Page 1

Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
First Published: 2016-09-19
Last Modified: 2018-10-19
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS,
INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND,
EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH
THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY,
CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15
of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment
generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications.
Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of
the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio
frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference
will not occur in a particular installation. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off and on, users are
encouraged to try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
• Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
• Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
• Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
• Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public domain version of
the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright©1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED "AS IS" WITH ALL FAULTS.
CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF
MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS
HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any examples, command display output, network
topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional
and coincidental.
Cisco and the Cisco logo are trademarks or registered trademarks of Cisco and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and other countries. To view a list of Cisco trademarks, go to this URL: www.cisco.com
go trademarks. Third-party trademarks mentioned are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship between Cisco and any
other company. (1721R)
©
2016–2017 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
Trademarks ?
PREFACE
CHAPTER 1
CHAPTER 2
Preface vii
Audience vii
Documentation Conventions vii
Related Documentation for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Software viii
Documentation Feedback x
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request x
Overview 1
Overview 1
Preparing the Site 5
Temperature Requirements 5
Humidity Requirements 5
Altitude Requirements 5
Dust and Particulate Requirements 6
Minimizing Electromagnetic and Radio Frequency Interference 6
CHAPTER 3
Shock and Vibration Requirements 7
Grounding Requirements 7
Planning for Power Requirements 7
Airflow Requirements 9
Rack and Cabinet Requirements 9
Clearance Requirements 10
Installing the Switch Chassis 13
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
Safety 13
Installation Options with Rack-Mount Kits, Racks, and Cabinets 14
Airflow Considerations 14
Installation Guidelines 14
Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch 16
Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount Kit 17
Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit 20
Grounding the Chassis 24
Starting the Switch 25
CHAPTER 4
CHAPTER 5
Connecting the Switch to the Network 29
Setting Up the Management Interface 29
Connecting to Host Servers 29
Guidelines for Connecting Ports 30
Maintaining Transceivers and Optical Cables 32
Replacing Modules 33
Replacing a Fan Module During Operations 33
Replacing a Power Supply Module 34
Removing an AC Power Supply 34
Removing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply 35
Removing a DC Power Supply 36
Installing an AC Power Supply 36
Installing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply 37
Installing a DC Power Supply 38
Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block 39
APPENDIX A
iv
Rack Specifications 43
Overview of Racks 43
General Requirements for Cabinets and Racks 43
Requirements Specific to Standard Open Racks 44
Requirements Specific to Perforated Cabinets 44
Cable Management Guidelines 44
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Page 5

Contents
APPENDIX B
System Specifications 45
Environmental Specifications 45
Switch Dimensions 45
Switch and Module Weights and Quantities 46
Transceiver and Cable Specifications 46
Switch Power Input Requirements 46
Power Specifications 47
650-W AC Power Supply Specifications 47
1200-W HVAC/HVDC Power Supply Specifications 47
930-W DC Power Supply (Port-Side Intake) Specifications 48
930-W DC Power Supply (Port-Side Exhaust) Specifications 48
Power Cable Specifications 49
AC Power Cables Supported by NX-OS Mode Switches 49
HVAC/HVDC Power Cables Supported by ACI-Mode and NX-OS Mode Switches 50
DC Power Cable Specifications 51
Regulatory Standards Compliance Specifications 51
APPENDIX C
APPENDIX D
APPENDIX E
LEDs 53
Switch Chassis LEDs 53
Lane Link LEDs 54
Fan Module LEDs 54
Power Supply LEDs 54
Additional Kits 57
Rack Mount Kit NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU 57
Rack Mount Kit N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT 57
Site Preparation and Maintenance Records 59
Site Preparation Checklist 59
Contact and Site Information 60
Chassis and Module Information 61
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
vi
Page 7

Preface
• Audience, on page vii
• Documentation Conventions, on page vii
• Related Documentation for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Software, on page viii
• Documentation Feedback, on page x
• Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request, on page x
Audience
This publication is for hardware installers and network administrators who install, configure, and maintain
Cisco Nexus switches.
Documentation Conventions
Command descriptions use the following conventions:
bold
DescriptionConvention
Bold text indicates the commands and keywords that you enter literally
as shown.
Italic
[x | y]
{x | y}
[x {y | z}]
variable
Italic text indicates arguments for which the user supplies the values.
Square brackets enclose an optional element (keyword or argument).[x]
Square brackets enclosing keywords or arguments separated by a vertical
bar indicate an optional choice.
Braces enclosing keywords or arguments separated by a vertical bar
indicate a required choice.
Nested set of square brackets or braces indicate optional or required
choices within optional or required elements. Braces and a vertical bar
within square brackets indicate a required choice within an optional
element.
Indicates a variable for which you supply values, in context where italics
cannot be used.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
vii
Page 8

Related Documentation for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Software
Preface
DescriptionConvention
string
Examples use the following conventions:
italic screen font
!, #
A nonquoted set of characters. Do not use quotation marks around the
string or the string will include the quotation marks.
DescriptionConvention
Terminal sessions and information the switch displays are in screen font.screen font
Information you must enter is in boldface screen font.boldface screen font
Arguments for which you supply values are in italic screen font.
Nonprinting characters, such as passwords, are in angle brackets.< >
Default responses to system prompts are in square brackets.[ ]
An exclamation point (!) or a pound sign (#) at the beginning of a line
of code indicates a comment line.
Related Documentation for Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS
Software
The entire Cisco NX-OS 9000 Series documentation set is available at the following URL:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps13386/tsd_products_support_series_home.html
Release Notes
The release notes are available at the following URL:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps13386/prod_release_notes_list.html
Configuration Guides
These guides are available at the following URL:
https://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps13386/products_installation_and_configuration_guides_list.html
The documents in this category include:
• Cisco Nexus 2000 Series NX-OS Fabric Extender Software Configuration Guide for Cisco Nexus 9000
Series Switches
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Fundamentals Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS High Availability and Redundancy Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Interfaces Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Layer 2 Switching Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Multicast Routing Configuration Guide
viii
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Page 9

Preface
Preface
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Quality of Service Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Security Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS System Management Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Unicast Routing Configuration Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Verified Scalability Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS VXLAN Configuration Guide
Other Software Documents
• Cisco Nexus 7000 Series and 9000 Series NX-OS MIB Quick Reference
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Programmability Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Software Upgrade and Downgrade Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS System Messages Reference
• Cisco Nexus 9000 Series NX-OS Troubleshooting Guide
• Cisco NX-OS Licensing Guide
• Cisco NX-OS XML Interface User Guide
Hardware Documents
• Cisco Nexus 3000 Series Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 92160YC-X NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 92300YC NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 92304QC NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9272Q NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 93108TC-EX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 93120TX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 93128TX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 93180LC-EX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 93180YC-EX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9332PQ NX-OS-Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9372PX and 9372PX-E NX-OS Mode Switches Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9372TX and 9372TX-E NX-OS Mode Switches Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9396PX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9396TX NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
ix
Page 10

Preface
Documentation Feedback
• Cisco Nexus 9504 NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9508 NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco Nexus 9516 NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
• Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information for the Cisco Nexus 3000 and 9000 Series
Documentation Feedback
To provide technical feedback on this document, or to report an error or omission, please send your comments
to nexus9k-docfeedback@cisco.com. We appreciate your feedback.
Obtaining Documentation and Submitting a Service Request
For information on obtaining documentation, using the Cisco Bug Search Tool (BST), submitting a service
request, and gathering additional information, see What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, at:
https://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml.
Subscribe to What's New in Cisco Product Documentation, which lists all new and revised Cisco technical
documentation as an RSS feed and delivers content directly to your desktop using a reader application. The
RSS feeds are a free service.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
x
Page 11

Overview
CHAPTER 1
Overview
• Overview, on page 1
The Cisco Nexus 9236C switch (N9K-C9236C) is a 1 rack unit (RU) switch that has the following ports:
• 36 100-Gigabit QSFP28 interface ports that support 100-, 50-, 40-, 25-, 10- and 1-Gigabit speeds. You
can use the following adapters with these ports:
• CVR-2QSFP28-8SFP which provides eight SFP/SFP+/SFP28 ports for each vertical pair of ports
on the switch. The top four SFP/SFP+/SFP28 ports connect to the upper QSFP28 port of the switch
pair, and the bottom SFP/SFP+/SFP28 ports connect to the lower QSFP28 port.
• CVR-QSFP-SFP10G which provides an SFP/SFP+ port for one QSFP/QSFP28 port on the switch.
Note
These ports also support breakout cables with four 10-Gigabit SFP+ transceivers
(such as the QSFP-4X10G-AOCxM and QSFP-4SFP10G-CUxM cables).
• 1 100/1000 management port
• 1 console port
• 2 software-defined ports
• 1 USB port for saving or loading switch configurations
The chassis for this switch includes the following user-replaceable components:
• Fan modules (four) with the following airflow choices:
• Port-side intake fan module with burgundy coloring (NXA-FAN-30CFM-B)
• Port-side exhaust fan module with blue coloring (NXA-FAN-30CFM-F)
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
1
Page 12
Overview
Overview
Note
Due to the airflow design though this switch (N9K-C9236C) when used in
conjunction with this fan (NXA-FAN-30CFM-F), it requires the fan to be run at
full speed at all time. This change was made as of release 7.0(3)I7(3).
• Power supply modules (two—one for operations and one for redundancy [n+1]) with the following
choices:
• 650-W port-side intake AC power supply with burgundy coloring (NXA-PAC-650W-PI)
• 650-W port-side exhaust AC power supply with blue coloring (NXA-PAC-650W-PE)
• 1200-W HVAC/HVDC dual-direction airflow power supply with white coloring (N9K-PUV-1200W)
• 930-W port-side intake DC power supply with green coloring (UCSC-PSU-930WDC)
• 930-W port-side exhaust DC power supply with gray coloring (UCS-PSU-6332-DC)
Note
Both power supplies should be the same type. Do not mix AC, DC, or
HVAC/HVDC power supplies.
Note
All fan modules and power supplies must use the same airflow direction during
operations. If you are using the 1200-W HVAC/HVDC power supplies, those
power supplies automatically use the same airflow direction as used by the other
modules in the switch.
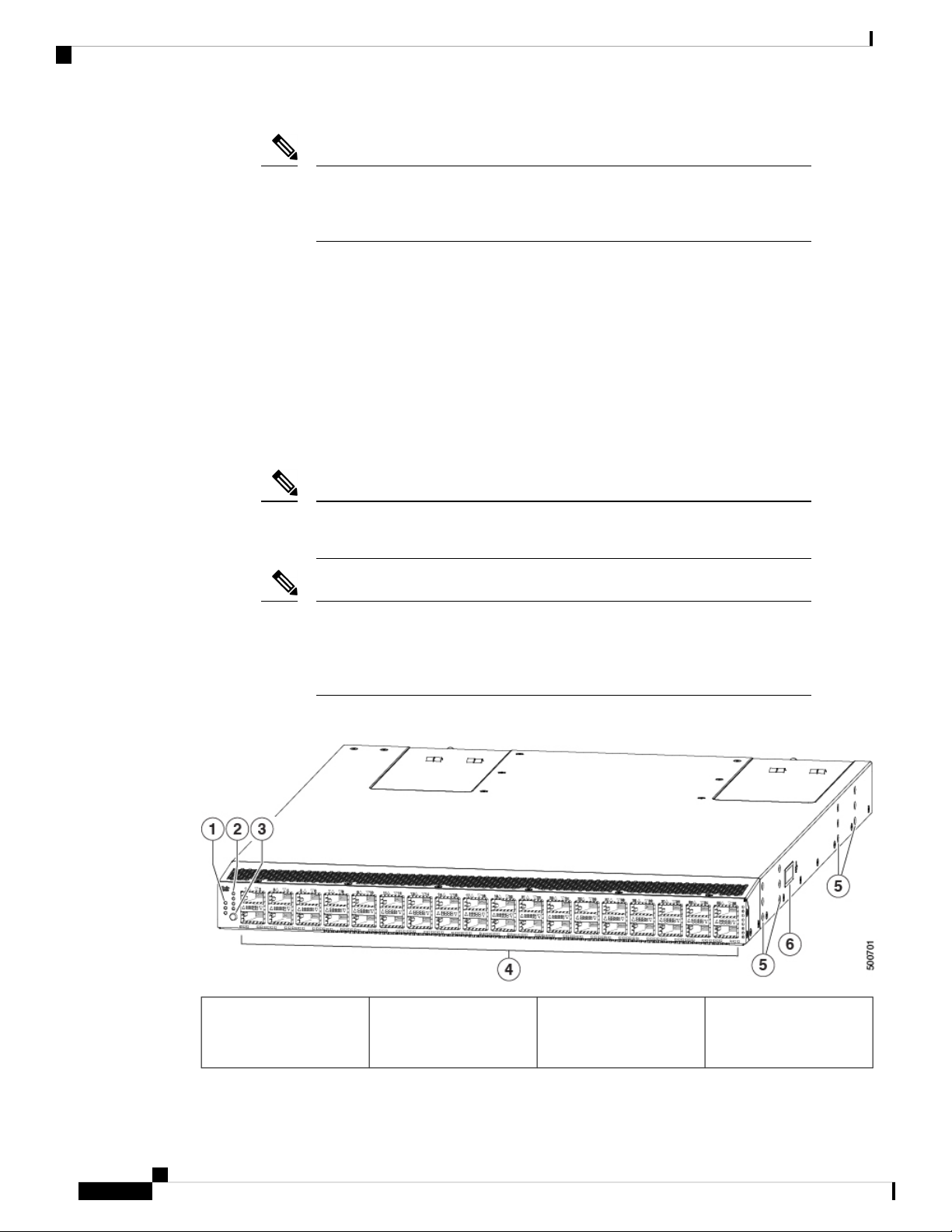
The following figure shows the switch features on the port side of the chassis.
1
4Beacon (BCN), Status
(STS), and Environment
36 100-Gigabit
QSFP+/QSFP28 ports
(ENV) LEDs
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
2
Page 13

