Page 1

Cisco Personal Assistant Installation and Administration Guide
Release 1.4
Revised November 29, 2004
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-4590-03
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCIP, CCSP, the Cisco Arrow logo, the Cisco Powered Network mark, Cisco Unity, Follow Me Browsing, FormShare, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.;
Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Aironet, ASIST, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCNA,
CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, the Cisco IOS logo, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo,
Empowering the Internet Generation, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ
Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Pac ke t, PIX,
Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX, Registrar, ScriptShare, SlideCast, SMARTnet, StrataView Plus, SwitchProbe, TeleRouter, The Fastest Way to Increase Your
Internet Quotient, TransPath, and VCO are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0403R)
IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
Copyright © 2004, Cisco Systems, Inc.
All rights reserved.
Page 3

Preface ix
Overview ix
Audience ix
Related Documentation x
Help and Document Conventions x
Using Help x
Document Conventions xi
Obtaining Documentation xi
Cisco.com xi
Ordering Documentation xii
Documentation Feedback xii
Obtaining Technical Assistance xii
Cisco Technical Support Website xii
Submitting a Service Request xiii
Definitions of Service Request Severity xiii
CONTENTS
CHAPTER
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information xiv
1 Planning for Personal Assistant 1-1
Understanding Personal Assistant 1-1
Personal Assistant Features 1-1
Cisco IP Telephony Terminology 1-3
Role of Personal Assistant in the Cisco IP Telephony Network 1-5
Personal Assistant and User Interactions 1-7
Understanding the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server 1-8
Speech-Recognition Server 1-8
Personal Assistant Server 1-9
License and Resource Managers 1-9
Interactions of the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server 1-10
Creating Server Clusters 1-10
Determining the Required Number of Personal Assistant Servers and Speech-Recognition
Servers 1-11
Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing 1-13
Creating a Personal Assistant Server Cluster With Failover 1-15
OL-4590-03
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant 1-16
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Using Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Without Personal Assistant 1-17
Defining Partitions and Call Search Spaces for Personal Assistant 1-18
Customizing Implementation of Personal Assistant 1-23
Using Personal Assistant Without Speech Recognition 1-23
Using Personal Assistant Without Rule-Based Call Routing 1-23
Preventing Toll Fraud 1-24
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant 2-1
Task List for Installing Personal Assistant on a New System 2-1
Installing Personal Assistant Software 2-2
Task List for Upgrading from Personal Assistant Version 1.3(x) 2-5
Stopping Personal Assistant Components 2-6
Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for Personal Assistant 2-6
Verifying That the Global Catalog Schema Includes Personal Assistant Attributes 2-6
Using an LDIF File 2-7
Disabling McAfee NetShield Services 2-8
Disabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant 2-8
Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant 2-9
Installing the Enhanced Text to Speech Server 2-9
Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the Corporate Directory 2-10
3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant 3-1
Setting Up Cisco IP Phone Route Plans 3-2
Creating a Phone Partition 3-2
Creating a Phone Calling Search Space 3-2
Assigning the Partition and Calling Search Space to Phones 3-3
iv
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls 3-3
Creating the Personal Assistant Partitions 3-4
Creating the Personal Assistant Calling Search Space 3-4
Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports and Configuring Error Handling 3-4
Updating the Calling Search Space for End-User Phones 3-7
Updating the Partition for Managed Phones 3-8
Setting Up the Personal Assistant Number 3-8
Adding Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User 3-9
Adding Media Ports for Personal Assistant 3-10
Configuring Cisco Unity in Cisco CallManager for Integration with Personal Assistant 3-12
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 5

Contents
CHAPTER
4 Configuring Personal Assistant 4-1
Personal Assistant Configuration Task List 4-1
Logging On to and Out of the Personal Assistant Administration Interface 4-3
Configuring Speech Recognition 4-4
Configuring Telephony Providers 4-7
Configuring the Corporate Directory 4-7
Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration (Personal Assistant Version 1.4(3) or
Later) 4-10
Configuring Personal Assistant Servers 4-10
Configuring Messaging 4-12
Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech 4-14
Creating a Simple Automated Attendant 4-15
Creating Dialing Rules 4-16
Configuring Directory Lookup Rules 4-17
Configuring Directory Hierarchies 4-18
Setting Up Systemwide Rules 4-19
Creating and Activating Systemwide Rules 4-19
Turning on Systemwide Rule Processing 4-20
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice Messaging System 4-20
Integrating Personal Assistant with an Octel Voice Messaging System 4-23
Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5 4-24
5 Preparing Users for Personal Assistant 5-1
Accessing the User Interface 5-1
Dialing Personal Assistant 5-2
Obtaining Help 5-2
Managing Users 5-2
How Administrative Changes Affect Users 5-3
6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant 6-1
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant 6-1
Unable to Access the User Web Interface 6-2
Search Results Include Multiple Copies of a User 6-2
Unable to Use Speech Commands 6-2
Users Cannot Make Conference Calls (Cisco CallManager 3.3 or Later) 6-3
Directed to Operator Too Often 6-3
Too Many Available Options 6-3
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Calls Transferred to Voice Mail Too Quickly 6-4
Dial Rules Not Working Properly 6-4
Calls Dropping 6-4
Callers Hear “We Are Experiencing Technical Difficulties, Please Call Back Later” 6-4
Personal Assistant Is Too Slow to Answer Calls 6-5
Callers Hear a Busy Tone When Calling Personal Assistant 6-5
A User Hears a Busy Tone When Calling Another User 6-5
Personal Assistant Does Not Recognize Users When They Call From Their Work Phones 6-6
Message Waiting Indicator Does Not Work 6-6
All Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail 6-7
Some Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail 6-7
Users Cannot Log On to Cisco Unity Voice Mail 6-7
Calendar-Based Call-Routing Rules Do Not Work 6-8
Users Hear Text to Speech Names Too Often 6-9
Personal Assistant Plays an Unexpected User Recorded Name 6-9
APPENDIX
Resolving Problems with Managing Personal Assistant 6-10
Speech Server or License Manager Is Not Recognized 6-10
Servers Displaying Connectivity Problem 6-10
Server Processor Is Running at Maximum 6-10
Personal Assistant Is Not Intercepting Calls 6-11
Personal Assistant Is Transferring Only Internal Calls or External Calls to Voice Mail 6-11
Troubleshooting Failed System Refreshes 6-11
Monitoring Server Status 6-12
Monitoring Performance 6-12
Collecting Call History Information 6-14
Starting and Stopping the Servers and License Manager 6-14
Collecting Trace and Debug Information 6-15
Integrating with Network Management Systems 6-16
CDP Support 6-16
Monitoring Personal Assistant Subsystem Status 6-17
Collecting System Logs with Syslog 6-17
A Personal Assistant Administration Page Reference A-1
vi
AA Prompt Configuration A-1
Control Center A-2
Corporate Directory Settings A-3
Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration A-6
Dial Rules Configuration A-6
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 7

I
NDEX
Contents
Directory Hierarchy Configuration A-7
Directory Lookup Rules A-8
Enhanced Text to Speech Configuration A-9
Messaging Configuration A-10
Miscellaneous Settings A-12
Reset User Information A-15
Server Configuration A-16
Server Status A-20
Speech Services Configuration A-21
Systemwide Rule Options A-25
Systemwide Rules A-25
Telephony Configuration A-26
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
vii
Page 8

Contents
viii
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 9

Overview
Preface
This preface describes who should read this publication and its document conventions.
The Cisco Personal Assistant Installation and Administration Guide provides you with the information
you need to understand, install, configure, and manage the Cisco
The following table provides an overview of the organization of this guide.
Personal Assistant application.
Audience
Chapter Description
Chapter 1, “Planning for Personal Assistant” Explains what Personal Assistant does for your
users, how it works, and how it fits into your IP
telephony network.
Chapter 2, “Installing and Upgrading
Personal Assistant”
Chapter 3, “Configuring Cisco CallManager for
Personal Assistant”
Chapter 4, “Configuring Personal Assistant” Provides procedures for configuring
Chapter 5, “Preparing Users for
Personal Assistant”
Chapter 6, “Troubleshooting Personal Assistant” Provides tips for resolving problems with
Appendix A, “Personal Assistant Administration
Page Reference”
Outlines the tasks and provides procedures for
installing and upgrading Personal
Provides procedures for configuring
Cisco
CallManager for use with
Personal
Personal
Describes information you should communicate to
your users.
Personal
Describes the fields on the pages used in the
Cisco
interface.
Assistant.
Assistant.
Assistant.
Personal Assistant Administration
Assistant.
OL-4590-03
Network engineers, system administrators, and telecom engineers should review this guide to learn the
steps required to properly set up Personal
Assistant in the network.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
ix
Page 10

Related Documentation
The tasks described in this guide are considered to be administration-level tasks. Because of the close
interaction of Personal
Cisco
CallManager as well.
Assistant with Cisco CallManager, these tasks require you to be familiar with
Related Documentation
For information about Cisco CallManager and additional information about Personal Assistant, refer to
the following publications:
• Cisco CallManager Administration Guide
• Personal Assistant end-user interface Help
Help and Document Conventions
The Personal Assistant Help system provides task-oriented Help and context-sensitive Help that is
available from every window that contains a Help menu or button.
Preface
Using Help
The Help system includes an index and is organized the same way as the Personal Assistant
documentation set.
You can access Help in any of the following ways:
• From the Help menu:
–
Access Help for the page you are viewing by selecting Help > For This Screen.
–
Access the contents of the Help system by selecting Help > Contents and Index.
• For a printed version of the manual associated with the application, or to view or search an Adobe
Acrobat version of the Help system, click the PDF button in the top left of the Help system. If you
have Adobe Acrobat installed (either as an independent application or as a plug-in to your browser),
the document opens.
From Acrobat, you can search the entire manual, print the entire manual or selected pages, or read
the manual online. Click the Bookmarks and Page button to view a table of contents for the
document in the left-hand margin if it is not already displayed. The bookmarks provide an easy way
to navigate through the document.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
x
OL-4590-03
Page 11
Preface
Document Conventions
The Cisco Personal Assistant Installation and Administration Guide uses the following conventions:
Convention Description
boldfaced text Boldfaced text is used for:
< >
(angle brackets)
italic text Arguments for which you supply values are in italics.
>
(right angle bracket)
• Key and button names. (Example: Click OK.)
• Information that you enter. (Example: Enter
Administrator in the User Name box.)
Angle brackets are used around parameters for which
you supply a value. (Example: In the Command Prompt
window, enter ping <IP Address>.)
A right angle bracket is used to separate selections that
you make:
• On menus. (Example: On the Windows Start menu,
click Settings
Modem Options.)
• In the graphical user interface of the
Personal
> Control Panel > Phone and
Assistant Administration.
Obtaining Documentation
The Cisco Personal Assistant Installation and Administration Guide also uses the following
conventions:
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com. Cisco also provides several
ways to obtain technical assistance and other technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain
technical information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/home/home.htm
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
xi
Page 12

Documentation Feedback
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Ordering Documentation
You can find instructions for ordering documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/es_inpck/pdi.htm
You can order Cisco documentation in these ways:
• Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order Cisco product documentation from
the Ordering tool:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/ordering/index.shtml
• Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order documentation through a local account representative by
calling Cisco Systems Corporate Headquarters (California, USA) at 408
North America, by calling 1 800
Preface
526-7208 or, elsewhere in
553-NETS (6387).
Documentation Feedback
You can send comments about technical documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the front cover of your
document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
For all customers, partners, resellers, and distributors who hold valid Cisco service contracts, Cisco
Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day, award-winning technical assistance. The Cisco Technical
Support Website on Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, Cisco Technical
Assistance Center (TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not hold a valid Cisco service
contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support Website
xii
The Cisco Technical Support Website provides online documents and tools for troubleshooting and
resolving technical issues with Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day,
365 days a year, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 13

Preface
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support Website requires a Cisco.com user ID and password.
If you have a valid service contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Note Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial number before submitting
a web or phone request for service. You can access the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support
Website by clicking the Too l s & R e so u rce s link under Documentation & Tools. Choose Cisco Product
Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down list, or click the Cisco Product
Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs. The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID
or model name; by tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command output.
Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial number label location highlighted.
Locate the serial number label on your product and record the information before placing a service call.
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and S4 service requests. (S3
and S4 service requests are those in which your network is minimally impaired or for which you require
product information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request Tool provides
recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the recommended resources, your service
request is assigned to a Cisco TAC engineer. The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
Obtaining Technical Assistance
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact the Cisco TAC by telephone.
(S1 or S2 service requests are those in which your production network is down or severely degraded.)
Cisco TAC engineers are assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your business
operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
USA: 1 800 553-2447
For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco has established severity
definitions.
Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is “down,” or there is a critical impact to your business operations. You
and Cisco will commit all necessary resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded, or significant aspects of your
business operation are negatively affected by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco
will commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the situation.
OL-4590-03
Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired, but most business operations
remain functional. You and Cisco will commit resources during normal business hours to restore service
to satisfactory levels.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
xiii
Page 14

Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco product capabilities, installation, or
configuration. There is little or no effect on your business operations.
Obtaining Additional Publications and Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is available from various online
and printed sources.
• Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides, and logo merchandise. Visit
Cisco Marketplace, the company store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
• The Cisco Product Catalog describes the networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as
ordering and customer support services. Access the Cisco Product Catalog at this URL:
http://cisco.com/univercd/cc/td/doc/pcat/
• Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and certification titles. Both new
and experienced users will benefit from these publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other
information, go to Cisco Press at this URL:
http://www.ciscopress.com
Preface
• Pack et magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for maximizing Internet and
networking investments. Each quarter, Packet delivers coverage of the latest industry trends,
technology breakthroughs, and Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and
troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies, certification and training
information, and links to scores of in-depth online resources. You can access Packet magazine at
this
URL:
http://www.cisco.com/packet
• iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to help growing companies
learn how they can use technology to increase revenue, streamline their business, and expand
services. The publication identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to
help solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help readers make sound
technology investment decisions. You can access iQ Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
• Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems for engineering
professionals involved in designing, developing, and operating public and private internets and
intranets. You can access the Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/ipj
• World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view current offerings at
this
URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
xiv
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 15

CHA P TER
1
Planning for Personal Assistant
Before you install Cisco Personal Assistant into your production network, you should take the time to
understand it and how it fits in the rest of the IP telephony network. You should also determine the best
server configuration to support your users.
Use the following sections to learn about the features and components of Personal Assistant, how it
works, and how it fits into your IP telephony network:
• Understanding Personal Assistant, page 1-1
• Understanding the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server, page 1-8
• Creating Server Clusters, page 1-10
• Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant, page 1-16
• Customizing Implementation of Personal Assistant, page 1-23
• Preventing Toll Fraud, page 1-24
Understanding Personal Assistant
Personal Assistant can selectively handle your incoming calls and help you make outgoing calls. The
following sections provide you with an overview of Personal
network:
• Personal Assistant Features, page 1-1
• Cisco IP Telephony Terminology, page 1-3
• Role of Personal Assistant in the Cisco IP Telephony Network, page 1-5
• Personal Assistant and User Interactions, page 1-7
Personal Assistant Features
Personal Assistant provides the following features:
Follow-Me Call Transferring
Users can tell Personal Assistant to use an alternate phone number as their primary location for a period
of time. Personal
a hotel room phone during a business trip.
Assistant routes calls to the follow-me phone. For example, a user could route calls to
Assistant and its role in the IP telephony
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-1
Page 16

Understanding Personal Assistant
Proxy Access
Users can give other users permission to access and manage their Personal Assistant accounts.
Rule-Based Call Routing
Personal Assistant can forward and screen incoming calls based on rules that users devise. Incoming
calls can be handled according to caller ID, date and time of day, or the meeting status of the user based
on the user calendar (considering information such as office hours, meeting schedules, vacations, or
holidays). Personal
call to a desk phone can be routed to a cell phone, home phone, or other phone, based on the call routing
rules that your users create. An incoming call can even generate an e-mail-based page.
To use rule-based call routing, you must allow Personal Assistant to intercept incoming calls. See the
“Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant” section on page 1-16 for additional information.
Your users set up these rules through a web-based interface, and activate different sets of rules through
the interface or by talking to Personal
Personal Assistant,” for information on how users access the user interface.
Simple Automated Attendant for Dial by Name
You can set up a simple automated attendant to allow callers to reach people by saying their names rather
than having to know their phone numbers. See the
page 4-15 for more information.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Assistant can also selectively route calls to other phone numbers. Thus, an incoming
Assistant over the phone. See Chapter 5, “Preparing Users for
“Creating a Simple Automated Attendant” section on
Speech-Enabled Directory Dialing
Users can dial phone numbers by telling Personal Assistant the applicable name. Personal Assistant
obtains the phone number from the corporate directory or personal address book.
To use any speech-enabled feature, you must add a sufficient number of speech and license servers to
your Personal
Assistant installation. See the “Creating Server Clusters” section on page 1-10 for
additional information.
Speech-Enabled Simple Ad Hoc Conferencing
Users can initiate conference calls by telling Personal Assistant to set up a conference call with the
desired participants or groups.
Speech-Enabled Voice-Mail Browsing
Users can use voice commands to browse, listen to, and delete voice mail messages.
Support for Multiple Locales
You can support users or outside callers who speak different languages. For your users,
Personal
Personal
Systemwide Rules
Assistant uses the language they select through the user web interface. If you create a
Assistant automated attendant, callers can switch between supported locales.
You can set up rules to apply to all calls that come through the Personal Assistant system. For example,
you might want to send all incoming calls to user voice mail after regular work hours. See the
“Setting
Up Systemwide Rules” section on page 4-19 for more information.
1-2
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 17

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Cisco IP Telephony Terminology
Personal Assistant and other components of the IP telephony network, such as Cisco CallManager, use
terminology and concepts that might not be familiar to you. The following sections explain these
concepts and how Personal
• Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports, page 1-3
• CTI Route Points and Media Ports, page 1-3
• Partitions and Calling Search Spaces, page 1-4
• Cisco CallManager Clusters, page 1-4
• How Personal Assistant Uses Directories, page 1-5
Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports
The Personal Assistant interceptor ports identify the phone extensions that Personal Assistant will
intercept from Cisco
and identify them in the Personal
Personal
Assistant to intercept the calls.
Assistant uses them:
CallManager. You configure these ports in Cisco CallManager as CTI route points
Understanding Personal Assistant
Assistant server configuration. The route points configuration allows
You can use wildcards when creating the route points so that one route point covers many extensions.
For example, the route point 1XXX covers all extensions from 1000 to 1999.
When you configure the interceptor ports, you should also set up the call forwarding configuration for
interceptor port error handling to allow calls to go through to the extension if the Personal
server is unavailable. The way you configure interceptor port error handling will differ depending on the
version of Cisco
Handling” section on page 1-23 for additional information on interceptor port error handling).
CallManager that the system uses (see the “Why You Need Interceptor Port Error
CTI Route Points and Media Ports
When you assign a phone number to a Personal Assistant server, you must define the extension as a
Computer Telephony Integration (CTI) route point in Cisco
Personal Assistant Number” section on page 3-8). The number you assign as the CTI route point is the
phone number your users use to access Personal Assistant.
A CTI route point is a virtual device that lets the Personal Assistant server receive multiple calls
simultaneously.
When a user calls the Personal Assistant server phone number that is defined as a CTI route point,
Personal
add one media port for each simultaneous Personal
Ports for Personal Assistant” section on page 3-10). For example, if you need 24 simultaneous sessions,
add 24 ports. Then, in the Personal Assistant server configuration, you enter 24 as the number of media
ports (see the
Assistant assigns the call to an available media port on the server. In Cisco CallManager, you
“Server Configuration” section on page A-16).
Assistant
CallManager (see the “Setting Up the
Assistant session you require (see the “Adding Media
OL-4590-03
If all media ports on a Personal Assistant server are in use, subsequent callers receive a busy signal
unless you have set up load balancing (see the
section on page 1-13).
Note If you use Personal Assistant to create an automated attendant, you also create a route point for the
attendant phone number. The attendant uses media ports in the same manner as Personal Assistant.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
“Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing”
1-3
Page 18

Understanding Personal Assistant
Partitions and Calling Search Spaces
In a Cisco CallManager setup, each phone extension is assigned to a partition and a calling search space.
A partition is a group of devices with similar reachability characteristics. Devices you can place in
partitions include IP phones, extensions, and gateways. By default, extensions are assigned to the “none”
partition. The “none” partition is a default setting in Cisco
non-existent partition.
A calling search space is an ordered list of partitions. When a user makes a call from an extension, the
call can only be completed if the dialed number is within a partition identified in the calling search space.
The calling search space always includes the none partition.
Calling search spaces and partitions make it possible to separate parts of your phone network. This can
be useful if you are providing phone service to a large building occupied by separate companies or
organizations (such as an office tower).
You must configure partitions and calling search spaces in Cisco CallManager to enable
Personal
Assistant to intercept calls and support rule-based call routing.
Cisco CallManager Clusters
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
CallManager that is treated as the null or
Cisco CallManager allows you to create clusters of Cisco CallManager systems that share a common
database. Cisco
across a converged IP network infrastructure to support IP telephony, to facilitate redundancy, and to
provide feature transparency and scalability.
If you are using Cisco CallManager clusters in your IP telephony network, it is important to understand
how Personal
Personal
Cisco CallManager Clusters and Personal Assistant
The pool of addresses that you create in Cisco CallManager to support Personal Assistant (interceptor
ports, CTI route points, translation patterns, and media ports) is registered with the primary
Cisco
CallManager server in the cluster. Each Personal Assistant server can register with multiple
primary Cisco
ports belong.
When the primary Cisco CallManager system of a media port goes down, the Personal Assistant server
is notified and attempts to register with the secondary Cisco
proceeding in a round-robin fashion. Once Personal
Cisco
CallManager server, it registers the media port with it. When the primary Cisco CallManager
system is online, the Personal
Cisco CallManager Clusters and Rule-Based Call Routing
To understand how Cisco CallManager clusters affect rule-based call routing, assume that you have two
users whose IP phones are configured within the same Cisco
Personal
to User B, the call is not intercepted as an incoming call; it is simply transferred. Any Personal
rules configured by User B do not take effect.
However, if these two users are in separate Cisco CallManager clusters, calls are not simply transferred.
Instead, the transferred call from User A (in Cisco
to User B (in Cisco
B has configured go into effect. This might erroneously cause calls for User A to have rules processed
and applied as if they were calls to User B.
CallManager clusters provide a mechanism for distributing call processing seamlessly
Assistant interacts with them. The number of clusters you have affects the number of
Assistant servers you need.
CallManager servers, based on the telephony provider to which these route points and
CallManager systems in the cluster,
Assistant establishes a connection with a secondary
Assistant server will re-register with it.
CallManager cluster. User A configures a
Assistant rule that forwards all her calls to the extension of User B. When the call is transferred
Assistant
CallManager Cluster 1) is treated as an incoming call
CallManager Cluster 2). Because it is treated as an incoming call, any rules that User
1-4
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 19

