Daewoo DTH 14 Q 1 FS TV SM Schematic


✔
Caution
: In this Manual, some parts can be changed for improving, their
performance without notice in the parts list. So, if you need the
latest parts information,please refer to PPL(Parts Price List) in
Service Information Center (http://svc.dwe.co.kr).

§CONTENTS
SPECIFICATIONS---------------------------------------------------------------- 2
SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 3
BLOCK DIAGRAM°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 4
GENERAL ALIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 6
DESCRIPTION OF THE CIRCUIT OPERATION°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 10
TROUBLE SHOOTING CHARTS°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 32
PRINTED CIRCUIT BOARDS °¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 40
REPLACEMENT PARTS LIST°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 41
EXPLODED VIEW°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 54
CIRCUIT DIAGRAM°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶°¶ 64
1
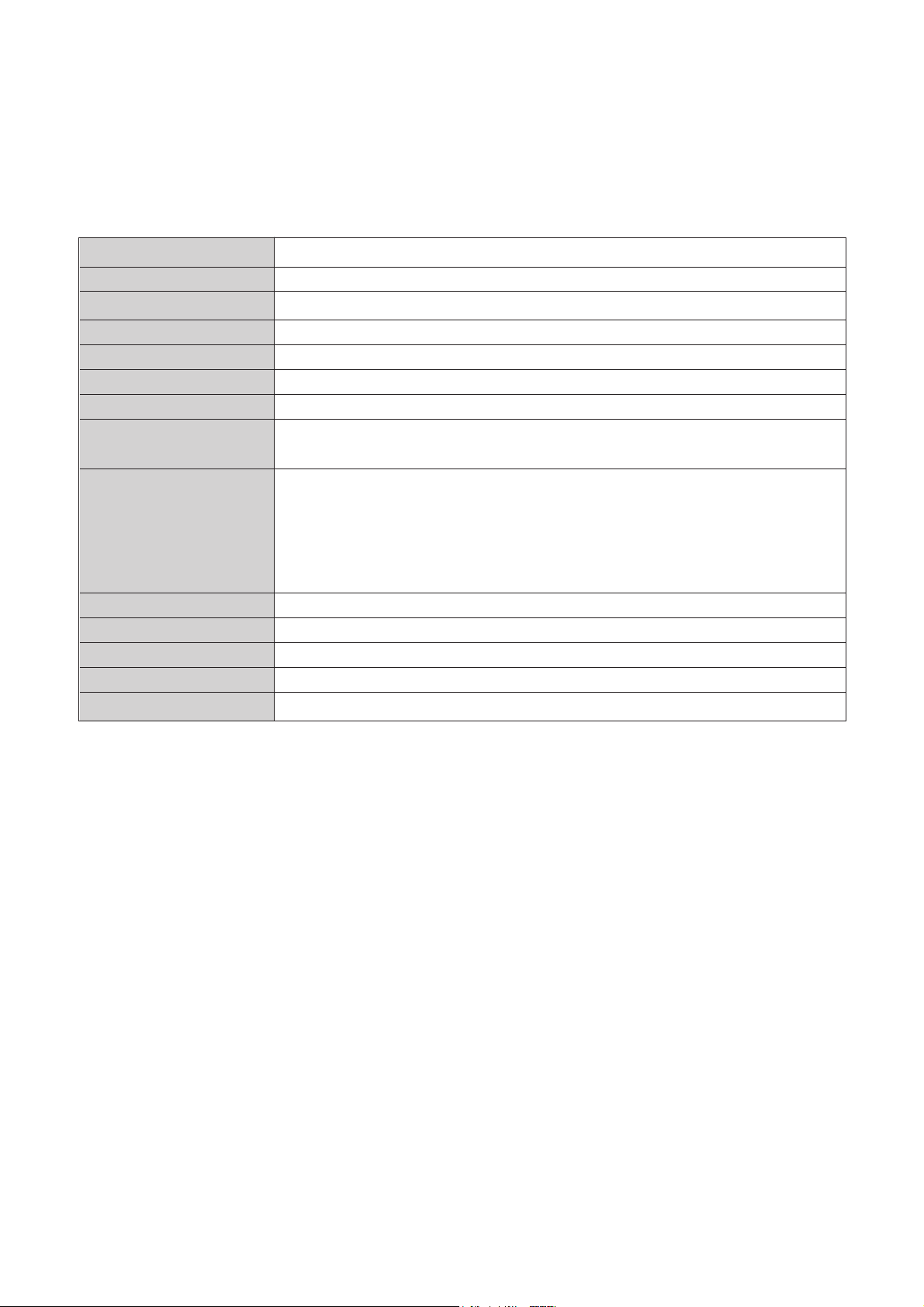
§ SPECIFICATIONS
CHASSIS CM-537
Receiving System NTSC/PAL-M/PAL-N
Main Voltage AC 100/220V, 50/60Hz
Power Consumption 60 Watts (14”) / 65 Watts (20”)
Sound Output 2.5W (16§ )
Antenna Impedance 75§ Unbalanced
Tuning System Frequency Synthesizer
Number of Memory 181 Channels
Channel
Reception Channel VHF TV LOW:CH2~6
HIGH:CH7~13
UHF TV CH14~CH69
CATV CH1~CH125
Remote Control Unit R-25C04
Screen Size 14” / 20”(diagonal)
Color Standard NTSC/PAL-N,M
Tuner Type Varactor Type with PLL
Aux. Terminal Input:Video,Audio
2
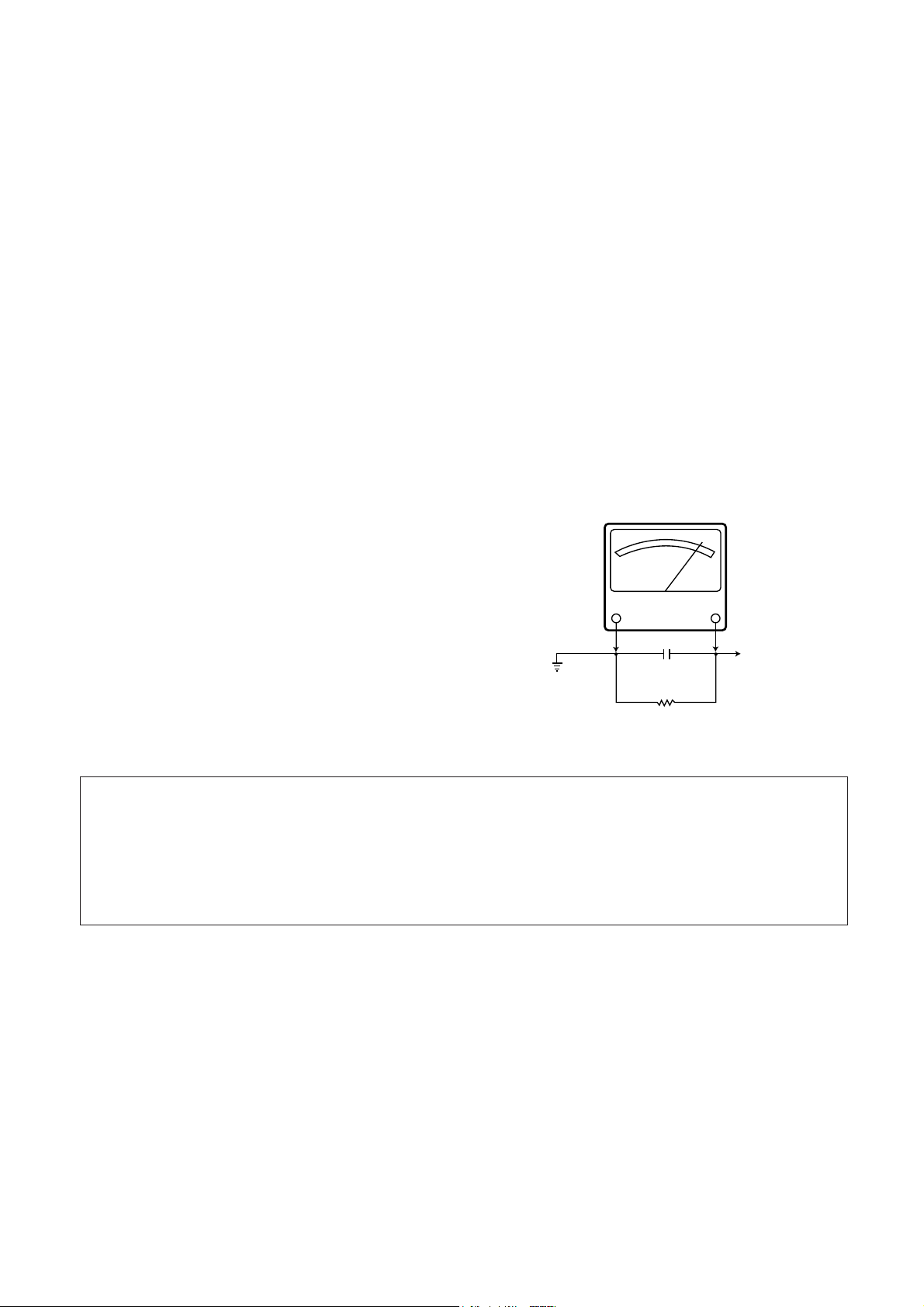
§ SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
10WATT
Good earth ground,
such as the water
pipe, conduit, etc.
1500 OHM
0.15MFD
AC VOLT METER
Place this probe
on each exposed
metallic part.
§ SAFETY PRECAUTION
WARNING: Service should not be attempted by anyone unfamiliar
with the necessary precaution on this receiver.
The following are the necessary precaution to be observed before
servicing.
1.Always discharge the picture tube anode to the CRT conductive
coating the picture tube. the picture tube is hightly evacuated
and if broken, glass fragments will be violently expelled. Use
shatterproofgoggles and keep picture tube away from the body
while handling.
2.When replacing chassis in the cabinet,always be certain that all
the protective devices are put back in place, such as;
nonmetallic control knobs, insulating covers, shields, isolation
resistor-capacitor network, etc
Plug the AC line cord directly into a AC outlet. Use an AC
voltmeter having 500 ohms per volt or more sensitivily in the
following manner.
Connect a 1500 ohm 10 watt resistor, paralleled by a 0.15 mfd,
AC type capacitor, between a known good earth ground( water
pipe, conduit etc) and the exposed metallic parts, one at a time.
Measure the AC voltage across the combination of 1500 ohm
resistor and 0.15 mfd capacitor.
Reverse the ac plug at the ac outlet and repeat AC voltage
measurements for each exposed metallic part. Voltage measured
must not exceed 0.3 volts RMS. This corresponds to 0.2 milliamp,
AC. Any value exceeding this limit constitutes a potential shock
hazard and must be corrected immediately.
3.Before retuning the set to the customer, always perform an AC
leakage current check on the exposed metallic parts of the
cabinet, such as antennas, terminals, screwheads, metal
overlays, control shafts etc, to be sure the set is safe to operate
without danger of electrical shock.
§ PRODUCT SAFETY NOTICE
Many electrical and mechanical parts in this chassis have special
safety-related characteristics. These characterictics are often
passed unnoticed by a visual inspection and the protection
afforded by them cannot necessarily be obtained by using
replacement components rated for higher volage, wattage,
etc.Replacement parts which have these special safety
characteristics are identified in this manual and its
§ SERVICE NOTES
1.When replacing parts or circuit boards, clamp the lead wires to
terminal before soldering.
2.When replacing a high wattage resistor(metal oxide film
resistor)in the circuit board keep the resistor min 1/2 inch away
from the circuit board.
supplements;electrical components having such features are
identified by shading on the schematic diagram and the parts list.