Overview
Overview
2
5Lane link status LEDs for
4x10-Gigabit port
configuration (1 LED lit
Screw holes (6) for
attaching a mounting
bracket
to show the lane being
checked or all LEDs off
when all 4 lanes are being
checked)
Grounding pad6Lane shift button3
To determine which transceivers, adapters, and cables are supported by this switch, see the Cisco Transceiver
Modules Compatibility Information document.
The following figure shows the switch features on the power supply side of the chassis.
1
Console port (1)6Power supply modules (1
or 2) (AC power supplies
shown) with slots
numbered 1 (left) and 2
(right)
2
USB port (1)7Fan modules (4) with slots
numbered from 1 (left) to
4 (right)
Management port (RJ-45)8L1 port (software defined)3
9L2 port (software defined)4
Screw holes (6) for
attaching a mounting
bracket
5
Grounding pad10Beacon (BCN) and Status
(STS) LEDs
Depending on whether you plan to position the ports in a hot or cold aisle, you can order the fan and power
supply modules with port-side intake or port-side exhaust airflow. For port-side intake airflow, the fan and
AC power supply modules have burgundy coloring (DC power supply modules have green coloring). For
port-side exhaust airflow, the fan and AC power supplies have blue coloring (DC power supply modules have
gray coloring). You can also order the 1200-W HVAC/HVDC power supply which has dual-direction airflow
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
3
Page 14

Overview
with white coloring. Dual-direction airflow modules automatically use the airflow direction of the other
modules installed in the switch.
The fan and power supply modules are field replaceable and you can replace one fan module or one power
supply module during operations so long as the other modules are installed and operating. If you have only
one power supply installed, you can install the replacement power supply in the open slot before removing
the original power supply.
Note
All of the fan and power supply modules must have the same direction of airflow. Otherwise, the switch can
overheat and shut down. If you are installing a dual-direction power supply, that module will automatically
use the same airflow direction as the other modules in the switch.
Overview
Caution
If the switch has port-side intake airflow (burgundy coloring for fan modules), you must locate the ports in
the cold aisle. If the switch has port-side exhaust airflow (blue coloring for fan modules), you must locate the
ports in the hot aisle. If you locate the air intake in a hot aisle, the switch can overheat and shut down.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
4
Page 15

Preparing the Site
• Temperature Requirements, on page 5
• Humidity Requirements, on page 5
• Altitude Requirements, on page 5
• Dust and Particulate Requirements, on page 6
• Minimizing Electromagnetic and Radio Frequency Interference, on page 6
• Shock and Vibration Requirements, on page 7
• Grounding Requirements, on page 7
• Planning for Power Requirements, on page 7
• Airflow Requirements, on page 9
• Rack and Cabinet Requirements, on page 9
• Clearance Requirements, on page 10
Temperature Requirements
The switch requires an operating temperature of 32 to 104 degrees Fahrenheit (0 to 40 degrees Celsius). If
the switch is not operating, the temperature must be between –40 to 158 degrees Fahrenheit (–40 to 70 degrees
Celsius).
CHAPTER 2
Humidity Requirements
High humidity can cause moisture to enter the switch. Moisture can cause corrosion of internal components
and degradation of properties such as electrical resistance, thermal conductivity, physical strength, and size.
The switch is rated to withstand from 5- to 95-percent (noncondensing) relative humidity.
Buildings in which the climate is controlled by air-conditioning in the warmer months and by heat during the
colder months usually maintain an acceptable level of humidity for the switch equipment. However, if the
switch is located in an unusually humid location, use a dehumidifier to maintain the humidity within an
acceptable range.
Altitude Requirements
This switch is rated to operate at altitudes from 0 to 13,123 feet (0 to 4,000 meters). If you operate this switch
at a higher altitude (low pressure), the efficiency of forced and convection cooling is reduced and can result
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
5
Page 16

Dust and Particulate Requirements
in electrical problems that are related to arcing and corona effects. This condition can also cause sealed
components with internal pressure, such as electrolytic capacitors, to fail or to perform at a reduced efficiency.
Dust and Particulate Requirements
Exhaust fans cool power supplies and system fans cool switches by drawing in air and exhausting air out
through various openings in the chassis. However, fans also ingest dust and other particles, causing contaminant
buildup in the switch and increased internal chassis temperature. Dust and particles can act as insulators and
interfere with the mechanical components in the switch. A clean operating environment can greatly reduce
the negative effects of dust and other particles.
In addition to regular cleaning, follow these precautions to avoid contamination of your switch:
• Do not permit smoking near the switch.
• Do not permit food or drink near the switch.
Preparing the Site
Minimizing Electromagnetic and Radio Frequency Interference
Electromagnetic interference (EMI) and radio frequency interference (RFI) from the switch can adversely
affect other devices, such as radio and television (TV) receivers. Radio frequencies that emanate from the
switch can also interfere with cordless and low-power telephones. Conversely, RFI from high-power telephones
can cause spurious characters to appear on the switch monitor.
RFI is defined as any EMI with a frequency above 10 kHz. This type of interference can travel from the switch
to other devices through the power cable and power source or through the air as transmitted radio waves. The
Federal Communications Commission (FCC) publishes specific regulations to limit the amount of EMI and
RFI that are emitted by computing equipment. Each switch meets these FCC regulations.
To reduce the possibility of EMI and RFI, follow these guidelines:
• Cover all open expansion slots with a blank filler plate.
• Always use shielded cables with metal connector shells for attaching peripherals to the switch.
When wires are run for any significant distance in an electromagnetic field, interference can occur to the
signals on the wires with the following implications:
• Bad wiring can result in radio interference emanating from the plant wiring.
• Strong EMI, especially when it is caused by lightning or radio transmitters, can destroy the signal drivers
and receivers in the chassis and even create an electrical hazard by conducting power surges through
lines into equipment.
Note
To predict and prevent strong EMI, you need to consult experts in radio frequency interference (RFI).
The wiring is unlikely to emit radio interference if you use a twisted-pair cable with a good distribution of
grounding conductors. If you exceed the recommended distances, use a high-quality twisted-pair cable with
one ground conductor for each data signal when applicable.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
6
Page 17

Preparing the Site
Shock and Vibration Requirements
Caution
If the wires exceed the recommended distances, or if wires pass between buildings, give special consideration
to the effect of a lightning strike in your vicinity. The electromagnetic pulse that is caused by lightning or
other high-energy phenomena can easily couple enough energy into unshielded conductors to destroy electronic
switches. You will want to consult experts in electrical surge suppression and shielding if you had similar
problems in the past.
Shock and Vibration Requirements
The switch has been shock- and vibration-tested for operating ranges, handling, and earthquake standards.
Grounding Requirements
The switch is sensitive to variations in voltage that is supplied by the power sources. Overvoltage, undervoltage,
and transients (or spikes) can erase data from memory or cause components to fail. To protect against these
types of problems, ensure that there is an earth-ground connection for the switch. You can connect the grounding
pad on the switch either directly to the earth-ground connection or to a fully bonded and grounded rack.
When you properly install the chassis in a grounded rack, the switch is grounded because it has a metal-to-metal
connection to the rack. Alternatively, you can ground the chassis by using a customer-supplied grounding
cable that meets your local and national installation requirements. For U.S. installations, we recommend
6-AWG wire. Connect your grounding cable to the chassis with a grounding lug (provided in the switch
accessory kit) and to the facility ground.
Note
You automatically ground AC power supplies when you connect them to AC power sources. For DC power
supplies, you must connect a grounding wire when wiring the power supply to the DC power source.
Planning for Power Requirements
The switch includes two power supplies (1-to-1 redundancy with current sharing) in one of the following
combinations:
• Two 650-W AC power supplies
• Two 1200-W HVAC/HVDC power supplies
• Two 930-W DC power supplies
Note
Both power supplies must be the same type. Do not mix AC, DC, and HVAC/HVDC power supplies in the
same chassis.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
7
Page 18

