Page 1

Note This feature is available on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router only.
Contents
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on
Cisco IOS XR Software
The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature lets you deploy Layer 3 Virtual Private Network (L3VPN)
services, over an IP core network, using L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling instead of MPLS. This allows
L2TPv3 tunnels to be configured as multipoint tunnels to transport IP VPN services across the core
IP network.
Feature History for Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR
Release Modification
Release 3.5.0 This feature was introduced on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.
Release 3.6.0 No modification.
OL-12284-01
• Prerequisites for Configuring MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-274
• Restrictions for Configuring MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-274
• Information About MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-274
• How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-277
• Configuration Examples for MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-293
• Additional References, page MPC-294
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-273
Page 2

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Prerequisites for Configuring MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Prerequisites for Configuring MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
The following prerequisites are required to implement MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels:
• You must be in a user group associated with a task group that includes the proper task IDs for
–
BGP commands
–
MPLS commands (generally)
–
MPLS Layer 3 VPN commands
For detailed information about user groups and task IDs, see the Configuring AAA Services on Cisco IOS
XR Software module of Cisco IOS XR System Security Configuration Guide.
Restrictions for Configuring MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
The following restrictions apply when you configure MPLS VPNs over IP tunnels:
• MPLS forwarding cannot be enabled on a provider edge (PE) router.
Information About MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
To implement MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, you must understand the following concepts:
• Overview: MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-274
• Advertising Tunnel Type and Tunnel Capabilities Between PE Routers—BGP, page MPC-275
• PE Routers and Address Space, page MPC-275
• Packet Validation Mechanism, page MPC-276
• Quality of Service Using the Modular QoS CLI, page MPC-276
• BGP Multipath Load Sharing for MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels, page MPC-276
• Inter-AS and CSC Support over IP Tunnels, page MPC-277
Overview: MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Traditionally, VPN services are deployed over IP core networks using MPLS, or L2TPv3 tunnels using
point-to-point links. However, an L2TPv3 multipoint tunnel network allows L3VPN services to be
carried through the core without the configuration of MPLS.
L2TPv3 multipoint tunneling supports multiple tunnel endpoints, which creates a full-mesh topology
that requires only one tunnel to be configured on each PE router. This permits VPN traffic to be carried
from enterprise networks across cooperating service provider core networks to remote sites.
Figure 24 illustrates the topology used for the configuration steps.
MPC-274
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 3
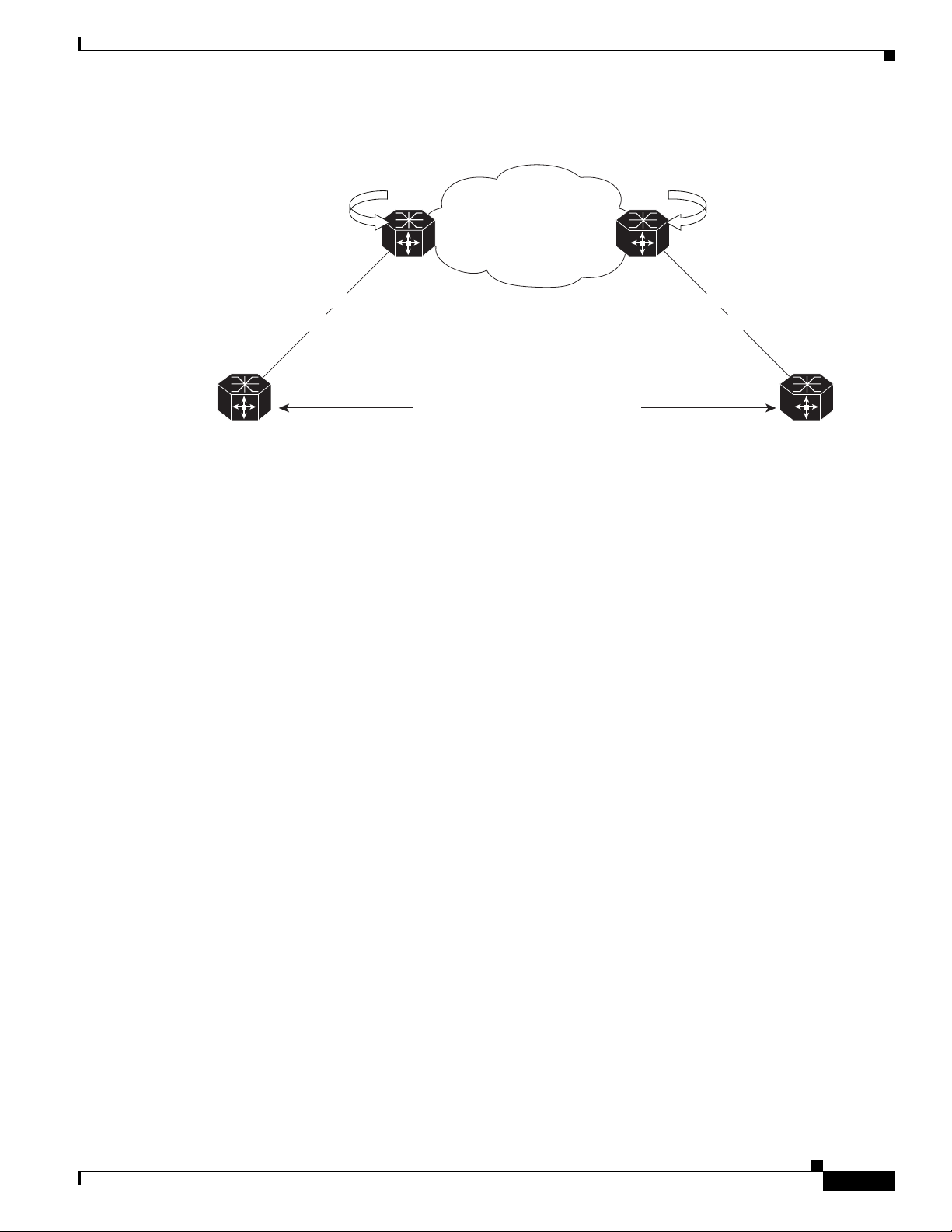
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Figure 24 Basic MPLS VPN over IP Topology
Information About MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
1.1.1.1
V4: 100.1.10.0/24
V6: 100.1.10.0/64
Prefix Advertised
V4: 110.0.0.1/18
V6: 110::1/120
PE-1 PE-2
IPv4
Network
(w/ ISIS)
3.3.3.3
V4: 200.1.10.0/24
V6: 200.1.10.0/64
Prefix Advertised
V4: 210.0.0.1/18
V6: 210::1/120
210625
Advertising Tunnel Type and Tunnel Capabilities Between PE Routers—BGP
Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) is used to advertise the tunnel endpoints and the subaddress family
identifier (SAFI) specific attributes (which contains the tunnel type, and tunnel capabilities). This
feature introduces the tunnel SAFI and the BGP SAFI-Specific Attribute (SSA) attribute.
These attributes allow BGP to distribute tunnel encapsulation information between PE routers. VPNv4
traffic is routed through these tunnels. The next hop, advertised in BGP VPNv4 updates, determines
which tunnel to use for routing tunnel traffic.
SAFI
The tunnel SAFI defines the tunnel endpoint and carries the endpoint IPv4 address and next hop. It is
identified by the SAFI number 64.
BGP SSA
The BGP SSA carries the BGP preference and BGP flags. It also carries the tunnel cookie, tunnel cookie
length, and session ID. It is identified by attribute number 19.
PE Routers and Address Space
One multipoint L2TPv3 tunnel must be configured on each PE router. To create the VPN, you must
configure a unique Virtual Routing and Forwarding (VRF) instance. The tunnel that transports the VPN
