1/1 Designed and manufactured by Secop for DANFOSS - DEHC.EI.100.E2.02 / 520N0556 August 2011
Danfoss can accept no responsibility for possible errors in catalogues, brochures and other printed material. Danfoss reserves the right to alter its products without notice. This also applies to products
already on order provided that such alterations can be made without subsequential changes being necessary in specifi cations already agreed.
All trademarks in this material are property of the respective companies. Danfoss and the Danfoss logotype are trademarks of Danfoss A/S. All rights reserved.
Instructions
Electronic Unit Type 105N4220,
160-254V, AC 50-60Hz for BD150F Compressor
Example for compressor speed: external frequency multiplied by 10 (270 Hz ⇒ 2,700 rpm).
If a signal with a frequency according to a speed
above maximum is applied, the compressor
works at maximum speed.
If a DC signal is supplied immediately after
a frequency signal, the compressor speed is
locked until another frequency is applied or the
DC signal is removed.
5. Adaptive control
(AEO - Adaptive Energy Optimizer)
The compressor adjusts its speed in steps to
any increasing or decreasing cooling demand,
within the minimum and maximum speed limits.
If the thermostat switches the compressor ON:
After a 60-minute running time, the speed will
increase stepwise every 15 minutes, depending
on the latest speed used, until the maximum is
reached.
If the thermostat switches the compressor OFF:
After each ON, the compressor either restarts
with lower speed steps than the recently used,
until the minimum is reached, or increases its
speed stepwise, after a new 60-minute running
time.
6. Earth connection
Earth connector to be applied to compressor
housing (10). The electronic unit is protected
by the electrical connection heatsink - toothed
washer - screw - compressor housing.
The electronic unit is working within a voltage
range of:
160-254V AC, 50- 60Hz or
12/24V DC with inverter
Max. allowable ambient temperature is 43°C.
The electronic is provided with a built-in thermal
protection which stops the compressor in case
of thermal overload.
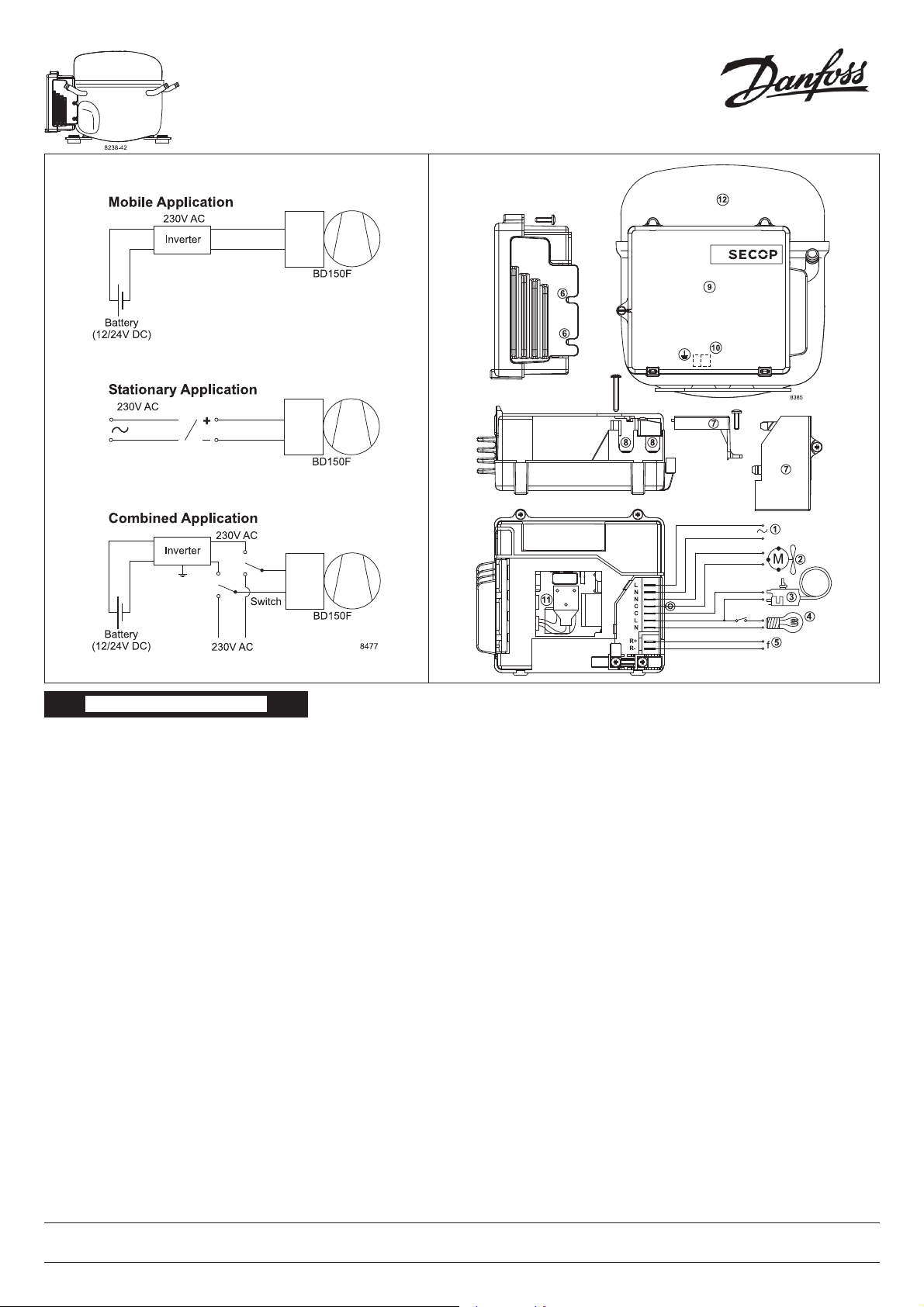
Use with 12/24V DC battery in a mobile application is possible by means of an inverter, 12/24V