Planning for Power Requirements
Note
For n+1 redundancy, you can use one or two power sources for the two power supplies. For n+n redundancy,
you must use two power sources and connect each power supply to a separate power source.
The power supplies are rated to output up to 650 W (AC power supplies), up to 1200 W (HVAC/HVDC power
supplies), or up to 930 W (DC power supplies), but the switch requires less than those amounts of power from
the power supply. To operate the switch you must provision enough power from the power source to cover
the requirements of both the switch and a power supply. Typically, this switch and a power supply require
275 W of power input from the power source, but you must provision as much as 640 W of power input from
the power source to cover peak demand.
Note
Some of the power supply modules have Underwriter Labs (UL) rating capabilities that exceed the switch
requirements. When calculating your power requirements, use the switch requirements to determine the amount
of power that is required for the power supplies.
To minimize the possibility of circuit failure, make sure that each power-source circuit that is used by the
switch is dedicated to the switch.
Preparing the Site
Note
Warning
Note
Warning
For AC input application, please refer to the following statement:
Statement 1005—Circuit Breaker
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the
protective devices are rated not greater than 20A (North America), 16A (Europe), and 13A (UK).
For DC input application, please refer to the following statement:
Statement 1005—Circuit Breaker
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection.
• Ensure that the protective devices are rated not greater than 40A when the switch is powered with regular
DC power supplies (rated 48-60VDC).
• Ensure that the protective devices are rated not greater than 10A when the switch is powered with HVDC
power supplies (rated 240-350VDC).
Note
For the power cables to use with the power supplies, see Power Cable Specifications, on page 49.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
8
Page 19
Preparing the Site
Airflow Requirements
The switch is positioned with its ports in either the front or the rear of the rack depending on your cabling
and maintenance requirements. You must have fan and power supply modules that move the coolant air from
the cold aisle to the hot aisle in one of the following ways:
• Port-side exhaust airflow—Cool air enters the chassis through the fan and power supply modules in the
cold aisle and exhausts through the port end of the chassis in the hot aisle.
• Port-side intake airflow—Cool air enters the chassis through the port end in the cold aisle and exhausts
through the fan and power supply modules in the hot aisle.
• Dual-direction airflow—The direction of the installed fan modules determines the airflow.
You can identify the airflow direction of each fan and power supply module by its coloring as follows:
• Blue coloring indicates port-side exhaust airflow.
• Burgundy coloring indicates port-side intake airflow.
Airflow Requirements
• White coloring on HVAC/HVDC power supplies indicates dual-direction airflow.
• Gray coloring on DC power supplies indicates port-side exhaust airflow.
• Green coloring on DC power supplies indicates port-side intake airflow.
Note
To prevent the switch from overheating and shutting down, you must position the air intake for the switch in
a cold aisle. The fan and power supply modules must have the same direction of airflow (even if their coloring
is different). If you must change the airflow direction for the switch, you must shutdown the switch before
changing the modules.
Rack and Cabinet Requirements
You can install the following types of racks or cabinets for your switch:
• Standard perforated cabinets
• Solid-walled cabinets with a roof fan tray (bottom-to-top cooling)
• Standard open four-post Telco racks
Work with your cabinet vendors to determine which of their cabinets meet the following requirements or see
the Cisco Technical Assistance Center (TAC) for recommendations:
• Use a standard 19-inch (48.3-cm), four-post Electronic Industries Alliance (EIA) cabinet or rack with
mounting rails that conform to English universal hole spacing per section 1 of the ANSI/EIA-310-D-1992
standard.
• The depth of a four-post rack must be 24 to 32 inches (61.0 to 81.3 cm) between the front and rear
mounting rails (for proper mounting of the bottom-support brackets or other mounting hardware).
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
9
Page 20

Clearance Requirements
Preparing the Site
• Required clearances between the chassis and the edges of its rack or the interior of its cabinet are as
follows:
• 4.5 inches (11.4 cm) between the front of the chassis and the interior of the cabinet (required for
cabling).
• 3.0 inches (7.6 cm) between the rear of the chassis and the interior of the cabinet (required for airflow
in the cabinet if used).
• No clearance is required between the chassis and the sides of the rack or cabinet (no side airflow).
Also, you must have power receptacles that are located within reach of the power cords that are used with the
switch.
Warning
Statement 1048—Rack Stabilization
Stability hazard. The rack stabilizing mechanism must be in place, or the rack must be bolted to the floor
before you slide the unit out for servicing. Failure to stabilize the rack can cause the rack to tip over.
Clearance Requirements
Provide the chassis with adequate clearance between the chassis and any other rack, device, or structure so
that you can properly install the chassis. Provide the chassis with adequate clearance to route cables, provide
airflow, and maintain the switch. For the clearances required for an installation of this chassis in a four-post
rack, see the following figure.
Depth of the chassis5Chassis1
Maximum extension of the bottom-support rails6Vertical rack-mount posts and rails2
Depth of the front clearance area (equal to the
7Chassis width3
depth of the chassis).
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
10
Page 21
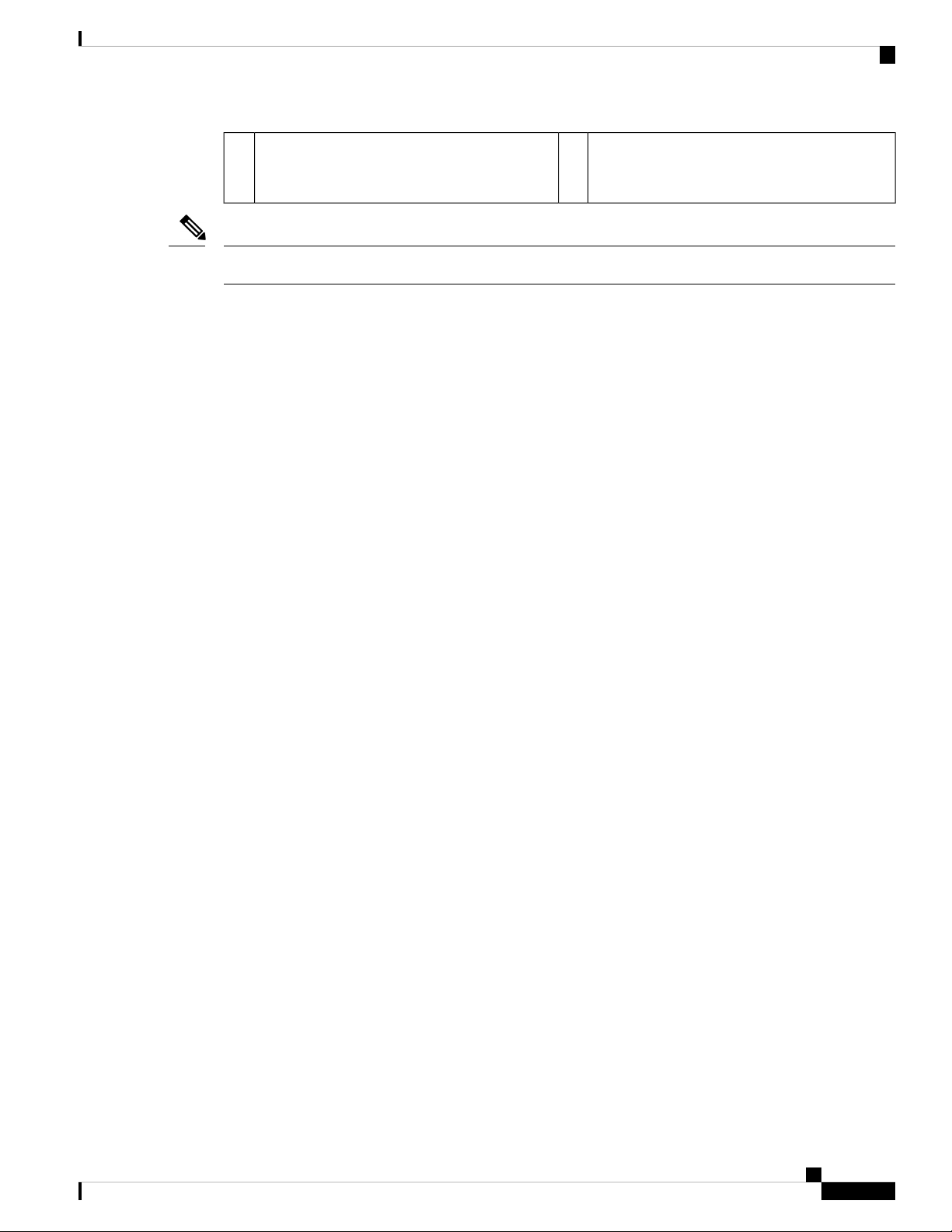
Preparing the Site
Width of the front clearance area (equal to the
4
width of the chassis with two rack-mount
brackets that are attached to it).
Note
Both the front and rear of the chassis must be open to both aisles for airflow.
Clearance Requirements
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
11
Page 22

Clearance Requirements
Preparing the Site
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
12
Page 23

Safety
CHAPTER 3
Installing the Switch Chassis
• Safety, on page 13
• Installation Options with Rack-Mount Kits, Racks, and Cabinets, on page 14
• Airflow Considerations, on page 14
• Installation Guidelines, on page 14
• Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch, on page 16
• Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount Kit, on page 17
• Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit, on page 20
• Grounding the Chassis, on page 24
• Starting the Switch, on page 25
Before you install, operate, or service the switch, see the Regulatory, Compliance, and Safety Information for
the Cisco Nexus 3000 and 9000 Series for important Safety Information.
Warning
Warning
Statement 1071—Warning Definition
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work
on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard
practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate
its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
Statement 1017—Restricted Area
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only
through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
13
Page 24

Installation Options with Rack-Mount Kits, Racks, and Cabinets
Installing the Switch Chassis
Warning
Statement 1030—Equipment Installation
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Installation Options with Rack-Mount Kits,Racks, andCabinets
The rack-mount kit enables you to install the switch into racks of varying depths. You can position the switch
with easy access to either the port connections or the fan and power supply modules.
You can install the switch using the following rack-mount options:
• Rack-mount kit (NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU) which you can order from Cisco. This option offers you easy
installation, greater stability, increased weight capacity, added accessibility, and improved removability
with front and rear removal.
• Rack-mount kit (N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT) which you can order from Cisco.
You can install the switch in the following types of racks:
• Open EIA rack
• Perforated EIA cabinet
The rack or cabinet that you use must meet the requirements listed the in General Requirements for Cabinets
and Racks, on page 43 section.
Note
You are responsible for verifying that your rack and rack-mount hardware comply with the guidelines that
are described in this doc.
Airflow Considerations
The switch comes with fan and power supply modules that have either port-side intake or port-side exhaust
airflow for cooling the switch. If you are positioning the port end of the switch in a cold aisle, make sure that
the switch has port-side intake fan modules with burgundy coloring. If you are positioning the fan and power
supply modules in a cold aisle, make sure that the switch has port-side exhaust fan modules with blue colorings.
All fan modules must have the same direction of airflow.
Installation Guidelines
When installing the switch, follow these guidelines:
• Ensure that there is adequate clearance space around the switch to allow for servicing the switch and for
adequate airflow.
• Ensure that you are positioning the switch in a rack so that it takes in cold air from the cold aisle and
exhausts air to the hot aisle. If there is blue coloring on the fan modules, the switch is configured for
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
14
Page 25

Installing the Switch Chassis
Installation Guidelines
port-side exhaust airflow and you must position the module side of the switch in a cold aisle. If there is
burgundy coloring on the fan modules, the switch is configured for port-side intake airflow and you must
position the port side of the switch in a cold aisle.
• Ensure that the chassis can be adequately grounded. If the switch is not mounted in a grounded rack, we
recommend connecting the system ground on the chassis directly to an earth ground.
• Ensure that the site power meets the power requirements for the switch. If available, you can use an
uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to protect against power failures.
Caution
Avoid UPS types that use ferroresonant technology. These UPS types can become
unstable with the switch, which can have substantial current draw fluctuations
because of fluctuating data traffic patterns.
• Ensure that circuits are sized according to local and national codes. Typically, this often requires one or
both of the following:
• AC power supplies typically require at least a 15-A or 20-A AC circuit, 100 to 240 VAC, and a
frequency of 50 to 60 Hz.
• HVAC/HVDC power supplies require the following:
• HVAC input voltage range of 230 to 277 VAC with a frequency of 50 to 60 Hz
• HVDC input voltage range of -240 to -380 VDC
• DC power supplies require the following:
• DC input voltage range of –48 to -60 VDC nominal (self-ranging, –40 to –60 VDC)
• DC line input current (steady state) of 23 A peak at –48 VDC
Caution
To prevent loss of input power, ensure the total maximum loads on the circuits
supplying power to the switch are within the current ratings for the wiring and
breakers.
Note
Warning
For AC input application, please refer to the statement below:
Statement 1005—Circuit Breaker
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent)
protection. Ensure that the protective devices is rated not greater than 20A (North
America), 16A (Europe), and 13A (UK).
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
15
Page 26

Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch
Note
For DC input application, please refer to the statement below:
Installing the Switch Chassis
Warning
Statement 1005—Circuit Breaker
This product relies on the building's installation for short-circuit (overcurrent)
protection. Ensure that the protective devices is rated not greater than 40A for
the regular DC power supplies (rated 48-60VDC) and 10A for the HVDC power
supplies.
Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch
Before you install the switch, be sure to unpack and inspect the switch for damage or missing components.
If anything is missing or damaged, contact your customer service representative immediately.
Tip
Keep the shipping container in case the chassis requires shipping at a later time.
Before you begin
Before you unpack the switch and before you handle any switch components, be sure that you are wearing a
grounded electrostatic discharge (ESD) strap. To ground the strap, attach it directly to an earth ground or to
a grounded rack or grounded chassis (there must be a metal-to-metal connection to the earth ground).
Step 1 Compare the shipment to the equipment list provided by your customer service representative and verify that you have
received all items, including the following:
• Accessory Kit
Note
For the contents of these kits, see the Additional Kits.
Step 2 Check for damage and report any discrepancies or damage to your customer service representative. Have the following
information ready:
• Invoice number of shipper (see packing slip)
• Model and serial number of the damaged unit
• Description of damage
• Effect of damage on the installation
Step 3 Check to be sure that each of the power supply and the fan tray modules have the expected direction of airflow as follows:
• Port-side intake airflow modules
• Burgundy (fan modules and AC power supplies)
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
16
Page 27

Installing the Switch Chassis
• Green (DC power supplies)
• Port-side exhaust airflow modules
• Blue (fan modules and AC power supplies)
• Gray (DC power supplies)
• Dual-direction airflow power-supply modules
• White (see the color of the fan modules to determine the airflow direction used)
Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount Kit
Note
All power supplies and fan modules must have the same direction of airflow.
Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount
Kit
To install the switch, you must attach front and rear mounting brackets to the switch, install slider rails on the
rear of the rack, slide the switch onto the slider rails, and secure the switch to the front of the rack. Typically,
the front of the rack is the side easiest to access for maintenance.
Note
You must supply the eight 10-32 or 12-24 screws required to mount the slider rails and switch to the rack.
Before you begin
• You have inspected the switch shipment to ensure that you have everything ordered.
• Make sure that the switch rack-mount kit includes the following parts:
• Front rack-mount brackets (2)
• Rear rack-mount brackets (2)
• Slider rails (2)
• M4 x 0.7 x 8-mm Phillips countersink screws (12)
• The rack is installed and secured to its location.
Step 1 Install two front rack-mount brackets and the two rear rack-mount brackets to the switch as follows:
a) Determine which end of the chassis is to be located in the cold aisle as follows:
• If the switch has port-side intake modules (fan modules with burgundy coloring), position the switch so that its
ports will be in the cold aisle.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
17
Page 28

Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount Kit
• If the switch has port-side exhaust modules (fan modules with blue coloring), position the switch so that its fan
and power supply modules will be in the cold aisle.
Installing the Switch Chassis
Note
If the power supply modules have white coloring, look at the fan modules to determine the airflow direction
for the switch.
b) Position the front rack-mount bracket and the rear rack-mount bracket so that its screw holes are aligned to the screw
holes on the side of the chassis.
Note
You can align the holes in the rack-mount bracket to the holes on the side of the chassis (see the two ways
to mount these brackets on a typical chassis, in following figure). The holes that you use depend on the
requirements of your rack and the amount of clearance required for interface cables (3 inches [7.6 mm]
minimum) and module handles (1 inch [2.5 mm] minimum).
c) Secure the front-mount bracket and the back-mount bracket to the chassis using four M4 screws and tighten each
screw to 12 in-lb (1.36 N·m) of torque.
d) Repeat Step 1 for the other front rack-mount bracket and the other back-mount bracket on the other side of the switch
and be sure to position that bracket the same distance from the front of the switch.
Note
Depending on the chassis depth, the back rack-mount bracket may not fit. In that case the back rack-mount
bracket is not needed.
Step 2 If you are not installing the chassis into a grounded rack, you must attach a customer-supplied grounding wire to the
chassis as explained in the Grounding the Chassis, on page 24 section. If you are installing the chassis into a grounded
rack, you can skip this step.
Step 3 Install the slider rails on the rack or cabinet as follows:
a) Determine which two posts of the rack or cabinet you should use for the slider rails. Of the four vertical posts in the
rack or cabinet, two will be used for the front mount brackets attached to the easiest accessed end of the chassis, and
the other two posts will have the slider rails.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
18
Page 29

Installing the Switch Chassis
b) Position a slider rail at the desired level on the back side of the rack and use 12-24 screws or 10-32 screws, depending
on the rack thread type, to attach the rails to the rack (see the following figure). Tighten 12-24 screws to 30 in-lb
(3.39 N·m) of torque and tighten 10-32 screws to 20 in-lb (2.26 N·m) of torque.
Installing the Switch using the NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU Rack-mount Kit
c) Repeat Step 3 to attach the other slider rail to the other side of the rack.
To make sure that the slider rails are at the same level, you should use a level tool, tape measure, or carefully count
the screw holes in the vertical mounting rails.
Step 4 Insert the switch into the rack and attach it as follows:
a) Holding the switch with both hands, position the two rear rack-mount brackets on the switch between the rack or
cabinet posts that do not have slider rails attached to them (see the following figure).
b) Align the two rear rack-mount guides on either side of the switch with the slider rails installed in the rack. Slide the
rack-mount guides onto the slider rails, and then gently slide the switch all the way into the rack until the front
rack-mount brackets come in contact with two rack or cabinet posts.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
19
Page 30

Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit
c) Holding the chassis level, insert screws (12-24 or 10-32, depending on the rack type) in each of the two front rack-mount
brackets (using a total of six screws) and into the cage nuts or threaded holes in the vertical rack-mounting rails (see
the following figure).
Installing the Switch Chassis
d) Tighten the 10-32 screws to 20 in-lb (2.26 N·m) or tighten the 12-24 screws to 30 in-lb (3.39 N·m).
Step 5 If you attached a grounding wire to the chassis grounding pad, connect the other end of the wire to the facility ground.
InstallingtheSwitchusingtheN3K-C3064-ACC-KITRack-mount
Kit
To install the switch, you must attach front and rear mounting brackets to the switch, install slider rails on the
rear of the rack, slide the switch onto the slider rails, and secure the switch to the front of the rack. Typically,
the front of the rack is the side easiest to access for maintenance.
Note
You must supply the eight 10-32 or 12-24 screws required to mount the slider rails and switch to the rack.
Before you begin
• You have inspected the switch shipment to ensure that you have everything ordered.
• Make sure that the switch rack-mount kit includes the following parts:
• Front rack-mount brackets (2)
• Rear rack-mount brackets (2)
• Slider rails (2)
• M4 x 0.7 x 8-mm Phillips countersink screws (12)
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
20
Page 31

Installing the Switch Chassis
• The rack is installed and secured to its location.
Step 1 Install two front-mount brackets to the switch as follows:
a) Determine which end of the chassis is to be located in the cold aisle as follows:
• If the switch has port-side intake modules (fan modules with burgundy coloring), position the switch so that its
ports will be in the cold aisle.
• If the switch has port-side exhaust modules (fan modules with blue coloring), position the switch so that its fan
and power supply modules will be in the cold aisle.
Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit
Note
If the power supply modules have white coloring, look at the fan modules to determine the airflow direction
for the switch.
b) Position a front-mount bracket so that four of its screw holes are aligned to the screw holes on the side of the chassis.
Note
You can align any four of the holes in the front rack-mount bracket to four of the six screw holes on the
side of the chassis (see the two ways to mount these brackets on a typical chassis, in following figure). The
holes that you use depend on the requirements of your rack and the amount of clearance required for interface
cables (3 inches [7.6 mm] minimum) and module handles (1 inch [2.5 mm] minimum).
1
the chassis
Front rack-mount bracket aligned to the module end
5Front rack-mount bracket aligned to the port end of
of the chassis
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
21
Page 32

Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit
2
6Four M4 screws used to attach the bracket to the
chassis
3
7Rear rack-mount guide aligned to the module end of
the chassis
4
8Two M4 screws used to attach the bracket to the
chassis
c) Secure the front-mount bracket to the chassis using four M4 screws and tighten each screw to 12 in-lb (1.36 N·m)
of torque.
d) Repeat Step 1 for the other front rack-mount bracket on the other side of the switch and be sure to position that bracket
the same distance from the front of the switch.
Step 2 Install the two rear rack-mount brackets on the chassis as follows:
a) Align the two screw holes on a rear rack-mount bracket to the middle two screw holes in the remaining six screw
holes on a side of the chassis. If you are aligning the guide to holes that are near the port connections end of the
chassis, see Callout 3 in the previous figure. Otherwise, see Callout 7 in the previous figure.
b) Attach the guide to the chassis using two M4 screws (see Callout 4 or 8 in the previous figure). Tighten the screws
to 12 in-lb (1.36 N·m) of torque.
c) Repeat Step 2 for the other rear rack-mount bracket on the other side of the switch.
Installing the Switch Chassis
Four M4 screws used to attach the bracket to the
chassis
Two M4 screws used to attach the bracket to the
chassis
Rear rack-mount guide aligned to the port end of the
chassis
Step 3 If you are not installing the chassis into a grounded rack, you must attach a customer-supplied grounding wire to the
chassis as explained in the Grounding the Chassis, on page 24 section.. If you are installing the chassis into a grounded
rack, you can skip this step.
Step 4 Install the slider rails on the rack or cabinet as follows:
a) Determine which two posts of the rack or cabinet you should use for the slider rails. Of the four vertical posts in the
rack or cabinet, two will be used for the front mount brackets attached to the easiest accessed end of the chassis, and
the other two posts will have the slider rails.
b) Position a slider rail at the desired level on the back side of the rack and use two 12-24 screws or two 10-32 screws,
depending on the rack thread type, to attach the rails to the rack (see the following figure). Tighten 12-24 screws to
30 in-lb (3.39 N·m) of torque and tighten 10-32 screws to 20 in-lb (2.26 N·m) of torque.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
22
Page 33

Installing the Switch Chassis
1
rack
c) Repeat Step 3 to attach the other slider rail to the other side of the rack.
To make sure that the slider rails are at the same level, you should use a level tool, tape measure, or carefully count
the screw holes in the vertical mounting rails.
Step 5 Insert the switch into the rack and attach it as follows:
a) Holding the switch with both hands, position the two rear rack-mount brackets on the switch between the rack or
cabinet posts that do not have slider rails attached to them (see the following figure).
Installing the Switch using the N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT Rack-mount Kit
Two customer-supplied 12-24 or 10-32 screws used
2Slider rail with screw holes aligned to screw holes in
to attach each slider rail to the rack
1
Front-mount brackets.3Align the two rear rack-mount bracket guides with
the slider rails installed in the rack.
2
Mounting rails on rack or cabinet posts.4Slide the rack-mount guides onto the slider rails until
the front rack-mount brackets come in contact with
the front rack-mount rails.
b) Align the two rear rack-mount guides on either side of the switch with the slider rails installed in the rack. Slide the
rack-mount guides onto the slider rails, and then gently slide the switch all the way into the rack until the front
rack-mount brackets come in contact with two rack or cabinet posts.
c) Holding the chassis level, insert two screws (12-24 or 10-32, depending on the rack type) in each of the two front
rack-mount brackets (using a total of four screws) and into the cage nuts or threaded holes in the vertical rack-mounting
rails (see the following figure).
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
23
Page 34

Grounding the Chassis
Installing the Switch Chassis
1
12-24 or 10-32 screws on each side.
Front-mount bracket.2
d) Tighten the 10-32 screws to 20 in-lb (2.26 N·m) or tighten the 12-24 screws to 30 in-lb (3.39 N·m).
Step 6 If you attached a grounding wire to the chassis grounding pad, connect the other end of the wire to the facility ground.
Mounting rails on rack or cabinet posts.3Fasten the chassis to the front of the rack with two
Grounding the Chassis
The switch chassis is automatically grounded when you properly install the switch in a grounded rack with
metal-to-metal connections between the switch and rack.
You can also ground the chassis, which is required if the rack is not grounded, by attaching a customer-supplied
grounding cable. Attach the cable to the chassis grounding pad and the facility ground.
Warning
Statement 1024—Ground Conductor
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence
of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician
if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
24
Page 35

