Page 1

Page 2

i
© Copyright 2005 Compex Systems Pte Ltd
All Rights Reserved
This document contains information, which is protected by copyright. Reproduction, adaptation
or translation without prior permission is prohibited, except as allowed under the copyright
laws.
Trademark Information
Compex®, ReadyLINK® and MicroHub® are registered trademarks of Compex, Inc. Microsoft
Windows and the Windows logo are the trademarks of Microsoft Corp. NetWare is the
registered trademark of Novell Inc. All other brand and product names are trademarks or
registered trademarks of their respective owners.
Notice: Copyrights © 2005 by Compex, Inc. All rights reserved. Reproduction, adaptation, or
translation without prior permission of Compex, Inc. is prohibited, except as allowed under the
copyright laws.
Manual Revision by Ann
Manual Number: U-0428-V1.3C Version 1.3, February 2005
Disclaimer
Compex, Inc. provides this manual without warranty of any kind, either expressed or implied,
including but not limited to the implied warranties of merchantability and fitness for a particular
purpose. Compex, Inc. may make improvements and/or changes to the product and/or
specifications of the product described in this manual, without prior notice. Compex, Inc will
not be liable for any technical inaccuracies or typographical errors found in this guide. Changes
are periodically made to the information contained herein and will be incorporated into later
versions of the manual. The information contained is subject to change without prior notice.
Your Feedback
We value your feedback. If you find any errors in this user’s manual, or if you have suggestions
on improving, we would like to hear from you. Please contact us at:
Fax: (65) 62809947
Email: feedback@compex.com.sg
Page 3

ii
FCC NOTICE
This device has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device,
pursuant to Part 15 of the FCC Rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable
protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This device generates, uses
and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the
instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no
guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation. If this device does cause
harmful interference to radio or television reception, the user is encouraged to try to correct the
interference by one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Connect the computer into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is
connected.
• Increase the separation between the computer and receiver.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Caution: Any changes or modifications not expressly approved by the grantee of this device
could void the user's authority to operate the equipment.
FCC Compliance Statement: This device complies with Part 15 of the FCC Rules. Operation
is subject to the following two conditions:
1. This device may not cause harmful interference, and
2. This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
This device must accept any interference received, including interference that may cause
undesired operation.
Products that contain a radio transmitter are labelled with FCC ID and may also carry the FCC
logo.
Caution: Exposure to Radio Frequency Radiation.
To comply with the FCC RF exposure compliance requirements, the following antenna
installation and device operating configurations must be satisfied:
a. For configurations using the integral antenna, the separation distance between the antenna(s)
and any person’s body (including hands, wrists, feet and ankles) must be at least 2.5cm (1
inch).
b. For configurations using an approved external antenna, the separation distance between the
antenna and any person’s body (including hands, wrists, feet and ankles) must be at least
20cm (8 inch).
The transmitter shall not be collocated with other transmitters or antennas.
Page 4

iii
ICES 003 Statement
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Declaration of Conformity
Compex, Inc. declares the following:
Product Name: Compex Wireless-A/G Dual-Band Network Access Point
Model No.: Compex WPE54AG conforms to the following Product Standards:
Radiated Emission Standards:
ETSI EN 300 328-2: July 2000; FCC: 47 CFR Part 15, Subpart B, ANSI C63.4-1992; 47 CFR
Part 15, Subpart C (Section 15.247), ANSI C63.4-1992.
Conducted Emission Standards:
ETS 300 826: Nov. 1997.
Immunity Standards:
IEC 801-2; IEC 801-3; IEC 801-4
Low Voltage Directive:
EN 60 950:1992+A1: 1993+A2: 1993+A3; 1995+A4; 1996+A11: 1997
Therefore, this product is in conformity with the following regional standards: FCC Class B
⎯ following the provisions of FCC Part 15 directive; CE Mark ⎯ following the provisions of
the EC directive.
This Class B digital apparatus complies with Canadian ICES-003.
Page 5

v
About This Document
The product described in this document, Compex Wireless-A/G Dual-Band Network Access
Point, Compex WPE54AG is a licensed product of Compex Systems Pte Ltd. This document
contains instructions for installing, configuring and using Compex WPE54AG. It also gives an
overview of the key applications and the networking concepts with respect to the product.
This documentation is for both Network Administrators and the end user who possesses some
basic knowledge in the networking structure and protocols.
It makes a few assumptions that the host computer has already been installed with TCP/IP and
already up & running and accessing the Internet. Procedures for Windows 98SE/ME/2000/XP
operating systems are included in this document. However, for other operating system, you may
need to refer to your operating system’s documentation for networking.
How to Use this Document
This document may become superseded, in which case you may find its latest version at:
http://www.compex.com.sg/prodspec.asp?f=Manual&s=1
The document is written in such a way that you as a user will find it convenient to find specific
information pertaining to the product. It comprises of chapters that explain in details on the
installation and configuration of Compex WPE54AG.
Firmware
This manual is written based on Firmware version 1.16 build 0405.
Conventions
In this document, special conventions are used to help and present the information clearly. The
Compex Wireless-A/G Dual-Band Network Access Point is often referred to as Compex
WPE54AG in this document. Below is a list of conventions used throughout.
NOTE
This section will consist of important features or instructions
CAUTION
This section concerns risk of injury, system damage or loss of data
WARNING
This section concerns risk of severe injury
Page 6
iv
Technical Support Information
The warranty information and registration form are found in the Quick Install Guide.
For technical support, you may contact Compex or its subsidiaries. For your convenience, you
may also seek technical assistance from the local distributor, or from the authorized
dealer/reseller that you have purchased this product from. For technical support by email, write
to
support@compex.com.sg.
Refer to the table below for the nearest Technical Support Centres:
Technical Support Centres
Contact the technical support centre that services your location.
U.S.A., Canada, Latin America and South America
Write
Compex, Inc.
840 Columbia Street, Suite B
Brea, CA 92821, USA
Call
Fax
Tel:
Tel:
Fax:
+1 (714) 482-0333 (8 a.m.-5 p.m. Pacific time)
+1 (800) 279-8891 (Ext.122 Technical Support)
+1 (714) 482-0332
Europe
Write
ReadyLINK Networktechnology Gmbh
Albert Einstein Straβe 34/M21
63322 Rödermark, Germany
Tel:
Fax:
+49 (0) 6074 - 98017 (8 a.m.-5 p.m. local time)
+49 (0) 6074 - 90668
Call
Support Email:
readylink@compex.com.sg
Asia, Australia, New Zealand, Middle East
and the rest of the World
Write
Compex Systems Pte Ltd
135, Joo Seng Road #08-01, PM Industrial Building
Singapore 368363
Call
Tel:
Tel:
Fax:
(65) 6286-1805 (8 a.m.-5 p.m. local time)
(65) 6286-2086 (Ext.199 Technical Support)
(65) 6283-8337
Internet access/
E-mail:
FTPsite:
support@compex.com.sg
ftp.compex.com.sg
Website:
http://www.cpx.com or http://www.compex.com.sg
Fax
Fax
Page 7

vi
References on Menu Command, Push Button, Radio Button, LED and Label appear in Bold.
For example, “Click on Ok.”
Page 8

vii
Copyrights © 2005 Compex Systems Pte Ltd...............................................................................i
Trademark Information.................................................................................................................i
Disclaimer........................................................................................................................................i
Your Feedback................................................................................................................................i
FCC NOTICE................................................................................................................................ii
Declaration of Conformity............................................................................................................ii
Technical Support Information.................................................................................................. iii
About This Document ..................................................................................................................iv
How to Use this Document...........................................................................................................iv
Drivers...........................................................................................................................................iv
Conventions...................................................................................................................................iv
Chapter 1 Product Overview.................................................................................... 1
1.1 Introduction..........................................................................................................................1
1.2 Features and Benefits...........................................................................................................1
1.3 Compex WPE54AG Package...............................................................................................3
1.4 When to use which mode.....................................................................................................3
1.4.1 The Access Point Mode.............................................................................................4
1.4.2 The Access Point Client Mode...................................................................................4
1.4.3 The Gateway Mode....................................................................................................5
1.4.4 The Wireless Routing Client Mode ...........................................................................6
1.4.5 The Wireless Ethernet Adapter Mode........................................................................7
1.4.6 The Wireless Bridge Link Mode................................................................................7
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation............................................................................. 8
2.1 Setup Requirements.............................................................................................................8
2.2 Compex WPE54AG Hardware Installation.......................................................................8
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface............................................................... 9
3.1 Access to the Web interface with uConfig..........................................................................9
3.2 Verify the IP address of Compex WPE54AG - The NpFind Utility...............................11
3.3 Direct access to web-based interface via Internet Explorer............................................12
Chapter 4 Common Configuration........................................................................ 17
4.1 Management Port Setup....................................................................................................17
4.1.1 To view the active DHCP leases..............................................................................19
4.1.2 To reserve specific IP addresses for predetermined DHCP clients..........................20
4.2 WLAN Setup ......................................................................................................................23
4.2.1 To configure the Basic setup of the wireless mode..................................................23
4.2.2 To configure the Advanced setup of the wireless mode...........................................26
Page 9

viii
4.3 Scan for Site Survey (For Wireless Client Mode Only)...................................................29
4.3.1 Show Link Information (For Wireless Client Mode Only)......................................30
4.4 Wireless Extended Features..............................................................................................31
4.4.1 Access Control – The Wireless Pseudo VLAN........................................................31
4.4.2 Wireless Setup - The Wireless Distributed System (WDS).....................................39
4.4.3 WMM Parameters (available in all modes except for Wireless Bridge Link)..........45
4.4.4 Long Distance Parameters (available in all modes).................................................47
4.5 WLAN Security..................................................................................................................49
4.5.1 How to set up WEP [Available in ALL modes].......................................................50
4.5.2 How to set up WPA-PSK [Available in AP/Gateway mode ONLY].......................52
4.5.3 How to set up 802.1x/RADIUS [Available in Access Point mode ONLY].............53
4.5.4 How to set up WPA EAP [Available in Access Point mode ONLY].......................54
4.6 STP Setup ( available in AP/Gateway modes)..................................................................56
4.7 SNMP Setup........................................................................................................................62
4.8 MAC Filtering....................................................................................................................62
Chapter 5 Further Configuration.......................................................................... 64
5.1 Setting up uConfig (only in Gateway mode) ....................................................................64
5.2 Configuring WAN Setup (Available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client mode).65
5.2.1 Dynamic IP..............................................................................................................66
5.2.2 Static IP ...................................................................................................................66
5.2.3 PPPoE......................................................................................................................67
5.2.4 Singapore ADSL......................................................................................................69
5.2.5 Australia BPA Cable................................................................................................70
5.2.6 PPTP........................................................................................................................71
5.3 Using NAT (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client mode)...............72
5.3.1 To set up a De-Militarised Zone host.......................................................................73
5.3.2 To set up port forwarding ........................................................................................74
5.4 Routing (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client mode).....................77
5.4.1 Static Routing ..........................................................................................................79
5.4.2 Dynamic Routing.....................................................................................................80
5.5 Implementing IP Filtering (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client
mode)
81
5.6 Applying Remote Management (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing
Client mode)........................................................................................................................
85
5.7 Enabling Parallel Broadband (Only available in Gateway mode).................................86
5.7.1 Load balancing.........................................................................................................86
5.7.2 Fail-Over Redundancy.............................................................................................87
5.7.3 To enable Parallel Broadband..................................................................................87
Chapter 6 System Utilities ...................................................................................... 89
6.1 Using the SYSTEM TOOLS Menu...................................................................................89
6.1.1 System Identity........................................................................................................89
Page 10

ix
6.1.2 WLAN Station List (Only available in AP and Gateway mode)..............................90
6.1.3 Set System’s Clock..................................................................................................90
6.1.4 Firmware Upgrade...................................................................................................91
6.1.5 Save or Reset Settings..............................................................................................92
6.1.6 Reboot System.........................................................................................................93
6.1.7 Change Password.....................................................................................................94
6.1.8 Logout......................................................................................................................94
6.2 Using the HELP menu.......................................................................................................95
6.2.1 Get Technical Support .............................................................................................95
6.2.2 About System ..........................................................................................................95
Appendix I Troubleshooting..................................................................................... 96
AI Solutions to Common Problems........................................................................................96
Appendix II Firmware Recovery............................................................................. 100
AII How to recover Compex WPE54AG from failed firmware..........................................100
Appendix III TCP/IP Configuration......................................................................... 102
AIII.1 Configure dynamic IP Address in Windows 98SE/ME..............................................102
AIII.2 Configure dynamic IP Address in Windows XP/2000................................................105
AIII.3 Configure static IP Address in Windows 98SE/ME...................................................107
AIII.4 Configure static IP Addres s in Windows XP/2000.....................................................108
Appendix IV Panel Views and Descriptions............................................................. 109
Appendix V Technical Specifications...................................................................... 111
Page 11

Chapter 1 Product Overview
1
Chapter 1 Product Overview
1.1 Introduction
The Compex NetPassage WPE54AG is a dual-band wireless access point that is
interoperable with all standard based 802.11a, 11g and 11b wireless devices. The
Compex NetPassage WPE54AG is a compact and high performance access point that is
designed with support for high security features like Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA),
IEEE 802.1x Authentication and 64-bit or 128-bit Wired Equivalent Privacy. Compex
exclusive wireless LAN technology Wireless Pseudo VLAN further enhances security in
wireless hotspot networks in isolating different users into their own VLANs. The
Compex NetPassage WPE54AG is capable of operating in 6 different modes: Access
Point Bridging, Access Point Client, Gateway, Wireless Routing Client, Wireless
Ethernet Adapter and Wireless Bridge Link; making it suitable for all kinds of wireless
applications.
1.2 Features and Benefits
Compex WPE54AG has been designed for high performance and offers a rich suite of
features, with which you should acquaint yourself to be able to exploit your Compex
WPE54AG’s full potential
• Wireless Distribution System
This unique feature allows linking of several access points, virtually creating a
larger wireless network infrastructure that allows desktops or laptops that are
connected to NetPassage WPE54AG to share their network resources wirelessly.
• Pseudo Virtual LAN
Compex unique Wireless Pseudo Virtual LAN technology is a feature that allows a
wireless client or groups of wireless client to be segmented wirelessly into its
individual workgroup or individual node thus enhancing the privacy of the wireless
clients. This is especially useful in public hotspot deployment.
• Secured Wireless Authentication
The Compex WPE54AG supports the latest wireless security standard—Wi-Fi
Protected Access. The wireless users now enjoy the freedom of wireless roaming
without worrying important data being exposed to outsiders. WPA has two different
modes: WPA-PSK for SOHO users and WPA-EAP for Enterprise users. WPE54AG
supports WPA-PSK and WPA-EAP that using IEEE 802.1x-based Extensible
Authentication Protocol (EAP) for secure and centralized user-based authentication.
The wireless clients are now able to authentication through a RADIUS server to the
Page 12

