Page 1

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware
Installation Guide
October 2008
Americas Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 527-0883
Text Part Number: OL-17468-02
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE
OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a Class A digital device, pursuant
to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference when the equipment is operated in a commercial
environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause
harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required
to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: The equipment described in this manual generates and may radiate radio-frequency energy. If it is not
installed in accordance with Cisco’s installation instructions, it may cause interference with radio and television reception. This equipment has been tested and found to
comply with the limits for a Class B digital device in accordance with the specifications in part 15 of the FCC rules. These specifications are designed to provide reasonable
protection against such interference in a residential installation. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a particular installation.
Modifying the equipment without Cisco’s written authorization may result in the equipment no longer complying with FCC requirements for Class A or Class B digital
devices. In that event, your right to use the equipment may be limited by FCC regulations, and you may be required to correct any interference to radio or television
communications at your own expense.
You can determine whether your equipment is causing interference by turning it off. If the interference stops, it was probably caused by the Cisco equipment or one of its
peripheral devices. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
• Turn the television or radio antenna until the interference stops.
• Move the equipment to one side or the other of the television or radio.
• Move the equipment farther away from the television or radio.
• Plug the equipment into an outlet that is on a different circuit from the television or radio. (That is, make certain the equipment and the television or radio are on circuits
controlled by different circuit breakers or fuses.)
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco Systems, Inc. could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH
ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES, INCLUDING,
WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO
OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
CCDE, CCENT, Cisco Eos, Cisco Lumin, Cisco Nexus, Cisco StadiumVision, Cisco TelePresence, Cisco WebEx, the Cisco logo, DCE, and Welcome to the Human Network
are trademarks; Changing the Way We Work, Live, Play, and Learn and Cisco Store are service marks; and Access Registrar, Aironet, AsyncOS, Bringing the Meeting To
You, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP, CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, CCSP, CCVP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems,
Cisco Systems Capital, the Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Collaboration Without Limitation, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Event Center, Fast Step, Follow Me Browsing,
FormShare, GigaDrive, HomeLink, Internet Quotient, IOS, iPhone, iQuick Study, IronPort, the IronPort logo, LightStream, Linksys, MediaTone, MeetingPlace,
MeetingPlace Chime Sound, MGX, Networkers, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, PCNow, PIX, PowerPanels, ProConnect, ScriptShare, SenderBase, SMARTnet,
Spectrum Expert, StackWise, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, TransPath, WebEx, and the WebEx logo are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.
and/or its affiliates in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply a partnership relationship
between Cisco and any other company. (0809R)
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses. Any examples, command display output, and figures included in the
document are shown for illustrative purposes only. Any use of actual IP addresses in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
© 2004–2008 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Page 3

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
CONTENTS
New and Changed Information vii
Preface xi
Audience xi
Organization xi
Conventions xii
Related Documentation xiv
Release Notes xiv
Compatibility Information xiv
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information xiv
Hardware Installation xiv
Cisco Fabric Manager xiv
Command-Line Interface xv
Intelligent Storage Networking Services Configuration Guides xv
Troubleshooting and Reference xv
Installation and Configuration Note xv
CHAPTER
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines xv
1 Product Overview 1-1
Chassis 1-2
Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM Blade Center 1-5
Integrated Supervisor Modules 1-5
Cisco MDS 9222i Integrated Supervisor Module 1-6
Cisco MDS 9216i Integrated Supervisor Module 1-6
Cisco MDS 9216A Integrated Supervisor Module 1-7
LEDs on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Integrated Supervisor Modules 1-9
Interface Modules 1-10
LEDs on the Interface Module 1-11
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Module Compatibility 1-12
Switching Modules 1-12
4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-13
48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-13
24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-14
12-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-15
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
i
Page 4

