Page 1

Copyright © 2015 ComAp a.s.
ComAp a.s..
Kundratka 2359/17, 180 00 Praha 8, Czech Republic
Tel: +420 266 790 611, Fax: +420 266 316 647
Technical support hotline: +420 266 790 666
E-mail: info@comap.cz, www.comap.cz
Compact Controller for Stand-by and Parallel Operating Gen-sets
Inteli New Technology
Modular Generator Controller
Multiple Internal engines application – SW configuration
SPI
IG-NT GC, IG-NTC GC, IS-NT, IG-NT-BB, IG-NTC-BB, IS-NTC-BB
Software version IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-3.2, July 2015
REFERENCE GUIDE
Page 2

2
Table of Contents
Table of Contents ............................................................................................................................................... 2
General guidelines .............................................................................................................................................. 4
What is described in this manual? ................................................................................................................. 4
Dangerous voltage ......................................................................................................................................... 5
Adjust set points ............................................................................................................................................. 5
Clarification of notation ................................................................................................................................... 5
Available Firmware and Archive sets ................................................................................................................. 6
General description ............................................................................................................................................ 7
Description of the controller system (with all options) .................................................................................... 7
Comparing of IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE 3.2 with standard gen-set fw .......................................................... 7
Available documentation ................................................................................................................................ 7
Example of interconnection GeCon x Engine controller ..................................................................................... 9
Functions .......................................................................................................................................................... 11
Basic description of SPI application ............................................................................................................. 11
Modified setpoints ........................................................................................................................................ 12
Controller modes .......................................................................................................................................... 13
Mains parameters out of limits during synchronising ................................................................................... 17
Active Power control modes in SPI .............................................................................................................. 17
PF control modes ......................................................................................................................................... 18
Load shedding .............................................................................................................................................. 19
Test on load – SPtM ..................................................................................................................................... 21
Power derating ............................................................................................................................................. 22
Protection mode settings .............................................................................................................................. 22
Circuit breakers operation sequence, GCB/MCB fail detection ................................................................... 23
External breaker control ............................................................................................................................... 29
Peak shaving based on Active and Apparent power ................................................................................... 29
Remote Alarm Messaging ............................................................................................................................ 30
Variable speed support ................................................................................................................................ 31
Force value – step by step guide ................................................................................................................. 32
Values for continuous writing from external sources ................................................................................... 34
User Buttons................................................................................................................................................. 34
User Mask function ...................................................................................................................................... 35
Remote Control Function ............................................................................................................................. 36
Virtual Peripheral Inputs-Outputs (VPIO) module ........................................................................................ 37
Shared Inputs and Outputs .......................................................................................................................... 37
Distributed Binary Inputs and Outputs ......................................................................................................... 39
Modbus Reading and Writing ....................................................................................................................... 40
User MODBUS ............................................................................................................................................. 40
Modbus Switches ......................................................................................................................................... 41
Power Formats ............................................................................................................................................. 41
PLC functions ............................................................................................................................................... 41
Multi language support ................................................................................................................................. 42
ECU interface customizing ........................................................................................................................... 42
Volt/PF control adjustment ........................................................................................................................... 42
Sync/load control adjustment ....................................................................................................................... 44
Protections and Alarm management ................................................................................................................ 47
Gen-set operation states .................................................................................................................................. 57
Inputs and Outputs ........................................................................................................................................... 58
Virtual and physical modules ....................................................................................................................... 58
Analog outputs ............................................................................................................................................. 58
Setpoints ........................................................................................................................................................... 60
ProcessControl ............................................................................................................................................. 60
Basic settings ............................................................................................................................................... 67
Comms settings............................................................................................................................................ 72
Delays/Timers .............................................................................................................................................. 78
Analog protect .............................................................................................................................................. 81
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 3

3
Gener protect ............................................................................................................................................... 83
Mains protect ................................................................................................................................................ 90
AMF settings ................................................................................................................................................ 92
Sync/Load ctrl............................................................................................................................................... 93
Volt/PF ctrl .................................................................................................................................................... 97
Force value ................................................................................................................................................... 99
Load shedding ............................................................................................................................................ 101
Timer settings ............................................................................................................................................. 103
Act. calls/SMS ............................................................................................................................................ 104
Date/Time ................................................................................................................................................... 107
Table of values ............................................................................................................................................... 108
Group: Gener values .................................................................................................................................. 108
Group: Mains values .................................................................................................................................. 115
Group: Sync/Load ctrl ................................................................................................................................ 120
Group: Volt/PF ctrl ...................................................................................................................................... 121
Group: Force value .................................................................................................................................... 121
Group: Load shedding ................................................................................................................................ 123
Group: Analog CU ...................................................................................................................................... 123
Group: Bin inputs CU ................................................................................................................................. 125
Group: Bin outputs CU ............................................................................................................................... 125
Group: Log Bout ......................................................................................................................................... 125
Group: Info ................................................................................................................................................. 129
Group: Statistics ......................................................................................................................................... 136
Table of binary input functions........................................................................................................................ 140
Table of analog input functions ...................................................................................................................... 177
Table of binary output functions ..................................................................................................................... 187
Controller configuration and monitoring ......................................................................................................... 222
Direct connection to the PC ....................................................................................................................... 222
GenConfig functions ................................................................................................................................... 222
InteliMonitor ................................................................................................................................................ 223
Modbus protocol ......................................................................................................................................... 223
Value and setpoint codes ........................................................................................................................... 223
Technical data ............................................................................................................................................ 223
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 4

4
General guidelines
Following described machine complies with the appropriate basic safety and health
requirement of the EC Low Voltage Directive No: 73/23 / EEC and EC
Electromagnetic Compatibility Directive 89/336 / EEC based on its design and type,
as brought into circulation by us.
What is described in this manual?
This manual describes IGS-NT -GeCon-MARINE- „MINT“ software configuration. The Generator controller
software configuration is designed for multiple sets applications with internal load sharer and synchronizer.
What is the purpose of this manual?
This manual provides general information on how to configure and operate the controller.
This manual is intended for use by:
Operators of gen-sets/generators
Gen-set/generator control panel builders
For everybody who is concerned with installation, operation and maintenance of the genset/generator
!! Warnings !!
Remote control
The IGS-NT controller can be remotely controlled. In case that maintenance needs to be done to the genset, check the following to ensure that the engine cannot be started.
To be sure:
Disconnect remote control via RS232 line
Disconnect input REMOTE START/STOP
or
Disconnect output STARTER and output GCB CLOSE/OPEN
The controller contains a large number of configurable setpoints, because of this it is impossible to describe
all of its functions. These are subject to change from SW version to SW version. This manual only describes
the product and is not guaranteed to be set for your application on arrival.
Text
PAGE (Capital letters in the frame) buttons on the front panel
Break Return (Italic) set points
Generator protections (Bold) Set point group
REMOTE START/STOP (Capital letters) binary inputs and outputs
Cyan background Valid for IS-NT only
Conformity declaration
Note:
ComAp believes that all information provided herein is correct and reliable and reserves the right to update
at any time. ComAp does not assume any responsibility for its use unless otherwise expressly undertaken.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 5

5
Be aware that the binary outputs can change state during and after software
reprogramming (before the controller is used again ensure that the proper
configuration and setpoint settings are set in the controller)!!!
Be aware that gen-set can automatically or remotely start !!!
Switch the controller to SEM mode and disconnect the Binary outputs Starter and Fuel
to avoid unexpected automatic start of gen-set and GCB closing.
!!! CAUTION !!!
Dangerous voltage
The terminals for voltage and current measurement should never be touched.
Properly connect the grounding terminals.
Do not disconnect the CT terminals for any reason.
Adjust set points
All setpoints are preadjusted to their typical values. But the set points in the “Basic settings” settings
group !!must!! be adjusted before the first startup of the gen-set.
!!! WRONG ADJUSTMENT OF BASIC PARAMETERS
CAN DESTROY THE GEN-SET !!!
The following instructions are for qualified personnel only. To avoid personal injury do
not perform any action not specified in this User guide !!!
WARNING – VERY IMPORTANT !!!
Clarification of notation
HINT
This type of paragraph points out details to help user installation/configuration.
NOTE:
This type of paragraph calls readers’ attention to a notice or related theme.
CAUTION!
This type of paragraph highlights a procedure, adjustment, etc. which may cause damage or improper
functioning of the equipment if not carried out correctly and may not be clear at first sight.
WARNING!
This type of paragraph indicates things, procedures, adjustments, etc. which demand a high level of
attention, otherwise personal injury or death may occur.
EXAMPLE:
This type of paragraph indicates examples of usage for illustrational purposes.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 6
6
Available Firmware and Archive sets
InteliGen NT GC
InteliGen NTC GC
InteliGen NT BaseBox
InteliGen NTC BaseBox
InteliSys NT BaseBox
InteliSys NTC BaseBox
IG-NT-GC-GeCon-MARINE-3.2
IG-NT-BB-GeCon-MARINE-3.2
IS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-3.2
InteliGen NT GC
InteliGen NTC GC
InteliGen NT BaseBox
InteliGen NTC BaseBox
InteliSys NT BaseBox
InteliSys NTC BaseBox
IG-GC-GeCon-MARINE -SPTM-
3.2
IG-BB-GeCon-MARINE -SPTM-
3.2
IS- GeCon-MARINE-SPTM-3.2
IG-GC-GeCon-MARINE -SPI-
3.2
IG-BB-GeCon-MARINE -SPI-3.2
IS- GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2
IG-GC-GeCon-MARINE -MINT-
3.2
IG-BB-GeCon-MARINE -MINT-
3.2
IS- GeCon-MARINE-MINT-3.2
IG-GC-GeCon-MARINE -
COMBI-3.2
IG-BB-GeCon-MARINE -
COMBI-3.2
IS- GeCon-MARINE-COMBI-3.2
For suitable firmware for your controller please consult this table:
Firmware (*.mhx)
Archives (*.ant)
Some features are available only in InteliGen NT Basebox, InteliGen NTC Basebox and InteliSys NT. These
features are highlighted by green background.
Features which are not available in InteliGenNT GC controller:
User MODBUS
Distributed Binary Inputs and Outputs
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 7

7
General description
PDF FILE
DESCRIPTION
IGS-NT & ID-DCU Accessory Modules 02-
2015.pdf
Thorough description of accessory modules for IGS-NT
family, technical data, information about installation of the
modules, how to connect them to controller and set them
properly.
IGS-NT Troubleshooting Guide 08-2014.pdf
How to solve most common troubles with InteliGen NT and
InteliSys NT controllers. Including the list of alarm massages.
IGS-NT Communication Guide 09-2014.pdf
Communication guide for IG/IS-NT controllers. It contains
information how to connect control unit and all
communication features descriptions
IGS-NT Installation Guide 08-2014.pdf
Installation guide for IG/IS-NT controllers. It contains
technical information about controler and extension modules
IGS-NT Application Guide 05-2013.pdf
Application guide for IG/IS-NT controllers. It refers to
application and typical installation settings and sites
structures
Description of the controller system (with all options)
NT Family controllers are comprehensive AMF-controllers for single and multiple generating sets operating
in stand-by or parallel modes. A modular construction allows upgrades to different levels of complexity in
order to provide the best solution for various customer applications.
NT Family controllers are equipped with a powerful graphic display showing icons, symbols and bar-graphs
for intuitive operation, which sets, together with high functionality, new standards in Gen-set controls.
The controller automatically starts the gen-set, closes the Gen-set C.B. when all conditions are met, then
stops the engine* (* sw GeCon opens GCB only, not stops the engine) on external signal or by pressing
push buttons.
Parallel to the Mains operation is a standard feature. Isolated parallel and Power Management System
support are optional. Forward and reverse synchronizing, Generator protections, Mains protection including
vector shift, load and power factor control are the major functions provided. Interfacing to foreign
synchronizers and load sharers is supported.
The key feature of the controller is its easy-to-use operation and installation. Predefined configurations for
typical applications are available as well as user-defined configurations for special applications.
Comparing of IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE 3.2 with standard gen-set fw
GeCon does not take care of Engine control
GeCon accepts in SEM mode external control of GCB and Engine
GeCon can control the engine via Binary start/stop output signals only – see below. The independent Engine
controller (e.g. ID-DCU) is expected.
Synchronizing and unloading timeouts can be disabled by setpoint setting (or Force value function)
All regulations (load, VAr sharing, frequency, voltage) can be disabled by setpoint change or by Force value.
Interface GeCon to engine controller is provided by I/O wires no by communication line.
Available documentation
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 8

8
IGS-NT Operator Guide 01-2014.pdf
Operator guide for IG/IS-NT
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 9

9
Example of interconnection
GeCon x Engine controller
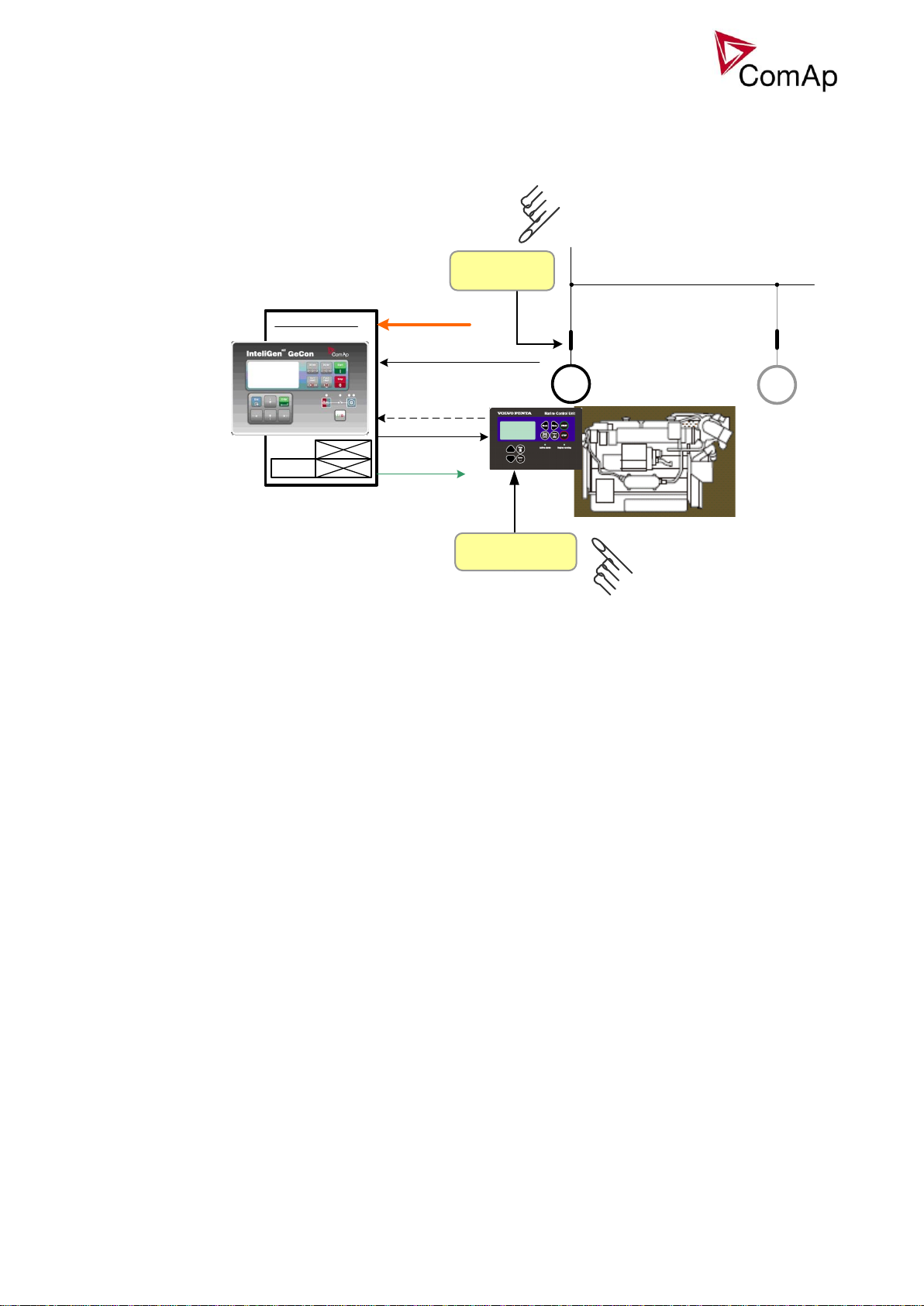
Schematic wiring:
Important signals/ interconnections:
From GeCon side:
BO: Start pulse, Stop pulse - for sending Start and Stop signals
Speed control (during synchronisation, regulation):
BO: Speed Up, Speed Down or Aout SG out
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 10

10
BI: ReadyToLoad – signal from Engine unit – it means that Engine is ready (speed is ok, no 2nd level
alarms) and can be loaded.
Other signals:
- Information about Warnings / SD in one unit can be sent to second unit.
- ECU – in case of Ecu communicating via CAN bus J1939 – GeCon can be connected to CAN1 for
showing ECU values on the display
- Interconnection on CAN2:
o For Time and Date synchronisation only- in case of IGS-NT and ID-DCU
o In case of connection IB-NT or I-LB+ - you can monitor both kind of units (IGS-NT, ID-DCU)
o In case of connection display – you can switch between both kind of units (IGS-NT, ID-DCU)
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 11

11
Functions
Basic description of SPI application
The SPI application is intended for single gen-sets and includes following main features:
Automatic startup and stop sequences with adjustable timing
Wide range of generator and engine protections, additional freely configurable protections
Parallel to the mains operation, many different load control modes (baseload, import/export control
and other)
Island operation
Integrated mains protection (mains decoupling relay) including vector shift
One breaker control (GCB) including synchronizing
MCB position sensing
Soft loading and unloading
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 12
12
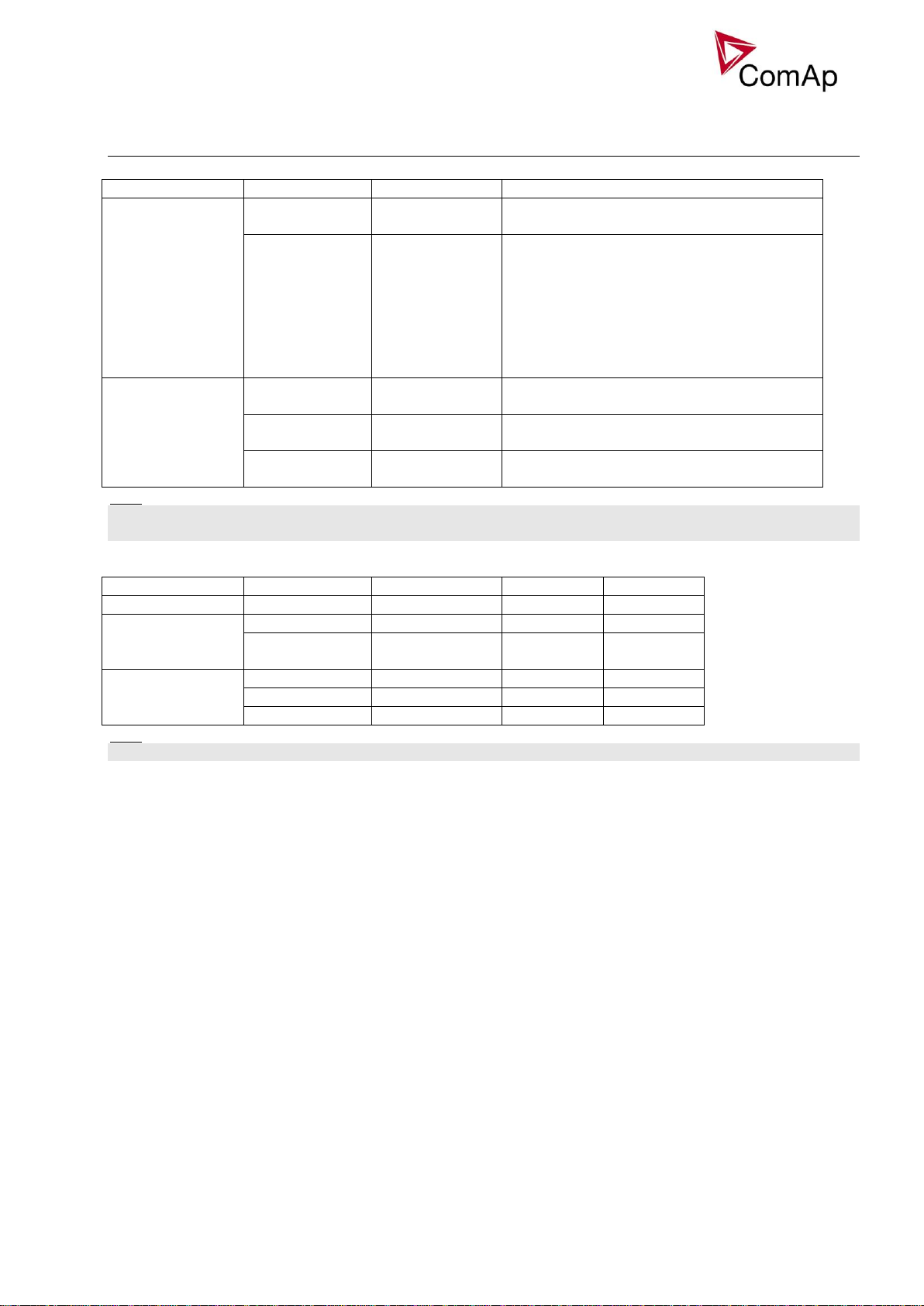
Modified setpoints
Group
Setpoint
Option
Function
Process control
StartStopBtn
ENABLED
DISABLED
Standard panel Start/Stop buttons function.
Panel Start/Stop buttons are disabled.
ProtectionMode
ACTIVE
NOT ACTIVE
ACTIVE:
2-nd level protections are evaluated, GCB
or MCB is controlled.
NOT ACTIVE:
2-nd level protections are evaluated, GCB
or MCB is NOT opened.
Exceptions are Emerg Stop and alarms
types Sdoverride.
Sync/Load ctrl
Sync timeout
1-1800s
NO TIMEOUT
Standard MINT function.
Unlimited synchronizing time.
GCB open level
1-100%
NO LEVEL
Standard MINT function.
No generator power open level detection.
GCB open del
1-1800s
NO TIMEOUT
Standard MINT function.
Unlimited unloading procedure.
“HAND”
SEM
AUT
Basic setting
ControllerMode
SEM
SEM
AUT
Process control
StartStopBtn
DISABLED
ENABLED
ENABLED
ProtectionMode
NOT ACTIVE
/ACTIVE
ACTIVE
ACTIVE
Sync/Load ctrl
Sync timeout
NO TIMEOUT
1-1800s
1-1800s
GCB open level
NO LEVEL
1-100%
1-100%
GCB open del
NO TIMEOUT
1-1800s
1-1800s
Below mentioned are GeCon specific setpoints only.
Hint:
All above mentioned setpoints can be Forced by Binary input(s) to another value (or switched between
ENABLED and DISABLED).
Based on setpoint settings there are three possible operational modes HAND – SEM - AUT:
Hint:
It is possible to configure (Force value) “HAND” – SEM switching via Binary input.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 13

