section)
x
Custom conguration of relay outputs
x
x
Two compressorsxx
Heating functionxx
Control of air humidity
x
x
Adaptive superheat
xxx
Adaptive liquid control
(zero superheat control for transcritical CO2 systems with liquid ejectors)
xxx
Adaptive defrosting
x
Product sensor
x
RS485 Lon, option (AK-OB55)
x
x
AK-CC55 Compact
Portfolio overview
The AK-CC55 portfolio contains four controllers with dierent functionalities and application settings, as outlined in
the table.
Table 1: AK-CC55 Portfolio
Function overview
Table 2: AK-CC55 function overview by type
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 6
Page 7
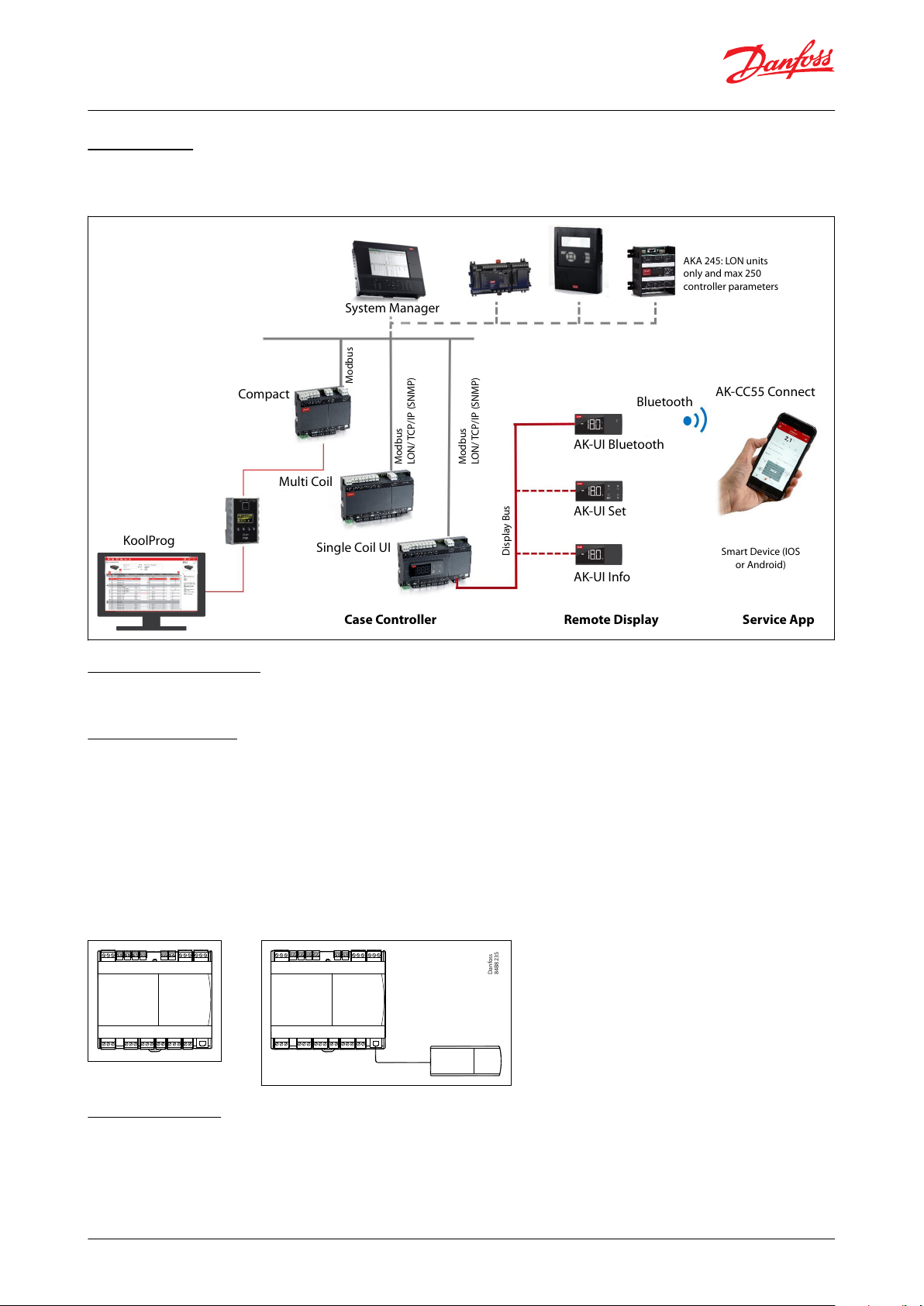
Danfoss
84B8235
Compact
System Manager
AKA 245: LON units
only and max 250
controller parameters
Multi Coil
KoolProg
Single Coil UI
AK-UI Info
AK-UI Set
AK-UI Bluetooth
Bluetooth
AK-CC55 Connect
Smart Device (IOS
or Android)
Modbus
LON/ TCP/IP (SNMP)
Display Bus
Modbus
LON/ TCP/IP (SNMP)
Modbus
Case Controller Remote Display Service App
AK-CC55 Compact
Connectivity
The diagram outlines the connectivity options presented by AK-CC55 for the design of system functionality.
Figure 2: Connectivity
Data communication
The AK-CC55 Compact controller has built-in MODBUS data communication only.
AK-CC55 Compact
Compact version for controlling one evaporator.
An application mode setting will congure inputs and outputs for the desired use. There are nine applications to
choose from.
Regulation is performed using a TXV in combination with a liquid line solenoid valve, controlling a compressor or an
AKV expansion valve.
AK-CC55 Compact is without display, and can be extended with one external display (see Figure 3 and Figure 4):
Figure 3: AK-CC55 Compact Figure 4: AK-CC55 Compact with external display.
External display
There are three versions available with dierent functions:
• AK-UI55 Info: Temperature display.
• AK-UI55 Set: Temperature display with control buttons on the front.
• AK-UI55 Bluetooth: Temperature display with Bluetooth communication, for use with AK-CC55 Connect Mobile
app.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 7
Page 8

AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 5: AK-UI55 Info Figure 6: AK-UI55 Set Figure 7: AK-UI55 Bluetooth
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 8
Page 9

Danfoss
84B3281
S5
S3
S4
S2
P
AKV
AK-CC55 Compact
Controller functionality
Functions
• Day/night thermostat with ON/OFF or modulating principle.
• Switch between thermostat settings via digital input.
• Adaptive superheat control.
• Modulating PWM control of brine valve
• Start of defrost via schedule, digital input, network or setting display.
• Natural, electric, simple hot gas, or warm brine defrost.
• Stop of defrost on time and/or temperature.
• Coordination of defrosting among several controllers in a line-up.
• Pulsing or ECO control of fans when thermostat is satised.
• Appliance cleaning function for documentation of HACCP procedure.
• Rail heat control via day/night load or dew point.
• Door function.
• Control of two compressors.
• Control of night blinds.
• Light control.
• Heat thermostat.
• High accuracy inputs:
◦ to guarantee a better measuring accuracy than stated in the standard EN ISO 23953-2 without subsequent
calibration (Pt1000 ohm sensor).
• Integrated MODBUS communication
Liquid injection by use of AKV
Liquid injection in the evaporator is controlled by an electronic injection valve of the type AKV. The valve operates
as both expansion valve and solenoid valve. The controller opens and closes the valve based on sensor readings.
The function contains an adaptive algorithm which independently adjusts the valve’s opening so that the
evaporator constantly supplies optimum amount of refrigerant.
Superheat is measured via:
Pressure sensor Pe and temperature sensor S2. By using a pressure sensor and temperature sensor, a correct
measurement of superheat is achieved under all conditions which ensures a very robust and precise control. The
signal from one pressure transmitter can be shared by max. 10 controllers, but only if there is no signicant pressure
dierence between the evaporators in question.
Figure 8: Liquid injection function with AKV valve
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 9
Page 10
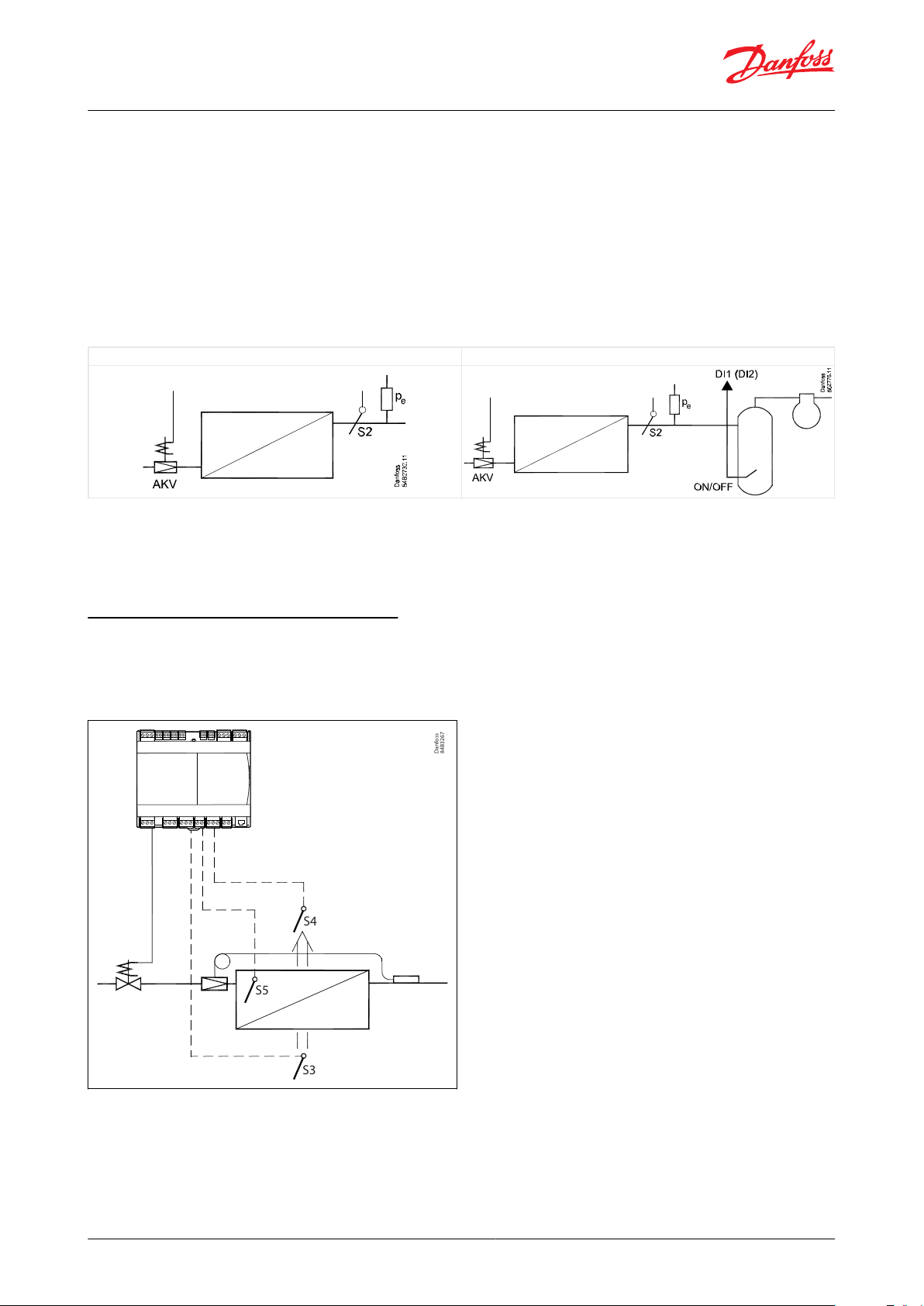
Dry expansion (MSS Control)
Adaptive liquid control (ALC)
S4
S5
S3
Danfoss
84B3267
AK-CC55 Compact
There are two parallel settings for superheat:
• Dry expansion, which does not allow liquid ow on the outlet of the evaporator.
• Adaptive liquid control in transcritical CO2 systems, which allows liquid ow. This type of control requires that the
controller receives an on/o signal from (for example) a suction accumulator in the suction line. A level switch in
the tank will register when the liquid level exceeds the max. level. When this happens, the controller will switch to
dry expansion, and then back to liquid control when the liquid level has dropped. The function is dened in
setting o02, o37 or o84.
The function can also be activated via data communication from a system unit. If the adaptive liquid control signal is
lost, the controller will automatically switch back to dry expansion.
Table 3: Liquid injection
WARNING:
Accidental actuation may allow liquid throughput to the compressor. It is the installer’s responsibility to ensure that
signal loss to the controller will not result in liquid throughput to the compressor. Danfoss accepts no
responsibility for damage resulting from inadequate installation.
Thermostatic expansion valve control
In the compact version the refrigeration (injection) can be controlled either by starting/stopping a compressor or by
opening/closing a solenoid valve in the liquid line.
Figure 9: AK-CC55 Compact with evaporator, solenoid
valve, expansion valve and sensor positions
Brine control
When changing from ON/OFF control to modulating control in TXV applications, a solenoid valve can be PWM
controlled with a set period time from 30 – 900 sec. A number of additional brine control parameters are available in
the injection control menu. When brine control is enabled, a dedicated brine defrost can also be set up in order to
force open the brine valve while defrosting.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 10
Page 11
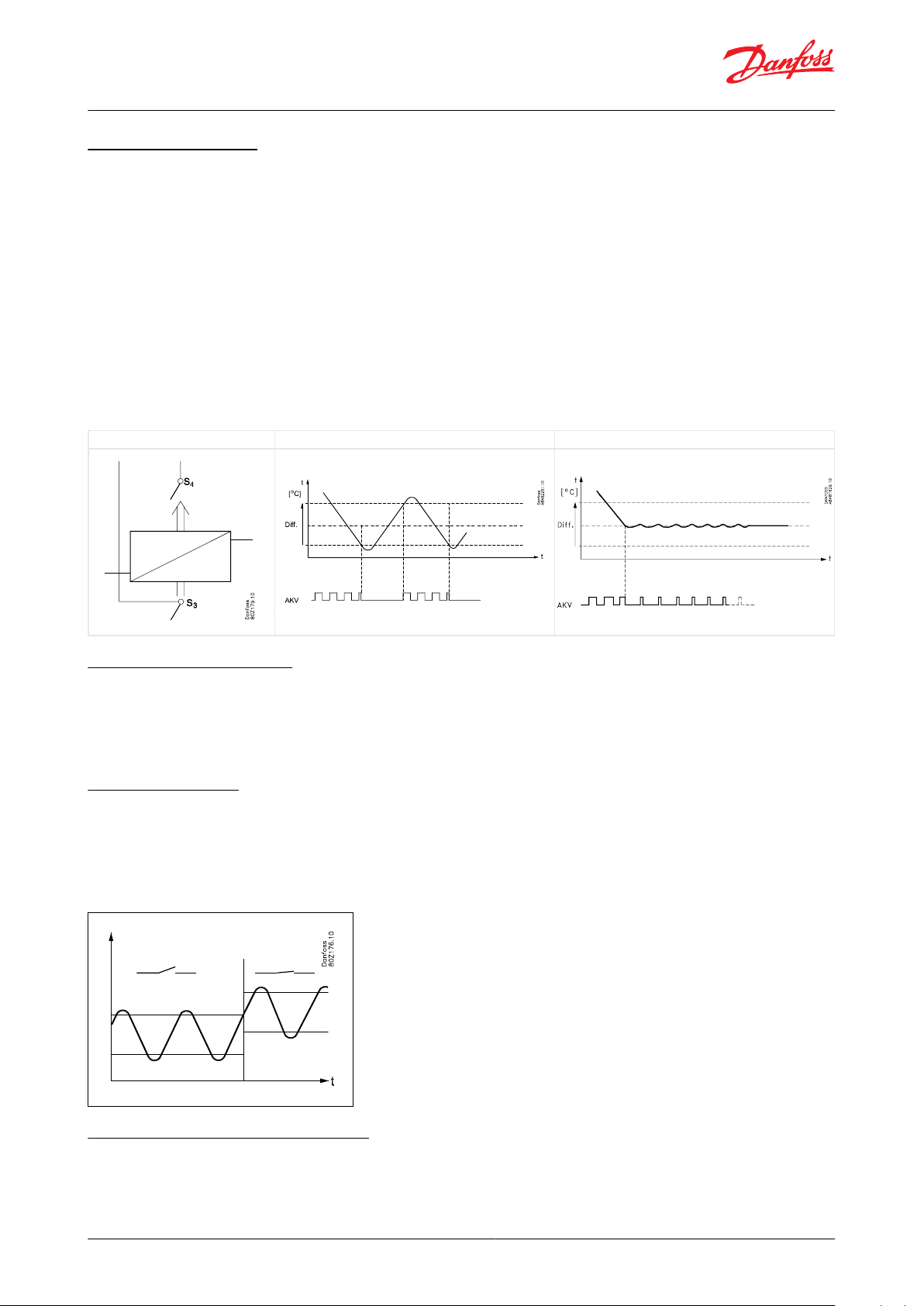
ON/OFF control
Modulating control
AK-CC55 Compact
Temperature control
The temperature in the appliance is registered by one or two temperature sensors which are located in the return air
before the evaporator (S3) or after the evaporator (S4) respectively. A setting for the thermostat, night thermostat,
alarm thermostat and display reading determines how much the two sensor values should inuence each individual
function, e.g. 50% of S4 will produce an equal value from both sensors.
The actual temperature control can take place in two ways:
1.
As an ordinary ON/OFF regulation with a dierential, or
2.
As a modulating control where the temperature variation will not be nearly as high as in ON/OFF control.
There is, however, a limit to the use of a modulating control as it can only be used in remote cabinets. It is not
recommended to use modulating thermostat control in low temperature applications. In applications with one
evaporator and one compressor, the thermostat function with ON/OFF control should be selected. In remote
cabinets, the thermostat function may either be selected for ON/OFF control or modulating control.
Table 4: Control methods
Temperature monitoring
Just as is possible for the thermostat, the alarm monitoring can be set with a weighting between S3 and S4 so that
you can decide how much the two sensor values should inuence the alarm monitoring. Minimum and maximum
limits can be set for alarm temperature and time delays. A longer time delay can be set for high temperature alarm.
This time delay is active for pull-down, after defrosting, appliance cleaning and start-up.
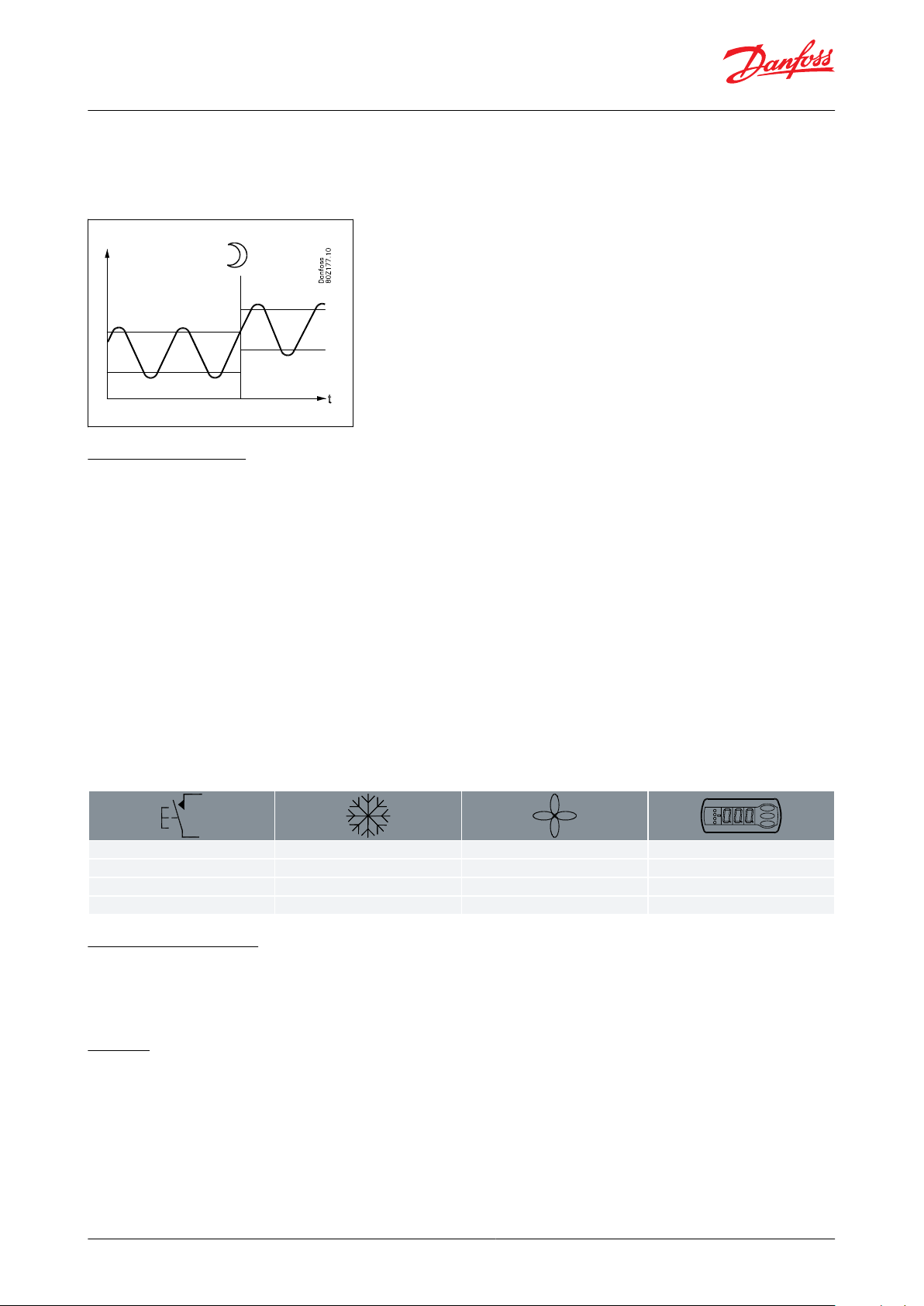
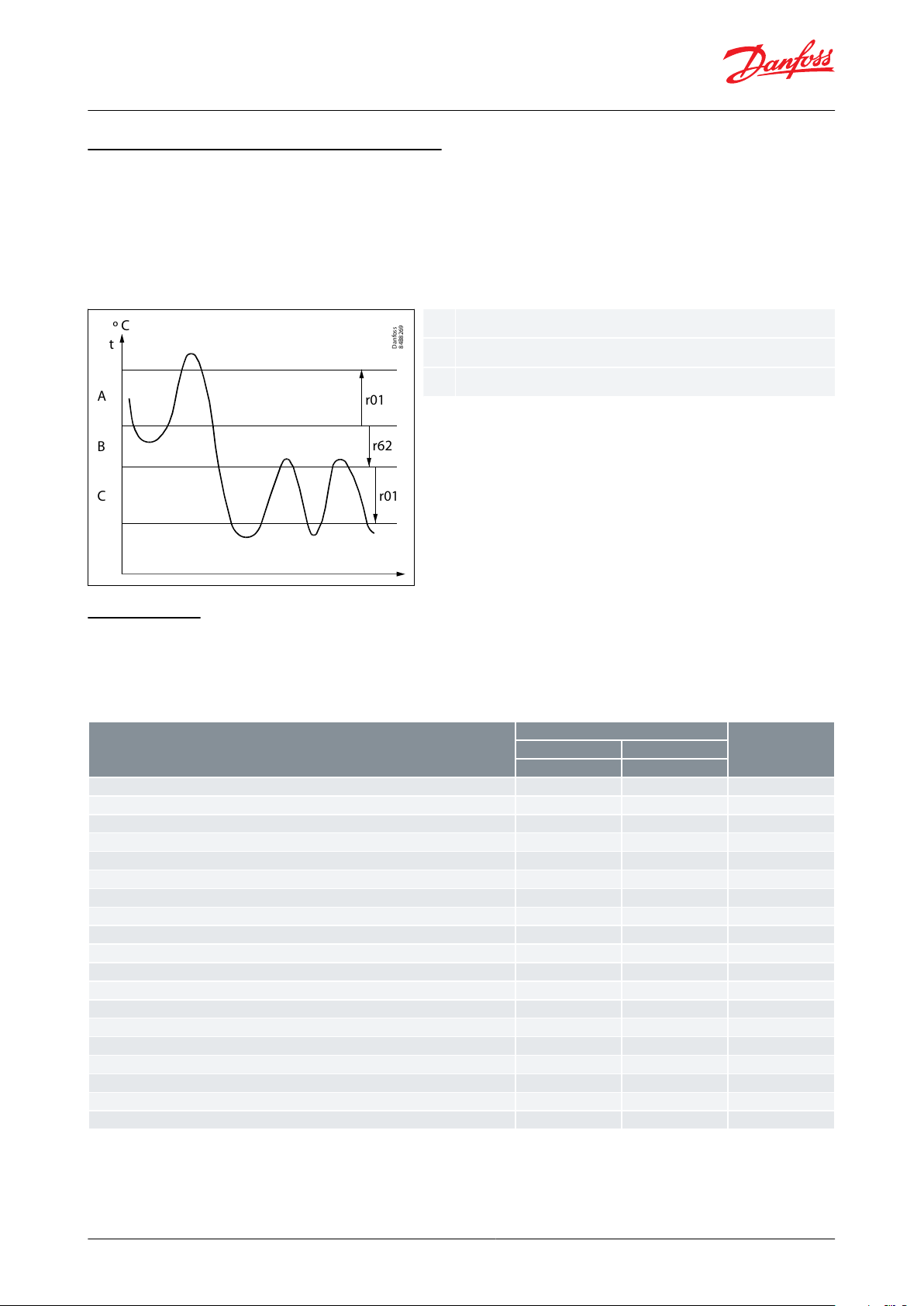
Thermostat bands
Thermostat bands can be used benecially for appliances where dierent product types are stored, which requires
dierent temperature conditions. It is possible to change between the two dierent thermostat bands via a contact
signal on a digital input. Separate thermostat and alarm limits can be set for each thermostat band – also for the
product sensor.
Figure 10: Thermostat band function with two dierent band settings
Night setback of thermostat value
In refrigeration appliances there may be big load dierences between the shop’s opening and closing hours,
especially if night lids/blinds are used. The thermostat reference may be raised here without it having any eect on
the product temperature.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 11
Page 12
-++°C1÷+
Fan2÷÷O3++°C
AK-CC55 Compact
Change-over between day and night operation can take place as follows:
• via an external switch connected to a digital input.
• via a signal from the data communication system.
Figure 11: Thermostat band function with Night setback
Appliance cleaning
This function makes it easy for the shop’s sta to carry out a cleaning of the appliance according to a standard
procedure. Appliance cleaning is activated via a pulse signal – as a rule via a key switch placed on the appliance or
via the AK-CC55 Connect mobile app.
Appliance cleaning is carried out via three phases:
1.
At the rst activation, the refrigeration is stopped, but the fans keep on operating in order to defrost the
evaporators. ”Fan” is shown on the display.
2.
At the second activation, the fans are also stopped and the appliance can now be cleaned. ”OFF” is shown on the
display.
3.
At the third activation, refrigeration is recommenced. The display will show the actual appliance temperature,
o97 setting.
When appliance cleaning is activated, a cleaning alarm is transmitted to the normal alarm recipient. A later
processing of these alarms will document that the appliance has been cleaned as often as planned.
There are no temperature alarms during appliance cleaning.
Table 5: Appliance cleaning function
Appliance shutdown
The function closes the AKV valve and all outputs are switched o. The cooling appliance is stopped like the “Main
switch”, but this happens without an “A45 standby alarm”. The function can be enabled by a switch on the DI input
or via a setting through data communication.
Defrost
Depending on the application, you may choose between the following defrost methods:
• Natural: Here the fans are kept operating during the defrost
• Electric: The heating element is activated
• Hot gas: Simple hot gas defrost can be selected in application modes where a compressor is controlled. The
compressor unit will operate during defrosting
• Brine defrost: The brine valve is forced open while defrosting (only possible when selecting modulating control in
TXV applications)
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 12
Page 13