Contents
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
4-Port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-16
LEDs on the Generation 2 Switching Modules 1-17
32-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-17
16-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module 1-18
Switching Module Features 1-19
LEDs on the Generation 1 Switching Module 1-20
Services Modules 1-21
18/4-Port Multiservice Module 1-21
18/4-Port Multiservice Federal Information Processing Standards Module 1-22
LEDs on the 18/4-Port Multiservice Module 1-23
14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module 1-23
LEDs on the 14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module 1-25
IP Storage Services Modules 1-25
LEDs on IP Storage Services Module 1-27
32-Port Fibre Channel Storage Services Module 1-27
LEDs on the Storage Services Module 1-29
32-Port Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module 1-29
LEDs on the Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module 1-31
Caching Services Module 1-31
LEDs on the Caching Services Module 1-34
CHAPTER
Power Supplies 1-35
Fan Module 1-36
Supported Transceivers 1-36
X2 Fibre Channel Transceivers 1-37
Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers 1-37
Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers 1-37
CWDM Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers 1-38
Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers 1-38
DWDM Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers 1-38
2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series 2-1
Preinstallation 2-2
Installation Options 2-2
Installation Guidelines 2-3
Required Equipment 2-4
Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch 2-4
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack 2-5
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance 2-11
Installing Front Rack-Mount Brackets for Cabinets with 26 Inches or Greater of Rail Spacings 2-12
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
ii
OL-17468-02
Page 5

Contents
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Installing Front Rack-Mount Brackets for Cabinets with Less Than 26 Inches of Rail Spacings 2-14
Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Rear-Facing into Cabinet 2-16
System Grounding 2-19
Proper Grounding Practices 2-19
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage 2-21
Establishing the System Ground 2-23
Required Tools and Equipment 2-23
Grounding the Chassis 2-24
Starting Up the Switch 2-26
Removing and Installing Components 2-28
Removing and Installing Switching and Services Modules 2-28
Removing a Caching Services Module 2-31
Removing Other Switching or Services Modules 2-32
Installing a Switching or Services Module, Including Caching Services Modules 2-33
Verifying Installation of a Switching or Services Module 2-34
Maintaining a Caching Services Module 2-35
Maintaining the Batteries on the Caching Services Module 2-35
Maintaining the Disk Drives on the Caching Services Module 2-35
Removing and Installing Power Supplies 2-36
Removing a Power Supply 2-36
Installing a Power Supply 2-36
Removing and Installing the Fan Module 2-38
Removing a Fan Module 2-39
Installing a Fan Module 2-39
Removing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series 2-40
CHAPTER
OL-17468-02
3 Connecting the Cisco MDS 9200 Series 3-1
Preparing for Network Connections 3-2
Connecting to the Console Port 3-2
Connecting to the COM1 Port 3-4
Connecting to the MGMT 10/100 Ethernet Port 3-5
Connecting to a Fibre Channel Port 3-6
Removing and Installing X2 Transceivers 3-6
Installing an X2 Transceiver 3-8
Removing an X2 Transceiver 3-8
Removing and Installing SFP Transceivers 3-8
Installing an SFP Transceiver 3-9
Removing an SFP Transceiver 3-10
Removing and Installing Cables into SFP Transceivers 3-11
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
iii
Page 6

Contents
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Installing a Cable into an SFP Transceiver 3-11
Removing a Cable from an SFP Transceiver 3-12
Maintaining SFP Transceivers and Fiber-Optic Cables 3-13
APPENDIX
APPENDIX
A Cabinet and Rack Installation A-1
Cabinet and Rack Requirements A-1
General Requirements for Cabinets and Racks A-1
Requirements Specific to Perforated Cabinets A-2
Requirements Specific to Solid-Walled Cabinets A-3
Requirements Specific to Standard Open Racks A-3
Requirements Specific to telco Racks A-3
Cisco MDS 9000 Family telco and EIA Shelf Bracket A-4
Rack-Mounting Guidelines A-4
Before Installing the Shelf Brackets A-5
Required Equipment A-5
Installing the Shelf Bracket Kit into a Two-Post telco Rack A-6
Installing the Shelf Bracket Kit into a Four-Post EIA Rack A-7
Installing the Switch on the Shelf Brackets A-8
Removing the Shelf Bracket Kit (Optional) A-9
B Technical Specifications B-1
Switch Specifications B-1
iv
Module Specifications B-2
Weight of Modules B-3
Power Specifications B-4
Specifications for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Power Supplies B-4
Component Power Requirements and Heat Dissipation Specifications B-5
X2 Transceiver Specifications B-7
Cisco 10-Gbps Fibre Channel X2 Transceivers B-7
General Specification for Cisco 10-Gbps Fibre Channel X2 Transceivers B-7
Environmental Conditions and Power Requirement Specifications for Cisco 10-Gbps Fibre
Channel X2 Transceivers
Cisco 10-Gbps Ethernet X2 Transceivers B-8
General Specification for Cisco 10-Gbps Ethernet X2 Transceivers B-9
Environmental and Power Requirements Specifications for Cisco 10-Gbps Ethernet X2
Transceiver
B-9
Cisco 10-Gbps Ethernet DWDM X2 Transceiver B-9
SFP and SFP+ Transceiver Specifications B-10
Cisco Fibre Channel SFP and SFP+ Transceivers B-10
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
B-8
OL-17468-02
Page 7