traffic across the core network resides in its own address space. A special purpose VRF called a Resolve
in VRF (RiV) is created to manage the tunnel address space. You also configure the address space under
the RiV that is associated with the tunnel and a static route in the RiV to route outgoing traffic through
the tunnel.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-275
Page 4
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Information About MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Packet Validation Mechanism
The MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels feature provides a simple mechanism to validate received packets
from appropriate peers. The multipoint L2TPv3 tunnel header is automatically configured with a 64-bit
cookie and L2TPv3 session ID. This packet validation mechanism protects the VPN from illegitimate
traffic sources. The cookie and session ID are not user-configurable, but they are visible in the packet as
it is routed between the two tunnel endpoints. Note that this packet validation mechanism does not
protect the VPN from hackers who are able to monitor legitimate traffic between PE routers.
Quality of Service Using the Modular QoS CLI
To configure the bandwidth on the encapsulation and decapsulation interfaces, use the modular QoS CLI
(MQC).
Note This task is optional.
Use the MQC to configure the IP precedence or Differentiated Services Code Point (DSCP) value set in
the IP carrier header during packet encapsulation. To set these values, enter a standalone set command
or a police command using the keyword tunnel. In the input policy on the encapsulation interface, you
can set the precedence or DSCP value in the IP payload header by using MQC commands without the
keyword tunnel.
Note You must attach a QoS policy to the physical interface—not to the tunnel interface.
If Modified Deficit Round Robin (MDRR)/Weighted Random Early Detection (WRED) is configured
for the encapsulation interface in the input direction, the final value of the precedence or DSCP field in
the IP carrier header is used to determine the precedence class for which the MDRR/WRED policy is
applied. On the decapsulation interface in the input direction, you can configure a QoS policy based on
the precedence or DSCP value in the IP carrier header of the received packet. In this case, an MQC policy
with a class to match on precedence or DSCP value will match the precedence or DSCP value in the
received IP carrier header. Similarly, the precedence class for which the MDRR/WRED policy is applied
on the decapsulation input direction is also determined by precedence or DSCP value in the IP carrier
header.
BGP Multipath Load Sharing for MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
BGP Multipath Load Sharing for EBGP and IBGP lets you configure multipath load balancing with both
external BGP and internal BGP paths in BGP networks that are configured to use MPLS VPNs. (When
faced with multiple routes to the same destination, BGP chooses the best route for routing traffic toward
the destination so that no individual router is overburdened.)
BGP Multipath Load Sharing is useful for multihomed autonomous systems and PE routers that import
both EBGP and IBGP paths from multihomed and stub networks.
MPC-276
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 5
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Inter-AS and CSC Support over IP Tunnels
The L3VPN Inter-AS feature provides a method of interconnecting VPNs between different VPN service
providers. Inter-AS supports connecting different VPN service providers to provide native IP L3VPN
services. For more information about Inter-AS, see Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs on
Cisco IOS XR Software.
Carrier Supporting Carrier (CSC) is implemented in circumstances in which one service provider needs
to use the transport services provided by another service provider. The service provider that provides the
transport is called the backbone carrier. The service provider, which uses the services provided by the
backbone carrier, is called a customer carrier. Backbone carriers with CSC, bridge two or more customer
carrier sites through an MPLS VPN/MPLS VPN over IP tunnels backbone. For more information about
CSC, see Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software.
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
The following procedures are required to configure MPLS VPN over IP:
• Configuring the Global VRF Definition, page MPC-277 (required)
• Configuring a Route-Policy Definition, page MPC-279 (required)
• Configuring a Static Route, page MPC-280 (required)
• Configuring an IPv4 Loopback Interface, page MPC-281 (required)
• Configuring a CFI VRF Interface, page MPC-283 (required)
• Configuring the Core Network, page MPC-284 (required)
• Configuring Inter-AS and CSC support over IP Tunnels, page MPC-285
• Verifying MPLS VPN over IP, page MPC-292 (optional)
Note All procedures occur on the local PE (PE1). Corresponding procedures must be configured on the remote
PE (PE2).
Configuring the Global VRF Definition
