Page 1

Frame 3 to 4
Power Installation Guide
Unidrive M600 to
M702 and HS70 to
HS72
Part Number: 0478-0254-03
Issue: 3
Page 2

Original Instructions
General Information
For the purposes of compliance with the EU Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC.
This guide covers the basic information that is required to install the drive, in applications where a drive malfunction
does not result in a mechanical hazard. When the drive is used in a safety related application, i.e. where a
malfunction might result in a hazard, it is essential to refer to this guide and the Control User Guide. The Control User
Guide is available for download from:
http://www.emersonindustrial.com/en-EN/controltechniques/downloads/userguidesandsoftware/Pages/downloads.aspx
or
www.emersonindustrial.com/en-EN/leroy-somer-motors-drives/downloads/Pages/manuals.aspx
The manufacturer accepts no liability for any consequences resulting from inappropriate, negligent or incorrect
installation or adjustment of the optional operating parameters of the equipment or from mismatching the variable
speed drive with the motor.
The contents of this guide are believed to be correct at the time of printing. In the interests of a commitment to a
policy of continuous development and improvement, the manufacturer reserves the right to change the specification
of the product or its performance, or the contents of the guide, without notice.
All rights reserved. No parts of this guide may be reproduced or transmitted in any form or by any means, electrical
or mechanical including photocopying, recording or by an information storage or retrieval system, without permission
in writing from the publisher.
Drive firmware version
This product is supplied with the latest firmware version. If this drive is to be connected to an existing system or
machine, all drive firmware versions should be verified to confirm the same functionality as drives of the same model
already present. This may also apply to drives returned from an Emerson Industrial Automation Service Centre or
Repair Centre. If there is any doubt please contact the supplier of the product.
The firmware version of the drive can be checked by looking at Pr 11.029
Environmental statement
Emerson Industrial Automation is committed to minimising the environmental impacts of its manufacturing operations
and of its products throughout their life cycle. To this end, we operate an Environmental Management System (EMS)
which is certified to the International Standard ISO 14001. Further information on the EMS, our Environmental Policy
and other relevant information is available on request, or can be found at:
http://www.emersonindustrial.com/en-EN/controltechniques/aboutus/environment/Pages/environment.aspx.
The electronic variable-speed drives manufactured by Emerson Industrial Automation have the potential to save
energy and (through increased machine/process efficiency) reduce raw material consumption and scrap throughout
their long working lifetime. In typical applications, these positive environmental effects far outweigh the negative
impacts of product manufacture and end-of-life disposal.
Nevertheless, when the products eventually reach the end of their useful life, they must not be discarded but should
instead be recycled by a specialist recycler of electronic equipment. Recyclers will find the products easy to
dismantle into their major component parts for efficient recycling. Many parts snap together and can be separated
without the use of tools, while other parts are secured with conventional fasteners. Virtually all parts of the product
are suitable for recycling.
Product packaging is of good quality and can be re-used. Large products are packed in wooden crates, while smaller
products come in strong cardboard cartons which themselves have a high recycled fibre content. If not re-used, these
containers can be recycled. Polythene, used on the protective film and bags for wrapping product, can be recycled
in the same way. Emerson Industrial Automation’s packaging strategy prefers easily-recyclable materials of low
environmental impact, and regular reviews identify opportunities for improvement.
When preparing to recycle or dispose of any product or packaging, please observe local legislation and best practice.
REACH legislation
EC Regulation 1907/2006 on the Registration, Evaluation, Authorisation and restriction of Chemicals (REACH)
requires the supplier of an article to inform the recipient if it contains more than a specified proportion of any
substance which is considered by the European Chemicals Agency (ECHA) to be a Substance of Very High Concern
(SVHC) and is therefore listed by them as a candidate for compulsory authorisation.
For current information on how this requirement applies in relation to specific Emerson Industrial Automation’s
products, please approach your usual contact in the first instance. Emerson Industrial Automation’s position
statement can be viewed at:
www.emersonindustrial.com/en-EN/controltechniques/aboutus/environment/reachregulation/Pages/reachregulation.aspx.
Copyright © February 2016 Emerson Industrial Automation.
The information contained in this guide is for guidance only and does not form part of any contract. The accuracy
cannot be guaranteed as Emerson have an ongoing process of development and reserve the right to change the
specification of their products without notice.
Control Techniques Limited. Registered Office: The Gro, Newtown, Powys SY16 3BE. Registered in England and
Wales. Company Reg. No. 01236886.
Moteurs Leroy-Somer SAS. Headquarters: Bd Marcellin Leroy, CS 10015, 16915 Angoulême Cedex 9, France.
Share Capital: 65 800 512 €, RCS Angoulême 338 567 258.
Issue Number: 3
Drive Firmware: 01.14.00.00
Page 3

Contents
1 Safety information ....................................................................................... 8
1.1 Warnings, Cautions and Notes ................................................................................ 8
1.2 Electrical safety - general warning ........................................................................... 8
1.3 System design and safety of personnel ................................................................... 8
1.4 Environmental limits ................................................................................................ 8
1.5 Access ..................................................................................................................... 9
1.6 Fire protection .......................................................................................................... 9
1.7 Compliance with regulations .................................................................................... 9
1.8 Motor ....................................................................................................................... 9
1.9 Mechanical brake control ......................................................................................... 9
1.10 Adjusting parameters ............................................................................................... 9
1.11 Electrical installation .............................................................................................. 10
2 Product information ..................................................................................11
2.1 Introduction ............................................................................................................ 11
2.2 Model number ........................................................................................................ 11
2.3 Nameplate description ........................................................................................... 12
2.4 Ratings .................................................................................................................. 13
2.5 Drive features ........................................................................................................ 15
2.6 Items supplied with the drive ................................................................................. 16
3 Mechanical installation ............................................................................. 17
3.1 Safety information .................................................................................................. 17
3.2 Planning the installation ......................................................................................... 18
3.3 Terminal cover removal ......................................................................................... 20
3.4 Dimensions and mounting methods ...................................................................... 23
3.5 Enclosure for standard drives ................................................................................ 27
3.6 Enclosure design and drive ambient temperature ................................................. 32
3.7 Heatsink fan operation ........................................................................................... 32
3.8 Enclosing standard drive for high environmental protection .................................. 32
3.9 Installation of high IP insert for size 3 and 4 .......................................................... 34
3.10 Size 3 and 4 internal braking resistor .................................................................... 37
3.11 External EMC filter ................................................................................................. 41
3.12 Terminal size and torque settings .......................................................................... 43
3.13 Routine maintenance ............................................................................................. 44
4 Electrical installation .................................................................................45
4.1 Power and ground connections ............................................................................. 46
4.2 AC Supply requirements ........................................................................................ 48
4.3 Supplying the drive with DC .................................................................................. 50
4.4 DC bus paralleling ................................................................................................. 51
4.5 24 Vdc supply ........................................................................................................ 52
4.6 Low voltage operation ........................................................................................... 53
4.7 Fan power supply .................................................................................................. 53
4.8 Ratings .................................................................................................................. 53
4.9 Output circuit and motor protection ....................................................................... 54
4.10 Braking .................................................................................................................. 57
4.11 Ground leakage ..................................................................................................... 62
4.12 EMC (Electromagnetic compatibility) ..................................................................... 63
5 Technical data ............................................................................................76
5.1 Drive technical data ............................................................................................... 76
5.2 Optional external EMC filters ................................................................................. 96
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 4

6 UL listing information ................................................................................98
6.1 General ..................................................................................................................98
6.2 Overload, overcurrent and overspeed protection ...................................................98
6.3 Short-circuit protection for branch circuits ..............................................................99
6.4 Control circuit protection ........................................................................................99
6.5 Wiring terminal markings ......................................................................................100
6.6 Environment .........................................................................................................100
6.7 Mounting ..............................................................................................................100
6.8 Listed accessories ................................................................................................101
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 5
Declaration of Conformity
G Williams
Vice President, Technology
Date: 30th November 2015
Control Techniques Ltd
The Gro
Newtown
Powys
UK
SY16 3BE
This declaration applies to the Unidrive M/HS product range comprising model numbers listed below:
Model
number
X Application
aaaa Basic series
bb Frame size 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11
c Voltage rating 1 = 100 V, 2 = 200 V, 4 = 400 V, 5 = 575 V, 6 = 690 V
ddddd Current rating Example 01000 = 100 A
e Drive format
The model number may be followed by additional characters that do not affect the ratings.
The variable speed drive products listed above have been designed and manufactured in accordance with the
following European harmonized standards:
EN 61800-5-1:2007
EN 61800-3: 2004
EN 61000-6-2:2005
EN 61000-6-4:2007
EN 61000-3-2:2006
EN 61000-3-3:2008
EN 61000-3-2: 2006 Applicable where input current < 16 A. No limits apply for professional equipment where input
power ≥1 kW.
These products comply with the Restriction of Hazardous Substances Directive - RoHS 2011/65/EU, the Low
Voltage Directive - LVD 2006/95/EC and the Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive - EMC 2004/108/EC.
Interpretation Nomenclature aaaa - bbc ddddde
M = Manufacturing Automation, E = Elevator, F = Flow, H = HVAC, CSD =
Compressor, EVC = Emerson Variable Scroll, HS = High Speed
M100, M101, M200, M201, M300, M400, M600, M700, M701, M702, F300,
H300, E200, E300, CSD1, HS30, HS70, HS71, HS72, M000, RECT
A = 6P Rectifier + Inverter (internal choke), D = Inverter, E = 6P Rectifier +
Inverter (external choke), N = 18P Rectifier + Inverter, T = 12P Rectifier +
Inverter
Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems - Part 5-1: Safety requirements Electrical, thermal and energy
Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems - Part 3: EMC requirements and specific
test methods
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-2: Generic standards - Immunity for industrial
environments
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 6-4: Generic standards - Emission standard for
industrial environments
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-2: Limits for harmonic current emissions
(equipment input current ≤16 A per phase)
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) - Part 3-3: Limitation of voltage changes, voltage
fluctuations and flicker in public, low voltage supply systems, for equipment with rated
current ≤16 A per phase and not subject to conditional connection
Moteurs Leroy-Somer
Usine des Agriers
Boulevard Marcellin Leroy
CS10015
16915 Angoulême Cedex 9
France
These electronic drive products are intended to be used with appropriate motors, controllers, electrical protection
components and other equipment to form complete end products or systems. Compliance with safety and EMC
regulations depends upon installing and configuring drives correctly, including using the specified input filters. The
drives must be installed only by professional installers who are familiar with requirements for safety and EMC. The
assembler is responsible for ensuring that the end product or system complies with all the relevant laws in the
country where it is to be used. Refer to the Product Documentation. An EMC data sheet is also available giving
detailed EMC information.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
5
Page 6
Declaration of Conformity
(including 2006 Machinery Directive)
Control Techniques Ltd
The Gro
Newtown
Powys
UK
SY16 3BE
This declaration applies to the Unidrive M/HS product range comprising model numbers listed below:
Model
number
X Application
aaaa Basic series
bb Frame size 01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06, 07, 08, 09, 10, 11
c Voltage rating 1 = 100 V, 2 = 200 V, 4 = 400 V, 5 = 575 V, 6 = 690 V
ddddd Current rating Example 01000 = 100 A
e Drive format
The model number may be followed by additional characters that do not affect the ratings.
This declaration relates to these products when used as a safety component of a machine. Only the Safe
Torque Off function may be used for a safety function of a machine. None of the other functions of the drive
may be used to carry out a safety function.
These products fulfil all the relevant provisions of the Machinery Directive 2006/42/EC and the EMC Directive 2014/
108/EC.
EC type examination has been carried out by the following notified body:
TUV Rheinland Industrie Service GmbH
Am Grauen Stein
D-51105 Köln
Germany
Notified body identification number: 0035
The harmonized standards used are shown below:
EC type-examination certificate numbers:
01/205/5270.01/14 dated 2014-11-11
01/205/5387.01/15 dated 2015-01-29
01/205/5383.02/15 dated 2015-04-21
EN 61800-5-1:2007
EN 61800-5-2:2007
EN ISO 13849-1:2008
EN ISO 13849-2:2008 Safety of machinery, Safety-related parts of control systems. Validation
EN 61800-3: 2004
EN 62061:2005
Interpretation Nomenclature aaaa - bbc ddddde
M = Manufacturing Automation, E = Elevator, F = Flow, H = HVAC, CSD =
Compressor, EVC = Emerson Variable Scroll, HS = High Speed
M300, M400, M600, M700, M701, M702, F300, H300, E200, E300, CSD1,
HS30, HS70, HS71, HS72, M000, RECT
A = 6P Rectifier + Inverter (internal choke), D = Inverter, E = 6P Rectifier +
Inverter (external choke), N = 18P Rectifier + Inverter, T = 12P Rectifier +
Inverter
Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems - Part 5-1: Safety requirements Electrical, thermal and energy
Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems - Part 5-2: Safety requirements Functional
Safety of Machinery, Safety-related parts of control systems, General principles for
design
Adjustable speed electrical power drive systems - Part 3: EMC requirements and
specific test methods
Safety of machinery, Functional safety of safety related electrical, electronic and
programmable electronic control systems
Moteurs Leroy-Somer
Usine des Agriers
Boulevard Marcellin Leroy
CS10015
16915 Angoulême Cedex 9
France
6
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 7

Person authorised to complete the technical file:
G Williams
Vice President, Technology
Date: 30th November 2015
C Hargis
Chief Engineer
Newtown, Powys, UK
IMPORTANT NOTICE
These electronic drive products are intended to be used with appropriate motors, controllers, electrical
protection components and other equipment to form complete end products or systems. It is the
responsibility of the installer to ensure that the design of the complete machine, including its safety-related
control system, is carried out in accordance with the requirements of the Machinery Directive and any
other relevant legislation. The use of a safety-related drive in itself does not ensure the safety of the
machine.
Compliance with safety and EMC regulations depends upon installing and configuring drives correctly,
including using the specified input filters. The drive must be installed only by professional installers who
are familiar with requirements for safety and EMC. The assembler is responsible for ensuring that the end
product or system complies with all relevant laws in the country where it is to be used. For more
information regarding Safe Torque Off, refer to the Control User Guide.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
7
Page 8
1 Safety information
WARNING
CAUTION
NOTE
1.1 Warnings, Cautions and Notes
A Warning contains information which is essential for avoiding a safety hazard.
A Caution contains information which is necessary for avoiding a risk of damage to the
product or other equipment.
A Note contains information, which helps to ensure correct operation of the product.
1.2 Electrical safety - general warning
The voltages used in the drive can cause severe electrical shock and/or burns, and could be lethal.
Extreme care is necessary at all times when working with or adjacent to the drive. Specific warnings
are given at the relevant places in this guide.
1.3 System design and safety of personnel
The drive is intended as a component for professional incorporation into complete equipment or a
system. If installed incorrectly, the drive may present a safety hazard.
The drive uses high voltages and currents, carries a high level of stored electrical energy, and is used
to control equipment which can cause injury.
Close attention is required to the electrical installation and the system design to avoid hazards either
in normal operation or in the event of equipment malfunction. System design, installation,
commissioning/start-up and maintenance must be carried out by personnel who have the necessary
training and experience. They must read this safety information and this guide carefully.
The STOP and Safe Torque Off functions of the drive do not isolate dangerous voltages from the
output of the drive or from any external option unit. The supply must be disconnected by an approved
electrical isolation device before gaining access to the electrical connections.
With the sole exception of the Safe Torque Off function, none of the drive functions must be
used to ensure safety of personnel, i.e. they must not be used for safety-related functions.
Careful consideration must be given to the functions of the drive which might result in a hazard,
either through their intended behavior or through incorrect operation due to a fault. In any application
where a malfunction of the drive or its control system could lead to or allow damage, loss or injury, a
risk analysis must be carried out, and where necessary, further measures taken to reduce the risk for example, an over-speed protection device in case of failure of the speed control, or a fail-safe
mechanical brake in case of loss of motor braking.
The Safe Torque Off function may be used in a safety-related application. The system designer is
responsible for ensuring that the complete system is safe and designed correctly according to the
relevant safety standards.
1.4 Environmental limits
Instructions in this guide regarding transport, storage, installation and use of the drive must be
complied with, including the specified environmental limits. Drives must not be subjected to
excessive physical force.
8
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 9

1.5 Access
Drive access must be restricted to authorized personnel only. Safety regulations which apply at the
place of use must be complied with.
1.6 Fire protection
The drive enclosure is not classified as a fire enclosure. A separate fire enclosure must be provided.
For further information, refer to section 3.2.5 Fire protection on page 18.
1.7 Compliance with regulations
The installer is responsible for complying with all relevant regulations, such as national wiring
regulations, accident prevention regulations and electromagnetic compatibility (EMC) regulations.
Particular attention must be given to the cross-sectional areas of conductors, the selection of fuses
or other protection, and protective ground (earth) connections.
This guide contains instruction for achieving compliance with specific EMC standards.
Within the European Union, all machinery in which this product is used must comply with the
following directives:
2006/42/EC: Safety of machinery.
2004/108/EC: Electromagnetic Compatibility.
1.8 Motor
Ensure the motor is installed in accordance with the manufacturer’s recommendations. Ensure the
motor shaft is not exposed.
Standard squirrel cage induction motors are designed for single speed operation. If it is intended to
use the capability of the drive to run a motor at speeds above its designed maximum, it is strongly
recommended that the manufacturer is consulted first.
Low speeds may cause the motor to overheat because the cooling fan becomes less effective. The
motor should be installed with a protection thermistor. If necessary, an electric forced vent fan should
be used.
The values of the motor parameters set in the drive affect the protection of the motor. The default
values in the drive should not be relied upon.
It is essential that the correct value is entered in Pr 00.046 motor rated current. This affects the
thermal protection of the motor.
Safety information
Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
1.9 Mechanical brake control
The brake control functions are provided to allow well co-ordinated operation of an external brake
with the drive. While both hardware and software are designed to high standards of quality and
robustness, they are not intended for use as safety functions, i.e. where a fault or failure would result
in a risk of injury. In any application where the incorrect operation of the brake release mechanism
could result in injury, independent protection devices of proven integrity must also be incorporated.
1.10 Adjusting parameters
Some parameters have a profound effect on the operation of the drive. They must not be altered
without careful consideration of the impact on the controlled system. Measures must be taken to
prevent unwanted changes due to error or tampering.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
9
Page 10