Before replacing any of these components, read the parts list in
this manual carefully. The use of substitute replacement parts
which do not have the same safety characteristics as specified in
the parts list may create shock, fire or other hazards.
3.Keep wires away form high voltage or high temperature
components.
3
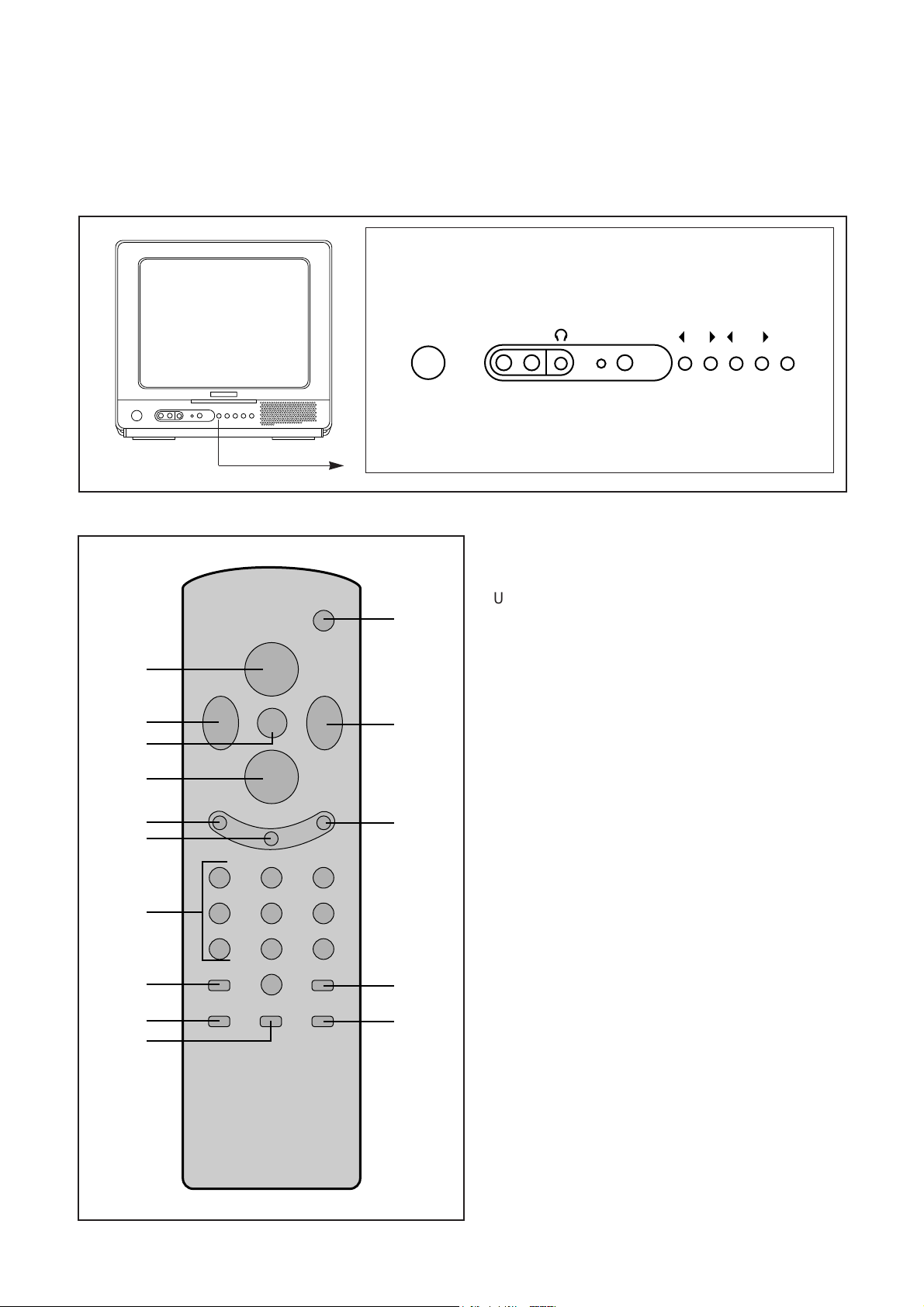
§ LOCATION OF CONTROLS
§ REMOTE CONTROL UNIT
POWER
2
3
VOL
¢‚
CH
¡ª
MENU
VOL
¢”
3
2
RECALL MUTE
5
CH
¡
ADD/ERA
6
123
8
9
456
789
SLEEP PREV.CH
0
TV/VIDEO AIR/CABLEAUTO.PICT
13
11
REMOTE CONTROLLER R-25C
MAIN POWER VIDEO AUDIO STAND-BY C H VOL MENU
1. POWER
Used to turn TV ON or OFF.
¡¡ªªCH¡¡
Â
Use these buttons to change channels on your
TV, or select items in the menu system.
¢¢‚‚
¢¢””
VOL
Use these buttons to change your TV’s
volume, to activate selections in the menu
system, or to change audio and video settings.
Use this button to turn TV’s menu system
on and off.
Press this button to display the channel
number
Use this button to add a channel to the TV’s
memory or erase the channel from memory.
Use to turn the TV’s sound on and off.
Use these buttons to change channels.
Use this button to program the TV to turn off
after a certain time.
Press this button to return to the previous
channel you were watching.
Press this button to return TV’s video
settings to their original level.
Use the button to set up your TV to receive
signals from an antenna (AIR) or a cable
system (CABLE)
Use the button to seiect TV or VIDEO mode.
1
3
7
10
12
2.
3.
4. MENU
5. RECALL
6. ADD/ERA
7. MUTE
8. 0-9
9. SLEEP
10. PREV.CH
11. AUTO.PICT.
12. AIR/CABLE
13. TV/VIDEO
5


§ GENERAL ALIGNMENT INSTRUCTIONS
THIS RECEIVER IS TRANSISTORIZED. SPECIAL CARE MUST BE TAKEN WHEN SERVICING. READ THE FOLLOWING
NOTES BEFORE ATTEMPTING ALIGNMENT.
• Alignment requires an exact procedure and should be undertaken only when necessary.
• The test equipment specified or its equivalent is required to perform the alignment properly.The use of a
equipment which does not meet these requirements may result in improper alignment.
• Correct matching of the equipment is essential. Failure to proper matching will result in responses which
cannot represent the true operation of the receiver.
• The AC Power line voltage should be kept within from 110 to 220 volts while alignment.
• Do not attempt to connect or disconnect any wire while the receiver is in operation.
Make sure the power cord is disconnected before replacing any parts in the receiver.
TEST EQUIPMENTS.
DC POWER SUPPLY ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ 0V~30V/500mA Class.
RF PATTERN GENERATOR¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ PHILIPS PM-5518
DIGITAL MULTI METER ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ FLUKE 8050A
WHITE BALANCE TESTER ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ¡ƒ NITSUKI 2840
6
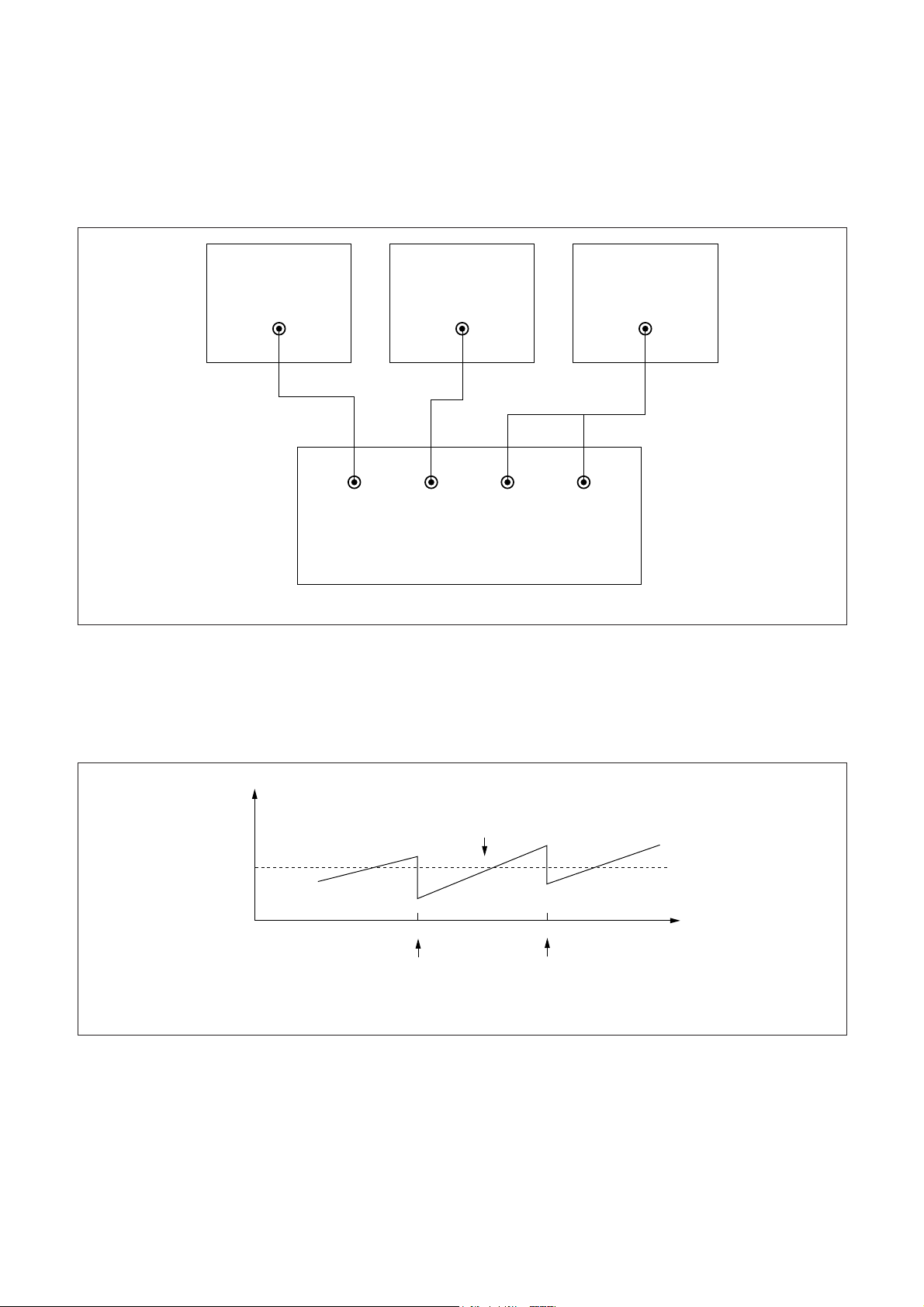
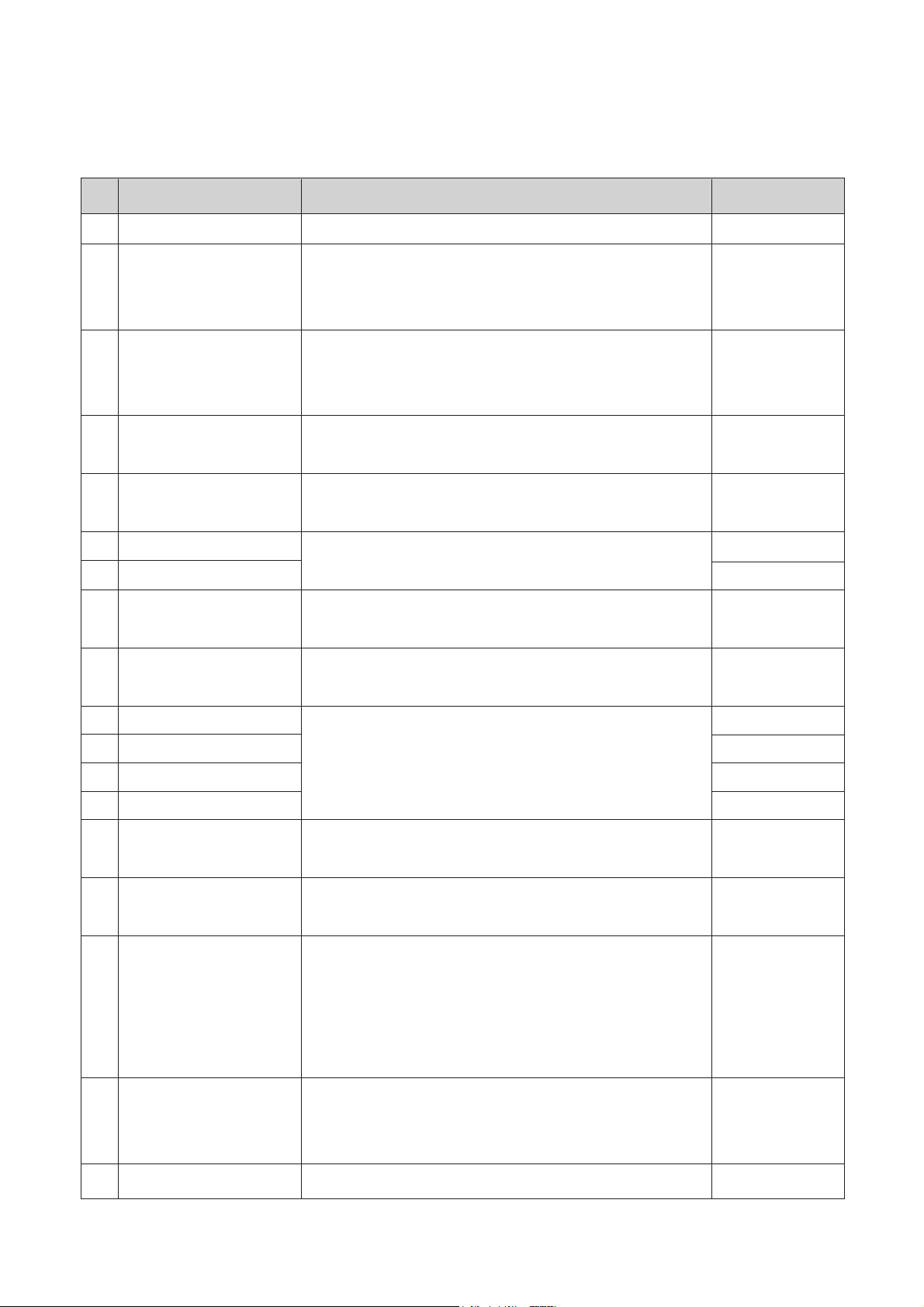
§ PIF VCO ADJUSTMENT
RF PATTERN
GENERATOR
PM-5518
DIGITAL MULTI
METER
DC POWER
SUPPLY
TP1
(L102)
TP3
(I501 #7)
TP4
(R701)
TP5
(I201)
[ADJUSTMENT SET]
(FIGURE 1)
[Measuring Instrument Connection]