Contents
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
General Specifications for Cisco 8-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP+ Transceivers B-11
Environmental and Power Requirements for Cisco 8-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP+
Transceivers
General Specifications for Cisco 4-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers B-13
Environmental and Power Requirement for Cisco 4-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers B-13
General Specifications for Cisco 2-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers B-14
Environmental and Power Requirement for Cisco 2-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers B-14
Maximum Environmental and Electrical Ratings for Cisco Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers B-15
Cisco Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet Transceivers B-15
General Specifications for Cisco Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers B-16
Environmental and Power Requirement Specifications for Cisco Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet
SFP Transceivers
Cisco CWDM SFP Transceivers B-17
Environmental and Optical Specifications for Cisco 2-Gbps CWDM SFP Transceivers B-18
Environmental and Optical Specifications for Cisco 4-Gbps CWDM SFP Transceivers B-19
Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Transceivers B-21
General Specifications for Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Transceivers B-21
Environmental and Power Requirement Specifications for Cisco Gigabit Ethernet
Transceivers
DWDM SFP Transceivers B-22
B-11
B-16
B-21
APPENDIX
C Cable and Port Specifications C-1
Cables and Adapters Provided C-1
Console Port C-2
Console Port Pinouts C-2
Connecting the Console Port to a Computer Using the DB-25 Adapter C-2
Connecting the Console Port to a Computer Using the DB-9 Adapter C-3
COM1 Port C-3
COM1 Port Pinouts C-3
Connecting the COM1 Port to a Modem C-4
MGMT 10/100/1000 Ethernet Port C-4
MGMT 10/100 Ethernet Port C-6
Supported Power Cords and Plugs C-7
Power Cords C-7
Supported Plugs for 6000-W AC, 2500-W AC, and 1900-W AC Power Supplies C-8
Supported Plugs for the 4000-W AC Power Supply C-10
Jumper Power Cord C-11
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
v
Page 8

Contents
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
APPENDIX
D Site Planning and Maintenance Records D-1
Site Preparation Checklist D-1
Contact and Site Information D-3
Chassis and Module Information D-4
vi
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 9