1.11 Electrical installation
1.11.1 Electric shock risk
The voltages present in the following locations can cause severe electric shock and may be lethal:
• AC supply cables and connections
• Output cables and connections
• Many internal parts of the drive, and external option units
Unless otherwise indicated, control terminals are single insulated and must not be touched.
1.11.2 Stored charge
The drive contains capacitors that remain charged to a potentially lethal voltage after the AC supply
has been disconnected. If the drive has been energized, the AC supply must be isolated at least ten
minutes before work may continue.
10
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 11
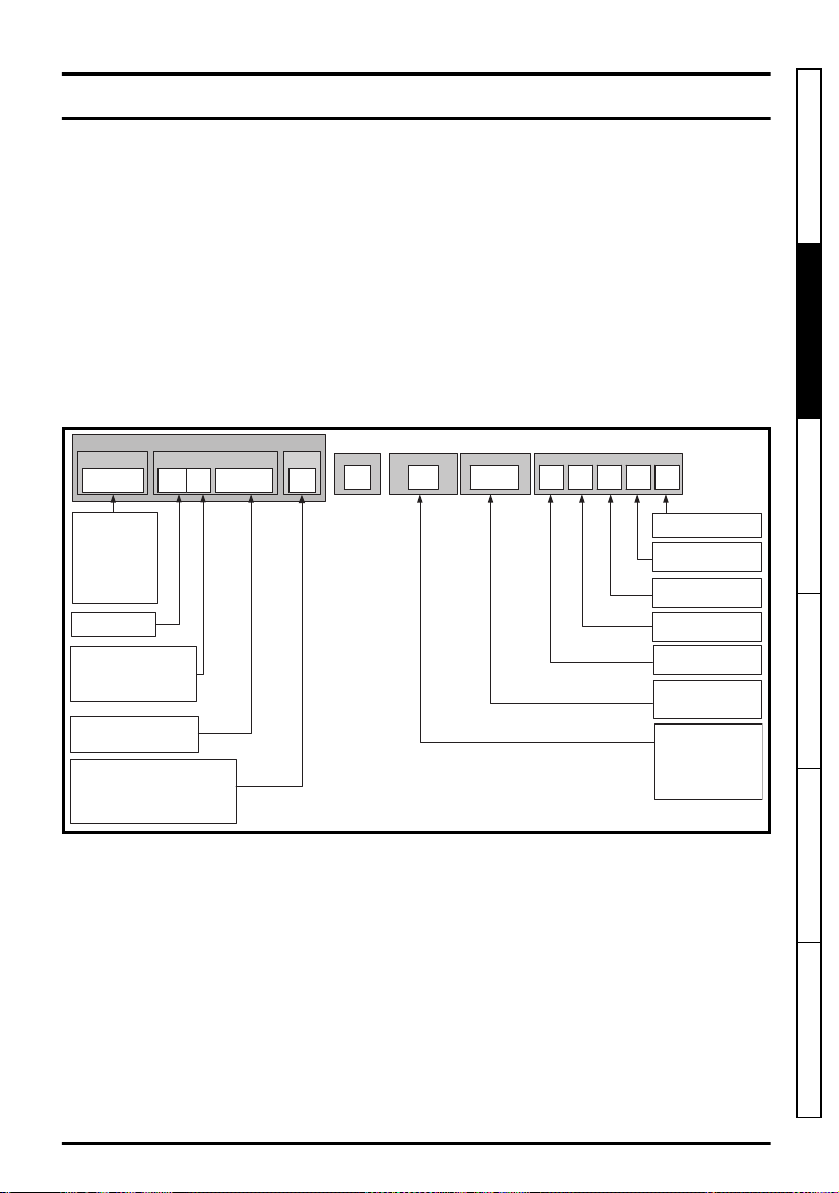
2 Product information
IdentificationLabel
ElectricalSpecifications
Derivative
UnidriveM600
UnidriveM700
UnidriveM701
UnidriveM702
UnidriveHS70
UnidriveHS71
UnidriveHS72
ProductLine
FrameSize
:
VoltageRating:
CurrentRating:
HeavyDutycurrentratingx 10
PowerFormat:
Reserved
0
OptionalBuild
CustomerCode
01
A B 1 00
CustomerCode:
00 = 50 Hz
01 = 60 Hz
Reserved:
ConformalCoating:
0 = Standard
IP / NEMA Rating:
1 = IP20 / NEMA 1
BrakeTransistor:
B = Brake
Cooling:
A = Air
Documentation
1
Documentation:
0-Suppliedseparately
1-English
2-French
3-Italian
4-German
5-Spanish
2-200V(200-240
-400V(380-480
-575V(500-575
-690V(500-690
± 10%)
4 ±
±
±
10%)
5 10%)
6 10%)
Power
Format
M600 - 03 4 00078 A
A - ACinACout(withinternalchoke)
D-DCin ACout(Inverter)
C- ACinDCout(Rectifier)
E- ACin ACout(withoutinternalchoke)
T - ACinACout(12P rectifier plus inverter)
2.1 Introduction
This guide provides the information necessary to install the following drive models:
Unidrive M600 to M702 frame 3 to 4
Unidrive HS70 to HS72 frame 3 to 4
This guide focuses on the drive power section, for example: electrical installation of the supply /
motor cables and mechanical installation of the drive.
For information about the drive control section, for example: parameter set up information, control
and encoder connections please refer to the Control User Guide.
2.2 Model number
The model numbers for the Unidrive M/HS product range are formed as illustrated below:
Figure 2-1 Model number
Safety information
Product information
Mechanical installation Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
11
Page 12
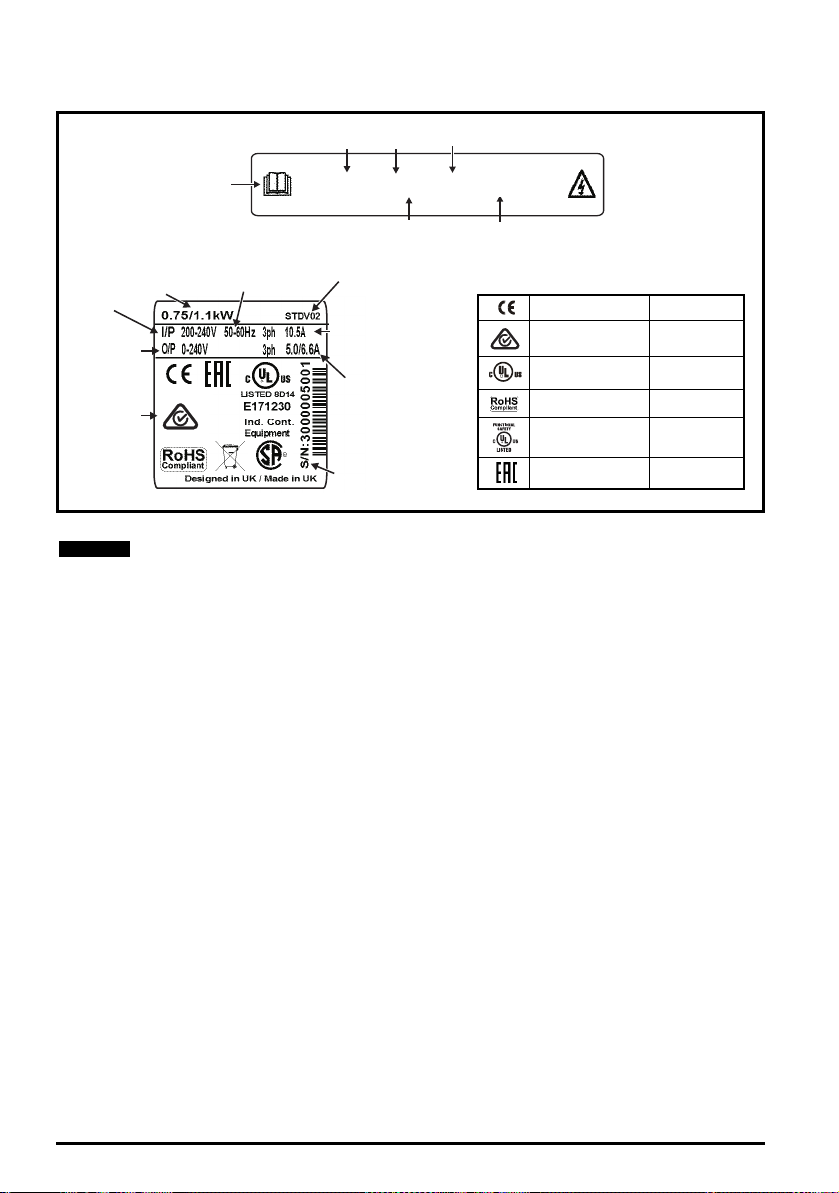
2.3 Nameplate description
Approvals
Inputvoltage
Output
voltage
HeavyDuty/
NormalDuty
powerrating
Customerand
datecode
Serial
number
Input
frequency
No.ofphases&
Typicalinputcurrentfor
NormalDutyrating
HeavyDuty/
NormalDutyrating
outputcurrent
Referto
UserGuide
Model
Frame
size
Voltage
HeavyDuty
currentrating
Driveformat
M600-03200050 A
Key to approvals
CE approval Europe
RCM regulatory
compliance mark
Australia
UL / cUL approval USA & Canada
RoHS compliant Europe
Functional safety USA & Canada
Eurasian conformity Eurasia
R
NOTE
Figure 2-2 Typical drive rating labels
Date code format
The date code is split into two sections: a letter followed by a number. The letter indicates
the year, and the number indicates the week number (within the year) in which the drive
was built. The letters go in alphabetical order, starting with A in 1990 (B in 1991, C in 1992
etc).
Example: A date code of Y28 would correspond to week 28 of year 2015.
12
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 13
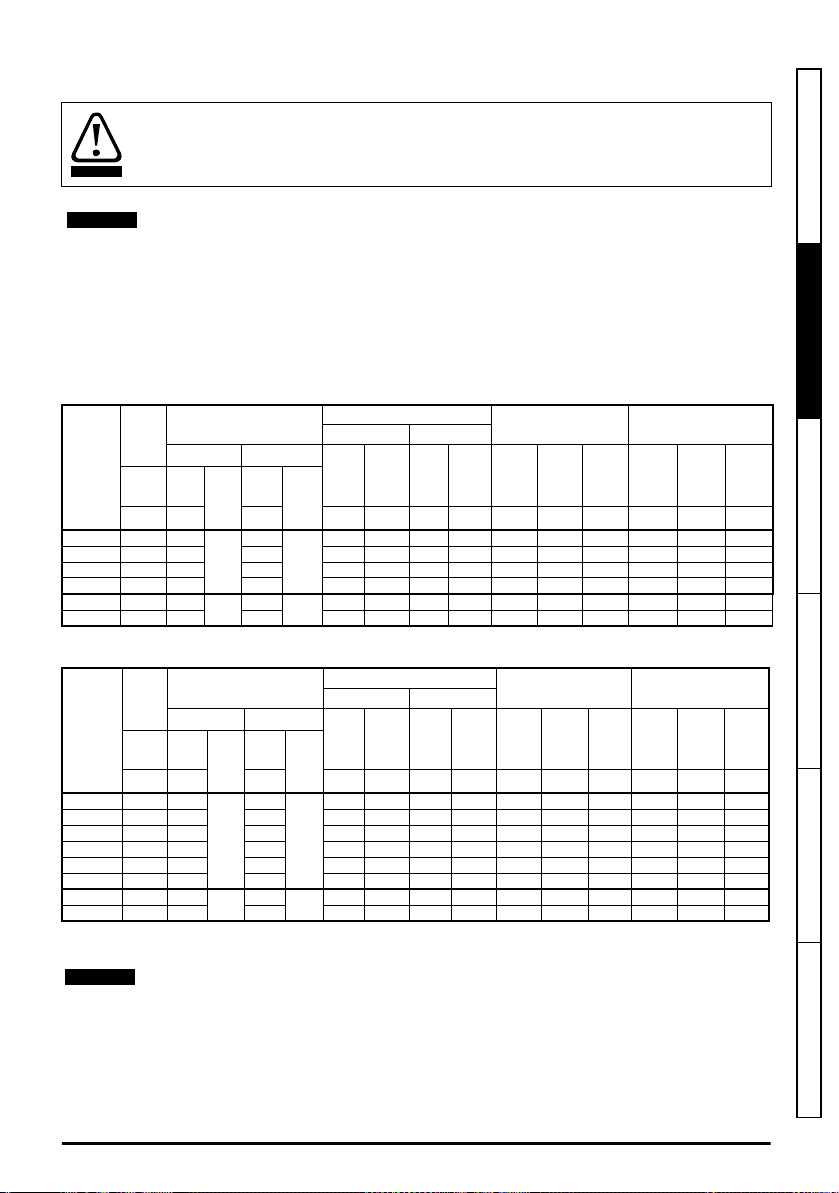
2.4 Ratings
WARNING
NOTE
NOTE
Fuses
The AC supply to the drive must be installed with suitable protection against overload and
short-circuits. The following section shows recommended fuse ratings. Failure to observe
this requirement will cause risk of fire.
Nominal cables sizes below are based on the cable installation method B2 (ref: IEC603645-52:2001) unless otherwise specified, and are provided as a guide only. Ensure cables
used suit local wiring regulations.
The continuous output current ratings given below are for maximum 40 °C (104 °F), 1000 m altitude
and 3 kHz switching frequency. Derating is required for higher switching frequencies, ambient
temperature >40 °C (104 °F) and high altitude. For further information, refer to Chapter 5 Technical
data on page 76.
Table 2-1 200 V drive ratings, cable sizes and fuse ratings
Max.
cont.
input
current
Model
3ph Nom
03200050 10.7 16
03200066 13 20 20 1.5 1.5 14 14 8 1.5 2 6.6 1.1 1.5
03200080 17.8 25 25 4 4 12 12 11 2.2 3 8 1.5 2
03200106 20.6 25 25 4 4 12 12 12.7 3 3 10.6 2.2 3
04200137 20.1 25
04200185 26.8 32 30 8 8 8 8 25 5.5 7.5 18.5 4 5
A A A
Fuse
IEC UL
Nom
Class
16
gG
25
gG
Class
CC, J
CC,
J or T*
Nominal cable size
European USA
Input Output Input Output
2
mm2mm
1.5 1.5 14 14 6.6 1.1 1.5 5 0.75 1
or
T*
6 6 10 10 18 4 5 13.7 3 3
AWG AWG A kW hp A kW hp
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Max.
Nom
Motor
cont.
output
current
power
@
230 V
power
@
230 V
Max.
cont.
output
current
Nom
power
@
230 V
Motor
power
@
230 V
Safety information
Product information
Mechanical installation Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Table 2-2 400 V drive ratings, cable sizes and fuse ratings
Max.
cont.
input
current
Model
3ph Nom
03400025 5 6
03400031 6.6 10 10 1.5 1.5 16 16 4.5 1.5 2 3.1 1.1 1.5
03400045 9.1 10 10 1.5 1.5 14 14 6.2 2.2 3 4.5 1.5 2.0
03400062 13.1 20 20 2.5 2.5 14 14 7.7 3 5 6.2 2.2 3.0
03400078 13.4 20 20 2.5 2.5 14 14 10.4 4 5 7.8 3 5.0
03400100 15.8 20 20 2.5 2.5 12 12 12.3 5.5 7.5 10 4 5.0
04400150 18.7 25
04400172 24.3 32 30 6 6 8 8 24 11 15 17.2 7.5 10.0
A A A
Fuse
IEC UL
Nom
Class
10
gG
25
gG
Class
CC, J
CC,
J or T*
Nominal cable size
European USA
Input Output Input Output
2
mm2mm
1.5 1.5 18 18 3.4 1.1 1.5 2.5 0.75 1.0
or
T*
4 4 10 10 18.5 7.5 10 15 5.5 10.0
AWG AWG A kW hp A kW hp
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Max.
Nom
power
@
400 V
Motor
power
@
460 V
cont.
output
current
* These fuses are fast acting.
Refer to Chapter 5 Technical data on page 76 for maximum fuse rating, maximum cable
size and peak currents.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Max.
cont.
output
current
Nom
power
@
400 V
Motor
power
@
460 V
13
Page 14
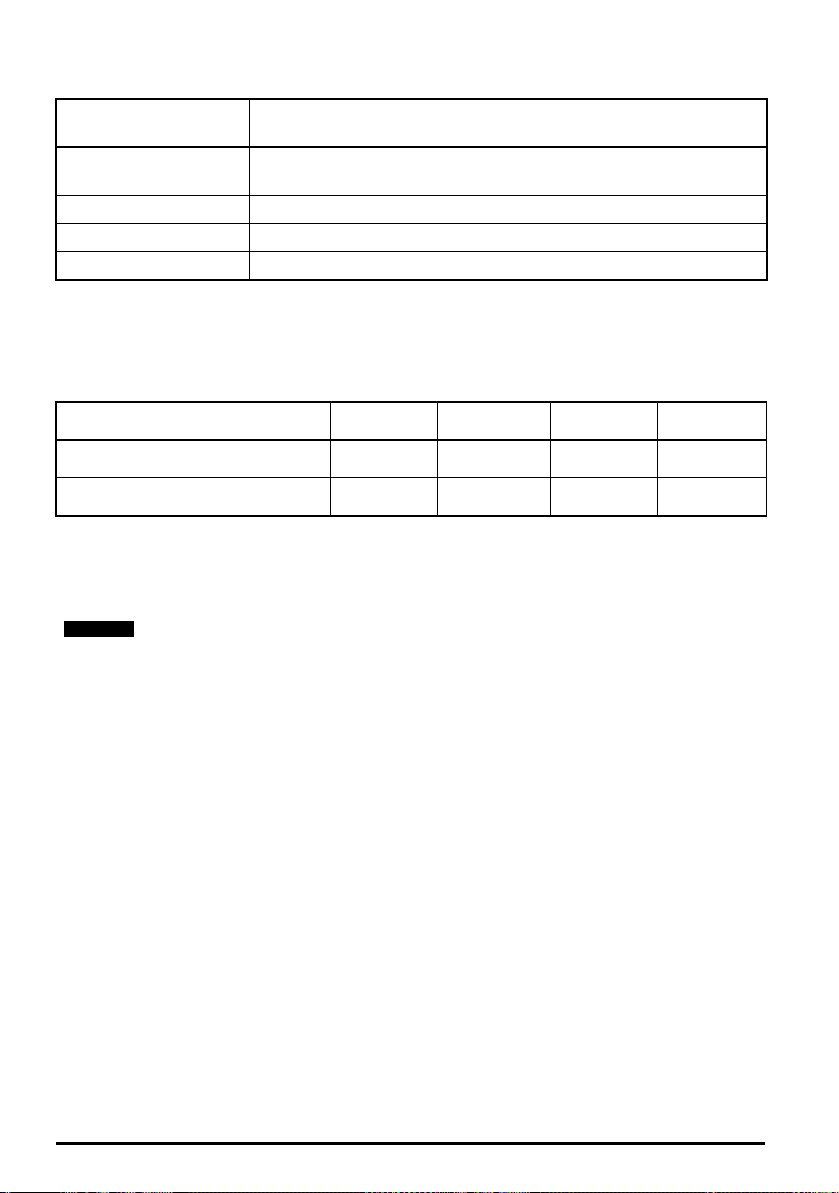
Table 2-3 Protective ground cable ratings
NOTE
Input phase
conductor size
≤ 10 mm
2
> 10 mm2 and ≤ 16 mm
Either 10 mm2 or two conductors of the same cross-sectional area as
the input phase conductor
2
The same cross-sectional area as the input phase conductor
> 16 mm2 and ≤ 35 mm216 mm
> 35 mm
2
Half of the cross-sectional area of the input phase conductor
2
Minimum ground conductor size
Typical short term overload limits
The maximum percentage overload limit changes depending on the selected motor. Variations in
motor rated current, motor power factor and motor leakage inductance all result in changes in the
maximum possible overload. Typical values are shown in the table below:
Table 2-4 Typical overload limits
Operating mode RFC from cold RFC from 100 %
Normal Duty overload with motor rated
current = drive rated current
Heavy Duty overload with motor rated
current = drive rated current
Open loop
from cold
110 % for 165 s 110 % for 9 s 110 % for 165 s 110 % for 9 s
200 % for 28 s 200 % for 3 s 150 % for 60 s 150 % for 7 s
Open loop
from 100 %
Generally the drive rated current is higher than the matching motor rated current allowing a higher
level of overload than the default setting.
The time allowed in the overload region is proportionally reduced at very low output frequency on
some drive ratings.
The maximum overload level which can be attained is independent of the speed.
Output current
The continuous output current ratings given on the rating label are for maximum 40 °C (104 °F), 1000
m altitude and 3 kHz switching frequency. Derating is required for higher switching frequencies,
ambient temperatures >40 °C (104 °F) and higher altitude. For derating information, refer to the
Chapter 5 Technical data on page 76.
Input current
The input current is affected by the supply voltage and impedance. The input current given on the
rating label is the typical input current and is stated for a balanced supply.
14
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 15
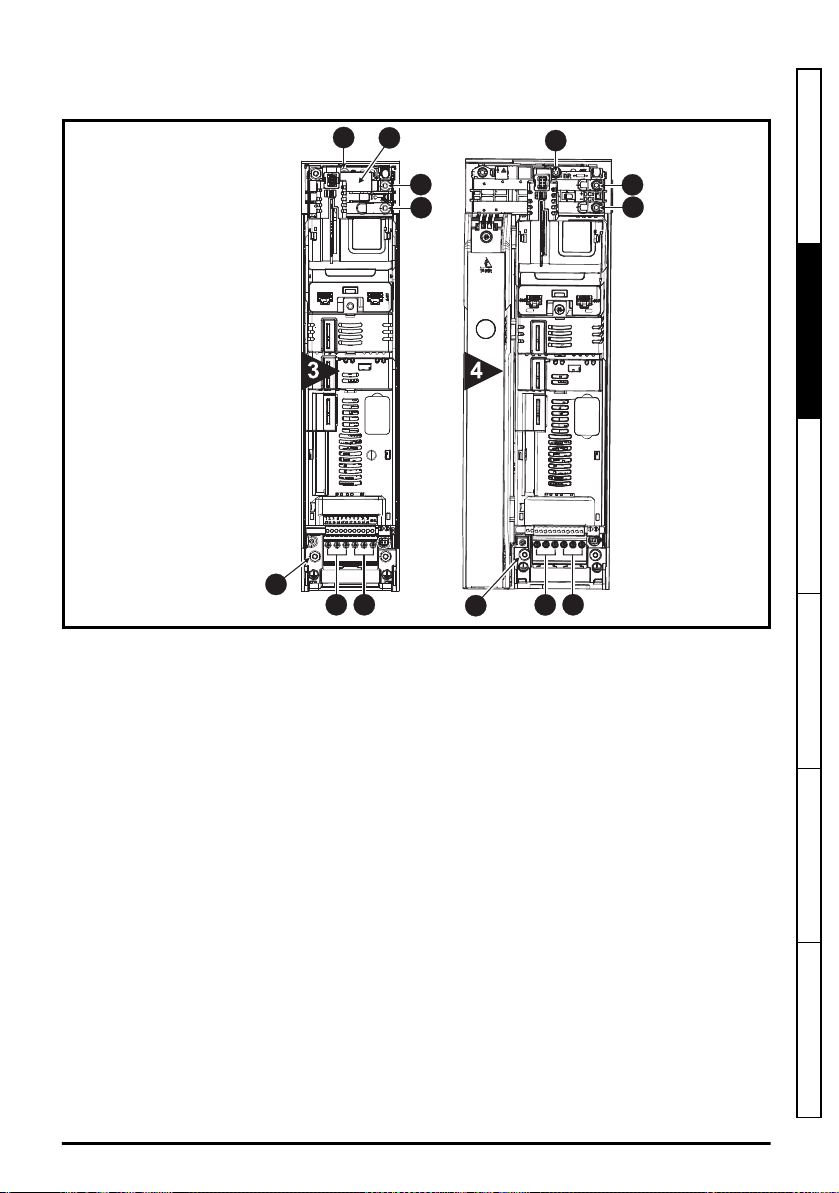
2.5 Drive features
1
2
3
4
6
5
7
1
3
4
6
5
7
Figure 2-3 Features of the drive power section
Key
1. Braking terminal 2. Internal EMC filter 3. DC bus + 4. DC bus -
5. Motor connections 6. AC supply connections 7. Ground connections
Safety information
Product information
Mechanical installation Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
15
Page 16
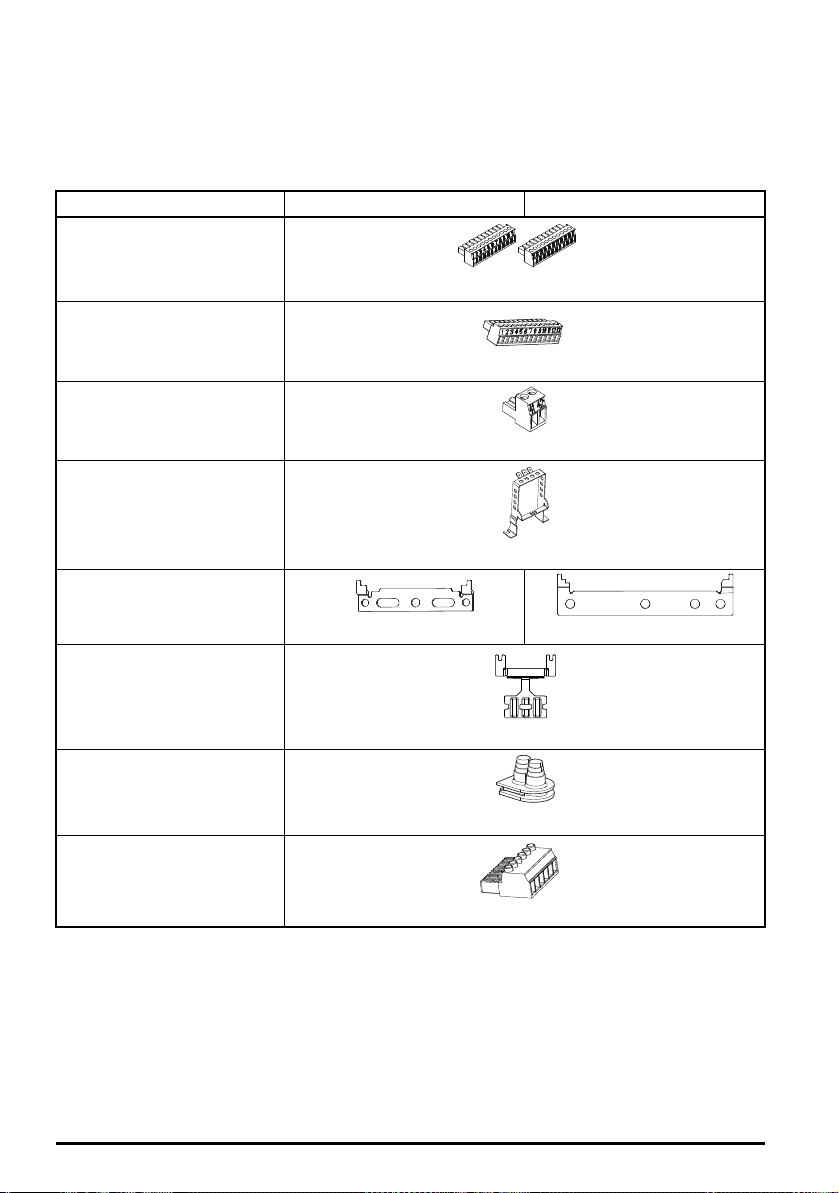
2.6 Items supplied with the drive
The drive is supplied with a copy of the Power Installation Guide and a copy of the Control Getting
Started Guide, a safety information booklet, the Certificate of Quality and an accessory kit box
including the items shown in Table 2-5.
Table 2-5 Parts supplied with the drive
Description Size 3 Size 4
Control connectors
(1 to 11 way and 21 to 31 way)
x 1* x 1*
Control connectors (1 to 13)
x 1**
Relay connector
x 1
Grounding bracket
x 1
Surface mounting brackets
x 2 x 2
Grounding clamp
x 1
DC terminal cover grommets
x 2
Supply and motor connector
x 1
* Supplied with Unidrive M600 / M700 / M701and HS70 / 71 only.
** Supplied with Unidrive M702 and HS72 only.
16
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 17
3 Mechanical installation
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
3.1 Safety information
Follow the instructions
The mechanical and electrical installation instructions must be adhered to. Any questions
or doubt should be referred to the supplier of the equipment. It is the responsibility of the
owner or user to ensure that the installation of the drive and any external option unit, and
the way in which they are operated and maintained, comply with the requirements of the
Health and Safety at Work Act in the United Kingdom or applicable legislation and
regulations and codes of practice in the country in which the equipment is used.
Stored charge
The drive contains capacitors that remain charged to a potentially lethal voltage after the
AC supply has been disconnected. If the drive has been energized, the AC supply must
be isolated at least ten minutes before work may continue.
Normally, the capacitors are discharged by an internal resistor. Under certain, unusual
fault conditions, it is possible that the capacitors may fail to discharge, or be prevented
from being discharged by a voltage applied to the output terminals. If the drive has failed
in a manner that causes the display to go blank immediately, it is possible the capacitors
will not be discharged. In this case, consult Emerson Industrial Automation or their
authorized distributor.
Competence of the installer
The drive must be installed by professional assemblers who are familiar with the
requirements for safety and EMC. The assembler is responsible for ensuring that the end
product or system complies with all the relevant laws in the country where it is to be used.
Enclosure
The drive is intended to be mounted in an enclosure which prevents access except by
trained and authorized personnel, and which prevents the ingress of contamination. It is
designed for use in an environment classified as pollution degree 2 in accordance with IEC
60664-1. This means that only dry, non-conducting contamination is acceptable.
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
17
Page 18
3.2 Planning the installation
NOTE
The following considerations must be made when planning the installation:
3.2.1 Access
Access must be restricted to authorized personnel only. Safety regulations which apply at the place
of use must be complied with.
The IP (Ingress Protection) rating of the drive is installation dependent. For further information, refer
to section 3.8
3.2.2 Environmental protection
The drive must be protected from:
• Moisture, including dripping water or spraying water and condensation. An anti-condensation
heater may be required, which must be switched off when the drive is running.
• Contamination with electrically conductive material
• Contamination with any form of dust which may restrict the fan, or impair airflow over various
components
• Temperature beyond the specified operating and storage ranges
• Corrosive gasses
3.2.3 Cooling
The heat produced by the drive must be removed without its specified operating temperature being
exceeded. Note that a sealed enclosure gives much reduced cooling compared with a ventilated one,
and may need to be larger and/or use internal air circulating fans.
For further information, refer to section 3.5
3.2.4 Electrical safety
The installation must be safe under normal and fault conditions. Electrical installation instructions are
given in Chapter 4
3.2.5 Fire protection
The drive enclosure is not classified as a fire enclosure. A separate fire enclosure must be provided.
For installation in the USA, a NEMA 12 enclosure is suitable.
For installation outside the USA, the following (based on IEC 62109-1, standard for PV inverters) is
recommended.
Enclosure can be metal and/or polymeric, polymer must meet requirements which can be
summarized for larger enclosures as using materials meeting at least UL 94 class 5VB at the point of
minimum thickness.
Air filter assemblies to be at least class V-2.
The location and size of the bottom shall cover the area shown in Figure 3-1. Any part of the side
which is within the area traced out by the 5° angle is also considered to be part of the bottom of the
fire enclosure.
Enclosing standard drive for high environmental protection
During installation it is recommended that the vents on the drive are covered to prevent
debris (e.g. wire off-cuts) from entering the drive.
Enclosure for standard drives
Electrical installation on page 45
.
on page 32.
on page 27.
18
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 19
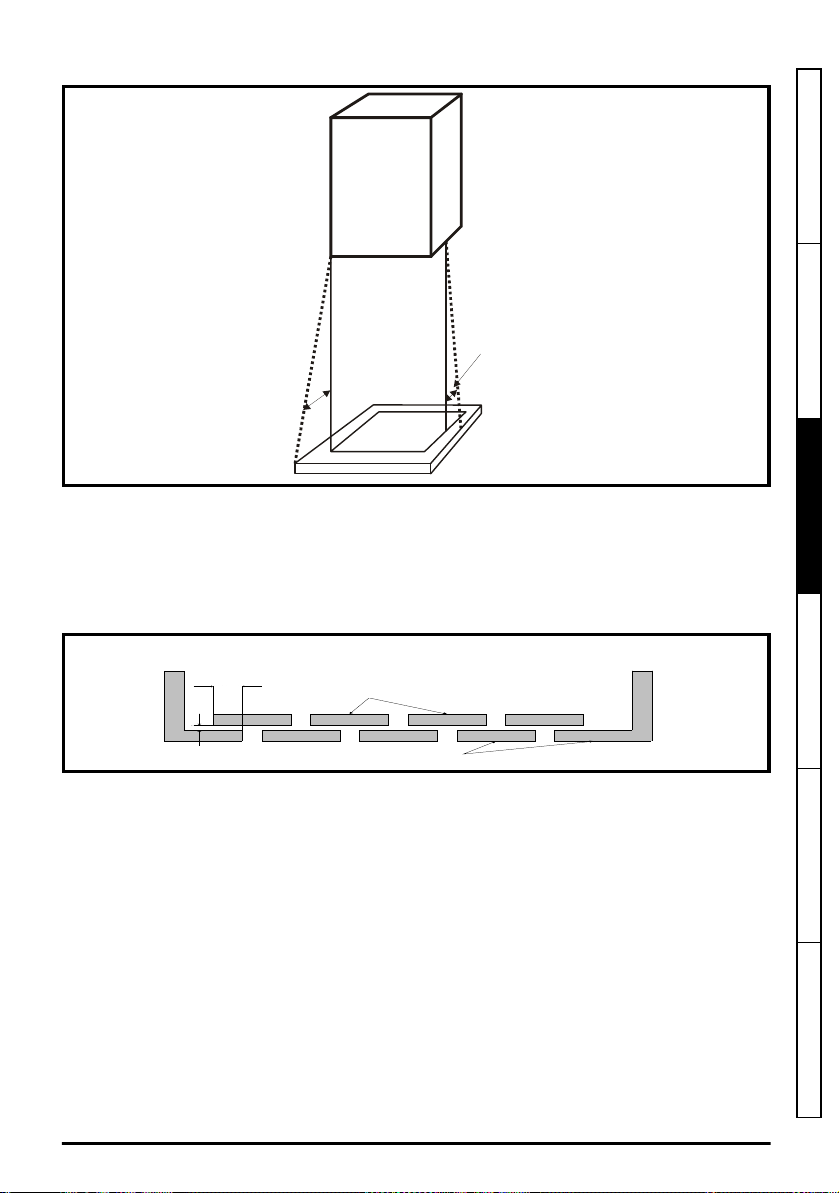
Figure 3-1 Fire enclosure bottom layout
Drive
5
o
5
o
N o t le s s
t ha n 2 X
B a ff le p la te s ( m a y b e
a b ov e o r b e lo w b o tt o m
o f e n cl o su r e)
X
B o tt o m o f f ir e
e n cl os u re
Not less
than 2
times ‘X’
Baffle plates (may be above or
below bottom of enclosure)
Bottom of fire enclosure
X
The bottom, including the part of the side considered to be part of the bottom, must be designed to
prevent escape of burning material - either by having no openings or by having a baffle construction.
This means that openings for cables etc. must be sealed with materials meeting the 5VB
requirement, or else have a baffle above. See Figure 3-2 for acceptable baffle construction. This
does not apply for mounting in an enclosed electrical operating area (restricted access) with concrete
floor.
Figure 3-2 Fire enclosure baffle construction
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
3.2.6 Electromagnetic compatibility
Variable speed drives are powerful electronic circuits which can cause electromagnetic interference if
not installed correctly with careful attention to the layout of the wiring.
Some simple routine precautions can prevent disturbance to typical industrial control equipment.
If it is necessary to meet strict emission limits, or if it is known that electromagnetically sensitive
equipment is located nearby, then full precautions must be observed. In-built into the drive, is an
internal EMC filter, which reduces emissions under certain conditions. If these conditions are
exceeded, then the use of an external EMC filter may be required at the drive inputs, which must be
located very close to the drives. Space must be made available for the filters and allowance made for
carefully segregated wiring. Both levels of precautions are covered in section 4.12
(Electromagnetic compatibility) on page 63
.
EMC
3.2.7 Hazardous areas
The drive must not be located in a classified hazardous area unless it is installed in an approved
enclosure and the installation is certified.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
19
Page 20
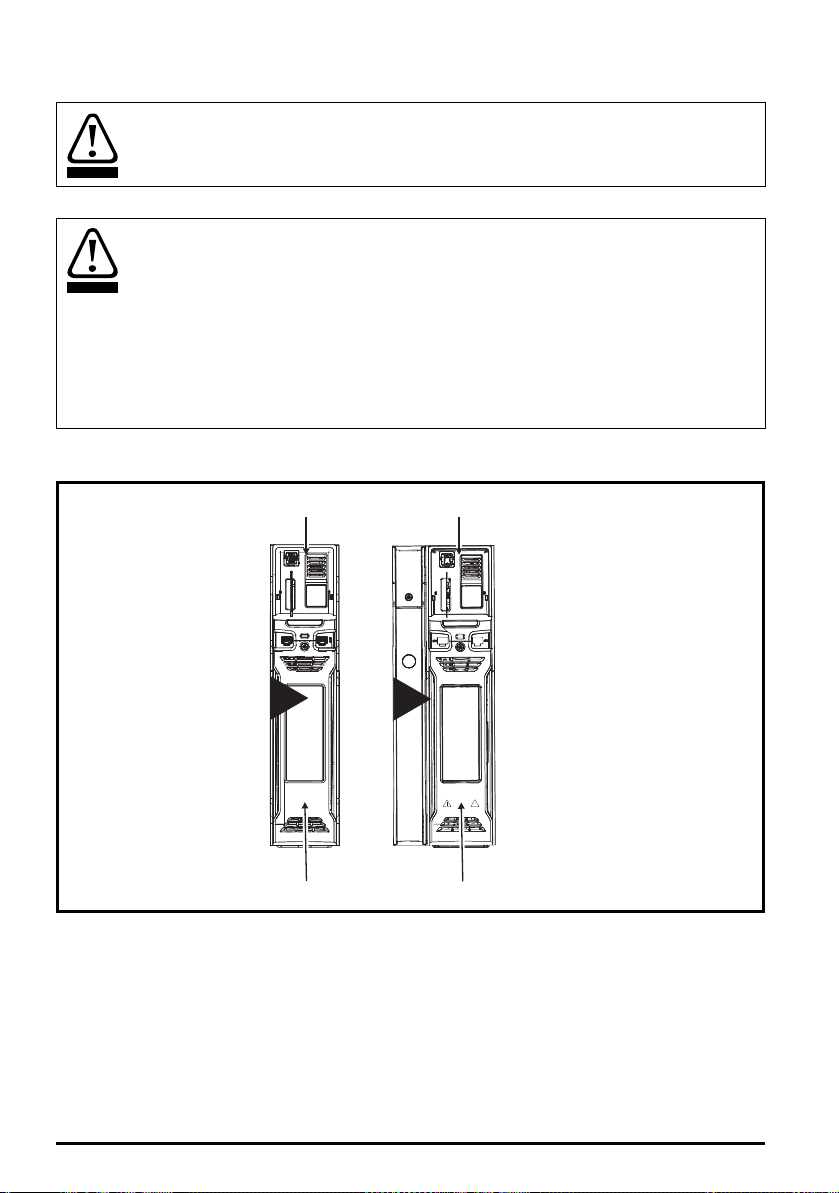
3.3 Terminal cover removal
WARNING
WARNING
3
DC/Braking
terminalcover
Control/ AC/
Motorterminalcover
4
Control/ AC/
Motorterminalcover
DC/Braking
terminalcover
Isolation device
The AC and / or DC power supply must be disconnected from the drive using an approved
isolation device before any cover is removed from the drive or before any servicing work
is performed.
Stored charge
The drive contains capacitors that remain charged to a potentially lethal voltage after the
AC and / or DC power supply has been disconnected. If the drive has been energized,
the power supply must be isolated at least ten minutes before work may continue.
Normally, the capacitors are discharged by an internal resistor. Under certain, unusual
fault conditions, it is possible that the capacitors may fail to discharge, or be prevented
from being discharged by a voltage applied to the output terminals. If the drive has failed
in a manner that causes the display to go blank immediately, it is possible the capacitors
will not be discharged. In this case, consult Emerson Industrial Automation or their
authorized distributor.
3.3.1 Removing the terminal covers
Figure 3-3 Location and identification of terminal covers (size 3 to 4)
20
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 21
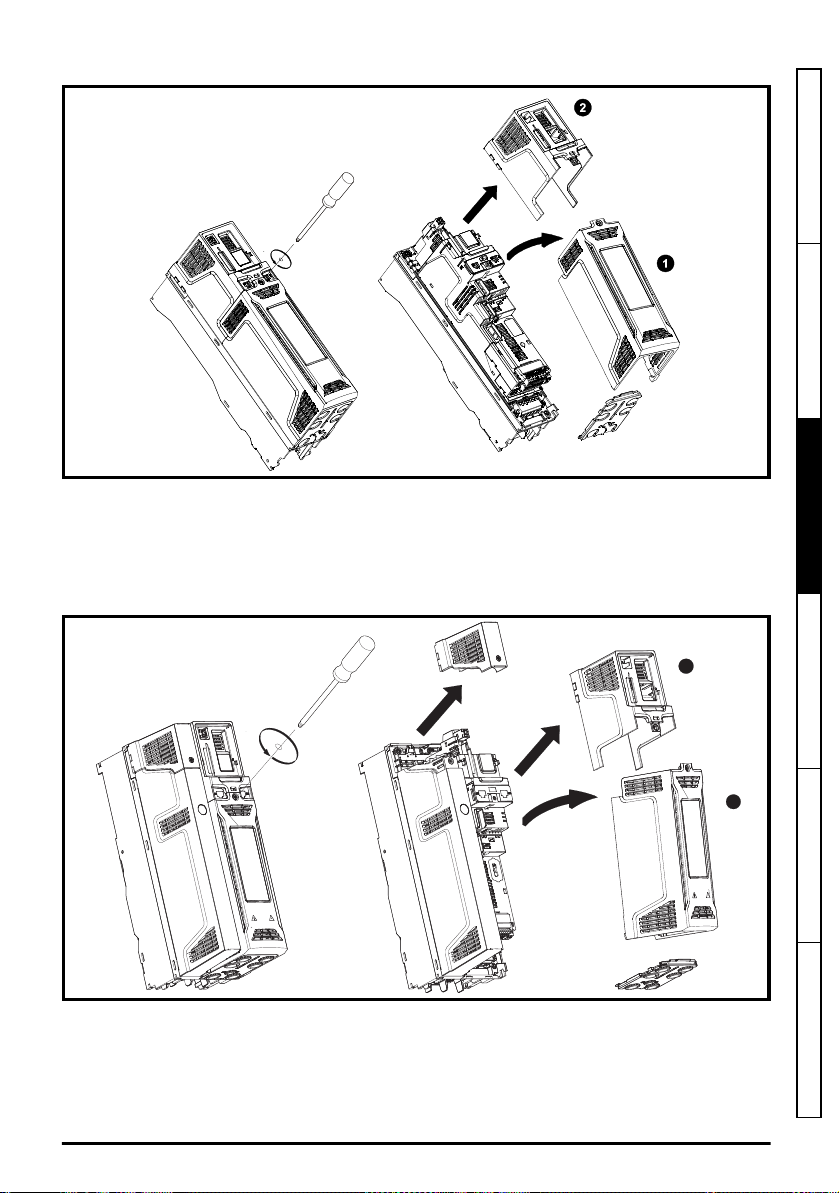
Figure 3-4 Removing the size 3 terminal covers
1
2
1. Control / AC / Motor terminal cover
2. DC / Braking terminal cover
The Control / AC / Motor terminal cover must be removed before removal of the DC / Braking
terminal cover. When replacing the terminal covers, the screws should be tightened to a maximum
torque of 1 N m (0.7 lb ft).
Figure 3-5 Removing the size 4 terminal covers
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
1. Control / AC / Motor terminal cover
2. DC / Braking terminal cover
The Control / AC / Motor terminal cover must be removed before removal of the DC / Braking
terminal cover. When replacing the terminal covers, the screws should be tightened to a maximum
torque of 1 N m (0.7 lb ft).
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
21
Page 22
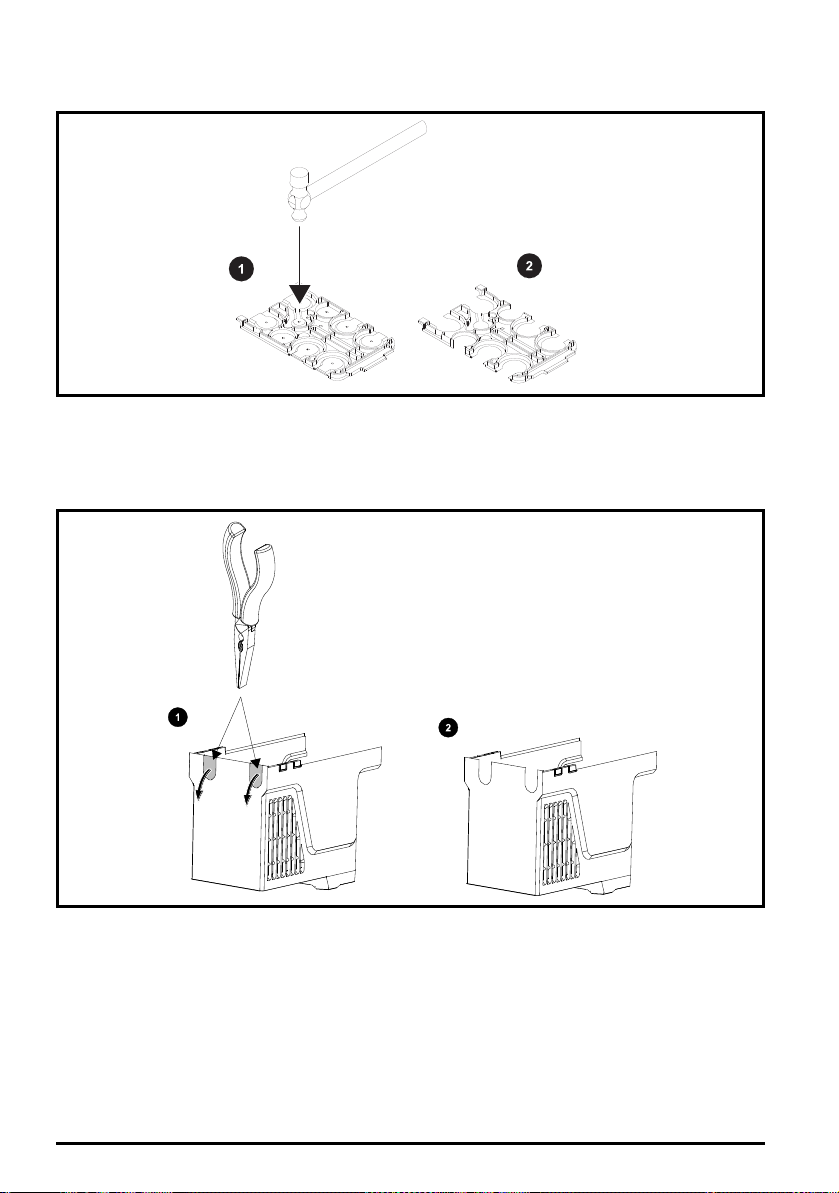
3.3.2 Removing the finger-guard and DC terminal cover break-outs
Figure 3-6 Removing the finger-guard break-outs
Place finger-guard on a flat solid surface and hit relevant break-outs with hammer as shown (1).
Continue until all required break-outs are removed (2). Remove any flash / sharp edges once the
break-outs are removed.
Figure 3-7 Removing the size 3 and 4 DC terminal cover break-outs
Grasp the DC terminal cover break-outs with pliers as shown (1) and pull down in the direction shown
to remove. Continue until all required break-outs are removed (2). Remove any flash / sharp edges
once the break-outs are removed. Use the DC terminal cover grommets supplied in the accessory
box (Table 2-5
22
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Parts supplied with the drive
on page 16) to maintain the seal at the top of the drive.
Issue Number: 3
Page 23
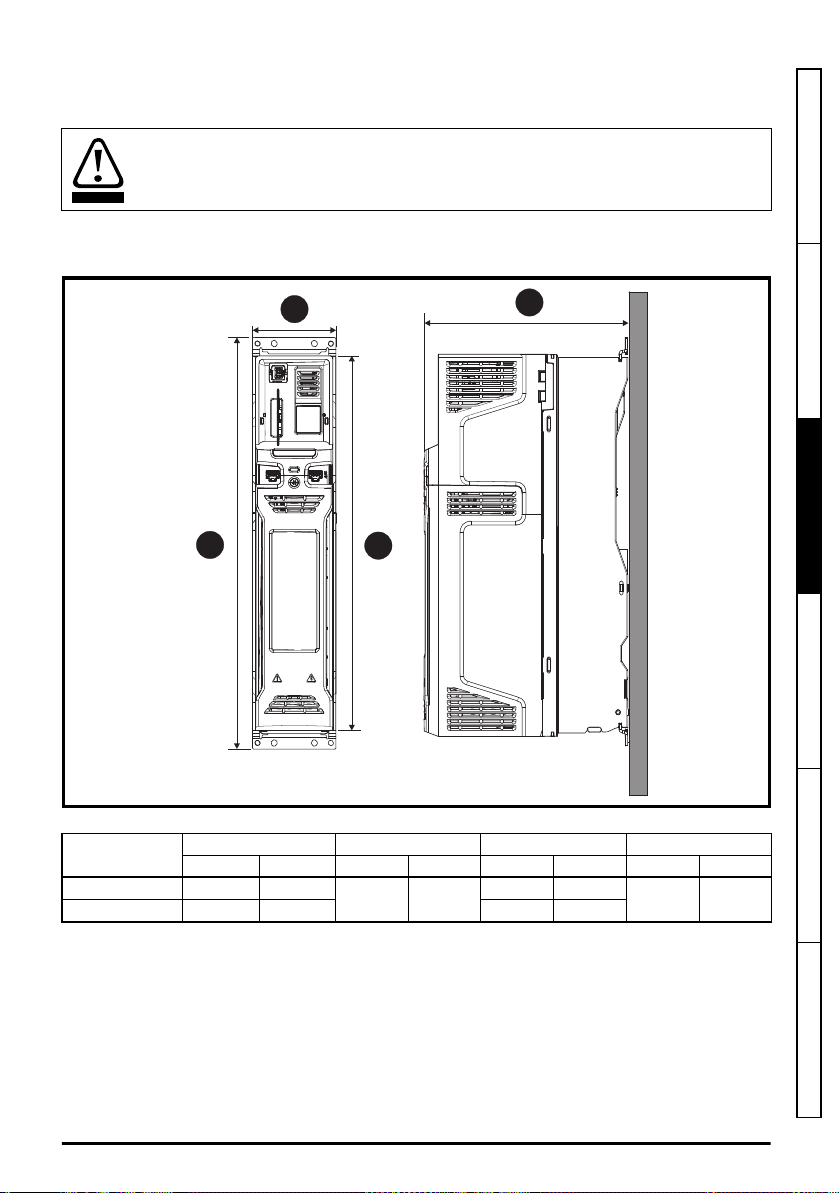
3.4 Dimensions and mounting methods
WARNING
H
H1
H2
W
D
Drive sizes 3 and 4 can be surface, through-panel or tile mounted using the appropriate brackets.
If the drive has been used at high load levels for a period of time, the heatsink can reach
temperatures in excess of 70 °C (158 °F). Human contact with the heatsink should be
prevented.
3.4.1 Drive dimensions
Figure 3-8 Drive dimensions (size 3 illustrated)
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Size
H1 H2 W D
mm in mm in mm in mm in
3 382 15.04
4 391 15.39 124 4.88
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
365 14.37
83 3.27
200 7.87
23
Page 24
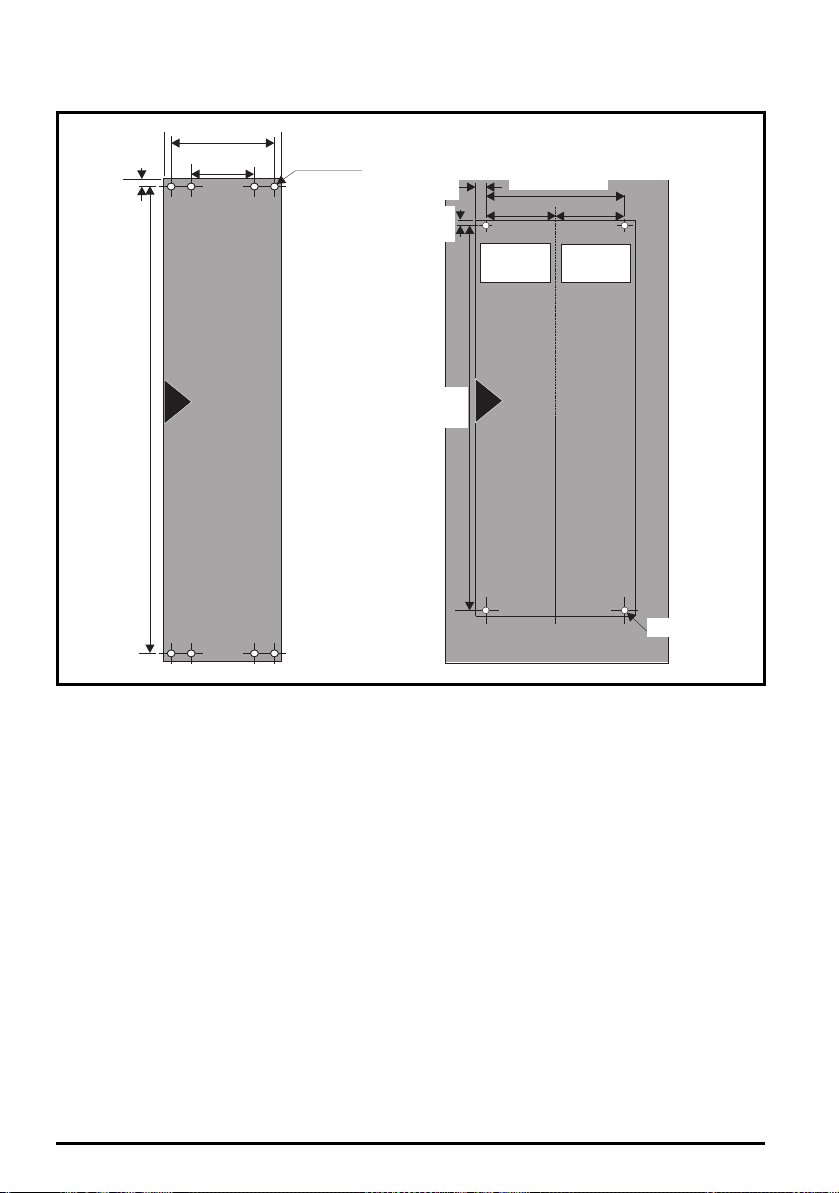
3.4.2 Surface mounting
6.0mm
(0.24in)
73.0mm(2.87in)
Æ
5.5mm
(0.22in)
370mm
(14.57in)
3
375mm
(14.76in)
8mm
(0.32in)
4
Æ
6.5mm
(0.26in)
x4holes
9mm
(0.35in)
53mm
(2.09in)
53mm
(2.09in)
106mm
(4.17in)
40mm
(1.58in)
Figure 3-9 Surface mounting dimensions
Surface mounting size 3
Each mounting bracket contains 5 mounting slots / holes, the outer holes (5.2 mm) x 2 should be
used for mounting the drive to the backplate as this allows the heatsink fan to be replaced without
removing the drive from the backplate. The inner slots / holes (6.2 mm) x 3 are used for Unidrive SP
size 1 retrofit applications.
Surface mounting size 4
The outer holes in the mounting bracket (6.5 mm) x 2 are to be used for surface mounting.
24
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 25
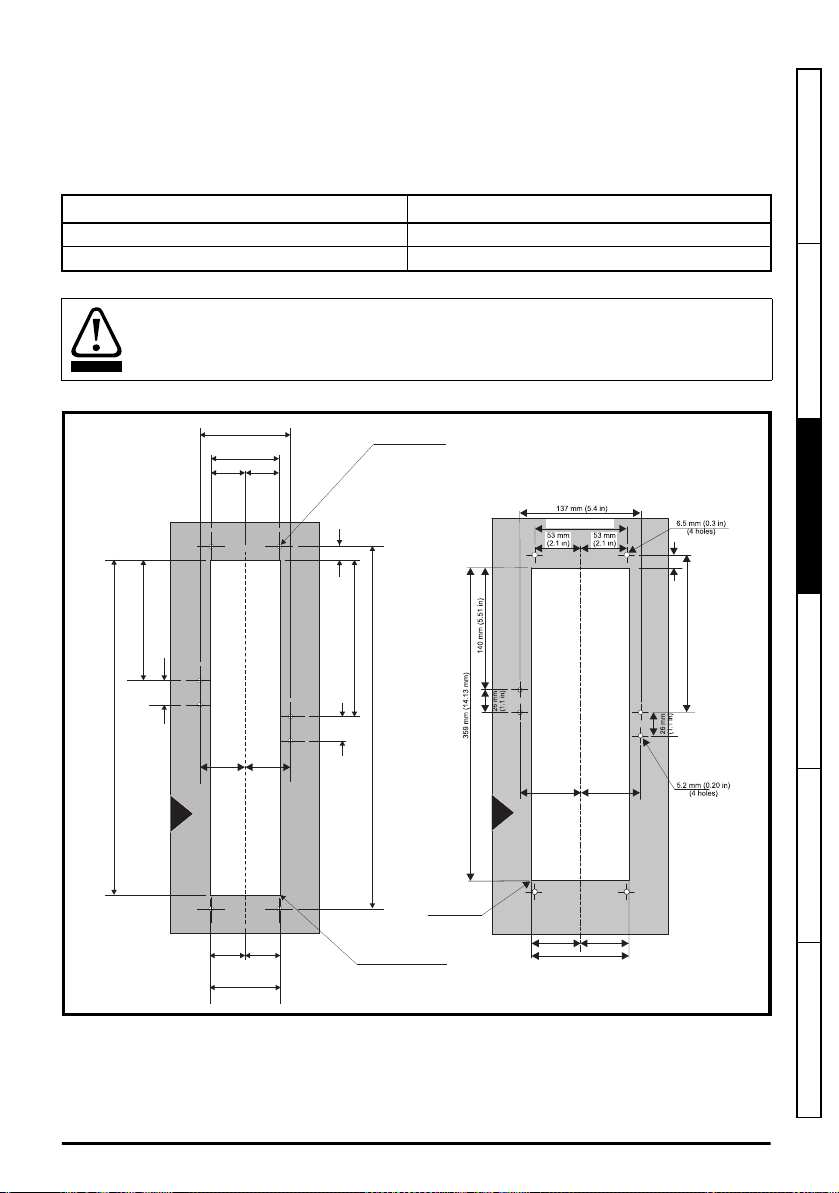
3.4.3 Through-panel mounting
WARNING
4
17mm
(0.67in)
68.5mm
(2.70in)
68.5mm
(2.70in)
117mm(4.61in)
168mm(6.61in)
58.5mm
(2.30in)
58.5mm
(2.30in)
4
106mm(4.17in)
97mm(3.82in)
36.5mm
(1.44in)
Æ5.20mm(0.21in)
x8holes
73mm(2.87in)
36.5mm
(1.44in)
15mm
(0.59in)
129mm(5.08in)
26mm(1.02in)
168mm(6.61in)
360mm(14.17in)
389mm(15.32in)
26mm(1.02in)
Radius1.0mm(0.04in)
38mm
(1.50in)
38mm
(1.50in)
76mm(2.99in)
3
48.5mm
(1.91in)
48.5mm
(1.91in)
Radius1.0mm
(0.04in)
The drive can be through-panel mounted using the appropriate brackets, see section 3.8
standard drive for high environmental protection
on page 32 for further details.
The through-panel mounting kit is not supplied with the drive and can be purchased separately,
below are the relevant part numbers:
Size CT part number
3 3470-0053
4 3470-0056
If the drive has been used at high load levels for a period of time, the heatsink can reach
temperatures in excess of 70 °C (158 °F). Human contact with the heatsink should be
prevented.
Figure 3-10 Through-panel mounting dimensions
Enclosing
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
25
Page 26
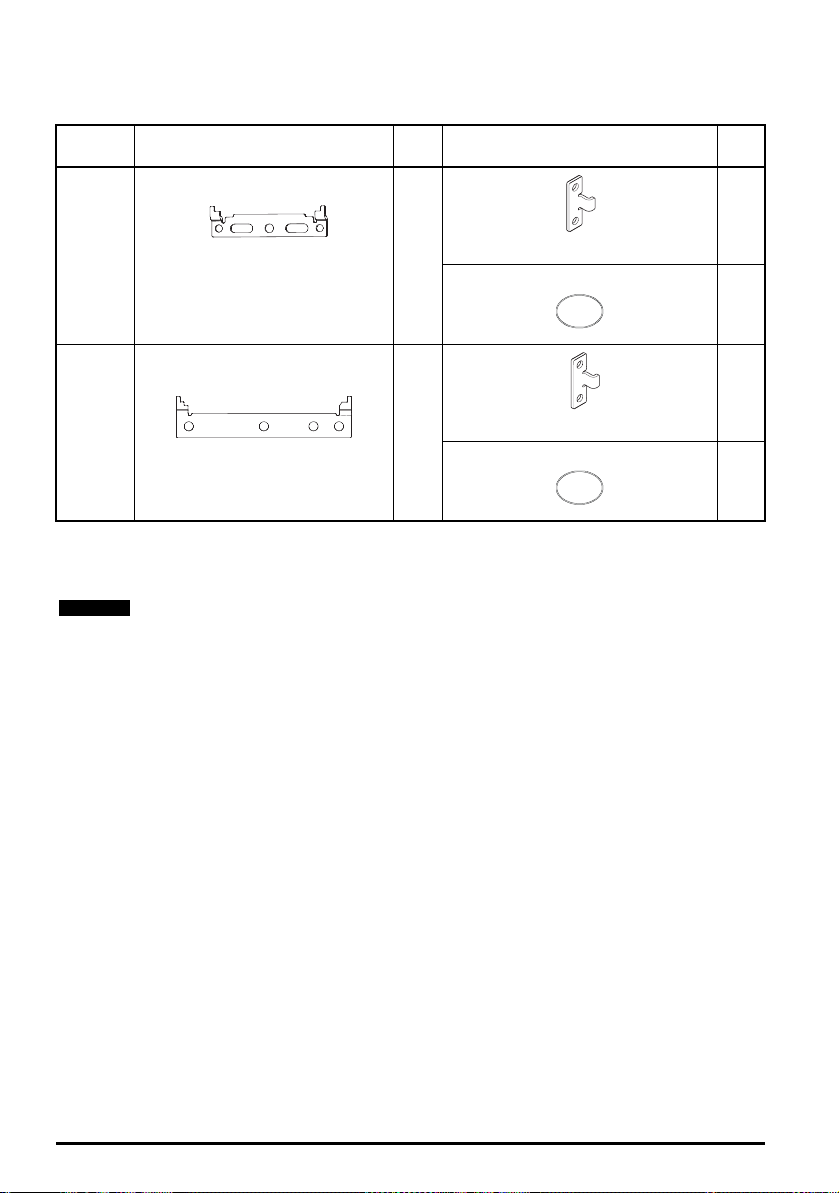
3.4.4 Mounting brackets
NOTE
Table 3-1 Mounting brackets
Frame
size
Surface Qty Through-panel* Qty
x 2
3
Outer hole size: 5.2 mm (0.20 in)
Centre hole / slot size: 6.2 mm (0.24 in)
4
Hole size: 6.5 mm (0.26 in)
x 2
x 2
Hole size: 5.2 mm (0.21 in)
Hole size: 5.2 mm (0.21 in)
* A gasket is supplied in the through-panel mounting kit, see section 3.8
high environmental protection
on page 32 for further details.
A retrofit kit is available for Unidrive M/HS size 4 that allows mounting of the drive in
applications previously using Unidrive SP size 2, the part number of this kit is 3470-0062.
A similar kit is not necessary for Unidrive M/HS size 3 because it has the same mounting
hole positions as Unidrive SP size 1.
x 1
x 2
x 1
Enclosing standard drive for
26
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 27
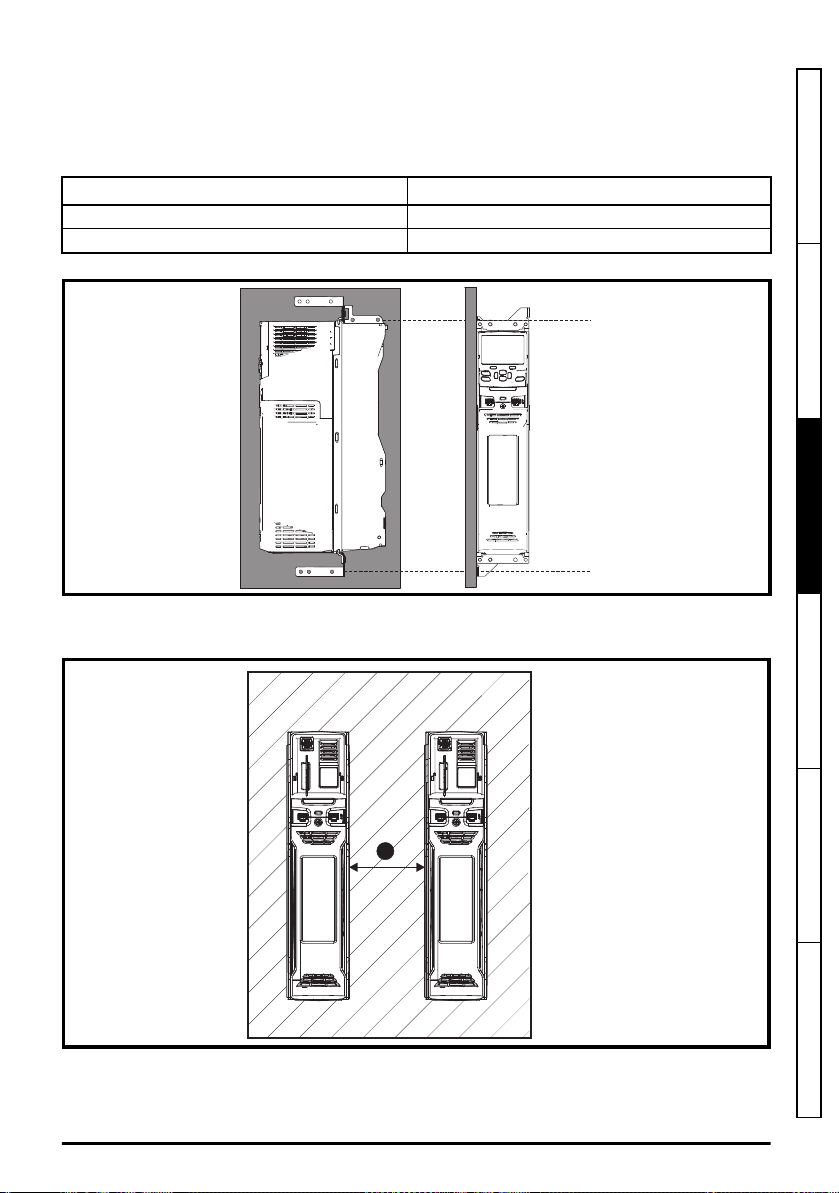
3.4.5 Tile mounting
Enclosure
A
Drive sizes 3 to 4 can be tile mounted where limited mounting space is available. The drive is
mounted sideways with the side panel against the mounting surface as shown in Figure 3-11. The tile
mounting kit is not supplied with the drive, it can be purchased separately using the following part
numbers:
Size CT part number
3 3470-0049
4 3470-0060
Figure 3-11 Tile mounting
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
3.5 Enclosure for standard drives
Figure 3-12 Recommended spacing between the drives
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
27
Page 28
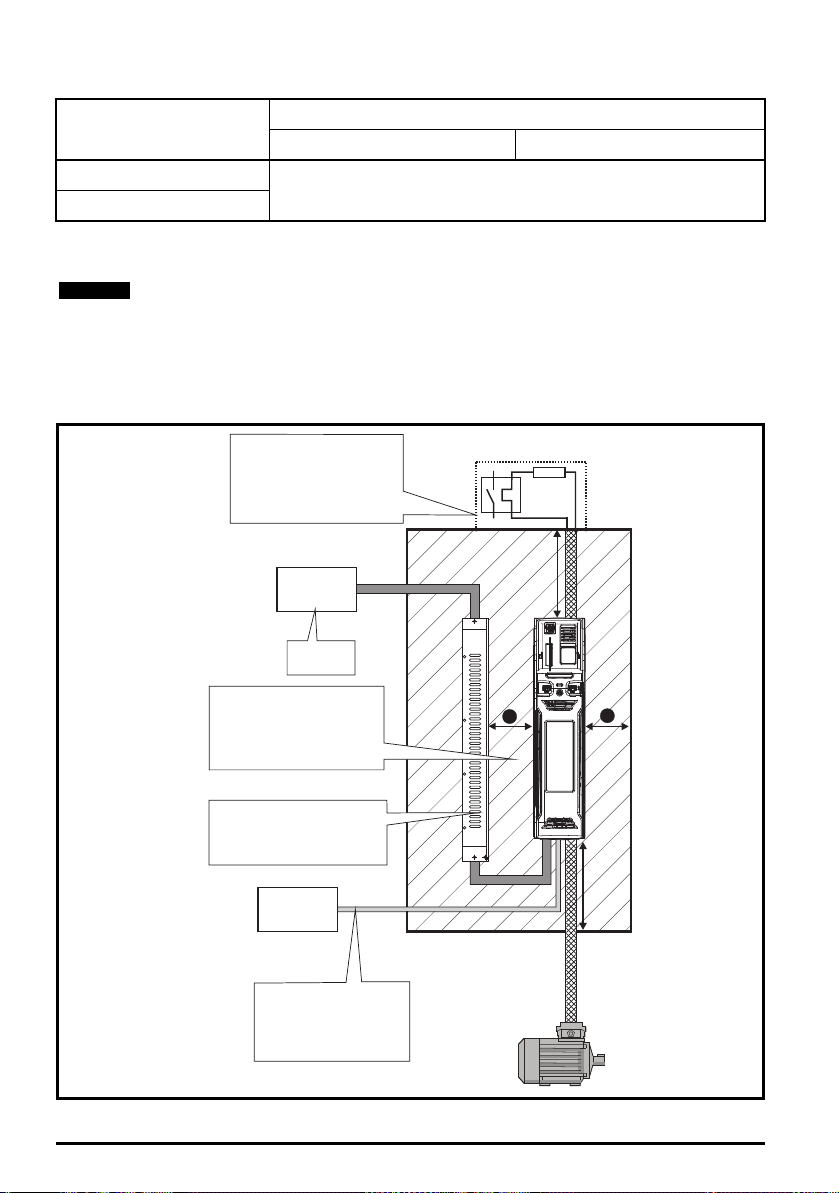
Table 3-2
NOTE
³100mm
(4in)
Enclosure
ACsupply
contactorand
fusesorMCB
Locateas
required
External
controller
Signalcables
Planforallsignalcables
toberoutedatleast
300mm(12in)fromthe
driveandanypowercable
Ensureminimumclearances
aremaintainedforthedrive
andexternalEMCfilter.Forced
orconvectionair-flowmustnot
berestrictedbyanyobjector
cabling
³100mm
(4in)
Optionalbrakingresistorandoverload
Locateas
Locateoptionalbraking
resistorexternalto
cubicle(preferablyneartoor
ontopofthecubicle).
Locatetheoverloadprotection
deviceasrequired
TheexternalEMCfiltercanbe
bookcasemounted(nexttothe
drive)orfootprintmounted(with
thedrivemountedontothefilter).
B
B
* 50 °C derating applies, refer to Table 5-5
(122 °F)
Spacing required between the drives (without high IP insert)
Drive Size
3
4
40°C 50°C*
Spacing (A)
0 mm (0.00 in)
Maximum permissible continuous output current @ 50 °C
on page 79.
When through-panel mounted, ideally drives should be spaced 30 mm (1.18 in) to
maximize panel stiffness.
3.5.1 Enclosure layout
Please observe the clearances in the diagram below taking into account any appropriate notes for
other devices / auxiliary equipment when planning the installation.
Figure 3-13 Enclosure layout
28
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 29