1. Connect the 12V DC POWER SUPPLY to TP4 and TP5.
2. Set the frequency of RF PATTERN GENERATOR with COLOR BAR PATTERN signal to 45.75MHz,
and connect the RF output to TP1.
3. Connect the DIGITAL MULTI METER to TP3.
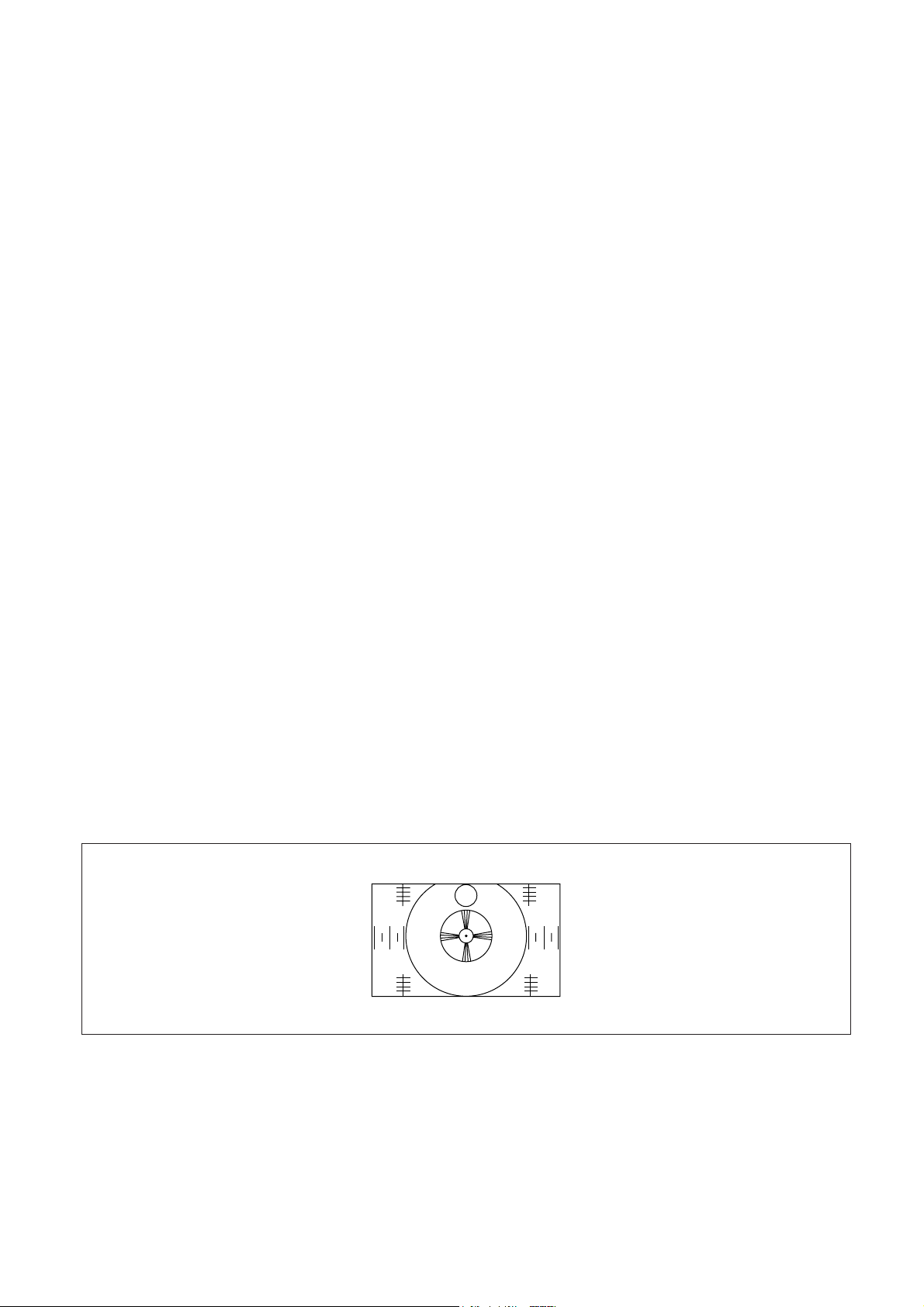
4. Adjust L506 so that the voltage of TP3 becomes 3.8V ± 0.1 Vdc within two DROP-POINTs (FIGURE 2).
V
adjust point
3.8V
core(L506) rotating
voltage drop points
(FIGURE 2)
§ SCREEN ADJUSTMENT
1. Push the 9D.SCR key of SERVICE REMOCON to obtain one line picture of screen.
2. Adjust the R,G,B Bias volume in order that the one line of screen may become white color.
7
3. Adjust the SCREEN VOLUME of FBT in order that the one line of screen disappear.
4
1
1
4
1
4
4
1
5 3 1
1 3 5
4. Push the 9D.SCR key of SERVICE REMOCON again.
§ FOCUS ADJUSTMENT
1. Receive the RETMA pattern.
2. Adjust the FOCUS volume of FBT to obtain the most clear picture.
§ RF AGC ADJUSTMENT
1. Input the COLOR BAR SIGNAL of 65dB to the ANTENNA INPUT of TV SET
2. Set the user control to AUTO PICTURE ON.
3. Turn completely the RF AGC volume R101 counter-clockwise and turn it clockwise until AGC voltage 6.0V is
obtained.
4. If there is the BEA T with strong signal(95 dB over), re-adjust it.
§ VERTICAL CENTER ADJUSTMENT
1. Receive the RETMA PATTERN.
3. Set the user control to AUTO PICTURE ON.
4. Adjust the R302 so that the horizontal center of the PATTERN may meet with the mechanical center of CRT.
§ HORIZONTAL CENTER ADJUSTMENT
1.Receive the RETMA PATTERN.
2.Set the user control to AUTO PICTURE ON.
3. Adjust the R501 in order that the circle may put in the center position of the screen.
(FIGURE 3) VERTICAL and HORIZONTAL center Adjustmemt
8
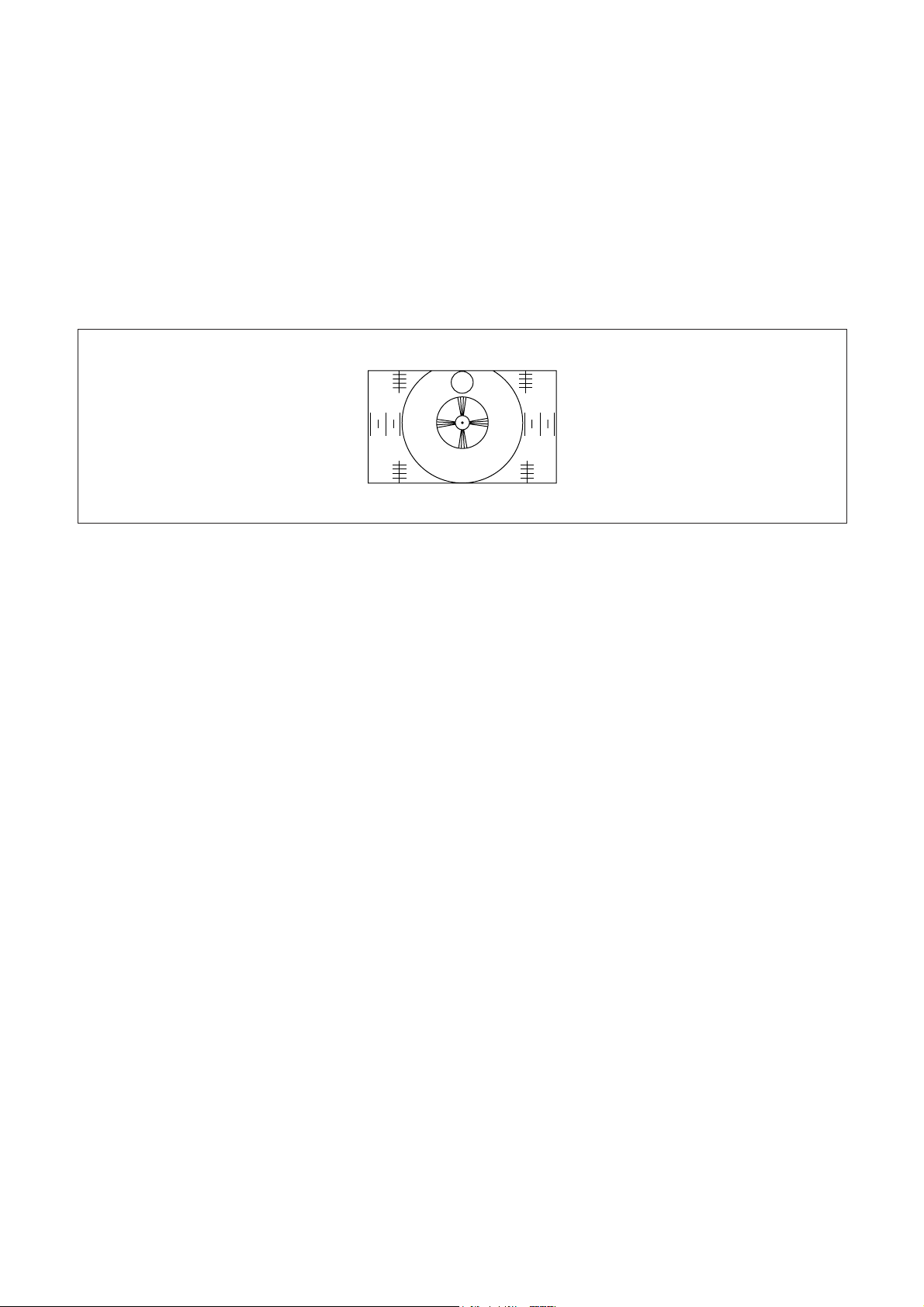
§ VERTICAL HIGHT ADJUSTMENT
4
1
1
4
1
4
4
1
5 3 1
1 3 5
1. Receive the RETMA PATTERN.
2. Set the user control to AUTO PICTURE ON.
3. Adjust the R301 so that the CENTER of circumference of big circle may meet with the upper and lower sides
of screen.