Chapter 1 Product Overview
2
authorized network through highly secured authentication methods like EAP-TLS,
EAP-TTLS, and EAP-PEAP.
• Smart Select
This feature will automatically scan and recommend the best channel that the access
point can utilize.
• Wireless Routing Client Capability
The Wireless Routing Client mode enables Internet Service Provider (ISP) or offices
to send their data packet wirelessly and these network packets will be routed
to a wired Local Area Network via the WPE54AG.
• Wireless Ethernet Adapter
The Wireless Ethernet Adapter mode enables any computers with an Ethernet
interface to be connected to the wireless LAN without the need to install any driver
software. This is extremely useful for machines with limited driver support, e.g.
Apple Macintosh machines and Linux machines.
• Parallel Broadband
This unique feature allows bandwidth aggregation and fail-over redundancy
capability when set to gateway mode which uses wireless distribution system to
wirelessly link all associated access point gateway together.
• Universal Configuration Software
Compex uConfig software allows users to get onto the web based configuration
interface of WPE54AG without the need to further manipulate the TCP/IP setup of
the workstation.
• Web-based Management Interface
Embedded with a HTTP server allows the configuration of the WPE54AG features
via a user friendly web-based management interface. In addition, firmware upgrade
can be done through this interface as well.
• IEEE 802.1x Authentication and Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
Compex WPE54AG supports latest wireless security Wi-Fi Protected Access (WPA)
using both Pre-Share Key and 802.1x EAP authentication. A wide range of IEEE
802.1x authentication methods like EAP-MD5, EAP-TLS, EAP-TTLS, EAP-PEAP
for strong mutual authentication and data encryption is supported.
• Wireless Pseudo Virtual LAN
Allows the creation of wireless virtual nodes or workgroups for wireless clients to
increase the privacy in a wireless LAN installation.
• SNMP
For easy remote management and monitoring of the NetPassage WPE54AG through
standard SNMP software.
Page 13

Chapter 1 Product Overview
3
• STP
Spanning-Tree Protocol provides path redundancy while preventing undesirable
loops in the network. It forces certain redundant data paths into a standby (blocked)
state. If one network segment in the Spanning-Tree Protocol becomes unreachable,
or if Spanning-Tree Protocol costs change, the spanning-tree algorithm reconfigures
the spanning-tree topology and re-establishes the link by activating the standby path.
1.3 Compex WPE54AG Package
Compex WPE54AG retail package contains the following items:
• 1 x Compex WPE54AG
• 1 x External Power Adapter
• 1 x 3dBi SMA Antenna
• 1 x Base Stand
• 1 x RJ45 MDIX cross-over Ethernet cable
• 1 x Quick Install Guide with Warranty Registration Form
• 1 x Product CD (including Quick Install Guide, User’s Manual, Firmware Recovery
Tool & Utilities)
1.4 When to use which mode
Compex WPE54AG is unique in the sense that it may operate in up to 5 different
complex modes in order to best suit any type of network application that you require.
This section presents a brief outline of the different network applications that can be
accommodated through the different modes of Compex WPE54AG.
Page 14
Chapter 1 Product Overview
4
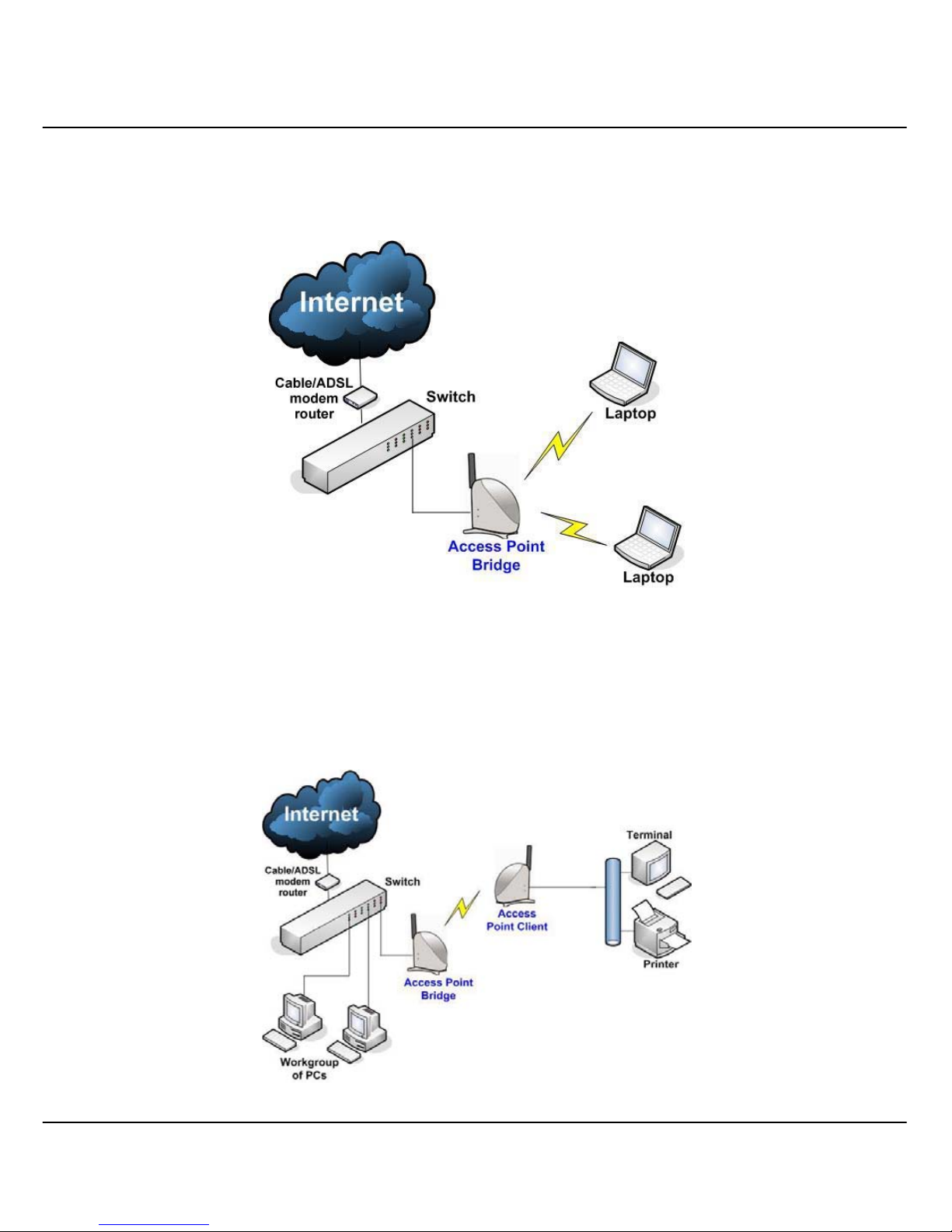
1.4.1 The Access Point Mode
This is the default mode of Compex WPE54AG. The Access Point mode
enables you to bridge wireless clients to the wired network infrastructure.
1.4.2 The Access Point Client Mode
In Access Point Client mode, Compex WPE54AG acts as a wireless client
which can operate wirelessly with another access point to perform transparent
bridging between two Fast Ethernet networks.
Page 15
Chapter 1 Product Overview
5
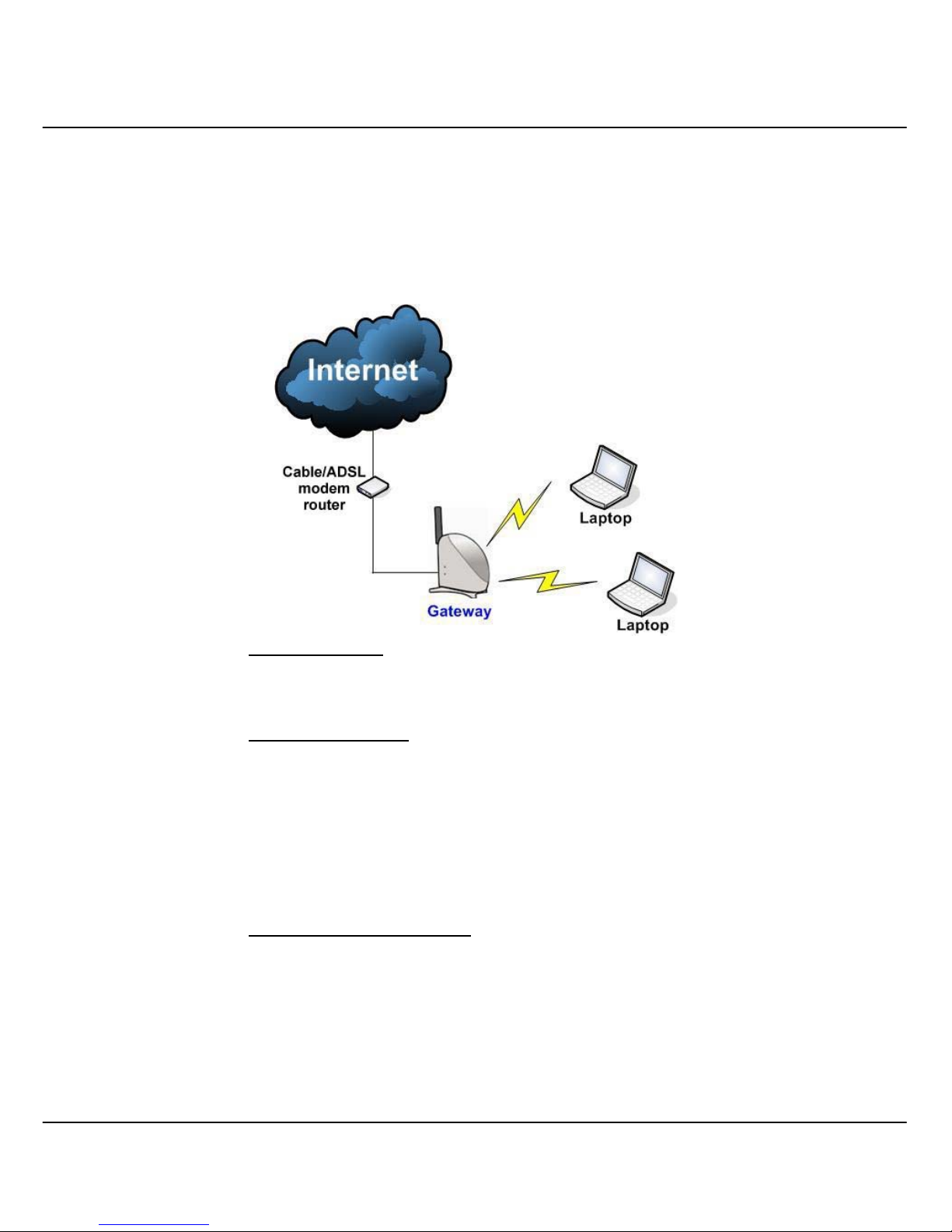
1.4.3 The Gateway Mode
Or put it more simply, Broadband Internet sharing in a wireless network!
Since Compex WPE54AG supports several types of broadband connections,
the first step in setting up Compex WPE54AG as a Broadband Internet
Gateway is to identify the type of broadband Internet access you are
subscribed to.
Static IP address
Use this type of connection if you have subscribed to a fixed IP address or to a
range of fixed IP addresses from your Internet Service Provider.
Dynamic IP address
When powered using this type of connection, Compex WPE54AG requests for
an IP address which will be automatically assigned to it by your Internet
Service Provider.
This type of connection applies for instance, to:
• Singapore Cable Vision subscribers
• @HOME Cable Service users
PPP over Ethernet (PPPoE)
Select this type of connection if you are using ADSL services in a country
utilising standard PPP over Ethernet for authentication.
For instance:
If you are in Germany which uses T-1 connection or
If you are using SingNet Broadband or Pacific Internet Broadband in
Singapore.
Page 16

Chapter 1 Product Overview
6
Singapore ADSL (Ethernet 512K)
This applies to ADSL subscribers in Singapore including SingTel Magix
SuperSurf users.
Australia BPA Cable
This connection type is customised for Big Pond Cable Internet users in
Australia.
PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol (PPTP) mode enables the
implementation of secure multi-protocol Virtual Private Networks (VPNs)
through public networks.
1.4.4 The Wireless Routing Client Mode
An application of this mode would be for the Ethernet port of the Wireless
Routing Client to be used for connection with other devices on the network
while accessing to the Internet would be achieved through wireless
communication with wireless ISP.
Page 17
Chapter 1 Product Overview
7
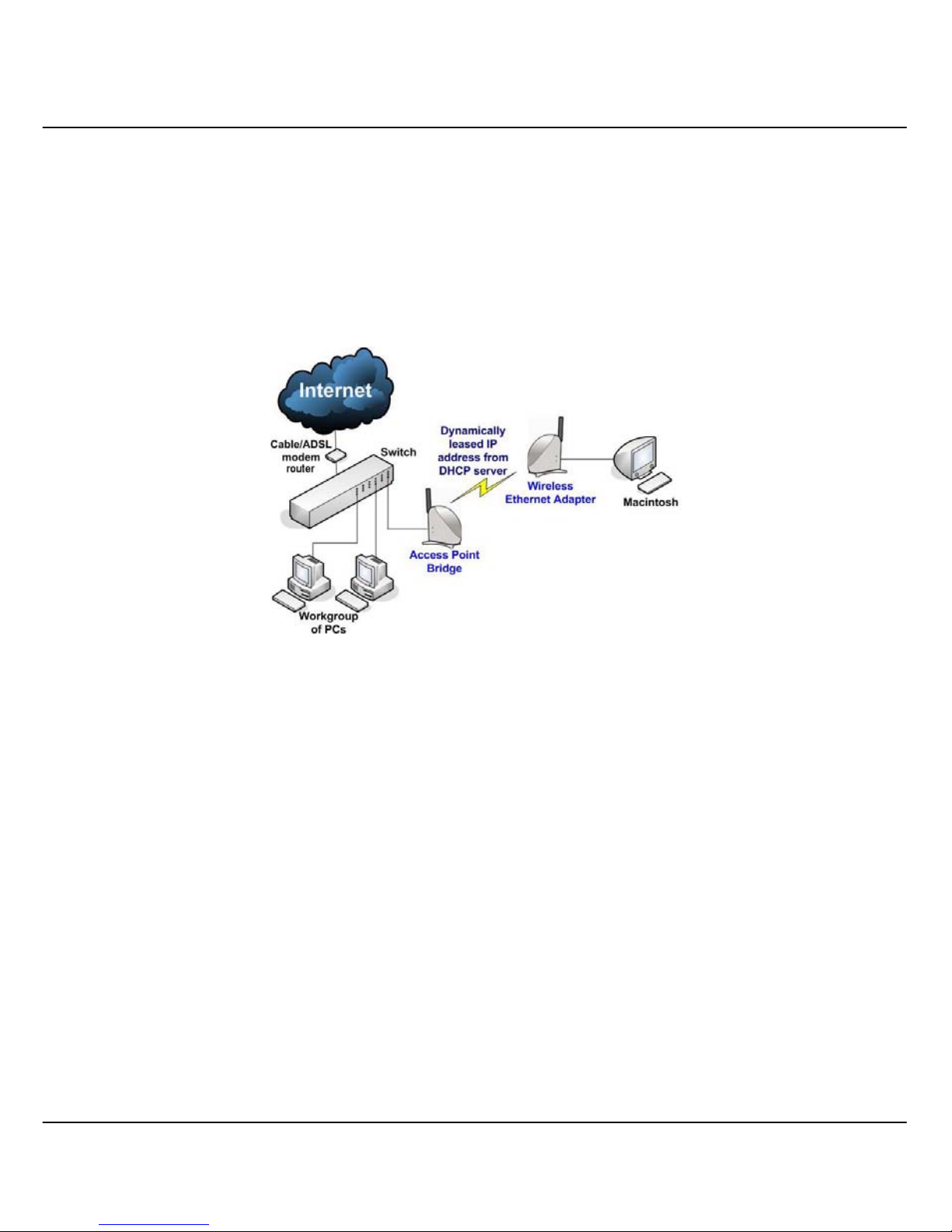
1.4.5 The Wireless Ethernet Adapter Mode
Similarly to the Access Point Client mode, Compex WPE54AG used in this
mode, is able to communicate wirelessly with another access point to perform
transparent bridging between two networks.
However here, the Wireless Ethernet Adapter connects a single wired
workstation only. No client software or drivers are required while using this
mode.
1.4.6 The Wireless Bridge Link Mode
The Wireless Bridge Link mode allows point-to-point communication
between different buildings. It enables you to bridge wireless clients that are
kilometres apart ( eg. within 100 metres between two buildings ) while
unifying the networks. In this scenario, you may configure two Compex
WPE54AG units to perform transparent bridging between two buildings.
Page 18

Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
8
Chapter 2 Hardware Installation
2.1 Setup Requirements
Before starting, please verify that the following is available:
• CAT5/5e networking cable
• At least one computer is installed with a Web browser and a wired or wireless
network interface adapter
• TCP/IP protocol is installed and IP address parameters are properly configured on
all your network’s nodes
2.2 Compex WPE54AG Hardware Installation
In three simple steps, you may power ON and begin configuring Compex WPE54AG.
1. You can choose to connect the external antenna to the SMA connector of Compex
WPE54AG.
2. Use the Ethernet cable to connect your PC to the socket labelled LAN on Compex
WPE54AG.
3. Attach the power adapter to the main electrical supply, and connect the power plug
onto the socket on Compex WPE54AG.
You may turn the device ON.
Page 19
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
9
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
There are two methods to access to the web-based Interface of Compex WPE54AG:
• Through our Compex Utility – uConfig
You can access to the web-based interface directly without the need to assign an IP address
to your PC.
• Enter IP address of Compex WPE54AG in the address bar of Internet Explorer
You need to assign an IP address to your PC, such as 192.168.168.xxx, where x can take
any value from 2 to 254.so that it is in the same subnet as Compex WPE54AG.
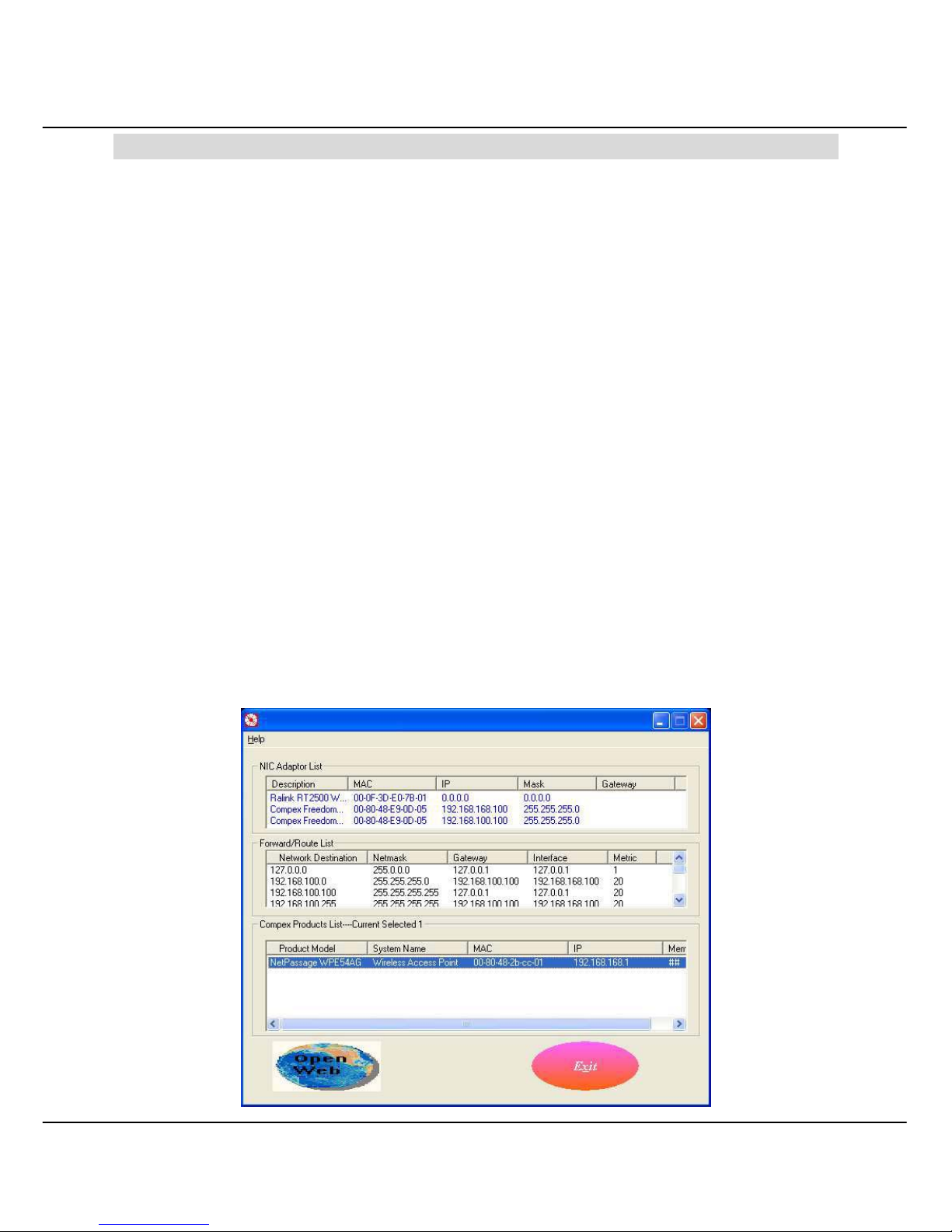
3.1 Access to the Web interface with uConfig
Compex has developed a powerful uConfig utility which will provide you hassle-free
access to the web-based configuration page. It has been designed to give you direct
access to the Web interface.
1. Insert the Product CD into your CD-ROM drive. The CD will run automatically.
2. From the Utilities section, select to install the uConfig utility to your hard disk.
3. When the utility has been installed, double-click on the uConfig icon.
Page 20
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
10
4. Select Compex WPE54AG in the Compex Products List section and click on Open
Web button.
5. At the login page, press the Log On! button to enter the configuration page.
6. You will then reach the home page of Compex WPE54AG’s web-based interface.
Page 21
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
11
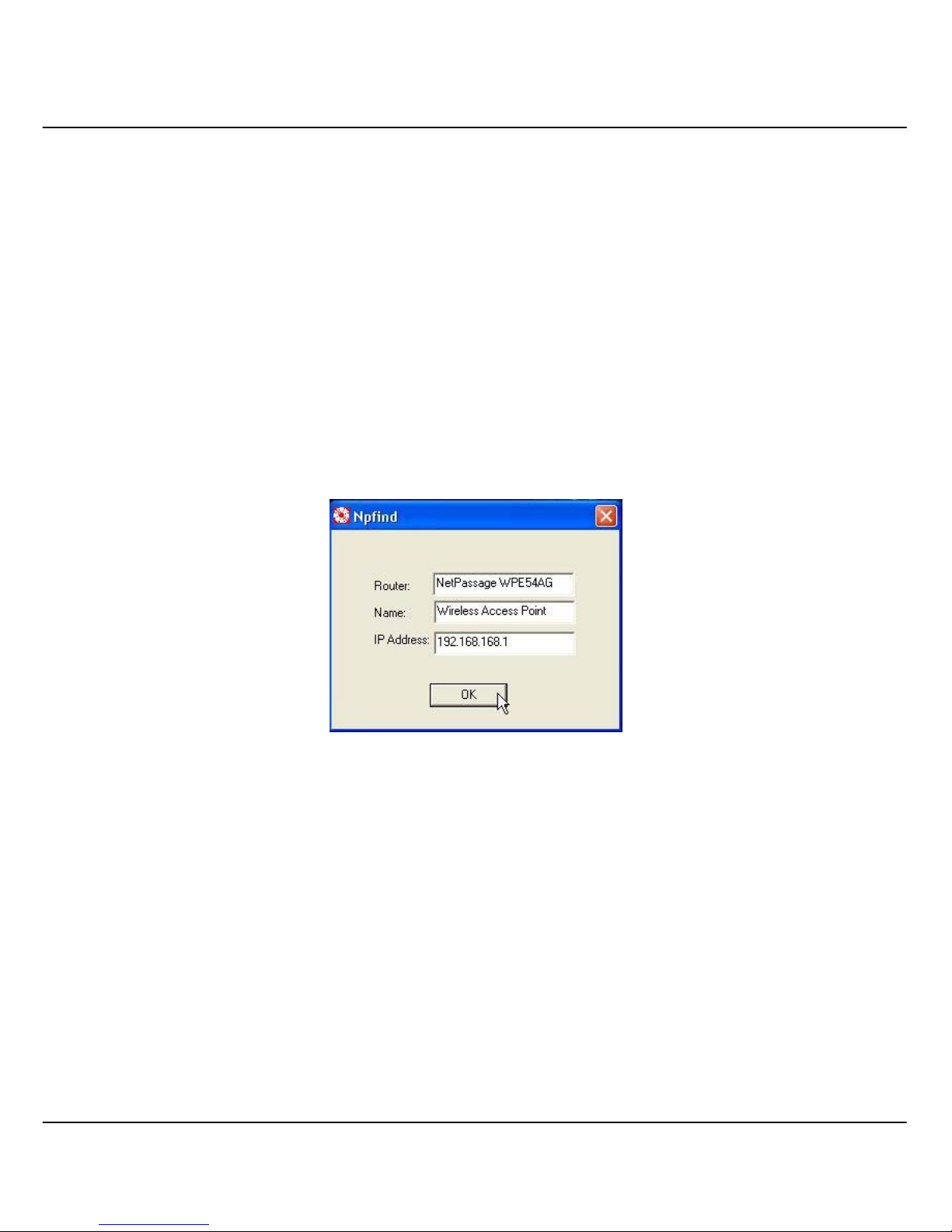
3.2 Verify the IP address of Compex WPE54AG - The NpFind Utility
Compex has designed another utility program NpFind, intended to help you verify the
IP address of your Compex product.
Follow the next steps to check the IP address of your Compex WPE54AG.
1. Insert the Product CD into the CD-ROM drive.
2. It will automatically run to the page shown below.
3. Click on Utilities.
4. Click on the NpFind program to run it.
The screen will automatically display the IP address of the Compex device detected.
Page 22
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
12
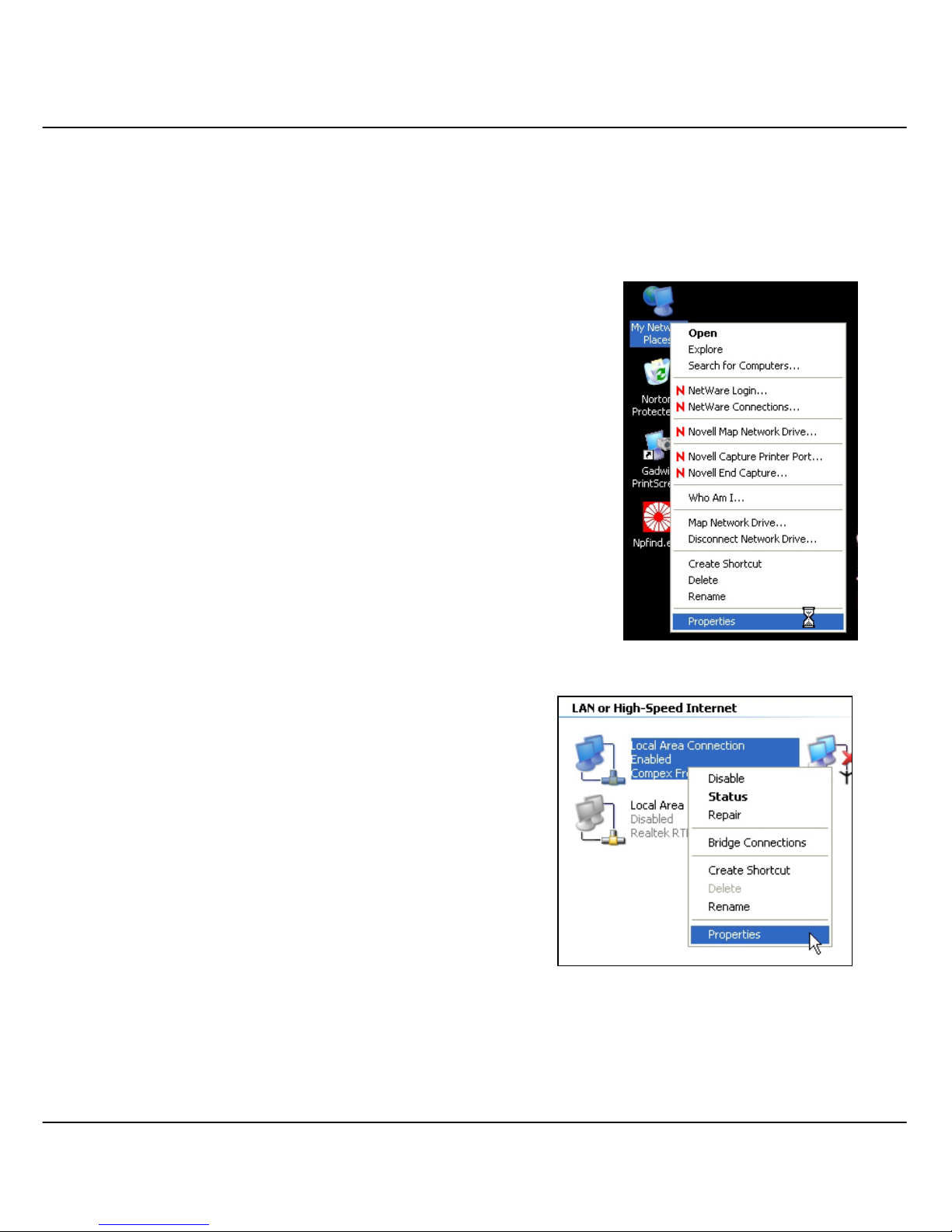
3.3 Direct access to web-based interface via Internet Explorer
For this method, you need to assign an IP address to your PC so that it belongs to the
same subnet as your Compex WPE54AG. In this example, we are using Windows XP
for illustration, for Windows 98/98SE/2000/NT/ME, kindly refer to Appendix III
“TCP/IP Configuration”.
1. Go to your desktop, right click on My Network
Places and select Properties.
2. Right click on your Ethernet adapter and
select Properties.
Page 23
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
13
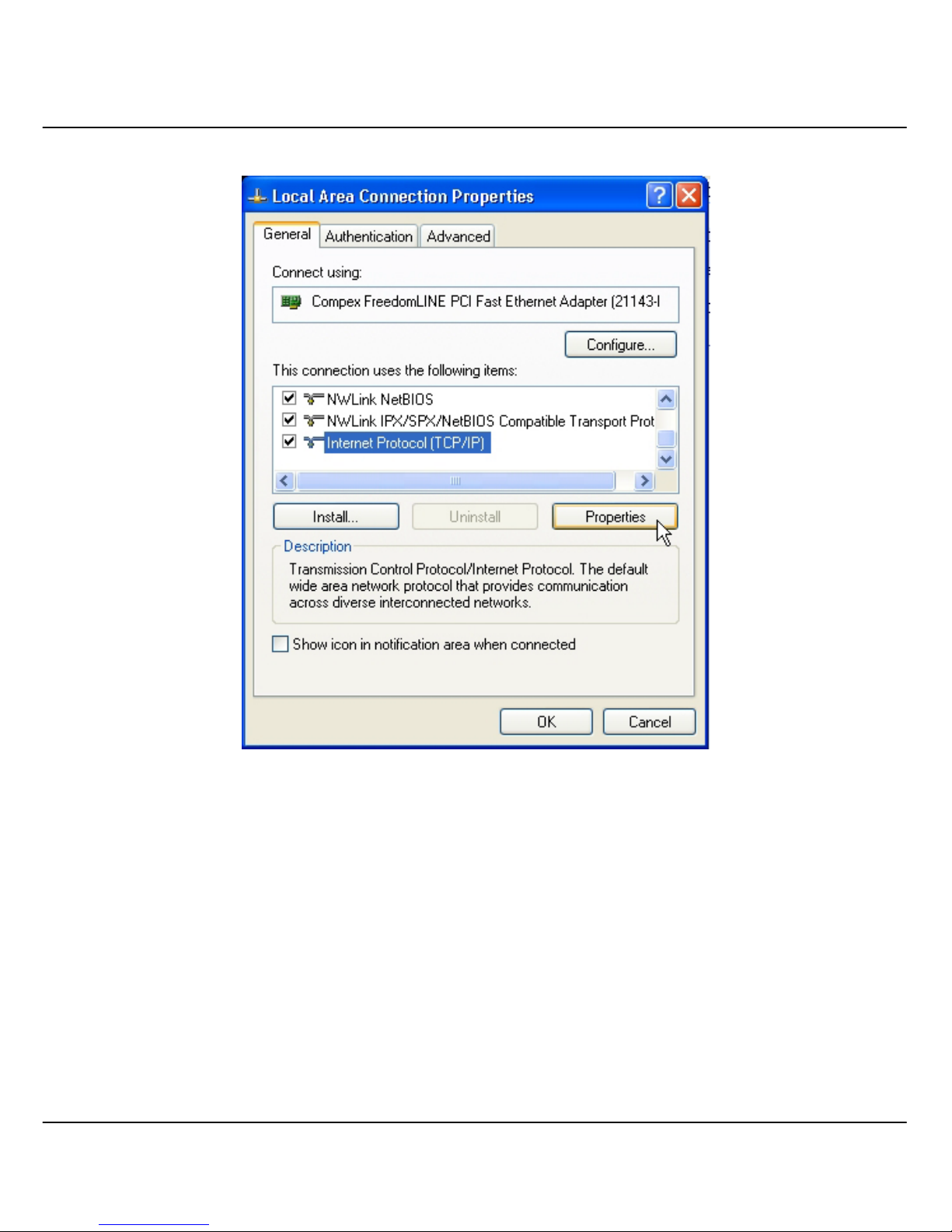
3. Next, select on Internet Protocol (TCP/IP) and click on Properties button.
Page 24
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
14
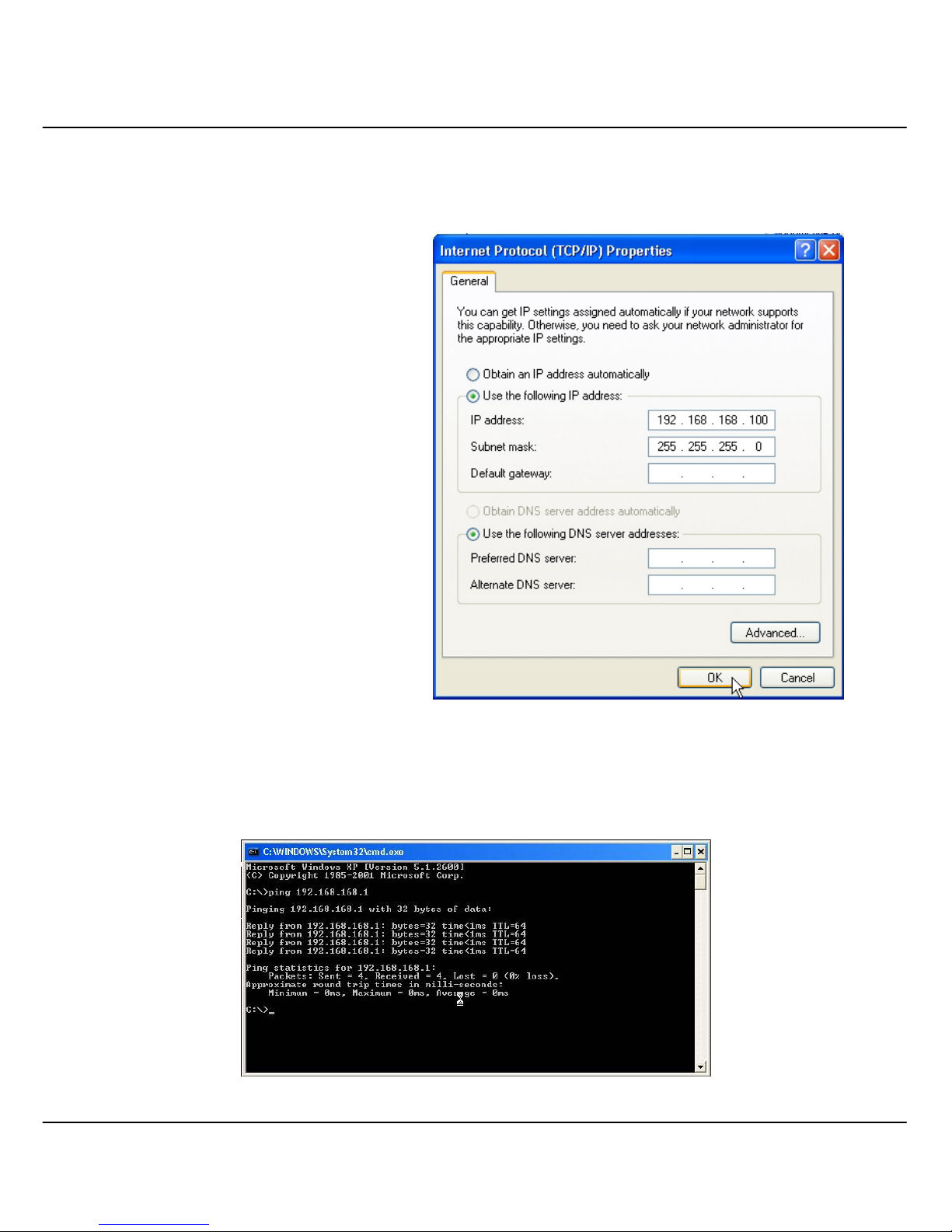
4. Since the default IP address for your Compex WPE54AG is 192.168.168.1, we need
to set your PC’s IP address to be the same subnet as your access point. Therefore, in
this example, we assign an IP address of 192.168.168.100 and subnet mask as
255.255.255.0.
5. Click OK button to update
the changes.
6. Now, you may open the MS-DOS prompt window and type in ping 192.168.168.1
to verify whether your PC can communicate with Compex WPE54AG.
7. If your TCP/IP settings are correct, you will get replies to the ping command:
Page 25
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
15
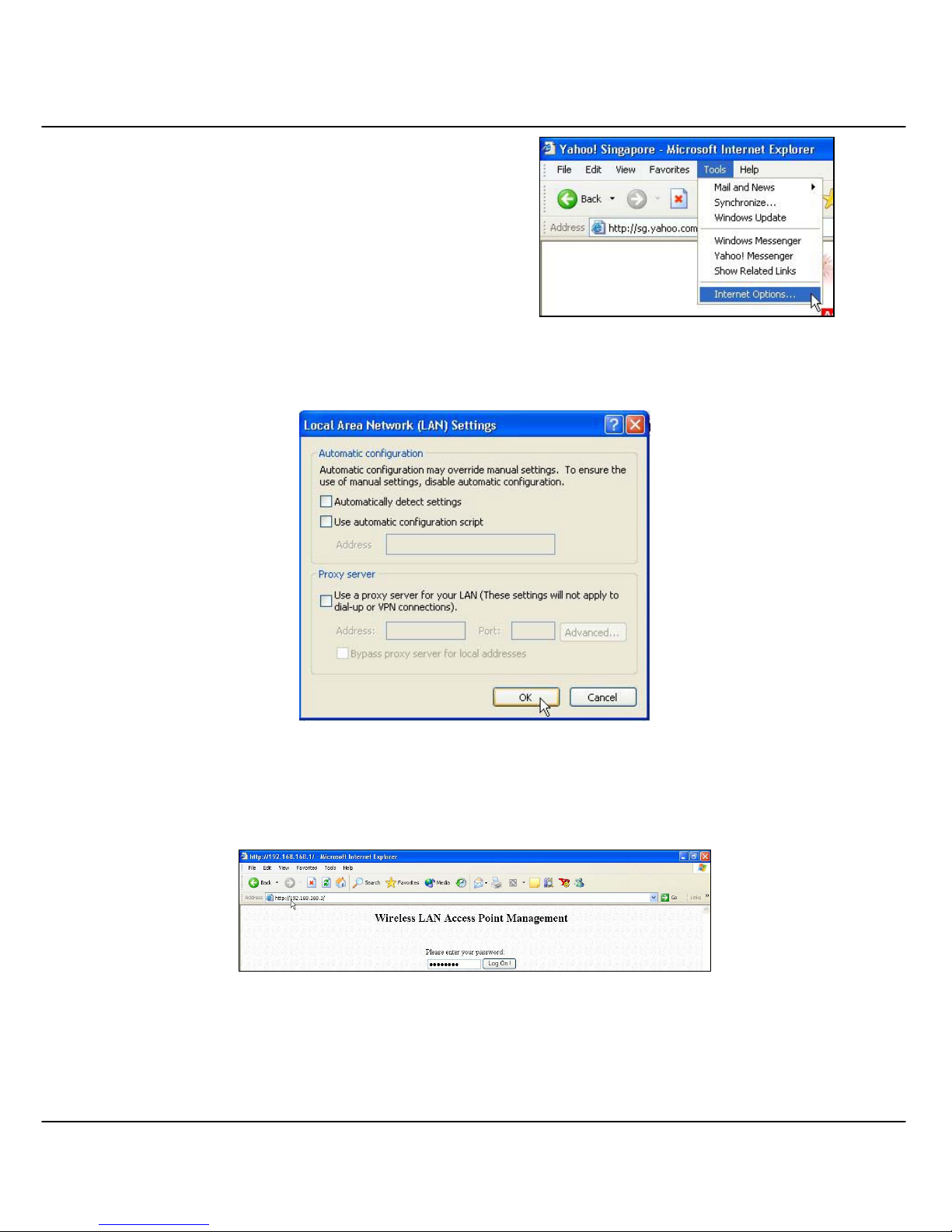
8. Launch your Web browser. Under the
Tools tab, select Internet Options.
9. Open the Connections tab and in the LAN Settings section, disable all the option
boxes. Click OK button to update the changes.
10. At the Address bar, enter http://192.168.168.1 and press Enter from your keyboard.
11. At the login page, click the Log On! button to enter the configuration pages.
Page 26
Chapter 3 Access to Web-based Interface
16
12. You will then reach the home page of Compex WPE54AG’s Web interface.
Page 27