13
Controller modes
OFF mode
Use OFF mode to block controller functions (even if is power on). OFF mode is used for controller firmware
or configuration change.
Binary outputs (e.g. GCB CLOSE/OPEN) are not energized, all closed Binary outputs are opened when
controller is switched to OFF mode.
Gen-set cannot be started and operated from IGS-NT-GeCon controller – no response for panel buttons and
Binary input commands.
Hint:
Switching to OFF mode is blocked on running engine to avoid accidental engine stop by mode change or by
firmware or configuration programming.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 14
14
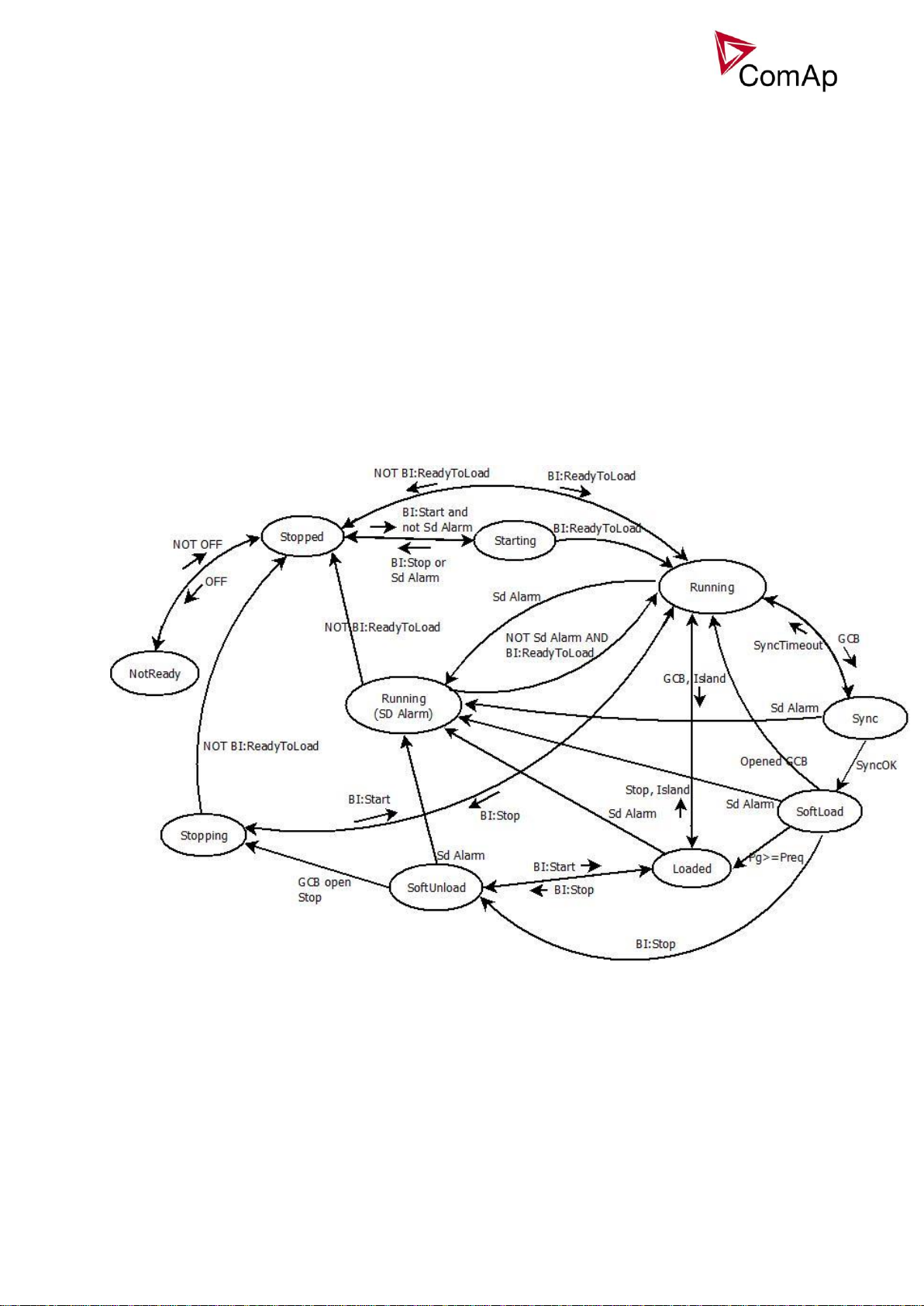
SEM mode
Engine start can be activated from
o Engine controller (e.g. ID-DCU, ID-MCU)
o GeCon panel – Start button
o GeCon BI: StartButton
o Remotely e.g. from InteliMonitor
GeCon BI: ReadyToLoad initiates GeCon “Running” state” - activates Gener protect: Min stab time a Max
stab time within the generator electric protections are activated.
Gen-set is loaded/unloaded from
o GeCon panel – GCB button
o GeCon BI: GCBButton
o Direct GCB “hand” control
o Remotely e.g. from InteliMonitor
o LBI: Gen unload
GCB closing from controller can be blocked by BI: GCB disable (does not block synchronization process)
Controller flow chart in SEM mode:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 15
15
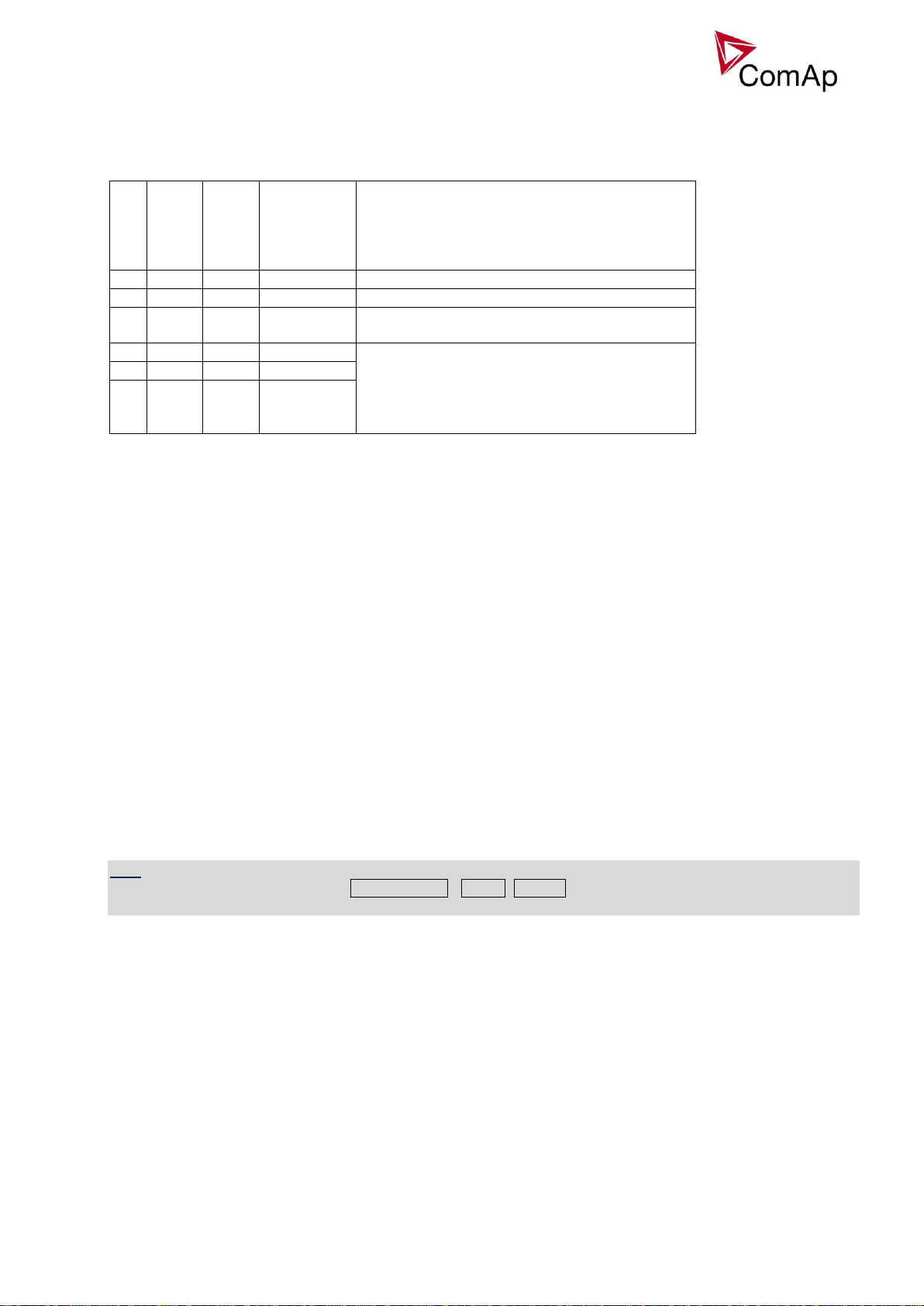
HAND mode
IG-EE GeCon
MINT
MCU
GCB feedback
GCB
close/open
Vg, Ig, Vb
RS232 - PC
Speed control
(Sync/Load ctrl)
GCB
START
STOP
(ReadyToLoad)
G
G
External Engine
Start / Stop
External GCB
Close / Open
generator
measuring
Process control: StartStopBtn = DISABLED
ProtectionMode = NOT ACTIVE
Sync/Load ctrl: Sync timeout = NO TIMEOUT
GCB open level = NO LEVEL
GCB open del = NO TIMEOUT
MCU
Hand mode is a special type of SEM mode. In Hand mode, the panel Start, Stop buttons are not working,
GCB is supposed to be controlled externally. The Hand mode is achieved by setpoints adjustment - see the
following picture.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 16
16
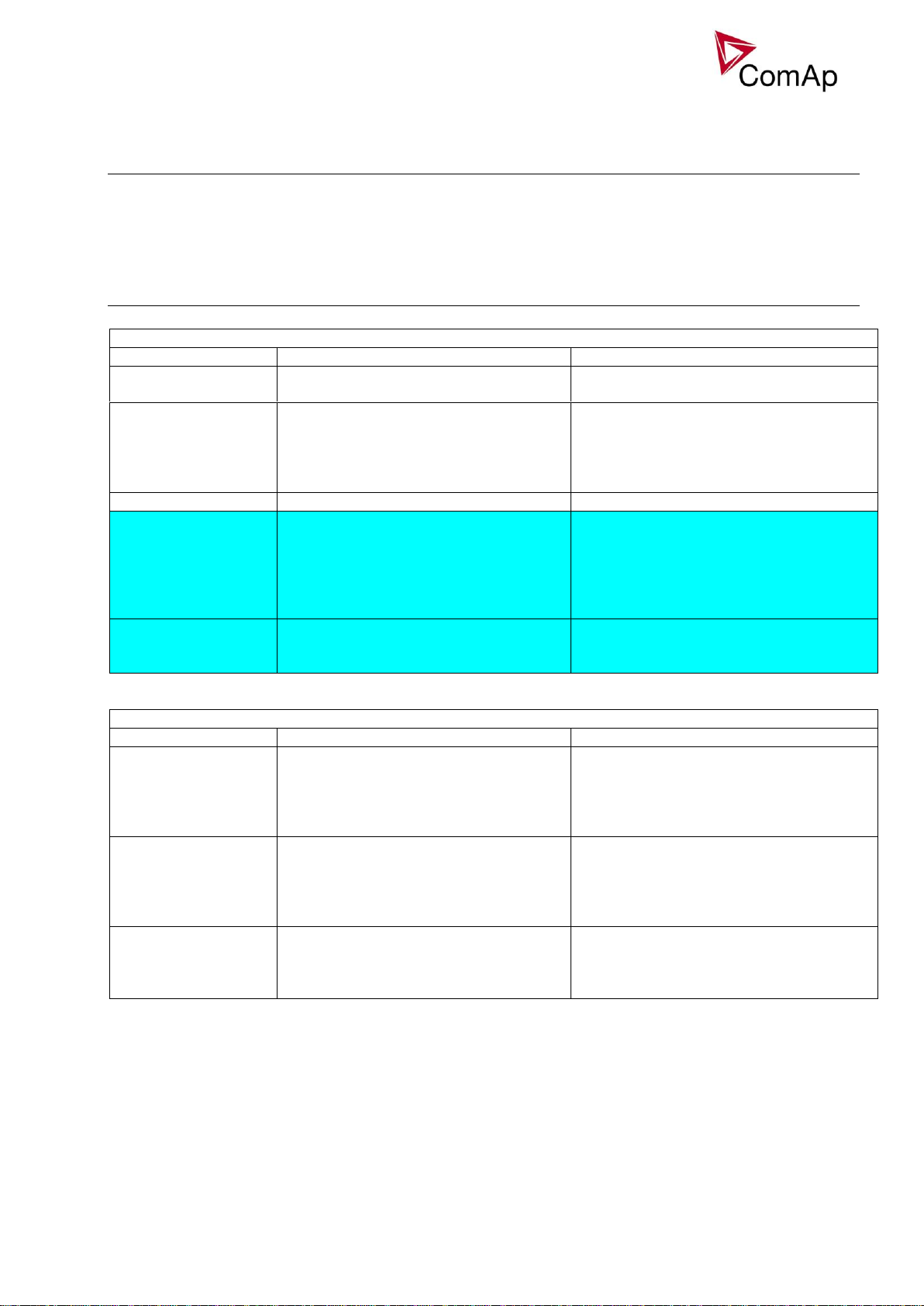
AUT mode
No.
Island
enable
Parallel
enable
Synchro
enable
Function
1
YES
YES
FORWARD
Basic SPI application
2
YES
NO
NO
SPM application
3
NO
YES
FORWARD
SPI application, no island (stand-by) operation
allowed
4
NO
NO
NO
Gen-set start is blocked. Binary output
StartBlocked indicates those states.
NO
NO
FORWARD
NO
YES
NO
Automatic mode is influenced by ProcessControl: Island enable, ParallelEnable, Synchro enable setpoints.
Following procedure corresponds to setting No.1 from table above.
1) After the input Rem start/stop is energized, controller starts the gen-set. If MCB feedack is active, the
controller will synchronize the gen-set to mains and ramp up the load, depending on the ProcessControl
set points adjustment.
2) If a mains failure is recognized, the controller will open the GCB to separate the failed mains from the
generator. After the mains breaker has been open (MCB feedback is de-energized), the controller will
close the GCB again to the island (stand-by) operation.
3) If mains recovers again, the GCB is open again to allow the MCB to be closed (manually or in general
not with a command from the controller). After both mains is present and MCB closed, the controller will
synchronize again with the healthy mains and close the GCB.
4) If input Rem start/stop is de-energized, controller will softly unload the gen-set back to the mains, then
open the GCB, cool down and stop the gen-set.
TEST mode
Use TEST mode for Gen-set start test if the Mains is OK or to transfer the load to the gen-set when Mains
fail is announced in advance.
HINT
The controller does not respond to GCB ON/OFF , STOP, START in Return To mains = ENABLED.
Gen-set automatically starts, when TEST mode is selected.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 17
17
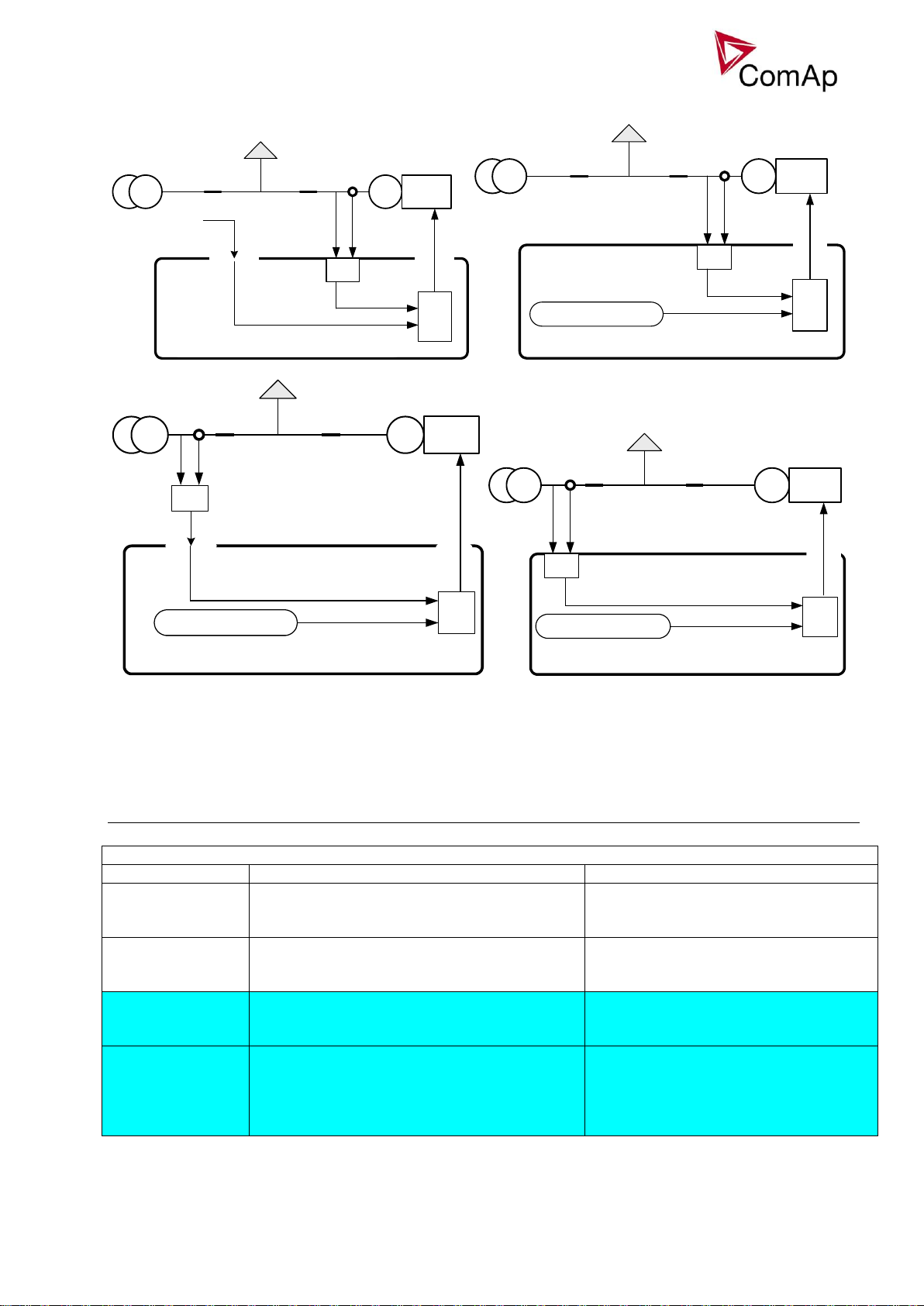
ProcessControl: Load ctrl PtM
Mode
Function
Related Setpoints – LBI – LBO - LAI
BASELOAD
Gen-set power is regulated to value
given by Base load setpoint.
ProcessControl: Base load
IM/EX
Gen-set load is controlled so, that the
mains import is maintained constant at
the level given by Import load setpoint –
I/E power is measured by controller on
auxiliary CT input or by analog input.
ProcessControl: Import load, I/E Pmmeas
ANEXT BASELOAD
Gen-set power is set by analog input.
Analog input: LdCtrlAnextBld
ANEXT IM/EX
Gen-set load is controlled so, that the
mains import is maintained constant at
the level given by the analog input
LdCtrl:AnExI/E – I/E power is measured
by controller on auxiliary CT input or by
analog input.
ProcessControl: I/E Pm-meas, Analog
input: PFCtrl:AnExI/E
T BY PWR
Gen-set power is controlled to keep the
required temperature, that is measured
via an analog input.
ProcessControl: TempByPwr Treq,
TempByPwr gain, TempByPwr int,
Analog input: LdCtrl:TByPwr
Another modes of active power control
Mode
Function
Related Setpoints – LBI – LBO - LAI
Export limit
Limits export to the mains in the
baseload mode. If the function is
enabled, the gen-set power is limited so
that mains import is always higher or
equal to the setpoint Import Load.
ProcessControl: Export limit = ENABLE,
Import load
Warming
The controller limits gen-set power for
requested time or until the water
temperature reach the requested value.
After warming the gen-set goes to the
requested (e.g. Baseload) power.
ProcessControl: Warming load;
Warming temp; Max warm time
Peak shaving
Automatic gen-set start/stop based on
object (load) consumption. Can be
based on measured kW or kVA.
ProcessControl: PeakLevelStart;
PeakLevelStop; PeakAutS/S del, Peak
kVA Start, Peak kVA Stop, PeakKVAS/S
del, LBO: PeakShaveAct
Mains parameters out of limits during synchronising
In case that mains parameters get out of permitted limits during synchronizing to mains (reverse or forward),
the regulation of gen-set speed and voltage according to mains frequency and voltage is interrupted. During
the state, when parameters reach out of limits, until “Mains fail” is issued, the engine speed and voltage
regulation output is kept on the last value.
Active Power control modes in SPI
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 18
18
Requested power
Actual power
Vgen
Igen
SpeedGoverrnor
output
Speed
governor
ProcessControl: Load ctrl PtM = ANEXT BASELOAD
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
LdCtrl:AnExtBld
Analog input:
Requested power
Actual power
ProcessControl: Baseload
Vgen
Igen
SpeedGoverrnor
output
Speed
governor
ProcessControl: Load ctrl PtM = BASELOAD
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
SpeedGoverrnor
output
Speed
governor
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
LdCtrl:I/E-Pm
Analog input:
Vmains
Imns 3
LoadCtrlPtm = IM / EX
I / E- Pm meas =
ANALOG INPUT
ProcessControl :
ProcessControl :
ProcessControl :
IM/ EX
Requested I/E power
Actual I/ E power
SpeedGoverrnor
output
Speed
governor
LoadCtrlPtm = IM / EX
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
Vmains
Imains ph3
ProcessControl :
IM/EX
ProcessControl :
I/E -Pm meas = IM3 CT INPUT
ProcessControl :
Requested I/
E power
Actual I/ E power
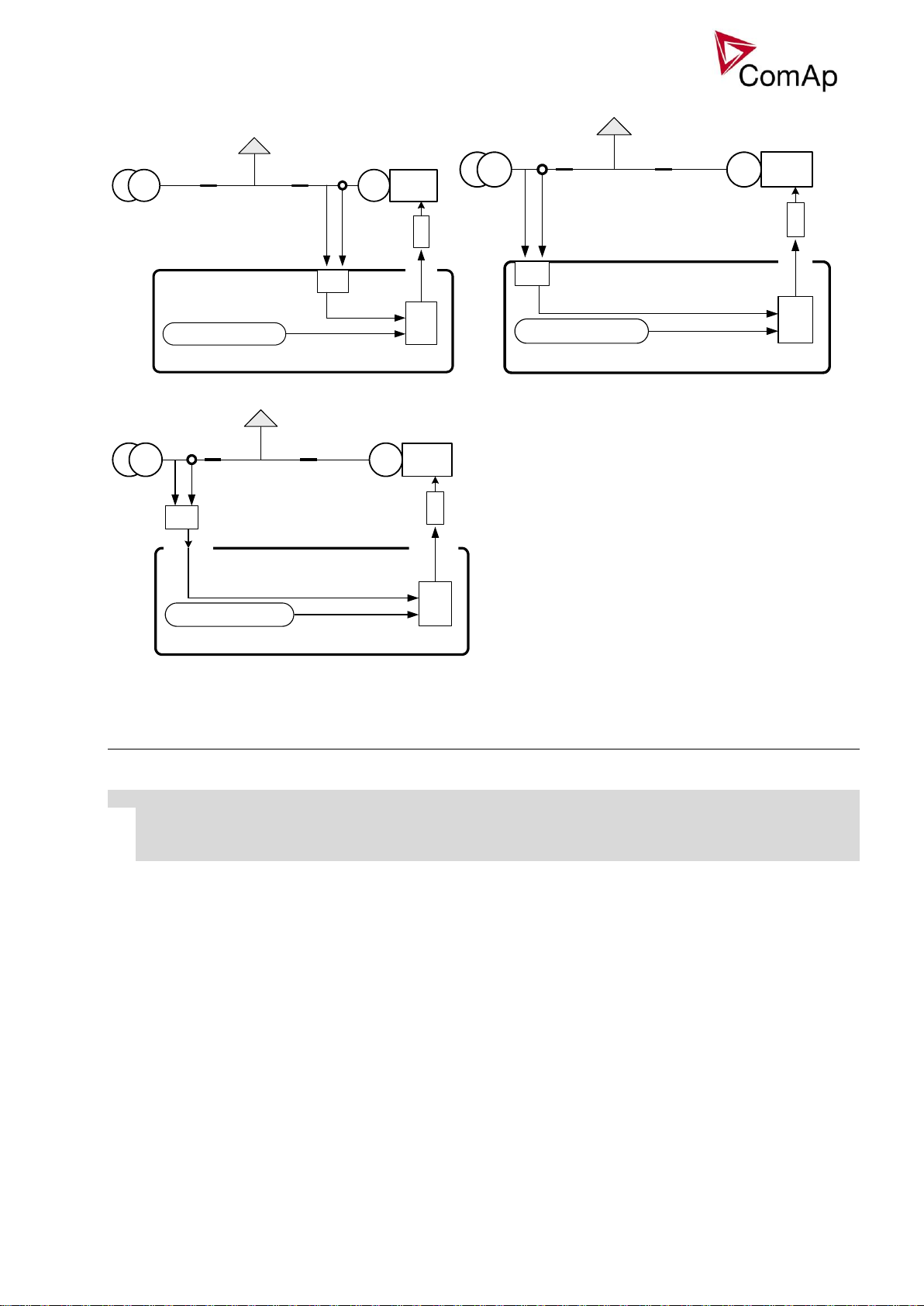
ProcCtrlSingle: PF ctrl PtM
Mode
Function
Setpoints
BASEPF
Gen-set power factor is maintained at
constant level adjusted by the setpoint
Base PF.
ProcCtrlSingle: PF ctrl PtM
PF-IM/EX
Gen-set power factor is controlled so, that the
mains power factor is maintained constant at
the level adjusted by setpoint Import PF
ProcCtrlSingle: Import PF,
I/E Qm-meas
ANEXT BASEPF
Gen-set power factor is maintained at
constant level given by the analog input
PFCtrl:AnExBPF
Analog input: PFCtrl:AnExBPF
ANEXT PF-IM/EX
Gen-set load is controlled so, that the mains
power factor is maintained constant at the
level given by the analog input PFCtrl:AnExI/E
– I/E power factor is measured by controller
on auxiliary CT input or by analog input.
ProcCtrlSingle: I/E Qm-meas
Analog input: PFCtrl:AnExI/E
PF control modes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 19
19
Requested PF
Actual PF
ProcessControl: Base PF
Vgen
Igen
AVRi output
AVR
ProcessControl: PF ctrl PtM = BASEPF
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
IG-AVRi
ProcessControl :
Import PF
AVR
ProcessControl :
ProcessControl :
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
IG-AVRi
Vmains
Imains ph3
PF ctrl PtM = PF IM/ EX
Actual I/ E PF
Requested I /E PF
I / E- Qm meas = IM3 CT INPUT
AVRiout pu t
Import PF
AVRi output
AVR
LOAD
GCBMCB
Controller
IG-AVRi
PfCtrl:I/E-Qm
Analog input:
Vmains
Imns 3
Actual I/E PF
Requested I/E PF
PF ctrl PtM = PF IM/EX
ProcessControl :
ProcessControl :
ProcessControl : I/E- Qm meas
= ANALOG INPUT
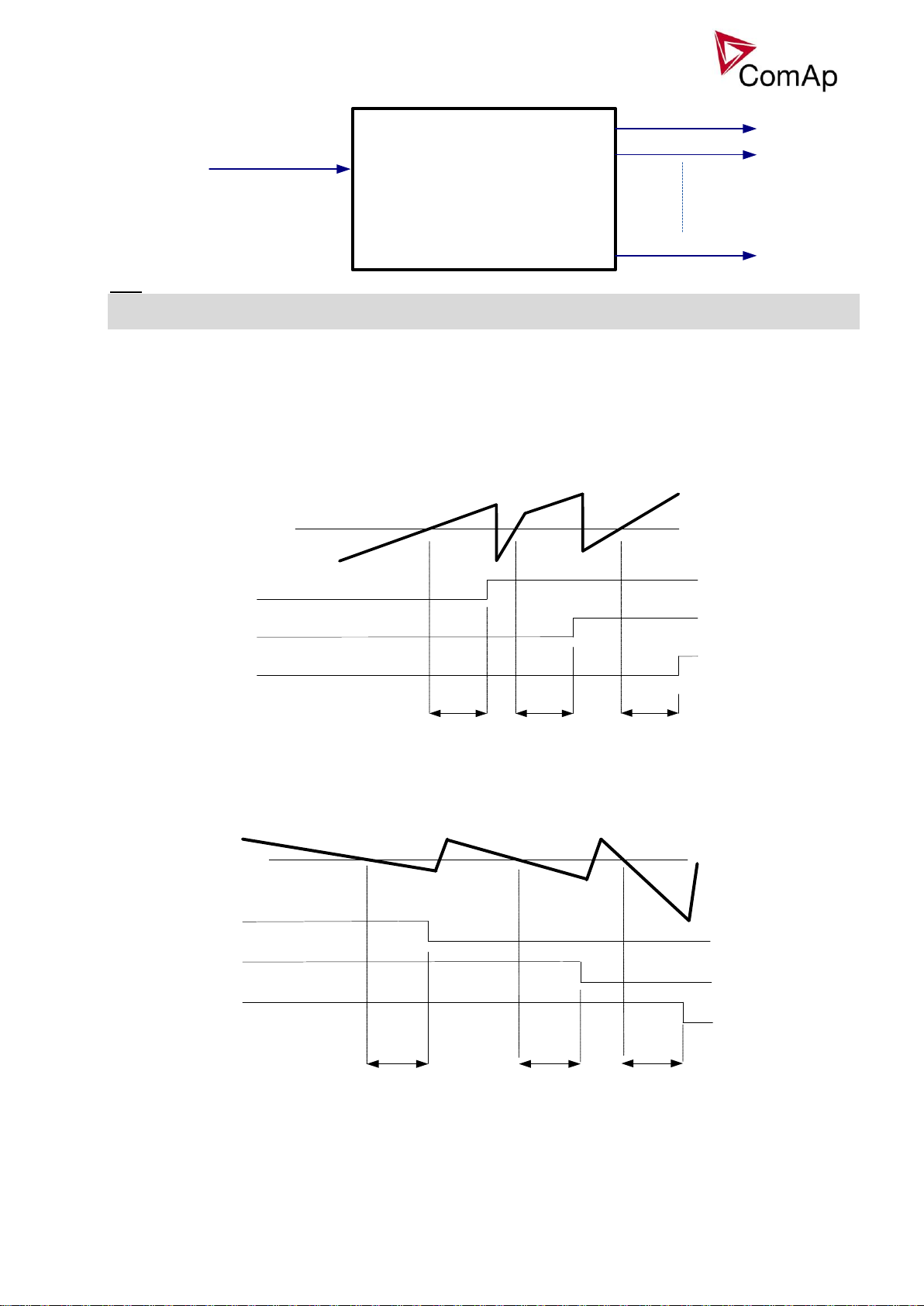
Load shedding
Load shedding function is dedicated for tripping of non-essential load in case of high generator current, or
drop of generator frequency above/below preadjusted limits, for preadjusted time.
All LOAD SHED outputs are activated (closed) to trip the unessential load when gen-set goes to island:
a) When GCB is closed after mains fail and gen-set starts in AUT mode.
b) When MCB opens from parallel to mains operation in AUT mode.
c) Before MCB is opened in SEM mode by button.
The load shedding function is active in all controller modes except OFF and MAN.
Load shedding has ten steps and each step is linked with its own Load shed x binary output. The non
essential load shedding is based on generator current and generator frequency. There is only one level for
current load shedding and one level for frequency load shedding for all 10 steps, as well for reconnection
level and delay. Load shed can only move from one step to the next, e.g. No LoadShed to LdShed S1 to
LdShed S2 to LdShed S10 and vice versa.
If manual reconnection of the load is desired, the AutoLd recon setpoint needs to be disabled (AutoLd recon
= DISABLED) and the MAN load recon binary input needs to be configured.
Rising edge on this input resets the controller to a lower stage, but only if the load is under the Ld recon level
at that moment.
The current load shedding can be activated in case any of phase current exceeds the adjusted limit. The
reconnection is able only in case all of the current values are below reconnection level.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 20
20
CurShedLev
CurRecLev
FreqShedLvl
FreqRecLvl
LdShed stage 1
LdShed stage 2
LdShed stage 10
ManualLdRecon
Load shedding:
Ld Shed delay
Ld recon delay
Ld shed
del
Ld shed
del
Ld shed
del
BO Load shed 1
BO Load shed 2
BO Load shed 3
Curr shed level
Gen-set current
closed
closed
closed
Ld recon del Ld recon delLd recon del
BO Load shed 2
Curr recon level
Gen-set current
BO Load shed 3
BO Load shed 1
opened
opened
opened
Hint:
If no Load Shedding outputs are configured, there is no record to history and no screen timer indication of
the activity of this function.
On the following pictures, the generator current load shedding is depicted. The current is evaluated from all 3
phases, each phase can activate the load shedding. On the picture, due to transparency, only 3 load shed
outputs are depicted, not all 10.
The generator frequency based load shedding is in fact the same, but fall below preadjusted limit is watched,
instead of exceeding of the limit as in case of current load shedding.
Load reconnection – automatic -> AutoLd recon = ENABLED
Load reconnection – manual -> AutoLd recon = DISABLED
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 21
21
BO Load shed 2
Curr recon level
BO Load shed 3
BO Load shed 1
BI Man load recon
opened
opened
opened
no action
Gen-set current
0 V batt
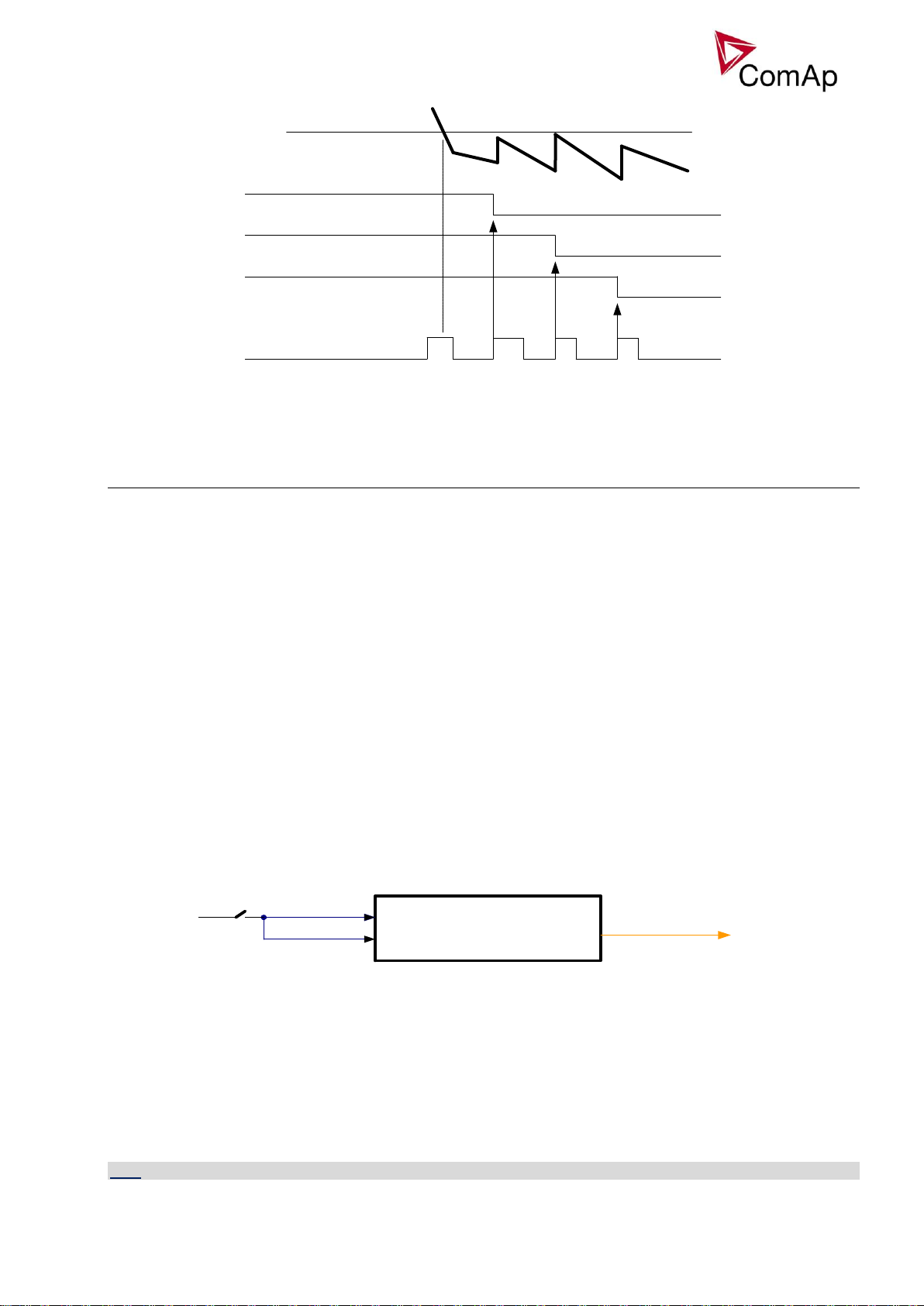
Test on load
Remote TEST
AMF settings:
ReturnTo mains = DISABLED
WrnTstOnLdFail
Test on load – SPtM
Affects the behavior in TEST mode. Before the activation of this function
1. adjust setpoint AMF settings: ReturnTo mains = DISABLED
2. adjust Process control: MFStart enable = YES.
3. switch controller to Test on load mode (see drawing below)
Gen-set starts and goes to load (synchronizes to the mains, closes GCB and opens MCB) automatically
when this input is closed even if Mains is OK.
Transmition of power from mains to generator
Behaviour of function depends on settings of setpoint ProcessControl:I/E-Pm meas. If the mains import is
measured (ProcessControl:I/E-Pm meas = IM3 CT INPUT or ANALO INPUT) then there is no time
limitation for unloading and opening of MCB. The MCB is opened when the Import/Export goes below 0 ± 5%
of Basic settings: Nomin power. If the setpoint ProcessControl:I/E-Pm meas = NONE then the MCB is
opened after delay given by setpoint AMF settings: BreakerOverlap.
Transmition of power from generator back to mains
GCB is opened when the power on gen-set is drops under level given by setpoint Sync/Load ctrl: GCB
open level at the least after delay given by setpoint AMF settings: BreakerOverlap.
Test on load with break (interruption)
The transfer of the load in TEST mode can be performed with interruption in case that the parallel to mains
operation is undesirable. Set setpoints ProcessControl:Parallel enable = NO or ProcessControl:Synchro
enable = NONE or REVERSE, ProcessControl:Island enable = YES: If the LBI Test on Load gets active the
load is passed from the mains to the gen-set with interruption. Controller opens MCB and closes GCB after
delay given by AMF settings:FwRet break. After deactivation of LBI Test on Load GCB is opened and and
MCB Is closed after delay given by AMF settings:FwRet break.
HINT
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 22
22
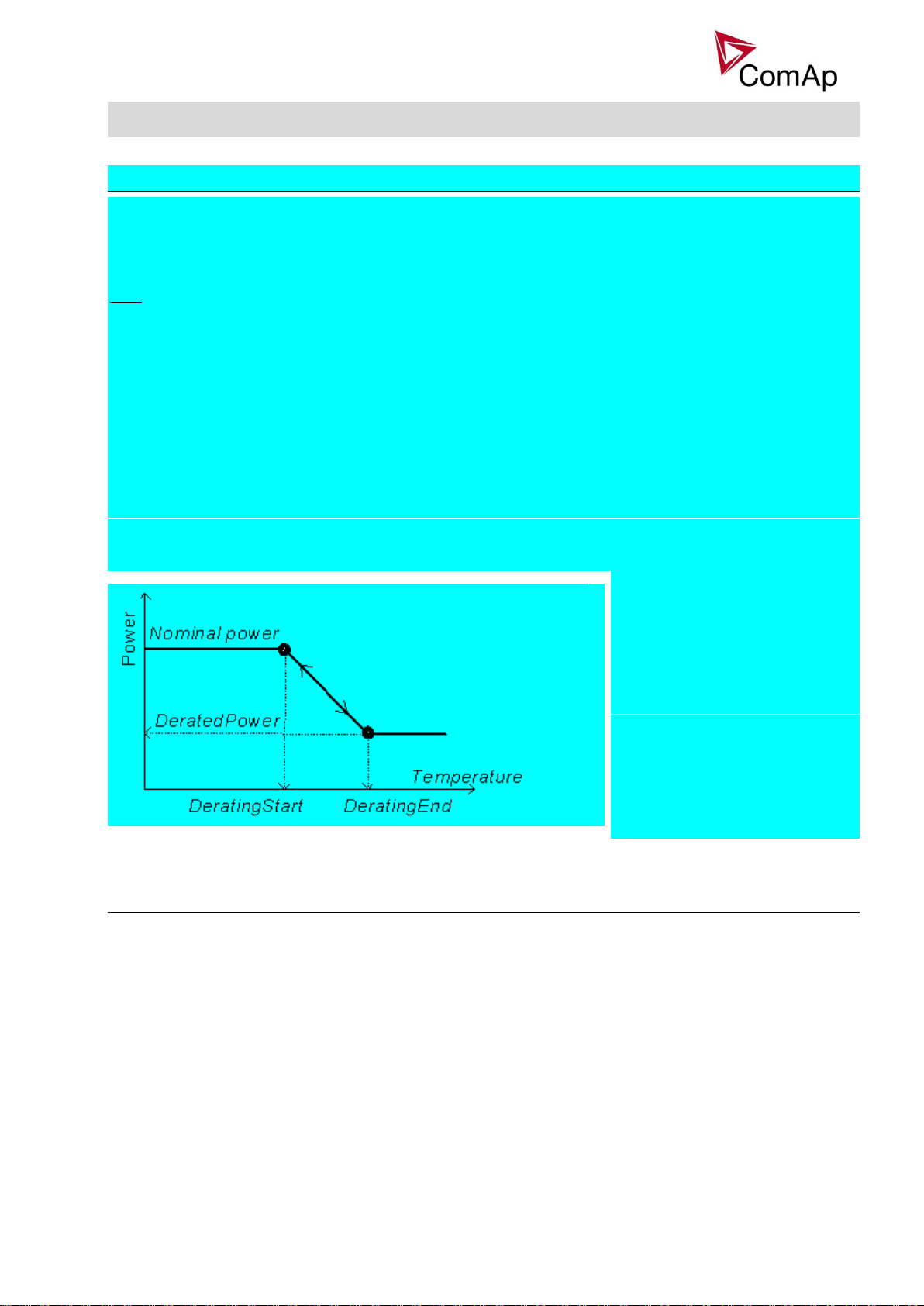
Temperature derating function
decreases genset power depend
on setpoints DeratingX strt,
DeratingX end and DeratedX pwr.
Temperature derating starts at
DeratingX strt temperature.
At DeratingX end temperature runs
genset at DeratedX pwr level.
Above DeratingX end temperature
Genset runs at constant DeratedX
pwr.
It is possible to configure both binary inputs (Remote TEST and Test on load) to only one controller physical
binary input internally.
Power derating
This function linearly decreases genset nominal power according to analog input value.
Gen-set power starts decreasing when temperature measured by Analog input PowerDeratingX exceeds
DeratingX strt value.
Gen-set power is at DeratedX pwr value when temperature measured by Analog input Power deratingX is
equal or higher than DeratingX end value.
Hint:
To use Power derating function configure at first Analog input PowerDeratingX to any IGS-NT or IS-AIN
analog input terminal by GenConfig.
When Power derating function is active the generator overload protection is based on the Derated power! ! !
Derated power value Pg derated is visible in the controller measure screen.
When derating function is not active the Derating power is equal to Nominal power.
Example :
Nomin power = 200 kW, Derating1 strt = 70 °C, Derating1 end = 100 °C, Derated1 pwr = 70 %.
Genset is running at Nominal power 200 kW. When temperature reached 70 °C the genset power starts
decreasing. When temperature reached 100 °C genset runs at 70 % of Nominal power = 140 kW. When
temperature increased above DeratingX end temperature level, gen-set power stays at DeratedX pwr level
140 kW.
Protection mode settings
Protections in this application are affected by Setpoint ProtectionMode (group ProcessControl).
This setpoint is active in MAN,SEM and AUT mode.
Setpoint ProtectionMode has 2 options of settings:
ACTIVE:
Standard setting – all protections are active, in case of 2nd level alarm the breaker is opened/controlled.
(2-nd level alarms are evaluated, GCB or MCB is controlled)
NOT ACTIVE:
2-nd level alarms are evaluated only , but GCB or MCB are NOT controlled (no actions).
Exceptions are Emergency Stop and Sd override alarms type.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 23
23
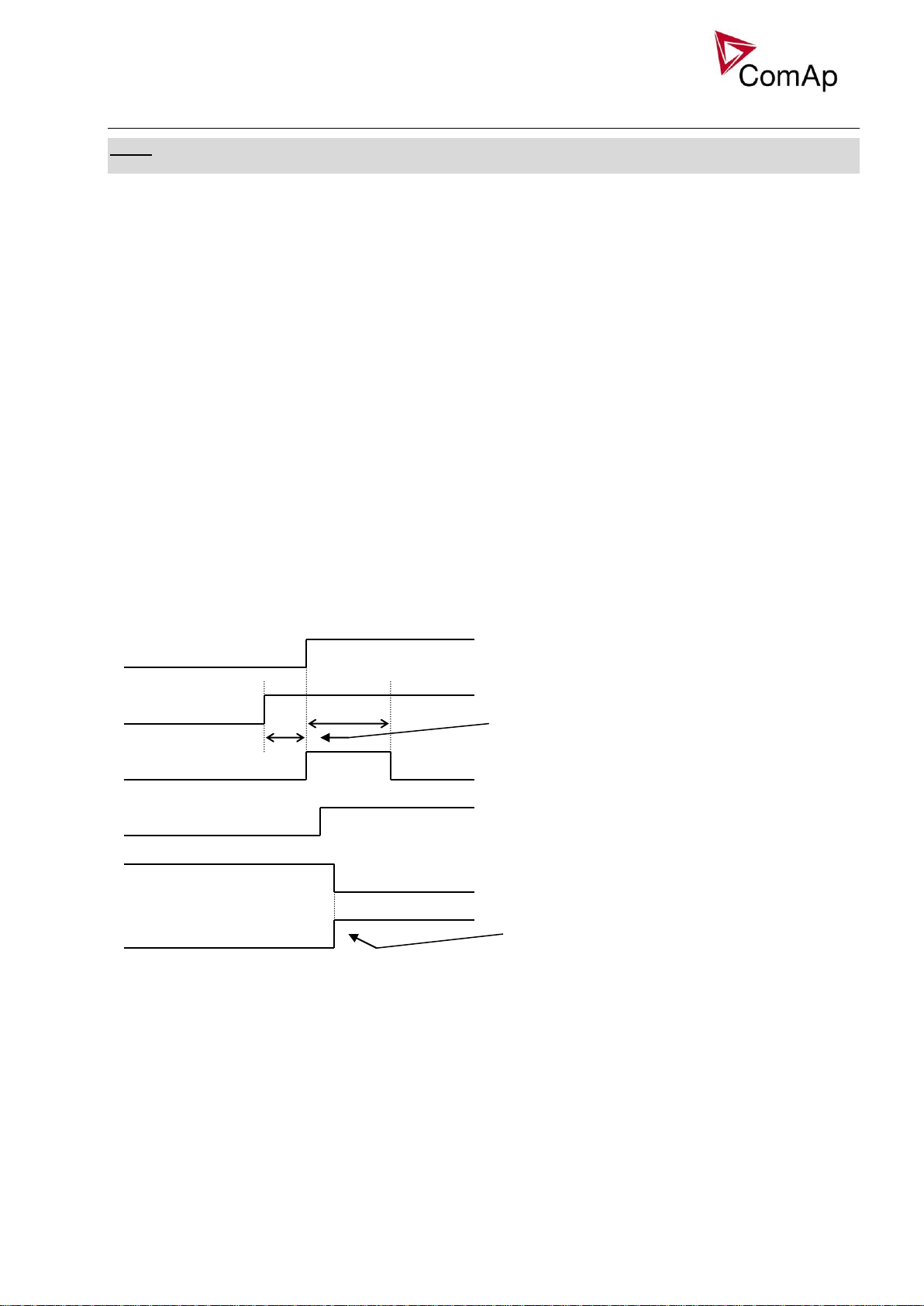
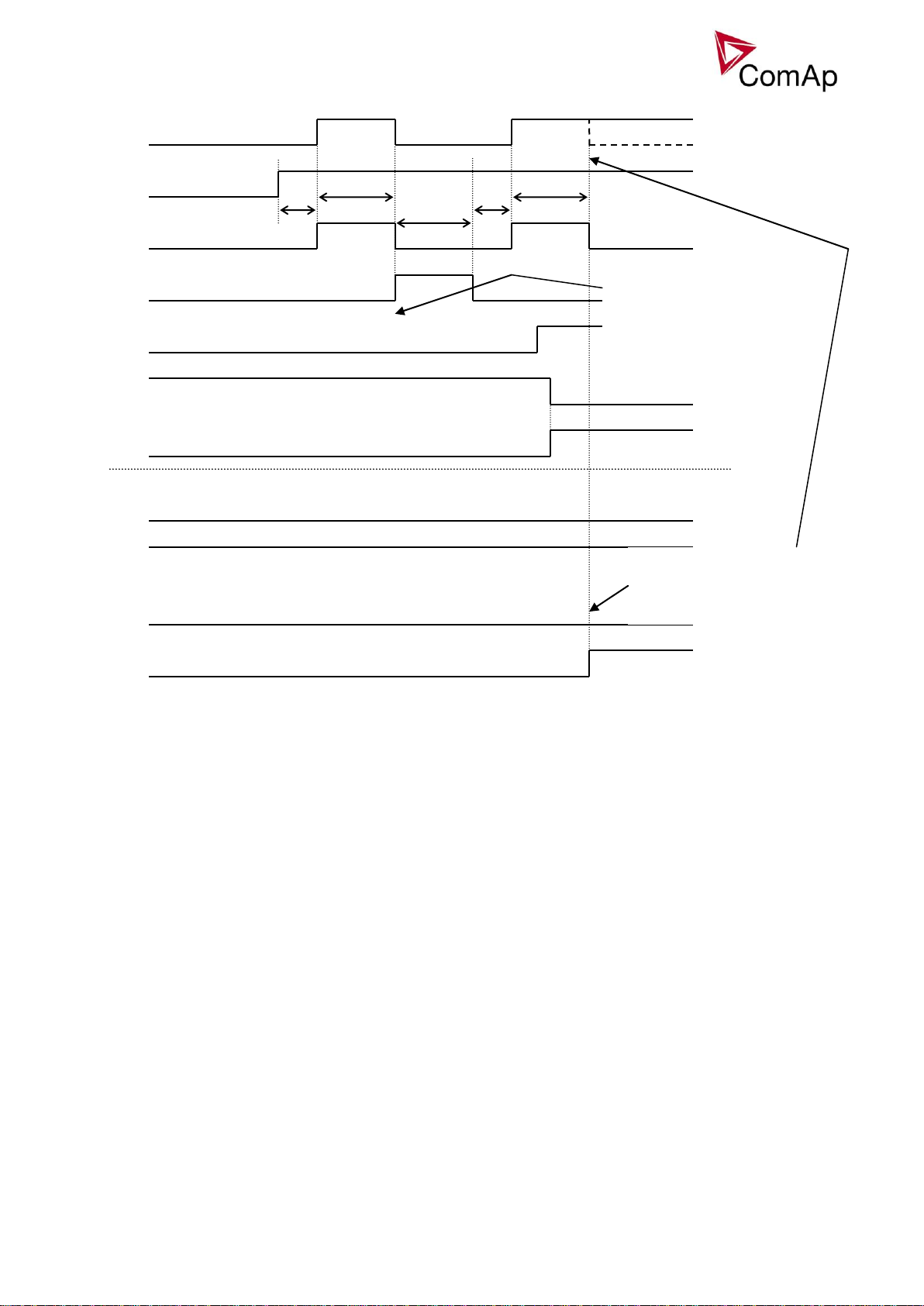
Circuit breakers operation sequence, GCB/MCB fail detection
2s
BO: CB status
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
minimum 1s from UV switching on,
together with MinStab time elapsing is
necessary before the CB is allowed to
close
When closing the CB, the CB status LBO
switches over only when both feedbacks
are in correct position
NOTE:
In the following text, “CB” abbreviation is used for MCB or GCB respectively.
Related binary inputs:
- CB fdb – CB feedback binary input
- CB fdb neg – negative CB feedback binary input. Used for increasing the reliability of CB status
evaluated by the controller. In case that it is not configured, negative value of CB fdb is calculated
internally within the controller.
Related binary outputs:
- CB close/open – output for circuit breaker. Equals to 1 during the time when CB is requested o be
closed.
- CB ON coil – output for closing coil of the CB. 2s pulse (5s if synchronising is not provided by the
particuilar CB) is used for closing the CB.
- CB OFF coil – output for opening coil of the CB. 2s pulse (5s if synchronising is not provided by the
particuilar CB) is used for opening the CB.
- CB UV coil – output for undervoltage coil of the CB. Permanently active, 2s negative pulse (5s if
synchronising is not provided by the particuilar CB) is used for CB opening request
- CB status – output indicating CB status as evaluated by the controller. This signal is used for lighting
LEDs on the panel, switching the regulations, CB fail evaluation, etc.
Possible CB sequences:
CB close command:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 24
24
2s
2s
1s
BO: CB OFF coil
2s
BO: CB status
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
If the CB is not closed after
the first attempt, it is only reset
by OFF pulse and no CB fail is
issued. This would be issued
after the second unsuccessfull
attempt.
BO: CB status = 0
BI: CB fdb neg = 1
BI: CB fdb = 0
BO: CB fail
ON pulse has finished and CB
status is not =1. CB fail is
issued immediatelly
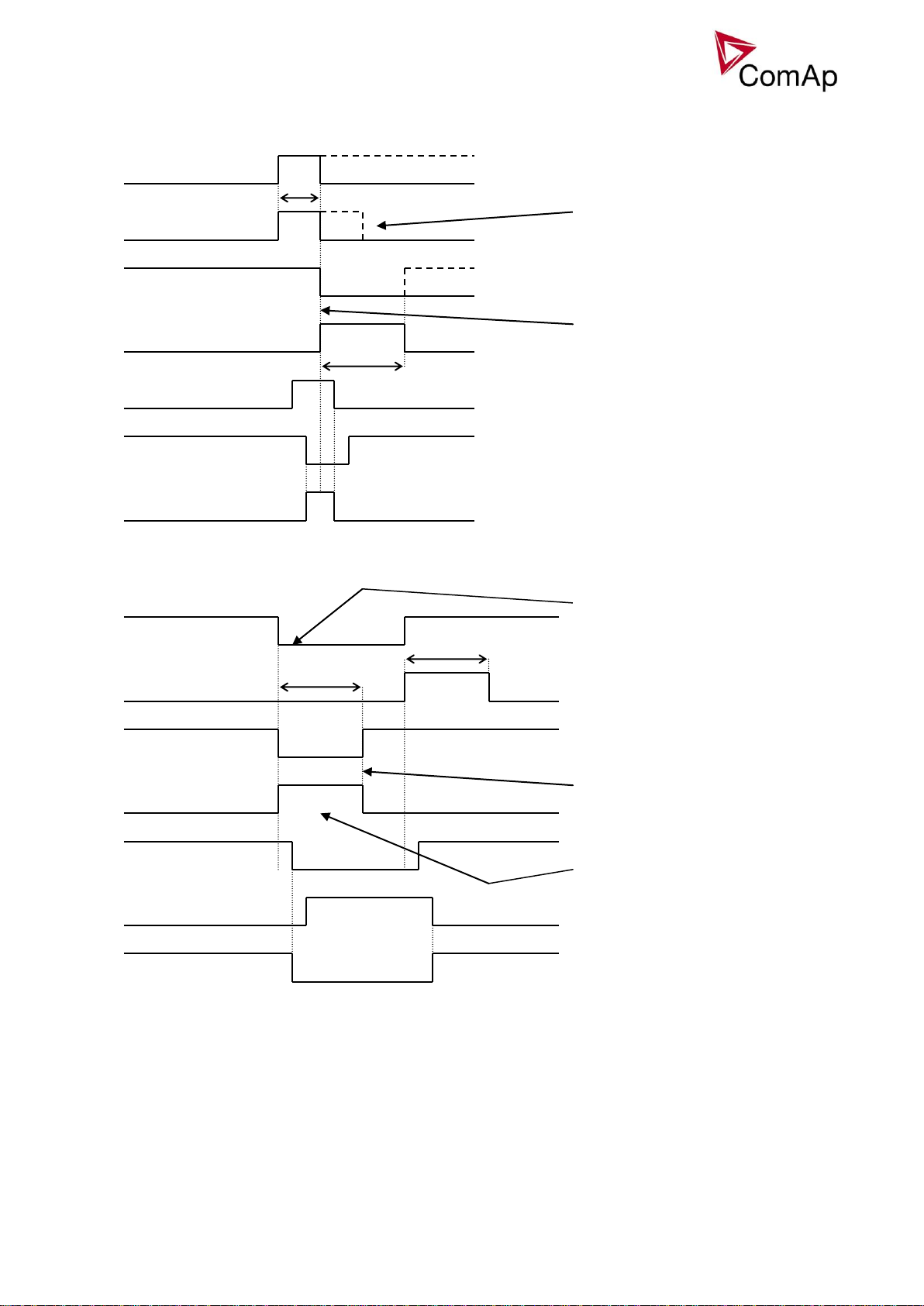
Repeated CB close command:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 25

