Page 1

MDS 3.0 Quality Measures
USER’S MANUAL
(v14.0)
Effective October 1, 2020
Page 2

QUALITY MEASURES (QM) USER’S MANUAL
CONTENTS
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures USER’S MANUAL (v14.0) ....................................................... i
QUALITY MEASURES (QM) USER’S MANUAL CONTENTS ................................. i
NOTABLE CHANGES TO THE MDS QUALITY MEASURES (QM)
USER’S MANUAL V14 .........................................................................................1
Chapter 1 QM Sample and Record Selection Methodology ......................................................3
Section 1: Definitions .......................................................................................................3
Section 2: Selecting the QM Samples ...............................................................................5
Section 3: Short Stay Record Definitions .........................................................................7
Section 4: Long Stay Record Definitions .........................................................................9
Section 5: Transition from the Pressure Ulcer to Skin Integrity Quality
Measures ................................................................................................................12
Section 6: Transition to the Patient Driven Payment Model ..........................................12
Chapter 2 MDS 3.0 Quality Measures Logical Specifications ................................................15
Section 1: Short Stay (SS) Quality Measures .................................................................16
Table 2-1 Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute Care: Pressure
Ulcer/Injury ................................................................................................16
Table 2-2 Percent of Residents Who Were Assessed and Appropriately
Given the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS) ..............................................17
Table 2-3 Percent of Residents Who Received the Seasonal Influenza
Vaccine (SS) ..............................................................................................18
Table 2-4 Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS) ...............................................................19
Table 2-5 Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS) ............................20
Table 2-6 Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)21
Table 2-7 Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 i
.....................................................................
Vaccine (SS
)
22
..
Page 3

Table 2-8 Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)23
.....................................................................
Table 2-9 Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)
24...................................
Table 2-10 Percent of Residents Who Newly Received an Antipsychotic
Medication (SS) .........................................................................................25
Table 2-11 Percent of Residents Who Made Improvements in Function
(SS) ............................................................................................................27
Section 2: Long Stay (LS) Quality Measures .................................................................30
Table 2-12 Percent of Residents Experiencing One or More Falls with
Major Injury (LS) .......................................................................................30
Table 2-13 Percent of High-Risk Residents With Pressure Ulcers (LS) ...............31
Table 2-14 Percent of Residents Assessed and AppropriatelyGiven the
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS) ...............................................................33
Table 2-15 Percent of Residents Who Received the Seasonal Influenza
Vaccine (LS) ..............................................................................................34
Table 2-16 Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS) ...............................................................35
Table 2-17 Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS) ............................36
Table 2-18 Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS) ......................................................................37
Table 2-19 Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal
Vaccine (LS) ..............................................................................................38
Table 2-20 Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS) ......................................................................39
Table 2-21 Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS)40
...................................
Table 2-22 Percent of Residents with a Urinary Tract Infection (LS) ...................41
Table 2-23 Percent of Low Risk Residents Who Lose Control of Their
Bowel or Bladder (LS) ...............................................................................42
Table 2-24 Percent of Residents Who Have/Had a Catheter Inserted and
Left in Their Bladder (LS) .........................................................................44
Table 2-25 Percent of Residents Who Were Physically Restrained (LS) ..............46
Table 2-26 Percent of Residents Whose Need for Help with Activities of
Daily Living Has Increased (LS) ...............................................................47
Table 2-27 Percent of Residents Who Lose Too Much Weight (LS) ....................49
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 ii
Page 4

Table 2-28 Percent of Residents Who Have Depressive Symptoms (LS) .............50
Table 2-29 Percent of Residents Who Received an Antipsychotic
Medication (LS) .........................................................................................52
Table 2-30 Prevalence of Falls (LS) 53 ...........
...........
Tabel 2-31 Prevalence of Antianxiety/Hypnotic Use (LS)
Table 2-32 Prevalence of Behavior Symptoms Affecting Others (LS)56
...............................................
...................................
.....
54
............
Table 2-33 Percent of Residents Whose Ability to Move Independently
Worsene
d (LS) ...........................................................................................57
Table 2-34 Percent of Residents Who Used Antianxiety or Hypnotic
Medication (LS) .........................................................................................60
Chapter 3 Technical Details .....................................................................................................61
Quality Measures (QM) Technical Details .....................................................................62
Section 1 Introduction .....................................................................................................63
Section 2 Steps Used in National QM Calculation .........................................................65
Section 3 Calculation of the Expected QM Score ..........................................................69
Section 4 Calculation of the Adjusted QM Score ...........................................................72
Chapter 4 Parameters Used for Each Quarter ..........................................................................73
Table 4-1. Logistic Regression Coefficients .........................................................74
Table 4-2. National Observed QM Means ............................................................75
Chapter 5 Episode and Stay Determination Logic ...................................................................76
Table 5-1: Possible Entry Dates When Entry Record is Missing ..........................79
Chapter 6 Specifications for the Facility Characteristics Report .............................................83
Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions ...........................85
APPENDIX A Quality Measure Identification Number by CMS Reporting Module..............1
Table A-1: Quality Measures (QMs) by CMS Reporting Module – Short
Stay ..............................................................................................................5
Table A-2: Quality Measures (QMs) by CMS Reporting Module – Long
Stay ..............................................................................................................7
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 iii
Page 5

NOTABLE CHANGES TO THE MDS QUALITY MEASURES (QM)
USER’S MANUAL V14
Transition from the Pressure Ulcer to Skin Integrity Measure
Beginning with the FY 2020 SNF QRP effective October 1, 2020, , Percent of Residents or
Patients with Pressure Ulcers That Are New or Worsened (Short Stay) (CMS ID: S002.02) will
be removed from the SNF QRP measure set and replaced with a modified version of that
measure, Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute Care: Pressure Ulcer/Injury (CMS ID: S038.02),
to include the addition of new or worsened unstageable pressure ulcers. This SNF QRP measure
will also be reported as a part of the NHQI effective 10/01/2020. For additional details on this
transition, please see Chapter 1 Section 5 of this manual.
Surveyor Quality Measures
The appendix on surveyor quality measures contained in previous versions of this user’s manual
has been removed from MDS QM User’s Manual V14, and the measures have been relocated to
Section 2 (Long Stay) of Chapter 2. Quality measure reports are available to State Surveyors and
facility staff through CMS’s CASPER reporting system. Quality measures available to facilities
through CASPER are also available to State Surveyors. Information regarding which measures
are available in CASPER is located in the Quality Measure by CMS Reporting Module, located
in Appendix A of this manual.
Measures Withdrawn from NQF Submission
The appendix on measures withdrawn from NQF submission contained in previous versions of
this user’s manual has been removed from MDS QM User’s Manual V14, and the measures have
been relocated to Section 1 (Short Stay) and Section 2 (Long Stay) of Chapter 2 respectively.
The following list contains measures that were previously approved or given time limited
endorsement by the National Quality Forum (NQF) but have been withdrawn from NQF
submission. The specifications for the Short Stay measures withdrawn from NQF submission can
be found in Chapter 2 Section 1 of this manual, and the specifications for the long stay measures
withdrawn from NQF submission can be found in Chapter 2 Section 2 of this manual.
• Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Short Stay) (CMS: N007.02) (NQF #0682 withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Short Stay) (CMS: N008.02) (NQF #0682A withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Short Stay) (CMS: N009.02) (NQF #0682B withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (Short Stay) (CMS: N010.02) (NQF #0682C withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Long Stay) (CMS: N020.02) (NQF #0683 withdrawn)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 1
Page 6

• Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Long Stay) (CMS: N021.02) (NQF #0683A withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Pneumococcal Vaccine
(Long Stay) (CMS: N022.02) (NQF #0683B withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the
Pneumococcal Vaccine (Long Stay) (CMS: N023.02) (NQF #0683C withdrawn)
• Percent of Residents Who Have Depressive Symptoms
(Long Stay) (CMS: N030.02) (NQF #0690 withdrawn)
• Percent of Low Risk Residents Who Lose Control of Their Bowel or Bladder
(Long Stay) (CMS: N025.02) (NQF #0685 withdrawn)
Renaming of Appendices
The Appendices contained in previous versions of this user’s manual have been renamed as
chapters. The only Appendix (A) in the MDS QM User’s Manual V14 contains the Quality
Measure Identification Number by CMS Reporting Module V1.8. The following list contains the
new chapter names in this user’s manual paired with the associated appendix name from
previous versions of this user’s manual:
• “Chapter 3: Technical Details,” previously “Appendix A: Technical Details”
• “Chapter 4: Parameters Used for Each Quarter,” previously “Appendix B: Parameters
Used for Each Quarter”
• “Chapter 5: Episode and Stay Determination Logic,” previously “Appendix C: Episode
and Stay Determination Logic”
• “Chapter 6: Specifications for the Facility Characteristics Report,” previously “Appendix
F: Specifications for the Facility Characteristics Report”
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 2
Page 7

Chapter 1
QM Sample and Record Selection Methodology
The purpose of this chapter is to describe the methodology that is used to select the short and
long stay samples as well as the key records that are used to compute the QMs for each of those
samples. The first section below will present definitions that are used to describe the selection
methodology. The second section describes the selection of the two samples. The third and
fourth sections describe the selection of the key records within each of the two samples.
The logic presented below depends upon the concepts of stays and episodes. Detailed
specifications for the identification of stays and episodes are presented in Appendix C of this
document.
Section 1: Definitions
Target period. The span of time that defines the QM reporting period (e.g., a calendar quarter).
Influenza Season. Influenza season is July 1 of the current year to June 30 of the following year
(e.g., July 1, 2019 through June 30, 2020 for the 2019 – 2020 influenza season).1
Stay. The period of time between a resident’s entry into a facility and either (a) a discharge, or
(b) the end of the target period, whichever comes first. A stay, thus defined, may include
interrupted stays lasting 3 calendar days or less. The start of a stay is either:
• An admission entry (A0310F = [01] and A1700 = [1]), or
• A reentry (A0310F = [01] and A1700 = [2]).
The end of a stay is the earliest of the following:
• Any discharge assessment (A0310F = [10, 11]), or
• A death in facility tracking record (A0310F = [12]), or
• The end of the target period.
Interrupted Stay. During a stay the resident had an interruption in their stay and resumed the
same stay within three consecutive calendar days. Interrupted stays apply only to Medicarecovered stays and pertain to both short- and long-stay resident episodes.
1
This definition is applicable to each of the long- and short-stay influenza vaccination measures. The short-stay
measures are identified as the following: NQF #0680 (CMS ID: N003.03); NQF #0680A (CMS ID: N004.03);
NQF #0680B (CMS ID: N005.03); NQF #0680C (CMS ID: N006.03). The long-stay measures are identified as
the following: NQF #0681 (CMS ID: N016.03); NQF #0681A (CMS ID: N017.03); NQF #0681B (CMS ID:
N018.03); NQF #0681C (CMS ID: N019.03).
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 3
Page 8

Episode. A period of time spanning one or more stays. An episode begins with an admission
(defined below) and ends with either (a) a discharge, or (b) the end of the target period,
whichever comes first. An episode starts with:
• An admission entry (A0310F = [01] and A1700 = [1]).
The end of an episode is the earliest of the following:
• A discharge assessment with return not anticipated (A0310F = [10]), or
• A discharge assessment with return anticipated (A0310F = [11]) but the resident did not
return within 30 days of discharge, or
• A death in facility tracking record (A0310F = [12]), or
• The end of the target period.
Admission. An admission entry record (A0310F = [01] and A1700 = [1]) is required when any
one of the following occurs:
• Resident has never been admitted to this facility before; or
• Resident has been in this facility previously and was discharged return not anticipated; or
• Resident has been in this facility previously and was discharged return anticipated and
did not return within 30 days of discharge.
Reentry. A reentry record (A0310F = [01] and A1700 = [2]) is required when all of the
following occurred prior to this entry; the resident was:
• Discharged return anticipated, and
• Returned to facility within 30 days of discharge.
Cumulative days in facility (CDIF). The total number of days within an episode during which
the resident was in the facility. It is the sum of the number of days within each stay included in
an episode. If an episode consists of more than one stay separated by periods of time outside the
facility (e.g., hospitalizations), and/or one or more stays with interruptions lasting 3 calendar
days or less, only those days within the facility would count towards CDIF. Any days outside of
the facility (e.g., hospital, home, etc.) would not count towards the CDIF total. The following
rules are used when computing CDIF:
• When counting the number of days until the end of the episode, counting stops with (a)
the last record in the target period if that record is a discharge assessment (A0310F = [10,
11]), (b) the last record in the target period if that record is a death in facility (A0310F =
[12]), or (c) the end of the target period is reached, whichever is earlier.
• When counting the duration of each stay within an episode, include the day of entry
(A1600) but not the day of discharge (A2000) unless the entry and discharge occurred on
the same day in which case the number of days in the stay is equal to 1.
o For example: if a resident is admitted on Monday and discharged the following
day (Tuesday), the duration of that episode would be 1 day.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 4
Page 9

• While death in facility records (A0310F = [12]) end CDIF counting, these records are not
used as target records because they contain only tracking information and do not include
clinical information necessary for QM calculation.
• Special rules for influenza vaccination measures. Influenza vaccination measures are
calculated only once per 12-month influenza season, which begins July 1 of a given year
and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year. For these measures, the target period begins
on October 1 and ends on March 31. This means that the end-of-episode date will be
March 31 for an episode that is ongoing at the end of the influenza season and that March
31 should be used as the end date when computing CDIF and for classifying stays as long
or short for the influenza vaccination measures.
o Note, the target period (i.e., October 1 – March 31) is different than the selection
period, which begins October 1 and ends June 30 of the following year. The
selection period for the influenza vaccination measures is discussed more in
Sections 3 and 4 below.
Short stay. An episode with CDIF less than or equal to 100 days as of the end of the target
period. Short stays may include one or more interruptions, indicated by Interrupted Stay
(A0310G1 = [1]).
Long stay. An episode with CDIF greater than or equal to 101 days as of the end of the target
period. Long stays may include one or more interruptions, indicated by Interrupted Stay
(A0310G1 = [1]).
Target date. The event date for an MDS record, defined as follows:
• For an entry record (A0310F = [01]), the target date is equal to the entry date (A1600).
• For a discharge record (A0310F = [10, 11]) or death-in-facility record (A0310F = [12]),
the target date is equal to the discharge date (A2000).
• For all other records, the target date is equal to the Assessment Reference Date (ARD,
A2300).
Section 2: Selecting the QM Samples
Two resident samples are selected for computing the QMs: a short-stay sample and a long-stay
sample. These samples are selected using the following steps:
1. Select all residents whose latest episode either ends during the target period or is ongoing
at the end of the target period. This latest episode is selected for QM calculation.
2. For each episode that is selected, compute the cumulative days in the facility (CDIF).
3. If the CDIF is less than or equal to 100 days, the resident is included in the short-stay
sample.
4. If the CDIF is greater than or equal to 101 days, the resident is included in the long-stay
sample.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 5
Page 10