Table 3-3 Spacing required between drive / enclosure and drive / EMC filter
NOTE
A
e
P
k T
in tTex t
–( )
-----------------------------------
=
Drive Size Spacing (B)
3 0 mm (0.00 in)
4 30 mm (1.18 in)
For EMC compliance:
1. When using an external EMC filter, one filter is required for each drive.
2. Power cabling must be at least 100 mm (4 in) from the drive in all directions
3.5.2 Enclosure sizing
1. Add the dissipation figures from section 5.1.3
to be installed in the enclosure.
2. If an external EMC filter is to be used with each drive, add the dissipation figures from section
5.2.1
EMC filter ratings
on page 96 for each external EMC filter that is to be installed in the
enclosure.
3. If the braking resistor is to be mounted inside the enclosure, add the average power figures from
for each braking resistor that is to be installed in the enclosure.
4. Calculate the total heat dissipation (in Watts) of any other equipment to be installed in the
enclosure.
5. Add the heat dissipation figures obtained above. This gives a figure in Watts for the total heat that
will be dissipated inside the enclosure.
Calculating the size of a sealed enclosure
The enclosure transfers internally generated heat into the surrounding air by natural convection (or
external forced air flow); the greater the surface area of the enclosure walls, the better is the
dissipation capability. Only the surfaces of the enclosure that are unobstructed (not in contact with a
wall or floor) can dissipate heat.
Calculate the minimum required unobstructed surface area
Power dissipation
Ae for the enclosure from:
on page 80 for each drive that is
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Where:
A
Unobstructed surface area in m2 (1 m2 = 10.9 ft2)
e
T
Maximum expected temperature in
ext
T
Maximum permissible temperature in oC
int
P
Power in Watts dissipated by
k
Heat transmission coefficient of the enclosure material in W/m2/oC
o
C
outside
all
heat sources in the enclosure
the enclosure
inside
the enclosure
Example
To calculate the size of an enclosure for the following:
• Two drives operating at the Normal Duty rating
• External EMC filter for each drive
• Braking resistors are to be mounted outside the enclosure
• Maximum ambient temperature inside the enclosure: 40 °C
• Maximum ambient temperature outside the enclosure: 30 °C
For example, if the power dissipation from each drive is 187 W and the power dissipation from each
external EMC filter is 9.2 W.
Total dissipation: 2 x (187 + 9.2) =392.4 W
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
29
Page 30
Power dissipation for the drives and the external EMC filters can be obtained from
NOTE
W
H
D
A
e
392.4
5.5 40 30–( )
---------------------------------
=
W
Ae2H D–
H D+
--------------------------
=
W
7.135 2 2× 0.6×( )–
2 0.6+
-----------------------------------------------------
=
Chapter 5
Technical data
on page 76.
The enclosure is to be made from painted 2 mm (0.079 in) sheet steel having a heat
transmission coefficient of 5.5 W/m2/oC. Only the top, front, and two sides of the
enclosure are free to dissipate heat.
The value of 5.5 W/m2/ºC can generally be used with a sheet steel enclosure (exact
values can be obtained by the supplier of the material). If in any doubt, allow for a greater
margin in the temperature rise.
Figure 3-14 Enclosure having front, sides and top panels free to dissipate heat
Insert the following values:
T
40 °C
int
T
30 °C
ext
k
5.5
P
392.4 W
The minimum required heat conducting area is then:
= 7.135 m2 (77.8 ft2)
(1 m2 = 10.9 ft2)
Estimate two of the enclosure dimensions - the height (H) and depth (D), for instance. Calculate the
width (W) from:
Inserting H = 2m and D = 0.6 m, obtain the minimum width:
=1.821 m (71.7 in)
If the enclosure is too large for the space available, it can be made smaller only by attending to one
or all of the following:
• Using a lower PWM switching frequency to reduce the dissipation in the drives
• Reducing the ambient temperature outside the enclosure, and/or applying forced-air cooling to
the outside of the enclosure
• Reducing the number of drives in the enclosure
• Removing other heat-generating equipment
30
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 31

