Compaq 8000 - Elite Convertible Minitower PC, 8100 - Elite Convertible Minitower PC User Manual
Page 1

Updated December 2009
Table of Contents:
Introduction ...........................................................................................1
What are the files and directories in a BIOS softpaq? ....................................... 2
In what operating systems can I update the PC BIOS? ....................................... 4
Will I lose my setup configurations when updating the BIOS? ........................... 4
How do I update my PC BIOS in Windows 7, Vista, or Windows XP? ................ 4
How do I update the BIOS in a DOS environment? ........................................... 5
How do I update the BIOS when not running Windows 7, Vista, Windows XP,
or DOS? ......................................................................................................... 6
What are the steps necessary to execute the HPQFlash utility? .......................... 9
What are the steps necessary to execute the HPQPwsd utility? ........................ 12
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable floppy for BIOS update? .... 12
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable CD for BIOS update? ......... 13
What are the steps necessary to create the BIOS image CD for F10 ROM flash
and recovery? ............................................................................................... 13
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable USB flash media (DOK) for
BIOS update? ................................................................................................ 14
What are the steps necessary to use SSM for BIOS update? ............................ 15
What are the steps necessary to use Altiris for BIOS update? .......................... 15
What if the PC does not complete the BIOS flash process? .............................. 18
What is a processor microcode update softpaq and how is it used? ................ 18
How can a processor microcode update be executed in Windows? ................. 19
What does the BIOS binary image naming convention indicate? ..................... 19
Can the BIOS POST splash screen be modified? .............................................. 19
How do I update the ME firmware in Windows 7, Vista, or Windows XP? ....... 20
How do I update the ME firmware in a DOS environment? ............................. 21
What are the steps necessary to use Altiris for ME firmware update? .............. 21
What if the ME firmware does not complete the update process? .................... 23
Can the ME firmware be restored to a previous version after updating? .......... 23
Summary ...................................................................................................... 23
Appendix A – Modifying a DOS boot diskette for Flashbin.exe ................ 24
For More Information ........................................................................... 25
Introduction
This whitepaper outlines Hewlett-Packard Business PC dc class BIOS flashing
options beginning with the 2005 products (e.g. dc7600). The BIOS (Basic Input
Output System) is the set of routines typically stored in read-only memory that
Page 2

enable a computer to load the operating system and communicate with the various
devices in the computer, such as storage drives, keyboard, monitor, printer, and
communications ports. As new processors, devices, and operating system features
are made available, the BIOS must be updated or flashed, in some situations, to
take advantage. The BIOS can be updated or restored in several methods. Users
or administrators can choose the best method depending on the operating
environment of the computer(s). BIOS updates are available in a softpaq
downloadable containing the BIOS image and upgrade instructions for the various
methods. Regardless of the BIOS flash method, business PC products provide a
high degree of upgrade reliability and offer failure safe recovery.
Starting with some 2006 products (e.g. dc7700), the biggest change is the
integration of an embedded Intel Management Engine (ME) which is used to
provide Active Management Technology (AMT), Alert Standard Format (ASF)
management, and other functions. Some HP Business PC products will only offer
ASF as configured from the factory. AMT capable PC products will allow the user
or administrator configuration of the management mode. AMT provides remote
access to a system regardless of the state of the operating system or power state as
long as the system is connected to a network. This ability to manage a system
when it is not powered on and/or fully operational is called Out-of-Band (OOB)
management. ASF is a subset of the monitoring features of AMT and does not offer
the rich range of OOB management options. ME is a hardware and firmware
platform resident solution. BIOS update softpaq images for systems incorporating
ME will contain a separate utility and binary for updating the ME firmware.
Another new feature for this product offering is the ability to update processor
microcode patches through HPQFlash in a Windows environment.
The remaining sections of this document attempts to ask about the typical BIOS
flash scenarios and provide the BIOS softpaq answers to these questions.
What are the files and directories in a BIOS softpaq?
BIOS updates are delivered to customers through downloadable softpaqs.
Softpaqs are self-executable programs which contain the BIOS image files and
utilities to allow the BIOS to be updated in various manners. Regardless of the
upgrade manner chosen by the user or administrator, HP business PC BIOS
provides flash recovery in the event of a BIOS flash failure. The softpaq is executed
by selecting the file SPXXXXX.exe where XXXXX is a unique identification number
assigned to each softpaq. The softpaq will present the user with information about
the softpaq contents, how to use the softpaq, and a brief explanation as to the PC
enhancements offered.
Page 3

After acknowledging the license agreement, the softpaq will allow the user or
administrator to extract the contents to any directory. The following files and
directories are an example of the extracted from a typical BIOS softpaq:
786xx.cab – Compressed BIOS image which can be used by System Software
Manager (SSM) to remotely update a system
SPxxxxx.cva – Identification file used in SSM remote BIOS upgrade
BIOS Flash.htm – Web document describing the softpaq contents and BIOS
upgrade methods
How to Use.txt – Text document describing the softpaq contents and BIOS
upgrade methods
DOS Flash (directory):
XXX_MMmm.bin – Binary BIOS image file required by Flashbin.exe
Assignpw.exe – DOS utility to assign administrative/setup password to
flsh.cpu
Flashbin.exe – DOS utility to update and/or restore BIOS
Flsh.cpu – Hardware specific driver required by Flashbin.exe to
update/restore the BIOS
BIOS CD (directory):
XXX_MMmm.iso – CD image containing the binary BIOS file for F10 and
flash recovery
Readme.txt – Text document describing the iso file image
HPQFlash (directory):
HPQFlash.exe – Windows application to update and/or restore BIOS
HPQFlash.txt – Text document describing HPQFlash.exe use and syntax
HPQPswd.exe – Windows application which allows the user (typically a
system administrator) to create an encrypted password file which can be
used with the /p option of the HPQFlash application
Page 4