Note that all residents who are selected in Step 1 above will be placed in either the short- or
long-stay sample and that the two samples are mutually exclusive. If a resident has multiple
episodes within the target period, only the latest episode is used.
Within each sample, certain key records are identified which are used for calculating individual
measures. These records are defined in the following sections.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 6
Page 11
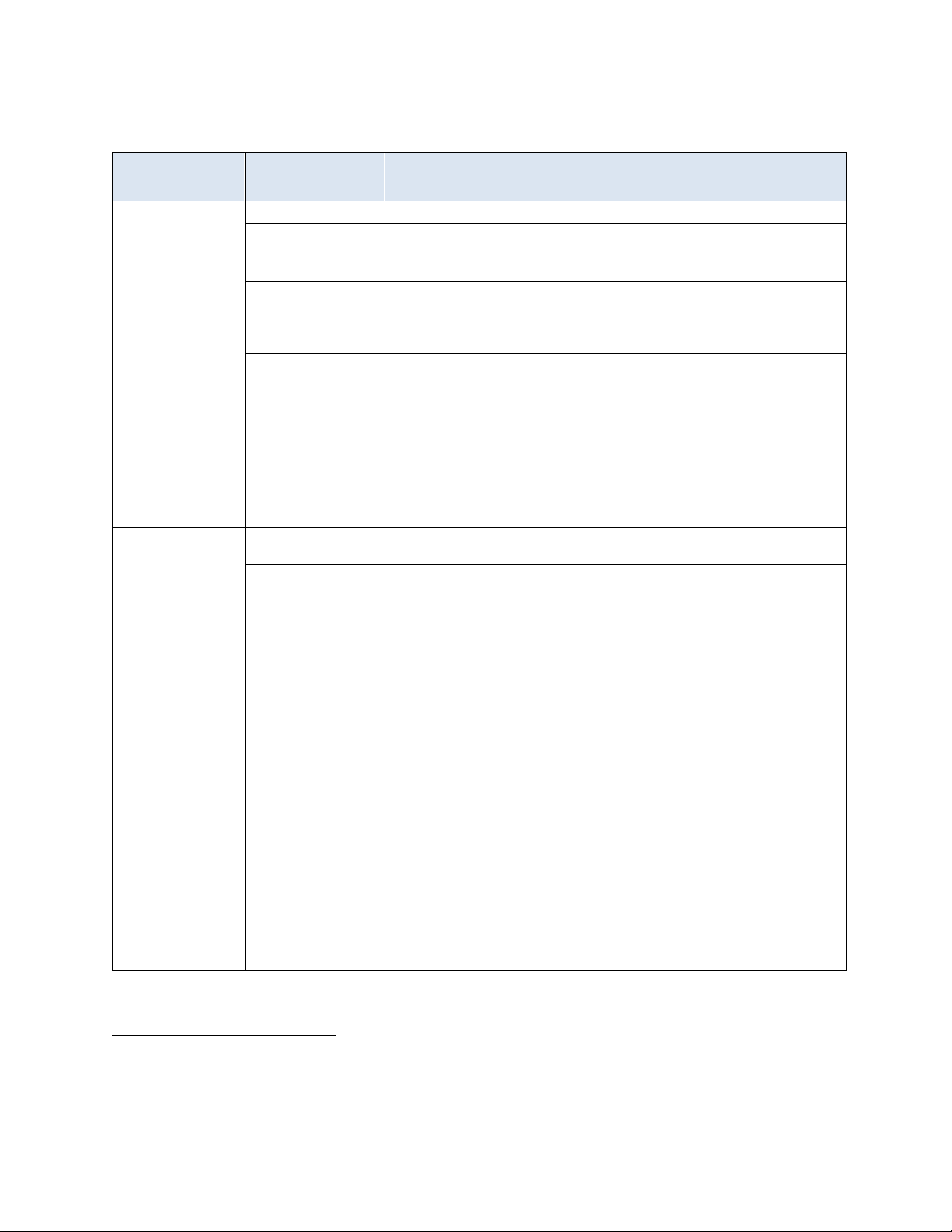
Section 3: Short Stay Record Definitions
ASSESSMENT
SELECTED PROPERTY
Target
assessment
Initial
assessment
Selection period Most recent 6 months (the short stay target period).
Qualifying RFAs2
Selection logic
Rationale
Selection period
Qualifying RFAs
Selection logic
Rationale
A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
A0310B
A0310F = [10, 11]
Latest assessment that meets the following criteria: (a) it is
cont
qualifying RFA, and (c) its target date is no more than 120 days
before the end of the episode.
Records with a qualifying RFA contain all of the items needed to
defi
date within the target period, but it must occur within 120 days
before the end of the resident’s selected episode (either the target
date of a discharge assessment or death in facility record that is the
last record in the target period or the end of the target period if the
episode is ongoing). 120 days allows 93 days between quarterly
assessments plus an additional 27 days to allow for late
assessments. The target assessment represents the resident’s
status at the end of the episode.
First assessment following the admission entry record at the
beginni
A0310A = [01] or
A0310B
A0310F = [10, 11]
Earliest assessment that meets the following criteria: (a) it is
cont
qualifying RFA, (c) it has the earliest target date that is greater than
or equal to the admission entry date starting the episode, and (d) its
target date is no more than 130 days prior to the target date of the
target record. The initial assessment cannot be the same as the
target assessment. If the same assessment qualifies as both the
initial and target assessments, it is used as the target assessment
and the initial assessment is considered to be missing.
Records with a qualifying RFA contain all of the items needed to
defi
within the target period. The initial assessment represents the
resident’s status as soon as possible after the admission that marks
the beginning of the episode. If the initial assessment is more than
130 days prior to the target assessment, it is not used and the initial
record is considered to be missing. This prevents the use of an
initial assessment for a short stay in which a large portion of the
resident’s episode was spent outside the facility. 130 days allows
for as many as 30 days of a 100-day stay to occur outside of the
facility.
= [01] or
ained within the resident’s selected episode, (b) it has a
ne the QMs. The target assessment need not have a target
ng of the resident’s selected episode.
= [01] or
ained within the resident’s selected episode, (b) it has a
ne the QMs. The initial assessment need not have a target date
(continued)
SELECTION SPECIFICATIONS
3
2
RFA: Reason For Assessment.
3
A short stay episode can span more than 100 calendar days because days outside of the facility are not counted in
defining a 100-day or less short stay episode.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 7
Page 12
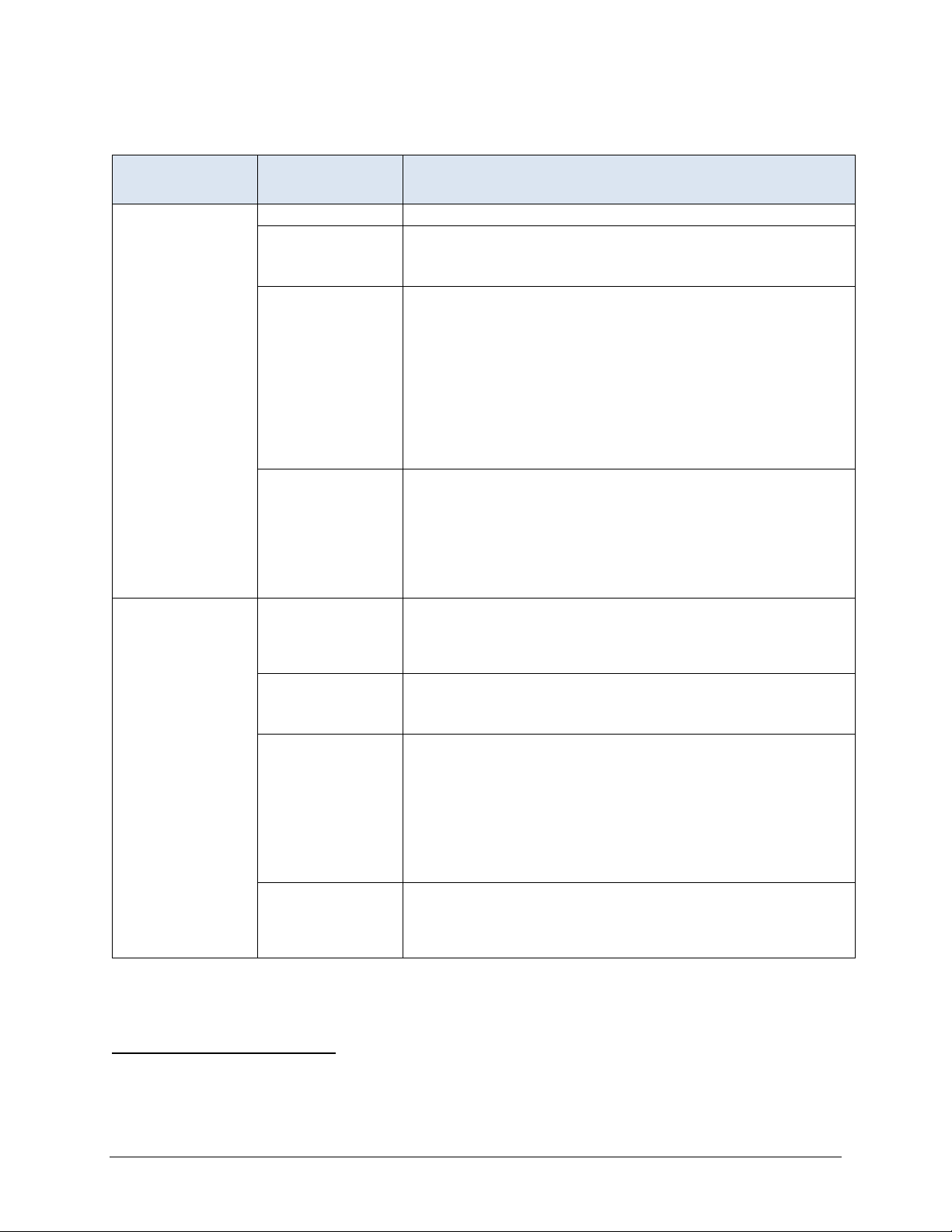
Short Stay Record Definitions (continued)
ASSESSMENT
SELECTED PROPERTY SELECTION SPECIFICATIONS
Look-back Scan Selection period Scan all qualifying RFAs within the current episode.
Qualifying RFAs A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
Influenza
vaccination
assessment
A0310B = [01]
A0310F = [10, 11]
Selection logic
Include the target assessment and qualifying earlier
assessments in the scan. Include an earlier assessment in the
scan if it meets all of the following conditions: (a) it is contained
within the resident’s episode, (b) it has a qualifying RFA, and
(c) its target date is on or before the target date for the target
assessment. The target assessment and qualifying earlier
assessments are scanned to determine whether certain events
or conditions occurred during the look-back period. These
events and conditions are specified in the definitions of
measures that utilize the look-back scan.
Rationale Some measures utilize MDS items that record events or
conditions that occurred since the prior assessment was
performed. The purpose of the look-back scan is to determine
whether such events or conditions occurred during the lookback period. All qualifying RFAs with target dates within the
episode are examined to determine whether the event or
condition of interest occurred at any time during the episode.
4
Selection period
All assessments with target dates on or after October 1 of the
most recently completed influenza season (i.e., the target date
must be on or between October 1 of the current year and June
30 of the following year).
Qualifying RFAs
A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
A0310B = [01]
A0310F = [10, 11]
Selection logic Select the record with the latest target date that meets all of
the following conditions:
a) It has a qualifying RFA, and
b) Target date is on or after October 1 of the most recently
c
fall on or between October 1 and June 30), and
c) A1600 (entry date) is on or before March 31 of the most
recently completed influenza season.
Rationale The selection logic defined above is intended to identify the
latest assessment that reports the influenza vaccine status for
a resident who was in the facility for at least one day from
October 1 through March 31.
or
or
ompleted influenza season (i.e., the target date must
4
The selection period uses a June 30th end date to ensure residents who are vaccinated between October 1 and
March 31, but do not have an assessment completed until after March 31, are captured in the measure sample.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 8
Page 13
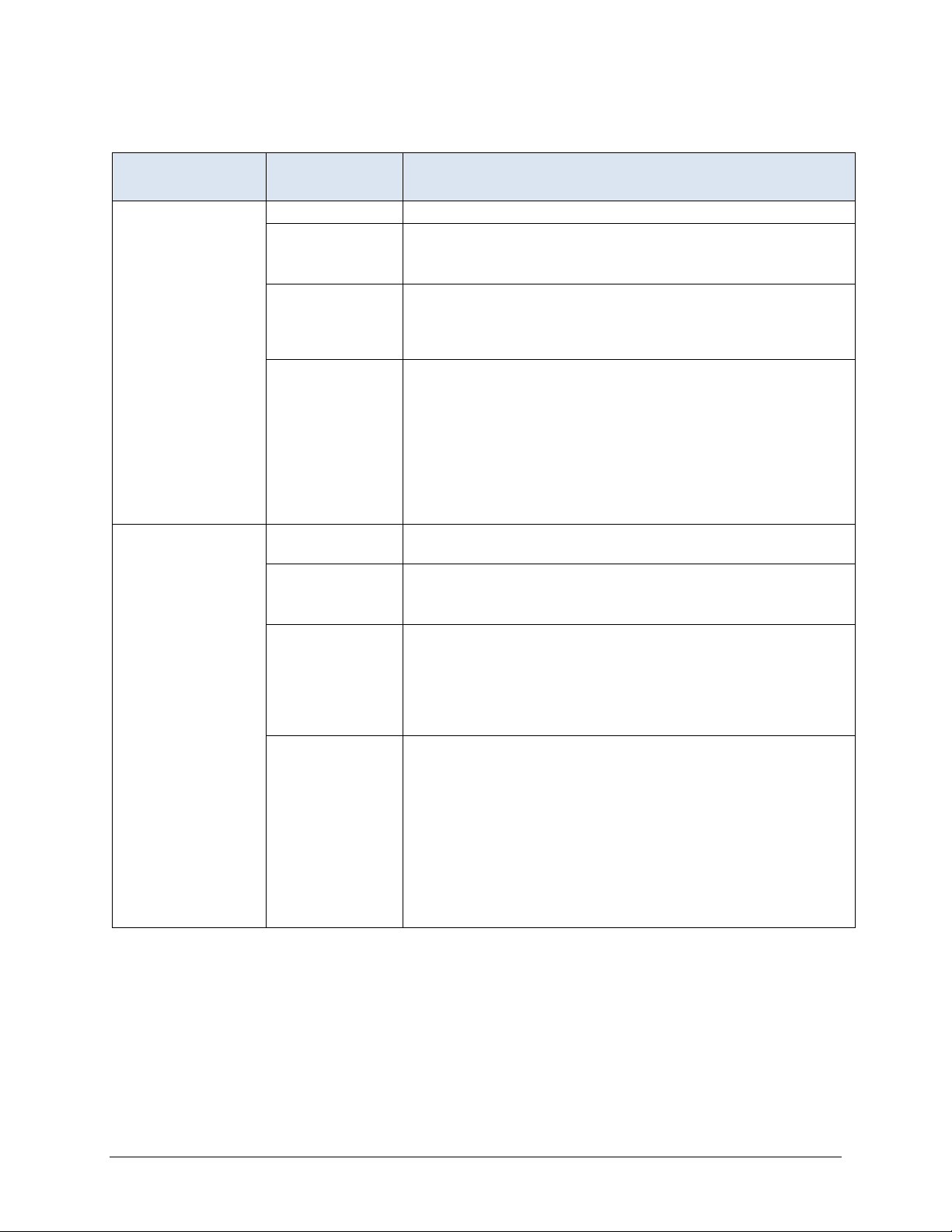
Section 4: Long Stay Record Definitions
ASSESSMENT
SELECTED PROPERTY
Target assessment Selection period Most recent 3 months (the long stay target period).
Qualifying RFAs A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
A0310B = [01] or
A0310F = [10, 11]
Selection logic Latest assessment that meets the following criteria: (a) it is
contained within the resident’s selected episode, (b) it has a
qualifying RFA, and (c) its target date is no more than 120
before the end of the episode.
Rationale Records with a qualifying RFA contain all of the items needed
to define the QMs. The target assessment need not have a
target date within the target period, but it must occur within 120
days of the end of the resident’s episode (either the last
discharge in the target period or the end of the target period if
the episode is ongoing). 120 days allows 93 days between
quarterly assessments plus an additional 27 days to allow for
late assessments. The target assessment represents the
resident’s status at the end of the episode.
Prior assessment Selection period Latest assessment that is 46 to 165 days before the target
assessment.
Qualifying RFAs A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
A0310B = [01] or
A0310F = [10, 11]
Selection logic Latest assessment that meets the following criteria: (a) it is
contained within the resident’s episode, (b) it has a qualifying
RFA, and (c) its target date is contained in the window that is
46 days to 165 days preceding the target date of the target
assessment. If no qualifying assessment exists, the prior
assessment is considered missing.
Rationale Records with a qualifying RFA contain all of the items needed
to define the QMs. The prior assessment need not have a
target date within the target period, but it must occur within the
defined window.
SELECTION SPECIFICATIONS
The window covers 120 days, which allows 93 days between
erly assessments plus an additional 27 days to allow for
quart
late assessments. Requiring a 45-day gap between the prior
assessment and the target assessment insures that the gap
between the prior and target assessment will not be small
(gaps of 45 days or less are excluded).
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 9
Page 14
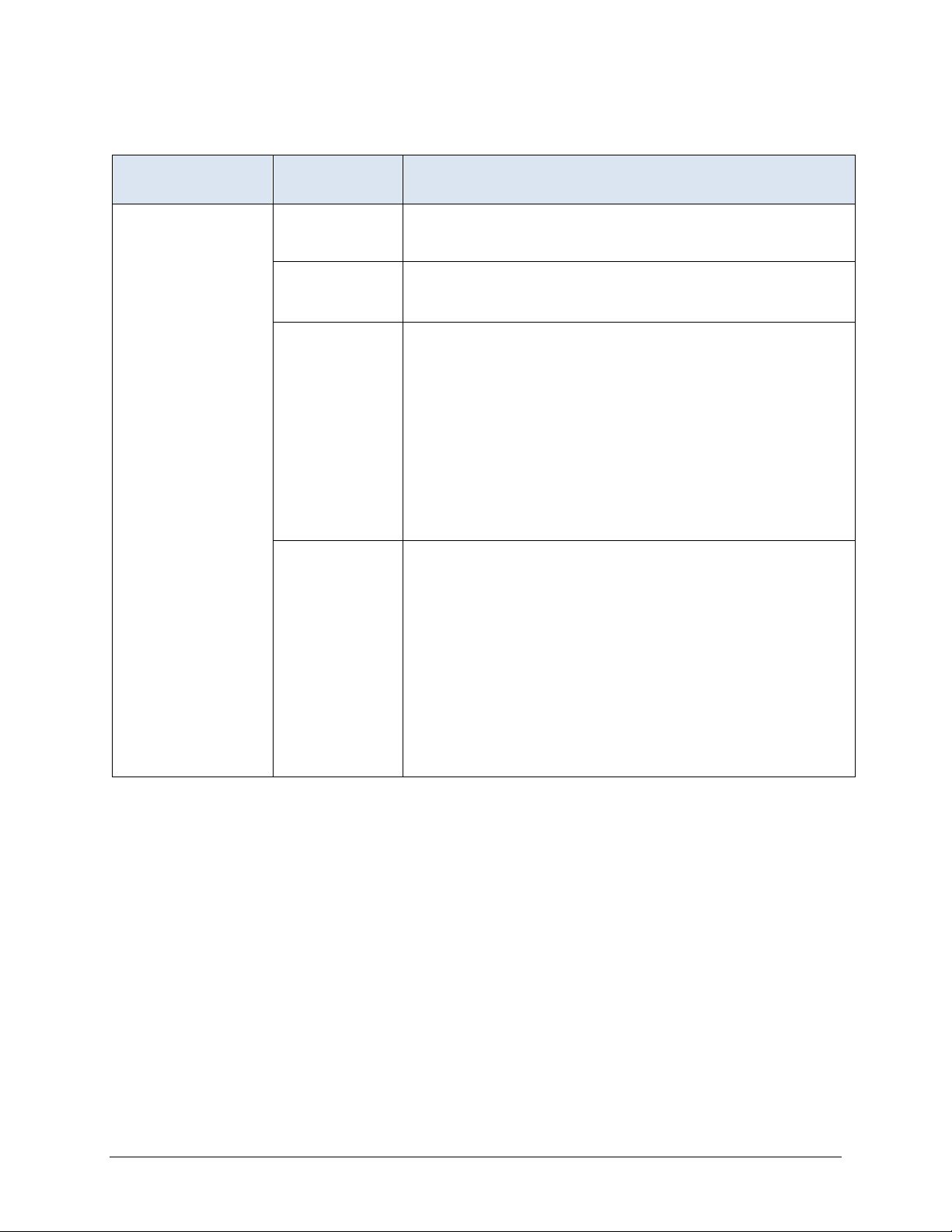
Long Stay Record Definitions (continued)
ASSESSMENT
SELECTED PROPERTY SELECTION SPECIFICATIONS
Look-back Scan Selection period Scan all qualifying RFAs within the current episode that have
target dates no more than 275 days prior to the target
assessment.
Qualifying RFAs A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
A0310B = [01]
A0310F = [10, 11]
Selection logic Include the target assessment and all qualifying earlier
assessments in the scan. Include an earlier assessment in the
scan, if it meets all of the following conditions: (a) it is
contained within the resident’s episode, (b) it has a qualifying
RFA, (c) its target date is on or before the target date for the
target assessment, and (d) its target date is no more than 275
days prior to the target date of the target assessment. The
target assessment and qualifying earlier assessments are
scanned to determine whether certain events or conditions
occurred during the look-back period. These events and
conditions are specified in the definitions of measures that
utilize the look-back scan.
Rationale Some measures utilize MDS items that record events or
conditions that occurred since the prior assessment was
performed. The purpose of the look-back scan is to determine
whether such events or conditions occurred during the lookback period. These measures trigger if the event or condition
of interest occurred any time during a one year period. A 275day time period is used to include up to three quarterly OBRA
assessments. The earliest of these assessments would have a
look-back period of up to 93 days, which would cover a total of
about one year. All qualifying RFAs with target dates in this
time period are examined to determine whether the event or
condition of interest occurred at any time during the time
interval.
or
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 10
Page 15
Long Stay Record Definitions (continued)
ASSESSMENT
SELECTED PROPERTY SELECTION SPECIFICATIONS
Influenza vaccination
assessment
Selection
5
period
Qualifying RFAs A0310A = [01, 02, 03, 04, 05, 06] or
Selection logic Select the record with the latest target date that meets all of
Rationale The selection logic defined above is intended to identify the
All assessments with target dates on or after October 1 of the
most recently completed influenza season (i.e., the target date
must be on or between October 1 of the current year and June
30 of the following year).
A0310B = [01]
A0310F = [10, 11]
the following conditions:
a) It has a qualifying RFA, and
b) Target date is on or after October 1 of the most recently
c
fall on or between October 1 and June 30), and
c) A1600 (entry date) is on or before March 31 of the most
r
latest assessment that reports the influenza vaccine status for
a resident who was in the facility for at least one day from
October 1 through March 31.
or
ompleted influenza season (i.e., the target date must
ecently completed influenza season.
5
The selection period uses a June 30th end date to ensure residents who are vaccinated between October 1 and
March 31, but do not have an assessment completed until after March 31, are captured in the measure sample.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 11
Page 16

