Page 1

Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
Software Release 8.6
Cisco Unified Communications Management Suite
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-25111-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this
URL: www.cisco.com/go/trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership
relationship between Cisco and any other company. (1110R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display
output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in
illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
© 2005-2011 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Preface vii
Audience vii
Conventions vii
Product Documentation viii
Related Documentation viii
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request ix
ix
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Prerequisites 1-1
Product Overview 1-1
Server and Client System Requirements 1-2
Server Requirements 1-2
Client Requirements 1-4
VMware Guidelines 1-5
Terminal Server Support for Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 1-7
Enabling and Disabling Terminal Services on a Windows Server 1-7
Enabling and Disabling FIPS on a Windows Server 1-7
Port Usage 1-8
2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor 2-1
Preparing to Install Service Monitor 2-1
Preparing the Server 2-2
Gathering Information to Provide During Installation 2-3
Ensuring That Required Ports Are Free 2-3
NTP Configuration Notes 2-3
Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor 2-4
OL-25111-01
Starting Cisco Unified Service Monitor 2-7
Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6 2-7
Upgrade Paths 2-8
Backing Up Service Monitor Files and Database 2-8
Understanding the Effect an Upgrade Has on Your Data 2-9
Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade 2-9
Deleting Cisco 1040 Configuration Files from TFTP Servers 2-10
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
iii
Page 4

Contents
Preventing Extra Processing After Upgrade 2-10
Configuring NTP 2-11
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6 2-11
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6 from 8.0 and 8.5 2-12
Adding Service Monitor to Unified Communications Manager 2-14
Performing Post-Upgrade Configuration for Cisco 1040s 2-15
Sample Cisco 1040 Sensor Configuration Files 2-16
Uninstalling and Reinstalling Service Monitor 2-17
Uninstalling Service Monitor 2-17
Reinstalling Service Monitor 2-18
Configuring Your System for SNMP Queries 2-19
CHAPTER
APPENDIX
3 Getting Started with Service Monitor 3-1
Configuring Security 3-1
Configuring Users (ACS and Local RBAC) 3-1
Configuring Users Using the Common Services Local Login Module 3-2
Enabling SSL Between the Browser and the Server 3-2
Configuring Service Monitor 3-3
A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade A-1
User Inputs for Typical Installation A-1
User Inputs for Custom Installation A-2
Password Information A-7
Password Rules for a New Installation A-7
Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords A-7
Password Rules for an Upgrade Installation A-8
Password Rules for Reinstallation A-8
Password Descriptions A-8
Common Services admin Password A-8
System Identity Account Password A-8
Common Services Guest Password A-9
Common Services Database Password A-9
Changing Passwords A-9
Changing the Common Services Admin Password A-9
Changing the casuser Password A-10
APPENDIX
iv
B Licensing B-1
Licensing Overview B-1
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 5

Verifying License Status B-1
Licensing Scenarios B-2
Licensing Messages B-3
Licensing Process B-3
Obtaining a PAK B-4
Obtaining a License File B-4
Registering a License File with Service Monitor B-4
Contents
APPENDIX
I
NDEX
C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS C-1
Cisco Secure ACS Support C-1
Service Monitor Integration Notes C-1
Common Services Local Login Module Authentication Roles C-2
Configuring the System Identity User in Common Services C-3
Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server C-3
Changing the AAA Mode to ACS in Common Services C-4
Registering an Application to Cisco Secure ACS from the Command Line C-5
Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in Cisco Secure ACS C-5
Verifying the Service Monitor and Cisco Secure ACS Configuration C-5
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
v
Page 6

Contents
vi
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 7

Audience
Preface
This manual describes Cisco Unified Service Monitor (Service Monitor) and provides instructions for
installing and upgrading it.
The audience for this document includes:
• IP communications and IP telephony management personnel.
• Administrative personnel monitoring the overall service levels of their organization.
• Network engineering personnel who evaluate and design IP network infrastructures.
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions:
Item Convention
Commands and keywords boldface font
Variables for which you supply values italic font
Displayed session and system information
Information you enter
Variables you enter
Menu items and button names boldface font
Selecting a menu item in paragraphs Option > Network Preferences
Selecting a menu item in tables Option > Network Preferences
screen font
boldface screen font
italic screen font
OL-25111-01
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material not covered in the
publication.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
vii
Page 8
Preface
Caution Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment
damage or loss of data.
Warning
This symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury.
Product Documentation
Note We sometimes update the documentation after original publication. Therefore, you should review the
documentation on Cisco.com for any updates.
Table 1 describes the product documentation that is available.
Table 1 Product Documentation
Document Title Available on Cisco.com at These URLs
Release Notes for Cisco Unified
Service Monitor 8.6
Cisco Unified Service Monitor 8.6
Compatibility Matrix
Installation Guide for Cisco
Unified Service Monitor 8.6
User Guide for Cisco Unified
Service Monitor 8.6
Context-sensitive online help Click the Help link in the upper-right hand corner of the window or the help button in
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6536/prod_release_notes_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6536/products_device_support_tables_list.ht
ml
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6536/prod_installation_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6536/products_user_guide_list.html
any dialog box.
Related Documentation
Note We sometimes update the documentation after original publication. Therefore, you should review the
documentation on Cisco.com for any updates.
Table 2 describes the additional documentation that is available.
Table 2 Related Documentation
Document Title Available on Cisco.com at These URLs
Quick Start Guide for Cisco 1040
Sensor
Release Notes for Cisco Unified
Operations Manager 8.6
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
viii
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/net_mgmt/cisco_unified_service_monitor/2.1/quick/
guide/1040qs21.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6535/prod_release_notes_list.html
OL-25111-01
Page 9
Preface
Table 2 Related Documentation (continued)
Document Title Available on Cisco.com at These URLs
Installation Guide for Cisco
Unified Operations Manager
(Includes Service Monitor) 8.6
User Guide for Cisco Unified
Operations Manager 8.6
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6535/prod_installation_guides_list.html
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6535/products_user_guide_list.html
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as an RSS feed and set content to be
delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free service. Cisco currently
supports RSS Version 2.0.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
ix
Page 10

Preface
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
x
OL-25111-01
Page 11

Prerequisites
• Product Overview, page 1-1
• Server and Client System Requirements, page 1-2
• Terminal Server Support for Windows 2003 and Windows 2008, page 1-7
• Port Usage, page 1-8
Product Overview
Cisco Unified Service Monitor (Service Monitor), a product from the Cisco Unified Communications
Management Suite, receives and analyzes data from these sources when they are installed in your voice
network and configured properly:
• Cisco Unified Communications Manager (Unified Communications Manager) clusters—Retain Call
Detail Records (CDRs) and Call Management Records (CMRs). CDRs include Mean Opinion Score
(MOS) values that were calculated on IP phones and voice gateways using the Cisco Voice
Transmission Quality (CVTQ) algorithm.
CHAP T ER
1
OL-25111-01
For Unified Communications Manager versions that Service Monitor supports, see Cisco Unified
Service Monitor 8.6 Compatibility Matrix. For information about configuring Unified
Communications Manager clusters to work with Service Monitor, see User Guide for Cisco Unified
Service Monitor.
• Sensors—Network Analysis Modules (NAMs) and Cisco 1040 Sensors (Cisco 1040s)—Compute
MOS for each RTP stream. Service Monitor obtains data from sensors every 60 seconds.
Service Monitor compares MOS against a threshold value—default or user-specified—for the codec in
use. When MOS drops below the threshold, Service Monitor generates SNMP traps and sends them to
up to four recipients. Service Monitor stores the data that it obtains in the database, where it is available
for display on Service Monitor reports. Service Monitor purges the database daily to maintain a
configurable number of days of data. (For more information, see the online help.)
If you configure Cisco Unified Operations Manager (Operations Manager) as a trap receiver for
Service Monitor, Operations Manager can further analyze, display, and act on the traps that Service
Monitor generates. Operations Manager can generate service quality events, display and track these
events on a real-time dashboard, and display and store event history. You can configure additional event
settings on Operations Manager to alert you if MOS drops below a threshold or if too many (configurable
number) service quality events occur during a period of time (configurable number of minutes). In
addition, you can configure Operations Manager to send notifications by e-mail, SNMP trap, and syslog
message.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
1-1
Page 12