HPQPswd.txt – Text document describing HPQFlash use and syntax
ROM.CAB – Compressed BIOS image file used by HPQFlash
ME Flash (directory):
Local-DOS (directory)
o FWUpdLcl.exe – DOS-based application to update the ME firmware
o Readme.txt – Text document describing FWUpdLcl DOS-based utility
use and syntax
Local-Win (directory)
o FWUpdLcl.exe – Windows-based application to update the ME
firmware
o Readme.txt – Text document describing FWUpdLcl use and syntax
o Xerces-c_2_7.dll – Library support file required for some versions of the
Windows update application.
XXX_bbbb.bin - Binary Management Engine image update file required by
the DOS or Windows update utility where "XXX" is the abbreviated ME
firmware version and "bbbb" is the build version number.
The softpaq contents will depend on the target system; therefore, not all softpaq
products will require all the files and directories previously mentioned. For
example, HP Business PC products, which do not integrate the Management
Engine, will not require the contents of the ME Flash directory. HP Business Blade
PC products do not support the Windows BIOS updates and will not require the
HPQFlash directory contents.
In what operating systems can I update the PC BIOS?
The BIOS can be updated or restored in Windows 7, Vista, or Windows XP using
the HPQFlash application. DOS environments can use the Flashbin.exe utility. In
situations with other Windows versions (2000, NT, 98, 95, ME), Linux, or other
operating systems, the BIOS can be updated using F10 setup “Flash System ROM”
feature.
Will I lose my setup configurations when updating the
BIOS?
F10 setup configuration options, passwords, and settings are not lost during BIOS
update or restore.
How do I update my PC BIOS in Windows 7, Vista, or
Windows XP?
In single PC situations, the user or administrator should use the HPQFlash
executable. For a system administrator with a network of Windows business PCs to
update, HPQFlash can be deployed through the use of System Software Manager
(SSM) to update all the appropriate PCs. HPQFlash requires the Windows
Management Interface (WMI) service to be installed and running on the target PC.
Page 5

How do I update the BIOS in a DOS environment?
The Flash Bin Firmware Upgrade Utility (Flashbin.exe) can be executed in a DOS
environment to upgrade or restore a PC BIOS image. The utility uses a driver
(flsh.cpu) for specific hardware flash operations. The BIOS binary image should be
included in the same directory as the utility and driver with the name format
XXX_MMmm.bin. The user can execute the utility by simply typing “flashbin”. The
current PC BIOS will be examined for compatibility with the binary image. If the
BIOS image file is an older BIOS version than the current PC BIOS, the user will be
warned. After the user confirms that the BIOS upgrade/restore should proceed, the
utility will begin the flashing process. The user will be warned not to reboot or
power cycle the PC during the flash process. However, if the process is interrupted
or does not complete successfully, the business PC flash recovery process will
automatically activate upon reboot. After the BIOS upgrade process has
successfully completed, the user must reboot or power cycle the PC for the new
BIOS image to take affect.
The Flashbin utility must be executed in a DOS environment. If the user does not
have DOS bootable media available, a DOS bootable floppy, USB flash media
(Disk On Key – DOK), or CD can be created to deliver the Flashbin utility, driver,
and BIOS image.
If the BIOS adminstrator/setup password has been established on the business PC,
the Flashbin utility driver must be assigned the password. Assign Password
(Assignpw.exe) can be used with DOS Flash if an administrative/setup password
has been previously set on the target PC. To assign a password to DOS Flash,
change directories to the directory that contains Flashbin.exe and type "assignpw
flsh.cpu". You will be prompted to type in the password. Press RETURN after you
have typed in the password. You may use the BACKSPACE key to correct mistakes.
You will then be prompted to confirm the password that you just entered. Pressing
ENTER before any password keys have been typed in will unassign the previously
assigned password. You may need to do this if the administrative/setup password
is deleted from the client machines. To assign a new password, just run the Assign
Password utility again.
Page 6

How do I update the BIOS when not running Windows 7,
Vista, Windows XP, or DOS?
BIOS can be updated using the F10 setup “Flash System ROM” feature. Reboot the
PC and press F10 to enter setup. In the File menu, select the “Flash System ROM”
item.
This flash utility will present the user with the option to select the media containing
the BIOS image file (7H1_MMmm.bin). F10 ROM based flash can accept the
binary file from the root directory of any removable media such as USB, legacy
floppy diskette, and CD. Please note that some systems may contain a BIOS image
that is too large for floppy media. Some models may not support a legacy floppy
drive with the exception of a USB floppy device. On those systems, Diskette will not
be listed as a media source choice. The BIOS CD Image file (XXX_MMmm.iso),
included in the softpaq, should be used to create a BIOS image CD. When
flashing with F10 ROM based flash, the CD media must be El-Torito compatible.
Page 7

When the media is selected, the user is presented with a list of valid binaries. If the
BIOS cannot read the media or media files, an error message will be displayed
and another media source can be selected.
Page 8

Once the desired binary image is selected and confirmed, the BIOS will begin the
flashing process. The flash process should not be interrupted. The percentage
completion will be displayed during the process.
The user is prompted when the process is completed. The new BIOS code will not
take effect until the PC is rebooted.
Page 9

