Crown CM-30, LM-201, LM-300A, LM-300AL, LM-301A Application Manual
...
CROWN MICROPHONE APPLICATION GUIDE:
TELECONFERENCING & DISTANCE LEARNING
© 2001 Crown Audio, Inc. All rights reserved PZM® and
are registered trademarks of Crown International.
Also exported as Amcron®
102100-2
11-01
PCC®
Crown International
P.O. Box 1000,
Elkhart, Indiana 46515-1000
(574) 294-8200 Fax (574) 294-8329
CROWN MICROPHONE
APPLICATION GUIDE
FOR TELECONFERENCING
AND DISTANCE LEARNING
Thanks to teleconferencing, we can hold meetings
with people in a nother location without having to
travel there. Distance learning lets a professor teach
thousands of students in various locations, all at the
same time , in a cos t-e f f ect ive ma nne r. It’ s also use d
for corporate training.
Both tele confe rencin g and dist ance lear ning ca n save
you or your company thousands of dol lars in travel
fees, not to mention the cost of hotels, meals, etc.
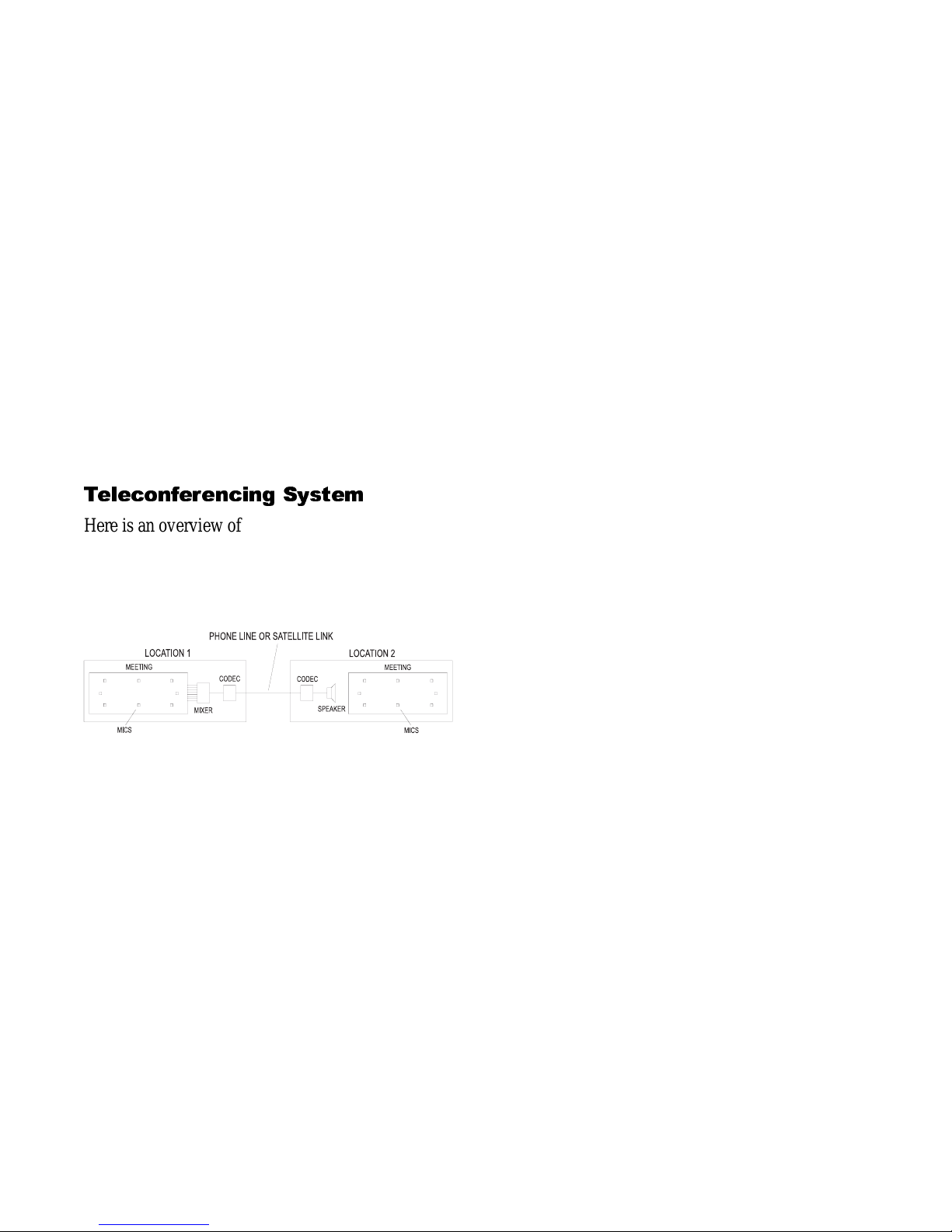
Teleconferencing System
Here is an overview of a typical teleconferencing
system (Fig. 1). Two meetings are set up around
conference tables. One meeting is in your company,
and the other mee ting is in anot her company.
