Page 1

Overview
Note You enable BAF output with the NODEPARMS tag ID. For more information, see the “NODEPARMS
CHA PTER
5
Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
This chapter describes how to configure the Cisco Billing and Measurements Server (BAMS) for
Bellcore AMA (Automatic Message Accounting) Format (BAF) records. BAMS provides a mediation
interface for Cisco Media Gateway Controller (MGC) systems. The purpose of BAMS is to provide
enhanced data collection and processing functions, which correspond to those found in a traditional
Class 4 tandem switch. BAMS does not include presentation graphics or database query functions;
rather, it is designed to produce output billing and measurement feeds for downstream systems that can
provide these functions.
Tag ID” section on page 4-9.
BAMS must be correctly configured with the following information:
• Billing design information
–
Billing zones
–
Zone relationships
–
Call types
–
Calling exceptions
–
Call type and structure code mapping for output records
• NPA-NXX LATA information
–
Zone assignment
–
LATA assignment
–
Toll-free prefix assignment
• Trunk group information
–
SigPathID to trunk group number
–
BearChanID to trunk group member
–
Trunk group connections
• International routing information
–
Country codes
OL-3351-01
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-1
Page 2

Generating BAF Records
Note Before configuring BAMS to generate billing and measurements, you should familiarize yourself with
Chapters 3 to 9 of this guide.
Note BAMS performs only limited data validation on the information provisioned into its tables. It is
important that you enter data carefully and understand the algorithms and their implementation.
BAMS values entered through the MML command-line interface are case sensitive; the verbs and
keywords are not.
Generating BAF Records
The following section explains how BAF records are generated from Cisco MGC switch data.
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Interworking of BAMS Configuration Tables
The first step in using BAMS is understanding the billing area that must be covered. Are there special
cases for billing within the area? Are there banded areas with special rating? Do some number prefixes
receive different treatment? Are special billing records required for these (or other) circumstances?
The answers to these questions are important in creating zones that are used to define interactions
between different origination and termination NPA-NXX combinations. These interactions also
determine the call types that are used to decide which BAF record to use for billing output. See the “Call
Area Provisioning Example” section on page 5-9 for more details.
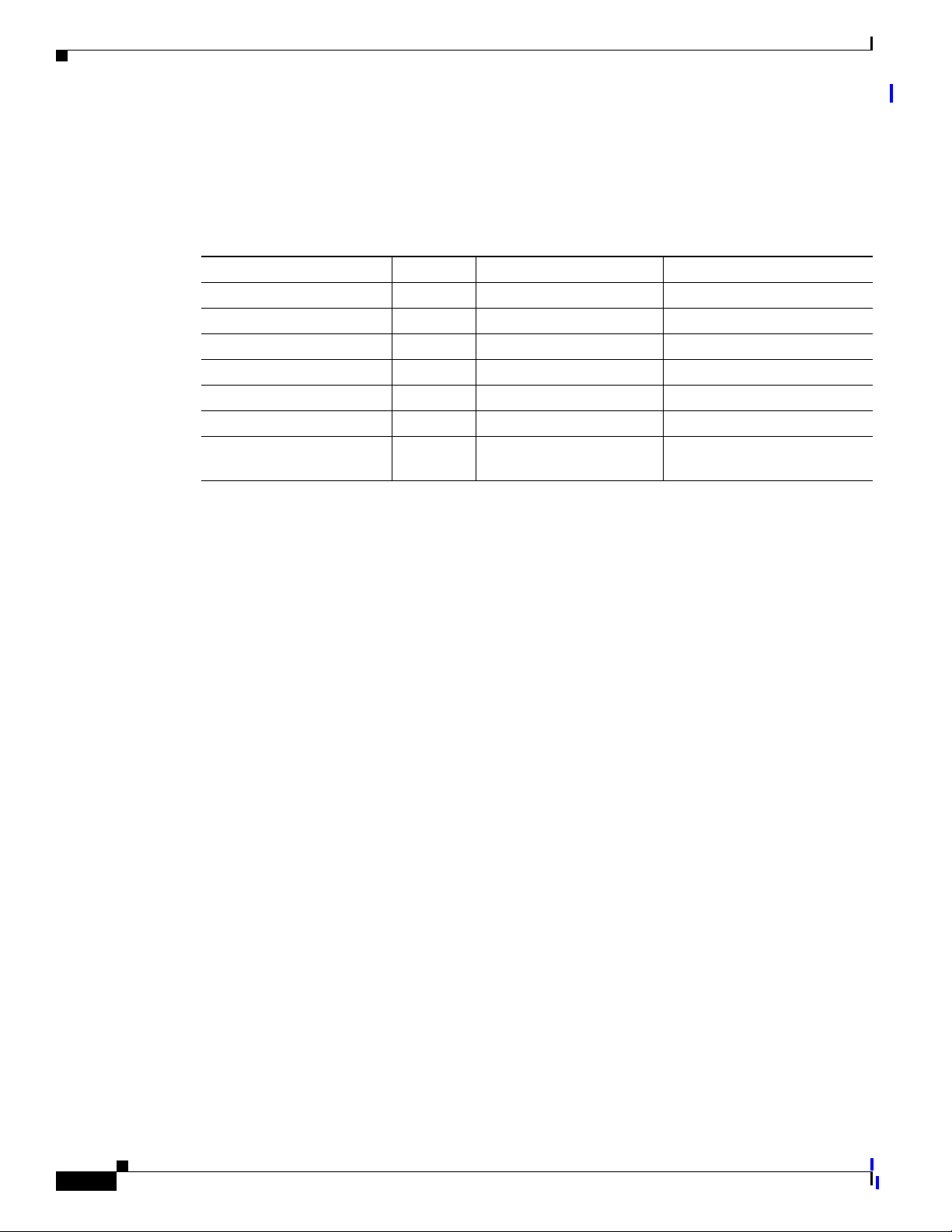
Once the billing area information has been gathered, it can be tabulated as shown in Table 5-1.
Table 5-1 Datafill Information Example
From To
1 202344 1 1 202345 1 FLAT
1 202344 1 1 202223 2 FLAT
2 202767 5 2 202333 3 MESSAGE
3 703298 8 1 202268 1 INTERLATA
Prerequisites for BAF Records
Results in
Map TypeLATA NPANXX Zone LATA NPANXX Zone
5-2
The following steps are required before Bellcore AMA Format (BAF) and Cisco Media Gateway
Controller (MGC) End of Call 1110 ASCII records can be generated:
1. The Billing and Measurements Server (BAMS) collects the individual call data blocks (CDBs)
generated by the Cisco MGC. This is performed by the Polling (POL) task.
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 3