25
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BO: CB fail
500 ms
<2s
BO: CB status = 0
BI: CB fdb neg = 1
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
CB fail – If any inconsistence between
the two feedback signals is detected, CB
fail is issued.
ON pulse is shortened/interrupted
and replaced by UV and OFF pulse
OFF pulse is activated until both
feedbacks return to the correct
position +2 seconds.
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
During CB opening the CB status
LBO is deactivated with change of
the first feddback status
Further behavior of UV output
depends on the system status. In
case of transition to cooling stays
off, if the Cb was opened manually
and the engine keeps running, it
activates again after timeout
elapses.
BO: CB status
CB fail – fdb mismatch:
CB open command:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 26
26
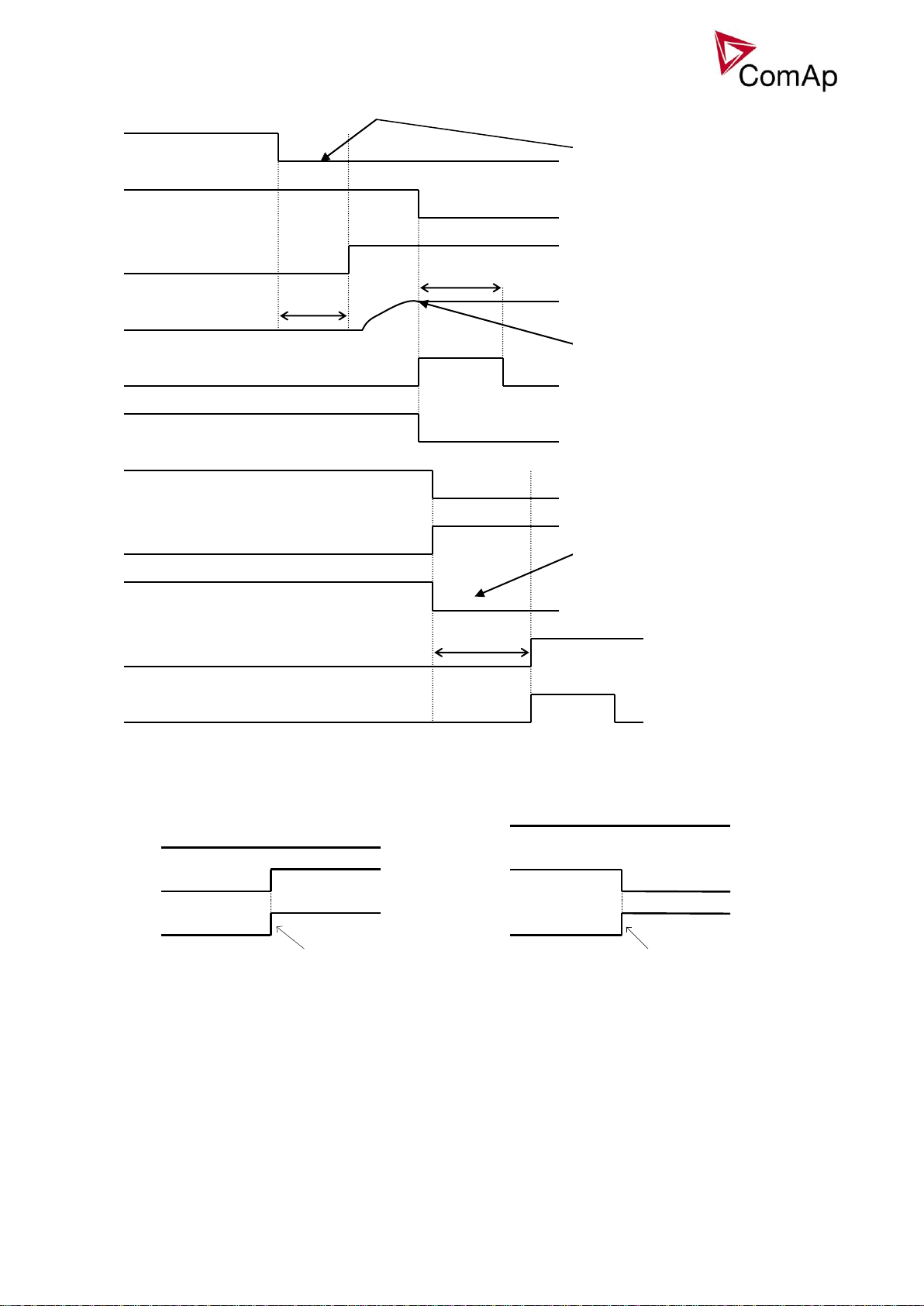
Transition closing -> opening (opening command is issued during closing pulse):
<2s
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
BO: CB status
BO: CB ON coil
Closing pulse is shortened, opening
sequence is started immediatelly
CB opening by protection or manual
command (button pressed)
2s
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
BO: CB status
BO: CB ON coil
OFF a UV pulse is always activated for
the full time. manual control (= CB
button) is deactivated during opening
pulse.
Here starts the standard closing
sequence – see CB close command.
In this moment, the reason for closing the
CB is activated again (e.g. Remote
Start/Stop is activated)
Transition opening -> closing (closing command is issued during opening pulse)
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 27
27
Alarm: GCB fail
BO GCB close/open
BI GCB feedback
Alarm detection:
immediatelly
active
closed
opened
Alarm: GCB fail
BI GCB feedback
BO GCB close/open
Alarm detection:
immediatelly
active
opened
closed
BO: MCB UV coil
FwRet break
RPM / fg / Ug
EmergStart del
2s
BO: MCB OFF coil
BI: MCB fdb neg
BI: MCB fdb
BO: Mains OK
BO: MCB status
BO: Fuel solenoid
FwRet break dealy is between MCB
status deactivation and command for
GCB closing.
BO: MCB close/open
Generator voltage is within limits
BO: GCB close/open
BO: GCB ON coil
If mains returns in this moment,
starting sequence is interrupted
and MCB stays closed. It is valid
until the moment when generator
voltage is within limits.
MCB opens on = GENRUN:
Other CB fail reasons:
When the BO CB close/open is in steady state and CB feedback is changed, the CB fail is detected
immediately (no delay).
When the BO CB close/open opens, there is 5 resp. 2 sec delay for the breaker to respond before a CB
fail is detected. In such case, if CB OFF coil is used for opening the CB and CB fail occurs during
opening the CB, the signal CB OFF coil is automatically extended until the breaker opening is detected
(evaluated as CB status).
2 sec when the CB is used for synchronizing
5 sec in other cases
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 28
28
Alarm: GCB fail
BO GCB close/open
BI GCB feedback
active
opened
opened
Time delay
5 sec
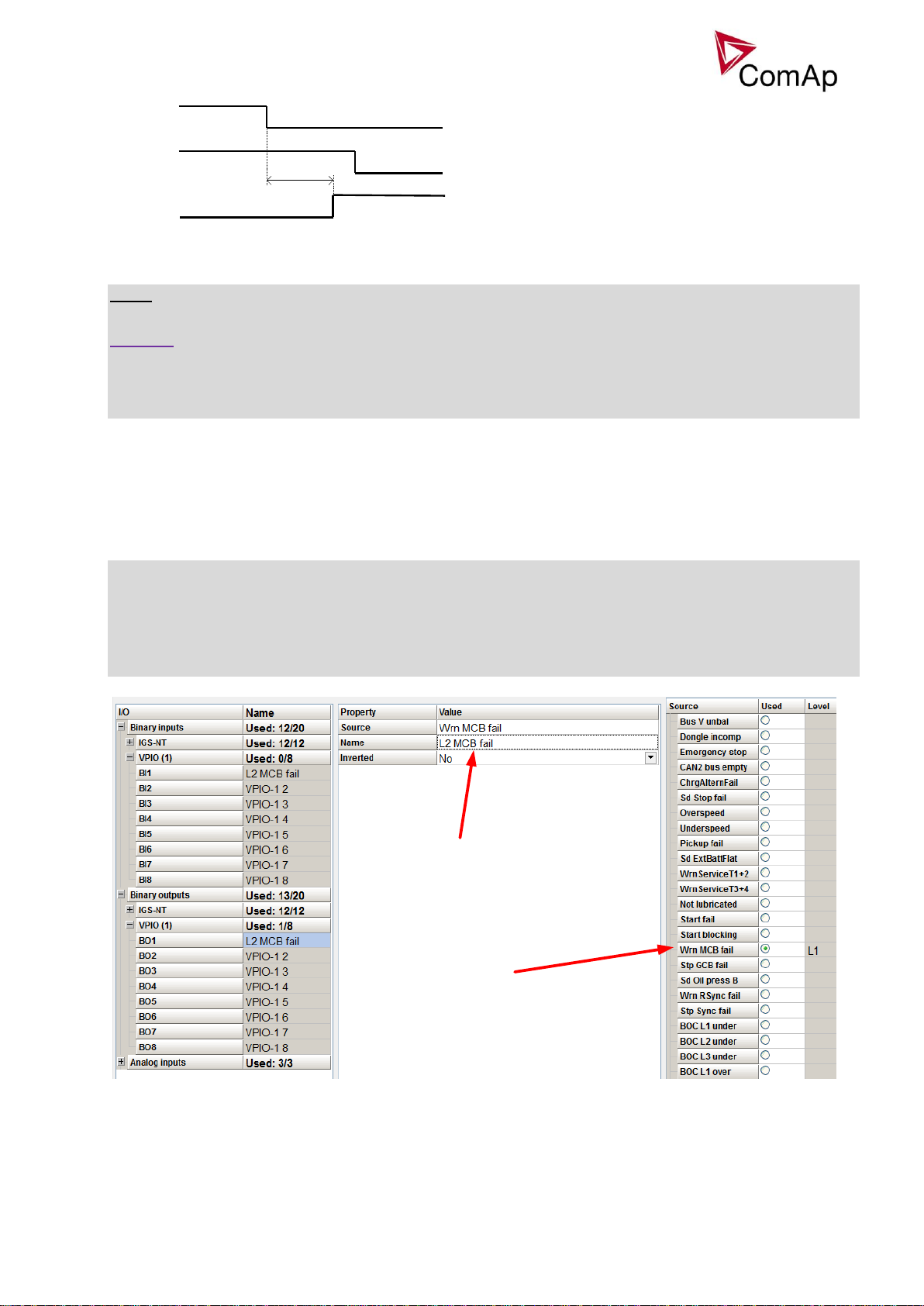
Rename the VPIO to suitable name
(e.g. L2 MCB fail, which indicates that it is
Level 2 alarm)
Choose Wrn MCB fail from Prg. States group on
any VPIO output
In case that CB fail is detected after switching the controller on (CB is closed), the CB OFF coil output is
activated immediatelly.
NOTE:
If the MCB or GCB feedback gets active during synchronization the breaker is imediately closed.
CAUTION!
In case that MCB feedback is active (MCB is expected as closed) and “MCB fail” is reported due to previous
incorrect manipulation of MCB, in the moment of Fault reset, the MCB fail is cleared and the controller
internally goes to “closed” state. I.e. MCB fdb status is confirmed and the output MCB close/open is
energized.
MCB fail Information
Opening of the MCB externally is allowed because external protection device may open it based on its
protections. The controller will try to reclose the breaker if Mains protect type protection is not configured
accordingly (e.g. external protection device/relay does not allow user to send this type of signal or such
wiring is impractical). After failed attempt to close the breaker, the controller issues standard alarm and in
AUT mode starts the engine and consequently closes GCB breaker.
Warning!
In this case, if the supposed opening of the MCB is caused merely by MCB feedback failure and
the actual position of the MCB is still closed, the controller will close GCB to the Mains voltage
directly without synchronizing because it cannot be distinguished what exactly happened. This
situation can be possibly harmful to the personnel or the equipment. Should this be the case, the
following solution is proposed:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 29
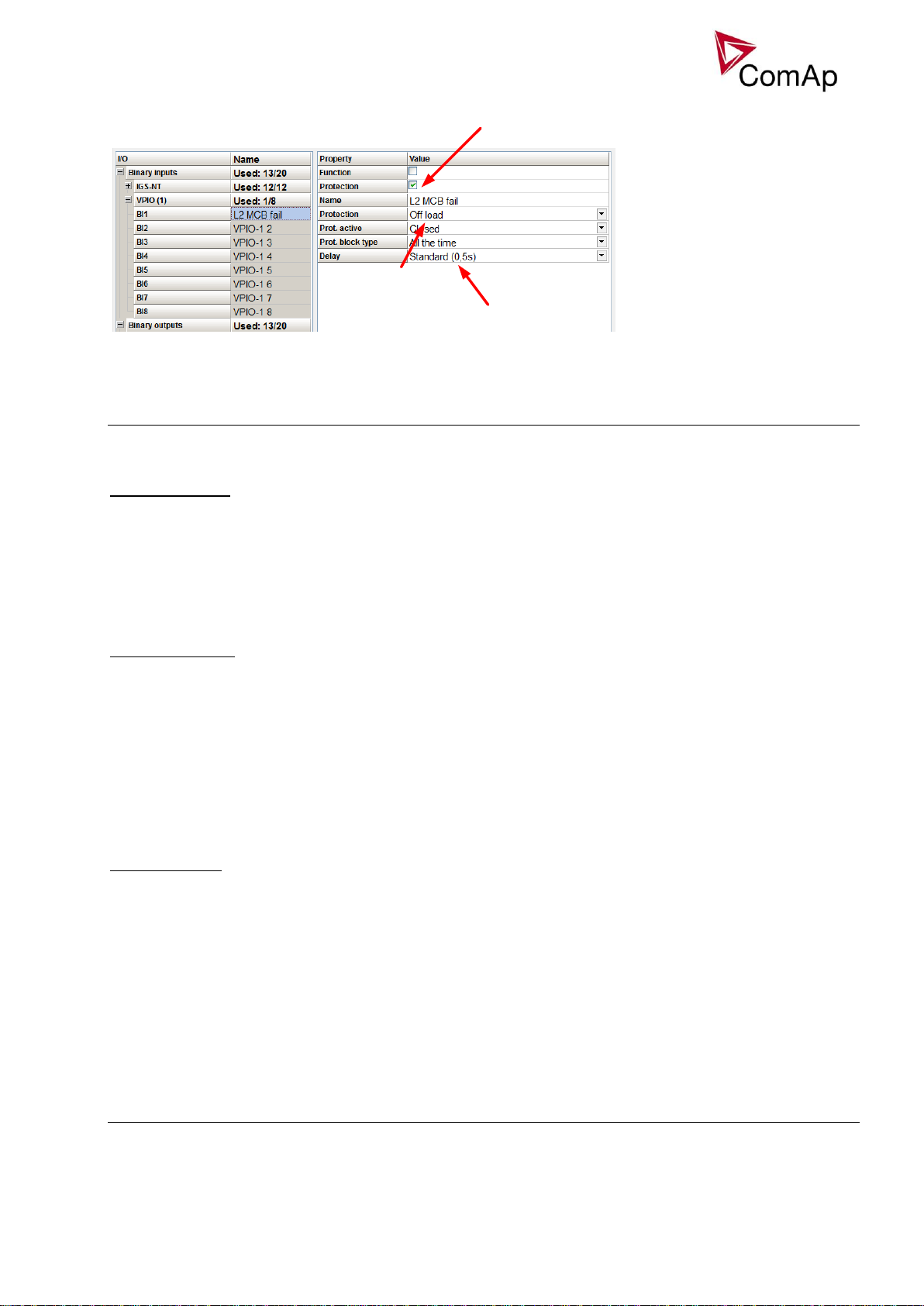
29
Adjust the delay if required (since the start of the engine
can take up considerable time, 0.5s should be sufficient)
Toggle on the protection for the interconnected VPIO input
(e.g. BI VPIO-1 1 is interconnected with BO VPIO-1 1)
Set the type of the
protection to Off load
External breaker control
This application accepts external breaker control in these situations:
MINT application:
Mode:MAN, SEM
External breaker control is accepted only when LBI:ReadyToLoad=1
Exceptions:
If the BUS voltage is >15V and GCBfdb=1 and LBI:ReadyToLoad=0 then BO GCB Fail and History record
are performed
SPtM application:
Mode:SEM
External MCB control is accepted
External GCB control is accepted only when LBI:ReadyToLoad=1
Exceptions:
If the Mains parameters are out of limits (voltage and frequency) and GCB and MCB are closed and
LBI:ReadyToLoad=1 – external control is not accepted – Wrn MCB fail and Wrn GCB fail are evaluated.
If the Mains voltage is > 15V and MCBfdb=1 and GCBfdb=1 and LBI:ReadyToLoad=0 then BO GCB Fail
and History record are performed.
SPI application:
Mode: SEM
External GCB control is accepted only when LBI:ReadyToLoad=1
Exceptions:
If the Mains parameters are out of limits (voltage and frequency) and GCB and MCB are closed and
LBI:ReadyToLoad=1 – external control is not accepted – Wrn MCB fail and Wrn GCB fail are evaluated.
If the Mains voltage is > 15V and MCBfdb=1 and GCBfdb=1 and LBI:ReadyToLoad=0 then BO GCB Fail
and History record are performed.
Peak shaving based on Active and Apparent power
The Peak shaving function is active only in AUT mode in parallel to Mains operation. Peak shaving is based
on Object P or Object Q (consumption of load). If load consumption increases over
ProcessControl:PeakLevelStart or ProcessControl:PeakKVAStart for period longer than
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 30
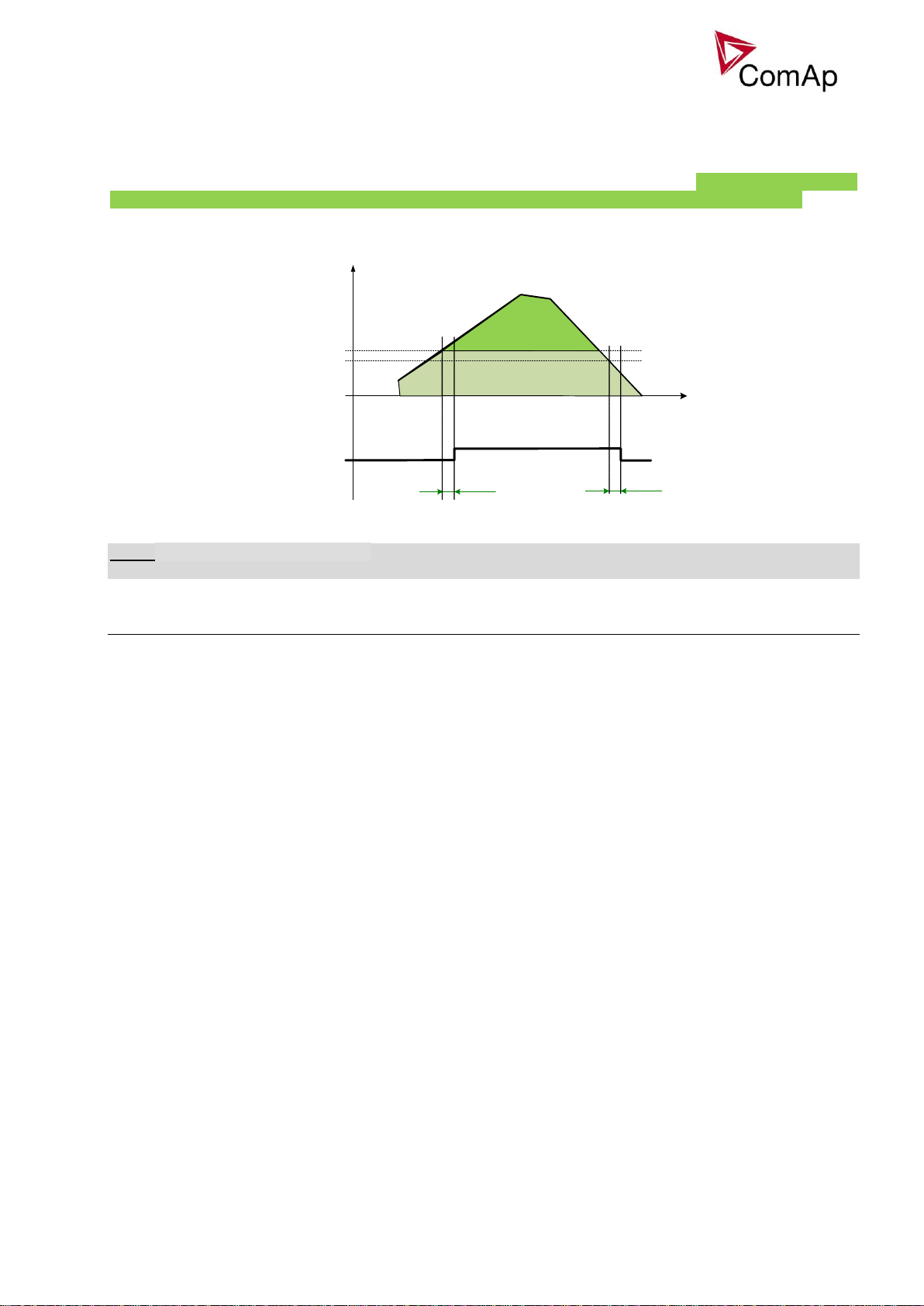
30
PeakLevelStart
PeakAutS/S del
Actual power [ kW
]
Time
PeakLevelStop
PeakAutS/S del
Sys start/stop
ProcessControl:PeakAutS/S or ProcessControl:PeakKVAS/S del the gen-set is started (BO Sys start/stop
is activated). If load consumption decreases below ProcessControl:PeakLevelStop or
ProcessControl:PeakKVAStop for period longer than ProcessControl:PeakAutS/S del or
ProcessControl:PeakKVAS/S del the gen-set is stopped. Both Peak shaving based on kW and kVA can
work simultaneously (SYS START/STOP is activated if at least one condition is fulfilled). Peak shaving based on
Apparent power is available in InteliGen-NT Basebox, InteliGen-NTC Basebox and InteliSys-NT only.
Figure: Example of peak shaving function based on Active power (the same function for Reactive power)
NOTE:
Function Peak Shaving based on Apparent power is not available for IG-NT-GC controller.
Remote Alarm Messaging
It is possible to use up to five channels for Active Call, Email and SMS upon defined type of Alarm. It is
possible to define protection type for all ENABLED channels to react. All the possibilities in the controller are:
History record, Alarm only, Warning, Mains protect and Mains protect with Reset. Find more information
about alarm types in the chapter Protections and alarm management.
Communication Types for Remote Alarm Messaging
Below there all types of communication available for each Active Call channel.
DATA-ANA: This option sends a complete archive to the recipient's PC via analog modem. An analog
modem must be connected either to one of controller COM ports or to one of I-LB modules connected to the
controller via CAN2 bus. The channel address must contain complete telephone number of the recipient's
PC where InteliMonitor is running in Active call receiving mode.
DATA-GSM: This option sends a complete archive to the recipient's PC via GSM modem. A GSM modem
with activated CSD data transfers must be connected either to one of controller COM ports or to one of I-LB
modules connected to the controller via CAN2 bus. The channel address must contain complete telephone
number of the recipient's PC where InteliMonitor is running in Active call receiving mode.
DATA-ISDN: This option sends a complete archive to the recipient's PC via ISDN modem. An ISDN modem
must be connected either to one of controller COM ports or to one of I-LB modules connected to the
controller via CAN2 bus. The channel address must contain complete telephone number of the recipient's
PC where InteliMonitor is running in Active call receiving mode.
DATA-CDMA: This option sends a complete archive to the recipient's PC via CDMA modem. A CDMA
modem must be connected either to one of controller COM ports or to one of I-LB modules connected to the
controller via CAN2 bus. The local CDMA network must allow point-to-point data transfers. The channel
address must contain complete telephone number of the recipient's PC where InteliMonitor is running in
Active call receiving mode.
SMS-GSM: This option sends a short text message (SMS) containing the actual Alarmlist contents to the
recipient's mobile phone via the GSM modem. The channel address must contain complete telephone
number of the recipient's mobile phone.
SMS-CDMA: This option sends a short text message (SMS) containing the actual Alarmlist contents to the
recipient's mobile phone via the CDMA modem. The channel address must contain complete telephone
number of the recipient's mobile phone.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 31

