PRELIMINARY
Frequency Generator for Integrated Core Logi c
Features
• Maximized EMI suppression using Cypress’s Spread
Spectrum technology
• Low jitter and tightly controlled clock skew
• Highly integrated device provi ding clocks requ ired for
CPU, core logic, and SDRAM
• Two copies of CPU clock
• Nine copies of SDRAM clock
• Seven copies of PCI clock
• One copy of synchronous APIC clock
• Three copies of 66-MHz outputs
• Two copies of 48-MHz outputs
• One copy of selectable 24- or 48-MHz clock
• One copy of double strength 14.31818-MHz reference
clock
• Power-down control
• SMBus interface for turning off unused clocks
Key Specifications
CPU, SDRAM Outputs Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter: .............250 ps
APIC, 48-MHz, 3V66, PCI Outputs
Cycle-to-Cycle Jitter:............................... ....................500 ps
CPU, 3V66 Output Skew:...........................................175 ps
SDRAM, APIC, 48-MHz Output Skew:....................... 250 ps
PCI Output Skew:....................................................... 500 ps
CPU to SDRAM Skew (@ 133 MHz) .......................± 0.5 ns
CPU to SDRAM Skew (@ 100 MHz).................4.5 to 5.5 ns
CPU to 3V66 Skew (@ 66 MHz)........................7.0 to 8.0 ns
3V66 to PCI Skew (3V66 lead).......................... 1.5 to 3.5 ns
PCI to APIC Skew.....................................................± 0.5 ns
Block Diagram
PWR_DWN#
SDATA
SCLK
(FS0:4*)
X1
XTAL
X2
OSC
SMBus
Logic
PLL 1
PLL2
PLL REF FREQ
Divider,
Delay,
and
Phase
Control
Logic
/2
VDDQ3
REF2X/FS3*
VDDQ2
CPU0:1
2
APIC
VDDQ3
3V66_0:2
2
PCI0/FS0*
PCI1/FS1*
PCI2/FS2*
PCI3:6
5
SDRAM0:8
9
VDDQ3
48MHz_0
48MHz_1/FS 4*
SI0/24_48#MHz*
W219B
with 133-MHz FSB
Table 1. Frequency Selections
FS4 FS3 FS2 FS1 FS0 CPU SDRAM 3V66 PCI APIC SS
0 0 0 0 0 75.3 113.0 75.3 37.6 18.8 OFF
0 0 0 0 1 95.0 95.0 63.3 31.6 15.8 –0.6%
0 0 0 1 0 129.0 129.0 86.0 43.0 21.5 OFF
0 0 0 1 1 150.0 113.0 75.3 37.6 18.8 OFF
0 0 1 0 0 150.0 150.0 75.0 37.5 18.7 OFF
0 0 1 0 1 110.0 110.0 73.0 36.6 18.3 OFF
0 0 1 1 0 140.0 140.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 0 1 1 1 144.0 108.0 72.0 36.0 18.0 OFF
0 1 0 0 0 68.3 102.5 68.3 34.1 17.0 OFF
0 1 0 0 1 105.0 105.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 1 0 1 0 138.0 138.0 69.0 34.5 17.0 OFF
0 1 0 1 1 140.0 105.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 1 1 0 0 66.8 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 0 1 100.2 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 1 0 133.6 133.6 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 1 1 133.6 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
1 0 0 0 0 157.3 118.0 78.6 39.3 19.6 OFF
1 0 0 0 1 160.0 120.0 80.0 40.0 20.0 OFF
1 0 0 1 0 146.6 110.0 73.3 36.6 18.3 OFF
1 0 0 1 1 122.0 91.5 61.0 30.5 15.2 –0.6%
1 0 1 0 0 127.0 127.0 84.6 42.3 21.1 OFF
1 0 1 0 1 122.0 122.0 81.3 40.6 20.3 –0.6%
1 0 1 1 0 117.0 117.0 78.0 39.0 19.5 OFF
1 0 1 1 1 114.0 114.0 76.0 38.0 19.0 OFF
1 1 0 0 0 80.0 120.0 80.0 40.0 20.0 OFF
1 1 0 0 1 78.0 117.0 78.0 39.0 19.5 OFF
1 1 0 1 0 166.0 124.5 83.0 41.5 20.7 OFF
1 1 0 1 1 133.6 133.6 89.0 44.5 22.2 OFF
1 1 1 0 0 66.6 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 0 1 100.0 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 1 0 133.3 133.3 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 1 1 133.3 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
Pin Configuration
REF2x/FS3*
VDDQ3
VDDQ3
3V66_0
3V66_1
3V66_2
FS0*/PCI0
FS1*/PCI1
FS2*/PCI2
VDDQ3
48MHz_0
FS4*/48MHz_1
SI0/24_48#MHz*
VDDQ3
Note:
1. Internal 250K pull-down or pull up resistors present on inputs
marked with * or ^ respectively. Design should not rely solely on
internal pull-up or pull down resistor to set I/O pins HIGH or LOW
respectively.
GND
GND
GND
PCI3
PCI4
PCI5
PCI6
GND
1
2
X1
3
X2
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
[1]
VDDQ2
48
47
APIC
46
VDDQ2
45
CPU0
44
CPU1
43
GND
42
VDDQ3
41
SDRAM0
40
SDRAM1
SDRAM2
39
W219B
38
37
36
35
34
33
32
31
30
29
28
27
26
25
GND
SDRAM3
SDRAM4
SDRAM5
VDDQ3
SDRAM6
SDRAM7
SDRAM8
GND
PWR_DWN#
SCLK
VDDQ3
GND
SDATA
^
Cypress Semiconductor Corporation • 3901 North First Street • San Jose • CA 95134 • 408-943-2600
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Revised December 21,2002
PRELIMINARY
I
W219B
Pin Definitions
Pin Name Pin No.