to 230V AC type, min. 300V peak voltage, min.
300W continuous power output. Examples of
application - see Fig. 1
1. Installation (see Fig. 2)
The connector (11) of the electronic unit (9) has
to be connected to the compressor (12) fi rst. The
total unit is then fi tted to the compressor housing
with two screws and toothed washers through the
recesses in the heatsink unit (6). All other terminals (except the earth connection under point 6)
and cord relief (8) are under the cover (7).
2. Power supply
Power supply L and N:
Power supply (1) is connected to L and N. Earth
connection is connected to terminal (10) on the
compressor housing (12).
3. Fan
Fan N and C:
A fan (2) can be connected to N and C. It will be
operated with power line voltage, and cut in and
out with the compressor if a conventional thermostat is used.
4. Thermostat connection (3) light connection (4)
The unit has 3 connec ti on options for thermostats.
4.1 Voltage signal application on-off (conventional thermostat)
Thermostats C, L and N:
Compressor control is an adaptive control, see
description under point 5.
4.2 Application of a thermostat provided with
DC signal out (min. 5V, max. 15V)
Signal input R+ and R- (5)
(fan operation not possible):
Connection with DC signal on-off to control unit,
with reinforced isolation in control unit (5).
The compressor unit runs in adaptive control
mode, see description under point 5.
4.3 Application of an electronic thermostat
with frequency output (min. 5V, max. 15V)
Signal input R+ and R- (5)
(fan connection not possible):
The refrigerator thermostat has to supply the
control unit (9) with a square signal (min. pulse
width 200 µs). The input terminals are reinforced
isolated. If the frequency is more than 100 Hz the
compressor goes into external reference control
mode. The compressor speed is con-trolled by
the external frequency (adaptive control is disabled). The control unit remains in this mode until
the power supply is disconnected. The compressor stops with an input signal below 198 Hz (min.
196 Hz, max. 199 Hz).
Compressor operation: if a frequency of above
203 Hz (min. 201 Hz, max. 205 Hz) is supplied,
the compressor starts.
Fig. 1
ENGLISH
Fig. 2
 Loading...
Loading...