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Note The prefix of the files polled by the POL task is the input prefix for FMT, the initial
processing task. Changing the parameter file-prefix1 or file-prefix2 in the Poll table
automatically changes the input prefix of the FMT task. This change takes effect on the
next startup of the system.
2. BAMS correlates the CDBs into a merged call structure. This is performed by the Correlation (COR)
task.
3. Each call type is categorized. This is performed by the Augmentation (AUG) task. The AUG task is
involved in the output of BAF records, as well as the BAF-to-CDR conversion task (CTB).
4. The ASCII Conversion (ASC) task outputs Cisco MGC End of Call 1110 ASCII files.
Identifying Call Types
Identification of call-type information is key to generating BAF records. The call type determines the
structure code and the call-type tables of the BAF record. Because the Cisco MGC generates partial
information in the CDBs, additional data within the CDBs is required for the unique identification of
each call scenario. BAMS provides the logic that determines the call type.
Identifying Call Types
Note the following:
• Each Cisco MGC serves a set of home NPA-NXXs.
• Each output BAF record needs to be put into a call category (for example, Flat rate, Message rate,
IntraLATA, InterLATA, Toll-Free, and so forth). The call category is important because it dictates
the BAF structure code and call-type fields.
Perform the following steps to identify call-type categories:
Step 1 Use the ZONE-INFO tag ID to define zone IDs. (For details, see the “Updating the Zone Information
Table” section on page 4-29.)
Step 2 Use the NPANXX tag ID to assign a zone ID and a LATA to each NPA-NXX. The zone narrowly defines
an area within the LATA as a call category. LATAs are centrally managed, and the system assumes that
you are using the correct source for the population of the LATA (for example, using Bellcore LERG
tables). Note that the LERG tables are not part of BAMS. (For details, see the “Updating the NPANXX
Table” section on page 4-13.)
Step 3 Use the RATING-TYPE tag ID to establish the calling relationships between zones. This tag ID
determines the call category (for example, flat rate, message rate, and so on). (For details, see the
“Updating the Rating Type Table” section on page 4-16.)
Step 4 Use the RATE-EXC tag ID to override certain call-category relationships defined with the NPANXX tag
ID. (For details, see the “Updating the Rating Exception Table” section on page 4-16.)
Step 5 Use the TRUNKGRP tag ID to determine if a call is originating or terminating. (For details, see the
“Updating the Trunk Group Table” section on page 4-26.)
OL-3351-01
Step 6 Use the MAPTYPE tag ID to specify which structure code to generate and which call type to assign each
call category. (For details, see the “Updating the Map Type Table” section on page 4-4.)
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-3
Page 4
Identifying Call Types
Default BAF Structure Codes and Call Types
Table 5-2 defines the default BAF structure codes and call types. The table lists the call categories, call
types, and answered and unanswered structure codes.
Table 5-2 BAF Structure Codes and Call Types
Call Category Call Type Answered Structure Code Unanswered Structure Code
FLAT 1 502 21
MESSAGE 1 20 21
INTRALATA 6 1 2
INTERLATA_ORIG 110 625 625
INTERLATA_TERM 119 625 653
INTERLATA_TANDEM 110 625 625
TOLL_FREE 141 360 –1 (A value of –1 means “do
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
not generate a record.”)
Example of BAF Structure Codes and Call Types Created from BAF Provisioning
The following example is a formatted printout of a binary record.
============================== BAF RECORD ================================
(000)Record Length : 97
(00)Hex Identifier : aa
( 0)Structure Code : 40625c
( 1)Call Type : 110c
( 2)Sensor Type : 118c
( 3)Sensor ID : 0012345c
( 4)Record Offce Type : 118c
( 5)Record Offce ID : 0067890c
( 6)Connect Date : 00713c
( 7)Timing Indicator : 00000c
( 8)Study Indicator : 0000000c
( 9)Off Hook Indicator : 0c
(10)Traffic sampld Ind : 0c
(11)Operator Action : 0c
(12)Service Feature : 000c
(13)Originating NPA : 703c
(14)Originating number : 7654321c
(15)Overseas Indicator : 0c
(16)Terminating NPA : 00804c
(17)Terminating number : 7654321c
(18)Connect Time : 1611272c
(19)Elapsed Time : 000000021c
(57)IC/INC Prefix : 00000c
( 6)Carrier Conn Date : 00713c
(18)Carrier Conn Time : 1611260c
(19)Carrier Elpsd Time : 000000020c
(58)IC/INC Call Status : 010c
(83)Trunk Group Number : 38004c
(59)Route Indicator : 1c
(85)Dial Indicator : 0c
(60)ANI/CPN Indicator : 3c
=============== Modules =================
Module 104 (Trunk ID)
5-4
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 5