REF2x/FS3 1 I/O Reference Clock with 2x Drive/Frequency Select 3: 3.3V 14.3 18-MHz c lock out-
X1 3 I Crystal Input: This pin has dual functions. It can be used as an external 14.318-
X2 4 I Crystal Output: An input connection for an external 14.318-MHz crystal connec-
PCI0/FS0 11 I/O PCI Clock 0/Frequency Selection 0 : 3.3V 33-MHz PCI clock outputs. This pin also
PCI1/FS1 12 I/O PCI Clock 1/Frequency Selection 1 : 3.3V 33-MHz PCI clock outputs. This pin also
PCI2/FS2 13 I/O PCI Clock 2/Frequency Selection 2 : 3.3V 33-MHz PCI clock outputs. This pin also
PCI3:6 15, 16, 18, 19 O PCI Clock 3 through 6: 3.3V 33-MHz PCI clock outputs. PCI0:6 can be individually
3V66_0:2 7, 8, 9 O 66-MHz Clock Output: 3.3V output clocks. The operating frequency is controlled
48MHz_0 21 O 48-MHz Clock Output: 3.3V fixed 48-MHz, non-spread spectrum clock output.
48MHz_1/
FS4
SIO/
24_48#MHz
PWR_DWN# 29 I Power Down Control: LVTTL-compatible input that places the device in power-
CPU0:1 45, 44 O CPU Clock Outputs: Clock outputs for the host bu s inter face. O utput fre quenc ies
SDRAM0:8 41, 40, 39, 37,
APIC 47 O Synchronous APIC Clock Outputs: Clock outputs ru nning syn chrono us wi th the
SDATA 25 I/O Data pin for SMBus circuitry.
SCLK 28 I Clock pin for SMBus circuitry.
VDDQ3 2, 6, 17, 24, 27,
VDDQ2 46, 48 P 2.5V Power Connection: Power supply for IOAPIC and CPU o utput buffers. Con-
GND 5, 10, 14, 20, 26,
22 I/O 48-MHz Clock Output/Frequency Selection 4: 3.3V fixed 48-MHz, non-spread
23 I/O Clock Output for Super I/O: This is the input clock for a Super I/O (SIO) device.
36, 35, 33, 32,
31
34, 42
30, 38, 43,
Pin
Type Pin Description
put. This pin also serves as the select strap to determine device ope rating frequency
as described in Table 1.
MHz crystal connection or as an external reference frequency input.
tion. If using an external reference, this pin must be left unconnected.
serves as the s elect st rap to det ermine d evice operating frequenc y as de scribed in
Table 1.
serves as the s elect st rap to det ermine d evice operating frequenc y as de scribed in
Table 1.
serves as the s elect st rap to det ermine d evice operating frequenc y as de scribed in
Table 1.
turned off via SMBus interface.
by FS0:4 (see Table 1).
spectrum clock ou tput. This pin al so serv es as the select strap t o determi ne devi ce
operating frequency as described in Table 1.
During power-up, it als o serves as a selection s trap. If it is sampled HIGH, the output
frequency for SIO is 24 MHz. If the input is sampled LOW, the output is 48 MHz.
down mode when held LOW.
depending on the configuration of FS0:4. Voltage swing is set by VDDQ2.
O SDRAM Clock Outputs: 3.3V outputs for SDRAM. The operating frequency is
controlled by FS0:4 (see Table 1).
PCI clock outputs. Voltage swing set by VDDQ2.
P 3.3V Power Con nection: Power supply for SDRAM output buffers, PCI outpu t buff-
ers, reference output buffers and 48-MHz output buffers. Connect to 3.3V.
nect to 2.5V or 3.3V.
G Ground Connections: Connect all ground pins to the common system ground
plane.
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 2 of 15
PRELIMINARY
W219B
Power-on
Reset
Timer
Output Three-state
Figure 1. Input Logic Selection Through Resistor Load Option
Overview
The W219B is a highl y i nteg rate d frequency timing gene rator,
supplying all the requi red clock sou rces for an Intel® architec-
ture platform using graphics integrated core logic.
Functional Description
I/O Pin Operation
Pin # 1, 1 1, 12, 13, 22, and 23 are dual-purpose l/O pins . Upon
power-up the pin acts as a logic input. An external 10-kΩ strapping resistor should be used. Figure 1 shows a suggested
method for strapping resistor conn ec tio ns .
After 2 ms, the pin becomes an output. Assuming the power
supply has stabilized by then, the specified output frequency
Output
Buffer
Hold
Output
Low
QD
Data
Latch
W219B
Output Strapping Resistor
Series Termination Resistor
Clock Load
10k
Ω
is delivered on the pins. If the power supply has not yet
reached full value, o utput frequen cy initia lly may be below target but will increase to target once supply voltage has stabilized. In either case, a short output clock cycle may be produced from the CPU clock outputs when the outputs are
enabled.