Alternatively, the user or administrator can use a Preboot eXecution Environment
(PXE) to boot to a PXE server, such as Altiris. The Flashbin utility can be executed in
the PXE DOS-like environment to perform the BIOS upgrade.
What are the steps necessary to execute the HPQFlash
utility?
The HPQFlash application is executed in the Windows environment by selecting the
HPQFlash.exe file. The initial HPQFlash application window will be presented as
follows reminding the user that additional applications should be closed before
proceeding.
The user must have administrative privilege on the PC to proceed with the BIOS
update. Otherwise, the application will respond with a warning message and exit
without updating the BIOS image. If the PC has an administrative or setup
password configured, HPQFlash will require the user to enter the setup password
before the BIOS can be successfully updated.
Page 10
If the user selects the Next button, entered the correct password (if needed), and
has the appropriate rights, the application will interrogate the current PC BIOS
image and compare it to the BIOS image file (ROM.CAB) in the same directory as
the FLashbin.exe. If the BIOS image file is not applicable to the PC, a warning
message will be displayed. If the image is applicable, HPQFlash will display the
current BIOS and the BIOS version contained in the ROM.CAB file.
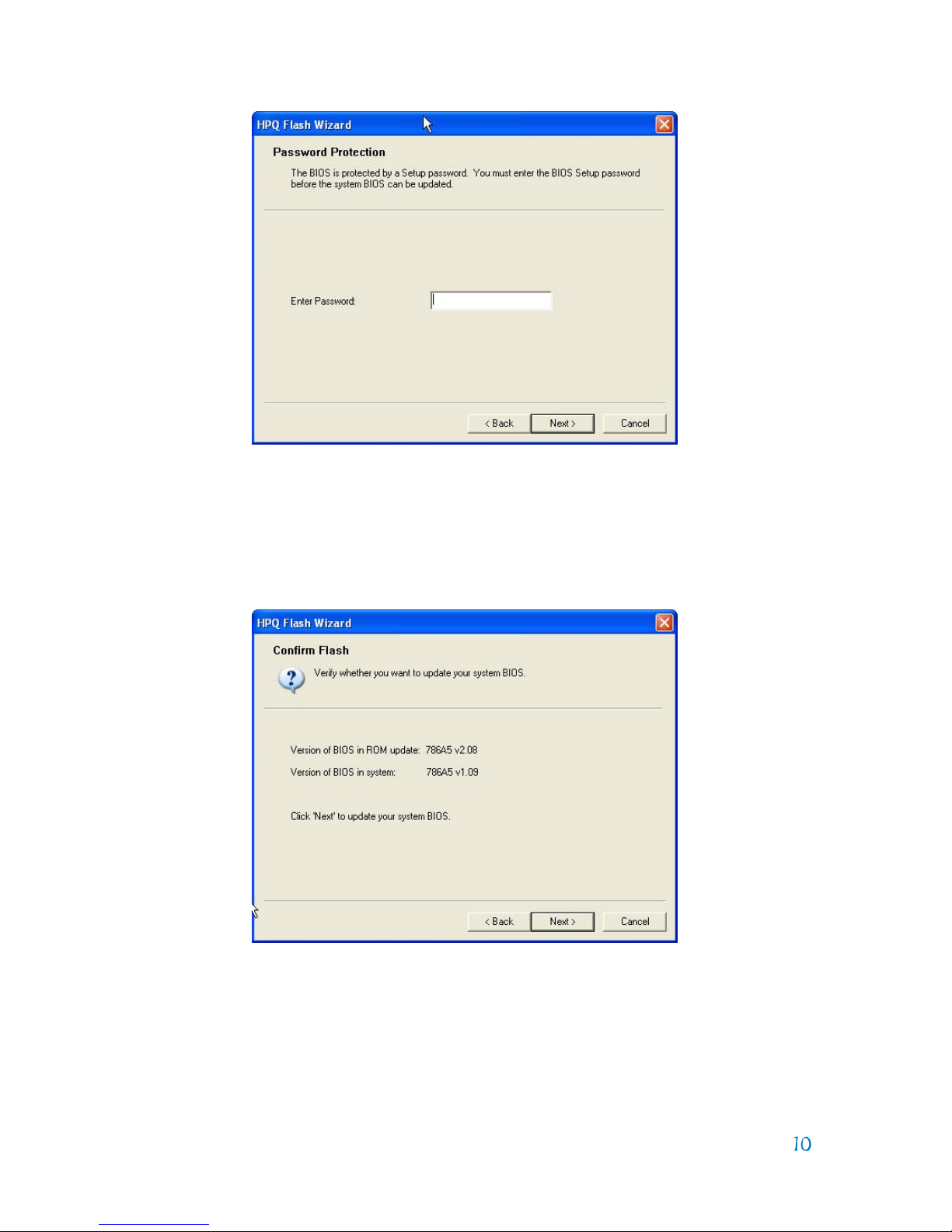
If the image file is applicable to the PC but is an older BIOS version than currently
installed, the user will receive the following warning; however the older image can
be restored to the PC if the user selects the Next button.
Page 11
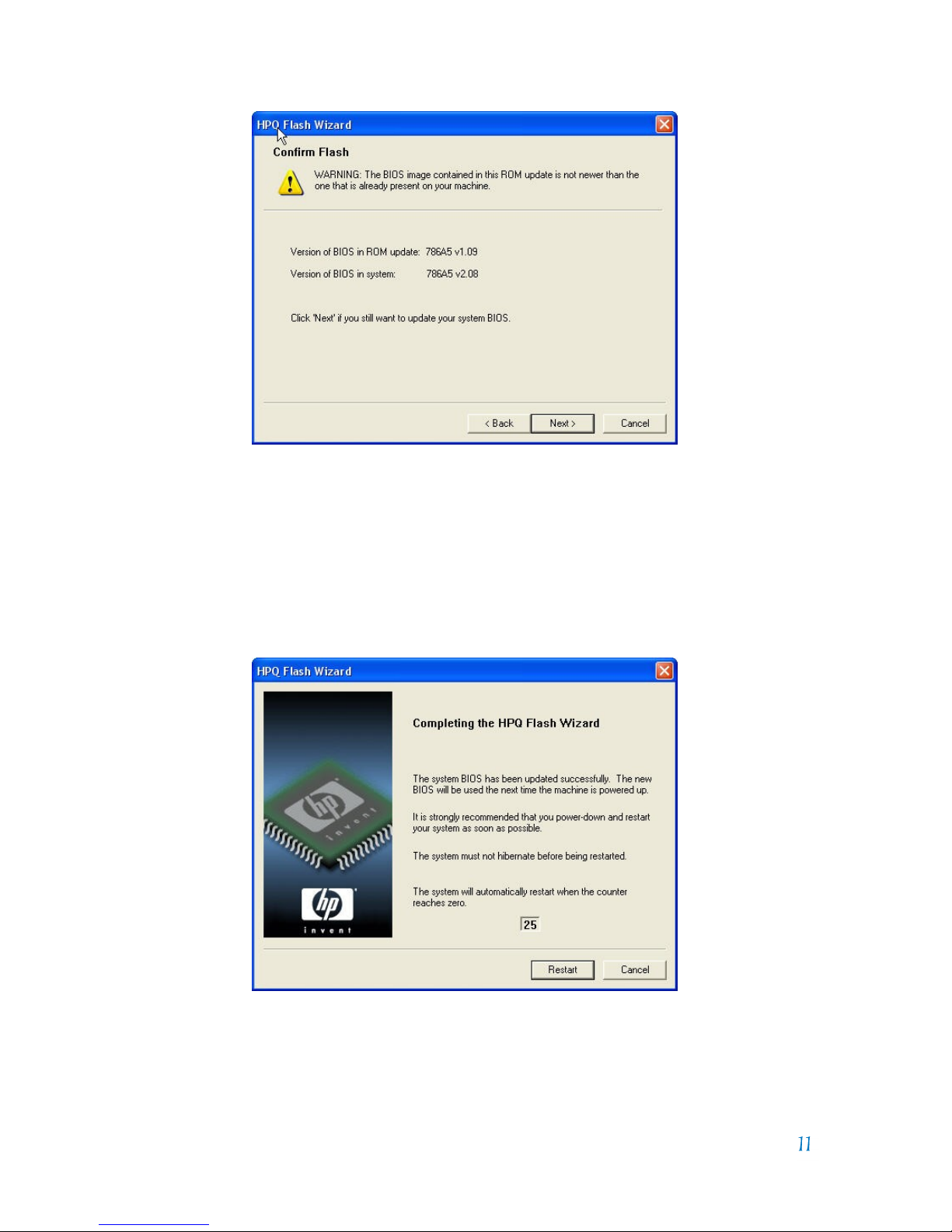
If Next is selected, the BIOS flashing process will begin, and the user is warned
not to interrupt the flashing process. Interrupting the flashing process can corrupt
the BIOS image. If the BIOS does not update successfully, the business PC would
enter flash recovery when rebooted.
After the flash process has successfully completed, the PC will be automatically
restarted or immediately if the user selects Restart before the timer expires. The
user can select Cancel to avoid the restart, but this is not recommended since the
updated BIOS image will not be in effect until the PC reboots.
Page 12
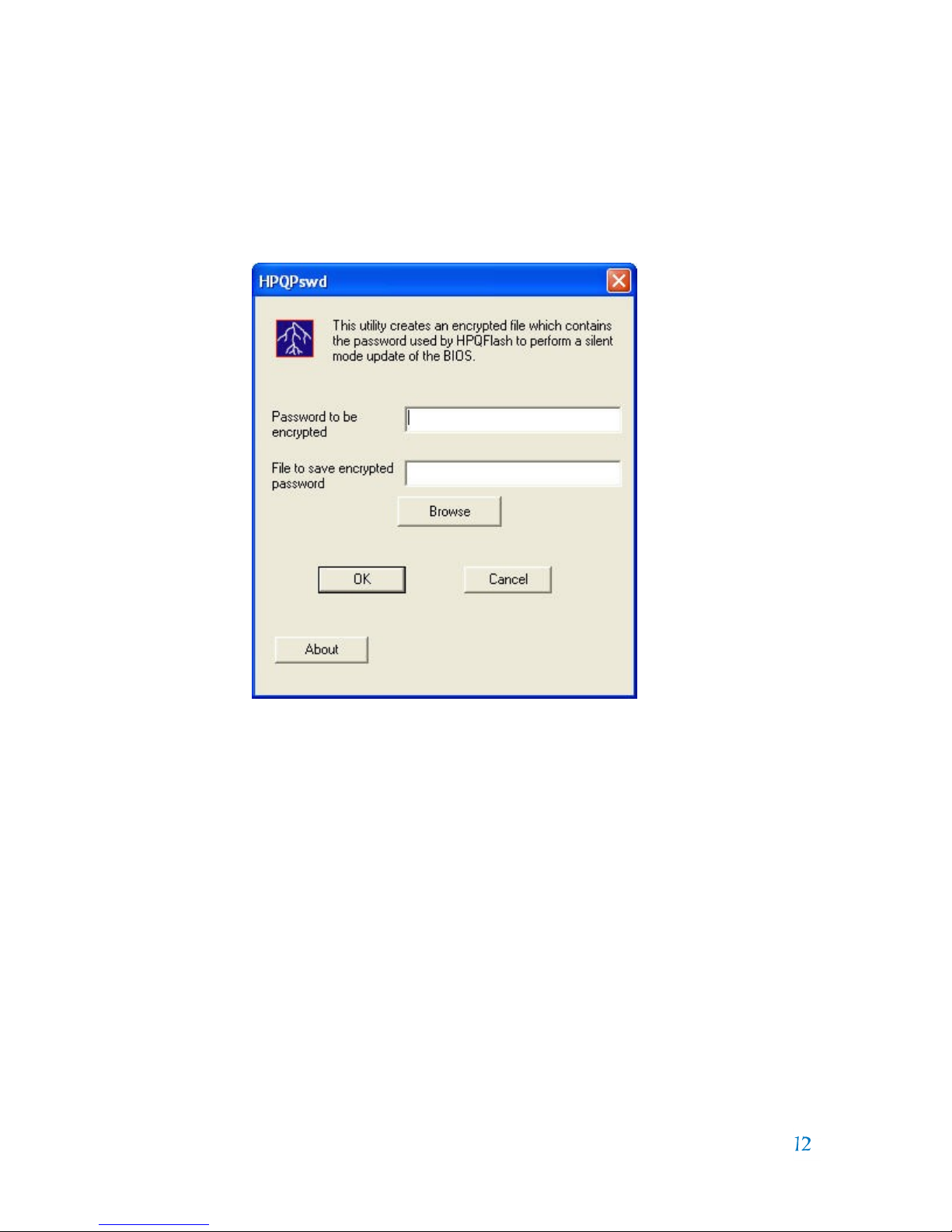
What are the steps necessary to execute the HPQPswd
utility?
The HPQPswd application is executed in the Windows environment by selecting the
HPQPswd.exe file. The initial HPQFlash application window will be presented as
follows options to the user or administrator.
As indicated in the image, this utility will create an encrypted password file
required to execute the HPQFlash application in a silent mode on an
administrative/setup password protected PC. HPQPswd utility is an application
which allows the user (typically a system administrator) to create an encrypted
password file which can be used with the /p option of the HPQFlash application.
This option is usually used along with the /s option to perform a silent mode
update of a PC BIOS on Hewlett-Packard computers which have a BIOS
administrative/setup password set. The password file can be named and stored in
any location. However, it is best to store the file in the same subdirectory as the
HPQFlash application. The HPQFlash application silent mode will execute without
user interaction.
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable floppy
for BIOS update?
Some products contain a BIOS image that is too large to fit on a diskette, or certain
models may not support a legacy floppy drive; therefore, the following information
would not be applicable to those products or models. To create an MS-DOS boot
disk from Windows XP Professional, the following steps can be executed:
Page 13