Section 5: Transition from the Pressure Ulcer to Skin Integrity Quality Measures
In order to reduce provider burden and duplication of measures, as well as to align measures
across the NHQI and the Skilled Nursing Facility (SNF) Quality Reporting Program (QRP), the
NHQI version of the quality measure, Percent of Residents or Patients with Pressure Ulcers That
Are New or Worsened (Short Stay) (CMS ID: N002.04), was replaced with the SNF QRP
version of the measure (CMS ID: S002.02) effective January 1, 2020. Beginning with the FY
2020 SNF QRP effective October 1, 2020, CMS ID: S002.02 will be removed from the SNF
QRP measure set and replaced with a modified version of that measure, Changes in Skin
Integrity Post-Acute Care: Pressure Ulcer/Injury (CMS ID: S038.02), to include the addition of
new or worsened unstageable pressure ulcers. This SNF QRP measure will also be reported as a
part of the NHQI effective 10/01/2020. The specifications for CMS ID: S038.02 can be found in
the Skilled Nursing Facility Quality Reporting Program Measure Calculations and Reporting
User’s Manual V3.0 on the SNF QRP website6 under the downloads section at the bottom of the
page.
Section 6: Transition to the Patient Driven Payment Model
The Medicare PPS Patient Driven Payment Model (PDPM)7 became effective October 1, 20198.
This payment change, including changes to the Medicare PPS assessment schedule and the
introduction of interrupted stays, may have moderate to small impacts on measures that include
Medicare Part A SNF stays that occur during a short-stay or long-stay episode. One example of a
small measure impact is seen in the Percent of Residents Who Newly Received an Antipsychotic
Medication (Short Stay) (NQF: None) (CMS ID: N011.02). The residents who are included in
this measure may have Medicare Part A SNF stays that are used to calculate this measure; these
stays may be ongoing while the PDPM policies become effective (i.e., Medicare Part A SNF
stays with an admission prior to the effective date of October 1, 2019, and discharges on or after
October 1, 2019). The remaining discussion refers to Medicare Part A SNF stays that are
embedded within an episode.
For Medicare Part A SNF stays with an admission prior to the implementation date of October 1,
2019, and discharges on or after October 1, 2019, the Medicare Part A SNF stay will use the
definitions and follow the measure specifications outlined in the MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual
Version 12.1 through September 30, 2019. Beginning October 1, 2019, the Medicare Part A SNF
stay will use the definitions and follow the measure specifications outlined in the MDS 3.0 QM
6
Please refer to the Skilled Nursing Facility Quality Reporting Program Measure Calculations and Reporting User’s
Manual V3.0 on the SNF QRP website: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-
struments/NursingHomeQualityInits/Skilled-Nursing-Facility-Quality-Reporting-Program/SNF-Quality-
In
Reporting-Program-Measures-and-Technical-Information.html
7
The Patient Driven Payment Model was finalized under the FY 2019 SNF PPS final rule (83 FR 39183 through
39265). Please refer to the FY 2019 SNF PPS final rule: https://www.govinfo.gov/content/pkg/FR-2018-08-
08/pdf/2018-16570.pdf
8
Quality measure scores calculated using the new PDPM specifications were publicly reported as of April 2020.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 12
Page 17

User’s Manual Version 13.0. The information from all available qualifying RFAs throughout the
episode may be used in the measure calculation. Two examples below illustrate this instruction:
• Resident entered the facility on August 1, 2019 and began a Medicare Part A SNF
stay on September 1, 2019 and was discharged from the Medicare Part A SNF stay on
October 30, 2019
– The PPS 5-Day and PPS 14-Day Assessments are completed prior to the October
1, 2019 PDPM implementation date
– The PPS Discharge Assessment is completed after the October 1, 2019 PDPM
implementation date
o If the PPS 5-Day and PPS 14-Day Assessments are initial, prior, or target
assessments for a quality measure, then measure calculations would be based
on QM specifications in the MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual Version 12.1 for the
PPS 5-Day and PPS 14-Day Assessments completed prior to October 1, 2019.
If the PPS Discharge Assessment is an initial, a prior, or a target assessment
for a quality measure, then measure calculations would be based on QM
specifications in the MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual Version 13.0 for the PPS
Discharge Assessment which is completed after October 1, 2019 in this
example. In this instance, if appropriate, measure calculations may utilize
information from the PPS 5-Day, PPS 14-Day, and PPS Discharge
Assessments because all assessments are valid Qualifying RFAs at the time
the assessment was completed. OBRA assessments (stand-alone or combined
with PPS assessments) may also be completed during the Medicare Part A
SNF stay and used in measure calculations9.
• Rationale: The resident began the Medicare Part A SNF stay before
October 1, 2019. The measure specifications follow the instructions in the
MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual Version 12.1 for all assessments completed
on or before September 30, 2019, which include PPS 14-Day
Assessments.
• Resident entered the facility on September 1, 2019 and began a Medicare Part A SNF
stay on October 1, 2019 and was discharged from the Medicare Part A SNF stay on
October 30, 2019
– PPS 5-Day and PPS Discharge Assessments are completed on or after the October
1, 2019 PDPM implementation date
o If the PPS 5-Day Assessment and/or PPS Discharge Assessment are initial,
prior, or target assessments for a quality measure, then measure calculations
would be based on QM specifications in the MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual
Version 13.0. In this instance, if appropriate, measure calculations may utilize
information from the PPS 5-Day and PPS Discharge Assessments because
9
Please refer to Chapter 1, Sections 3 and 4 to identify Qualifying RFAs for short and long stay measure
calculations.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 13
Page 18

those are the only PPS assessments that are valid Qualifying RFAs. OBRA
assessments (stand-alone or combined with PPS assessments) may also be
completed during the Medicare Part A SNF stay and used in measure
calculations10.
• Rationale: The resident began the Medicare Part A SNF stay on or after
October 1, 2019. The measure specifications follow the instructions in the
MDS 3.0 QM User’s manual Version 13.0, which, with respect to PPS
assessments, only require a PPS 5-Day and PPS Discharge Assessment
for quality measure calculations; all other interim PPS assessments used
in quality measure calculations no longer exist under the PDPM. Note,
Interim Payment Assessments (IPAs) are also part of the PPS item sets. If
applicable, IPAs may also be completed during the Medicare Part A SNF
stay; however, data from IPAs are used for PPS payment purposes only
and are not used in measure calculations.
10
Please refer to Chapter 1, Sections 3 and 4 to identify Qualifying RFAs for short and long stay measure
calculations.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 14
Page 19

Chapter 2
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures Logical Specifications
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 15
Page 20

Section 1: Short Stay (SS) Quality Measures
Table 2-1
Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute Care: Pressure Ulcer/Injury11
(CMS ID: S038.02) (NQF: None)
This quality measure is calculated using the SNF Quality Reporting Program measure Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute Care:
Pressure Ulcer/Injury (CMS ID: S038.02). To review the measure logic specifications for CMS ID: S038.02, please refer to the SNF
Quality Reporting Program Measure Calculations and Reporting User’s Manual V3.0 on the SNF QRP website12 under the downloads
section at the bottom of the page. The measure logical specifications can be found in Chapter 7, Table 7-5.
11
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
12
Please refer to the SNF Quality Reporting Program Measure Calculations and Reporting User’s Manual V3.0 on the SNF QRP website:
https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/NursingHomeQualityInits/Skilled-Nursing-Facility-Quality-Reporting-
gram/SNF-Quality-Reporting-Program-Measures-and-Technical-Information.html
Pro
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 16
Page 21

Table 2-2
Percent of Residents Who Were Assessed and Appropriately Given the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N003.03) (NQF #0680)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who are assessed and/or given, appropriately, the influenza vaccination during the most recent
influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting any of the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident received the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season, either in the facility (O0250A = [1]) or outside the facility (O0250C
[2]); or
=
2. Resident was offered and declined the influenza vaccine (O0250C = [4]); or
3. Resident was ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (O0250C = [3]) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to eggs or other components of the
v
accine, history of Guillian-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous influenza vaccination, bone marrow transplant within the past 6
months).
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
the most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year, and
r
eports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 17
Covariates
Page 22

Table 2-3
Percent of Residents Who Received the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N004.03) (NQF #0680A)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who received the influenza vaccination during the most recent influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident received the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season, either in the facility (O0250A = [1]) or outside the facility (O0250C
[2]).
=
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
reports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 18
Covariates
Page 23

Table 2-4
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N005.03) (NQF #0680B)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who are offered and declined the influenza vaccination during the most recent influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident was offered and declined the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season (O0250C = [4]).
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
reports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 19
Covariates
Page 24

Table 2-5
Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N006.03) (NQF #0680C)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who did not receive, due to medical contraindication, the influenza vaccination during the most recent
influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident was ineligible for the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season due to medical contraindication(s) (O0250C = [3]) (e.g.,
aphylactic hypersensitivity to eggs or other components of the vaccine, history of Guillian-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous
an
influenza vaccination, bone marrow transplant within the past 6 months).
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
r
eports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31
Not applicable
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 20
Page 25

Table 2-6
Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N007.02) (NQF #0682 – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of short-stay residents whose pneumococcal vaccine status is up to date during the 12-month reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting any of the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Pneumococcal vaccine status is up to date (O0300A = [1]); or
2. Were offered and declined the vaccine (O0300B = [2]); or
3. Were ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (O0300B = [1]) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to components of the vaccine; bone marrow
ansplant within the past 12 months; or receiving a course of chemotherapy within the past two weeks).
tr
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is less than 5 years (i.e., resident has not yet reached fifth birthday on target date).
Not applicable
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 21
Covariates
Page 26

Table 2-7
Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N008.02) (NQF #0682A – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who received the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Pneumococcal vaccine status is up to date (O0300A = [1]).
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is less than 5 years (i.e., resident has not yet reached fifth birthday on target date).
Covariates
Not applicable
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 22
Page 27

Table 2-8
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N009.02) (NQF #0682B – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who were offered and declined the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Were offered and declined the vaccine (O0300B = [2]).
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is less than 5 years (i.e., resident has not yet reached fifth birthday on target date).
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 23
Page 28