Installing the Switch Chassis
Starting the Switch
Warning
Step 1 Use a wire-stripping tool to remove approximately 0.75 inch (19 mm) of the covering from the end of the grounding
wire. We recommend 6-AWG wire for the U.S. installations.
Step 2 Insert the stripped end of the grounding wire into the open end of the grounding lug. Use a crimping tool to crimp the
lug to the wire, see the following figure. Verify that the ground wire is securely attached to the grounding lug by attempting
to pull the wire out of the crimped lug.
Statement 1046—Installing or Replacing the Unit
When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last.
Before you begin
Before you can ground the chassis, you must have a connection to the earth ground for the data center building.
3Chassis grounding pad1
2
Step 3 Secure the grounding lug to the chassis grounding pad with two M4 screws, see the previous figure. Tighten the screws
to 11 to 15 in-lb (1.24 to 1.69 N·m) of torque.
Step 4 Prepare the other end of the grounding wire and connect it to the facility ground.
Grounding cable, with 0.75
in. (19 mm) of insulation that
is stripped from one end,
which is inserted into the
grounding lug and crimped
in place
2 M4 screws are used to
secure the grounding lug to
the chassis
Starting the Switch
You start the switch by connecting it to its dedicated power source. If you need n+1 redundancy, you must
connect each of the power supplies to one or two power sources. If you need n+n redundancy, you must
connect each power supply in a switch to a different power source.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
25
Page 36

Starting the Switch
Installing the Switch Chassis
Before you begin
• The switch must be installed and secured to a rack or cabinet.
• The switch must be adequately grounded.
• The rack must be close enough to the dedicated power source so that you can connect the switch to the
power source by using a designated power cables.
• You have the designated power cables for the power supplies that you are connecting to the dedicated
power sources.
Note
Depending on the outlet receptacle on your AC power distribution unit, you might
need an optional jumper power cord to connect the switch to your outlet receptacle.
• The switch is not connected to the network (this includes any management or interface connections).
• The fan and power supply modules are fully secured in their chassis slots.
All of the fan slots must be filled with fan modules and the power supply slots must be filled with the
same types of power supplies (do not mix AC and DC power supplies).
Step 1 For each AC power supply, do the following:
a) Using the recommended AC power cable for your country or region, connect one end to the AC power supply.
b) Connect the other end of the power cable to the AC power source.
Step 2 For each HVAC/HVDC power supply, connect it to a power source as follows:
a) Using the recommended high voltage power cable for your country or region, connect the Anderson Power Saf-D-Grid
connector on the power cable to the power receptacle on the power supply. Make sure that the connector clicks when
fully pushed into the receptacle.
b) Connect the other end of the power cable to a power source.
• When connecting to an HVAC power source, insert the C14 or LS-25 plug in a receptacle for the HVAC power
source.
• When connecting to an HVDC power source, do the following:
1. Verify that the power is turned off at a circuit breaker for the power source terminals.
2. Remove the nuts from each of the terminal posts for the power supply.
3. Place the power cable negative-wire terminal ring on the negative terminal for the power source and secure
them with a terminal nut.
4. Place the power cable positive-wire terminal ring on the positive terminal for the power source and secure
them with a terminal nut.
5. Place the power cable ground-wire terminal ring on the ground terminal for the power source and secure
them with a terminal nut.
6. If there is a safety cover for the power source terminals, place and secure it over the terminals to avoid an
electrical shock hazard.
7. Turn on the power at the power source circuit breaker.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
26
Page 37

Installing the Switch Chassis
Step 3 For each DC power supply, do the following:
a) Turn off the circuit breaker for the power source to avoid an electrical shock hazard.
b) Verify that the power cable wires from the power source are connected to a connector block.
c) Insert the connector block into the receptacle on the power supply. Make sure that the connector block clicks when
fully inserted in the receptacle and does not pull out.
d) If there is a safety cover for the terminals, place and secure it over the terminals to avoid an electrical shock hazard.
e) Turn on the power at the circuit breaker for the DC power source.
Step 4 Verify that the power supply LED is on and green.
Step 5 Listen for the fans; they should begin operating when the power supply is powered.
Step 6 After the switch boots, verify that the following LEDs are lit:
• On the fan modules, the Status (STA or STS) LED is green.
If a fan module Status LED is not green, try reinstalling the fan module.
• After initialization, the switch chassis Status (labeled as STA or STS) LED is green.
Step 7 Verify that the system software has booted and the switch has initialized without error messages.
Starting the Switch
A setup utility automatically launches the first time that you access the switch and guides you through the basic
configuration. For instructions on how to configure the switch and check module connectivity, see the appropriate Cisco
Nexus 9000 Series configuration guide.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
27
Page 38

Starting the Switch
Installing the Switch Chassis
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
28
Page 39

Connecting the Switch to the Network
• Setting Up the Management Interface, on page 29
• Connecting to Host Servers, on page 29
• Guidelines for Connecting Ports, on page 30
• Maintaining Transceivers and Optical Cables, on page 32
Setting Up the Management Interface
The management port (MGMT ETH) provides out-of-band management, which enables you to use the
command-line interface (CLI) to manage the switch by its IP address. This port uses a 10/100/1000 Ethernet
connection with an RJ-45 interface.
Before you begin
The switch must be powered on.
CHAPTER 4
Step 1 Connect the RJ-45, UTP cable to the MGMT ETH port on the switch.
Step 2 Connect the other end of the cable to a 10/100/1000 Ethernet port on a network device.
What to do next
You are ready to connect the interface ports on each of the line cards to the network.
Connecting to Host Servers
The switch has 36 ports that connect to host servers. You can configure each of these ports for 100-, 40-, 25-,
10-, or 1-Gigabit speeds as follows:
• For 100 Gigabits per second, use QSFP28 transceivers on both ends of each optical cable.
• For 40 Gigabits per second, use QSFP+ transceivers on both ends of each optical cable.
• For 25 Gigabits per second, you can do either of the following:
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
29
Page 40

Guidelines for Connecting Ports
• For 10-Gigabit connectivity, you can do one of the following:
Connecting the Switch to the Network
• Use a breakout cable with a QSFP28 transceiver on one end and four SFP25 transceivers on the
other ends. To configure one or more ports to use this cable, use the interface breakout module
module_number port low_port_number[-high_port_number] map 25g-4x command. For the Cisco
Nexus 9236C switch, use 1 for the module_number. If you are configuring only one port, use the
port number in place of low_port_number. If you are configuring a range of ports, specify the port
numbers from low to high, such as port 2-15.
Note
You can use a breakout cable that is up to 9.8 feet (3 meters) in length.
• Use a CVR-2QSFP28-8SFP adapter for each 100-Gigabit port to operate at 25-Gigabits and configure
the port or range of ports to operate at 25-Gigabits by using the interface breakout module
module_number port low_port_number[-high_port_number] map 25g command. For the Cisco
Nexus 9236C switch, use 1 for the module_number. If you are configuring only one port, use the
port number in place of low_port_number. If you are configuring a range of ports, specify the port
numbers from low to high, such as port 2-15.
• Use a QSFP-to-SFP adapter, such as the CVR-QSFP-SFP10G adapter, so that you can connect
SFP+ or SFP transceivers to the QSFP28/QSFP+ ports. The 10-Gigabit speed is automatically set
up through the adapter connection.
• Use a breakout cable with a QSFP+ transceiver on the switch end and four SFP+ transceivers on
the other cable ends. To configure one or more ports to use this cable, use the interface breakout
module module_number port low_port_number[-high_port_number] map 10g-4x command. For
the Cisco Nexus 9236C switch, use 1 for the module_number. If you are configuring only one port,
use the port number in place of low_port_number. If you are configuring a range of ports, specify
the port numbers from low to high, such as port 2-15.
To determine which transceivers and cables are supported by this switch, see
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/products-device-support-tables-list.html.
To see the transceiver specifications and installation information, see
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/products-installation-guides-list.html.
Guidelines for Connecting Ports
You can use 100-Gigabit Quad Small Form Factor Pluggable 28 (QSFP28) or 40-Gigabit QSFP+ transceivers
for connections to other network devices using speeds of 100, 40, 25, or 10 Gigabits per second (you can use
breakout cables for 25- and 10-Gigabit connections).
For information about the transceivers currently being used with the switch, use the show inventory all
command.
Prevent damage to the fiber-optic cables that can separate from their cables. Keep the transceivers disconnected
from their fiber-optic cables when installing the transceiver in the line card. Before removing such a transceiver
from the switch, remove the cable from the transceiver.
To maximize the effectiveness and life of your transceivers and optical cables, do the following:
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
30
Page 41

Connecting the Switch to the Network
• Wear an ESD-preventative wrist strap that is connected to an earth ground whenever handling transceivers.
The switch is typically grounded during installation and provides an ESD port to which you can connect
your wrist strap.
• Do not remove and insert a transceiver more often than is necessary. Repeated removals and insertions
can shorten its useful life.
• Keep the transceivers and fiber-optic cables clean and dust free to maintain high signal accuracy and to
prevent damage to the connectors. Contamination causes increased attenuation (loss of light), and should
be kept below 0.35 dB.
• Inspect routinely for dust and damage. If you suspect damage, clean and then inspect fiber ends under a
microscope to determine if damage has occurred.
Guidelines for Connecting Ports
• Clean these parts before installation to prevent dust from scratching the fiber-optic cable ends.
• Clean the connectors regularly; the required frequency of cleaning depends upon the environment.
In addition, clean connectors if they are exposed to dust or accidentally touched. Both wet and dry
cleaning techniques can be effective; refer to your site's fiber-optic connection cleaning procedures.
• Do not touch the ends of connectors. Touching the ends can leave fingerprints and cause other
contamination.
Warning
Warning
Warning
• To minimize the chance of damaging transceivers when installing them, slide them gently into their
switch slots. Never force transceivers all the way into the slots. If the transceiver stops part way into the
slot, it might be upside down. Remove the transceiver before turning it over and reinstalling it. If positioned
correctly, the transceiver slides all the way into the slot and clicks when fully installed.
Statement 1051—Laser Radiation
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or
view directly with optical instruments.
Statement 1053—Class 1M Laser Radiation
Class 1M laser radiation when open. Do not view directly with optical instruments.
Statement 1055—Class I and Class 1M Laser
Class I (CDRH) and Class 1M (IEC) laser products.
Warning
Statement 1056—Unterminated Fiber Cable
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the end of the unterminated fiber cable or connector. Do not
view directly with optical instruments. Viewing the laser output with certain optical instruments (for example,
eye loupes, magnifiers, and microscopes) within a distance of 100 mm may pose an eye hazard.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
31
Page 42

Maintaining Transceivers and Optical Cables
Maintaining Transceivers and Optical Cables
Transceivers and fiber-optic cables must be kept clean and dust free to maintain high signal accuracy and
prevent damage to the connectors. Contamination increases attenuation (loss of light) and should be below
0.35 dB.
Consider the following maintenance guidelines:
• Transceivers are static sensitive. To prevent ESD damage, wear an ESD-preventative wrist strap that is
connected to the grounded chassis.
• Do not remove and insert a transceiver more often than is necessary. Repeated removals and insertions
can shorten its useful life.
• Keep all optical connections covered when not in use. Clean them before using to prevent dust from
scratching the fiber-optic cable ends.
• Do not touch the ends of connectors. Touching the ends can leave fingerprints and cause other
contamination.
Connecting the Switch to the Network
• Clean the connectors regularly; the required frequency of cleaning depends upon the environment. In
addition, clean connectors if they are exposed to dust or accidentally touched. Both wet and dry cleaning
techniques can be effective; refer to the fiber-optic connection cleaning procedures for your site.
• Inspect routinely for dust and damage. If you suspect damage, clean and then inspect fiber ends under a
microscope to determine if damage has occurred.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
32
Page 43