1. Insert a blank, floppy diskette into the PC.
2. From Windows Explorer, right-click the 3 1/2 Floppy (A:) drive and choose
Format. The Format 3 1/2 Floppy (A:) window appears.
3. In the Format Options section, select Create an MS-DOS startup disk. To format
the disk, choose Start.
If Windows XP is not accessible, a bootable diskette can be created using FreeDOS
(http://www.freedos.org/). FreeDOS is available as an ISO image and as a
diskette distribution in 1.44MB format. For your convenience, a 1.44MB boot disk
image is also available.
After the disk is formatted with either method, additional steps are required to
prepare the diskette (see Appendix A) before copying the contents of the DOS
Flash directory (i.e. Flashbin.exe, Assignpw.exe, and BIOS image file
(XXX_MMmm.bin)) to the media. Assignpw.exe is required if PC to be updated has
administrator/setup password set.
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable CD for
BIOS update?
A bootable, El-Torito compatible, CD can be created for BIOS update. Most third
party CD burning software supports the creation of a bootable CD emulating a
floppy, and a subset of those also support the creation of a bootable CD emulating
a hard disk. The BIOS image of some products are too large to fit on a diskette.
For these platforms, the ISO image must be made from a bootable hard drive
image. This is most easily done using bootable USB flash media (e.g. DOK) as the
image source. To conserve space, ensure the partition is just large enough to hold
the BIOS image. For BIOS images that can fit on a floppy diskette, bootable CD
with floppy emulation would require the user to create a bootable floppy diskette
such as in the manner described in the previous question. The third party CD
software can create an image from the floppy and transfer this to the CD. Once
the CD burning process is complete, the business PC can be booted from the CD,
and the Flashbin utility can be executed.
If the adminstrator/setup password has been established on the business PC, the
Flashbin utility driver must be assigned the password. Assign Password
(Assignpw.exe) can be used with DOS Flash if an administrative/setup password
has been previously set on the target PC. To assign a password to DOS Flash,
change directories to the directory that contains Flashbin.exe and type "assignpw
flsh.cpu". This procedure should be executed on the floppy diskette files before
creating the CD media.
What are the steps necessary to create the BIOS image CD
for F10 ROM flash and recovery?
The softpaq BIOS CD Image file (XXX_MMmm.iso) allows the user or administrator
to create binary image CD that can be used to locally restore or update the system
BIOS. This feature requires that a system is available with CD burning software
and a compatible CD-R/RW drive installed.
Page 14