Table 2-9
Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the Pneumococcal Vaccine (SS)
(CMS ID: N010.02) (NQF #0682C – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of short-stay residents who did not receive, due to medical contraindication, the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month
reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Were ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (O0300B = [1]) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to components of the vaccine; bone marrow
ransplant within the past 12 months; or receiving a course of chemotherapy within the past two weeks).
t
Denominator
All short-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected target assessment is less than 5 years (i.e., resident has not yet reached fifth birthday on target date).
Not applicable.
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 24
Page 29

Table 2-10
Percent of Residents Who Newly Received an Antipsychotic Medication (SS)13
(CMS ID: N011.02) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of short-stay residents who are receiving an antipsychotic medication during the target period but not on their initial
assessment.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Short-stay residents for whom one or more assessments in a look-back scan (not including the initial assessment) indicates that antipsychotic medication was
ved:
recei
1. N0410A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7].
Note that residents are excluded from this measure if their initial assessment indicates antipsychotic medication use or if antipsychotic medication use is
known on the initial assessment (see exclusion #3, below).
un
Denominator
A
ll short-stay residents who do not have exclusions and who meet all of the following conditions:
1. The resident has a target assessment, and
2. The resident has an initial assessment, and
3. The target assessment is not the same as the initial assessment.
Exclusions
he following is true for all assessments in the look-back scan (excluding the initial assessment):
1. T
1.1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012: (N0410A = [-]).
2. Any of the following related conditions are present on any assessment in a look-back scan:
2.1. Schizophrenia (I6000 = [1]).
2.2. Tourette’s syndrome (I5350 = [1]).
2.3. Huntington’s disease (I5250 = [1]).
13
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 25
Page 30

Measure Specifications Continued
3. The resident’s initial assessment indicates antipsychotic medication use or antipsychotic medication use is unknown:
3.1. For initial assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012: (N0410A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, -]).
Covariates
Not applicable
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 26
Page 31

Table 2-11
Percent of Residents Who Made Improvements in Function (SS)14
(CMS ID: N037.03) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of short-stay residents who were discharged from the nursing home that gained more independence in transfer,
locomotion, and walking during their episodes of care.
Measure Specifications
NOTE:
1. A “valid preceding PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment” refers to the date of the earliest assessment if a resident has both a PPS
5-
Day assessment (A0310B = [01]) and an OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A = [01]).
2. A “valid discharge assessment” refers to a discharge assessment with a date closest to the valid preceding PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA
Admission assessment where a return is not anticipated (A0310F = [10]).
3. The PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment should be used to calculate the tercile cutoffs. If resident has both a PPS 5-Day
ass
essment and an OBRA Admission assessment, calculate covariate using the assessment with the earlier date. Terciles are recalculated in each
quarter.
Numerator
Short-stay residents who:
1. Have a change in performance score that is negative ([valid discharge assessment] - [valid preceding PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission
ass
essment] < [0]).
Performance is calculated as the sum of G0110B1 (transfer: self- performance), G0110E1 (locomotion on unit: self-performance), and G0110D1 (walk in
corridor: self-performance), with 7’s (activity occurred only once or twice) and 8's (activity did not occur) recoded to 4's (total dependence).
Denominator
Short-stay residents who meet all of the following conditions, except those with exclusions:
1. Have a valid discharge assessment (A0310F = [10]), and
2. Have a valid preceding PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]) or OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A = [01]).
14
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 27
Page 32

Measure Specifications Continued
Exclusions
1. Residents satisfying any of the following conditions:
1.1. Comatose (B0100 = [1]) on the PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment, whichever was used in the QM.
1.2. Life expectancy of less than 6 months (J1400 = [1]) on the PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment, whichever was used in the
.
QM
1.3. Hospice (O0100K2 = [1]) on the PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment, whichever was used in the QM.
1.4. Information on Transfer: self-performance, walk in corridor: self-performance, or locomotion on unit: self-performance is missing on any of the
as
sessments used to calculate the QM (G0110B1, G0110D1, or G0110E1 = [-]) (i.e., valid discharge assessment, and PPS 5-Day assessment or
OBRA Admission assessment, whichever was used in the QM).
1.5. Residents with no impairment (sum of G0110B1, G0110D1 and G0110E1 = [0]) on the PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission
assessment, whichever was used in the QM.
1.6. Residents with an unplanned discharge on any assessment during the care episode (A0310G = [2])
Covariates
All covariates used throughout this measure are calculated using the valid preceding PPS 5-Day assessment or OBRA Admission assessment described in the
NOTE at the top of the measure specifications.
1. Age on t
(A0900) from the date of assessment (A2300)
If (MONTH(A2300) > MONTH(A0900)) or (MONTH(A2300) = MONTH(A0900) and
DAY(A2300) >= DAY(A0900)) then Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900) else Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900)-1
1.1 Covariate Age Category ≤ 54 = 1 if Age ≤ 54 and Covariate Age Category ≤ 54 = 0 if Age >54)
1.2 Covariate Age Category 54 to 84 = 1 if Age >54 and ≤ 84 and Covariate Age Category 54 to 84 = 0 if Age ≤ 54 or Age > 84) (reference)
1.3 Covariate Age Category >84 = 1 if Age >84 and Covariate Age Category >84 = 0 if Age ≤ 84)
2. Gender
2.1 Covariate = 1 if (A0800 = [2]) (Female)
2.2 Covariate = 0 if (A0800 = [1]) (Male)
3. Severe cognitive impairment
3.1 Covariate = 1 if (C1000 = [3] and C0700 = [1]) or BIMS summary score (C0500) < [7]
3.2 Covariate = 0 if (C1000 = [0, 1, 2, ^, -] or C0700 = [0, ^, -]) and (C0500 = [>7, ^, -, 99])
4. Long Form ADL (LFADL) Scale (G0110A1 + G0110B1 + G0110E1 + G0110G1 + G0110H1 + G0110I1 + G0110J1). If any (G0110A1, G0110B1,
G
he PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]) or OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A = [01]) as calculated by subtracting date of birth
If Covariate has not been set to 1 or 0 based on logic in 3.1 and 3.2, then Covariate = [0].
0110E1, G0110G1, G0110H1, G0110I1, G0110J1) = [7, 8], recode the item to equal [4].
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 28
Page 33

4.1 Covariate = 0 if LFADL = (middle tercile15 or highest tercile) or if any (G0110A1, G0110B1, G0110E1, G0110G1, G0110H1, G0110I1,
G0110J1) = [-]
Covariate = 1 if LFADL = lowest tercile
4.2 Covariate =0 if (lowest tercile or highest tercile)
C
ovariate = 1 if LFADL = middle tercile (reference)
4.3 Covariate =0 if (lowest tercile or middle tercile)
ovariate = 1 if LFADL = highest tercile
C
5. Heart failure
5.1 Covariate = 1 if (I0600 = [1])
C
ovariate = 0 if (I0600 = [0, -])
6. CVA, TIA, or Stroke
6.1 Covariate = 1 if (I4500 = [1])
ovariate = 0 if (I4500 = [0, -])
C
7. Hip Fracture
7.1 Covariate = 1 if (I3900 = [1])
ovariate = 0 if (I3900 = [0, -])
C
8. Other Fracture
8.1 Covariate = 1 if (I4000 = [1])
ovariate = 0 if (I4000 = [0, -])
C
Covariates Continued
15
Long Form ADL Scale terciles are recalculated in each quarter using the PPS 5-Day or OBRA Admission assessment.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 29
Page 34

Section 2: Long Stay (LS) Quality Measures
Table 2-12
Percent of Residents Experiencing One or More Falls with Major Injury (LS)16
(CMS ID: N013.02) (NQF: 0674)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who have experienced one or more falls with major injury reported in the target period or look-back
period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with one or more look-back scan assessments that indicate one or more falls that resulted in major injury (J1900C = [1, 2]).
Denominator
All long-stay nursing home residents with one or more look-back scan assessments except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
esident is excluded if the following is true for all look-back scan assessments:
R
1. The number of falls with major injury was not coded (J1900C = [-]).
Not applicable.
16
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 30
Covariates
Page 35

Table 2-13
Percent of High-Risk Residents With Pressure Ulcers (LS)17
(CMS ID: N015.03) (NQF: 0679)
Measure Description
This measure captures the percentage of long-stay, high-risk residents with Stage II-IV or unstageable pressure ulcers
Measure Specifications
Numerator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment that meet the following condition:
1. Stage II-IV or unstageable pressure ulcers are present, as indicated by any of the following six conditions:
1.1. (M0300B1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]) or
1.2. (M0300C1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]) or
1.3. (M0300D1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]) or
1.4. (M0300E1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]) or
1.5. (M0300F1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]) or
1.6. (M0300G1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, or 9]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment who meet the definition of high risk, except those with exclusions. Residents are defined as high-risk
hey meet one or more of the following three criteria on the target assessment:
if t
1. Impaired bed mobility or transfer indicated, by either or both of the following:
1.1. Bed mobility, self-performance (G0110A1 = [3, 4, 7, 8]).
1.2. Transfer, self-performance (G0110B1 = [3, 4, 7, 8]).
2. Comatose (B0100 = [1]).
3. Malnutrition or at risk of malnutrition (I5600 = [1]) (checked).
17
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 31
Page 36

Measure Specifications Continued
Exclusions
1. Target assessment is an OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A = [01]) or a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]).
2. If the resident is not included in the numerator (the resident did not meet the pressure ulcer conditions for the numerator) and any of the following
onditions are true:
c
2.1. (M0300B1 = [-]).
2.2. (M0300C1 = [-]).
2.3. (M0300D1 = [-]).
2.4. (M0300E1 = [-]).
2.5. (M0300F1 = [-]).
2.6. (M0300G1 = [-]).
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 32
Page 37

Table 2-14
Percent of Residents Assessed and AppropriatelyGiven the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N016.03) (NQF #0681)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who are assessed and/or given, appropriately, the influenza vaccination during the most recent influenza
season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting any of the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident received the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season, either in the facility (O0250A= [1]) or outside the facility
O0250C = [2]); or
(
2. Resident was offered and declined the influenza vaccine (O0250C = [4]); or
3. Resident was ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (O0250C = [3]) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to eggs or other components of the
v
accine, history of Guillian-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous influenza vaccination, bone marrow transplant within the past 6
months).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
reports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 33
Page 38

Table 2-15
Percent of Residents Who Received the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N017.03) (NQF #0681A)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who received the influenza vaccination during the most recent influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident received the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season, either in the facility (O0250A = [1]) or outside the facility (O0250C
[2]).
=
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
reports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 34
Covariates
Page 39

Table 2-16
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N018.03) (NQF #0681B)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who are offered and declined the influenza vaccination during the most recent influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident was offered and declined the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season (O0250C = [4]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
reports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 35
Covariates
Page 40

Table 2-17
Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N019.03) (NQF #0681C)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who did not receive, due to medical contraindication, the influenza vaccination during the most recent
influenza season.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected influenza vaccination assessment:
1. Resident was ineligible for the influenza vaccine during the most recent influenza season due to medical contraindication(s) (O0250C = [3]) (e.g.,
aphylactic hypersensitivity to eggs or other components of the vaccine, history of Guillain-Barré Syndrome within 6 weeks after a previous
an
influenza vaccination, bone marrow transplant within the past 6 months).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected influenza vaccination assessment. This includes all residents who have an entry date (A1600) on or before March 31 of
he most recently completed influenza season and have an assessment with a target date on or after October 1 of the most recently completed influenza season
t
(i.e., the target date must fall on or between October 1 and June 30), except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident’s age on target date of selected influenza vaccination assessment is 179 days or less.
Notes
This measure is only calculated once per 12-month influenza season which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year and
r
eports data for residents who were in the facility for at least one day during the target period of October 1 through March 31.
Not applicable.
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 36
Page 41

Table 2-18
Percent of Residents Assessed and Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N020.02) (NQF #0683 – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents whose pneumococcal vaccine status is up to date.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting any of the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Have an up to date pneumococcal vaccine status (O0300A = [1]); or
2. Were offered and declined the vaccine (O0300B = [2]); or
3. Were ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to components of the vaccine; bone marrow transplant within
t
he past 12 months; or receiving a course of chemotherapy within the past two weeks) (O0300B = [1]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 37
Page 42

Table 2-19
Percent of Residents Who Received the Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N021.02) (NQF #0683A – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who received the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Pneumococcal vaccine status is up to date (O0300A = [1]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 38
Page 43

Table 2-20
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered and Declined the Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N022.02) (NQF #0683B – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who were offered and declined the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Were offered and declined the vaccine (O0300B = [2]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 39
Page 44

Table 2-21
Percent of Residents Who Did Not Receive, Due to Medical Contraindication, the Pneumococcal Vaccine (LS)
(CMS ID: N023.02) (NQF #0683C – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who did not receive, due to medical contraindication, the pneumococcal vaccine during the 12-month
reporting period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Residents meeting the following criteria on the selected target assessment:
1. Were ineligible due to medical contraindication(s) (O0300B = [1]) (e.g., anaphylactic hypersensitivity to components of the vaccine; bone marrow
t
ransplant within the past 12 months; or receiving a course of chemotherapy within the past two weeks).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment.
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 40
Page 45

Table 2-22
Percent of Residents with a Urinary Tract Infection (LS)18
(CMS ID: N024.02) (NQF: 0684)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percentage of long stay residents who have a urinary tract infection.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment that indicates urinary tract infection within the last 30 days (I2300 = [1]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Target assessment is an admission assessment (A0310A = [01]) or a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]).
2. Urinary tract infection value is missing (I2300 = [-]).
Covariates
Not applicable.
18
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 41
Page 46

Table 2-23
Percent of Low Risk Residents Who Lose Control of Their Bowel or Bladder (LS)
(CMS ID: N025.02) (NQF #0685 – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who frequently lose control of their bowel or bladder.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment that indicates frequently or always incontinence of the bladder (H0300 = [2, 3]) or bowel (H0400 = [2,
]).
3
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exc
lusions
1. Target assessment is an admission assessment (A0310A = [01]) or a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]).
2. Resident is not in numerator and H0300 = [-] or H0400 = [-].
3. Residents who have any of the following high-risk conditions:
3.1. Severe cognitive impairment on the target assessment as indicated by (C1000 = [3] and C0700 = [1]) or (C0500 ≤ [7]).
3.2. Totally dependent in bed mobility self-performance (G0110A1 = [4, 7, 8]).
3.3. Totally dependent in transfer self-performance (G0110B1 = [4, 7, 8]).
3.4. Totally dependent in locomotion on unit self-performance (G0110E1 = [4, 7, 8]).
4. Resident does not qualify as high risk (see #3 above) and both of the following two conditions are true for the target assessment:
4.1. C0500 = [99, ^, -], and
4.2. C0700 = [^, -] or C1000 = [^, -].
5. Resident does not qualify as high risk (see #3 above) and any of the following three conditions are true:
5.1. G0110A1 = [-].
5.2. G0110B1 = [-].
5.3. G0110E1 = [-].
6. Resident is comatose (B0100 = [1]) or comatose status is missing (B0100 = [-]) on the target assessment.
7. Resident has an indwelling catheter (H0100A = [1]) or indwelling catheter status is missing (H0100A = [-]) on the target assessment.
8. Resident has an ostomy (H0100C = [1]) or ostomy status is missing (H0100C = [-]) on the target assessment.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 42
Page 47

Not applicable.
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 43
Page 48

Table 2-24
Percent of Residents Who Have/Had a Catheter Inserted and Left in Their Bladder (LS)19
(CMS ID: N026.03) (NQF #0686)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of residents who have had an indwelling catheter in the last 7 days.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment that indicates the use of indwelling catheters (H0100A = [1]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Target assessment is an admission assessment (A0310A = [01]) or a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]).
2. Target assessment indicates that indwelling catheter status is missing (H0100A = [-]).
3. Target assessment indicates neurogenic bladder (I1550 = [1]) or neurogenic bladder status is missing (I1550 = [-]).
4. Target assessment indicates obstructive uropathy (I1650 = [1]) or obstructive uropathy status is missing (I1650 = [-]).
1. Frequent bowel incontinence on prior assessment (H0400 = [2, 3]).
1.1. Covariate = [1] if (H0400 = [2, 3]).
1.2. Covariate = [0] if (H0400 = [0, 1, 9, -]).
2. Pressure ulcers at stages II, III, or IV on prior assessment:
2.1. Covariate = [1] if any of the following are true:
2.1.1. (M0300B1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]), or
2.1.2. (M0300C1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]), or
2.1.3. (M0300D1 = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9]).
2.2. Covariate = [0] if the following is true:
19
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 44
Covariates
Page 49