31
IB-E-MAIL: This option sends an e-mail containing the actual Alarmlist contents and latest 20 history records
(only date, time, reason) to the recipient's mailbox via the IB-COM module or IG-IB module. The channel
address must contain valid e-mail address of the recipient.
NOTE:
The SMTP settings (SMTP authent,SMTP user name, SMTP password, SMTP address, Contr mailbox) must
be properly adjusted for sending e-mails.
Example of setting
There is an example of setting of Remote Alarm Messaging. In this case active calls we be triggered on
Mains protect and Mains protect with Reset alarms. Message is sent via email to
emailAddress@domain.com (Channel 1 – available for NTC controller or with any controller with connected
IB-NT or I-LB+), archive is sent via ISDN modem to the number +111222333444 (Channel 2) and SMS is
sent to the number +999111333555 (Channel 3).
It is also possible to adjust number of attempts that controller performs in case of not successful Active Call –
Comms settings:ActCallAttempt. The language of messages can be changed –
Comms settings:Acall+SMS lang (use Translator and Languages tabs in GenConfig to adjust languages).
Up to five channels can be used.
Variable speed support
This fw contains variable speed support which is used on Hybrid ship (ship with DC bus).
Variable speed control is usually used on ship where the gen-sets work in long term period on small load. By
changing speed on genset is possible to achieve lower fuel consumption.
Frequency (and Voltage) are usually control according to current load.
For variable speed is used:
Setpoints:
Nominal freq 30..65 Hz (step 1 Hz) FV (Basic settings Group)
ForceBlock6Del 0-60s (step 0,1s) FV (Delays/Timers Group)
GenNomV, BusNomV FV (Basic settings Group)
Voltage dependence on frequency
In generator is induced magnetic flux, which is almost constant in various RPM.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 32

32
30Hz
50Hz
138V
230V
voltage
frequency
Magnetic flux =U/f ~konstant
It is necessary to change nominal frequency together with nominal voltage – due to their dependence.
Temporary blocking of fix frequency and voltage protections
Temporary blocking of frequency and voltage fix protections
After submitting a request for change of nominal frequency and voltage the generator needs some time for
performing the changes. During this time the fix frequency and voltage protections (connected to nominal
values) must be blocked.
The time need for blocking of these protections is set by setpoint:
ForceBlock6Del 0-60s (step 0,1s) FV (Delays/Timers Group)
HINT
With larger frequency range the regulation can be rougher, in this case the AC/DC inverter is expected.
WARNING!
Used generator should be designed for variable rotation.
With frequency changes the nominal value of Voltage must be also changed.
Force value – step by step guide
In this chapter there is complete step by step guide which shows how to use Force value function of the
controller.
Forcing of values is used to change particular setpoint temporarily by activation of related Binary Input. This
is used to change function of controller under given conditions (e.g. there are two different periods during the
day when Export limit given by distribution network is required or not).
WARNING!
Setpoints must not be written continuously (e.g. via Modbus connection)! If continuous change of setpoints
is required, combination of External values and Force value function needs to be used. The memory that
holds setpoints is designed for up to 105 writings. Than memory may be damaged!
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 33