Offsets Among Clock Signal Groups
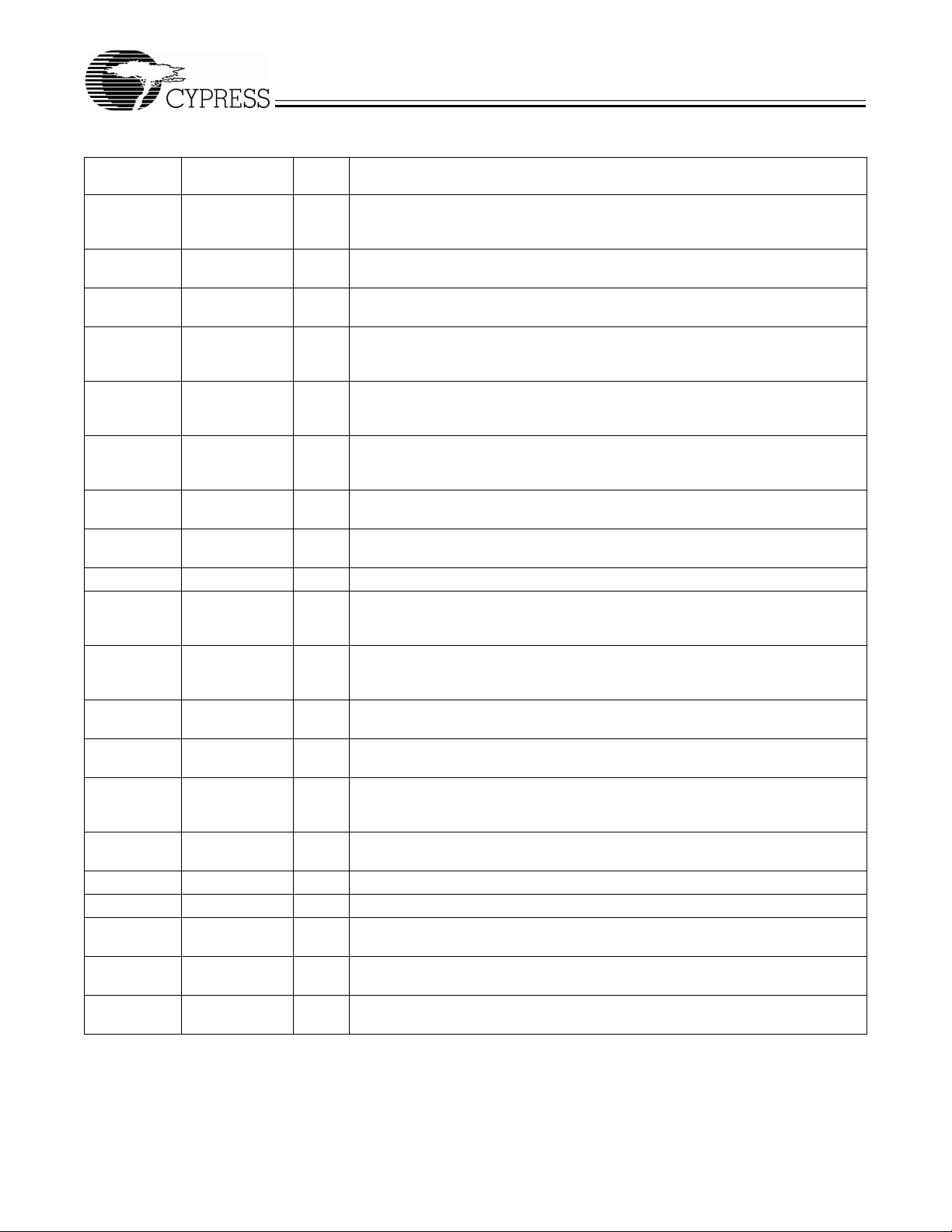
Figure 2 and Figure 3 represent the phase relationship amon g
the different groups of clo ck outputs from W219B when it is
providing a 66-MHz CPU clock and a 100-MHz CPU clock,
respectively. It should be noted that when CPU clock is operating at 100 MHz, CPU clock output is 180 degrees out of
phase with SDRAM clock outputs.
CPU 66-MHz
SDRAM 100-MHz
3V66 66-MHz
PCI 33-MHz
REF 14.318-MHz
USB 48-MHz
APIC
0 ns
CPU 66 Period
SDRAM 100 Period
Hub-PC
Figure 2. Group Offset Waveforms (66.8 CPU Clock, 100.2 SDRAM Clock)
40 ns30 ns20 ns10 ns
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 3 of 15
CPU 100-MHz
SDRAM 100-MHz
3V66 66-MH z
PCI 33-MHz
REF 14.318-MHz
USB 48-MHz
APIC
0 ns
PRELIMINARY
40 ns30 ns20 ns10 ns
CPU 100 Period
SDRAM 100 Period
Hub-PC
W219B
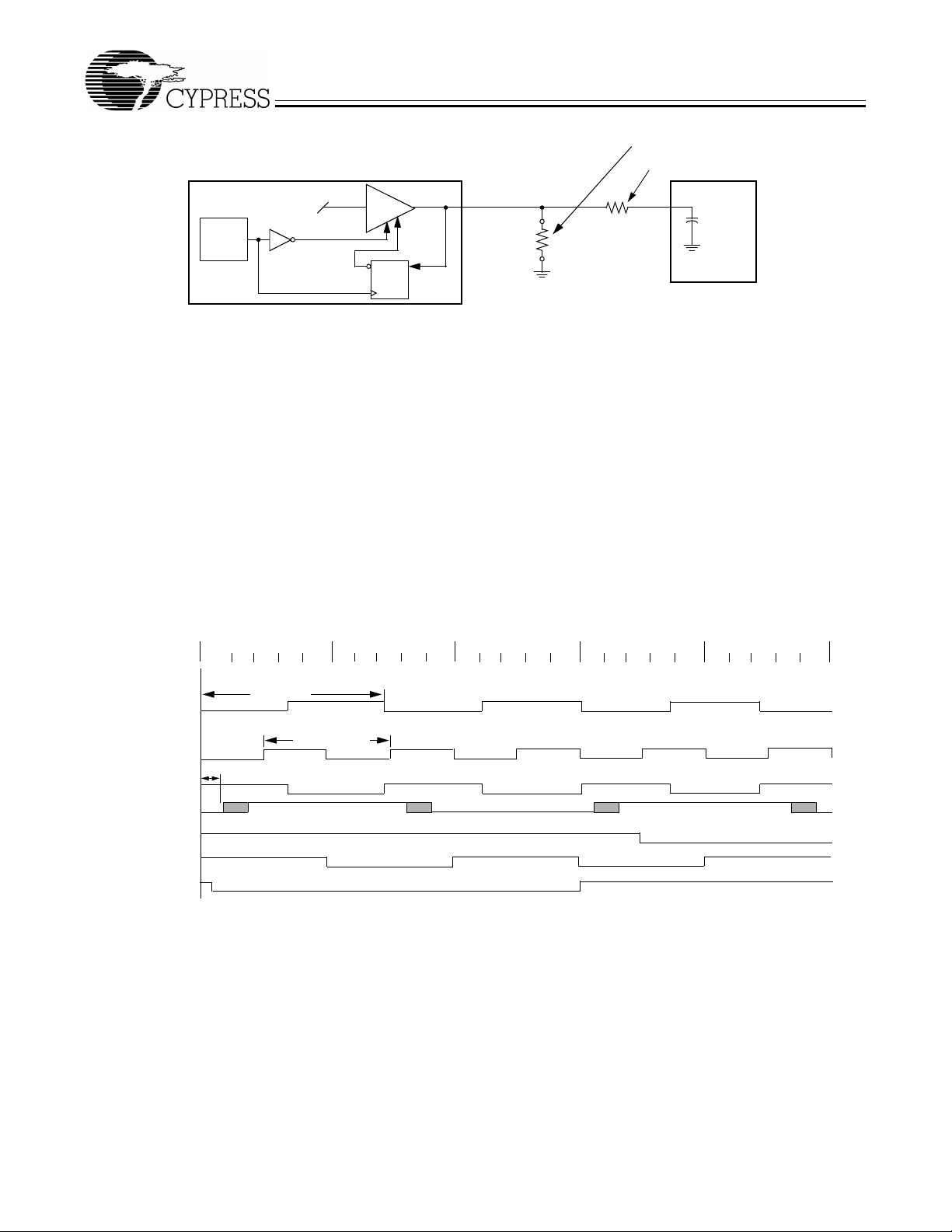
Figure 3. Group Offset Waveforms (100.2 CPU Clock, 100.2 SDRAM Clock)
Power-Down Control
W219B provides one PWRDWN # s ignal to pla ce the d evic e in low-p ower mo de. In low -powe r mode , the PLLs a re turne d of f an d
all clock outputs are driven LOW.