CHAPTER 5
Replacing Modules
• Replacing a Fan Module During Operations, on page 33
• Replacing a Power Supply Module, on page 34
Replacing a Fan Module During Operations
All fan and power supply modules must have the same airflow direction or else an error can occur with the
switch overheating and shutting down. You can determine the airflow direction of a fan module by the color
of the stripe on the front of the module. If the fan module has a blue stripe for port-side exhaust airflow, the
power supplies must have blue coloring for the same airflow direction. If the fan module has a burgundy stripe
for port-side intake airflow, the power supplies must have burgundy coloring for the same airflow direction.
To avoid over heating the switch, make sure that the fan modules are positioned in one of the following ways:
• For port-side exhaust airflow with blue coloring, position the fan modules in a cold aisle.
• For port-side intake airflow with burgundy coloring, position the ports in a cold aisle.
Before you begin
Before you can replace a fan module, ensure that both of the following conditions exist:
• The replacement fan module must have the same airflow direction as the other modules in the chassis.
If you must replace the fan module during operations and both of the above conditions are not met, leave the
fan module that you need to replace in the chassis to preserve the designed airflow until you have the required
module.
Step 1 Remove the fan module that you need to replace as follows:
a) Place the removed module on an antistatic surface or in an antistatic bag. If possible, repack the module in its packing
materials for safe shipping or storage.
Step 2 Follow these steps to replace the missing fan module within two minutes to avoid a shutdown.
a) Remove the replacement fan module from its packing materials and place it on an antistatic surface.
Hold the module by its handle and do not touch the electrical connectors on its backside. Also, to protect the electrical
connectors, avoid letting them come in contact with anything other than the electrical connectors inside the chassis.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
33
Page 44

Replacing a Power Supply Module
b) Position the fan module in front of the open fan slot (be sure that the backside of the module with the electrical
connectors is positioned to enter the slot first) and slide the module all the way into the chassis until its front side
comes in contact with the chassis. For the last 0.2 inches (0.5 cm), carefully mount the module onto the chassis
connectors by pushing more firmly, but do not force the module if it does not move further (excessive force can
damage the connectors).
Replacing Modules
Note
c) Verify that the STS LED turns on and becomes green.
If the STS LED does not turn on, slide the module out of the chassis, and visually check the electrical connectors on
the back side of the chassis for damage. If damaged, contact Cisco Technical Assistance for help. If undamaged,
repeat the previous step to reinstall the module.
If you are not able to push the module all the way into the slot, carefully slide the module out of the slot
and check its electrical connectors for damage. If damaged, contact Cisco Technical Assistance for help.
If undamaged, repeat this step to reinstall the module.
Replacing a Power Supply Module
The switch requires two power supplies for redundancy. With one power supply providing the necessary
power for operations, you can replace the other power supply during operations so long as the new power
supply has the same airflow direction as the other modules in the chassis.
You can replace a power supply with another supported power supply that has the same power source type
(AC, DC, HVAC, or HVDC) and the same wattage rating as the other installed power supply. Additionally,
the airflow direction of the power supply must match or conform to the airflow direction of the installed fan
modules. For the airflow direction used by the switch, see the coloring of the fan modules. The following list
describes the power supplies supported by this switch.
• NXA-PAC-650W-PE (650-W, port-side exhaust (blue latch) power supply requiring an AC power source)
• NXA-PAC-650W-PI (650-W, port-side intake (burgundy latch) power supply requiring an AC power
source)
• N9K-PUV-1200W (1200-W, dual-direction (white latch) high-voltage AC/DC power supply requiring
a high-voltage AC or DC power source)
• UCS-PSU-6332-DC (930-W, port-side exhaust (blue latch) power supply requiring DC power source)
• UCSC-PSU-930WDC (930-W, port-side intake (burgundy latch) power supply requiring DC power
source)
Removing an AC Power Supply
To remove an AC power supply, you must first disconnect the power cable and then remove the module from
the chassis.
Before you begin
• To replace a power supply during operations, you must have a functioning power supply providing power
to the switch while you replace the other power supply. If there is only one power supply installed in the
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
34
Page 45

Replacing Modules
Removing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply
switch and you need to replace it, install the new power supply in the open slot and power it up before
removing the original power supply.
• Ensure that the chassis is grounded. For grounding instructions, see Grounding the Chassis, on page 24.
Step 1 Pull the power cord out from the power receptacle on the power supply to be removed and verify that the LED turns
off.
Note
Note
The LED might be on and amber colored to indicate that the input power has been disconnected.
If you need to remove an Anderson's Saf-D-Grid power cable connector from a high-voltage power supply,
press the tab at the top of the connector and pull the connector out of the power supply.
Step 2 Remove the power supply from the chassis by pushing and holding its thumb latch to the left and pulling the power supply
part way out of the chassis.
Step 3 Place your other hand under the power supply to support it while you slide it out of the chassis.
Either place the power supply on an antistatic surface or pack it in its packing materials.
Step 4 If the power supply slot is to remain empty, install a blank power supply filler panel (part number N2200-P-BLNK).
What to do next
You are ready to install the replacement power supply.
Removing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply
You can remove one power supply while the other one provides power to the switch.
To disconnect the power supply from its power cables, you must shut off the power from the power source
and then either disconnect a connector for the power cables or release each of three cables from the power
supply (requires a standard screw driver).
Step 1 Turn off the circuit breaker for the power feed to the power supply that you are replacing.
Be sure that the LEDs turn off on the power supply that you are removing.
Step 2 Remove the power cable from the power supply by pressing the tab on the top of the Anderson Power SAF-D-Grid
connector and pull the cable and connector out of the power supply.
Step 3 Grasp the power supply handle while pressing the release latch towards the power supply handle.
Step 4 Place your other hand under the power supply to support it while you slide it out of the chassis.
Caution
Do not touch the electrical connectors on the back side of the module and prevent anything else from coming
into contact with and damaging the connectors.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
35
Page 46

Removing a DC Power Supply
What to do next
You are ready to install an HVAC/HVDC power supply in the open slot.
Removing a DC Power Supply
You can remove one power supply while the other one provides power to the switch.
To disconnect the power supply from its power cables, you must shut off the power from the power source
and then either disconnect a connector for the power cables or release each of three cables from the power
supply (requires a standard screw driver).
Step 1 Turn off the circuit breaker for the power feed to the power supply that you are replacing.
Be sure that the LEDs turn off on the power supply that you are removing.
Step 2 Remove the power cable from the power supply by doing the following:
• To remove an orange power cable connector from a 48-V DC power supply, do the following:
Replacing Modules
1. Push the orange plastic button on the top of the connector block inward toward the power supply.
2. Pull the connector block out of the power supply.
• To remove an Anderson Power Products Saf-D-Grid power cable connector from a high-voltage power supply, press
on the tab at the top of the Saf-D-Grid connector and pull the connector out of the power supply.
Step 3 Grasp the power supply handle while pressing the release latch towards the power supply handle.
Step 4 Pull the power supply out of the bay.
What to do next
You are ready to install a DC power supply in the open slot.
Installing an AC Power Supply
You can replace one power supply while the other one provides power to the switch.
Before you begin
• The power supply that you are installing must be capable of using the same airflow direction as the fan
trays installed in the same switch and it must use the same type of power source as the other power supply
installed in the same switch (do not mix AC and DC power supplies in the same switch).
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
36
Page 47

Replacing Modules
Installing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply
Note
DC power supplies with green coloring have the same port-side intake airflow
direction as the power supplies with red coloring, and DC power supplies with
gray coloring have the same port-side exhaust airflow direction as the power
supplies with blue coloring. HVAC/HVDC power supplies automatically use the
same airflow direction as the installed fan modules. If the power supply that you
are replacing has a different color handle than the replacement power supply,
verify that it has or will have the same airflow direction as the other modules in
the switch.
• An AC power source must be within reach of the power cable that will be used with the replacement
power supply. If you are using n+n power redundancy, there must be a separate power source for each
power supply installed in the chassis. Otherwise, only one power source is required.
• There must be an earth ground connection to the chassis that you are installing the replacement module.
Typically, the chassis is grounded by its metal-to-metal connection with a grounded rack. If you need to
ground the chassis, see Grounding the Chassis, on page 24.
Step 1 Holding the replacement power supply with one hand underneath the module and the other hand holding the handle, turn
the power supply so that its release latch is on the right side and align the back end of the power supply (the end with the
electrical connections) to the open power supply slot before carefully sliding the power supply all the way into the slot
until it clicks into place.
Note
If the power supply does not fit into the open slot, turn the module over before sliding it carefully into the open
slot.
Step 2 Test the installation by trying to pull the power supply out of the slot without using the release latch.
If the power supply does not move out of place, it is secured in the slot. If the power supply moves, carefully press it all
the way into the slot until it clicks in place.
Step 3 Attach the power cable to the electrical outlet on the front of the power supply.
Step 4 Make sure that the other end of the power cable is attached to the appropriate power source for the power supply.
Note
Depending on the outlet receptacle on your power distribution unit, you might need the optional jumper cable
to connect the switch to your outlet receptacle.
Step 5 Verify that the power supply is operational by making sure that the power supply LED is green. For information on
what the power supply LEDs indicate, see Power Supply LEDs, on page 54.
Installing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply
You can replace one power supply while the other one provides power to the switch.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
37
Page 48

Installing a DC Power Supply
Note
DC power supplies with green coloring have the same port-side intake airflow direction as the power supplies
with red coloring, and DC power supplies with gray coloring have the same port-side exhaust airflow direction
as the power supplies with blue coloring. HVAC/HVDC power supplies automatically use the same airflow
direction as the installed fan modules. If the power supply that you are replacing has a different color handle
than the replacement power supply, verify that it has or will have the same airflow direction as the other
modules in the switch.
Before you begin
Replacing Modules
• If you are using DC power for the replacement power supply, the circuit breaker for the power feed to
the power supply that you are replacing must be turned off.
• If you are using n+n power redundancy, there must be a separate power source for each power supply
installed in the chassis (power sources must be of the same type—do not mix AC and DC power sources
for the same switch). Otherwise, only one power source is required.
• There must be an earth ground connection to the chassis that you are installing the replacement module.
Typically, the chassis is grounded by its metal-to-metal connection to a grounded rack. If you need to
ground this chassis by another means, see Grounding the Chassis, on page 24.
Step 1 Holding the replacement power supply with one hand underneath the module and the other hand holding the handle, turn
the power supply so that its release latch is on the right side and align the back end of the power supply (the end with the
electrical connections) to the open power supply slot before carefully sliding the power supply all the way into the slot
until it clicks into place.
Note
If the power supply does not fit into the open slot, turn the module over before sliding it into the open slot.
Step 2 Test the installation by trying to pull the power supply out of the slot without using the release latch.
If the power supply does not move out of place, it is secured in the slot. If the power supply moves, carefully press it all
the way into the slot until it clicks in place.
Step 3 If the DC power cables and a grounding cable are already connected to an electrical connector block, insert the block
into the power receptacle on the power supply.
If the electrical cables have not been connected to the electrical connector block, wire them as described in Wiring a 48
V DC Electrical Connector Block, on page 39.
Step 4 Make sure that the other end of the power cable is connected to the appropriate power source for the power supply.
Step 5 If using a DC power source, turn on the circuit breaker for the DC power source connected to the power supply.
Step 6 Verify that the power supply is operational by making sure that the power supply LED is green. For information on
what the power supply LEDs indicate, see Power Supply LEDs, on page 54.
Installing a DC Power Supply
This topic is for installing the 48-V DC power supply into switch chassis. If you need to install a high voltage
(HVAC/HVDC) power supply, see Installing an HVAC/HVDC Power Supply, on page 37.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
38
Page 49