Server and Client System Requirements
Service Monitor 8.6 can be installed in two modes—Enterprise Network Deployment mode and
Managed Service Provider (MSP) Network Deployment mode. You can specify the mode that you need
to use, when you install the product. You need to choose which mode to install based on your
requirements. See User Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor for more details.
Server and Client System Requirements
• Server Requirements, page 1-2
• Client Requirements, page 1-4
• VMware Guidelines, page 1-5
Server Requirements
Note • For Service Monitor to coreside on a system with other applications in the Cisco Unified
Communications Management Suite, see the coresidence requirements in Installation Guide for
Cisco Unified Operations Manager 8.6.
• Service Monitor supports VMware for virtualization. For more information, see VMware
Guidelines, page 1-5.
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Table 1-1 lists the server requirements for a standalone installation of Service Monitor.
1-2
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 13
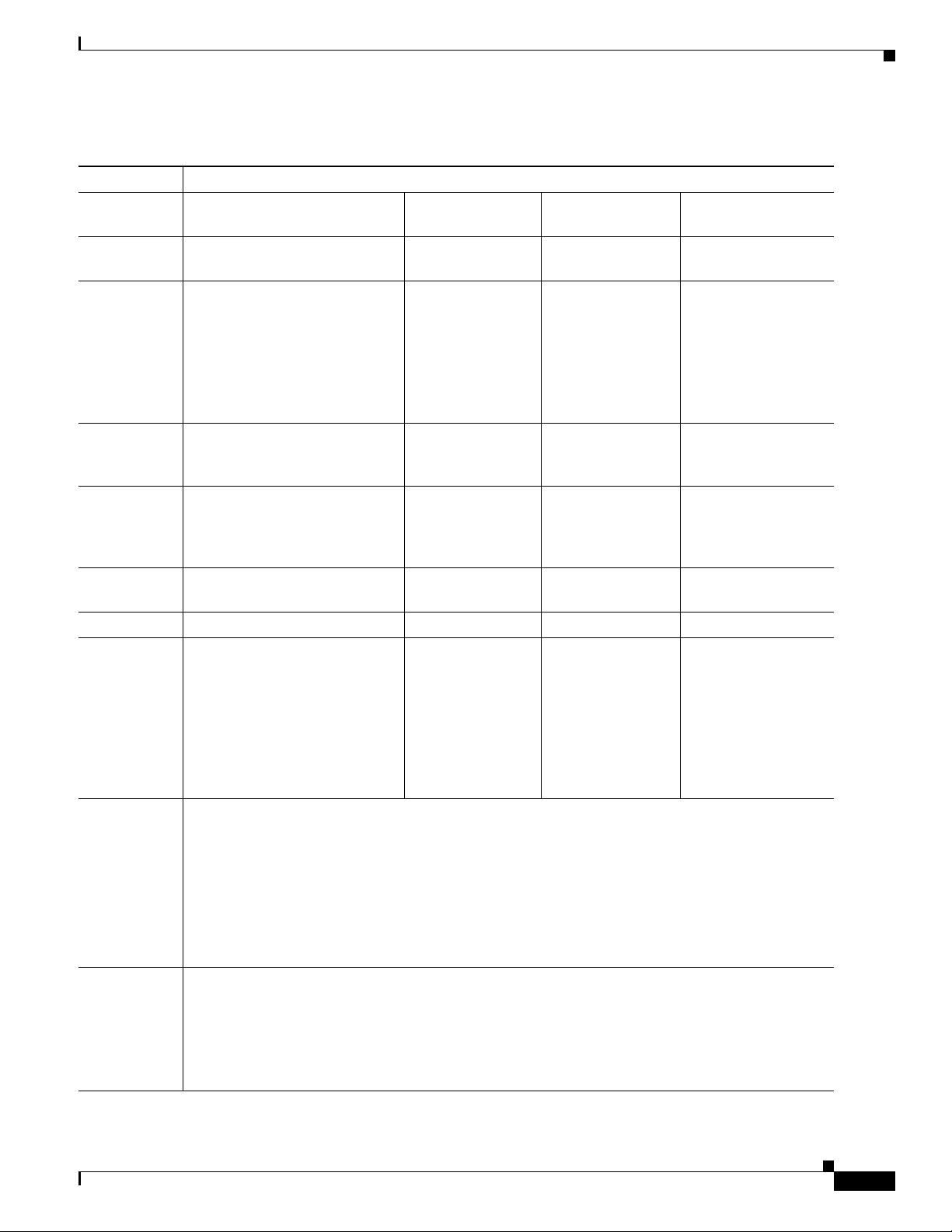
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Table 1-1 Server Requirements for Service Monitor Standalone Installation
Description Specifications
System
Up to 1,000 phones Up to 10,000
parameters
Call rate
Up to 50 Up to 150 Up to 500 Up to 500
(CDRs/min)
NAM/1040
Up to 100 Up to 1000 Up to 5000 Up to 5000
Sensor
RTP Stream
rate
(Streams/min)
phones
Server and Client System Requirements
Up to 30,000
phones
Up to 45,000 phones
CDR/ RTP
Up to 50/100 Up to 150/800 Up to 500/1500 Up to 500/1500
S t r e a m r a t e
(together)
Processor Two processors or dual core, 2
GHz minimum each
Memory
(RAM)
Page file
1
2
Disk space
4 GB 4 GB 4 GB 4 GB
8GB 8GB 8GB 8GB
3
• 84 GB recommended
• NTFS file system (required
for secure operation).
• At least 200 MB in
Windows temporary
directory (%TEMP%)
Software
4 5 6 7
• Windows Server 2003 Standard Edition or Enterprise Edition with Service Pack 2 (32 Bit);
• Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition or Enterprise Edition (32 bit) with Service Pack 2
• VMware ESX 3.5 or ESXi 4.x. For requirements, see VMware Guidelines.
• ODBC Driver Manager
9
3.5.10 or later.
Two processors or
dual core, 2 GHz
minimum each
Four processors,
quad core or two
dual core, 2 GHz
minimum each
Four processors, quad
core or two dual core,
2 GHz minimum each
8
• NTP-Configure the server to use Network Time Protocol (NTP) to synchronize with the
timeserver that is used by Cisco Unified Communications Managers in your network. See NTP
Configuration Notes, page 2-3.
Hardware
• Color monitor.
• CD-ROM drive.
• Support for one or two 1-GB NICs (one is required, and the second is for failover support; both
NIC cards must have the same IP address)
1. If server RAM size is less than 4 GB, then a warning message appears.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
1-3
Page 14
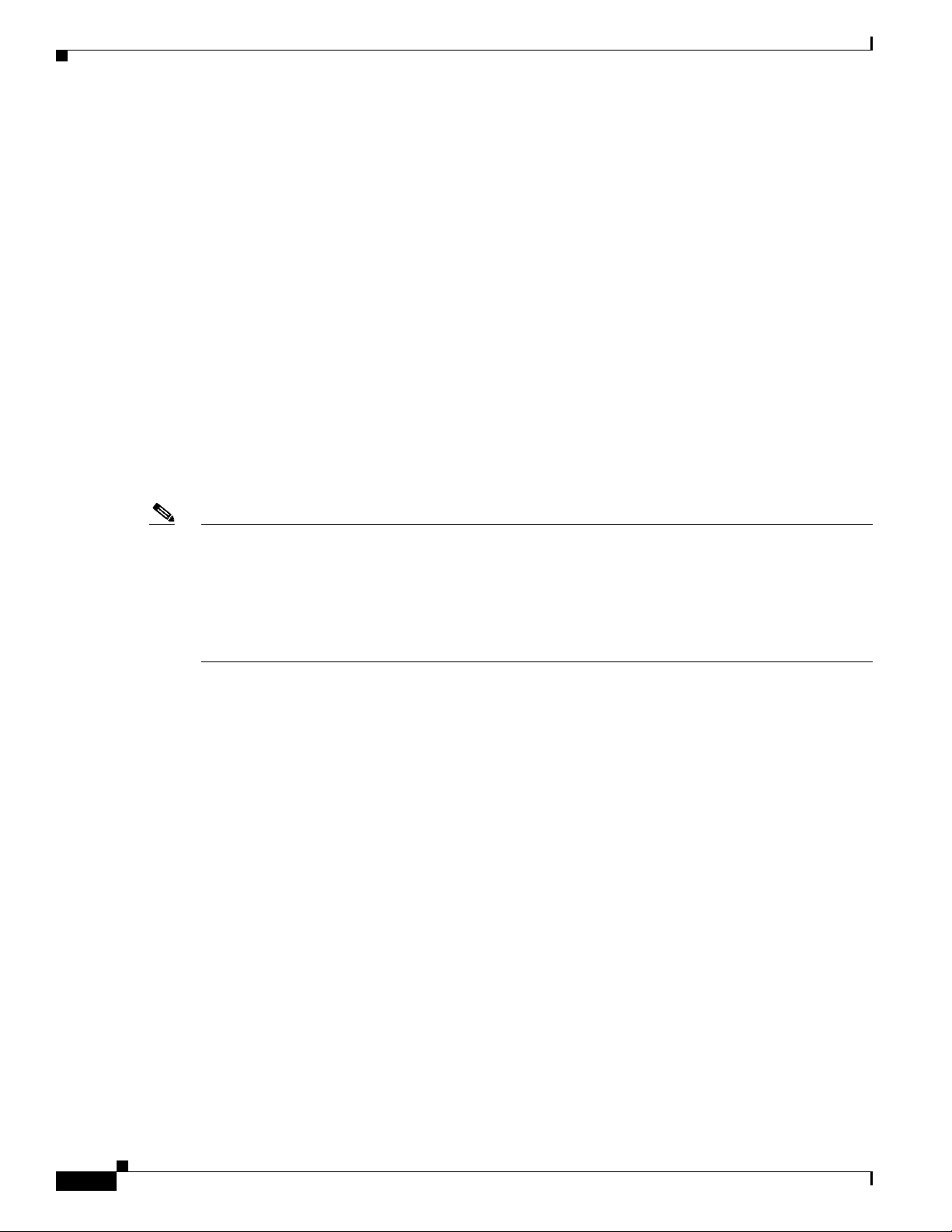
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Server and Client System Requirements
2. While configuring the page file, you should set both the minimum and maximum file size parameters to same size. Page size also needs to be
changed from automatic to manual. This ensures that Windows creates a page file of the required size.
3. Do not install Service Monitor on a FAT file system
4. You must install Service Monitor on a dedicated system. Do not install Service Monitor on a Primary Domain Controller (PDC) or Backup
Domain Controller (BDC). Do not install Service Monitor in an encrypted directory. Service Monitor does not support directory encryption.
5. Immediately following installation, the TCP/IP stack should be hardened to avoid denial of service attacks. Ensure these steps are taken before
using the product.
—Apply Windows security patches. See Microsoft Security Updates for Denial of Service Attacks for details. The system that you use for
your Operations Manager server should meet all security guidelines that Microsoft recommends for Windows 2003 or 2008 Server.
(CSCsy83124) See the NSA website for security guidance: http://www.nsa.gov.
—Specifically, the TCP/IP stack should be hardened to avoid denial of service attacks. Refer to the section "Security Consideration for
Network Attacks" on page 121 of the The Windows Server 2003 - Security Guide, v2.1 which can be downloaded from the NSA website.
—On the Windows Server 2003 Enterprise Edition or 2008 Standard or Enterprise Edition server, block remote access to all TCP/UDP ports
except for those ports used by Operations Manager required for external access.
6. The default locale for your Windows operating system must be set to US-English.
7. Windows Terminal Services is supported in Remote Administration mode only. Use of Windows Terminal Services or Remote Desktop and
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) to remotely control the server is not recommended for performing day-to-day operations (for example,
running reports, keeping dashboards open, and so on).
8. Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition (64 bit) and Windows Server 2008 R2 Edition are not supported Operation Systems
9. To verify the version of ODBC Driver Manager, from the Windows desktop, choose Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative Tools
> Data Sources (ODBC). Select the About tab. If necessary, install Microsoft Data Access Component (MDAC) 2.5 or later
Note • If your browser is configured to use a proxy server for your LAN, Service Monitor cannot open some
report windows. Disable proxy server settings in Internet Options. (From the Connections tab, click
LAN Settings.)
• When using Service Monitor, disable any software on your desktop that you use to prevent popup
windows from displaying. Service Monitor must be able to open multiple windows to display
information.
Client Requirements
Table 1-1 lists the client hardware and software requirements.
1-4
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 15
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Table 1-1 Minimum Client Hardware and Software Requirements
Component Minimum Requirement
Hardware/software
Processor Dual Core, 2 GHz minimum (Windows PC or Apple Mac)
Memory 2 GB RAM minimum
• Color monitor with video card set to 256 colors (For optimum viewing on the Service
Monitor display, We recommend that you use the highest native resolution supported by
the client PC and monitor. A large, high-resolution display will also allow for less
scrolling through information presented and increase operator efficiency. The minimum
resolution recommended is 1440 x 900.)
• Any PC or server platform with a Pentium IV processor, 1.0 GHz or greater, running one
of the following:
–
Windows XP Professional Service Pack 2
–
Windows 2003 Server (Standard and Enterprise Editions) without Windows
Terminal Services
–
Windows Server 2008 Enterprise Edition SP2
–
Windows Server 2008 Standard Edition SP2
Server and Client System Requirements
Browser
• Microsoft Internet Explorer 8.x or 9.x
• Firefox 3.6, 4.0 or 5.0
Note We strongly recommend that you use a browser from a client system to perform
Adobe Flash Player 10 or later.
VMware Guidelines
Service Monitor supports VMware ESX 3.5 and ESXi 4.x. Service Monitor must have the same system
resources available to it inside the virtualization environment that it has for a standard (nonvirtual)
installation. When determining the performance of Service Monitor in your virtual setup, you must take
into account that the VMware instance will use some system resources that would normally be available
to Service Monitor in a standard installation. Additional requirements for running Service Monitor in a
virtualization environment might vary with your environment and system load. For more information,
see Best Practices for Cisco Unified Communication Suite on Virtualization at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6535/prod_white_papers_list.html
The following configurations are supported for Service Monitor in a virtual environment:
• An instance of Service Monitor, supporting up to 45,000 phones
• Each of these products installed on a separate virtual machine:
day-to-day operations (for example, running reports). Use of Windows Terminal
Services, Remote Desktop, or VNC to perform day-to-day operations is not
recommended.
OL-25111-01
–
Operations Manager
–
Service Monitor
–
Service Statistics Manager
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
1-5
Page 16
Server and Client System Requirements
–
Provisioning Manager
• Each product installed on one virtual machine, supporting up to 10,000 phones and 1,000 IP devices.
Note For more information, see Best Practices for Cisco Unified Communication Suite on Virtualization at the
following website:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps6535/prod_white_papers_list.html.
When setting up Service Monitor in a VMware environment, keep in mind the following guidelines:
• Resources must be reserved at 100% of requirements for the virtual machine.
• To use a licensed Service Monitor in a VMware environment, you must configure your virtual
machine with a static MAC address.
Note You can run Service Monitor in Evaluation mode with a dynamic MAC address. However,
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
before you can run a licensed copy of Service Monitor, you must set up a static MAC
address.
To set up a static MAC address, do the following:
Step 1 Power down the virtual machine.
Step 2 In the Inventory panel, select the virtual machine.
Step 3 Click the Summary tab and then click Edit Settings.
Step 4 In the Hardware list, select Network Adapter.
Step 5 For MAC address, select Manual.
Step 6 Change the current MAC address of the virtual machine to a static MAC address in the following range:
00:50:56:00:00:00 to 00:50:56:3F:FF:FF.
When assigning a static MAC address, we recommend choosing a complex address. An example of a
complex MAC address is 00:50:56:01:3B:9F. A less complex MAC address is 00:50:56:11:11:11,
because of the repeating ones (1).
1-6
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 17

Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Terminal Server Support for Windows 2003 and Windows 2008
Note Choosing a complex address makes it less likely that you will choose an address being used by
another customer. This can prevent accidental licensing overlap between different customers.
Step 7 Click OK.
Terminal Server Support for Windows 2003 and Windows 2008
You can install Service Monitor on a system with Terminal Services enabled in Remote Administration
mode. However, you cannot install Service Monitor on a system with Terminal Services enabled in
Application mode.
If you have enabled Terminal Services in Application mode, you should disable the Terminal Server,
reboot the system, and start the installation again.
Table 1-2 summarizes the Terminal Services features in Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 Server.
.
Table 1-2 Terminal Services on Windows 2003 and Windows 2008 Server
Windows 2003 /Windows 2008
Server Features
Terminal Server Remote access and virtual system. Each client has its own virtual
OS environment.
Remote Desktop Administration Remote access only. All clients use the same (and the only)
operating system.
Note Do not use terminal services to perform day-to-day tasks in
Cisco Unified Communications Management Suite
applications, such as viewing the Service Level View in
Operations Manager or viewing reports in Service Monitor.
Enabling and Disabling Terminal Services on a Windows Server
To enable or disable Terminal Server, go to Manage Your Server > Add or Remove a Role > Terminal
Server.
To enable or disable Remote Desktop Administration, go to Control Panel > System > Remote.
Enabling and Disabling FIPS on a Windows Server
Sometimes, Federal Information Processing Standard (FIPS) compliant encryption algorithms are
enabled for Group security policy on Windows server.
OL-25111-01
When FIPS compliance is activated, the SSL authentication may fail on the Service Monitor server. To
allow Service Monitor to work properly, disable FIPS compliance.
To enable or disable FIPS on Windows 2003 server:
Step 1 Go to Start > Settings > Control Panel > Administrative tools > Local Security Policy.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
1-7
Page 18
Port Usage
Step 2 Click Local Polices > Security Options.
Step 3 Select System cryptography: Use FIPS compliant algorithms for encryption, hashing, and signing.
Step 4 Right-click the selected policy and click Properties.
Step 5 Select Enabled or Disabled to enable or disable FIPS compliant algorithms.
Step 6 Click Apply.
Port Usage
Note The ports in Table 1-3 and Table 1-4 should not be scanned.
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
The Local Security Policy window appears.
You must reboot the server for the changes to take effect.
Before you install Service Monitor, ensure that the ports listed in Table 1-3 and Table 1-4 are free.
Table 1-3 lists the ports that Service Monitor uses. Common Services is installed with Service Monitor.
Table 1-4 lists the ports that Common Services uses.
Table 1-3 Service Monitor Port Usage
Protocol Port Number Service Name
TCP 22 SFTP—Service Monitor uses SFTP to obtain data from Unified
Communications Manager versions 5.x and later.
UDP 53 DNS.
UDP 67 and 68 DHCP.
TCP 2000 SCCP—Service Monitor uses SCCP to communicate with Cisco 1040s.
TCP 43459 Database.
UDP 5666 Syslog—Service Monitor receives syslog messages from Cisco 1040s.
TCP 5665–5680 Interprocess communication between the user interface and back-end
processes.
These ports must be free.
Note Service Monitor uses TFTP to find the configuration file for a given Cisco 1040. Service Monitor by
default uses port 69 on the TFTP servers.
1-8
Common Services is also installed on the Service Monitor system. Table 1-4 lists the ports used by
Common Services.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 19
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
Table 1-4 Common Services Port Usage
Port
Protocol
TCP 23 Telnet.
TCP 25 Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
TCP 49 TACACS+ and ACS.
UDP 69 Trivial File Transfer Protocol (TFTP).
UDP 161 Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP).
TCP 443 Common Services HTTP server in SSL mode.
TCP 514 Remote Copy Protocol.
UDP 514 Syslog.
UDP 1431 Trap Listener to MAC Notification Traps.
TCP 1741 Common Services HTTP Protocol.
— 2002 Communicate with Cisco Secure ACS server when AAA mode is ACS.
TCP 8898 Log Server.
TCP 9007 Tomcat shutdown.
TCP 9009 Ajp13 connector used by Tomcat.
TCP 15000 Log server.
UDP 16236 UT Host acquisition.
TCP 40050-
TCP 40401 LicenseServer.
TCP 42340 Daemon Manager - Tool for Server Processes.
UDP 42342 OSAGENT.
TCP 42344 ANI HTTP Server.
UDP 42350 Event Services Software (ESS) (alternate port is 44350/udp.)
TCP 42351 Event Services Software (ESS) Listening (alternate port is 44351/tcp.)
TCP 42352 ESS HTTP (alternate port is 44352/tcp.)
TCP 42353 ESS Routing (alternate port is 44352/tcp.)
TCP 43441 CMF Database.
TCP 50001 SOAPMonitor.
Number Service Name
If IIS is on your system, even when IIS is disabled, you will be asked if you want
to select an HTTPS port other than 443 during installation or upgrade. To avoid
port conflict, select another port.
CSTM ports used by Common Services applications, such as Device and
40070
Credential Repository (DCR).
Port Usage
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
1-9
Page 20

Port Usage
Chapter 1 Prerequisites
1-10
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 21

CHAP T ER
2
Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
This section contains the following topics:
• Preparing to Install Service Monitor, page 2-1
• Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor, page 2-4
• Starting Cisco Unified Service Monitor, page 2-7
• Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6, page 2-7
• Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6, page 2-11
• Uninstalling and Reinstalling Service Monitor, page 2-17
• Configuring Your System for SNMP Queries, page 2-19
Preparing to Install Service Monitor
To ensure a successful Service Monitor installation, do the following before you install Cisco Unified
Service Monitor (Service Monitor):
• Make sure that your hardware and software meet the requirements for the server. See Server
Requirements, page 1-2.
• Prepare the Service Monitor server for installation. See Preparing the Server, page 2-2.
• Verify that the ports that Service Monitor and Common Services use are not being used. See
Ensuring That Required Ports Are Free, page 2-3.
• Gather information that you might need to provide during the Service Monitor installation. See
Gathering Information to Provide During Installation, page 2-3.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-1
Page 22
Preparing to Install Service Monitor
Preparing the Server
Note The system that you use for your Service Monitor server should meet all the security guidelines that
Microsoft recommends for Windows 2003 Server. See the NSA website for security guidance
(http://www.nsa.gov/ia/mitigation_guidance/security_configuration_guides/operating_systems.shtml).
Specifically, the TCP/IP stack should be hardened to avoid denial of service attacks. Refer to the section
"Security Consideration for Network Attacks" on page 121 of the The Windows Server 2003 - Security
Guide, v2.1 which can be downloaded from the NSA website.
Service Monitor is already installed on a server when you install Operations Manager. To activate
Service Monitor on such a server, register your PAK on Cisco.com and install the license file for Cisco
Unified Service Monitor. (See Licensing, page B-1.)
Before installing, reinstalling, or upgrading Service Monitor, do the following:
• Verify that the Primary and Active regional settings on your Windows system are set to either US
English or Japanese. Other options are not supported by Service Monitor.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
You can set the Active regional settings in Control Panel > Regional and Language Options >
Regional Options.
• Set the correct date and time on the system. For more information, see Common Services online
help.
• Verify that the drive that you choose to install Service Monitor on is an NTFS file system.
• Verify that the fully qualified domain name of the system on which Service Monitor is installed is
Domain Name System (DNS) resolvable. The IP address must be resolvable to the DNS, and the
DNS must be resolvable to the IP address (forward and reverse lookup, in DNS terms). To check
name resolution on the Service Monitor server, in a command prompt, run the command
NMSROOT\bin>smNameRes.exe.
Note NMSROOT is the directory where Service Monitor is installed on your system. If you
selected the default directory during installation, it is C:\PROGRA~1\CSCOpx.
• Disable the virus scan software on your system. You can restart it after the installation is complete.
• Disable Cisco Security Agent if it is running on your system. You can restart it after the installation
is complete.
• Close all open or active programs. Do not run other programs during the installation process.
Do not install Service Monitor on:
• A Primary Domain Controller (PDC) or Backup Domain Controller (BDC).
• An Advanced Server with terminal services enabled in application server mode.
2-2
You must install Service Monitor on a system with a static IP address.
You can perform the following tasks either before or after you complete the installation:
• Configure the Service Monitor server to use the same NTP server that Unified Communications
Manager uses. See NTP Configuration Notes, page 2-3.
• Obtain the license file or files for Service Monitor. See Licensing, page B-1.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 23

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Read through the following installation notes:
• Service Monitor is installed in the default directory SystemDrive:\Program Files\CSCOpx
where SystemDrive is the Windows operating system installed directory.
If you select another directory during installation, the application is installed in that directory.
The destination folder should not contain the following special characters:
! @ # $ % ^ & * ( ) + | } { " [ ] ; ' / ? < > , . ` =
If errors occur during installation, check the installation log file in the root directory on the drive
where the operating system is installed. Each installation creates a new log file; for example:
C:\Ciscoworks_install_YYYYMMDD_hhmmss.log, where YYYYMMDD denotes the year, month and
date of installation and hhmmss denotes the hours, minutes and seconds of installation.
For example:
C:\Ciscoworks_install_20060721_182205.log
• You can click Cancel at any time to end the installation. However, any changes to your system will
not be undone. For example, if any new files were installed or if there were any changes to the
system files, you need to manually clean up the installation directories.
Preparing to Install Service Monitor
• To monitor Service Monitor using a third-party SNMP management tool, see Configuring Your
System for SNMP Queries, page 2-19.
Gathering Information to Provide During Installation
During installation, you will need to set passwords for various user accounts and for the database. For
more information about the user accounts and for password rules, see Password Information, page A-7.
You might need to supply mail settings—such as HTTPS port—and security certificate information. For
more information, see User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade, page A-1. You will also
need to supply the license file location or select Evaluation only. For more information, see Licensing,
page B-1.
Ensuring That Required Ports Are Free
The ports that Service Monitor and Common Services use must be free. For a list of ports, see Port
Usage, page 1-8.
NTP Configuration Notes
The clocks on Service Monitor and Unified Communications Manager servers must be synchronized for
Service Monitor reports to include complete and up-to-date information and accurately reflect activity
during a given time period. These notes offer a starting point and do not provide complete instructions
for configuring NTP.
To get st a r t ed:
OL-25111-01
1. Talk with your Unified Communications Manager administrators to determine the time server with
which Service Monitor should synchronize. You might find Cisco IP Telephony Clock
Synchronization: Best Practices, a white paper on Cisco.com, useful; read it at this URL:
http://cisco.com/en/US/products/sw/voicesw/ps556/prod_white_papers_list.html.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-3
Page 24

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2. Use your system documentation to configure NTP on the Windows Server 2003 system where
Service Monitor will be installed. Configure NTP with the time server being used by
Cisco Unified Communication Managers in your network. You might find How to configure an
authoritative time server in Windows Server, useful; look for it at this URL:
http://support.microsoft.com/kb/816042.
Note This website is Copyright © 2010, Microsoft Corporation.
We also recommend that you configure your NAMs to use the same NTP server that Unified
Communications Manager instances use.
Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor
To ensure that your system is ready for the installation, perform the necessary tasks in Preparing to
Install Service Monitor, page 2-1.
Note Windows Management Instrumentation (WMI) services must not run during installation; WMI services
can lock processes and cause the installation to terminate unexpectedly. The installation procedure will
notify you if WMI services are running and ask permission to stop the services and restart them after
installation completes.
Note We recommend that you do not terminate the installation while it is running.
Step 1 As the local administrator, log in to the machine on which you will install the Service Monitor software.
Step 2 Unzip the file that you obtained through the eDelivery system.
Step 3 Click the setup.exe file.
The Cisco Unified Service Monitor Setup Program window opens.
Step 4 Read any messages and acknowledge them to continue:
• If WMI Services are running on the system—A message is displayed stating that, for the installation
to proceed, the script will stop WMI Services, complete the installation, and restart WMI Services.
To continue, click OK.
• If IIS is detected (even if it is disabled)—A message is displayed. To avoid port conflict with IIS,
click OK: in a later step you will be prompted to select an HTTPS port other than 443.
The Welcome window appears.
Step 5 Click Next. The Software License Agreement window appears.
Step 6 Select the I accept the terms of the license agreement radio button and click Next.
2-4
Step 7 The Licensing Information window appears.
Step 8 Select one of the following, and then click Next:
• License File Location—Browse to enter the location.
• Evaluation Only—You can complete the installation and then register the license file later.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 25

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Note For instructions on obtaining a license file, see Licensing Process, page B-3.
The installation program checks the name lookup and DHCP. If a static IP address is not configured
on your system, the DHCP-Enabled Network Adapters dialog box appears. Click Yes .
If you are installing on a virtual machine with a dynamic MAC address, another warning message
will be displayed. Click Yes . (Although you can complete the installation, Service Monitor will not
be functional. For more information, see VMware Guidelines, page 1-5.)
The Setup Type window appears.
Step 9 Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Typical—To install Service Monitor 8.6 while entering the least amount of input.
• Custom—To install Service Monitor 8.6, select the destination directory, and enter passwords for
user and database.
If you choose the Typ i c a l installation mode, the following information will be supplied for you for the
Common Services installation: guest password, Common Services database password, Mail Settings,
and self-signed certificate information. The remainder of this procedure is written for a Typical
installation.
Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor
If you choose the Custom installation mode, you will be prompted to enter the above information during
the installation process.
Step 10 Click Next. The Select Components window appears.
Step 11 Select the Install Cisco Unified Service Monitor 8.6 radio button. Click Next.
The installation program checks dependencies and system requirements. The System Requirements
window displays the results of the requirements check and advises whether the installation can continue.
One of the following might occur:
• If there is not enough disk space for the installation, or the correct operating system is not present,
or the minimum required RAM is not available, the installation program displays an error message
and stops.
• If your system has less than 4 GB of RAM, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
WARNING: System memory is less than the requirement for Cisco Unified Service
Monitor system to support high call volume.
Please refer to Service Monitor documentation for more details and upgrade the
memory to at least 4GB if you have high call volume.
• If your disk space is less than 73000 MB, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
Current disk space <nnnn> MB is less than Recommended disk space 73000 MB and it
may affect performance.
OL-25111-01
Note The disk space displayed in the System Requirements window is the least amount you need
to install and start Service Monitor. The Recommended disk space (see table on page 1-2)
is the minimum space necessary to use Service Monitor.
• If other minimum requirements are not met, the installation program displays an appropriate
message and continues installing.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-5
Page 26