0 ns 25 ns 50 ns 75 ns
Center
1 2
VCO Internal
CPU 100MHz
3V66 66MHz
APIC 33MHz
PCI 33MHz
PwrDwn
SDRAM 100MHz
REF 14.318MHz
USB 48MHz
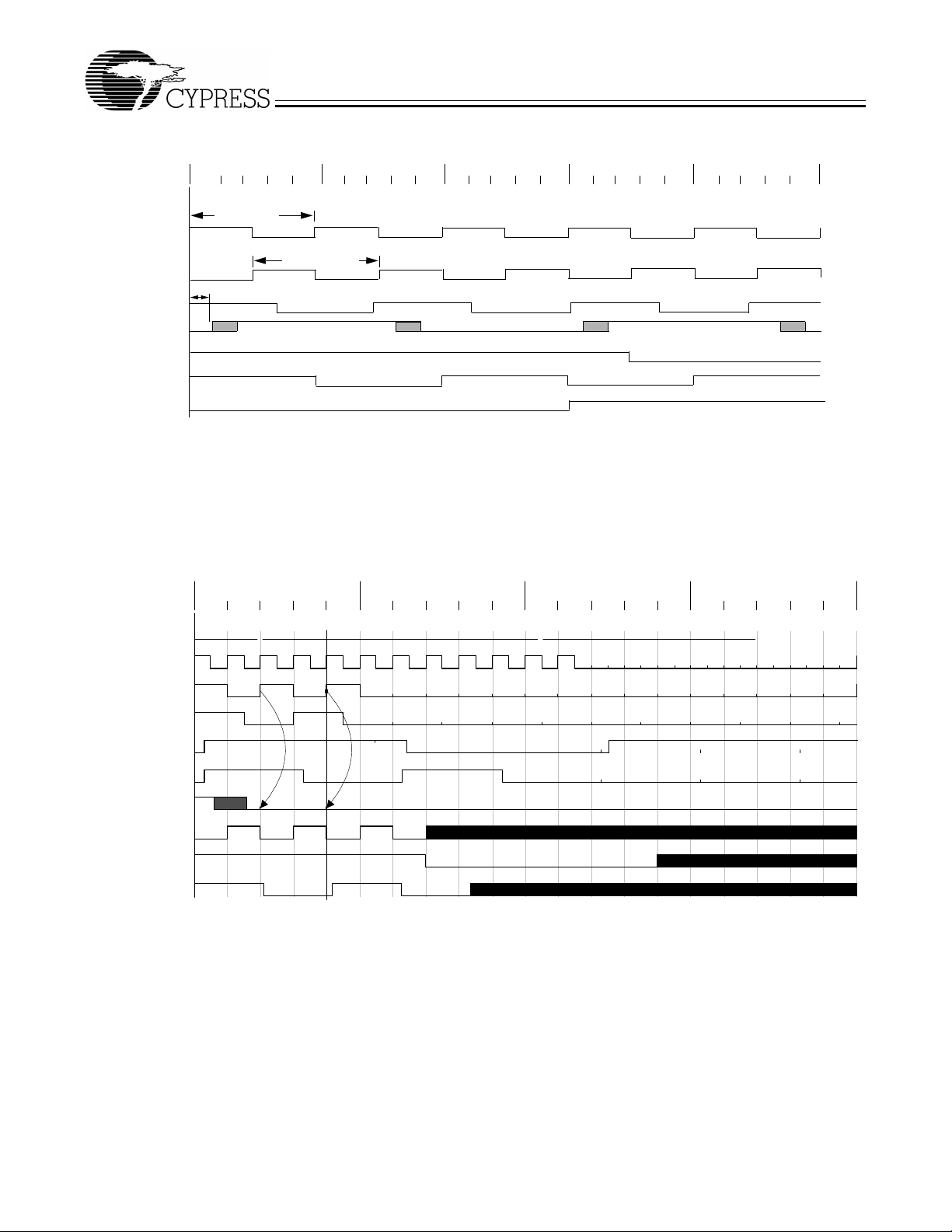
Figure 4. PWRDWN# Timing Diagram
Notes:
2. Once the PWRDWN# signal is sampled LOW for two consecutive rising edges of CPU, clocks of interest will be held LOW on the next HIGH-to-LOW transition.