§ WHITE BALANCE ADJUSTMENT
1.Execute HEAT RUN of the TV SET over 30 minutes with SERVICE REMOCON.
2.Connect the signal output of WHITE BALANCE TESTER (Nitsuki 2840) to the ANTENNA (or VIDEO IN) input
of the TV SET. Stick and fix the SENSOR to the center position of CRT.
3. Adjust the R,G,B BIAS and G,B DRIVE VOLUME in order that R,G,B of the HIGH and LOW BEAM may meet
with the CENTER LED of each measuring instrument.
4. At this time, the memorized coordinates of the WHITE BALANCE TESTER, unless otherwise specified, use
following coordinates and color temperature (PAL:9600K 3~5ftL 265¡¿295 , NTSC: 10850K 3~5ftL 274¡¿289)
§ SUB-BRIGHT ADJUSTMENT
1. Receive the RETMA PATTERN.
2. Set the user control to AUTO PICTURE ON.
3. Turn the SUB-BRIGHT CONTROL VOLUME (R540) and adjust the gradation pattern as shown.
4. The status that the border between 15% and 20% can be distinguished.
9
§ DESCRIPTION OF CIRCUIT OPERATION
§ FEATURE OF THE CM-537
•VIDEO, CHROMA, DEFLECTION in one-chip IC.
•Automatic switching of 3-SYSTEM(NTSC, PAL-M, PAL-N).
•FS(Frequency Synthesizer ) Tunning System.
•Function of LAST MEMORY against the electric failure (E2PROM:24LC028).
•Separation of PIF and SIF(SAW filter :DSW1013P)
•Minimization of Ringing by applying Ringing-less FBT(2001SPND)
•Auto-compensation of the vertical height level against the frequency change of AC power .
•OVER CURRENT PROTECTION Circuit.
•Elimination Circuit of POP NOISE.
§ OPERATION CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH BLOCK
A.¥-COM BLOCK
1. ¥-COM(DMC42C522N, I701) PIN DESCRIPTION/OPERATION
PIN NAME/(ABBREV) FUNCTION REMARK
1 NTSC-M 3-SYSTEM SWITCHING CMOS
(RCO/PWM14) PUSH PULL
2 PAL-M 3-SYSTEM SWITCHING CMOS
(R83) PUSH PULL
3 AC POWER DOWN MAIN POWER DOWN Detect input:active LOW CMOS
(R03/INT3) PUSH PULL
4 SD INPUT SYNC. signal INPUT H: signal detect
(RO2/INT2) L: no signal
5 REMOTE CONTROL REMOTE CONTROL signal input
INPUT REMOTE CONTROL IC : M50560-388GP/M50560-001
(R01/INT1TIM1) (CUSTOM CODE: 14H)
6 KEY RETURN IN 0 ·KEY MATRIX COLUMN 0
(R00/INT0/TIM0) ·HOLD MODE : WAKE-UP using INT1 PUSH PULL
7 Xin SYSTEM CLOCK : 4.1943 MHz
8 Xout
9 RESET SYSTEM RESET
10 KEY RETURN IN 1 KEY MATRIX COLUMN 1
(R82)
11 Vss GND
12 KEY RETURN IN 2 KEY MATRIX COLUMN 2
(R81)
13 KEY SCAN OUT 0 · KEY MATRIX ROW 0
& TIMER · Active HIGH when ON TIMER is set.
(R80)
10
PIN NAME/(ABBREV) FUNCTION REMARK
14 Vdd +5V
15 KEY SCAN OUT 1 · KEY MATRIX COLUMN 1
& CLOCK · TUNER CLOCK & EEPROM CLOCK
(R23)
16 KEY SCAN OUT 2 · KEY MATRIX COLUMN 2
& DATA · TUNER DATA & EEPROM DATA
(R22)
17 ENABLE · TUNER ENABLE CMOS
(R20/PCL) PUSH PULL
18 AFC · AFC voltage from MAIN IC(LA7688) : DC 0 ~Vdd A/D CONV
(R21/AFC IN) CENTER : 2.5V 4BIT
19 OSC in
20 OSC out
21 /H-Sync · SYNC. signal for OSD H. position.
(HD) · 0~5V PULSE/Active LOW INPUT
· OSD CLOCK
22 /V-Sync · SYNC. signal for OSD V. position.
(VD) · 0~5V PULSE/Active LOW INPUT
23 R(R60/OSD R) · Active “HIGH” OUTPUT
24 G(R61/OSD G) · Dot pattern OF OSD
25 B(OSD B)
26 OSD Ys
27 50/60 IN · 3-SYSTEM SWITCHING CMOS
(R13) · 50Hz: LOW(PAL-N) , 60Hz: HIGH (PAL-M, NTSC-M)
28 /C.IDENT IN · 3-SYSTEM SWITCHING CMOS
(R12) · “LOW” (INPUT) signal detected with NO-COLOR.
29 OCP IN · OVER CURRENT PROTECTION INPUT: active HIGH CMOS
(R11) · TV POWER turns OFF when HIGH signal detected for
10ms.
· The u-COM observe this pin immediately after
POWER ON.
30 SCREEN OUT · HIGH signal OUTPUT indicating SCREEN adjustment. CMOS
(R10) · Goes HIGH when REMOCON KEY;9DH detected.
· Toggled when 9DH detected.
31 VIDEO MUTE OUT · Active LOW, Normal : HIGH CMOS
11
PIN NAME/(ABBREV) FUNCTION REMARK
32 POWER · Active HIGH
· LOW state at initial condition (RESET). except
· Toggle LOW/HIGH when POWER KEY input is detected. HEAT-RUN mode
(LOW ¡ POWER OFF / HIGH ¡ POWER ON)
· Automatically turns to LOW when SLEEP TIMER
(count down) counts “0”.
· Automatically turns to LOW when the OFF TIMER is set
and the clock(TV) indicates OFF-TIME.
· Automatically turns to HIGH when the ON TIMER is set
and the clock (TV) indicates ON-TIME.
33 TV/VIDEO · TV: HIGH / VIDEO: LOW CMOS
(R31) · VIDEO MUTE(#31) is activated for a moment PUSH PULL
when this pin is togglled.
(VIDEO MUTE MODE needs OPTION diodes)
34 SOUND MUTE · Active HIGH, Normal : LOW CMOS
(R30) · HIGH out ¡ MUTE. PUSH PULL
· Following action make the TV set to be MUTE
for a moment.
1. Channel selecting
direct selecting, sequential channel selecting,
AUTO PROGRAM
2. POWER ON/OFF
· When MUTE KEY is detected following changes
are occurred for a moment.
1. VOLUME level ¡ LOW
2. SOUND MUTE(#34) ¡ HIGH
3. Color of OSD : GREEN ¡ RED
35 VOLUME · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT CMOS
(PWM82) · 64 STEP (2bit/step) VOLUME CONTROL
· Following action make the VOLUME level to “0”
(MUTE) for a moment.
1. Channel selecting
2. TV/VIDEO selecting
36 BRIGHTNESS · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT
(PWM81) · 64 step (2bit/step) BRIGHTNESS CONTROL
37 CONTRAST · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT
(PWM80) · 64 step (2bit/step) CONTRAST CONTROL
38 SHARPNESS · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT
(RC3/PWM63) · 64 step (2bit/step) SHARPNESS CONTROL
39 COLOR · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT
(RC2/PWM62) · 64 step (2bit/step) COLOR CONTROL
40 TINT · Active HIGH, PWM OUTPUT
(RC3/PWM63) · 64 step (2bit/step) TINT CONTROL
2.Function of LAST MEMORY
Always holds a previous DATA by saving the signal of the data,clock,enable on the E2PROM.
12
33
10
14
8
1
µ-COM
(I701)
TV(H)
/VI(L)
SIF
Filter
I501
LA7688
VIDEO
DET
VIDEO
SWITCH
9V
R,G,B OUT
Q503
EXT.VIDEO
(JV01/JV02)
B. VIDEO BLOCK
17
21
41
1
2
27
28
I701
µ-COM
I501
LA7685J
NTSC-M
50/60
COLOR
/KILLER
PAL-M
VCO
X502
X503
Q506
9V
R766
R774
Q502
Q705
X501
7.6V
9V
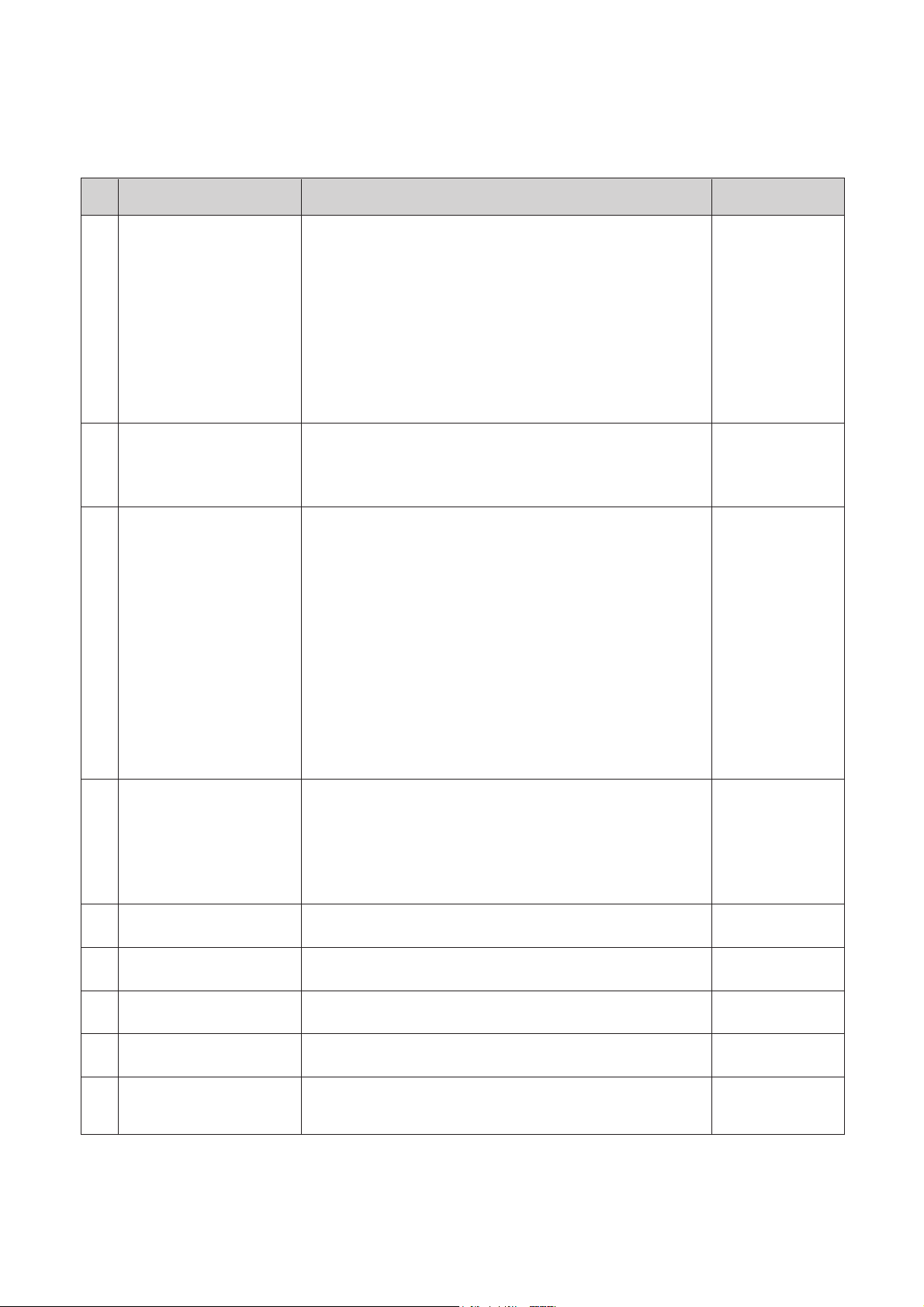
1. TV/VIDEO SWITCHING
1) SWITCHING BLOCK DIAGRAM
2) CIRCUIT OPERATION
•After going out to the #8 of I501, the detected signals go into the #10 of I501through 4.5MHz BPF(Band Pass
Filter, Z502) : TV SIGNAL.