Perform this task to configure the global VRF definition.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. vrf vrf-name
3. address-family ipv4 unicast
OL-12284-01
4. import route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 | as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
5. export route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 | as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
6. exit
7. address-family ipv6 unicast
8. import route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 | as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-277
Page 6
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
9. export route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 | as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
10. end
or
commit
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
vrf vrf-name
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# vrf vrf-name
Step 3
address-family ipv4 unicast
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Enters global configuration mode.
Specifies a name assigned to a VRF.
Specifies an IPv4 address-family address.
Step 4
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf)#
address-family ipv4 unicast
import route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 |
as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# import
route-target 500:99
export route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 |
as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# export
route-target 700:44
exit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# exit
address-family ipv6 unicast
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf)#
address-family ipv6 unicast
Configures a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) import
route-target extended community.
Configures a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) export
route-target extended community.
Exits interface configuration mode.
Specifies an IPv6 address-family address.
MPC-278
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 7
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Command or Action Purpose
Step 8
import route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 |
as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# import
route-target 500:99
Step 9
export route-target [0-65535.0-65535:0-65535 |
as-number:nn | ip-address:nn]
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# import
route-target 700:88
Step 10
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# end
or
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-vrf-af)# commit
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Configures a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) import
route-target extended community.
Configures a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) export
route-target extended community.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
Configuring a Route-Policy Definition
Perform this task to configure a route-policy definition for CE-PE EBGP.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. route-policy name pass
3. end policy
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-279
Page 8
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
route-policy name pass
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# route-policy
ottawa_admin pass
Step 3
end policy
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-rpl)# end policy
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Enters global configuration mode.
Defines and passes a route policy.
End of route-policy definition.
Configuring a Static Route
Perform this task to add more than 4K static routes (Global/VRF).
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. router static
3. maximum path ipv4 1-140000
4. maximum path ipv6 1-140000
5. end
or
commit
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
Step 2
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
router static
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters static route configuration subcommands.
MPC-280
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# router static
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 9
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Command or Action Purpose
Step 3
maximum path ipv4 1-140000
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router (config-static)# maximum
path ipv4 1-140000
Step 4
maximum path ipv6 1-140000
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-static)# maximum
path ipv6 1-140000
Step 5
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-static)# end
or
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-static)# commit
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Enters the maximum number of static ipv4 paths that can be
configured.
Enters the maximum number of static ipv6 paths that can be
configured.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
Configuring an IPv4 Loopback Interface
The following task describes how to configure an IPv4 Loopback interface.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. interface type interface-id
3. ipv4 address ipv4-address
4. end
or
commit
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-281
Page 10