Installing Cisco Unified Service Monitor
Step 12 Click Next. The Enter Admin Password window appears:
a. Enter a password for the admin user, confirm, and click Next.
Note Note the password. You will need it to log in to Service Monitor until you have configured
The Enter System Identity Account Password window appears
b. Enter a System Identity Account password (and confirm), and click Next. The Create casuser dialog
box appears.
c. Click Yes to continue with the installation.
Note • If you selected the Custom installation mode, during this part of the installation you will be asked
to enter the following information: guest password, Common Services database password, Mail
Settings, and self-signed certificate information.
• If you need to change the HTTPS port from 443 to another number, the Mail Settings information
page will be displayed.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
security and created other users.
Step 13 The Summary window appears, displaying the current settings. Click Install. As the installation
proceeds, additional informational messages are displayed.
Step 14 Click OK on additional messages as they are displayed to ensure that the installation progresses:
• You will see a dialog box with the following message displayed:
Before you reboot this system, configure automatic time synchronization on it using
NTP. Configure this system to use the time server that is used by Cisco Unified
Communications Managers in your network.
For more information, see NTP Configuration Notes, page 2-3.
• If Windows SNMP service is not installed on your system, you will see this message:
Windows SNMP service is not installed on your system. This installation will continue.
To install support for system application and host resources MIBs, you must install
the Windows SNMP service, using Add/Remove Programs from the Control Panel.
If you installed Service Monitor for evaluation only, you will see this message:
Please obtain a valid license key from Cisco.com within 90 days.
A Restart window appears. The Yes, I want to restart my computer now radio button is selected.
Step 15 Click Finish. (You must restart your computer before you start Step 16.)
Step 16 After the installation completes:
a. Verify that Service Monitor was installed correctly by starting Service Monitor. See Starting Cisco
Unified Service Monitor, page 2-7.
2-6
Note You should wait approximately fifteen minutes after the installation completes before starting
Service Monitor. This allows all of the process to start. If you do not wait, you may receive the
following HTTP Status 500 error message:
that prevented it from fulfilling this request.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
The server encountered an internal error ()
OL-25111-01
Page 27

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
b. Exclude the NMSROOT\databases directory from virus scanning. Problems can arise if database
files are locked because of virus scanning.
Note NMSROOT is the directory where Service Monitor is installed on your system. If you selected
the default directory during installation, it is C:\Program Files\CSCOpx.
Starting Cisco Unified Service Monitor
Before starting Service Monitor, do the following:
• Ensure that you restarted your system after you completed the installation or upgrade to
Service Monitor 8.6.
• Disable any popup blocker utility that is installed on your client system.
Starting Cisco Unified Service Monitor
Note By default, SSL is not enabled in Common Services. See “Setting up Browser-Server Security” in
Common Services online help for information about how to enable SSL.
Step 1 Enter the appropriate address in your browser as follows:
• If you upgraded to Service Monitor 8.6 and had previously enabled SSL in Common Services, type
https://servername:port number where:
–
servername is the IP address or DNS name of the server where Service Monitor resides
–
port number is either 443 (the default) or the HTTPS port you entered during the upgrade. A
login page is displayed.
• If SSL is not enabled, type http://servername:1741 where servername is the IP address or DNS name
of the server where Service Monitor resides. A login page is displayed.
Step 2 Enter a username and password. If you do not have a username, you can do the following:
• Enter admin for the user ID.
• Enter the password that you entered for the admin user during installation and press Enter.
The Service Monitor home page appears.
Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6
OL-25111-01
This section contains the following information:
• Upgrade Paths, page 2-8
• Backing Up Service Monitor Files and Database, page 2-8
• Understanding the Effect an Upgrade Has on Your Data, page 2-9
• Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9
• Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-7
Page 28

Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6
• Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9
• Deleting Cisco 1040 Configuration Files from TFTP Servers, page 2-10
• Preventing Extra Processing After Upgrade, page 2-10
• Configuring NTP, page 2-11
Upgrade Paths
You can upgrade from Service Monitor 8.0, Service Monitor 8.0.1, Service Monitor 8.5 to Service
Monitor 8.6.
To save existing call data so that you can continue to run reports against it, you must migrate the call
data before you start the upgrade. For more information, see Planning for Data Migration and Migrating
Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9.
During the upgrade, configuration data—TFTP servers, trap receivers, credentials, and so on—is
automatically migrated.
Upgrading from Enterprise Network Deployment mode to MSP Network Deployment mode is not
supported. To change from MSP mode to Enterprise mode, you must uninstall Service Monitor and
freshly install it again.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Backing Up Service Monitor Files and Database
The upgrade procedure does not back up your system. You should perform a backup before you upgrade.
Step 1 Back up the Service Monitor database:
a. Log in to the system where Service Monitor is installed.
b. Stop the daemon manager using this command:
net stop crmdmgtd
c. From NMSROOT\databases\qovr, copy the files qovr.db and qovr.log to a tape, an external drive, or
a network directory (not a local directory). Doing so ensures data integrity in case of hardware
failure and ensures that backup data does not exhaust local disk space.
Note Ensure that you know the qovr database password. In case you do not know the password,
modify the password before you proceed. For instructions, see “Changing the Password for
the Service Monitor Database” in User Guide for Service Monitor 8.6.
d. Restart the daemon manager using the following command:
net start crmdmgtd
Note To restore the database, perform steps 1a and 1b, restore the saved files, and perform step 1c.
2-8
Step 2 Back up Service Monitor configuration data using the Common Services backup described in the
Common Services online help.
The Common Services online help is only available through the Common Services pages, which are
located in the Administration tab.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 29

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
To access the Common Services online help, you can use the following procedure:
1. Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security. The Setting up
Security page appears.
2. Click Help. The online help opens.
Note You must restore the Service Monitor configuration data and additionally restore the database.
To restore both the Service Monitor database and configuration data requires two steps: restoring the
database manually and restoring the configuration data (using the procedures referenced in Step 2 b).
Understanding the Effect an Upgrade Has on Your Data
To migrate report data (also know as call data), you must run the call migration tool before you start the
upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6. For more information, see Planning for Data Migration and Migrating
Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9.
When you upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6:
Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6
• Service Monitor configuration data—such as credentials and threshold settings—is retained.
• Common Services data is retained.
Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade
Migrating call data is optional. However, to keep the data, you must migrate it before you start the
upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6. You can find the call migration tool in the zip file that contains the
Service Monitor product on Cisco.com.
Note When you perform a data migration using the CMT tool, and an upgrade from Service Monitor 8.0 to
Service Monitor 8.6, the grading of the previous calls will be Unknown after the upgrade, in CDR,
CVTQ, and Sensor reports. The reason is that the grading logic is absent in 8.0. Grading will work
properly for the new calls that are made.
Global MOS Threshold settings cannot be retained for upgrades from Service Monitor 8.0 to 8.6. Two
configurable MOS settings were introduced in Service Monitor 8.5, so the data was not available in 8.0.
To configure global MOS threshold settings after the upgrade is complete, select Administration >
Global > Threshold.
The README_QOVR_CMT.TXT. file that is included with the Call Migration Tool provides estimates
of the time that data migration takes and the disk space it uses. It also explains the effect that running
the tool has on Operations Manager and Service Statistics Manager, if they are installed in your network.
OL-25111-01
Step 1 Download the zip file (CUSM8_6.zip) that contains the Service Monitor product from Cisco.com. You
can navigate to the file as follows:
a. Go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/partner/products/ps6536/tsd_products_support_series_home.html.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-9
Page 30

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Preparing to Upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6
b. If you have not already logged in to Cisco.com, log in.
c. Click the Download Software link.
d. Follow the online instructions to select Cisco Unified Service Monitor 8.6 and download the zip file.
Step 2 Extract the QOVR_CMT.zip file from the \install\CallMigrationTool folder in the CUSM8_6.zip file.
Step 3 Extract the README_QOVR_CMT.TXT file from the QOVR_CMT.zip file and use the information in
it to plan for and execute the migration.
Deleting Cisco 1040 Configuration Files from TFTP Servers
We recommend that you delete existing Cisco 1040 configuration and binary image files from your
existing TFTP servers before you perform the upgrade. Delete the following files:
• Cisco 1040 Sensor configuration files: One QOVDefault.CNF file and a QoVMACAddress.CNF file
for each Cisco 1040.
• Binary image file: For example, SvcMonAA2_nn.img
Preventing Extra Processing After Upgrade
If you are monitoring calls from Unified Communications Manager 6.x or later, you should consider
that:
• During the upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6, all processes are stopped. Service Monitor is not
available to receive data files from Unified Communications Manager 6.x or later.
• After the upgrade completes:
–
Unified Communications Manager sends all backlogged data files to Service Monitor; this takes
time.
–
Service Monitor drops old files.
To avoid this processing, before you upgrade, you can:
• Prevent Unified Communications Manager 7.x and later from sending backlogged data. To do so,
edit the billing server and uncheck the Resend on Failure check box. For more information, see
Unified Communications Manager Configuration in User Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
8.6.
• For Unified Communications Manager software releases earlier than 7.x, prevent them from sending
data by deleting the Service Monitor Application Billing Server from Unified Communications
Manager and restarting the CDR Repository Manager service. See Removing Service Monitor from
Unified Communications Manager, page 2-10. You can add Service Monitor to Unified
Communications Manager and restart the CDR Repository Manager service again after the upgrade
completes.
2-10
Removing Service Monitor from Unified Communications Manager
This procedure is recommended if you are performing an upgrade to Service Monitor 8.6 and you are
monitoring calls from Unified Communications Manager 6.x.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 31

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Note You can configure Unified Communications Manager 7.x and later to not resend data on failure. For
more information, see Unified Communications Manager Configuration in User Guide for Cisco Unified
Service Monitor 8.6.
Step 1 Launch Unified Communications Manager Serviceability.
Step 2 Select Tools > CDR Management.
Step 3 Scroll down to Billing Applications Server Parameters and look for the Service Monitor server that you
want to upgrade. You can identify the server from entries in the Hostname/IP Address and User Name
columns; (smuser will be displayed in the User Name column).
Step 4 Select the check box for the Service Monitor server that you will upgrade.
Step 5 Click Delete Selected.
Step 6 Restart the CDR Repository Service:
a. From Unified Communications Manager Serviceability, select Tools > Control Center - Network
Services.
b. From the list of servers, select the publisher.
c. Scroll down to CDR Services.
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
d. Select the Cisco CDR Repository Manager radio button.
e. Click the Restart button.
Configuring NTP
If you plan to add Unified Communications Managers to Service Monitor and have not already
configured the Service Monitor server to use NTP, do so before or after you upgrade. For more
information, see NTP Configuration Notes, page 2-3.
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Before you perform the upgrade, you must:
• Disable the virus scan software on your system. You can restart it after the upgrade is complete.
• Disable Cisco Security Agent if it is running on your system. You can restart it after the upgrade is
complete.
Note Immediately after you upgrade, Cisco 1040s are unable register to Service Monitor until you complete
the tasks listed in Performing Post-Upgrade Configuration for Cisco 1040s, page 2-15.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-11
Page 32

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6 from 8.0 and 8.5
Step 1 Make sure you have taken the appropriate steps to migrate the report data (also know as call data), see
Planning for Data Migration and Migrating Call Data Before the Upgrade, page 2-9.
Step 2 As the local administrator, log in to the machine on which you will install the Service Monitor software.
Step 3 Unzip the file that you obtained through the eDelivery system.
Step 4 Click the setup.exe file.
The Cisco Unified Service Monitor Setup Program window opens.
Step 5 Read any messages and acknowledge them to continue:
• If WMI Services are running on the system—A message is displayed stating that, for the installation
to proceed, the script will stop WMI Services, complete the installation, and restart WMI Services.
To continue, click OK.
• If IIS is detected (even if it is disabled)—A message is displayed. To avoid port conflict with IIS,
click OK: in a later step you will be prompted to select an HTTPS port other than 443.
The Welcome window appears.
Step 6 Click Next. The Software License Agreement window appears.
Step 7 Select the I accept the terms of the license agreement radio button and click Next.
Step 8 The Licensing Information window appears.
Step 9 Select one of the following, and then click Next:
• License File Location—Browse to enter the location.
• Evaluation Only—You can complete the installation and then register the license file later.
Note For instructions on obtaining a license file, see Licensing Process, page B-3.
The installation program checks the name lookup and DHCP. If a static IP address is not configured
on your system, the DHCP-Enabled Network Adapters dialog box appears. Click Yes .
If you are installing on a virtual machine with a dynamic MAC address, another warning message
will be displayed. Click Yes . (Although you can complete the installation, Service Monitor will not
be functional. For more information, see VMware Guidelines, page 1-5.)
The Setup Type window appears.
Step 10 Select one of the following radio buttons:
• Typical—To install Service Monitor 8.6 while entering the least amount of input.
• Custom—To install Service Monitor 8.6, select the destination directory, and enter passwords for
user and database.
If you choose the Typ i c a l installation mode, the following information will be supplied for you for the
Common Services installation: guest password, Common Services database password, Mail Settings,
and self-signed certificate information. The remainder of this procedure is written for a Typical
installation.
2-12
If you choose the Custom installation mode, you will be prompted to enter the above information during
the installation process.
Step 11 Click Next. The Select Components window appears.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 33