•The external VIDEO signals from JV01(or JV02) go into the #14 of I501 : VIDEO SIGNAL.
•Output pulse from the #33 of the ¥-COM(TV:HIGH, VIDEO:LOW) go into #1 of I501 through a buffer(Q504 and
Q507).
•According to the input pulse of the #1, TV/VIDEO switching circuit let out the video signals to the RGB generator
block inside I501.
2. OUTLINE AND OPERATION OF 3-SYSTEM AUTO SWITCHING
1) SWITCHING BLOCK DIAGRAM
2) CIRCUIT OPERATION
•If 50[Hz] detected. #21 of the I501 goes down to LOW level. This out goes into the Q506 (and #27 of the I701),
and then X501 oscillates (#1 and #2 of the I701 are deactivated.).
13
¢¡PAL-N system
•If 60[Hz] detected, #21 of the I501 goes up to HIGH level and the system operates as PAL-M or NTSC-M.
¤ In the case that Base voltage of Q705 is LOW, the voltage driven from R766 and R774 is applied to the #28
of the I701.
¤ŁIn the case that Base voltage of Q705 is HIGH, according to the voltage change of the #28 of the I701, the
comparator in the I701 switch over the system.
(PAL-M¢¡NTSC-M, NTSC-M¢¡PAL-M)
•HIGH signal of the #1 of I701 makes X502 oscillates.(NTSC-M)
•HIGH signal of the #2 of I701 makes X503 oscillates.(PAL-M)
3) FREQUENCY CHARACTERISTICS OF EACH SYSTEM
COLOR VHF UHF
SCANNING
NUMBER
LINE
FREQUENCY
(Fh) (Fsc)
FIELD
FREQUENCY
CHROMINANCE
SUB CARRIER
NTSC M M 525line 15,734[Hz] 60[Hz] 3.579545[MHz]
PAL M M 525line 15,734[Hz] 60[Hz] 3.575611[MHz]
PAL M 625line 15,625[Hz] 50[Hz] 3.582056[MHz]
C. SOUND BLOCK
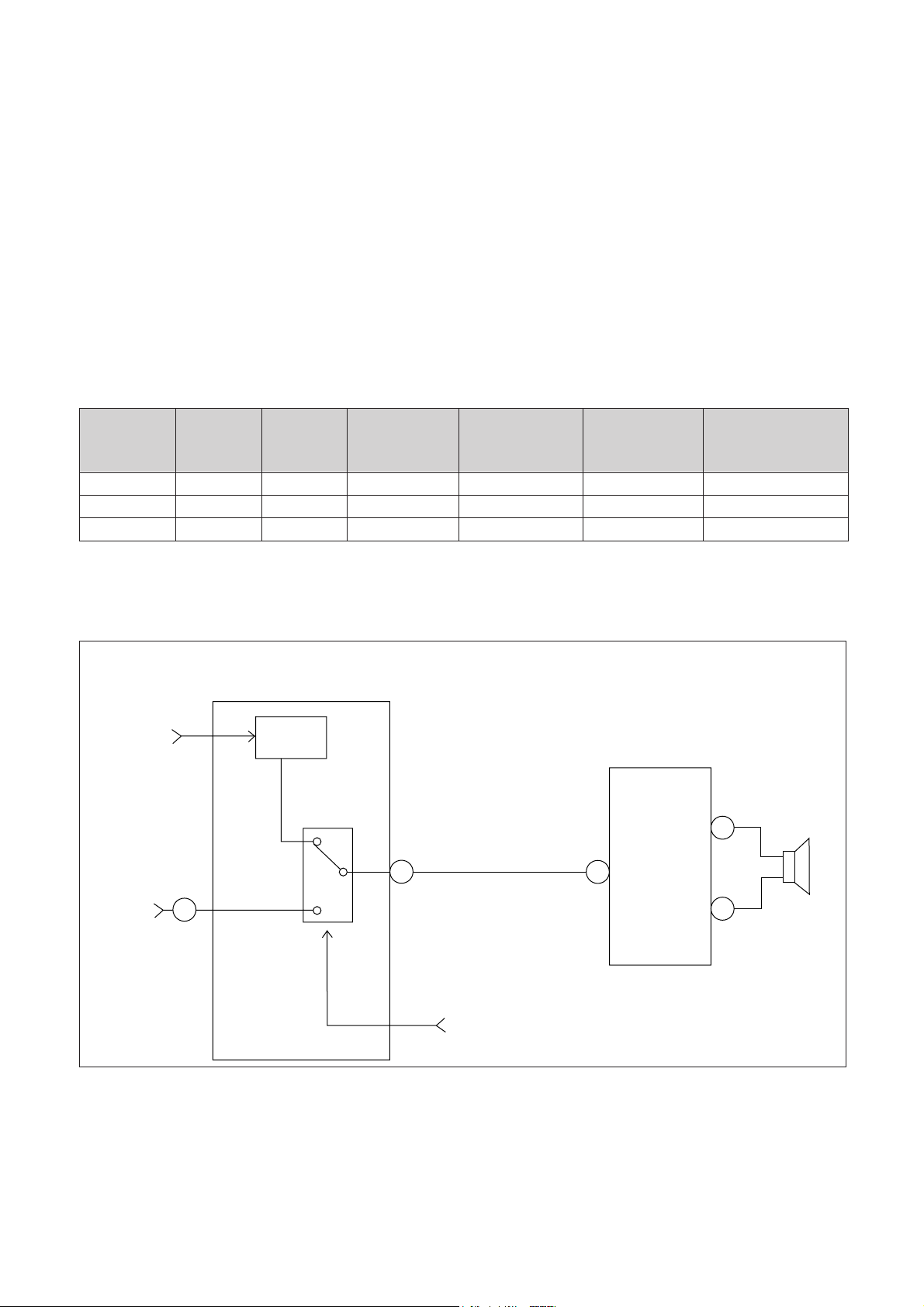
1. SOUND BLOCK DIAGRAM
I501
LA7688
FM
DET
AUDIO
SWITCH
51
I601
TDA7056A
6
3
8
EXT.
AUDIO
(JV01/JV02)
SIF
12
SP
from the µ-COM(#33)
2. EXPLANATION OF OPERATION
1) The TV audio signal is detected and goes into the audio switch in I501.
2) The external audio signal from JV01(or JV02) goes into the #12 of I501.
3) The audio switch in I501 alternates audio signals according to the TV/VIDEO control input from the I701.
4) The selected audio signal (#51 of I501) go into the #3 of I601.
14
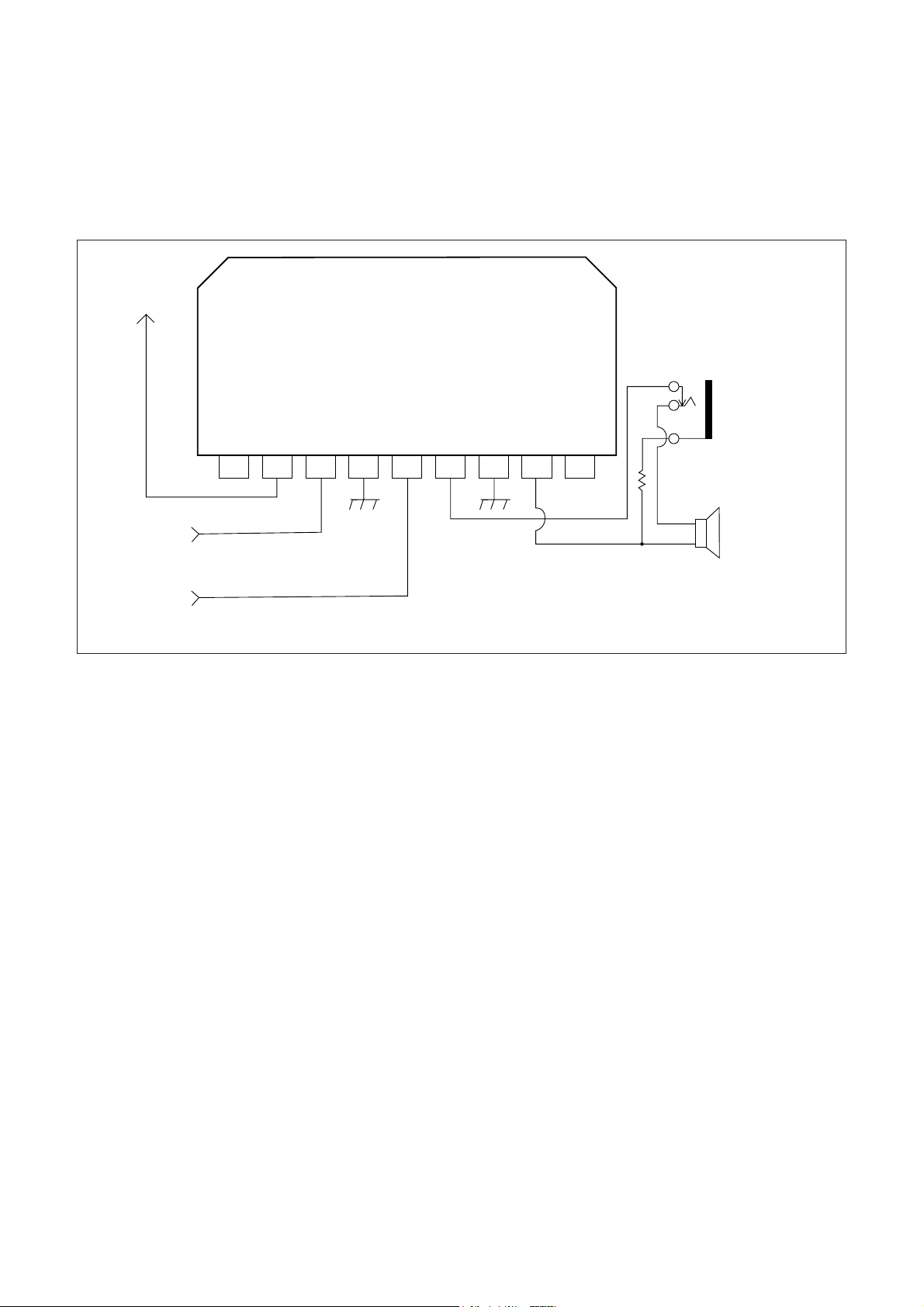
3.SOUND AMP IC
1 2 4 63 5 7 8 9
33V
From
#51
of I501
From
#35
of I701
N.C VP IN
S.GND
Volume OUT(+) P.GND OUT(–) N.C
TDA7056A
Earphone
Jack
SPEAKER
16 ohm
3W
SP01
1) BLOCK DIAGRAM
2) EXPLAINATION OF THE OPERATION
•The audio signal from the I501 goes into the #3 of the I601.