How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
interface type interface-id
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# interface
Loopback0
Step 3
ipv4 address ipv4-address
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# ipv4 address
1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
Step 4
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# end
or
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# commit
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters interface configuration mode and enables a
Loopback interface.
Enters an IPv4 address and mask for the associated IP
subnet. The network mask can be specified in either of two
ways:
• The network mask can be a four-part dotted decimal
address. For example, 255.0.0.0 indicates that each bit
equal to 1 means that the corresponding address bit
belongs to the network address.
• The network mask can be indicated as a slash (/) and
number. For example, /8 indicates that the first 8 bits of
the mask are ones, and the corresponding bits of the
address are the network address.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
MPC-282
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 11

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Configuring a CFI VRF Interface
Perform this task to associate a VPN routing and forwarding (VRF) instance with an interface or a
subinterface on the PE routers.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. interface type interface-id
3. vrf vrf-name
4. ipv4 address ipv4-address
5. ipv6 address ipv6-address
6. dot1q vlan vlan-id
7. end
or
commit
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
interface type interface-id
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# interface
GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1.1
Step 3
vrf vrf-name
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# vrf v1
Step 4
ipv4 address ipv4-address
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# ipv4 address
100.1.10.2 255.255.255.0
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters interface configuration mode and enables a
GigabitEthernet interface.
Specifies a VRF name.
Enters an IPv4 address and mask for the associated IP
subnet. The network mask can be specified in either of two
ways:
• The network mask can be a four-part dotted decimal
address. For example, 255.0.0.0 indicates that each bit
equal to 1 means that the corresponding address bit
belongs to the network address.
• The network mask can be indicated as a slash (/) and
number. For example, /8 indicates that the first 8 bits of
the mask are ones, and the corresponding bits of the
address are network address.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-283
Page 12

How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
ipv6 address ipv6-address
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# ipv6
100::1:10:2/64
Step 6
dot1q native vlan vlan-id
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# dot1q native
vlan 665
Step 7
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# end
or
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-if)# commit
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Enters an IPv6 address.
This argument must be in the form documented in
RFC 2373, where the address is specified in hexadecimal
using 16-bit values between colons, as follows:
• IPv6 name or address: Hostname or X:X::X%zone
• IPv6 prefix: X:X::X%zone/<0-128>
Enters the trunk interface ID. Range is from 1 to 4094
inclusive (0 and 4095 are reserved).
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
Configuring the Core Network
To configure the core network, refer to the procedures documented in Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs
on Cisco IOS XR Software.
The tasks are presented as follows:
• Assessing the needs of MPLS VPN customers
• Configuring routing protocols in the core
• Configuring MPLS in the core
• Enabling FIB in the core
• Configuring BGP on the PE routers and route reflectors
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
MPC-284
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 13