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
How Personal Assistant Uses Directories
With Personal Assistant, you must have a supported LDAP directory installed, to meet network
requirements. The directory contains records for each user in your organization, and includes
information such as name, phone extension, e-mail address, and office location. This LDAP directory is
typically called the corporate directory. Personal
Personal
Personal Assistant also uses the directory to maintain Personal Assistant configuration information and
some Personal
user). For this information, Personal
uses.
You can also use the Cisco CallManager directory as the corporate directory, but this is not required.
Many installations prefer a corporate directory that is independent from Cisco
Personal
integrated with Cisco
for information on identifying the directory to Personal Assistant.
The Personal Assistant system configuration includes a setting for unique user name attribute. This is
the name of the field within your directory that is unique for each user. Ask your directory administrator
for the name of this field if you do not know it. See the
page A-3 for information on updating the Personal Assistant configuration with this information.
Assistant to dial a number by telling Personal Assistant the applicable name.
Assistant user information (for example, the call routing rules and spoken name of a
Assistant fully supports this separation. Or, your corporate directory might already be
CallManager. See the “Configuring the Corporate Directory” section on page 4-7
Understanding Personal Assistant
Assistant accesses this directory when a user asks
Assistant automatically uses the directory that Cisco CallManager
CallManager, and
“Corporate Directory Settings” section on
Role of Personal Assistant in the Cisco IP Telephony Network
Personal Assistant interacts with many elements in your IP telephony network. Some network elements
need to be informed of the presence of Personal
Personal
voice-over-IP network in place before installing Personal
Assistant and do not require such information. You should have a fully-functional
Assistant; other elements interact indirectly with
Assistant in your telephony network.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-5
Page 20
Understanding Personal Assistant
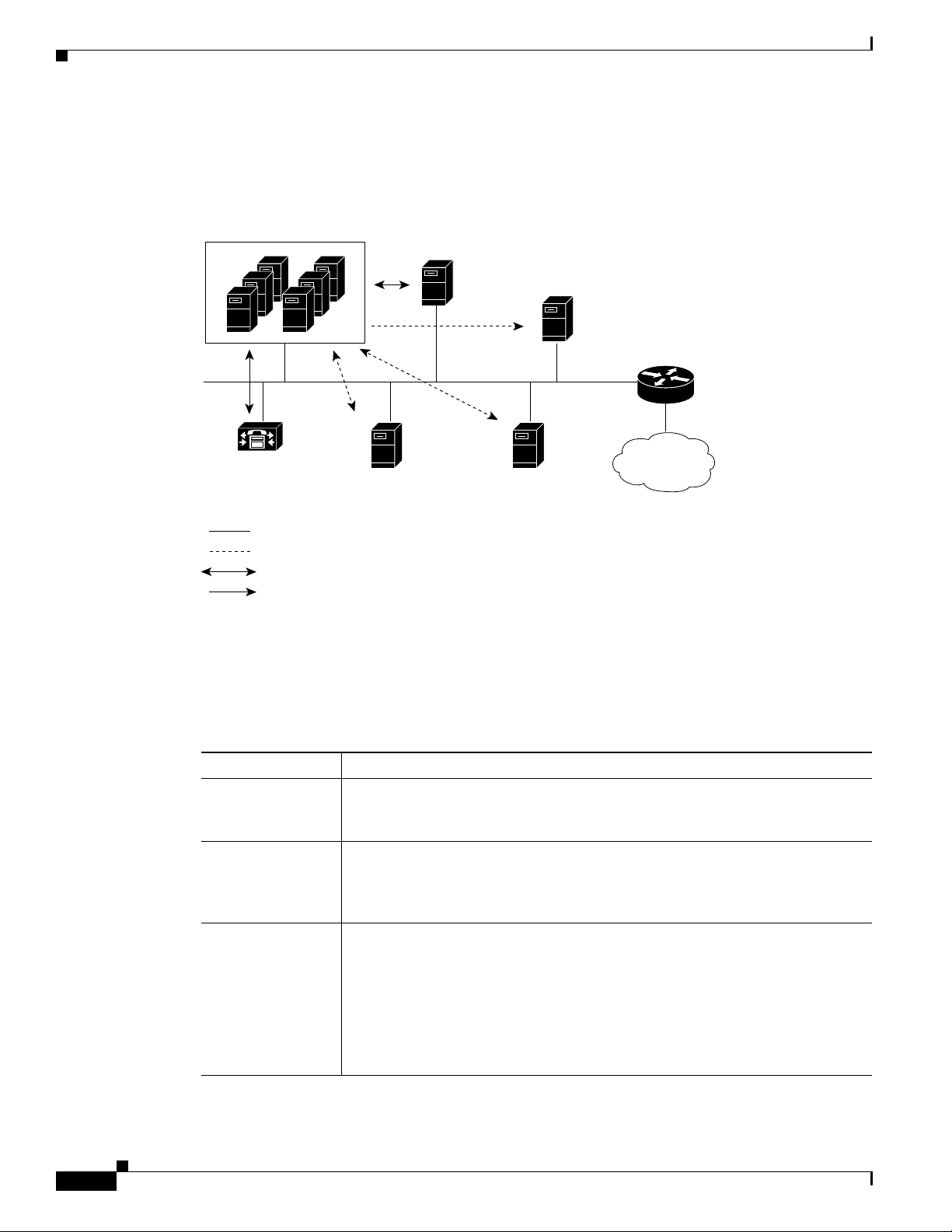
Figure 1-1 illustrates the connection of Personal Assistant to the IP telephony network.
Figure 1-1 Personal Assistant in the IP Telephony Network
Personal Assistant
server clusters
LDAP
directory
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
SMTP paging
server
Gateway
Ethernet
Cisco CallManager
Cisco Unity Microsoft
Exchange
Personal Assistant and the target system require configuration
Only Personal Assistant requires configuration
Communication is two way
Communication is one way
Table 1-1 further describes the components of the IP telephony network that are critical to using
Personal Assistant. For information on supported software versions, refer to the “Software
Requirements” section of the Release Notes for Personal Assistant Version 1.4. The release notes are
available at http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps2026/prod_release_notes_list.html.
Ta b l e 1-1 Software Requirements for Using Personal Assistant
System Usage
Call intercepting Cisco CallManager sends incoming calls to Personal Assistant for processing.
Personal
Assistant uses Cisco CallManager to connect Personal Assistant users
to dialed numbers.
LDAP directory The LDAP directory contains corporate and personal directories, with names,
phone numbers, e-mail addresses, and so on. Personal
directory to look up numbers when a Personal
Personal
Assistant dial a number.
Voice mail Personal Assistant connects users to their voice mailboxes, and sends incoming
calls to voice mail when a call routing rule of a Personal
that a call should be directed to voice mail.
With Cisco Unity systems, Personal Assistant can only work with the G.711
Mu-Law wave file record format.
With Octel systems, Personal Assistant can only redirect calls to the system.
Users cannot browse Octel voice mail from within Personal
PSTN
51292
Assistant uses the
Assistant user requests that
Assistant user indicates
Assistant.
1-6
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 21

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Table 1-1 Software Requirements for Using Personal Assistant (continued)
System Usage
Personal calendar Personal Assistant accesses the Exchange calendar of a user when evaluating a
call routing rule that includes calendar-based options.
SMTP paging
server
Web br ows e r
Personal Assistant sends e-mail pages to a Personal Assistant user when a call
routing rule indicates that the user should be paged.
You access web-based interfaces to manage and use Personal Assistant.
application
Personal Assistant and User Interactions
The following sections can assist you in understanding how Personal Assistant interacts with users:
• Interaction Terminology, page 1-7
• Incoming Call Handling, page 1-7
• Access to Personal Assistant, page 1-8
Understanding Personal Assistant
Interaction Terminology
The following terms can be useful in understanding how Personal Assistant works:
• A grammar includes a list of words and possible sequences in which a user can state them.
• An utterance is a user response or command that Personal Assistant recognizes as valid.
• A dialog is a prompt from Personal Assistant, followed by a response from the user.
• A session represents any interaction with Personal Assistant or call interception by
Personal
(interaction), or when Personal
Incoming Call Handling
The following sequence illustrates the processes involved when incoming calls arrive at extensions
configured to use Personal
1. An incoming call arrives at a Personal Assistant-enabled number.
2. Because a Personal Assistant interceptor port (CTI route point) is configured for this extension,
Cisco
3. Personal Assistant retrieves user information from the LDAP directory.
4. If the user has configured rules, the rules initiate depending on the type of destination included in
the rules:
–
–
–
Assistant. For example, a session occurs when a user uses the dial-by-name feature
Assistant routes a call based on a user rule (interception).
Assistant:
CallManager routes the call to Personal Assistant.
Calendar information—Personal Assistant accesses information from the Exchange Server.
An e-mail or page—Personal Assistant sends e-mail by using the messaging system.
Phone number—Personal Assistant transfers the call through Cisco CallManager.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-7
Page 22

Understanding the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server
Access to Personal Assistant
The following sequence illustrates the processes involved when users access Personal Assistant:
1. Users dial the Personal Assistant number (the extension of the CTI route-point configured for
Personal
2. The call is routed to the first available media port. If no port is available, the call is rejected and the
caller hears a busy signal.
3. If a media port is available, the speech channel opens, and Personal Assistant plays a welcome
prompt. Users can then dial other users by name or access voice mail.
If speech resources are not available, Personal Assistant opens a non-speech session with the user,
enabling the user to use the phone keypad for touch-tone dial-by-name.
4. If users use dial-by-name to call another user:
a. User says: “Call ‘John Smith’.”
b. The command is received and processed by the speech-recognition server.
c. The user name is passed to Personal Assistant, and Personal Assistant retrieves user
d. Based on the confidence level, Personal Assistant either prompts the user, or transfers the call.
Assistant in Cisco CallManager).
information from the LDAP directory.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Understanding the Personal Assistant Server and
Speech-Recognition Server
Personal Assistant has a modular structure, which allows you to install various pieces of the product on
different server platforms. This provides a fault-tolerant redundant structure that you need for ensuring
that the Personal
The following sections provide information about the Personal Assistant servers and their interactions
with each other:
• Speech-Recognition Server, page 1-8
• Personal Assistant Server, page 1-9
• License and Resource Managers, page 1-9
• Interactions of the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server, page 1-10
Speech-Recognition Server
If you plan to implement any of the speech-enabled features of Personal Assistant, you must install at
least one speech-recognition server. During installation, you are given the option to install a
speech-recognition server, and you can either install it on the same system as the Personal
server or on a separate one.
The speech-recognition server prompts users and recognizes user responses based on a pre-defined
grammar, which includes a list of words and possible sequences in which a user can state them. During
a call to Personal
commands. Also, the Help included with the Personal
by using examples of valid prompts and responses.
Assistant system is always available to your users.
Assistant, you can ask for help and Personal Assistant will tell you the available
Assistant end-user interface defines this grammar
Assistant
1-8
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 23

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
For specific items, such as user names in the corporate directory, the grammar is generated and
automatically compiled during the system refresh (see the
page 4-4). As new users are added to the directory, their names are automatically recognized after the
refresh.
Personal Assistant Server
The Personal Assistant server manages the interaction between the user and Personal Assistant,
processes call routing and dial rules, and manages the overall configuration of the Personal
system.
You must install the Personal Assistant server during installation, and you manage its functions and
processes from the administrator web-based interface (see the
Personal Assistant Administration Interface” section on page 4-3 for information about accessing the
interface).
You can have more than one Personal Assistant server configured. In fact, you should do this if you want
to provide failover protection (see the
Understanding the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server
“Configuring Speech Recognition” section on
Assistant
“Logging On to and Out of the
“Creating Server Clusters” section on page 1-10 for details).
License and Resource Managers
The license and resource managers are subcomponents of the Personal Assistant server; they are
installed with it. However, they actually work in conjunction with the speech-recognition and
Personal
services, they are closely linked, in that every system that functions as a license manager also functions
as a resource manager.
License Manager
The license manager maintains the license for the speech-recognition software. The speech-recognition
servers work only if there is at least one active license manager with a valid license. Although every
Personal
license manager.
You only need one license manager within a single Personal Assistant server cluster, although Cisco
recommends that you define two license managers for redundancy.
Resource Manager
The resource manager manages the interaction between the Personal Assistant server cluster and the
speech-recognition servers in the speech-recognition server cluster. Although every Personal
server includes a resource manager, only one resource manager is used as the active connection between
the Personal
automatically chooses the resource manager to be used, and if that manager becomes disabled, another
resource manager takes over.
Once a resource manager establishes a connection between a Personal Assistant server and an available
speech-recognition server for a particular call, the Personal
server interact directly for the duration of that call. The resource manager is not a permanent
communication link between the servers.
Assistant servers. Although the license manager and resource managers provide different
Assistant server includes a license manager, not every Personal Assistant server needs an active
Assistant server cluster and the speech-recognition server cluster. Personal Assistant
Assistant
Assistant server and speech-recognition
OL-4590-03
The resource manager does not manage communication between Personal Assistant servers;
Personal
Assistant servers communicate directly.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-9
Page 24
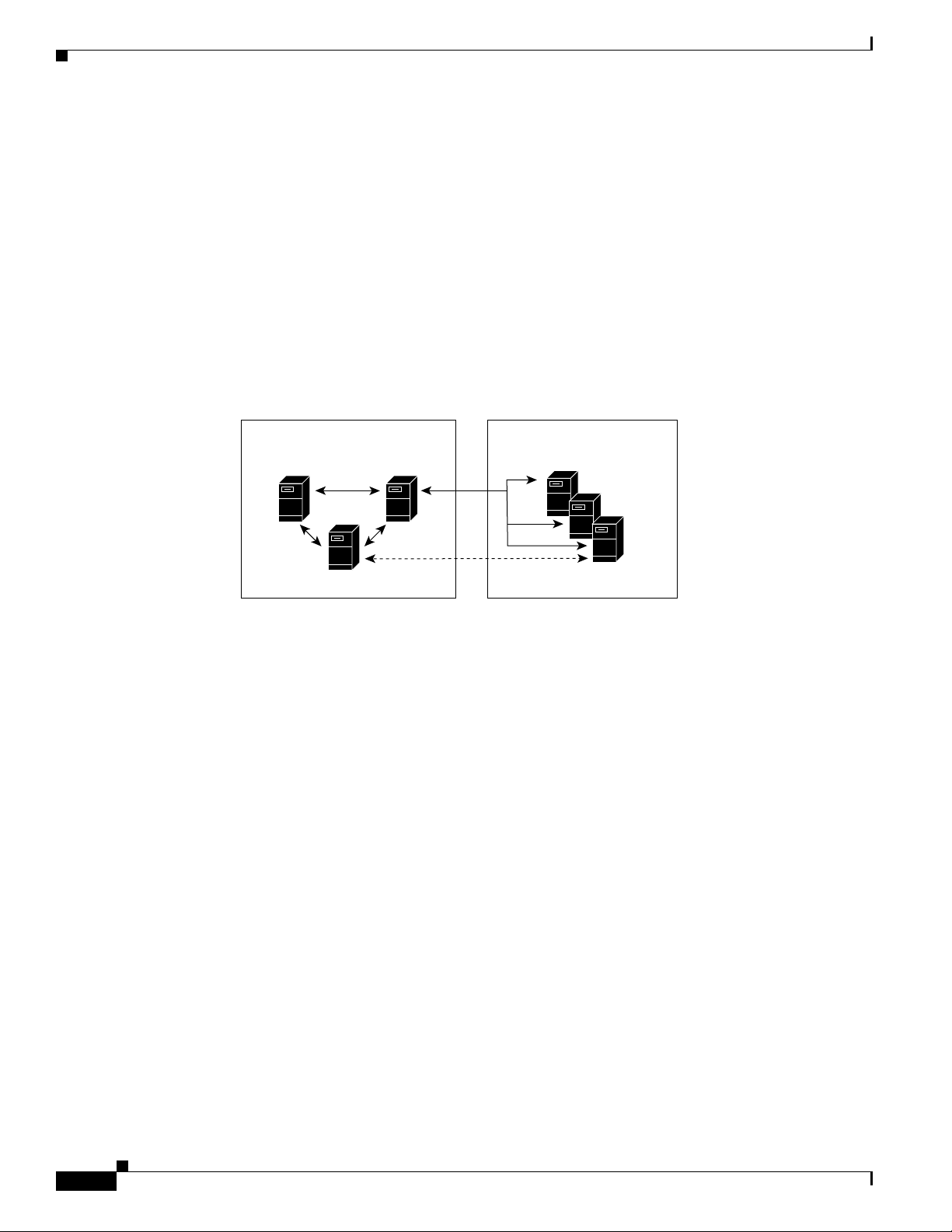
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Creating Server Clusters
Interactions of the Personal Assistant Server and Speech-Recognition Server
Personal Assistant separates the speech-recognition functions from call routing and other basic
functions of the Personal
interaction between the cluster of Personal
servers. This section describes how the clusters interact, and what you need to do to enable the
interaction.
Figure 1-2 illustrates the Personal Assistant server structure. The dotted line between Personal Assistant
server B and speech-recognition server 3 illustrates the direct interaction between these servers after the
connection is established through the resource manager on Personal
Figure 1-2 Personal Assistant Server Structure
Assistant server. Because these functions are separate, you must configure the
Assistant servers and the cluster of speech-recognition
Assistant server C.
Personal Assistant
Server Cluster
PA server A
PA server B
PA server C
license mgr,
resource mgr
Speech-Recognition
Server Cluster
1
2
3
51291
Figure 1-2 assumes that you are installing Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition servers on
separate platforms. However, you can install the Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition
servers on the same platform. When installed on the same platform, the servers still establish
communications through a resource manager, even if the resource manager is on the same system. In
fact, you could create a redundant Personal
Personal
Assistant server, license manager, and speech-recognition server. Logically, this minimal
cluster looks the same as the one illustrated in
Assistant speech cluster with two systems, each running a
Figure 1-2.
To enable the interaction between the Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition servers, you
must identify the license managers to a Personal
Assistant server. See the “Configuring Speech
Recognition” section on page 4-4 for information on how to do this.
Creating Server Clusters
Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition servers work together in server clusters. This makes
it possible to share the load among servers, and to set up failover relationships so that if a server becomes
disabled, another server can take over with minimal interruption for your users.
To set up the server clusters, you must:
1. Determine your server and speech-recognition requirements and install the Personal Assistant
server and speech-recognition software on an applicable number of servers.
The number of servers required is based on the number of sessions each server supports, the number
of users you are supporting, and how many users you are willing to support per session.
It is also affected by the number of Cisco CallManager clusters you have, and the distribution of
WAN connections between them.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-10
OL-4590-03
Page 25

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
During server installation, you must specify the same Cisco CallManager publisher for all of the
Personal
2. Configure the Personal Assistant servers.
During server configuration, you can configure the Personal Assistant servers either to balance the
call load among themselves or to support failover. If you use failover, you need more servers than
you would otherwise need for a given number of media ports.
3. Configure the speech-recognition servers.
You must also identify at least one license manager for the speech software. The speech software
requires that an active, valid license be available at all times for it to work. See the
Speech Recognition” section on page 4-4 for information about adding speech-recognition servers
to the server cluster.
See the following sections for detailed discussions on determining the number of Personal Assistant
servers required, how to use load balancing, and how failover affects your calculations:
• Determining the Required Number of Personal Assistant Servers and Speech-Recognition Servers,
page 1-11
• Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing, page 1-13
Creating Server Clusters
Assistant and speech-recognition servers in the same Personal Assistant cluster.
“Configuring
• Creating a Personal Assistant Server Cluster With Failover, page 1-15
Determining the Required Number of Personal Assistant Servers and Speech-Recognition Servers
The quantity of servers you install should be adequate to support the number of sessions defined in the
Personal
the cluster).
The number of Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition servers that are required in your
clusters depends on several factors:
• The number of concurrent calls to Personal Assistant that you need to support. For example, a sales
Assistant server cluster (that is, the sum of sessions on all active Personal Assistant servers in
and marketing organization that is very phone-dependent would probably need more servers than an
engineering group that uses the phone less frequently.
When considering this, you should make separate calculations of the number of simultaneous
sessions with Personal
Assistant and the number of simultaneous sessions with the
speech-recognition server. For example:
–
Call-interception sessions—the number of users who will set up rules to enable
Personal
–
Speech-recognition sessions—the number of users who will access voice mail and dial other
Assistant to intercept calls for them.
users by name.
OL-4590-03
• The server model that you use. A more powerful server can support more concurrent calls than a less
powerful server.
• Whether you run the Personal Assistant servers and speech-recognition servers on the same system.
Running both servers on a single system reduces the number of concurrent calls the server can
support.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-11
Page 26
Creating Server Clusters
• Whether you enable automatic failover for Personal Assistant server redundancy. Failover ensures
that if a server goes down, another server takes over the responsibilities of the failed server. If you
configure failover, you should enable only half of the ports that would otherwise be supported on a
server.
• The number of Cisco CallManager clusters in your network, and the distribution of WAN links
between them.
Because you can easily add and remove servers from a cluster, you do not have to be precise on your first
estimate. As users become familiar with Personal
increases, you can add servers to accommodate the increased usage.
Estimated Number of Simultaneous Sessions
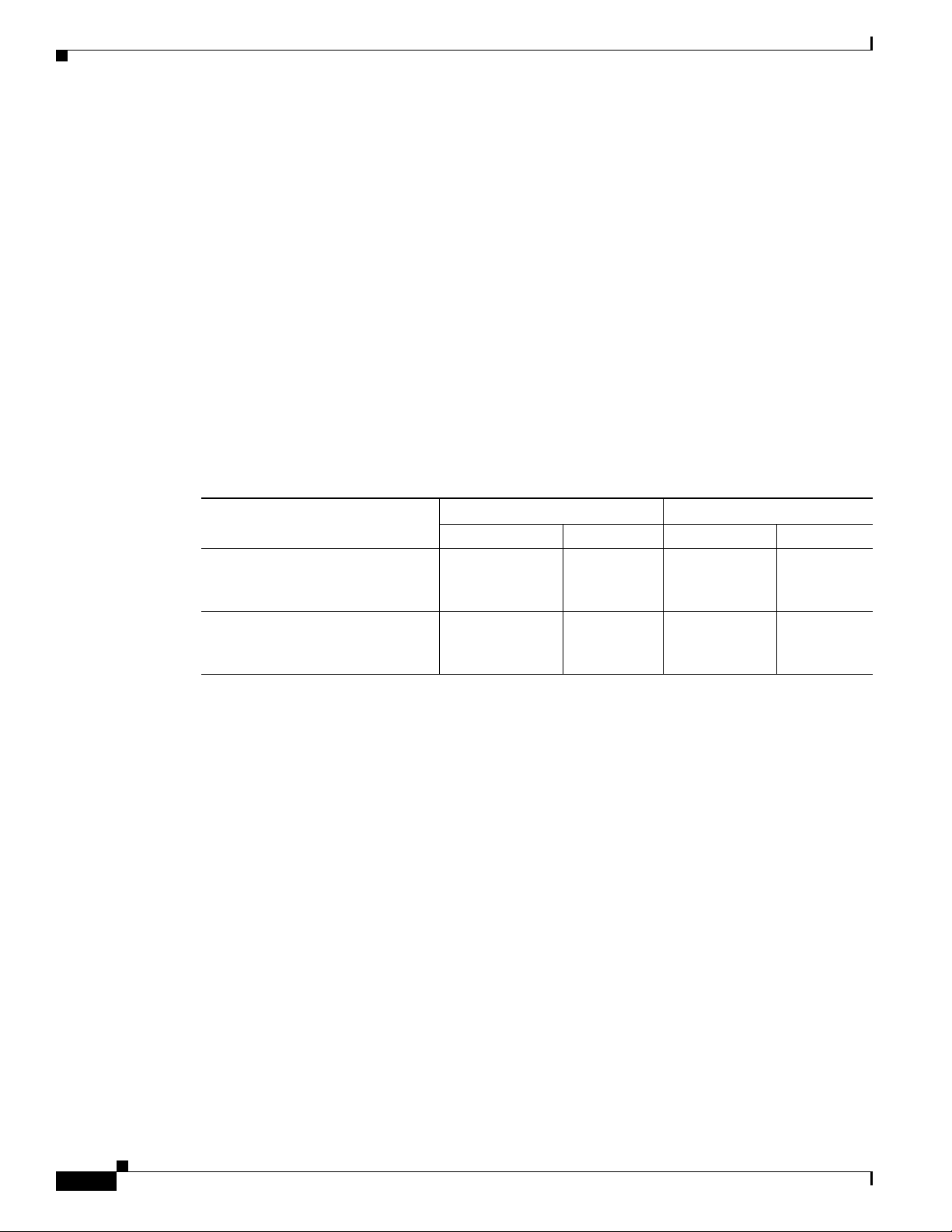
Table 1-2 explains the estimated number of simultaneous sessions supported on each server platform,
based on server model and session type. However, depending on your particular system usage, these
values can vary considerably. Use the information in
needs.
Ta b l e 1-2 Estimated Number of Simultaneous Sessions
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Assistant, and their use of Personal Assistant
Table 1-2 as a starting point to estimate your server
MCS-7825 Series MCS-7835 Series
Server Installation
Personal Assistant server and
Interceptor Ports
1
Media Ports
50 sessions 24 sessions 70 sessions 36 sessions
2
Interceptor Ports1Media Ports
2
speech-recognition server installed
on different systems
Personal Assistant server and
22 sessions 20 sessions 30 sessions 24 sessions
speech-recognition server installed
on the same system
1. We recommend that you estimate approximately 25 users per session using interceptor ports.
2. We recommend that you estimate approximately 50 users per session using media ports.
When evaluating the information in Table 1-2, keep in mind that:
• Media port sessions indicate how many simultaneous sessions use speech-recognition features such
as dialing by name, browsing voice mail, and initiating conference calls. In these sessions, users are
directly interacting with Personal
• Interceptor port sessions indicate how many simultaneous sessions involve Personal Assistant
Assistant.
intercepting incoming calls for users. In these sessions, once users have configured their dial rules,
they do not directly interact with Personal
Assistant. Personal Assistant seamlessly routes the
incoming calls based on the dial rules.
• As an initial guideline, we recommend that you estimate approximately 25 users per
call-interception session, and approximately 50 users per speech-recognition session.
• These estimates represent the system capacities and might not necessarily reflect the number of
licenses you have purchased.
Using the Session Estimates in Your Planning
To estimate how many ports you need to support your users, consider the following example:
1. Determine the number of users, for example 1750.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-12
OL-4590-03
Page 27