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
New and Changed Information
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide applies to Cisco MDS NX-OS Release 4.1(1b)
and earlier Cisco MDS SAN-OS releases.
Table 1 lists the new and changed features available with each supported Cisco MDS NX-OS release and
SAN-OS release for the Cisco MDS 9500 Series, with the latest release first.
Note As of NX-OS Release 4.1(1b), SAN-OS has been changed to NX-OS. References to SAN-OS releases
before 4.1(1b) still apply.
Table 1 Documented Features for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Changed in
Feature Description
4/44-port 8-Gbps
Host-Optimized
Fibre Channel
switching module
SFP+ Transceivers Added the SFP+ transceivers information. 4.1(1b) “Technical
Cisco MDS Fibre
Channel
Bladeswitch
overview
18/4-port
Multiservice
(MSM-18/4)
module
18/4-port
Multiservice
(MSM-18/4)
module
Added 4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized
Fibre Channel switching module. The
switching module offers 48 autosensing
1-, 2-, 4- and 8-Gbps Fibre Channel ports
and can be used in any of the Cisco MDS
9500 Series chassis and in the Cisco MDS
9222i Switches, when running NX-OS
4.1(1b).
Description of the Cisco MDS Fibre
Channel Bladeswitch for IBM
BladeCenter.
Added information on IPv6 support. 3.3(1a) The “1 8/4-Port
Added information on SAN extension
support.
Release Where Documented
4.1(1b) Product Overview
chapter.
Specifications”
section on page B-1
3.3(1a) Product Overview
chapter.
Multiservice Module”
section on page 1-21.
3.3(1a) The “1 8/4-Port
Multiservice Module”
section on page 1-21.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
vii
Page 10
New and Changed Information
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Table 1 Documented Features for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (continued)
Changed in
Feature Description
18/4-port
Multiservice
Added the Storage Media Encryption
information.
(MSM-18/4)
module
Cisco MDS 9222i
Mutiservice
Modular Switch
18/4-port
Multiservice
Added the new 18/4 Fibre Channel port
and 4 Gigabit Ethernet IP services port
Multiservice Modular Switch.
Added the new 18/4-port Multiprotocol
Services module.
(MSM-18/4)
module
18/4-port
Multiservice FIPS
Added the new 18/4-port Multiprotocol
Services FIPS module.
(MSFM-18/4)
module
48-port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
switching module
Added 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel
switching module. The switching module
offers 48 autosensing 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel ports and can be used in
any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series chassis
and in the Cisco 9216i and 9216A
Switches.
24-port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
switching module
Added 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel
switching module. The switching module
offers 24 autosensing 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel ports and can be used in
any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series chassis
and in the Cisco 9216i and 9216A
Switches.
Release Where Documented
3.2(1) The “1 8/4-Port
Multiservice Module”
section on page 1-21.
3.2(1) The “Product
Overview” section on
page 1-1, the
“Chassis” section on
page 1-2,
“Cisco MDS 9222i
Integrated Supervisor
Module” section on
page 1-6, and the
“Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.2(1) The “1 8/4-Port
Multiservice Module”
section on page 1-21
and the “Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.2(1) The “18/4-Port
Multiservice Federal
Information
Processing Standards
Module” section on
page 1-22 and the
“Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.0(1) The “48-Port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
Switching Module”
section on page 1-13
and the “Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.0(1) The “24-Port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
Switching Module”
section on page 1-14
and the “Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
viii
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 11
New and Changed Information
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Table 1 Documented Features for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (continued)
Changed in
Feature Description
12-port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
switching module
Added 12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel
switching module. The switching module
can be used in any of the Cisco MDS 9500
Series chassis and in the Cisco MDS
9216i and 9216A Switches.
4-port 10-Gbps
Fibre Channel
switching module
Added 4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel
switching module. The switching module
offers four dedicated bandwidth Fibre
Channel ports running at 10 Gbps with no
oversubscription.
X2 transceiver Added X2 transceiver. The X2 transceiver
is a small form-factor pluggable
optimized for 10-Gbps applications.
Fibre Channel SFP
transceiver
Gigabit Ethernet
Added 4-Gbps Fibre Channel SFP trans-
ceiver.
Added Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver.
SFP transceiver
32-port Fibre
Channel Storage
Added 32-port Fibre Channel Storage
Services Module (SSM).
Services Module
(SSM)
14/2-port
Multiprotocol
Added 14/2-port Multiprotocol Services
module.
Services
(MPS-14/2) module
Release Where Documented
3.0(1) The “12-Port 4-Gbps
Fibre Channel
Switching Module”
section on page 1-15
and the “Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.0(1) The “4-Port 10-Gbps
Fibre Channel
Switching Module”
section on page 1-16
and the “Technical
Specifications”
section on page B-1.
3.0(1) The “X2 Fibre
Channel
Transceivers” section
on page 1-37 and the
“X2 Transceiver
Specifications”
section on page B-7.
3.0(1) The “Fibre Channel
SFP Transceivers”
section on page 1-37
and the “Cisco Fibre
Channel SFP and
SFP+ Transceivers”
section on page B-10.
Not release
specific
The “Supported
Transceivers” section
on page 1-36 and the
“Cisco Gigabit
Ethernet
Transceivers” section
on page B-21.
2.0(2b) The “32-Port Fibre
Channel Storage
Services Module”
section on page 1-27.
2.0(1b) The “14/2-Port
Multiprotocol
Services Module”
section on page 1-23.
OL-8494-01
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
ix
Page 12

New and Changed Information
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
x
OL-17468-02
Page 13