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
17
Chapter 4 Common Configuration
This chapter illustrates the following features, which are available in ALL the operating modes
of Compex WPE54AG, unless stated otherwise.
• Management Port
• WLAN Setup
• WLAN Security
• SNMP Setup
4.1 Management Port Setup
This section shows you how to customize the parameters of Compex WPE54AG to suit
the needs of your network. It also explains how to make use of the built-in DHCP server
of Compex WPE54AG.
Setting up your LAN
You can opt to adjust the default values of Compex WPE54AG and customize them to
your network settings.
LAN SETUP
Click on Management Port from the CONFIGURATION menu.
In the Management Port
Setup page, refer to the
table below to replace the
default settings of Compex
WPE54AG with appropriate
values to suit the needs of
your network.
Click on Apply to save your new parameters.
Page 28
Chapter 4 Common Configuration
18
This table describes the parameters that can be modified in the Management Port
Setup page.
Parameters Description
IP Address
The IP address of Compex WPE54AG is set by default to
192.168.168.1.
Network Mask
The Network Mask serves to identify the subnet in which Compex
WPE54AG resides. The default network mask is 255.255.255.0.
DHCP Start IP
Address
This is the first IP address that the DHCP server will assign. The
value that you input here should belong to the same subnet as
Compex WPE54AG. For example, if the IP address and network
mask of your Compex WPE54AG are 192.168.168.1 and
255.255.255.0 respectively, the DHCP Start IP Address should be
192.168.168.X, where X can take any value from 2 to 254. This value
is pre-set to 192.168.168.100.
DHCP End IP
Address
This is the last IP address that the DHCP server can assign. It should
also belong to the same subnet as Compex WPE54AG. For instance,
if the IP address and network mask of your Compex WPE54AG are
192.168.168.1 and 255.255.255.0 respectively, the DHCP End IP
Address should be 192.168.168.X, where X can take any value from
2 to 254. It is pre-set as 192.168.168.254.
DHCP Gateway IP
Address
Inserting a DHCP gateway IP address will enable the DHCP server to
automatically assign an IP address to any PC belonging to a different
subnet or LAN.
Always use these
DNS servers
If this checkbox is enabled, the DHCP server will also resolve the
DNS queries of the computers. Otherwise, you will have to set up
DNS information manually for every PC in your network.
Primary DNS IP
Address
Your ISP usually provides the IP address of the DNS server.
Secondary DNS IP
Address
This optional field is reserved for the IP address of a secondary DNS
server.
DHCP Server
If you disable the DHCP server, you will need to manually configure
the TCP/IP parameters of each PC in your network.
Page 29
Chapter 4 Common Configuration
19
4.1.1 To view the active DHCP leases
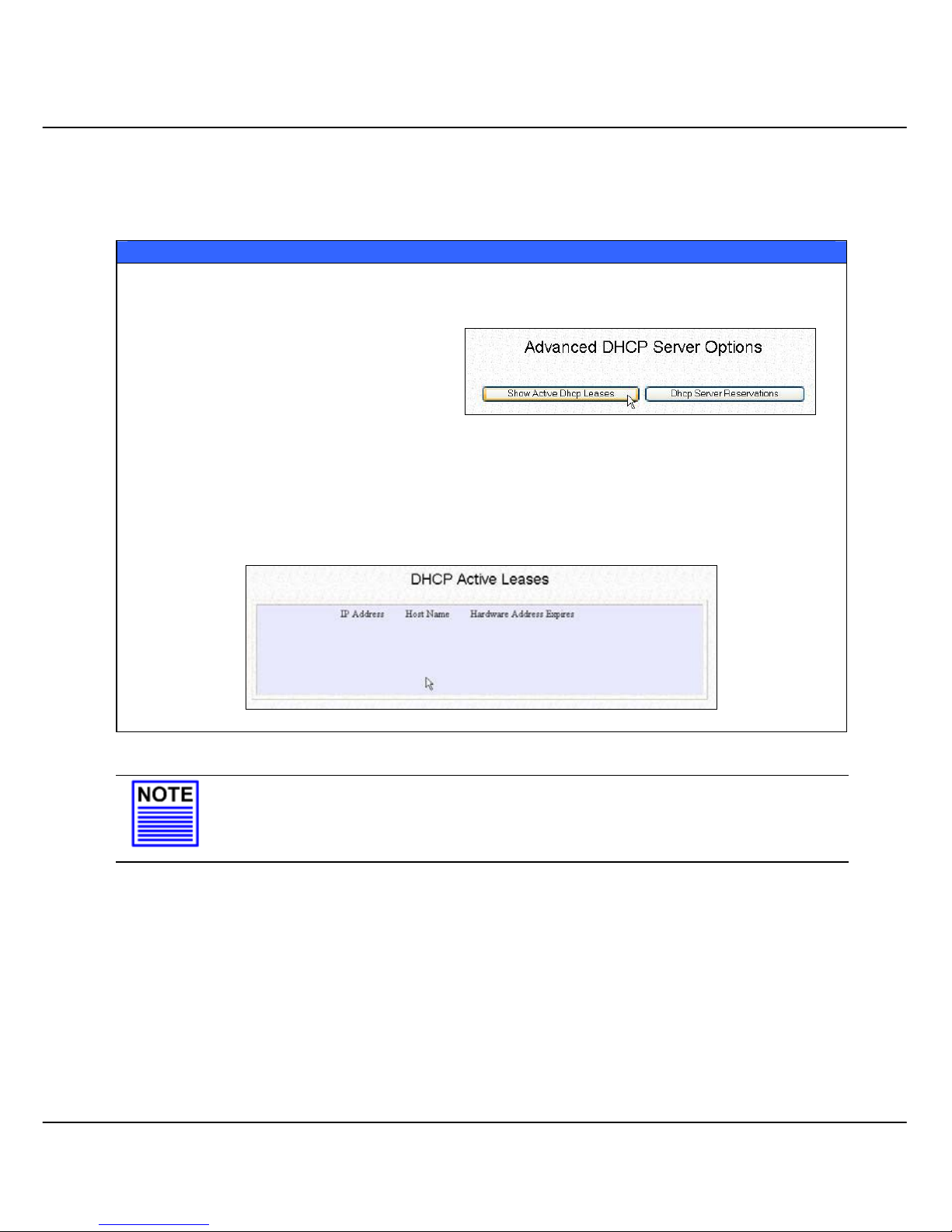
The following will guide you to a page display of the active IP address leases
that have been allocated by the built-in DHCP server of Compex WPE54AG.
View Active DHCP Leases
Click on Management Port from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Go to the Advanced DHCP Server
Options section, click on the Show
Active DHCP leases button.
The DHCP Active Leases table displays:
The IP Address that has been allocated to the DHCP client
The Host Name of the DHCP client
Its Hardware (MAC) Address
The date and time at which the IP address leased expires
NOTE
Invalid date and time displayed in the Expires column indicates that the clock of
your Compex WPE54AG has not been properly set. Please refer to the SYSTEM
TOOLS section for more details on how to set the system clock.
Page 30
Chapter 4 Common Configuration
20
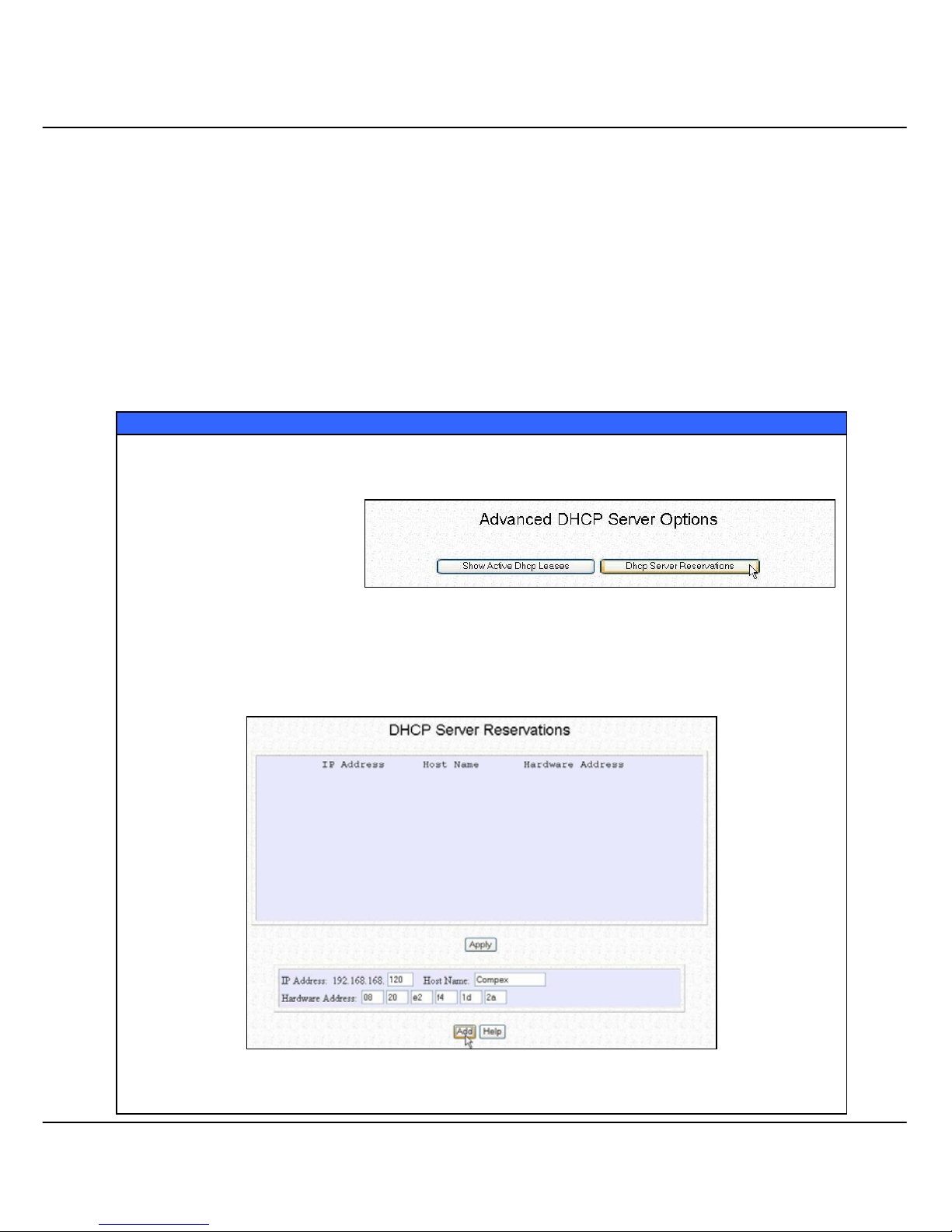
4.1.2 To reserve specific IP addresses for predetermined DHCP clients
Making an IP address reservation lets you inform the DHCP server to exclude
that specific address from the pool of free IP addresses it draws on for
dynamic IP address allocation.
For instance, if you set up a publicly accessible FTP/HTTP server within your
private LAN, while that server would require a fixed IP address, you would
still want the DHCP server to dynamically allocate IP addresses to the rest of
the PCs on the LAN.
The following shows you how to reserve a particular IP address.
Reserve Specific IP addresses
Click on Management Port from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Go to the Advanced DHCP
Server Options section,
click on the DHCP Server
Reservations button.
Fill in:
The host portion of the IP Address to reserve.
The Host Name, if there is any, else, leave it blank.
The Hardware Address, in pairs of two hex values
Click on Add button.
Page 31