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
2. Choose a server, for example the MCS-7835-H1-IPC1.
3. Determine how to install the Personal Assistant components, for example, whether you want the
Personal
4. Determine how many sessions you must support for your users:
–
1750 users divided by 25 = 70 call-interception sessions
–
1750 users divided by 50 = 35 speech-recognition sessions
You need enough servers to support at least this number of sessions. When you configure the servers,
you specify the actual number of ports in use, so if you intend to use fewer than the maximum, take
this into consideration when determining the number of servers that you need.
5. Use the information in Table 1-2 to determine that if you install the Personal Assistant server and
the speech-recognition server on separate MCS-7835-H1-IPC1 systems (for a total of two systems)
you can support:
–
70 call-interception sessions
–
36 speech-recognition sessions
Therefore, you can support 1750 users by using two MCS-7835-H1-IPC1 systems: one system for
the Personal
6. Be sure to add the servers by using the Personal Assistant administrative interface:
Creating Server Clusters
Assistant server and speech-recognition servers on separate systems.
Assistant server and one system for the speech-recognition server.
–
Add the speech-recognition servers to the System Configuration settings. See the “Configuring
Speech Recognition” section on page 4-4.
–
Add the Personal Assistant servers to the Server Configuration settings. See the “Configuring
Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10.
7. You also must add the number of supported ports by using the Personal Assistant administrative
interface:
–
Add the supported number of media ports in the Server Configuration settings. See the
“Configuring Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10. Although your selected server
configuration supports up to 36 ports, you only need 35 ports for your users.
–
Add the interceptor port addresses in Server Configuration settings. See the “Configuring
Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10. In this setting, enter the interceptor ports that
cover all 1750 users. Although your configuration supports 70 simultaneous sessions, the
interceptor ports must cover all users you are supporting.
8. Consider configuring load balancing (see the “Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load
Balancing” section on page 1-13) or adding failover servers (see the “Creating a Personal Assistant
Server Cluster With Failover” section on page 1-15) for greater redundancy.
Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing
A single Personal Assistant server can handle a number of simultaneous sessions, which you define
when you set the number of media ports (see the
all media ports are being used, new callers receive a busy signal from Personal Assistant unless you set
up load balancing among the Personal
Assistant servers in each Personal Assistant server cluster.
If you are not using failover servers, and if a Personal Assistant server becomes disabled, no other server
takes over the media ports of the disabled server. This reduces the number of available simultaneous
sessions with Personal
Assistant. However, you can set up load balancing in the cluster to mitigate the
effects of a disabled server.
“Server Configuration” section on page A-16). When
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-13
Page 28
Creating Server Clusters
To create a simple Personal Assistant server cluster, do not specify failover servers in the server
configurations when you configure each server through the Personal
(See the
“Configuring Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10 for information on configuring
the Personal Assistant servers into a cluster, and the “Server Configuration” section on page A-16 for
reference information on the server configuration settings.)
The following sections describe how to configure load balancing:
• Configuring Load Balancing, page 1-14
• Effect of Load Balancing on Users Who Access Personal Assistant, page 1-14
• Effect of Load Balancing on Rule-Based Call Routing, page 1-15
Configuring Load Balancing
Personal Assistant load balancing is based on the “call forward busy” and “call forward no answer”
numbers assigned to each Personal
these settings correctly in Cisco
calls for busy servers without the knowledge of your users.
If you create a chain of servers, your users will need only one phone number to reach Personal Assistant.
This can make it easier for your users to use Personal
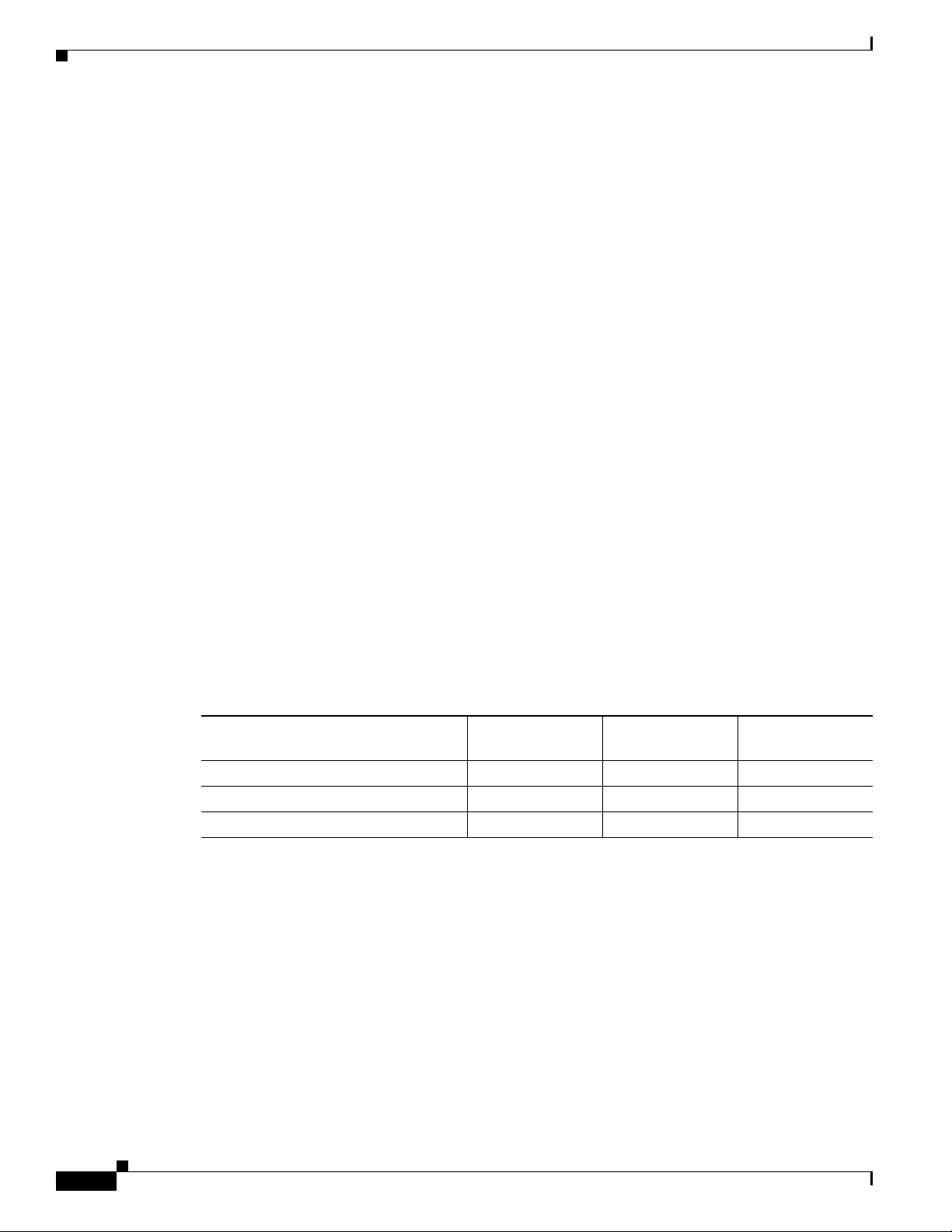
Table 1-3 shows an example setup in which three Personal Assistant servers are chained so that they
share the call load. In this example, users have been told to call extension 5600 to reach
Personal
call. If it does not have an available media port, the call is forwarded to 5700 (Personal
2). If Personal
forwarded to 5800 (Personal
available media port, the call is forwarded to 5600 (Personal
Personal
Assistant. If Personal Assistant Server 1 has an available media port, it handles an incoming
Assistant by calling Personal Assistant Server 2 or 3 directly.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Assistant administration interface.
Assistant server phone number (CTI route point). If you configure
CallManager, the Personal Assistant servers in the cluster can answer
Assistant.
Assistant Server
Assistant Server 2 has an available media port, it handles the call; otherwise, the call is
Assistant Server 3). If Personal Assistant Server 3 does not have an
Assistant Server 1). Users can also reach
Ta b l e 1-3 Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing
Personal Assistant
Cisco CallManager Setting
Server 1
CTI route point (phone number) 5600 5700 5800
Call forward busy 5700 5800 5600
Call forward no answer 5700 5800 5600
Effect of Load Balancing on Users Who Access Personal Assistant
If you are using load balancing without a failover server, and if a Personal Assistant server becomes
disabled, all calls that the server is currently handling are cut off. However, if Personal
already completed its role in the call process (for example, has transferred a call based on call-routing
rules), the call remains in progress. Subsequent calls to the disabled server are forwarded to another
server based on the “call forward no answer number” configured in Cisco
number of available simultaneous sessions is reduced because the active server must support the sessions
from the disabled server in addition to its normal load.
Personal Assistant
Server 2
CallManager. However, the
Personal Assistant
Server 3
Assistant has
1-14
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 29

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Effect of Load Balancing on Rule-Based Call Routing
If you are not using failover servers, and if a Personal Assistant server becomes disabled, the interceptor
port route points registered with that particular server are unavailable. Because the remaining servers
were not configured as failover servers, these interceptor ports cannot re-register with these servers.
Instead, Personal
for the affected users will be unavailable and all calls will ring directly through to the applicable
extensions.
Assistant cannot intercept calls for these extensions. Thus, all rule-based call routing
Creating a Personal Assistant Server Cluster With Failover
If load balancing, as explained in the “Setting Up Personal Assistant Server Load Balancing” section on
page 1-13, does not provide you with sufficient redundancy, you can configure failover servers in the
Personal Assistant cluster.
If you are using failover and a Personal Assistant server becomes disabled, the failover server takes
control of the media ports and interceptor ports that were configured on the disabled server. For example,
if you configured 15 media ports on the disabled server, the failover server would add 15 media ports to
its configuration. Thus, if you use failover servers, you must have twice as many servers for a given
number of media ports as would be required if you were not using failover servers.
Although the failover server takes on the media and interceptor ports of the disabled server, it cannot
take over active calls. Any active calls on the disabled server are dropped. However, if Personal
has completed its role in the call process (for example, it had transferred a call based on call-routing
rules), the call remains in progress.
In addition to taking over the disabled server ports, the failover server registers itself with
Cisco
CallManager as the disabled server CTI route point.
Creating Server Clusters
Assistant
When the disabled server becomes active again, it asks the failover server to return its ports. The failover
server returns the ports as they become available; no active calls are dropped. When the reactivated
server regains all media ports, it reregisters itself as the CTI route point with Cisco
There are two main techniques for setting up failover servers:
• Using Active Personal Assistant Servers for Failover, page 1-15
• Using Spare Personal Assistant Servers for Failover, page 1-16
Using Active Personal Assistant Servers for Failover
When you use an active Personal Assistant server as a failover server, the server works as a regular
Personal
However, if the primary server becomes disabled, the failover server must be able to handle the media
and interceptor ports of the disabled server, as well as its own. Thus, you must have sufficient capacity
on the failover server to accommodate the ports defined on the disabled server.
For example, if you are using two MCS-7835-H1-IPC1 Personal Assistant servers, each server supports
a maximum of 36 media ports (see
you must reduce the media ports on each server to no more than 18. So, if server A goes down, server B
will take over the 18 ports of server A, and server B will temporarily run with 36 ports (its original 18
plus the 18 of server A).
Assistant server managing calls with users. The server is not idle.
Table 1-2). If you use the servers as failover servers for each other,
CallManager.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-15
Page 30

Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
If you defined more than 18 media ports on server A and server B, the servers will not be able to take on
the full load of the other server if it becomes disabled. For example, if you define 18 ports on server A
and 24 on server B, and server A fails, Personal
load exceeded 36, calls would be dropped (because each server supports a maximum of 36 media ports)
and the quality of service experienced by your users would deteriorate.
In general, if you use active Personal Assistant servers as failovers, you should divide the ports per server
in half, and double the number of Personal
Although you can assign more than one Personal Assistant server to handle failover for any given server
(for example, server A could use server B and server C as failovers), only one server is actually used if
a server becomes disabled. The disabled server ports are not distributed among the designated failover
servers.
Using Spare Personal Assistant Servers for Failover
When you use a spare Personal Assistant server as a failover server, it sits idle unless an active server
becomes disabled.
To create a spare server, do not define a CTI route point in Cisco CallManager for that server. When an
active server becomes disabled, the spare server registers itself with Cisco
point, in place of the disabled server.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Assistant assigns 42 ports to B. If the simultaneous call
Assistant servers in the cluster.
CallManager as the CTI route
When adding a spare server to a Personal Assistant server cluster, do not define any media ports or
interceptor ports (see the
being used for anything except failover.
Because a spare failover server does not have any active ports, it can take over for a fully-loaded
Personal
spare servers, you can configure 36 media ports on the active server. If the active server becomes
disabled, the spare will be able to take over the 36 media ports.
Because servers should seldom become disabled, you can have fewer failover servers than you have
active servers. For example, you might define two failover servers for six active servers. The ratio you
use depends on your network reliability and uptime service level agreements. The key is that a failover
server must be able to take over all the media ports you define on an active server.
Assistant server. For example, if you are using MCS-7835-H1-IPC1 systems for your active and
“Server Configuration” section on page A-16), thus preventing the server from
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
Personal Assistant interacts with Cisco CallManager to intercept incoming calls to user extensions. By
intercepting these calls, Personal
can configure a rule that instructs Personal
Although Cisco CallManager does not require that you set up partitions, you must create partitions if
you install Personal
Personal
If you are not yet using partitions and calling search spaces in Cisco CallManager, the following
examples provide tips on setting them up with the minimum amount of effort. If you do not set up and
configure partitions and calling search spaces, Personal
however, still use the speech features provided by Personal
speech-enabled voice mail access (see the
The following sections provide examples of using partitions and calling search space in your IP
telephony network before and after adding Personal
• Using Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Without Personal Assistant, page 1-17
Assistant.
Assistant and want to enable the rule-based call routing feature or
Assistant can redirect them based on user rules. For example, a user
Assistant to send all incoming calls to voice mail.
Assistant cannot intercept user calls. You can,
Assistant, such as dial-by-name and
“Speech-Recognition Server” section on page 1-8).
Assistant:
1-16
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 31

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
• Defining Partitions and Call Search Spaces for Personal Assistant, page 1-18
Using Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Without Personal Assistant
To illustrate partitions and calling search spaces, consider this example in which partitions and calling
search spaces are used without Personal
The following partitions were created to support lobby phones, employee phones, and calls destined for
the PSTN.
Partition Name Designated Devices Assigned to Partition
Lobby All lobby phones
Employee All employee IP phones
PSTN All externally destined route patterns (local PSTN)
The following calling search spaces were created and the partitions were assigned to them to provide
different services. For example, to disallow external calls from the lobby phones, the cssLobby calling
search space does not include the PSTN partition.
Assistant:
Calling Search Space Partitions Assigned To
cssLobby Employee
Lobby
cssEmp Lobby
Employee
PSTN
cssGW Lobby
Employee
The following partitions and calling search spaces were assigned to individual extensions.
Cisco CallManager Setting User 1001 User 1002 User 3000 User 5555
Phone extension 1001 1002 3000 5555
Partition Employee Employee Lobby PSTN
Calling search space cssEmp cssEmp cssLobby cssGW
When User 3000 dials User 1001, Cisco CallManager looks in the calling search space of User 3000,
cssLobby. Because cssLobby includes the Employee partition in which the extension of User 1001
exists, the call goes through successfully.
However, if User 3000 dials User 5555, the call cannot be completed, because the cssLobby calling
search space does not include the PSTN partition in which the extension of User 5555 exists. Effectively,
this means that people using the lobby phone cannot make outside calls.
Devices (such as lobby IP phones) that can dial only internal
numbers.
Devices (such as employee IP phones) that can dial both
internal and external numbers.
PSTN voice gateway used for outside callers to access lobby
and employee phones.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-17
Page 32

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
On the other hand, User 5555 can dial User 3000, because the calling search space of User 5555, cssGW,
includes the Lobby partition in which the extension of User 3000 exists.
To understand how Personal Assistant uses partitions and call search spaces to intercept user calls, see
the
“Defining Partitions and Call Search Spaces for Personal Assistant” section on page 1-18.
Defining Partitions and Call Search Spaces for Personal Assistant
You need to create or update partitions and calling search spaces in Cisco CallManager to support
Personal
settings and add ones specific to Personal
Cisco
The following sections provide examples of using partitions and calling search spaces with
Personal
• Adding Personal Assistant to Existing Partitions, page 1-18
• Adding Personal Assistant Without Previously Defined Partitions, page 1-20
Assistant. If you are already using these features, you simply need to update your existing
Assistant. If you are not currently using these features in
CallManager, you must add a minimal set to enable Personal Assistant to intercept calls.
Assistant:
Adding Personal Assistant to Existing Partitions
To understand how Personal Assistant uses partitions and calling search spaces, recall that the previous
example (the
page 1-17) showed partitions (Employee, Lobby, and PSTN) and calling search spaces (cssLobby,
cssEmp, and cssGW). To add Personal Assistant to this scenario, you must do the following:
1. Add a Personal Assistant partition, for example PA, and a Personal Assistant managed phones
partition, for example PAManaged.
Add the interceptor ports (to intercept incoming calls) to the PA partition.
Add the phones of all employees who will use Personal Assistant to the PAManaged partition.
Leave other employees phones in the NonPAManaged partition, and add the following devices and
ports to it:
–
–
Partition Name Designated Devices Assigned to Partition
Lobby All lobby phones
NonPAManaged All employee IP phones not managed by
PA Personal Assistant interceptor ports
PAManaged All employee IP phones managed by
PSTN All externally destined route patterns (local PSTN)
“Using Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Without Personal Assistant” section on
CTI route point (the pilot port to access Personal Assistant)
Media ports (to support Personal Assistant sessions)
Personal
Assistant, Personal Assistant CTI route
point, and Personal
Personal
Assistant
Assistant media ports
1-18
2. Add the PA partition to the cssLobby, cssEmp, and cssGW calling search spaces. Be sure to add the
PA partition to the top of the list to force Cisco
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
CallManager to search the PA partition first.
OL-4590-03
Page 33

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
3. Create the calling search space for Personal Assistant, in this example, cssPA, and add the partitions
indicated in the following table to it.
Calling Search
Space
cssPA PAManaged
cssLobby PA
cssEmp PA
cssGW PA
Partitions Assigned To
Devices that will not have Personal Assistant evaluate the
Lobby
NonPAManaged
PSTN
NonPAManaged
Lobby
Lobby
NonPAManaged
PSTN
Lobby
NonPAManaged
called number for interception.
Devices (such as lobby IP phones) that can dial internal
numbers and access Personal
Devices (such as employee IP phones) that can dial internal
and external numbers and access Personal
PSTN voice gateway used for outside callers to access
lobby phones, employees, and Personal
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
Assistant.
Assistant.
Assistant.
4. Change the partition of User 1002 to PAManaged (see the “Why You Need a Partition for
Personal Assistant Managed Phones” section on page 1-22 for a complete explanation of this task)
Cisco CallManager
Setting
User 1001 User 1002 User 1003
PA Interceptor Port
Route Point
Phone extension 1001 1002 1003 1XXX
Partition NonPAManaged PAManaged-
NonPAManaged PA
Employee
Calling search space cssEmp cssEmp cssEmp cssPA
With Personal Assistant now added to this example, you can understand how user calls are intercepted.
When User 1001 calls User 1002, Cisco CallManager uses the calling search space of User 1001,
cssEmp. Cisco
1XXX (where X matches any digit), which exists in the PA partition. Therefore, Cisco
routes the call to Personal
CallManager determines that the best match to extension 1002 within the cssEmp is
CallManager
Assistant instead of sending it to the phone of User 1002. Personal Assistant
processes the active call routing rules of User 1002 and uses the applicable rule. If no rule applies, the
call goes directly to the extension of User 1002, because the calling search space of Personal
Assistant,
cssPA, contains the partition PAManaged, which is the partition in which the extension of User 1002
exists. If the applicable rule instructs Personal
1003, Cisco
calling search space of Personal
CallManager finds the best match to extension 1003 in the NonPAManaged partition of the
Assistant, cssPA, and sends the call directly to User 1003.
Assistant to transfer User 1002 calls to the phone of User
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-19
Page 34

Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
Note that because cssPA contains the NonPAManaged partition and does not contain the PA partition,
Personal
Assistant does not intercept the call a second time to process the active call routing rules of
User 1003.
When User 1002 calls User 1001, Cisco CallManager uses the calling search space of User 1002,
cssEmp, and finds the best match to extension 1001 in the NonPAManaged partition. (While cssEmp
includes the PA partition, and 1XXX in the PA partition is a match for extension 1001, 1001 exists in the
NonPAManaged partition and is the best match.) The call is sent directly to extension 1001. Because
Personal
Assistant does not intercept the call, no call routing rules are applied.
Adding Personal Assistant Without Previously Defined Partitions
If you are not already using partitions, then you must create a minimal set in order to implement
rule-based call routing by using Personal
When you have not yet created any partitions or calling search spaces specific to your needs, all of your
IP phones currently exist by default in the “none” partition in Cisco
partition exists in all calling search spaces, you can selectively enable Personal
extensions. If Personal
Assistant is not intercepting the dialed number, Cisco CallManager will find the
number in the none partition, and ring the applicable phone.
You can selectively support Personal Assistant depending on how you assign the partitions and calling
search spaces. Consider this example:
Assistant.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
CallManager. Because the none
Assistant for different
1. Create a Personal Assistant partition, for example PA, and a Personal Assistant managed phones
partition, for example PAManaged.
Add the interceptor ports (to intercept incoming calls) to the PA partition.
Add the phones of all employees who will use Personal Assistant to the PAManaged partition.
(Placing these phones in the PAManaged partition effectively removes them from the “none”
partition.)
Leave all other phones in the “none” partition, including the CTI route point (the pilot port to access
Personal
Assistant) and the media ports (to support Personal Assistant sessions).
Partition Name Designated Devices Assigned to Partition
none All other phones (including lobby phones, employee
IP phones not managed by Personal
and the Personal
Assistant CTI route point and media
Assistant), PSTN,
ports
PA Personal Assistant interceptor ports
PAManaged All employee IP phones managed by
Personal
2. Next, create the following calling search spaces:
–
cssPA—Add the PAManaged partition to it.
Assistant
1-20
–
cssPhones—Add the PA partition to it.
Note that every calling search space includes the “none” partition by default.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 35

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Calling Search
Space
cssPA PAManaged
cssPhones PA
3. Update each IP phone extension that you want managed with the new PAManaged partition and the
cssPhones calling search space.
If you do not want to enable Personal Assistant on a particular phone (such as a lobby phone), you
can leave the extension assigned to the none partition, but you must update the calling search space.
If you need to update hundreds or thousands of user extensions, consider using the
Cisco
CallManager Bulk Administration Tool (BAT).
Partitions Assigned To
Devices that will not have Personal Assistant evaluate the
none
none
called number for interception.
Devices (such as employee IP phones) that can dial internal
and external numbers and access Personal
Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
Assistant.
Cisco CallManager
Setting
User 1001 User 1002 User 1003
PA Interceptor Port
Route Point
Phone extension 1001 1002 1003 1XXX
Partition none PA Ma na ge d none PA
Calling search space cssPhones cssPhones cssPhones cssPA
4. It is important to understand how these changes affect User 1001 and User 1002.
In this example, we have reconfigured the phone of User 1002 to use Personal Assistant by adding
it to the PAManaged partition. We have also left the phone of User 1001 in the “none” partition.
Finally, we have updated the calling search spaces to search the Personal
Assistant partition (PA).
These changes enable the call routing rules of User 1002 to be applied to all incoming calls. To
complete the configuration, we have created the 1XXX interceptor port (X matches any digit) in the
PA partition so that Personal
Assistant will intercept calls to the extension of User 1002.
When User 1001 calls User 1002, Cisco CallManager uses the calling search space of User 1001,
cssPhones. Cisco
is 1XXX, which exists in the PA partition. Therefore, Cisco
Personal
Assistant instead of sending it to the phone of User 1002. Personal Assistant processes the
CallManager determines that the best match to extension 1002 within cssPhones
CallManager routes the call to
active call routing rules of User 1002 and uses the applicable rule. If no rule applies, the call goes
directly to the extension of User 1002, because the calling search space of Personal
Assistant,
cssPA, contains the partition PAManaged, which is the partition in which the extension of User 1002
exists. If the applicable rule instructs Personal
phone of User 1003, Cisco
CallManager finds the best match to extension 1003 in the “none”
partition of the calling search space of Personal
Assistant to transfer the calls of User 1002 to the
Assistant, cssPA, and sends the call directly to User
1003.
OL-4590-03
Note that because cssPA contains the NonPAManaged partition and does not contain the PA
partition, Personal
Assistant does not intercept the call a second time to process the active call
routing rules of User 1003.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-21
Page 36

Intercepting Calls with Personal Assistant
When User 1002 dials User 1001, Cisco CallManager uses the calling search space of User 1002,
cssPhones, and finds that 1XXX, in the PA partition matches. Because Cisco
the best match within the partitions of the calling search space, it continues to search and finds 1001
in the “none” partition. Cisco
CallManager rings the phone of User 1001.
Why You Need a Partition for Personal Assistant Managed Phones
When you create the partitions needed for Personal Assistant, you create a partition that will contain the
phones that Personal
create a partition that will contain the interceptor port route points (in our examples, PA). This section
explains why you need both partitions.
Recall how Cisco CallManager routes calls:
1. Cisco CallManager identifies the calling search space assigned to the extension from which the call
is made. For example, if User A calls User B, the calling search space of the phone of User A is used
to complete the call.
2. Cisco CallManager tries to find the best match for the called extension, searching top to bottom in
the list of partitions contained in the calling search space. If the first match uses wildcards (for
example, 1XXX), subsequent partitions are searched in an attempt to find a better match. If an exact
match is found, it is used, even if a wildcard match exists in a partition higher in the list of partitions
in the calling search space.
Assistant will manage (in our examples, this partition is PAManaged). You also
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
CallManager looks for
Because you are going to use wildcards when you create interceptor port route addresses, you must
prevent Cisco
CallManager from finding exact matches to use in place of the interceptor addresses.
Consider an example of a call between non-Personal Assistant users:
• The PA partition includes 1XXX as the interceptor route points.
• The NonPAManaged partition includes the extensions of User 1001 and User 1003.
• The cssEmp calling search space includes the PA and NonPAManaged partitions, in that order.
• The extensions of User 1001 and User 1003 use the cssEmp calling search space.
Now, when User 1001 calls User 1003, Cisco CallManager first checks the PA partition, and finds a
match: 1XXX. However, because this match uses wildcards, the search continues to the NonPAManaged
partition, where an exact match, 1003, is found. Cisco
of User 1003, found in the NonPAManaged partition. Thus, Personal
CallManager then routes the call to the extension
Assistant has no role in the call.
Now, consider the case of a phone in the PAManaged partition:
• The PA partition includes 1XXX as the interceptor route points.
• The NonPAManaged partition includes the extension of User 1001 and User 1003.
• The PAManaged partition includes the extension of User 1002.
• The cssEmp calling search space includes the PA and NonPAManaged partitions, in that order.
• The extensions of User 1001, User 1003, and User 1002 use the cssEmp calling search space.
In this example, when User 1001 calls User 1002, Cisco CallManager first checks the PA partition, and
finds a match: 1XXX. Again, because this match uses wildcards, the search continues to the
NonPAManaged partition, but this time, an exact match is not found because the extension of User 1002
is no longer in the NonPAManaged partition. Cisco
route point found in the PA partition. Thus, Personal
CallManager routes the call based on the 1XXX
Assistant intercepts the call, and applies the call
routing rules of User 1002 to it.
1-22
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 37

Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
Why You Need Interceptor Port Error Handling
You configure interceptor port error handling to tell Cisco CallManager how to route calls to
Personal
interceptor port error handling, and if Personal
called, and the caller will hear a fast busy tone.
The way you configure interceptor port error handling differs according to which version of
Cisco
Cisco CallManager Version 3.x
If you are using Cisco CallManager version 3.x, when you create an interceptor port, you create two
entities: a route point, and a translation pattern. Cisco
handling. Each translation pattern must match the set of numbers in the corresponding interceptor port
route point. The translation patterns must not be placed in the PA partition, as this could cause a match
even when the Personal
Cisco CallManager Version 4.0 or Later
If you are using Cisco CallManager version 4.0 or later, you configure interceptor port error handling by
setting the Forward No Answer destination and calling search space to the same values as the directory
number configured for the interceptor CTI route point.
Assistant users when the Personal Assistant server is unavailable. If you do not configure
CallManager you are using, as follows.
Assistant server is available.
Customizing Implementation of Personal Assistant
Assistant is unavailable, a user phone will not ring when
CallManager uses the translation pattern for error
Customizing Implementation of Personal Assistant
Personal Assistant provides users with the ability to access their voice mail, to call other users by using
speech commands, and to configure rules for handling incoming calls. If you choose not to use some of
these features, the following sections can assist you in determining what you need to do:
• Using Personal Assistant Without Speech Recognition, page 1-23
• Using Personal Assistant Without Rule-Based Call Routing, page 1-23
Using Personal Assistant Without Speech Recognition
You can use Personal Assistant without using the speech-recognition capability. Without speech
recognition, your users can interact with Personal
instead of talking to Personal
through voice mail, and they must spell out names using the keypad.
If you do not want to use speech recognition, do not install speech-recognition servers.
Assistant, the user must learn the key sequences required to navigate
Using Personal Assistant Without Rule-Based Call Routing
If you do not allow Personal Assistant to intercept incoming calls, you can use Personal Assistant
without rule-based call routing. Without rule-based call routing, your users cannot have
Personal
If you do not want to use rule-based call routing, do not configure partitions and calling search spaces
in Cisco
recognition, you must configure the CTI route point and media ports in Cisco
Assistant intercept and handle their incoming calls.
CallManager. You also do not need to configure intercept ports. However, if you use speech
Assistant only by using the touch-tone interface. Thus,
CallManager.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
1-23
Page 38

Preventing Toll Fraud
Preventing Toll Fraud
To prevent or limit name-dialing transfers from Personal Assistant to external numbers, we recommend
that you use one of the following solutions:
• Configure your Cisco CallManager route plans, partitions, and calling search spaces to disable
Personal
• Configure Personal Assistant to operate in speech-enabled Auto Attendant mode so that callers and
employees can access names in the corporate directory only from an external or internal route point.
• Configure an internal (non-DID) route point for Personal Assistant so that employees can access all
Personal
In addition, you can customize Personal Assistant to use the following restriction settings:
• Restrict access to Personal Assistant only to Cisco CallManager users.
• Restrict access to Personal Assistant only to registered phones.
• Enforce PIN authentication from personal destinations.
For details on how to configure these settings, see the “Miscellaneous Settings” section on page A-12.
Assistant from making long-distance calls.
Assistant functionality only from the office.
Chapter 1 Planning for Personal Assistant
1-24
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 39

CHA P TER
2
Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Task List for Installing Personal Assistant on a New System, page 2-1
• Installing Personal Assistant Software, page 2-2
• Task List for Upgrading from Personal Assistant Version 1.3(x), page 2-5
• Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for Personal Assistant, page 2-6
• Disabling McAfee NetShield Services, page 2-8
• Disabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant, page 2-8
• Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant, page 2-9
• Installing the Enhanced Text to Speech Server, page 2-9
• Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the Corporate Directory, page 2-10
Task List for Installing Personal Assistant on a New System
Personal Assistant consists of three components that you can install separately or together on one
system: the Personal
server; and the speech recognition server.
Although you configure some Personal Assistant settings during installation, you do most of the
configuration after installation by using the Personal
Use the following task list to install Personal Assistant on a system that is not running a previous version
of Personal
Personal Assistant Version 1.3(x)” section on page 2-5.
1. Before installing Personal Assistant on a new system, review the planning information in Chapter 1,
2. Verify the hardware and software requirements for the Personal Assistant 1.4 system. Refer to the
3. Review the system limitations and restrictions on how Personal Assistant can be configured in the
Assistant. If you are upgrading Personal Assistant, see the “Task List for Upgrading from
“Planning for Personal Assistant.” You must have a clear understanding of how many users you need
to support and the best configuration of the Personal Assistant components for your requirements,
as you will need this information to make decisions during the installation process.
“System Requirements and Supported Software” section of the Release Notes for Personal Assistant
Ve r s i o n 1 . 4 . The release notes are available at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps2026/prod_release_notes_list.html.
network. Refer to the
Notes for Personal Assistant Version 1.4.
Assistant web interfaces for end users and administrators; the Personal Assistant
Assistant administration interface.
“Personal Assistant Configuration on the Network” section of the Release
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-1
Page 40

Installing Personal Assistant Software
4. If the system uses Active Directory for the corporate directory, prepare the directory system to work
with Personal
Personal Assistant” section on page 2-6.
5. If McAfee NetShield is installed on the Personal Assistant server, disable the virus-scanning
services so that they do not interfere with the installation program. See the
NetShield Services” section on page 2-8. Otherwise, skip to Task 6.
6. If Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant is installed on the Personal Assistant server,
disable the Cisco Security Agent service so that it does not interfere with the installation program.
See the
Otherwise, skip to Task 7.
7. Install the Personal Assistant server, speech recognition server, and user and administrative
interfaces. See the
8. Install the enhanced Text to Speech server, if applicable. See the “Installing the Enhanced Text to
Speech Server” section on page 2-9.
9. Configure Cisco CallManager. See Chapter 3, “Configuring Cisco CallManager for
Personal Assistant.”
10. Configure Personal Assistant. See Chapter 4, “Configuring Personal Assistant.”
11. Load user information from the corporate directory. See the “Refreshing the System—Updating
User Information from the Corporate Directory” section on page 2-10.
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Assistant. See the “Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for
“Disabling McAfee
“Disabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant” section on page 2-8.
“Installing Personal Assistant Software” section on page 2-2.
12. When the refresh has completed, re-enable the Cisco Security Agent service, if applicable. See the
“Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant” section on page 2-9.
13. When the refresh has completed, if applicable, re-enable the McAfee NetShield services that you
disabled in Task
5. Refer to the virus-scanning software documentation for information about
re-enabling the services.
Installing Personal Assistant Software
If you are integrating Personal Assistant with Cisco Unity or Microsoft Exchange in a Windows 2000
domain, you cannot use the same product code to install both Windows
You must first install Windows
Personal
To Install Personal Assistant Software
Step 1 Log on to the computer from which you are running the Personal Assistant Installation program as a
Assistant installation.
local administrator.
Step 2 Insert the Personal Assistant Installation CD into the CD-ROM drive. The Personal Assistant installation
program automatically launches.
Step 3 If prompted, enter the product key.
Step 4 Click OK. The welcome window opens.
Step 5 Click Next. The End-User License Agreement window opens.
2000, restart the system, and join the domain before proceeding with the
2000 and Personal Assistant.
2-2
Step 6 Read the agreement, and click I Agree to accept the terms and continue. Or, click Exit to cancel the
installation. The Cisco
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
Personal Assistant Components window opens.
OL-4590-03
Page 41

Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Step 7 Do the following substeps on the Cisco Personal Assistant Components window:
a. Choose the Personal Assistant components to install:
• Cisco Personal Assistant Server—Manages the interaction between the user and
Cisco
Personal Assistant, processes call routing and dial rules, and manages the overall
configuration of the Cisco
• Cisco Personal Assistant Speech Recognition Server—Processes speech commands.
• Cisco Personal Assistant Web Administration—Is used to administer and access
Personal
Assistant by using a web browser.
During installation, the selected components install on the same system. If you want to install
components on different systems, choose only those components you want installed together at
this time. You must perform subsequent installations to install the remaining components on
different systems.
b. To install Personal Assistant on an Windows 2000 Domain, select Use a Domain Account and enter
the following:
• Account—Domain administrator account.
• Password—Password for the domain administrator account.
• Domain—Domain in which you are installing Cisco Personal Assistant.
If you are installing multiple Personal Assistant servers, you must install them in the same
Windows
2000 domain.
Installing Personal Assistant Software
Personal Assistant system.
If you chose to install only the Personal Assistant Speech Recognition Server, skip to Step 12.
Otherwise, continue with Step 8.
Step 8 Click Next. The Cisco Personal Assistant Locales window opens.
Step 9 Check the check boxes for the desired locales.
Step 10 Click Next. The Cisco CallManager Database Location window opens.
Step 11 On the Cisco CallManager Database Location window, enter the settings from the Cisco CallManager
publisher:
• Host name—The DNS name or IP address of the Cisco CallManager publisher.
• Windows 2000 username and password—The settings on the server that is the Cisco CallManager
publisher.
• SQL Server username and password—The SQL server used by Cisco CallManager publisher. Enter
the information only if you are installing Personal
Personal
Assistant version 1.4(3) or later, the installation program does not display the SQL Server
Assistant version 1.4(2) or earlier. Note that for
username and password fields.
These settings must match those on the Cisco CallManager publisher server. For example, if you do not
have a password set for Windows
2000 on that system, do not enter it here. However, a user name is
required.
Note You must specify the same Cisco CallManager publisher for all of the Personal Assistant and
speech-recognition servers in the same Personal
Assistant cluster.
You must be able to access the Cisco CallManager system from the computer on which you are
installing Personal
Cisco
CallManager system. If it cannot reach Cisco CallManager, it generates an error and the
Assistant. When you click Next, the installer verifies connectivity to the
installation will not continue.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-3
Page 42

Installing Personal Assistant Software
Step 12 Click Next. The Ready to Install Cisco Personal Assistant window opens.
If an error message appears saying, “Connected successfully using the information supplied, but could
not find a Call Manager database on the server. Please check the information and retry,” exit the
installation program and do the following procedure “
Cisco CallManager Database (Personal Assistant 1.4(2) and Earlier).” When you are done creating the
data source, repeat this procedure.
Step 13 Click Next.
The Personal Assistant components you selected are installed. Installation takes approximately 10 to 15
minutes to complete. Once complete, the Cisco Product Activation window opens.
Step 14 Click Yes to restart the computer. Click No to continue installing other applications. Note that you must
restart before using Personal
If you are installing Personal Assistant version 1.4(2) or 1.4(1) and if the installation of
Personal
Assistant reports errors about connecting to the Cisco CallManager database, do the following
procedure to create a system data source in the ODBC Data Source Administrator to use TCP/IP to
connect to the Cisco
Otherwise, skip the procedure.
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
To Manually Create a System Data Source for the
Assistant.
CallManager database. Do the procedure on each Personal Assistant server.
To Manually Create a System Data Source for the Cisco CallManager Database (Personal Assistant 1.4(2) and
Earlier)
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools > Data Sources
(ODBC).
Step 2 Click the System DSN tab, and click Add.
Step 3 In the Create New Data Source dialog box, click SQL Server from the list, and click Finish.
Step 4 In the Create a New Data Source to SQL Server dialog box, enter a name (for example, PACCMDB) and
a description for the data source in the applicable fields.
Step 5 In the Server list, click the hostname or IP address of the Cisco CallManager publisher server.
Note The ODBC sources on all servers in the Personal Assistant cluster must use the same publisher
database.
Step 6 Click Next.
Step 7 Click Client Configuration.
Step 8 In the Add Network Library Configuration dialog box, confirm that the correct Cisco CallManager
hostname or IP address appear in the Server Alias and Server Name fields.
Step 9 Under Network Libraries, click TCP/IP.
Step 10 Update the information in the Port Number field, if applicable.
Step 11 Click OK.
2-4
Step 12 Click With SQL Server Authentication Using a Login ID and Password Entered by the User, then
enter the Login ID and Password for the Cisco
Step 13 Click Next until you get to the last page, then Click Finish.
Step 14 In the dialog box that appears, click Test Data Source.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
CallManager publisher database.
OL-4590-03
Page 43

Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Task List for Upgrading from Personal Assistant Version 1.3(x)
Confirm that the test completes successfully.
Step 15 Click OK to complete the configuration.
Task List for Upgrading from Personal Assistant Version 1.3(x)
Use the following task list to upgrade Cisco Personal Assistant on a system that is currently running a
1.3(x) version of the software. The task list assumes the currently-installed Personal
component was installed correctly and is functioning.
Personal Assistant will be out of service while the system is upgraded. Plan to upgrade the product on a
day and time where the elimination of the Personal
Assistant service will have the least impact.
If you are installing Personal Assistant on a server that does not have a version already installed, see the
“Task List for Installing Personal Assistant on a New System” section on page 2-1.
Caution Do not upgrade from Personal Assistant version 1.2(x) directly to version 1.4. For this upgrade, you must
first upgrade to Personal
Administration Guide for version 1.3 for instructions.
Assistant version 1.3. Refer to the Cisco Personal Assistant Installation and
Upgrading from Personal Assistant version 1.1(x) is not supported.
Assistant
1. If McAfee NetShield is installed on the Personal Assistant server, disable the virus-scanning
services so that they do not interfere with the installation program. See the
“Disabling McAfee
NetShield Services” section on page 2-8. Otherwise, skip to Task 2.
2. If Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant is installed on the Personal Assistant server,
disable the Cisco Security Agent service so that it does not interfere with the installation program.
See the
“Disabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant” section on page 2-8.
Otherwise, skip to Task 3.
3. Upgrade Cisco CallManager to the required version. See Tab le 1-1 on page 1-6 for the required
version, and refer to the Cisco CallManager documentation for upgrade instructions.
4. Stop all Personal Assistant components to remove Personal Assistant services from the telephony
network. See the
5. Install the Personal Assistant server, speech recognition server, and user and administrative
interfaces. See the
6. If you are upgrading to the enhanced Text to Speech server, install the enhanced server. See the
“Stopping Personal Assistant Components” section on page 2-6.
“Installing Personal Assistant Software” section on page 2-2.
“Installing the Enhanced Text to Speech Server” section on page 2-9.
7. Reload user information from the corporate directory. See the “Refreshing the System—Updating
User Information from the Corporate Directory” section on page 2-10.
8. When the refresh has completed, re-enable the Cisco Security Agent service, if applicable. See the
“Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant” section on page 2-9.
9. When the refresh has completed, if applicable, re-enable the McAfee NetShield services that you
disabled in Task
1. Refer to the virus-scanning software documentation for information about
re-enabling the services.
OL-4590-03
10. If you are upgrading to the enhanced Text to Speech server, configure the Text to Speech. See the
“Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech” section on page 4-14.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-5
Page 44

Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for Personal Assistant
11. If Cisco CallManager is configured in a cluster, specify the Cisco CallManager internal directory
configuration. See the
(Personal Assistant Version 1.4(3) or Later)” section on page 4-10.
“Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration
Stopping Personal Assistant Components
To Stop Personal Assistant Components
Step 1 Log on to the computer from which you are running the Personal Assistant upgrade program as a local
administrator.
Step 2 In the Personal Assistant administration interface, select System > Control Center. Personal Assistant
opens the Control Center page.
Step 3 Click Stop All in each of the three sections of the page to stop all Personal Assistant Servers, license
managers, and speech recognition servers.
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for
Personal
Verifying That the Global Catalog Schema Includes Personal Assistant Attributes
Ta b l e 2-1 Personal Assistant Attributes
Assistant
Do the following two subsections, if applicable.
If you are using Active Directory for the corporate directory, and if you have users defined in multiple
domains, you must use the global catalog server when you configure the corporate directory.
If you use the global catalog server, the global catalog schema must include the attributes specific to
Personal
In addition to the attributes listed, if you create directory hierarchies that use other attributes (for
example, City=San Jose), ensure that the additional attributes are also included in the schema.
Verify with your Active Directory administrator that the global catalog schema has the applicable
attributes.
Active Directory Attribute Name Attribute Name in Personal Assistant
sAMAccountName Unique Attribute
givenName First Name
sn Last Name
alias Nick Name
telephoneNumber Work Phone
Assistant, as listed in Tabl e 2-1.
2-6
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 45

Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Table 2-1 Personal Assistant Attributes (continued)
Active Directory Attribute Name Attribute Name in Personal Assistant
mobile Cell Phone
homeNumber Home Phone
pager Pager Address
mail E-mail Address
Using an LDIF File
LDIF is a standard format used to import and export data from an LDAP directory. You can set up
Personal
the system refreshes and when it restarts. By default, Personal
result in a large amount of network traffic, depending on the size of the data and the complexity of the
system. Instead of having each server in a multiple Personal
resource-intensive LDAP query, you can set up an LDIF file at a shared location and configure each
server to read from it.
Note that Personal Assistant will still use LDAP queries for functions such as name-dialing, searching
the corporate directory to copy users to the address book, and so on.
To use an LDIF file, you first set up the system to generate the LDIF file that includes attributes specific
to Personal
file. The
Assistant to read from an LDIF file to obtain information from the corporate directory when
Assistant. When you later configure the corporate directory, you specify the location of this
“To Configure the Corporate Directory” procedure on page 4-8 will alert you when to do this.
Setting Up Active Directory as the Corporate Directory for Personal Assistant
Assistant uses an LDAP query, which can
Assistant cluster run a large,
Table 2-2 lists the Personal Assistant attributes required in the LDIF file. Note that in addition to the
listed fields, if you configured directory hierarchies that use other attributes (for example, City=San
Jose), you must include the additional attributes in the file. See the
below for an example of how to set up an LDIF file for Personal Assistant.
Ta b l e 2-2 LDIF File Attributes
LDAP Attribute Name Attribute Name in Personal Assistant
cn, uid, or sAMAccountName Unique Attribute
givenName First Name
sn Last Name
alias Nick Name
telephoneNumber Work Phone
mobile Cell Phone
homeNumber Home Phone
pager Pager Address
mail E-mail Address
“Sample LDIF File Creation” section
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-7
Page 46

Disabling McAfee NetShield Services
Sample LDIF File Creation
For example, assume that the directory is Active Directory and that you are setting up the LDIF file
Paldifdata.ldif in the directory C:/Ldif. To create the file, run the ldifde command, as follows:
ldifde -s global-catalog-server -t 3268 -d “dc=sample,dc=com” -r “(ObjectCategory=Person)” -p
SubTree -l “givenName,sn,alias,homePhone,telephoneNumber,mobile,pager,mail” -n -f
“C:/Ldif/Paldifdata.ldif”
The example produces the following output:
dn: CN=jdoe,CN=users,CN=sample,CN=com
changetype: add
mail: jdoe@sample.com
givenName: John
sn: Doe
telephoneNumber: 12345
Disabling McAfee NetShield Services
If McAfee NetShield is installed on the Personal Assistant server, the virus-scan services must be
disabled before you run the Personal
or upgrade process. (The task list alerts you when to re-enable the services.)
Assistant installation program in order to speed up the installation
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
To Disable McAfee NetShield Services
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2 In the right pane, double-click each of the services listed below. For each service, on the General tab,
click Stop, click Disabled in the Startup Type list, and then click OK.
• Network Associates Alert Manager
• Network Associates McShield
• Network Associates Task Manager
Step 3 Close the Services MMC.
Disabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant
To Disable the Cisco Security Agent Service
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2 In the right pane, double-click Cisco Security Agent.
Step 3 Click the General tab, and click Stop.
Step 4 In the Startup Type list, click Disabled, and click OK.
Step 5 Click OK to close the Cisco Security Agent Properties dialog box.
2-8
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 47

Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant
Step 6 Close the Services MMC.
Re-Enabling Cisco Security Agent for Cisco Personal Assistant
To Re-Enable the Cisco Security Agent Service
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2 In the right pane, double-click Cisco Security Agent.
Step 3 On the General tab, in the Startup Type list, click Automatic.
Step 4 Click Start.
Step 5 Click OK to close the Cisco Security Agent Properties dialog box.
Step 6 Close the Services MMC.
Installing the Enhanced Text to Speech Server
The platform requirements for the enhanced Text to Speech server are the same as the requirements for
the Personal
Personal Assistant Version 1.4. The release notes are available at
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps2026/prod_release_notes_list.html.
The enhanced Text to Speech server can be installed on the Personal Assistant server or on a separate
server, but not on the Cisco
able to connect to the Text to Speech server. Otherwise enhanced text to speech generation will fail and
the default text to speech server will be used instead.
Do the following two procedures, if applicable.
To Install the Enhanced Text to Speech Server and Any Applicable Locale(s)
Step 1 Log on to the computer from which you are installing the Text to Speech server as a local administrator.
Step 2 If you are installing the Text to Speech server on the Personal Assistant server, as a best practice, we
recommend that you stop one of the Personal
a. On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
b. In the right pane, double-click PATTSServer.
c. Click the General tab, and click Stop. If a message appears saying that the PATTServer service
could not be stopped, click OK.
d. Close the Services MMC.
Step 3 Insert the Cisco Personal Assistant Enhanced TTS Server CD1 in the CD-ROM drive.
Assistant server. Refer to the “Hardware Requirements” section of the Release Notes for
CallManager or Cisco Unity server. The Personal Assistant server must be
Assistant services. Do the following substeps:
OL-4590-03
If the installation program does not appear, browse to the root directory of the CD, and double-click
Setup.exe.
Step 4 Follow the on-screen prompts until you are prompted to select the components to install.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-9
Page 48

Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the Corporate Directory
Step 5 Check the Enhanced TTS Server check box.
Step 6 Check the check box(es) of the locale(s) that you want to install.
Step 7 Enter a port number between 1024 and 65535 on which to run the TTS server, in the TTS Port Number
field, and click Next. (The default is 6666.)
We recommend that you make note of this number. This is the port number that you will enter on the
Enhanced TTS Configuration page of the Administration interface.
Step 8 Continue to follow the on-screen prompts until the setup is complete.
Step 9 When the setup is complete, click OK.
To install additional locales, do the following procedure.
To Install Additional Enhanced Text to Speech Server Locales
Step 1 Ensure that you are logged on to the computer from which you are installing the additional enhanced
Text to Speech server locales as a local administrator.
Step 2 If you are installing the additional locales on the Personal Assistant server, as a best practice, we
recommend that you stop one of the Personal
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
Assistant services. Do the following substeps:
a. On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
b. In the right pane, double-click PATTSServer.
c. Click the General tab, and click Stop. If a message appears saying that the PATTServer service
could not be stopped, click OK.
d. Close the Services MMC.
Step 3 Insert the Cisco Personal Assistant Enhanced TTS Server CD2 in the CD-ROM drive.
If the installation program does not appear, browse to the root directory of the CD, and double-click
Setup.exe.
Step 4 Follow the on-screen prompts until you are prompted to select the components to install.
Step 5 Check the check boxes for the applicable locales, and click Next.
Step 6 Continue to follow the on-screen prompts until the setup is complete.
Step 7 When the setup is complete, click OK.
Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the
Corporate Directory
Do the following procedure to have Personal Assistant load speech recognition grammars and user
information from the corporate directory.
Ensure that the virus-scanning services are disabled during the first system refresh.
2-10
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 49

Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
To Refresh the System
Step 1 Log on to the Personal Assistant administration interface.
Step 2 Select System > Speech Services. The Speech Services Configuration page appears.
Step 3 Click Refresh Now.
Note that the refresh can take up to an hour, depending on the size of the corporate directory, the number
of locales installed, and the number of directory hierarchies configured.
Step 4 After the refresh has completed, verify that the refresh was successful by clicking Last Refresh Details.
Step 5 If the refresh was not successful, the Personal Assistant services may not run and some
Personal
a. On the Speech Services Configuration page, verify that the entry in the License Key field is valid.
Assistant features may be unavailable. Do the following substeps:
If the Number of Licenses field does not display the correct number speech ports and available
locales, re-enter the license key, and click Save to update the information.
b. Verify the DNS names or IP addresses in the Speech Recognition Server Hosts and the Speech
Recognition License Manager Hosts lists. If any information is incorrect, make the applicable
modifications, and click Save to update the information.
c. Navigate to the Control Center page and verify that the license manager is running. If the license
manager has not started, click the Start button on the same line as the server name.
Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the Corporate Directory
d. Return to the Speech Services Configuration page and click Refresh Now.
e. After the refresh has completed, verify that the refresh was successful by clicking Last Refresh
Details.
If the refresh was not successful, contact Cisco TAC to resolve the problem before proceeding.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
2-11
Page 50

Refreshing the System—Updating User Information from the Corporate Directory
Chapter 2 Installing and Upgrading Personal Assistant
2-12
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 51

CHA P TER
3
Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
After installing Personal Assistant, you must complete tasks in Cisco CallManager, as described in the
following sections:
• Setting Up Cisco IP Phone Route Plans, page 3-2
• Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls, page 3-3
• Setting Up the Personal Assistant Number, page 3-8
• Adding Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User, page 3-9
• Adding Media Ports for Personal Assistant, page 3-10
• Configuring Cisco Unity in Cisco CallManager for Integration with Personal Assistant, page 3-12
Cisco Personal Assistant Configuration Wizard
The Cisco Personal Assistant Configuration Wizard is a tool that can be used to automatically configure
most of the objects that Cisco
that you install Personal
CallManager needs for integration with Personal Assistant the first time
Assistant.
OL-4590-03
Note that the wizard can only be used with Personal Assistant version 1.4(3) or later.
If you use the wizard to complete the tasks in Cisco CallManager automatically, you will still have to do
the tasks in the following two sections to configure phones manually:
• Assigning the Partition and Calling Search Space to Phones, page 3-3
• Updating the Partition for Managed Phones, page 3-8
You can download the wizard for free from the Personal Assistant Software Download page at
http://www.cisco.com/cgi-bin/tablebuild.pl/assist.
For more information on using the wizard—including instructions for installing and running it—refer to
the Personal
Software Download page.
Note that to access the software download page, you must b e logged on to Cisc o.com as a registered user.
Understanding the Cisco CallManager Examples
The setup sections in this chapter represent an example setup, with sample values included for reference
only. Your particular configuration depends on the needs of your network. For the examples, the
following calling search spaces and partitions are used:
• EmployeeCSS—includes the PA and Employee partitions
Assistant Configuration Wizard Readme file, also available on the Personal Assistant
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-1
Page 52