33
Add or remove Force value
Change position of Force value functions (priority)
Change the name of the source setpoint
(available only for Force value 1-16 setpoints)
Select the value that should be forced (i.e.
the value of the particular setpoint)
Rename binary input that
triggers the forcing
ID of binary input
(1 for ForceValueIn 1 etc.)
Select source setpoint or value
Setpoints that are available for forcing may be identified by Force value button on the right side in GenConfig
(see the figure below).
When the button is clicked, Force value dialog appears.
For example if we add Force value:Force value 1 to be forced to ProcessControl:Export limit as value 0
(DISABLED) by Binary Input FORCEVALUEIN 1 we can change the function of Export limit from ENABLED to
DISABLED by activation of FORCEVALUEIN 1. It is possible to rename the setpoint to e.g.
Force value:ExportDisabled and Binary Input as well to e.g. DISABLEEXPLIM. The function will not change
(only the corresponding names).
It is possible to use several force value functions for one setpoint. If more than one forcing Binary Input is
active, the one with the highest position (lowest number in the Force value dialog) is used.
It is possible as well to use one Binary Input to force multiple setpoints (e.g. in case of complex function
change).
NOTE:
It is possible only to force value or setpoint in other setpoint if their dimension and range are the same (e.g.
only value with dimension in hours and which is Integer 16 to a setpoint with dimension hours and which is
as well Integer 16). You may use PLC block Convert to change the dimension and range if needed.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 34

34
Values for continuous writing from external sources
This function is especially designed for continuous writing of setpoints from external sources (e.g. via
Modbus connection).
WARNING!
Setpoints must not be written continuously (e.g. via Modbus connection)! If continuous change of setpoints
is required, combination of External values and Force value function needs to be used. The memory that
holds setpoints is designed for up to 105 writings. Than memory may be damaged!
It is possible to use up to four different External values for continuous writing from external sources. The
values are adjusted by setpoints in Force value group. Default (also initial) value may be adjusted, rate of
change of ExtValueX (by Binary Inputs EXTVALUEX UP and EXTVALUEX DOWN) can be adjusted as well as
high and low limit of the value.
There are two way, how to adjust External values. One is using Binary Inputs mentioned above. Second one
is to write the value directly using e.g. Modbus. External values then may be converted using PLC block
convert and force into setpoint which is then continuously forced (note: NOT WRITTEN) by the value of
ExtValueX. This way internal memory is safe and no damage may occur.
External values are reverted back to their default (initial) value (given by corresponding setpoint) when
Binary Input for their reset is active (and they change to the previous value after Binary Input deactivates).
When the Binary Input is active the External value cannot be changed by Modbus writing or by using Binary
Inputs for up and down value.
NOTE:
External values are not available for external writing when any Binary Input (up, down or reset) related to
them is active.
Note also that when the controller is reset (powered down and up again), all external values are reverted
back to their default (initial) values.
HINT
For information on how to write (or read) objects from controller via Modbus, please refer to the latest
Communication guide for InteliGen and InteliSys.
User Buttons
There are several User Buttons available in the controller. It is possible to set them on Soft Buttons in
InteliVision 5 or 8.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 35

35
Selects which button is this function mapped to
(0 – first button, 1 – second button and so on)
Choose UserButton index and
its function (ON/OFF etc.)
Choose which colour will be
available for this button
Select which condition triggers
which coulour
Adjust text for the button
when it is active or inactive
ON
Pressing the button changes the state of log. Binary Output USER BUTTON X to closed.
When the output is closed and the button is pressed state is not changed.
OFF
Pressing the button changes the state of log. Binary Output USER BUTTON X to opened.
When the output is opened and the button is pressed state is not changed.
ON/OFF
Pressing the button changes the state of log. Binary Output USER BUTTON X to opened or
closed depending on previous state (it is changed to the opposite state).
PULSE ON
Pressing the button issues log. Binary Output USER BUTTON X to close for one second.
NOTE:
Repeated pressing of button during the closed period (one second) causes issuing other
puls of length of one second to be generated from the moment of button pushing.
Available functions for soft buttons are listed in the following table.
HINT
It is possible to lock User Button with password (go to tab Commands in GenConfig). User Buttons 1-5, 6-8
and 9-16 can be locked separately. It is also possible to use User Buttons in SCADA diagrams.
User Mask function
In GenConfig you can easily set any object in Screen Editor to show or hide based on activation of particular
Logical Binary Input available for users. Below, there is diagram showing the setup of User Mask function in
Screen Editor.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 36

36
Select the proper function
Show = appears when LBI gets active
Hide = disappears when LBI gets active
None = no function
Select the object
Select which User Mask is used for
this object
NOTE:
Masking of screens in InteliVision 5 supports only Show function
Use also other masking functions (masking can react on several internal states, e.g. activation of Timers).
Remote Control Function
It is possible to remotely control several Binary Outputs in the controller. You can either use Remote
Switches tool in InteliMonitor (select Remote switches in menu for corresponding controller), import Remote
Switches tool to a SCADA diagram in Line Diagram Editor or use external device via Modbus (register
#46361 and command #26 (1A hex), for more information on Modbus please refer to the InteliGen/InteliSys
Communication guide).
Remote Switch will activate or deactivate depending on remote control so it can be used to manually control
devices, simulate malfunctions while commissioning etc.
Figure: Remote Switches tool in InteliMonitor, Remote Switches tools in Line Diagram Editor and Mobus commands
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 37

37
LBO:RemoteControl1 LBI:Emerg. manual
Remote Switch
command
Vitual Output
Virtual Input
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
VPIO module
Remote Switches may be easily used to trigger logical Binary Input function and all other related functions as
normal switch on Binary Input. Module VPIO (Virtual Peripheral Inputs- Outputs) can be added to
configuration and it will copy the state of Remote Switch on virtual output to its counterpart virtual input.
Refer to the figure below for example.
Virtual Peripheral Inputs-Outputs (VPIO) module
For the controller there are several modules available. One of them is Virtual Peripheral Inputs-Outputs
module which is particularly usefull for connection of logical Binary Output functions to logical Binary Input
functions. This way internal controller function may easily trigger other internal controller functions without
unnecessary wiring or usage of PLC functions.
Module is functioning the same way as normal module with 8 outputs and 8 inputs, but the difference is, that
each input copies its counterpart output. It is possible to select any logical Binary Output function for one of
the outputs of VPIO module. Inputs on VPIO module work the same way as standard input of the controller
(i.e. it can be assigned function and protection).
For example of this function please refer to the chapter Remote Control function.
Shared Inputs and Outputs
It is possible to share Binary and Analog values between all the controllers via CAN bus, thus saving
physical Inputs and Outputs and excess wiring.
Figure: Using of Remote Switches to trigger logical binary inputs
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 38

38
SHBOUT (1) SHBIN (1)
SHBOUT (2)
Not Received
Module SHBIN (2) is not
inserted
SHBOUT (3)SHBIN (3)
SHBIN (2)
Not Received
Module SHBIN (3) is not
inserted
Not Received
Module SHBIN (1) is not
inserted
CAN
CAN
Controller 1 Controller 2
Controller 3
Shared Binary Inputs and Outputs may be used exactly in the same way as standard physical Inputs and
Outputs. If SHBIN or SHAIN modules are configured, at least one corresponding module of SHBOUT or
SHAOUT (respectively) is needed. If it is not configured, corresponding protection appears because SHBIN
or SHAIN will be missing. See the figure below for more information.
CAUTION!
For proper function of Shared Binary and Analog Inputs and Outputs, only one source of Shared Binary or
Analog Outputs must be configured (i.e. it is not possible to configure in one controller SHBOUT1 and to
another one as well SHBOUT1).
HINT
Controller sends Shared Binary Outputs each 100ms if there are any changes in any bit position. If there are
no changes, controller sends the information with period 1s.
Figure: Adding of various modules
Figure: Principal Scheme (same for shared Binary I/O and shared Analogue I/O
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 39

39
SHBIN (1)
SHBOUT (2)
Not Received
Module SHBIN (2) is not
inserted
SHBOUT (3)SHBIN (3)
CAN
Controller 2
Controller 3
Not Transimitted
Module SHBOUT (1) is not
inserted
Level 1, Level 2 or no protection is displayed
DISTBOUT
DISTBIN
-01
DISTBIN
-02
DISTBIN
-03
DISTBIN
-04
Controller CAN 1
DISTBOUT
DISTBIN
-01
DISTBIN
-02
DISTBIN
-03
DISTBIN
-04
Controller CAN 2
DISTBOUT
DISTBIN
-01
DISTBIN
-02
DISTBIN
-03
DISTBIN
-04
Controller CAN 3
DISTBOUT
DISTBIN
-01
DISTBIN
-02
DISTBIN
-03
DISTBIN
-04
Controller CAN 4
CAN communication
Distributed Binary Inputs and Outputs
It is possible to share Binary and Analog values between all the controllers via CAN bus, thus saving
physical Inputs and Outputs and excess wiring.
DISTBIN and DISTBOUT work in a different way than SHBIN and SHBOUT. Each controller has one pack of
eight DISTBOUT available (if not configured or no function is assigned to any output, it does not broadcast
them). The number of DISTBOUT module is not shown in the configuration and it is always corresponding to
the CAN address of the controller (e.g. the controller with address 5 will be broadcasting DISTBOUT-05
which can be received if module DISTBIN-05 is configured in another controller. Up to 32 DISTBIN modules
can be configured (meaning that the controller will be receiving all DISTBOUT from all the controller, even
his own).
It is not possible to change the name of DISTBIN inputs or add protections.
In the example below you can see 4 controllers with various DISTBIN and DISTBOUT configuration.
NOTE:
HINT
Controller sends Distributed Binary Outputs each 100ms if there are any changes in any bit position. If there
are no changes, controller sends the information with period 1s.
NOTE:
DISTBIN and DISTBOUT function is not available for IM-NT-GC and IG-NT(C)-GC controller.
NOTE:
DISTBIN and DISTBOUT function is conditioned by IGS-NT-LSM+PMS dongle.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 40

40
Modbus Reading and Writing
User Modbus register number
Standard Modbus register number
Communication object number
Value, Setpoint, Alarm state
Select type
Select object
Controller supports Modbus Slave functions (an external device may write or read from a controller). Modbus
registers corresponding to objects in the controller can be exported to text form in GenConfig.
Figure: Exporting of Modbus registers
If Modbus Master function is required extension module I-CB/Modbus connected via CAN1 can be used. For
more information on how to use this module please refer to InteliGen/InteliSys Communication Guide and to
I-CBEdit manual.
User MODBUS
Users can define Modbus registers from 42873 to 43000. Values, setpoints and Alarm states can be
specified for these new Modbus registers to prepare the Modbus protocol for batch reading and writing or to
standardize Modbus protocol between FW versions or branches.
NOTE:
User MODBUS function is not available for IM-NT-GC controller.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 41

41
Modbus Switches
Register for writing
Modbus register number
Value for back-reading
Modbus register number
ModbusSw1
46337
ModbusSw1
40547
ModbusSw2
46338
ModbusSw2
40548
Register port for writing
Input value
LBO ModbusSw16 ………………….ModbusSw1
ModbusSw1 (46337)
000F HEX
0000 0000 0000 1111
Register port for writing
Input value
LBO ModbusSw32 ………………….ModbusSw17
ModbusSw2 (46338)
F000 HEX
1111 0000 0000 0000
Group
PLC Block
IS-NT-GeCon
MARINE
3.0
IG-NT-GeCon
MARINE
3.0
Logical function
OR/AND
128
32
The “Modbus Switches” contains of two groups of LBOs named “ModbusSw1” and “ModbusSw2”. Both
registers are available on Modbus for simple writing (using command 6 or 16). The particular bits of these
registers are available as binary status for universal use in logical binary outputs of the controller as
“ModbusSw1..ModbusSw32”. No password is required for writing of those registers. There are two Values
“ModbusSw1” and “ModbusSw2” in group “Log Bout” available for back-reading.
NOTE:
The LSB of ModbusSw1 (46337) corresponds with LBO “ModbusSw1”
The LSB of ModbusSw2 (46338) corresponds with LBO “ModbusSw17”
The Values ModbusSw1 and ModbusSw2 have the position of LSB opposite-wise.
Examples:
Power Formats
IGS-NT family allows user to choose from several Power Formats that affect dimensions in which values and
some setpoints are interpreted or adjusted. Power formats may be changed in Miscellaneous tab in
GenConfig. There are following Power Formats available:
1 kW kVAr kVA kX V
0,1 kW kVAr kVA kX V
0,01 MW MVAr MVA MX kV
0,01 MW MVAr MVA MX V
NOTE:
Range of some setpoints and values is changed significantly when different Power Formats are selected.
Last Power Format is designed to be used in combined Power/High Voltage and Low Voltage instalations.
High voltage is then interpreted in Volts (e.g. 33256V instead of 33kV).
Last two Power Formats can be used in combination on one CAN bus.
PLC functions
Following functions are available in IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE firmware.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 42

42
XOR/RS
128
32
Comparators
Comp Hyst
16
4
Comp Time
16
4
Comp Win
16
4
Math operations
Math Fc
16
2
Ext Math Fc 8 2
Interp. Fc’B’ 8 1
Math AxB/C 4
Regulators
PID Ana B 4 2
PID Bin 4 2
Ramp functions
Ramp 4 2
Up/Down 4 2
Inc/Dec 2 2
Mov Avg 2 1
Time functions
Timer 4 1
Delay
16
Delay „B“
8
8
Others
Ana Switch
16
2
Force Hist 4 4
Force Prot 4 4
Jump 4 4
Mux Const. 4 4
Counter 4 1
Decomp 4 4
Convert
10
10
Multi language support
NT Family controllers support up to three Languages that is possible to switch during controller duty. Every
terminal (i.e. Remote display or PC-InteliMonitor) can be switched to different language. Use PC-GenConfig
- Translator tool to translate texts to another language.
Default application archives contain all texts in English only.
ECU interface customizing
The list of available ECU interfaces can be found in GenConfig / Modules / ECU list.
In sw GeCon is possible to configure the any ECU communicating via J1939, but controller can read
information only. Writing any information is not possible. ECUs comunicate via modbus are not supported.
Volt/PF control adjustment
IG-AVRi output connection
Every time refer to corresponding AVR manual before interface connecting. Use no droop AVR.
IG-AVRi-TRANS (AC power supply for AVRi) has to be supplied from gen-set voltage.
AVRi outputs can be connected as symmetrical: OUT1-OUT2 or unsymmetrical OUT1-OCOM or OUT2OCOM.
Potentiometer on the AVRi defines maximal OUT1, OUT2 voltage range.
Use symmetrical (OUT1,OUT2) AVRi output to connect the AVRi to AVR auxiliary voltage input.
Use unsymmetrical output if an external AVR potentiometer has to be replaced with AVRi.
AVRi output voltage should change generator voltage typically in range 10 % of Nominal voltage.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 43

43
100.0 %
10 V
0 V
AVR DCout bias
0 %
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
s
e
t
t
o
m
i
n
i
m
u
m
2 V
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
s
e
t
t
o
m
a
x
i
m
u
m
OUT1 – OCOM [V]
100.0 %
10 V
0 V
AVR DCout bias
0 %
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
s
e
t
t
o
m
i
n
i
m
u
m
2 V
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
s
e
t
t
o
m
a
x
i
m
u
m
OUT2 – OCOM [V]
[V]
100.0 %
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
=
m
a
x
i
m
u
m
AVR DCout bias
10 V
Out1 to Out2
0 V
0 %
-10 V
A
V
R
i
p
o
t
=
m
i
n
i
m
u
m
50 %
AVRi output voltage
Out1 - OCOM
Out2 - OCOM
Out1 – Out2
Bias \ Pot
Min
Max
Min
Max
Min
Max
0 %
0 0 2
10
- 2 V
-10 V
50 %
1 5 1 5 0 V
0 V
100 %
2
10 0 0
+ 2 V
10 V
For more details please refer to Installation guide – chapter AVR interface examples.
AVRi Out1 or Out 2 to GND output voltage depends on AVRi trim setting
AVRi Out1 to Out 2 output voltage
Voltage control adjustment
HINT:
To judge optimal adjusting induce generator voltage jumps by AVR DCout bias change or by Nominal
voltage change .
AVRi output OCOM is common output. GND was used instead of OCOM
PF control adjustment
The genset should be cca 30 % loaded in parallel to mains and baseload mode.
1) Set the same values PF gain, PF int as in voltage control loop.
2) Set Process control: #SysLdCtrl PtM = BASELOAD, #SysBaseLoad = 30 % of Nominal load,
#SysPFCtrl PtM = BASEPF, #SysPwrFactor = 1.0.
3) Start and synchronize the gen-set in MAN Mode by pressing GCB ON/OFF
4) When running in parallel 30% loaded increase slowly PF gain to unstable point and then decrease
value by 30 % to insure stable performance.
5) Adjust PF int (usually setting to 100% gives optimal performance).
Hint:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
1) Set Voltage gain, Voltage int to zero and AVR DCout bias to 50%.
2) Start always with AVRi pot min adjustment (fully counterclockwise).
3) Start the gen-set in MAN Mode to nominal speed, without load.
4) Adjust generator voltage to nominal value by the potentiometer present on the AVR. If there is no
potentiometer on the AVR, use AVR DCout bias to adjust the nominal voltage.
5) Change AVR DCout bias to 0% and 100% to check generator voltage control range (typically 10
% of nominal voltage). Adjust voltage control range by AVRi trim.
6) Set AVR DCout bias to be Nominal voltage on generator (50%).
7) When gen-set is running unloaded increase carefully Voltage gain to unstable point and then
decrease value by 30 % to insure stable performance.
8) Adjust Voltage int (usually setting to 100% gives optimal performance).
Page 44

44
RPMRPM
Volt [V] Volt [V]
0 V
+10 V- 10 V
Speed governor
voltage output1500 0 V
- 10 V
1500
+10 V
Speed governor
voltage output
+ 5 % of nominal+ 5 % of nominal
- 5 % of nominal - 5 % of nominal
To judge optimal adjusting induce generator power jumps by SysBaseLoad change or by soft changes of
AVR DCout bias.
Sync/load control adjustment
HINT:
Use isochronous speed governor.
Two wire shielded connection from IGS-NT SPEED GOVERNOR output (SG OUT, SG COM) to Speed
governor auxiliary input is recommended.
A full range change of the IGS-NT speed governor output (from SpeedGovLowLim to SpeedGovHiLim)
should cause 5-10% change of the engine speed (SpeedGovLowLim ~ 95% RPMnom, Speed gov bias ~
100% RPMnom, SpeedGovHiLim ~ 105% RPMnom.
IMPORTANT
Speed governor has to be adjusted for optimum performance before Sync / load control adjusting.
Check generator phase sequence before the first GCB connection.
SpeedRegChar = POSITIVE SpeedRegChar = NEGATIVE
Before optimal Sync/load setpoints adjusting disconnect GCB OPEN/CLOSE output or set Phase window =
0 to avoid paralleling.
Synchronizer adjustment
1) Start the engine in MAN Mode.
2) Set the engine RPM by speed trim on speed governor or by Speed gov bias and SpeedGovLowLim and
SpeedGovHiLim to Nominal frequency.
3) To start synchronizing press GCB ON/OFF button. GCB LED starts to flash to indicate synchronization.
To stop synchronization press again GCB ON/OFF .
Slip control adjusting:
4) Adjust Freq gain to unstable speed control and decrease value by 30 % to insure stable performance.
5) Adjust Freq int to stable (fast and smooth) slip control. Synchroscope movement on the controller
measure screen should slow down and stop (in any position, because Angle control is off).
Angle control adjusting:
6) Set Angle gain. Synchroscope on the controller measure screen should move slowly and stop in “up“
position. Set Angle gain to unstable value (synchroscope swings) and decrease value by 30 % to
insure stable performance.
Load control adjustment
Prior to Sync/Load control adjustment, the Volt/PF control has to be adjusted! Load control loop is active in
parallel to mains mode only (MCB feedback closed). Switch off other engines while adjusting.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 45

45
MAINS
LOAD
GEN
P > 0 Import
P > 0 Consumption
P> 0 Generation
Q> 0 Import
Q> 0 Consumption
Q> 0 Generation
Cos > 0 C
Consumption P
Capacitive LOAD
Cos > 0 L
Consumption P
Inductive LOAD
P
Q
Cos < 0 L
Export P
Import Q
Cos < 0 C
Export P
Export Q
Cos > 0 C
Import P
Export Q
Cos > 0 L
Import P
Import Q
P
Q
Cos < 0 L
Consumption P
Generation Q
Cos < 0 C
Consumption P
Consumption Q
Cos > 0 C
Generation P
Consumption Q
Cos > 0 L
Generation P
Generation Q
P
Q
1) Set #SysLdCtrl PtM = Baseload, set Baseload value to 30 % of Nominal power of one gen-set.
2) Set Load gain to the same value as Slip freq gain. Set Load int to zero.
3) Start the gen-set in MAN Mode, press GCB ON/OFF button to synchronize and close gen-set to mains.
4) When GCB is closed, gen-set load slowly increases to Base load value. Check that gen-set power is
positive (CT polarity!).
5) Increase Load gain to unstable load control and decrease value by 30 % to insure stable performance.
When Load int factor is set to zero gen-set load can differ from required Baseload.
6) To adjust and optimize Load int change several times Base load between 30 and 70 % of Nominal
power. Usually setting Load int to 100% gives optimal performance.
7) When gen-set is running full load check if
a. Speed governor output voltage value is not limited (not reached SpeedGovLowLim or
SpeedGovHiLim)
b. Speed governor actuator isn’t mechanically limited or operates in small section of throttle range.
Active and reactive power terminology
Mains
Exported active power is supplied to the mains. It is displayed in negative numbers e.g. –20kW.
Imported active power is consumed from the mains. It is displayed in positive numbers e.g. +20kW.
When reactive power is imported (>0) InteliMains-NT displays L (inductive) character of the load.
When reactive power is exported (<0) InteliMains-NT displays C (capacitive) character of the load.
Load
Active power consumed by Load is displayed in positive numbers e.g. 20kW.
When reactive power is positive (>0) InteliMains-NT displays L (inductive) character of the load.
When reactive power is negative (<0) InteliMains-NT displays C (capacitive) character of the load.
Genset
Generated active power is displayed in positive numbers e.g. 20kW.
When reactive power is positive (>0) IGS-NT displays L (inductive) character of the load.
When reactive power is negative (<0) IGS-NT displays C (capacitive) character of the load.
Synchronizer adjustment
7) Start the engine in SEM Mode.
8) Set the engine RPM by speed trim on speed governor or by Speed gov bias and SpeedGovLowLim and
SpeedGovHiLim to Nominal frequency.
9) To start synchronizing press GCB ON/OFF button. GCB LED starts to flash to indicate synchronization.
To stop synchronization press again GCB ON/OFF .
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 46

46
Slip control adjusting:
10) Adjust Freq gain to unstable speed control and decrease value by 30 % to insure stable performance.
11) Adjust Freq int to stable (fast and smooth) slip control. Synchroscope movement on the controller
measure screen should slow down and stop (in any position, because Angle control is off).
Angle control adjusting:
12) Set Angle gain. Synchroscope on the controller measure screen should move slowly and stop in “up“
position. Set Angle gain to unstable value (synchroscope swings) and decrease value by 30 % to
insure stable performance.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 47

47
Protections and Alarm management
Setpoint group
Analog protections
Configurable
Analog protect
Generator protections
Configurable
Gener protect
Mains protections – should not be used in MINT
application
Configurable
Mains protect
Fix protections
Fix
Gener protect – part of them,
Analog protect – part of them
ALARM/EVENT KIND
LEVEL
DESCRIPTION
Warning
1
The alarm appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log.
Activates the output Common Wrn as well as the standard alarm outputs.
Alarm Only
1
The alarm appears only in the Alarmlist.
Activates the output Common Al as well as the standard alarm outputs.
HistRecOnly
1
The event is recorded into the history.
Activates the output Common Hst for one second. Standard alarm outputs
are not activated.
AL indication
1
The event is only indicated in the Alarmlist.
It disappear for the alarmist automatically as soon as the cause
disappears.
Standard alarm outputs are not activated.
A+H indication
1
The event is only indicated in the Alarmlist and recorded into the history
log.
It disappear for the alarmist automatically as soon as the cause
disappears.
Standard alarm outputs are not activated.
Shutdown
2
The alarm appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log.
It causes immediate open the GCB (Stop pulse to Engine is not send)
The GCB cant be closed while there is a Shutdown alarm in the Alarmlist.
Activates the output Common Sd as well as the standard alarm outputs.
Slow Stop
2
The alarm appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log.
It causes stop of the gen-set by the standard stop sequence, i.e. including
unloading and cooling phase.
The gen-set can't be started again while there is a Slow stop alarm in the
Alarmlist.
Activates the output Common Stp as well as the standard alarm outputs.
Protection groups
There are two groups of protections in the controller: fix and customer configurable.
Protection types
Because of limited (adjustable) GeCon influence to the Engine and GCB (depends on configuration and
wiring) the GeCon protection system is more focused to fail indication. All Protection types are available
because of IGS-NT system compatibility even if some Protection types have the same result in GeCon (e.g.
BO, Stp, Sd).
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 48

48
Off Load
2
The event appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log. It
does not require confirmation, diappears by itself.
It causes immediate opening of the GCB. In AUT and SEM modes the genset remains running for 60 seconds and then it is stopped by the standard
stop sequence. In MAN mode the gen-set remains running until the
operator changes it's operational state manually.
If the controller is in AUT or SEM mode and all previously active Off load
alarms disappeared the gen-set is automatically started back and
connected to the load if the condition for the gen-set to be running persists
(e.g. Rem start/stop is active ..).
This event is used to put the gen-set temporarily off the load for any
reason.
Activates the output Common OfL.
Low Power
2
The event appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log. It
does not require confirmation, diappears by itself.
It causes reduction of the required gen-set load to the Min Power PtM
during parallel-to-mains operation or local baseload operation.
If all previously active Low power alarms disappeared the gen-set is
automatically ramped back to the original required load, which is given
according to the currently active load control mode (Load ctrl PtM) in PtM
operation.
Activates the output Common LoP.
This alarm type is not overriden by the input Sd Override.
Note:
Available in IS-NT only.
BrkOpen
2
The event appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log.
It causes immediate opening of the GCB (without unloading) and engine
stays running (stop pulse is not send).
The gen-set can't be started again while there is a BO alarm in the
Alarmlist.
Activates the output Common BO as well as the standard alarm outputs.
Mains Protect
2
The protection is only recorded into the history log.
In applications which control the MCB this protection causes opening of the
MCB. The gen-set can continue operation in island mode if required. The
MCB can be closed back as soon as there isn't any mains protection active
(including the built-in mains protections).
In applications which do not control the MCB this protection causes
opening of the GCB. The controller waits then for the MCB to open. After
that the gen-set can continue operation in island mode if required. As soon
as there isn't any mains protection active (including the built-in mains
protections) the GCB is opened again and the controller waits for the MCB
to close. After that the gen-set can continue operation in parallel-to-mains
mode if required.
Activates the output Common MP.
This alarm type is not overriden by the input Sd Override.
Sd Override
2
The alarm appears in the Alarmlist and is recorded into the history log.
It causes immediate opening of the GCB (without unloading) and engine
stays running (stop pulse is not send).
The gen-set can't be started again while there is a Sd override alarm in the
Alarmlist.
Activates the standard alarm outputs.
This alarm type is not overriden by the input Sd Override.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 49