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
(244)TrunkID : 380030234c
Module 104 (Trunk ID)
(244)TrunkID : 680042113c
Module 000 (Final Module)
============================== End of BAF Record =========================
Exception and Special Processing
Overriding Call Types
In some cases, a carrier might want to override a call type. Some examples include:
• Calls between a subset of NPA-NXXs in two different zones being treated differently from all other
NPA-NXXs in the same zones
• InterLATA calls being treated as intraLATA calls for record-generation purposes
Use the RATE-EXC tag ID to override the default call-type classification. For more information, see the
“RATE-EXC Tag ID” section on page 4-16.
Exception and Special Processing
Processing 7-Digit Numbers
If only 7 digits are populated in the calling and called numbers, the system acts as if each incoming trunk
group visible to BAMS has a default NPA and prefixes this NPA to each 7-digit number. The full
NPA-NXX is required for BAMS to perform the zone analysis. Each trunk has a default originating and
terminating NPA, defined in the orgnpa and trmnpa fields, in the Trunk Group table. These fields are
used only if the incoming number is 7 digits.
Processing Toll-Free Calls
A toll-free call can be identified if its dialed number prefix is contained in the Tollfree table. The default
toll-free prefixes are: 800, 877, 888, 1800, 1877, and 1888. Toll-free calls have their own call-type
category. A zone analysis is still performed, but the call type is overridden with the toll-free call type.
Processing International Calls
Records for international calls are processed like all other records, using zone analysis. Based on the
default case, international numbers are classified as interLATA calls.
Processing LNP Calls
Local number portability (LNP) calls are processed like all other records, using zone analysis. The only
special processing involved is the propagation of BAF module 720. This module is generated in response
to the presence of the lnp_dip field in the CDB.
OL-3351-01
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-5
Page 6