Replacing Modules
Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block
You can replace one power supply while the other one provides power to the switch.
Before you begin
• The circuit breaker for the DC power source for the power supply must be turned off.
• The power supply that you are installing must be capable of using the same airflow direction as the fan
trays installed in the same switch
• A DC power source must be within reach of the power cable that will be used with the replacement power
supply. If you are using n+n power redundancy, there must be a separate power source for each power
supply installed in the chassis (do not mix AC and DC power sources for the same switch). Otherwise,
only one power source is required.
• There must be an earth ground connection to the chassis that you are installing the replacement module.
Typically, the chassis is grounded by its metal-to-metal connection to a grounded rack. If you need to
ground this chassis by another means, see Grounding the Chassis, on page 24.
Step 1 Holding the replacement power supply with one hand underneath the module and the other hand holding the handle, turn
the power supply so that its release latch is on the right side and align the back end of the power supply (the end with the
electrical connections) to the open power supply slot before carefully sliding the power supply all the way into the slot
until it clicks into place.
Note
If the power supply does not fit into the open slot, turn the module over before carefully sliding it into the open
slot.
Step 2 If the DC power cables and a grounding cable are already connected to an electrical connector block, insert the block
into the power receptacle on the power supply.
If the electrical cables have not been connected to the electrical connector block, wire them as described in Wiring a 48
V DC Electrical Connector Block, on page 39.
Step 3 Turn on the circuit breaker for the DC power source connected to the power supply.
Step 4 Verify that the power supply is operational by making sure that the power supply LED is green. For information on
what the power supply LEDs indicate, see Power Supply LEDs, on page 54.
Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block
You must connect the ground, negative, and positive DC power cables to a connector block in order to connect
the power cables to a 48 V DC power supply.
Note
The recommended wire gauge is 8 AWG. The minimum wire gauge is 10 AWG.
Warning
Statement 342—Before Connecting to System Power Supply
High leakage currentearth connection essential before connecting to system power supply.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
39
Page 50

Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block
Replacing Modules
Warning
Statement 1024—Ground Conductor
This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence
of a suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician
if you are uncertain that suitable grounding is available.
Before you begin
You must turn off the circuit breaker for the DC power cables that you are connecting to prevent electrocution.
Step 1 Verify that the circuit breaker for the power feed to the replacement power supply is turned off.
Step 2 Remove the DC power connector block from the power supply by doing the following:
a) Push the orange plastic button on the top of the connector block inward toward the power supply.
b) Pull the connector block out of the power supply.
Step 3 Strip 0.6 inches (15 mm) of insulation off the DC wires that you are using.
Step 4 Orient the connector as shown in the following figure with the orange plastic button on top.
-48V (-DC) cable4Wire retainer lever1
Grounding cable (8 AWG recommended)5Orange plastic button on top of the connector2
-48V Return (+DC) cable3
Step 5 Use a small screwdriver to depress the spring-loaded wire retainer lever on the lower spring-cage wire connector. Insert
your green (ground) wire into the aperture and then release the lever.
Step 6 Use a small screwdriver to depress the spring-loaded wire retainer lever on the middle spring-cage wire connector. Insert
your black (DC negative) wire into the aperture and then release the lever.
Step 7 Use a small screwdriver to depress the spring-loaded wire retainer lever on the upper spring-cage wire connector. Insert
your red (DC positive) wire into the aperture and then release the lever.
Step 8 Insert the connector block back into the power supply. Make sure that your red (DC positive) wire aligns with the power
supply label, "+ DC".
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
40
Page 51

Replacing Modules
Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block
Step 9 Verify that the other ends of the cables are attached to the DC power source and ground. You are then ready to turn on
the DC power source.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
41
Page 52

Wiring a 48 V DC Electrical Connector Block
Replacing Modules
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
42
Page 53

Rack Specifications
• Overview of Racks, on page 43
• General Requirements for Cabinets and Racks, on page 43
• Requirements Specific to Standard Open Racks, on page 44
• Requirements Specific to Perforated Cabinets, on page 44
• Cable Management Guidelines, on page 44
Overview of Racks
You can install the switch in the following types of cabinets and racks, assuming an external ambient air
temperature range of 0 to 104°F (0 to 40°C):
• Standard perforated cabinets
• Solid-walled cabinets with a roof fan tray (bottom to top cooling)
• Standard open racks
APPENDIX A
Note
If you are selecting an enclosed cabinet, we recommend one of the thermally validated types, either standard
perforated or solid-walled with a fan tray.
Note
We do not recommend that you use racks that have obstructions (such as power strips), because the obstructions
could impair access to field-replaceable units (FRUs).
General Requirements for Cabinets and Racks
The cabinet or rack must also meet the following requirements:
• Standard 19-inch (48.3 cm) (two- or four-post EIA cabinet or rack, with mounting rails that conform to
English universal hole spacing per section 1 of ANSI/EIA-310-D-1992). For more information, see
Requirements Specific to Perforated Cabinets, on page 44.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
43
Page 54

Requirements Specific to Standard Open Racks
• The minimum vertical rack space requirement per chassis is:
• For a one RU (rack unit) switch, 1.75 inches (4.4 cm)
• For a one and a half RU (rack unit) switch, 2.63 (6.68 cm)
• For a two RU (rack unit) switch, 3.5 inches (8.8 cm)
• For a three RU (rack unit) switch, 5.25 inches (13.3 cm)
• The width between the rack-mounting rails must be at least 17.75 inches (45.0 cm) if the rear of the
device is not attached to the rack. For four-post EIA racks, this measurement is the distance between the
two front rails.
Four-post EIA cabinets (perforated or solid-walled) must meet the following requirements:
• The minimum spacing for the bend radius for fiber-optic cables should have the front-mounting rails of
the cabinet offset from the front door by a minimum of 3 inches (7.6 cm).
• The distance between the outside face of the front mounting rail and the outside face of the back mounting
rail should be 23.0 to 30.0 inches (58.4 to 76.2 cm) to allow for rear-bracket installation.
Rack Specifications
Requirements Specific to Standard Open Racks
If you are mounting the chassis in an open rack (no side panels or doors), ensure that the rack meets the
following requirements:
• The minimum vertical rack space per chassis must be one rack unit (RU), equal to 1.75 inches (4.4 cm)
two rack units (RUs), equal to 3.5 inches (8.8 cm).
• The distance between the chassis air vents and any walls should be 2.5 inches (6.4 cm).
Requirements Specific to Perforated Cabinets
A perforated cabinet has perforations in its front and rear doors and side walls. Perforated cabinets must meet
the following requirements:
• The front and rear doors must have at least a 60 percent open area perforation pattern, with at least 15
square inches (96.8 square cm) of open area per rack unit of door height.
• The roof should be perforated with at least a 20 percent open area.
• The cabinet floor should be open or perforated to enhance cooling.
The Cisco R Series rack conforms to these requirements.
Cable Management Guidelines
To help with cable management, you might want to allow additional space in the rack above and below the
chassis to make it easier to route all of the fiber optic or copper cables through the rack.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
44
Page 55

System Specifications
• Environmental Specifications, on page 45
• Switch Dimensions, on page 45
• Switch and Module Weights and Quantities, on page 46
• Transceiver and Cable Specifications, on page 46
• Switch Power Input Requirements, on page 46
• Power Specifications, on page 47
• Power Cable Specifications, on page 49
• Regulatory Standards Compliance Specifications, on page 51
Environmental Specifications
APPENDIX B
SpecificationEnvironment
32 to 104°F (0 to 40°C)Ambient operating temperatureTemperature
–40 to 158°F (–40 to 70°C)Ambient nonoperating
Relative
humidity
Operating
Nonoperating
Switch Dimensions
8 to 80% with humidity gradation of 10% per hour
5 to 95%
0 to 13,123 feet (0 to 4,000 meters)OperatingAltitude
HeightDepthWidthSwitch
1.72 inches (4.4 cm) (1 RU)22.5 inches (57.1 cm)17.3 inches (43.9 cm)Cisco Nexus 9236C
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
45
Page 56

Switch and Module Weights and Quantities
Switch and Module Weights and Quantities
System Specifications
QuantityWeight per UnitComponent
118.2 lb (8.3 kg)Cisco Nexus 9236C Chassis (N9K-C9236C)
Fan Module
– Port-side exhaust (blue) (NXA-FAN-30CFM-F)
– Port-side intake (burgundy) (NXA-FAN-30CFM-B)
Power Supplies
– 650-W AC port-side exhaust (blue) (NXA-PAC-650W-PE)
– 650-W AC port-side intake (burgundy) (NXA-PAC-650W-PI)
– 1200-W HVAC/HVDC dual-direction (white) (N9K-PUV-1200W)
– 930-W DC port-side exhaust (gray) (UCS-PSU-6332-DC)
– 930-W DC port-side intake (green) (UCSC-PSU-930WDC)
Transceiver and Cable Specifications
To determine which transceivers, adapters, and cables are supported by this switch, see https://www.cisco.com/
c/en/us/support/interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/products-device-support-tables-list.html.
To see the transceiver specifications and installation information, see https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/
interfaces-modules/transceiver-modules/products-device-support-tables-list.html.
0.92 lb (0.4 kg)
0.92 lb (0.4 kg)
—
2.42 lb (1.1 kg)
2.42 lb (1.1 kg)
2.42 lb (1.1 kg)
2.42 lb (1.1 kg)
2.42 lb (1.1 kg)
4—
2 (1 for
operations
and 1 for
redundancy)
Switch Power Input Requirements
The following table lists the typical amount of power that the switch consumes. It also lists the maximum
amount of power that you must provision for the switch and power supply for peak conditions.
Note
Some power supplies have UL listed capabilities that are greater than the maximum power requirements for
a switch. To determine the power consumption characteristics for the switch, use the typical and maximum
requirements that are listed in the following table.
Switch
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
46
Typical Power
Consumption (AC or DC)
Maximum Power
Consumption (AC or DC)
Heat Dissipation
Requirement
2183.77 BTUs per hour640 W275 WCisco Nexus 9236C
Page 57

System Specifications
Power Specifications
Power specifications include the specifications for each type of power supply module.
650-W AC Power Supply Specifications
These specifications apply to the following power supplies:
• NXA-PAC-650W-PE
• NXA-PAC-650W-PI
Power Specifications
SpecificationCharacteristic
AC input voltage
Maximum AC input current
Efficiency rating
Nominal range: 100 and 240 VAC (Range: 90-132
VAC, 180-264 VAC)
Nominal range: 50 to 60 Hz (Range: 47-63 Hz)AC input frequency
7.6 A at 100 VAC
3.65 A at 208 VAC
760 A at 100 VACMaximum input volt-amperes
650 WMaximum output power per power supply
33 A (sub-cycle duration)Maximum inrush current
12 ms at 650 WMaximum hold-up time
12 VDCPower supply output voltage
12 VDCPower supply standby voltage
Climate Savers Platinum Efficiency (80Plus Platinum
certified)
RSP1Form factor
1200-W HVAC/HVDC Power Supply Specifications
These specifications apply to the 1200-W HVAC/HVDC (N9K-PUV-1200W) power supplies.
SpecificationCharacteristic
Input voltage
• AC (for 1230 W output)
• DC (for 1230 W output)
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
Nominal (Range)
• 200 to 277 VAC
• –240 to –380 VDC
Nominal: 50 to 60 Hz (Range: 47-63 Hz)AC input frequency
47
Page 58