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Preface
This preface describes the audience, organization, and conventions of the
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide. It also provides information on how to obtain
related documentation.
Audience
To use this installation guide, you must be familiar with electronic circuitry and wiring practices and
preferably be an electronic or electromechanical technician.
Organization
This guide is organized as follows:
Chapter Title Description
Chapter 1 Product Overview Provides an overview of the Cisco MDS 9200 Series and its
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco
Chapter 3 Connecting the
Appendix A Cabinet and Rack
Appendix B Technical
Appendix CCable and Port
Appendix D Site Planning and
MDS 9200 Series
Cisco MDS 9200
Series
Installation
Specifications
Specifications
Maintenance
Records
components.
Describes how to install the Cisco MDS 9200 Series, and how to
install modules, power supplies, and fan assemblies.
Describes how to connect the Cisco MDS 9200 Series, including
the modules.
Provides guidelines for selecting an enclosed cabinet, the
procedure for installing a switch using the optional telco and
EIA Shelf Bracket Kit.
Lists specifications for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches and
components including modules, power, and transceivers.
Lists cable and port specifications for the Cisco MDS 9200
Series.
Provides site planning and maintenance records.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
xi
Page 14

Preface
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions for notes, cautions, and safety warnings.
Notes and Cautions contain important information that you should be aware of.
Note Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to material that are not covered
in the publication.
Caution Means reader be careful. You are capable of doing something that might result in equipment damage or
loss of data.
Safety warnings appear throughout this publication in procedures that, if performed incorrectly, can
cause physical injuries. A warning symbol precedes each warning statement.
Warning
Waarschuwing
Varoitus
Attention
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause
bodily injury. Before you work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards
involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for
preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each
warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that
accompanied this device.
Dit waarschuwingssymbool betekent gevaar. U verkeert in een situatie die
lichamelijk letsel kan veroorzaken. Voordat u aan enige apparatuur gaat
werken, dient u zich bewust te zijn van de bij elektrische schakelingen
betrokken risico's en dient u op de hoogte te zijn van standaard maatregelen
om ongelukken te voorkomen. Voor vertalingen van de waarschuwingen die in
deze publicatie verschijnen, kunt u het document Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information (Informatie over naleving van veiligheids- en andere
voorschriften) raadplegen dat bij dit toestel is ingesloten.
Tämä varoitusmerkki merkitsee vaaraa. Olet tilanteessa, joka voi johtaa
ruumiinvammaan. Ennen kuin työskentelet minkään laitteiston parissa, ota
selvää sähkökytkentöihin liittyvistä vaaroista ja tavanomaisista
onnettomuuksien ehkäisykeinoista. Tässä julkaisussa esiintyvien varoitusten
käännökset löydät laitteen mukana olevasta Regulatory Compliance and
Safety Information -kirjasesta (määräysten noudattaminen ja tietoa
turvallisuudesta).
Ce symbole d'avertissement indique un danger. Vous vous trouvez dans une
situation pouvant causer des blessures ou des dommages corporels. Avant de
travailler sur un équipement, soyez conscient des dangers posés par les
circuits électriques et familiarisez-vous avec les procédures couramment
utilisées pour éviter les accidents. Pour prendre connaissance des
traductions d’avertissements figurant dans cette publication, consultez le
document Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformité aux
règlements et consignes de sécurité) qui accompagne cet appareil.
Statement 1071
xii
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 15