AK-CC55 Compact
Start of defrost
A defrost can be started in dierent ways:
Interval:
Defrost is started at xed time intervals like e.g. every eighth hour. An interval must ALWAYS be set to a "higher"
value than the period set between two defrostings when a schedule or network signal is used.
Week schedule:
Here defrost can be started at xed times of the day and night. However, max. 6 defrosts per day.
Contact:
Defrost is started with a contact signal on a digital input.
Figure 12: Defrost start
Network:
The defrost start signal is received from a system manager via data communication.
Max. thermostat runtime:
When the aggregate time has passed a preset value, a defrost will be initiated.
Manual:
An extra defrost can be activated from the defrost button on the AK-UI55 Set display via the app, or via the
parameter setting. All the mentioned methods can be used in parallel – if just one of them is activated, a defrost will
be started.
Stop of defrost
Defrosting can be stopped by either:
• Time
• Temperature (with time as safety)
Compressor run during hot gas defrost
If the defrosting method is set to “Gas,” the compressor will be “On” during the defrost cycle. (Only for application
situations that include a compressor output).
Fans
The fans can be stopped or operated during defrosting. They can also run and then be stopped at a set temperature.
The temperature signal is obtained from the defrost stop sensor.
Defrost sequence
1.
Pump down
2.
Defrost
3.
Waiting position after defrost
4.
Drip o
5.
Delay of fan
Real-time clock
The controller has a built-in real-time clock which can be used to start defrosts. This clock has a power reserve of
four days.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 13
Page 14
System manager
Max 10.
Danfoss
84B8268
AK-CC55 Compact
If the controller is equipped with data communication, the clock will automatically be updated from a Danfoss
system manager.
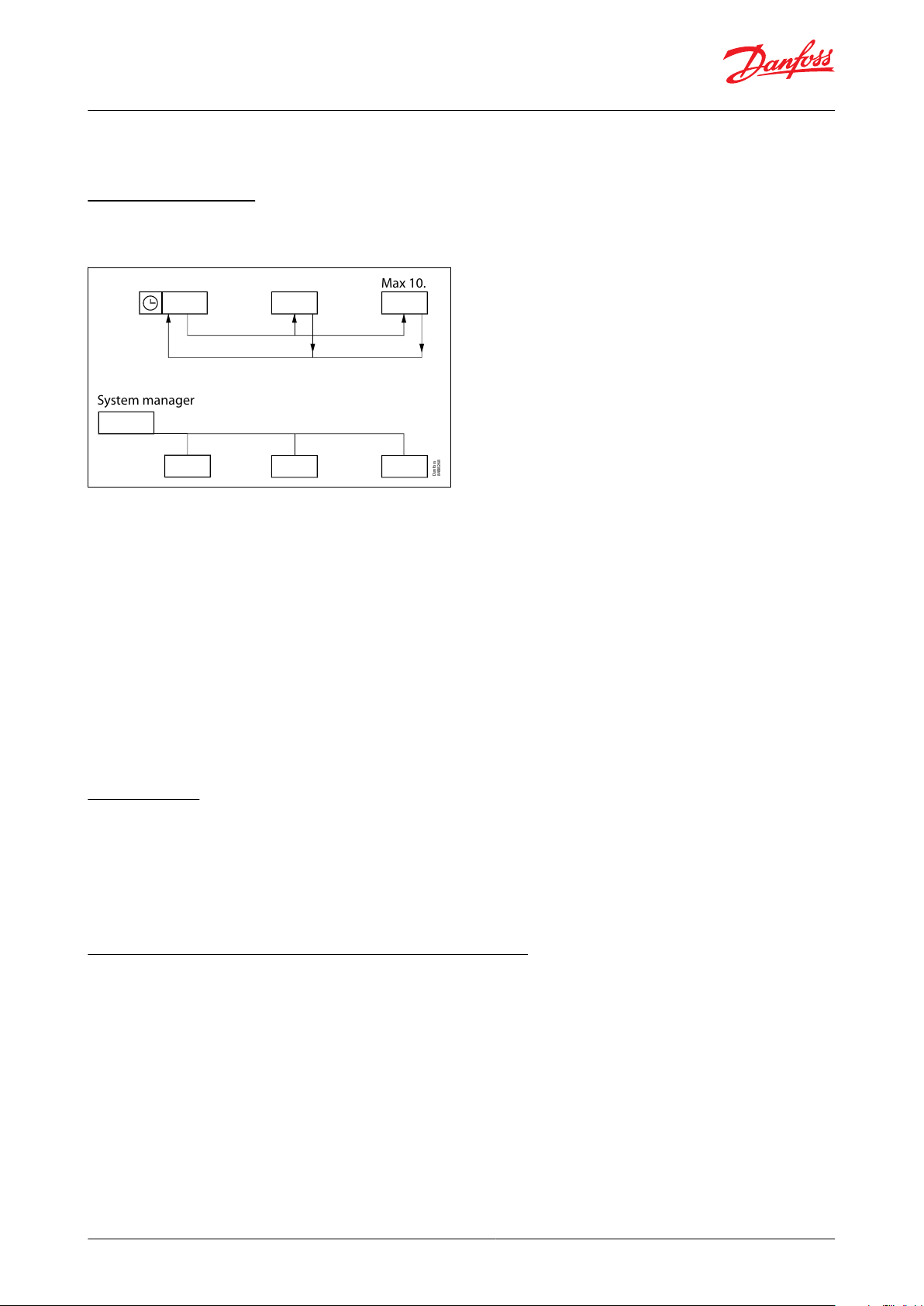
Coordinated defrost
There are two ways in which coordinated defrost can be arranged.
Figure 13: Coordinated defrost options
Either with wire connections between the controllers or via data communication:
Wire connections
The digital input DI2 must be congured for coordinated defrost and wiring must be connected between the
relevant controllers. When one controller starts a defrost, all the other controllers will follow suit and likewise start a
defrost. After the defrost, the individual controllers will move into waiting position. When all are in waiting position
there will be a change-over to refrigeration.
Coordination via data communication
Here the system manager handles the coordination. The controllers are gathered in defrosting groups and the
system manager ensures that defrosting is started in the group according to a weekly schedule.
When a controller has completed defrosting, it sends a message to the system manager and then goes into a
waiting position. When every controller in the group is in a waiting position, refrigeration is again permitted in all
the individual controllers.
Melt function
This function will prevent the air ow in the evaporator from being reduced by frost created by uninterrupted
operation for a long time.
The function is activated if the thermostat temperature has remained in the range between -5 °C and +10 °C for a
longer period than the set melting interval. The refrigeration will then be stopped during the set melting period.
The frost will be melted so that the air ow and hence the evaporator’s capacity will be greatly improved.
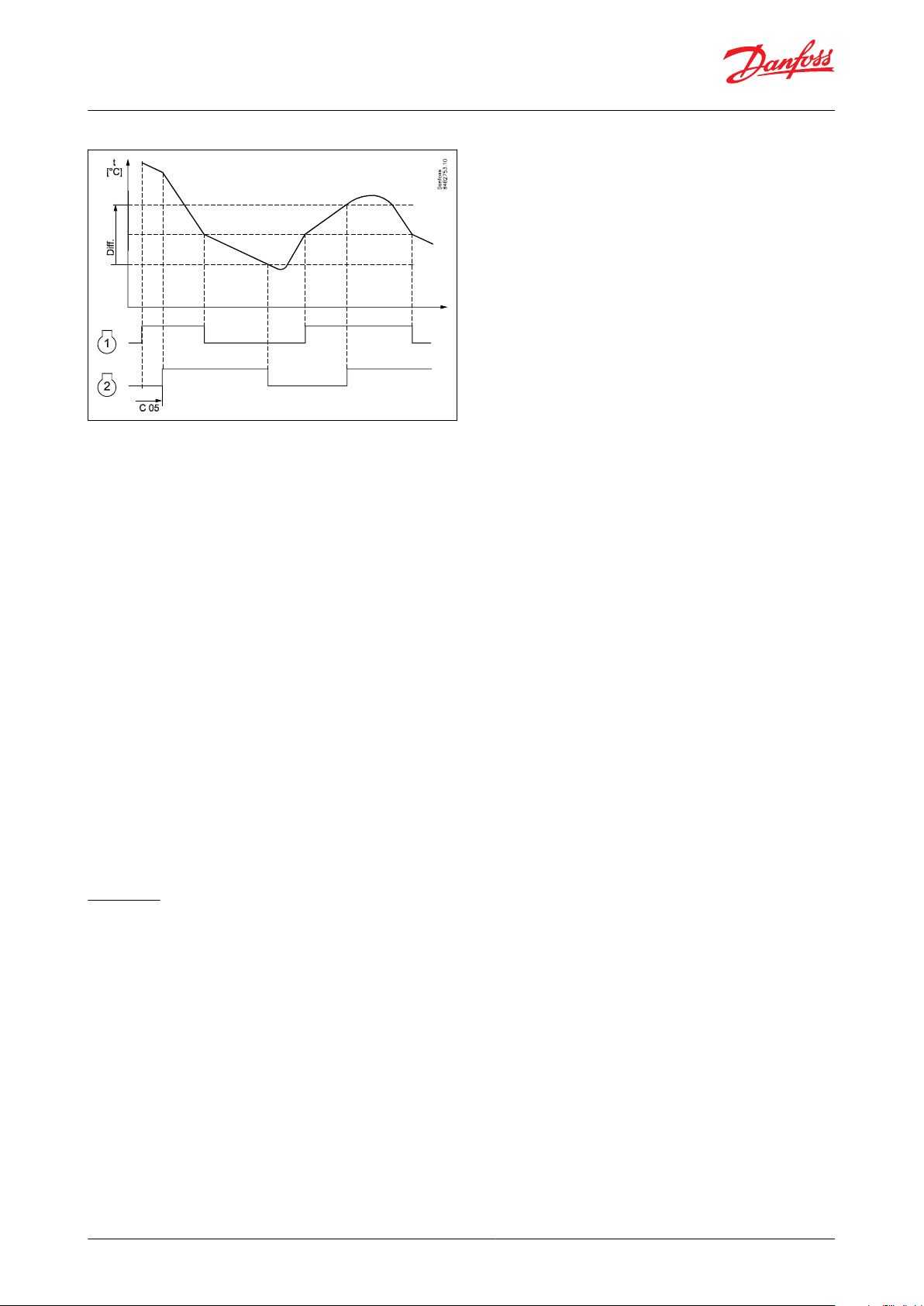
Control of two compressors (only with custom set-up)
Two compressor steps can be controlled cyclic or sequentially. At cyclic control, two compressors must be of the
same size, while in sequential control compressor step 1 can be larger than step 2.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 14
Page 15
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 14: Control of two compressors.
Cyclic control
When the controller demands refrigeration, it will rst cut in the compressor with the shortest operating time. After
the time delay, the second compressor will be cut in.
When the temperature has dropped to ”the middle of the dierential”, the compressor with the longest operation
time will be cut out.
The running compressor will continue until the temperature has reached the cut-out value. Then it will cut out.
When the temperature again reaches the middle of the dierential, a compressor will again be started.
If one compressor cannot maintain the temperature within the dierential, the second compressor will also be
started.
If one of the compressors has run on its own for two hours, the compressors will be changed over so that
operational time is balanced.
The two compressors must be of a type that can start up against a high pressure.
The compressor's settings for ”Min. On time” and ”Min. O time” will always have top priority during normal
regulation. But if one of the override functions is activated, like e.g. defrost, door open function, case shutdown,
forced closing, the ”Min. On time” will be disregarded.
Sequential control
Compressor steps are controlled in the same manner as described for cyclic control, but compressor step 1 will
always be started rst and cut out as the last one. No time equalization is available in sequential control mode.
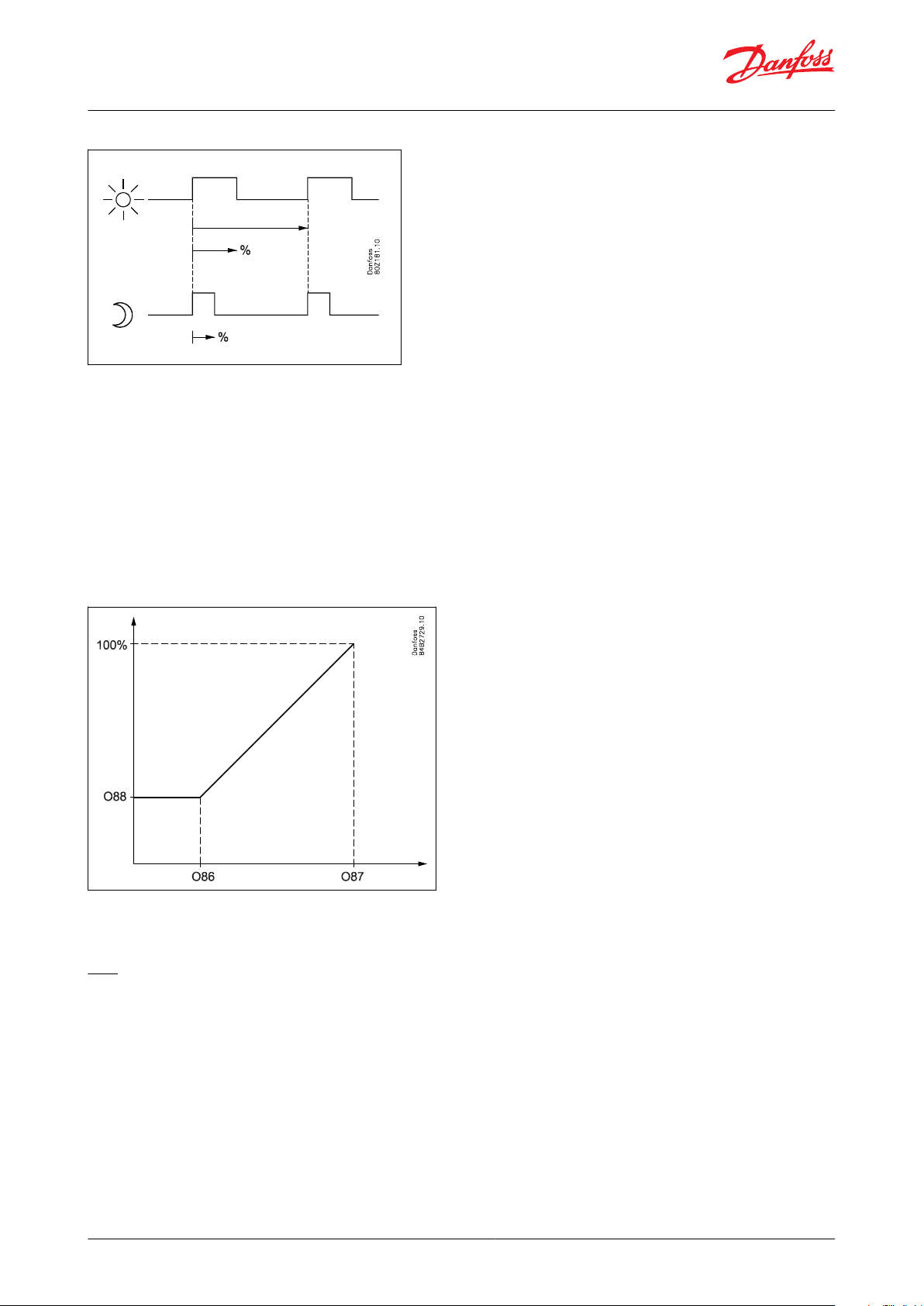
Rail heat
It is possible to pulse-control the power to the rail heat in order to save energy. Pulse control can either be
controlled according to day/night load or dewpoint.
Relay or analogue output
A relay output can be used when long cycle times are permitted. If fast pulsing is required, the AO1/PWM output
can be used. The output must be connected to an external power solid state relay. The cycle time must be
congured for the relay output in o43 or for analogue output in P82.
Pulse control according to day and night
Various ON periods can be set for day and night operation. A cycle time is set as well as the percentage part of the
period in which the rail heat is ON.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 15
Page 16
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 15: Rail heat control, day/night load.
Pulse control according to dewpoint
In order to use this function, a system manager of the type AK-SM is required which can measure ambient
temperature and humidity to calculate dewpoint and distribute to the appliance controllers. For this the rail heat’s
ON period is controlled according to the distributed dewpoint.
Two dewpoint values are set in the appliance control:
• One where the eect must be max. i.e. 100%. (o87)
• One where the eect must be min. (o86)
At a dewpoint which is equal to or lower than the value in 086, the eect will be the value indicated in o88. In the
area between the two dewpoint values, the controller will manage the power to be supplied to the rail heat.
Figure 16: Rail heat control, dewpoint
During defrosting
During defrosting rail heat will be active, as selected in setting d27.
Fan
Pulse control
To obtain energy savings, it is possible to pulse control the power supply to the evaporator fans.
Pulse control can be accomplished in one of the following ways:
• during the thermostat’s cut-out period (cold room)
• during night operation and during the thermostat’s cut-out period (appliance with night blinds) (The function is
not actual when r14=2, i.e. modulating regulation).
A period of time is set as well as the percentage of this period of time where the fans have to be operating.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 16
Page 17

AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 17: Fan cycle time
Cut-out of fans during plant breakdowns
If the refrigeration in a breakdown situation stops, the temperature in the cold room may rise quickly as a result of
the emission of heat from large fans. In order to prevent this situation, the controller can stop the fans if the
temperature at S5 exceeds a set limit value. The fans will start running again when the S5 temperature has dropped
2K below the set limit. (The function can also be used as a type of MOP function. Here the load on the compressors
is limited until the S5 temperature has fallen below the congured value).
ECO operations (only with custom set-up)
Reduced fan speed is permitted when the night blind is down. (Fan with changeover between high and low speed).
ECO operation is not permitted if the heat function is activated.
Light function
The function can be used for controlling the light in a refrigeration appliance or in a cold room. It can also be used
for controlling a motorised night blind.
The light function can be dened in several ways:
• The light is controlled via a signal from a door contact. The light is kept on for a set time after the door has been
closed.
• The light is controlled via the day/night function
• The light is controlled via a DI input
• The light is controlled via the data communication from a system manager. Here there are two operational options
if data communication should fail:
◦ The light can go ON
◦ The light can stay in its current mode
The light load must be connected to the NC terminals on the relay.
This ensures that the light remains ON in the appliance if power to the controller should fail.
A setting denes how light is controlled when regulation is stopped via r12 Main switch = OFF (see o98). The light is
switched o when the appliance cleaning function is activated.
Night blind
Motorised night blinds can be controlled automatically from the controller. The night blinds will follow the status of
the light function. When the light is switched on, the night blinds open, and when the light is switched o, the night
blinds close again. When the night blinds are closed, it is possible to open them using a switch signal on the digital
input. If this pulse signal is activated, the night blinds will open and the refrigeration appliance can be lled with
new products. If the pulse signal is activated again, the blinds close.
When the night blind function is used, the thermostat function can control with dierent weighting between the S3
and S4 sensors. A weighting during day operation and another when the blind is closed.
A night blind is opened when the appliance cleaning function is activated.
A setting can dene that the night blind is opened when "r12" (Main switch) is set to o (see o98).
When the night blind rolls down, the fan will be stopped for the set time. The night blind can thereby roll down to
the correct position.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 17
Page 18
Danfoss
84B8269
A
r01
r01
t
º C
r62
B
C
ABC
Refrigeration
Neutral zone
Heat
Function
Input / Settings menu
Setting
DI1
DI2
o02
o37
None++
0
DI Status++
1
Door function++
2
Door alarm++
3
Defrost start++
4
Main switch++
5
Night setback++
6
Thermostat band++
7
Alarm at closed++
8
Alarm at open++
9
Case cleaning++
10
Forced cooling++
11
Open blinds++
12
Coordinated defrost
+
13
Forced closing++
14
Shutdown++
15
Light control++
16
Leak detection++
20
Adaptive liquid control
++21
AK-CC55 Compact
Heating function (only with custom set-up)
The heating function is used to prevent the temperature from becoming too low, e.g. in a cold room, etc. The limit
for when the heating function cuts o is set as an oset value below the current cut-out limit for the refrigeration
thermostat. This ensures that refrigeration and heating do not occur simultaneously. The dierence for the heating
thermostat has the same value as for the refrigeration thermostat. To prevent that the heating thermostat cuts in
during short-term drops in air temperature, a time delay can be set for when to change from refrigeration to
heating.
Figure 18: Heating function
Digital inputs
There are two digital inputs, DI1 and DI2, with dry contact function, and one digital input DI3 with high voltage
signal.
They can be used for the following functions:
Table 6: Function table and DI settings
Example: If DI1 is to be used to start a defrost, o02 must be set to 4.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 18
Page 19

Danfoss
84B8235
Master control function
Description
MC Ther. toggle
Master control signal used for switching case load ON/OFF depending on the load condition
MC Load request
Master control signal used to control the load balance between multiple case controllers on the same suction line
MC Max. Te
oset
Requested
oset to actual evaporating temperature in order to keep the air temperature at the actual setpoint
MC Liquid control
Master control signal allowing switch to adaptive liquid control
AK-CC55 Compact
Forced closing
The AKV valves can be closed with an external signal ("Forced closing").
The function must be used in connection with the compressor’s safety circuit, so that there will be no injection of
liquid into the evaporator when the compressor is stopped by the safety controls and cannot start again (however
not at low pressure – LP).
Via a setting (see o90 Fan at forced closing) it is possible to dene whether the fan should be ON or OFF during
forced closing and whether an ongoing defrost is suppressed (i.e. put in standby position for a period of upto 10
minutes before it is cancelled) - this feature can be used in CO2 systems to eliminate excessive heating while
compressors cannot run.
The signal can be received from the DI-input or via the data communication.
Door contact
The door contact function can via the digital inputs be dened for two dierent applications:
Alarm monitoring:
The controller monitors the door contact and delivers an alarm message if the door has been opened for a longer
period than the set alarm delay.
Alarm monitoring and stop of refrigeration:
When the door is opened, the refrigeration is stopped, i.e. the injection, the compressor and the fan are stopped and
light switches on. If the door remains open for a longer time than the set restart time, refrigeration will be resumed.
This will ensure that refrigeration is maintained even if the door is left open or if the door contact should be
defective. If the door remains open for a longer period than the set alarm delay, an alarm will also be triggered.
Display
The controller has one plug for an external display.
One of the following display types can be connected:
• AK-UI55 Info (temperature display).
• AK-UI55 Set (temperature display and operation).
• AK-UI55 Bluetooth (temperature display and app interface).
The connection between the display and the controller must be made using an AK-UI55 cable.
The distance between the controller and the display must not exceed 100 m.
Figure 19: Controller with one display
Override
The controller contains a number of override functions which can be used together with Master Control functions in
the Danfoss gateway/system manager:
Table 7: Override functionality
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 19
Page 20

Master control function
Description
MC Night setback
Master control signal for changing between day and night time operation
MC Case shutdown
Master control signal used to shut down a case for a time period. During shutdown there will be no alarm monitoring
MC Forced closing
Master control signal that will close the injection valve
MC Forced cooling
Master control signal that will provide forced cooling
MC Defrost start
Master control signal for starting a defrost. At adaptive defrost the defrost might be skipped if the defrost is not needed
MC Defrost state
Read out the actual state of the defrost
MC Hold after defrost
Master control signal used for co-ordinated defrost control to hold cabinets from returning to normal refrigeration after a defrost
until all cabinets have terminated defrost
MC Stop defrost
Master control signal used to prevent a defrost start in a controller.
MC Light signal
Master control signal for control of light via a data communication signal from the system manager
MC Actual dewpoint
Master control signal sending the actual measured dewpoint from the system manager to the controller over the network.
MC Po load factor
Calculated load factor for the refrigerated appliance. Used for suction pressure optimization.
MC Bluetooth lock
Master control signal that will lock down all Bluetooth data communication
MC Min. delta T
Required minimum delta temperature across evaporator (S3 - Te) in order to keep the air temperature at the actual setpoint
AK-CC55 Compact
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 20
Page 21