The following steps describe how the file can be used:
1. Obtain a blank CD and place it in the CD-R/RW drive.
2. Execute XXX_MMmm.iso. This will launch the CD burning software.
3. To make the BIOS binary image CD, follow instructions provided by the
application.
4. Place the newly created BIOS binary image CD in the CD drive of the
computer to be updated or restored and cycle system power.
5. Follow the procedures detailed in the “How do I update the BIOS when not
running Windows 7, Vista, Windows XP, or DOS?” section.
What are the steps necessary to create a bootable USB
flash media (DOK) for BIOS update?
A USB Flash Media Device can be made “bootable” in order to execute the
Flashbin.exe utility. Please read the following requirements and procedure
completely before attempting to make the USB flash media device bootable. If you
are not comfortable with the steps, please do not attempt this procedure. Data loss
can result from improper execution.
Requirement:
Microsoft Windows (Win 95 OSR2 or later) Startup diskette or DOS Bootable
diskette with fdisk.exe and sys.com files on the diskette.
HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool (SP27608.exe) This softpaq can be
downloaded from http://h50178.www5.hp.com/local_drivers/17550/SP27608.exe
Procedure steps:
1. Download and execute the HP USB Disk Storage Format Tool softpaq.
2. Insert the USB flash media device into any of the computer’s USB ports.
3. Execute the Format Tool and select the USB device to format.
4. Enter Volume Label if desired.
Page 15