2.2.1. (M0300B1 = [0, -, ^]) and
2.2.2. (M0300C1 = [0, -, ^]) and
2.2.3. (M0300D1 = [0, -, ^]).
3. All covariates are missing if no prior assessment is available.
Covariates Continued
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 45
Page 50

Table 2-25
Percent of Residents Who Were Physically Restrained (LS)
(CMS ID: N027.02) (NQF #0687)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay nursing facility residents who are physically restrained on a daily basis.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment that indicates daily physical restraints,
here:
w
1. Trunk restraint used in bed (P0100B = [2]), or
2. Limb restraint used in bed (P0100C = [2]), or
3. Trunk restraint used in chair or out of bed (P0100E = [2]), or
4. Limb restraint used in chair or out of bed (P0100F = [2]), or
5. Chair prevents rising used in chair or out of bed (P0100G) = [2]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident is not in numerator and any of the following is true:
1. (P0100B = [-]), or
2. (P0100C = [-]), or
3. (P0100E = [-]), or
4. (P0100F = [-]), or
5. (P0100G = [-]).
Not applicable.
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 46
Page 51

Table 2-26
Percent of Residents Whose Need for Help with Activities of Daily Living Has Increased (LS)20
(CMS ID: N028.02) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents whose need for help with late-loss Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) has increased when compared to
the prior assessment.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with selected target and prior assessments that indicate the need for help with late-loss Activities of Daily Living (ADLs) has increased
en the selected assessments are compared. The four late-loss ADL items are self-performance bed mobility (G0110A1), self-performance transfer
wh
(G0110B1), self-performance eating (G0110H1), and self-performance toileting (G0110I1).
An increase is defined as an increase in two or more coding points in one late-loss ADL item or one point increase in coding points in two or more late-loss
AD
L items. Note that for each of these four ADL items, if the value is equal to [7, 8] on either the target or prior assessment, then recode the item to equal [4]
to allow appropriate comparison.
Residents meet the definition of increased need of help with late-loss ADLs if either of the following are true
1. At least two of the following are true (note that in the notation below, [t] refers to the target assessment, and [t-1] refers to the prior assessment):
1.1 Bed mobility: ([Level at target assessment (G0110A1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110A1[t-1])]) > [0], or
1.2 Transfer: ([Level at target assessment (G0110B1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110B1[t-1])]) > [0], or
1.3 Eating: ([Level at target assessment (G0110H1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110H1[t-1])]) > [0], or
1.4 Toileting: ([Level at target assessment (G0110I1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110I1[t-1])]) > [0].
2. At least one of the following is true:
2.1 Bed mobility: ([Level at target assessment (G0110A1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110A1[t-1])]) > [1], or
2.2 Transfer: ([Level at target assessment (G0110B1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110B1[t-1])]) > [1], or
2.3 Eating: ([Level at target assessment (G0110H1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110H1[t-1])]) > [1], or
2.4 Toileting: ([Level at target assessment (G0110I1[t])] - [Level at prior assessment (G0110I1[t-1])]) > [1].
20
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 47
Page 52

Measure Specifications Continued
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target and prior assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. All four of the late-loss ADL items indicate total dependence on the prior assessment, as indicated by:
1.1. Bed Mobility (G0110A1) = [4, 7, 8] and
1.2. Transferring (G0110B1) = [4, 7, 8] and
1.3. Eating (G0110H1) = [4, 7, 8] and
1.4. Toileting (G0110I1) = [4, 7, 8].
2. Three of the late-loss ADLs indicate total dependence on the prior assessment, as in #1 AND the fourth late-loss ADL indicates extensive assistance
value 3) on the prior assessment.
(
3. If resident is comatose (B0100 = [1, -]) on the target assessment.
4. Prognosis of life expectancy is less than 6 months (J1400 = [1, -]) on the target assessment.
5. Hospice care (O0100K2 = [1, -]) on the target assessment.
6. The resident is not in the numerator and
6.1. Bed Mobility (G0110A1 = [-]) on the prior or target assessment, or
6.2. Transferring (G0110B1 = [-]) on the prior or target assessment, or
6.3. Eating (G0110H1) = [-]) on the prior or target assessment, or
6.4. Toileting (G0110I1 = [-]) on the prior or target assessment.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 48
Covariates
Page 53

Table 2-27
Percent of Residents Who Lose Too Much Weight (LS)
(CMS ID: N029.02) (NQF #0689)
Measure Description
The measure captures the percentage of long-stay residents who had a weight loss of 5% or more in the last month or 10% or more in the last 6 months who
were not on a physician prescribed weight-loss regimen noted in an MDS assessment during the selected quarter.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay nursing home residents with a selected target assessment which indicates a weight loss of 5% or more in the last month or 10% or more in the last 6
onths who were not on a physician prescribed weight-loss regimen (K0300 = [2]).
m
Denominator
Long-stay nursing home residents with a selected target assessment except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Target assessment is an OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A= [01]) or a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B= [01])
2. Prognosis of life expectancy is less than 6 months (J1400 = [1]) or the Prognosis item is missing (J1400 = [-]) on the target assessment.
3. Receiving Hospice care (O0100K2 = [1]) or the Hospice care item is missing (O0100K2 = [-]) on the target assessment.
4. Weight loss item is missing (K0300= [-]) on the target assessment.
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 49
Covariates
Page 54

Table 2-28
Percent of Residents Who Have Depressive Symptoms (LS)
(CMS ID: N030.02) (NQF #0690 – Withdrawn)
Measure Description
The measure reports the percentage of long-stay residents who have had symptoms of depression during the 2-week period preceding the MDS 3.0 target
assessment date.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment where the target assessment meets either of the following two conditions:
CONDITION A (The resident mood interview must meet Part 1 and Part 2 below)
PART 1:
• Little interest or pleasure in doing things half or more of the days over the last two weeks (D0200A2 = [2, 3]).
or
• Feeling down, depressed, or hopeless half or more of the days over the last two weeks (D0200B2 = [2, 3]).
PART 2:
The resident interview total severity score indicates the presence of depression (D0300 ≥ [10] and D0300 ≤ [27]).
CONDITION B: (The staff assessment of resident mood must meet Part 1 and Part 2 below)
PART 1:
• Little interest or pleasure in doing things half or more of the days over the last two weeks (D0500A2 = [2, 3]).
or
• Feeling or appearing down, depressed, or hopeless half or more of the days over the last two weeks (D0500B2 = [2, 3]).
PART 2:
The staff assessment total severity score indicates the presence of depression (D0600 ≥ [10] and D0600 ≤ [30]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. Resident is comatose or comatose status is missing (B0100 = [1, -]).
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 50
Page 55

Measure Specifications Continued
2. Resident is not included in the numerator (the resident did not meet the depression symptom conditions for the numerator) AND both of the following
are true:
2.1. D0200A2 = [^, -] or D0200B2 = [^, -] or D0300 = [99, ^, -].
2.2. D0500A2 = [^, -] or D0500B2 = [^, -] or D0600 = [^, -].
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 51
Page 56

Table 2-29
Percent of Residents Who Received an Antipsychotic Medication (LS)21
(CMS ID: N031.03) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of long-stay residents who are receiving antipsychotic drugs in the target period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment where the following condition is true: antipsychotic medications received. This condition is defined as
llows:
fo
1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012: (N0410A = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]).
Denominator
Long-stay nursing home residents with a selected target assessment except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. The resident did not qualify for the numerator and any of the following is true:
1.1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012: (N0410A = [-]).
2. Any of the following related conditions are present on the target assessment (unless otherwise indicated):
2.1. Schizophrenia (I6000 = [1]).
2.2. Tourette’s syndrome (I5350 = [1]).
2.3. Tourette’s syndrome (I5350 = [1]) on the prior assessment if this item is not active on the target assessment and if a prior assessment is
lable.
avai
2.4. Huntington’s disease (I5250 = [1]).
Not applicable.
21
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 52
Covariates
Page 57

Table 2-30
Prevalence of Falls (LS)22
(CMS ID: N032.02) (NQF#: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of long-stay residents who have had a fall during their episode of care.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with one or more look-back assessments that indicate the occurrence of a fall (J1800 = [1]).
Denominator
All long-stay nursing home residents with one or more look-back scan assessments except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident is excluded if the following is true for all of the look-back scan assessments:
1. The occurrence of falls was not assessed (J1800 = [-]).
Covariates
Not applicable.
22
This measure is not reported on NHC and is only available on the CASPER QM reports
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 53
Page 58

Tabel 2-31
Prevalence of Antianxiety/Hypnotic Use (LS)23
(CMS ID: N033.02) (NQF#: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of long-stay residents who are receiving antianxiety medications or hypnotics but do not have evidence of psychotic or
related conditions in the target period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment where any of the following conditions are true:
1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012:
1.1. Antianxiety medications received (N0410B = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]), or
1.2. Hypnotic medications received (N0410D = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]).
Denominator
All long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. The resident did not qualify for the numerator and any of the following is true:
1. For assessments with target date on or after 04/01/2012: N0410B = [-] or N0410D = [-].
2. Any of the following related conditions are present on the target assessment (unless otherwise indicated):
1. Schizophrenia (I6000 = [1]).
2. Psychotic disorder (I5950 = [1]).
3. Manic depression (bipolar disease) (I5900 = [1]).
4. Tourette’s syndrome (I5350 = [1]).
5. Tourette’s syndrome (I5350 = [1]) on the prior assessment if this item is not active on the target assessment and if a prior assessment is
avai
lable.
6. Huntington’s disease (I5250 = [1]).
7. Hallucinations (E0100A = [1]).
23
This measure is not reported on NHC and is only available on the CASPER QM reports.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 54
Page 59

8. Delusions (E0100B = [1]).
9. Anxiety disorder (I5700 = [1]).
10. Post-traumatic stress disorder (I6100 = [1]).
11. Post-traumatic stress disorder (I6100 = [1]) on the prior assessment if this item is not active on the target assessment and if a prior assessment
available.
is
Not applicable.
Measure Specifications Continued
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 55
Page 60

Table 2-32
Prevalence of Behavior Symptoms Affecting Others (LS)24
(CMS ID: N034.02) (NQF#: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percentage of long-stay residents who have behavior symptoms that affect others during the target period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment where any of the following conditions are true:
1. The presence of physical behavioral symptoms directed towards others (E0200A = [1, 2, 3]), or
2. The presence of verbal behavioral symptoms directed towards others (E0200B = [1, 2, 3]), or
3. The presence of other behavioral symptoms not directed towards others (E0200C = [1, 2, 3]), or
4. Rejection of care (E0800 = [1, 2, 3]), or
5. Wandering (E0900 = [1, 2, 3]).
Denominator
All residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
Resident is not in numerator and any of the following is true:
1. The target assessment is a discharge (A0310F = [10, 11].
2. E0200A is equal to [-, ^].
3. E0200B is equal to [-, ^].
4. E0200C is equal to [-, ^].
5. E0800 is equal to [-, ^].
6. E0900 is equal to [-, ^].
Covariates
Not applicable.
24
This measure is not reported on NHC and is only available on the CASPER QM reports.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 56
Page 61

Table 2-33
Percent of Residents Whose Ability to Move Independently Worsened (LS)25
(CMS ID: N035.03) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the percent of long-stay residents who experienced a decline in independence of locomotion during the target period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment and at least one qualifying prior assessment who have a decline in locomotion when comparing their
get assessment with the prior assessment. Decline identified by:
tar
1. Recoding all values (G0110E1 = [7, 8]) to (G0110E1 = [4]).
2. An increase of one or more points on the “locomotion on unit: self-performance” item between the target assessment and prior assessment (G0110E1
on
target assessment – G0110E1 on prior assessment ≥1).
Denominator
Long-stay residents who have a qualifying MDS 3.0 target assessment and at least one qualifying prior assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
esidents satisfying any of the following conditions:
R
1. Comatose or missing data on comatose (B0100 = [1, -]) at the prior assessment.
2. Prognosis of less than 6 months at the prior assessment as indicated by:
2.1. Prognosis of less than six months of life (J1400 = [1]), or
2.2. Hospice use (O0100K2 = [1]), or
2.3. Neither indicator for being end-of-life at the prior assessment (J1400 ≠ [1] and O0100K2 ≠ [1]) and a missing value on either indicator (J1400 =
[-] or O
3. Resident totally dependent during locomotion on prior assessment (G0110E1 = [4, 7, or 8]).
4. Missing data on locomotion on target or prior assessment (G0110E1 = [-]).
5. Prior assessment is a discharge with or without return anticipated (A0310F = [10, 11]).
6. No prior assessment is available to assess prior function.
0100K2 = [-]).
25
This measure is used in the Five-Star Quality Rating System.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 57
Page 62

6.1. Target assessment is an OBRA Admission assessment (A0310A = [01]), a PPS 5-Day assessment (A0310B = [01]), or the first assessment after
an admission (A0310E = [1]).
Covariates used to risk-adjust this measure include:
1. Eating (self-performance) from prior assessment
1.1 Needs Help Covariate = 1 if (G0110H1 = [2, 3]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110H1 = [-, 0, 1, 4, 7, 8]).
1.2 Dependence Covariate = 1 if (G0110H1 = [4,7,8)] and Covariate = 0 if (G0110H1 = [-, 0,1,2,3]).
2. Toileting (self-performance) from prior assessment
2.1 Needs Help Covariate = 1 if (G0110I1 = [2, 3]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110I1 = [-, 0, 1, 4, 7, 8]).
2.2 Dependence Covariate = 1 if (G0110I1 = [4,7,8]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110I1 = [-, 0,1,2,3]).
3. Transfer (self-performance) from prior assessment
3.1 Needs Help Covariate = 1 if (G0110B1 = [2,3]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110B1 = [-, 0, 1, 4, 7, 8]).
3.2 Dependence Covariate = 1 if (G0110B1 = [4,7,8]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110B1 = [-, 0,1,2,3]).
4. Walking in Corridor (self-performance) from prior assessment
4.1 Independence Covariate = 1 if (G0110D1 = [0,1]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110D1 = [-, 2, 3, 4, 7, 8]).
4.2 Needs Some Help Covariate = 1 if (G0110D1 = [2]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110D1 = [-, 0, 1, 3, 4, 7, 8]).
4.3 Needs More Help Covariate = 1 if (G0110D1 = [3]) and Covariate = 0 if (G0110D1 = [-, 0, 1, 2, 4, 7, 8]).
5. Severe cognitive impairment from prior assessment
5.1 Covariate = 1 if (C1000 = [3] and C0700 = [1]) or BIMS summary score (C0500 ≤ [7]).
Covariate = 0 if (C1000 = [0, 1, 2, ^, -] or C0700 = [0, ^, -]) and (C0500 = [>7, ^, -, 99])
If Covariate has not been set to 1 or 0 based on logic in 5.1 and 5.2, then Covariate = [0].
6. Linear Age
If (MONTH(A2300) > MONTH(A0900)) or(MONTH(A2300) = MONTH(A0900) and
DAY(
A2300) >= DAY(A0900)) then Linear Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900) else Linear Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900)-1
7. Gender
7.1 Covariate = 1 if (A0800= [2]) (Female).
Covariate = 0 if (A0800= [1]) (Male).
8. Vision
8.1 Covariate = 1 if B1000 change score >0 with change score calculated from B1000 on the prior assessment to B1000 on the latest assessment with
n-missing after the prior assessment.
no
Covariate = 0 if either of the following criteria are met:
Measure Specifications Continued
Covariates
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 58
Page 63