Danfoss
84B8281
S₄
S₃
S₅
S₂
S₃
S₅
S₄
40
41
42
5V
s
A1
43
44
AI2
45
46
AI3
47
48
AI4
49
50
AI5
60
61
DI2
DI1
70
71
AO1
PWM
83
84
85
B
A
MODBUS
115 - 230V AC
L
N
1
2
3
8
9
7
10
11
12
DO2
13
14
DO3
16
15
17
DO4
Danfoss
84B3236
DO1
AK-CC55 Compact
Applications
The chapter outlines application examples:
• Standard display case
• Cold rooms
An application setting will congure inputs and outputs so that the controller’s operation interface is reecting the
selected application.
In application 4 and 9, users can custom dene the functions of relay 2, 3 and 4, e.g.:
• Controlling two compressors
• Controlling the night blind
• Controlling the heat function
• ECO operations of fans
Figure 20: Standard display case, upright or normal, with one evaporator
Figure 21: Cold room conguration with door, light and heat control function
AK-CC55 Compact connections and application options
Figure 22: Electrical connections AK-CC55 Compact
AK-CC55 Compact is optimised for control of one evaporator plus dierent combinations of light, rail heat and alarm
relays.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 21
Page 22

No.
Application description
DO1
DO2
DO3
DO4
AO1
AI1
AI2
AI3
AI4
AI5/ DI1
DI2
1
TXV appl.S3S4S52
TXV appl.S3S4S53
TXV appl.S3S4S54
TXV appl./ User def. cong.
User def.
User def.
User def.S3S4S55
EEV appl.PeS2S3S4S56
EEV appl.PeS2S3S4S57
EEV appl.PeS2S3S4S58
EEV appl.PeS2S3S4S59
EEV appl./ User def. cong.
User def.
User def.
User def.PeS2S3S4
S5
Pe
Evaporating pressure
S2
Gas outlet of evaporator
S3
Return air temperature
S4
Discharge air temperature
S5
Evaporator temperature
AK-CC55 Compact
It has 4 Digital Outputs (DO), known as DO1 – DO4, one Analogue Output (AO), known as AO1, 4 Analogue Inputs
(AI), known as AI1 – AI4, an input that can be used as either an AI5 or as a DI (Digital Input) DI1, and one Digital Input
(DI2).
It has 9 dierent application options (Application 1 – Application 9) to control the functions of the input and output
relays.
Table 8: Application with digital and analogue in/output specication
= Optional use
Table 9: Sensor description
Application set-ups and IO connections
AK-CC55 Compact is designed for control of one evaporator + dierent combinations of light, rail heat and alarm
relays.
The most important variations are:
Applications 1-4: TEV applications
Control of compressor or solenoid valve, alarm relay, lights, rail heat
Application 4: Congurable outputs, e.g.: Dual compressor operation, heat function, night blind, ECO fan
Applications 5-9: EEV applications
Control of AKV valve, compressor, alarm relay, light, rail heat.
9: Congurable outputs, e.g.: Dual compressor operation, heat function, night blind, ECO fan
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 22
Page 23

115 – 230 V AC
Comp. Alarm Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S3 S4 S5
AI5
DI1
1
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
Danfoss
84B3257
115 – 230 V AC
Comp. Light Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S3 S4 S5
AI5
DI1
2
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
Danfoss
84B3258
115 – 230 V AC
Comp. Railheat Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S3 S4 S5
AI5
DI1
3
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
Danfoss
84B3259
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 23: Connections for application 1
Figure 24: Connections for application 2
Figure 25: Connections for application 3
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 23
Page 24

115 – 230 V AC
Comp. DO2 DO3
Custom set-up
DO4
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S3 S4 S5
AI5
DI1
4
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
Danfoss
84B3260
115 – 230 V AC
AKV Comp. Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S2Pe
5V s
S3 S4
AI5
S5
5
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
P
1 3 2
Danfoss
84B3261
115 – 230 V AC
AKV Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S2Pe
5V s
S3 S4
AI5
S5
6
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
P
1 3 2
Alarm
Danfoss
84B3262
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 26: Connections for application 4
Figure 27: Connections for application 5
Figure 28: Connections for application 6
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 24
Page 25

115 – 230 V AC
AKV Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S2Pe
5V s
S3 S4
AI5
S5
7
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
P
1 3 2
Light
Danfoss
84B3263
115 – 230 V AC
AKV Fan Defrost
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S2Pe
5V s
S3 S4
AI5
S5
8
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
P
1 3 2
Railheat
Danfoss
84B3264
115 – 230 V AC
AKV
1 2 3 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
L N
40
0 – 10 V/
PWM
S2Pe
5V s
S3 S4
AI5
S5
9
41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 83 84
B-A
+
MODBUS
85
DI2 AO1
60 61 70 71
P
1 3 2
DO2 DO3
Custom set-up
DO4
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17
Danfoss
84B3265
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 29: Connections for application 7
Figure 30: Connections for application 8
Figure 31: Connections for application 9
Product identication
The controller is provided with labels from the factory, indicating a generic application. When selecting the required
application, specic labels are provided so that you can mount the relevant one.
The application number is indicated on the left-hand side of the labels. Use the label tting the selected application.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 25
Page 26

Danfoss
84B8266
230 V AC (115 AC)
AK-CC55 Compact
Some of the labels are applicable to multiple application options.
Figure 32: Labels used to indicate application number
AK-CC55 Compact connections
Data communication
Figure 33: Data communication
IMPORTANT:
It is important that the installation of the data communication cable is performed correctly with sucient distance
to high voltage cables.
AKV info
Figure 34: AKV info
230 V or 115 V
AC coil
Max. 0.5 A
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 26
Page 27

A
AKS 32R
B
out
C
ABC
Black
Brown
Blue
AO1/
PWM
60 61 70 71
SSR
Danfoss
80G8234
AK-CC55 Compact
External solid state relay for rail heat
Figure 35: External solid state relay for rail heat
0 / 10 V Pulse Width Modulated (PWM)
Max. 15 mA.
AKS 32R info
Figure 36: AKS 32R info
NOTE:
A ratiometric pressure transmitter with a 5 V, 10 – 90% voltage output signal must be used.
The signal from one pressure transmitter can be received by up to 10 controllers. There must not be a signicant
pressure drop from the pressure transmitter's position in the suction line to the individual evaporators.
Coordinated defrost via cable connections
Figure 37: Coordinated defrost via cable connections
Max. 10
The following controllers can be connected in this way:
EKC 204A, AK-CC 210, AK-CC 250, AK-CC 450, AK-CC 550 and AK-CC55.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 27
Page 28

Danfoss
84B8235
AK-CC55 Compact
Refrigeration is resumed at the same time when all controllers have terminated defrost.
External display AK-UI55
Figure 38: External display AK-UI55
(Total length: max. 100 m)
Connections
AI1
Pressure transmitter
AKS 32R
Connect to terminal 40, 41 and 42.
(Use cable 060G1034: Black=40, Brown=41, Blue=42)
The signal from one pressure transmitter can be received by up to 10 controllers. But only if there are no signicant
pressure drops between the evaporators to be controlled. See Figure 36: AKS 32R info.
AI2 - AI5
Primarily for temperature inputs
• S2
Pt 1000 ohm sensor AKS11, placed at the evaporator outlet
• S3, S4, S5
Pt 1000 AKS11, PTC 1000 EKS111, NTC5K EKS211 or NTC10K EKS221 sensor. All have to be of the same type.
• S3, air sensor, placed in the warm air before the evaporator
• S4, discharge air sensor, placed in the cold air after the evaporator
(the need for either S3 or S4 can be selected in the conguration)
• S5, defrost sensor, placed in the evaporator
(If the DI1 input is used for a temperature measurement, it will appear as AI5.))
DI1
Digital input signal
The dened function is active when the input is short-circuited or opened, depending on the function dened in
o02.
DI2
Digital input signal.
The dened function is active when the input is short-circuited or opened, depending on the function dened in
o37.
AO1
Analogue output signal
• Analogue 0 – 10 V (currently not used)
• Pulse width modulated signal
Can be used for fast pulse control of rail heat via an external power solid state relay.
MODBUS
For data communication.
• Terminal 83 = B-
• Terminal 84 = A+
• Terminal 85 = screen
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 28
Page 29

AK-CC55 Compact
Supply voltage
• 230 V AC or 115 V AC
DO1
• AKV valve
Connection of expansion valve type AKV, AKVA, AKVH or AKVP.
The coil must be a 230 V or 115 V AC coil
• Compressor
Connection of a relay. The coil must be a 230 V or 115 V AC coil. Max. 0.5 A.
• Solenoid valve
The coil must be a 230 V or 115 V AC coil. Max. 0.5 A.
DO2
• Alarm
There is a connection between terminal 10 and 12 in alarm situations and when the controller is without power.
DO2 has reinforced insulation that can be used with 24 V.
• Light, Rail heat, Compressor/Liquid line valve
There is connection between terminal 10 and 11 (10 and 12 at light) when the function is ON.
DO3
• Fan
There is connection between terminal 13 and 14 when the fan is ON.
DO4
• Defrost
There is connection between terminal 15 and 16 when defrosting takes place.
DO2-DO4 + AO1 and Application 4 / 9
Here, the dierent outputs can be custom dened in q02-q09
Display (RJ12 plug)
If readings/operation of the controller is required, an external display can be connected. The max. cable length is
100 m.
Electric noise
Cables for sensors, low voltage DI inputs and data communication must be kept separate from other electric cables:
• Use separate cable trays
• Keep a distance between cables of at least 10 cm
• Long cables at the low voltage DI input should be avoided
Installation considerations
Accidental damage, poor installation, or site conditions, can give rise to malfunctions of the control system, and
ultimately lead to a plant breakdown.
Every possible safeguard is incorporated into our products to prevent this. However, a wrong installation could still
present problems. Electronic controls are no substitute for normal, good engineering practice.
Danfoss will not be responsible for any goods, or plant components, damaged as a result of the above defects. It is
the installer's responsibility to check the installation thoroughly, and to t the necessary safety devices.
Special reference is made to the necessity of signals to the controller when the compressor is stopped and to the
need of liquid receivers before the compressors.
Your local Danfoss agent will be pleased to assist with further advice, etc.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 29
Page 30

AK-CC55 Compact
Operation
The controller can be operated in dierent ways depending on the user interface.
The following options are available:
• Via data commmunication
• Via AK-UI55 Setting display
• Via AK-UI55 Bluetooth display
Operation via data communication
Via system manager's display
All AK-CC55 controllers can be operated from a central location, e.g. AK-SM 800.
Data communication is to take place via MODBUS.
Via system manager and service tool
Operation can also be performed from a central location with PC software "Service Tool" connected to a system
manager AK-SM 720 via MODBUS.
Programming via KoolProg
Programming by use of PC software type KoolProg® via interface MMIMYK connected to RJ12 display connector.
Direct operation
Operation via AK-UI55 setting display
The display can be located at a distance of up to 100 meters from the controller.
Smart phone and app via AK-UI55 Bluetooth display
The "AK-CC55 connect" app is used for smart phone operation.
AK-CC55 connect can be downloaded freely to a compatible iOS/Android smartphone device.
Menu operation is established by activating Bluetooth communication to the app.
Operation via AK-UI55 Set
Display AK-UI55 Set
The values will be shown with three digits, and with a setting you can determine whether the temperature is to be
shown in °C or in °F.
The keyboard can be locked and unlocked by pressing arrow up and down at the same time if the parameter P89
has enabled this feature.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 30
Page 31

Lights in event of alarm — press on alarm button — alarm relay is reset — alarm code displayed — e.g. “A1”
Lights up in event of:
Energy optimization
Cooling
Defrosting
Fan operation
Up arrow / Down arrow / Arrow to left:
Navigation in the menu and setting of values.
Long press (3 seconds) will start a defrost,
“-d-” is shown in the display.
Ongoing defrosting can be stopped by a long press.
Long press (3 seconds) gives access to the
information menu “InF”
SET:
Long press (3 seconds) gives access to the “SEt” menu.
If the operation is locked with a password, “PS” is shown. Enter the code.
Shows the setting for a chosen parameter / saves a changed setting.
Short press gives access to entering of the thermostat’s cut-out limit.
Danfoss
84B8265
Display readout
Denomination
-d-
Defrost is in progress
Err
The temperature cannot be displayed due to a sensor error
Er1
The display cannot load data from the controller. Disconnect and then reconnect the display
Er2
Lost display communication
ALA
The alarm button is activated. The rst alarm code is then shown
- - -
At top position of the menu or when max. value has been reached, the three dashes are shown in the top of the display
- - -
At bottom position of menu or when min. value has been reached, the three dashes are shown in the bottom of the display
Loc
The menu operation is locked. Unlock by pressing (for 3 seconds) on the ‘up arrow’ and ‘down arrow’ simultaneously
UnL
The menu operation is unlocked
- - -
The parameter has reached min. or max. limit
PS
A password is required for access to the menu
Fan
Appliance cleaning has been initiated. The fans are running
OFF
Appliance cleaning is activated and the appliance can now be cleaned
OFF
The main switch is set to O
SEr
The main switch is set to service / manual operation
CO2
Flashes: Will display in event of a refrigerant leakage alarm, but only if the refrigerant is set up for CO
2
AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 39: Operating via AK-UI55 Set
Table 10: Messages provided by the display
Factory setting
If you need to return to the factory-set values, do the following:
• Cut o the supply voltage to the controller
• Keep up "∧" and down "∨" arrow buttons depressed at the same time as you reconnect the supply voltage
• When FAc is shown in the display, select "yes"
NOTE:
The OEM factory setting will either be the Danfoss factory settings or a user dened factory setting if one has been
made.
The user can save his setting as OEM factory setting via parameter o67.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 31
Page 32

SET
Set
(PS)
<
cFg SET r12 Main switch
<
o61 Application
r--
Menu groups
See also the following pages.
o03 MODBUS address
A-- r89 Food type
c-- r00 Cut-out temperature
d-- o30 Refrigerant type
n-- o20 Min. transmitter range
F-- o21 Max. transmitter range
t-- d01 Defrost method
o-- d03 Defrost interval
p-- d10 Defrost sensor
q-- d04 Max. defrost time
u-- d02 Defrost stop temperature
< <
(Return) (Return)
SET button, 3 s: Configuration settings
PS: Password (if any)
Danfoss
84B3291
<
Inf
StA SET See control state message
App SET See selected application
in SET
AI1
(PE)
Read input status
out SET do1
*
Read output status
AI2
**
buS SET MODBUS quality do2
*
AI3
**
SoF SET See SW version do3
*
AI4
**
< do4
Ao1
*
AI5
**
(Return)
<
di1
**
(Return)
di2
**
**
<
(Return)
Info button, 3 s: Information for service
use
Output status
When you want info on a relay
output, the dot will show whether
the relay is activated (energized)
for e.g.:
do4 = not activated
do.4 = activated
Danfoss
84B3292
*
**
StA
The output's function (determined at
conguration). DOs and AOs can also be forced
controlled from this menu, when r12 Main switch
has been set to position "service". Forced control of
a function can also be performed in codes q11 to
q27.
The input's function (determined at conguration)
See control state message in Table 43
AK-CC55 Compact
Parameter groups when operating via display
Figure 40: SET button parameter list
Figure 41: Info button parameter list
Get a good start
With the following procedure you can start regulation very quickly:
1.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 32
Open parameter r12 and stop the regulation (in a new and not previously set unit, r12 will already be set to 0
which means stopped regulation.)
Select application based on the wiring diagrams on page Page 22
Open parameter o61 and set the application number
For network. Set the address in o03
Then select a set of presets from the "Food type" help table
Open parameter r89 and set the number for the array of presettings. The few selected settings will now be
transferred to the menu
Page 33

Setting of presettings (r89).
After setting 1-5, setting is returned to 0.
12345
Food type
Vegetables
Milk
Meat/sh
Frozen food
Ice cream
Temperature (r00)
8 °C
0 °C
-2 °C
-20 °C
-24 °C
Max. temp. setting (r02)
10 °C
4 °C
2 °C
-16 °C
-20 °C
Min. temp. setting (r03)
4 °C
-4 °C
-6 °C
-24 °C
-28 °C
Upper alarm limit (A13)
14 °C
8 °C
8 °C
-15 °C
-15 °C
Lower alarm limit (A14)
0 °C
-5 °C
-5 °C
-30 °C
-30 °C
Upper alarm limit for S6 (A22)
14 °C
8 °C
8 °C
-15 °C
-15 °C
Lower alarm limit for S6 (A23)
0 °C
-5 °C
-5 °C
-30 °C
-30 °C
AK-CC55 Compact
7.
Set the desired cut-out temperature r00
8.
Select refrigerant via parameter o30 (only application 5-9)
9.
Set the pressure transmitter min. and max. range via parameter o20 and o21 (only application 5-9)
10.
Set the desired defrost method in d01
11.
Set the interval time between defrost starts in d03
12.
Set the desired defrost sensor in d10
13.
Set the maximum defrost time in d04
14.
Set the defrost stop temperature in d02
15.
Open parameter r12 and start the regulation
16.
Go through the parameter list and change the factory values where needed
17.
Get the controller up and running on network:
◦ MODBUS: Activate scan function in system unit
Table 11: Food type settings
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 33
Page 34