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Configuring Inter-AS and CSC support over IP Tunnels
These tasks describe how to configure Inter-AS and CSC support over IP tunnels:
• Configuring the ASBRs to Exchange VPN-IPv4 Addresses for IP Tunnels, page MPC-285
(required)
• Configuring the Backbone Carrier Core for IP Tunnels, page MPC-288
• Configuring CSC-PE Routers for IP Tunnels, page MPC-288
Configuring the ASBRs to Exchange VPN-IPv4 Addresses for IP Tunnels
Perform this task to configure an external Border Gateway Protocol (eBGP) autonomous system
boundary router (ASBR) to exchange VPN-IPv4 routes with another autonomous system for IP tunnels
Note This procedure is supported on the Cisco XR 12000 Series Router.
SUMMARY STEPS
1. configure
2. router bgp autonomous-system-number
3. address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
4. address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
5. neighbor ip-address
6. remote-as autonomous-system-number
7. address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
8. route-policy route-policy-name {in}
9. route-policy route-policy-name {out}
10. neighbor ip-address
11. remote-as autonomous-system-number
12. update-source interface-type interface-number
13. address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
14. address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
15. end
or
commit
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-285
Page 14
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
router bgp autonomous-system-number
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config)# router bgp 120
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)#
Step 3
address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)#
address-family ipv4 tunnel
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)#
Step 4
address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Enters global configuration mode.
Enters Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) configuration mode
allowing you to configure the BGP routing process.
Configures IPv4 tunnel address family.
Configures VPNv4 address family.
Step 5
Step 6
Step 7
Step 8
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(cconfig-bgp-af)#
address-family vpnv4 unicast
neighbor ip-address
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)# neighbor
172.168.40.24
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
remote-as autonomous-system-number
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as
2002
address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
address-family vpnv4 unicast
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
route-policy route-policy-name {in}
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
route-policy pass-all in
Places the router in neighbor configuration mode for BGP
routing and configures the neighbor IP address
172.168.40.24 as an ASBR eBGP peer.
Creates a neighbor and assigns it a remote autonomous
system number.
Configures VPNv4 address family.
Applies a routing policy to updates that are received from a
BGP neighbor.
• Use the route-policy-name argument to define the name
of the of route policy. The example shows that the route
policy name is defined as pass-all.
• Use the in keyword to define the policy for inbound
routes.
MPC-286
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 15

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Command or Action Purpose
Step 9
route-policy route-policy-name {out}
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
route-policy pass-all out
Step 10
neighbor ip-address
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)# neighbor
175.40.25.2
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
Step 11
remote-as autonomous-system-number
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as
2002
Step 12
update-source interface-type interface-number
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Applies a routing policy to updates that are sent from a BGP
neighbor.
• Use the route-policy-name argument to define the name
of the of route policy. The example shows that the route
policy name is defined as pass-all.
• Use the out keyword to define the policy for outbound
routes.
Places the router in neighbor configuration mode for BGP
routing and configures the neighbor IP address 175.40.25.2
as an VPNv4 iBGP peer.
Creates a neighbor and assigns it a remote autonomous
system number.
Allows BGP sessions to use the primary IP address from a
particular interface as the local address.
Step 13
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
update-source loopback0
address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
address-family ipv4 tunnel
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
Configures IPv4 tunnel address family.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-287
Page 16

How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Command or Action Purpose
Step 14
address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
address-family vpnv4 unicast
Step 15
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)# end
or
RP/0/0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)# commit
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Configures VPNv4 address family.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
Configuring the Backbone Carrier Core for IP Tunnels
Configuring the backbone carrier core requires setting up connectivity and routing functions for the CSC
core and the CSC-PE routers. To do so, you must complete the following high-level tasks:
• Verify IP connectivity in the CSC core.
• Configure IP tunnels in the core.
• Configure VRFs for CSC-PE routers.
• Configure multiprotocol BGP for VPN connectivity in the backbone carrier.
Configuring CSC-PE Routers for IP Tunnels
Perform this task to configure a CSC-PE for IP tunnels.
For information on how to configure CSC-CE routers, see the Implementing MPLS Layer 3 VPNs on
Cisco IOS XR Software module.
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
SUMMARY STEPS
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-288
1. configure
2. router bgp as-number
3. address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
OL-12284-01
Page 17