49
Default protections in SPI
Fix – firmware based
Generator:
Corresponding setpoints
IDMT overcurrent
BO
Basic settings: Nomin current; Gener protect: 2Inom del
IDMT Active power
BO
Gener protect: OverldStrtEval; 2POvrldStrtEvDel
IDMT EarthFault Current
BO
Gener protect: NomEthFltCurr, 2EthFltCurr del
Shortcurrent
BO
Gener protect: Ishort; Ishort del
Generator voltage: Ug1>, Ug1<,
Ug2>, Ug2<, Ug3>, Ug3<
BO
Gener protect: Gen >V; Gen <V; Gen V del.
Generator frequency: fg<, fg>
BO
Gener protect: Gen >f; Gen <f; Gen V del
Default – configurable
Reverse power
BO
Gener protect: Reverse power; ReversePwr del
EarthFaultCurr
BO
Gener protect: EarthFaultCurr; EthCurr del
Excitation Loss
BO
Gener protect: ExcitationLoss, ExctLoss del
Gen Current unbalance
BO
Gener protect: Gen I unbal; Gen I unb del
Gen Voltage unbalance
BO
Gener protect: Gen V unbal;Gen V unb del
Mains:
Vector shift
MP
Mains protect: VectorS prot; Vector S limit
Mains voltage
MP
Mains protect: Mains >V MP; Mains <V MP; Mains V del
Mains frequency
MP
Mains protect: Mains >f; Mains <f; Mains f del
Default - configurable
Mains frequency
MP
Mains protect: Mains >f; Mains <f; Mains f del
Analog protection:
Batt <V, Batt >V
Wrn
Analog protect: Batt >V; Batt <V; Batt V del
Basic settings:
VoltProtselect = PHASE-NEUTRAL
Mains protect: Mains >V MP
Mains <V MP
Mains V del
Mains >f
Mains <f
Mains f del
MP L1 under
MP L2 under
MP L3 under
MP L1 over
MP L2 over
MP L3 over
Mains V L1-N
MP fmns under
MP fmns over
Mains freq
Mains V L2-N
Mains V L3-N
Mains voltage and frequency protections - limits and indications
Hint
Mains protect is a setpoints group that contain setpoints related to mains protection evaluation. MP L1
under, Mains L1-N and etc. are alarms that occurs when mains protection is evaluated.
For more information about Mains protection see chapter Setpoints / Mains protect of this manual
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 50

50
MP L12 under
MP L23 under
MP L31 under
MP L12 over
MP L23 over
MP L31 over
Mains V L1-L2
MP fmns under
MP fmns over
Mains freq
Mains V L2-L3
Mains V L3-L1
Mains protect: Mains >V MP
Mains <V MP
Mains V del
Mains >f
Mains <f
Mains f del
Basic settings:
VoltProtselect = PHASE-PHASE
Mains protect: VectorS prot
VectorS CB sel
VectorS limit
VectorShiftTrp
VectorShiftAct
Basic settings:
VoltProtSelect = PHASE-NEUTRAL
Gener protect: Gen >V BOC
Gen <V BOC
Gen V Sd
Gen V del
Gen >f
Gen <f
Gen f del
BOC L1 under
BOC L2 under
BOC L3 under
BOC L1 over
BOC L2 over
BOC L3 over
Gen V L1-N
BOC fms under
BOC fms over
Gen freq
Gen V L2-N
Gen V L3-N
BOC L12 under
BOC L23 under
BOC L31 under
BOC L12 over
BOC L23 over
BOC L31 over
Gen V L1-L2
BOC fms under
BOC fms over
Gen freq
Gen V L2-L3
Gen V L3-L1
Basic settings:
VoltProtSelect = PHASE-PHASE
Gener protect: Gen >V BOC
Gen <V BOC
Gen V Sd
Gen V del
Gen >f
Gen <f
Gen f del
Vector shift protection - limits and indications
HINT
For more information about Vector Shift Protection see chapter Setpoints / Mains protect of this manual or
chapter Vector Shift Protection of NPU User Guide 1.9.
Generator voltage and frequency protections - limits and indications
HINT
Gener protect is a setpoints group that contain setpoints related to mains protection evaluation. BOC L1
under, Gen V L1-N and etc are alarms that occurs when genset protection is evaluated.
For more information about Genset protection see chapter Setpoints / Gener protect of this manual.
Shutdown override
If the Binary input Sd override is closed, all 2nd level protections are disabled to allow engine run in an
emergency situation, e.g. sprinkler devices power supply.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 51

51
All protections are shown in Alarmlist and recorded into History, but the controller doesn’t stop the engine
because of them. If the input is deactivated and some protections are still active or not yet reset, the
controller starts to take these protections into account and consequently stops the engine.
Take in account, that the binary outputs, signalizing activation of the particular protection are active
independently on the state of BI: SdOverride.
Hint:
All 2nd level protections are locked out, except of these:
- Emergency stop
- Binary and analog protections configured as Sd override type. In fact this protection type means:
"Unoverridable shutdown", i.e. it works the same way as standard shutdown protection, however it
can not be overriden (blocked) by the Sd override input.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 52

52
Circuit breakers operation sequence, GCB/MCB fail detection
BO: CB status
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
minimum 1s from UV switching on,
together with MinStab time elapsing is
necessary before the CB is allowed to
close
When closing the CB, the CB status LBO
switches over only when both feedbacks
are in correct position
Note:
In the following text, “CB” abbreviation is used for MCB or GCB respectively.
Related binary inputs:
- CB fdb – CB feedback binary input
- CB fdb neg – negative CB feedback binary input. Used for increasing the reliability of CB status
evaluated by the controller. In case that it is not configured, negative value of CB fdb is calculated
internally within the controller.
Related binary outputs:
- CB close/open – output for circuit breaker. Equals to 1 during the time when CB is requested o be
closed.
- CB ON coil – output for closing coil of the CB. 2s pulse (5s if synchronising is not provided by the
particular CB) is used for closing the CB.
- CB OFF coil – output for opening coil of the CB. 2s pulse (5s if synchronising is not provided by the
particular CB) is used for opening the CB.
- CB UV coil – output for undervoltage coil of the CB. Permanently active, 2s negative pulse (5s if
synchronising is not provided by the particular CB) is used for CB opening request
- CB status – output indicating CB status as evaluated by the controller. This signal is used for lighting
LEDs on the panel, switching the regulations, CB fail evaluation, etc.
Possible CB sequences:
CB close command:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 53

53
2s
2s
1s
BO: CB OFF coil
2s
BO: CB status
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
If the CB is not closed after
the first attempt, it is only reset
by OFF pulse and no CB fail is
issued. This would be issued
after the second unsuccessfull
attempt.
BO: CB status = 0
BI: CB fdb neg = 1
BI: CB fdb = 0
BO: CB fail
ON pulse has finished and CB
status is not =1. CB fail is
issued immediatelly
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BO: CB fail
500 ms
<2s
BO: CB status = 0
BI: CB fdb neg = 1
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB ON coil
1s
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
CB fail – If any inconsistence between
the two feedback signals is detected, CB
fail is issued.
ON pulse is shortened/interrupted
and replaced by UV and OFF pulse
OFF pulse is activated until both
feedbacks return to the correct
position +2 seconds.
Repeated CB close command:
CB fail – fdb mismatch:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 54

54
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
During CB opening the CB status
LBO is deactivated with change of
the first feddback status
Further behavior of UV output
depends on the system status. In
case of transition to cooling stays
off, if the Cb was opened manually
and the engine keeps running, it
activates again after timeout
elapses.
BO: CB status
<2s
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
BO: CB status
BO: CB ON coil
Closing pulse is shortened, opening
sequence is started immediatelly
CB opening by protection or manual
command (button pressed)
CB open command:
Transition closing -> opening (opening command is issued during closing pulse):
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 55

55
Alarm: GCB fail
BO GCB close/open
BI GCB feedback
Alarm detection:
immediatelly
active
closed
opened
Alarm: GCB fail
BI GCB feedback
BO GCB close/open
Alarm detection:
immediatelly
active
opened
closed
Alarm: GCB fail
BO GCB close/open
BI GCB feedback
active
opened
opened
Time delay
5 sec
2s
2s
BO: CB OFF coil
BI: CB fdb neg
BI: CB fdb
BO: CB close/open
BO: CB UV coil
BO: CB status
BO: CB ON coil
OFF a UV pulse is always activated for
the full time. manual control (= CB
button) is deactivated during opening
pulse.
Here starts the standard closing
sequence – see CB close command.
In this moment, the reason for closing the
CB is activated again (e.g. Remote
Start/Stop is activated)
Transition opening -> closing (closing command is issued during opening pulse)
Other CB fail reasons:
When the BO CB close/open is in steady state and CB feedback is changed, the CB fail is detected
immediately (no delay).
When the BO CB close/open opens, there is 5 resp. 2 sec delay for the breaker to respond before a CB
fail is detected. In such case, if CB OFF coil is used for opening the CB and CB fail occurs during
opening the CB, the signal CB OFF coil is automatically extended until the breaker opening is detected
(evaluated as CB status).
2 sec when the CB is used for synchronizing
5 sec in other cases
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 56

56
In case that CB fail is detected after switching the controller on (CB is closed), the CB OFF coil output is
activated immediately.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 57

57
Gen-set operation states
Not ready
Gen-set is not ready to start
Init
Fw and archive incompatibility or invalid values in setpoint – controller does not work
Starting
Waiting for ReadyToLoad signal
Running
Waiting for GCB connection or start synchronizing
Soft load
Gen-set power is ramping up
Loaded
Gen-set is loaded
Soft unld
Gen-set power is ramping down
Stopping
Stopping procedure before the BI ReadyToLoad is opened.
Stopped
Stopped - initial state – waiting for engine start. LBI:ReadytoLoad is deactived.
MainsOper
Mains is present (MCB is closed, GCB is opened)
IslOper
Island operation (MCB is opened, GCB is closed)
Brks Off
GCB, MCB opened
Synchro
Gen-set is synchronizing (MCB is closed, GCB is
opened)
ParalOper
Gen-set is in parallel with mains (MCB is closed,
GCB is closed)
Gen-set can operate in following states
Breakers conditions
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 58

58
Inputs and Outputs
Module name
BIN
BOUT
AIN
AOUT
IMPULSE
Note
IGS-NT
controller
x x x x
Number of I/O depends on type.
IGS-PTM
8 8 4 1 -
Standard I/O extension module.
IS-AIN8
- - 8 - -
Standard I/O extension module.
IS-AIN8TC
- - 8 - -
8 thermocouple inputs
IS-BIN16/8
16 8 - - -
Standard I/O extension module.
Inteli AIN8
- - 8 - 2
Inteli AIN8TC
- - 8 - -
Inteli IO8/8
8 8 - 2 -
Inteli IO16/0
16 0 - 2 -
Inteli AIO9/1
- - 2 1 -
I-CB
x x x x -
Configurable communication bridge.
IGL-RA15
-
15 - - - 15 Green, Red, Yellow LED panel.
I-AOUT8
- - - 8 -
8 Analog outputs
VPIO
8 8 - - -
Virtual periphery I/O module.
SHBIN
8 - - - -
SHared (virtual) Binary INput module
SHBOUT
- 8 - - -
SHared (virtual) Binary OUTput module
SHAIN
- - 8 - -
Shared (virtual) Analog INput module
SHAOUT
- - - 8 -
Shared (virtual) Analog OUTput module
PLC x x x x - Programmable (internal) logic module.
Requested power range
Controller analog output setting
0 – 1000 kW
Low limit: -250 kW
High limit: 1000 kW
Low – High kW
Low limit: Low - (High – Low)/4 kW
High limit: High kW
Virtual and physical modules
Number of I/O can be extended and project wiring can be reduced using the following extension and virtual
modules.
HINT
For more details about Virtual peripherals (Shared and Internal virtual I/O periphery and PLC) see last
version of IGS-NT-Application guide-x.x.pdf.
CAUTION!
Usage of any 3rd-party peripheral modules in cooperation with ComAp controller is not recommended.
ComAp can’t guarantee the proper function of controller with none-ComAp peripheral modules.
Analog outputs
IS-NT controller has one analogue output, free configurable. To this output there can be configured any
analogue value, which is in the controller. To scale the output use the internal calculator in the GenConfig
PC tool.
If the output range 4 to 20 mA is needed, the limits for analog output should be set according to an example
in the following table:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 59

59
This setting ensures that 0 kW (Low kW) will correspond to 4 mA.
No analog output is available on IG-NT controller. Use extension unit IGS-PTM (one analog output) or IAOUT8 (eight analog outputs).
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 60

60
Setpoints
Password protection
Any setpoint can be password protected - 7 levels of password is available. The password is a four-digit
number. Only setpoints associated with the entered password level can be modified.
Even though one level may have been set from the front panel, the affected setpoints are not accessible
from InteliMonitor (direct or Modem) until this level is set in IMON (InteliMONitor). Setpoints opened from
front panel are automatically closed 15 minutes after the last key has been pressed or when wrong value of
password is set. Any password can be changed once that level password or higher has been entered.
The controller programming (configuration) requires the highest password - 7 level.
ProcessControl
BaseLoad [ kW – MW*]
This setpoint is used for adjusting of the requested gen-set power in Baseload mode, i.e. if the setpoint Load
ctrl PtM is set to BASELOAD
Step: 0,1 kW / 1 kW / 0,01 MW*
Range: 0,1 kW – 650,00 MW*
ForceValue possibility: No
*Note:
The actual setpoint units and range depend on setting of the Power format (see GenConfig manual).
Hint:
If you set this setpoint to a higher value than the system is available to produce, the total produced power is
limited with the sum of Nomin power setpoints of all gen-sets in the system.
Base PF [ ]
This setpoint is used for adjusting of the requested gen-set power factor value if the power factor control
mode is set to BASEPF (setpoint PF ctrl PtM).
Values over 1.00 mean capacitive load character, i.e. setting 0.95 means 0.95L and setting 1.05 means
0.95C.
Step: 0,01
Range: 0,60 - 1,20
Import load [ kW ]
This setpoint is used for adjusting of the requested mains import if the gen-set load control mode is set to
IMP/EXP (Load ctrl PtM = IMP/EXP)
This setpoint is also used for adjusting of the maximum allowed export if export limit function is active (Export
limit = ENABLED).
Range: -32000 .. 32000 [kW]
NOTE:
Negative value of import is export, i.e. the power flows into the mains.
NOTE:
The actual setpoint units and range depend on setting of the Power format in GenConfig.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 61

61
Import PF [ - ]
The setpoint is used to adjust the requested power factor at the mains when PF ctrl PtM = PF-IM/EX. Values
over 1.00 mean capacitive load character.
Step: 0,01
Range: 0,60 - 1,20
EXAMPLE:
Setting 0.95 means 0.95L and setting 1.05 means 0.95C.
Load ctrl PtM [ BASELOAD / IM/EX / ANEXT BASELOAD /
ANEXT IM/EX / T BY PWR ] (FV)
Load ctrl PtM selects control mode for parallel to mains operation.
BASELOAD Gen-set is loaded at preadjusted level ProcessControl: Base load.
IM/EX Gen-set is loaded according to imported/exported power from/to mains to achieve
ProcessControl: Import load.
ANEXT BASELOAD Gen-set is loaded according to the requested value given by an external device via
Analog input LdCtrl:AnExBld.
ANEXT IM/EX Gen-set is loaded according to imported/exported power from/to mains to achieve the
requested value given by an external device via Analog input LdCtrl:AnExI/E.
T BY PWR Gen-set power is changed to keep required temperature, measured via an analog input.
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
For “digital” external load control select mode ANEXT BASELOAD and as the source for LdCtrl:AnExBld
select value ExtValue1-4. This value can be set using a command transmitted e.g. over CAN bus or
ModBus.
PF ctrl PtM [ BASEPF / PF-IM/EX ANEXT BASEPF / ANEXT PF-IM/EX ]
(FV)
PF ctrl PtM selects control mode of power factor for parallel to mains operation.
BASEPF Gen-set power factor is kept at the level given by Process control:Base PF.
PF-IM/EX Gen-set power factor is controlled according to imported/exported reactive power
from/to mains to achieve ProcessControl: Import PF.
ANEXT BASEPF Gen-set power factor is kept at the level given by an external device via Analog
input PFCtrl:AnExBPF.
ANEXT PF-IM/EX Gen-set power factor is controlled according to imported/exported reactive power
from/to mains to achieve the requested value given by an external device via Analog
input PFCtrl:AnExI/E.
Force value possibility: Yes
I/E-Pm meas [ NONE / IM3 CT INPUT / ANALOG INPUT ]
Import / Export measurement selection when one of power I/E modes selected.
NONE No source for I/E active power measurement available. If selected, power control
defaults to Baseload (BASELOAD, ANEXT BASELOAD, T BY PWR).
IM3 CT INPUT Mains I/E active power (Pm) is measured and calculated from controller’s Im3
current terminal. The value is multiplied by 3 to estimate the aggregate mains
power.
ANALOG INPUT Mains I/E active power is measured by an external device and the controller
measures this value via analog input LdCtrl:I/E-Pm.
Hint:
Earth fault current protection may be used only if I/E-Pm meas = ANALOG INPUT or NONE.
I/E-Qm meas [ NONE / IM3 CT INPUT / ANALOG INPUT ]
Import / Export measurement selection when one of PF I/E modes selected.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 62

62
NONE No source for I/E reactive power measurement available. If selected, power factor
control defaults to BasePF (BASEPF, ANEXT BASEPF).
IM3 CT INPUT Mains I/E reactive power (Qm) is measured and calculated from controller’s Im3
current terminal. The value is multiplied by 3 to estimate the aggregate mains
reactive power.
ANALOG INPUT Mains I/E reactive power is measured by an external device and the controller
measures this value via analog input PFCtrl:I/E-Qm.
Hint:
Earth fault current protection may be used only if I/E-Qm meas = ANALOG INPUT or NONE.
If I/E-Pm meas is set to IM3 CT INPUT, then I/E-Qm meas should be logically set to IM3 CT INPUT as well,
because IM3 CT INPUT is common input for both parameters.
PeakLevelStart [ kW – MW* ] (FV)
Load consumption level the gen-set has to stop at. Function is inactive when PeakAutS/Sdel = OFF. Genset
start is PeakAutS/Sdel delayed after the consumption of the Load exceeds the PeakLevelStart limit.
Step: 0,1 kW / 1 kW / 0,01 MW*
Range: PeakLevelStop to 320,00 MW*
Force value possibility: Yes
*Note:
The actual setpoint units and range depend on setting of the Power format (see GenConfig manual).
PeakLevelStop [ kW – MW* ] (FV)
Load consumption level the gen-set has to start at. Genset stop is PeakAutS/Sdel delayed after
PeakLevelStop limit is reached. Load consumption (P factory) is calculated (not directly measured) as a sum
of gen-set (Act power) and mains (P mains) active power.
Step: 0,1 kW / 1 kW / 0,01 MW*
Range: 0,00 to PeakLevelStart MW*
Force value possibility: Yes
*Note:
The actual setpoint units and range depend on setting of the Power format (see GenConfig manual).
PeakAutS/S del [ s ] (FV)
Delay for automatic Peak start/stop function. Set OFF to disable Peak aut start function.
Step: 1s
Range: OFF, 1 – 3200 s
Force value possibility: Yes
Export limit [ DISABLED / ENABLED ] (FV)
Protection against power export to the mains. The function limits gen-set requested power to hold import
power higher or equal to the setpoint Import Load.
Force value possibility: Yes
Derating1 strt [ X ] (FV)
Derating2 strt [ X ] (FV)
The starting values for the power derating function. The gen-set nominal power is decreased according to
the adjusted curve.
The setpoint actual physical dimension is given by the related analog input and the value assigned to it.
Step: 1 X
Range: ± 32000 X
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
DeratingX strt unit [X] depends on DeratingPowerX analog input unit.It can be e.g.°C in case of temperature
derating function.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 63

63
Derating1 end [ X ] (FV)
Process control:
Derating1Start [X]
Derating1End [X]
Derated1Power [%]
Power derating 1
analog input
Nominal power
influences Overload
protection etc.
Power derating
Process control:
Derating2Start [X]
….
Power derating 2
analog input
Derating2 end [ X ] (FV)
Ending value for power limitation – at this value the gen-set power is limited to DeratedX pwr value and it
won’t go lower for higher input values.
The setpoint actual physical dimension is given by the related analog input and the value assigned to it.
Step: 1 X
Range: ± 32000 X
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
To record the power derating activity into the History:
-Configure the binary output Derating X act to a virtual periphery input.
-Configure either “History record” or “Warning”-type alarm to this input to record power derating
activity in History and optionally to indicate it in Alarmlist.
Derated1 pwr [ % ] (FV)
Derated2 pwr [ % ] (FV)
The ratio of decreasing of the gen-set nominal power at DeratingX end level.
Step: 1 % of Nomin power
Range: 0 - 100 % of Nomin power
Force value possibility: Yes
Hints:
DeratedX pwr = 90% means the nominal power reduction to 90%, not by 90%.
Derating ratio is set to zero and functions are not active when Analog inputs PowerDeratingX are not
configured (e.g. in default configuration).
When Power derating function is active, the generator nominal power is decreased to DeratedX pwr and so
Overload protection (BOC Overload) is based on this Derated power!
The generator nominal power is reduced according to the bigger restriction – the more reduced channel out
of the two.
TempByPwr Treq [ °C ] (FV)
Requested temperature value for temperature control by generator power.
Before use, you have to configure the analog input LdCtrl:TbyPwr.
Step: 1 °C
Range: ± 32000 C
Force value possibility: Yes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 64

64
TempByPwr gain [ % ]
Gain factor for Temperature by generator power control loop.
Step: 0,01 %
Range: 0,00 – 100,0 %
TempByPwr int [ % ]
Integration factor for Temperature by generator power control loop.
Step: 0,01 %
Range: 0,00 – 100,0 %
Overheat prot [ ENABLED / DISABLED ] (FV)
ENABLED: If the temperature measured from analog input “LdCtrl:TbyPwr” exceeds the value TbyPwr
Treq the gen-set power is decreased gradually to Min Power PtM. If the temperature
decreases below TbyPwr Treq the gen-set increases the power gradually to the original
requested value (Baseload, Imp/Exp....).
DISABLED: Overheat protection function is disabled. No power change if the temperature measured from
analog input “LdCtrl:TbyPwr” exceeds the value TbyPwr Treq.
Force value possibility: Yes
Island enable [ NO / YES ] (FV)
NO, YES: Enables or disables island operation.
Force value possibility: Yes
The setpoint is used to enable/disable the island operation, i.e. supplying the load while the mains is
disconnected.
Island mode is recognized if the mains breaker is open, e.g. the feedback input MCB feedback is
not active.
Parallel mode is recognized if the mains breaker is closed, e.g. the feedback input MCB feedback
is active.
If the island mode is recognized and island operation is disabled the controller will open the generator
breaker, cool-down the gen-set and stop it. While this situation persists the controller behavior is following:
The gen-set start in AUT mode is blocked, it can be started in MAN mode only.
The GCB can't be closed.
The message OfL StartBlck is present in the alarm list (see the alarm output OfL StartBlck).
ParallelEnable [ NO / YES ] (FV)
NO, YES: Enables or disables Mains parallel operation.
Force value possibility: Yes
The setpoint is used to enable/disable the parallel operation, i.e. supplying the load in parallel with the mains.
Island mode is recognized if the mains breaker is open, e.g. the feedback input MCB feedback is
not active.
Parallel mode is recognized if the mains breaker is closed, e.g. the feedback input MCB feedback
is active.
If the parallel mode is recognized and parallel operation is disabled the controller will open the generator
breaker, cool-down the gen-set and stop it. While this situation persists the controller behavior is following:
The gen-set start in AUT mode is blocked, it can be started in MAN mode only.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 65

65
MFStart
enable
Parallel
Enable
ForwSync
Enable
RevSync
Enable
Island
enable
Description
- OFF
- - -
Not Ready - ParalDisabled
OFF
ON
OFF
-
-
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, doesn't close GCB
OFF
ON
ON - OFF
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, synchronizes, closes GCB, at
Mains fail both MCB and GCB are opened
OFF
ON
OFF
ON
OFF
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, doesn't close GCB, if the Mains
fails, MCB is opened, gen-set keeps
running
OFF
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, GCB is not closed, if Mains fails,
MCB openes and GCB closes
OFF
ON
ON
OFF
ON
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, synchronizes, closes GCB, if Mains
fails, opens MCB, stays in Island
OFF
ON
ON
ON
ON
Gen-set starts after Rem start/stop is
closed, synchronizes, closes GCB, if Mains
fails, MCB is opened, gen-set runs in
Island, reverse synchr., MCB closes
ON
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
Gen-set starts after Mains fail, doesn't
close GCB - Island operation disabled
ON
ON
OFF
OFF
ON
Gen-set starts after Mains fail, goes to
Island, if Mains returns, GCB is opened,
MCB is closed
ON
ON
ON
OFF
ON
Gen-set starts after Mains fail, opens MCB,
closes GCB, if Mains returns, opens GCB,
closes MCB, synchronizes GCB, closes
GCB
ON
ON
OFF
ON
ON
Gen-set starts after Mains fail, opens MCB,
closes GCB, if the Mains returns,
synchronizes, closes MCB
ON
ON
ON
ON
ON
Gen-set starts after Mains fail,
synchronizes, closes GCB, if Mains fails,
MCB is opened, gen-set runs in Island,
reverse synchr., MCB closes
The GCB can't be closed.
The message OfL StartBlck is present in the alarm list (see the alarm output OfL StartBlck).
Synchro enable [ NONE / FORWARD / REVERSE / BOTH ] (FV)
Enable or disable forward/reverse synchronization.
NONE: No synchronizing is enabled.
FORWARD: GCB synchronizing is enabled.
REVERSE: MCB synchronizing is enabled.
BOTH: GCB and MCB synchronizing are enabled.
Force value possibility: Yes
MFStart enable [ NO / YES ] (FV)
NO, YES: Enables or disables automatic Mains failure start.
Force value possibility: Yes
Examples of settings:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 66

66
#Neutral cont. [ EACH / COMMON ]
StartStopBtn= DISABLED
ProtectionMode = NOT ACTIVE
Setting for systems where engine is started separately. and
protection are controlled externally (not from controller).
StartStopBtn= ENABLED
ProtectionMode = ACTIVE
Standard settings for system where engine start/stop and GCB is
controlled from controller.
Setpoint changes behavior of binary output Neutral CB C/O which is used for Neutral contactor control.
EACH: Four pole GCB’s are supposed on the engine.
a) When GCB is opened (after start, before stop):
Binary output Neutral CB C/O (Neutral contactor) closes when Generator voltage is higher than 75%
of Nominal voltage.
Binary output Neutral CB C/O (Neutral contactor) opens when Generator voltage is lower than 50%
of Nominal voltage.
b) Binary output Neutral CB C/O (Neutral contactor) is opened when gen-set is running in parallel to the
mains (MCB is closed) .
COMMON: Three pole GCB’s are supposed for the gen-set.
a) When MCB is opened Neutral contactor closes when Generator voltage (at least one phase) is
higher than 75% of Nominal voltage.
b) When MCB is opened Neutral contactor opens when all phases of Genset voltage are lower than
50% of Nominal voltage.
c) When MCB is closed Neutral contactor opens.
Hint:
Configure Binary output Neutral CB C/O and Binary input Neutral CB fdb Prior to Neutral contactor function
is used.
Neutral contactor fail is detected when no feedback comes within 400ms or when MCB and Neutral
contactor are closed for more than 400 ms.
WatchedContr
Range 1…..16 [controller CAN address]
This setpoint defines the address of the controller which is the master one in the redundancy controller
system. Master controller has this setpoint adjusted to 0. The redundant controller has this setpoint adjusted
to address of it’s master. The slave evaluates the activity of the master via CAN bus. In case there is
detected any problem with master, BO:CtrlHBeat FD on the slave controller is activated.
ProtectionMode [ ACTIVE / NOT ACTIVE ] (FV)
ACTIVE:
Standard setting – all protections are active.
2-nd level protections are evaluated, GCB or MCB is controlled.
NOT ACTIVE:
2-nd level protections are just evaluated, but GCB or MCB is NOT opened (no actions).
Exceptions are Emergency Stop and alarms types Sd override.
Recommended settings
StartStopBtn [ ENABLED / DISABLED ] (FV)
ENABLED: Standard settings for systems where engine start/stop and GCB is controlled from controller.
DISABLED: Disables the engine Start and Stop buttons and corresponding Binary start/stop signals.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 67