Calculating the air-flow in a ventilated enclosure
V
3k P
T
in tTex t
–
---------------------------
=
P
o
P
l
-------
V
3 1.3× 323.7×
40 30–
---------------------------------------
=
The dimensions of the enclosure are required only for accommodating the equipment. The
equipment is cooled by the forced air flow.
Calculate the minimum required volume of ventilating air from:
Where:
V
Air-flow in m3 per hour (1 m3/hr = 0.59 ft3/min)
T
Maximum expected temperature in °C outside
ext
T
Maximum permissible temperature in °C
int
P
Power in Watts dissipated by
k
Ratio of
all
heat sources in the enclosure
the enclosure
inside
the enclosure
Where:
P0 is the air pressure at sea level
PI is the air pressure at the installation
Typically use a factor of 1.2 to 1.3, to allow also for pressure-drops in dirty air-filters.
Example
To calculate the size of an enclosure for the following:
• Three drives operating at the Normal Duty rating
• External EMC filter for each drive
• Braking resistors are to be mounted outside the enclosure
• Maximum ambient temperature inside the enclosure: 40 °C
• Maximum ambient temperature outside the enclosure: 30 °C
For example, dissipation of each drive: 101 W and dissipation of each external EMC filter: 6.9 W
(max).
Total dissipation: 3 x (101 + 6.9) = 323.7 W
Insert the following values:
T
40 °C
int
T
30 °C
ext
k
1.3
P
323.7 W
Then:
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
=
126.2 m3/hr (74.5 ft3 /min)
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
(1 m3/ hr = 0.59 ft3/min)
31
Page 32

3.6 Enclosure design and drive ambient temperature
Drive derating is required for operation in high ambient temperatures
Totally enclosing or through panel mounting the drive in either a sealed cabinet (no airflow) or in a
well ventilated cabinet makes a significant difference on drive cooling.
The chosen method affects the ambient temperature value (T
) which should be used for any
rate
necessary derating to ensure sufficient cooling for the whole of the drive.
The ambient temperature for the four different combinations is defined below:
1. Totally enclosed with no air flow (<2 m/s) over the drive
T
= T
rate
+ 5 °C
int
2. Totally enclosed with air flow (>2 m/s) over the drive
T
= T
rate
int
3. Through panel mounted with no airflow (<2 m/s) over the drive
T
= the greater of T
rate
+5 °C, or T
ext
int
4. Through panel mounted with air flow (>2 m/s) over the drive
T
= the greater of T
rate
ext
or T
int
Where:
T
= Temperature outside the cabinet
ext
T
= Temperature inside the cabinet
int
T
= Temperature used to select current rating from tables in Chapter 5
rate
Technical data
on
page 76.
3.7 Heatsink fan operation
The drive is ventilated by an internal heatsink mounted fan. The fan housing forms a baffle plate,
channelling the air through the heatsink chamber. Thus, regardless of mounting method (surface
mounting or through-panel mounting), the installing of additional baffle plates is not required.
Ensure the minimum clearances around the drive are maintained to allow air to flow freely.
The heatsink fan on all sizes is a variable speed fan. The drive controls the speed at which the fan
runs based on the temperature of the heatsink and the drive's thermal model system. The maximum
speed at which the fan operates can be limited in Pr
derating. Refer to section 3.13.1
Fan removal procedure
06.045
. This could incur an output current
on page 44 for information on fan removal.
3.8 Enclosing standard drive for high environmental protection
An explanation of environmental protection rating is provided in section 5.1.10
page 85.
The standard drive is rated to IP20 pollution degree 2 (dry, non-conductive contamination only)
(NEMA 1). However, it is possible to configure the drive to achieve IP65 rating (sizes 3 to 4) (NEMA
12) at the rear of the heatsink for through-panel mounting (some current derating is required). Refer
to Chapter 5
Technical data
on page 76.
This allows the front of the drive, along with various switchgear, to be housed in a high IP enclosure
with the heatsink protruding through the panel to the external environment. Thus, the majority of the
heat generated by the drive is dissipated outside the enclosure maintaining a reduced temperature
inside the enclosure. This also relies on a good seal being made between the heatsink and the rear
of the enclosure using the gaskets provided.
32
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
IP / UL Rating
Issue Number: 3
on
Page 33

Figure 3-15 Example of IP65 (sizes 3 to 4) (NEMA 12) through-panel layout
IP20
(NEMA1)
IP65(sizes3to4)(NEMA 12)enclosure
Drivewith
highIP insert
installed
Gasket
seal
NOTE
Drive
Gasket
Enclosure
rearwall
Safety information Product information
The main gasket should be installed as shown in Figure 3-16.
On drive sizes 3 and 4, in order to achieve the high IP rating at the rear of the heatsink it is necessary
to seal a heatsink vent by installing the high IP insert as shown in Figure 3-18 and Figure 3-19 on
page 36.
The heatsink fans have conformal coated PCBs and have sealant at cable entry points.
This means that the electronics of the fan are rated to IP54. Dripping, splashing or sprayed
water can impede the operation of the fan, therefore if the environment is such that the fan
may be subjected to more than occasional dripping or sprayed water while operational,
then suitable drip protection covers should be employed.
Figure 3-16 Installing the gasket
To seal the space between the drive and the backplate, use two sealing brackets as shown in Figure
3-17.
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
33
Page 34

Figure 3-17 Through panel mounting
Throughpanel
securingbracket
Enclosure
rearwall
Throughpanel
securingbracket
3.9 Installation of high IP insert for size 3 and 4
The standard drive is rated to IP20 pollution degree 2 (dry, non-conductive contamination only)
(NEMA 1). However, it is possible to configure the drive to achieve IP65 rating sizes 3 to 4 (NEMA
12) at the rear of the heatsink for through-panel mounting (some current derating is required).
On drive sizes 3 and 4, in order to achieve the high IP rating at the rear of the heatsink it is necessary
to seal a heatsink vent by installing the high IP insert as shown in Figure 3-18.
34
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 35

Figure 3-18 Installation of high IP insert for size 3
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
1. To install the high IP insert, firstly place a flat head screwdriver into the slots highlighted (1).
2. Pull the hinged baffle down to expose the ventilation hole, install the high IP insert into the
ventilation hole in the heatsink (2).
3. Ensure the high IP insert is securely installed by firmly pressing it into place (3).
4. Close the hinged baffle as shown (1).
5. To remove the high IP insert, reverse the above instructions.
The guidelines in Table 3-4 should be followed.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
35
Page 36

Figure 3-19 Installation of high IP insert for size 4
1. To install the high IP insert, firstly place a flat head screwdriver into the slots highlighted (1).
2. Pull the hinged baffle up to expose the ventilation hole, install the high IP insert into the
ventilation hole in the heatsink (2).
3. Ensure the high IP insert is securely installed by firmly pressing it into place (3).
4. Close the hinged baffle as shown (1).
5. To remove the high IP insert, reverse the above instructions.
The guidelines in Table 3-4 should be followed.
36
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 37

Table 3-4 Environmental considerations
NOTE
NOTE
WARNING
Environment High IP insert Comments
Clean Not installed
Dry, dusty (non-conductive) Installed
IP65 compliance Installed
A current derating must be applied to the drive if the high IP insert is installed. Derating
information is provided in Chapter 5
Technical data
Failure to do so may result in nuisance tripping.
Safety information Product information
Regular cleaning recommendedDry, dusty (conductive) Installed
on page 76
When designing an IP65 (NEMA 12) enclosure (Figure 3-15
4) (NEMA 12) through-panel layout
on page 33), consideration should be made to the
Example of IP65 (sizes 3 to
dissipation from the front of the drive.
Table 3-5 Power losses from the front of the drive when through-panel mounted
Frame size Power loss
3
4
≤
≤
50 W
75 W
3.10 Size 3 and 4 internal braking resistor
Size 3 and 4 have been designed with an optional space-saving heatsink mounted resistor. The
resistor can be installed within the heatsink fins of the drive. When the heatsink resistor is used, an
external thermal protection device is not required as the resistor is designed such that it will fail safely
under any fault conditions. The in-built software overload protection is set-up at default to protect the
resistor. The resistor is rated to IP54 (NEMA 12).
Table 3-6 Size 3 and 4 internal braking resistor part numbers
Frame size Part number
3 1220-2752
4 1299-0003
The internal / heatsink mounted braking resistors must only be used with the following
drives. Brake resistor 1220-2752 must only be used with size 3 drives. Brake resistor
1299-0003 must only be used with size 4 drives.
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
37
Page 38

3.10.1 Internal braking resistor installation instructions
Brake resistor bung
1
Figure 3-20 Brake resistor installation on size 3
• Remove the terminal covers.
• Remove the internal EMC filter as shown in Figure 4-11
filter
• Remove the brake resistor bung (1) from the hole in the chassis, the closed end of the bung will
• Feed brake resistor bung onto outer insulation of brake resistor cable. The wider end of the bung
• Install the braking resistor to the heatsink using the captive screws. The screws should be tighten
• Route the cables through the provided hole at the rear of the heatsink as shown in Figure 3-20
• Crimp the cable ends and make appropriate connections. The brake terminals must be tightened
• Replace the terminal covers on the drive, tighten to a maximum torque of 1 N m (0.7 lb ft).
on page 66.
need to be pierced so that the cable has access to be routed through.
should be inserted first. The Narrow end should align with end of insulation.
to a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.5 lb ft).
and take the cable out from the front side of the drive. Ensure the cables are routed between the
fins of the heatsink, and the cables are not trapped between the heatsink fins and the resistor.
to a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.5 Ib ft).
Removal of the size 3 internal EMC
38
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 39