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
21
Reserve Specific IP addresses (continued…)
Press the Apply button to make your new entry effective.
The DHCP Reservations page will then be refreshed to illustrate the currently reserved IP
addresses.
If you do not need the DHCP server to reserve an IP address anymore, you can delete the
DHCP Server Reservation thus:
Delete DHCP Server Reservation
Select the reserved IP address to delete.
Click on Delete.
The DHCP Server Reservations table will then be refreshed to reflect your changes.
Page 32

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
22
NOTE
When creating a DHCP reservation, you can opt to key in either the Host
Name or the Hardware Address of the DHCP client.
If you have entered both, the DHCP server will first check the hardware
address.
If a match in hardware address has been found, the Host Name will then be
ignored.
Page 33

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
23
4.2 WLAN Setup
This section shows how to perform the following functions:
Basic:
This function performs a basic setup of the wireless modes of operation.
Security:
This function performs data encryption and protection for the router.
Advanced:
This function furthers the basic configuration of the router by setting the system’s
additional parameters such as Access Control, WDS, WMM and Long Distance
Parameters.
Statistics:
This function uses the Scan Feature to monitor and interpret the statistics data
collected.
It also covers the Show Link Information option featured ONLY
in wireless client
mode.
4.2.1 To configure the Basic setup of the wireless mode
The following will guide you to configure the basic setup of the wireless mode
you have selected.
Basic Setup Wireless Mode
Double-click on WLAN Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu. You will see the submenus expanded under WLAN Setup. Click on Basic.
The default operating mode of Compex WPE54AG is the Access Point mode.
Page 34

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
24
Make your selection from
the Network Mode dropdown list.
Click on the Apply button
to access the setup page of
your selected mode.
Basic Setup Wireless Mode (continued…)
In the Mode Setup page:
The Access Point Name field appears when
Compex WPE54AG is in AP/Gateway
mode and refers to the identity of the
device.
In AP/Gateway mode, the ESSID uniquely
identifies each WLAN.
The Wireless Profile drop-down list
provides a selection of network
environment types in which to operate
Compex WPE54AG:
Page 35

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
25
• 802.11a;
• 802.11b only;
• 802.11b/g mixed, when both b and g
clients are present;
• 802.11g only
Choose a Country that you are located.
Click on the Edit Country Setting button
to select your country.
Click on the Apply button to update the
changes.
Page 36

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
26
4.2.2 To configure the Advanced setup of the wireless mode
The following will guide you to configure the advanced setup of the wireless
mode you have selected.
Advanced Setup Wireless Mode
Double-click on WLAN Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu to expand into the four
sub-menus. From here, click on Advanced.
In the WLAN Advanced Setup page:
Page 37

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
27
Setup Wireless Mode (continued…)
The Beacon Interval is the amount of time
between beacon transmissions. A beacon is
a guidance signal sent by the access point to
announce its presence to other access
points. It also sends information, such as
timestamp, SSID, and other parameters
regarding the access point to other access
points that are within the specified range.
The access point needs the beacon interval
to know when to receive the beacon from
the other access point.
The Data Beacon Rate (DTIM) determines
how often the beacon contains a delivery
traffic indication message (DTIM). The
DTIM tells power-save client devices that a
packet is waiting for them. If the beacon
period is set at 100, its default setting, and
the data beacon rate is set at 1, its default
setting, then the access point sends a beacon
containing a DTIM every 100 Kμsecs. One
Kμsec equals 1,024 microseconds.
The RTS/CTS Threshold value determines
the minimum size of a packet in bytes that
would trigger the RTS/CTS mechanism.
The Frag Threshold value indicates the
maximum size that a packet can reach
without being fragmented. This value
ranges from 256 to 2346 bytes.
The Transmit Power drop-down list lets
you pick from a range of transmission
power.
Enabling Radio Off When Ethernet No
Link option allows your AP to turn off the
radio signal so that no wireless clients can
connect to it. This might occur when your
This value extends from 256 to 2346 bytes,
where a value of 0 indicates that all the
packets should be transmitted using RTS.
In AP/Gateway mode ONLY
:
Page 38

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
28
Ethernet cable is disconnected to the
network)
If this function is enabled, the wireless
radio will be turned off if there is no
Ethernet connection. The wireless radio will
be turned back on when the Ethernet link is
restored.
The turning ON or OFF delay takes about
60 seconds after detecting whether the
Ethernet link is UP or DOWN respectively.
The Auto Reboot Timer is the time setting
for the access point to automatically reboot.
NOTE
The values illustrated in the examples are suggested values for their respective
parameters.
Page 39

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
29
4.3 Scan for Site Survey (For Wireless Client Mode Only)
This feature only available in wireless client mode (Access Point Client, Wireless
Routing Client and Wireless Ethernet Adapter).
• When a Compex WPE54AG is connected to wired network and a set of wireless
stations, it is referred to as a Basic Service Set (BSS). The MAC address of
Compex WPE54AG is used as entry here.
• SSID refers to the network name which uniquely identifies the network to which
Compex WPE54AG is connected.
• Chan refers to the channel being used for transmission.
• Auth refers to the types of authentication, such as WPA, WPA-PSK, etc being used
by the access point.
• Alg refers to the types of algorithm, such as WEP, TKIP, etc being used by the
access point.
• Signal describes the strength of the signal received in percentage.
Scan For Site Survey
In the Mode Setup page, click on the Site Survey button.
Page 40