67
Basic settings
!!! VERY IMPORTANT !!!
The maximum input current to the controller current terminals is 11 Amps. Higher value is
displayed as measured limit, e.g. 15 Amps from CT is measured and displayed as 11 Amps.
Take special care when selecting CT’s. All available 5 Amp CT’s do not have a range up to 11
Amps.
Nomin power [ kW ] (FV)
Nominal power of the generator.
Step: 1 kW
Range: 1 – 32000 kW
Force value: Yes
Nomin current [ A ] (FV)
This is the current limit for the generator. IDMT over current and short current protections are based on this
setpoint. See Generator protections: 2Inom del, Ishort setpoints. Nominal current can be different from
generator rated current value.
Step: 1 A
Range: 1 - 10000 A
Force value: Yes
CT ratio prim [ A ]
Gen-set phases Current Transformers ratio – primary side.
Step: 1 A
Range: 1 – 10000 A
CT ratio sec [ /5A / /1A ]
Gen-set phases Current Transformers ratio – secondary side selection /5A or /1A. Available in IG-xxC and
IS-NT versions. In standard IG-EE/NT units only 5 A range available.
Im3/ErFltCurCTp [ A ]
Earth Fault protection Current Transformer ratio – primary side.
Step: 1 A
Range: 1 – 10000 A
Im3/ErFltCurCTs [ /5A / /1A ]
Earth Fault protection Current Transformer ratio – secondary side selection /5A or /1A. Available in IG-xxC
and IS-NT versions. In standard IG-EE/NT units only 5 A range available.
VT ratio [ /1 ]
Gen-set Voltage Transformers ratio.
Step: 0,1 V / V
Range: 0,1 – 500,0 V / V
Vg InpRangeSel [ 277 V / 120 V ]
Gen-set voltage sensing inputs range selection. Available in IG-xxC and IS-NT versions. In standard IGEE/NT units only 277 V range available.
Hint:
The range 277 V is suitable for both European (230 V) and American (277 V) measurement.
The range 120 V is intended for high-voltage applications where voltage transformers with output range 100
V are used, or for alternative American (120 V) measurement.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 68

68
Vb VT ratio [ /1 ]
Bus Voltage Transformers ratio.
Step: 0,1 V / V
Range: 0,1 – 500,0 V / V
Hint:
Set VT ratio to 1,0 if no Voltage Transformers are used.
Vb InpRangeSel [ 277 V / 120 V ]
Bus voltage sensing inputs range selection. Available in IG-xxC and IS-NT versions. In standard IG-EE/NT
units only 277 V range available.
GenNomV [ V ] (FV)
Nominal generator voltage (phase to neutral).
Step: 1V
Range: 80 – 30000 V
Force value: Yes
Hint:
The nominal value can be externally changed using Force value function. However, it is intended for
changes between standard nominal voltages only (230 / 120 V) using Force value X source setpoints.
It is prohibited to use another controller values as a source for Force value in this case!!!
GenNomVph-ph [ V ]
Nominal generator voltage (phase to phase).
Step: 1V
Range: 130 – 60000 V
Hint:
If one of the nominal voltages is changed, the other is automatically adjusted to correspond with the new
value. E.g. if GenNomV is changed to 220 V, the GenNomVph-ph is changed to 220*1,73 = 381 V.
MainsNomV [ V ] (FV)
Nominal bus voltage (phase to neutral).
Step: 1V
Range: 80 – 30000 V
Force value: Yes
Hint:
The nominal value can be externally changed using Force value function. However, it is intended for
changes between standard nominal voltages only (230 / 120 V) using Force value X source setpoints.
It is prohibited to use another controller values as a source for Force value in this case!!!
MainsNomVph-ph [ V ]
Nominal bus voltage (phase to phase).
Step: 1V
Range: 130 – 30000 V
Hint:
Both Gen and Bus nominal voltages must be set to the same value when no PT is used.
FixVoltProtSelect [ PHASE-NEUTRAL / PHASE-PHASE ]
PHASE-NEUTRAL: The generator and mains/bus voltage are displayed as phase-to-neutral voltages.
PHASE-PHASE: The generator and mains/bus voltage are displayed as phase-to-phase voltages.
Nominal freq [ Hz ] (FV)
Nominal generator frequency
Step: 1Hz
Range: 35 – 65 Hz
Force value: Yes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 69

69
In case of change value of this setpoint, the setpoint is blocked for next change for time ForceBlock6Del.
Hint:
The nominal value can be externally changed using Force value function. However, it is intended for
changes between standard nominal frequencies only (50 / 60 Hz) using Force value X source setpoints.
It is prohibited to use another controller values as a source for Force value in this case!!!
Nom frg offset [ Hz ] (FV)
Nominal generator frequency
Step: 0,01 [Hz]
Range: -2.00 .. 2.00 [Hz]
Force value: Yes
The setpoint adjusts offset of nominal system frequency (Nominal Freq) with step 0.01 Hz.
Controller regulates to the Nominal Freq + Nom frq offset frequency.
The value Nominal Freq + Nom frq offset is used as 100% for generator and mains/bus frequency
protections and as requested value for frequency regulation (except synchronizing) if the setpoint Freq reg
loop is set to ALL THE TIME.
Gear teeth [ - ]
Step: 1 [ - ]
Range: 1…500
Force value: No
Number of teeth on the engine’s flywheel for the pick-up sensor.
This setpoint was added based on the customer's request to display RPM.
GeCon just shows RPM value, but this value is NOT used for control of system.
EngCoolTime [ s ]
Step: 1 [ s ]
Range: 0 …..3600s
Force value: No
Setpoint for setting of respecting time for Cooling.
In the case of a request to stop the engine the GeCon send Stop pulse (after opening GCB). This Stop pulse
is send to the Engine controller (Engine controller should to be move from Running state to Cooling).
After the time EngCoolTime count down the GeCon send second Stop pulse which should move Engine
controller from Cooling state to Stopped.
Hint:
Time in setpoint EngCoolTime must be longer than CoolingTime in EngineControler otherwise second Stop
pulse from GeCon will shorten required Cooling time in Engine controller.
ControllerMode [ OFF / SEM / AUT / MAN ] (FV)
Equivalent to Controller mode changes by MODE or MODE buttons.
Force value: Yes
Hint:
Mode change can be separately password protected.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 70

70
FltRes GoToSEM [ DISABLED / ENABLED ] (FV)
OFF
The backlight is off all the time
NO TIMEOUT
The backlight is on all the time
DISABLED: Controller stays in AUT mode after Fault reset .
ENABLED: Automatic switch from AUT to SEM mode after Fault reset to avoid automatic engine start. This
function is active for all 2nd-level protections (Shut down, Slow stop, ElProt, Off-load).
Force value: Yes
Hint:
Set to ENABLED to avoid automatic engine start when Fault reset button is pressed after shut down in
automatic mode.
Local buttons [ PANEL / EXTBUTTONS / BOTH ]
PANEL: Only the buttons on the controller front panel are enabled.
EXTBUTTONS: Only the external signals (copies of the panel buttons) are enabled.
BOTH: Both controller buttons and external signals are enabled.
Hint:
This switch is valid for these signals: GCBButton, MCBButton, FaultResButton, HornResButton, StartButton,
StopButton.
DispBaklightTO [min] (FV)
Range [units] OFF, 1-240 min, NO TIMEOUT [min]
This setpoint adjusts timeout after which the display (internal display or IS display #1) backlight is switched
off.
NOTE:
When IntelliVision is used this setpoint does not adjust its behavior. Its backlight is adjusted by internal
IntelliVision "setpoint".
DispBlkStrtOff [- ] (FV)
Range [units] DISABLED, ENABLED [-]
If this setpoint is in ENABLED position the display backlight is temporarily switched off during gen-set start.
UserBtn pulse [s ] (FV)
Step: 0,1 [ s ]
Range: 0,2 …10 s
Force value: Yes
Setpoint UserBtn pulse allows user to choose the duration of UserButton pulse.
ResetActAlarms [ DISABLED / ENABLED ]
DISABLED: If Fault reset is activated (from any source), only inactive (normally displayed) alarms are
reset. So only inactive alarms can be cleared from the Alarmlist.
ENABLED: If Fault reset is activated (from any source), all currently present (including inverse displayed
= active) alarms are reset (asterisk in Alarmlist disappears for all present alarms). I.e. after an active (inverse
displayed) alarm later on becomes inactive (normally displayed), it is cleared automatically from the Alarmlist
if previously reset.
Hint:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 71

71
ENABLED mode corresponds to the way that IG and IS controllers (previous generation) handled the
alarms.
ConvCoefPulse1 - 4 [ ]
This setpoint adjusts the rate of increasing of the PulseCounter1 – 4 (integrating internal counters that can
be seen at PulseCounter1-4). The setpoint assigns number of pulses (BI:PulseCounter1 – 4) to increase the
PulseCounter integrating value by 1.
Step: 1/X
Range: 1 – 65000 1/X
Example:
Number of pulses on the physical input BI: PulseCounter1: 10
ConvCoefPulse1 = 2
Value of the PulseCounter1 integrating counter: 5
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 72

72
Comms settings
Gen-set name
User-defined name, used for controller identification at remote connections. Gen-set name is max 15
characters long and has to be entered using PC software.
Hint:
The setpoint can be changed using PC SW only (e.g. InteliMonitor). Gen-set name isn’t affected by
GenConfig SW.
LB/UART Log [ENABLED / DISABLED]
Enables history logging of IG-IB / I-LB connection.
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
If communication via IG-IB is interrupted for more than 5s, it is automatically terminated. If it is established
again after this period, it is considered as a newly created connection and a new record “Terminal” is done
into history in case of LB/UART Log = ENABLED. This may cause overfilling of the history in case of some
monitoring tools, e.g. InteliSupervisor.
Contr. addr [ ]
Controller CAN bus and RS-485 identification number. Each controller in the group has to have its own
unique number.
Step: 1
Range: 1 to 32
Hint:
When opening Direct or Modem connection to the controller (using PC monitoring/control SW), the Contr.
address has to correspond to the Gen-set setting in PC SW.
RS232(1) mode [ DIRECT / MODEM (HW) / MODEM (SW) /
MODBUS-DIRECT / MODBUS-MDM(HW) / ECU link]
Communication protocol selection for RS232(1) line.
DIRECT: Connection to a local PC running InteliMonitor. RS232 or RS485 (with internal or
external converter) lines can be used. Set this also for IG-IB connected via RS232 line.
MODEM (HW): Analog/GSM/ISDN modem connection. Select this for standard modems with HW flow
control. If selected and no CTS signal is detected, communication may not work
correctly.
MODEM (SW): Analog/GSM/ISDN modem connection. Select this for modems without HW flow control
– controller will use SW flow control signals XOn, Xoff, so only TxD and RxD signals
need to be connected between the controller and the modem.
MODBUS-DIRECT Modbus protocol for direct connection to PLC / external SCADA terminal.
Communication speed can be selected via setpoint RS232(1)MBCSpd.
MODBUS-MDM(HW)Modbus protocol for modem (remote) connection to PLC / external SCADA terminal.
Communication speed can be selected via setpoint RS232(1)MBCSpd.
ECU-LINK Port redirected to connect the ECU with special (not J1939) interface, e.g. Cummins
Modbus.
Hint:
Detail description of Modbus protocol see in Communication guide.
RS232(2) mode [ DIRECT / MODEM (HW) / MODEM (SW) /
MODBUS-DIRECT / MODBUS-MDM(HW) / ECU-LINK]
Communication protocol selection for RS232(2) line.
Description is the same like for RS232(1) mode.
Available only in IS-NT and in IG-xxC versions.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 73

73
RS232(1)MBCSpd [ 9600 bps / 19200 bps / 38400 bps / 57600 bps ]
Defines the communication speed on RS232(1) line when ModBus mode is selected.
RS232(2)MBCSpd [ 9600 bps / 19200 bps / 38400 bps / 57600 bps ]
Defines the communication speed on RS232(2) line when ModBus mode is selected. Available only in IS-NT
and in IG-xxC versions.
RS232(1)MdmIni [ ]
Auxiliary modem initialization string – executed after the default modem initialization string. Used with
modem connected to the RS232(1) communication port.
Hint:
Applicable only for MODEM(HW), MODEM(SW) and MODBUS-MDM(HW) modes.
Use for special AT command setting of your modem if default string does not initiate the modem properly. AT
commands must be separated using semicolon “;”, max. length 31 characters.
The setpoint can be changed only using PC SW when configuring IG-EE/NT.
RS232(2)MdmIni [ ]
Auxiliary modem initialization string – executed after the default modem initialization string. Used with
modem connected to the RS232(2) communication port.
Available only in IS-NT and in IG-xxC versions.
Hint:
Applicable only for MODEM(HW), MODEM(SW) and MODBUS-MDM(HW) modes.
Use for special AT command setting of your modem if default string does not initiate the modem properly. AT
commands must be separated using semicolon “;”, max. length 31 characters.
The setpoint can be changed only using PC SW when configuring IG-EE/NT.
RS485(1) conv. [ DISABLED / ENABLED ]
If set to ENABLED, the communication RS232(1) port is redirected to the built-in RS485 converter. That
means the remote display RS485 line (for IG-Disp connection) is blocked and the converter is used for
communication with superior system or ECU.
Available in all controllers except of IS-NT.
Hint:
Applicable only for DIRECT, MODBUS-DIRECT modes.
This converter is not isolated!
RS485(2) conv. [ DISABLED / ENABLED ]
If set to ENABLED, the communication RS232(2) port is redirected to the built-in isolated RS485 converter.
Available only in IS-NT and in IG-xxC versions.
Hint:
Applicable only for DIRECT, MODBUS-DIRECT modes.
CAN bus mode [ 32C / 8C ]
CAN bus speed selection.
32C: High speed CAN (250 kbps) applicable up to 32 controllers, CAN bus length limited up to 200
meters.
8C: Low speed CAN (50 kbps) applicable up to 8 controllers, CAN bus length limited up to 900 meters.
Hint:
Low speed use for long distance connection only. Set all connected controllers to the same speed.
If having problems with needed CAN bus length, see Communication guide / I-CR module.
CAN2emptDetect [ DISABLED / ENABLED ] (FV)
Enables the detection of missing intercontroller CAN connection. If enabled and no other controllers are
detected on the CAN bus (the complete bus, not only within the logical group), this protection activates.
Force value: Yes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 74

74
CANAddrSwitch1
MODEM
The address is used for modem connection via I-LB
OTHER
The address is used for direct connection to any other device as e.g. IV8 or I-RD.
MODEM
The address is used for modem connection via I-LB
OTHER
The address is used for direct connection to any other device as e.g. IV8 or I-RD
FIXED
The ethernet connection is adjusted fixedly according to the setpoints IP address, Net
mask, Gateway IP, DNS IP. .
This method should be used for classic ethernet or Internet connection. When this type
of connection is opening the controller is specified by it's IP address. That means it
would be inconvenient if the IP address were not fixed (static).
AUTOMATIC
The ethernet connection settings is obtained automatically from the DHCP server.
The obtained settings is then copied to the related setpoints (it is not possible to set
those setpoints manually in this setting, for more information please see the following
setpoints: IP address, Net mask, Gateway IP and DNS IP). If the process of obtaining
the settings from DHCP server is not successful the value 000.000.000.000 is copied to
the setpoint IP address and the module continues trying to obtain the settings.
This method is beneficial for AirGate connection as it makes the connection very easy,
in fact "plug and play". When this type of connection is opening the controller is
specified by it's AirGate ID and the IP address does not play any role.
The setpoint selects function of the terminal address 122 at the CAN2 line. See the latest communication
guide for details about this topic.
CANAddrSwitch2
The setpoint selects function of the terminal address 125 at the CAN2 line. See the latest communication
guide for details about this topic.
IP address
In fixed settings mode this setpoint is used to adjust the IP address of the ethernet interface of the
controller. Ask your IT specialist for help with this setting.
In Automatic settings mode this setpoint is used to display the IP address, which has been assigned
by the DHCP server. It is not possible to change the setpoint value manually in this setting (the value
is immediately reverted back by controller communication module IB-COM).
IP Addr mode
The setpoint is used to select the method how the ethernet connection is adjusted.
CAUTION!
If you need to use fixed ethernet settings you should consult the proper setting with your IT specialist.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 75

75
Net mask
DISABLED
This is a standard mode, in which the controller listens to the incoming traffic and answers
the TCP/IP queries addressed to him. This mode requires the controller to be accessible
from the remote device (PC), i.e. it must be accessible at a public and static IP address if
you want to connect to it from the Internet.
ENABLED
This mode uses the "AirGate" service, which hides all the issues with static/public address
into a black box and you do not need to take care about it. You just need only a
connection to the Internet. The AirGate server address is adjusted by the setpoint AirGate
addr.
In fixed settings mode this setpoint is used to adjust the network mask of the network segment
where the controller is connected.
In Automatic settings mode this setpoint is used to display the network mask which has been
assigned by the DHCP server. It is not possible to change the setpoint value manually in this setting
(the value is immediately reverted back by controller communication module IB-COM).
Gateway IP
In fixed settings mode this setpoint is used to adjust the IP address of the gateway of the network
segment where the controller is connected.
In Automatic settings mode this setpoint is used to display the gateway IP address which has been
assigned by the DHCP server. It is not possible to change the setpoint value manually in this setting
(the value is immediately reverted back by controller communication module IB-COM).
A gateway is a device which connects the respective segment with the other segments and/or Internet.
ComApProtoPort
Range [units] 1 .. 255 [-]
This setpoint is used to adjust the port, which is used for ethernet connection to a PC with any of ComAp PC
program (i.e. InteliMonitor, GenConfig). This setpoint should be adjusted to 23, which is the default port
used by all ComAp PC programs. A different value should be used only in special situations as e.g. sharing
one public IP address among many controllers or to overcome a firewall restrictions.
AirGate
Range DISABLED, ENABLED [-]
This setpoint selects the ethernet connection mode.
AirGate IP
Range max. 32 characters [-]
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 76

76
This setpoint is used for entering the domain name or IP address of the AirGate server. Use the free AirGate
server provided by ComAp at address airgate.comap.cz if your company does not operate it's own AirGate
server.
SMTP authent
Range DISABLED, ENABLED [-]
Switch this setpoint to ENABLED position if your SMTP server requires authentificated access. You have
also adjust SMTP user name and SMTP password. Ask your internet provider or IT manager for this
information.
NOTE:
Most of public free SMTP servers require authentification. You will get instructions when you register to the
freemail service.
SMTP user name
Range max. 32 characters [-]
Use this setpoint to enter the user name for the SMTP server if SMTP authentification is enabled.
SMTP password
Range max. 32 characters [-]
Use this setpoint to enter the password for the SMTP server if SMTP authentification is enabled.
SMTP address
Range max. 32 characters
CAUTION!
Proper setting of SMTP-related setpoints as well as controller mailbox are essential for sending alerts via e-
mails.
This setpoint is used for entering the domain name (e.g. smtp.yourprovider.com) or IP address (e.g.
74.125.39.109) of the SMTP server. Please ask your internet provider or IT manager for this information.
NOTE:
You may also use one of free SMTP servers, e.g. smtp.gmail.com. However, please note that some free
SMTP servers may cause delays (in hours..) when sending e-mails.
NOTE:
If you do not want to send active e-mails, you may leave this setpoint blank, as well as other setpoints
related to SMTP server and e-mail settings.
Contr mailbox
Range max. 32 characters
Enter an existing e-mail address into this setpoint. This address will be used as sender address in active
e-mails that will be sent from the controller. Do not enter your or other recipient's e-mail address.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 77

77
Recipient's addresses are to be entered into the setpoints AcallCH1-Addr, AcallCH2-Addr and AcallCH3-
Addr.
NOTE:
Most of SMTP server will reject sending e-mails that contain nonexisting address in the sender address field.
Time zone
Range [units] - [-]
This setpoint is used to select the time zone where the controller is located. See your computer time zone
setting (click on the time indicator located in the rightmost position of the the windows task bar) if you are not
sure about your time zone.
NOTE:
If the time zone is not selected properly the active e-mails may contain incorrect information about sending
time, which may result in confusion when the respective problem actually occured.
DNS IP
Range [units] - [-]
In fixed settings mode this setpoint is used to adjust the domain name server (DNS), which is
needed to traslate domain names in e-mail addresses and server names into correct IP addresses.
In Automatic settings mode this setpoint is used to display DNS server, which has been assigned by
the DHCP server. It is not possible to change the setpoint value manually in this setting (the value is
immediately reverted back by controller communication module IB-COM).
ECU Diag (FV)
Range [units] DISABLED, ENABLED [-]
This setpoint is used to disable reading of diagnostic codes from the ECU if an external diagnostic tool is
connected to the engine.
A message ECU Diag disabled is displayed in the alarm list while ECU diagnostics is disabled.
SHxOcol detect [ DISABLED / ENABLED ]
This setpoint is used to enable/disable evaluation of collisions of virtual shared peripherial modules. A
collision means that there is more than one source (shared outputs module) active on the CAN2 bus.
NOTE:
In certain situations multiple sites with bus tie breakers may need to have more shared outputs sources as
the CAN bus line is in some points interrupted according to bus tie breakers position. Normally a collision
would be indicated if there were more sources on the bus and this setpoint can be used to disable the
evaluation of collisions in this special case.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 78

78
Delays/Timers
BINARY INPUT
BinInp delayX
physical
closed
Engine running
state
RunOnlyBlkDelX
PROTECTION
active
inactive
PROTECTION BLOCKED
BINARY INPUT
BinInp delayX
physical
closed
Engine running
state
RunOnlyBlkDel
PROTECTION
active
inactive
Horn timeout [ s ] (FV)
The maximum amount of time the Binary output Horn is closed (horn, buzzer will sound). OFF = the output
won’t be activated, NO TIMEOUT = the output stays closed until the alarm has been reset.
Step: 1s
Range: OFF, 1 – 3600 s, NO TIMEOUT
Force value: Yes
RunOnlyBlkDel1 [ s ]
Delay for Engine running Alarms activation – group 1 – see drawing below.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 3000,0 s
RunOnlyBlkDel2 [ s ]
Delay for Engine running Alarms activation – group 2.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 3000,0 s
RunOnlyBlkDel3 [ s ] (FV)
Delay for Engine running Alarms activation – group 3.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 3000,0 s
Force value: Yes
BinInp delay 1 [ s ] (FV)
Binary input protection is activated when input is closed for longer time than BinInp delay 1. To use this
delay, Binary input must be configured in GenConfig for Property – Delay = BinInp delay 1.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 600,0 s
Force value: Yes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 79

79
BinInp delay 2 [ s ] (FV)
DriveConfig: I/O, Property, Protection active = Closed
BINARY INPUT
BinInp delay
physical
BINARY INPUT
Internal value
no change
BINARY INPUT
BinInp delay
physical
BINARY INPUT
closed
Internal value
BINARY INPUT
BinInp delay
physical
BINARY INPUT
Internal value
DriveConfig: I/O, Property, Protection active = Opened
opened
Binary input protection is activated when input is closed for longer time than BinInp delay 2. To use this delay
Binary input must be configured in GenConfig for Property – Delay = BinInp delay 2.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 600,0 s
Force value: Yes
BinInp delay 3 [ s ] (FV)
Binary input protection is activated when input is closed for longer time than BinInp delay 3. To use this delay
Binary input must be configured in GenConfig for Property – Delay = BinInp delay 3.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 600,0 s
Force value: Yes
Hint:
BinInp delay is active only for Binary inputs configured as protection.
If these setpoints are not used, default BI delay is 0,5s.
ForceBlockDel1 [ s ] (FV)
ForceBlockDel2 [ s ] (FV)
ForceBlockDel3 [ s ] (FV)
ForceBlockDel4 [ s ] (FV)
ForceBlockDel5 [ s ] (FV)
ForceBlockDel6 [ s ] (FV)
Delays for Force block protection activation after the corresponding Binary input Force block is opened.
Protection deactivation is without delay. Protection is activated/deactivated independent on engine running
or not running state – it depends only on the corresponding Force block X input.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0,0 – 60,0 s
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 80

80
BINARY INPUT
ForceBlock del
FORCE BLOCK
Protection
closed
BINARY INPUT
Prot. block type = Force block
closed
active
active
inactive
BinInpDelayX
Force value: Yes
Service time 1 [ h ]
Service time 2 [ h ]
Service time 3 [ h ]
Service time 4 [ h ]
Running hours down counters are decremented when engine is running. Service alarm is indicated in Alarm
list and History record is activated when at least one of the counters reaches zero. Service time X setpoints
are actual counter values.
Step: 1 h
Range: 0 – 65535 h
Hint:
Once a service time has elapsed the corresponding Service time X setpoint must be adjusted again to a nonzero value to clear the alarm and begin a new countdown.
You can rename the particular timers using Translator to indicate specific service intervals – e.g. “OilChange
time”, “SparkPlug time”, ...
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 81

81
Analog protect
The content depends on programmable protections settings. This list contains pre-set protections from
default archives:
Batt >V [ V ]
Warning level for battery over voltage.
Step: 0,1 V
Range: 8,0 – 40,0 V
Batt <V [ V ]
Warning level for low battery voltage.
Step: 0,1 V
Range: 8,0 – 40,0 >V
Batt volt del [ s ]
Delay for battery voltage alarms.
Step: 1 s
Range: 0 – 600,0 s
Max+CylDifPmin [ C ]
Max+CylDifPmin = Maximum positive Cylinder temperature Difference at minimal gen-set Power level.
Maximum positive deviation of one cylinder temperature from the average at the PminCylDifEval load. Alarm
can be activated depending on Block type (set in GenConfig ->Software configuration->Analog inputs) – all
the time or after some time after start (depends on RunOnlyBlkDelX time).
Step: 1 C
Range: ± 32000 C
Max-CylDifPmin [ C ]
Max-CylDifPmin = Maximum negative Cylinder temperature Difference at minimal gen-set Power level.
Maximum negative deviation of one cylinder temperature from the average at the PminCylDifEval. load.
Alarm can be activated depending on Block type (set in GenConfig ->Software configuration->Analog inputs)
– all the time or after some time after start (depends on RunOnlyBlkDelX time).
Step: 1 C
Range: ± 32000 C
Max+CylDifPnom [ C ]
Max-CylDifPnom = Maximum positive Cylinder temperature Difference at nominal gen-set Power level.
Maximum positive deviation of one cylinder temperature from the average at the Nomin power. Alarm can be
activated depending on Block type (set in GenConfig ->Software configuration->Analog inputs) – all the time
or after some time after start (depends on RunOnlyBlkDelX time).
Step: 1 C
Range: ± 32000 C
Max-CylDifPnom [ C ]
Max-CylDifPnom = Maximum negative Cylinder temperature Difference at nominal gen-set Power level.
Maximum negative deviation of one cylinder temperature from the average at the Nomin power. Alarm can
be activated depending on Block type (set in GenConfig ->Software configuration->Analog inputs) – all the
time or after some time after start (depends on RunOnlyBlkDelX time).
Step: 1 C
Range: ± 32000 C
PminCylDifEval [ kW – MW* ]
Minimum gen-set Power for Cylinder temperature Difference evaluation. The protection is not evaluated, if
the gen-set power is lower than this limit.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 82