Figure 3-21 Brake resistor installation on size 4
Brake resistor bung
1
• Remove the terminal covers.
• Remove the brake resistor bung from the hole (1) in the chassis, the closed end of the bung will
need to be pierced so that the cable has access to be routed through.
• Feed brake resistor bung onto outer insulation of brake resistor cable. The wider end of the bung
should be inserted first. The Narrow end should align with end of insulation.
• Install the braking resistor to the heatsink using the captive screws. The screws should be tighten
to a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.5 lb ft).
• Route the cables through the provided hole at the rear of the heatsink as shown in Figure 3-21
and take the cable out from the front side of the drive. Ensure the cables are routed between the
fins of the heatsink, and the cables are not trapped between the heatsink fins and the resistor.
• Crimp the cable ends and make appropriate connections. The brake terminals must be tightened
to a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.5 Ib ft).
• Replace the terminal covers on the drive, tighten to a maximum torque of 1 N m (0.7 lb ft).
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
39
Page 40

3.10.2 External brake resistor
1
2
118mm(4.65in)
15.5mm
(0.61in)
Æ 4.5mm(0.18in)
x2holes
1.5mm
(0.06in)
30.5mm
(1.20in)
80mm(3.15in)
130mm(5.12in)
Æ 4.5x6mm(0.18in)
x2holes
R=1.5mm
(0.06)
External brake resistors are available from Emerson Industrial Automation for drive sizes 3 to 4. They
can be mounted in the enclosure as per mounting recommendation in Figure 3-13
layout
on page 28 using mounting bracket part number 6541-0187 (shown in Figure 3-23). Figure 322 below shows the brake resistor mounted on the mounting bracket. Two M4 screws and nuts (2)
can be used to fix the brake resistor to the mounting bracket. One M4 nut with washer (1) is provided
to use for the ground connection. The brake resistor is equipped with a thermal switch, the thermal
switch should be integrated in the control circuit by the user.
Figure 3-22 Brake resistor with the mounting bracket
1. Ground connection (1 x M4 nut and washer).
2. Attaching the brake resistor to the mounting bracket (using 2 x M4 screws and nuts).
Figure 3-23 Mounting bracket dimensions
Enclosure
40
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 41

Figure 3-24 Brake resistor dimensions
60mm(2.36in)
68mm(2.68in)
118mm(4.65in)
130mm(5.12in)
Æ 4.5mm(0.18in)
x4holes
15mm
(0.59in)
3.11 External EMC filter
The external EMC filter for size 3 and 4 drives can be footprint mounted or bookcase mounted as
shown in Figure 3-25 and Figure 3-26.
Figure 3-25 Footprint mounting the EMC
filter
Figure 3-26 Bookcase mounting the EMC
filter
Safety information Product information
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
3.11.1 Optional external EMC filters
Table 3-7 EMC filter cross reference
Model CT part number
200 V
03200050 to 03200106 4200-3230
04200137 to 04200185 4200-0272
400 V
03400025 to 03400100 4200-3480
04400150 to 04400172 4200-0252
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
41
Page 42

3.11.2 EMC filter ratings
Y
ED
Z
L
1
'
L
2
'
L
3
'
X
X
Y
V
Y
A
B
H
CW
Z
Z
CS
U1
V1 W1
Netz / Line
Last / Load
PE
U2
V2 W2
Table 3-8 Optional external EMC filter details
CT part
number
Maximum
continuous
current
(104 °F)
@ 50 °C
(122 °F)
Voltage
rating
IEC UL
IP
rating
Power dissipation
at rated current
@ 40 °C
(104 °F)
@ 50 °C
(122 °F)
A A V V W W mA mA MΩ
4200-3230 20 18.5 250 300
4200-3480 16 15 528 600 13 11 10.7 151
4200-0272 27 24.8 250 300 33 28 6.8 137
20 17 2.4 60
20
4200-0252 25 23 528 600 28 24 11.1 182
Figure 3-27 External EMC filter
Ground leakage
Balanced
supply
phase-to-
phase and
phase-to-
ground
Worst
case@ 40 °C
Discharge
resistors
1.68
V: Ground stud
Z: Bookcase mounting slot
diameter.
Table 3-9 Size 3 external EMC filter dimensions
CT part
number
4200-3230
4200-3480
Table 3-10 Size 4 external EMC filter dimensions
CT part
number
4200-0272
4200-0252
42
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
A B C D E H W V/X Y/Z CS
384 mm
(15.12 in)
A B C D E H W V/X Y/Z CS
395 mm
(15.55 in)
X: Threaded holes for footprint mounting
of the drive
CS: Cable size
414 mm
(16.30 in)
425 mm
(16.73 in)
56 mm
(2.21 in)
100 mm
(3.94 in)
41 mm
(1.61 in)
60 mm
(2.36 in)
33 mm
(1.30 in)
426 mm
(16.77 in)
437 mm
(17.2 in)
Y: Footprint mounting hole diameter
M5
5.5 mm
(0.22 in)
83 mm
(3.27 in)
123 mm
(4.84 in)
M6
6.5 mm
(0.26 in)
Issue Number: 3
2.5 mm
(14 AWG)
6 mm
(10 AWG)
2
2
Page 43

3.11.3 EMC filter torque settings
Table 3-11 Optional external EMC Filter terminal data
CT part
number
4200-3230
4200-3480
4200-0252
4200-0272
connections
Max cable
size
2
4 mm
(12 AWG)
2
6 mm
(10 AWG)
Power
Max torque
0.8 N m
(0.59 lb ft)
1.8 N m
(0.88 lb ft)
Ground stud
Ground
connections
size
M5
M6
Table 3-12 Fastener details for drive footprint mounting on external EMC filter
Type Size 3 Size 4
Screw specification Property class 8.8. standard metric, coarse thread
Thread size M5 M6
Length (mm) 12 12
Washer Helical spring, split spring or conical spring
Torque (N m) 6.0 10.0
3.12 Terminal size and torque settings
Table 3-13 Drive control and relay terminal data
Model Connection type Torque setting
All Plug-in terminal block 0.5 N m (0.4 lb ft)
Safety information Product information
Max torque
2.5 N m
(1.8 lb ft)
5.0 N m
(3.7 lb ft)
Mechanical installation
Electrical installation Technical data UL listing information
Table 3-14 Drive power terminal data
Frame
size
3 and 4
AC and motor terminals DC and braking Ground terminal
Recommended Maximum Recommended Maximum Recommended Maximum
Plug-in terminal block T20 Torx (M4)
0.7 N m
(0.5 lb ft)
0.8 N m
(0.6 lb ft)
2.0 N m
(1.4 Ib ft)
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
2.5 N m
(1.8 Ib ft)
T20 Torx (M4) / M4 Nut
(7 mm AF)
2.0 N m
(1.4 Ib ft)
2.5 N m
(1.8 Ib ft)
43
Page 44
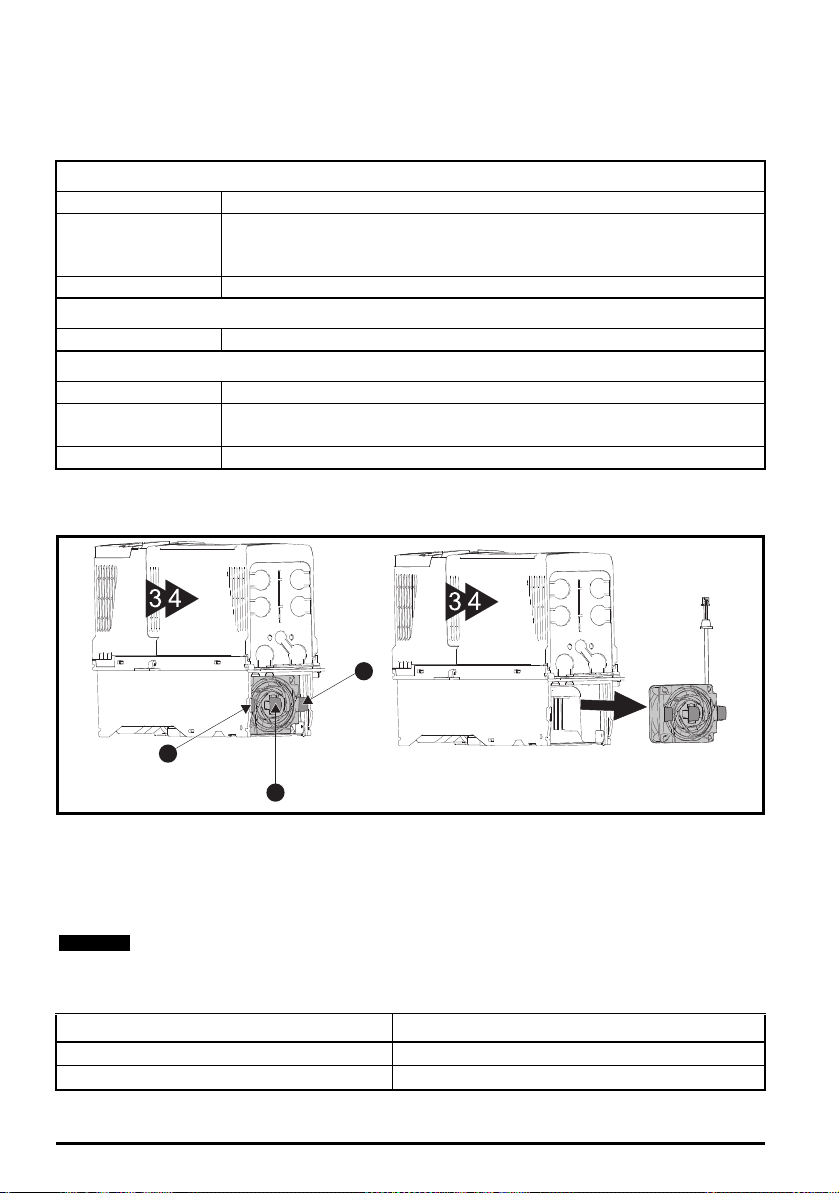
3.13 Routine maintenance
1
1
2
NOTE
The drive should be installed in a cool, clean, well ventilated location. Contact of moisture and dust
with the drive should be prevented. Regular checks of the following should be carried out to ensure
drive / installation reliability are maximized:
Environment
Ambient temperature Ensure the enclosure temperature remains at or below maximum specified
Dust
Moisture Ensure the drive enclosure shows no signs of condensation
Enclosure
Enclosure door filters Ensure filters are not blocked and that air is free to flow
Electrical
Screw connections Ensure all screw terminals remain tight
Crimp terminals
Cables Check all cables for signs of damage
3.13.1 Fan removal procedure
Figure 3-28 Removal of the size 3 and 4 heatsink fan (size 3 shown)
Ensure the drive remains dust free – check that the heatsink and drive fan
are not gathering dust. The lifetime of the fan is reduced in dusty
environments.
Ensure all crimp terminals remains tight – check for any discoloration which
could indicate overheating
Ensure the fan cable is disconnected from the drive prior to attempting fan removal.
1. Press the two tabs inwards to release the fan from the drive frame.
2. Using the central fan tab, withdraw the fan assembly from the drive housing.
Replace the fan by reversing the above instructions.
If the drive is surface mounted using the outer holes on the mounting bracket, then the
heatsink fan can be replaced without removing the drive from the backplate.
Table 3-15 Heatsink fan part numbers
Model Fan part number
Size 3 3251-0029
Size 4 3251-0245
44
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 45

4 Electrical installation
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Electric shock risk
The voltages present in the following locations can cause severe electric shock and may be
lethal:
AC supply cables and connections
DC and brake cables, and connections
Output cables and connections
Many internal parts of the drive, and external option units
Unless otherwise indicated, control terminals are single insulated and must not be touched.
Isolation device
The AC and / or DC power supply must be disconnected from the drive using an approved
isolation device before any cover is removed from the drive or before any servicing work
is performed.
STOP function
The STOP function does not remove dangerous voltages from the drive, the motor or any
external option units.
Safe Torque Off function
The Safe Torque Off function does not remove dangerous voltages from the drive, the
motor or any external option units.
Stored charge
The drive contains capacitors that remain charged to a potentially lethal voltage after the
AC and / or DC power supply has been disconnected. If the drive has been energized,
the AC and / or DC power supply must be isolated at least ten minutes before work may
continue. Normally, the capacitors are discharged by an internal resistor. Under certain,
unusual fault conditions, it is possible that the capacitors may fail to discharge, or be
prevented from being discharged by a voltage applied to the output terminals. If the drive
has failed in a manner that causes the display to go blank immediately, it is possible the
capacitors will not be discharged. In this case, consult Emerson Industrial Automation or
their authorized distributor.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Equipment supplied by plug and socket
Special attention must be given if the drive is installed in equipment which is connected to
the AC supply by a plug and socket. The AC supply terminals of the drive are connected
to the internal capacitors through rectifier diodes which are not intended to give safety
isolation. If the plug terminals can be touched when the plug is disconnected from the
socket, a means of automatically isolating the plug from the drive must be used (e.g. a
latching relay).
Permanent magnet motors
Permanent magnet motors generate electrical power if they are rotated, even when the
supply to the drive is disconnected. If that happens then the drive will become energized
through its motor terminals. If the motor load is capable of rotating the motor when the
supply is disconnected, then the motor must be isolated from the drive before gaining
access to any live parts.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
45
Page 46

4.1 Power and ground connections
L1
L2
L2L1L3
U V W
Optional EMC
filter
Optional
line reactor
Fuses
L3
Mains
Supply
Motor
Optional ground
connection
Supply
PE
AC Connections
3
DC Connections
BR
+DC
-DC
Internal
EMC filter
Ground connection
studs
Additional ground
connection
Figure 4-1 Size 3 power and ground connections
46
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 47

Figure 4-2 Size 4 power and ground connections
L1 L2
L2L1 L3 U V W
Optional EMC
filter
Optional
line reactor
Fuses
L3
Mains
Supply
Motor
Optional ground
connection
Supply
PE
AC Connections
BR
+DC
-DC
4
DC / Brake connections
1
Ground connection
studs
Additional ground
connection
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
47
Page 48

4.1.1 Ground connections
WARNING
NOTE
WARNING
WARNING
Electrochemical corrosion of grounding terminals
Ensure that grounding terminals are protected against corrosion i.e. as could be caused
by condensation.
The drive must be connected to the system ground of the AC supply. The ground wiring must
conform to local regulations and codes of practice.
For further information on ground cable sizes, refer to Table 2-3
ratings
on page 14.
Protective ground cable
On size 3 and 4, the supply and motor ground connections are made using the M4 studs located
either side of the drive near the plug-in power connectors. See Figure 4-1 and Figure 4-2 for details.
The ground loop impedance must conform to the requirements of local safety regulations.
The drive must be grounded by a connection capable of carrying the prospective fault
current until the protective device (fuse, etc.) disconnects the AC supply.
The ground connections must be inspected and tested at appropriate intervals.
4.2 AC Supply requirements
AC supply voltage:
200 V drive: 200 V to 240 V ±10 %
400 V drive: 380 V to 480 V ±10 %
Number of phases: 3
Maximum supply imbalance: 2 % negative phase sequence (equivalent to 3 % voltage imbalance
between phases).
Frequency range: 45 to 66 Hz
For UL compliance only, the maximum supply symmetrical fault current must be limited to 100 kA
Table 4-1 Supply fault current used to calculate maximum input currents
Model Symmetrical fault level (kA)
All 100
4.2.1 Supply types
All drives are suitable for use on any supply type i.e TN-S, TN-C-S, TT and IT. Drives are suitable for
use on supplies of installation category III and lower, according to IEC60664-1. This means they may
be connected permanently to the supply at its origin in a building, but for outdoor installation
additional over-voltage suppression (transient voltage surge suppression) must be provided to
reduce category IV to category III.
Operation with IT (ungrounded) supplies:
Special attention is required when using internal or external EMC filters with ungrounded
supplies, because in the event of a ground (earth) fault in the motor circuit the drive may
not trip and the filter could be over-stressed. In this case, either the filter must not be
used (removed) or additional independent motor ground fault protection must be
provided. For instructions on removal, refer to Figure 4-11 and Figure 4-12 on page 66.
For details of ground fault protection contact the supplier of the drive.
48
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 49

A ground fault in the supply has no effect in any case. If the motor must continue to run with a ground
WARNING
fault in its own circuit then an input isolating transformer must be provided and if an EMC filter is
required it must be located in the primary circuit. Unusual hazards can occur on ungrounded supplies
with more than one source, for example on ships. Contact the supplier of the drive for more
information.
If an SI-Applications Plus module is installed in the drive, then the drive must not be used
on a corner-grounded or centre-grounded delta supply if the supply voltage is above 300
V. If this is required, please contact the supplier of the drive for more information.
4.2.2 Supplies requiring line reactors
Input line reactors reduce the risk of damage to the drive resulting from poor phase balance or
severe disturbances on the supply network.
Where line reactors are to be used, reactance values of approximately 2 % are recommended.
Higher values may be used if necessary, but may result in a loss of drive output (reduced torque at
high speed) because of the voltage drop.
For all drive ratings, 2 % line reactors permit drives to be used with a supply unbalance of up to 3.5 %
negative phase sequence (equivalent to 5% voltage imbalance between phases).
Severe disturbances may be caused by the following factors, for example:
• Power factor correction equipment connected close to the drive.
• Large DC drives having no or inadequate line reactors connected to the supply.
• Across the line (DOL) started motor(s) connected to the supply such that when any of these
motors are started, the voltage dip exceeds 20 %.
Such disturbances may cause excessive peak currents to flow in the input power circuit of the drive.
This may cause nuisance tripping, or in extreme cases, failure of the drive.
Drives of low power rating may also be susceptible to disturbance when connected to supplies with a
high rated capacity.
Line reactors are particularly recommended for use with the following drive models when one of the
above factors exists, or when the supply capacity exceeds 175 kVA:
03200050, 03200066, 03200080, 03200106,
03400025, 03400031, 03400045, 03400062
Model sizes 03400078 to 04400172 have an internal DC choke so they do not require AC line
reactors except for cases of excessive phase unbalance or extreme supply conditions.
When required, each drive must have its own reactor(s). Three individual reactors or a single threephase reactor should be used.
Reactor current ratings
The current rating of the line reactors should be as follows:
Continuous current rating:
Not less than the continuous input current rating of the drive
Repetitive peak current rating:
Not less than twice the continuous input current rating of the drive
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
49
Page 50

Table 4-2 2 % line reactors
L
Y
100
----------
V
3
-------
×
1
2π fI
------------
×=
Drive
model
number
03200050 200 INL2001 4401-0143 13.5 0.79 1.8 156 70 125
03200066 200 INL2001 4401-0143 13.5 0.79 1.8 156 70 125
03200080 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
03200106 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
04200137 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
04200185 200 INL2003 4401-0145 26.8 0.32 2.5 156 80 125
03400025 400 INL4001 4401-0148 6.6 2.94 1.3 80 75 130
03400031 400 INL4001 4401-0148 6.6 2.94 1.3 80 75 130
03400045 400 INL4002 4401-0149 9.1 1.62 1.8 156 70 125
03400062 400 INL4011 4401-0234 13 1.12 2.5 156 80 125
03400078 400 INL4011 4401-0234 13 1.12 2.5 156 80 125
03400100 400 INL4003 4401-0151 15.8 1.05 2.6 156 80 125
04400150 400 INL4004 4401-0152 18.7 0.79 3.5 156 60 145
04400172 400 INL4005 4401-0153 24.3 0.61 4.9 156 75 145
Voltage
Line reactor
rating
designation
V A mH kg mm mm mm
CT Part
number
Line
reactor
current
rating
Inductance Weight Length Width Height
4.2.3 Input inductor calculation
To calculate the inductance required (at Y %), use the following equation:
Where:
I
= drive rated input current (A)
L
= inductance (H)
f
= supply frequency (Hz)
V
= voltage between lines
4.3 Supplying the drive with DC
All drive sizes have the option to be powered from an external DC power supply. Refer to section
4.1
Power and ground connections
The DC supply connections for size 3 and 4 are located under the DC / Braking terminal cover.
Figure 4-3 shows DC supply connections and cable routing.
50
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
on page 46 to identify the location of DC supply connections.
Issue Number: 3
Page 51

Figure 4-3 DC supply connections (size 3 shown)
NOTE
The Internal EMC filter and plastics have been removed from the above image to
demonstrate the routing of the DC cables.
4.4 DC bus paralleling
DC bus paralleling using standard cable / busbars is supported by all frame sizes.
On frame sizes 3 and 4, terminal and enclosure design enables the DC bus of a number of drives to
be connected together using pre-made busbars. The diagram below shows how the busbar links
connect the DC bus of several drives together.
The connecting of the DC bus between several drives is typically used to:
1. Return energy from a drive which is being overhauled by the load to a second motoring drive.
2. Allow the use of one braking resistor to dissipate regenerative energy from several drives.
Figure 4-4 DC bus paralleling (size 3 shown)
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
There are limitations to the combinations of drives which can be used in this configuration.
For application data, contact the supplier of the drive.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
51
Page 52

The DC bus paralleling kit is not supplied with the drive but available to order from the
NOTE
supplier of the drive.
Table 4-3 DC bus paralleling kit part numbers
Size CT part number
3 3470-0048
4 3470-0061
4.5 24 Vdc supply
The 24 Vdc supply connected to control terminals 1 & 2* provides the following functions:
• It can be used to supplement the drive's own internal 24 V supply when multiple option modules
are being used and the current drawn by these module is greater than the drive can supply.
• It can be used as a back-up power supply to keep the control circuits of the drive powered up
when the line power supply is removed. This allows any fieldbus modules, application modules,
encoders or serial communications to continue to operate.
• It can be used to commission the drive when the line power supply is not available, as the display
operates correctly. However, the drive will be in the Under voltage trip state unless either line
power supply or low voltage DC operation is enabled, therefore diagnostics may not be possible.
(Power down save parameters are not saved when using the 24 V back-up power supply input).
• If the DC bus voltage is too low to run the main SMPS in the drive, then the 24 V supply can be
used to supply all the low voltage power requirements of the drive.
Select
(06.067) must also be enabled for this to happen.
Table 4-4 24 Vdc Supply connections
Function Sizes 3 and 4
Supplement the drive’s internal supply
and back-up supply for the control circuit
Low Under Voltage Threshold
Terminal
1, 2*
* Terminal 9 on
The working voltage range of the control 24 V power supply is as follows:
1 0 V
2 +24 Vdc
Nominal operating voltage 24.0 Vdc
Minimum continuous operating voltage 19.2 V
Maximum continuous operating voltage 28.0 V
Minimum start up voltage 21.6 V
Maximum power supply requirement at 24 V 40 W
Recommended fuse 3 A, 50 Vdc
Minimum and maximum voltage values include ripple and noise. Ripple and noise values must not
exceed 5 %.
52
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Unidrive M702
and
Unidrive HS72.
Issue Number: 3
Page 53

4.6 Low voltage operation
NOTE
WARNING
With the addition of a 24 Vdc power supply to supply the control circuits, the drive is able to operate
from a low voltage DC supply with a range from 24 Vdc to the maximum DC volts. It is possible for
the drive to go from operating on a normal line power supply voltage to operating on a much lower
supply voltage without interruption.
Going from low voltage operation to normal mains operation requires the inrush current to be
controlled. This may be provided externally. If not, the drive supply can be interrupted to utilise the
normal soft starting method in the drive.
To fully exploit the new low voltage mode of operation, the under voltage trip level is now user
programmable. For application data, contact the supplier of the drive.
The working voltage range of the low voltage DC power supply is as follows:
Size 3 to 4
Minimum continuous operating voltage: 26 V
Minimum start up voltage: 32 V
Maximum over voltage trip threshold: 230 V drives: 415 V
400 V drives: 830 V
4.7 Fan power supply
The fans installed on all drive sizes are supplied internally by the drive.
4.8 Ratings
See section 2.4
Maximum continuous input current
The values of maximum continuous input current are given to aid the selection of cables and fuses.
These values are stated for the worst case condition with the unusual combination of stiff supply with
high imbalance. The value stated for the maximum continuous input current would only be seen in
one of the input phases. The current in the other two phases would be significantly lower.
The values of maximum input current are stated for a supply with a 2 % negative phase-sequence
imbalance and rated at the maximum supply fault current given in section 4.2
requirements
The nominal cable sizes given in section 2.4
wiring regulations for the correct size of cables. In some cases a larger cable is required to avoid
excessive voltage drop.
Ratings
on page 13.
AC supply
on page 65.
Ratings
on page 13 are only a guide. Refer to local
The nominal output cable sizes in section 2.4
maximum current matches that of the drive. Where a motor of reduced rating is used the
cable rating may be chosen to match that of the motor. To ensure that the motor and cable
are protected against over-load, the drive must be programmed with the correct motor
rated current.
Ratings
on page 13 assume that the motor
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Fuses
The AC supply to the drive must be installed with suitable protection against overload and
short-circuits. Nominal fuse ratings are shown in section 2.4
to observe this requirement will cause risk of fire.
A fuse or other protection must be included in all live connections to the AC supply.
Fuse types
The fuse voltage rating must be suitable for the drive supply voltage.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Ratings
on page 13. Failure
53
Page 54

4.8.1 Main AC supply contactor
WARNING
Normal capacitance
Shield or armour
separated from the cores
High capacitance
Shield or armour close
to the cores
The recommended AC supply contactor type for size 3 to 4 is AC1.
4.9 Output circuit and motor protection
The output circuit has fast-acting electronic short-circuit protection which limits the fault current to
typically no more than five times the rated output current, and interrupts the current in approximately
20 µs. No additional short-circuit protection devices are required.
The drive provides overload protection for the motor and its cable. For this to be effective,
Current (00.046
) must be set to suit the motor.
Rated
Rated Current (00.046
overload.
There is also provision for the use of a motor thermistor to prevent over-heating of the motor, e.g. due
to loss of cooling.
) must be set correctly to avoid a risk of fire in the event of motor
4.9.1 Motor cable types
Since capacitance in the motor cable causes loading on the output of the drive, ensure the cable
length does not exceed the values given in Table 5-21 and Table 5-22.
Use 105 °C (221 °F) (UL 60/75 °C temp rise) PVC-insulated cable with copper conductors having a
suitable voltage rating, for the following power connections:
• AC supply to external EMC filter (when used)
• AC supply (or external EMC filter) to drive
• Drive to motor
• Drive to braking resistor
4.9.2 High-capacitance / reduced diameter cables
The maximum cable length is reduced from that shown in Table 5-21 and Table 5-22 if high
capacitance or reduced diameter motor cables are used.
Most cables have an insulating jacket between the cores and the armor or shield; these cables have
a low capacitance and are recommended. Cables that do not have an insulating jacket tend to have
high capacitance; if a cable of this type is used, the maximum cable length is half that quoted in the
tables, (Figure 4-5 shows how to identify the two types).
Figure 4-5 Cable construction influencing the capacitance
The maximum motor cable lengths specified in section 5.1.22
types
is shielded and contains four cores. Typical capacitance for this type of cable is 130 pF/m (i.e.
from one core to all others and the shield connected together).
54
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Maximum motor cable lengths and
Issue Number: 3
Page 55