BAF Output Provisioning Example
Processing Transit/Tandem Calls
InterLATA calls can originate at, terminate at, or pass through the Cisco MGC generating the BAF records.
Originating records are distinguished from terminating records by the appropriate use of the BAF calltype
field in the Map Type table. BAMS identifies a call as an originating interLATA call if only the egress
trunk group is populated. Similarly, BAMS identifies a terminating call as an interLATA call if only the
ingress trunk group is populated.
However, it is also possible for a call to transit, or pass through the Cisco MGC. If the ingress and egress
fields are populated, this call can be identified. BAMS does not support BAF record types for tandem calls.
Rather, BAMS separates interLATA calls into three subcategories: originating, terminating, and tandem.
The Map Type table provides user-configurable record types. By default, structure code 625/call type 110
is used for interLATA tandem calls.
BAF Output Provisioning Example
The following example shows a BAF output provisioning script.
set-node:1:
prov-sta::srcver=”new”,dstver=”baf”,confirm
set-nodename::name="london"
prov-add:poll:host-name1=”va-lewis”,rem-dir1=”/opt/CiscoMGC/var/bam”,file-prefix1=”cdr*”,fi
le-suffix1=”.bin”,action=”R”,interval=1,timeout=5,maxtries=3,host-name2=”va-clark”,rem-dir2
=”opt/CiscoMGC/var/bam”,file-prefix2=”cdr*”,file-suffix2=”.bin”
prov-add:SWITCHINFO:sensortype="118",sensorid="999999",recoffctype="118",recoffcid="999999"
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=2002,connection=”D”,orgnpa=120,trmnpa=120,circuits=300
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=2017,connection=”T”,orgnpa=121,trmnpa=120,circuits=300
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=1,info=”zones 1-10 same dpc as w/2002”
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=11,info=”zones 11-18 same dpc as w/2017”
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120200,lata=1,zone=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120201,lata=1,zone=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120202,lata=1,zone=2
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120203,lata=1,zone=3
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120204,lata=1,zone=4
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120205,lata=1,zone=5
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120206,lata=1,zone=6
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120207,lata=1,zone=7
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=120208,lata=1,zone=8
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121700,lata=2,zone=11
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121701,lata=2,zone=11
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121702,lata=2,zone=12
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121703,lata=2,zone=13
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121704,lata=2,zone=14
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121705,lata=2,zone=15
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121706,lata=2,zone=16
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121707,lata=2,zone=17
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=121708,lata=2,zone=18
prov-add:ALM-PARMS:maxlines=10000,msgdisclvl=5,msgfwdlvl=3
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”FLAT”,calltype=”1”,answered=”502”,unanswered=”20”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”MESSAGE”,calltype=”1”,answered=”20”,unanswered=”20”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”INTRALATA”,calltype=”6”,answered=”1”,unanswered=”1”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”INTERLATAORIGINATING”,calltype=”110”,answered=”625”,unanswered=”6
25”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”INTERLATATERMINATING”,calltype=”119”,answered=”625”,unanswered=”6
53”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”INTERLATATANDEM”,calltype=”110”,answered=”625”,unanswered=”625”
prov-add:MAPTYPE:maptype=”TOLLFREE”,calltype=”141”,answered=”360”,unanswered=”-1”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=1,trmzone=11,ratetype=”FLAT”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=2,trmzone=12,ratetype=”MESSAGE”
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
5-6
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 7