Figure 1. Teleconferencing system.
People at your mee ting are picked up by microphones. The sound of their voices is sent over standard telephone lines, or a satellite link, to the other
meeting location. There, the people can hear you
through a loudspeaker.
Similarly, mics at their location pick them up. Their
voices are sent over phone lines or satellite to your
location. You hear them through a loudspeaker. You
can talk back and forth, almost as if they were with
you at the conference table.
There might be cameras and video monitors set up so
that you can see the other people, and they can see
you.
A teleconferencing syst em is made of the following
components:
• Microphones
These pick u p the vo ice of each pa rticipan t. M ics ca n
be on the conference table or on a lectern. The mics
might be swit chable: each user can turn his or her
mic on and off.
• Mixer
This electronic device combines all the mic signals
into one audio si gnal.
• Telephone coupler or codec
Short for co der-decoder, a codec takes t he audio signal from the mixer, and sends it over the telephone
lines. On the sending end, it digitally codes the audio
into a telephone signal. On the receiving end, it
decodes the te lephone signal back into audio.
Some codecs also send and receive video. Video signals must b e sent via sate llite, whic h relays th e signal
to the distant location.
Some systems combine a mixer and codec into one
unit. Other systems combine mics, mixer and codec
into one unit.
• Telephone lines
Supplied by the telephone company, standard phone
lines (or high-speed phone lines) carry your audio
signal to the dista nt me eting loc ation. The re, a cod ec
converts t he phone signal back into audio, whi ch i s
fed to a speaker. The meeting par ticipants can hear
you through this speaker.
• Loudspeaker
In your meeting room, a loudspeaker plays the voices
of the peopl e from the distant meeting.
• Video cameras and TV monitors
This is an option. Cameras and mon it ors let you see
the people at the distant meeting, and let them see
you. In many systems, the cameras automat ically
switch to show the person speaking.

Distance Learning System
Now let’s explain a distance learning system (Fig. 2).
T ypica lly , students will be in one or more classrooms,
and a professor will be in another location. The professor talks to the students through a clip-on or lavalier microphone. The mic signal is sent by phone
lines or satellite to the classr oo ms. There, seve ra l
loudspeakers play the prof essor’s voice to the students. The stud ents can see the professor over a TV
monitor.
Figure 2
In the classroom, each student or pair of students has
a desk mic or hanging mic. Students can switch on
the mic when they want to as k the teacher a q uestion .
The mic signals are sent by phone lines or satellite to
the teache r. The teacher and studen t can talk back
and forth, alm ost as if they were in the same room .
Figure 3
The parts of a distance learning system are the same
as in a teleconference system. Crown makes one part
of these systems: the microphones.
You should contact a consultant, codec manufacturer
or system integrator t o d esign and install your complete system.
How to Send Clear Audio
When you tra nsm it aud io to the distant m eetin g, th e
audio should be cl ear and easy to understand. But
there are som e prob lem s tha t pr even t clea r so und :
Reverberation
This is the sound reflected off the room walls, floor
and ceiling. Too muc h reverberation makes the
speech sound hollow , distant, and blurred.
Background noise
This is noise from ven tila tion ducts, fluo re sce nt li ght
ballasts, video equipment, and equipment cooling
fans. Too much noise makes the speech hard to hear
and understand.
Feedback
This is the squealing or ringing sound you hear when
the mics pick up the sound of the loudspeaker. The
speech sound picked up by the mics is fed to a loudspeaker, and the loudsp eaker sound re-enters the
microphone. This creates a feedback loop and makes
an annoying ringing sound.
Here are some ways to prevent all these problems.
The result will be clear, intelligible audio:
• Place mics close to talkers. Put tab le-top mics
within arm’s length. Talk into lectern mics about 8
inches away. Wear a lavalier mic on th e ch est.
• Use directional mics. Some examples of directional
mics are cardi oid, superc ardioid, and hypercardi oid.
These mics are designed to reject feedback, noise and
reverberation.
• Use boundary mics on conference tables. A boundary mic is a low profile unit that lies on the conference table surface. It picks up less room ac oustics
than a conve nt ion a l mic o n a desk stand , so th e
boundary mic sounds clear er. Also, a mic o n a desk
stand picks up table-top sound reflections. These
reflections cause phase interference, which may give
the voice a strange tone quality. The boundary mic is
designed to eliminate phase interference, so it sounds
natural.
 Loading...
Loading...