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Setting Up Cisco IP Phone Route Plans
• PACSS—includes the PAManagedEmployee and Employee partitions
The examples are based on a single Cisco CallManager cluster. If you have more than one cluster, you
must repeat the configuration in each cluster. The route points and translation patterns (if applicable)
will be different in each cluster, but you can use the same partition and calling search space names, and
the same Personal
For detailed information about how Personal Assistant uses calling search spaces and partitions, see the
“Partitions and Calling Search Spaces” section on page 1-4.
Assistant user name.
Setting Up Cisco IP Phone Route Plans
Before configuring Personal Assistant, you must ensure that the Cisco IP Phones are added and
registered with Cisco
assistance adding and registering the Cisco IP Phones.
The following sections provide an example setup for your network:
• Creating a Phone Partition, page 3-2
• Creating a Phone Calling Search Space, page 3-2
• Assigning the Partition and Calling Search Space to Phones, page 3-3
CallManager. Refer to the Cisco CallManager documentation and Help if you need
• Using Partitions and Calling Search Spaces Without Personal Assistant, page 1-17
Creating a Phone Partition
If you have not already created a partition for the Cisco IP Phones, do the following procedure to create
one.
To Create a Phone Partition
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Partitions page of the Cisco CallManager administration interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New Partition. The Partition Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Partition Name and Description field, enter a descriptive name (for example, “Employee”).
Optionally, you can include a description.
Step 4 Click Insert to add the new partition.
Creating a Phone Calling Search Space
If you do not already have a calling search space defined for the Cisco IP Phones, do the following
procedure to create one.
3-2
To Create a Calling Search Space
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Calling Search Spaces page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 53

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
Step 2 Click Add a New Calling Search Space. The Calling Search Space Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Calling Search Space Name field, enter a descriptive name (for example, “EmployeeCSS”).
Step 4 In the Available Partitions list box, select the Employee partition and add it to the Selected Partitions
list box by clicking the arrow buttons between the two list boxes.
Step 5 Click Insert to add the new calling search space.
Assigning the Partition and Calling Search Space to Phones
After you have created the Employee partition and calling search space, you must configure the IP
phones to use them.
You can use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to change the partition and calling search space on
phones in much less time than it takes to make the changes to each phone individually. If you prefer to
make the changes individually on each phone, do the following procedure. For instructions on using the
BAT, refer to the Cisco
CallManager documentation.
To Assign a Partition and Calling Search Space to Phones
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Phones page of the Cisco CallManager administration interface.
Step 2 In the search field, select Device Name Is Not Empty and click Find.
Cisco CallManager lists all of the phones in the bottom frame.
Step 3 Click the phone whose configuration you want to change. The Phone Configuration page opens.
Step 4 Click the line number you want to configure in the left-hand column. The Directory Number
Configuration page opens.
Step 5 Change the partition to Employee, and the calling search space to EmployeeCSS.
Step 6 Click Insert to save your changes.
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
Personal Assistant can intercept incoming calls and route them according to user-defined rules. To
enable Personal
configure two Personal
interceptor port route points, and update the calling search space and change the partition on the end-user
phones.
The following sections describe the steps involved in configuring Cisco CallManager to enable
Personal
Assistant to intercept calls between two extensions, such as 1006 and 1007, you must
Assistant partitions and a calling search space, create the Personal Assistant
Assistant to intercept calls:
OL-4590-03
• Creating the Personal Assistant Partitions, page 3-4
• Creating the Personal Assistant Calling Search Space, page 3-4
• Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports and Configuring Error Handling, page 3-4
• Updating the Calling Search Space for End-User Phones, page 3-7
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-3
Page 54

Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
• Updating the Partition for Managed Phones, page 3-8
Creating the Personal Assistant Partitions
Do the following procedure to create the two Personal Assistant partitions:
• PA—The partition that will contain the route points used as Personal Assistant interceptor ports.
Used to intercept calls to the phones that Personal
• PAManagedEmployee—The partition for phones whose calls will be intercepted by
Personal
To Create Personal Assistant Partitions
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Partitions page of the Cisco CallManager administration interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New Partition. The Partition Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Partition Name field, enter a descriptive name (for example, “PA”).
Step 4 Click Insert to add the new partition.
Step 5 Repeat Step 2 through Step 4 to create the PAManagedEmployee partition.
Assistant.
Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Assistant manages.
Creating the Personal Assistant Calling Search Space
To Create a Personal Assistant Calling Search Space
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Calling Search Spaces page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New Calling Search Space. The Calling Search Space Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Calling Search Space Name field, enter a descriptive name (for example, “PACSS”).
Step 4 In the Available Partitions list box, select the PAManagedEmployee and Employee partitions, and add
them to the Selected Partitions list box by clicking the arrow buttons between the two list boxes. Arrange
the partitions so that PAManagedEmployee is at the top of the list.
If you are using any other partitions, add them to this list.
Step 5 Click Insert to add the new calling search space.
Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports and Configuring Error Handling
When you configure the Personal Assistant servers, you assign the route points you create here to the
individual servers. Thus, you should define route points based on how you will divide the managed
phones between servers.
3-4
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 55

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
These route points coincide with the phone extensions. The most efficient way to configure
Personal
Assistant is to use wildcards to define a single route point that covers many extensions. For
example, the single route point 1XXX covers extensions 1000 to 1999. To define a route point that covers
a single extension, enclose the last digit in square brackets. For example, 240[5] covers only the
extension 2405.
In addition to creating the Personal Assistant interceptor port route points, you configure interceptor port
error handling to enable Cisco
Personal
Assistant server is unavailable.
CallManager to route calls to Personal Assistant users when the
See the applicable section, depending on the Cisco CallManager version you are using:
• Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Port Route Points and Configuring Error
Handling—Cisco CallManager Version 4.0 and Later, page 3-5
• Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Port Route Points and Configuring Error
Handling—Cisco CallManager Version 3.x, page 3-6
Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Port Route Points and Configuring Error
Handling—Cisco
CallManager Version 4.0 and Later
When the system uses Cisco CallManager version 4.0 or later, you configure the error handling at the
same time that you create each Personal
To Create Route Points and Configure Error Handling for the Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List CTI Route Points page of the Cisco CallManager administration
Assistant interceptor port route point.
interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New CTI Route Point. The CTI Route Point Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Device Name field, enter a unique meaningful name to identify this as a Personal Assistant route
point interceptor number. (For example, if you are creating the 1XXX route point, “PA1XXX” or
“PARP1XXX” might be useful names.)
Step 4 From the Device Pool menu, select the applicable device pool.
Step 5 From the Calling Search Space menu for the device, select the calling search space that is configured for
Personal
Step 6 Click Insert to add the new CTI route point.
Step 7 Click OK to add a directory number for line 1 of the CTI Route Point. The Directory Number
Assistant (for example, “PACSS”).
Configuration window for line 1 opens.
Step 8 In the Directory Number field, enter the phone number to be used for a Personal Assistant interceptor
port (for example, “1XXX”).
Step 9 From the Partition menu, select the phone partition that is configured for Personal Assistant (for
example, “PA”).
OL-4590-03
Step 10 From the Calling Search Space menu for the line, select the same calling search space that you chose for
the device in
Step 5.
Do not leave <None> as the calling search space for line 1.
Step 11 Click No Voice Mail in the Voice Mailbox Profile list. Otherwise, Personal Assistant cannot mark user
messages with the sender name.
Step 12 In the Forward No Answer Destination field, enter the same phone number that you entered in the
Directory Number field in
Step 8.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-5
Page 56

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
Step 13 In the Calling Search Space menu for the Forward No Answer field, click the same calling search space
that you chose for the directory number in
Step 14 Repeat Step 12 and Step 13 for Forward Busy and Forward on Failure.
Step 15 Click Insert.
Step 16 Repeat Step 2 through Step 15 to create any additional route points.
Step 10.
Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Port Route Points and Configuring Error
Handling—Cisco
CallManager Version 3.x
When the system uses Cisco CallManager version 3.x, you configure error handling by creating a
corresponding translation pattern for each Personal
Do the following two procedures to define the route points and translation patterns that will be used as
Personal
To Create Route Points for the Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports
Assistant interceptor ports.
Assistant interceptor port that you configure.
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List CTI Route Points page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New CTI Route Point. The CTI Route Point Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Device Name field, enter a unique meaningful name to identify this as a Personal Assistant route
point interceptor number. For example, if you are creating the 1XXX route point, “PA1XXX” or
“PARP1XXX” might be useful names.
Step 4 From the Device Pool menu, select the applicable device pool.
Step 5 From the Calling Search Space menu for the device, select the calling search space that is configured for
Personal
Step 6 Click Insert to add the new CTI route point.
Step 7 Click OK to add a directory number for line 1 of the CTI Route Point. The Directory Number
Assistant (for example, “PACSS”).
Configuration window for line 1 opens.
Step 8 In the Directory Number field, enter the phone number to be used for a Personal Assistant interceptor
port (for example, “1XXX”).
Step 9 From the Partition menu, select the phone partition that is configured for Personal Assistant (for
example, “PA”).
Step 10 From the Calling Search Space menu for the line, select the same calling search space that you chose for
the device in
Step 5.
Do not leave <None> as the calling search space for line 1.
Step 11 If the system uses Cisco CallManager version 3.2 or later, click No Voice Mail in the Voice Mailbox
Profile list. If the system uses Cisco
Otherwise, Personal
Step 12 Click Insert.
Step 13 Repeat Step 2 through Step 12 to create any additional route points.
Assistant cannot mark user messages with the sender name.
CallManager version 3.1, leave the Voice Message Box field blank.
3-6
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 57

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Step 14 Continue with the following “To Create Translation Patterns to Correspond to the Personal Assistant
Route Points” procedure.
To Create Translation Patterns to Correspond to the Personal Assistant Route Points
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Translation Patterns page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New Translation Pattern. The Translation Pattern Configuration window opens.
Step 3 In the Translation Pattern field, enter one of the directory numbers of the route points you configured
(for example, “1XXX”).
Step 4 In the Partition field, select Employee.
Step 5 In the Calling Search Space field, select PAC S S .
Step 6 Deselect Provide Outside Dial Tone.
Step 7 Click Insert to save your changes.
Step 8 Repeat Step 2 through Step 7 for every route point you configured in the previous “To Create Route
Points for the Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports” procedure.
Setting Up Personal Assistant to Intercept Calls
Updating the Calling Search Space for End-User Phones
After adding Personal Assistant to your network, you need to update the calling search space assigned
to the end-user phones.
To Update a Calling Search Space for End-User Phones
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Calling Search Spaces page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 In the search field, enter EmployeeCSS and click Find, or to list all calling search spaces, click Find
with no search argument.
Step 3 Select EmployeeCSS from the calling search space list.
The Calling Search Space Configuration page opens.
Step 4 In the Available Partitions list box, select the PA partition, and add it to the Selected Partitions list box
by clicking the arrow buttons between the two list boxes.
Step 5 Rearrange the order of the partitions to ensure that the PA partition is first.
Step 6 Click Update to update the calling search space.
Step 7 If you are using other calling search spaces for phones, repeat Step 2 through Step 6 to update them.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-7
Page 58

Setting Up the Personal Assistant Number
Updating the Partition for Managed Phones
To convert a phone to Personal Assistant management, assign the phone to the PAManagedEmployees
partition. You can do a phased deployment of Personal
subset of your phones at a time.
You can use the Bulk Administration Tool (BAT) to change the partition on phones in much less time
than it takes to make the changes to each phone individually. If you prefer to make the changes
individually on each phone, do the following procedure. For instructions on using the BAT, refer to the
Cisco
CallManager documentation.
To Update the Partition for Managed Phones
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List Phones page of the Cisco CallManager administration interface.
Step 2 To view all phones, select Device Name Is Not Empty, or enter a limited search string to view the phone
subset you want to configure, and click Find.
Cisco CallManager lists the phones in the bottom frame.
Step 3 Click the phone whose configuration you want to change. The Phone Configuration page opens.
Step 4 In the left-hand column, click the line number you want to configure. The Directory Number
Configuration page opens.
Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Assistant by changing the partition of only one
Step 5 Change the partition to PAManagedEmployee.
Step 6 Click Insert to save your changes.
Setting Up the Personal Assistant Number
You must configure a CTI route point in Cisco CallManager to identify the phone number that is used to
access Personal
to configure the automated attendant number.
To Set Up the Personal Assistant Number
Step 1 Navigate to the Find and List CTI Route Points page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 Click Add a New CTI Route Point. The CTI Route Point Configuration page opens.
Step 3 In the Device Name field, enter a unique name (for example, “PANumber”) to identify this as the
Personal
Step 4 From the Device Pool menu, select the applicable device pool.
Step 5 From the Calling Search Space menu for the device, select the Personal Assistant calling search space
you configured (for example, “PACSS”).
Step 6 Click Insert to add the new CTI route point.
Step 7 Click OK to add a directory number for line 1 of the CTI Route Point. The Directory Number
Configuration window for line 1 opens.
Assistant. If you are also setting up an automated attendant, do the following procedure
Assistant access number.
3-8
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 59

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Step 8 In the Directory Number field, enter the phone number to be used for calling Personal Assistant (for
example, “4000”).
Step 9 From the Partition menu, select the phone partition you configured (for example, “Employees”).
Step 10 From the Calling Search Space menu for the line, select the Personal Assistant calling search space you
configured (for example, “PACSS”).
Ensure that you set the Calling Search Space for the line to the Calling Search Space for the device. Do
not leave <None> as the Calling Search Space for the line.
Step 11 Assign the Call Forward No Answer and Call Forward Busy to the PAC S S calling search space.
Step 12 If you want to use load balancing and have configured multiple CTI route points, enter the extension to
forward to in the Call Forward No Answer and Call Forward Busy Destination field.
Step 13 Click Insert and Close.
For additional assistance, refer to the documentation and Help included with Cisco CallManager.
Adding Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User
Adding Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User
You need to add Personal Assistant as a JTAPI user. The settings you enter here are used when
configuring a JTAPI telephony provider in Personal
To Add Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User
Step 1 In Cisco CallManager, select User > Add a New User.
Step 2 Complete the following required fields:
• First Name—Use a descriptive name (for example, “Personal”).
• Last Name—Use a descriptive name (for example, “Assistant”).
• UserID—Use a descriptive name (for example, “PA”).
• User Password and Confirm Password—Enter and confirm a password.
• PIN and Confirm PIN—Enter and confirm a PIN.
Step 3 Check the Enable CTI Application Use check box.
Step 4 Click Insert to create the user.
Step 5 In the left-hand column, click Device Association.
Step 6 In the User Devices Assignment window, fill in the search field and click Select Devices to list the route
Assistant.
points. Check the check boxes associated with the Device Name fields for the route points used as the
Personal
Step 7 Click Update to save your changes.
Assistant number, the automated attendant number, and the interceptor ports.
OL-4590-03
Tip If you do not select all of the CTI route points defined for the use of Personal Assistant, callers will hear
a busy tone when calling Personal
Assistant or the automated attendant, or calls to certain extensions
will not be intercepted.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-9
Page 60

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Adding Media Ports for Personal Assistant
Adding Media Ports for Personal Assistant
Media ports terminate the media between Personal Assistant and the end-user Cisco IP Phones. Add a
media port for each simultaneous Personal
simultaneous sessions, add 24 ports.
After configuring these ports in Cisco CallManager, you must also enter the number of ports in the
Personal
Assistant administration interface (see the “Configuring Personal Assistant Servers” section on
page 4-10).
You create media ports as Cisco7960 devices, even if you are using other types of phones in your
network.
This section contains two procedures for adding media ports. Do the applicable procedure for your
version of Cisco
• To Add Media Ports for Personal Assistant (Cisco CallManager 4.0 and Later), page 3-10
• To Add Media Ports for Personal Assistant (Cisco CallManager 3.3 and Earlier), page 3-11
To Add Media Ports for Personal Assistant (Cisco CallManager 4.0 and Later)
CallManager:
Assistant session you require. For example, if you need 24
Step 1 In Cisco CallManager, select Device > Add a New Device.
Step 2 From the Device Type drop-down list box, select Phone, and click Next.
Step 3 From the Phone Type drop-down list box, select Cisco7960, and click Next. The Phone Configuration
options page opens.
Step 4 Enter the MAC address, as follows:
Enter the extension number, preceded by an adequate number of nines (as a place holder for all
unoccupied digits to the left of the extension) so that the end result is a 12-digit number. For example,
if the extension is 5001, the MAC address should be 999999995001.
Step 5 From the Device Pool menu, select the applicable device pool.
Step 6 From the Phone Button Template menu, select Standard 7960.
Step 7 Click Insert to add the Device.
Step 8 When you are asked if you want to configure line 1, click OK. The Directory Number Configuration
page opens.
Step 9 In the Directory Number field, enter the extension assigned to this port (for example, “5001”).
Step 10 From the Partition menu, select the phone partition you configured (for example, “Employees”).
Step 11 From the Voice Mail Profile menu, select NoVoiceMail. (Note that if you do not set this to NoVoiceMail,
Personal
Step 12 From the Calling Search Space menu, select the calling search space configured for Personal Assistant
Assistant cannot mark user messages with the sender name.)
(for example, “PACSS”).
Step 13 Ensure that no values are entered for the Call Forward and Pickup settings.
3-10
Step 14 In the Maximum Number of Calls field, enter 2.
Step 15 In the Busy Trigger field, enter 1.
Step 16 Click Add.
Step 17 Repeat Step 1 through Step 16 for each port that you need to add.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 61

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
For example, if you need 24 simultaneous sessions, follow these steps to create 24 media ports. Assign
consecutive numbers to the ports (for example, “4001–4024”).
To Add Media Ports for Personal Assistant (Cisco CallManager 3.3 and Earlier)
Step 1 In Cisco CallManager, select Device > Add a New Device.
Step 2 From the Device Type drop-down list box, select Phone, and click Next.
Step 3 From the Phone Type drop-down list box, select Cisco7960, and click Next. The Phone Configuration
options page opens.
Step 4 Enter the MAC address, as follows:
Enter the extension number, preceded by an adequate number of nines (as a place holder for all
unoccupied digits to the left of the extension) so that the end result is a 12-digit number. For example,
if the extension is 5001, the MAC address should be 999999995001.
Step 5 From the Device Pool menu, select the applicable device pool.
Step 6 From the Phone Button Template menu, select Standard 7960.
Step 7 Click Insert to add the Device.
Step 8 When you are asked if you want to configure line 1, click OK. The Directory Number Configuration
page opens.
Adding Media Ports for Personal Assistant
Step 9 In the Directory Number field, enter the extension assigned to this port (for example, “5001”).
Step 10 From the Partition menu, select the phone partition you configured (for example, “Employees”).
Step 11 From the Voice Mail Profile menu, select NoVoiceMail. (Note that if you do not set this to NoVoiceMail,
Personal
Step 12 From the Calling Search Space menu, select the Personal Assistant calling search space you configured
Assistant cannot mark user messages with the sender name.)
(for example, “PACSS”).
Step 13 From the Call Waiting menu, select Off.
Step 14 Ensure that no values are entered for the Call Forward and Pickup settings.
Step 15 Click Insert to save your changes.
Step 16 Repeat Step 1 through Step 15 for each port that you need to add.
For example, if you need 24 simultaneous sessions, follow these steps to create 24 media ports. Assign
consecutive numbers to the ports (for example, “4001–4024”).
Tip You can use the Cisco Bulk Administrator Tool (BAT) to configure several ports at once.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
3-11
Page 62

Chapter 3 Configuring Cisco CallManager for Personal Assistant
Configuring Cisco Unity in Cisco CallManager for Integration with Personal Assistant
Configuring Cisco Unity in Cisco CallManager for Integration
with Personal
When adding Cisco Unity to Cisco CallManager, and setting the calling search space that you use for
voice mail ports and for message waiting indicators, ensure that it contains the PAManagedEmployees
partition, but not the PA partition. Otherwise, the message waiting indicators will not work.
You assign partitions and calling search spaces to voice mail ports on the Feature > Voice Mail > Cisco
Voice Mail Port > Voice Port Configuration page of the Cisco CallManager Administration interface.
You use the Cisco CallManager Administration interface to assign partitions and calling search spaces
to message waiting indicators in one of the following ways:
• On the Feature > Voice Mail > Message Waiting > Message Waiting Configuration page.
• On the Service Parameters Configuration page by going to Service > Service Parameters, and
Refer to the documentation included with Cisco Unity and Cisco CallManager for detailed instructions
on integrating Cisco
Assistant
clicking Cisco Messaging Interface for the applicable server. Set the calling search spaces on the
Service Parameters Configuration page only when a simplified message desk interface
(SMDI)-compliant external voicemail system is used.
Unity with Cisco CallManager.
3-12
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 63

CHA P TER
4
Configuring Personal Assistant
The following sections describe how to configure Personal Assistant:
• Personal Assistant Configuration Task List, page 4-1
• Logging On to and Out of the Personal Assistant Administration Interface, page 4-3
• Configuring Speech Recognition, page 4-4
• Configuring Telephony Providers, page 4-7
• Configuring the Corporate Directory, page 4-7
• Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration (Personal Assistant Version
1.4(3) or Later), page 4-10
• Configuring Personal Assistant Servers, page 4-10
• Configuring Messaging, page 4-12
• Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech, page 4-14
• Creating a Simple Automated Attendant, page 4-15
• Creating Dialing Rules, page 4-16
• Configuring Directory Lookup Rules, page 4-17
• Configuring Directory Hierarchies, page 4-18
• Setting Up Systemwide Rules, page 4-19
• Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice Messaging System, page 4-20
• Integrating Personal Assistant with an Octel Voice Messaging System, page 4-23
• Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5, page 4-24
Personal Assistant Configuration Task List
Personal Assistant does not function until you complete a minimal configuration. After installing
Personal
Personal
various directories, voice mail systems, and other servers that Personal
OL-4590-03
Assistant, you use the administration interface to create speech server clusters and
Assistant server clusters, and to configure the connections between these clusters and the
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
Assistant should use. The
4-1
Page 64

Personal Assistant Configuration Task List
following task list helps you understand what you must do to make Personal Assistant operational, and
also indicates which configuration steps are optional. The cross-references lead to sections that provide
details for each configuration step.
1. Log on to the Personal Assistant Administration interface. See the “Logging On to and Out of the
Personal Assistant Administration Interface” section on page 4-3.
2. If you are using Personal Assistant speech-recognition capabilities, create and configure the speech
server clusters. See the
3. Create the telephony providers that the Personal Assistant servers will require. You must create
these providers before you create the server clusters. See the
section on page 4-7.
4. Identify the corporate directory to Personal Assistant. See the “Configuring the Corporate
Directory” section on page 4-7.
5. Create and configure the Personal Assistant server clusters. See the “Configuring Personal Assistant
Servers” section on page 4-10.
6. If you are using Personal Assistant version 1.4(3) or later and if Cisco CallManager is using its
internal directory, specify the Cisco
“Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration (Personal Assistant Version
1.4(3) or Later)” section on page 4-10.
7. Configure the following messaging features, as applicable to your configuration:
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
“Configuring Speech Recognition” section on page 4-4.
“Configuring Telephony Providers”
CallManager internal directory configuration. See the
• Calendar-based call routing rules.
• The ability for users to create call routing rules that send e-mail pages to them.
• The ability for users to access voice mail while calling Personal Assistant, or to create call
routing rules that send callers directly to voice mail.
• Automatic notification from Personal Assistant when user PINs have been changed (only
available if the system is configured to use the Cisco
CallManager PIN).
See the “Configuring Messaging” section on page 4-12.
8. Identify the operator to whom Personal Assistant will transfer calls if a user has problems with
Personal
Note From the Miscellaneous Settings page, you can also set up logging, and can modify
Assistant. See the “Miscellaneous Settings” section on page A-12.
additional settings. Many settings on the Miscellaneous Settings page are optional, and need
to be changed only if you find the default settings inappropriate for your network.
9. If you are using the enhanced Text to Speech feature, configure the settings for your enhanced
Tex t
to Speech server. See the “Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech” section on page 4-14.
10. If you want to use Personal Assistant as a simple automated attendant, which would allow callers to
dial users by name rather than by number (thus enabling callers to find an employee without
knowing the phone number), configure the AA prompt and route point. See the
“Creating a Simple
Automated Attendant” section on page 4-15 and the “Configuring Personal Assistant Servers”
section on page 4-10.
11. If you want to make dialing easier for users, you can configure dial rules that will automatically
modify the numbers they dial. For example, if your phone system requires you to dial 9 to access an
outside line, you can set up Personal
automatically add a 9 to the front of the number. See the
Assistant to look for dialed numbers that are 7 digits and
“Creating Dialing Rules” section on
page 4-16.
4-2
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 65