•I601 amplifies this audio signal correspond to the volume control signal from I701.
•The amplified audio signal from the #6 and #8 drives the speaker (s).
¡ AUDIO MUTE function is activated by the I701(SOFTWARE MUTE).
15
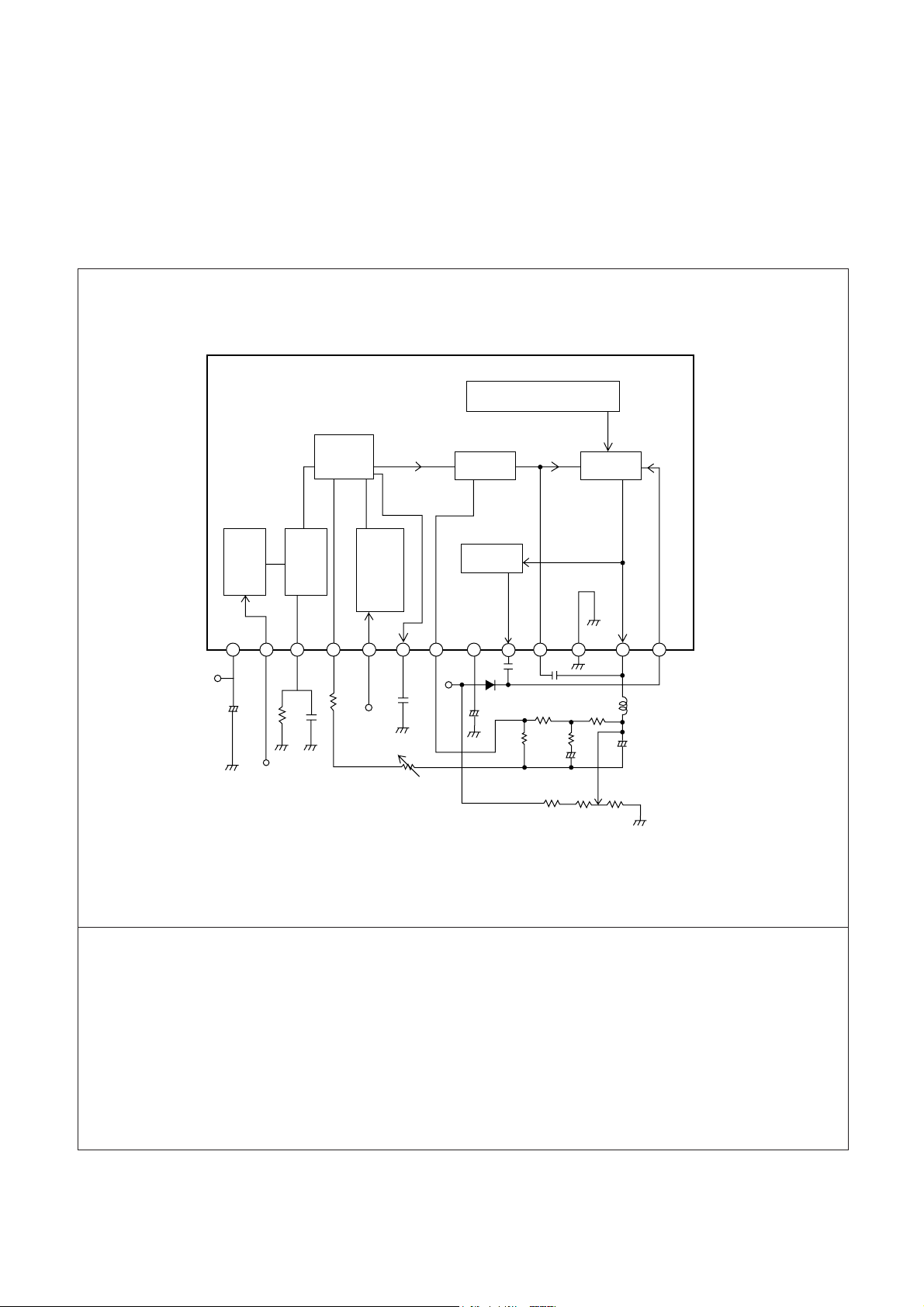
D. DEFLECTION BLOCK
Ramp
Generator
Vert. Drive
Vert. Out
THERMAL PROTECTION
Vert.
Trig.
Input
One
Shot
Multi
Vert.
Size
Control
S.W
Pump UP
+B1
9V
+
VERT.
TR1G.
1N
50/60
Hz
Vert. Height.
+B7
25V
+
+
+
10~20P
vert
center
DY
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
9
10 11 12 13
LA7837
This block can be separated into two parts, VERTICAL and HORIZONTAL.
Only the VERTICAL circuit is explained here, comprehensibly.
1. BLOCK DIAGRAM OF VERTICAL IC
# 1: B+ (12V)
# 2: VERTICAL TRIGGER INPUT
# 3: TIME CONSTANT & MUTE
# 4: VERTICAL HEIGHT CONTROL
# 5: 50/60[Hz] VERTICAL SIZE CONTROL SIGNAL
INPUT
# 6: RAMP WAVEFORM GENERATION
# 7: AC/DC FEEDBACK INPUT TO VERTICAL
# 8: POWER SUPPLY (VBB): 25V
# 9:PUMP UP OUTPUT
#10:OSC BLOCKING
#11:GND
#12:VERTICAL OUTPUT
#13:POWER SUPPLY FOR VERTICAL OUTPUT
16
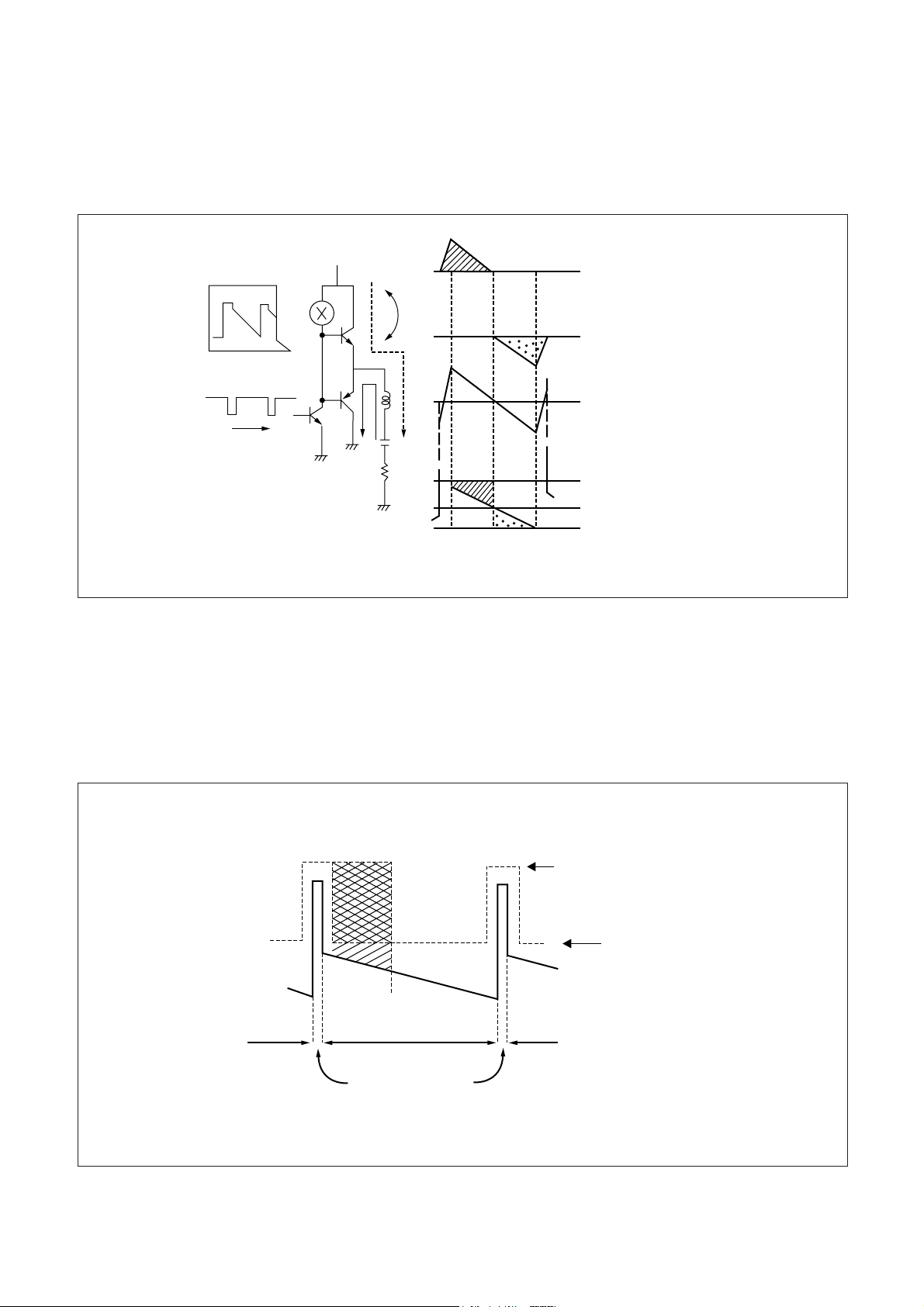
2. OPERATION OF VERTICAL
GND
(b) Q3 Collector
Current i1
GND
(c) Q4 Collector
Current i2
VCC (e)Emitter Voltage
1/2 VCC
GND
(d) Current of
Deflection coil
i1 + i2
GND
(a)
VCC
Q3
Q4
Q2
i2
i1
VCC1
VERTICAL OUTPUT WAVE
1) In the picture above, (a) shows a fixed Vcc, and (+)(-)current of deflection coil is (d) whichk is sum of (b) and
(c), and (e) shows EMITTER voltage of Q3,Q4.
2) Collector loss of Q3 is i1 Vce1 which is the product of obligue region of (b),(e).Collector loss of Q4 is product
of dot region of (c),(e).
3) To reduce collector loss of Q3,if bring down the voltage during scanning time as shown in the picture (b) ,
Vce1 become lower so that the loss diminish.