3. PWRDWN# is an asynchronous input and metastable conditions could exist. This signal is synchronized inside W219B.
4. The shaded sections on the SDRAM, REF, and USB clocks indicate “Don’t Care” states.
5. Diagrams shown with respect to 100 MHz. Similar operation when CPU is 66 MHz.
[2, 3, 4, 5]
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 4 of 15
PRELIMINARY
Spread Spectrum Frequency Timing Generator
The device generates a clock that is frequency modulated in
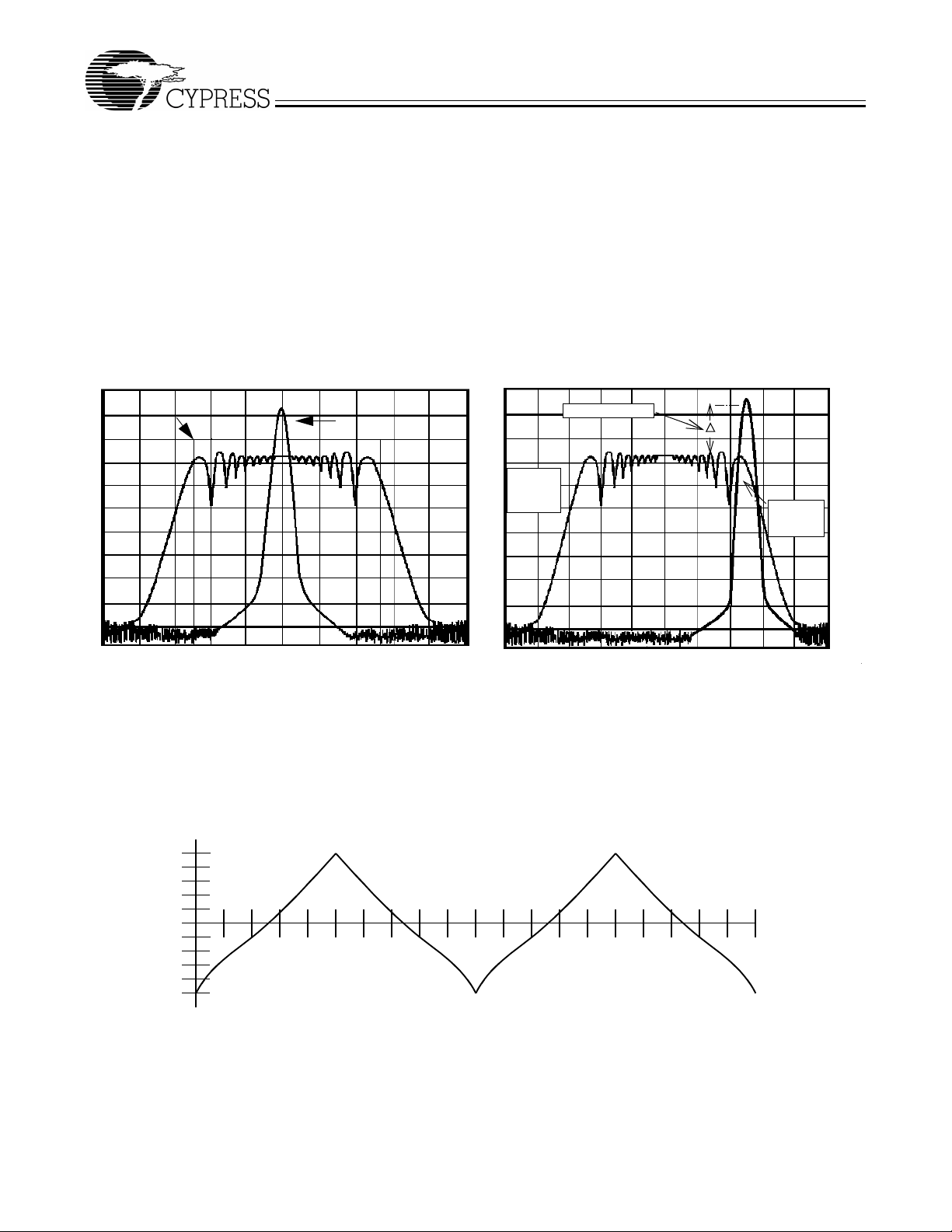
order to increase th e bandwidt h that it occu pies. By inc reasing
the bandwidth of the fundamental and its harmonics, the amplitudes of the radiated electromagnetic emissions are reduced. This effect is depicted in Figure 5.
As shown in Figure 5, a harmonic of a modulated clock has a
much lower amplit ude than that of an unmodulated si gnal. The
reduction in amplitude is dependent on the harmonic number
and the frequency deviation or spread. The equation for the
reduction is:
dB = 6.5 + 9*log
SSFTG
Amplitude (dB)
(P) + 9*log10(F)
10
Typical Clock
W219B
Where P is the pe rcentage of deviation and F is the frequenc y
in MHz where the reduction is measured.
The output clock is modulated with a waveform depicted in
Figure 6. This waveform, as discusse d in “Spread Spectrum
Clock Generation for the Reduction of Radiated Emi ssions” by
Bush, Fessler, and Hardin produces the maximum reduction
in the amplitude of radiated electromagnetic emissions. The
deviation selected for this chip is ±0.45% or –0.6% of the selected frequency. Figure 6 details the Cypress spreading pattern. Cypress does of fer option s with more spread a nd greater
EMI reduction. Con tact your l ocal Sales re presen tative for d etails on these devices.
EMI Reduction
Spread
Spectrum
Enabled
Amplitude (dB)
Non-
Spread
Spectrum
Frequency Span (MHz)
Center Spread
Frequency Span (MHz)
Down Spread
Figure 5. Clock Harmonic with and without SSCG Modu lation Frequency Do main Representation
MAX.
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
FREQUENCY
MIN.
90%
100%
10%
20%
30%
40%
50%
60%
70%
80%
Figure 6. Typical Modulation Profile
90%
100%
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 5 of 15

PRELIMINARY
1 bit 7 bits 1 1 8 bits 1
Start bit Slave Address R/W Ack Command Code Ack Byte Count = N
Ack Data Byte 1 Ack Data Byte 2 Ack ... Data Byte N Ack Stop
1 bit 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 8 bits 1 1
Figure 7. An Example of a Block Write
Serial Data Interface
The W219B features a two-pin, serial data interface that can
be used to configure inte rnal regi ster settin gs that con trol particular device functions .