5. Select the format option “Create a DOS startup disk”, set the dropdown menu
box to the device containing the DOS system files, and select “Start”.
After the USB flash media is made bootable, the Flashbin.exe, Assignpw.exe, and
BIOS image file (XXX_MMmm.bin) can be copied to the media. Boot the PC to be
updated from the USB media and execute the Flashbin.exe as prescribed previously
in the “How do I update the BIOS in a DOS environment?” section.
What are the steps necessary to use SSM for BIOS update?
System administrators can use the BIOS update softPaq with System Software
Manager (SSM) to update the BIOS on target PCs on a network. Place this softPaq
in your SSM Filestore folder then update the database. SSM is a free utility
provided by Hewlett-Packard Company. For information on SSM and this remote
BIOS update method, access the System Software Manager website
(www.hp.com/go/ssm).
What are the steps necessary to use Altiris for BIOS
update?
This section contains instructions for using Altiris Deployment server to deliver a
BIOS update. This information assumes that an Altiris Deployment server has been
Page 16

successfully configured. The basic steps required for BIOS update through the
Altiris Deployment server is as follows:
1. Copy Flashbin.exe, Adminpw.exe, and BIOS image to the server
2. Create Flash.bat
3. Create the Altiris ROM Flash Event
4. Connect the Client PC to the Altiris Console
Step 1: Copy Flashbin.exe, Adminpw.exe, and BIOS image to the server
1. Create a “ROMFlash” folder in the Altiris eXpress folder
2. Copy the following files to the ROMFlash folder:
a) Flashbin.exe
b) Assignpw.exe
c) XXX_MMmm.bin (desired BIOS update image)
Step 2: Create Flash.bat
1. Open a command box
2. Start|Run: cmd
3. cd\express
4. cd ROMFlash
5. edit flash.bat
6. Type in the following, where [Altiris Sever Name] is the name of the server
a) net use k: \\[Altiris Sever Name]\express
b) k:
c) cd romflash
d) flashbin /l:us /f /flsh.cpu default
7. Save the file
8. Exit Cmd
Step 3: Create ROM Flash Event in Altiris
1. Select File | New | Event
This creates a new Event in the Events frame (bottom, left section)
2. Type in the name of the Event: ROM Flash
3. Double click the new event
Brings up an Event Properties form
4. Click “Add”
5. Select “Run Script”
Brings up a new form
6. Select “Run the script from file:”
Page 17

7. Click on the “folder” button
The button to the right of “Run the script from file”, button has image of a
folder on it)
8. Select the file “flash.bat” created in the previous section
9. Click “Open”
10. Select “DOS (from BootWorks)”
11. Click “OK”
12. The Events Properties Form should show:
Task: Run Script
Details: [path of the file]
13. Click “OK”
Step 4: Connecting the Test Unit to the Altiris Console
1. Connect the client PC to the LAN with the Altiris Server
2. On the client: Access the Altiris eXpress folder on the server
a) Click Start | Run
b) Type in the path to the server: \\[server name]\express
3. Run Aclient.exe
a) Double click on Aclient
b) Follow the instructions
4. When Aclient is properly installed and the system is connected to the Altiris
Console, the Altiris icon in the Windows Taskbar (next to the clock) will
become blue
5. On the server:
a) Right click on the client computer name
b) Select properties
c) Check “Apply regular license”
The ROM Flash Event Setup is completed and will be delivered to the client PC.
Page 18

What if the PC does not complete the BIOS flash process?
HP business PC products provide flash disaster recovery if the BIOS flash process
fails to complete. The BIOS will automatically detect that the BIOS flash process
did not properly complete and boot in recovery mode. With most business PC
models, the user or administrator will be presented with the following screen.
It will boot the PC in a recovery mode and search the root directory of the
removable media sources (floppy, USB, or CD) for a compatible binary image. The
BIOS CD image file (XXX_MMmm.iso), included in the softpaq, should be used to
create a BIOS image CD if the user or administrator desires to use CD media for
BIOS recovery. When flashing during recovery, the CD media, containing the
BIOS image file, must be El-Torito compatible. Floppy or USB media sources can
simply contain the BIOS binary image file in the root directory. Once a binary
image is located, the BIOS update process will be attempted again. The automatic
flash recovery will continue until the BIOS is successfully updated or restored.
If no binary image is found, the PC will attempt to boot to diskette or USB flash
media. The boot media must have DOS in order for the disaster recovery mode to
successfully boot.
What is a processor microcode update softpaq and how is
it used?
Typical processors download code from the BIOS during initialization referred to as
microcode. If a new, supported processor is installed in the business PC which
requires a microcode currently not adequately provided by the BIOS, the BIOS will
issue a POST warning “1801-Microcode Update Error”. To add this microcode to
Page 19