Preface
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Warnung
Avvertenza
Advarsel
Dieses Warnsymbol bedeutet Gefahr. Sie befinden sich in einer Situation, die
zu einer Körperverletzung führen könnte. Bevor Sie mit der Arbeit an
irgendeinem Gerät beginnen, seien Sie sich der mit elektrischen
Stromkreisen verbundenen Gefahren und der Standardpraktiken zur
Vermeidung von Unfällen bewußt. Übersetzungen der in dieser
Veröffentlichung enthaltenen Warnhinweise finden Sie im Dokument
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Informationen zu
behördlichen Vorschriften und Sicherheit), das zusammen mit diesem Gerät
geliefert wurde.
Questo simbolo di avvertenza indica un pericolo. La situazione potrebbe
causare infortuni alle persone. Prima di lavorare su qualsiasi
apparecchiatura, occorre conoscere i pericoli relativi ai circuiti elettrici ed
essere al corrente delle pratiche standard per la prevenzione di incidenti. La
traduzione delle avvertenze riportate in questa pubblicazione si trova nel
documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Conformità alle
norme e informazioni sulla sicurezza) che accompagna questo dispositivo.
Dette varselsymbolet betyr fare. Du befinner deg i en situasjon som kan føre
til personskade. Før du utfører arbeid på utstyr, må du vare oppmerksom på de
faremomentene som elektriske kretser innebærer, samt gjøre deg kjent med
vanlig praksis når det gjelder å unngå ulykker. Hvis du vil se oversettelser av
de advarslene som finnes i denne publikasjonen, kan du se i dokumentet
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information (Overholdelse av forskrifter og
sikkerhetsinformasjon) som ble levert med denne enheten.
Aviso
¡Advertencia!
Varning!
Este símbolo de aviso indica perigo. Encontra-se numa situação que lhe
poderá causar danos físicos. Antes de começar a trabalhar com qualquer
equipamento, familiarize-se com os perigos relacionados com circuitos
eléctricos, e com quaisquer práticas comuns que possam prevenir possíveis
acidentes. Para ver as traduções dos avisos que constam desta publicação,
consulte o documento Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Informação de Segurança e Disposições Reguladoras) que acompanha este
dispositivo.
Este símbolo de aviso significa peligro. Existe riesgo para su integridad física.
Antes de manipular cualquier equipo, considerar los riesgos que entraña la
corriente eléctrica y familiarizarse con los procedimientos estándar de
prevención de accidentes. Para ver una traducción de las advertencias que
aparecen en esta publicación, consultar el documento titulado Regulatory
Compliance and Safety Information (Información sobre seguridad y
conformidad con las disposiciones reglamentarias) que se acompaña con
este dispositivo.
Denna varningssymbol signalerar fara. Du befinner dig i en situation som kan
leda till personskada. Innan du utför arbete på någon utrustning måste du vara
medveten om farorna med elkretsar och känna till vanligt förfarande för att
förebygga skador. Se förklaringar av de varningar som förkommer i denna
publikation i dokumentet Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
(Efterrättelse av föreskrifter och säkerhetsinformation), vilket medföljer
denna anordning.
OL-8494-01
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
xiii
Page 16

Preface
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Related Documentation
The documentation set for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family includes the following documents. The
documentation set for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family includes the following documents. To find a
document online, use the Cisco MDS NX-OS Documentation Locator at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/ps5989/products_documentation_roadmap09186a00804500c1.html.
Release Notes
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes for Cisco MDS NX-OS Releases
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes for Storage Services Interface Images
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Release Notes for Cisco MDS 9000 EPLD Images
Compatibility Information
• Cisco MDS 9000 NX-OS Hardware and Software Compatibility Information
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Interoperability Support Matrix
• Cisco MDS Storage Services Module Interoperability Support Matrix
• Cisco MDS NX-OS Release Compatibility Matrix for Storage Service Interface Images
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
• Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family
Hardware Installation
• Cisco MDS 9124 Multilayer Fabric Switch Quick Start Guide
• Cisco MDS 9500 Series Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
• Cisco MDS 9100 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Cisco Fabric Manager
xiv
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Quick Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Database Schema
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Data Mobility Manager Configuration Guide
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 17

Preface
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Command-Line Interface
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Software Upgrade and Downgrade Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Storage Services Module Software Installation and Upgrade Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Quick Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Command Reference
Intelligent Storage Networking Services Configuration Guides
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Data Mobility Manager Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Storage Media Encryption Configuration Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Secure Erase Configuration Guide - For Cisco MDS 9500 and 9200 Series
Troubleshooting and Reference
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Troubleshooting Guide
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family MIB Quick Reference
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family SMI-S Programming Reference
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family System Messages Reference
Installation and Configuration Note
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family SSM Configuration Note
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Port Analyzer Adapter Installation and Configuration Note
• Cisco 10-Gigabit X2 Transceiver Module Installation Note
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family CWDM SFP Installation Note
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family CWDM Passive Optical System Installation Note
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
OL-8494-01
For information on obtaining documentation, submitting a service request, and gathering additional
information, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new and
revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
Subscribe to the What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation as a Really Simple Syndication (RSS) feed
and set content to be delivered directly to your desktop using a reader application. The RSS feeds are a free
service and Cisco currently supports RSS version 2.0.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
xv
Page 18