4.9.3 Motor winding voltage
The PWM output voltage can adversely affect the inter-turn insulation in the motor. This is because of
the high rate of change of voltage, in conjunction with the impedance of the motor cable and the
distributed nature of the motor winding.
For normal operation with AC supplies up to 500 Vac and a standard motor with a good quality
insulation system, there is no need for any special precautions. In case of doubt the motor supplier
should be consulted. Special precautions are recommended under the following conditions, but only
if the motor cable length exceeds 10 m:
• AC supply voltage exceeds 500 V
• DC supply voltage exceeds 670 V, i.e regenerative / AFE supply.
• Operation of 400 V drive with continuous or very frequent sustained braking
• Multiple motors connected to a single drive
For multiple motors, the precautions given in section 4.9.4
For the other cases listed, it is recommended that an inverter-rated motor be used taking into
account the voltage rating of the inverter. This has a reinforced insulation system intended by the
manufacturer for repetitive fast-rising pulsed voltage operation.
Users of 575 V NEMA rated motors should note that the specification for inverter-rated motors given
in NEMA MG1 section 31 is sufficient for motoring operation but not where the motor spends
significant periods braking. In that case an insulation peak voltage rating of 2.2 kV is recommended.
If it is not practical to use an inverter-rated motor, an output choke (inductor) should be used. The
recommended type is a simple iron-cored component with a reactance of about 2 %. The exact value
is not critical. This operates in conjunction with the capacitance of the motor cable to increase the
rise-time of the motor terminal voltage and prevent excessive electrical stress.
Multiple motors
should be followed.
4.9.4 Multiple motors
Open-loop only
If the drive is to control more than one motor, one of the fixed V/F modes should be selected
(Pr
05.014
The maximum motor cable lengths specified in section 5.1.22
types
It is recommended that each motor is connected through a protection relay since the drive cannot
protect each motor individually. For connection, a sinusoidal filter or an output inductor must be
connected as shown in Figure 4-7, even when the cable lengths are less than the maximum permissible.
For high DC voltages or when supplied by a regen system, a sinusoidal filter is recommended. For
details of filter or inductor sizes refer to the supplier of the drive.
= Fixed or Squared). Make the motor connections as shown in Figure 4-6 and Figure 4-7.
Maximum motor cable lengths and
on page 90 apply to the sum of the total cable lengths from the drive to each motor.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
55
Page 56

Figure 4-6 Preferred chain connection for multiple motors
Motor protection
relay
Chain connection (preferred)
connection
Inductor
Motor protection
relay
Figure 4-7 Alternative connection for multiple motors
4.9.5 / ∆ motor operation
The voltage rating for and ∆ connections of the motor should always be checked before
attempting to run the motor.
The default setting of the motor rated voltage parameter is the same as the drive rated voltage, i.e.
400 V drive 400 V rated voltage
230 V drive 230 V rated voltage
56
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 57

A typical 3 phase motor would be connected in for 400 V operation or ∆ for 230 V operation,
WARNING
NOTE
however, variations on this are common e.g. 690 V ∆ 400 V.
Incorrect connection of the windings will cause severe under or over fluxing of the motor, leading to a
very poor output torque or motor saturation and overheating respectively.
4.9.6 Output contactor
If the cable between the drive and the motor is to be interrupted by a contactor or circuit
breaker, ensure that the drive is disabled before the contactor or circuit breaker is opened
or closed. Severe arcing may occur if this circuit is interrupted with the motor running at
high current and low speed.
A contactor is sometimes required to be installed between the drive and motor for safety purposes.
The recommended motor contactor is the AC3 type.
Switching of an output contactor should only occur when the output of the drive is disabled.
Opening or closing of the contactor with the drive enabled will lead to:
1. OI ac trips (which cannot be reset for 10 seconds)
2. High levels of radio frequency noise emission
3. Increased contactor wear and tear
The Drive Enable terminal when opened provides a Safe Torque Off function. This can in many
cases replace output contactors.
For further information see the
Control User Guide
.
4.10 Braking
Braking occurs when the drive is decelerating the motor, or is preventing the motor from gaining
speed due to mechanical influences. During braking, energy is returned to the drive from the motor.
When motor braking is applied by the drive, the maximum regenerated power that the drive can
absorb is equal to the power dissipation (losses) of the drive.
When the regenerated power is likely to exceed these losses, the DC bus voltage of the drive
increases. Under default conditions, the drive brakes the motor under PI control, which extends the
deceleration time as necessary in order to prevent the DC bus voltage from rising above a user
defined set-point.
If the drive is expected to rapidly decelerate a load, or to hold back an overhauling load, a braking
resistor must be installed.
Table 4-5 shows the default DC voltage level at which the drive turns on the braking transistor.
However the braking resistor turn on and the turn off voltages are programmable with
Lower Threshold
(06.073) and
Braking IGBT Upper Threshold
(06.074).
Braking IGBT
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Table 4-5 Default braking transistor turn on voltage
Drive voltage rating DC bus voltage level
200 V 390 V
400 V 780 V
When a braking resistor is used, Pr
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
00.015
should be set to Fast ramp mode.
57
Page 58

High temperatures
WARNING
NOTE
CAUTION
Parameter
Size 3 Size 4
200 V
drive
400 V
drive
200 V
drive
400 V
drive
Braking resistor rated power Pr 10.030 50 W 100 W
Braking resistor thermal time constant Pr 10.031 3.3 s 2.0 s
Braking resistor resistance Pr 10.061 75 Ω 38 Ω
Braking resistors can reach high temperatures. Locate braking resistors so that damage
cannot result. Use cable having insulation capable of withstanding high temperatures.
4.10.1 Heatsink mounted braking resistor
A resistor has been especially designed to be mounted within the heatsink of the drive (size 3 and 4).
See section 3.10
resistor is such that no thermal protection circuit is required, as the device will fail safely under fault
conditions. On size 3 and 4 the in built software overload protection is set-up at default for the
designated heatsink mounted resistor. The heatsink mounted resistor is not supplied with the drive
and can be purchased separately.
Table 4-6 provides the resistor data for each drive rating.
Size 3 and 4 internal braking resistor
for mounting details. The design of the
The internal / heatsink mounted resistor is suitable for applications with a low level of
regen energy only. See Table 4-6.
Braking resistor overload protection parameter settings
Failure to observe the following information may damage the resistor.
The drive software contains an overload protection function for a braking resistor. On
size 3 and 4 this function is enabled at default to protect the heatsink mounted resistor.
Below are the parameter settings.
For more information on the braking resistor software overload protection, see
Pr
10.030,
Pr
10.031
and Pr
10.061
software overload protection
full descriptions in
on page 62
.
section 4.10.3 Braking resistor
If the resistor is to be used at more than half of its average power rating, the drive
cooling fan must be set to full speed by setting Pr
06.045
to 11.
Table 4-6 Heatsink mounted braking resistor data
Parameter Size 3 Size 4
Part number 1220-2752 1299-0003
DC resistance at 25 °C 75
Ω
Peak instantaneous power over 1 ms at nominal resistance 8 kW 16 kW
Average power over 60 s * 50 W 100 W
Ingress Protection (IP) rating IP54
Maximum altitude 2000 m
* To keep the temperature of the resistor below 70 °C (158 °F) in a 30 °C (86 °F) ambient, the
average power rating is 50 W for size 3, 100 W for size 4. The above parameter settings ensure this
is the case.
58
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
37.5
Ω
Page 59

4.10.2 External braking resistor
WARNING
Overload protection
When an external braking resistor is used, it is essential that an overload protection device
is incorporated in the braking resistor circuit; this is described in
When a braking resistor is to be mounted outside the enclosure, ensure that it is mounted in a
ventilated metal housing that will perform the following functions:
• Prevent inadvertent contact with the resistor
• Allow adequate ventilation for the resistor
When compliance with EMC emission standards is required, external connection requires the cable
to be armored or shielded, since it is not fully contained in a metal enclosure. See section
4.12.5
Compliance with generic emission standards
on page 70 for further details.
Internal connection does not require the cable to be armored or shielded.
Table 4-7 Minimum resistance values and peak power rating for the braking resistor at 40 °C (104 °F)
Model
Minimum resistance
*
Instantaneous power
rating
Ω kW kW
200 V
03200050
03200066 1.9
03200080 2.8
22 7.7
03200106 3.6
04200137
04200185 6.3
18 9.4
400 V
03400025
03400031 2.0
03400045 2.8
74 9.2
03400062 4.6
03400078
03400100 6.6
04400150
04400172 12.6
50 13.6
37 18.3
* Resistor tolerance: ±10 %. The minimum resistance specified are for stand-alone drive systems
only. If the drive is to be used as part of a common DC bus system different values may be
required. See
Braking resistor software overload protection
on page 62.
Figure 4-8 on page 61.
Continuous power
rating
1.5
4.6
1.5
5.0
9.0
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
59
Page 60

For high-inertia loads or under continuous braking, the continuous power dissipated in the braking
resistor may be as high as the power rating of the drive. The total energy dissipated in the braking
resistor is dependent on the amount of energy to be extracted from the load.
The instantaneous power rating refers to the short-term maximum power dissipated during the on
intervals of the pulse width modulated braking control cycle. The braking resistor must be able to
withstand this dissipation for short intervals (milliseconds). Higher resistance values require
proportionately lower instantaneous power ratings.
In most applications, braking occurs only occasionally. This allows the continuous power rating of the
braking resistor to be much lower than the power rating of the drive. It is therefore essential that the
instantaneous power rating and energy rating of the braking resistor are sufficient for the most
extreme braking duty that is likely to be encountered.
Optimization of the braking resistor requires careful consideration of the braking duty.
Select a value of resistance for the braking resistor that is not less than the specified minimum
resistance. Larger resistance values may give a cost saving, as well as a safety benefit in the event
of a fault in the braking system. Braking capability will then be reduced, which could cause the drive
to trip during braking if the value chosen is too large.
The following external brake resistors are available from the supplier of the drive for sizes 3 and 4.
Table 4-8 External brake resistors (40° C ambient) for drive sizes 3 and 4
Part
number
1220-
2201
1220-
2401
1220-
2801
Part
desc
DBR,
100 W,
20R, 130
x 68, TS
DBR,
100 W,
40R, 130
x 68, TS
DBR,
100 W,
80R, 130
x 68, TS
Ohmic
value
Pr10.061
20 Ω 100 W 2.0 MW 2300 W 1000 W 650 W 250 W 20
40 Ω 100 W 1.6 MW 1900 W 900 W 610 W 240 W 16
80 Ω 100 W 1.25 MW 1500 W 775 W 570 W 230 W 12.5
Cont
power
rating
Pr10.030
Max inst
power
rating
ton = 1 ms
Pulse
power
1/120 s
(ED 0.8 %)
Pulse
power
5/120 s
(ED 4.2 %)
Pulse
power
10/120 s
(ED 8.3 %)
Pulse
power
40/120 s
(ED 33 %)
Time
constant
Pr10.031
The brake resistors can be used in a series or parallel to get the required resistance and power
depending on the size of the drive as per Table 4-7. The brake resistor is equipped with a thermal
switch. The thermal switch should be integrated in the control circuit by the user.
60
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 61

The resistor combinations shown in Table 4-9 below can be made using one or more brake resistor/s
Optional
EMC
filter
Stop
Start /
Reset
Thermal
protection
device
Braking resistor
Drive
Main contactor
power supply
+DC
BR
from Table 4-8 above. Pr
in Table 4-8 above. Refer to description of Pr
4.10.3 Braking resistor software overload protection
10.030
, Pr
10.031
and Pr
10.030
10.061
should be set as per information provided
, Pr
10.031
and Pr
10.061
in
section
on page 62 for more information.
Table 4-9 Resistor combinations
Heavy
Model
03200050 0.7 135 101
03200066 1.1 92 69
03200080 1.5 68 51
03200106 2.2 46 34
03400025 0.7 540 405
03400031 1.1 370 277
03400045 1.5 271 203
03400062 2.2 184 138
03400078 3.0 135 101
03400100 4.0 101 76
04200137 3.0 34 25
04200185 4.0 26 19
04400150 5.5 74 56
04400172 7.5 54 40
duty
kW Ω Ω Vdc Ω Ω
150 %
Peak
power
200 %
Peak
power
Braking
voltage
390 22
780
390 18
780 37
Resistor
Min. value
74
50
Resistor
combinations
1 x 40 = 40
2 x 80 = 40 (when
connected in parallel)
1 x 80 = 80
2 x 40 = 80 (when
connected in series)
1 x 20 = 20
2 x 40 = 20 (when
connected in parallel)
1 x 40 = 40
2 x 80 = 40 (when
connected in parallel)
Thermal protection circuit for the braking resistor
The thermal protection circuit must disconnect the AC supply from the drive if the resistor becomes
overloaded due to a fault. Figure 4-8 shows a typical circuit arrangement.
Figure 4-8 Typical protection circuit for a braking resistor
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
See Figure 4-1 on page 46 and Figure 4-2 on page 47 for the location of the +DC and braking
resistor connections.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
61
Page 62

4.10.3 Braking resistor software overload protection
Pr 10.031
Resistor pulse power rating x Braking time
Resistor continuous power rating
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
=
WARNING
The drive software contains an overload protection function for a braking resistor. In order to enable
and set-up this function, it is necessary to enter three values into the drive:
•
Braking Resistor Rated Power
•
Braking Resistor Thermal Time Constant
•
Braking Resistor Resistance
This data should be obtained from the manufacturer of the braking resistor. The braking resistor
thermal time constant can be calculated from resistor data sheet values using the following equation:
Pr
10.039
gives an indication of braking resistor temperature based on a simple thermal model. Zero
indicates the resistor is close to ambient and 100 % is the maximum temperature the resistor can
withstand. A ‘Brake Resistor’ alarm is given if this parameter is above 75 % and the braking IGBT is
active. A Brake R Too Hot trip will occur if Pr
(default value) or 1.
If Pr
10.037
but instead the braking IGBT will be disabled until Pr
for applications with parallel connected DC buses where there are several braking resistors, each of
which cannot withstand full DC bus voltage continuously. With this type of application it is unlikely the
braking energy will be shared equally between the resistors because of voltage measurement
tolerances within the individual drives. Therefore with Pr
resistor has reached its maximum temperature the drive will disable the braking IGBT, and another
resistor on another drive will take up the braking energy. Once Pr
drive will allow the braking IGBT to operate again.
See the
Pr
10.039
This software overload protection should be used in addition to an external overload protection
device.
is equal to 2 or 3, a Brake R Too Hot trip will not occur when Pr
Parameter Reference Guide
.
(10.030)
(10.061)
(10.031)
10.039
reaches 100 %, when Pr
10.039
for more information on Pr
10.037
is set to 0
10.039
10.031
, Pr
reaches 100 %,
10.037
falls below 95 %. This option is intended
10.037
set to 2 or 3, then as soon as a
10.039
has fallen below 95 % the
10.030
, Pr
and
4.11 Ground leakage
The ground leakage current depends upon whether the internal EMC filter is installed or not. The
drive is supplied with the filter installed. Instructions for removing the internal filter are given in
section 4.12.2
With internal filter installed:
Size 3 to 4:
* Proportional to the supply voltage and frequency.
With internal filter removed:
62
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Internal EMC filter
28 mA* AC at 400 V 50 Hz
30 µA DC with a 600 V DC bus (10 MΩ)
<1 mA
When the internal filter is installed the leakage current is high. In this case a permanent
fixed ground connection must be provided, or other suitable measures taken to prevent a
safety hazard occurring if the connection is lost.
on page 65.
Issue Number: 3
Page 63

4.11.1 Use of residual current device (RCD)
WARNING
There are three common types of ELCB / RCD:
1. AC - detects AC fault currents
2. A - detects AC and pulsating DC fault currents (provided the DC current reaches zero at least
once every half cycle)
3. B - detects AC, pulsating DC and smooth DC fault currents
• Type AC should never be used with drives.
• Type A can only be used with single phase drives
• Type B must be used with three phase drives
Only type B ELCB / RCD are suitable for use with 3 phase inverter drives.
If an external EMC filter is used, a delay of at least 50 ms should be incorporated to ensure spurious
trips are not seen. The leakage current is likely to exceed the trip level if all of the phases are not
energized simultaneously.
4.12 EMC (Electromagnetic compatibility)
The requirements for EMC are divided into three levels in the following three sections:
• section 4.12.3, General requirements for EMC, this is for all applications, to ensure reliable
operation of the drive and minimise the risk of disturbing nearby equipment. The immunity
standards specified in Chapter 5.1.25
met, but no specific emission standards are applied.
• section 4.12.4, Requirements for meeting the EMC standard for power drive systems, IEC618003 (EN 61800-3:2004).
• section 4.12.5, Requirements for meeting the generic emission standards for the industrial
environment, IEC61000-6-4, EN 61000-6-4:2007.
The recommendations of section 4.12.3 will usually be sufficient to avoid causing disturbance to
adjacent equipment of industrial quality. If particularly sensitive equipment is to be used nearby, or in
a non-industrial environment, then the recommendations of section 4.12.4 or section 4.12.5 should
be followed to give reduced radio-frequency emission.
In order to ensure the installation meets the various emission standards described in:
• The EMC data sheet available from the supplier of the drive
• The Declaration of Conformity at the front of this manual
• Chapter 5
The correct external EMC filter must be used and all of the guidelines in section 4.12.3
requirements for EMC Ground (earth) connections
generic emission standards
Technical data
on page 76
on page 70 must be followed.
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
on page 67 and section 4.12.5
on page 93 will be
General
Compliance with
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Technical data UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
63
Page 64

Table 4-10 Drive and EMC filter cross reference
WARNING
NOTE
Model CT part number
200 V
03200050 to 03200106 4200-3230
04200137 to 04200185 4200-0272
400 V
03400025 to 03400100 4200-3480
04400150 to 04400172 4200-0252
High ground leakage current
When an EMC filter is used, a permanent fixed ground connection must be provided which
does not pass through a connector or flexible power cord. This includes the internal EMC
filter.
The installer of the drive is responsible for ensuring compliance with the EMC regulations
that apply in the country in which the drive is to be used.
4.12.1 Grounding hardware
The drive is supplied with a grounding bracket and grounding clamp to facilitate EMC compliance.
They provide a convenient method for direct grounding of cable shields without the use of "pig-tails”.
Cable shields can be bared and clamped to the grounding bracket using metal clips or clamps1 (not
supplied) or cable ties. Note that the shield must in all cases be continued through the clamp to the
intended terminal on the drive, in accordance with the connection details for the specific signal.
1
A suitable clamp is the Phoenix DIN rail mounted SK14 cable clamp (for cables with a maximum
outer diameter of 14 mm).
• See Figure 4-9 for details on installing the grounding clamp.
• See Figure 4-10 for details on installing the grounding bracket.
Figure 4-9 Installation of grounding clamp (size 3 and 4)
Loosen the ground connection nuts and slide the grounding clamp in the direction shown. Once in
place, the ground connection nuts should be tightened with a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.47 lb ft).
64
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 65

Figure 4-10 Installation of grounding bracket (all sizes -size 3 shown)
WARNING
WARNING
WARNING
Loosen the ground connection nuts and slide the grounding bracket in the direction shown. Once in
place, the ground connection nuts should be tightened with a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.47 lb ft).
On size 3 and 4 the grounding bracket is secured using the power ground terminal of the
drive. Ensure that the supply ground connection is secure after installing / removing the
grounding bracket. Failure to do so will result in the drive not being grounded.
A faston tab is located on the grounding bracket for the purpose of connecting the drive 0 V to ground
should the user require to do so.
4.12.2 Internal EMC filter
It is recommended that the internal EMC filter be kept in place unless there is a specific reason for
removing it.
If the drive is used with ungrounded (IT) supplies, the internal EMC filter must be
removed unless additional motor ground fault protection is installed.
For instructions on removal refer to section 4.12.2. For details of ground fault protection
contact the supplier of the drive.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
If the drive is used as a motoring drive as part of a regen system, then the internal EMC filter must be
removed.
The internal EMC filter reduces radio-frequency emission into the line power supply. Where the
motor cable is short, it permits the requirements of EN 61800-3:2004 to be met for the second
environment - see section 4.12.4
Systems)
on page 69 and section 12.1.27
Compliance with EN 61800-3:2004 (standard for Power Drive
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
on page 254. For
longer motor cables the filter continues to provide a useful reduction in emission levels, and when
used with any length of shielded motor cable up to the limit for the drive, it is unlikely that nearby
industrial equipment will be disturbed. It is recommended that the filter be used in all applications
unless the instructions given above require it to be removed, or where the ground leakage current of
28 mA for size 3 is unacceptable. See section 4.12.2 for details of removing and installing the internal
EMC filter.
The supply must be disconnected before removing the internal EMC filter.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
65
Page 66

Figure 4-11 Removal of the size 3 internal EMC filter
Remove the screw and nut (1) and (2) as shown above.
Lift away from the securing points and rotate away from the drive. Ensure the screw and nut are
replaced and re-tightened with a maximum torque of 2 N m (1.47 lb ft).
Figure 4-12 Removal of the size 4 internal EMC filter
To electrically disconnect the Internal EMC filter, remove the screw as highlighted above (1).
66
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 67

4.12.3 General requirements for EMC Ground (earth) connections
Optional
ground
connection
External
controller
0V
If the control circuit 0V
is to be grounded, this
should be done at the
system controller only to
avoid injecting noise
currents into the 0V circuit
Metal backplate
Grounding bar
PE
~
PE
If ground connections are
made using a separate
cable, they should run
parallel to the appropriate
power cable to minimise
emissions
Use four core cable to
connect the motor to the drive.
The ground conductor in the
motor cable must be connected
directly to the earth terminal of
the drive and motor.
It must not be connected directly
to the power earth busbar.
The incoming supply ground
should be connected to a
single power ground bus bar
or low impedance earth
terminal inside the cubicle.
This should be used as a
common 'clean' ground for all
components inside the cubicle.
3 phase AC supply
Optional EMC
filter
Metal backplate
safety bonded to
power ground busbar
The grounding arrangements should be in accordance with Figure 4-13, which shows a single drive
on a back-plate with or without an additional enclosure.
Figure 4-13 shows how to configure and minimise EMC when using unshielded motor cable.
However shielded cable is a better option, in which case it should be installed as shown in section
4.12.5
Compliance with generic emission standards
Figure 4-13 General EMC enclosure layout showing ground connections
on page 70.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
67
Page 68

Cable layout
Optional braking resistor and overload
Do not place sensitive
(unscreened) signal circuits
in a zone extending
300 mm (12”) all around the
Drive, motor cable, input
cable from EMC filter and
unshielded braking resistor
cable (if used)
300 mm
(12 in)
NOTE
Figure 4-14 indicates the clearances which should be observed around the drive and related ‘noisy’
power cables by all sensitive control signals / equipment.
Figure 4-14 Drive cable clearances
Any signal cables which are carried inside the motor cable (i.e. motor thermistor, motor brake) will
pick up large pulse currents via the cable capacitance. The shield of these signal cables must be
N
connected to ground close to the motor cable, to avoid this noise current spreading through the
control system.
68
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 69

4.12.4 Compliance with EN 61800-3:2004 (standard for Power Drive
CAUTION
CAUTION
Systems)
Meeting the requirements of this standard depends on the environment that the drive is intended to
operate in, as follows:
Operation in the first environment
Observe the guidelines given in section 4.12.5
page 70. An external EMC filter will always be required.
This is a product of the restricted distribution class according to IEC 61800-3
In a residential environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the
user may be required to take adequate measures.
Operation in the second environment
In all cases a shielded motor cable must be used, and an EMC filter is required for all drives with a
rated input current of less than 100 A.
The drive contains an in-built filter for basic emission control. In some cases feeding the motor cables
(U, V and W) once through a ferrite ring can maintain compliance for longer cable lengths.
For longer motor cables, an external filter is required. Where a filter is required, follow the guidelines
in section 4.12.5
Compliance with generic emission standards
Where a filter is not required, follow the guidelines given in section 4.12.3
EMC Ground (earth) connections
on page 67.
The second environment typically includes an industrial low-voltage power supply network
which does not supply buildings used for residential purposes. Operating the drive in this
environment without an external EMC filter may cause interference to nearby electronic
equipment whose sensitivity has not been appreciated. The user must take remedial
measures if this situation arises. If the consequences of unexpected disturbances are
severe, it is recommended that the guidelines in section 4.12.5
emission standards
be adhered to.
Compliance with generic emission standards
.
General requirements for
Compliance with generic
on
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Refer to section 5.1.25
Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
compliance with EMC standards and definitions of environments.
Detailed instructions and EMC information are given in the
the supplier of the drive.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
on page 93 for further information on
EMC Data Sheet
which is available from
Technical data UL listing information
69
Page 70

4.12.5 Compliance with generic emission standards
≥
100 mm
(4 in)
≥
100 mm
(4 in)
Do not modify
the filter wires
Sensitive
signal
cable
≥
300 mm
(12 in)
Use the recommended filter and shielded motor cable. Observe the layout rules given in Figure 4-15
and Figure 4-17. Ensure the AC supply and ground cables are at least 100 mm from the power
module and motor cable.
Figure 4-15 Supply and ground cable clearance (sizes 3 to 4)
Figure 4-16 Sensitive signal circuit clearance
Avoid placing sensitive signal circuits in a zone 300 mm (12 in) in the area immediately surrounding
the power module. Ensure good EMC grounding.
70
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 71

Figure 4-17 Grounding the drive, motor cable shield and filter
Ensure direct
metal contact
at drive and
filter mounting
points (any
paint must be
removed).
Motor cable shield
(unbroken) electrically
connected to and held
in place by grounding
clamp.
Connect the shield of the motor cable to the ground terminal of the motor frame using a link that is as
short as possible and not exceeding 50 mm (2 in) long.
A complete 360° termination of the shield to the terminal housing of the motor is beneficial.
From an EMC consideration it is irrelevant whether the motor cable contains an internal (safety)
ground core, or if there is a separate external ground conductor, or where grounding is through the
shield alone. An internal ground core will carry a high noise current and therefore it must be
terminated as close as possible to the shield termination.
Figure 4-18 Grounding the motor cable shield
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Unshielded wiring to the optional braking resistor(s) may be used provided the wiring runs internally to
the enclosure. Ensure a minimum spacing of 300 mm (12 in) from the signal wiring and the AC supply
wiring to the external EMC filter. If this condition cannot be met then the wiring must be shielded.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
71
Page 72