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
30
Scan For Site Survey (continued…)
The Site Survey provides a list of the BSS and SSID available, the Chan (channels), Auth
(Authentication), Alg (Algorithm) being used, and the strength of the Signal received.
To configure to a different
SSID:
Select the radio button
corresponding to the SSID you
want to configure to.
Click on the Apply button to
effect the change and return to
the Setup page.
Click on the Refresh button.
4.3.1 Show Link Information (For Wireless Client Mode Only)
This function offers a summary of the link data when Compex WPE54AG is
in the wireless client mode, i.e., either of the Access Point Client, Wireless
Routing Client or the Wireless Ethernet Adapter mode.
Show Link Information
In the Mode Setup page, go to
the Link Information section.
Click on the Show Link Information button. When an access point is connected to a wired
network and a set of wireless stations, it is referred to as a Basic Service Set (BSS).
The Link Information table
illustrates the following data:
State refers to the MAC address
of the BSS.
Page 41

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
31
Current Channel is the channel being presently used for transmission.
Signal Strength, given in percentage form, shows the intensity of the signal received and
hence the connection strength.
4.4 Wireless Extended Features
The Wireless Extended Features are ONLY
available when Compex WPE54AG
operates in all modes as tabulated below:
Features Mode
Access Control Access Point and Gateway
Wireless Distributed System (WDS) Access Point and Gateway
WMM Parameters All modes except for Wireless
Bridge Link
Outdoor Parameters All modes
4.4.1 Access Control – The Wireless Pseudo VLAN
A VLAN is a group of PCs or other network resources that behave as if they
were connected to a single network segment.
Those stations which are assigned to the same VLAN share network resources
and bandwidth as if they were connected to the same segment. Conversely,
only the stations within the same VLAN can access each other.
A Wireless Pseudo VLAN acts by segregating a single wireless LAN into
multiple virtual LANs so that communication is possible only among wireless
clients within the same VLAN.
When operating in the Gateway mode, Compex WPE54AG lets you create
VLANs containing either a single user, and referred to as Wireless Pseudo
VLAN Per Node, or a group of users, termed Wireless Pseudo VLAN Per
Group.
When operating in the Access Point mode, Compex WPE54AG allows you to
define Tag VLANs in addition to the Wireless Pseudo VLAN Per Node and the
Wireless Pseudo VLAN Per Group.
To learn more about Compex’s exclusive Wireless Pseudo VLAN, please
refer to the whitepaper available online at
www.cpx.com or
www.compex.com.sg.
Page 42

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
32
4.4.1.1 Wireless Pseudo VLAN Per Node
When implemented, this mode isolates each wireless client into its own
pseudo VLAN. Wireless clients can therefore access resources on the wired
network but are unable to see each other or access each other’s data.
The following steps demonstrate how to set up a Wireless Pseudo VLAN per
Node.
Wireless Pseudo VLAN – Per Node
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced, which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.
Go to the Extended Features
section, and click on the Access
Control button.
The Wireless Pseudo VLAN
function is Disabled by default.
Select Per Node from the dropdown list.
Click on the Apply button.
Page 43

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
33
4.4.1.2 Wireless Pseudo VLAN Per Group
Compex WPE54AG can configure up to four ‘groups’ of wireless clients
identified by their MAC address. Whenever a wireless client requests network
access, Compex WPE54AG will first verify whether its MAC address is
present in any of the Pseudo VLAN groups. If it is, Compex WPE54AG will
grant it access to all the wired system resources and to all other wireless
clients belonging to the same Pseudo VLAN group only.
The following steps demonstrate how to set up Wireless Pseudo VLAN
Groups.
Wireless Pseudo VLAN – Per Group
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced, which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.
Click on the Access Control
button.
Page 44

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
34
Wireless Pseudo VLAN – Per Group (continued…)
The Wireless Pseudo VLAN
function is Disabled by default.
Select Pseudo VLAN from the
drop-down list.
Click on the Apply button.
The MAC Address List enables you to manage specific VLAN groups by adding or deleting
clients through their MAC address.
Click on the Add button.
Select a group number from the
Group ID drop-down list.
Fill in the Mac Addr field with
the MAC address of the client in
the format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or
xx-xx-xx-xx-xx-xx, where x is
any value within the range 0-9 or
a-f.
Click on the Apply button.
The updated Mac Address List page will appear as shown.
Page 45

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
35
Delete client from a group
If you want to delete a particular
client from a group:
Select the client to delete from
the Mac Address List.
Click on the Delete button.
This Delete MAC Address page
will appear to confirm whether
you want to delete the selected
client.
If you do not want to delete the
client:
Click on Apply button.
If you want to remove the client
from the group:
Click on Delete button.
Page 46

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
36
4.4.1.3 Tag VLAN - [Available in Access Point mode ONLY]
While a port-based VLAN is limited in size since it can only exist within the
confines of a single Ethernet switch, a Tag VLAN is designed to extend the
wired VLAN to individual wireless clients.
Here, each VLAN is identified by a ‘tag’, which the switch associates with
specific ports. The switch will then pass this tag information with every data
packet transmitted. By using the same tag on each access point in the network,
full client roaming can be implemented while complying with VLAN
integrity.
Wireless Pseudo VLAN – Tag VLAN
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced, which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.:
Go to the Extended Features
section.
Click on the Access Control button.
The Wireless Pseudo VLAN
function is Disabled by default.
Select Tag VLAN from the dropdown list.
Click on the Apply button.
The Tag VLAN page enables you to manage specific VLAN groups by adding or deleting
clients through their MAC address.
Page 47

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
37
Click on the Add button.
Select a group number from the
Group ID drop-down list.
Fill in the Mac Addr field with
the MAC address of the client in
the format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or
xx-xx-xx-xx-xx, where x is any
value between 0-9 or a-f.
Click on the Apply button.
The updated Mac Address List
page will appear as shown on the
right.
Repeat Step 4 if you need to add
more clients or to configure
more groups.
Page 48

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
38
Delete client from a Tag VLAN
If you want to delete a particular
client from a group:
Select the client to delete from
the Mac Address List.
Click on the Delete button.
The Delete MAC Address page
will appear to confirm whether
you want to delete the selected
client.
If you want to remove the client
from the group:
Click on Delete.
Else click on Apply.
Click on the corresponding Group checkbox to enable a particular VLAN.
If you enable Guest domain, even those stations which are not identified in the MAC
address list will still be allowed to access the Internet though they will not be able to
communicate with each other
Page 49

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
39
4.4.2 Wireless Setup - The Wireless Distributed System (WDS)
A distribution system links up several Compex WPE54AG’s and the areas they serve,
creating a wider network in which mobile users can roam while still staying connected
to the available network resources.
In a WDS, Compex WPE54AG can drive a cell of wired and wireless clients while at the
same time, connecting to other gateways. This requires the operational frequency
channel to be the same within the cell controlled by your gateway as well as for its
wireless links to the other gateways.
4.4.2.1 Star Configuration WDS
In a star configuration WDS, links are established between one root Compex
WPE54AG and several satellite gateways positioned to increase the area
covered.
Here, the root gateway connects to the Internet and maintains three WDS links
while each satellite gateway uses one port only for communication with the
root.
Page 50

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
40
4.4.2.2 Chain Configuration WDS
A chain configuration WDS spans an area in length, for instance a long
corridor. Satellite access points are chained together starting from a root
access point.
Compex WPE54AG at either end of the chain will have only one WDS port
enabled, while the access points in the middle will have two WDS ports
configured to associate with the neighboring Compex WPE54AG upward and
downward in the chain.
WDS - Chain
Configuration
Page 51

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
41
The following steps will guide you in setting up WDS in your Compex
WPE54AG.
WDS Configuration Setup
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.
Go to the Extended Features
section. Click on the WDS
Configuration button.
As illustrated on the WDS
Setup, the WDS feature is
Disabled by default.
Select Enable from the WDS
Global Control drop-down list
to operate WDS.
Click on the Apply button.
Please note that if you auto select your frequency
channel (SmartSelect), you are not allowed to activate
WDS Global Control.
At the WDS Status page:
Click on the Add button to
expand your WDS.
NOTE
To configure WDS, all your access points must be in the same channel; and
both your access points at opposite WDS link must have each other’s wireless
MAC address
Page 52

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
42
WDS Configuration Setup (continued…)
On the Add WDS Link screen
that appears:
Fill up the Partner Address
field with the MAC address of
the device to include in your
WDS, using the format xx-xxxx-xx-xx-xx or
xx:xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or a mix of:
and -, and where x can take any
hexadecimal value 0-9 or a-f.
Use the Status option to control whether you want to Enable this particular WDS link or to
Disable it.
Click on the Apply button.
The WDS Status page will be
updated as shown on the right.
If you want to modify the status
entry for a WDS link:
Select the radio button on the
left of that particular link as
illustrated below left.
Click on the Edit button.
At the Edit WDS Link page
which shows:
Select whether to enable or to
disable the WDS link.
Click on the Apply button for
the changes you made to take
effect.
Page 53

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
43
WDS Configuration Setup (continued…)
If you want to delete a WDS
link:
Select the radio button on the
left of that particular link.
Click on the Remove button.
An updated WDS Status
page will be displayed.
To view WDS Statistics
Info:
Click on the hyperlink of the
selected Partner Address.
The Link ( Partner Address
) Statistics table shown on
the left will be displayed.
Click on the Back button to
return to the WDS Status
page.
Page 54

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
44
NOTE
• If WDS Global Control is Disabled
, every WDS link will be closed
regardless of its status.
When WDS Global Control is set to Enabled
, the status of every WDS
link that you want to include still needs to be individually Enabled
.
• In the WDS Statistics table, each entry corresponds to a particular WDS
link.
• Although the WDS nodes may belong to different SSIDs, they MUST
be
configured in the same channel and use the same WEP keys (if the
encryption feature is enabled) to be able to communicate with one another.
If the WDS-enabled access points are required to support too many operational
wireless clients, you may find end-to-end throughput to be low (depending on
the applications). For instance, end-to-end latency may become an issue in a
very long WDS chain configuration.
Page 55

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
45
4.4.3 WMM Parameters (available in all modes except for Wireless Bridge
Link)
WMM stands for Wireless Multi-Media. WMM is a QoS (Quality of Service )
standard in IEEE 802.11E that we can adopt to improve and support the
voice, video and multimedia applications. QoS can be realized through 4
different Access Categories (AC). Each AC type consists of an independent
transmit queue and a channel access function with its own parameters that
include Cwmin,Cwmax, AIFS, TxopLimit, ACM and Ack-policy.
The following steps demonstrate how to configure these WMM Parameters.
WMM Parameters
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced, which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.
Go to the Extended Features
section, and click on the
WMM Parameters button.
The WMM Setup function is
WMM by default.
Select WMM from the dropdown list
Click on the Apply button.
Page 56

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
46
Depending on the mode you set up, you have to select either AP (Access Point) or BSS (
Basic Service Set) WMM Parameters. For instance, if the mode is AP, select AP WMM
Parameters. The following parameters are described :
CWmin : It is the minimum Contention Window. It is a random number drawn from this
interval or window for the backoff mechanism.
CWmax : It is the maximum Contention Window. It is a random number drawn from this
interval or window for the backoff mechanism.
AIFS : Arbitrary Inter-frame Space. It is the minimum time interval between the wireless
medium becoming idle and the start of transmission of a frame.
TXOP Limi t : Transmission Opportunity. It is the minimum duration for which a QSTA can
transmit after obtaining a TXOP.
ACM : Admission Control Management.
Ack Policy: Acknowledge Policy
Page 57

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
47
4.4.4 Long Distance Parameters (available in all modes)
These parameters determine the distance between wireless clients to ensure
that the wireless point-to-point communication takes place efficiently and
effortlessly.
The following steps demonstrate how to configure these Long Distance
Parameters.
Long Distance Parameters
From WLAN Setup under Configuration, click on Advanced, which shows the WLAN
Advanced Setup page.
Go to the Extended Features
section, and click on the Long
Distance Parameters button.
The Long Distance Parameters
function is Disable by default.
Select Enable from the dropdown list
Click on the Apply button.
To copy the reference data, click
on Show Reference Data.
Page 58

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
48
The parameters are described below:
Outdoor:
The Outdoor parameter is disabled by default. If set to Enable, the Outdoor parameters will
be configured for outdoor communication over short or long distances specified.
Distance:
This parameter determines the distance between different buildings. It should be entered in
meters.
Slot Time:
This parameter determines the slot time allocated by each wireless client ( that is, the
sending and the receiving clients) to initate and/or recieve data transmission.
ACK Timeout:
This parameter determines the timeout allowed for the sending client to receive the
acknowledgment response from the receiving client.
CTS Timeout:
This Clear-to-Send time is the one in which the wireless clients are ready to initiate and/or
receive data transmission within a specified timeout.
Page 59

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
49
4.5 WLAN Security
This section illustrates how to make your WLAN more secure. All the nodes in your
network MUST share the same wireless settings to be able to communicate.
We will illustrate how to configure each type of security mode individually
To start with, follow the common preliminary steps described below to select the most
appropriate security approach for protecting your wireless communications.
Selecting Security Mode
Click on WLAN Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu to select Security.
Make a selection from the
Security Mode drop down
menu.
The Security Mode is set to
NONE by default.
Click on Apply.
Page 60

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
50
4.5.1 How to set up WEP [Available in ALL modes]
The guidelines below will help you to set up Compex WPE54AG for using
WEP.
Security Mode -WEP
At the WEP Setup page:
Select whether to use WEP 64bit
or WEP 128 bit.
Click on Apply.
Compex WPE54AG lets you define up to four different WEP keys.
Specify the key entry format, by selecting either:
• Use Alphanumeric Characters
• Use Hexadecimal
Enter your WEP keys in the Key fields.
Security Mode –WEP (continued…)
When using 64-bit encryption:
Your WEP key has to be either 5 alphanumeric characters or 10 hex characters long.
Page 61

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
51
When using 128-bit encryption:
Your WEP key has to be either 13 alphanumeric characters or 26 hex characters long.
Select which of the keys defined to Encrypt data with.
Click on Save and Reboot your Compex WPE54AG.
A Hexadecimal value can only take in numbers 0-9 and letters A-F and is NOT casesensitive.
Page 62

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
52
4.5.2 How to set up WPA-PSK [Available in AP/Gateway mode ONLY]
The guidelines below will help you to set up Compex WPE54AG for using
WPA-PSK. (Please take note that the WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK and WPA-
PSK-AUTO security modes share the same functions).
Security Mode –WPA-PSK, WPA2-PSK, WPA-PSK-AUTO
At the WLAN Security Setup
page:
Select WPA-PSK mode.
Click on Apply button.
Specify the key entry format by
selecting either:
• Passphrase (Alphanumeric
characters)
• Hexadecimal
Fill in the pre-shared network
key.
If you are using the Passphrase format, your entry can consist of a minimum of 8
alphanumeric characters or a maximum of 63 alphanumeric characters.
Otherwise, when using the Hexadecimal format, your entry MUST
consist of 64
hexadecimal characters.
The Cipher Type is set to TKIP.
Define the GTK update (Group Transient Key update), or the length of time after which
Compex WPE54AG will automatically generate a new master key.
Page 63