Preface
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
xvi
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 19

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
CHAP T ER
1
Product Overview
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series of multilayer modular fabric switches supports storage area network (SAN)
applications. The Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches provide scalability, multitransport capability,
security, and manageability to enterprise SANs. The Cisco MDS 9200 Series shares a consistent
architecture with the Cisco MDS 9500 Series of multilayer directors, making it an intelligent and
flexible fabric switch series. The Cisco MDS 9200 Series includes the Cisco MDS 9222i Multiservice
Modular Switch, the Cisco MDS 9216i Multilayer Fabric Switch, and the Cisco MDS 9216A Multilayer
Fabric Switch.
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series provides the following features:
• An interface module providing local and remote management interfaces for the supervisor module.
• A spare slot for an optional hot-swappable switching or services module.
• Redundant and hot-swappable power supplies and fan modules.
• Power and cooling management and environmental monitoring.
• Switch module port interfaces that support field-replaceable, hot-swappable X2 transceivers.
• Switch module port interfaces that support field-replaceable, hot-swappable small form-factor
pluggable (SFP) and Enhanced small form-factor pluggable (SFP+) transceivers.
• Nondisruptive code load and activation.
OL-17468-02
• Redundant and self-monitoring system clocks.
The Cisco MDS 9222i Multiservice Modular Switch provides an 18-port Fibre Channel switching and
4-port Gigabit Ethernet IP services module, and a modular expansion slot to host Cisco MDS 9000
Family Switching and Services modules.
The Cisco 9216i Switch includes a nonremovable supervisor module with an integrated 14-port Fibre
Channel and 2-port Gigabit Ethernet switching module. The integrated supervisor module supports IP
services on the 2 Gigabit Ethernet ports. It also provides switching and local and remote management.
The Cisco 9216A Switch includes a nonremovable supervisor module with an integrated 16-port Fibre
Channel switching module. The integrated supervisor module provides switching and local and remote
management.
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series enhances the Cisco MDS 9216 Switch with a flexible backplane that is
designed to meet the requirements of future modules in the Cisco MDS 9000 Family, while maintaining
backward compatibility with all existing modules. The Cisco MDS 9200 Series is also compatible with
all existing Cisco MDS 9216 power supplies and fan trays, and provides a COM1 port interface that is
compatible with a standard RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter.
For information on how to configure the Cisco MDS 9200 Series, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI
Configuration Guide and the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-1
Page 20