Data Protocol
The clock driver s eri al protocol accepts onl y blo ck w ri tes fro m
the controller . The bytes must be accessed i n sequential order
from lowest to highest byte with the ability to stop after any
complete byte has been transferred. Indexed bytes are not
allowed.
A block write beg ins with a slave address and a wri te condition.
After the comm and code the core logic issues a byt e count
which describes how many more bytes will follow in the message. If the host had 20 bytes to send, the first byte would be
the number 20 (14h), followed by the 20 bytes of data. The
byte count may n ot be 0. A block writ e com mand i s all owed to
Table 2. Example of Possible Byte Count Value
Byte Count Byte Notes
MSB LSB
0000 0000 Not allowed. Must have at least one byte.
0000 0001 Data for functional and frequency select register (currently byte 0 in spec)
0000 0010 Reads first two bytes of data. (byte 0 then byte1)
0000 0011 Reads first three bytes (byte 0, 1, 2 in order)
0000 0100 Reads first four bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3 in order)
0000 0101 Reads first five bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4 in order)
0000 0110 Reads first six bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 in order)
0000 0111 Reads first seven bytes (byte 0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6 in order)
0010 0000 M ax. byte count supported = 32
transfer a maximum of 32 data bytes. The slave receiver address for W219B is 11010010. Figure 7 shows an example of
a block write.
The command code and the byte count bytes are required as
the first two bytes of any transfer. W219B expects a command
code of 0000 0000. The byte count byte is the number of additional bytes required for the transfer, not counting the command code and byte count bytes. Additionally, the byte count
byte is required to be a minimum of 1 byt e and a max imum of
32 bytes to satisfy the above requirement. Table 2 shows an
example of a possible byte count value.
A transfer is considered val id a fter th e ac k nowl edge bit corresponding to the byte coun t is read by th e co ntro lle r. The command code and byte count bytes are ignored by the W219B.
However, these bytes must be included in the data write sequence to maintain proper byte allocation.
[6]
[7]
[7]
W219B
Table 3. Serial Data Interface Control Functions Summary
Control Function Description Common Application
Output Disable Any individual clock output(s) can be disabled.
(Reserved) Reserved func tion for future dev ice revision or pro-
Notes:
6. The acknowledgment bit is returned by the slave/receiver (W219B).
7. Bytes 6 and 7 are not defined for W219B.
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 6 of 15
Disabled outputs are act iv ely held LOW.
duction device testing.
Unused outputs are di sable d to redu ce EMI and system power. Examples are clock outputs to unused
PCI slots.
No user application. Register bit mu st be written as 0.

PRELIMINARY
Serial Configuration Map
1. The serial bits will be read by the clock driver in the followin g
order:
Byte 0 - Bits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
Byte 1 - Bits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
Byte N - Bits 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2, 1, 0
Byte 0: Control Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Function
Bit 7 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 6 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 5 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 4 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 3 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 2 23 24/48 MHz 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 1 21, 22 48 MHz 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 0 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Byte 1: Control Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Description
Bit 7 32 SDRAM7 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 6 33 SDRAM6 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 5 35 SDRAM5 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 4 36 SDRAM4 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 3 37 SDRAM3 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 2 39 SDRAM2 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 1 40 SDRAM1 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 0 41 SDRAM0 1 (Active/Inactive)
[8]
[8]
2. All unused register bits (reserved and N/A) should be written to a “0” level.
3. All register bits labeled “Initialize to 0" must be written to
zero during initial ization. Failure to do so may result in higher than normal operating current. The controller will read
back the written value.
W219B
Byte 2: Control Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Description
Bit 7 -- Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 6 19 PCI6 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 5 18 PCI5 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 4 16 PCI4 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 3 15 PCI3 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 2 13 PCI2 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 1 12 PCI1 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 0 11 PCI0 1 (Active/Inactive)
Note:
8. Inactive means outputs are held LOW and are disabled from switching. These outputs are designed to be configured at power-on and are not expected to be
configured during the normal modes of operation.
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 7 of 15
[8]

PRELIMINARY
Byte 3: Reserved Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Description
Bit 7 31 SDRAM8 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 6 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 5 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 4 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 3 47 APIC 1 (Active/Inactive)
Bit 2 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 1 - Reserved 1 Reserved
Bit 0 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Byte 4: Reserved Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Function
Bit 7 - SEL3 0 See Table 4
Bit 6 - SEL2 0 See Table 4