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
53
Press the Save button.
Click on Reboot to restart the system, after which your settings will become effective.
A Hexadecimal value can only take in numbers 0-9 and letters A-F and is NOT
case-
sensitive.
For selecting WPA2-PSK and WPA-PSK-AUTO, you can use the above procedure of
selecting WPA-PSK. However, for WPA ( actually is the same as WPA1) , AES is not
mandatory whereas AES is mandatory for WAP2.
4.5.3 How to set up 802.1x/RADIUS [Available in Access Point mode ONLY]
The guidelines below will help you to set up Compex WPE54AG for using
802.1x/RADIUS.
Security Mode –802.1x/RADIUS
At the WLAN Security Setup
page:
Select 802.1x mode.
Click on Apply button.
Key in the IP address of the
Primary RADIUS Server in
your WLAN.
You can optionally add in the IP
address of a Secondary
RADIUS Server, if any.
Page 64

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
54
[Refer to the section on How to set up WEP.]
Press the Save button.
Click on Reboot to restart the system, after which your settings will become effective.
The RADIUS authentication server MUST
be in the same subnet as Compex WPE54AG.
4.5.4 How to set up WPA EAP [Available in Access Point mode ONLY]
The guidelines below will help you to set up Compex WPE54AG for
using WPA-EAP. (Please take note that the WPA or WPA1-EAP,
WPA2-EAP and WPA-EAP_AUTO have the same functions).
Security Mode –WPA-EAP, WPA2-EAP, WPA-EAP-AUTO
At the WLAN Security Setup
page:
Select WPA-EAP mode.
Click on Apply button.
The Cipher Type is set to TKIP.
Key in the IP address of the
Primary RADIUS Server in
your WLAN.
You can optionally add in the IP
address of a Secondary
RADIUS Server, if any.
Page 65

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
55
Security Mode –WPA-EAP, WPA2-EAP, WPA-EAP-AUTO (continued…)
You can key in a different Authentication Port but it MUST
match the corresponding port of
the RADIUS server.
Enter the Shared Secret Key, used to validate client-server RADIUS communications.
Specify the Maximum Retransmissions. For greater security, key in the minimum
permissible 1, else the maximum allowed is 10.
Define the GTK update (Group Transient Key update), or the length of time after which
Compex WPE54AG will automatically generate a new master key.
Press the Save button.
Click on Reboot to restart the system, after which your settings will become effective.
The RADIUS authentication server MUST be in the same subnet as Compex WPE54AG.
For selecting WPA2-EAP and WPA-EAP-AUTO, you can use the above procedure of
selecting WPA-EAP. However, for WPA ( actually is the same as WPA1) , AES is not
mandatory whereas AES is mandatory for WPA2.
Page 66

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
56
4.6 STP Setup ( available in AP/Gateway modes)
Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is a link
management protocol that helps to prevent
undesirable loops occur in the network. For an
Ethernet network to function properly, only one
active path can exist between two stations. If a
loop exists in the network topology, duplication of
messages will occur and this might confuse the
forwarding algorithm and allow duplicate frames
to be forwarded.
In short, the main purpose of activating STP is to
prevent looping when you have redundant paths in
the network. Without activating STP, redundant
topology will cause broadcast storming.
To establish path redundancy, STP creates a
tree
that spans all of the switches in an extended
network, forcing redundant paths into a standby,
or blocked, state. but establishes the redundant
links as a backup if the initial link should fail. If
STP costs change, or if one network segment in
the STP becomes unreachable, the spanning tree
algorithm reconfigures the spanning tree
topology and re-establishes the link by activating
the standby path. Without spanning tree in place,
it is possible that both connections may be
simultaneously live, which could result in an
endless loop of traffic on the
LAN.
Page 67

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
57
Spanning-Tree Protocol operation is transparent to end stations, which are unaware
whether they are connected to a single LAN segment or a switched LAN of multiple
segments.
The figure shown below explains the implementation of STP in a network. AP#1 is
physically connected to a switch whilst another 4 access points (AP#2, AP#3, AP#4 and
AP#5) are connected to AP#1 wirelessly. Redundant paths were found in this network,
without enabling STP function, broadcast storm will occur in this network, resulted
duplicated frames to be forwarded.
When STP is enabled, the STP-enabled access points will first try to find the root access
point using the following criteria:
a. use the access point that is configured with the smallest STP priority.
Default priority set in the access points is 32768.
b. If the STP priority values are the same, the access point with smallest MAC
address will be chosen as root.
Page 68

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
58
Once the root access point is determined, the STP algorithm will start to calculate the
path cost from each access point to the root access point. Based on the path cost in the
following table,
Bandwidth STP Cost
4Mbps 250
10Mbps 100
16Mbps 62
45Mbps 39
100Mbps 19
155Mbps 14
622Mbps 6
1Gbps 4
10Gbps 2
The path with the smallest cost will be used and extra redundant paths will be disabled.
Page 69

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
59
To explain the effect of STP & Pseudo VLAN on the wireless clients, we will compare 3
separate scenarios.
Scenario #1
– (No STP, No Pseudo VLAN)
Referring to the illustration below, if the Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and Pseudo
VLAN are not implemented in a network, all clients (Notebook#1, #2, #3 & #4,) can
access to one another, resulting low level of data security. If redundant paths were found
in this network, broadcast packets will be duplicated and forwarded endlessly resulting
in a broadcast storm.
Scenario #2
– (With STP, No Pseudo VLAN)
When STP is enabled, extra redundant network paths between access points will be
disabled, hence preventing multiple active network paths in between any two network
access points.
If one of the access points is down, the STP algorithm will reactivate one of the
redundant paths so that the network connection will not be lost.
All wireless users will be able to communicate with each other if they are associated to
the access points of the same WDS zone.
Page 70

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
60
Scenario #3
– (With STP and Pseudo VLAN)
In this example, both STP and Pseudo VLAN are implemented in this network. All
wireless users are unable to communicate with one another. This is one of the measures
to ensure data privacy between wireless users in the network.
Page 71

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
61
Enabling STP Setup
Click on STP Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu
Select Enable from the STP Status
radio button.
STP Status:
Activate Spanning Tree Protocol
(STP) function makes your network
more resilient to link failure and also
provides a protection from loop.
Priority:
Specify the configurable value that is appended as the most significant portion of a AP.
This value specifies which access point acts as the central reference point, or Root AP, for
the STP system — the lower the priority value, the more likely the access point is to become
the Root AP. If the priority values are all the same, then the system will search for the
smallest MAC address of the access point and set it as the Root AP.
Hello Time:
Specify the time in seconds that elapses between the configuration messages (also known as
Hello BPDUs) generated by an AP that assumes itself to be the Root AP.
Forwarding Delay:
Specify the time in seconds that an AP spends in the listening and learning states, that is,
listening for configuration messages.
Max Aging Time:
Specify the maximum age in seconds at which the stored configuration message information
is judged to be too old and is discarded.
If an AP does not receive a configuration message after the Max Aging Time, the system
will assume that the link between itself and the Root AP has gone down and will then
reconfigures the network to cater for the change.
Click on the Apply button.
Page 72

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
62
4.7 SNMP Setup
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) is a set of communication protocols that
separates the management architecture from the architecture of the hardware devices.
Enabling SNMP
Click on SNMP Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu
Select Enable from the SNMP State drop-down list.
The default Read Password is set to public while the default Read/Write Password is
private.
Click on the Apply button.
4.8 MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering acts as a security measures by controlling the users from accessing to the
network. This can be easily done by adding the user’s MAC address to the listing and
from there, you can choose whether the particular user is allowed to access to the
network or not. Simply click on the radio button besides Allow PCs listed to access
network, or Prevent PCs listed from accessing network to activate the function.
Page 73

Chapter 4 Common Configuration
63
Enabling MAC Filtering
Click on MAC Filtering from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Select Enable from the MAC Filtering
drop-down list.
Click on the Add button to add in the
MAC address of the user.
Fill in the Filtered Mac Address field
with the MAC address of the client in
the format xx:xx:xx:xx:xx or xx-xx-xx-
xx-xx-xx, where x is any value within
the range 0-9 or a-f.
Click on the Apply button to update the
changes.
Referring to the figure shown on the
right, notice that the MAC Address has
been added to the list.
Next, you can choose whether you wish
to allow/prevent the user to/from access
to the network.
Simply click on the radio button besides
Allow PCs listed to access network, or
Prevent PCs listed from accessing
network.
Click Apply button to update the
changes.
NOTE
When Mac Filtering is enabled with allow access policy, the Mac Address list
cannot be empty.
Page 74

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
64
Chapter 5 Further Configuration
This chapter provides guidelines in:
• Setting up uConfig (only in Gateway mode)
• Configuring WAN Setup (only in Gateway or Wireless Routing Client mode )
• Using NAT
• Routing
• Implementing IP Filtering
• Applying Remote Management
• Enabling Parallel Broadband
5.1 Setting up uConfig (only in Gateway mode)
This option is ONLY
available when Compex WPE54AG operates in Gateway mode.
uConfig Set up
Click on uConfig IP Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Fill in the IP Address.
Key in the Network Mask.
Click on Save button.
Reboot the system to make your
changes effective.
Page 75

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
65
5.2 Configuring WAN Setup (Available in Gateway and Wireless Routing
Client mode)
The WAN setup allows you to set up Compex WPE54AG for broadband Internet
connection.
Described below are the common steps you should start with to select or change the
broadband connection type.
Changing WAN Type
Click on WAN Setup from the CONFIGURATION menu.
The setup page of the WAN type
that you have last implemented
will be displayed.
Since Compex WPE54AG
operates in Dynamic IP Address
Allocation mode by default,
initially the Dynamic IP setup
page will appear.
Press the Change button (which
appears on the setup pages of all
the WAN Types), to reach the
Select WAN Type page.
Select the WAN type you want to switch to.
Click on Save.
The setup page of the WAN type that you have selected will then appear.
Page 76

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
66
5.2.1 Dynamic IP
In the default dynamic IP addressing mode, your ISP automatically assigns
the IP address of Compex WPE54AG to it.
This type of connection applies to most Cable Internet subscribers, for
instance:
• Singapore Cable Vision subscribers.
• @HOME Cable Service users.
Changing WAN Type – Dynamic IP Configuration
At the Dynamic IP WAN Setup
page:
You can review the:
- IP Address
- Network Mask
- Gateway IP Address
- Primary DNS
- Secondary DNS
Your ISP dynamically allocates these parameters to Compex WPE54AG.
5.2.2 Static IP
If you have subscribed to a specific IP address or to a fixed range of IP
addresses from your ISP, follow the procedure summarized below.
Changing WAN Type – Static IP Configuration
At the Static IP WAN Setup
page:
Replace the default IP Address,
Network Mask and Gateway
IP Address fields with the
relevant values given by your
ISP.
Click on the Save button.
Click on the Reboot button to restart the system and let the changes to take effect.
Page 77

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
67
5.2.3 PPPoE
Select this connection type if you have subscribed to ADSL in a country
utilizing standard PPPoE for authentication, for instance:
• If you are in Germany which uses T-1 connection.
• If you are a SingNet Broadband or Pacific Internet Broadband user in
Singapore.
The next steps will guide you in setting up Compex WPE54AG.
Changing WAN Type – PPPoE Configuration
At the PPPoE WAN Setup
page:
Fill in the relevant fields
following the parameters of your
broadband Internet account.
The Status section gives you a
summary of your connection
settings such as:
- IP address
- Network Mask
- Gateway IP Address
- Primary & Secondary DNS
If you are offline, pressing the Connect button will immediately initiate a connection.
Click on the Save button.
Click on the Reboot button to restart the system and allow the changes to take effect.
Page 78

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
68
PPPoE Parameter Description
MTU
The MTU or Maximum Transmission Unit is the largest packet size
allowed by the ISP. It is set by default to 1462 though it can vary
between 1400 and 1492.
Username
This refers to your broadband account username.
Password
This refers to your broadband account password.
Service Name
This optional field allows you to key in the service name of your
ADSL subscription.
On-Demand
If enabled, the NetPassage router will automatically connect to the
ISP whenever a LAN client makes an Internet request.
Idle Timeout
This field is relevant only if the On-Demand option is enabled and
allows you to specify a maximum lapse of idle time allowed before
Compex WPE54AG automatically goes offline. It will only reconnect when a LAN client makes an Internet request.
If the field is set to 0, this feature will be disabled and Compex
WPE54AG will remain online unless disconnected by the ISP.
Always-On
If this feature is enabled, Compex WPE54AG will remain
permanently connected to the Internet.
Reconnect Time
Factor
This field is relevant only if the Always-On option is enabled and
allows you to specify a maximum lapse of offline time following
which, NetPassage should automatically reconnect to the Internet.
The default value has been set to 30 seconds.
Use non-standard
PPPoE Ethernet type
This applies to certain Ethernet-based ADSL modem requiring nonstandard PPPoE for authentication. In case of doubts, do NOT
enable this checkbox.
Page 79

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
69
5.2.4 Singapore ADSL
Other ADSL subscribers in Singapore, including SingTel Magix SuperSurf
users, should opt for this type of connection.
Changing WAN Type – Singapore ADSL Configuration
At the Singapore ADSL WAN
Setup page:
Key in the Username of your
Internet account.
Insert your account Password.
Enter an Idling Timeout value,
in the range of 30-3600 seconds.
Entering 0 will disable this
feature.
The Status section gives you a summary of your connection settings such as:
- IP address
- Network Mask
- Gateway IP Address
- Primary & Secondary DNS
If you are offline, pressing the Connect button will immediately initiate a connection.
Click on the Save button.
Press the Reboot button to restart the system and allow the changes to take effect.
Page 80

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
70
5.2.5 Australia BPA Cable
This type of connection has been especially customized for Big Pond Cable
Internet users in Australia
Changing WAN Type – Singapore ADSL Configuration
At the Australia BPA WAN
Setup page:
Key in the Username of your
Internet account.
Insert your account Password.
Enter the IP address of your
Authentication Server, as
defined by your ISP.
Fill in an Idling Timeout value,
in the range of 30-3600 seconds.
Entering 0 will disable this
feature.
The Status section gives you a summary of your connection settings such as:
- IP address
- Network Mask
- Gateway IP Address
- Primary & Secondary DNS
If you are online, pressing the Disconnect button will immediately end your connection.
Click on the Save button.
Press the Reboot button to restart the system and allow the changes to take effect.
Page 81