82
Gen-set power
Cylinder temperature
deviation from average
Max+CylDifPmin
Max-CylDifPmin
Max+CylDifPnom
Nominal power
PminCylDifEval
Max-CylDifPnom
+
-
Average temperature
Step: 0,1 kW / 1 kW / 0,01 MW*
Range: 0,0 kW – Nominal power*
*Note:
The actual setpoint units and range depend on setting of the Power format (see GenConfig manual).
CylDifEvalDel [ s ]
Cylinder temperature Difference Evaluation Delay.
Step: 1s
Range: 0 – 600 s
Cylinder temperature deviation protection type: warning
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 83

83
Gener protect
Pgen [%]
<=100
101
102
105
110
120
150
2POvrldStEvDel [s]
0,1 No action
10 5 2 1 0,5
0,2
0,2 No action
20
10 4 2 1 0,4
0,5 No action
50
25
10 5 2,5
1
1,0 No action
100
50
20
10 5 2
1,5 No action
150
75
30
15
7,5 3 2,0 No action
200
100
40
20
10
4
2,5 No action
250
125
50
25
12,5
5
5,0 No action
500
250
100
50
25
10
10,0
No action
1000
500
200
100
50
20
2POvrldStEvDel * OverldStrtEval
Reaction time =
Pgen - OverldStrtEval
Hint:
Generator protections are ignored when Process control: ProtectionMode = NOT ACTIVE. This is important
in the case the GCB and engine is not controlled from controller.
The content depends on programmable protections (Universal states) settings. This list contains pre-set
protections from default archives + fixed protections, which are always present.
Electric protection are evaluated when LBI:ReadyToLoad=1 and max stab time was finished.
OverldStrtEval [ % ] (FV)
Specifies the overload level, where the protection evaluation starts (see figure at 2PovrldStEvDel). Under
this level the protection is not active.
Step: 1 % of Nomin power
Range: 100 – 200 %
Force value: Yes
2POvrldStEvDel [ s ]
IDMT curve shape selection. 2PovrldStEvDel is the Reaction time of IDMT protection for 200% overload
Pgen = 2* OverldStrtEval.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0,0 - 600,0 s
Protection: BreakerOpen & Cool-down.
IDMT is inverse proportional to the generator overload. The higher the overload gets the less time will elapse
before the protection activates.
When the IDMT protection is activated the GCB is opened, the event is recorded in the Alarmlist and History,
and the engine will cool down and stop.
Where Reaction time is the amount of time from IDMT detection to the opening of the GCB.
Hint:
The maximum allowable Reaction time is 3600 sec.
Reaction time is the amount of time from IDMT detection to the opening of the GCB.
Following example shows reaction times for OverldStrtEval = 100% in dependence on generator power and
setpoint 2PovrldStEvDel value:
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 84

84
20,0
No action
2000
1000
400
200
100
40
50,0
No action
No action
2500
1000
500
250
100
Pgen [%]
<=110
111
112
115
120
150
200
2POvrldStEvDel [s]
0,1 No action
11
5,5
2,2
1,1
0,275
0,123
0,2 No action
22
11
4,4
2,2
0,55
0,245
0,5 No action
55
27,5
11
5,5
1,375
0,612
1,0 No action
110
55
22
11
2,75
1,223
1,5 No action
165
82,5
33
16,5
4,125
1,834
2,0 No action
220
110
44
22
5,5
2,445
2,5 No action
275
137,5
55
27,5
6,875
3,056
5,0 No action
550
275
110
55
13,75
6,112
10,0
No action
1100
550
220
110
27,5
12,223
20,0
No action
2200
1100
440
220
55
24,445
50,0
No action
No action
2750
1100
550
137,5
61,112
Pgen
Nominal power
2POvrldStEvDel
Maximal Reaction time
Reaction time
OverldStrtEval
Following example shows reaction times for OverldStrtEval = 110% in dependence on generator power and
setpoint 2PovrldStEvDel value:
Min Power PtM [ % ] (FV)
Minimum Power in Parallel to the Mains is the minimal value of the gen-set power in parallel to the mains.
Gen-set is never loaded below this level (even if the active load control loop requests a lower level). There is
no indication or alarm when Min Power PtM level is reached.
Step: 1 % of Nomin power
Range: 0 – 100 % of Nomin power
Force value: Yes
Hint:
If the setpoint Base load is lower than setpoint Gener protect: Min power PtM, the gen-set requested load is
set to Gener protect: Min power PtM.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 85

85
Igen [%]
<=100
101
102
105
110
120
150
200
2Inom del
0,1 No action
10 5 2 1 0,5
0,2
0,1
0,2 No action
20
10 4 2 1 0,4
0,2
0,5 No action
50
25
10 5 2,5 1 0,5
1,0 No action
100
50
20
10 5 2 1 2,0 No action
200
100
40
20
10 4 2
5,0 No action
500
250
100
50
25
10
5
10,0
No action
No action
500
200
100
50
20
10
20,0
No action
No action
No action
400
200
100
40
20
2Inom del * Nomin current
Reaction time =
Igen - Nomin current
The value of Min Power PtM is ignored during Warming procedure.
The setpoint is used as a limit for Low power protection: if it becomes active, the load is ramped-down using
setpoint Sync/Load strl: Load ramp, to Min power PtM. After protection becomes inactive, the power
limitation is automatically terminated.
Ishort [ % ]
If the level set in this setpoint is reached, the GCB is opened with delay defined in Ishort del. Intended for
shortcurrent detection.
Step: 1 % of Nomin current
Range: 100 - 500 % of Nomin current
Protection: BreakerOpen & Cool-down.
Ishort del [ s ]
Delay for generator shortcurrent protection.
Step: 0,02 s
Range: 0,00 – 10,00 s
Hint:
Ishort del can be set to 0,01 s but this value is rounded to the proximate controller evaluation period.
2Inom del [ s ]
IDMT curve shape selection. 2Inom del is the Reaction time of IDMT protection for 200% overcurrent
Igen = 2* Nominal current.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0,0 - 60,0 s
Protection: BreakerOpen & Cool-down.
IDMT is inversely proportional to the generators overcurrent. The higher the overcurrent gets the less time
will elapse before the protection is activated.
When the IDMT protection is activated the GCB is opened, the event is recorded in the Alarmlist and History,
and the engine will cool down and stop.
Where Reaction time is the amount of time from IDMT detection to the opening of the GCB.
Hint:
The maximum allowable Reaction time is 900 sec.
Reaction time is the amount of time from IDMT detection to the opening of the GCB.
Igen is the maximum current of the three phases of generator current.
EXAMPLE of Reaction time for different over current levels.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 86

86
50,0
No action
No action
No action
No action
500
250
100
50
!!! VERY IMPORTANT !!!
The maximum input range of the controller current terminals is 11 Amps. Anything over this
value is displayed as measured limit, e.g. 15 Amps from CT is measured and displayed as 11
Amps.
Take special care when selecting CT’s. All available 5 Amp CT’s do not have a range up to 11
Amps.
Igen
Nominal current
Ishort
2Inom del
Maximal Reaction time
Reactiontime
IDMTCurrEval [ ENABLED/DISABLED ] (FV)
Activation/deactivation of IDMT current protection.
Gen >V [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for generator over voltage in % of nominal voltage.
Step: 1 % ,(0=OFF)
Range: Gen <V BO – 150 % of GenNomV or GenNomVph-ph respectively
Protection: BreakerOpen
Gen <V [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for generator under voltage in % of nominal voltage.
Step: 1 % (0=OFF)
Range: 50 – Gen >V BO % of GenNomV or GenNomVph-ph respectively
Protection: BreakerOpen
Hint:
All three phases are checked for generator voltage protection. Minimum or maximum out of three is used.
Gen V del [ s ]
Delay for generator under and over voltage protection.
Step: 0,02 s
Range: 0,00 – 600,00 s
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 87

87
Gen >f [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for generator over frequency in % of nominal frequency.
Step: 0,1 % (0=OFF)
Range: Gen<f – 150,0 % of Nominal freq
Protection: BreakerOpen
Gen <f [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for generator under frequency in % of nominal frequency.
Step: 0,1 % (0=OFF)
Range: 50,0 – Gen>f % of Nominal freq
Protection: BreakerOpen
Hint:
The generator frequency is evaluated from the L3 phase.
Gen f del [ s ]
Delay for generator under frequency and over frequency protection.
Step: 0,02 s
Range: 0,00 – 600,00 s
Min stab time [ s ]
This is the minimum time the controller will wait, after switching the engine to nominal RPM, to close the
GCB (the delay ensures that the GCB is closed with correct generator frequency/voltage).
Step: 1s
Range: 1 – Max stab time s
Force value: Yes
Max stab time [ s ]
This is the maximum time the controller will wait for generator voltage and frequency to build up, after
switching the engine to nominal RPM.
Step: 1s
Range: Min stab time – 3600 s
Force value: Yes
Hint:
When generator voltage in Max stab time does not reach defined limits (see Gener protect group), an alarm
occurs and the gen-set will cool down and stop.
Reverse power [%] (FV)
Range 0 .. 50 [%]
This setpoint adjusts the threshold level for the generator reverse (negative) power protection. The threshold
is adjusted in % of the generator nominal power.
The protection activates if the generator power drops below the threshold for time longer than ReversePwr
del.
NOTE:
The generator reverse power protection is Breaker open (BO) type.
ReversePwr del [s]
Range 0 .. 600.0 [s]
The setpoint adjusts the delay for generator reverse power protection. The threshold for the protection is
adjusted by setpoint Reverse power.
Nom EthFltCurr [A] (FV)
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 88

88
Range [units] 0 .. 10000 [A]
This setpoint adjust the level of EarthFault Current when IDMT protection starts to get evaluated. Time of
evaluation of this protection is given by the setpoint 2EthFltCur del. When the EarthFault Current goes below
the level given by Nom EthFltCurr, protection starts decreasing its thermal counter. For more information
about this protection, refer to the setpoint 2EthFltCur del.
2EthFltCur del OFF, 0.1 .. 600.0 [s]
Range [units] OFF, 0.1 .. 600.0 [s]
This setpoint adjusts the reaction time of the IDMT EarthFault Current protection if the current is 200% of the
base level given by the setpoint Nom EthFltCurr.
The reaction time of the IDMT EarthFault Current protection is not fixed; it depends on how much is the
current above the limit (base level). The higher is the current the shorter the reaction time will be.
EXAMPLE OF IDMT CURRENT PROTECTION CURVE
NOTE:
The IDMT EarthFault Current protection is Breaker open and cool down (BO) type.
NOTE:
This protection's internal counter accumulates and it starts continuously decreasing when the EarthFault
Current goes below Nom EthFltCurr. This function prevents the protection from completely reseting when the
EarthFault Current goes below Nom EthFltCurr for only a short period of time. This behavior emulates circuitbreaker with thermal current protection.
ExcitationLoss [%]
Range [units] 0 .. 150 [%]
This setpoint adjusts excitation loss protection level. Corresponding level in kVA is calculated from nominal
power of gen-set as a negative percentage given by this setpoint (e.g. this setpoint is adjusted to 50% and
nominal power of gen-set is 200 kW, therefore excitation loss protection level is set to -100 kVAr)
Delay for this protection is given by the setpoint ExctLoss del.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 89

89
This protection is breaker off and cooldown type. For more information on protection types please refer to the
section Alarm types.
ExctLoss del [s]
Range [units] OFF, 0.1 .. 600.0 [s]
This setpoint adjusts the delay for loss of excitation protection. Threshold of this protection is given by the
setpoint ExcitationLoss.
EarthFaultCurr [ A ]
Threshold for generator Earth fault current protection. The value is measured via the 4th current terminal In /
Im3.
Step: 1 A
Range: 0 – 10000 A
Protection: BreakerOpen.
EthFltCurr del [ s ]
Delay for generator Earth fault current protection.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0– 600,0 s
Hint:
Earth fault current protection based on limits above is active only if I/E-Pm meas = ANALOG INPUT or
NONE.
Gen V unbal [ % ]
Threshold for generator voltage unbalance alarm in % of nominal voltage. The voltage unbalance is
calculated as a maximum difference between phase voltages.
Step: 1%
Range: 0 – 200% of GenNomV or GenNomVph-ph respectively
Gen V unb del [ s ]
Delay for generator voltage unbalance alarm.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0 – 600,0 s
Protection: BreakerOpen.
Gen I unbal [ % ]
Threshold for generator current asymmetry (unbalance) in % of nominal current. The current unbalance is
calculated as a maximum difference between phase currents.
Step: 1%
Range: 0 – 200% of Nomin current
Gen I unb del [ s ]
Delay for generator current asymmetry (unbalance).
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0 – 600,0 s
Protection: BreakerOpen.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 90

90
Mains protect
The content depends on programmable protections settings. This list contains pre-set protections from
default archives + fixed protections, which are always present:
Mains >V MP [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for mains over voltage.
Step: 1%
Range: Mains<V MP – 150 % of MainsNomV or MainsNomVph-ph respectively
Protection: Mains protection.
Force value possibility: Yes
Mains <V MP [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for mains under voltage.
Step: 1 %
Range: 50 – Mains>V MP % of MainsNomV or MainsNomVph-ph respectively
Protection: Mains protection.
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
All three phases are checked for mains voltage protection. Minimum or maximum out of three is used.
For high voltage applications, the MainsNomVph-ph can be used for nominal voltage setting.
Mains V del [ s ]
Delay for mains under and over voltage protection.
Step: 0,02 s
Range: 0,00 – 600,00 s
Mains >f [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for mains over frequency in % of nominal frequency.
Step: 0,1%
Range: Mains<f - 150,0 % of Nominal freq
Protection: Mains protection.
Force value possibility: Yes
Mains <f [ % ] (FV)
Threshold for mains under frequency in % of nominal frequency.
Step: 0,1%
Range: 50,0 - Mains>f % of Nominal freq
Protection: Mains protection.
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
The mains frequency is evaluated from the L3 phase.
Mains f del [ s ]
Delay for mains under frequency and over frequency protection.
Step: 0,02 s
Range: 0,00 – 600,00 s
VectorS prot [ DISABLED / PARALLEL ONLY / ENABLED ] (FV)
DISABLED: Vector shift protection is disabled.
PARALLEL ONLY: Vector shift protection is enabled only if the gen-set is running in parallel with mains
(= MCB+GCB status active).
ENABLED: Vector shift protection is enabled if MCB status is active.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 91

91
Force value possibility: Yes
Hint:
If ENABLED is selected, it is likely that Vector shift protection will trip the MCB before other mains
protections. It senses the fast changes in mains voltage angle position, which occur with every mains failure,
even if the gen-set is not running in parallel with mains.
VectorS limit [ ]
Vector shift protection threshold level.
Step: 1°
Range: 1 – 45°
Hint:
To be sure of proper adjusting of VectorS limit, check Max VectorS value on the controller or PC software
screen. Max VectorS value is set to zero when transiting to parallel, and then accumulates the maximum
reached value (positive only) during parallel operation. Thus, during the normal operation, only the
“background noise” is accumulated (usually max 3°), and the protection level should be set to approximately
twice the value of this “noise”.
Mains V unbal [ % ]
Threshold for mains voltage unbalance alarm in % of nominal voltage. The voltage unbalance is calculated
as a maximum difference between phase voltages.
Step: 1%
Range: 0 – 200% of MainsNomV or MainsNomVph-ph respectively
Mains Vunb del [ s ]
Delay for mains voltage unbalance alarm.
Step: 0,1s
Range: 0 – 600,0 s
Protection: Mains protection
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 92

92
AMF settings
FwRet break [ s ] (FV)
Delay between GCB opening and MCB closing during the return to mains when reverse synchronizing is not
enabled.
Delay between MCB opening and GCB closing in TEST Mode, when Return To mains = ENABLED and
power cut comes.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0 – 60,0 s
Force value possibility: Yes
Mains ret del [ s ] (FV)
Delay after the mains return to the start of synchronizing of MCB (SPtM) or GCB (SPI).
Step: 1 s
Range: 0 – 3600 s
Force value possibility: Yes
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 93

93
Sync/Load ctrl
Voltage match
1 2 3
Note:
1 1 0 Phase L3 is out of voltage window
Voltage match
1 2 3
Note:
1 1 1 All phases are in voltage window
IG/IS-NT
MCB
LOAD
GCB
4
Vm Im
MCB GCB
3x10 kV 3x230/400VAC
Vg Ig
L1, L2, L3, N
G
4
T1
T2
3
SpeedRegChar [ POSITIVE / NEGATIVE ]
Switch between speed governor characteristic.
POSITIVE: When the controller Speed governor output voltage increases – engine speed increases.
NEGATIVE: When the controller Speed governor output voltage decreases – engine speed increases.
Hint:
When set to NEGATIVE, Binary outputs Speed Up and Speed Dn still work without inversion.
Voltage window [ % ] (FV)
Maximum difference between generator and mains/bus voltage.
Step: 0,1 % of GenNomV
Range: 0,0 – 100,0 % of GenNomV
Force value: Yes
Hint:
See Voltage phases match indication on the controller Synchronizing screen.
Example 1.
Example 2.
GtoM AngleReq [ ]
Requested phase difference between generator and mains voltage during synchronizing. Use this setpoint
for phase correction of potential transformers connection.
Step: 1
Range: -45 to +45
Following is an example of the controller connection to a high voltage system.
T1 shifts phase +30 and no shift is on T2.
GtoM AngleReq = +30 for this example.
Phase window [ ] (FV)
Maximum phase angle (mains/bus x generator voltage) difference between requested and actual angle for
synchronizing.
Step: 1
Range: 0 – 90
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 94

94
Force value: Yes
Hint:
If you want to lock out the GCB closing during synchronizing loop test, set Phase window = 0. This allows the
control loop to be tested while actual GCB closing is blocked.
Dwell time [ s ] (FV)
The period of time that the phase angle must be within Phase window and voltage difference within Voltage
window before a breaker (GCB/MCB) is closed.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 0,0 – 25,0 s
Force value: Yes
Freq gain [ % ]
Gain of frequency control loop.
Step: 0,1 %
Range: 0,0 % - 200,0 %
Freq int [ % ]
Relative integration factor of frequency control loop.
Step: 1 %
Range: 0 % – 100 %
Freq reg loop [ GCB OPEN / SYNC ONLY ] (FV)
GCB OPEN: Frequency control is active during running unloaded period and during synchronizing.
SYNC ONLY: Frequency control is active during synchronizing only.
Force value: Yes
Angle gain [ % ]
Gain of angle control loop.
Step: 0,1%
Range: 0,0 % to +200,0 %
Speed gov bias [ V ] (FV)
Speed control DC output bias level of SPEED GOVERNOR voltage output.
Step: 0,01 V
Range: SpeedGovLowLim to SpeedGovHiLim V
Force value: Yes
SpdGovPWM rate [ Hz ]
Pulse-Width Modulation rate of the Speed Regulator pulse output.
Step: 1 Hz
Range: 500 – 3000 Hz
Hint:
This adjusting can be used for some Cummins and CAT engines speed governor interfaces. We recommend
to keep the default setting (1200 Hz) for all other speed governor types (coming out through the analog
interface +/- 10V).
SpeedGovLowLim [ V ]
Low limit for voltage on analog output of Speed Regulator.
Step: 0,01 V
Range: -10,00 V – SpeedGovHiLim
SpeedGovHiLim [ V ]
High limit for voltage on analog output of Speed Regulator.
Step: 0,01 V
Range: SpeedGovLowLim - 10,00 V
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 95

95
TauSpeedActuat [ s ]
Time constant of the speed actuator connected to the binary Up/Down outputs. This is to match the reaction
of the controller’s regulator with the actual reaction time of the actuator.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 1,0 - 300,0 s
Load ramp [ s ] (FV)
Increasing or decreasing load rate. In seconds / Nomin power.
Step: 1 s
Range: 0 – GCB open del s
Force value: Yes
When the timer is countdown then the state soft load or unload is terminated.
Load gain [ % ]
Gain of power control loop.
Step: 0,1 %
Range: 0 – 200,0 %
Load int [ % ]
Relative integration factor of power control loop.
Step: 1 %
Range: 0 – 100 %
Hint:
Load gain and Load int setpoints are active only when gen-set operates in parallel to the mains, when GCB
and MCB are closed. This is valid for both single and multiple applications.
RampStartLevel [ % ]
Value of initial load, on which starts the load ramping according to Load ramp setting.
Step: 1 %
Range: 0 – 100 %
GCB open level [ % ] (FV)
Power level for opening the GCB while soft unload is in progress. If this level isn’t reached, the GCB opens
after GCB open del time.Setting = NO LEVEL disables this GCB open criteria.
Step: % of Nomin power
Range: NO LEVEL, 1 to 100 %
GCB open del [ s ] (FV)
The timeout to unload the gen-set. Should the load ramp fail to bring the gen-set power down to GCB open
level to allow the opening of GCB, the breaker will open after GCB open del. Setting = NO TIMEOUT
disables this GCB open timeout criteria.
Step: 1 s
Range: Load ramp – 1800, NO TIMEOUT
Force value: Yes
Hint:
It is possible to open GCB by panel button or externally.
Sync timeout [ s ] (FV)
Maximum allowed time for forward or reverse synchronization.
Step: 1 s
Range: 1 – 1800 s, NO TIMEOUT
Hint:
If the synchronizing does not succeed within (Sync timeout / 10, but minimum 60) s, the speed regulator
output is reset and synchronisation is automatically started again. So if you set the Sync timeout to
sufficiently high value, the synchronizing cycle can be internally repeated up to 10 times.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 96

96
If NO TIMEOUT is selected, then the time for synchronizing has no limitation and can only be interrupted by
pressing the GCB or STOP button in SEM mode or removing a corresponding request input in AUT mode. In
the NO TIMEOUT case, the synchronization is restarted every 1800 / 10 = 180 s.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 97

97
Volt/PF ctrl
Operation mode
Island
Parallel to mains
Gen-set state
Running,
GCB opened
Loaded island
GCB closed
MCB opened
Synchronizing
Loaded in parallel
GCB closed
Active loop:
Volt gain, int;
Active loop:
Volt gain, int;
Active loop:
Volt gain, int;
Active loop:
PF control
AVRRegChar [ POSITIVE / NEGATIVE ]
Switch between AVR characteristic.
POSITIVE: When the controller and AVRi output voltage increases – generator voltage increases.
NEGATIVE: When the controller and AVRi output voltage decreases – generator voltage increases.
Hint:
When set to NEGATIVE, Binary outputs AVR Up and AVR Dn still work without inversion.
Voltage gain [ % ]
Gain of voltage control loop.
Step: 0,1 %
Range: 0,0 to +200,0 %
Voltage int [ % ]
Relative integration factor of voltage control loop. Increasing of integration value causes quicker response.
Step: 1 %
Range: 0 – 100 %
Hint:
Voltage gain and Voltage int setpoints are active (adjust AVR) when GCB is open to maintain the Nominal
voltage or to match voltage during synchronizing. Voltage loop operates as well in single island operation.
PF gain [ % ]
Gain of power factor control loop.
Step: 0,1 %
Range: 0,0 – 200,0 %
PF int [ % ]
Relative integration factor of power factor control loop. Increasing of integration value causes quicker
response.
Step: 1 %
Range: 0 – 100 %
Hint:
When any gain setpoint is set to zero, the corresponding control loop is switched OFF.
PF gain and PF int setpoints are active only when the gen-set runs parallel to mains.
VoltRegOut behaviour in single-gen-set applications
AVR DCout bias [ % ] (FV)
AVRi voltage output bias level. This is a basic voltage level of the output if there is no regulation loop active.
Step: 0,1 %
Range: 0 – 100,0 %
Force value: Yes
Hint:
Real voltage level depends on AVRi outputs connection and output level potentiometer setting. Maximum
range is 10 V.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 98

98
TauVoltActuat [ s ]
Time constant of the voltage regulator connected to the binary Up/Down outputs. This is to match the
reaction of the controller‘s regulator with the actual reaction time of the voltage regulator.
Step: 0,1 s
Range: 1,0 - 300,0 s
Force value: Yes
Hint:
Use this for older generators where motorised potentiometer is used for voltage adjust to the AVR.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 99

99
Force value
Force value 1-16 [ X ]
„Source“ setpoints containing the alternative values for selected „target“ setpoints. The setpoint with index X
corresponds to the Force value Xth function. Procedure description see in GenConfig-x.y User guide.
Hint:
As the “source” for Force value channel can be used any compatible value in the controller (in general all
values and setpoints of types integer8,16,32). In that case the corresponding Force value X setpoint is
unused on that channel.
ExtValue1LoLim [ X ]
ExtValue2LoLim [ X ]
ExtValue3LoLim [ X ]
ExtValue4LoLim [ X ]
ExtValueX low limit. The value is not decreased under this limit, even if the request still exists (via binary
input ExtValueX down).
Step: 1 X
Range: -32000 – ExtValueXHiLim X
ExtValue1HiLim [ X ]
ExtValue2HiLim [ X ]
ExtValue3HiLim [ X ]
ExtValue4HiLim [ X ]
ExtValueX high limit. The value is not increased above this limit, even if the request still exists (via binary
input ExtValueX up).
Step: 1 X
Range: ExtValueXLoLim – 32000 X
ExtValue1 rate [ X/s ] (FV)
ExtValue2 rate [ X/s ] (FV)
ExtValue3 rate [ X/s ] (FV)
ExtValue4 rate [ X/s ] (FV)
ExtValueX rate of change per second. If the binary input ExtValueX down or ExtValueX up is active, the
value is changed according to this rate.
Step: 1 X/s
Range: 1 – 10000 X/s
Hint:
If binary input ExtValueXreset is active, the corresponding ExtValueX is held at its default value, regardless
of the activity of inputs Up and Down and regardless of incoming external set commands.
Using this function in combination with Force value you can externally control selected setpoints’ values and
achieve some special behaviour of the controller.
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
Page 100

100
ExtValue1deflt [ X ] (FV)
ExtValue2deflt [ X ] (FV)
ExtValue3deflt [ X ] (FV)
ExtValue4deflt [ X ] (FV)
ExtValueX default (starting) value. If ExtValueX is changed from this default value using Modbus command,
the new value is kept in ExtValueX until another command arrives or until the controller has been switched
off. If the binary input ExtValueXreset is active, the ExtValueX is held at this value regardless of other
conditions.
Step: 1 X
Range: -32000 – 32000 X
Inteli NT GeCon-MARINE SPI, SW Version 3.2, ©ComAp – July 2015
IGS-NT-GeCon-MARINE-SPI-3.2.PDF
 Loading...
Loading...