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=3,trmzone=13,ratetype=”INTRALATA”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=4,trmzone=14,ratetype=”INTERLATA”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=5,trmzone=15,ratetype=”INTERLATA”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=6,trmzone=16,ratetype=”FLAT”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=7,trmzone=17,ratetype=”FLAT”
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=7,trmzone=18,ratetype=”FLAT”
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”baf*bin”,polled=2,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm
=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”acc_h*”,polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=
6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”acc_d*”,polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=99,agelevel=6,delage=99,
delalarm=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”acc_r*”,polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=
6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”cdr*bin”,polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm
=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”*finished”,polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=20,agelevel=6,delage=5,
delalarm=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”elkup*”,polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=
6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”esyn*”,polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”esem*”,polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”ebaf*”,polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”cdr*csv”,polled=2,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm
=6
prov-add:MSC-PARMS:type=”baf*csv”,polled=2,alarm=5,agealarm=5,agelevel=6,delage=5,delalarm
=6
prov-add:MSC-THRES:interval=15,put=80,plt=60,uut=95,iut=50000,mil=80,mal=85,crl=90,key=1
prov-add:P01FILTER:answered=1,noanswer=1,busy=1,other=1
prov-add:SKIPCDB:id=1020
prov-add:NODEPARMS:activate=1,statoutput=0,bafoutput=1,asciibafoutput=1,asciioutput=0,
lookupinfo=1,bafinfo=1,dynamicaccumes=0,sup-zero-counts=0,interval-minutes=15,
nailed-cfg=0,p01output=0,p01prefix="p01_",enable-h323=0,extasciioutput=0,nicsoutput=0
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=1800
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=800
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=1888
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=888
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=1877
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=877
prov-dply::
BAF Output Provisioning Example
Bulk Provisioning
You accomplish bulk provisioning by preparing a batch file that contains the correct sequence of
provisioning commands. The command-line instruction to execute the bulk-provisioning batch file is as
follows:
mml -b filename containing commands [-o outputfilename]
BAMS does not monitor each command’s execution status, but the results are placed in the MML session
log file. You specify the log filename (that is, outputfilename) with the -o parameter, as shown above.
Note The batch file must begin with a prov-sta command and end with a prov-dply command. These
commands denote the beginning and the end of the provisioning session.
The following is an example of a batch file named mml.script:
set-node:2:
prov-sta::srcver=new,dstver=sample,confirm
OL-3351-01
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-7
Page 8

BAF Output Provisioning Example
set-nodename::name="virginia"
prov-add:poll:host-name1="va-harley",rem-dir1="/opt/CiscoMGC/var/bam",file-prefix1="cdr*",
file-suffix1=".bin",host-name2="va-davidson",rem-dir2="/opt/CiscoMGC/var/bam",file-prefix2
="cdr*",file-suffix2=".bin",action="R",interval=5,timeout=5,maxtries=3
prov-ed:NODEPARMS:asciioutput=0,statoutput=1,bafoutput=1,lookupinfo=0
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=1,info="herndon virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=2,info="springfield virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=3,info="reston virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=4,info="falls church virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=5,info="ashburn virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=6,info="sterling virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=7,info="dulles virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=8,info="arlington virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=9,info="tysons corner virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=10,info="vienna virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=11,info="leesburg virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=12,info="middleburg virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=13,info="hamilton virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=14,info="herndon virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=15,info="herndon virginia"
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=16,info="herndon virginia"
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516121,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=703111,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516112,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516123,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516134,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516145,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516156,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516167,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516178,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516189,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516190,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516103,LATA=132,ZONE=1
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=804111,LATA=132,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616311,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616321,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616331,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616341,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616351,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616361,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616371,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616381,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616391,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616301,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=616312,LATA=123,ZONE=2
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516546,LATA=132,ZONE=3
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=516489,LATA=132,ZONE=4
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=212123,LATA=132,ZONE=5
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=212321,LATA=132,ZONE=6
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=212456,LATA=132,ZONE=7
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=212789,LATA=132,ZONE=8
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=207123,LATA=120,ZONE=9
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=207321,LATA=120,ZONE=10
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=207456,LATA=120,ZONE=11
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=530123,LATA=726,ZONE=12
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=530321,LATA=726,ZONE=13
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=530456,LATA=726,ZONE=14
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=804456,LATA=726,ZONE=15
prov-add:npanxx:NPANXX=757123,LATA=726,ZONE=16
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=1,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=2,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=3,RATETYPE="INTRALATA"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=5,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="INTRALATA"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=9,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=10,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=11,RATETYPE="INTRALATA"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=12,RATETYPE="FLAT"
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
5-8
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 9