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
71
5.2.6 PPTP
The Point-to-Point Tunnelling Protocol (PPTP) is a networking technology
which, enables the implementation of secure multi-protocol Virtual Private
Networks (VPNs) through public networks, enabling remote users to access
corporate networks securely at a lower cost
Changing WAN Type – PPTP Configuration
At the PPTP WAN Setup page:
Key in the Client IP address.
Enter the Network Mask.
Fill in the Username of your
Internet account.
Insert your account Password.
Enter the IP address of your
VPN Server.
Fill in an Idling Timeout value,
in the range of 30-3600 seconds.
Entering 0 will disable this
feature.
Click on the Save button.
Press the Reboot button to restart the system and let the changes take effect.
Page 82

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
72
5.3 Using NAT (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client mode)
NAT, also known as Network Address Translation, functions by transforming the
private IP address of packets originating from hosts on your network so that they appear
to be coming from a single public IP address and by restoring the destination public IP
address to the appropriate private IP address for packets entering the private network.
The multiple PCs on your network would then appear as a single client to the WAN
interface.
Enabling NAT
Click on NAT from the CONFIGURATION menu.
By default, the NAT Status
radio button is enabled.
To change the NAT Status:
Select the appropriate radio
button.
Click on the Apply button.
NOTE
Disabling NAT will disable Internet Sharing. Broadband Internet sharing
requires this option to be Enabled
.
When NAT is enabled, your network is not accessible to the WAN. However,
implementing virtual servers allows you to host Internet servers such as Web servers,
FTP servers or Mail servers on your network, in spite of NAT.
Page 83

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
73
5.3.1 To set up a De-Militarised Zone host
A De-Militarised Zone host, or DMZ host, is a separate neutral client sitting
between your private network and the WAN.
It initiates WAN connections upon request from your network clients, and
forwards the request packets. Similarly, outside users can access only the
DMZ host.
You can host Web pages or public information that can be served to the
outside world, on the DMZ host.
Setting up DMZ
Click on NAT from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Ensure the NAT Status is
enabled.
At the Advanced NAT Options
section:
Click on DMZ.
Key in the IP address of the PC you wish to place within the DMZ in the Private IP
Address field.
The default Private IP Address is set to 0.0.0.0. For illustration, we entered 192.168.168.55
Click on the Apply button to confirm your entry.
Disable DMZ
Enter 0.0.0.0 as the Private IP
Address.
Click on the Apply button.
Page 84

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
74
5.3.2 To set up port forwarding
Port forwarding allows Compex WPE54AG to redirect any incoming Internet
request bearing a public IP address to a specific PC on your network, based on
the incoming packet’s TCP/UDP port number.
You can thus use TCP port forwarding to hide your web-server behind
Compex WPE54AG for added security while using UDP port forwarding lets
you run a secure multiplayer game server.
The following diagram shows a Compex WPE54AG with a public IP address
of 203.120.90.3 and a private IP address of 192.168.168.1. All incoming
packets with port number 80 will be forwarded to the Web server, known on
the LAN as 192.168.168.5, while those with port number 21 will be directed
to the FTP server which has a private IP address of 192.168.168.8.
Page 85

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
75
Set up Port Forwarding – For Known Server
Click on NAT from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Ensure whether the NAT Status
is enabled.
At the Advanced NAT Options
section:
Click on Port Forwarding.
The NAT Static Port Based
Entries table illustrated by the
screen shot displays the list of
current port-based entries.
Click on the Add button.
For standard server applications:
HTTP/FTP/POP3/Netmeeting,
go to the Known Server
section:
Complete the Private IP
Address field.
Pick the appropriate selection from the Server Type drop down list.
Click on Add button.
We illustrated with a POP3 server having Private IP Address of 192.168.168.45.
Page 86

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
76
Set up Port Forwarding – For Custom Server
Otherwise, in order to set up
Internet applications which are
not defined in the Known
Server section, go to Custom
Server:
Key in the Private IP Address.
Define the Port numbers to use.
Select the relevant Protocol from the drop down list.
Identify the Server Type.
Click on Add button.
We entered a Private IP Address of 192.168.168.55, defined ports 15 to 89 as the
application Ports, selected UDP from the Protocol drop-down list and labelled the Server
Type as LAN Game.
The updated NAT Static Port Based Entries will reflect your new entry.
If you want to assign more servers in your LAN, click on the Add button.
Delete a table entry
If you want to delete any of the
table entries:
Select the entry to delete.
Click on the Delete button.
The table will be refreshed.
Page 87

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
77
The following is a non-exhaustive list of well-known port numbers:
Application Port Number
Echo 7
Daytime 13
FTP 21
SMTP (Simple Mail Transfer, i.e., email) 25
Telnet 23
Time 37
Name server 42
Gopher 70
WWW (World Wide Web) 80
5.4 Routing (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client mode)
Compex WPE54AG supports both static routing so that you can manually add entries
into its routing table and dynamic routing, where it will automatically update the routing
table, whenever necessary.
NOTE
The default settings of Compex WPE54AG are sufficient to allow broadband
Internet sharing. There is NO need to configure any further routing
information.
Please note that improper routing settings will cause undesired effects!
Page 88

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
78
The diagram illustrates a Compex WPE54AG (X) functioning as Internet gateway to
wireless clients while another Compex WPE54AG (Y) connects to the office’s remote
resources.
The routing table of X can be modified so that if its wireless clients intend to use the
remote office resources, data packets are automatically redirected to Y.
Page 89

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
79
5.4.1 Static Routing
The following will show you how to add entries to your gateway’s routing
table so that it may re-route IP packets to another network, which is very
useful if your network has more than one router.
Static Routing
Click on Routing from the CONFIGURATION menu.
The IP Routing Table
illustrated by the screen shot on
the left displays the list of
current routing entries.
If you want to add a static route
in the IP Routing Table:
Click on the Add button.
Specify the Destination IP
Address of your new entry.
Fill in the Gateway IP Address.
Click on Apply.
The new entry will appear in the updated IP Routing Table.
If you want to add more routes, click on the Add button.
Delete Static Routing
If you want to delete any of the
table routes:
Select the entry to delete. Click
on the Delete button.
The table will be refreshed.
Page 90

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
80
5.4.2 Dynamic Routing
When using dynamic routing, Compex WPE54AG can continuously update its
routing table with the latest routing information, thus automatically adjusting
to any physical changes in the network topology.
Compex WPE54AG supports RIP1 (Routing Information Protocol) and RIP2
(Routing Information Protocol version 2), and periodically broadcasts its
routing tables to neighboring routers. The best route is chosen if there are
multiple routes to a destination.
The next steps will guide you in setting up dynamic routing.
Dynamic Routing
Click on Routing from the CONFIGURATION menu.
By defaul t, Dynamic Routing is
disabled.
Select which dynamic routing
protocol to implement from the
Routing Protocol drop down
list.
Click on the Apply button.
Reboot the system.
From then on, the IP Routing Table will be dynamically updated.
Page 91

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
81
5.5 Implementing IP Filtering (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing Client
mode)
Enabling the IP Filtering function causes Compex WPE54AG to decide, according to
predefined rules, whether to block all outgoing packets or to let them pass.
Compex WPE54AG provides granularity and latitude in monitoring the traffic in your
network by allowing you to define IP filtering rules, based on these 3 factors:
• Source IP Address
This would allow you to selectively restrict Internet activity originating from a
specific PC or group of PCs.
• TCP Port
You may choose to prevent certain applications such as FTP or Telnet, which use a
commonly known port number.
• Time frame
For example, you may restrict Internet access from your children’s PC to certain
time frames such as between 19H30 and 21H45.
For instance, let us assume that an IP filtering rule has been defined as:
TCP Port 23 from any IP on any day at any time (Port 23 is usually used for Telnet).
If the sent radio button is selected, all outgoing packets will be sent except those
belonging to Telnet sessions. On the other hand, if the discarded radio button is
selected, all outgoing packets will be blocked except for those belonging to Telnet
sessions. We illustrated the second case below.
Page 92

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
82
IP Filtering
Click on IP Filtering from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Select either the Sent or
Discarded radio button to accept
or reject any packet conforming
to the rules.
Click on the Add button to set
the new rule in the IP Filter
Configuration GUI.
Insert a Rule Name for this new
packet filtering rule.
From the IP Address drop down
list, select whether to apply the
rule to:
A Range of IP addresses
In this case, you will have to
define (From) which IP address
(To) which IP address, your
range extends.
A Single IP address
Here, you need only specify the
source IP address in the (From)
field.
Any IP address
You may here, leave both, the
(From) as well as the (To)
fields, blank.
Page 93

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
83
IP Filtering (continued…)
At the Destination Port drop
down list, select either:
A Range of TCP ports
In this case, you will have to
define (From) which port (To)
which port, your rule applies.
A Single TCP port
Here, you need only specify the
source port in the (From) field.
Any IP port
You may here, leave both, the
(From) as well as the (To)
fields, blank.
From the Day of the Week drop
down list, select whether the rule
should apply to:
A Range of days
Here, you will have to select
(From) which day (To) which
day
Any day
In this case, you may skip both
the (From) as well as the (To)
drop down fields.
Page 94

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
84
IP Filtering (continued…)
At the Time of the Day drop
down list, you may also choose
to apply the rule to:
A Range of time
In which case, you have to
specify the time in the format
HH:MM, where HH may take
any value from 00 to 23 and
MM, any value from 00 to 59.
Any time
Here, you may leave both
(From) and (To) fields blank.
Click on the Apply button to make the new rule effective.
The Filtering Configuration table will then be updated.
If you want to define more IP Filtering rules, click on the Add button.
Delete IP Filtering
We illustrated deleting the rule called Finance.
To delete an existing IP filtering rule:
Select the radio button
corresponding to the rule to
delete.
Click on Delete.
The Filtering Configuration
table will then be refreshed.
Page 95

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
85
Delete IP Filtering (continued…)
We illustrated editing the rule called Purchasing.
If you want to edit an existing IP
filtering rule:
Select the radio button
corresponding to the rule to edit.
Click on Edit.
You will then return to the IP
Filtering Configuration GUI,
from which you can re-define
the rule.
5.6 Applying Remote Management (Only available in Gateway and Wireless Routing
Client mode)
Making use of remote management, you only require Internet access to be able to
manage your network.
This feature is especially helpful for those who work away from the office or from
home.
Remote Management
Click on Remote Management from the CONFIGURATION menu.
Specify the HTTP Port number
and the Telnet Port number.
The standard entry for HTTP
Port is 80 and 23 for Telnet Port.
Click on Save button.
Press the Reboot button to
restart the system so that the
changes can take effect.
Page 96

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
86
Remote Management (continued…)
If you want to disable the
Remote Management feature:
Key in 0 for both the HTTP
Port and the TELNET Port.
Click on Save button.
Press the Reboot button to
restart your computer so that the
changes can take effect.
5.7 Enabling Parallel Broadband (Only available in Gateway mode)
Compex WPE54AG is equipped with Compex’s exclusive Parallel Broadband
technology, which translates into scalable Internet bandwidth as well as Load Balancing
and Fail-Over Redundancy features.
Since there is no restriction to the type of broadband Internet account that a Compex
WPE54AG can connect to, your network may run with one Compex WPE54AG on
Cable Internet, while the rest connect to ADSL.
The diagram below illustrates an application of Parallel Broadband in a network with 3
Compex WPE54AGs, X, Y and Z.
5.7.1 Load balancing
Building your network around multiple Compex WPE54AGs arranged in
cascade and running under Parallel Broadband, creates an aggregate
bandwidth and enables you to balance the Internet traffic generated by your
private network over multiple broadband connections. For instance, Z might
share its load with X and Y so that each Compex WPE54AG serves
approximately the same number of users.
Page 97

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
87
5.7.2 Fail-Over Redundancy
In case one of your broadband connections should fail, the affected Compex
WPE54AG will automatically switch over to other operational broadband
channels so that your network is not disrupted. For instance, when the WAN
connection to Z is down, Z will redirect its traffic to Y, and hence providing
Fail-Over Redundancy of Internet access to wireless clients of Z.
To learn more about Parallel Broadband, please read the whitepaper at
www.cpx.com or www.compex.com.sg
5.7.3 To enable Parallel Broadband
Before enabling the Parallel Broadband feature, verify whether:
• Each Compex WPE54AG is correctly configured to connect to its
specific broadband Internet account.
• You need to enable DHCP on all Compex WPE54AGs in Parallel
broadband. It is recommended that each WPE54AG leases IP in a nonoverlapping IP address pool.
• All Compex WPE54AG are interconnected in a chain manner using
WDS as illustrated in the section on WLAN Basic Setup.
• Each Compex WPE54AG is running in Gateway mode with the Parallel
Broadband option enabled.
Parallel Broadband
Load Balancing &
Fail-Over Redundancy
Page 98

Chapter 5 Further Configuration
88
Enable Parallel Broadband
Click on Parallel Broadband from the CONFIGURATION menu.
By default the Parallel
Broadband feature is disabled.
Enable the Parallel Broadband
Status.
Click on Apply button.
Repeat this for the other
Compex WPE54AGs in your
network.
Page 99

Chapter 6 System Utilities
89
Chapter 6 System Utilities
This chapter provides guidelines in using:
• The SYSTEM TOOLS menu
• The HELP menu
6.1 Using the SYSTEM TOOLS Menu
6.1.1 System Identity
If your network operates with several Compex WPE54AGs, you would find it
useful to have a means of identifying each individual device.
In certain cases, your Internet Service Provider might request for a System
Name before allowing you to access the Internet. This System Name also
serves as a DHCP Client ID during negotiations with the DHCP Server for
dynamic IP address allocation.
You can define the System Identity of Compex WPE54AG to be also utilized
as System Name or as DHCP Client ID.
System Identity
Click on System Identity from the SYSTEM TOOLS menu.
Enter the DHCP Client ID
assigned by your ISP in the
System Name field.
Fill in the name of a person to
contact in the System Contact
field.
Fill up the System Location
field. If there are multiple
devices in your network or
building, this entry might help to
identify the device.
Click on the Apply button to
effect the changes.
Page 100

Chapter 6 System Utilities
90
6.1.2 WLAN Station List (Only available in AP and Gateway mode)
This option allows you to view the wireless clients in the wireless network.
WLAN Station List ( Available in AP mode)
Click on WLAN Station List from the SYSTEM TOOLS menu.
Click on the Refresh button to
get the latest information on the
availability of wireless clients in
the wireless network.
WLAN Station List (Available in Gateway mode)
Click on WLAN Station List from the SYSTEM TOOLS menu.
Click on the Refresh button to
get the latest information on the
availability of wireless clients in
the wireless network.
6.1.3 Set System’s Clock
Synchronizing the built-in clock of Compex WPE54AG with the time kept by
your workstation will enable you to effectively manage and operate the timebased functions provided by Compex WPE54AG.
Set System’s Clock
Click on Set System’s Clock from the SYSTEM TOOLS menu.
 Loading...
Loading...