R-W
RW*
If the operation is protected by one or more passwords, reading and setting the parameter will be limited to:
R or W
This setting can be seen with password no. _ or higher (3 is the highest level).
This setting can be performed with password no. _ or higher (3 is the highest level).
The asterisk indicates in which application from 1-9 the parameter is applicable
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Cutout 1
0-0
r00*********r03
r02
2.0 °C
Dierential
1-2
r01*********0.1 °C
20.0 °C
2.0 °C
Max cutout limit
0-2
r02*********r03
50.0 °C
50.0 °C
Min cutout limit
0-2
r03*********-50.0 °C
r02
-50.0 °C
Temperature unit
0=Celsius, 1=Fahrenheit
1-2
r05*********010
S4 Air OFF evap. A - Adjustment
1-2
r09*********-10.0 °C
10.0 °C
0.0 °C
S3 Air ON evap. A - Adjustment
1-2
r10*********-10.0 °C
10.0 °C
0.0 °C
Main switch
-1=Manual, 0=Stop,
1=Start
0-2
r12*********-110
Night oset
1-2
r13*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
0.0 °C
Thermostat mode
2=Modulating, 1=ON/OFF
1-2
r14*********121
Thermostat sensor S4 %
1-2
r15*********0 %
100 %
100%
Melt interval
1-2
r16*********0 h
10 h
1 h
Melt period
1-2
r17*********0 min
30 min
5 min
Cutout 2
0-2
r21*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
2.0 °C
Thermostat sensor S4 %
night
1-2
r61*********0 %
100 %
100%
Air heater neutral zone
1-2
r62**
0.0 °C
50.0 °C
5.0 °C
Air heater start delay
1-2
r63**
0 min
240 min
240 min
Food type
0=None, 1=Vegetables,
2=Dairy, 3=Meat and sh,
4=Frozen food, 5=Ice
cream
1-2
(1)
r89*********050
S4 frost protection
1-2
r98*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
-50.0 °C
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Alarm delay A
1-2
A03*********0 min
240 min
30 min
Door open alarm delay
1-2
A04*********0 min
240 min
60 min
Alarm delay pulldown A
1-2
A12*********0 min
240 min
90 min
High alarm limit 1
1-2
A13*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
8.0 °C
Low alarm limit 1
1-2
A14*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
-30.0 °C
High alarm limit 2
1-2
A20*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
8.0 °C
Low alarm limit 2
1-2
A21*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
-30.0 °C
Alarm delay DI 1
1-2
A27****
0 min
240 min
30 min
Alarm delay DI 2
1-2
A28*********0 min
240 min
30 min
Alarm sensor S4% A
1-2
A36*********0 %
100 %
100%
AK-CC55 Compact
AK-UI55 display menu (SW ver. 2.0x)
Thermostat
Table 12: Thermostat
(1)
(1)
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
Alarm settings
Table 13: Alarm settings
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 34
Page 35

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Min ON time
1-2
c01******
0 min
30 min
0 min
Min OFF time
1-2
c02******
0 min
30 min
0 min
Delay between comp.
1-2
c05**
0 s
999 s
5s
Step control mode
1=Sequential, 2=Cyclic
1-2
c08**12
2
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Defrost method
0=None, 1=Electrical,
2=Hot gas, 3=Brine, 4=Air/
Ocycle
1-3
d01*********041
Defrost stop limit A
1-2
d02*********0.0 °C
50.0 °C
6.0 °C
Defrost start interval
1-2
d03*********0 h
240 h
8h
Max defrost time
1-2
d04*********0 min
360 min
45 min
Time staggering power up
1-2
d05*********0 min
240 min
0 min
Drip o time
1-2
d06*********0 min
60 min
0 min
Fan start delay
1-2
d07*********0 min
60 min
0 min
Fan start temperature
1-2
d08*********-50.0 °C
10.0 °C
-5.0 °C
Fan control during defrost
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=OFF at
drip, 3=OFF at high temp
1-2
d09*********031
Defrost stop method
0=Time, 1=S5 sensor,
2=S4 sensor
1-2
d10*********020
Pump down delay
1-2
d16*********0 min
60 min
0 min
Max thermostat runtime
1-2
d18*********0 h
240 h
0h
Rail heat during defrost
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=Normal
control
1-2
d27*********021
Display delay after defrost
1-2
d40*********5 min
240 min
30 min
Fan stop temperature
1-2
d41*********-20.0 °C
20.0 °C
0.0 °C
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Max superheat limit
1-2
n09*****n10
20.0 °C
12.0 °C
Min superheat limit
1-2
n10*****2.0 °C
n09
3.0 °C
MOP temperature
1-2
n11*****-50.0 °C
15.0 °C
15.0 °C
AKV Period time
1-2
(1)
n13*****3 s
6 s
6 s
Brine valve - Period time
1-2
n63****
30 s
900 s
300 s
Brine valve max OD
1-2
n64****
n65
100 %
100%
Brine valve min OD
1-2
n65****
0 %
n64
0%
Brine valve windup
1-2
n66****
0.2
1.0
1.0
Brine valve Kp
1-2
n67****
0.5
10.0
4.0
Brine valve Tn
1-2
n68****
60 s
1800 s
300 s
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Fan stop high S5 temp.
1-2
F04*********-50.0 °C
50.0 °C
50.0 °C
Fan pulsing mode
0=No pulsing, 1=Pulsing
cutout, 2=Pulsing cutout
night
1-2
F05*********020
Fan period time
1-2
F06*********1 min
30 min
5 min
Fan ON cycle
1-2
F07*********0 %
100 %
100%
AK-CC55 Compact
Compressor
Table 14: Compressor
Defrost
Table 15: Defrost
Injection control
Table 16: Injection control
(1)
(1)
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
Fan control
Table 17: Fan control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 35
Page 36

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min.value
Max.value
Fact.value
Defrost schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t00*********010
Def. start 1 - Hours
1-2
t01*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 1 - Minutes
1-2
t11*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Def. start 2 - Hours
1-2
t02*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 2 - Minutes
1-2
t12*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Def. start 3 - Hours
1-2
t03*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 3 - Minutes
1-2
t13*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Def. start 4 - Hours
1-2
t04*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 4 - Minutes
1-2
t14*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Def. start 5 - Hours
1-2
t05*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 5 - Minutes
1-2
t15*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Def. start 6 - Hours
1-2
t06*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Def. start 6 - Minutes
1-2
t16*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Time hours
0-1
t07*********0 h
23 h
0 h
Time minutes
0-1
t08*********0 min
59 min
0 min
Time date
0-1
t45*********1311
Time month
0-1
t46*********1121
Time year
0-1
t47*********0
100
0
Monday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t51*********011
Tuesday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t52*********011
Wednesday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t53*********011
Thursday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t54*********011
Friday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t55*********011
Saturday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t56*********011
Sunday - Follow schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
1-2
t57*********011
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Delay of outputs at power
up
1-2
o01*********0 s
600 s
5s
DI1
Conguration
0=None, 1=DI status,
2=Door function, 3=Door
alarm, 4=Defrost start,
5=Main switch, 6=Night
setback, 7=Thermostat
band, 8=Alarm at closed,
9=Alarm at open, 10=Case
cleaning, 11=Forced cooling, 12=Open blinds,
13=Coordinated defrost,
14=Forced closing,
15=Shutdown, 16=Light
control, 20=Leak detection, 21=Adaptive liquid
control
1-2
(1)
o02****021
0
Network address
1-3
(1)
o03*********0
240
0
Access code 3
3-3
o05*********0
999
0
Temperature sensor type
0=Pt 1000, 1=PTC 1000,
2=NTC 5k, 3=NTC 10k
1-3
(1)
o06*********030
Max hold time
1-2
o16*********0 min
360 min
20 min
Display air S4%
1-2
o17*********0 %
100 %
100%
Pe Min range
1-3
(1)
o20*****-1.0 Bar
5.0 Bar
-1.0Bar
Pe Max range
1-3
(1)
o21*****6.0 Bar
200.0 Bar
12.0Bar
AK-CC55 Compact
Defrost schedule
Table 18: Defrost schedule
Miscellaneous
Table 19: Miscellaneous
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 36
Page 37

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Refrigerant
0=Not seleted, 6=R13,
7=R13b1, 2=R22, 8=R23,
14=R32, 11=R114,
3=R134a, 12=R142b,
24=R170, 15=R227,
25=R290, 16=R401A,
18=R402A, 19=R404A,
21=R407A, 22=R407B,
20=R407C, 37=R407F,
49=R407H, 23=R410A,
32=R413A, 30=R417A,
31=R422A, 33=R422D,
34=R427A, 35=R438A,
40=R448A, 41=R449A,
48=R449B, 43=R450A,
44=R452B, 45=R454B,
9=R500, 4=R502,
10=R503, 17=R507,
36=R513A, 26=R600,
27=R600a, 5=R717,
28=R744, 46=R1233zdE,
38=R1234ze, 39=R1234yf,
47=R1234zeZ, 29=R1270,
42=R452A, 1=User de-
ned display, 13=User de-
ned
1-3
(1)
o30*****0490
DI2 Conguration
0=None, 1=DI status,
2=Door function, 3=Door
alarm, 4=Defrost start,
5=Main switch, 6=Night
setback, 7=Thermostat
band, 8=Alarm at closed,
9=Alarm at open, 10=Case
cleaning, 11=Forced cooling, 12=Open blinds,
13=Coordinated defrost,
14=Forced closing,
15=Shutdown, 16=Light
control, 20=Leak detection, 21=Adaptive liquid
control
1-2
(1)
o37*********0210
Light control mode
1=Day and night, 2=Network, 3=Door switch,
4=Network (Fallback),
5=Digital input
1-2
o38****15
1
MC Light signal
0=OFF, 1=ON
1-2
o39****010Rail heat ON cycle day
1-2
o41*********0 %
100 %
100%
Rail heat ON cycle night
1-2
o42*********0 %
100 %
100%
Rail heat period time
1-2
o43****
6 min
60 min
6min
Case cleaning mode
0=OFF, 1=Fans run,
2=Cleaning
0-1
o46*********020
Application mode
1=1. Comp/Alarm/Fan/
Defrost, 2=2. Comp/
Light/Fan/Defrost, 3=3.
Comp/Railheat/Fan/
Defrost, 4=4. Comp/
Custom, 5=5. EEV/
Comp/Fan/Defrost, 6=6.
EEV/Alarm/Fan/Defrost,
7=7. EEV/Light/Fan/
Defrost, 8=8. EEV/
Rail/Fan/Defrost, 9=9.
EEV/Custom
1-3
(1)
o61*********195
Access code 2
2-2
o64*********0
999
0
Make new factory
0=OFF, 1=ON
3-3
(1)
o67*********010
Rail heat control mode
0=ON, 1=Day/Night timer,
2=Dew point ctrl.
1-2
o85*********020
Dewpoint min limit
1-2
o86*********-10.0 °C
o87
8.0 °C
Dewpoint max limit
1-2
o87*********o86
50.0 °C
17.0 °C
Rail heat min ON cycle
1-2
o88*********0 %
100 %
30%
Door restart inj. delay
1-2
o89*********0 min
240 min
30 min
Fan at forced closing
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=OFF and
suppress defrost, 3=ON
and suppress defrost
1-2
o90*********031
Light at Main switch OFF
0=OFF, 1=Normal ctrl.
1-2
o98****01
0
AK-CC55 Compact
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 37
Page 38

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Alarm relay priority
0=Not used, 1=High Priority, 2=Medium priority,
3=All
1-2
P41****03
2
Blinds max open time
1-2
P60**
0 min
60 min
5 min
Fan stop at blinds closing
1-2
P65****
0 s
300 s
0 s
Rail heat PWM - Period
time
1-2
P82*********4 s
60 s
10 s
Refrigerant factor K1
1-3
(1)
P83*****-999
999
300
Refrigerant factor K2
1-3
(1)
P84*****-999
999
300
Refrigerant factor K3
1-3
(1)
P85*****-999
999
300
Max superheat liquid ctrl.
1-2
P86*****P87
20.0 °C
3.0 °C
Min superheat liquid ctrl
1-2
P87*****0.0 °C
P86
1.0 °C
Access code 1
1-1
P88*********0
999
0
Display lock
0=OFF, 1=ON
1-2
P89*********010
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
DO2
Conguration
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan
ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail
heat, 5=Alarm, 6=Light,
7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/
LLSV, 9=Compressor 2,
10=Air heater
1-3
(1)
q02**010
6
DO3
Conguration
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan
ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail
heat, 5=Alarm, 6=Light,
7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/
LLSV, 9=Compressor 2,
10=Air heater
1-3
(1)
q03**010
8
DO4
Conguration
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan
ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail
heat, 5=Alarm, 6=Light,
7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/
LLSV, 9=Compressor 2,
10=Air heater
1-3
(1)
q04**010
9
AO1
Conguration
0=None, 1=Rail heat PWM
1-3
(1)
q09*********010
EEV override A
1-2
(2)
q11*****0 %
100 %
0%
Compressor 1 - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q12******010Fan - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q13*********010
Defrost A - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q14*********010
Rail heat - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q15****010Alarm relay - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q16****010Light - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q17****010Compressor 2 - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q19**010Blinds - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q21**010Air heater - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q23**010Fan ECO - override
0=MAN OFF, 1=MAN ON
1-2
(2)
q24**010Rail heat PWM - override
1-2
(2)
q27*********0 %
100 %
0%
High temperature - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q28*********031
Low temperature - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q29*********031
Sensor errors - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q30*********031
AK-CC55 Compact
(1)
(1)
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
Control
Table 20: Control
(1)
(1)
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
DO cong and manual
Table 21: DO cong and manual
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 38
Page 39

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
DI alarms - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q31*********032
Defrost - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q32*********033
Miscellaneous - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q33*********032
Injection - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q34*********032
Control stopped - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q35*********033
Leak detection - Priority
0=Disabled, 3=Low,
2=Medium, 1=High
1-2
q36*********032
Food temp. sensor
1=Thermostat air,
2=Alarm air, 3=S3 Air ON
evap.
1-2
(1)
q39*********132
Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Control state A
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer, 3=Min OFF timer,
4=Drip o, 10=Main
switch OFF, 11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4, 13=Not_used,
14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay,
17=Door open, 18=Melt
period, 19=Modulating
temp. control, 20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control,
24=Start injection,
25=Manual control,
26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing,
29=Case cleaning,
30=Forced cooling,
31=Door open, 32=Power-up delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller, 48=Adaptive liquid
control
0-X
u00*********0480
S5 Evaporator A
0-X
u09*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
DI1 Status
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u10****010Defrost time A
0-X
u11*********0 min
900 min
0 min
S3 Air ON evap. A
0-X
u12*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Night condition
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u13*********010
S4 Air OFF evap. A
0-X
u16*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Thermostat air temp. A
0-X
u17*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Thermostat runtime A
0-X
u18*********0 min
999 min
0 min
S2 Gas outlet A
0-X
u20*****-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Superheat A
0-X
u21*****-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Superheat reference A
0-X
u22*****-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
EEV opening A
0-X
u23*****0 %
100 %
0%
Pe Evap. pressure
0-X
u25*****-1.0 Bar
200.0 Bar
0.0Bar
Te Evap. temp.
0-X
u26*****-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
DI2 Status
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u37*********010
Display readout 1
0-X
u56*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Alarm air temp. A
0-X
u57*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Compressor 1
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u58******010Fan
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u59*********010
Defrost A
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u60*********010
AK-CC55 Compact
(1)
(1)
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
In order to change this parameter the regulation must be stopped via the parameter r12 Main switch = OFF.
(2)
(2)
In order to change this parameter the parameter r12 Main switch must be set in position "SEr" allowing manual control of outputs.
In order to change this parameter the parameter r12 Main switch must be set in position "SEr" allowing manual control of outputs.
Service
Table 22: Service
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 39
Page 40

Function
Values
R-W
Code123456789Min. value
Max. value
Fact. value
Rail heat
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u61****010Alarm relay
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u62****010Light
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u63****010Compressor 2
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u67**010Blinds
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u82**010Air heater
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
u84**010Railheat power
0-X
u85*********0 %
100 %
0%
Thermostat band
1=Band 1, 2=Band 2
0-X
u86*********121
Thermostat cutin temp.
0-X
u90*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
4.0 °C
Thermostat cutout temp.
0-X
u91*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
2.0 °C
Brine valve opening
0-X
U02****
0 %
100 %
0%
Fan ECO
0=OFF, 1=ON
0-X
U37**010Network status
0-X
U45*********0 %
100 %
0%
Rail heat PWM
0-X
U59*********0 %
100 %
0%
Food temperature A
0-X
U72*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
Defrost sensor temperature A
0-X
U73*********-200.0 °C
200.0 °C
0.0 °C
AK-CC55 Compact
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 40
Page 41