Diminish if Q3 Collector Loss
OUTPUT VOLTAGE
17
Blanking Time
Voltage
Sanning Time
Voltage
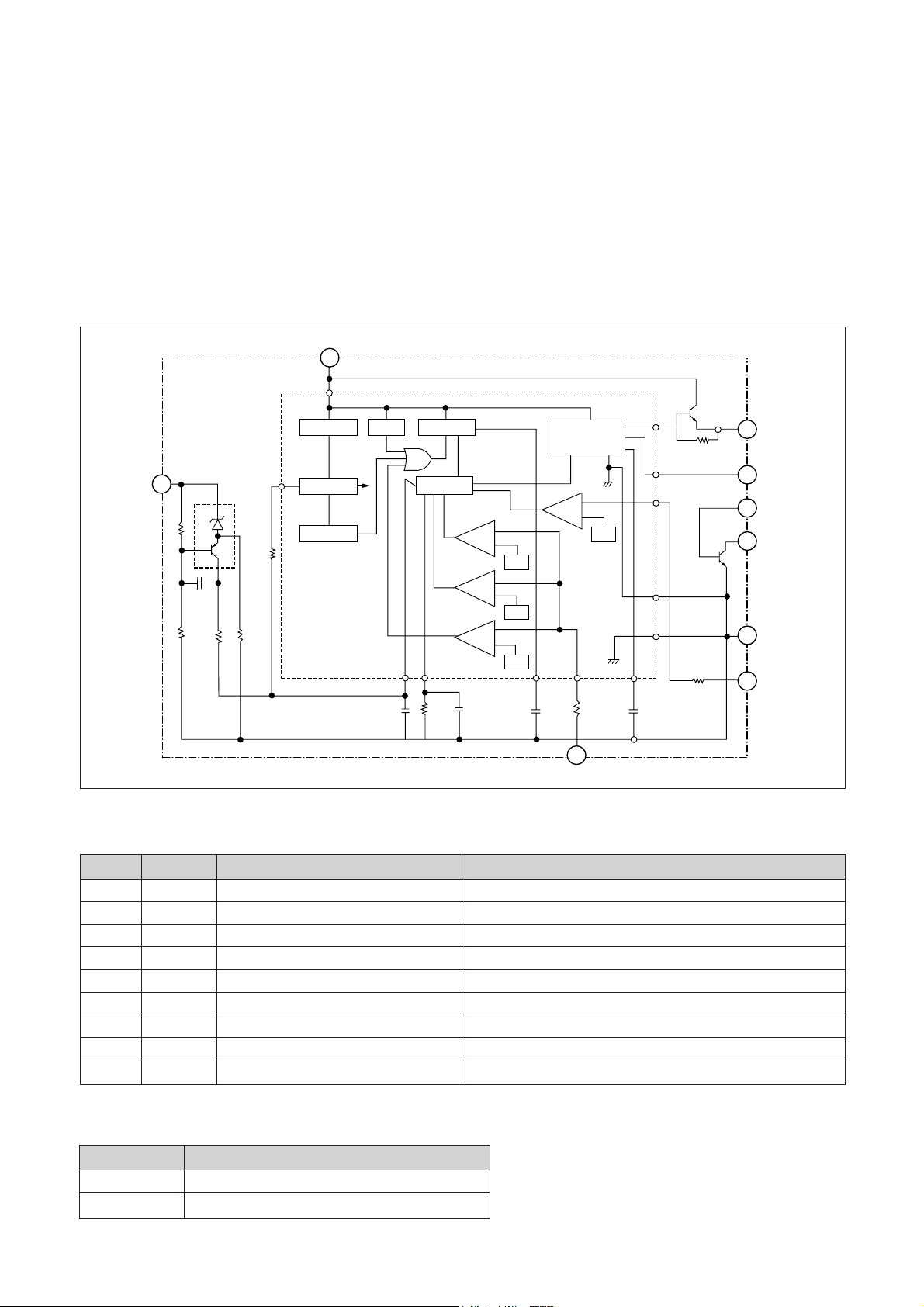
E. POWER BLOCK
INH-1
REF
OCP
REF
INH-2
REF
INH-3
REF
9
7
6
8
4
3
1
2
5
START UP
PRE REG OSC
T.S.D
OVP LATCH
V IN
INH
PROPOTIONAL
DRIVE
Tr2
R6
PNP +2Di
R7 R8 R9
Tr1
R4
R4
R3
R1
C1 C4 R5C2 C3R2
DIRVE
SINK
B
C
GND
OCP
SENS
This chassis designed for free voltage(AC 100V ~ AC 220V ) power. power block contains power IC, SMPS
transformer and several passive components.
The power IC STR-S5707 has power transistor. oscillator circuit, voltage comparator circuit, thermal protection
circuit, OCP(over current protection) circuit insiude.
1.STR-S5707 BLOCK DIAGRAM
2.PIN DESCRIPTION
PIN NO SYMBOL NAME FUNCTION
1 C COLLECTOR POWER TRANSISTOR COLLECTOR
2 GND GROUND GROUND(POWER TRANSISTOR EMITTER)
3 B BASE POWER TRANSISTOR BASE
4 SINK SINK BASE CURRENT (Is) INPUT
5 OCP OVER CURRENT PROTECTION OVERCURRENT SENSING SIGNAL INPUT
6 INH INHIBIT / LATCH SYNC, OFF TIME/LATCH CIRCUIT CONTROL INPUT
7 F/B(SENS) FEED BACK(SENSING) INPUT CONSTANT VOLTAGE CONTROL SIGNAL INPUT
8 DRIVE DRIVE BASE DRIVE CURRENT (Id) OUTPUT
9 Vin Vin SUPPLY VOLTAGR FOR CONTROL CIRCUIT
3. OTHER FUNCTION
Symbol Function
OVP Built-in Overvoltage Protection Circuit
TSD Built-in Thermal Shutdown Circuit
18
Rs(R803,R804)
Ln
L1
9
V
IN
2
GND
C806
D804
AC
IN
Fig .1 Start-up Circuit
1
Fig .2 V
IN Terminal Voltage Circuit Current VIN
IN
20mA
200µA
4.9V 7.5V8V
Vin
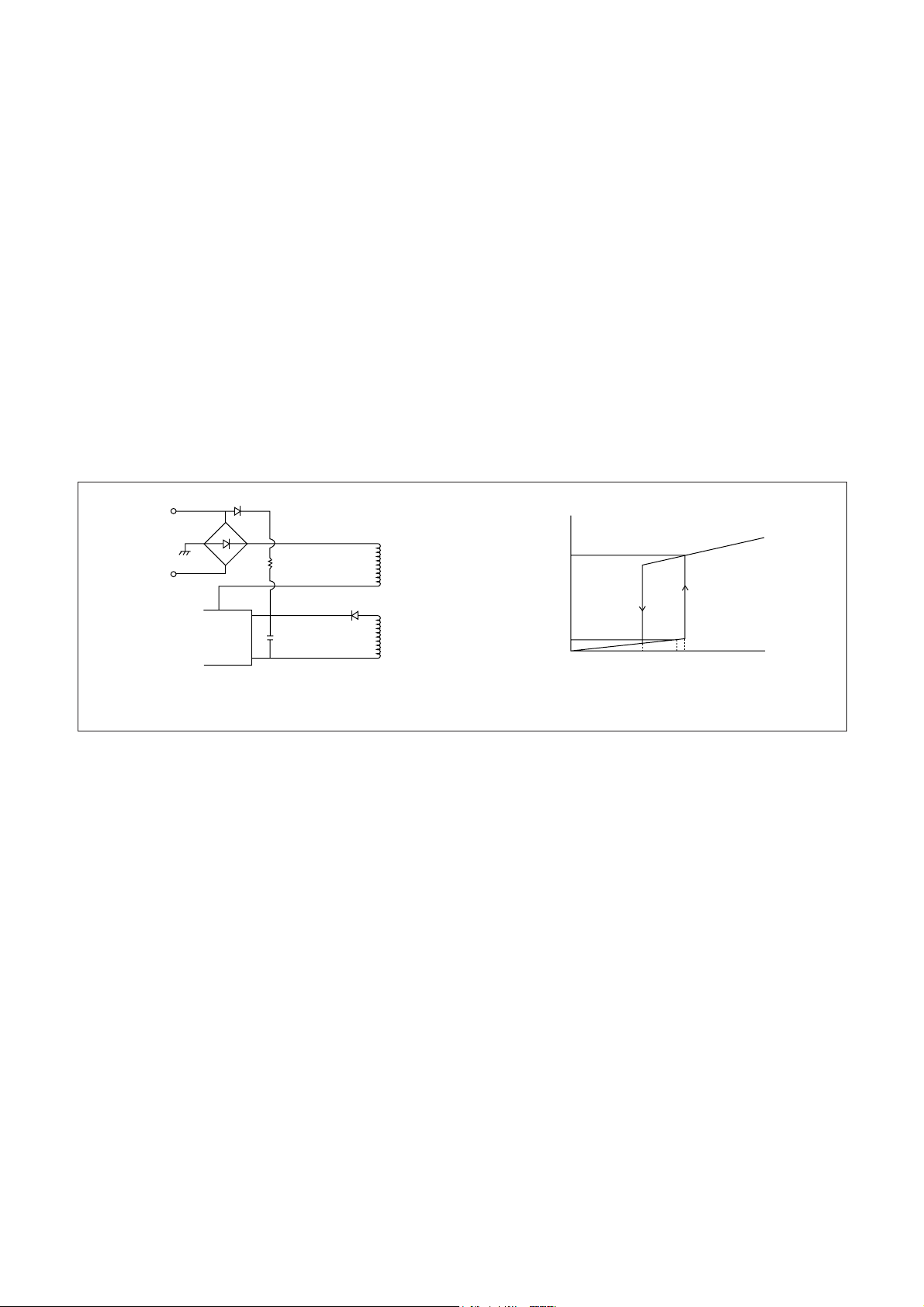
4. EXPLAINATION OF CIRCUIT OPERATION
1) VIN terminal, start-up circuit
A start-up circuit is to start and stop a operation of a control IC by detecting a voltage appearing at a VIN
terminal (pin-9). At start up of a power supply, when a voltage at the VIN terminal reaches to 8V by charging up
C806 by the function of a start-up resistor, Rs, a control circuit starts operating by the function of the start-up
circuit. As shown in Fig. 2, since a circuit current is suppressed 200§¸ maximum ( at V
IN = 7.5V ) until the
control circuit starts its operation.
After the control circuit starts its operation, power source is obtained by smoothing voltage appearing at L1
winding. Once the control circuit starts operating, as its voltage doesn’t reach the fixed voltage at once, V
IN
terminal voltage starts dropping. However, as a shut-down voltage is set low (at 4.9V), while VIN terminal
voltage reaches a shutdown voltage, L1 winding voltage reaches the fixed voltage earlier so that the control
circuit can continue on operating.