• B1000 change score ≤ 0 with change score calculated from B1000 on the prior assessment to B1000 on the latest assessment with non-
missing B1000 after prior assessment.
• B1000 is not missing on the prior assessment, B1000 is missing on the target assessment, and no intermediate assessment has a non-missing
alue for B1000.
v
If Covariate has not been set to 1 or 0 based on logic in 8.1 and 8.2, then Covariate = [0].
9. Oxygen use
9.1 Covariate = 1 where (O0100C2 = [0]) on prior and (O0100C2 = [1]) on the latest assessment with non-missing O0100C2 after prior assessment.
Covariate = 0 if (O0100C2 = [0]) on the latest assessment with non missing O0100C2 after prior assessment or
• O0100C2 is not missing on the prior assessment, O0100C2 is missing on the target assessment, and no intermediate assessment has a non-
issing value for O0100C2.
m
If Covariate has not been set to 1 or 0 based on logic in 9.1, then Covariate = [0].
10. All covariates are missing if no prior assessment is available.
Covariates Continued
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 59
Page 64

Table 2-34
Percent of Residents Who Used Antianxiety or Hypnotic Medication (LS)
(CMS ID: N036.02) (NQF: None)
Measure Description
This measure reports the prevalence of antianxiety or hypnotic medication use (long stay) during the target period.
Measure Specifications
Numerator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment where any of the following conditions are true:
1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012:
1.1 Antianxiety medications received (N0410B = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]), or
1.2 Hypnotic medications received (N0410D = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7]).
Denominator
Long-stay residents with a selected target assessment, except those with exclusions.
Exclusions
1. The resident did not qualify for the numerator and any of the following is true:
1.1. For assessments with target dates on or after 04/01/2012: (N0410B = [-] or N0410D = [-]).
2. Any of the following related conditions are present on the target assessment (unless otherwise indicated):
2.1. Life expectancy of less than 6 months (J1400 = [1]).
2.2. Hospice care while a resident (O0100K2 = [1]).
Covariates
Not applicable.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 60
Page 65

Chapter 3
Technical Details
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 61
Page 66

Quality Measures (QM) Technical Details
List of Contents:
Section 1 Introduction ............................................................................................63
Section 2 Steps Used In National QM Calculation ................................................65
Section 3 Calculation of the Expected QM Score .................................................69
Section 4 Calculation of the Adjusted QM Score ..................................................72
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 62
Page 67

Section 1
Introduction
This chapter presents technical details regarding the calculation of the nursing home quality
measures (QMs), including the methodology used for risk adjustment.
Overview of QM Calculations
The QMs are created from counts of nursing facility long stay residents or short stay residents
who have certain conditions or problems (e.g., falls resulting in major injury). For example,
facility-level scores for the long stay falls QM are computed by: 1) counting residents in the
facility who had a fall resulting in major injury and 2) computing the percent of residents in the
facility who had valid MDS data and who experienced such a fall. The detailed logic for
defining the resident-level outcomes for each QM is presented in the QM Sample and Record
Selection Methodology section and in the Quality Measure Logic Specifications section of this
manual. This logic is listed under the "Numerator" entry for each QM.
A Note on Risk Adjustment
Risk adjustment refines raw QM scores to better reflect the prevalence of problems that facilities
should be able to address. Two complementary approaches to risk adjustment are applied to the
QMs.
One approach involves exclusion of residents whose outcomes are not under nursing facility
control (e.g., outcome is evidenced on admission to the facility) or the outcome may be
unavoidable (e.g., the resident has end-stage disease or is comatose). All of the QMs, except the
vaccination QMs, are shaped by one or more exclusions. For each QM, the prevalence of the
outcome across all residents in a nursing facility, after exclusions, is the facility-level observed
QM score.
A second approach involves adjusting QM scores directly, using logistic regression. This
method of adjustment employs resident-level covariates that are found to increase the risks of an
outcome. Detailed specifications for resident-level covariates are presented in the Quality
Measure Logical Specifications section of this manual. This approach involves the following
steps:
• First, resident-level covariates were used in a logistic regression model to calculate a
resident-level expected QM score (the probability that the resident will evidence the
outcome, given the presence or absence of characteristics measured by the covariates).
Section 3 of this Appendix presents the details for calculating expected scores for
residents.
• Then, an average of all resident-level expected QM scores for the nursing facility was
calculated to create a facility-level expected QM score.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 63
Page 68

• The final facility-level adjusted QM score was based on a calculation which combines the
facility-level expected score and the facility-level observed score. The details for
calculating facility-level adjusted scores are presented in Section 4 of this Appendix. The
parameters used for each release of the QMs are presented in Appendix B.
Only four of the QMs are adjusted using resident level covariates for public reporting:
• S038.02: Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute Care: Pressure Ulcer/Injury
• N037.03: Percent of Residents Who Improved Performance on Transfer, Locomotion,
and Walking in the Corridor (Short Stay)
• N026.03: Percent of Residents Who Have/Had a Catheter Inserted and Left in Their
Bladder (Long Stay)
• N035.03: Percent of Residents Who Declined in Independence in Locomotion (Long
Stay)
The remaining QMs are not adjusted using resident-level covariates. For these measures,
facility-level observed QM scores are reported.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 64
Page 69

Section 2
Steps Used in National QM Calculation
Introduction
This section outlines the processing steps used to calculate QMs. The description below uses Q1
2019 as the target period. The dates associated with these steps would be updated, as
appropriate, for subsequent quarterly releases of the QMs. It is important to note two items that
recurred throughout the process:
Every step in file construction and QM calculation proceeded in parallel for two samples of
residents and facilities: a “Long stay” (LS) sample and a “Short stay” (SS) sample.
• Two “target periods” were defined:
– a “Current Period” which was one quarter, Q1 2019, for LS residents and two
quarters, Q4 2018 and Q1 2019, for SS patients. Data from the current periods were
used as the target period for final QM reporting;
– a “Current Year”, Q2 2018 through Q1 2019, of data were used to estimate logistic
regressions for risk adjustment.
Processing Steps:
1. MDS Selection. All MDS records for U.S. nursing facilities in Q2 2018 through Q1 2019
were selected.
2. Episode Creation. Using the definitions contained elsewhere in this document, episodes
were created from the available data. Each episode, which may include one or more
interruptions, indicated by Interrupted Stay (A0310G1 = [1]), was classified as either long or
short stay depending upon the number of cumulative days in the facility. Only the latest
episode was retained for each resident.
3. Sampling for LS QMs. Nursing facilities and residents were sampled to provide data for LS
QM and covariate calculations.
a. “Current Period” LS resident sample: residents were included in this sample if they
had a long stay episode that ended within the last quarter of the target period (i.e., Q1
2019).
b. “Current Year” LS resident sample: residents were included in this sample if they had
a long stay episode in the target period (Q2 2018 through Q1 2019).
c. “Influenza Season” LS resident sample: includes residents with an influenza
vaccination target assessment for the most recently completed influenza season,
which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year.
Only sampled once a year for the annual calculation of the influenza vaccination
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 65
Page 70

QMs, which occurs after the most recent influenza season has been completed (i.e.,
after the end of June).
4. Sampling for SS QMs. Nursing facilities and residents were sampled to provide data for SS
QM and covariate calculations.
a. “Current Period” SS resident sample: residents were included in this sample if they
had a short stay episode that ended within the last two quarters of the target period
(i.e., Q4 2018 and Q1 2019).
b. “Current Year” SS resident sample: residents were included in this sample if they had
a short stay episode in the target period (Q2 2018 through Q1 2019).
c. “Influenza Season” SS resident sample: includes residents with an influenza
vaccination target assessment for the most recently completed influenza season,
which begins on July 1 of a given year and ends on June 30 of the subsequent year.
Only sampled once a year for the annual calculation of the influenza vaccination
QMs, which occurs after the most recent influenza season has been completed (i.e.,
after the end of June).
5. Resident-level QM Calculation Files. At this point, resident-level QM calculation files were
created, separately for each LS resident sample and each SS resident sample, using the
specified target, prior, initial, and influenza vaccination assessments for each resident record
as appropriate.
6. Resident-level QM and Covariate Calculation Files. Next, resident-level QM scores were
calculated (and covariate values were calculated for the risk-adjusted QMs), separately for
each LS resident and SS resident.
a. Resident-level QM calculation (all QMs):
i. Resident exclusions: For each QM, excluded residents were assigned a missing
value for that QM. Residents with missing covariate values were also assigned a
missing value for that QM.
ii. QM values: does the resident “trigger” the QM?
1. If “Yes”, then store a value of 1 for that QM in the resident-level QM
calculation record appropriate to that resident for a sample.
2. If “No”, then store a value of 0 for that QM in the resident-level QM
calculation record appropriate to that resident for a sample.
b. Resident-level covariate calculation (risk-adjusted QMs):
i. Resident exclusions: For each QM, excluded residents were assigned a missing
value for that QM. Residents with missing covariate values were also assigned a
missing value for that QM.
ii. Covariate: does the resident “trigger” the covariate?
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 66
Page 71

1. If “Yes”, then store a value of 1 for that covariate in the resident-level QM
calculation record appropriate to that resident for a sample.
2. If “No”, then store a value of 0 for that covariate in the resident-level QM
calculation record appropriate to that resident for a sample.
7. Logistic Regressions. With the resident-level files complete, and all relevant exclusions
applied, logistic regressions for the risk-adjusted QMs were estimated using the Current Year
LS and SS samples (Q2 2018 through Q1 2019).
a. Input: LS or SS resident-level file.
b. Dependent variable: was the QM triggered? (yes = 1, no = 0).
c. Predictors: resident-level covariates.
d. Calculation of logistic regressions: (See Section 3 in this Appendix).
e. Output values: logistic regression constant term and resident-level covariate
coefficients for each of the risk-adjusted QMs. The resulting values are given in
Table B.1 of Appendix B.
The logistic regression results calculated for Q1 2019 will remain in effect for QM
calculation in subsequent quarters. Recalculation may occur sometime in the future if
deemed appropriate.
8. Resident-level Expected QM Scores. For the QMs that were risk adjusted, resident-level
expected QM scores were calculated for each resident for the Current Period LS and SS
samples. (See Section 3 in this Appendix for calculation formulas).
a. Input: logistic regression constant term and resident-level covariate coefficients from
the previous step for each adjusted QM.
b. Output values: resident-level expected QM scores for each resident, for each of the
risk-adjusted QMs.
9. National Mean QMs. National mean observed QMs were needed for calculating the facility-
level adjusted QM scores below. The overall national mean observed QM scores for the
Current Period LS and SS samples were calculated, for each risk adjusted QM:
a. Numerator: for each QM, count the total number or residents that triggered the QM
and sum for the nation.
b. Denominator: for each QM, count the total number of residents retained after
exclusions and sum for the nation. Note that the sample will include only those
residents with non-missing data for the component covariates.
c. Overall national mean observed QM score: divide the numerator by the denominator.
10. Facility-level Observed QM Scores. For all QMs, the facility-level observed QM scores were
calculated for the Current Period LS and SS samples -- for the QMs that were not risk
adjusted, these are the measures that will be publicly reported.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 67
Page 72

a. Numerator: for each QM, count the total number of residents who triggered the QM
in each facility and sum for the nursing facility.
b. Denominator: for each QM, count the total number of residents retained after
exclusions for each facility and sum for the nursing facility. Note that the sample will
include only those residents with non-missing data for the component covariates.
c. Facility-level observed QM scores: divide the numerator by the denominator for each
QM and nursing facility.
11. Facility-level Expected QM Scores. For the risk-adjusted QMs, the facility-level expected
QM scores are calculated for the Current Period LS and SS samples. This is done by
averaging the resident-level expected QM scores for each QM within each nursing facility.
Note that the sample will include only those residents with non-missing data for the
component covariates.
12. Facility-level Adjusted QM Scores. Finally, for the risk-adjusted QMs, the facility-level
adjusted QM scores were calculated for the Current Period LS and SS samples.
a. Input -- for each of the risk-adjusted QMs
i. Facility-level observed QM scores
ii. Facility-level expected QM scores
iii. National mean observed QM scores
b. Calculation: (See Section 4 of this Appendix for calculation formulas)
c. Output: Facility-level adjusted QM scores for the five risk-adjusted QMs
13. Final Facility-level Output File. The final facility-level output files for the Current Period
LS and SS QMs contained the following:
a. For all QMs:
i. Facility numerator counts
ii. Facility denominator counts
iii. Facility-level observed QM scores (publicly reported for the unadjusted QMs)
b. For the risk-adjusted QMs: Facility-level adjusted QM scores (publicly reported
scores)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 68
Page 73

Section 3
Calculation of the Expected QM Score
For the QMs adjusted with resident-level covariates, the resident-level expected QM score was
calculated as an intermediate step to obtaining an adjusted QM score for the facility. This
section describes the technical details referred to in Section 2 of this chapter.
Calculating Resident-level Expected QM Scores
The resident-level expected score for a QM is an estimate of the risk that a resident will trigger
the QM. This estimate is based on consideration of the resident-level covariates associated with
the QM.
For each of the risk-adjusted QMs, a resident-level logistic regression was estimated. Data came
from the short stay and long stay samples described in the prior section of this appendix. The
resident-level observed QM score was the dependent variable. The predictor variables were one
or more resident-level covariates associated with the QM. Calculation of the QM and covariate
scores is described in Section 2 (Step 5) of this Appendix.
Each logistic regression had the following form:
[1]
QM triggered (yes = 1; no = 0)= B
0
+ B
∗COV
1
A
+ B
∗COV
2
+ ⋯+ B
B
∗COV
N
N
where B0 is the logistic regression constant, B1 is the logistic regression coefficient for the first
covariate, COVA is the resident-level score for the first covariate, B2 is the logistic regression
coefficient for the second covariate (where applicable), and COVB is the resident-level score for
the second covariate (where applicable), and so on.
Each resident’s expected QM score could then be calculated with the following formula:
[2] Resident-level expected QM Score =
1
[1 + e
−X
]
where e is the base of natural logarithms and x is a linear combination of the constant and the
logistic regression coefficients times the covariate scores (from Formula [1], above). A covariate
score will be 1 if the covariate is triggered for that resident, and 0 if not
.
As an example, consider the actual calculation used for the expected score for the LS "Percent of
re
sidents who have/had a catheter inserted and left in their bladder" QM (N026.03). The
covariates for that QM are indicators of bowel incontinence and pressure ulcers at stages II – IV
on the prior assessment. The equation used for this QM (with the parameters from Table B.1 for
Q1 2018) is:
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 69
Page 74

[3] N026.03 =
1
(
−
[1 + e
where B0 is the logistic regression constant, B1 is the logistic regression coefficient for BowInc,
the resident-level covariate indicating bowel incontinence, and B2 is the logistic regression
coefficient for PresUlcer, the resident-level covariate indicating pressure ulcers at stages II – IV.
The N026.03 score for a resident who triggers the bowel incontinence and pressure ulcers at
stages II – IV covariates (covariate scores = 1) is expected to be:
B0+B
∗BowInc +B2∗PresUlcer
1
[4] 0.1747 =
1
[1 + e
−(−4.281009+0.4587008 ∗1+2.26932 ∗1)
)
]
]
For a resident who does not trigger the bowel incontinence or pressure ulcers at stages II – IV
covariates (covariate scores = 0), the N026.03 score is expected to be:
[5] 0.0136 =
1
[1 + e
Thus, a resident who is bowel incontinent and has pressure ulcers at stages II – IV (i.e. covariates
= 1) is over twelve times as likely to report having a catheter inserted and left in their bladder
(17.47 percent) compared to a resident who is not bowel incontinent and does not have pressure
ulcers at stages II – IV (1.36 percent).
For a resident who triggers only the bowel incontinence covariate (covariate score = 1) and not
the pressure ulcers at stages II – IV covariate (covariate score = 0), the N026.03 score is
expected to be:
−(−4.281009+0.4587008 ∗0+2.26932 ∗0)
[6] 0.0214 =
]
1
]
[1 + e
−(−4.281009+0.4587008 ∗1+2.26932∗0)
For a resident who does not trigger the bowel incontinence covariate (covariate score = 0) and
triggers only the pressure ulcers at stages II – IV covariate (covariate score = 1), the N026.03
score is expected to be:
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 70
Page 75