the BIOS, a processor microcode softpaq is provided to update the BIOS.
Processor microcode changes can be updated in the BIOS without having to
change the entire BIOS. Binary file microcode image is uXX_MMmm.bin where the
“u” indicates microcode, XX is the general BIOS family, MM is major version, and
mm is the minor version. Microcode updates can only be accomplished by using
Flashbin.exe utility.
Microcode update images are offered for the general BIOS family and can be
applied to any particular BIOS of that family. For example, microcode image
u7D_0101.bin can be applied to any BIOS in the 786D family such as 786D1 or
786D2. Minor version numbers are incremented to indicate minimal changes to
the microcode typically involving an updated version of a previous released
microcode. Major version number changes indicate a greater degree of change to
the microcode source such as the addition of a new processor microcode.
How can a processor microcode update be executed in
Windows?
With the latest version of HPQFlash to support the 2007 HP Business PC products
(e.g. dc7800), processor microcode patches can be updated in a Windows
environment. As detailed in the previous section, the microcode softpaq specific to
the general BIOS family can be downloaded containing the image file
uXX_MMmm.bin. This image file must be copied to the same directory as the
HPQFlash.exe utility. Once that process has been completed, the microcode
update can be executed by running the command “HPQFlash –u uXX_MMmm.bin”
from the directory containing the utility and microcode image file. To log the
operation output, the command can be extended to “HPQFlash –u uXX_MMmm.bin
–l <logfile> where the logfile value is replaced with the file name target.
What does the BIOS binary image naming convention
indicate?
Binary image format is XXX_MMmm.bin. The XXX portion indicates the BIOS
family. The MM is the major version number. The mm is the minor version number.
The BIOS family is a collection of BIOS products all originating from the same basic
code source. For example, 7HX would indicate a BIOS image from the 786H BIOS
family. Minor version numbers are incremented to indicate minimal changes to the
BIOS source code typically involving minor problem fixes. Major version number
changes indicate a greater degree of change to the BIOS source code such as new
feature additions, additional hardware support, or significant POST modifications.
Can the BIOS POST splash screen be modified?
The Image Flash (Flashi.exe) utility can be used to replace the POST splash image
stored in the BIOS part or save the current image. This DOS utility is typically
provided for re-sellers who may want to be able to put their own logo in place of
the standard Hewlett-Packard image. Error checking is done to insure that an
image that does not meet the requirements above cannot be flashed into the ROM
part. The utility allows browsing through directories on the current disk. The
Page 20

images found can be viewed and a background color and a foreground color can
be chosen from the colors in the image's palette. The utility also has a command
line option to quickly flash a new image.
The image stored in the BIOS will be compressed with RLE4. If the image being
flashed is already in RLE4, the image flashed will be identical to the original except
the second byte in the Bitmap Header will be a checksum. If an uncompressed
bitmap is flashed, the Image Flash Utility will encode it using RLE4 and save it.
Therefore, when using the save (/s) feature to get the current image, the newly
saved image will be in RLE4 format, regardless of the format of the original image.
Usage to Flash Image:
Normal: Flashi.exe
Command Line Mode: Flashi.exe [Image_File] [Foreground_Color]
[Background_Color]
The normal execution method will provide the user with additional interaction so
that the image can be selected from various files and a preview can be seen before
the image is committed to the BIOS.
There is only a command line mode to save the current image. You cannot save
the current image under an existing file name.
Usage to Save Current Splash Image (command line only):
Command Line Mode: Flashi.exe /s name
How do I update the ME firmware in Windows 7, Vista, or
Windows XP?
FWUpdLcl.exe utility in the ME Flash\Local-Win directory is designed to update the
ME firmware within a local Windows environment. For more information and utility
options, view the readme.txt file located in the ME Flash\Local-Win folder. The ME
can be updated by executing the following command "FWUpdLcl.exe
<XXX_bbbb.bin> -generic". The ME Flash folder contains a binary update image
for the ME. The binary image file is named XXX_bbbb.bin where "XXX" is the
abbreviated ME firmware version and "bbbb" is the build version number. For
example, 210_1028.bin is the ME update file version 2.1.0 with the build number of
1028. The update binary image and the Local-Win folder contents can be copied
to any Windows accessible media such as a CD/DVD or USB flash media device,
including HP Drive Key and M-Systems DiskOnKey.
The following image shows the successful completion of the ME FW update process
in a Windows XP environment. The update process will stay at the “Performing
Update…” step for most of the time.
Page 21

After the update is complete, the ME firmware is executing the update image, a
system reboot is not immediately required.
How do I update the ME firmware in a DOS environment?
Another FWUpdLcl.exe version is included for ME firmware within a local DOS
environment. For more information, view readme.txt located in the ME Flash\LocalDOS folder. The ME can be updated by executing the following command
"FWUpdLcl.exe <XXX_bbbb.bin>" from the directory containing the utility and
update image file. The ME Flash folder contains a binary update image for the
ME. The binary image file is named XXX_bbbb.bin where "XXX" is the abbreviated
ME firmware version and "bbbb" is the build version number. The update binary
image and the Local-DOS folder contents can be copied to any DOS media such
as a USB flash media device, including HP Drive Key and M-Systems DiskOnKey®.
The update process output is similar to the Windows-based version.
What are the steps necessary to use Altiris for ME firmware
update?
This section contains instructions for using Altiris Deployment server to deliver a ME
firmware update. This information assumes that an Altiris Deployment server has
been successfully configured. The basic steps required for ME firmware update
through the Altiris Deployment server is as follows:
1. Copy FWUpdLcl.exe and ME firmware update image to the server
2. Create MEflash.bat
3. Create the Altiris ME Flash Event
4. Connect the Client PC to the Altiris Console
Page 22