930-W DC Power Supply (Port-Side Intake) Specifications
System Specifications
SpecificationCharacteristic
35 A (cold turn on); 70 A (hot turn on)Maximum inrush current
Maximum output Watts
• For 200 to 277 VAC
• For 192 to 400 VDC
Power supply output voltage
• For 200 to 277 VAC
• For 192 to 400 VDC
Efficiency rating
Per power supply
• 1230 W
• 1230 W
Per power supply
• 12 VAC at 100 A
• 12 VDC at 100 A
12 V at 2.5 APower supply standby voltage
Climate Savers Platinum Efficiency (80Plus Platinum
certified)
RSP1Form factor
930-W DC Power Supply (Port-Side Intake) Specifications
These specifications apply to the 930-W DC (UCSC-PSU-930WDC) port-side intake power supplies.
SpecificationCharacteristic
DC input voltage range
Nominal range: -48 to -60 VDC nominal (Range: -40
to -60 VDC)
23 A at -48 VDCMaximum DC input current
1104 WMaximum input W
930 WMaximum output power per power supply
35 A (sub-cycle duration)Maximum inrush current
8 ms at 930 WMaximum hold-up time
12 VDCPower supply output voltage
12 VDCPower supply standby voltage
Greater than 92% at 50% loadEfficiency rating
RSP1Form factor
930-W DC Power Supply (Port-Side Exhaust) Specifications
These specifications apply to the 930-W DC (UCS-PSU-6332-DC) power supplies.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
48
Page 59

System Specifications
Power Cable Specifications
SpecificationCharacteristic
23 A at -48 VDCMaximum DC input current
1104 WMaximum input W
930 WMaximum output power per power supply
35 A at +35° CelciusMaximum inrush current
8 ms at 50 % loadMaximum hold-up time
12 VDCPower supply output voltage
12 VDCPower supply standby voltage
Efficiency rating
Climate Savers Platinum Efficiency (80Plus Platinum
certified)
1UForm factor
Power Cable Specifications
The following sections specify the power cables that you order and use with AC, HVAC/HVDC, and DC
power supplies.
AC Power Cables Supported by NX-OS Mode Switches
CAB-C13-C14-2M
CAB-C13-C14-AC
CAB-C13-CBN
Cord Set DescriptionPower Cord Part NumberPower Type
Power Cord Jumper, C13-C14
Connectors, 6.6 feet (2.0 m)
Power cord, C13 to C14 (recessed
receptacle), 10 A, 9.8 feet (3 m)
Cabinet jumper power cord, 250
VAC, 10 A, C14-C13 connectors,
2.3 feet (0.7 m)
250 V, 10 A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-250V-10A-ARArgentina
CAB-9K10A-AUAustralia
CAB-9K10A-EUEuropean Union
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
250 VAC, 10 A, 3112 plug, 8.2 feet
(2.5 m)
250 V, 10 A, 6.9 feet (2.1 m)CAB-250V-10A-BRBrazil
250 VAC, 10 A, CEE 7/7 plug, 8.2
feet (2.5 m)
10 A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-IND-10AIndia
49
Page 60

HVAC/HVDC Power Cables Supported by ACI-Mode and NX-OS Mode Switches
System Specifications
Cord Set DescriptionPower Cord Part NumberPower Type
250 V, 10 A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-250V-10A-ISIsrael
CAB-9K10A-ITItaly
250 VAC, 10 A, CEI 23-16/VII
plug, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)
CAB-9K12A-NANorth America
125 VAC, 13 A, NEMA 5-15 plug,
8.2 feet (2.5 m)
NEMA L6-20-C13, 6.6 feet (2.0 m)CAB-AC-L620-C13North America
200/240V, 6A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-N5K6A-NANorth America
250 V, 10 A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-250V-10A-CNPeoples Republic of China
250 V, 10 A, 8.2 feet (2.5 m)CAB-250V-10A-IDSouth Africa
CAB-9K10A-SWSwitzerland
250 VAC, 10 A, MP232 plug, 8.2
feet (2.5 m)
CAB-9K10A-UKUnited Kingdom
250 VAC, 10 A, BS1363 plug (13
A fuse), 8.2 (2.5 m)
NO-POWER-CORDAll except Argentina, Brazil, and
Japan
No power cord included with
switch
HVAC/HVDCPowerCablesSupported byACI-Mode andNX-OSMode Switches
Japan
Cord Set DescriptionPower Cord Part NumberPower Type
CAB-HVAC-SD-0.6MHVAC
2-foot (0.6 m) cable with
Saf-D-Grid and SD connectors
CAB-HVAC-C14-2MHVAC
6.6-foot (2.0 m) cable with
Saf-D-Grid and C14 connector (use
for up to 240 V)
CAB-HVAC-RT-0.6MHVAC
2-foot (0.6 m) cable with
Saf-D-Grid and RT connector
CAB-HVDC-3T-2MHVDC
6.6-foot (2.0 m) cable with
Saf-D-Grid and three terminal
connectors
NO-POWER-CORDAll except Argentina, Brazil, and
No power cord included with
switch
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
50
Page 61

System Specifications
DC Power Cable Specifications
DC Power Cable Specifications
Cord Set DescriptionPower CordPower Supply
(customer supplied)UCSC-PSU-930WDC (port-side
intake airflow)
CAB-48DC-40A-8AWGUCS-PSU-6332-DC (port-side
exhaust airflow)
NO-POWER-CORDAll except Argentina, Brazil, and
Japan
8 AWG insulated cable (10 AWG
minimum) for each power supply
8-AWG cable with 3-pin keyed
power supply connector and three
wires (power source connection)
No power cord included with
switch
Regulatory Standards Compliance Specifications
The following table lists the regulatory standards compliance for the switch.
Table 1: Regulatory Standards Compliance: Safety and EMC
DescriptionSpecification
Regulatory compliance
Safety
Products should comply with CE Markings according to directives 2004/108/EC
and 2006/95/EC.
• UL 60950-1 Second Edition
• CAN/CSA-C22.2 No. 60950-1 Second Edition
• EN 60950-1 Second Edition
• IEC 60950-1 Second Edition
• AS/NZS 60950-1
• GB4943
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
51
Page 62

System Specifications
System Specifications
DescriptionSpecification
EMC: Emissions
EMC: Immunity
RoHS
• 47CFR Part 15 (CFR 47) Class A
• AS/NZS CISPR22 Class A
• CISPR22 Class A
• EN55022 Class A
• ICES003 Class A
• VCCI Class A
• EN61000-3-2
• EN61000-3-3
• KN22 Class A
• CNS13438 Class A
• EN55024
• CISPR24
• EN300386
• KN 61000-4 series
The product is RoH-6 compliant with exceptions for leaded-ball grid-array (BGA)
balls and lead press-fit connectors.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
52
Page 63

LEDs
• Switch Chassis LEDs, on page 53
• Lane Link LEDs, on page 54
• Fan Module LEDs, on page 54
• Power Supply LEDs, on page 54
Switch Chassis LEDs
The BCN, STS, and ENV, LEDs are located on the left side of the front of the switch. The port LEDs appear
as triangles pointing up or down to the nearest port.
APPENDIX C
StatusColorLED
Flashing blueBCN
GreenSTS
Amber
Red
GreenENV
Amber
The operator has activated this LED
to identify this switch in the
chassis.
This switch is not being identified.Off
The switch is operational.
The switch is booting up.Flashing amber
Temperature exceeds the minor
alarm threshold.
Temperature exceeds the minor
alarm threshold.
The switch is not receiving power.Off
Fans and power supply modules are
operational.
At least one fan or power supply
module is not operating.
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
53
Page 64

Lane Link LEDs
LEDs
StatusColorLED
Lane Link LEDs
The Lane Link LEDs indicate which of the break out lanes are being checked. If none of the Lane Link LEDs
is lit, all four lanes are being checked.
Green(port)
Amber
Off
Port admin state is 'Enabled', SFP
is present and the interface is
connected (that is, cabled, and the
link is up).
Port admin state is 'Disabled, or the
SFP is absent, or both.
Port admin state is 'Enabled' and
SFP is present, but interface is not
connected.
DescriptionLED Lit
Checking lane 1.1
Checking lane 2.2
Checking lane 3.3
Fan Module LEDs
The fan module LED is located below the air holes on the front of the module.
Power Supply LEDs
The power supply LEDs are located on the left front portion of the power supply. Combinations of states
indicated by the Okay ( ) and Fault ( ) LEDs indicate the status for the module as shown in the following
table.
Checking lane 4.4
Checking all four lanesNone
StatusColorLED
The fan module is operational.GreenSTS
The fan module is not operational (fan is probably not functional).Red
Fan module is not receiving power.Off
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
54
Page 65

LEDs
LEDs
green
LED
LED
Status
Power supply is on and outputting power to the switch.OffGreen
OffFlashing
Power supply is connected to a power source but not outputting power to the
switch—power supply might not be installed in the chassis.
Power supply is not receiving power.OffOff
Flashing amberGreen
Power supply warning—possibly one of the following conditions:
• High voltage
• High power
• Low voltage
• Power supply installed in chassis but not connected to a power source
• Slow power supply fan
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
55
Page 66

LEDs
LEDs
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
56
Page 67

Additional Kits
• Rack Mount Kit NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU, on page 57
• Rack Mount Kit N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT, on page 57
Rack Mount Kit NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU
The following table lists and illustrates the contents for the 1-RU rack-mount kit (NXK-ACC-KIT-1RU).
• Front brackets (2)
• Rear brackets (2)
• Slider rails (2)
• M4 Phillips pan-head screws
(6)
APPENDIX D
QuantityDescriptionIllustration
1Rack-mount kit
Rack Mount Kit N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT
The following table lists and illustrates the contents for the 1-RU rack-mount kit (N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT).
• Front-mount angled bracket
(2)
• Rear-mount slider bracket (2)
• Slider rails (2)
• M4 x 7 mm mounting screws
(16)
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
QuantityDescriptionIllustration
1Rack-mount kit
57
Page 68

Rack Mount Kit N3K-C3064-ACC-KIT
Additional Kits
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
58
Page 69

Site Preparation and Maintenance Records
• Site Preparation Checklist, on page 59
• Contact and Site Information, on page 60
• Chassis and Module Information, on page 61
Site Preparation Checklist
Planning the location and layout of your equipment rack or cabinet is essential for successful switch operation,
ventilation, and accessibility.
The following table lists the site planning tasks that we recommend that you complete before you install the
switch. Your completion of each task ensures a successful switch installation.
Space evaluation:
Space and layout
APPENDIX E
Verification Time and DatePlanning Activity
Floor covering
Impact and vibration
Lighting
Physical access
Maintenance access
Environmental evaluation:
Ambient temperature
Humidity
Altitude
Atmospheric contamination
Airflow
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
59
Page 70

Contact and Site Information
Power evaluation:
Site Preparation and Maintenance Records
Verification Time and DatePlanning Activity
Input power type
Power receptacles
Receptacle proximity to the
equipment
Dedicated (separate)
circuits for power
redundancy
UPS for power failures
Grounding: proper wire
gauge and lugs
Circuit breaker size
Grounding evaluation:
Data center ground
Cable and interface equipment
evaluation:
Cable type
Connector type
Cable distance limitations
Interface equipment
(transceivers)
EMI evaluation:
Distance limitations for
signaling
Site wiring
RFI levels
Contact and Site Information
Use the following worksheet to record contact and site information for the installation.
Contact person
Contact phone
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
60
Page 71

Site Preparation and Maintenance Records
Contact e-mail
Building/site name
Data center location
Floor location
Address (line 1)
Address (line 2)
City
State/Provence
Contact person
ZIP/postal code
Country
Chassis and Module Information
Chassis and Module Information
Use the following worksheet to record information about the switch.
Contract number
Chassis serial number
Product number
Use the following worksheet to record network-related information.
Switch IP address
Switch IP netmask
Hostname
Domain name
IP broadcast address
Gateway/router address
DNS address
Use the following worksheet to record information about the modules in the switch.
Fan module 1
NotesModule Serial NumberModule TypeModule Slot
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
61
Page 72

Site Preparation and Maintenance Records
Fan module 2
Fan module 3
Fan module 4
Power Supply 1
Power Supply 2
Site Preparation and Maintenance Records
NotesModule Serial NumberModule TypeModule Slot
Cisco Nexus 9236C NX-OS Mode Switch Hardware Installation Guide
62
 Loading...
Loading...