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=13,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=14,RATETYPE="INTRALATA"
prov-add:rating-type:ORGZONE=15,TRMZONE=16,RATETYPE="INTRALATA"
prov-add:RATE-EXC:orgnpanxx=516121,trmnpanxx=516112,ratetype="MESSAGE"
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=900222
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8003,CONNECTION="D",ORGNPA=804,TRMNPA=703,circuits=3000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8004,CONNECTION="T",ORGNPA=703,TRMNPA=804,circuits=6000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8005,CONNECTION="T",ORGNPA=516,TRMNPA=516,circuits=6000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8006,CONNECTION="T",ORGNPA=616,TRMNPA=616,circuits=6000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8007,CONNECTION="D",ORGNPA=212,TRMNPA=212,circuits=3000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8008,CONNECTION="D",ORGNPA=207,TRMNPA=207,circuits=3000
prov-add:trunkgrp:TRUNKGRP=8009,CONNECTION="D",ORGNPA=530,TRMNPA=530,circuits=3000
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="baf*bin",polled=2,alarm=5,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=
5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="acc_h*",polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="acc_d*",polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=30,agelevel=6,delage=30,delalarm
=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="acc_r*",polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="cdr*",polled=1,alarm=5,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="elkup*",polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="esyn*",polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=9,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-PARMS:type="esem*",polled=1,alarm=6,agealarm=9,agelevel=6,delage=30,delalarm=5
prov-ed:MSC-THRES:interval=60,put=80,plt=65,uut=90,iut=50000,mil=80,mal=85,crl=90,key=1
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="FLAT",calltype="1",answered="502",unanswered="20"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="MESSAGE",calltype="1",answered="20",unanswered="20"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="INTRALATA",calltype="6",answered="1",unanswered="-1"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="INTERLATAORIGINATING",calltype="110",answered="625",unanswered="1"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="INTERLATATERMINATING",calltype="119",answered="625",unanswered="1"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="INTERLATATANDEM",calltype="110",answered="625",unanswered="-1"
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype="TOLLFREE",calltype="141",answered="360",unanswered="-1"
prov-ed:ALM-PARMS:maxlines=20000,msgdisclvl=5,msgfwdlvl=3
prov-dply::
Call Area Provisioning Example
Once the file is created, it must be executed from outside of MML. To execute it, you use the following
command:
mml -b filename
Example:
$mml -b mml.script
Call Area Provisioning Example
Figure 5-1 shows a hypothetical BAMS provisioning scenario. A fictional metropolitan city, River City,
has been designed to include multiple call zones, local access and transport areas (LATAs), and
numerous central offices.
Designing a Billing Plan
Before any provisioning is done, a plan must be developed that determines how BAMS constructs billing
records for the implementation in question. Many different methods can be used to accomplish a desired
result. BAMS is designed to allow a customer to design billing applications that are unique to any
configuration.
OL-3351-01
Caution Customer billing-system expert inputs are necessary for anyone wishing to configure BAMS for BAF.
The information in the following sections is provided by way of example only.
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-9
Page 10

Call Area Provisioning Example
Assumptions Used in This Example
In Figure 5-1, some origination points can call to any point within the metropolitan area, with no toll
charged. A call type is determined by BAMS as a relationship between zones. BAMS can be configured
to specify that a certain call type produces, or does not produce, a billing record. Obviously, the
downstream billing system can determine which records are billable and which are informational only.
Keep in mind the following general information about the metropolitan area shown in Figure 5-1:
• There are three LATAs, labeled 1, 2, and 3.
• Any zone that is adjacent to another zone within the same LATA is marked as FLAT.
• Calls that cross LATAs are marked as interLATA.
• A call that originates and terminates in zones that are not adjacent, but that are in the same LATA,
is designated as MESSAGE to indicate a banded billing rate.
From the North American Bell System, the concept of LATAs is a traditional boundary concept that is
supported by BAMS. These are geographic regions, defined by NPANXX containment. BAF output
sometimes requires LATA assignment for certain record types. Because BAMS is not geared toward
local exchange routing guide (LERG) data, a downstream system could use the LATA designation for
other purposes.
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
LERG data is not resident on BAMS.
5-10
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 11

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Figure 5-1 River City Metropolitan Example
Zone 1
202–344
202–345
202–261
202–268
River City
202–223
202–224
202–225
Call Area Provisioning Example
VSC3000
202–333
202–334
202–335
LATA - 1
LATA - 2
202–767
202–768
202–769
Zone 5
Zone 6
703–551
703–552
703–553
Zone 2
703–434
703–435
703–436
202–878
202–879
202–880
703–333
703–334
703–335
LATA - 3
Zone 7
703–545
703–546
703–547
LATA - 1
LATA - 2
LATA - 3
LATA - 3
Zone 3
LATA - 2
703–621
703–622
Zone 4
703–298
703–299
Zone 8
Zone Membership
Each NPANXX combination that is supported within the metropolitan area must be a member of a zone.
Otherwise, the unknown call origination or termination point is considered to be out of the calling area,
and the call is tagged as INTERLATAORIGINATING or INTERLATATERMINATING.
OL-3351-01
LATA - 3
Zone 9
Central Office
46598
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-11
Page 12