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Step 12 Select all radio buttons. Click Next.
The installation program checks dependencies and system requirements. The System Requirements
window displays the results of the requirements check and advises whether the installation can continue.
One of the following might occur:
• If there is not enough disk space for the installation, or the correct operating system is not present,
or the minimum required RAM is not available, the installation program displays an error message
and stops.
• If your system has less than 4 GB of RAM, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
WARNING: System memory is less than the requirement for Cisco Unified Service
Monitor system to support high call volume.
Please refer to Service Monitor documentation for more details and upgrade the
memory to at least 4GB if you have high call volume.
• If your disk space is less than 73000 MB, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
Current disk space <nnnn> MB is less than Recommended disk space 73000 MB and it
may affect performance.
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Note The disk space displayed in the System Requirements window is the least amount you need
to install and start Service Monitor. The Recommended disk space (see table on page 1-2)
is the minimum space necessary to use Service Monitor.
• If other minimum requirements are not met, the installation program displays an appropriate
message and continues installing.
Step 13 Click Next. The Enter Admin Password window appears:
a. Enter a password for the admin user, confirm, and click Next.
Note Note the password. You will need it to log in to Service Monitor until you have configured
security and created other users.
The Enter System Identity Account Password window appears
b. Enter a System Identity Account password (and confirm), and click Next. The Create casuser dialog
box appears.
c. Click Yes to continue with the installation.
Note • If you selected the Custom installation mode, during this part of the installation you will be asked
to enter the following information: guest password, Common Services database password, Mail
Settings, and self-signed certificate information.
• If you need to change the HTTPS port from 443 to another number, the Mail Settings information
page will be displayed.
OL-25111-01
Step 14 The Summary window appears, displaying the current settings. Click Install. As the installation
proceeds, additional informational messages are displayed.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-13
Page 34

Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Step 15 Click OK on additional messages as they are displayed to ensure that the installation progresses:
• You will see a dialog box with the following message displayed:
Before you reboot this system, configure automatic time synchronization on it using
NTP. Configure this system to use the time server that is used by Cisco Unified
Communications Managers in your network.
For more information, see NTP Configuration Notes, page 2-3.
• If Windows SNMP service is not installed on your system, you will see this message:
Windows SNMP service is not installed on your system. This installation will continue.
To install support for system application and host resources MIBs, you must install
the Windows SNMP service, using Add/Remove Programs from the Control Panel.
If you installed Service Monitor for evaluation only, you will see this message:
Please obtain a valid license key from Cisco.com within 90 days.
A Restart window appears. The Yes, I want to restart my computer now radio button is selected.
Step 16 Click Finish. (You must restart your computer before you start Step 16.)
Step 17 After the installation completes:
a. Verify that Service Monitor was installed correctly by starting Service Monitor. See Starting Cisco
Unified Service Monitor, page 2-7.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Note You should wait approximately fifteen minutes after the installation completes before starting
Service Monitor. This allows all of the process to start. If you do not wait, you may receive the
following HTTP Status 500 error message:
that prevented it from fulfilling this request.
b. Exclude the NMSROOT\databases directory from virus scanning. Problems can arise if database
The server encountered an internal error ()
files are locked because of virus scanning.
Adding Service Monitor to Unified Communications Manager
If you removed a Service Monitor Application Billing Server from Unified Communications Manager
before upgrading, add the Service Monitor Application Billing Server back to Unified Communications
Manager.
Note Perform this task on Unified Communications Manager version 5.x and later only. Perform this task only
while Service Monitor is up and running.
Step 1 Launch Unified Communications Manager Serviceability.
Step 2 Select Tools > CDR Management.
Step 3 Scroll down to Billing Applications Server Parameters and click Add New.
2-14
Step 4 Enter data in the following fields:
• Host Name / IP Address—Enter the IP address of the system where Cisco Unified Service Monitor
is installed.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 35

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
• User Name—Enter smuser.
Note Do not enter any username other than smuser.
• Password—Enter a password. The default password is smuser. To change this password:
–
Change it in Service Monitor first. (For more information, see the online help.)
–
Enter the same password that you entered for smuser while configuring other settings in Service
Monitor.
Note If you changed the password in Service Monitor and Unified Communications Manager does
not immediately accept the new password, wait one minute and enter the new password
again.
• Select SFTP Protocol.
• Directory Path—Enter /home/smuser/.
Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Note Do not enter any directory path other than /home/smuser.
Step 5 Click Add. In some cases, for CDR/CMR files to be delivered to a newly added billing server, you must
first restart the CDR Repository Management Service:
a. From Unified Communications Manager Serviceability, select Tools > Control Center - Network
Services.
b. From the list of servers, select the publisher.
c. Scroll down to CDR Services.
d. Select the Cisco CDR Repository Manager radio button.
e. Click the Restart button.
Performing Post-Upgrade Configuration for Cisco 1040s
This section provides the minimum steps required to enable Cisco 1040s to register with
Service Monitor 8.6. For complete configuration procedures, including how to add NAMs and Unified
Communications Managers to Service Monitor, see the configuration checklists in User Guide for Cisco
Unified Service Monitor.
Step 1 Start Service Monitor. See Starting Cisco Unified Service Monitor, page 2-7.
Step 2 Configure the default configuration file:
OL-25111-01
a. Select Administration > Configuration > Cisco 1040 > Setup. The Setup page appears.
b. Update the Default Configuration to TFTP Server fields:
–
Image Filename—Enter SvcMonAB2_102.img.
–
Primary Service Monitor—Enter an IP address or DNS name.
–
Secondary Service Monitor—(Optional) Enter an IP address or DNS name.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-15
Page 36

Upgrading to Service Monitor 8.6
Note Occasionally, updated binary image files might be released. For the names of supported binary image
files, see Cisco Unified Service Monitor 8.6 Compliance Matrix.
c. Click OK. Service Monitor stores the default configuration file locally and copies it to the TFTP
servers that are configured in Service Monitor.
d. Copy the binary image file, SvcMonAB2_102.img, from NMSROOT\ImageDir on the Service
Monitor server to the root location on the TFTP server. (NMSROOT is the directory where Service
Monitor is installed; its default location is C:\Program Files\CSCOpx.)
e. Verify that the newly created QOVDefault.CNF file is on the TFTP server. If it is not, upload it to
the root location on the TFTP server from the Service Monitor image file directory,
NMSROOT\ImageDir. For examples of the configuration files, see Sample Cisco 1040 Sensor
Configuration Files, page 2-16.
Note If you use Unified Communications Manager as a TFTP server, Service Monitor cannot copy
configuration files to Unified Communications Manager due to security settings on the latter. You will
need to manually upload the configuration file as described in Step 2e. After uploading the configuration
file, reset the TFTP server on Unified Communications Manager. For more information, see Unified
Communications Manager documentation.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Step 3 Wait a few minutes and verify that the Cisco 1040s have registered to Service Monitor. If they have not,
reset the Cisco 1040s by disconnecting them from power and connecting them again.
Warning
Before disconnecting a Cisco 1040 Sensor, read the regulatory compliance and safety information in
Quick Start Guide for Cisco 1040 Sensor.
Sample Cisco 1040 Sensor Configuration Files
Service Monitor creates these files when you edit the configuration through the user interface and when
a Cisco 1040 uses the default configuration file to register. These samples are provided to enable you to
confirm that the contents of a sensor configuration file are correct.
Note Always use the Service Monitor user interface to edit sensor configuration files to ensure that Service
Monitor functions properly. Do not edit Cisco 1040 Sensor configuration files on the TFTP server.
Default 1040 Sensor Configuration File—QOVDefault.CNF
In the default configuration file, the ID, A000, is a placeholder; an IP address or alternatively a DNS
name is provided for the Receiver. The last updated data and time represent the last time that the default
configuration was updated from the Service Monitor user interface.
Receiver=10.92.99.22;;
ID=A000
Image=SvcMonAB2_102.img
LastUpdated=11_16_2010-6_59_46.78
CDPGlobalRunState=true
SyslogPort=UDP:5666
SkinnyPort=TCP:2000
2-16
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 37

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Uninstalling and Reinstalling Service Monitor
MAC-Specific 1040 Sensor Configuration File—QOV001120FFCF18.CNF
In a MAC-specific configuration file, the default ID, A000, has been replaced by the sensor MAC
address; the receiver DNS name is included, although an IP address could appear instead. The last
updated date and time represent the last time that the configuration file was updated; this could be when
the sensor registered with Service Monitor or when a user edited the configuration file from the Service
Monitor user interface.
Receiver=qovr-weekly;;
ID=001120FFCF18
Image=SvcMonAB2_102.img
LastUpdated=11_13_2010-4_3_57.578
CDPGlobalRunState=true
SyslogPort=UDP:5666
SkinnyPort=TCP:2000
Uninstalling and Reinstalling Service Monitor
This section contains the following:
• Uninstalling Service Monitor, page 2-17
• Reinstalling Service Monitor, page 2-18
Uninstalling Service Monitor
Caution You must use the Cisco Unified Service Monitor uninstallation program to remove Service Monitor from
your system. If you try to remove the files and programs manually, you can seriously damage your
system.
Use this procedure to uninstall Service Monitor.
Step 1 As the local administrator, log in to the system on which Service Monitor is installed, and select Start >
All Programs > Cisco Unified Service Monitor > Uninstall Cisco Unified Service Monitor to start
the uninstallation process.
Note If WMI Services are running on the system, a message is displayed stating that, for the
uninstallation to proceed, the script will stop WMI Services, complete the uninstallation, and
restart WMI Services. To continue, click Ye s.
A confirmation dialog box is displayed.
Step 2 Click Ye s if you want to proceed with uninstallation.
OL-25111-01
Step 3 Click Finish and restart your system.
Step 4 Delete any files that remain in the NMSROOT directory. NMSROOT is the directory where Service
Monitor was installed; its default location is C:\Program Files\CSCOpx.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-17
Page 38

Uninstalling and Reinstalling Service Monitor
Reinstalling Service Monitor
Note To reinstall Service Monitor on a system with Operations Manager, you must reinstall both Operations
Manager and Service Monitor; see Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Operations Manager (Includes
Service Monitor).
The existing database is preserved when you reinstall Service Monitor. However, the reinstallation
procedure does not perform a backup prior to copying and installing new files on your system. To
perform a backup, see Backing Up Service Monitor Files and Database, page 2-8.
For information about passwords that you will be asked to set during reinstallation, see User Inputs for
Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade, page A-1. Be sure to read Fixing Problems That Can Occur
After You Change Passwords, page A-7.
Use this procedure to install Service Monitor 8.6 on a system where Service Monitor 8.6 is already
installed.
Step 1 As the local administrator, log in to the machine on which you will reinstall the Service Monitor
software.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
Step 2 Unzip the file that you obtained through the eDelivery system.
Step 3 Click the setup.exe file.
The Cisco Unified Service Monitor Setup Program window opens.
Step 4 Read any messages and acknowledge them to continue:
• If WMI Services are running on the system—A message is displayed stating that, for the installation
to proceed, the script will stop WMI Services, complete the installation, and restart WMI Services.
Click OK.
• A message is displayed stating that a database backup will not be performed. Click OK.
The Welcome window appears.
Step 5 Click Next. The Software License Agreement window appears.
Step 6 Select the I accept the terms of the license agreement radio button and click Next.
The installation program checks the name lookup and DHCP. The Setup Type dialog box appears.
Step 7 Select the Typical radio button and click Next. The Select Applications window appears.
Step 8 Select all radio buttons. Click Next.
The installation program checks dependencies and system requirements.
The System Requirements window displays the results of the requirements check and advises whether
the installation can continue. One of the following might occur:
• If there is not enough disk space for the installation, the installation program displays an error
message and stops.
• If your system has less than 4 GB of RAM, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
WARNING: System memory is less than the requirement for Cisco Unified Service
Monitor system to support high call volume.
Please refer to Service Monitor documentation for more details and upgrade the
memory to at least 4GB if you have high call volume.
2-18
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 39

Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
• If your disk space is less than 73000 MB, you can continue with the installation after reading this
message:
Current disk space <nnnn> MB is less than Recommended disk space 73000 MB and it may
affect performance.
Note The disk space displayed in the System Requirements window is the least amount you need
to install and start Service Monitor. The Recommended disk space (see table on page 1-2)
is the minimum space necessary to use Service Monitor.
• If other minimum requirements are not met, the installation program displays an appropriate
message and continues installing.
Step 9 Click Next. The Change casuser Password window appears.
Step 10 Enter and confirm a password or click Next to have the system generate a random password for you. The
Summary window appears, displaying the current settings.
Step 11 Click Install.
Step 12 The Summary window appears, displaying the current settings.
Step 13 Click Install. The reinstallation proceeds and the Setup Complete window appears.
Step 14 Click Finish.
Configuring Your System for SNMP Queries
Configuring Your System for SNMP Queries
Service Monitor implements the system application MIB. If you want to use a third-party SNMP
management tool to make SNMP queries against the server where Service Monitor is installed, Windows
SNMP service must be installed.
Note To improve security, the SNMP set operation is not allowed on any object ID (OID) in the system
application MIB. After installation of Service Monitor, you should modify the credentials for Windows
SNMP service to not use a default or well-known community string.
You can install Windows SNMP service before or after you install Service Monitor. Use this procedure
to determine whether Windows SNMP service is installed.
Step 1 Verify that Windows SNMP service is installed on the server where you will install Service Monitor. To
do so:
a. Open the Windows administrative tool Services window.
b. Verify the following:
–
SNMP Service is displayed on the Windows administrative tool Services window; if so,
Windows SNMP service is installed.
–
SNMP service status is Started; if so, SNMP service is running.
Step 2 If Windows SNMP service is not installed, install it.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
2-19
Page 40

Configuring Your System for SNMP Queries
Note Windows online help provides instructions for adding and removing Windows components, such as
Windows SNMP service. To locate the instructions, try selecting the Index tab in Windows online help
and entering a keyword or phrase, such as install SNMP service.
Chapter 2 Installing, Uninstalling, and Upgrading Service Monitor
2-20
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 41

Getting Started with Service Monitor
This section contains the following topics:
• Configuring Security, page 3-1
• Configuring Service Monitor, page 3-3
Configuring Security
Service Monitor relies on security that you configure using Common Services. To get started, see these
topics:
• Configuring Users (ACS and Local RBAC), page 3-1
• Enabling SSL Between the Browser and the Server, page 3-2
For more information, see Setting Up Security in the Common Services online help.
CHAP T ER
3
Configuring Users (ACS and Local RBAC)
What Service Monitor users can see and do is determined by the user role. Service Monitor supports two
Common Services modes for authenticating users:
• Local RBAC—You select a supported login module to provide authentication and authorization. By
default, Common Services uses the Local login module to assign roles, along with privileges
associated with those roles. For more information, refer to Configuring Users Using the Common
Services Local Login Module, page 3-2.
• ACS—In ACS mode, authentication and authorization is provided by Cisco Secure Access Control
Server (ACS). Cisco Secure ACS specifies the privileges associated with roles, ensuring that users
perform only certain tasks.
To use ACS mode, Cisco Secure ACS must be installed on your network and Service Monitor must
be registered with Cisco Secure ACS. For more information, see Security Configuration with
Cisco Secure ACS, page C-1.
Note When Operations Manager and Service Monitor coreside on the same machine, the AAA
mode configuration in use is same for both the products.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
3-1
Page 42

Configuring Security
Configuring Users Using the Common Services Local Login Module
Step 1 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security > Local User Setup.
The Local User Setup page appears.
Step 2 Click Add. The User Information page appears.
Step 3 Enter the user information.
Step 4 Click OK.
To understand how each user role relates to tasks in Service Monitor, view the Permission Report.
Step 1 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Reports > Permission
Report > Generate Report. A new window opens.
Step 2 From the Go to list, select Cisco Unified Service Monitor to view the task list for Service Monitor.
Chapter 3 Getting Started with Service Monitor
Enabling SSL Between the Browser and the Server
When you start Service Monitor, the login page always opens in secure mode, providing secure access
between the client browser and the Service Monitor server. In secure mode, Secure Socket Layer (SSL)
is used to encrypt the transmission channel between the browser and the server. To use secure mode
throughout Service Monitor, enable SSL in Common Services.
Note If you enable SSL on a system with Service Monitor and Operations Manager, SSL is enabled for both
applications.
Step 1 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security > Browser-Server
Security Mode Setup. The Browser-Server Security Mode Setup dialog box appears.
Step 2 Select the Enable radio button.
Step 3 Click Apply.
Step 4 Log out from Service Monitor, and close all browser sessions.
Step 5 Restart the daemon manager from the command line by entering these commands:
net stop crmdmgtd
net start crmdmgtd
Step 6 Restart the browser and use the secure URL to restart Service Monitor:
https://<servername>:<https port>
3-2
Note If you enter http://<servername>:1741 in your browser and SSL is enabled, you will be directed
to the secure URL.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 43

Chapter 3 Getting Started with Service Monitor
Configuring Service Monitor
The Service Monitor CDR Call Report relies on system-defined data and user-defined dial plans. To
define dial plans—and call categories—see Configuring Call Classification in User Guide for Cisco
Unified Service Monitor.
Note If you use Service Statistics Manager for long-term reporting on Service Monitor data:
• Be aware that Service Statistics Manager relies on Service Monitor to categorize call data.
• Ensure that you configure call classification in Service Monitor before you install or upgrade to
Service Statistics Manager 8.6.
To configure Service Monitor, see the appendix Configuration Checklists and Tips in User Guide for
Cisco Unified Service Monitor.
Configuring Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
3-3
Page 44

Configuring Service Monitor
Chapter 3 Getting Started with Service Monitor
3-4
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 45

User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
This appendix provides information on the user inputs during Service Monitor installation,
reinstallation, and upgrade.
This appendix contains:
• User Inputs for Typical Installation, page A-1
• User Inputs for Custom Installation, page A-2
• Password Information, page A-7
User Inputs for Typical Installation
Table A- 1 lists information you need to supply when installing Service Monitor for the first time in
Typical mode.
APPENDIX
A
Table A-1 User Inputs for New Installation: Typical
Settings Value
Applications to install Select the applications you want to install.
Password for admin user No default values.
Enter the admin password. For more information on passwords, see
Password Information.
Password for System
Identity account
No default values.
Enter the System Identity account password. For more information on
passwords, see Password Information.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-1
Page 46

User Inputs for Custom Installation
Table A-1 User Inputs for New Installation: Typical (continued)
Settings Value
Password for casuser The password is generated randomly if you leave the field blank.
Mail Settings:
• HTTPS port
• Administrator’s e-mail
address
• SMTP server name
Table A- 2 lists information you need to enter during an upgrade installation in Typical mode.
Table A-2 User Inputs for Upgrade Installation: Typical
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Note Appears if IIS was detected on your system, and you indicated
that you would like to avoid port conflict between IIS and Service
Monitor by reconfiguring the default HTTPS port. Otherwise,
Mail Settings appears only during a Custom installation.
The default values are:
• Port number 443—Enter a value from the range that is displayed.
• admin@domain.com.
• localhost name.
Settings Value
Password for casuser
account
The password is generated randomly if you leave the field blank. (See
Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords,
page A-7.)
Applications to install Select the applications you want to install.
Table A- 3 lists information you need to enter while reinstalling in Typical mode.
Table A-3 User Inputs for Reinstallation: Typical
Settings Value
Password for casuser
account
The password is generated randomly if you leave the field blank. (See
Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords,
page A-7.)
Applications to install Select the applications you want to install.
User Inputs for Custom Installation
Table A- 4 lists the information you must enter while installing for the first time in Custom mode.
Table A-4 User Inputs for a New Installation: Custom
A-2
Settings Value
Destination folder The default location is System drive:\Program Files\CSCOpx. Select another
location if you want to install in a specific location. We recommend that you
specify a short path for the destination folder.
Applications to
Select the applications you want to install.
install
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 47

Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Table A-4 User Inputs for a New Installation: Custom (continued)
Settings Value
Password for users
admin and guest
No default values. Enter the admin and guest passwords. For more information
on passwords, see Password Information.
(Mandatory)
Password for System
Identity account
(Mandatory)
Password for user
No default values.
Enter the system identity account password. For more information on
passwords, see Password Information.
The password is generated randomly if you leave the field blank.
casuser
Password for the
database
Enter the database password. For more information on passwords, see
Password Information.
(Mandatory)
Mail Settings:
(Mandatory)
• HTTPS port
• Administrator’s
e-mail address
• SMTP server
The default values are:
• 443—If IIS is installed on your server, enter a port number from the range
displayed.
• admin@domain.com.
• localhost name.
name
Data for the
Self-signed
Certificate:
(Mandatory)
• Country Code
• State
• City
• Organization
By default, the self-signed certificate is generated using the organization that
Windows is registered to, and the host name.
You must enter the host name. You can leave the other fields blank.
Note Common Services allows you to create security certificates to enable
SSL communication between your client browser and management
server. Self-signed certificates are valid for five years from the date of
creation. When a certificate expires, the browser prompts you to install
the certificate again from the server where you have installed Common
Services. In Typical mode, this certificate is automatically generated.
Name
User Inputs for Custom Installation
OL-25111-01
• Organization
Unit Name
• Host name
• E-mail Address
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-3
Page 48

User Inputs for Custom Installation
Table A- 5 lists the information you must enter during an upgrade installation in Custom mode.
Note If Service Statistics Manager is installed in your network and you change either of the following:
• The password for the user admin
• The destination location (the directory in which Service Monitor is installed)
Service Statistics Manager stops collecting data from Service Monitor. You can reenable data collection
by performing the procedures that are documented in Release Notes for Cisco Unified Service Statistics
Manager 1.3.
Table A-5 User Inputs for an Upgrade Installation: Custom
Settings Value
Applications to
install
Password for users
admin and guest
(Optional)
Password for System
Identity account
(Mandatory)
Password for the user
casuser (Optional)
Password for the
database (Optional)
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Select the applications you want to install.
You can change the passwords for the admin and guest users. To keep the
existing passwords, leave the fields blank. (See Fixing Problems That Can
Occur After You Change Passwords, page A-7.)
No default values.
Enter the System Identity account password. For more information on
passwords, see Password Information.
If you do not enter a password, the setup program generates a random password
for you.
(See Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords,
page A-7.)
Leave the fields blank to use the existing password.
A-4
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 49

Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Table A-5 User Inputs for an Upgrade Installation: Custom (continued)
Settings Value
Mail Settings:
You can choose to keep the existing information.
(Optional)
• HTTPS port
• Administrator’s
e-mail address
• SMTP server
name
Data for the
Self-signed
Certificate:
(Mandatory)
• Country Code
• State
• City
• Organization
• Organization
Unit Name
• E-mail Address
You can change the Self-signed certificate information. By default, the
installation program uses the existing self-signed certificate information.
If you want to generate a new certificate, uncheck the Keep Existing Certificate
check box, and enter the country code, state, city, company, organization, and
host name for HTTPS.
You must enter the host name. You can leave the other fields blank.
Note Common Services allows you to create security certificates to enable
SSL communication between your client browser and management
server. Self-signed certificates are valid for five years from the date of
creation. When the certificate expires, the browser prompts you to
install the certificate again from the server where you have installed
Common Services. In Typical mode, this certificate is automatically
generated.
User Inputs for Custom Installation
Table A- 6 lists the information you must enter while reinstalling in Custom mode.
Note If you have Service Statistics Manager installed and you change either of the following:
• The password for the user admin
• The destination location (the directory in which Service Monitor is installed)
Service Statistics Manager stops collecting data from Service Monitor. You can reenable data collection
by performing the procedures that are documented in Release Notes for Cisco Unified Service Statistics
Manager 1.3.
Table A-6 User Inputs for Reinstallation: Custom
Settings Value
Destination folder The default location is System drive:\Program Files\CSCOpx.
We recommend that you specify a short path for the destination folder.
Password for users
admin and guest
(Optional)
You can change the passwords for the admin and guest users. To keep the
existing passwords, leave the fields blank.
(If you change the password for the admin user, see Fixing Problems That Can
Occur After You Change Passwords, page A-7.)
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-5
Page 50

User Inputs for Custom Installation
Table A-6 User Inputs for Reinstallation: Custom (continued)
Settings Value
Password for System
Identity account
(Mandatory)
Password for user
casuser (Optional)
Password for the
database (Optional)
Mail Settings:
(Optional)
• HTTPS port
• Administrator’s
e-mail address
• SMTP server
name
Data for the
Self-signed
Certificate:
(Mandatory)
• Country Code
• State
• City
• Organization
Name
• Organization
Unit Name
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
You can change the passwords for the System Identity account. To keep the
existing passwords, leave the fields blank.
If you do not enter a password, the setup program generates a random password
for you. (See Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords,
page A-7.)
Leave the fields blank to retain the existing password.
You can choose to keep the existing information.
By default, the self-signed certificate is generated using the organization that
Windows is registered to, and the host name.
You must enter the host name. You can leave the other fields blank.
Note Common Services allows you to create security certificates to enable
SSL communication between your client browser and management
server. Self-signed certificates are valid for five years from the date of
creation. When the certificate expires, the browser prompts you to
install the certificate again from the server where you have installed
Common Services. In Typical mode, this certificate is automatically
generated.
A-6
• Hostname
• E-mail Address
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 51

Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Password Information
This topic provides information on the use of passwords during installation.
It contains:
• Password Rules for a New Installation, page A-7
• Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords, page A-7
• Password Rules for an Upgrade Installation, page A-8
• Password Rules for Reinstallation, page A-8
• Password Descriptions, page A-8
• Changing Passwords, page A-9
Password Rules for a New Installation
The following rules apply for a new installation:
• In Typical mode, admin, casuser, and System Identity account passwords are mandatory. The
installation program generates guest and database passwords randomly.
Password Information
• In Custom mode, admin, guest, System Identity account, and database passwords are mandatory.
You can either enter the casuser password or allow the installation program to randomly generate it.
Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords
During upgrade and reinstallation, you might change the passwords for the admin user and for the
casuser account. Table A - 7 lists the problems that can occur and provides steps you can take to resolve
them.
Table A-7 Potential Problems
Password Changed Potential Problem Workaround
admin Service Statistics Manager
loses contact with Operations
Manager and Service
Monitor.
casuser Service Monitor credentials
fail when accessing a Unified
Communications Manager
version 4.x system for which
Windows authentication is
configured.
If Service Statistics Manager is installed in
your network, reestablish contact by
performing the procedures in Release Notes
for Cisco Unified Service Statistics Manager
1.3.
The casuser password on the Service Monitor
server must match the casuser password on
the Unified Communications server. Log in
to the Windows server where Unified
Communications Manager is installed and
update the casuser password.
OL-25111-01
Note If you do not know the casuser
password on the Service Monitor
server, change it; see Changing the
casuser Password.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-7
Page 52

Password Information
Password Rules for an Upgrade Installation
During an upgrade installation, the casuser password is requested; other passwords are retained.
Password Rules for Reinstallation
The following rules apply for reinstallation:
• In Typical mode, the installation program retains passwords for admin, guest, and database.You can
either enter the casuser password or allow the installation program to randomly generate it. (See
Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You Change Passwords, page A-7.)
• In Custom mode, you can choose to enter new admin, guest, system identity account, and database
passwords or retain most existing passwords. You can either enter the casuser password or allow the
installation program to randomly generate it. (See Fixing Problems That Can Occur After You
Change Passwords, page A-7.)
Password Descriptions
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
The types of passwords are as follows:
• Common Services admin Password, page A-8
• System Identity Account Password, page A-8
• Common Services Guest Password, page A-9
• Common Services Database Password, page A-9
Common Services admin Password
When entering the password for the admin user, include a minimum of five characters.
The admin user account is the default administrator; you must use the admin username and password to
log in to Service Monitor after initial installation. (Be sure to write down the password.)
You are prompted to enter this password in both Typical and Custom modes of installation.
System Identity Account Password
When entering the System Identity account password, use a minimum of five characters.
You are prompted to enter this password in both Typical and Custom modes of installation.
The System Identity account is used in a multiple-server environment. Communication among multiple
servers is enabled by a “trust” model addressed by certificates and shared secrets. For more information,
see the Common Services online help.
A-8
Note You need a System Identity account to configure security with Cisco Secure ACS (which must be
installed on a separate server) and to configure the DCR in master and slave mode. (Operations Manager
supports the DCR; Service Monitor does not support it.)
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 53

Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Common Services Guest Password
When entering the password for the Common Services guest account, use a minimum of five characters.
Use this password to log into the Common Services server as a guest user. You are prompted to enter
this password in Custom installation mode. In Typical mode, this password is randomly generated.
Common Services Database Password
When entering database passwords:
• Use a minimum of five characters and a maximum of 15 characters.
• Do not start the password with a number.
• Do not insert spaces between characters.
• Do not use any special characters.
Changing Passwords
Password Information
These topics explain how to change the passwords for the admin user and casuser accounts using utilities
(or the Common Services user interface, if possible):
• Changing the Common Services Admin Password
• Changing the casuser Password
Changing the Common Services Admin Password
Note If you change the admin password and Service Statistics Manager is in your network, it will lose contact
with Operations Manager and Service Monitor. To reestablish contact, perform the procedures in
Release Notes for Cisco Unified Service Statistics Manager 1.3.
You can change your Common Services Admin password either by using the Common Services user
password recovery utility or from the user interface.
• Changing the Admin Password Using the Password Recovery Utility
• Changing the Admin Password from Common Services
Changing the Admin Password Using the Password Recovery Utility
Step 1 Stop the daemon manager by entering the following at the shell prompt:
net stop crmdmgtd
OL-25111-01
Step 2 Go to NMSROOT\bin directory and enter:
NMSROOT
\bin\resetpasswd username
where NMSROOT is the directory where you have installed Service Monitor.
A message appears:
Enter new password for username:
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-9
Page 54

Password Information
Step 3 Enter the new password for username.
Step 4 Start the daemon manager by entering the following at the command prompt:
net start crmdmgtd
Changing the Admin Password from Common Services
Step 1 Log in with username admin.
Step 2 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security > Local User Setup.
The Local User Setup page appears.
Step 3 Click Modify My Profile.
The My Profile window appears.
Step 4 Enter the password in the Password field.
Step 5 Re-enter the password in the Verify field.
Step 6 Enter the e-mail ID in the E-mail field.
Step 7 Click OK.
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Changing the casuser Password
Caution Changing the casuser password might cause Service Monitor credential failure when accessing a Unified
Communications Manager version 4.x system for which Windows authentication is configured. Be
prepared to log into the Windows server where Unified Communications Manager is installed to update
the casuser password to match the new casuser password that you enter.
Step 1 At the command prompt, enter:
NMSROOT
Three options are displayed:
1. Randomly generate the password
2. Enter the password
3. Exit.
Step 2 Enter 2, and press Enter.
A message appears, prompting you to enter the password.
Step 3 Confirm the password.
If a local user policy is configured on the Service Monitor server and you enter a password that does not
match the password policy, the application exits with an error message. For more information, see
Setting up Local User Policy in the Common Services online help.
\setup\support\resetCasuser.exe
A-10
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 55

Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
Password Information
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
A-11
Page 56

Password Information
Appendix A User Inputs for Installation, Reinstallation, and Upgrade
A-12
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 57

Licensing
This appendix provides licensing information for Cisco Unified Service Monitor (Service Monitor). It
contains the following sections:
• Licensing Overview, page B-1
• Licensing Process, page B-3
Licensing Overview
Service Monitor features software-based product registration and license key technologies. Licensing
ensures that you possess a licensed copy of Service Monitor.
Note • Licensing uses node-locking technology. The license file can only be used with the MAC address
that you supply.
• To license, install, and run Service Monitor on VMware, you must configure a static address for the
virtual machine.
APPENDIX
B
To determine whether Service Monitor is licensed, see Verifying License Status, page B-1. If you do not
have a license or you want to upgrade your license, see Licensing Scenarios, page B-2. For information
about messages that are displayed during product evaluation, see Licensing Messages, page B-3.
Verifying License Status
Step 1 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Administration > Licensing.
The Licensing Information page appears, displaying the information in the following table.
Column Description
Name Abbreviated product name—For Service Monitor, this is SM.
Version Product version—A.b.c, where A is the major version number, b is the
OL-25111-01
minor version number, and c is the service pack number. For
example, SM Standard 8.6 indicates version 8.6 without service
packs.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
B-1
Page 58

Licensing Overview
Appendix B Licensing
Column Description
Size Limit—Number of phones that Service Monitor is licensed to
support, up to a maximum value.
Note The licensing process permits you to install any valid
licenses, even if, as a result, the number of phones exceeds
the maximum value. To move a license from one Service
Monitor server to another, you must open a service request.
For more information, see Obtaining Documentation and
Submitting a Service Request.
Status One of the following:
• Purchased—You have a registered, licensed product.
• Evaluation—This license will expire on the expiration date;
Service Monitor will stop running.
Expiration Date Date on which Service Monitor stops running—Applies to evaluation
licenses. The evaluation period lasts for 90 days.
Note To view the installed software version, select the About link in the upper-right corner of the Service
Monitor home page.
Licensing Scenarios
Table B- 1 describes what to do in different scenarios if you do not have a licensed, registered copy of
Service Monitor or if you want to increase the number of phones supported.
Table B-1 How to Obtain and Register a License
Scenario What to Do
Installing with a purchased license.
Installing with an evaluation license.
Note The evaluation license is
limited to monitoring 10,000
phones.
1. Before installing, obtain a license file. See Licensing
Process, page B-3.
Note You can install Service Monitor without the license
file. You can upgrade your license after installation.
See Registering a License File with Service Monitor,
page B-4.
2. During installation, select License File Location, and
provide the location of your license file.
During installation, select Evaluation Only. Evaluation
versions are active for 90 days, after which you are required to
purchase a license.
To upgrade to a purchased license after installation, obtain a
PAK and license file for the Service Monitor software version.
For information on the licensing process, see Licensing
Process, page B-3.
B-2
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 59

Appendix B Licensing
Table B-1 How to Obtain and Register a License (continued)
Scenario What to Do
Upgrading a license—Either of these:
• Upgrading from an evaluation
license to a purchased license
• Installing an incremental license
to support additional phones
Moving Service Monitor to another
server.
Licensing Messages
If you have installed the evaluation version of Service Monitor, you must obtain the license file from
Cisco.com to continue to use the product after the 90-day evaluation period. For details, see Licensing
Process, page B-3.
Licensing Process
See Licensing Process, page B-3.
Call the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for
assistance. For more information, see Obtaining
Documentation and Submitting a Service Request.
Before expiry of the evaluation license, you will see the following prompt:
This software is provided for evaluation purposes only and will expire in XX days. If this
is not an evaluation copy, please click this link for information about obtaining a valid
purchase license. Click here for current licensing information. Otherwise, please contact
your Cisco representative for purchasing information.
This message is displayed as an alert after you log in and try to access Service Monitor. If you fail to
upgrade your evaluation license, all Service Monitor processes will run, but access to Service Monitor
functionality will be prohibited.
Licensing Process
The Service Monitor license file includes support for a set number of phones. You can purchase
incremental licenses to support additional phones and monitor up to a maximum number of phones with
a single Service Monitor. For each incremental license that you purchase, you will receive a PAK, and
you must use that PAK to obtain a license file.
This process applies to new installations and license upgrades:
1. Obtain a Product Authorization Key (PAK)—The PAK is used to register Service Monitor, and any
additional phone support that you might purchase for Service Monitor, on Cisco.com, and it contains
resource limitations. See Obtaining a PAK, page B-4.
2. Obtain a license file—A license file is sent to you after you register the PAK on Cisco.com. See
Obtaining a License File, page B-4.
3. Copy the license file to the server where Service Monitor is to be installed. If Service Monitor is
already installed and you are upgrading your license file, you must register the license file with
Service Monitor. See Registering a License File with Service Monitor, page B-4.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
B-3
Page 60

Licensing Process
Obtaining a PAK
The PAK is located on the software claim certificate. The software claim certificate is available in one
of these ways:
• If your order included hardware, a printed software claim certificate is included in the package.
• If your order did not include hardware, you can obtain the software claim certificate through the
eDelivery system; for information on eDelivery, see
http://www.cisco.com/web/partners/tools/edelivery.html.
Obtaining a License File
Note If you plan to install Service Monitor on a VMware server, you must supply a static MAC address to
obtain a license file. Service Monitor does not work when a dynamic MAC address is configured for the
virtual machine. For more information, see VMware Guidelines, page 1-5.
Appendix B Licensing
Step 1 Register the PAK and the MAC address of the system where Service Monitor is installed with Cisco.com
at http://www.cisco.com/go/license. You will be asked to log in. You must be a registered user of
Cisco.com to log in.
Note The MAC address is required because licensing uses node-locking technology. The license file
can only be used with the MAC address that you supply.
The license file will be e-mailed to you. After you obtain the license file, register the license with the
Service Monitor server.
Registering a License File with Service Monitor
Caution This procedure registers a license even when, as a result, license size exceeds the maximum number of
phones that Service Monitor supports on a single server. When the number of phones in Service Monitor
exceeds the limit, data from additional phones is not collected or analyzed.
Step 1 Copy the license file to the Service Monitor server, into a directory with read permission for the
username casuser or the user group casuser.
B-4
Note If you copy a folder that contains the license file to the Service Monitor server, be sure to provide
read permission for casuser on the folder as well as on the license file.
Step 2 Install the license:
a. Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Administration >
Licensing. The License Information page appears.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 61