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
4. address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
5. neighbor A.B.C.D
6. remote-as as-number
7. update-source interface-type interface-number
8. address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
9. address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
10. vrf vrf-name
11. rd {as-number:nn | ip-address:nn | auto}
12. address-family {ipv4 unicast}
13. allocate-label all
14. neighbor A.B.C.D
15. remote-as as-number
16. address-family {ipv4 labeled-unicast}
17. route-policy route-policy-name in
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
DETAILED STEPS
Command or Action Purpose
Step 1
configure
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router# configure
Step 2
router bgp as-number
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config)# router bgp 2
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)#
Step 3
address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp)#
address-family vpnv4 unicast
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)#
Step 4
address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
18. route-policy route-policy-name out
19. end
or
commit
Enters global configuration mode.
Configures a BGP routing process and enters router
configuration mode.
• Range for 2-byte numbers is 1 to 65535. Range for
4-byte numbers is 1.0 to 65535.65535.
Configures VPNv4 address family.
Configures IPv4 tunnel address family.
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)#
address-family ipv4 tunnel
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-289
Page 18

How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Command or Action Purpose
Step 5
neighbor A.B.C.D
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-af)# neighbor
10.10.10.0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
Step 6
remote-as as-number
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)# remote-as
888
Step 7
update-source interface-type interface-number
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
update-source loopback0
Step 8
address-family {vpnv4 unicast}
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Configures the IP address for the BGP neighbor.
Configures the AS number for the BGP neighbor.
Allows BGP sessions to use the primary IP address from a
particular interface as the local address.
Configures VPNv4 unicast address family.
Step 9
Step 10
Step 11
Step 12
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr)#
address-family vpnv4 unicast
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
address-family {ipv4 tunnel}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)#
address-family ipv4 tunnel
vrf vrf-name
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-nbr-af)# vrf
9999
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf)#
rd {as-number:nn | ip-address:nn | auto}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf)# rd auto
address-family {ipv4 unicast}
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf)#
address-family ipv4 unicast
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-af)#
Configures IPv4 tunnel address family.
Configures a VRF instance.
Configures a route distinguisher.
Note Use the auto keyword to automatically assign a
unique route distinguisher.
Configures IPv4 unicast address family.
MPC-290
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 19
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Command or Action Purpose
Step 13
allocate-label all
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-af)#
allocate-label all
Step 14
neighbor A.B.C.D
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-af)#
neighbor 10.10.10.0
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr)#
Step 15
remote-as as-number
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr)#
remote-as 888
Step 16
address-family {ipv4 labeled-unicast}
How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Allocate labels for all local prefixes and prefixes received
with labels.
Configures the IP address for the BGP neighbor.
Enables the exchange of information with a neighboring
BGP router.
Configures IPv4 labeled-unicast address family.
Step 17
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr)#
address-family ipv4 labeled-unicast
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr-af)#
route-policy route-policy-name in
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr-af)#
route-policy pass-all in
Applies the pass-all policy to all inbound routes.
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-291
Page 20

How to Configure MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Command or Action Purpose
Step 18
route-policy route-policy-name out
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr-af)#
route-policy pass-all out
Step 19
end
or
commit
Example:
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr-af)#
end
or
RP/0/RP0/CPU0:router(config-bgp-vrf-nbr-af)#
commit
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Applies the pass-all policy to all outbound routes.
Saves configuration changes.
• When you issue the end command, the system prompts
you to commit changes:
Uncommitted changes found, commit them before
exiting(yes/no/cancel)?
[cancel]:
–
Entering yes saves configuration changes to the
running configuration file, exits the configuration
session, and returns the router to EXEC mode.
–
Entering no exits the configuration session and
returns the router to EXEC mode without
committing the configuration changes.
Verifying MPLS VPN over IP
To verify the configuration of end-end (PE-PE) MPLS VPN over IP provisioning, use the following
show commands:
• show cef recursive-nexthop
• show bgp ipv4 tunnel
• show bgp vpnv4 unicast summary
• show bgp vrf v1 ipv4 unicast summary
• show bgp vrf v1 ipv4 unicast prefix
• show cef vrf v1 ipv4 prefix
• show cef ipv6 recursive-nexthop
• show bgp vpnv6 unicast summary
–
Entering cancel leaves the router in the current
configuration session without exiting or
committing the configuration changes.
• Use the commit command to save the configuration
changes to the running configuration file and remain
within the configuration session.
MPC-292
• show bgp vrf v1 ipv6 unicast summary
• show bgp vrf v1 ipv6 unicast prefix
• show cef vrf v1 ipv6 prefix
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 21