Call Area Provisioning Example
Note Zoning provides a mechanism for differentiating between rating types (for example, flat rate and
message calls).
In the example in Figure 5-1, the following commands would be used to assign zone membership in
zone 1:
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=202344,zone=1,lata=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=202345,zone=1,lata=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=202261,zone=1,lata=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=202268,zone=1,lata=1
As a further example, the following commands would be used to assign zone membership in zone 9:
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=703545,zone=9,lata=3
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=703546,zone=9,lata=3
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=703547,zone=9,lata=3
Free Calling Between Zones
Assume that the billing design in this example states that, if a call originates in one zone and is intended
for an adjacent zone, the call type should be FLAT. The following commands implement FLAT for
adjacent zones. Note that the calling plan must be implemented in both directions, because zone A might
be allowed to call zone B for free, but not the other way around.
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=2,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=2,TRMZONE=1,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=5,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=5,TRMZONE=1,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=1,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=1,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=2,TRMZONE=3,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=3,TRMZONE=2,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=2,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=2,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=3,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=3,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=3,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=8,TRMZONE=3,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=8,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=8,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=7,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=8,TRMZONE=9,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=9,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=7,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=5,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=4,TRMZONE=5,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=6,TRMZONE=5,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=5,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=6,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=7,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=6,TRMZONE=9,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=9,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=9,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=7,TRMZONE=9,RATETYPE="FLAT"
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
5-12
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
Page 13

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Banded Message Rates
In Figure 5-1, many zones are not adjacent to other zones. The following commands set up MESSAGE
rate call types for calls from zone 6 and zone 8, which are not adjacent to each other but are in the same
LATA. In the example shown in Figure 5-1, many zone relationships of this type could occur.
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=6,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=8,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="MESSAGE"
Configuring Trunk Groups for InterLATA Calls
Calls that cross LATA boundaries are normally considered toll calls, unless the zones are adjacent or an
exception case is entered with the RATE-EXC tag ID. Because the default call type is interLATA (when
either originating or terminating NPANXX is not found in the Zone Information table), the only
provisioning required is on the ingress or egress trunk group.
For BAF billing records, the connectivity of the ingress or egress trunk determines the BAF direction of
the calls. When configured properly, BAMS marks interLATA calls as INTERLATAORIGINATING or
INTERLATATERMINATING. Because many telephone plan areas require only 7-digit dialing, the
Trunk Group table is also used to populate default originating and terminating NPAs when fewer than
10 digits are received for the A number or the B number. Finally, each trunk group has multiple circuits,
and the count of the number of circuits is captured in the Trunk Group table for different measurement
calculations.
Call Area Provisioning Example
Although there are many trunk groups, in the example shown in Figure 5-1, we configure only a few
trunk groups for Direct (to an end office) and a few trunk groups for Tandem (to an access tandem type
office). All trunk groups must be provisioned in the table for proper BAMS operation. Only a small
sample is shown here:
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=123,connection="D",orgnpa=703,trmnpa=202,circuits=72
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=124,connection="T",orgnpa=703,trmnpa=201,circuits=24
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=223,connection="D",orgnpa=703,trmnpa=202,circuits=72
prov-add:TRUNKGRP:trunkgrp=227,connection="T",orgnpa=703,trmnpa=408,circuits=96
Configuring Adjacent Area Codes
Adjacent area codes present no problem to BAMS, because the key for the various lookup tables is based
on the entire NPA-NXX (6-digit) string. Trunk groups must be provisioned, and, in the case of fewer
than 10-digit dialing, they must indicate default originating and terminating NPAs.
Configuring IntraLATA Calls
Cases might occur where a billing design does not use FLAT, or designates calls for adjacent zones to
something other than flat rate so that the downstream system can treat those calls differently. The
following example shows configuration for intraLATA calls between zones within the same LATA:
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=5,trmzone=4,ratetype="INTRALATA"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=5,trmzone=6,ratetype="INTRALATA"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=5,trmzone=6,ratetype="INTRALATA"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:orgzone=5,trmzone=6,ratetype="INTRALATA"
OL-3351-01
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-13
Page 14