Figure 4-19 Shielding requirements of optional external braking resistor
+DC
BR
Optional external
braking resistor
Enclosure
+DC
BR
Optional external
braking resistor
Enclosure
OR
If the control wiring is to leave the enclosure, it must be shielded and the shield(s) clamped to the
drive using the grounding bracket as shown in Figure 4-20. Remove the outer insulating cover of the
cable to ensure the shield(s) make direct contact with the bracket, but keep the shield(s) intact until
as close as possible to the terminals. Alternatively, wiring may be passed through a ferrite ring, part
number 3225-1004.
Figure 4-20 Grounding of signal cable shields using the grounding bracket
72
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 73

4.12.6 Variations in the EMC wiring
From the Drive
To the motor
Back-plate
Enclosure
Isolator
Coupling bar
From the
Drive
To the
motor
(If required)
Interruptions to the motor cable
The motor cable should ideally be a single length of shielded or armored cable having no
interruptions. In some situations it may be necessary to interrupt the cable, as in the following
examples:
• Connecting the motor cable to a terminal block in the drive enclosure
• Installing a motor isolator / disconnect switch for safety when work is done on the motor
In these cases the following guidelines should be followed.
Terminal block in the enclosure
The motor cable shields should be bonded to the back-plate using uninsulated metal cable-clamps
which should be positioned as close as possible to the terminal block. Keep the length of power
conductors to a minimum and ensure that all sensitive equipment and circuits are at least 0.3 m (12
in) away from the terminal block.
Figure 4-21 Connecting the motor cable to a terminal block in the enclosure
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Using a motor isolator / disconnect-switch
The motor cable shields should be connected by a very short conductor having a low inductance.
The use of a flat metal coupling-bar is recommended; conventional wire is not suitable.
The shields should be bonded directly to the coupling-bar using uninsulated metal cable-clamps.
Keep the length of the exposed power conductors to a minimum and ensure that all sensitive
equipment and circuits are at least 0.3 m (12 in) away.
The coupling-bar may be grounded to a known low-impedance ground nearby, for example a large
metallic structure which is connected closely to the drive ground.
Figure 4-22 Connecting the motor cable to an isolator / disconnect switch
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
73
Technical data UL listing information
Page 74

Surge immunity of control circuits - long cables and connections outside a building
Signal from plant Signal to drive
0V 0V
30V zener diode
e.g. 2xBZW50-15
Signal from plant Signal to drive
0V 0V
2 x 15V zener diode
e.g. 2xBZW50-15
The input/output ports for the control circuits are designed for general use within machines and small
systems without any special precautions.
These circuits meet the requirements of EN 61000-6-2:2005 (1 kV surge) provided the 0 V
connection is not grounded.
In applications where they may be exposed to high-energy voltage surges, some special measures
may be required to prevent malfunction or damage. Surges may be caused by lightning or severe
power faults in association with grounding arrangements which permit high transient voltages
between nominally grounded points. This is a particular risk where the circuits extend outside the
protection of a building.
As a general rule, if the circuits are to pass outside the building where the drive is located, or if cable
runs within a building exceed 30 m, some additional precautions are advisable. One of the following
techniques should be used:
1. Galvanic isolation, i.e. do not connect the control 0 V terminal to ground. Avoid loops in the
control wiring, i.e. ensure every control wire is accompanied by its return (0 V) wire.
2. Shielded cable with additional power ground bonding. The cable shield may be connected to
ground at both ends, but in addition the ground conductors at both ends of the cable must be
bonded together by a power ground cable (equipotential bonding cable) with cross-sectional
area of at least 10 mm2, or 10 times the area of the signal cable shield, or to suit the electrical
safety requirements of the plant. This ensures that fault or surge current passes mainly through
the ground cable and not in the signal cable shield. If the building or plant has a well-designed
common bonded network this precaution is not necessary.
3. Additional over-voltage suppression - for the analog and digital inputs and outputs, a zener diode
network or a commercially available surge suppressor may be connected in parallel with the
input circuit as shown in Figure 4-23 and Figure 4-24.
If a digital port experiences a severe surge its protective trip may operate (I/O Overload trip). For
continued operation after such an event, the trip can be reset automatically by setting Pr
10.034
to 5.
Figure 4-23 Surge suppression for digital and unipolar inputs and outputs
Figure 4-24 Surge suppression for analog and bipolar inputs and outputs
74
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 75

Surge suppression devices are available as rail-mounting modules, e.g. from Phoenix Contact:
Unipolar TT-UKK5-D/24 DC
Bipolar TT-UKK5-D/24 AC
These devices are not suitable for encoder signals or fast digital data networks because the
capacitance of the diodes adversely affects the signal. Most encoders have galvanic isolation of the
signal circuit from the motor frame, in which case no precautions are required. For data networks,
follow the specific recommendations for the particular network.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation
Electrical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data UL listing information
75
Page 76

5
Technical data
5.1 Drive technical data
5.1.1 Power and current ratings
For a full explanation of ‘Normal Duty’ and ‘Heavy Duty’ refer to the
The continuous current ratings given are for maximum 40 °C (104 °F), 1000 m altitude and 3 kHz
switching frequency. Derating is required for higher switching frequencies, ambient temperature >40
°
C (104 °F) and high altitude. For further information, refer to Chapter 5.1.2
ratings (Derating for switching frequency and temperature)
on page 77.
Table 5-1 200 V drive ratings (200 V to 240 V ±10 %)
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Max
Nominal
Model
03200050 6.6 1.1 1.5 7.2 5 7.5 10 0.75 1
03200066 8 1.5 2 8.8 6.6 9.9 13.2 1.1 1.5
03200080 11 2.2 3 12.1 8 12 16 1.5 2
03200106 12.7 3 3 13.9 10.6 15.9 21.2 2.2 3
04200137 18 4 5 19.8 13.7 20.5 27.4 3 3
04200185 25 5.5 7.5 27.5 18.5 27.7 37 4 5
cont
output
current
power
at 230 V
A kW hp A A A A kW hp
Motor
power
at 230 V
Peak
current
Max
cont
output
current
Table 5-2 400 V drive ratings (380 V to 480 V ±10 %)
Control User Guide
Open
loop
peak
current
RFC
peak
current
.
Power and current
Nominal
power
at 230 V
at 230 V
Motor
power
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Max
Nominal
Model
03400025 3.4 1.1 1.5 3.7 2.5 3.7 5.0 0.75 1.0
03400031 4.5 1.5 2.0 4.9 3.1 4.6 6.2 1.1 1.5
03400045 6.2 2.2 3.0 6.8 4.5 6.7 9.0 1.5 2.0
03400062 7.7 3.0 5.0 8.4 6.2 9.3 12.4 2.2 3.0
03400078 10.4 4.0 5.0 11.4 7.8 11.7
03400100 12.3 5.5 7.5 13.5 10.0 15.0
04400150 18.5 7.5 10.0 20.3 15.0 22.5
04400172 24.0 11.0 15.0 26.4 17.2 25.8
76
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
cont
output
current
power
at 400 V
A kW hp A A A A kW hp
Motor
power
at 460 V
Peak
current
Max
cont
output
current
Open
loop
peak
current
RFC
peak
current
15.6
20.0
30.0
34.4
Nominal
power
at 400 V
3.0 5.0
4.0 5.0
5.5 10.0
7.5 10.0
at 460 V
Issue Number: 3
Motor
power
Page 77

5.1.2 Power and current ratings (Derating for switching frequency and
temperature)
Table 5-3 Maximum permissible continuous output current @ 40 °C (104 °F) ambient
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Nominal
Model
kW hp
200 V
03200050 1.1 1.5 6.6 0.75 1.0 5.0
03200066 1.5 2.0 8.0 1.1 1.5 6.6
03200080 2.2 3.0 11 10.2 1.5 2.0 8.0 7.5
03200106 3.0 3.0 12.7 12.1 10.2 2.2 3.0 10.6 8.8 7.5
04200137 4.0 5.0 18 3.0 3.0 13.7
04200185 5.5 7.5 25 24 22 4.0 5.0 18.5 17.6 16
400 V
03400025 1.1 1.5 3.4 0.75 1.0 2.5
03400031 1.5 2.0 4.5 1.1 1.5 3.1
03400045 2.2 3.0 6.2 5.0 1.5 2.0 4.5 3.7
03400062 3.0 5.0 7.7 6.2 5.0 2.2 3.0 6.2 5.8 4.5 3.8
03400078 4.0 5.0 10.4 7.6 5.7 3.0 5.0 7.8 7.6 5.7 4.4
03400100 5.5 7.5 12.3 10.5 7.6 5.8 4.0 5.0 10 9.2 7.7 5.7 4.4
04400150 7.5 10 18.5 14.6 11.1 5.5 10 15.0 14.4 11.5 9.4
04400172 11 15 24 21.8 19.2 14.6 11.2 7.5 10 17.2 16.1 14.4 11.5 9.4
Maximum permissible continuous output
rating
current (A) for the following switching
2
kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz
frequencies
Nominal
rating
kW hp
Maximum permissible continuous output
current (A) for the following switching
2
kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz
frequencies
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data
UL listing information
77
Page 78

Table 5-4 Maximum permissible continuous output current @ 40 °C (104 °F) ambient with
high IP insert installed
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Model
200 V
03200050 6.6 5.0
03200066 8.0 6.6
03200080 11.0 9.7 8.0 6.9
03200106 12.3 11.9 11.1 10.0 9.0 6.4 4.7 10.6 10.4 9.3 7.8 6.8
04200137 14.5 13.5 12.2 10.5 9.6 13.7 13.5 12.2 10.5 9.6
04200185 14.5 13.5 12.2 10.5 9.6 14.5 13.5 12.2 10.5 9.6
400 V
03400025 3.4 3.3 2.5
03400031 4.5 4.4 4.1 3.6 3.3 3.1
03400045 5.1 5.0 4.7 4.4 4.1 3.6 3.3 4.5 4.4 4.1 3.6 3.2
03400062 7.7 7.4 6.7 6.2 5.7 5.0 6.2 5.6 4.5 3.8
03400078 8.3 7.6 6.9 6.0 5.2 7.8 7.6 6.9 5.3 4.0
03400100 8.3 7.6 6.9 6.0 5.2 8.3 7.6 6.9 5.3 4.0
04400150 8.6 8.4 6.9 8.6 8.4 6.9
04400172 8.6 8.4 6.9 8.6 8.4 6.9
Maximum permissible continuous output current
for the following switching frequencies
2
kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz2kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz
(A)
Maximum permissible continuous output current
for the following switching frequencies
(A)
78
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 79

Table 5-5 Maximum permissible continuous output current @ 50 °C (122 °F)
NOTE
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Model
200 V
03200050 6.6 5.0
03200066 8.0 6.6
03200080 11 10.5 9.1 8.0 7.0
03200106 12.7 12.6 12.2 11.7 10.5 9.1 10.6 9.6 8.1 7.0
04200137 18 13.7
04200185 22.2 20.2 18.5 17.9 16.2 14.8
400 V
03400025 3.4 2.5
03400031 4.5 3.1
03400045 6.2 5.9 5.4 4.4 4.5 4.2 3.4
03400062 7.6 7.2 6.9 6.4 5.9 5.4 4.4 7.6 5.8 4.5 3.8
03400078 10.4 9.3 8.5 6.9 5.1 7.8 7.0 5.1 3.9
03400100 11.9 11.2 10.5 9.3 8.5 6.9 5.2 10.0 8.3 7.0 5.2 3.9
04400150 18 17.5 17 16.3 15.8 12.2 9.3 15 14.8 13.2 10.6 8.6
04400172 18 17.5 17 16.3 15.8 12.2 9.3 17.2 16.8 14.8 13.2 10.6 8.6
Maximum permissible continuous output current
for the following switching frequencies
2
kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz2kHz3kHz4kHz6kHz8kHz12kHz16kHz
(A)
Maximum permissible continuous output current
for the following switching frequencies
(A)
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
55 °C ratings are available on request.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data
UL listing information
79
Page 80

5.1.3 Power dissipation
Table 5-6 Losses @ 40° C (104° F) ambient
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Nominal
Model
200 V
03200050 1.1 1.5 88 93 95 99 104 113 122 0.75 1 74 78 8 0 84 87 94 101
03200066 1.5 2 95 100 102 107 113 122 133 1.1 1.5 8 5 89 91 9 4 99 108 116
03200080 2.2 3 117 123 126 133 139 151 146 1.5 2 92 97 99 105 109 118 111
03200106 3 3 129 136 141 149 158 168 157 2.2 3 109 115 118 126 134 124 116
04200137 4 5 171 180 187 201 216 244 273 3 3 138 145 151 163 174 198 221
04200185 5.5 7.5 227 239 248 266 284 308 314 4 5 176 185 192 207 221 237 241
400 V
03400025 1.1 1.5 76 80 84 94 103 123 141 0.75 1 67 71 7 6 83 92 108 124
03400031 1.5 2 84 88 92 104 115 137 160 1.1 1.5 66 69 73 82 91 107 124
03400045 2.2 3 99 104 112 125 139 167 157 1.5 2 79 83 88 99 109 131 125
03400062 3 5 108 114 122 137 153 149 147 2.2 3 93 98 105 118 123 118 127
03400078 4 5 138 145 158 186 212 201 197 3 5 109 115 125 145 161 166 165
03400100 5 7.5 155 163 179 209 208 201 200 4 5 131 138 151 163 163 166 165
04400150 7.5 10 214 225 244 283 322 325 310 5.5 10 180 189 205 238 262 274 286
04400172 11 15 269 283 307 325 329 325 315 7.5 10 199 210 227 249 262 274 286
rating
kW hp
Drive losses (W) taking into account
any current derating for the given
2
kHz3 kHz 4 kHz 6 kHz 8 kHz
conditions
12
kHz
16
kHz
Nominal
rating
kW hp
Drive losses (W) taking into account any current
derating for the given conditions
2
khz3 kHz 4kHz 6kHz 8 kHz
12
kHz
16
kHz
80
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 81

Table 5-7 Losses @ 40°C (104° F) ambient with high IP insert installed
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Model
200 V
03200050 88 93 95 99 104 113 122 74 78 80 84 87 94 101
03200066 95 100 102 107 113 122 133 85 89 91 94 99 108 116
03200080 117 123 126 133 140 158 157 92 97 99 105 109 118 112
03200106 122 128 124 122 118 98 84 109 115 119 127 122 120 122
04200137 138 145 151 151 146 142 146 145 153 160 161 155 152 155
04200185 204 215 205 194 189 187 199 176 185 192 202 193 191 200
400 V
03400025 76 80 84 94 103 123 137 67 71 76 83 92 108 124
03400031 84 88 92 102 105 110 134 66 69 73 82 91 107 126
03400045 80 84 85 89 92 109 134 79 83 88 96 100 109 130
03400062 108 114 117 122 135 172 203 93 98 105 118 122 136 155
03400078 112 118 134 155 173 221 267 109 115 126 155 173 195 205
03400100 112 118 134 155 173 221 267 106 112 126 155 173 195 205
04400150 100 105 114 132 153 197 207 103 108 118 136 156 202 214
04400172 96 101 111 131 152 197 207 100 105 114 133 157 202 214
Drive losses (W) taking into consideration any
current derating for the given conditions
2
kHz3 kHz 4 kHz 6 kHz 8 kHz
12
kHz
Drive losses (W) taking into consideration any
current derating for the given conditions
16
kHz 2 kHz3 kHz 4 kHz 6 kHz 8 kHz
12
kHz
16
kHz
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data
UL listing information
81
Page 82

Table 5-8 Losses @ 50° C (122° F) ambient
Normal Duty Heavy Duty
Model
200 V
03200050 88 93 95 99 104 113 122 74 78 80 84 87 94 101
03200066 95 100 102 107 113 122 133 85 89 91 94 99 108 116
03200080 117 123 126 133 139 144 139 92 97 99 105 109 118 113
03200106 129 136 140 143 147 151 150 109 115 118 126 121 117 116
04200137 171 180 187 201 216 253 297 138 145 151 163 174 198 228
04200185 203 214 223 244 265 312 334 176 185 192 207 217 230 247
400 V
03400025 76 80 84 118 103 123 141 67 71 76 83 92 108 124
03400031 84 88 92 104 115 137 160 66 69 73 82 91 107 124
03400045 99 104 112 125 132 146 155 79 83 88 99 109 122 121
03400062 106 106 109 114 117 145 155 118 124 132 148 148 140 139
03400078 138 145 158 175 194 225 225 109 115 125 148 160 166 172
03400100 152 152 160 175 194 225 230 131 138 152 158 160 170 172
04400150 213 213 227 262 300 323 325 180 189 205 240 253 276 297
04400172 212 212 227 262 300 318 321 200 211 226 240 253 276 297
Drive losses (W) taking into accou nt any current
derating for the given conditions
2
kHz3 kHz 4 kHz 6 kHz 8 kHz
12
kHz
Drive losses (W) taking into account any current
derating for the given conditions
16
kHz 2 kHz3 kHz 4 kHz 6 kHz 8 kHz
12
kHz
16
kHz
Table 5-9 Power losses from the front of the drive when through-panel mounted
Frame size Power loss
3 ≤ 50 W
4 ≤ 75 W
5.1.4 Temperature, humidity and cooling method
Ambient temperature operating range:
- 20 °C to 55 °C (- 4 °F to 131 °F).
Output current derating must be applied at ambient temperatures >40 °C (104 °F).
Cooling method: Forced convection
Maximum humidity: 95 % non-condensing at 40 °C (104 °F)
82
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 83

5.1.5 Supply requirements
AC supply voltage:
200 V drive: 200 V to 240 V ±10 %
400 V drive: 380 V to 480 V ±10 %
Number of phases: 3
Maximum supply imbalance: 2 % negative phase sequence (equivalent to 3 % voltage imbalance
between phases).
Frequency range: 45 to 66 Hz
For UL compliance only, the maximum supply symmetrical fault current must be limited to 100 kA
5.1.6 Line reactors
Input line reactors reduce the risk of damage to the drive resulting from poor phase balance or
severe disturbances on the supply network.
Where line reactors are to be used, reactance values of approximately 2 % are recommended.
Higher values may be used if necessary, but may result in a loss of drive output (reduced torque at
high speed) because of the voltage drop.
For all drive ratings, 2 % line reactors permit drives to be used with a supply unbalance of up to 3.5 %
negative phase sequence (equivalent to 5% voltage imbalance between phases).
Severe disturbances may be caused by the following factors, for example:
• Power factor correction equipment connected close to the drive.
• Large DC drives having no or inadequate line reactors connected to the supply.
• Across the line (DOL) started motor(s) connected to the supply such that when any of these
motors are started, the voltage dip exceeds 20 %.
Such disturbances may cause excessive peak currents to flow in the input power circuit of the drive.
This may cause nuisance tripping, or in extreme cases, failure of the drive.
Drives of low power rating may also be susceptible to disturbance when connected to supplies with a
high rated capacity.
Line reactors are particularly recommended for use with the following drive models when one of the
above factors exists, or when the supply capacity exceeds 175 kVA:
03200050, 03200066, 03200080, 03200106,
03400025, 03400031, 03400045, 03400062
Model sizes 03400078 to 04400172 have an internal DC choke so they do not require AC line
reactors except for cases of excessive phase unbalance or extreme supply conditions.
When required, each drive must have its own reactor(s). Three individual reactors or a single threephase reactor should be used.
Reactor current ratings
The current rating of the line reactors should be as follows:
Continuous current rating:
Not less than the continuous input current rating of the drive
Repetitive peak current rating:
Not less than twice the continuous input current rating of the drive
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Technical data
UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
83
Page 84

Table 5-10 2 % line reactors
Drive
model
number
03200050 200 INL2001 4401-0143 13.5 0.79 1.8 156 70 125
03200066 200 INL2001 4401-0143 13.5 0.79 1.8 156 70 125
03200080 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
03200106 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
04200137 200 INL2002 4401-0144 20.6 0.48 2.4 156 80 125
04200185 200 INL2003 4401-0145 26.8 0.32 2.5 156 80 125
03400025 400 INL4001 4401-0148 6.6 2.94 1.3 80 75 130
03400031 400 INL4001 4401-0148 6.6 2.94 1.3 80 75 130
03400045 400 INL4002 4401-0149 9.1 1.62 1.8 156 70 125
03400062 400 INL4011 4401-0234 13 1.12 2.5 156 80 125
03400078 400 INL4011 4401-0234 13 1.12 2.5 156 80 125
03400100 400 INL4003 4401-0151 15.8 1.05 2.6 156 80 125
04400150 400 INL4004 4401-0152 18.7 0.79 3.5 156 60 145
04400172 400 INL4005 4401-0153 24.3 0.61 4.9 156 75 145
Voltage
Line reactor
rating
designation
V A mH kg mm mm mm
CT Part
number
Line
reactor
current
rating
Inductance Weight Length Width Height
5.1.7 Motor requirements
No. of phases: 3
Maximum voltage:
200 V drive: 240 V
400 V drive: 480 V
5.1.8 Storage
-40 °C (-40 °F) to +55 °C (131 °F) for long term storage, or to +70 °C (158 °F) for short term
storage.
Storage time is 2 years.
Electrolytic capacitors in any electronic product have a storage period after which they require
reforming or replacing.
The DC bus capacitors have a storage period of 10 years.
The low voltage capacitors on the control supplies typically have a storage period of 2 years and are
thus the limiting factor.
Low voltage capacitors cannot be reformed due to their location in the circuit and thus may require
replacing if the drive is stored for a period of 2 years or greater without power being applied.
It is therefore recommended that drives are powered up for a minimum of 1 hour after every 2 years
of storage. This process allows the drive to be stored for a further 2 years.
5.1.9 Altitude
Altitude range: 0 to 3,000 m (9,900 ft), subject to the following conditions:
1,000 m to 3,000 m (3,300 ft to 9,900 ft) above sea level: de-rate the maximum output current from
the specified figure by 1% per 100 m (330 ft) above 1,000 m (3,300 ft)
For example at 3,000 m (9,900 ft) the output current of the drive would have to be de-rated by 20 %.
84
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 85

5.1.10
The drive is rated to IP20 pollution degree 2 (dry, non-conductive contamination only) (NEMA 1).
However, it is possible to configure the drive to achieve IP65 rating (sizes 3 to 4) (NEMA 12) at the
rear of the heatsink for through-panel mounting (some current derating is required).
The IP rating of a product is a measure of protection against ingress and contact to foreign bodies
and water. It is stated as IP XX, where the two digits (XX) indicate the degree of protection provided
as shown in Table 5-11.
Table 5-11 IP Rating degrees of protection
Protection against contact and ingress of
foreign bodies
0 No protection 0 No protection
1
2
3
4
5
6
7 - 7 Protection against immersion
8 - 8 Protection against submersion
Table 5-12 UL enclosure ratings
IP / UL Rating
First digit Second digit
Protection against ingress of water
Protection against large foreign bodies φ >
50 mm (large area contact with the hand)
Protection against medium size foreign
bodies φ > 12 mm (finger)
Protection against small foreign bodies φ >
2.5 mm (tools, wires)
Protection against granular foreign bodies
φ
> 1mm (tools, wires)
Protection against dust deposit, complete
protection against accidental contact.
Protection against dust ingress, complete
protection against accidental contact.
UL rating Description
Type 1
Type 12
Enclosures are intended for indoor use, primarily to provide a degree
of protection against limited amounts of falling dirt.
Enclosures are intended for indoor use, primarily to provide a degree
of protection against dust, falling dirt and dripping non-corrosive
liquids.
Protection against vertically falling drops of
1
water
Protection against spraywater (up to 15 °
2
from the vertical)
Protection against spraywater (up to 60 °
3
from the vertical)
Protection against splashwater (from all
4
directions)
Protection against heavy splash water (from
5
all directions, at high pressure)
Protection against deckwater (e.g. in heavy
6
seas)
5.1.11 Corrosive gasses
Concentrations of corrosive gases must not exceed the levels given in:
• Table A2 of EN 50178:1998
• Class 3C2 of IEC 60721-3-3
This corresponds to the levels typical of urban areas with industrial activities and/or heavy traffic, but
not in the immediate neighborhood of industrial sources with chemical emissions.
5.1.12 RoHS compliance
The drive meets EU directive 2011/65/EU for RoHS compliance.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Technical data
UL listing information
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
85
Page 86

5.1.13 Vibration
NOTE
Maximum recommended continuous vibration level 0.14 g r.m.s. broad-band 5 to 200 Hz.
This is the limit for broad-band (random) vibration. Narrow-band vibration at this level
which coincides with a structural resonance could result in premature failure.
Bump Test
Testing in each of three mutually perpendicular axes in turn.
Referenced standard:IEC 60068-2-29: Test Eb:
Severity: 18 g, 6 ms, half sine
No. of Bumps: 600 (100 in each direction of each axis)
Random Vibration Test
Testing in each of three mutually perpendicular axes in turn.
Referenced standard:IEC 60068-2-64: Test Fh:
Severity: 1.0 m²/s³ (0.01 g²/Hz) ASD from 5 to 20 Hz
-3 dB/octave from 20 to 200 Hz
Duration: 30 minutes in each of 3 mutually perpendicular axes.
Sinusoidal Vibration Test
Testing in each of three mutually perpendicular axes in turn.
Referenced standard: IEC 60068-2-6: Test Fc:
Frequency range: 5 to 500 Hz
Severity: 3.5 mm peak displacement from 5 to 9 Hz
10 m/s² peak acceleration from 9 to 200 Hz
15 m/s² peak acceleration from 200 to 500 Hz
Sweep rate: 1 octave/minute
Duration: 15 minutes in each of 3 mutually perpendicular axes.
EN 61800-5-1:2007, Section 5.2.6.4. referring to IEC 60068-2-6
Frequency range: 10 to 150 Hz
Amplitude: 10 to 57 Hz at 0.075 mm pk
57 to 150 Hz at 1g p
Sweep rate: 1 octave/minute
Duration: 10 sweep cycles per axis in each of 3 mutually perpendicular axes
5.1.14
By electronic control: unlimited
By interrupting the AC supply: ≤20 (equally spaced)
5.1.15 Start up time
This is the time taken from the moment of applying power to the drive, to the drive being ready to run
the motor:
For faster start up time a 24V backup supply can be used, see section 4.5
page 52.
Starts per hour
Sizes 3 and 4 = 2.5 s
24 Vdc supply
on
86
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 87