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
12. Personal Assistant looks up callers in the corporate directory when an internal caller is placing a call
to another user. In order for Personal
the number as written in the corporate directory. If the numbers do not match, Personal
will not be able to determine the caller. This can happen, for example, if you enable 5-digit calling
on the internal network, but you use 7- or 10-digit numbers in the corporate directory.
If you want Personal Assistant to be able to identify callers (which is required for effective call
routing rule processing), configure directory lookup rules. See the
Rules” section on page 4-17.
13. If you have a large number of users, users might encounter problems when trying to dial a party by
name. For example, there might be too many parties that have the same or similar names. To help
users narrow the Personal
specify a location or department to search. See the
page 4-18.
14. If you want to set up rules to apply to all calls that come through the Personal Assistant system,
create and configure systemwide rules. See the
page 4-19.
15. If you are using Cisco Unity, configure the integration with the messaging system to enable voice
mail browsing for your users. See the
Messaging System” section on page 4-20.
Logging On to and Out of the Personal Assistant Administration Interface
Assistant to find the caller, the number of the caller must match
Assistant
“Configuring Directory Lookup
Assistant search, you can create directory hierarchies that will let users
“Configuring Directory Hierarchies” section on
“Setting Up Systemwide Rules” section on
“Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice
16. If you are using Octel voice messaging, configure the integration with the messaging system to allow
Personal
Personal Assistant with an Octel Voice Messaging System” section on page 4-23.
17. If you are using Exchange 5.5, configure the integration with Exchange to allow Personal Assistant
to send e-mail for refresh notification, PIN changes, and paging. See the
Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5” section on page 4-24.
Assistant to distinguish between internal and external Octel numbers. See the “Integrating
“Integrating
Logging On to and Out of the Personal Assistant Administration
Interface
You must log on to the Personal Assistant Administration interface to view or change the
Personal
accounts. You must use an account with administrative privileges on the Windows
the administration interface in order to change the Personal
To Log On to and Out of the Personal Assistant Administration Interface
Step 1 From a supported web browser window, open the Personal Assistant Administrator page by using the
format http://<PA host>/pasystemadmin, where PA
administration interface.
For example, if you installed the administration interface on a server named paserver, the URL would be
http://paserver/pasystemadmin.
The Log on screen displays.
Step 2 Enter a Windows 2000 local user name that has administrator authority, and its password. The user name
must be defined on the system that is running the administrator interface.
Assistant configuration. Personal Assistant manages logons based on Windows 2000 local user
2000 system running
Assistant configuration.
host is the server on which you installed the
OL-4590-03
Step 3 Click Login. Personal Assistant logs you on to the system, and you can access the various configuration
pages.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-3
Page 66

Configuring Speech Recognition
Step 4 Click Session > Logout in the menu bar to log out of the system when you are finished configuring
Personal
Assistant.
The system automatically logs you out after 30 minutes of inactivity.
Configuring Speech Recognition
You must configure speech services to create speech server clusters. This allows users to talk to
Personal
See the
recognition with Personal Assistant, you can skip this configuration.
You can also fine-tune speech recognition if users are having problems with the speech recognition
interface. See the
address include:
• Users being asked too often to confirm their commands.
• Users being transferred to the operator too often because:
Assistant over the phone, for example, dialing parties by name rather than by phone number.
“To Configure Speech Recognition” procedure on page 4-4. If you are not using speech
“To Fine-Tune Speech Recognition” procedure on page 4-5. Problems that you can
–
There are a large number of similarly named people in your corporate directory.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
–
Errors occur in Personal Assistant understanding spoken commands.
–
Users ask for help from Personal Assistant too often during a session.
Make sure you have the license document included in the Personal Assistant package.
Personal Assistant uses defaults for all speech recognition parameters, and these should work well with
most installations. Before fine-tuning the speech recognition parameters, confirm that any reported
problems are widespread. If changes are necessary, trial and error is the only way to determine effective
settings for these parameters for your specific needs.
To Configure Speech Recognition
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Speech Services. The Speech Services
Configuration page opens.
Step 2 If you want Personal Assistant to automatically refresh cached user information from the corporate
directory on a daily schedule, check the Daily Automatic Refresh check box, and set the time by using
the Refresh Schedule hour and minute lists. This ensures that the corporate directory information stays
up-to-date, and that the speech recognition software has the data required to understand spoken
commands.
Note Depending on the size of your corporate directory, the number of locales installed, and the
number of directory hierarchies configured, it can take a significant amount of time to fetch this
information, compile it, and publish it to the speech servers. Pick a time when directory updates
are complete for the day, and there is reduced user access to Personal Assistant and the directory.
4-4
Step 3 If you want Personal Assistant to send you the refresh status by e-mail when a refresh has completed,
check the Send Refresh Status check box, and enter your e-mail address in the Administrator E-mail
Address field.
Step 4 In the License Key field, enter your speech recognition license key.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 67

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
After clicking Save, Personal Assistant displays the number of licenses, which is the maximum number
of simultaneous speech ports and locales available when using this license key.
Step 5 Create the speech server cluster by doing the following substeps:
a. For each speech server, in the Speech Recognition Server Hosts field, enter the server IP address or
DNS name, and click Add. Note that the speech servers are not activated until the next refresh.
b. Identify one or two Personal Assistant servers that should be used as the license manager hosts. All
Personal
actively used for distributing licenses.
c. In the Speech Recognition License Manager Hosts field, enter the IP address or DNS name of the
Personal
servers, so that there is a backup license manager. Speech recognition works when there is at least
one active license manager.
Step 6 From the Available Locales list, select the locales you want to support, and click >>. You can select
multiple locales by using Ctrl-Click or Shift-click. Personal
locale only if your license key allows it.
Step 7 From the Default Locale list, select the language Personal Assistant will initially use in the
speech-recognition interface and on the user web interface.
Note that if you do not set a default locale, users will not have speech recognition and will be unable to
access the user web interface.
Configuring Speech Recognition
Assistant servers include license managers, but you must identify which ones will be
Assistant server you want to use, and click Add. Cisco recommends that you identify two
Assistant allows you to add more than one
Note Users can later select a different locale for their use by using the user web interface.
Personal
Assistant uses the locale the user selects once it identifies who is calling or who is
logging on to the user web interface.
Step 8 Click Save to save and activate your changes.
Tip Select System > Miscellaneous Settings and enter the operator extension so that users are transferred to
the operator if they encounter too many speech recognition problems.
To Fine-Tune Speech Recognition
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Speech Services. The Speech Services
Configuration page opens.
Step 2 If you are trying to resolve problems in which users are being transferred to the operator too quickly, you
can make any of the following changes:
• If users are being transferred to the operator because there are many similarly named people in your
phone directory, change the Maximum Number for Disambiguation parameter.
The Maximum Number for Disambiguation setting determines the number of options (people,
numbers, and so on) a user can select from when trying to call a person with a common name, such
as John Smith. By increasing this number, Personal
Assistant presents additional selections and
reduces transfers to the operator.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-5
Page 68

Configuring Speech Recognition
If Maximum Number for Disambiguation is set to “3,” a user will be presented with up to three
selections if there are multiple people with the requested name. Therefore, if three people in your
company share the name “John Smith,” Personal
for each of the three, allowing users to select the applicable John Smith. If there are more than three
people with the name John Smith, the user is transferred to the operator.
• If Personal Assistant is being interrupted too often and fails to provide users with the applicable
prompts, uncheck the Allow Barge-In check box.
Barge-In allows a user to interrupt Personal Assistant and issue a command in the middle of a
prompt. However, in situations with excessive background noise, Personal
accepting the noise as valid interruptions.
• If users are being transferred to the operator because they are encountering speech-recognition
errors, increase the number of errors allowed. When the Max Error Count per Dialog is reached
during a dialog, or the Max Error Count per Call is reached during an entire session, the user is
transferred to the operator. However, if you set the values too high, users can become frustrated
while using Personal
• If users are being transferred to the operator because they are requesting help too often, you can
increase the number of times they are allowed to request help. When the Max Help Count per Dialog
is reached during a dialog, or the Max Help Count per Call is reached during an entire
Personal
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Assistant plays the recorded name and extension
Assistant might be
Assistant.
Assistant session, the user is transferred to the operator.
Step 3 If you are trying to resolve problems in which users are being asked to confirm their commands too often,
you can change the Rejection Confidence Level and Reconfirm Confidence Level parameters.
The speech-recognition software assigns a percentage confidence level to every recognized utterance.
The default Rejection Confidence Level is 45 percent.
• If the software is less confident that it understood the speaker than the Rejection Confidence Level,
Personal
Assistant tells the user it did not understand the request: “Sorry, I didn’t understand.” The
user can then repeat or rephrase the request.
• If the confidence level is between Rejection Confidence Level and the Reconfirm Confidence Level
percentages, Personal
Assistant tells the speaker its interpretation of the request and asks the
speaker to confirm the interpretation: “John Smith? Is this correct?” The speaker can then say yes
or no. If yes, Personal
Assistant completes the request. If no, the speaker must repeat or rephrase the
request.
• If the confidence level is higher than the Reconfirm Confidence Level, Personal Assistant initiates
the request without asking for confirmation: “Calling John Smith.” The speaker can stop
Personal
Assistant by saying “cancel” or “no.”
If you set Reconfirm Confidence Level too high, users will have to reconfirm most commands. If you set
it too low, Personal
Step 4 Click Save to save and activate your changes.
Step 5 If you are installing or upgrading Personal Assistant, continue to follow the applicable task list.
Assistant might initiate too many unintended tasks.
Otherwise, if you added or removed a speech server or license manager, click Refresh Now to update
the Personal
Assistant configuration and load the new servers with the information required for them to
operate correctly. (Ensure that the refresh is successful by clicking Last Refresh Details when the
refresh is complete. If the refresh is not successful, see the
“Troubleshooting Failed System Refreshes”
section on page 6-11 to resolve the problem before proceeding.)
4-6
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 69

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Configuring Telephony Providers
You must configure the telephony interface between Personal Assistant and the Cisco CallManager
clusters so that Personal
enter here must correspond to the Personal
“Adding Personal Assistant as a JTAPI User” section on page 3-9).
You must create one JTAPI provider and one Skinny provider for every Cisco CallManager cluster in
which Personal
have five Cisco
must define at least ten providers (five JTAPI, five Skinny).
Personal Assistant uses both JTAPI and Skinny protocols, and must have providers for both. JTAPI is
used for interceptor ports and route points; Skinny is used for media ports.
See the “Configuring Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10 for more information on server
configuration.
To Configure Telephony Providers
Assistant servers have their phone numbers and route points defined. For example, if you
CallManager clusters in which Personal Assistant servers have numbers defined, you
Assistant can successfully receive and transfer phone calls. The settings you
Configuring Telephony Providers
Assistant user you created in Cisco CallManager (see the
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Telephony. The Telephony Configuration
page opens.
Step 2 In the Provider Group Name field, enter a meaningful name for the provider group you are adding. When
configuring Personal
field.
Step 3 In the Provider Type field, select the type of telephony service the group is providing.
Step 4 Identify the provider, based on provider type:
• JTAPI—For JTAPI providers, enter the DNS name or IP address of the CTI Manager for the
Cisco
CallManager cluster, and click Add. You can identify more than one CTI Manager, but they
must be in the same cluster. Then, enter the user name and password for the Personal
added to Cisco
Cisco
CallManager.
• Skinny—Enter the DNS name or IP address of the Cisco CallManager server, and click Add. You
can identify more than one server, but they must be in the same cluster. Do not enter a user name
and password for Skinny providers.
Step 5 Click Insert to add the provider to the left-hand list of providers.
Tip To view or modify the configuration for a provider, or to delete it, click the provider name in the left-hand
list. The provider settings are loaded into the page, and you change them if required.
Assistant servers, you will select providers based on the names you enter in this
Assistant user
CallManager. Personal Assistant uses this information to log into
Configuring the Corporate Directory
You must identify the corporate directory so that Personal Assistant can look up information such as
phone numbers and locations for all of the employees in the corporation. Personal
information to find the phone number for an employee when someone tries to phone the employee by
using the employee name.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Assistant uses this
4-7
Page 70

Configuring the Corporate Directory
Before you begin the procedure, you must know some details about the corporate directory. Review the
procedure and contact your directory administrator to obtain any information you do not know.
To Configure the Corporate Directory
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Corporate Directory Settings. The
Corporate Directory Settings page opens.
Step 2 In the Unique User Attribute Name field, enter the unique identifier attribute field used in the corporate
directory.
Personal Assistant uses this attribute to identify each user. For example, even if two users have the same
name (John Smith), they have unique e-mail addresses.
The field that you use depends on your corporate directory. Use the applicable field, as follows:
• For Cisco CallManager DC Directory—enter cn
• For Active Directory—enter sAMAccountName
• For Netscape Directory—enter either cn or uid
For any other directory, ask the directory administrator for the name of the unique field.
Note that the name is case sensitive.
Step 3 In the Directory Server URL field, enter the URL for the corporate directory, including the port number.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
The value that you enter depends on your corporate directory. Use the applicable value, as follows: (Note
that these options use the default port numbers for each type of directory.)
• For Cisco CallManager DC Directory—Enter ldap://<Fully qualified domain name of the corporate
directory server>:8404.
• For Active Directory, single domain—If your users are contained in a single domain, enter
ldap://<Fully qualified domain name of the domain controller>:389.
• For Active Directory, multiple domains—If you have defined users in multiple domains, enter
ldap://<Fully qualified domain name of the Global Catalog server>:3268.
• For Netscape Directory—Enter ldap://<IP address of the Netscape Directory server>:389.
For any other directory, ask the directory administrator for the value to use.
Step 4 If the directory requires authentication for access, enter the administrator name in the Directory Admin
DN field, and enter the password in the Directory Admin Password field.
The value that you enter in the Directory Admin DN field depends on your corporate directory. Use the
applicable value, as follows:
• For Cisco CallManager DC Directory—Enter cn=Directory Manager,o=domain.com.
• For Active Directory—Enter <Active Directory administrator user ID>@<Fully qualified domain
name>.
• For Netscape Directory—Enter cn=Directory Manager.
Note that Directory Manager is the default administrator user ID for Cisco CallManager DC Directory
and for Netscape Directory. If your system uses a different administrator user ID, use the applicable
value.
For any other directory, ask the directory administrator for the value to use.
Step 5 In the Directory Search Base DN for Users field, enter the Distinguished Name (DN) for the user node
of your corporate directory.
4-8
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 71

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
The value that you enter depends on your corporate directory. Use the applicable value, as follows:
• For Cisco CallManager DC Directory—Enter ou=<Root user DC Directory node>,o=<Fully
qualified domain name>. For example: ou=Users,o=Domain.com.
• For Active Directory—Enter a comma-separated list of each component of the distinguished name
for the user node in Active Directory. For example: if the node is
UserNode1.Subdomain1.Domain.com, enter dc=UserNode1,dc=Subdomain1,dc=Domain,dc=com.
• For Netscape Directory—Enter ou=People,o=<Fully qualified domain name>. For example:
ou=People,o=UserNode1.Subdomain1.Domain.com.
For any other directory, ask the directory administrator for the value to use.
Step 6 In the Directory Search Filter field, enter an LDAP expression for restricting the entries retrieved. For
example, you can limit the Personal Assistant directory lookups to a specific location, thus allowing
users to use name dialing for employees only in the selected area. If your directory includes a “location”
field, and “newyork” is a valid location in your directory, a directory search filter for limiting searches
to New York would be “(location=newyork).”
The expression you enter depends on your corporate directory:
• For Cisco CallManager DC Directory—If the user search base is set to the root node or domain,
append !(description=ciscoPABUser) to the Directory Search Filter. For example,
(&(objectclass=person)(!(description=ciscoPABUser))). Otherwise, Personal
unable to distinguish between users in the corporate directory and users in the address book.
Configuring the Corporate Directory
Assistant will be
• For Active Directory—If your message store is Exchange 5.5, enter
(&(objectclass=user)(objectcategory=Person)). Otherwise, enter
(&(objectclass=user)(objectcategory=Person)(legacyExchangeDN=*)).
• For Netscape Directory—Enter (objectClass=person).
Note that the instructions above are valid for the typical configuration. The expression you enter might
need additional search-filter parameters, depending on how your directory is structured. The expression
must be valid for the directory you are using. If you do not know what to enter, refer to the documentation
supplied with the directory, or ask your directory administrator for information on valid LDAP
expressions for your corporate directory.
Step 7 Click Te st to have Personal Assistant validate the search filter.
Step 8 If you are using an LDIF file, check the Use LDIF File check box, and in the LDIF File Location field,
enter the UNC path for the file that you created in the
“Using an LDIF File” section on page 2-7. For
example, enter \\Paserver\ldif\paldifdata.ldif.
Step 9 Click Te st to have Personal Assistant validate the LDIF file.
Step 10 If the system uses Active Directory, and if the LDAP directory has a restriction on the number of results
returned per query, check the Limit Page Size check box, and fill in the Number of Results Per Page.
Otherwise, uncheck the check box.
Consult your LDAP administrator to determine the page size to use.
Step 11 Click Save to save your changes.
If you are installing or upgrading Personal Assistant, continue to follow the applicable task list.
Otherwise, changes to corporate directory settings take effect on the next refresh. If you need the changes
to take effect immediately, go to the Speech Services Configuration page, and click Refresh Now.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-9
Page 72

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration (Personal Assistant Version 1.4(3) or Later)
Specifying the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory
Configuration (Personal
Personal Assistant uses the directory Cisco CallManager is using to maintain system configuration
information such as corporate directory settings and some user information such as call routing rules and
user recorded names. In a typical configuration, Cisco
Directory. When Cisco
publisher server. If Cisco
configuration to have Personal
same cluster if the publisher is unavailable.
Note that because Personal Assistant can only read information from a subscriber server, it cannot
update configuration information unless the publisher is in service.
To specify the Cisco CallManager internal directory configuration, you identify the subscriber servers
in the Cisco
Do the following procedure only if you are using Personal Assistant version 1.4(3) or later and if
Cisco
To Specify the Cisco CallManager Internal Directory Configuration
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Cisco CallManager Directory. The
Cisco
Step 2 In the Cisco CallManager Subscriber Server field, enter the host name or the IP address of the subscriber
server, and click Add.
Personal Assistant adds the server to the list of subscriber servers for the Cisco CallManager cluster.
Step 3 Repeat Step 2 for each subscriber server.
CallManager cluster.
CallManager is using its internal directory.
CallManager Internal Directory Configuration page opens.
Assistant Version 1.4(3) or Later)
CallManager uses its internal directory, DC
CallManager is in a cluster, Personal Assistant maintains information on the
CallManager is using its internal directory, you can specify the directory
Assistant read information from an available subscriber server in the
Step 4 Click Save to save and activate your changes.
Configuring Personal Assistant Servers
You must configure each Personal Assistant server to define its operating characteristics and to add it to
the server cluster.
To Configure Personal Assistant Servers
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select Servers > Server Configuration. The Server
Configuration page opens.
This page has two columns:
• The left column lists the Personal Assistant servers you have already added to the Personal Assistant
server cluster. Click a server name to view and change the server properties. The primary
Personal
Assistant server is indicated by a red arrow.
4-10
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 73

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
• The right column contains the settings for the selected server. When you initially open the page, this
column is empty of settings, so that you can add a new Personal
to add a new Personal
before entering settings.
Step 2 Enter settings for a new server, or change the existing settings, as applicable. See the “Server
Configuration” section on page A-16 for explanations of each setting. At a minimum, you must
configure the following settings to enable a fully-functional server:
• Server Name—A unique name for the server. This is not the same as the DNS name or IP address
of the server. Instead, it is a name used internally by Personal
convention that is meaningful to you.
• Hostname or IP Address—The DNS name or IP address of the Personal Assistant server.
• Route Address Provider—The telephony provider you created to supply JTAPI services for the route
point. See the
the provider. The provider you select must be in the same Cisco CallManager cluster in which the
route points are defined.
• Route Address—The CTI route point for the Personal Assistant server, as defined in
Cisco
CallManager. This is the phone number users dial to contact Personal Assistant. See the “CTI
Route Points and Media Ports” section on page 1-3 and the “Setting Up Personal Assistant Server
Load Balancing” section on page 1-13 for detailed information on the CTI route address.
• Media Port Provider—The telephony provider you created to supply Skinny services for the media
ports. See the
the provider. The provider you select must be in the same Cisco CallManager cluster in which the
Personal
• Media Port Beginning Address—The start of the range of ports defined in Cisco CallManager that
will be used to terminate calls to Personal
assigned to an available port in this range.
Configuring Personal Assistant Servers
Assistant server. If you later want
Assistant server while viewing the properties of an existing server, click New
Assistant. Choose a naming
“Configuring Telephony Providers” section on page 4-7 for information on creating
“Configuring Telephony Providers” section on page 4-7 for information on creating
Assistant route point is defined.
Assistant. When Personal Assistant answers a call, it is
• Number of Media Ports—The number of ports you want to support on the server. This number
determines how many simultaneous speech-recognition sessions the server can handle. The number
you choose depends on the server platform you are using, and whether you are using failover. See
the
“Creating Server Clusters” section on page 1-10 for information about the maximum ports that
are available for the various hardware platforms and installation configurations.
• Interceptor Port Provider—The telephony provider you created to supply JTAPI services for the
route points used as Personal
Assistant interceptor ports. See the “Configuring Telephony
Providers” section on page 4-7 for information on creating the provider. The provider you select
must be in the same Cisco CallManager cluster in which the route points are defined.
• Interceptor Ports—The phone extensions for which you want this Personal Assistant server to
intercept incoming calls. Personal
the applicable call routing rules. This list is central to the functions of Personal
Personal
Assistant to intercept calls to these extensions requires careful planning and changes to the
extension properties in Cisco
Assistant intercepts calls to these extensions so that it can apply
Assistant; setting up
CallManager.
The extensions you enter must be defined in Cisco CallManager. If you defined route points by using
wildcards, such as 25XX, you can enter them here.
Read the following sections for detailed explanations and examples:
–
Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports and Configuring Error Handling, page 3-4
–
Partitions and Calling Search Spaces, page 1-4
–
Defining Partitions and Call Search Spaces for Personal Assistant, page 1-18
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-11
Page 74

Configuring Messaging
Step 3 Save your changes as applicable:
Tip Do not configure the debug or trace settings unless instructed to by Cisco Technical Support. Debug and
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
–
Adding Personal Assistant Without Previously Defined Partitions, page 1-20
• Failover Server Names—The ordered list of servers that should take over for the server if it becomes
disabled. Using the Personal
number of telephony ports you can define for the servers. See the
on page 1-10 for an explanation of configuring Personal Assistant clusters with and without failover.
• If you are creating a new server, click Insert. Personal Assistant saves the server settings and adds
the new server to the list in the left column.
• If you are updating an existing server, click Save. Personal Assistant saves and activates your
changes.
trace settings can have an adverse effect on server performance, and they generate a large amount of data
that only Cisco can interpret. These features exist so that Cisco can use them to help identify and fix any
problems you encounter with the software. See the
on page 6-15 for more information.
You can remove a server by selecting it in the left column, and then clicking Delete when the server
properties are displayed.
The Personal Assistant server restarts automatically when any changes, except those made to the trace
and debug settings, are saved. To manually start or stop the servers, or to verify that a particular server
is up and running, use the Control Center by selecting System
Stopping the Servers and License Manager” section on page 6-14 for details.
Assistant failover capability requires careful planning, and affects the
“Creating Server Clusters” section
“Collecting Trace and Debug Information” section
> Control Center. See the “Starting and
Configuring Messaging
Personal Assistant can provide e-mail paging, calendar-based call routing services, and direct access to
the voice mail system. Personal
call routing, and if you are using Cisco
you are already using. Personal
their PINs have been changed. You must configure the messaging parameters to enable these services
for your users. If you do not want to enable one or more of these services, leave the settings for the
service blank.
Personal Assistant must have administrator access to Microsoft Exchange to obtain a user calendar
information. This information is used when evaluating call routing rules that include calendar-based
conditions.
You must have the voice mail server set up and configured on a system separate from Personal Assistant.
Personal Assistant must have administrator access to the voice mail system to obtain user mailbox
account information and stored voice mail messages. These voice mail settings are also used to redirect
calls to user voice mail without ringing the user phone, based on the user rules that include voice mail
as a destination.
If you are using Cisco Unity, and you do not know the Cisco Unity mailbox name, do the following two
procedures in the order listed. Otherwise, skip to the
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-12
Assistant integrates with Microsoft Exchange to provide calendar-based
Unity, Personal Assistant can integrate with the Exchange server
Assistant can also automatically send e-mail notification to users when
“To Configure Messaging” procedure on page 4-13.
OL-4590-03
Page 75

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
To Identify the Cisco Unity System Mailbox Name
Step 1 On the Cisco Unity server, on the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Microsoft Exchange >
System Manager.
Step 2 Expand Servers.
Step 3 Expand <Cisco Unity Partner Exchange Server Name>.
Step 4 Expand First Storage Group.
Step 5 Expand Mailbox Store.
Step 6 Click Mailboxes.
Step 7 From the list of mailboxes in the right pane, identify the Cisco Unity mailbox.
The name is typically either Unity Messaging or Unity Messaging System <Server Name>. If you
cannot identify the mailbox, see your Cisco
To Configure Messaging
Configuring Messaging
Unity administrator.
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Messaging. The Messaging Configuration
page opens.
Step 2 To enable calendar-based call routing rule services, do the following substeps:
a. In the Calendar Server Name field, enter the Exchange server name. (You can use a DNS name or
an IP address.)
b. In the Calendar Mailbox Name field, enter the first and last name of the Exchange administrator
account. See the
“Messaging Configuration” section on page A-10 for detailed information on the
account name you must enter.
Step 3 To enable e-mail paging, do the following substeps:
a. In the Paging SMTP Server Name field, enter the DNS name or IP address of your e-mail paging
server.
b. In the Paging SMTP Server Port field, enter the SMTP port used to send messages to the SMTP
server.
c. In the Paging SMTP Domain Name field, enter the domain in which the paging SMTP server
belongs.
Step 4 To allow users to access their voice mail through Personal Assistant, or to create call routing rules that
send incoming calls directly to voice mail, identify the voice mail servers to Personal
Assistant by doing
the following substeps, as applicable:
a. If you are using Cisco Unity, enter the mailbox name for the Cisco Unity system profile in the
Mailbox Name field, and enter the number of ports allowed by your license in the Number of
Cisco
Unity Licenses field. Use the name that you identified in the “To Identify the Cisco Unity
System Mailbox Name” procedure on page 4-13. The number of ports determines the allowed
number of simultaneous voice mail sessions. These fields are optional for other voice mail systems.
b. In the Redirection Delay field, enter the time in milliseconds to delay transferring the call to the
desired voice mailbox after a call is transferred to the voice mail system. This delay ensures that a
call connects to the voice mail system before Personal
Assistant enters the DTMF sequence to
redirect the call to the desired mailbox.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-13
Page 76

Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech
We recommend that you use 2000 milliseconds for a Cisco Unity system, and 4000 milliseconds for
other systems, such as Octel.
c. Add each voice mail server to the list of servers by entering the Voice Mail Server Name (for
example, unity1), the Pilot Number (the phone number used to reach voice mail), and the internal
and external DTMF Redirection Sequences required to direct a call to a specific voice mailbox.
Click Add Server after entering the information.
The voice mail server name is required only for Cisco Unity voice mail systems. The name must be
an unqualified DNS name, for example, unity1 rather than unity1.cisco.com. Do not use IP
addresses. See the
these fields.
Step 5 If you configure the system to use the Cisco CallManager PIN, and if you want Personal Assistant to
automatically send e-mail notification to users when their PINs are changed, check the Notify Users of
PIN Change check box, and enter your corporate e-mail address in the Administrator E-mail Address
field. (Personal
Note that Personal Assistant does not send e-mail notification if the system is configured to use the
Cisco
Unity subscriber phone password as the Personal Assistant PIN.
Step 6 If you are using Cisco Unity, select a field from the Unique Attribute for Corporate Directory list and a
field from the Unique Attribute for Message Store list whose entries are likely to match. For example,
select cn for the corporate directory field and sAMAccountName for the message store field. The fields
are used to integrate Cisco
subscribers can browse voice mail.
To validate your choice of attributes, click Test Attributes, enter a value on which to search, and click
Test Va lu e .
Step 7 If you are using Cisco Unity, and you want Personal Assistant to use the name the user already recorded
in the Cisco
Names. Personal
Personal
Assistant loads only subscriber names recorded in CCITT Mu-Law format (G.711 Mu-Law).
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
“Messaging Configuration” section on page A-10 for more information about
Assistant uses this e-mail address as the return address for the message.)
Unity with Personal Assistant so that users who are also Cisco Unity
Unity voice mail system as the Personal Assistant user spoken name, click Load Recorded
Assistant plays this name to callers when they try to call the user. Note that
Step 8 Click Save to save and activate your changes.
Configuring Enhanced Text to Speech
If you installed the enhanced Text to Speech server, you must configure Personal Assistant to use it.
Otherwise, Personal
To Configure Enhanced Text To Speech
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Enhanced TTS. The Enhanced TTS
Configuration page opens.
Step 2 In the TTS Server Name field, enter the name or IP address of the enhanced Text to Speech server.
Step 3 In the TTS Port Number field, enter the TTS Port Number you specified when you installed the enhanced
Text to Speech server.
Step 4 In the TTS License Key field, enter the license key for the enhanced Text to Speech feature.
Step 5 Click Save to save and activate your changes.
The Number of Licenses shows the number of ports available for your TTS license key.
Assistant uses the default Text to Speech server.
4-14
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 77

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Step 6 Click Te st to validate the configuration.
Note that while the Personal Assistant server and the TTS server are not required to be in the same
domain, the test cannot display configuration information if they are in different domains.
Creating a Simple Automated Attendant
You can use Personal Assistant as an automated attendant to provide callers who are not
Personal
without knowing their extensions, and without involving a live operator.
When someone calls the automated attendant number, Personal Assistant plays a welcome prompt you
supply, and then presents the caller with the dial-by-name speech interface, including spoken Help. This
is the same interface your regular Personal
other than dial-by-name.
If a caller enters a number on the keypad, Personal Assistant verifies that a user is associated with the
number in the corporate directory before transferring the caller. Callers to the automated attendant can
reach only those phone numbers that are associated with a person in the corporate directory.
If you support multiple locales, you can set up the automated attendant so that callers can select the
language they are most comfortable with. Personal
your default locale. Your prompt should direct callers to press 8 if they want to change languages. You
might want to include multiple languages in your default locale prompt to assist callers who do not know
your default language. For example, if your default locale is American English, but you are supporting
Canadian French callers, your English prompt might include a short statement in French instructing the
French speaker to press 8 and select French.
Assistant users with the ability to dial users by name. This allows callers to contact users
Assistant users can use, but it does not include any features
Assistant initially plays the prompt associated with
Creating a Simple Automated Attendant
To Create an Automated Attendant
Step 1 Create a route point for the automated attendant in Cisco CallManager. This is the phone number people
will use to connect to the automated attendant.
Step 2 Record a welcome prompt for the automated attendant. The file must be a WAV file in CCITT Mu-Law
format (G.711 Mu-Law). You can use any recording software that will save a file in this format.
Personal
Step 3 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > AA Prompt.
Step 4 Enter the path of the prompt file you created in Step 2, or browse to the location to which you saved the
Assistant does not include a recorder.
file, and click Update.
Note that if you support multiple locales, you can have separate prompts for each locale. For each locale,
enter the applicable prompt file path, and click Update.
To verify that the correct prompt file is loaded, click the locale. To restore the default prompt, click
Restore. (The Restore button is not displayed when the default prompt is used.)
Step 5 Select Servers > Server Configuration, and from the left-hand column list of servers, select the
Personal
new Personal
Step 6 In the AA Route Address field, enter the route point that you created in Step 1.
Assistant server that you want to manage the automated attendant. (Alternatively, configure a
Assistant server for the automated attendant to use.)
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-15
Page 78

Creating Dialing Rules
Step 7 Click Save. The automated attendant is now operational.
Creating Dialing Rules
You can create global dialing rules to automatically modify outgoing phone numbers. These changes
only affect the user when he or she uses Personal
outside of Personal
rules will not be applied. The user must be connected to Personal
through Personal
Global dialing rules are applied before any dialing rules that users create for Personal Assistant.
Rules can distinguish between phone numbers based on the initial string of digits in the number, on the
length of the number, or both. Rules can remove numbers from the front of the dialed number, add
numbers to the front, or both.
For example, you can create a rule that if the number of digits of the phone number is 7, then prefix the
number with 9. This rule then automatically enters a 9 when dialing an outside number.
Assistant. For example, if a user simply picks up the phone and dials a number, these
Assistant for the rules to be applied.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Assistant; they do not apply to the telephony system
Assistant and dialing the number
To Configure Dialing Rules
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Dial Rules. The Dial Rules Configuration
page opens.
The page is divided into two sections:
• Add Rule—This section contains fields and the Add Rule button.
• List of Dial Rules—This is a list of rules, in order of priority. Rules are applied from top to bottom.
If a phone number satisfies the conditions of a rule, the rule is applied and no subsequent rules are
considered.
Step 2 Enter information in the fields in the Add Rule section to create the desired dialing rule. Each field is
optional, but you must at least fill in either the Number of Prefix Digits to Remove field or the New
Prefix field in order for the rule to be applied.
• Phone Number Prefix—Enter one or more digits at the beginning of the number the user dials. The
distinguishing string of digits can be as many digits as the number itself.
• Number of Digits—Enter the total number of digits in the phone number the user dials. Do not count
hyphens or spaces.
• Number of Prefix Digits to Remove—Enter the number of digits that Personal Assistant will delete
from the front of the dialed number. For example, if you enter 4, and the dialed number is
1-500-555-6262, Personal
• New Prefix—Enter the string of digits that Personal Assistant will add to the front of the dialed
Assistant removes 1500, and leaves 555-6262.
number, after removing the specified number of digits. For example, you might need to add a prefix
of 9 in order to dial an external number.
• Priority (Personal Assistant version 1.4(5) and later only)—Enter the position for the rule in the list
of rules. If you do not specify a priority, the rule will be placed at the bottom of the list.
4-16
Step 3 Click Add Rule. Personal Assistant adds the rule to the list of rules.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 79

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Tip To change a rule, find it in the list of rules, modify the properties as desired, and click Update on the line
with the rule.
To change the priority of a rule, use the up and down arrows until the rule is correctly positioned. For
Personal
Assistant version 1.4(5) and later, you can also enter the applicable value in the New Priority
field, and click Update on the line with the rule.
To delete a rule, find it in the list of rules, and click the Delete icon on the same line as the rule.
Configuring Directory Lookup Rules
You can create directory lookup rules to automatically modify incoming internal phone numbers so that
the user information associated with the number can be found in the corporate directory.
For example, if you use 5-digit numbers to call within your phone network, but the corporate directory
uses 7- or 10-digit number versions of the 5-digit numbers, Personal
a 5-digit number to the caller. By creating directory lookup rules, you can convert the 5-digit number to
the type of number used in the directory, so that Personal
the number.
Directory lookup rules do not modify the number that is dialed. These rules only convert the number to
something that can be found in the corporate directory for information lookup purposes.
Rules can distinguish between phone numbers based on the initial string of digits, on the length of the
number, or both. They can remove numbers from the front of the dialed number, add numbers to the
front, or both.
Configuring Directory Lookup Rules
Assistant will be unable to match
Assistant can find the caller associated with
To Configure Directory Lookup Rules
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Directory Lookup Rules. The Directory
Lookup Rules page opens.
The page is divided into two sections:
• Add Rule—This section contains a fill-in-the-blank sentence and the Add Rule button.
• List of Directory Lookup Rules—This is a list of your rules, in order of priority. Rules are applied
from top to bottom. If a number satisfies the conditions of a rule, the rule is applied and no
subsequent rules are considered.
Step 2 Enter information in the fields in the Add Rule section to create the desired directory lookup rule. Each
field is optional, but you must at least fill in either the Number of Prefix Digits to Remove field or the
New Prefix field in order for the rule to be applied.
• Phone Number Prefix—Enter one or more digits at the beginning of the number the user dials. The
distinguishing string of digits can be as many digits as the number itself.
• Total Number of Digits—Enter the total number of digits in the phone number the user dials. Do not
count hyphens or spaces.
• Number of Prefix Digits to Remove—Enter the number of digits that Personal Assistant will delete
from the front of the dialed number. For example, if you enter 4, and the dialed number is
1-500-555-6262, Personal
Assistant removes 1500, and leaves 555-6262.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-17
Page 80

Configuring Directory Hierarchies
• New Prefix—Enter the string of digits that Personal Assistant will add to the front of the dialed
number, after removing the specified number of digits. For example, you can add an area code and
initial digits to a 5-digit extension, turning 56565 into 5555556565. Personal
resulting number to look up the calling party in the corporate directory.
• Priority (Personal Assistant version 1.4(5) and later only)—Enter the position for the rule in the list
of rules. If you do not specify a priority, the rule will be placed at the bottom of the list.
Step 3 Click Add Rule. Personal Assistant adds the rule to the list of rules.
Tip To change a rule, find it in the list of rules, modify the properties as desired, and click Update on the line
with the rule.
To change the priority of a rule, use the up and down arrows until the rule is correctly positioned. For
Personal
field, and click Update on the line with the rule.
To delete a rule, find it in the list of rules, and click the Delete icon on the same line as the rule.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Assistant uses the
Assistant version 1.4(5) and later, you can also enter the applicable value in the New Priority
Configuring Directory Hierarchies
A directory hierarchy is a set of groupings of directory entries. These groupings can make directory
searches more accurate and manageable for callers who are trying to dial a party by name rather than by
phone number. For example, a caller can narrow a search by first stating the location or department in
which to search. Locations and departments are the types of directory hierarchy groups you can define.
Create directory hierarchies if callers are having problems with speech recognition due to the large
number of similarly-named people in the corporate directory.
Changes to the directory hierarchy configuration take effect the next time the system refreshes.
To Configure Directory Hierarchies
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select System > Directory Hierarchy. The Directory
Hierarchy Configuration page opens.
This page includes a list of the nodes in the hierarchy that already exist at the bottom of the page.
To see the nodes for each type of hierarchy, select the type of hierarchy (Location or Department) in the
Hierarchy Type field.
Step 2 In the Hierarchy Type field, select the type of node you want to create. The type you select will determine
how callers can select the group. For example, if you create a location, callers can select it by saying
“Location” while talking to Personal
Step 3 In the Name field, enter a meaningful name for the group.
Assistant on the phone.
4-18
Step 4 In the Primary Spoken Name field, enter the primary name that callers will use to select the group. This
can be the same name used in the Name field.
Step 5 In the Alternate Spoken Name field, enter any aliases for the primary spoken name, clicking Add after
entering each alias. Adding aliases allows callers to select the group by different names. For example, if
the primary name is NewYorkCity, likely aliases might be NYC, NewYork, BigApple, and so forth.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 81

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Step 6 In the LDAP Search Filter field, enter the LDAP search filter that defines the group. You must know the
correct LDAP expression used by your corporate directory, and the specific names of the fields in your
directory, to create a valid filter. If you are using an LDIF file, Personal
with information from the file, to create the hierarchies.
To see if the expression is valid and returns the entries that you expect, click Tes t Fil t er.
Step 7 Click Save. Personal Assistant adds the node to the list of nodes.
Tip To change a node, click it in the list of nodes. Personal Assistant opens the Update Hierarchy Node page,
where you can change certain node characteristics. You cannot change the hierarchy type. To change the
hierarchy type, you must create a new node of the desired type.
The list of nodes includes a count of the number of entries in the corporate directory that match the node
filter. This number is determined when Personal Assistant refreshes directory information.
Setting Up Systemwide Rules
Assistant uses this filter, along
Setting Up Systemwide Rules
You can set up rules to apply to all calls that come through the Personal Assistant system. For example,
you might want to send all calls to user voice mailboxes after regular work hours.
To set up systemwide rules, you create and activate systemwide rule sets, and turn on systemwide rule
processing. Turning on systemwide rule processing involves setting the conditions under which
Personal
For example, you can create and activate a systemwide rule set with a single rule to direct calls to voice
mail. You set the systemwide rule processing condition to “Apply System Rules When No User Rule is
Applicable.” A user activates a rule set with the single rule, for example to forward calls from the
extension 1234 to a mobile phone number. When a call comes in for that user from extension 1234,
Personal
from any other extension, Personal
systemwide rule to forward the call to the user voice mailbox.
Creating and Activating Systemwide Rules
To create and activate systemwide rules, you set up destinations and destination groups, callers and caller
groups, a personal address book, and rules and rule sets, in much the same way a user would.
However, when creating systemwide rules, in addition to regular destinations, you can select from one
of five virtual destinations—User Work Phone, User Home Phone, User Mobile Phone, User Pager, User
Voice Mail—that map to actual user destination values when a rule is applied.
You can also use the call-forwarding rule tester to see how Personal Assistant would forward an
incoming call based on your systemwide rules. Note that the call-forwarding rule tester for systemwide
rules always assumes that the option Always Apply System Rules is selected.
Assistant applies active rules to incoming calls.
Assistant determines that the user rule applies, and applies it. When a call comes in for that user
Assistant determines that the user rule does not apply and uses the
OL-4590-03
For example, you can create the rule “Direct the call to destination User Voice Mail and do not screen
the call.” When Personal
number, and routes the call there.
Assistant intercepts a call, it searches the directory for the user voice mail
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-19
Page 82

Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice Messaging System
To Create and Activate Systemwide Rules
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select Systemwide Rules > Systemwide Rules. The
Systemwide Rule Sets page opens.
Step 2 Use the systemwide rule sets pages to create and activate systemwide rule sets.
Refer to the Cisco Personal Assistant User Guide for instructions on how to set up destinations and
destination groups, callers and caller groups, a personal address book, and rules and rule sets.
Note To return to the main configuration page of the Personal Assistant Administration interface from
the Systemwide Rule Sets page, click System Configuration
Configuration.
Turning on Systemwide Rule Processing
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
> Return to System
Turning on systemwide rule processing involves setting the conditions under which Personal Assistant
applies active rules to incoming calls.
To Turn on Systemwide Rule Processing
Step 1 In the Personal Assistant Administration, select Systemwide Rules > Systemwide Rule Options. The
System Rule Options page opens.
Step 2 Select one of the following options:
• Never Apply System Rules—Use only user rules and turn off systemwide rule processing.
• Always Apply System Rules (Ignore User Rules)—Use only systemwide rules and turn off user rule
processing.
• Apply System Rules When No User Rule is Applicable—Process calls by using the active user rules
first. If no user rule applies, use the systemwide rules.
• Apply User Rules When No System Rule is Applicable—Process calls by using the active
systemwide rules first. If no systemwide rule applies, use the user rules.
Use caution when setting the Always Apply System Rules and Apply User Rules When No System Rule
Is Applicable options. The systemwide rules will take precedence over user rules.
Step 3 Click Save.
Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice
Messaging System
When Personal Assistant is integrated with a Cisco Unity voice messaging system, Personal Assistant
users can use speech or touch-tone key pad commands over the phone to navigate through the
Cisco
Unity voice mail system.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-20
OL-4590-03
Page 83

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Do the following six procedures, in the order given, to configure and test the integration.
To Add the Personal Assistant Server to the Domain of the Cisco Unity Server
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Settings > Control Panel > System.
Step 2 Click the Network Identification tab.
Step 3 Click Properties.
Step 4 In the Identification Changes dialog box, click Domain, and enter the name of the domain to which the
Cisco
Unity server belongs. (For example, “Unified.cisco.com.”)
Step 5 Click OK.
Step 6 In the Domain Username and Password dialog box, enter the name and password of an account that has
permission to add computers to the domain.
Step 7 Click OK three times.
Step 8 Click Ye s to restart the server.
Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice Messaging System
You must configure two Personal Assistant services— PAServer and PAWebAdmin—to log on as an
account with domain administrator privileges for the Cisco
Unity domain.
To Configure Two Personal Assistant Services to Log on with Cisco Unity Domain Administrator Privileges
Step 1 On the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Administrative Tools > Services.
Step 2 In the right pane, double-click PAServe r.
Step 3 Click the Log On tab.
Step 4 Click This Account.
Step 5 Click Browse.
Step 6 In the Select User dialog box, in the Look In list, click the name of the domain to which the Cisco Unity
server belongs.
Step 7 Double-click the name of an account with Cisco Unity domain administrator privileges.
Step 8 Enter and confirm the password.
Step 9 Click Apply.
Step 10 Click the General tab.
Step 11 Click Stop.
Step 12 Click Start.
Step 13 Click OK.
OL-4590-03
Step 14 Repeat Step 2 through Step 13 with the PAWebAdmin service.
Step 15 When you are done setting the accounts, close the Services window.
If the Cisco Unity message store is Exchange 5.5, skip to the “To Add the Outlook Path to the System
Path Variable” procedure on page 4-22.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-21
Page 84

Integrating Personal Assistant with a Cisco Unity Voice Messaging System
If the Cisco Unity message store is Exchange 2003 or Exchange 2000, do the following procedure to
enable the Exchange administrator to access all of the Exchange user mailboxes. Otherwise,
Personal
Assistant will not be able to access the Exchange user mailboxes.
To Grant Send-As and Receive-As Permissions to the Account That the Personal Assistant Services Log On As
Step 1 On the Cisco Unity Server, click Start > Programs > Microsoft Exchange > System Manager.
Step 2 Expand Servers.
Step 3 Right-click <Cisco Unity Server Name>, and click Properties.
Step 4 Click the Security tab.
Step 5 Click <Administrator User Name> in the list.
Step 6 If the Allow Inheritable Permissions from Parent check box is not in the Permissions list (the
administrator user does not have inherited permissions), skip to
list, uncheck the Allow Inheritable Permissions from Parent check box. The Security window opens.
Step 7 In the Security window, click Copy.
Step 8 In the Permissions list, check the Receive As and Send As check boxes.
Step 9 Click Advanced.
Step 10 At the top of the Access Control window, click Deny Permissions, and click Remove.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Step 8. Otherwise, in the Permissions
Step 11 Repeat Step 10 for the other three deny statements.
Step 12 Click OK twice.
If you are using Personal Assistant version 1.4(3) or later, skip to the “To Ensure That the
Personal Assistant Server Can Connect to the Cisco Unity Server by Using the DNS Name” procedure
on page 4-23.
If you are using Personal Assistant version 1.4(2) or earlier, do the following procedure. Otherwise,
Personal
Assistant will not be able to use the Mail control panel.
To Add the Outlook Path to the System Path Variable
Step 1 On the Personal Assistant server, log on to Windows by using an account that is a member of the Local
Administrators group.
Step 2 Right-click My Computer, and click Properties.
Step 3 Click the Advanced tab.
Step 4 Click Environment Variables.
Step 5 Under System Variables, click Path.
Step 6 Click Edit.
Step 7 Append ;%PAROOT%\bin\outlook to the end of the entry in the Variable Value field.
Step 8 Click OK three times.
4-22
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 85

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
The Personal Assistant server must be able to connect to the Cisco Unity server by using the DNS name
<Cisco
Unity server name>.<Cisco Unity domain name>.cisco.com. To enable the Personal Assistant
server to resolve the Cisco
Cisco
Unity server to the Personal Assistant server hosts file.
To Ensure That the Personal Assistant Server Can Connect to the Cisco Unity Server by Using the DNS Name
Step 1 On the Personal Assistant server, open a command window, enter ping <Cisco Unity Server
Name>.<Cisco
Step 2 If the connection is successful, skip to the following “To Test the Integration with Cisco Unity”
procedure. Otherwise, continue with Step 3.
Step 3 Browse to the directory C:\Winnt\System32\Drivers\Etc, and open the hosts file in Notepad.
Step 4 Add an entry in the following format:
<Cisco Unity Server IP Address> <Cisco Unity Server Name>.<Cisco Unity Domain
Name>.cisco.com.
For example: 172.16.10.1 mlewando.unified.cisco.com
Note that there is a space between the IP address and the DNS name.
Integrating Personal Assistant with an Octel Voice Messaging System
Unity server name, you might need to add the name and IP address of the
Unity Domain Name>.cisco.com, and press Enter.
Step 5 Save and close the file.
Step 6 Open a command window, enter ping <Cisco Unity Server Name>.<Cisco Unity Domain
Name>.cisco.com, and press Enter to verify that the Cisco
name you entered in
To Test the Integration with Cisco Unity
Step 1 Call the Personal Assistant number from any user extension.
Step 2 Say “voice mail.”
Step 3 When you access Cisco Unity voice mail for the first time, a Personal Assistant profile in Exchange is
automatically created and you are transferred to the Cisco
Cisco
Unity, continue to follow the tasks in the “Personal Assistant Configuration Task List” section on
page 4-1. If your call is not transferred to Cisco Unity, continue with Step 4.
Step 4 If your call is not transferred to Cisco Unity, the Personal Assistant profile in Exchange may not have
been created correctly. To verify whether the profile was created and to manually create it if necessary,
see the
Step 5 Repeat Step 1 through Step 3.
“Users Cannot Log On to Cisco Unity Voice Mail” section on page 6-7.
Step 4.
Unity server can by accessed by using the
Unity number. If your call is transferred to
Integrating Personal Assistant with an Octel Voice Messaging
System
When Personal Assistant is integrated with Octel voice messaging systems, Personal Assistant allows
users to forward incoming calls to their Octel mailboxes by using rules. Personal
which calls Octel would treat as internal calls (calls from callers who have an Octel mailbox on the same
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Assistant distinguishes
4-23
Page 86

Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5
Octel system as the people who are being called), and which calls Octel would treat as external calls
(calls from callers who do not have Octel mailboxes). Based on this determination, Personal
sends the applicable DTMF redirection sequence to the Octel server when forwarding the call.
By default, Personal Assistant uses the following heuristics to determine if an incoming call is internal
or external to the Octel system.
Personal Assistant identifies both the user who made the call and the called user, and then looks up their
mailbox and pilot# information in Personal
A call is considered internal to Octel only if all of the following conditions are true:
• The caller ID is known.
• The caller and called numbers map to Octel mailboxes on the same Octel server.
• The caller ID length does not exceed 7 digits.
Instead of having Personal Assistant use heuristics, you can explicitly define which extensions are
internal to Octel by using the MailboxInfo.properties file. The MailboxInfo.properties file is in the
Program Files\Cisco Systems\Personal Assistant\Etc directory.
A Sample MailboxInfo.properties File
# MailboxInfo.properties
# Contains information about valid Octel mailbox numbers.
# Comment lines begin with '#'.
#
# Patterns may include digits 0-9, 'X' to match any digit, or a range, as in “[2-4]”.
# Mailbox mask may include digits and 'X' only and will
# be used along with calling number to find the mailbox number.
#
# Format
# include : number-pattern to include : voicemail-pilot # : mailbox-mask
# exclude : number pattern to exclude
#
include : 251XX : 28000 : XXXXX
exclude : 2512[3-8]
exclude : 25130
The sample MailboxInfo.properties file shows that all 5-digit phone extensions starting with 251
(matching 251XX) have a matching Octel mailbox (mask XXXXX) on an Octel server with pilot number
28000, except for extensions 25123 to 25128 and extension 25130.
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Assistant
Assistant settings.
Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5
If you are using Exchange 5.5, add the internet mail service connector on the Exchange 5.5 server.
Otherwise, Personal
paging.
To Add the Internet Mail Service Connector
Step 1 On the Exchange server, on the Windows Start menu, click Programs > Microsoft Exchange >
Microsoft Exchange Administrator.
Step 2 In the left pane, expand <Organization>.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-24
Assistant will be unable to send e-mail for refresh notification, PIN changes, and
OL-4590-03
Page 87

Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
Step 3 Expand <Site>.
Step 4 Expand Configurations.
Step 5 Click Connections.
Step 6 Click File > New Other > Internet Mail Service.
Step 7 In the Internet Mail Wizard window, click Next.
Step 8 Click Next.
Step 9 In the list, click the name of the Exchange server.
Step 10 Click Next.
Step 11 Click No, and click Next.
Step 12 Click Use DNS to Send Mail, and click Next.
Step 13 Click All Internet Mail Addresses, and click Next.
Step 14 Enter @<Fully qualified domain name of the site>, and click Next.
Step 15 Click Create/Use the Mailbox Called Administrator, and click Next.
Step 16 Enter the password for the service account, and click Next.
Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5
Step 17 Click Finish.
Step 18 Click OK to close the status message boxes, if applicable.
Step 19 Close Exchange Administrator.
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
4-25
Page 88

Integrating Personal Assistant with Exchange 5.5
Chapter 4 Configuring Personal Assistant
4-26
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 89

CHA P TER
5
Preparing Users for Personal Assistant
There are some configuration changes that you can make that affect how users use Personal Assistant.
You should communicate these changes if you make them.
In general, you might find deployment of Personal Assistant to be easier if you link the user interface to
your corporate intranet in a location that can be easily found. This will relieve your users of having to
find the URL some other way, making it easy for them to access Personal
bookmark it for subsequent use. A corporate web page is also a good place to list the phone numbers that
users should use to access Personal
The following sections can assist you in determining what information to communicate with your users
to prepare them to use Personal
• Accessing the User Interface, page 5-1
• Dialing Personal Assistant, page 5-2
• Obtaining Help, page 5-2
• Managing Users, page 5-2
• How Administrative Changes Affect Users, page 5-3
Assistant through the phone.
Assistant:
Assistant for the first time and
Accessing the User Interface
To enable users to access the Personal Assistant user interface, you must provide them with the URL and
the user name and password.
URL
To access the Personal Assistant user interface, users open a supported web browser and enter the
following URL:
http://<PAhost>/pauseradmin
where PAhost is the computer name of the server on which you install the Personal Assistant web
administration component.
User Name and Password
Users log in to Personal Assistant by using the unique user attribute configured for your system, for
example their e-mail address.
The password is the same password defined for access to the Cisco CallManager user interface. To
change or reset the password, use the Cisco
OL-4590-03
CallManager user interface.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
5-1
Page 90

Dialing Personal Assistant
Dialing Personal Assistant
You need to tell users what number to dial to access Personal Assistant in order to use the dial-by-name
feature, to access their voice mail, or to use other features of the telephony interface. The
Personal
You also need to tell users the PIN to use to access protected features such as call-forwarding rules and
voice mail browsing. By default, Personal
Cisco
Personal
Assistant access number is the extension you configured as the CTI route point.
CallManager. Alternatively, if the system is integrated with Cisco Unity, you can set up
Assistant to use the Cisco Unity subscriber phone password as the PIN.
Obtaining Help
Users can access Help with the Personal Assistant web user interface in any of the following ways:
• From the Help menu:
–
Access Help for the page you are viewing by selecting Help > For This Screen.
–
Access the contents of the Help system by selecting Help > Contents and Index.
Chapter 5 Preparing Users for Personal Assistant
Assistant uses the same PIN established for access to
• To print a copy of the manual associated with the application, or to view or search an Adobe Acrobat
version of the Help system, click the PDF button in the top left corner of the Help system. If you
have Adobe Acrobat Reader installed (either as an independent application or as a plug-in to your
browser), the document opens.
From Acrobat Reader, you can search the entire manual, print the entire manual or selected pages,
or read the manual online. If the table of contents for the document is not already displayed on the
left side of the page, click the
easy way to navigate through the document.
• Users can access Help in the telephony interface at any time by saying “help.”
Managing Users
You can manage some Personal Assistant users through the Reset User Information page. Select
System
You can make the following changes:
• Reset the user PIN—You can make this change if the system is configured to use the
> Reset User Information to open the page.
Cisco
This is useful if a user forgets a PIN. Changing the PIN does not affect the user configuration. The
user can also reset the PIN through the user interface.
You can also configure Personal Assistant to automatically notify users of PIN changes by e-mail.
For more information about automatic PIN change notification, see the
section on page A-10.
Bookmarks and Page button to view it. The bookmarks provide an
CallManager PIN. Personal Assistant requires the new PIN the next time the user(s) log on.
“Messaging Configuration”
5-2
Note If the system is configured to use the Cisco Unity subscriber phone password as the PIN, you
cannot reset the PIN through any Personal
in Cisco Unity. Also, users will not receive e-mail notification of PIN changes.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
Assistant interface. The phone password must be reset
OL-4590-03
Page 91

Chapter 5 Preparing Users for Personal Assistant
• Reset the recorded name—You can erase the name a user recorded, which forces the user to rerecord
the name the next time they call Personal
the user interface.
• Delete the user from the Personal Assistant system—You can remove user account data from the
Personal
Assistant directory.
When you delete a user record from the corporate directory, user account data—destinations and
destination groups, callers and caller groups, rules and rule sets, personal address book information,
personal settings, and the recorded name—remains in the Personal
we highly recommend that when a user is deleted from the network, you also delete their
Personal
Assistant account information.
You might also delete a user account if information has become associated with a user incorrectly.
For example, if a device (such as a cell phone) is transferred from one user to another, and the old
user has rules that include the device, the new user might receive unexpected and undesired calls.
Deleting the old user account ensures that the new user will not receive calls inadvertently
transferred to the device.
Note that you cannot use the Personal Assistant interface to reset a user password, because the password
Personal
Assistant uses is the same as the one used for accessing the Cisco CallManager user interface.
To change the password, use the Cisco
How Administrative Changes Affect Users
Assistant. The user can also reset the spoken name through
Assistant directory. Therefore,
CallManager user interface.
For more information about using the Reset User Information page, see the “Reset User Information”
section on page A-15.
How Administrative Changes Affect Users
Some of the changes you make by using the Personal Assistant Administrative interface directly affect
how users can use Personal
• Stopping or restarting servers—If you do not have multiple Personal Assistant servers and speech
recognition servers configured on your network, stopping or restarting servers can temporarily
disrupt user access to Personal
• Configuring dial rules—Both you and users have the ability to configure dial rules. Administrative
dial rules take priority over user-configured dial rules.
• Configuring directory hierarchies—You can create locations and departments to help users narrow
a dial-by-name directory search. For example, if you create a location called NewYork, users can
tell Personal
Assistant to search the NewYork location for Roger Smith. This is useful when dialing
a person with a common name.
• Setting call pickup duration—Both you and users can modify the call pickup timeout. The
user-configured setting takes priority.
Note The value specified for call pickup duration must be less than the Call Forward No Answer
(CFNA) value set in Cisco
information, you should notify them of the maximum timeout value to set.
Assistant. For example:
Assistant.
CallManager. Because users do not have access to this
OL-4590-03
• Allowing calls only from Cisco CallManager users—You can configure Personal Assistant to
restrict access to users who are registered in the Cisco
• Disallowing calls from unknown phones—You can configure Personal Assistant to accept user calls
CallManager directory.
only from user work, home, mobile, and personal destination numbers that are listed in the corporate
directory.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
5-3
Page 92

How Administrative Changes Affect Users
• Enforcing Authentication by PIN from personal destinations—Both you and users can configure
Personal
in the corporate directory. When you configure Personal
priority over the user-configured setting. Otherwise, the user setting is used.
• Configuring Personal Assistant to apply rules only to calls to corporate destinations—You can
configure Personal
in the corporate directory.
• Allowing callers to transfer directly to voice mail—You can have Personal Assistant allow a caller
to transfer to voice mail when the call is not picked up at the first user destination.
• Notifying users of PIN changes—If the system is configured to use the Cisco CallManager PIN, you
can have Personal
changed.
Both you and users have the ability to change the PIN. When you reset the PIN, you must enter a
non-blank PIN, therefore, you should let the user know the new PIN, if applicable.
• Disabling rules on calls made through Personal Assistant—You can configure Personal Assistant to
allow another JTAPI application (such as IPMA) to intercept a call before Personal
When this option is set and a call is made through Personal
applied.
• Setting up systemwide rules—Both you and users have the ability to create and activate call-routing
rules. Whether Personal
depends on the rule-application condition you set. Because user rules can be overridden, this feature
should be used with caution.
Chapter 5 Preparing Users for Personal Assistant
Assistant to require a PIN when users call from any phone except their work phone listed
Assistant to do this, your setting takes
Assistant to apply active call-forwarding rules only to calls to destinations listed
Assistant automatically send users e-mail notification when their PINs have
Assistant does.
Assistant, call-routing rules are not
Assistant applies your rule or the user-configured rule to an incoming call
5-4
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 93

CHA P TER
Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
This chapter contains the following sections:
• Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant, page 6-1
• Resolving Problems with Managing Personal Assistant, page 6-10
• Troubleshooting Failed System Refreshes, page 6-11
• Monitoring Server Status, page 6-12
• Monitoring Performance, page 6-12
• Collecting Call History Information, page 6-14
• Starting and Stopping the Servers and License Manager, page 6-14
• Collecting Trace and Debug Information, page 6-15
• Integrating with Network Management Systems, page 6-16
6
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
The following sections provide resolutions to problems users might encounter:
• Unable to Access the User Web Interface, page 6-2
• Search Results Include Multiple Copies of a User, page 6-2
• Unable to Use Speech Commands, page 6-2
• Users Cannot Make Conference Calls (Cisco CallManager 3.3 or Later), page 6-3
• Directed to Operator Too Often, page 6-3
• Too Many Available Options, page 6-3
• Calls Transferred to Voice Mail Too Quickly, page 6-4
• Dial Rules Not Working Properly, page 6-4
• Calls Dropping, page 6-4
• Callers Hear “We Are Experiencing Technical Difficulties, Please Call Back Later”, page 6-4
• Personal Assistant Is Too Slow to Answer Calls, page 6-5
• Callers Hear a Busy Tone When Calling Personal Assistant, page 6-5
• A User Hears a Busy Tone When Calling Another User, page 6-5
• Personal Assistant Does Not Recognize Users When They Call From Their Work Phones, page 6-6
OL-4590-03
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
6-1
Page 94

Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
• Message Waiting Indicator Does Not Work, page 6-6
• All Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail, page 6-7
• Some Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail, page 6-7
• Users Cannot Log On to Cisco Unity Voice Mail, page 6-7
• Calendar-Based Call-Routing Rules Do Not Work, page 6-8
• Users Hear Text to Speech Names Too Often, page 6-9
Unable to Access the User Web Interface
If users cannot access the Personal Assistant user web interface pages, it may be that the systemwide
default locale for the speech-recognition interface and user web interface has not been set. If the Default
Locale field on the Speech Services Configuration page of the Personal
interface is blank, move applicable locales from the available locales list to the supported locales list.
Then, click the default locale in the list. See the
for instructions.
If users cannot log on to the Personal Assistant user web interface, verify that they are using the correct
logon name. The logon name should match the unique user attribute that you defined on the Corporate
Directory settings page of the Personal
organization uses the employee e-mail address as the unique user attribute, verify that users are entering
an e-mail address and not another attribute, such as a phone number.
Assistant Administration interface. For example, if your
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
Assistant Administration
“Speech Services Configuration” section on page A-21
Search Results Include Multiple Copies of a User
If Personal Assistant returns multiple copies of a user when you search for users in the
Personal
that the corporate directory search filter includes the string !(description=CiscoPABUser), if the user
search base is set to the root of the directory. The full entry in the Directory Search Filter field should
be (&(objectclass=person)(!(description=CiscoPABUser))). Otherwise, Personal
distinguish between users in the corporate directory and users in the personal address book. See the
“Corporate Directory Settings” section on page A-3 for instructions on setting the directory search filter.
Assistant user web interface, and if your directory is Cisco CallManager DC Directory, ensure
Unable to Use Speech Commands
If users cannot use speech commands and instead must use touch-tone dialing to interact with
Personal
• Verify that the speech recognition server is up and running. See the “Starting and Stopping the
• Establish whether you have recently added a new speech-recognition server or additional license
• Consider whether you have an adequate number of speech-recognition servers to handle the number
Assistant:
Servers and License Manager” section on page 6-14.
manager hosts. If you have, you must refresh the servers before they can support users. See the
“Configuring Speech Recognition” section on page 4-4.
of users. See the
speech licenses to accommodate usage.
“Creating Server Clusters” section on page 1-10. You might want to add more
Assistant cannot
6-2
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 95

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
Users Cannot Make Conference Calls (Cisco CallManager 3.3 or Later)
If you are using Cisco CallManager version 3.3 or later and if users are unable to make conference calls,
it may be that the Cisco
that not all Cisco
Do the following procedure to verify the ad hoc conferencing parameter and reset it, if applicable.
To Verify the Ad Hoc Conferencing Service Parameter in Cisco CallManager
Step 1 Navigate to the Service Parameters Configuration page of the Cisco CallManager administration
interface.
Step 2 Click <Cisco CallManager server> in the Server list, and click Cisco CallManager in the Service list.
The Service Parameters Configuration page appears.
Step 3 Under Clusterwide Parameters (Feature - General), confirm that the ad hoc conferencing parameter is
set correctly, depending on the Cisco
CallManager service parameter for ad hoc conferencing is not set correctly. Note
CallManager service releases and support patch releases contain the parameter.
CallManager version:
Cisco CallManager 4.1
Cisco CallManager 4.0
Cisco CallManager 3.3
Note that the parameter is not present in some engineering specials and service releases of the versions
listed.
If the value is incorrect, click the correct value, and click Update.
Caution The ad hoc conferencing parameter may be used by other telephony applications in your
system. We highly recommend that you contact your telephony system administrator before
changing the value.
Directed to Operator Too Often
If users report that they are being directed to the operator too often when using Personal Assistant, check
the speech recognition settings on the Personal
Recognition” section on page 4-4.
Drop Ad Hoc Conference should be set to Never.
Drop Ad Hoc Conference When Controller Leaves should be set to False.
Drop Ad Hoc Conference When Creator Leaves should be set to False.
Assistant server. See the “Configuring Speech
Too Many Available Options
If users report they are given too many options when using dial-by-name, you should reduce the Max
Disambiguate parameter of the speech recognition settings on the Personal
OL-4590-03
Assistant server.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
6-3
Page 96

Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
Calls Transferred to Voice Mail Too Quickly
By using the miscellaneous settings in the Personal Assistant Administration interface, you can
designate the call pickup time. This determines how long Personal
up before it moves on to the next defined dial rule.
However, users can also configure the call pickup time (by selecting Preferences > Settings from the user
interface), and the user setting takes precedence over the setting in the Personal
Administration. For example, if the server setting is 20 seconds, but a user has set call pickup time to 10
seconds, Personal
If users state that they are being transferred too quickly to voice mail, check the call pickup setting in
both the administrator and user interfaces.
Assistant uses 10 seconds as the call pickup time.
Dial Rules Not Working Properly
You can configure dial rules through the Personal Assistant administration and user interfaces. However,
rules configured in the administration interface take priority over those configured through the user
interface. Therefore, if a user has configured a dial rule that conflicts with or produces different results
from the one you configured as the administrator, the user rules are ignored.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
Assistant waits for a call to be picked
Assistant
Calls Dropping
Under normal circumstances, users should not experience dropped calls while using Personal Assistant.
However, if you have recently changed settings on the Personal
the server might have restarted. If you do not have any failover servers, Personal
been unavailable during this restart.
If a user is actively interacting with Personal Assistant when the server becomes unavailable, the call
will drop. However, if Personal
transfer, the call will not be dropped.
To prevent calls from being dropped while Personal Assistant is being used, limit the changes and
restarts to the Personal
consider adding one in order to more reliably support your users.
Assistant server to off-peak times. Also, if you do not have a failover server,
Assistant has already completed its role in the call, such as a successful
Assistant server and saved the settings,
Assistant might have
Callers Hear “We Are Experiencing Technical Difficulties, Please Call Back Later”
If users call Personal Assistant and consistently hear this message, there are two main problems to check
for:
• Problems with the speech recognition subsystem. The speech or license servers are not running, or
the speech package is not available in the expected location in
\Speech\Grammar\Static\<Locale>\Pa in the Personal
problem:
–
Use the control center (System > Control Center) to see if the speech servers and license
managers are running. Try stopping and restarting them to see if this resolves the problem.
Assistant installation directory. To solve this
6-4
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
Page 97

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
–
Refresh the speech grammar by clicking Refresh Now on the Speech Services Configuration
page (System
(look for xcopy errors in the Personal
Cisco
TAC.
• The time changed on the Personal Assistant server, or there is a large time difference between the
speech servers and the Cisco
–
Ensure that the times are consistent on these machines, which typically obtain their time from
the domain controller when the servers reside in a Windows domain.
> Speech Services). If the problem persists, verify that the package was created
Assistant log on the primary server), and contact
CallManager servers. To solve this problem:
Personal Assistant Is Too Slow to Answer Calls
If it takes a long time for Personal Assistant to answer calls to the Personal Assistant number, it is likely
that you are using IP addresses for speech server or license managers in your configuration, and your
DNS server is not set up to resolve an IP address to an IP address.
To resolve the problem, either reconfigure your DNS server to add IP address to the same IP address
mapping, or change the Personal
managers by using DNS host names.
Assistant configuration to identify the speech servers and license
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
Callers Hear a Busy Tone When Calling Personal Assistant
When callers to the Personal Assistant number hear a busy tone, you might have one of the following
problems:
• Callers always hear busy tone—If callers always hear a busy signal, it could mean any of the
following problems exist:
–
Personal Assistant is not running. Check the status of the servers by using the control center
(System
–
No media ports are defined. Check the server configuration (Servers > Server Configuration)
and add ports if necessary. You must also create the ports in Cisco
“Configuring Personal Assistant Servers” section on page 4-10 and the “Adding Media Ports for
Personal Assistant” section on page 3-10 for more information.
–
The Personal Assistant CTI route points are not assigned to the JTAPI user for
Personal
automated attendant number (if any), and all route points used as Personal
ports.
• Callers occasionally hear a busy tone—Either add more media ports or install additional
Personal
is heavier than the existing setup can handle.
> Control Center).
Assistant. You must assign the route points used for the Personal Assistant number, the
Assistant servers. When callers occasionally hear a busy tone, the call load from your users
A User Hears a Busy Tone When Calling Another User
CallManager. See the
Assistant interceptor
OL-4590-03
If two users each have phone DNs that exactly match the DNs of Personal Assistant interceptor port
route points that are configured in Cisco
contact one another by using Personal
CallManager, the users will hear a busy tone when trying to
Assistant.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
6-5
Page 98

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
For example, user A has the DN 2001 and user B has the DN 2002. Two Personal Assistant interceptor
port route points with the DNs 2001 and 2002 are defined in Cisco
to call user B, Cisco
rejected and user A hears a busy tone.
Check the DNs of both users in Cisco CallManager against the Personal Assistant interceptor port route
points. To avoid the problem, we recommend that you use wildcards for the interceptor port route points.
See the
page 3-4.
If the DNs and interceptor port route points are not the problem, verify that the user phones are in the
correct partition. See the
“Creating Personal Assistant Interceptor Ports and Configuring Error Handling” section on
CallManager cannot transfer the call to Personal Assistant. Instead the call is
“Updating the Partition for Managed Phones” section on page 3-8.
CallManager. When user A attempts
Personal Assistant Does Not Recognize Users When They Call From Their Work Phones
If a user calls Personal Assistant from his or her work phone, and if Personal Assistant prompts the user
for an extension or first and last name:
• Verify that the user work phone is set correctly in the corporate directory. If applicable, modify the
entry and do a system refresh. Note that the user will not be recognized until the refresh has
completed successfully.
• Ensure that the directory lookup rule correctly translates the user work phone to the work phone
number as it is represented in the corporate directory, if applicable. See the
Rules” section on page A-8.
• Check whether a refresh or a server restart is in progress. During these processes, Personal Assistant
reads information from the corporate directory and cannot recognize users until the refresh or restart
has successfully completed.
“Directory Lookup
Message Waiting Indicator Does Not Work
If the message waiting light on the phones no longer lights when a new message is received, the problem
might be in the calling search space configuration.
When setting the calling search space that you use for voice mail ports and for message waiting
indicators, ensure that it contains the PAManagedEmployees partition, but not the PA partition.
Otherwise, the message waiting indicators will not work.
You assign partitions and calling search spaces to voice mail ports on the Feature > Voice Mail > Cisco
Voice Mail Port > Voice Port Configuration page of the Cisco CallManager Administration interface.
You use the Cisco CallManager Administration interface to assign partitions and calling search spaces
to message waiting indicators in one of the following ways:
• On the Feature > Voice Mail > Message Waiting > Message Waiting Configuration page.
• On the Service Parameters Configuration page by going to Service > Service Parameters, and
clicking Cisco Messaging Interface for the applicable server. Set the calling search spaces on the
Service Parameters Configuration page only when a simplified message desk interface
(SMDI)-compliant external voice mail system is used.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
6-6
OL-4590-03
Page 99

Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
All Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail
If users are transferred to the main voice mail number when they try to access voice mail in
Personal
configuration (System
DNS name, for example unity1 rather than unity1.domain.com. Do not use IP addresses.
If the DNS name is not the problem, reinstall the Personal Assistant servers and specify a Cisco Unity
domain and administrative user when asked for Windows domain information.
Assistant, rather than being taken directly to the applicable voice mailbox, check the messaging
> Messaging). Ensure that the voice mail servers are identified by unqualified
Some Users Cannot Browse Voice Mail
If users in general can access voice mail, but some users cannot, there is probably a problem with the
Cisco
Unity user setup information, or a consistency problem with Cisco CallManager.
Make sure the user voice mailbox number matches the user extension in Cisco CallManager, and that the
user ID is the same in Cisco
If the mailbox number and extension are not the problem, check the Personal Assistant messaging
configuration (System
in Personal
Assistant.
Unity and Cisco CallManager.
> Messaging), and ensure that the user voice mail server is properly configured
Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
Finally, if you are using more than one voice mail server, users can select the voice mail number when
configuring Personal
voice mail number has been selected.
Assistant user settings. Check the user configuration to ensure that the correct
Users Cannot Log On to Cisco Unity Voice Mail
If users cannot log on to the voice mail system from Personal Assistant, it is likely that the
Personal
be automatically created the first time someone accesses voice mail through the Personal
server.
Do the following two procedures to verify whether the profile was created and to manually create it, if
applicable.
To Verify the Personal Assistant Profile in the Outlook Client
Step 1 On the Personal Assistant Server, click Start > Settings > Control Panel.
Step 2 Double-click the Mail icon.
Note If a memory error message appears, it may be that the Outlook path has not been added to the
Assistant voice mail profile in the Outlook Client was not created correctly. The profile should
system path variable. Add the Outlook path and repeat this procedure.
Assistant
OL-4590-03
If the profile window is blank, Personal Assistant failed to create the profile. Skip to the “To Manually
Create the Personal Assistant Voice Mail Profile in the Outlook Client” procedure on page 6-8. When
you are done creating the profile, repeat this procedure to verify it.
If the Cisco Unity System Profile Properties window opens, skip to Step 3.
Step 3 Click Properties.
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
6-7
Page 100

Resolving Problems with Using Personal Assistant
Step 4 In the Microsoft Exchange Server window, verify the Cisco Unity server name in the Microsoft
Exchange Server field.
If the server name is incorrect, enter the correct name or IP address. For example: amishak. (Do not use
the fully qualified domain name.)
Step 5 Ve r i f y t h e C i sc o Unity system mailbox name in the Mailbox Name field.
If the mailbox name is incorrect, enter the correct name.
Step 6 If the mailbox name is not underlined, click Check Name, to verify the name.
Depending on how your system is configured, you might be prompted for the domain, user name, and
password.
The mailbox name should be underlined, and the Check Name button should be disabled.
Step 7 Click OK twice.
To Manually Create the Personal Assistant Voice Mail Profile in the Outlook Client
Step 1 On the Personal Assistant server, browse to the directory
C:\Program
Step 2 Under [Service1], set Homeserver to the Microsoft Exchange server name.
Files\Cisco Systems\Personal Assistant\Bin, and open the file paUnity.prf in Notepad.
Chapter 6 Troubleshooting Personal Assistant
Step 3 Under [Service1], set MailboxName to the Administrator Mailbox Firstname Lastname.
Step 4 Save the changes, and close the file.
Step 5 Open a command prompt (DOS) window.
Step 6 Change the directory to C:\Program Files\Cisco Systems\Personal Assistant\Bin\Outlook.
Step 7 Run the new profile setup program by entering newprof.exe -p -s, and then pressing Enter.
Step 8 When the Newprof window appears, browse to the directory
C:\Program
Step 9 Click Execute.
Step 10 When you are done creating the profile, repeat the “To Verify the Personal Assistant Profile in the
Files\Cisco Systems\Personal Assistant\Bin, and click the file paUnity.prf.
Outlook Client” procedure on page 6-7.
Calendar-Based Call-Routing Rules Do Not Work
If a user has set up calendar-based call routing rules, and the rules are not working properly, you might
have an incorrect messaging configuration, or the user meeting information might not yet be
synchronized (thus making it unavailable for Personal
Check the messaging configuration (System > Messaging) to ensure that the correct calendar server
name and calendar mailbox name are configured. If you are using Cisco
use “Unity Messaging” in the Calendar Mailbox Name field, unless the account uses a different name.
If you are using Exchange without Cisco
on the Exchange server. See the
“Messaging Configuration” section on page A-10 for more information
Unity, use the first and last name of the administrator account
and for detailed instructions.
Assistant).
Unity with Microsoft Exchange,
6-8
Cisco Personal Assistant 1.4 Installation and Administration Guide
OL-4590-03
 Loading...
Loading...