[7] 0.1180 =
1
[1 + e
Thus, a resident who has pressure ulcers at stages II – IV (i.e. covariates = 1) is over five times
as likely to report having a catheter inserted and left in their bladder (11.80 percent) compared to
a resident who is bowel incontinent (2.14 percent). The parameters used for calculating the
resident-level expected QM scores are presented in Table B.1 of Appendix B.
Calculating Facility-level Expected QM Scores
Once an expected QM score has been calculated for all residents at risk, the facility-level
expected QM score is simply the average of all resident-level scores for each of the risk-adjusted
QMs.
−(−4.281009+0.4587008 ∗0+2.26932 ∗1)
]
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 71
Page 76

Section 4
Calculation of the Adjusted QM Score
The risk-adjusted QM score is a facility-level QM score adjusted for the specific risk for that QM
in the nursing facility. The risk-adjusted QM score can be thought of as an estimate of what the
nursing facility's QM rate would be if the facility had residents with average risk.
The facility-level adjusted score is calculated using the following scores:
• The facility-level observed QM score,
• The facility-level average expected QM score, and
• The national average observed QM score.
The actual calculation of the adjusted score uses the following equation:
1
[8] Adj =
[1 + e
−y
]
where
Adj is the facility-level adjusted QM score, and
Obs
y = (Ln (
)−Ln (
1 −Obs
Obs is the facility-level observed QM rate,
Exp
)+ Ln (
1 −Exp
Nat
))
1 −Nat
Exp is the facility-level expected QM rate,
Nat is the national observed QM rate, and
Ln indicates a natural logarithm.
e is the base of natural logarithms
Note that the adjusted QM rate (Adj) is calculated differently in two special cases:
1. When Obs equals 0.00, then Adj is set to 0.00 (without using the equation).
2. When Obs equals 1.00, then Adj is set to 1.00 (without using the equation).
The adjusted QM score equation will produce adjusted scores in the range of 0 to 1. These
adjusted scores can then be converted to percentages for ease of interpretation.
These adjusted score calculations are applied to QMs that use expected scores based on residentlevel covariates (See Section 3 of this Appendix). The national average observed QM rates,
required for these calculations, are presented in Appendix B.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 72
Page 77

Parameters Used for Each Quarter
Chapter 4
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 73
Page 78

o
N
o
Introduction
This chapter presents the model parameters that were estimated for the risk adjusted QMs for the
following time period:
• The period ending March 31, 2018 referred to as Q1 2018.
The purpose of this document is to present the logistic regression coefficients used in the risk
adjustment calculations that were applied to the risk-adjusted QMs. For details regarding the use
of these parameters, please refer to Chapter 3.
Logistic Regression Coefficients
Five QMs are risk adjusted. The logistic regression coefficients used are presented in Table 4-1.
Where risk adjustment involves the use of more than one resident-level covariate, coefficients
are listed in the order presented in the LS and SS matrices that are presented in the MDS 3.0
Quality Measures Logical Specifications section of this manual. The calculations in Table 4-1
are based on calculations for the Current Year sample ending with Q1 2018.
Table 4-1. Logistic Regression Coefficients
QM Constant (Intercept) Resident-Level Covariates
S038.02
N037.03 0.7823972
For the Constant and Resident-Level Covariates, please refer to the latest
ersion of the Risk Adjustment Appendix File for CMS ID: S038.02 in the
v
SNF Measure Calculations and Reporting User’s Manual, found at the
following URL:
A
ssessment-Instruments/NursingHomeQualityInits/Skilled-Nursing-FacilityQuality-Reporting-Program/SNF-Quality-Reporting-Program-Measures-andTechnical-Information.html
https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-Initiatives-Patient-
1. Covariate 1.1 (Age Category≤54)
2. Covariate 1.2 (Age Category 54 to
84)
(reference category)
3. Covariate 1.3 (Age Category>84) -0.16045
4. Covariate 2.1 (Female) 0.0272314
5. Covariate 3.1 (Cognitive
Impairment)
6. Covariate 4.1 (ADL Lowest Tercile)
7. Covariate 4.2 (ADL Middle Tercile)
reference category)
(
8. Covariate 4.3 (ADL Highest Tercile) -0.2748568
9. Covariate 5.1 (Heart Failure) -0.0636875
10. Covariate 6.1 (CVA/TIA/Stroke) -0.1366926
No
data
N
d
a
t
a
-0.053567
0.0
-0.5714708
-0.161358
0.0
d
a
t
a
11. Covariate 7.1 (Hip Fracture) 0.2954314
12. Covariate 8.1 (Other Fracture) 0.233453
N026.03 -4.281009
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 74
1. Covariate 1.1 (Bowel Incontinence) 0.4587008
2. Covariate 2.1 (Pressure Ulcer) 2.26932
Page 79

Table 4-1. Logistic Regression Coefficients (continued)
QM Constant (Intercept) Resident-Level Covariates No data
N035.03 -2.469571
1. Covariate 1.1 (Help with Eating) 0.0095926
2. Covariate 1.2 (Dependence
Eating)
3. Covariate 2.1 (Help with
Toileting)
4. Covariate 2.2 (Dependence
Toileting)
5. Covariate 3.1 (Help with
Transfer)
6. Covariate 3.2 (Dependence with
Transfer)
7. Covariate 4.1 (Independence
with Walking)
8. Covariate 4.2 (Some Help with
Walking)
9. Covariate 4.3 (More Help with
Walking)
10. Covariate 5 (Severe Cognitive
Impairment)
11. Covariate 6 (Age) 0.008044
0.5191111
0.2583423
0.4434241
0.0760023
0.4310152
0.0428471
-0.1233525
-0.6388195
0.1311536
12. Covariate 7 (Female) 0.0277615
13. Covariate 8 (Impaired Vision) 0.3495715
14. Covariate 9 (Oxygen Use) 0.8450993
National Observed Means
The national observed QM means are updated for each quarterly release. Table 4-2 presents
these means for Q1 2018, as an example.
Table 4-2. National Observed QM Means
QM Q1 2018
26
NA
S038.02
N037.03 0.6458298
N026.03 0.0227849
N035.03 0.1854863
26
Please refer to the latest version of the Risk Adjustment Appendix File for CMS ID: S038.02 in the SNF Measure
Calculations and Reporting User’s Manual found at the following URL: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Quality-
Initiatives-Patient-Assessment-Instruments/NursingHomeQualityInits/Skilled-Nursing-Facility-QualityReporting-Program/SNF-Quality-Reporting-Program-Measures-and-Technical-Information.html
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 75
Page 80

Episode and Stay Determination Logic
Chapter 5
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 76
Page 81

MDS 3.0 Episode and Stay Determination
Logic
Introduction
Several CMS applications are based upon the identification of stays and episodes using MDS 3.0
data. This chapter provides definitions and detailed logic that can be used by these applications.
This chapter begins with definitions of key terms and concepts. It then explains how stays and
episodes are identified in a well-defined assessment data stream (i.e., when all assessment
completion and submission rules are followed). It concludes with detailed logic that handles
exceptional cases (e.g., missing entry or discharge records).
Definitions
An episode consists of one or more stays, and a stay is the period of time between a resident’s
entry into a facility and either (a) a discharge, or (b) the end of the target period, whichever
comes first. A stay may include one or more interruptions lasting 3 calendar days or less.
Because an episode is built from a set of one or more stays, the episode can be identified if the
stays have been built properly. Therefore, this section will describe how to build stays.
Three properties of each stay must be determined:
• The starting date.
• The ending date.
• The stay type (admission or reentry).
The starting date is the date the resident entered the facility (either for the first time or after a
previous discharge). The ending date is either (a) the discharge date, or (b) the end of the target
period, whichever is earlier. The stay type is defined as follows:
Admission. An admission occurs when any one of the following conditions apply:
• The resident has never been admitted to this facility before; or
• The resident has been in this facility previously and was discharged return not
anticipated; or
• The resident has been in this facility previously and was discharged return anticipated
and did not return within 30 days of discharge.
Reentry. A reentry occurs when both of the following conditions apply:
• The resident has a discharge return anticipated, and
• The resident returned to the facility within 30 days of discharge.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 77
Page 82

Rules for a Well- Constructed Data Stream
In a well-constructed data stream (where all records are submitted and correctly coded), the
following logic will correctly determine the starting date, ending date, and type for each stay.
This logic assumes that the resident’s records have been sorted in reverse chronological order
(see the end of this section for sorting details). Stays and episodes must be contained within a
single facility, so the following logic applies to the records for a single facility.
1. If the first (latest) record that is on or before the end of the reporting period is a discharge
(A0310F = [10, 11, 12]), then the stay end date is equal to the discharge date (A2000).
Otherwise, the stay is ongoing and the stay end date is equal to the end of the reporting
period.
2. If the stay end date of the resident’s latest stay chronologically precedes the beginning of
the target period27, then the episode is not included in the sample. If the stay is ongoing
or if the discharge occurs within the target period, then continue.
3. Scan backwards chronologically until an entry record (A0310F = [01]) is encountered.
The stay start date is equal to the entry date (A1600) on the entry record.
4. Look at the chronologically preceding record. The stay type is defined as follows:
4.1. If a chronologically preceding record is found and if it is a discharge return
anticipated (A0310F = [11]) and if the discharge date of the discharge record is
within 30 days of the stay start date defined above, then the stay type is a reentry.
Otherwise, the stay type is an admission. Admissions occur under any of the
following conditions:
4.1.1. No chronologically preceding record is found.
4.1.2. A chronologically preceding record is found and it is a discharge return not
anticipated (A0310F = 10).
4.1.3. A chronologically preceding record is found and it is a discharge return
anticipated (A0310F = 11) and the discharge date is 31 days or more before
the stay start date.
5. If the stay was classified as an admission stay, then scanning would stop because this
would mark the beginning of the episode. If the stay was a reentry, then the scan logic
would continue with the stay that ended with the record found in Step #4 (if any). Stays
would continue to be scanned and classified until one of the following conditions
occurred:
27
The span of time that defines the application’s reporting period (e.g., a calendar quarter).
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 78
Page 83

5.1. An admission stay was identified, or
5.2. No more records were found for the same resident and facility, or
5.3. An application-specific rule was met. For example, for short stay Quality Measures
(QMs), processing stops when the number of cumulative days in the facility (CDIF)
exceeded 100 days (CDIF is the sum of the number of days within each of the stays
that are contained in the episode).
Handling Missing Records
Exceptions to the rules will occur when entry and/or discharge records are missing from a
resident’s data stream. When this occurs, starting and/or ending dates must be imputed and the
stay type must be determined as accurately as possible. The following rules will describe how
these situations are handling. This discussion will refer to three types of records:
• Entry record (where A0310F= [01]).
• Discharge record (where A0310F= [10, 11, 12]).
• A normal assessment (where A0310F= [99]).
Missing Entry Records
In the scan logic described above, if a normal assessment is immediately preceded chronologically
by a discharge record or if there is no chronologically preceding record, then an entry record is
missing. In this case the stay start date and type must be imputed. The imputation rules are as
explained below. In these rules, the assessment that is preceded chronologically by a discharge or
that has no preceding record is termed the “problem assessment”.
The table below is used to impute the entry date when there is a missing entry record.
Table 5-1: Possible Entry Dates When Entry Record is Missing
Type of Problem
Assessment
PPS 5-Day A0310B = [01] A2300 - 7 days A2300
OBRA Admission A0310A = [01] A2300 - 13 days A2300
Other OBRA A0310A = [02,03,04,05,06] A2300 - 106 days A2300
Discharge A0310F = [10,11,12] A1600 A1600
Reasons for
Assessment
Possible Entry Dates
Earliest Date
Latest Date
The table above lists various types of problem assessments and shows the earliest and latest
possible entry dates that are associated with each one. The following steps explain how to use
this table to impute an entry date and stay type when a problem assessment is chronologically
preceded by a discharge assessment or where no record precedes the problem assessment.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 79
Page 84

1. Use the table above to classify the problem assessment. Classify the assessment using
the reason for assessment items indicated in the table. If the problem assessment
qualifies for more than one of the rows in the table, use the first (top-most) row for which
it qualifies.
2. Determine the earliest and latest entry date associated with the selected row.
3. Determine the entry date (A1600) that is reported on the problem assessment.
4. Determine a tentative entry date, as follows:
4.1. If the entry date (A1600) on the problem assessment falls between the earliest and
latest entry date in the table, set the tentative entry date equal to this value of A1600.
4.2. Otherwise, set the tentative entry date equal to the date that is listed in the “earliest
date” column of the table.
5. Determine a final imputed entry date, as follows:
5.1. If the problem assessment is chronologically preceded by a discharge record, add
one day to the discharge date (A2000) on the discharge record and compare the
resulting date with the tentative entry date (A1600 from the assessment). Set the
final imputed entry date equal to the later of these two dates.
5.2. If there is no record that chronologically precedes the problem assessment, then set
the final imputed entry date equal to the tentative entry date.
6. Determine the stay type, as follows:
6.1. If the problem assessment is chronologically preceded by a discharge record,
determine the stay type using the normal logic described above.
6.2. If there is no record that chronologically precedes the problem assessment, then set
the stay type as an admission stay.
MISSING DISCHARGE RECORDS
In the scan logic described above, if an entry record is immediately preceded chronologically by
a normal assessment, then a discharge record is missing. In this case, the end date of the
chronologically preceding stay and the stay type of the current stay must be imputed. The
imputation rules are as follows. In these rules, the assessment that chronologically precedes the
entry record is termed the “ending index assessment”. The “current stay” is the stay that begins
with the entry record. The “chronologically preceding stay” is the stay that contains the ending
index assessment.
1. The end date of the chronologically preceding stay is set equal to the assessment
reference date that is recorded on the ending index assessment.
2. Set the stay type of the current stay as follows:
2.1. Determine the value of A1700 that is recorded on the entry record of the current stay.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 80
Page 85

2.2. If A1700 is equal to [1] (admission), then set the stay type for the current stay to
“admission”.
2.3. If A1700 is equal to [2] (reentry), then set the stay type for the current stay to
“reentry”.
Multiple Entry Records
If there are two or more entry records which are adjacent to one another in the resident’s data
stream, keep the latest entry record and ignore the earlier adjacent entry record(s).
Multiple Discharge Records
If there are two or more discharge records which are adjacent to one another in the resident’s
data stream, keep the latest discharge record and ignore the earlier adjacent discharge record(s).
Sorting Rules
As noted above, stays are identified from the records for a given resident and facility that are
sorted in reverse chronological order. Sorting criteria must be applied to handle the case where
there is more than one record on a given target date. The exact sorting criteria are as follows:
a) State ID +
b) Facility internal ID +
c) Resident internal ID +
d) Target date (descending) +
e) Record type (descending) +
f) Assessment internal ID (descending)
Note that record type (record_type) is defined as follows:
1. If A0310F = 01 (the record is an entry record), then record_type = [1].
2. Else if A0310F = 99 (the record is not an entry or discharge), then:
a. If the item subset code28 is equal to NC (comprehensive assessment), then
record_type = [7].
b. Else if the item subset code is equal to NQ (quarterly assessment), then record_type =
[6].
c. Else if the item subset code is equal to NP (PPS assessment), then record_type = [5].
d. Else record_type = [2] (this condition should not occur).
3. Else if A0310F = [10] (discharge, return not anticipated), then record_type = [8].
4. Else if A0310F = [11] (discharge, return anticipated), then record_type = [9].
28
The item subset code is contained in the field ITM_SBST_CD.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 81
Page 86

5. Else if A0310F = [12] (death in facility), then record_type = [10].
Also note that the assessment internal ID is used as the final tie-breaker on the assumption that
records that should be later in the sort sequence will be submitted and processed later than the
other records. The record processing timestamp would be a slightly better field to use for this
purpose. However, it is available only to users who have direct access to the ASAP database.
The assessment internal ID was therefore adopted as a reasonable substitute for the timestamp so
that all users would have access to the same sorting fields.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 82
Page 87

Chapter 6
Specifications for the Facility Characteristics Report
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 83
Page 88