Call Area Provisioning Example
Configuring Toll-Free Calls
Different countries have different designations for toll-free dialing. For this reason, BAMS maintains the
Tollfree table for the NPANXX combinations that are considered toll free.
Note Any 800, 888, or 877 NPA results in a toll-free BAF record, overriding any zone or rating type
designations.
Standard North American entries are provided here:
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=1800
prov-add:TOLLFREE:digits=1877
Configuring a Metropolitan Calling Plan
Suppose that one set of NPANXXs could call FLAT to any zone in Figure 5-1. This could happen if you
set up an overlay zone that covers the entire area. The LATA field would be set up for each NPANXX,
as appropriate.
To configure a metropolitan calling plan, perform the following steps:
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Step 1 Set up zone membership, zone 10 for the overlay:
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=202388,zone=10,lata=1
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=703488,zone=10,lata=3
Step 2 Set up zone relationships so that the super-zone can call any other zone as FLAT, and any other zone can
call the super-zone as FLAT.
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=1,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=2,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=3,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=4,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=5,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=6,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=7,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=8,RATETYPE="FLAT"
prov-add:RATING-TYPE:ORGZONE=10,TRMZONE=9,RATETYPE="FLAT"
Configuring for a Rating Exception
Sometimes cases occur in which a particular NPANXX calling another NPANXX needs to be classified
as a rating exception. For these cases, you can place an entry in the Rating Exception table, as follows:
prov-add:RATE-EXC:orgnpanxx=202344,trmnpanxx=703299,ratetype="FLAT"
prov-add:RATE-EXC:orgnpanxx=703299,trmnpanxx=202344,ratetype="FLAT"
BAMS Provisioning Worksheets
Start from a worksheet for provisioning BAF by providing the following information:
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-14
OL-3351-01
Page 15

Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
Step 1 Determine if the network is switched or is nailed up.
Note For a nailed up (Cisco SC2200) connection, define the field values in the Nailed Connection table using
the SIGPATH tag ID. The fields are SIGPATH, BEARCHAN, TRUNKGRP, and TRUNKNUM.
SIGPATH and BEARCHAN parameters are both hex entries and should be prefixed by 0x.
Step 2 Enter switch data in the Switch Information table. (Refer to the “SWITCHINFO Tag ID” section on
page 4-19.)
Step 3 Define the Trunk Group table. You need to determine if each trunk is tandem or direct, default NPA for
originating, or default NPA for terminating.
Note Define the Zone Information table by entering a number and a description for each zone.
Step 4 Assign an NPANXX to each zone. (Refer to the “NPANXX Tag ID” section on page 4-13.)
Step 5 Assign a rate type (zone to zone). (Refer to the“RATING-TYPE Tag ID” section on page 4-17.)
Step 6 Define the structure code/call type for every rate type. (Refer to the“MAPTYPE Tag ID” section on
page 4-4.)
Step 7 Define the toll-free NPAs. (Refer to the“TOLLFREE Tag ID” section on page 4-26.)
Step 8 Define rating exception cases. (Refer to the“RATE-EXC Tag ID” section on page 4-16.)
BAF Configuration Parameters
Step 9 Define the country codes. (Refer to the“COUNTRY Tag ID” section on page 4-3.)
BAF Configuration Parameters
Updating BAF Structure Codes
Use the MAPTYPE tag ID to update selected BAF structure codes, such as category codes and call types.
Refer to the “MAPTYPE Tag ID” section on page 4-4 for field name descriptions and values.
Example:
prov-rtrv:MAPTYPE:
prov-ed:MAPTYPE:maptype=map type mnemonic,answered=new structure code,unanswered=new
structure code,calltype=new BAF call type number
Adding a New Zone ID
Use the ZONE-INFO tag ID to add new zone IDs. Refer to the “ZONE-INFO Tag ID” section on
page 4-29 for field name descriptions and values.
Example:
prov-rtrv:ZONE-INFO:
prov-add:ZONE-INFO:zone=<zone number>,desc="<description>"
OL-3351-01
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
5-15
Page 16

BAF Configuration Parameters
Adding a New NPANXX (Zone Membership)
Use the NPANXX tag ID to add new NPANXX information. Refer to the “NPANXX Tag ID” section on
page 4-13 for field name descriptions and values.
Example:
prov-rtrv:NPANXX:npanxx=<areacode and exchange 6 digits>
prov-add:NPANXX:npanxx=<6digits>,lata=<latanumber>,zone=<zonenumber>
Chapter 5 Configuring BAMS for BAF Output
5-16
Cisco Billing and Measurements Server User’s Guide
OL-3351-01
 Loading...
Loading...