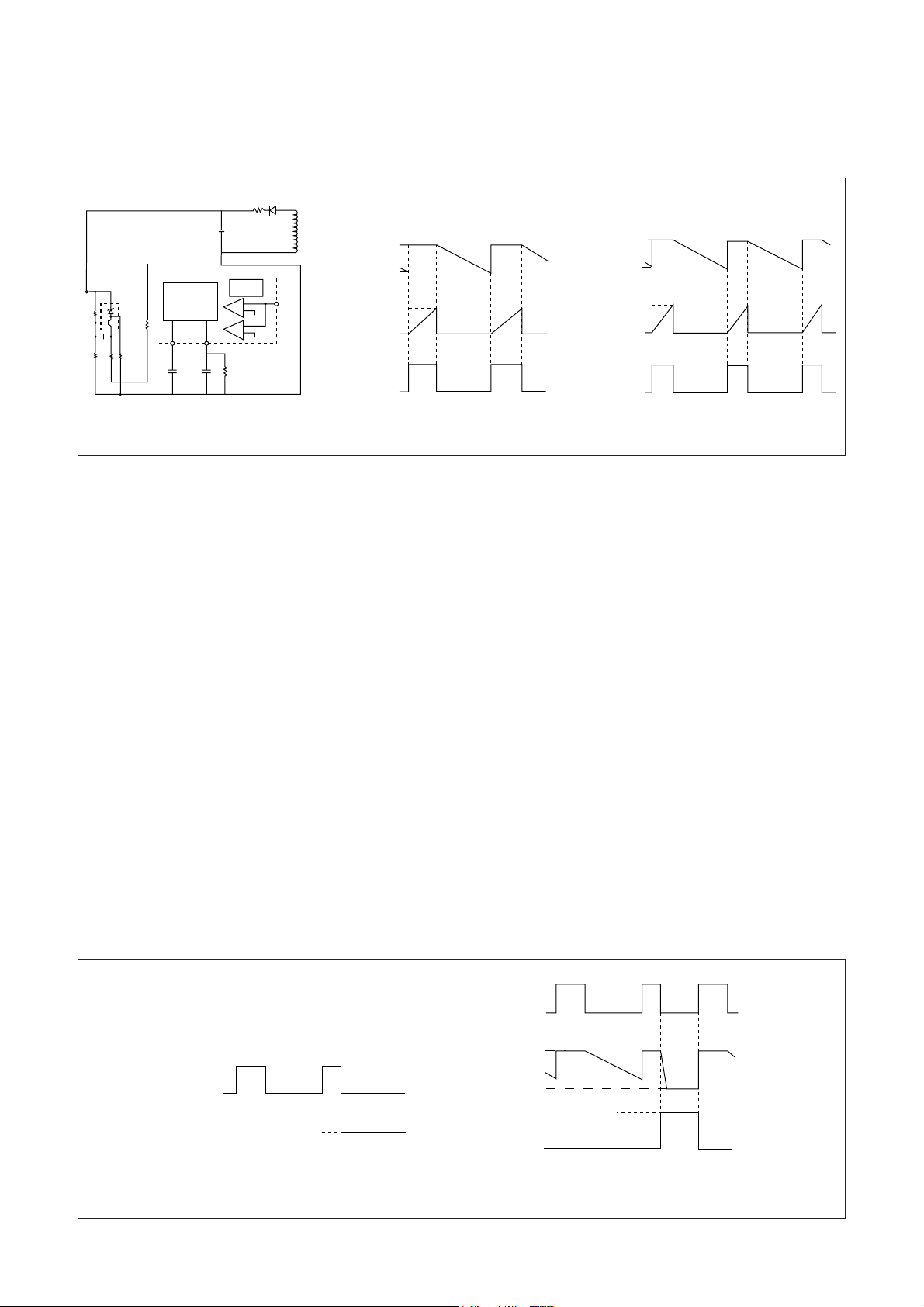
2) Osciliator, F/B terminal voltage (Pin #7)
A oscillator generates pulse signals which turns a power transistor on and off by making use of charge and
discharge of CI and C2 incorporated in the Hybrid IC.
Constant voltage control of a switch-mode power supply is performed by changing both ON- time and OFFtime except when the load is light (ex. remote control stand-by mode of TVs).
Fig. 4 shows how the oscillator works when the Hybrid IC independently operates (with no F/B nor INH
signals). When the power thransistor is on, C2 Is charged to the set voltage (approx 2.3V at Ta =25°C). On the
other hand, C1 starts charging up through R1 from almost 0V and the voltage across C1 increases in
accordance with the inclination determined by the product of C1 and R1. When the voltage across C1 reaches
approx. 0.75V (Tc=25°C). the output from the oscillator is reversed and the power transistor turns off. At the
same time C1 is quickly discharged by the function of a internal circuit of the oscillator and the voltage across it
decreases to almost 0V. When the power transistor turns off, C2 starts discharging through R2 and the voltage
across C2 decreases in accordance with the inclination derermined by the product of C2 decreases to about
1V. the output from the oscillator is reversed again and the transistor consequently turns on. The power
transistor continues turning on and off by repeating the above-mentioned operations.
19
As the circuit in Fig. 3 shows, the ON-time is controlled by changing a current charged by C1, which is as the
R6
R7
PIN +2Di
Reg
Drive
Cfrcu1
R7 R8 R9
R1
R2
C1 C2
+
–
+
–
OSD
L1
COMP 1
COMP 2
VTH1
VTH2
INH
Tre
Fig 3 Oscillator Circuit Configulation
C2 ACROSS
Voltage
C1 ACROSS
Voltage
Osc.
Output
PTR
Fig 4 Operation Waveforms of Oscillator without F/B nor
INH Signal
1V
2.3V
0V
0V ON
OFF
0.75V
Fig 5 Operation Waveforms of Oscillator with F/B Signal
C2 ACROSS
Voltage
C1 ACROSS
Voltage
Osc.
Output
PTR
1V
2.3V
0V
0V
0.75V
result of that the detection winding (L1),which detects a change of voltage in a secondary side, connected to the
sensing terminal (Pin No. 7) has the current in accordance with an output signal from an output voltage
detection circuit (an error amplifier) built in. As an AC input voltage to the power supply gets the higher and a
load current the smaller, the current flowing to the SENS terminal gets the larger, and the ON-time gets the
shorter.
3) Function of INH terminal (Pin #6), control of OFF-time
Signal to the INH terminal is used as inputs to COMP.1 and COMP.2 inside of the control IC. A threshold voltage
of COMP.1 VTH1 is set at 0.75V (Ta=25°C) and an input signal to a drive circuit becomes almost 0V (the power
transistor is in OFF mode) when a voltage at the INH terminal reaches the VTH1. As long as the INH terminal
voltage does not get lower than VTH1. the power transistor sustains OFF mode. On the other hand, a threshold
voltage of COMP.2 VTH2, is set at 1.5V (Ta=25°C).When the INH terminnal voltage reaches VTH2, an output from
COMP.2 reverses and, as a result, C2 starts firing and a voltage across C2 drops to almost 0V in a moment. As
the result of this immediate discharge of C2, the OFF-time of the oscillator which has been determined by the
product of C2 and R2 (⁄ 55 ¥ sec) can be quicker up to approx. 2¥sec. As long as the INH terminal voltage
does not get lower than V
TH2, AVoltage across C2 stays at almost 0V and a output from the oscillator keeps the
power transistor being on. The relation between the INH terminal voltage and the function of the oscillator
described above is shown in Fig. 6 and Fig. 7
Osc.
Output
PTR
Fig .6 Operation Waveforms of INH Terminal(VTH1)
INH
Ter. Voltage
ON
OFF
TH1
V
20
Osc.
Output
PTR
C2 ACROSS
Voltage
Fig .7 Operation Waveforms of INH Terminal(VTH2)
2.3V
0V
INH
Ter. Voltage.
ON OFF
V
TH2
9
VIN
6
INH
2
GND
C808
R807 L1
D805
D803
S1
+
Fig 8 Operation Circuit
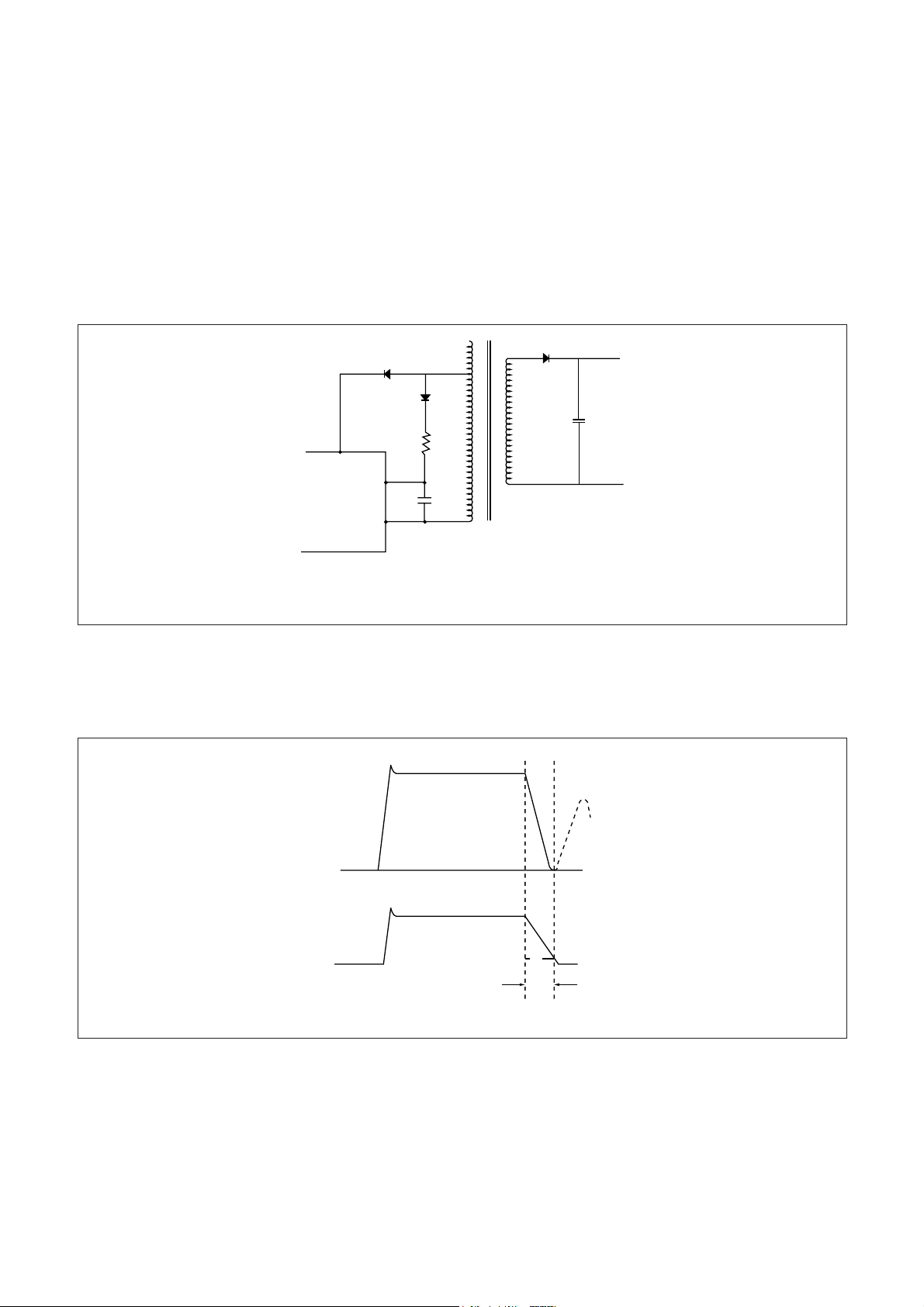
4) Quasi-resonant operation
0V
0V
Fig 9 Waveforms of VCE and VINH at Quasi-resonant Operation
VCE
INH Terminal
Voltage
tr
V
THI
By inputting a voltage signal which is synchronized with the energy discharge time of a secondary winding of a
transformer to the. INH terminal, quasi-resonant operation can be achieved. As shown in Fig. 8 , the voltage of
L1 winding which is synchronized. with the energy discharge time of a secondary winding. S1. shall be input to
the INH terminal through D805 and R807. Since V
TH2 is set at 1.5V typical, a voltage at the INH terminal. VINH,
shall be set at 2V.
Fig. 9 shows waveforms of VCE, Ic and VINH of the transistor, voltage across C808 in the oscillator as well as an
output from the oscillator when operating in quasi-resonant mode.
when the power transistor turns off and a voltage higher than VTH2 is applied to the INH terminal, C808
immediately discharges and then starts charging again. Even after the discharge of energy of a secendary
winding is completed, VINH does not immediately increases. When it gets lower than VTH2 after the time,tr, which
is determined by the production of internal impedance of the IC and CINH, has past, the transistor turns on.
21
 Loading...
Loading...