Specifications for Facility Characteristics Report
cord Selection
Re
The Facility Characteristic Report is populated using data from records selected using the
standard QM episode and record selection logic as given in the QM User’s Manual. The
Facility Characteristics measures can be processed with the QM measures. Each Facility
Characteristic measure is computed using all residents (both short-stay and long-stay residents).
Most of the Facility Characteristic measures are populated using data from a look-back scan of
the assessment records selected for each resident. For each resident, the look-back scan begins
with the target assessment selected for QM processing. The resident’s records are scanned in
reverse chronological order (by ARD) and all data items required for the Facility Characteristics
report are populated from data that are available from each assessment. As assessments are
scanned, each required item is initially populated with the item value from the target assessment.
If the value from the target assessment is a valid (non-missing) value, then the scan for that item
stops. If the value for the target assessment is not a valid value (a missing value), then the scan
continues with the earlier assessments in reverse chronological order. Once a valid value is
found for an item, that value is used for the report (i.e., the value is not changed if additional
values are present in earlier records).
A “valid value” is any value that is one of the “normal” responses to an item. Missing non-valid
values are:
1. A dash (“-”) indicating that the item was not assessed.
2. A caret (“^”) indicating that the item was skipped.
3. A null (.) indicating that the item is inactive.
Note that the diagnosis code items (I8000A through I8000J) are not used in the measure
specifications below and are therefore not included in the look-back scan.
For each resident, the look-back scan continues until any of the following conditions is satisfied:
• All required items have been populated with valid values, as defined above, or
• All selected records for a resident have been scanned.
Note that scanning stops for a resident as soon as either of these conditions is satisfied.
Measure Specifications
The definitions in the following table are applied to a look-back scan of the records selected for
a resident as described in the prior section on Record Selection. Counts of the number of
residents within each facility that meet the numerator criteria for each measure below are used as
the numerator to produce facility percentages for the report.
The denominator used to produce the facility percentages in the report will vary for different
measures, depending on missing data. If missing data precludes determination of the status for a
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 84
Page 89

measure as indicated in the “Exclusions” section, then the resident is excluded from both the
numerator and denominator in the facility percentage.
Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions
Measure Description and Definition
Gender
Male
Female
Age
<25 years old
Description: Resident is included if Item A0800 (Gender) is equal to 1
(Male). Records with dashes (not assessed) in A0800 are excluded from
the male/female counts.
Numerator: A0800 = 1 (Male).
Exclusions: A0800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A0800 (Gender) is equal to 2
(Female). Records with dashes (not assessed) in A0800 are excluded
from the male/female counts.
Numerator: A0800 = 2 (Female).
Exclusions: A0800 missing
Calculation of Age, based on Items A0900 (Birth Date) and A2300
(Assessment Reference Date ARD):
IF (MONTH(A2300) > MONTH(A0900)) OR
(MONTH(A2300) = MONTH(A0900) AND
DAY(A2300) >= DAY(A0900)) THEN
Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900) ELSE
Age = YEAR(A2300)-YEAR(A0900)-1
Description: Age less than 25 years old.
25-54 years old
55-64 years old
65-74 years old
75-84 years old
Numerator:
Record triggers if age < 25.
Description: Age of 25 through 54 years old.
Numerator:
Record triggers if age >= 25 and <= 54.
Description: Age of 55 through 64 years old.
Numerator:
Record triggers if age >= 55 and <= 64.
Description: Age of 65 to 74 years old.
Numerator:
Record triggers if age >= 65 and <= 74.
Description: Age of 75 through 84 years old.
Numerator:
Record triggers if age >= 75 and <= 84.
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 85
Page 90

Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions (continued)
Measure
Description and Definition
85+ years old
Diagnostic Characteristics
Psychiatric
Diagnosis
Intellectual Disability (ID)
(Mental retardation as
defined at 483.45(a)) or
Developmental Disability
(DD)
Description: Age of 85 years of age or older.
Numerator:
Record triggers if age >= 85.
Description: Resident is included as having a psychiatric
diagnosis if any of the following is true:
• Any psychiatric mood disorders are checked (=1) in items
I5700 through I6100, or
• Item I5350 (Tourette’s Syndrome) is checked (=1), or
• Item I5250 (Huntington’s Disease) is checked (=1).
Numerator:
• Any of the following items are checked (-1): I5250,
I5350, I5700 through I6100.
Exclusions: No value I5250, I5350, I5700 through I6100 = 1 and any
value I5250, I5350, I5700 through I6100 is missing
Description: Resident is counted as having ID/DD if any of the
following items are checked:
•
A1550A (Down syndrome).
A1550B (Autism).
•
A1550C (Epilepsy).
•
A1550D (Other organic condition related to ID/DD).
•
•
A1550E (ID/DD with no organic condition).
Hospice
Numerator:
A1550A, B, C, D, or E is checked (= 1).
Exclusions: No value A1550A, B, C, D, or E = 1 and any value A1550A,
B, C, D, or E missing
Description: Resident is included if Item O0100K2 (Hospice care)
is checked.
Numerator: O0100K2 is checked (=1).
Exclusions: O0100K2 missing
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 86
Page 91

Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions (continued)
Measure
Description and Definition
Prognosis
Life expectancy of less than
6 months
Discharge Plan
Discharge planning IS NOT
already occurring for the
resident to return to the
community.
Discharge planning IS
already occurring for the
resident to return to the
community.
Referral
Referral not needed.
Description: Resident is included if item J1400 (Prognosis) is coded 1
(Yes).
Numerator: J1400 = 1 (Yes).
Exclusions: J1400 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item Q0400A (Discharge Plan) is
coded 0 (No).
Numerator: Q0400A = 0 (No).
Exclusions: Q0400A missing
Description: Resident is included if Item Q0400A (Discharge Plan) is
coded 1 (Yes).
Numerator: Q0400A = 1 (Yes).
Exclusions: Q0400A missing
Description: Resident is included if Item Q0600 (Referral) is coded 0 (No
- Referral not needed).
Referral is or may be
needed, but has not been
made.
Referral has been made.
Numerator: Q0600 = 0 (No - Referral not needed).
Exclusions: Q0600 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item Q0600 (Referral) is coded 1
(Yes – Referral is or may be needed).
Numerator: Q0600 = 1 (No - Referral is or may be needed).
Exclusions: Q0600 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item Q0600 (Referral) is coded 2
(Yes - Referral made).
Numerator: Q0600 = 2 (Yes - Referral made).
Exclusions: Q0600 missing
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 87
Page 92

Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions (continued)
Measure
Description and Definition
Type of Entry
Admission
Reentry
Entered Facility From
Community (private
home/apartment
board/care, assisted living,
group home)
Another nursing home or
swing bed
Description: Resident is included if Item A1700 (Type of Entry) is coded
1, (Admission).
Numerator: A1700 = 1 (Admission).
Exclusions: A1700 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1700 (Type of Entry) is coded
2, (Reentry).
Numerator: A1700 = 2 (Reentry).
Exclusions: A1700 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
01 (Community).
Numerator: A1800 = 01 (Community).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
02 (Another nursing home or swing bed).
Acute hospital
Psychiatric hospital
Inpatient rehabilitation
facility
Numerator: A1800 = 02 (Another nursing home or swing bed).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
03 (Acute hospital).
Numerator: A1800 = 03 (Acute hospital).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
04 (Psychiatric hospital).
Numerator: A1800 = 04 (Psychiatric hospital).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
05 (Inpatient rehabilitation facility).
Numerator: A1800 = 05 (Inpatient rehabilitation facility).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
(continued)
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 88
Page 93

Table 6-1: Facility Characteristics Report Measure Definitions (continued)
Measure
Description and Definition
ID/DD facility
Hospice
Long Term Care Hospital
(LTCH)
Other
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
06 (ID/DD facility).
Numerator: A1800 = 06 (ID/DD facility).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
07 (Hospice).
Numerator: A1800 = 07 (Hospice).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
09 (Long Term Care Hospital (LTCH)).
Numerator: A1800 = 09 (Long Term Care Hospital (LTCH)).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
Description: Resident is included if Item A1800 (Entered From) is coded
99 (Other).
Numerator: A1800 = 99 (Other).
Exclusions: A1800 missing
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 89
Page 94

MDS 3.0 Quality Measures
USER’S MANUAL
APPENDIX A
Quality Measure Identification Number
by CMS Reporting Module
Effective: October 1, 2020
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-1
Page 95

Quality Measure Identification Number by CMS Reporting Module V1.8
The table below documents CMS quality measures (QM) calculated using MDS 3.0 data and
reported in a CMS reporting module. A unique CMS identification number (ID) is specified for
each QM. The table serves two purposes:
• The table indicates which QMs are associated with a CMS reporting module.
• The table documents the CMS ID—the link to QM specification detail in the CMS’ MDS
QM User’s Manual. As various QM specifications are revised, the QM is given a new
CMS ID and the older QM logical version (i.e., CMS ID) is retained. This allows for the
possibility of a transition period when more than one version of the same QM can be
reported simultaneously across reporting modules (e.g., a MDS 3.0 item set update). The
National Quality Forum (NQF) identification number is included for reference.
The following CMS reporting modules are included:
CASPER Reporting Quality Measure Reports contain quality measure information at the
national, state, facility and resident level for a single reporting period. Users are able to
specify the reporting time frame. State and National comparison group data are calculated
monthly on the first day of the month. Data calculation is delayed by two months in order to
allow for submission of late and corrected assessments. Comparison data are not
recalculated if assessments with target dates that fall in periods for which comparison group
data were already calculated. Quality Measure data are calculated weekly for the
assessments accepted into the national database since the previous week’s data calculation.
Note: Quality measure reports available to facilities through CMS’s CASPER reporting
system are also available to State Surveyors.
Nursing Home Compare (NHC), CMS’ website contains quality measure information (as well
as other details) for Medicare and Medicaid-certified US nursing homes. (Note: information
for those nursing homes reporting less than 20 residents for both short stay and long stay
quality measures for the reporting period is not included.). The QM information is updated
and posted quarterly. NHC reports the average adjusted QM values across the most recent
four quarters.
Five-Star Quality Rating System contains information on health inspections, staffing and
quality measures. QMs are updated and posted quarterly. The Five Star module reports the
weighted average adjusted QM values across the most recent four quarters.
Facility and Resident Quality Measure Preview Reports, available in the facility’s shared
folders on CMS’ QIES website, display the quarterly numerator, denominator and reported
percent values for each of the publicly reported MDS 3.0 quality measures and also displays
the list of residents who triggered one or more of the publicly reported MDS 3.0 Quality
Measures. The preview reports allow the provider to see their measure percent values prior
to being posted on the Nursing Home Compare website. The preview reports indicate the
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-2
Page 96

measure values for the most recent quarter (i.e., the QM value is based on a one quarter look
back period). The quality measure data correspond with the NHC reporting cycle.
QMs by CMS Reporting Module—Column Headers
Quality Measure Label: A brief definition of the quality measure. The label refers to the one
sentence definition of the QM as reported in the MDS 3.0 QM User’s Manual. The QM label
wording may not be identical across reporting modules. The User should refer to the CMS ID
for QM cross-reference among reporting modules.
Short or Long Stay: Refers to the nursing home (NH) population used to calculate the quality
measure. The short stay quality measure specifications are based on NH residents whose
episode is less than or equal to 100 cumulative days in the nursing home at the end of the target
period. The long stay quality measure specifications are based on NH residents whose episode
is greater than or equal to 101 cumulative days in the NH at of the end of the target period.
CMS ID: the unique CMS identification number depicted as
S = provider type (N = Nursing Home)
nnn = three-digit QM ID
vv = logic version number for a QM (e.g., 01, 02, 03)
Examples of incrementing the CMS ID:
N123.01 – first logic version of the nursing home measure 123
N123.02– second logic version of nursing home measure 123
NQF ID: Specifies the National Quality Forum QM identification number for those QM
endorsed by NQF. For further details refer to the National Quality Forum website:
https://www.qualityforum.org/qps/
Effective Date: Specifies the date the QM was first implemented (i.e., effective).
CASPER: Certification and Survey Provider Enhanced Reports (CASPER) Quality Measure
Reports. For further details refer to references and manuals page of the QIES Technical Support
Office website: https://qtso.cms.gov/providers/nursing-home-mdsswing-bed-
providers/reference-manuals
NHC: CMS’ Nursing Home Compare website contains detailed information about all Medicare
and Medicaid-certified nursing homes in the US, including quality measures. For further details
refer to the Nursing Home Compare website:
https://www.medicare.gov/NursingHomeCompare/search.aspx?bhcp=1
Five-Star: CMS’ Five-Star Quality Rating System contains information on health inspections,
staffing and quality measures. For further details see the Nursing Home Compare Five-Star
Quality Rating System Technical Users’ Guide: https://www.cms.gov/Medicare/Provider-
Enrollment-and-Certification/CertificationandComplianc/Downloads/cutpointstable.pdf
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-3
Page 97

Provider Preview: Facility and Resident Quality Measure Preview Reports. For further details
refer to the QIES Technical Support Office website: https://qtso.cms.gov/
Specifications for all CMS ID quality measures are contained in Chapter 2 of this user’s manual.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-4
Page 98

0682A
drawn)
Table A-1: Quality Measures (QMs) by CMS Reporting Module – Short Stay
Quality Measure (QM) Label CMS ID NQF ID
SHORT STAY QMs
Changes in Skin Integrity Post-Acute
Care: Pressure Ulcer/Injury
S038.02 NA 10/1/20
Percent of Residents Who Were
Assessed and Appropriately Given the
N003.03 0680 10/1/12 NO
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Received the
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine
N004.03 0680A 10/1/12 NO NO NO
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered
and Declined the Seasonal Influenza
N005.03 0680B 10/1/12 NO NO NO
Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Did Not
Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza
N006.03 0680C 10/1/12 NO NO NO
Vaccine
Percent of Residents Assessed and
Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal
Vaccine
N007.02
0682
(with-
drawn)
Effective
Date CASPER29 NHC
YES YES YES YES
10/1/12 NO
YES
YES
Five-
Star
NO
NO
Provider
Preview
YES
YES
YES
YES
YES
Percent of Residents Who Received the
Pneumococcal Vaccine
N008.02
(with-
10/1/12 NO NO NO
YES
29
The quality measure reports available to facilities through CASPER are also available to State Surveyors.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-5
Page 99

Quality Measure (QM) Label CMS ID NQF ID
SHORT STAY QMs
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered
and Declined the Pneumococcal Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Did Not
Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Pneumococcal
Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Newly
Received an Antipsychotic Medication
Percentage of Residents Who Made
Improvements in Function
Effective
Date CASPER29 NHC
0682B
N009.02
(with-
10/1/12 NO NO NO
drawn)
0682C
N010.02
(with-
10/1/12 NO NO NO
drawn)
N011.02 NA 4/1/12
N037.03 NA 10/1/16
Five-
Star
Provider
Preview
YES
YES
YES YES YES YES
YES YES YES YES
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-6
Page 100

Table A-2: Quality Measures (QMs) by CMS Reporting Module – Long Stay
Quality Measure (QM) Label CMS ID NQF ID
LONG STAY QMs
Percent of Residents Experiencing One
or More Falls with Major Injury
Percent of High-Risk Residents with
Pressure Ulcers
N013.02 0674 10/1/10
N015.03 0679 10/1/18
Percent of Residents Assessed and
Appropriately Given the Seasonal
N016.03 0681 10/1/10 NO
Influenza Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Received the
Seasonal Influenza Vaccine
N017.03 0681A 10/1/10 NO NO NO
Percent of Residents Who Were Offered
and Declined the Seasonal Influenza
N018.03 0681B 10/1/10 NO NO NO
Vaccine
Percent of Residents Who Did Not
Receive, Due to Medical
Contraindication, the Seasonal Influenza
N019.03 0681C 10/1/10 NO NO NO
Vaccine
Effective
Date CASPER30 NHC
YES YES YES YES
YES YES YES YES
YES
Five-
Star
NO
Provider
Preview
YES
YES
YES
YES
Percent of Residents Assessed and
Appropriately Given the Pneumococcal
Vaccine
N020.02
0683
(with-
drawn)
10/1/10 NO
YES
NO
YES
30
The quality measure reports available to facilities through CASPER are also available to State Surveyors.
MDS 3.0 Quality Measures User’s Manual V14 – Effective October 1, 2020 A-7
 Loading...
Loading...