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Configuration Examples for MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
Configuration Examples for MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels
This section provides the following examples:
• Configuring an L2TPv3 Tunnel: Example, page MPC-293
• Configuring the Global VRF Definition: Example, page MPC-293
• Configuring a Route-Policy Definition: Example, page MPC-293
• Configuring a Static Route: Example, page MPC-294
• Configuring an IPv4 Loopback Interface: Example, page MPC-294
• Configuring a CFI VRF Interface: Example, page MPC-294
Configuring an L2TPv3 Tunnel: Example
The following example shows how to configure an L2TPv3 tunnel:
tunnel-template t1
encapsulation l2tp
!
source Loopback0
!
Configuring the Global VRF Definition: Example
The following example shows how to configure an L2TPv3 tunnel:
vrf v1
address-family ipv4 unicast
import route-target
1:1
!
export route-target
1:1
!
address-family ipv6 unicast
import route-target
1:1
!
export route-target
1:1
!
Configuring a Route-Policy Definition: Example
The following example shows how to configure a route-policy definition:
configure
route-policy pass-all
pass
end-policy
!
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-293
Page 22

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Additional References
Configuring a Static Route: Example
The following example shows how to configure a static route:
configure
router static
maximum path ipv4 <1-140000>
maximum path ipv6 <1-140000>
end-policy
!
Configuring an IPv4 Loopback Interface: Example
The following example shows how to configure an IPv4 Loopback Interface:
configure
interface Loopback0
ipv4 address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255
!
Configuring a CFI VRF Interface: Example
The following example shows how to configure an L2TPv3 tunnel:
configure
interface GigabitEthernet0/0/0/1.1
vrf v1
ipv4 address 100.1.10.2 255.255.255.0
ipv6 address 100::1:10:2/64
dot1q vlan 101
!
Additional References
For additional information related to this feature, refer to the following references:
Related Documents
Related Topic Document Title
Cisco IOS XR L2VPN command reference document MPLS Virtual Private Network Commands on Cisco IOS XR
Software
Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 on Cisco IOS XR Software
Routing (BGP, EIGRP, OSPF, and RIP) commands:
complete command syntax, command modes,
command history, defaults, usage guidelines, and
examples
Routing (BGP, EIGRP, OSPF, and RIP) configuration Cisco IOS XR Routing Configuration Guide
Cisco IOS XR Routing Command Reference
MPC-294
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
Page 23

Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
Additional References
Related Topic Document Title
Cisco IOS XR L2VPN command reference document MPLS Virtual Private Network Commands on Cisco IOS XR
Software
Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 Layer 2 Tunnel Protocol Version 3 on Cisco IOS XR Software
MPLS LDP configuration: configuration concepts,
task, and examples
MPLS Traffic Engineering Resource Reservation
Protocol configuration: configuration concepts, task,
and examples
Cisco CRS-1 router getting started material Cisco IOS XR Getting Started Guide
Information about user groups and task IDs Configuring AAA Services on Cisco IOS XR Software module of the
Implementing MPLS Label Distribution Protocol on Cisco IOS XR
Software
Implementing RSVP for MPLS-TE and MPLS O-UNI on Cisco IOS
XR Software
Cisco IOS XR System Security Configuration Guide
Standards
Standards Title
No new or modified standards are supported by this
feature, and support for existing standards has not been
modified by this feature.
—
MIBs
MIBs MIBs Link
— To locate and download MIBs using Cisco IOS XR software, use the
Cisco MIB Locator found at the following URL and choose a
platform under the Cisco Access Products menu:
http://cisco.com/public/sw-center/netmgmt/cmtk/mibs.shtml
RFCs
RFCs Title
RFC 3931 Layer Two Tunneling Protocol - Version 3 (L2TPv3)
RFC 2547 BGP/MPLS VPNs
OL-12284-01
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
MPC-295
Page 24

Additional References
Technical Assistance
Description Link
The Cisco Technical Support website contains
thousands of pages of searchable technical content,
including links to products, technologies, solutions,
technical tips, and tools. Registered Cisco.com users
can log in from this page to access even more content.
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Implementing MPLS VPNs over IP Tunnels on Cisco IOS XR Software
MPC-296
Cisco IOS XR MPLS Configuration Guide
OL-12284-01
 Loading...
Loading...