AK-CC55 Compact
Operation via AK-UI55 Bluetooth
Access to parameters via Bluetooth and app
1.
App can be downloaded from App Store and Google Play.
◦ Name = AK-CC55 Connect
◦ Start the app.
2.
Click on the display’s Bluetooth button for 3 seconds.
◦ The Bluetooth light will then ash while display is showing the controller’s address.
3.
Connect to the controller from the app.
Figure 42: AK-UI55 Bluetooth
Display info:
• Loc
• The operation is locked and cannot be operated via Bluetooth.
• Unlock from the system manager.
Figure 43: Connect to controller Figure 44: Controller dashboard Figure 45: Set-up menu
The functions are described on Page 42 – Page 54.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 41
Page 42

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Main switch
Start / stop of refrigeration. With this setting refrigeration can be started, stopped or a manual override of
the outputs can be allowed. (For manual control the
value is set at -1. Then the outputs can be force controlled. Start / stop of refrigeration can also be accomplished with the external switch function connected
to a DI input.Stopped control will give a ”Main switch
OFF" alarm.
-1=Manual, 0=Stop, 1=Start
r12
r12 Main switch
Delay of outputs at
power up
Delay of output signal after start-up After start-up or a
power failure the controller’s functions can be delayed so that overloading of the electricity supply network is avoided. Here you can set the time delay.
o01
o01 DelayOfOutp.
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Main switch
Start / stop of refrigeration. With this setting refrigeration can be started, stopped or a manual override of
the outputs can be allowed. (For manual control the
value is set at -1. Then the outputs can be force controlled. Start / stop of refrigeration can also be accomplished with the external switch function connected
to a DI input.Stopped control will give a ”Main switch
OFF" alarm.
-1=Manual, 0=Stop, 1=Start
r12
r12 Main switch
Application mode
Selection of application The controller covers several
applications for control of a refrigerated case. Here
you set which of the possible applications is required.This menu can only be set when regulation is
stopped, i.e. “r12 Main Switch” is set to 0.
1=1. Comp/Alarm/Fan/Defrost, 2=2. Comp/Light/Fan/
Defrost, 3=3. Comp/Railheat/Fan/Defrost, 4=4. Comp/
Custom, 5=5. EEV/Comp/Fan/Defrost, 6=6. EEV/
Alarm/Fan/Defrost, 7=7. EEV/Light/Fan/Defrost, 8=8.
EEV/Rail/Fan/Defrost, 9=9. EEV/Custom
o61
o61 Appl. mode
DO2 Conguration
Select the function of the digital output
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail heat,
5=Alarm, 6=Light, 7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/LLSV,
9=Compressor 2, 10=Air heater
q02
q02 DO2 Cong.
DO3 Conguration
Select the function of the digital output
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail heat,
5=Alarm, 6=Light, 7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/LLSV,
9=Compressor 2, 10=Air heater
q03
q03 DO3 Cong.
DO4 Conguration
Select the function of the digital output
0=None, 1=Fans, 2=Fan ECO, 3=Defrost, 4=Rail heat,
5=Alarm, 6=Light, 7=Blinds, 8=Compressor/LLSV,
9=Compressor 2, 10=Air heater
q04
q04 DO4 Cong.
AO1 Conguration
Select the function of the analogue output
0=None, 1=Rail heat PWM
q09
q09 AO1 Cong.
DI1 Conguration
Select the function of the digital input
0=None, 1=DI status, 2=Door function, 3=Door alarm,
4=Defrost start, 5=Main switch, 6=Night setback,
7=Thermostat band, 8=Alarm at closed, 9=Alarm at
open, 10=Case cleaning, 11=Forced cooling,
12=Open blinds, 13=Coordinated defrost, 14=Forced
closing, 15=Shutdown, 16=Light control, 20=Leak detection, 21=Adaptive liquid control
o02
o02 DI1 Cong.
DI2 Conguration
Select the function of the digital input
0=None, 1=DI status, 2=Door function, 3=Door alarm,
4=Defrost start, 5=Main switch, 6=Night setback,
7=Thermostat band, 8=Alarm at closed, 9=Alarm at
open, 10=Case cleaning, 11=Forced cooling,
12=Open blinds, 13=Coordinated defrost, 14=Forced
closing, 15=Shutdown, 16=Light control, 20=Leak detection, 21=Adaptive liquid control
o37
o37 DI2 Cong.
Refrigerant
Select the type of refrigerant. If the required refrigerant is not part of the list, the user dened option can
be used. Please contact Danfoss for detailed informationWarning: Wrong selection of refrigerant may
cause damage to the system.
0=Not seleted, 6=R13, 7=R13b1, 2=R22, 8=R23,
14=R32, 11=R114, 3=R134a, 12=R142b, 24=R170,
15=R227, 25=R290, 16=R401A, 18=R402A, 19=R404A,
21=R407A, 22=R407B, 20=R407C, 37=R407F,
49=R407H, 23=R410A, 32=R413A, 30=R417A,
31=R422A, 33=R422D, 34=R427A, 35=R438A,
40=R448A, 41=R449A, 48=R449B, 43=R450A,
44=R452B, 45=R454B, 9=R500, 4=R502, 10=R503,
17=R507, 36=R513A, 26=R600, 27=R600a, 5=R717,
28=R744, 46=R1233zdE, 38=R1234ze, 39=R1234yf,
47=R1234zeZ, 29=R1270, 42=R452A, 1=User dened,
13=User dened display
o30
o30 Refrigerant
Refrigerant factor K1
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
P83
P83 RfgFac.K1
AK-CC55 Compact
AK-CC55 Connect menu (SW ver. 2.0x)
Start / Stop
Table 23: Start / Stop
Conguration
Table 24: Conguration
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 42
Page 43

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Refrigerant factor K2
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
P84
P84 RfgFac.K2
Refrigerant factor K3
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
P85
P85 RfgFac.K3
Refrigerant factor
A1
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
x65
--- Rfg.Fac.A1
Refrigerant factor
A2
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
x66
--- Rfg.Fac.A2
Refrigerant factor
A3
Refrigerant factor for a custom refrigerant - please
contact Danfoss for detailed information
x67
--- Rfg.Fac.A3
Pe Min range
Minimum measuring range for sensor
o20
o20 MinTransPres
Pe Max range
Maximum measuring range for sensor
o21
o21 MaxTransPres
Temperature sensor
type
Sensor type for S3, S4 and S5. Normally a Pt 1000 sensor with great signal accuracy is used. But you can also use a sensor with another signal accuracy. That
may either be a PTC sensor (1000 ohm at 25°C) All the
mounted sensors S3-S5 must be of the same type. 0 =
Pt 10001 = PTC 10002 = NTC 5k3 = NTC 10k
0=Pt 1000, 1=PTC 1000, 2=NTC 5k, 3=NTC 10k
o06
o06 SensorCong
Defrost method
Select method of defrost
0=None, 1=Electrical, 2=Hot gas, 3=Brine, 4=Air/
Ocycle
d01
d01 Def. method
Defrost stop method
Here you dene whether a defrost cycle is to be stopped by time or by a temperature sensor
0=Time, 1=S5 sensor, 2=S4 sensor
d10
d10 DefStopSens.
Defrost stop limit A
When the selected defrost stop sensor reaches the set
limit, the defrost cycle is terminated
d02
d02 Def.StopTemp
Food type
When changing the food type the controller will automatically adapt temperature setpoints and alarm limits according to the selected food type. Please be
aware that the setting will revert to "None" after having been changed.
0=None, 1=Vegetables, 2=Dairy, 3=Meat and sh,
4=Frozen food, 5=Ice cream
r89
r89 Food type
Food temp. sensor
Select the temperature to be used for the food temperature representation
1=Thermostat air, 2=Alarm air, 3=S3 Air ON evap.
q39
q39 Food sensor
Network address
Network address of the controller
o03
o03 Unit addr.
Service pin
If the controller is built into a LonWorks network with
data communication, it must have an address, and
the system manager must know this address.The address is sent to the system manager when the menu is
set in pos. ON.
IMPORTANT:
Before you set o04, you MUST set the application
mode of the controller (The function is not used
when the data communication is MODBUS)
0=OFF, 1=ON
o04
o04 Service pin
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Thermostat air
temp. A
Thermostat temperature
u17
u17 Ther. air
Food temperature A
Read out of food temperature
U72
U72 Food temp.
S3 Air ON evap. A
Actual sensor value
u12
u12 S3 air temp.
S4 Air OFF evap. A
Actual sensor value
u16
u16 S4 air temp.
Night condition
Status at the day-/night operation (night operation:
on/o)
0=OFF, 1=ON
u13
u13 Night Cond.
Thermostat cutin
temp.
Readout of the actual cutin value for the thermostat
u90
u90 Cutin temp.
Thermostat cutout
temp.
Readout of the actual cut out value for the thermostat
u91
u91 Cutout temp.
AK-CC55 Compact
Thermostat control
Table 25: Thermostat control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 43
Page 44

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Thermostat runtime
A
Read the ongoing cutin time for the thermostat or the
duration of the last completed cutin
u18
u18 Ther runtime
Thermostat band
Readout of which thermostat used for regulation: 1=
Thermostat band 12= Thermostat band 2
1=Band 1, 2=Band 2
u86
u86 Ther. band
Air heater
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u84
u84 Heat relay
Thermostat mode
Here it is dened how the thermostat is to operate. Either as an ordinary ON/OFF thermostat or as a modulating thermostat.When operation is ”modulating” the
valve will limit the ow of refrigerant so that the temperature variation will be less than for the ON/OFF
thermostat.The thermostat dierential (r01) must not
be set lower than 2K for ""modulating"".In a decentralised plant you must select the ON/OFF thermostat
setting."
2=Modulating, 1=ON/OFF
r14
r14 Therm. mode
Cutout 1
Set point. The thermostat’s cutout value when the
given thermostat band is in use
r00
r00 Cutout
Cutout 2
Set point. The thermostat’s cutout value when the
given thermostat band is in use
r21
r21 Cutout 2
Dierential
When the temperature is higher than the set cutout +
the set dierential, the compressor relay will be cut in.
It will cut out again when the temperature comes
down to the set cutout limit
r01
r01 Dierential
Max cutout limit
Setpoint limitation - The controller’s setting range for
the thermostat setpoint may be narrowed down, so
that much too high or much too low values are not
set accidentally - with resulting damages.To avoid a
too high setting of the setpoint, the max. allowable
reference value may be lowered
r02
r02 Max cutout
Min cutout limit
Setpoint limitation - The controller’s setting range for
the thermostat setpoint may be narrowed down, so
that much too high or much too low values are not
set accidentally - with resulting damages.To avoid a
too low setting of the setpoint, the min. allowable reference value may be increased
r03
r03 Min cutout
Thermostat sensor
S4 %
Selection of thermostat sensor. Here you dene the
sensor the thermostat is to use for its control function.
S3, S4, or a combination of them. With the setting 0%,
only S3 is used. With 100%, only S4.
r15
r15 Ther. S4 %
Thermostat sensor
S4 % night
Selection of thermostat sensor S4% during night operation with night blinds. Here you dene the sensor
the thermostat is to use for its control function. S3, S4,
or a combination of them. With the setting 0%, only
S3 is used. With 100%, only S4.
r61
r61 Ther.S4% Ngt
Night oset
Night setback value.The thermostat’s reference will be
the setpoint plus this value when the controller
changes over to night operation.
r13
r13 Night oset
S4 frost protection
Frost protection on S4 air temperature. If the S4 temperature sensors measures a temperature lower than
the set limit, refrigeration will be stopped in order to
protect produce from ice formation. Refrigeration will
start again when the S4 temperature has risen 2K
above the set limit
r98
r98 S4 Min Lim
Air heater neutral
zone
Heat function. Set the width of the Neutral Zone for
changeover from cooling to heating "
r62
r62 Heat NZ
Air heater start delay
Time delay on transition from refrigeration phase to
heating phase (there is not time delay on transition
from heating phase to refrigeration phase)
r63
r63 HeatStartDel
Melt interval
Melt function. Only for control of MT cases/rooms (-5
to +10°C). The function ensures that the evaporator
will not be blocked by ice crystals. Here you set how
often the function is to stop the refrigeration and
hence transform the ice crystals to water.
r16
r16 MeltInterval
Melt period
Melt period. Here you set how long an on-going melt
function is to last
r17
r17 Melt period
AK-CC55 Compact
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 44
Page 45

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Alarm status
Actual alarm status
0=OFF, 1=ON
x16
--- Sum alarm
Alarm air temp. A
Measured temperature for alarm thermostat
u57
u57 Alarm air
High alarm limit
Readout of actual high alarm limit for the temperature monitoring
y10
--- High al. lim
Low alarm limit
Readout of actual low alarm limit for the temperature
monitoring
y11
--- Low al. lim
S3 Air ON evap. A
Actual sensor value
u12
u12 S3 air temp.
S4 Air OFF evap. A
Actual sensor value
u16
u16 S4 air temp.
Reset alarms
Command for resetting all alarms, unless they are still
active
0=OFF, 1=ON
x15
--- Reset alarm
Alarm sensor S4% A
Signal to the alarm thermostat Here you have to dene the ratio between the sensors which the alarm
thermostat has to use. S3, S4 or a combination of the
two. With setting 0% only S3 is used. With 100% only
S4 is used
A36
A36 Alarm S4 %
High alarm limit 1
Upper alarm limit. The limit value is set in absolute
value. The limit value will be raised with the night o-
set during night operation.
A13
A13 HighLim Air
Low alarm limit 1
Lower alarm limit. The limit value is set in absolute
value
A14
A14 LowLim Air
High alarm limit 2
Upper alarm limit. The limit value is set in absolute
value. The limit value will be raised with the night o-
set during night operation.
A20
A20 HighLim2 Air
Low alarm limit 2
Lower alarm limit. The limit value is set in absolute
value
A21
A21 LowLim2 Air
Alarm delay A
Alarm delay (short alarm delay on air temperature). If
the upper or the lower alarm limit values are exceeded, a timer function will commence. The alarm will
not become active until the set time delay has been
passed. The time delay is set in minutes
A03
A03 Alarm delay
Alarm delay pulldown A
Alarm delay at tempeature pulldown conditions (long
alarm delay). This time delay is used during start-up,
during defrost, immediately after a defrost. There will
be change-over to the normal time delay when the
temperature has dropped below the set upper alarm
limit.
A12
A12 Pulldown del
Door open alarm
delay
Time delay for door alarm
A04
A04 DoorOpen del
Door restart inj. delay
Start of refrigeration when door is open. If the door
has been left open, refrigeration will be started after
the set time.
o89
o89 DoorInjStart
Alarm delay DI 1
Time delay for digital input alarm
A27
A27 Al.Delay DI1
Alarm delay DI 2
Time delay for digital input alarm
A28
A28 Al.Delay DI2
AK-CC55 Compact
Alarm limits and delays
Table 26: Alarm limits and delays
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 45
Page 46

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Thermostat air
temp. A
Thermostat temperature
u17
u17 Ther. air
S3 Air ON evap. A
Actual sensor value
u12
u12 S3 air temp.
S4 Air OFF evap. A
Actual sensor value
u16
u16 S4 air temp.
EEV opening A
Actual status of output function
u23
u23 EEV OD %
Pe Evap. pressure
Actual sensor signal
u25
u25 EvapPress Pe
Te Evap. temp.
Temperature converted from pressure
u26
u26 EvapTemp Te
S2 Gas outlet A
Actual sensor value
u20
u20 S2 temp.
Superheat A
Readout of actual superheat at the outlet of the evaporator
u21
u21 Superheat
Superheat reference
A
Read out of the actual superheat reference
u22
u22 SuperheatRef
Brine valve opening
Actual status of output function
U02
U02 PWM OD %
Min superheat limit
Min. value for the superheat reference
n10
n10 Min SH
Max superheat limit
Max. value for the superheat reference
n09
n09 Max SH
MOP temperature
MOP temperature. The valve opening degree is reduced until the evaporating temperature reaches the
set MOP limit. If no MOP function is required, select
highest value, which corresponds to OFF
n11
n11 MOP temp.
AKV Period time
Period time for the pulse width modulation
n13
n13 AKV Period
Min superheat liquid ctrl
Min. value for the superheat reference during adaptive liquid control
P87
P87 SH Min Liq.
Max superheat liquid ctrl.
Max. value for the superheat reference during adaptive liquid control
P86
P86 SH Max Liq.
Brine valve - Period
time
Period time for the pulse width modulation
n63
n63 Pwm Period
Brine valve max OD
Expert setting - please contact Danfoss for further info
n64
n64 Pwm Max. OD
Brine valve min OD
Expert setting - please contact Danfoss for further info
n65
n65 Pwm Min. OD
Brine valve windup
Expert setting - please contact Danfoss for further info
n66
n66 PwmWindUpFac
Brine valve Kp
Expert setting - please contact Danfoss for further info
n67
n67 Pwm Kp fact.
Brine valve Tn
Expert setting - please contact Danfoss for further info
n68
n68 Pwm Tn sec
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Defrost sensor temperature A
Actual temperature of selected defrost stop sensor
U73
U73 Def.StopTemp
S5 Evaporator A
Actual sensor value
u09
u09 S5 temp.
AK-CC55 Compact
Injection control
Table 27: Injection control
Defrost control
Table 28: Defrost control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 46
Page 47