Step 1: Copy FWUpdLcl.exe and ME firmware update image to the server
1. Create a “MEFlash” folder in the Altiris eXpress folder
2. Copy the following files to the MEFlash folder:
a) FWUpdLcl.exe (located in softpaq subdirectory “ME Flash\Local-
DOS”)
b) XXX_bbbb.bin (located in softpaq subdirectory “ME Flash”)
Step 2: Create Flash.bat
1. Open a command box
2. Start|Run: cmd
3. cd\express
4. cd MEFlash
5. edit meflash.bat
6. Type in the following, where [Altiris Sever Name] is the name of the server
a) net use k: \\[Altiris Sever Name]\express
b) k:
c) cd MEflash
d) fwupdlcl <XXX_bbbb.bin>
7. Save the file
8. Exit Cmd
Step 3: Create ME Flash Event in Altiris
1. Select File | New | Event
This creates a new Event in the Events frame (bottom, left section)
2. Type in the name of the Event: ME Flash
3. Double click the new event
Brings up an Event Properties form
4. Click “Add”
5. Select “Run Script”
Brings up a new form
6. Select “Run the script from file:”
7. Click on the “folder” button
The button to the right of “Run the script from file”, button has
image of a folder on it)
8. Select the file “meflash.bat” created in the previous section
9. Click “Open”
10. Select “DOS (from BootWorks)”
11. Click “OK”
Page 23

12. The Events Properties Form should show:
Task: Run Script
Details: [path of the file]
13. Click “OK”
Step 4: Connecting the Test Unit to the Altiris Console
1. Connect the client PC to the LAN with the Altiris Server
2. On the client: Access the Altiris eXpress folder on the server
a. Click Start | Run
b. Type in the path to the server: \\[server name]\express
3. Run Aclient.exe
a. Double click on Aclient
b. Follow the instructions
4. When Aclient is properly installed and the system is connected to the Altiris
Console, the Altiris icon in the Windows Taskbar (next to the clock) will
become blue
5. On the server:
a. Right click on the client computer name
b. Select properties
c. Check “Apply regular license”
The ME Flash Event Setup is completed and will be delivered to the client PC.
What if the ME firmware does not complete the update
process?
The ME retains a recovery image of the current firmware during the update process.
If for any reason the ME cannot successfully complete the update, the ME will
continue to function properly with the current firmware image.
Can the ME firmware be restored to a previous version
after updating?
The ME firmware cannot be regressed to a previous version after successfully
completing the update process. The ME firmware can only be updated to a newer
image.
Summary
HP’s Business PC BIOS provides update methods to allow the user or administrator
to manage the BIOS upgrades and ME firmware in a flexible manner. HPQFlash
offers a familiar, Windows application interface that allows the user to confidently
update the BIOS and processor microcode. Setup-based-flash and recovery
provides a convenient, local upgrade method which is not dependent on the PC
Page 24

operating system. The Flashbin utility provides a traditional DOS upgrade
operation for local or remote situations. Administrators can use the remote
management capabilities of such tools as SSM and Altiris to deliver enterprise wide
upgrade ability.
Regardless of the BIOS flash method, business PC products provide a high degree
of upgrade reliability and offer failure safe recovery. We are confident that HP will
remain the premier provider of comprehensive BIOS upgrade solutions in the
industry.
Appendix A – Modifying a DOS boot diskette for
Flashbin.exe
Most of the HP Business PC BIOS images will not fit on a 1.44MB floppy diskette.
Also, many product configurations may not include a standard flo9ppy disk drive.
For those situations, a bootable USB flash media (e.g., DOK) is the easiest to use as
the image source. However, for those images that will fit on a 1.44MB floppy
image, this appendix provides the instructions necessary to create a DOS bootable
flash diskette.
In order to copy Flashbin.exe, flsh.cpu, and the BIOS binary image onto the
Windows XP MS-DOS boot diskette, the following modifications must be made:
Driver directory
o Delete all files except COMMAND.COM and CONFIG.SYS
In order to copy Flashbin.exe, flsh.cpu, and the BIOS binary image onto the
FreeDOS boot diskette, the following modifications must be made:
FreeDOS directory
o Delete all the files except FDAUTO.BAT and GPL.COM
o Modify FDAUTO.BAT to contain the following statements:
@echo off
set disksrc=A:
set bootsrc=realdisk
set cputype=80386
Driver directory
o Delete all files except HIMEM.EXE
Root directory
o Modify FDCONIG.SYS to contain the following statements:
!FILES=20
!BUFFERS=20
!LASTDRIVE=Z
!SET PATH=A:\FREEDOS
!SWITCHES=/F /N
!SHELLHIGH=A:\COMMAND.COM A:\ /D /K
A:\FREEDOS\FDAUTO.BAT
!echo=Welcome to FreeDOS (http://www.freedos.org)!
Page 25

© 2009 Hewlett-Packard Development Company, L.P. The information contained herein
is subject to change without notice. The only warranties for HP products and services
are set forth in the express warranty statements accompanying such products and
services. Nothing herein should be construed as constituting an additional warranty. HP
shall not be liable for technical or editorial errors or omissions contained herein. Itanium
is a trademark or registered trademark of Intel Corporation or its subsidiaries in the
United States and other countries.
604759-001, December 2009
For More Information
For the HP sales office nearest you, refer to your local phone directory, or call the
HP regional office listed below.
Corporate and North American headquarters
Hewlett-Packard
3000 Hanover Street
Palo Alto, CA 94304-1185
Phone: (650) 857-1501
Fax: (650) 857-5518
Regional headquarters
Latin America
Hewlett-Packard
Waterford Building, 9th Floor
5200 Blue Lagoon Drive
Miami, Florida 33126 USA
Phone: (305) 267-4220
Europe, Africa, Middle East
Hewlett-Packard
Route du Nant-d’Avril 150
CH-1217 Meyrin 2
Geneva, Switzerland
Phone: (41 22) 780-8111
Asia Pacific
Hewlett-Packard Asia Pacific Ltd.
Hewlett-Packard Hong Kong Ltd.
9/F, Cityplaza One
111 King’s Road
Taikoo Shing
Hong Kong
Phone: (852) 2599-7777
 Loading...
Loading...