Appendix B Licensing
b. Click the Update button. The Select License File dialog box appears.
c. Browse to and select the license file:
–
Click the Browse button.
–
Browse to the location where you copied the license file in Step 1.
–
Select the license file.
–
Click OK. The Licensing Information page is updated. For more information, see Table B- 2 .
If you purchased more than one license, repeat Step 2 to install each additional license.
If you encounter errors, ensure that the license file:
–
Is in a directory with read permission for the username casuser or the user group casusers.
–
Contains the correct MAC address in HOSTID=<MAC>. (Use a text editor to view the contents
of the license file.) If the value of HOSTID is not correct, you must open a service request. See
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request.
Table B-2 License Registration Result
Licensing Process
License registered.… Expected Result on Licensing Information Page
Upgrade from an evaluation license Entry in the Status column changes from Evaluation to
Purchased.
Increase number of phones supported Entry in the Size column increases per license size.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
B-5
Page 62

Licensing Process
Appendix B Licensing
B-6
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 63

APPENDIX
C
Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
To configure Service Monitor to use Cisco Secure ACS for authentication and authorization, work
through these topics in order:
• Cisco Secure ACS Support, page C-1
• Service Monitor Integration Notes, page C-1
• Common Services Local Login Module Authentication Roles, page C-2
• Configuring the System Identity User in Common Services, page C-3
• Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server, page C-3
• Changing the AAA Mode to ACS in Common Services, page C-4
• Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in Cisco Secure ACS, page C-5
• Verifying the Service Monitor and Cisco Secure ACS Configuration, page C-5
Cisco Secure ACS Support
Service Monitor supports the ACS mode of authentication and authorization. To use this mode, you must
have a Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS), installed in your network on a server separate from
the one where Service Monitor is installed. For the supported software version, see Tab le 1 -1 .
Service Monitor Integration Notes
Service Monitor (and Common Services) integrate with Cisco Secure ACS as shared profile components.
Multiple instances of the same application—for example, Service Monitor—can use the same Cisco
Secure ACS server for authentication and authorization.
When you register Cisco Unified Service Monitor (and Common Services) with Cisco Secure ACS, the
applications tasks—such as adding data source credentials to Service Monitor—and user roles—such as
Network Administrator—for the application are imported into Cisco Secure ACS.
You only need to register one instance of an application with Cisco Secure ACS for tasks and roles to be
imported. If you register an application a second time, any changes that you have made to role settings,
such as creating custom roles, are lost.
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
C-1
Page 64

Appendix C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
Common Services Local Login Module Authentication Roles
Note The Service Monitor integration with Cisco Secure ACS does not enable you to selectively filter out
specific devices. For example, a user in a role that includes the task:
• Data Source Credentials: add, edit and verify—Can add, edit, or verify credentials in
Service Monitor for any NAM or any Unified Communications Manager.
• Cisco 1040: view details—Can view details from Service Monitor for any Cisco 1040.
Common Services Local Login Module Authentication Roles
Common Services login modules enable you to use a source other than the native mechanism for
authentication, that is the Common Services Local login module.
After you authenticate, authorization is controlled by your role. A role is a set of tasks that you have the
privilege to perform. By default, the Common Services Local login module authorization scheme has six
roles. Roles are listed in Table C- 1 from least privileged to most privileged.
Table C-1 Common Services User Roles and Privileges
Role Description
Non-ACS Mode—Common Services Local Login Module
Help Desk Privileges to view some information in Service Monitor and Common
Services.
Example: Generate and view reports and view details for Cisco 1040.
(Cannot perform modifications.)
Network Operator Privilege to perform all Service Monitor tasks and some Common Services
tasks.
Example: Set up Service Monitor; add, modify, verify data source
credentials.
Network Administrator Privilege to perform all Service Monitor tasks and several Common
Services tasks. User can also perform Network Operator tasks.
Example: Same as Network Operator.
System Administrator Privilege to perform all system administration tasks.
Example: Enable and disable debugging; set logging level.
Super Admin This role is not supported in Service Monitor.
For tasks that are defined for Service Monitor and Common Services and the roles with privileges to
perform the tasks, see the Permission Report in Common Services. (Select Administration > Server
Administration (Common Services) > Reports > Permission Report > Generate Report.)
C-2
Note For more information, see Common Services online help.
We recommend that you do not modify the default Common Services roles. However, you can create
your own custom roles for Service Monitor on Cisco Secure ACS.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 65

Appendix C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
Configuring the System Identity User in Common Services
Configuring the System Identity User in Common Services
Before you integrate the Service Monitor server with Cisco Secure ACS, ensure that you create and
assign all privileges to a system identity user in Common Services. This topic explains how to set up a
local user as the system identity user. (To use the Common Services admin user as the system identity
user, see the topic Setting up system identity account in Common Services online help.)
1. Create a local user and assign all roles to the user. (See Configuring Users Using the Common
Services Local Login Module, page 3-2.)
Note If the System Identity User is not configured with all Common Services Local login module
roles (see Table C- 1 ), authorization fails when you try perform certain tasks in Service
Monitor and Common Services.
2. Update the System Identity User, replacing the username with the one that you created in step 1.
(Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security > Multi-Server
Trust Management > System Identity Setup.
For more information, see Common Services online help.
Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server
Perform these tasks in Cisco Secure ACS before you change the Common Services AAA mode to ACS:
1. Configure ACS Administrators.
Configure an administrator user with all privileges in Cisco Secure ACS.
Note If you do not configure the administrator user with all privileges, Service Monitor
registration with Cisco Secure ACS fails.
Note the username and password for the administrator; you will need to enter them when you change
the AAA mode to ACS in Common Services.
2. Add the Service Monitor server to Cisco Secure ACS as a AAA Client.
Configure the Service Monitor server as a AAA client in Cisco Secure ACS and do the following:
–
Select authentication by TACACS + (CISCO IOS).
–
Note the shared secret that you enter; you will need to enter it in Common Services when you
change the AAA mode to ACS in Common Services.
3. Add the System Identity User and Common Services users to Cisco Secure ACS.
You can create a group and add users to it.
4. Note whether the Service Monitor and Common Services applications are already registered with
Cisco Secure ACS. To find out, select Shared Profile Components and look for:
OL-25111-01
–
Cisco Unified Service Monitor
–
Common Services
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
C-3
Page 66

Appendix C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
Changing the AAA Mode to ACS in Common Services
For details about how to perform each of the previous tasks, see the Common Services online help.
Changing the AAA Mode to ACS in Common Services
Before you perform this procedure, complete the tasks in Configuring the System Identity User in
Common Services, page C-3 and Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server, page C-3.
Step 1 Select Administration > Server Administration (Common Services) > Security > AAA Mode Setup.
The AAA Mode Setup page appears.
Step 2 Next to Select a Type, select the ACS radio button. The page refreshes, displaying appropriate options.
Step 3 Under Server Details, enter an IP address for the Cisco Secure ACS server and enter a port.
Step 4 Under Login, enter:
• ACS Admin Name—Enter the name of the administrator you created in step 1. (See Setting Up the
Cisco Secure ACS Server, page C-3.)
• ACS Admin Password—Enter the password for the administrator you created in step 1. (See Setting
Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server, page C-3.)
• ACS Shared Secret Key— Enter the shared secret you entered when you added the Service Monitor
server to Cisco Secure ACS as a AAA client in step 2. (See Setting Up the Cisco Secure ACS Server,
page C-3.)
Step 5 Decide whether to select Register all installed applications with ACS.
Note If Service Monitor is registered with ACS and you register it again, you lose any custom roles
that were previously configured in Cisco Secure ACS for Service Monitor. The same is true for
Common Services. (To selectively register an application, see Registering an Application to
Cisco Secure ACS from the Command Line, page C-5.)
Step 6 Select the appropriate radio button (HTTP or HTTPS) under Current ACS Administrative Access
Protocol.
Step 7 Click Apply to complete the mode change. An ACS verification status message is displayed; do one of
the following:
• Click OK—Registers Service Monitor and Common Services tasks and users to ACS; overwrites
any existing custom roles for Service Monitor and Common Services.
• Click Cancel—Prevents registration to ACS from occurring.
C-4
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 67

Appendix C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in Cisco Secure ACS
Step 8 Restart the daemon manager for the changes to take effect. From the command line, enter these
commands:
net stop crmdmgtd
net start crmdmgtd
Registering an Application to Cisco Secure ACS from the Command Line
A script, <NMSROOT>\bin\AcsRegCli.pl, enables you register applications to Cisco Secure ACS.
Note NMSROOT is the directory where Service Monitor is installed. If you chose the default, it is
C:\PROGRA~1\CSCOpx.
Following are the available parameters when running the script from the CLI:
AcsRegCli.pl -register <application name>
Replace application name with any of the following:
• qovr—Registers Service Monitor only
• cmf—Registers Common Services only
• all—Registers all applications on the server (Cisco Unified Service Monitor and Common Services).
Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in Cisco Secure ACS
You must ensure that the System Identity User in Cisco Secure ACS is assigned all roles and that
Common Services users or user groups have been assigned the proper privileges.
In Cisco Secure ACS, select Shared Profile Components > Cisco Unified Service Monitor. For more
information, see these documents:
• User Guide for Cisco Secure Access Control Server 4.x
• Common Services online help. Look for these topics:
–
Roles in ACS
–
Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in ACS
Verifying the Service Monitor and Cisco Secure ACS Configuration
OL-25111-01
After performing the tasks beginning with Assigning Roles to Users and User Groups in Cisco Secure
ACS, page C-5 through Configuring the System Identity User in Common Services, page C-3, verify the
configuration as follows:
1. Log in to Service Monitor with a username defined in Cisco Secure ACS.
2. Try to perform tasks, to ensure that you can perform only those tasks that you are entitled to perform
based on the role assigned to you in Cisco Secure ACS.
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
C-5
Page 68

Verifying the Service Monitor and Cisco Secure ACS Configuration
For example, if your privilege is Help Desk, then:
–
You should be able to view the Cisco 1040s that are managed by Service Monitor.
–
You should not be able to add Cisco 1040s for Service Monitor to manage, and you should not
be able to delete them.
If you encounter difficulties, see Authentication Failure in ACS Mode in Common Services online help.
Appendix C Security Configuration with Cisco Secure ACS
C-6
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
Page 69

INDEX
A
AAA mode 3-1
ACS mode
authentication 3-1
user roles and privileges, configuring C-5
audience for this document vii
authentication
ACS mode 3-1
Local RBAC mode 3-1
B
backup procedure 2-8
C
call classification
data
configuring in Service Monitor 3-3
recording from Service Statistics Manager 2-9
reporting
CDR Call Report 3-3
Service Statistics Manager reports 3-3
call data, migrating 2-9
cautions
license limit, surpassing B-4
significance of viii
Cisco Secure Access Control Server (ACS) 3-1
Cisco Secure Agent, disabling 2-2
Common Services, ports used by 1-9
configuring
SSL 3-2
users 3-2
D
daemon manager, stopping and starting 2-8
database backup 2-8
data migration
tool, downloading 2-9
understanding 2-9
documentation viii
audience for this vii
typographical conventions in vii
E
eDelivery system, about B-4
I
installation preparation 2-2
integrating CiscoWorks Server with ACS
AAA mode setup C-4
ACS support C-1
before you begin C-3
roles
assigning to users C-5
CiscoWorks authentication C-2
IP address, static 2-2
L
license
file
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
IN-1
Page 70

Index
obtaining B-4
registering B-4
PAK, obtaining B-4
process B-3
scenarios B-2
status, verifying B-1
locale setting 2-2
M
MAC address, importance of static B-4
N
non-ACS mode
authentication 3-1
CiscoWorks Local Login module 3-2
users, configuring 3-2
NTP configuration 2-3
P
security, Windows 2003 Server guidelines 2-2
Service Statistics Manager
call categories 3-3
call classification data, recording 2-9
installation, order of 3-3
server, stopping 2-11
upgrade, order of 2-11, 3-3
software claim certificate, obtaining B-4
SSL, enabling 3-2
T
terminal services
application mode 1-7
remote desktop administration 1-7
typographical conventions in this document vii
U
upgrade preparation 2-7
users, configuring 3-1
PAK, obtaining B-4
Permission Report 3-1
preparation
for installation 2-2
for upgrade 2-7
R
regional settings 2-2
registration, license B-4
report data, migrating 2-9
S
secure mode 3-2
Secure Socket Layer 3-2
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
IN-2
V
verification, license status B-1
virus scan, disabling 2-2
VMware
guidelines 1-5
MAC address, static B-4
software version 1-5
W
warnings
significance of viii
Windows 2003 Service security guidelines 2-2
OL-25111-01
Page 71

Index
OL-25111-01
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
IN-3
Page 72

Index
IN-4
Installation Guide for Cisco Unified Service Monitor
OL-25111-01
 Loading...
Loading...