5.1.16
Unidrive Mxxx models:
In all operating modes (Open loop, RFC-A, RFC-S) the maximum output frequency is limited to 550
Hz.
Unidrive HSxx models:
In open loop mode the maximum achievable output frequency is 3,000 Hz.
In RFC-A and RFC-S modes, the maximum achievable output frequency is 1,250Hz.
In RFC-S mode the speed is also limited by the voltage constant (Ke) of the motor unless field
weakening operation is enabled. Ke is a specific constant for the servo motor being used. It can
normally be found on the motor data sheet in V/k rpm (volts per 1,000 rpm).
It is recommended that a minimum ratio of 12:1 is maintained between the switching frequency and
the maximum output frequency to maintain the quality of the output waveform. If this minimum ratio is
exceeded, extra motor losses will result due to the increased harmonic content of the output
waveform.
5.1.17
Speed:
The absolute frequency and speed accuracy depends on the accuracy of the crystal used with the
drive microprocessor. The accuracy of the crystal is 100 ppm, and so the absolute frequency/speed
accuracy is 100 ppm (0.01 %) of the reference, when a preset speed is used. If an analog input is
used the absolute accuracy is further limited by the absolute accuracy of the analog input.
The following data applies to the drive only; it does not include the performance of the source of the
control signals.
Open loop resolution:
Closed loop resolution
Current:
The resolution of the current feedback is 10 bit plus sign.
Accuracy: typical 2 %
Output frequency / speed range
Accuracy and resolution
Preset frequency reference: 0.1 Hz
Precision frequency reference: 0.001 Hz
Preset speed reference: 0.1 rpm
Precision speed reference: 0.001 rpm
Analog input 1: 11 bit plus sign
Analog input 2: 11 bit plus sign
worst case 5 %
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Technical data
5.1.18
The heatsink fan generates the majority of the sound pressure level at 1 m produced by the drive. The
heatsink fan is a variable speed fan. The drive controls the speed at which the fan runs based on the
temperature of the heatsink and the drive's thermal model system.
Table 5-13 gives the sound pressure level at 1 m produced by the drive when running at maximum
normal and heavy duty current and when the heatsink fan is running at minimum speed.
Table 5-13 Acoustic noise data
*At 40 °C ambient and 3 kHz switching frequency.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Acoustic noise
Size
3 62.8 50.9 42.9
4 62.6 56.9 45.8
Max ND operation
dBA
Max HD operation*
dBA
Min fan speed
dBA
87
UL listing information
Page 88

5.1.19 Overall dimensions
WARNING
H Height including surface mounting brackets
W Width
D Projection forward of panel when surface mounted
F Projection forward of panel when through-panel mounted
R Projection rear of panel when through-panel mounted
Table 5-14 Overall drive dimensions
Size
3
4
H W D F R
382 mm
(15.04 in)
391 mm
(15.39 in)
83 mm
(3.27 in)
124 mm
(4.88 in)
Dimension
200 mm
(7.87 in)
134 mm
(5.28 in)
67 mm
(2.64 in)
67 mm
(2.64 in)
5.1.20
Table 5-15 Overall drive weights
Weights
Size Model kg lb
3
4 All variants 6.5 14.30
034300078, 034300100 4.5 9.9
All other variants 4.0 8.8
5.1.21 Input current, fuse and cable size ratings
The input current is affected by the supply voltage and impedance.
Typical input current
The values of typical input current are given to aid calculations for power flow and power loss. The
values of typical input current are stated for a balanced supply.
Maximum continuous input current
The values of maximum continuous input current are given to aid the selection of cables and fuses.
These values are stated for the worst case condition with the unusual combination of stiff supply with
bad balance. The value stated for the maximum continuous input current would only be seen in one
of the input phases. The current in the other two phases would be significantly lower.
The values of maximum input current are stated for a supply with a 2 % negative phase-sequence
imbalance and rated at the maximum supply fault current given in Table 5-16.
Table 5-16 Supply fault current used to calculate maximum input currents
Model Symmetrical fault level (kA)
All 100
Fuses
The AC supply to the drive must be installed with suitable protection against overload and
short-circuits. Table 5-17 and Table 5-18 shows the recommended fuse ratings. Failure to
observe this requirement will cause risk of fire.
88
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 89

Table 5-17 AC Input current and fuse ratings (200 V)
NOTE
CAUTION
Model
03200050
03200066
03200080
03200106
04200137
04200185
Typical
input
current
Maximum
continuous
input
current
A A A A A A A
8.2
9.9
14
16
17
23
10.4
12.6
Maximum
overload
input
current
15.8
20.9
17
20
20 30 25 25
28 41 32 32 30 30
25
34
Nominal Max
16
20
25
* These fuses are fast acting.
Table 5-18 AC Input current and fuse ratings (400 V)
Model
03400025
03400031
03400045
03400062
03400100
04400150
04400172
Typical
input
current
Maximum
continuous
input
current
A A A A A A A
5
6
8
11
12
14
17
22
13
13
16
19
24
Maximum
overload
input
current
5
7
9
7
9
13
21
20
25
30
35
Nominal Max
10 10
20 20 20 2003400078
25 25
32 32 30 30
* These fuses are fast acting.
Fuse rating
IEC UL / USA
Nominal Max
Class
20
25 gG
25
gG
IEC UL / USA
Class
25 25
Fuse rating
Nominal Max
gG
gG
10 10
25 25
25
Class
CC, J or
T*
CC, J or
T*
Class
CC, J or
T*
CC, J or
T*
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Ensure cables used suit local wiring regulations.
The nominal cable sizes below are only a guide. The mounting and grouping of cables
affects their current-carrying capacity, in some cases smaller cables may be acceptable
but in other cases a larger cable is required to avoid excessive temperature or voltage
drop. Refer to local wiring regulations for the correct size of cables.
Table 5-19 Cable ratings (200 V)
Cable size (IEC) mm
Model
Nominal Max
03200050
03200066
03200080
03200106
04200137
04200185
Input Output Input Output
Install
method
1.5
4 B2
4 4
6
8
8 B2
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
2
Nominal Max
1.5
6
8 8 8
Install
method
4 B2
8 B2
Cable size (UL) AWG
Nominal Max Nominal Max
14
10
12 12
10
8
Technical data
14
10
10
8
UL listing information
89
Page 90

Table 5-20 Cable ratings (400 V)
Cable size (IEC)
Model
Nominal Max
03400025
03400031 16 16
03400045
03400078
03400100 12 12
04400150
04400172
Input Output Input Output
method
1.5
4 B2
2.5 2.5
4
6 6
6 B2
Install
2
mm
Nominal Max
1.5
4
Install
method
4 B2
6 B2
Nominal Max Nominal Max
Cable size (UL)
AWG
18
14 1403400062
10
10
8 8
8
18
10
10
8
5.1.22
Maximum motor cable lengths and types
Since capacitance in the motor cable causes loading on the output of the drive, ensure the cable
length does not exceed the values given in Table 5-21 and Table 5-22.
Use 105 °C (221 °F) (UL 60/75 °C temp rise) PVC-insulated cable with copper conductors having a
suitable voltage rating, for the following power connections:
• AC supply to external EMC filter (when used)
• AC supply (or external EMC filter) to drive
• Drive to motor
• Drive to braking resistor
Table 5-21 Maximum motor cable lengths (200 V drives)
200 V Nominal AC supply voltage
Maximum permissible motor cable length for each of the following switching
Model
03200050 65 m (210 ft)
03200066 100 m (330 ft)
03200080 130 m (425 ft)
03200106 200 m (660 ft)
04200137
04200185
2
kHz
200 m (660 ft)
3
kHz
150 m
(490 ft)
150 m
(490 ft)
4
kHz
frequencies
6
kHz
100 m
(330 ft)
100 m
(330 ft)
8
kHz
75 m
(245 ft)
75 m
(245 ft)
12 kHz 16 kHz
50 m
(165 ft)
50 m
(165 ft)
37 m
(120 ft)
37 m
(120 ft)
90
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 91

Table 5-22 Maximum motor cable lengths (400 V drives)
400 V Nominal AC supply voltage
Maximum permissible motor cable length for each of the following
Model
03400025 65 m (210 ft)
03400031 100 m (330 ft)
03400045 130 m (425 ft)
03400062
03400078
03400100
04400150
04400172
2
kHz
200 m (660 ft)
200 m (660 ft)
3
kHz
switching frequencies
4
kHz
150 m
(490 ft)
150 m
(490 ft)
6
kHz
100 m
(330 ft)
100 m
(330 ft)
8
kHz
75 m
(245 ft)
75 m
(245 ft)
12
kHz
50 m
(165 ft)
50 m
(165 ft)
16
kHz
37 m
(120 ft)
37 m
(120 ft)
• Cable lengths in excess of the specified values may be used only when special techniques are
adopted; refer to the supplier of the drive.
• The default switching frequency is 3 kHz for Open-loop and RFC-A and 6 kHz for RFC-S mode.
The maximum cable length is reduced from that shown in Table 5-21 and Table 5-22 if high
capacitance or reduced diameter motor cables are used, refer to Chapter 4.9.2
reduced diameter cables
on page 54.
High-capacitance /
5.1.23 Braking resistor values
Table 5-23 Braking resistor resistance and power rating at 40 °C (104 °F) (200 V)
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Model
Minimum
resistance *
Ω
Instantaneous power
rating
kW kW
03200050
03200066 2.2
03200080 3.1
22 7.7
03200106 4.2
04200137
04200185 7.4
18 9.4
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Continuous
power rating
1.7
5.1
Technical data
UL listing information
91
Page 92

Table 5-24 Braking resistor resistance and power rating at 40 °C (104 °F) (400 V)
Minimum
Model
resistance *
Ω
03400025
03400031 2.3
03400045 3.1
74 9.2
Instantaneous power
rating
kW kW
Continuous
power rating
1.7
03400062 5.1
03400078
03400100 7.3
04400150
04400172 13.9
50 13.6
37 18.3
6.4
12.5
* Resistor tolerance: ±10 %. The minimum resistance specified are for stand-alone drive systems
only. If the drive is to be used as part of a common DC bus system different values may be required.
See
Braking resistor software overload protection
on page 62.
5.1.24 Torque settings and maximum cable size
Table 5-25 Drive control and relay terminal data
Model Connection type Torque setting
All Plug-in terminal block 0.5 N m (0.4 lb ft)
Table 5-26 Drive power terminal data
Frame
size
3 and 4
AC and motor terminals DC and braking Ground terminal
Recommended Maximum Recommended Maximum Recommended Maximum
Plug-in terminal block T20 Torx (M4)
0.7 N m
(0.5 lb ft)
0.8 N m
(0.6 lb ft)
2.0 N m
(1.4 Ib ft)
2.5 N m
(1.8 Ib ft)
T20 Torx (M4) / M4 Nut
(7 mm AF)
2.0 N m
(1.4 Ib ft)
2.5 N m
(1.8 Ib ft)
Table 5-27 Plug-in terminal block maximum cable sizes
Frame size Terminal block description Max cable size
All
11 way control connectors
2 way relay connector
3
4
6 way AC power connector
1.5 mm2 (16 AWG)
2.5 mm2 (12 AWG)
6 mm2 (10 AWG)
Table 5-28 External EMC filter terminal data
CT part
number
4200-0252
4200-0272
4200-3230
4200-3480
92
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Max cable size Max torque Ground stud size Max torque
16 mm
(6 AWG)
4 mm
(12 AWG)
Power
connections
2
2
1.8 N m
(1.4 lb ft)
0.8 N m
(0.59 lb ft)
Ground
connections
M6
M5
4.8 N m
(2.8 lb ft)
3.0 N m
(2.2 lb ft)
Issue Number: 3
Page 93

5.1.25 Electromagnetic compatibility (EMC)
This is a summary of the EMC performance of the drive. For full details, refer to the
which can be obtained from the supplier of the drive.
Table 5-29 Immunity compliance
Standard Type of immunity Test specification Application Level
IEC61000-4-2
EN61000-4-2
IEC61000-4-3
EN61000-4-3
IEC61000-4-4
EN61000-4-4
IEC61000-4-5
EN61000-4-5
IEC61000-4-6
EN61000-4-6
IEC61000-4-11
EN61000-4-11
IEC61000-6-1
EN61000-6-1:2007
IEC61000-6-2
EN61000-6-2:2005
IEC61800-3
EN61800-3:2004
1
See section 4.12.6
grounding and external surge protection of the control ports.
Electrostatic
discharge
Radio frequency
radiated field
Fast transient burst
Surges
Conducted radio
frequency
Voltage dips and
interruptions
Generic immunity standard for the residential,
commercial and light - industrial environment
Generic immunity standard for the industrial
environment
Product standard for adjustable speed power drive
systems (immunity requirements)
Variations in the EMC wiring
6 kV contact discharge
8 kV air discharge
10 V/m prior to modulation
80 - 1000 MHz
80 % AM (1 kHz) modulation
5/50 ns 2 kV transient at 5
kHz repetition frequency via
coupling clamp
5/50 ns 2 kV transient at 5
kHz repetition frequency by
direct injection
Common mode 4 kV
1.2/50 µs waveshape
Differential mode
2 kV1.2/50 µs waveshape
Lines to ground
10V prior to modulation
0.15 - 80 MHz
80 % AM (1 kHz) modulation
-30 % 10 ms
+60 % 100 ms
-60 % 1 s
<-95 % 5 s
on page 73 for possible requirements regarding
Module enclosure
Module enclosure
Control lines
Power lines
AC supply lines:
line to ground
AC supply lines:
line to line
Signal ports to
1
ground
Control and power
lines
AC power ports
Meets immunity requirements for first
and second environments
EMC Data Sheet
Level 3
(industrial)
Level 3
(industrial)
Level 4
(industrial harsh)
Level 3
(industrial)
Level 4
Level 3
Level 2
Level 3
(industrial)
Complies
Complies
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data
UL listing information
93
Page 94

Emission
The drive contains an in-built filter for basic emission control. An additional optional external filter
provides further reduction of emission. The requirements of the following standards are met,
depending on the motor cable length and switching frequency.
Table 5-30 Size 3 emission compliance (200 V drives)
Motor cable
length (m)
Using internal filter:
0 – 2 C3 C4
Using internal filter and ferrite ring (2 turns):
0 – 10 C3 C4
10-20 C3 C4
Using external filter:
0 – 20 R (C1) R (C1) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2)
20 – 100 I (C2) I (C2) C3 C3 C3 C3 C3
2 3 4 6 8 12 16
Switching Frequency (kHz)
Table 5-31 Size 3 emission compliance (400 V drives)
Motor cable
length (m)
Using internal filter:
0 – 5 C3 C4
Using internal filter and ferrite ring (2 turns):
0 – 10 C3 C4
Using external filter:
0 – 20 R (C1) R (C1) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2)
20 – 100 I (C2) I (C2) C3 C3 C3 C3 C3
2 3 4 6 8 12 16
Switching Frequency (kHz)
Table 5-32 Size 4 emission compliance (200 V drives)
Motor cable
length (m)
Using internal filter:
0 – 2 C3 C4
Using internal filter and ferrite ring (2 turns):
0 – 4 C3 C4
Using external filter:
0 – 20 R (C1) R (C1) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2)
20 – 100 I (C2) I (C2) C3 C3 C3 C3 C3
94
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
2 3 4 6 8 12 16
Switching Frequency (kHz)
Issue Number: 3
Page 95

Table 5-33 Size 4 emission compliance (400 V drives)
CAUTION
Motor cable
length (m)
Using internal filter:
0 – 4 C3 C4
Using internal filter and ferrite ring (2 turns):
0 – 10 C3 C4
Using external filter:
0 – 20 R (C1) R (C1) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2) I (C2)
20 – 100 I (C2) I (C2) C3 C3 C3 C3 C3
Key
(shown in decreasing order of permitted emission level):
2 3 4 6 8 12 16
Switching Frequency (kHz)
E2R EN 61800-3:2004 second environment, restricted distribution (Additional measures may be
required to prevent interference)
E2U EN 61800-3:2004 second environment, unrestricted distribution
I Industrial generic standard EN 61000-6-4:2007
EN 61800-3:2004 first environment restricted distribution (The following caution is required
by EN 61800-3:2004)
This is a product of the restricted distribution class according to IEC 61800-3. In a
residential environment this product may cause radio interference in which case the user
may be required to take adequate measures.
R Residential generic standard EN 61000-6-3:2007
EN 61800-3:2004 first environment unrestricted distribution
EN 61800-3:2004 defines the following:
• The first environment is one that includes residential premises. It also includes establishments
directly connected without intermediate transformers to a low-voltage power supply network
which supplies buildings used for residential purposes.
• The second environment is one that includes all establishments other than those directly
connected to a low-voltage power supply network which supplies buildings used for residential
purposes.
• Restricted distribution is defined as a mode of sales distribution in which the manufacturer
restricts the supply of equipment to suppliers, customers or users who separately or jointly have
technical competence in the EMC requirements of the application of drives.
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Technical data
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
UL listing information
95
Page 96

IEC 61800-3:2004 and EN 61800-3:2004
The 2004 revision of the standard uses different terminology to align the requirements of the
standard better with the EC EMC Directive.
Power drive systems are categorized C1 to C4:
Category Definition
Corresponding code
used above
C1 Intended for use in the first or second environments R
Not a plug-in or movable device, and intended for use in
C2
the first environment only when installed by a
I
professional, or in the second environment
C3
C4
Intended for use in the second environment, not the first
environment
Intended for use in the second environment in a system
rated at over 400A, or in a complex system.
E2U
E2R
Note that category 4 is more restrictive than E2R, since the rated current of the PDS must exceed
400 A or the supply voltage exceed 1000 V, for the complete PDS.
5.2 Optional external EMC filters
Table 5-34 EMC filter cross reference
Model CT part number
200 V
03200050 to 03200106 4200-3230
04200137 to 04200185 4200-0272
400 V
03400025 to 03400100 4200-3480
04400150 to 04400172 4200-0252
5.2.1
Table 5-35 Optional external EMC filter details
4200-3230 20 18.5 250 300
4200-0272 27 24.8 250 300 33 28 6.8 137
4200-3480 16 15 528 600 13 11 10.7 151
4200-0252 25 23 528 600 28 24 11.1 182
EMC filter ratings
Part
number
(104 °F)
Maximum
continuous
current
@ 50 °C
(122 °F)
A A V V W W mA mA M
Voltage
rating
IEC UL
IP
rating
20
Power
dissipation at
rated current
@ 40 °C
(104 °F)
@ 50 °C
(122 °F)
20 17 2.4 60
Ground leakage
Balanced
supply
phase-to-
phase and
phase-to-
ground
Worst
case@ 40 °C
Discharge
resistors
Ω
1.68
96
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Page 97

5.2.2 Overall EMC filter dimensions
Table 5-36 Optional external EMC filter dimensions
Part
number
4200-3230 426 16.77 83 3.27 41 1.61 1.9 4.20
4200-0272 437 17.20 123 4.84 60 2.36 4.0 8.82
4200-3480 426 16.77 83 3.27 41 1.61 2.0 4.40
4200-0252 437 17.20 123 4.84 60 2.36 4.1 9.04
H W D
mm inch mm inch mm inch kg lb
Dimension (mm)
Weight
5.2.3 EMC filter torque settings
Table 5-37 Optional external EMC Filter terminal data
Part
number
4200-0252
4200-0272
4200-3230
4200-3480
Power
connections
Max cable size Max torque Ground stud size Max torque
16 mm
(6 AWG)
2
4 mm
(12 AWG)
2
1.8 N m
(1.4 lb ft)
0.8 N m
(0.59 lb ft)
connections
M6
M5
Ground
5.0 N m
(3.7 lb ft)
2.5 N m
(1.8 lb ft)
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
Technical data
UL listing information
97
Page 98

6
UL listing information
6.1 General
6.1.1 Scope of approvals
All models are listed to both US and Canadian safety requirements.
The UL file number is: E171230.
The Manufacturing Location Code is: 8D14.
6.1.2 Manufacturers name
The manufacturer is Emerson Industrial Automation.
6.1.3 Electrical ratings
The electrical ratings are tabulated in
6.1.4 Multiple wiring arrangements
The drives are not intended for use in applications that require different wiring arrangements. The
drives are not multiple rated.
6.1.5 Model numbers
The way in which the model numbers for the
section 2.1
Introduction
on page 11.
6.1.6 Plenum rating
The drives are suitable for installation in a compartment (duct) handling conditioned air when
installed as enclosed types with the intended Type 1 terminal kit.
6.1.7 Operating temperature
The drives are rated for use at 40 °C ambient temperature.
Operation at 50 °C is permitted with derated output. Refer to Table 5-5 on page 79 for further
information.
Operation at 55 °C is permitted with derated output, 55 °C ratings are available on request.
6.1.8 Installation warnings, cautions and notes
The appropriate installation warnings, cautions and notes are located in Chapter 1
information
on page 8.
Table 2-1 and Table 2-2 on page 13.
Unidrive M/HS
product range is formed is illustrated in
Safety
6.2 Overload, overcurrent and overspeed protection
6.2.1 Degree of protection level
The devices incorporate solid state overload protection for the motor load. The protection levels are
expressed as a percentage of full-load current. Refer to the
information.
In order for the motor protection to work properly, the motor rated current must be entered into
Pr
00.046
or Pr
05.007
.
The protection level may be adjusted below 150 % if required. Refer to the
further information.
The drive incorporates solid state motor overspeed protection. However, this feature does not
provide the level of protection provided by an independent, high-integrity overspeed protection
device.
98
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Control User Guide
Control User Guide
for further
for
Issue Number: 3
Page 99

6.2.2 Thermal memory protection
The drives are provided with motor load and speed sensitive overload protection with thermal
memory retention.
The thermal memory protection complies with UL requirements for shutdown, loss of power and
speed sensitivity.
For a full explanation of the thermal protection system refer to the
In order to comply with UL requirements for thermal memory retention it is necessary to set the
Thermal Protection Mode
be set to 1.
(Pr
04.016
) to zero; and the
Low Speed Protection Mode
Control User Guide.
(Pr
04.025
) must
6.2.3 Use with motors with thermal protectors
The drive is provided with a means to accept and act upon a signal from a thermal sensor or switch
imbedded in the motor or from an external protective relay. Refer to the
further information.
Control User Guide
for
6.2.4 Specific overcurrent protective device
The drive is not required to be connected to a supply source with a specific overcurrent protective
device other than those specified in section 2.4
Ratings
on page 13.
6.3 Short-circuit protection for branch circuits
6.3.1 Short-circuit rating
The drive is suitable for use on a circuit capable of delivering not more than 100,000 RMS
symmetrical amperes, 600 Vac maximum, when protected by the overcurrent protective devices as
described in section 2.4
Unless otherwise indicated in section 2.4
class CC, J or T rated 600 Vac.
Unless otherwise indicated in section 2.4
type with category control number DIVQ or DIVQ7, rated 600 Vac.
6.3.2 Solid state short-circuit protection
The drive is provided with solid state short-circuit protection. Integral solid state protection does not
provide branch circuit protection. Branch circuit protection must be provided in accordance with the
National Electrical Code and any additional local codes.
6.3.3 Common DC bus systems
Frame sizes 3 and 4 are approved for use in modular drive systems using a common DC bus.
For permitted combinations of converter and inverter, along with the required branch circuit
protection, contact Emerson Industrial Automation.
Ratings
on page 13
Ratings
Ratings
.
on page 13, branch fuses may be any UL listed
on page 13, circuit breakers may be any UL listed
Safety information Product information Mechanical installation Electrical installation Technical data
6.4 Control circuit protection
6.4.1 Control circuit wiring
All control circuits are located in limited voltage, limited current isolated secondary circuits. Additional
wiring protection is not required.
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
Issue Number: 3
99
UL listing information
Page 100

6.4.2 Supplemental fuse
When the control circuits are supplied with an external 24 V supply, a supplemental fuse is required
as described in section 4.5
24 Vdc supply
on page 52.
6.4.3 Listed accessory kits
All drives are supplied with an accessory kit box, refer to Table 2-5
page 16.
Parts supplied with the drive
on
6.5 Wiring terminal markings
6.5.1 Marking for proper connection
All main terminals are plainly marked. There are no multiple circuit arrangements.
6.5.2 Terminal connection of ground supply conductor.
The terminals for the connection of the grounded supply circuit conductor are identified by means of
an earth symbol (IEC 60417, symbol No. 5019).
Ground connections must use UL listed closed loop (ring) terminals.
6.5.3 User relay contact
An isolated user relay contact is provided that may be wired in the field to become part of a class 1 or
class 2 circuit. This is described in the
6.5.4 Type of conductors
Use copper conductors only.
6.5.5 Temperature rating of conductors
Use 75 °C rated conductors only.
6.5.6 Torque values
Torque values for field wiring terminals are provided in
settings
on page 43
.
Control User Guide.
section 3.12 Terminal size and torque
6.6 Environment
6.6.1 Environment
Drives are intended for operation in pollution degree 2 environments.
Drives are supplied as open type.
Drives are classed as Enclosed Type 1 when installed with the intended Type 1 terminal kit.
Drives are classed as Type 12 when through hole mounted using the Type 12 kit (high IP kit).
6.7 Mounting
6.7.1 Surface mounting
All drives are suitable for Surface mounting. Mounting instructions are given in
3.4 Dimensions and mounting methods
on page 23
.
6.7.2 Bookcase mounting
In order to minimize the width of the installation, drives may be mounted side by side with or without
airspace between them.
6.7.3 Tile mounting
Frame sizes 3 and 4 are suitable for tile mounting. The drive is mounted sideways with the side panel
against the mounting surface. Tile mounting kits are available.
100
Unidrive M/HS Frame 3 and 4 Power Installation Guide
section
Issue Number: 3
 Loading...
Loading...