Bit 5 - SEL1 0 See Table 4
Bit 4 - SEL0 0 See Table 4
Bit 3 - FS(0:4) Override 0 0 = Select operating frequency by FS(0:4) strapping
1 = Select operating frequency by SEL(0:4) bit settings
Bit 2 - SEL4 0 See Table 4
Bit 1 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 0 - Test Mode 0 0 = All output enable
1 = All output three-stated
W219B
Byte 5: Reserved Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Description
Bit 7 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 6 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 5 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 4 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 3 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 2 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 1 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 0 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Byte 6: Reserved Register (1 = Enable, 0 = Disable)
Bit Pin# Name Default Pin Description
Bit 7 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 6 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 5 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 4 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 3 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Bit 2 - Reserved 1 Reserved
Bit 1 - Reserved 1 Reserved
Bit 0 - Reserved 0 Reserved
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 8 of 15
PRELIMINARY
Table 4. Additional Frequency Selections through Serial Data Interface Data Bytes
Input Conditions Output Frequency
Data Byte 4, Bit 3 = 1
Bit 2
SEL_4
0 0 0 0 0 75.3 113.0 75.3 37.6 18.8 OFF
0 0 0 0 1 95.0 95.0 63.3 31.6 15.8 –0.6%
0 0 0 1 0 129.0 129.0 86.0 43.0 21.5 OFF
0 0 0 1 1 150.0 113.0 75.3 37.6 18.8 OFF
0 0 1 0 0 150.0 150.0 75.0 37.5 18.7 OFF
0 0 1 0 1 110.0 110.0 73.0 36.6 18.3 OFF
0 0 1 1 0 140.0 140.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 0 1 1 1 144.0 108.0 72.0 36.0 18.0 OFF
0 1 0 0 0 68.3 102.5 68.3 34.1 17.0 OFF
0 1 0 0 1 105.0 105.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 1 0 1 0 138.0 138.0 69.0 34.5 17.0 OFF
0 1 0 1 1 140.0 105.0 70.0 35.0 17.5 OFF
0 1 1 0 0 66.8 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 0 1 100.2 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 1 0 133.6 133.6 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
0 1 1 1 1 133.6 100.2 66.8 33.4 16.7 ±0.45%
1 0 0 0 0 157.3 118.0 78.6 39.3 19.6 OFF
1 0 0 0 1 160.0 120.0 80.0 40.0 20.0 OFF
1 0 0 1 0 146.6 110.0 73.3 36.6 18.3 OFF
1 0 0 1 1 122.0 91.5 61.0 30.5 15.2 –0.6%
1 0 1 0 0 127.0 127.0 84.6 42.3 21.1 OFF
1 0 1 0 1 122.0 122.0 81.3 40.6 20.3 –0.6%
1 0 1 1 0 117.0 117.0 78.0 39.0 19.5 OFF
1 0 1 1 1 114.0 114.0 76.0 38.0 19.0 OFF
1 1 0 0 0 80.0 120.0 80.0 40.0 20.0 OFF
1 1 0 0 1 78.0 117.0 78.0 39.0 19.5 OFF
1 1 0 1 0 166.0 124.5 83.0 41.5 20.7 OFF
1 1 0 1 1 133.6 133.6 89.0 44.5 22.2 OFF
1 1 1 0 0 66.6 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 0 1 100.0 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 1 0 133.3 133.3 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
1 1 1 1 1 133.3 100.0 66.6 33.3 16.6 –0.6%
Bit 7
SEL_3
Bit 6
SEL_2
Bit 5
SEL_1
Bit 4
SEL_0
CPU SDRAM 3V66 PCI APIC
W219B
Spread
Spectrum
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 9 of 15

DC Electrical Characteristics
PRELIMINARY
[9]
W219B
DC parameters must be sustainable under steady state (DC) conditions.
Absolute Maximum DC Power Supply
Parameter Description Min. Max. Unit
V
DDQ3
V
DDQ2
T
S
3.3V Core Supply Voltage –0.5 4.6 V
2.5V I/O Supply Voltage –0.5 3.6 V
Storage Temperature –65 150 °C
Absolute Maximum DC I/O
Parameter Description Min. Max. Unit
V
i/o3
V
i/o3
3.3V Core Supply Voltage –0.5 4.6 V
2.5V I/O Supply Voltage –0.5 3.6 V
ESD prot. Input ESD Protection 2000 V
DC Operating Requirements
Parameter Description Condition Min. Max. Unit
V
DD3
V
DDQ3
V
DDQ2
V
DD3 =
V
ih3
V
il3
I
il
V
DDQ2 =
V
oh2
V
ol2
V
DDQ3 =
V
oh3
V
ol3
V
DDQ3 =
V
poh3
V
pol3
3.3V±5%
2.5V±5%
3.3V±5%
3.3V±5%
3.3V Core Supply Voltage 3.3V±5% 3.135 3.465 V
3.3V I/O Supply Voltage 3.3V±5% 3.135 3.465 V
2.5V I/O Supply Voltage 2.5V±5% 2.375 2.625 V
3.3V Input High Voltage V
DD3
2.0 V
+ 0.3 V
DD
3.3V Input Low Voltage GND – 0.3 0.8 V
Input Leakage Current
[10]
0<Vin<V
DDQ3
–5+5µA
2.5V Output High Voltage Ioh=(–1 mA) 2.0 V
2.5V Output Low Voltage Iol=(1 mA) 0.4 V
3.3V Output High Voltage Ioh=(–1 mA) 2.4 V
3.3V Output Low Voltage Iol=(1 mA) 0.4 V
PCI Bus Output High Voltage Ioh=(–1 mA) 2.4 V
PCI Bus Output Low Voltage Iol=(1 mA) 0.55 V
C
in
C
xtal
C
out
L
pin
T
a
Note:
9. Multiple Supplies: The voltage on any input or I/O pin cannot exceed the power pin during power-up. Power supply sequencing is NOT required.
10. Input Leakage Current does not include inputs with pull-up or pull-down resistors.
Input Pin Capacitance 5 pF
Xtal Pin Capacitance 13.5 22.5 pF
Output Pin Capacitance 6 pF
Pin Inductance 0 7 nH
Ambient Temperature No Airflow 0 70 °C
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 10 of 15

AC Electrical Characteristics
TA = 0°C to +70°C, V
= 14.31818 MHz
f
XTL
Parameter Description
T
Period
T
HIGH
T
LOW
T
RISE
T
FALL
T
Period
T
HIGH
T
LOW
T
RISE
T
FALL
T
Period
T
HIGH
T
LOW
T
RISE
T
FALL
Host/CPUCLK Period 15.0 15.5 10.0 10.5 7.5 8.0 ns 11
Host/CPUCLK High Time 5.2 N/A 3.0 N/A 1.87 N/A ns 14
Host/CPUCLK Low Time 5.0 N/A 2.8 N/A 1.67 N/A ns
Host/CPUCLK Rise Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
Host/CPUCLK Fall Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
SDRAM CLK Period 10.0 10.5 10.0 10.5 10.0 10.5 ns 11
SDRAM CLK High Time 3.0 N/A 3.0 N/A 3.0 N/A ns 14
SDRAM CLK Low Time 2.8 N/A 2.8 N/A 2.8 N/A ns
SDRAM CLK Rise Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
SDRAM CLK Fall Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
APIC CLK Period 60.0 64.0 60.0 N/A 60.0 64.0 ns 11
APIC CLK High Time 25.5 N/A 25.5 N/A 25.5 N/A ns 14
APIC CLK Low Time 25.3 N/A 25.30 N/A 25.30 N/A ns
APIC CLK Rise Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
APIC CLK Fall Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
= 3.3V±5%, V
DDQ3
PRELIMINARY
[9]
= 2.5V±5%
DDQ2
66.6-MHz Host 100-MHz Host 133-MHz Host
W219B
Unit NotesMin. Max. Min. Max. Min. Max.