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Defrost A
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u60
u60 Def. relay
Defrost time A
Read the duration of the ongoing defrost or the duration of the last completed defrost.
u11
u11 Defrost time
Start defrost
Command for starting a defrost
0=OFF, 1=ON
x09
--- Def. Start
Stop defrost
Command for stopping an ongoing defrost cycle
0=OFF, 1=ON
x10
--- Def. Stop
Defrost method
Select method of defrost
0=None, 1=Electrical, 2=Hot gas, 3=Brine, 4=Air/
Ocycle
d01
d01 Def. method
Defrost stop method
Here you dene whether a defrost cycle is to be stopped by time or by a temperature sensor
0=Time, 1=S5 sensor, 2=S4 sensor
d10
d10 DefStopSens.
Defrost stop limit A
When the selected defrost stop sensor reaches the set
limit, the defrost cycle is terminated
d02
d02 Def.StopTemp
Max defrost time
Max duration of a defrost cycle. The setting is also
used as a safety time if the defrost is stopped on temperature. If the selected defrost stop sensor does not
reach the set defrost stop temperature limit within
the set time, the defrost will be stopped anyway.
d04
d04 Max Def.time
Defrost start interval
The function is zeroset and will start the timer function at each defrost start. When the time has expired
the function will start a defrost. The function is used
as a simple defrost start, or it may be used as a safeguard if the normal signal fails to appear. If master/
slave defrost without clock function or without data
communication is used, the interval time will be used
as max. time between defrosts. If a defrost start via
data communcation does not take place, the interval
time will be used as max. time between defrosts.When there is defrost with clock function or data communication, the interval time must be set for a
somewhat longer period of time than the planned
one. In connection with power failure the interval
time will be maintained, and when the power returns
the interval time will continue from the maintained
value. he interval time is not active when set to 0
d03
d03 Def.Interval
Time staggering
power up
Time staggering for defrost cutins during start-up The
function is only relevant if you have several refrigeration appliances or groups where you want the defrost
to be staggered in relation to one another. The function is furthermore only relevant if you have chosen
defrost with interval start. The function delays the interval time by the set number of minutes, but it only
does it once, and this at the very rst defrost taking
place when voltage is connected to the controller.
The function will be active after each and every power failure.
d05
d05 Time stagg.
Max thermostat runtime
Defrost on demand – aggregate refrigeration time Set
here is the refrigeration time allowed without defrosts. If the time is passed, a defrost will be started.
With setting = 0 the function is not in use.
d18
d18 MaxTherRunT.
Pump down delay
Set the time where the evaporator is emptied of refrigerant prior to the actual defrost cycle
d16
d16 Pump dwn del
Drip o time
Here you set the time that is to elapse from a defrost
and until the compressor is to start again. (The time
when water drips o the evaporator).
d06
d06 DripO time
Max hold time
Max. standby time after coordinated defrost. When a
controller has completed a defrost it will wait for a
signal which tells that the refrigeration may be resumed. If this signal fails to appear for one reason or
another, the controller will itself start the refrigeration
when this standby time has elapsed.
o16
o16 MaxHoldTime
Fan control during
defrost
Fan operation during defrost Here you can set how
the fan is to operate during defrost.0: Stopped (Runs
during pump down)1: Running (stopped during "fan
delay")2: Running during pump down and defrost. After that stopped3: Running during pump down and
defrost until defrost stop sensor reaches fan stop temperature limit
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=OFF at drip, 3=OFF at high temp
d09
d09 FanDuringDef
Fan start delay
Delay of fan start after defrost. Here you set the time
that is to elapse from compressor start after a defrost
and until the fan may start again. (The time when remaining water is transformed into ice on the evaporator).
d07
d07 FanStartDel
Fan start temperature
Temperature limit for starting the fans after a defrost.
When the measured S5 evaporator temperature is
getting below the set limit, the fans are started
d08
d08 FanStartTemp
AK-CC55 Compact
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 47
Page 48

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Fan stop temperature
If the fan control during defrost has been set up for it,
the fans can be stopped during the defrost if the defrost sensor exceeds the set temperature limit
d41
d41 Def Fan Stop
Rail heat during defrost
Dene how railheat is controlled during defrost0: Railheat is OFF all the time1: Railheat is ON all the time2:
Normal railheat control
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=Normal control
d27
d27 Railh.at def
Display delay after
defrost
Set the maximum time the display should show the
defrost code "-d-" after a defrost. The normal temperature readout is normally started when the temperature in the case is OK again or if a high temperature
alarm is raised.
d40
d40 Disp. d del.
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Defrost schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t00
t00 Def.Schedule
Def. start 1 - Hours
t01
t01 Def. 1 hr.
Def. start 1 - Minutes
t11
t11 Def. 1 min.
Def. start 2 - Hours
t02
t02 Def. 2 hr.
Def. start 2 - Minutes
t12
t12 Def. 2 min.
Def. start 3 - Hours
t03
t03 Def. 3 hr.
Def. start 3 - Minutes
t13
t13 Def. 3 min.
Def. start 4 - Hours
t04
t04 Def. 4 hr.
Def. start 4 - Minutes
t14
t14 Def. 4 min.
Def. start 5 - Hours
t05
t05 Def. 5 hr.
Def. start 5 - Minutes
t15
t15 Def. 5 min.
Def. start 6 - Hours
t06
t06 Def. 6 hr.
Def. start 6 - Minutes
t16
t16 Def. 6 min.
Monday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t51
t51 Mon.Schedule
Tuesday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t52
t52 Tue.Schedule
Wednesday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t53
t53 Wed.Schedule
Thursday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t54
t54 Thu.Schedule
Friday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t55
t55 Fri.Schedule
Saturday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t56
t56 Sat.Schedule
Sunday - Follow
schedule
0=No, 1=Yes
t57
t57 Sun.Schedule
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Compressor 1
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u58
u58 Comp1/LLSV
Compressor 2
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u67
u67 Comp2 relay
Min ON time
Minimum time the compressor is to run once it has
been started.
c01
c01 Min. On time
Min OFF time
Minimum time the compressor has to be stopped
c02
c02
Min.O time
Delay between
comp.
Time delay for couplings of two compressors. The
step delay is the time that has to elapse from the rst
compressor cuts in and until the next compressor can
cut in.
c05
c05 Step delay
Step control mode
Selection of step control mode for compressors. At sequential mode compressor 1 will always be the rst to
start and the last to stop. In cyclic mode the run time
between the compressor will be equalized.
1=Sequential, 2=Cyclic
c08
c08 Step mode
AK-CC55 Compact
Defrost schedules
Table 29: Defrost schedules
Compressor
Table 30: Compressor
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 48
Page 49

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Fan
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u59
u59 Fan relay
Fan ECO
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
U37
U37 Fan Eco
Fan pulsing mode
Pulse operation of fan 0: No pulse operation 1: Pulse
operation when the thermostat is cut out2: Pulse operation when the thermostat is cut out, but only during night operation
0=No pulsing, 1=Pulsing cutout, 2=Pulsing cutout
night
F05
F05 FanPulseMode
Fan period time
Periodtime for pulsing of fan
F06
F06 Fan cycle
Fan ON cycle
ON time for fan. The ON period is set as a percentage
of the period time
F07
F07 Fan ON %
Fan stop high S5
temp.
Fan stop temperature The function stops the fans in
an error situation, so that they will not provide power
to the appliance. If the defrost sensor registers a higher temperature than the one set here, the fans will be
stopped. There will be re-start at 2 K below the setting. The function is not active during a defrost or
start-up after a defrost.
F04
F04 FanStop temp
Fan at forced closing
You can set whether fans should be operational or
stopped if the function "Forced closing" is activated
here. 0: Fans are OFF1: Fans are ON2: Fans are OFF and
defrost is not permitted3: Fans are ON and defrost is
not permitted
0=OFF, 1=ON, 2=OFF and suppress defrost, 3=ON and
suppress defrost
o90
o90 Fan ForcedCl
Fan stop at blinds
closing
When blinds are closing the fans are stopped in the
dened time delay in order to ensure that the blinds
are closed correctly
P65
P65 BlindFanStop
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Dewpoint
Actual dewpoint received from system manager via
network
x18
--- Dew point
Rail heat
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u61
u61 Railh. relay
Railheat power
Readout of the actual rail power in %
u85
u85 Rail DutyC %
Rail heat PWM
Actual status of output function
U59
U59 Railheat PWM
Rail heat control
mode
The rail heat can be controlled in several ways: 0: Railheat is running all the time 1: Pulse control is used
with a timer function following the day/night operation 2: Pulse control is used with a dew point function.
This function requires that a signal is received about
the dew point value. The value is measured by a system manager and sent to the controller via the data
communication.
0=ON, 1=Day/Night timer, 2=Dew point ctrl.
o85
o85 Railh. mode
Rail heat ON cycle
day
Railheat power during day time. The ON period is set
as a percentage of the period
o41
o41 Railh.ONday%
Rail heat ON cycle
night
Railheat power during night time. The ON period is
set as a percentage of the period time
o42
o42 Railh.ONngt%
AK-CC55 Compact
Fan control
Table 31: Fan control
Railheat control
Table 32: Railheat control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 49
Page 50

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Rail heat period
time
Periodtime for pulsing of railheat
o43
o43 Railh.cycle
Rail heat PWM - Period time
Period time for the pulse width modulation
P82
P82 RailCyclePWM
Rail heat min ON cycle
Lowest permitted rail heat power. When the measured dew point is below the dened minimum limit
the rail heat will run with the set minimum power
o88
o88 Rail Min ON%
Dewpoint min limit
If the measuered dew point is below the set value the
rail heat is running at minimum heat
o86
o86 DewP Min lim
Dewpoint max limit
If the measured dew point is above the set value the
rail heat is maximum
o87
o87 DewP Max lim
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state
A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer, 3=Min
OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF, 11=Thermostat cutout, 12=Frost protection S4, 13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan
delay, 17=Door open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp.
control, 20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant
selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced
cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up delay, 33=Air heating,
45=Shut down controller, 48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl.
state
Night condition
Status at the day-/night operation (night operation: on/o)
0=OFF, 1=ON
u13
u13 Night
Cond.
Light
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u63
u63 Light relay
Blinds
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u82
u82 Blinds
relay
Light control
mode
Conguration of light function1: Light is controlled via day/
night status 2: Light is controlled via data communication and
master control parameter "MC Light signal" 3: Light is controlled by door contact on DI input. When the door is opened the
relay will cut in. When the door is closed again there will be a
time delay of two minutes before the light is switched o. 4: As
"2" but if there are any 15-minute network errors, the light will
switch on and the night blind will open. 5: Light is controlled
via DI input signal
1=Day and night, 2=Network, 3=Door switch, 4=Network (Fallback), 5=Digital input
o38
o38 Light
cong
Light at
Main switch
OFF
Dene how light and blinds are to be controlled at Main switch
OFF 0: Light is switched o and night blinds are open when the
main switch is o 1: Light and night blinds are independent of
main switch.
0=OFF, 1=Normal ctrl.
o98
o98 Light
MS=O
Blinds max
open time
Time delay from when blinds have been opened manually until
they close again
P60
P60 BlindOpenTim
Case cleaning mode
The status of the function can be followed here or the function
can be started manually.0 = Normal operation (no cleaning) 1 =
Only fans are running to defrost the evaporator. All other outputs are O. 2 = Cleaning with stopped fans. All outputs are O.
If the function is controlled by a digital input signal, the relevant status can be seen here in the menu.
0=OFF, 1=Fans run, 2=Cleaning
o46
o46 Case
clean
AK-CC55 Compact
Light/Blinds/Cleaning control
Table 33: Light/Blinds/Cleaning control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 50
Page 51

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Control state A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Normal ctrl., 1=Hold after defrost, 2=Min ON timer,
3=Min OFF timer, 4=Drip o, 10=Main switch OFF,
11=Thermostat cut-out, 12=Frost protection S4,
13=Not_used, 14=Defrost, 15=Fan delay, 17=Door
open, 18=Melt period, 19=Modulating temp. control,
20=Emergency control, 23=Adaptive superheat control, 24=Start injection, 25=Manual control, 26=No refrigerant selected, 16=Forced closing, 29=Case cleaning, 30=Forced cooling, 31=Door open, 32=Power-up
delay, 33=Air heating, 45=Shut down controller,
48=Adaptive liquid control
u00
u00 Ctrl. state
Display readout 1
Read out of the temperature shown on the display
u56
u56 Display air
Display air S4%
Signal to the display sensor. Here you have to dene
the ratio between the sensors which the display has
to use. S3, S4 or a combination of the two. With setting 0% only S3 is used. With 100% only S4 is used
o17
o17 Disp. S4 %
Display readout adjustment
Correction of the display´s temperature.If the temperature at the products and the temperature received
by the controller are not identical, an oset adjustment of the display temperature can be carried out."
r04
r04 Disp. Adj. K
Temperature unit
Select whether temperatures are to be shown as °C or
as °F.
0=Celsius, 1=Fahrenheit
r05
r05 Temp.unit
Display lock
With this setting it is possible to lock the keypad operation of the local display. When not used for some
time, the local display will lock the button operations
and a special key combination is required in order to
use the keypad
0=OFF, 1=ON
P89
P89 LockDispKey
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Alarm relay
Actual status of output function
0=OFF, 1=ON
u62
u62 Alarm relay
Alarm relay priority
Set which alarm priorities that are to activate the
alarm relay: 0=Not used, alarm relay is not used1:
High, alarm with high priority will activate relay2: Medium, alarms with high or medium priority will activate the alarm relay3: All, all alarms will activate alarm
relay
0=Not used, 1=High Priority, 2=Medium priority,
3=All
P41
P41 Al.Rel.Prio
Mute alarm
When muting alarms, the alarm relay will stop signalling the alarm until a new alarm arises
0=OFF, 1=ON
q38
q38 Mute Alarm
High temperature Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q28
q28 Hi Temp Prio
Low temperature Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q29
q29 Lo Temp Prio
Sensor errors - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q30
q30 Sensor Prio
DI alarms - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q31
q31 DIAlarm Prio
Defrost - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q32
q32 Defrost Prio
Miscellaneous - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q33
q33 Misc Prio
AK-CC55 Compact
Display control
Table 34: Display control
Alarm relay priorities
Table 35: Alarm relay priorities
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 51
Page 52

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Injection - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q34
q34 Inject Prio
Control stopped Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q35
q35 CtrlOFF Prio
Leak detection - Priority
Select the priority of the alarms associated to the
alarm group. Be aware - by selecting "Disable" the
alarms will not be shown on the display or be routed
to the alarm relay or to the network.
0=Disabled, 3=Low, 2=Medium, 1=High
q36
q36 Leak Prio
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Access code 3
Access code for local display
o05
o05 Acc. code 3
Access code 2
Access code for local display
o64
o64 Acc. code 2
Access code 1
Access code for local display
P88
P88 Acc. code 1
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Network status
Quality of the network communication
U45
U45 Comm. status
Network address
Network address of the controller
o03
o03 Unit addr.
Baudrate
Communication speed of network
1=Auto, 2=9600 Baud, 3=19200 Baud, 4=38400 Baud
x96
--- Bus baudrate
Parity and stop bit
Select parity and stop bit of Modbus messages
0=None, 1=Even, 2=Odd
x97
--- Parity bit
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
S3 Air ON evap. A Adjustment
Correction of sensor signal e.g. due to long sensor cable
r10
r10 Adjust S3
S4 Air OFF evap. A Adjustment
Correction of sensor signal e.g. due to long sensor cable
r09
r09 Adjust S4
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Make new factory
With this command you save the controller’s actual
settings as a new basic setting (the earlier factory settings are overwritten).
0=OFF, 1=ON
o67
o67 Make factory
Reset to factory settings
Command which will revert all controller settings to
factory values.
0=OFF, 1=ON
z06
--- Reset factory
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Superheat ctrl.
mode A
Select how to control the superheat of the evaporator. At adaptive control the superheat reference is
adapted automatically to give the best utilization of
the evaporator surface. At load based control the superheat reference is increased at high loads
1=Adaptive, 2=Load based
n21
n21 SH mode
Superheat close A
Minimum superheat limit where the valve is closing
x68
--- SH close
AFidentForce A
Expert setting - contact Danfoss for further information
x69
--- AFidentForce
Superheat Kp min A
Min limit for
amplication factor of PI controller ad-
justing the valve opening degree (expert setting)
x70
--- SH Kp min
Superheat Kp max A
Max limit for
amplication factor of PI controller ad-
justing the valve opening degree (expert setting)
x71
--- SH Kp max
Superheat Tn A
Integration time of PI controller adjusting the valve
opening degree (expert setting)
x72
--- SH Tn
Te feedback gain A
Gain factor for feedback of evaporating temperature
signal Te to PI controller controlling the superheat
(expert setting)
x73
--- Te-gain
Kp MTR control A
Amplication
factor for modulating temperature con-
trol (Expert setting)
x77
--- MTR Kpfactor
AK-CC55 Compact
Miscellaneous
Table 36: Miscellaneous → Access codes
Table 37: Miscellaneous → Network
Table 38: Miscellaneous → Sensor adjustment
Table 39: Miscellaneous → Factory reset
Advanced
Table 40: Advanced → Advanced injection control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 52
Page 53

Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Tn MTR control A
Integration time for modulating temperature control
(Expert setting)
x78
--- MTR Tn sec
AFident A
Expert readout - contact Danfoss for further information
x79
--- AFident
Calculated Max OD
A
Calculated maximum opening degree of injection
valve (expert readout)
x80
--- Max OD %
Superheat close liquid ctrl. A
Minimum limit of superheat where the valve is closing duting adaptive liquid control
x87
--- SH close Liq
AFident Ee
Expert readout - contact Danfoss for further information
Y20
--- AFident Ee
Aver.OD Ee
Expert readout - contact Danfoss for further information
Y21
--- Aver.OD Ee
Emergency OD day
Average opening degree of liquid line solenoid valve
during day operation
z01
--- EmerC OD day
Emergency OD
night
Average opening degree of liquid line solenoid valve
during night operation
z02
--- EmerC OD ngt
Function
Description
Values
Code
Short name
Regulation condition A
Readout of the actual control state of the controller
0=Main switch OFF, 1=Injection start, 2=Superheat
ctrl., 3=Fill evap., 4=Defrost, 5=Post defrost, 6=Forced
closing, 7=Injection fault, 8=Emergency control,
9=Modulating ctrl., 10=Melt period, 11=Door open,
12=Case cleaning, 13=Cutout, 14=Forced cooling,
15=Shut down
x62
--- Reg. Cond.
MC Actual cutin
temp.
x63
--- Cutin temp.
MC Actual cutout
temp.
x64
--- Cutout temp.
MC Ther. toggle
Master control signal used for switching case load
ON/OFF depending on load condition
0=No action, 1=Toggle ON, 2=Toggle OFF
x81
--- TherToggle
MC Load request
Master control signal used to control load balance between multiple case controllers on the same suction
line
x82
--- LoadReq
MC Max Te oset
Requested oset to actual evporating temperature in
order to keep the air temperature at the actual set
point
x84
--- MaxTeOset
MC Liquid control
Master control signal allowing switch to adaptive liquid control
0=OFF, 1=ON
x85
--- MC Liq. Ctrl
MC Night setback
Master control signal for changing between day and
night time operation
0=OFF, 1=ON
x06
--- Night setbck
MC Case shutdown
Master control signal used to shut down a case for a
time period. During shut down there will be no alarm
monitoring
0=OFF, 1=ON
x17
--- Case shutdwn
MC Forced closing
Master control signal that will close the injection
valve
0=OFF, 1=ON
x07
--- Forced close
MC Forced cooling
Master control signal that will provide forced cooling
0=OFF, 1=ON
x08
--- Forced cool.
MC Defrost start
Master control signal for starting a defrost. At adaptive defrost the defrost might be skipped if the defrost is not needed
0=OFF, 1=ON
x13
--- MC def.start
MC Defrost state
Read out the actual state of the defrost
0=OFF, 1=ON
x14
--- DefrostState
MC Hold after defrost
Master control signal used for co-ordinated defrost
control to hold cabinets from returning to normal refrigeration after a defrost until all cabinets have terminated defrost
0=OFF, 1=ON
x11
--- HoldAfterDef
MC Stop defrost
Master control signal used to prevent a defrost start in
a controller.
0=OFF, 1=ON
x12
--- Disable def.
MC Light signal
Master control signal for control of light via data communication signal from system manager
0=OFF, 1=ON
o39
o39 Light remote
MC Actual dewpoint
Master control signal sending the actual measured
dew point from system manager to controller over
the network.
x03
--- Act.DewPoint
MC Po load factor
x83
--- Load factor
MC Bluetooth lock
Master control signal that will lock down all Bluetooth
datacommunication
0=OFF, 1=ON
aaa
--- BT lock
MC Min delta T
Required minimum delta temperature across evaporator (S3 - Te) in order to keep the air temperature at
the actual set point
y04
--- Min Delta T
AK-CC55 Compact
Table 41: Advanced → Master control
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 53
Page 54

Code
Alarm text
Description
E01
Hardware failure
The controller has a hardware failure
E06
Clock lost time
Clock has lost valid time
E20
Pe Evap. pressure A - Sensor error
Sensor signal is out of range. Please check the sensor for correct operation
E24
S2 Gas outlet A - Sensor error
Sensor signal is out of range. Please check the sensor for correct operation
E25
S3 Air ON evap. A - Sensor error
Sensor signal is out of range. Please check the sensor for correct operation
E26
S4 Air OFF evap. A - Sensor error
Sensor signal is out of range. Please check the sensor for correct operation
E27
S5 Evaporator A - Sensor error
Sensor signal is out of range. Please check the sensor for correct operation
A01
High temperature alarm A
The alarm temperature has been above the max alarm limit for a longer time period than the set alarm delay.
A02
Low temperature alarm A
The alarm temperature has been below the min alarm limit for a longer time period than the set alarm delay.
A04
Door open alarm
The door has been open for a too long time
A05
Max defrost hold time exceeded
The controller has been waiting longer time than permitted after a co-ordinated defrost.
A11
Refrigerant not selected
The refrigerant has not been selected hence control can not be initiated
A15
DI alarm 1
Alarm signal from digital input signal
A16
DI alarm 2
Alarm signal from digital input signal
A45
Main switch set OFF
The controller manin switch has been set to either Stop or Manaual control. Alternatively a digital input set
up for "main switch" function, has stopped control
A59
Case in cleaning mode
A case cleaning operation has been started on a case
AA2
CO2 leak detected
CO2 is leaking from the refrigerantion system
AA3
Refrigerant leak detected
Refrigerant is leaking from the refrigeration system
a04
Wrong IO conguration
Inputs and outputs have not been congured correctly
AK-CC55 Compact
Fault message
In an error situation the alarm LED on the front will be on and the alarm relay will be activated (depending on
priority). If you push the alarm button for 3 seconds you can see the alarm report in the display. (Alarm priorities can
be changed. See the Table 35: Alarm relay priorities.) Here are the messages that may appear:
Table 42: Fault message
NOTE:
Data communication
The importance of individual alarms can be dened with a setting. The setting must be carried out in the group
"Alarm destinations"
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 54
Page 55

Ctrl. State/
Code
Operating status
Description
Push the info button for 3 seconds to see status. If there is a status code, it will be shown on the display. The individual status codes have the
following meanings:
S0
Normal ctrl.
The controller is running normal control. There is no other control taking priority
S1
Hold after defrost
The controller is waiting for other controllers to terminate coordinated defrost
S2
Min ON timer
The compressor is restricted from starting until the minimum ON timer expires
S3
Min OFF timer
The compressor is restricted from stopping until the minimum OFF timer expires
S4
Drip o
The defrost has terminated and the controller is waiting for drip delay to expire, while the water is dripping o the
evaporator
S10
Main switch OFF
The controller has been stopped because the parameter r12 Main switch has been set in OFF or Service position or
the controller has been stopped via Main switch function on DI input
S11
Thermostat cut-out
The air temperature has reached the thermostat cut-out value
S12
Frost protection S4
The air o temperature is below the minimum S4 frost limit (r98, S4 frost protection)
S14
Defrost
The controller is running a defrost cycle
S15
Fan delay
The evaporator fans are waiting to start after a defrost cycle (d07, Fan start delay and d08, Fan start temperature)
S16
Forced closing
The injection valve has been forced closed via a signal on a digital input or from the system manager (compressor
pack is restricted from starting)
S17
Door open
DI signal indicates that the cold room door is open
S18
Melt period
The controller has stopped refrigeration for a short while to turn ice crystals into water and thereby improve air
ow through the evaporator
S19
Modulating temp. control
The air temperature is controlled close to the set point via a modulating temperature control
S20
Emergency control
(1)
The air temperature is controlled according to an emergency procedure due to sensor error (Pe, S2, S3 or S4)
S23
Adaptive superheat control
The superheat of the evaporator is optimized
S24
Start injection
The liquid injection into the evaporator has started
S25
Manual control
Main switch has been set in Service position for manual control of outputs
S26
No refrigerant selected
The refrigerant type has not been selected (parameter o30 Refrigerant)
S29
Case cleaning
A case cleaning operation has been initiated via parameter o46 Case cleaning mode or via a signal on a digital
input or via the AK-CC55 Connect app
S30
Forced cooling
The thermostat has been overruled to run forced cooling via a signal on a digital input
S32
Power-up delay
The controller has just been powered up and the output control is waiting for the power-up delay to expire (parameter o01, Delay of outputs at power-up)
S33
Air heating
The air heater is energized in order to raise the air temperature (parameters r62, Air heater neutral zone and r63, Air
heater start delay)
S45
Shut down controller
The control has been stopped due to a digital input signal or from the system manager
S48
Adaptive liquid control
The superheat control is running adaptive liquid control with reduced superheat for transcritical CO2 systems with
ejectors. Signal is provided via digital input or from the system manager
AK-CC55 Compact
Operating status
Table 43: Operating status
(1)
(1)
Emergency control:
Emergency control:
• If Pe or S2 sensor fails, the controller will operate with a safe opening degree based on normally registered opening degree during day and
• If Pe or S2 sensor fails, the controller will operate with a safe opening degree based on normally registered opening degree during day and
night operation.
night operation.
• If S3 or S4 sensor fails, the thermostat will operate with a registered ON/OFF duty cycle during day and night operation.
• If S3 or S4 sensor fails, the thermostat will operate with a registered ON/OFF duty cycle during day and night operation.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 55
Page 56

Electrical data
Value
Supply voltage AC [V]
115 V / 230 V, 50/60 Hz
Voltage variation range max. [V]
85 – 265 V
Power consumption [VA]
5 VA
Power ON indicator
Green LED
Electrical cable dimensioning [mm2]
Max.1.5 mm2 multi-core cable
Sensor and measuring data
Value
Sensor S2
Pt 1000 AKS11
Sensor S3, S4, S5
Pt 1000 AKS11
PTC 1000 EKS111
NTC5K EKS211
NTC10K EKS221 sensor
(All 3 must be of the same type)
Temperature measuring accuracy
Pt1000: -60 – 120 °C. ±0.5 K
PTC1000: -60 – 80 °C. ±0.5 K
NTC5K: -40 – 80 °C. ±1.0 K
NTC10K: -40 – 120 °C. ±1.0 K
Pt1000 sensor specication
±0.3 K at 0 °C
±0.005 K per degree
Pe measuring
AKS 32R Ratiometric pressure transmitter: 10-90%
Input and output relay
specications
Input/output
Description
Digital input
DI1
DI2
Signal from dry contact functions
Requirements to contacts: Gold plating
Cable length must be max. 15 m
Use auxiliary relays when the cable is longer
Open loop: 12 V
Contact 3.5 mA
Solid state output
DO1 (for AKV coil)
115V / 230 V AC
Max. 0.5 A (No overload protection!)
Max. 1 x 20 W AKV for 115 V AC
2 x 20 W AKV for 230 V AC
Note: 2 EC coils are not supported.
Relays
DO2
DO3
DO4
115 V / 230 V AC
Load max.: CE. 8 (6)A
UL. 8A res. 3FLA 18LRA
Load min.: 1VA
Inrush: DO2 DO3 TV-5 80A
Analogue output/ PWM
AO1
0 / 10 V Pulse Width Modulated
(PWM) max. 15 mA.
0 – 10 V variable, max. 2 mA
AK-CC55 Compact
Product specication
Technical data
Electrical specications
Table 44: Electrical specications
Sensor and measuring data
Table 45: Sensor and measuring data
Input and output relay specications
Table 46: Input and output relay specications
NOTE:
• DO2 to DO4 are 16 A relays.
• Max. load must be observed.
• DO2 / DO3 is recommended for load with high inrush current e.g. EC Fan and LED light.
• All relays are sealed for use with ammable refrigerant like Propane R290.
• Compliance with EN 60 335-2-89: 2010 Annex BB.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 56
Page 57

Danfoss
84B3239
Danfoss
84B3242
Function data
Value
Display
LED 3 digit
External display, AK-CC55 Compact
1 external display
External display connection
RJ12
Max. display cable length [m]
100 m
Data communication built-in
MODBUS
Clock battery backup power reserve
4 days
Mounting
DIN rail
Environmental conditions
Value
Ambient temperature range, operation
0 – 55 °C
Ambient temperature range, transport
-40 – 70 °C
Enclosure rating IP
IP20
Relative humidity range [%]
20 – 80%, non-condensing
Shocks/Vibrations
No shocks and vibrations allowed
AK-CC55 Compact
Function data
Table 47: Function data
Environmental conditions
Table 48: Environmental conditions
Dimensions
Measurements are in mm.
Figure 46: AK-CC55 Compact
Figure 47: AK-CC55 Set
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 57
Page 58

Control
Certication
Mark
Country
Compact
EMC/LVD/RoHS
CEEUCompact
UL recognized
cURus
NAM (US and Canada)
Compact
ACMA (EMC)
RCM
Australia/New Zealand
Compact
LVE/EMC/RoHS
EAC
Russia, Kazakhstan, belarus
Compact
LVD/EMC/RoHS
UA
Ukraine
Display module
Certication
Mark
Country
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
REDCEEU
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
FCC
FCC ID
USA
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
IC (ISED)
IC ID
Canada
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
CMIIT
CMITT ID
China
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
ACMA (EMC/Wireless)
RCM
Australia
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
RSM (EMC/Wireless)
RCM
New Zealand
AK-UI55 Bluetooth
EMC/LVD/Wireless
UA
Ukraine
AK-UI55 Info
EMC/LVD
UA
Ukraine
AK-UI55 Info
ACMA (EMC)
RCM
Australia
AK-UI55 Info
RSM (EMC)
RCM
New Zealand
AK-UI55 Info
RoHS
EAC
Russia, Kazakhstan, belarus
AK-UI55 Set
EMC/LVD
UA
Ukraine
AK-UI55 Set
ACMA (EMC)
RCM
Australia
AK-UI55 Set
RSM (EMC)
RCM
New Zealand
AK-UI55 Set
RoHS
EAC
Russia, Kazakhstan, belarus
AK-CC55 Compact
Certicates, declarations, and approvals
The list contains all certicates, declarations, and approvals for this product type. Individual code number may have
some or all of these approvals, and certain local approvals may not appear on the list.
Some approvals may change over time. You can check the most current status at danfoss.com or contact your local
Danfoss representative if you have any questions.
Table 49: Controller
Table 50: Display module
Controllers/displays/option module:
CB certicate including all deviation according to IEC 60730-1 and 2-9
Relays:
Tested according to IEC 60079-15
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 58
Page 59

AK-CC55 Compact
Statements for the AK-UI55 Bluetooth display
FCC COMPLIANCE STATEMENT
CAUTION:
Changes or modications not expressly approved could void your authority to use this equipment This device
complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation to the following two conditions: (1) This device may not cause
harmful interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference received, including interference that may
cause undesired operation.
INDUSTRY CANADA STATEMENT
This device complies with Industry Canada license-exempt RSS standard(s). Operation is subject to the following
two conditions: (1) this device may not cause interference, and (2) this device must accept any interference,
including interference that may cause undesired operation of the device.
Le présent appareil est conforme aux CNR d'Industrie Canada applicables aux appareils radio exempts de licence.
L'exploitation est autorisée aux deux conditions suivantes : (1) l'appareil ne doit pas produire de brouillage, et (2)
l'utilisateur de l'appareil doit accepter tout brouillage radioélectrique subi, même si le brouillage est susceptible
d'en compromettre le fonctionnement.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 59
Page 60

Online support
Play Store
App Store
Danfoss oers a wide range of support along with our products, including digital product information, software,
mobile apps, and expert guidance. See the possibilities below.
The Danfoss Product Store
The Danfoss Product Store is your one-stop shop for everything product related—no matter where
you are in the world or what area of the cooling industry you work in. Get quick access to essential
information like product specs, code numbers, technical documentation, certications, accessories,
and more.
Start browsing at store.danfoss.com.
Find technical documentation
Find the technical documentation you need to get your project up and running. Get direct access to
our ocial collection of data sheets, certicates and declarations, manuals and guides, 3D models
and drawings, case stories, brochures, and much more.
Start searching now at www.danfoss.com/en/service-and-support/documentation.
Danfoss Learning
Danfoss Learning is a free online learning platform. It features courses and materials specically
designed to help engineers, installers, service technicians, and wholesalers better understand the
products, applications, industry topics, and trends that will help you do your job better.
Create your Danfoss Learning account for free at www.danfoss.com/en/service-and-support/learning.
Get local information and support
Local Danfoss websites are the main sources for help and information about our company and
products. Find product availability, get the latest regional news, or connect with a nearby expert—all
in your own language.
Find your local Danfoss website here: www.danfoss.com/en/choose-region.
AK-CC55 Connect
Make service easy with the free AK-CC55 Connect app. Via a Danfoss Bluetooth display you can
connect to an AK-CC55 case controller and get a visual overview of the display functions. The app
ensures smooth interaction with a Danfoss AK-CC55 case controller in a user-friendly design.
Download the app here:
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its
products without notice. This also applies to products already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential
changes being necessary in specications already agreed. All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and
the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
© Danfoss | Climate Solutions | 2021.04 BC365212986197en-000101 | 60
 Loading...
Loading...