T
Period
T
HIGH
T
LOW
T
RISE
T
FALL
T
Period
T
HIGH
T
LOW
T
RISE
T
FALL
, tp
tp
ZL
, tp
tp
LZ
t
stable
Notes:
11. Period, jitter, offset, and skew measured on rising edge at 1.25 for 2.5V clocks and at 1.5V for 3.3V clocks.
12. T
HIGH
13. T
LOW
14. The time specified is measured from when V
operating within specification.
15. T
RISE
0.4V and V
3V66 CLK Period 30.0 N/A 30.0 N/A 30.0 N/A ns 11, 13
3V66 CLK High Time 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A ns 14
3V66 CLK Low Time 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A ns
3V66 CLK Rise Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
3V66 CLK Fall Time 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 0.4 1.6 ns 15
PCI CLK Period 15.0 16.0 15.0 16.0 15.0 16.0 ns 11, 12
PCI CLK High Time 5.25 N/A 5.25 N/A 5.25 N/A ns 14
PCI CLK Low Time 5.05 N/A 5.05 N/A 5.05 N/A ns
PCI CLK Rise Time 0.5 2.0 0.5 2.0 0.5 2.0 ns 15
PCI CLK Fall Time 0.5 2.0 0.5 2.0 0.5 2.0 ns 15
Output Enable Delay (Al l outputs) 30.0 N/A 30.0 N/A 30.0 N/A ns
ZH
Output Disable Delay
ZH
(All outputs)
All Clock Stabilization from
12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A ns 15
12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A 12.0 N/A ms 15
Power-Up
is measured at 2.0V for 2.5V outputs, 2.4V for 3.3V outputs.
is measured at 0.4V for all outputs.
and T
are measured as a transition through the threshold region Vol = 0.4V and Voh = 2.0V (1 mA) JEDEC specification for 2.5V outputs, and Vol =
FALL
= 2.4V for 3.3V.
oh
achieves its nominal operating level (typical condition V
DDQ3
= 3.3V) until the frequency output is stable and
DDQ3
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A P age 11 of 15

PRELIMINARY
Group Skew and Jitter Limits
Output Group Pin-Pin Skew Max. Cycle-Cycle Jitter Duty Cycle Nom Vdd
CPU 175 ps 250 ps 45/55 2.5V 1.25V
SDRAM 250 ps 250 ps 45/55 3.3V 1.5V
APIC 250 ps 500 ps 45/55 2.5V 1.2 5V
48MHz 250 ps 500 ps 45/55 3.3V 1.5V
3V66 175 ps 500 ps 45/55 3.3V 1.5V
PCI 500 ps 500 ps 45/55 3.3V 1.5V
REF N/A 1000 ps 45/55 3.3V 1.5V
Test Poi nt
Test Load
T
PERIOD
Duty Cycle
Clock Output Wave
2.5V Clocking
Interface
1.25
Output
Buffer
T
HIGH
2.0
0.4
W219B
Skew, Jitter
Measure Point
T
LOW
T
RISE
3.3V Clocking
Interface
2.4
1.5
0.4
T
RISE
T
FALL
T
PERIOD
Duty Cycle
T
HIGH
T
T
FALL
LOW
Figure 8. Output Buffer
Ordering Information
Ordering Code Package Name Package Type
W219B H 48-pin SSOP (300 mils)
Intel is a registered trademark of Intel Corporation.
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 12 of 15

Layout Example
PRELIMINARY
C1
10 µF
G
+2.5V Supply
FB
0.005 µF
G
G
G
G
+3.3V Supply
FB
10 µF
0.005 µF
C4
G G
1
2
G
3
4
5
G
6
VDDQ3
C3
G
VG
G
G
V
G
7
8
G
9
10
11
G
W219B
12
VDDQ2
G
V
48
G
47
V
46
G
45
44
43
G
V
42
G
41
40
39
G
38
G
37
W219B
C2
3.3V
13
G
14
15
G
16
VG
17
G
18
19
G
20
21
22
23
G
24
C1 & C3, C5 = 10 – 22
Each supply plane or strip should have a
C5
20µF
G
0.1
µ
F
C6
G
FB = Dale ILB1206 - 300 (300
Ceramic Caps
= VIA to GND plane layer
G
Note:
All VDD by pass capacitors = 0.1 µF
5
Ω
VDDQ3
(Core)
Ω @ 100 MHz) or TDK ACB2012L-120
V = VIA to respectiv e supply plane trace
36
G
35
V
34
G
33
32
31
30
G
29
28
G
V
27
G
26
G
25
C2 & C4 = 0.005
µF
ferrite bead and capacitors
µF
G
G
C6 = 0.1 µF
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 13 of 15

ng so indemnifies Cypress Semiconductor against all charges.
Package Diagram
PRELIMINARY
48-Pin Shrink Small Outline Package (SSOP, 300 mils)
W219B
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 14 of 15
© Cypress Semiconductor Corporation, 2001. The information contained herein is subject to change without notice. Cypress Semiconductor Corporation assumes no responsibility for the use
of any circuitry other than circuitry embodied in a Cypress Semiconductor product. No r does it convey or imply any license under patent or other rights. Cypress Semiconductor does not autho rize
its products for use as critical components in life-support systems where a malfunction or failure may reasonably be expected to result in significant injury to the user. The inclusion of Cypress
Semiconductor products in life-support systems application implies that the manufacturer assume s all risk of such use and in doi

PRELIMINARY
Document Title: W219B Frequency Generator for Integrated Core Logic with 133-MHz FSB
Document Number: 38-07220
REV. ECN NO.
** 110485 10/21/01 SZV Change from Spec number: 38-00884 to 38-07220
*A 122837 12/21/02 RBI Add Power up Requirements to Electrical Characteristics
Issue
Date
Orig. of
Change Description of Change
W219B
Information
Document #: 38-07220 Rev. *A Page 15 of 15
 Loading...
Loading...