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Chassis
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Note The Cisco MDS 9200 Series requires Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x, 3.x, and NX-OS 4.1(1b). The
Cisco MDS 9222i Switch requires MDS SAN-OS Release 3.x and NX-OS 4.1(1b).
The following hot-swappable, field-replaceable modules are supported by the Cisco MDS 9200 Series:
• 4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9248-48K9)
• 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9148)
• 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9124)
• 12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9112)
• 4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9704)
• 32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9032)
• 16-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module (DS-X9016)
• 18/4-port Multiservice (MSM-18/4) module (DS-X9304-18K9)
• 18/4-port Multiservice FIPS (MSFM-18/4) module (DS-X9304-18FK9
• 14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module (DS-X9302-14K9)
• 8-port IP Storage Services (IPS-8) module (DS-X9308-SMIP)
• 4-port IP Storage Services (IPS-4) module (DS-X9304-SMIP)
Chassis
• Storage Services Module (SSM) (DS-X9032-SSM)
• Advanced Services Module (ASM) (DS-X9032-SMV)
• Caching Services Module (CSM) (DS-X9560-SMC)
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Chassis, page 1-2
• Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM Blade Center, page 1-5
• Integrated Supervisor Modules, page 1-5
• Interface Modules, page 1-10
• Cisco MDS 9000 Family Module Compatibility, page 1-12
• Switching Modules, page 1-12
• Services Modules, page 1-21
• Fan Module, page 1-36
• Supported Transceivers, page 1-36
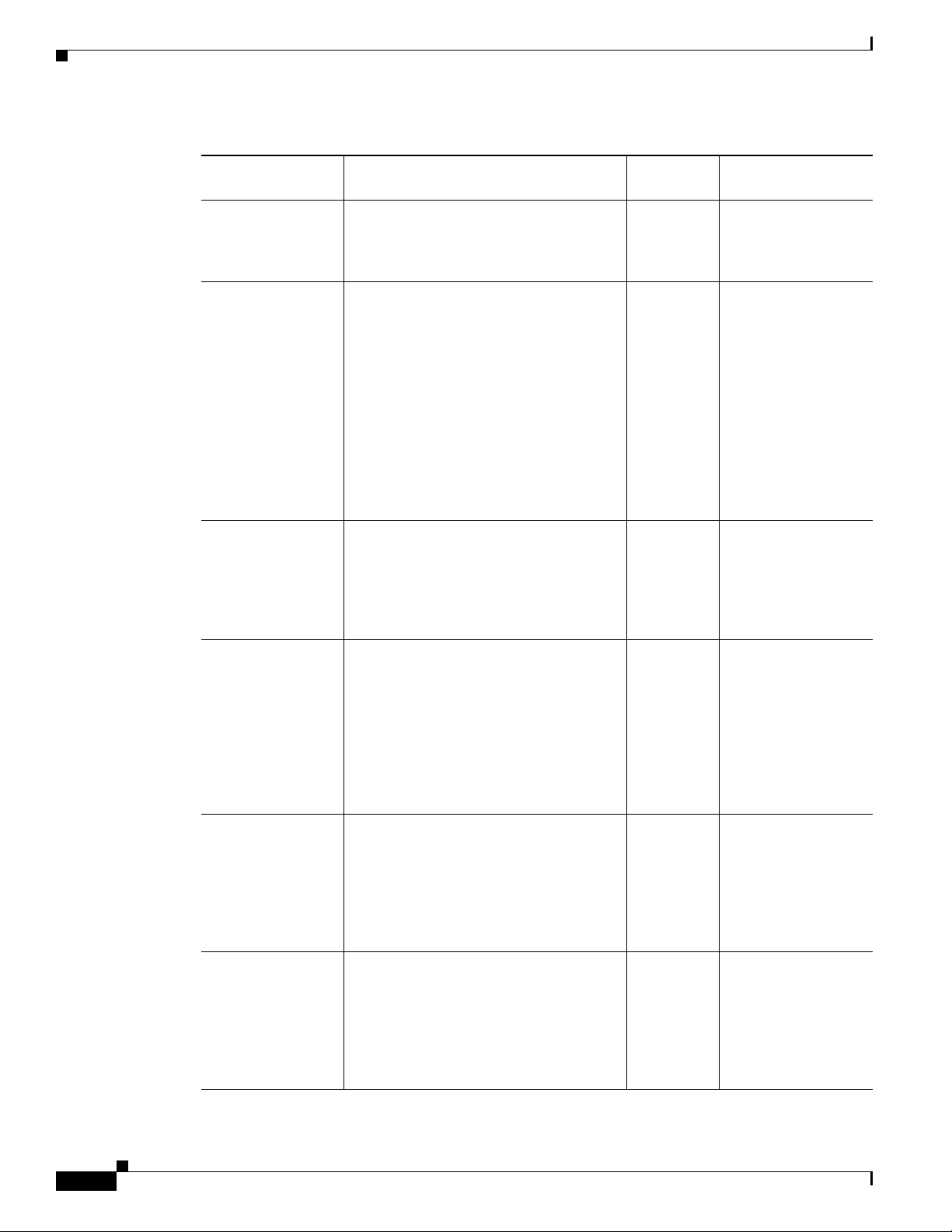
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches have a two-slot chassis. The Cisco MDS 9222i (see Figure 1-1)
has a nonremovable supervisor module (in slot 1) with an integrated 18-port Fibre Channel switching
and 4-port Gigabit Ethernet IP services module, and a modular expansion slot to host Cisco MDS 9000
Family Switching and Services modules. See the “Cisco MDS 9222i Integrated Supervisor Module”
section on page 1-6.
1-2
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 21
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Chassis
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
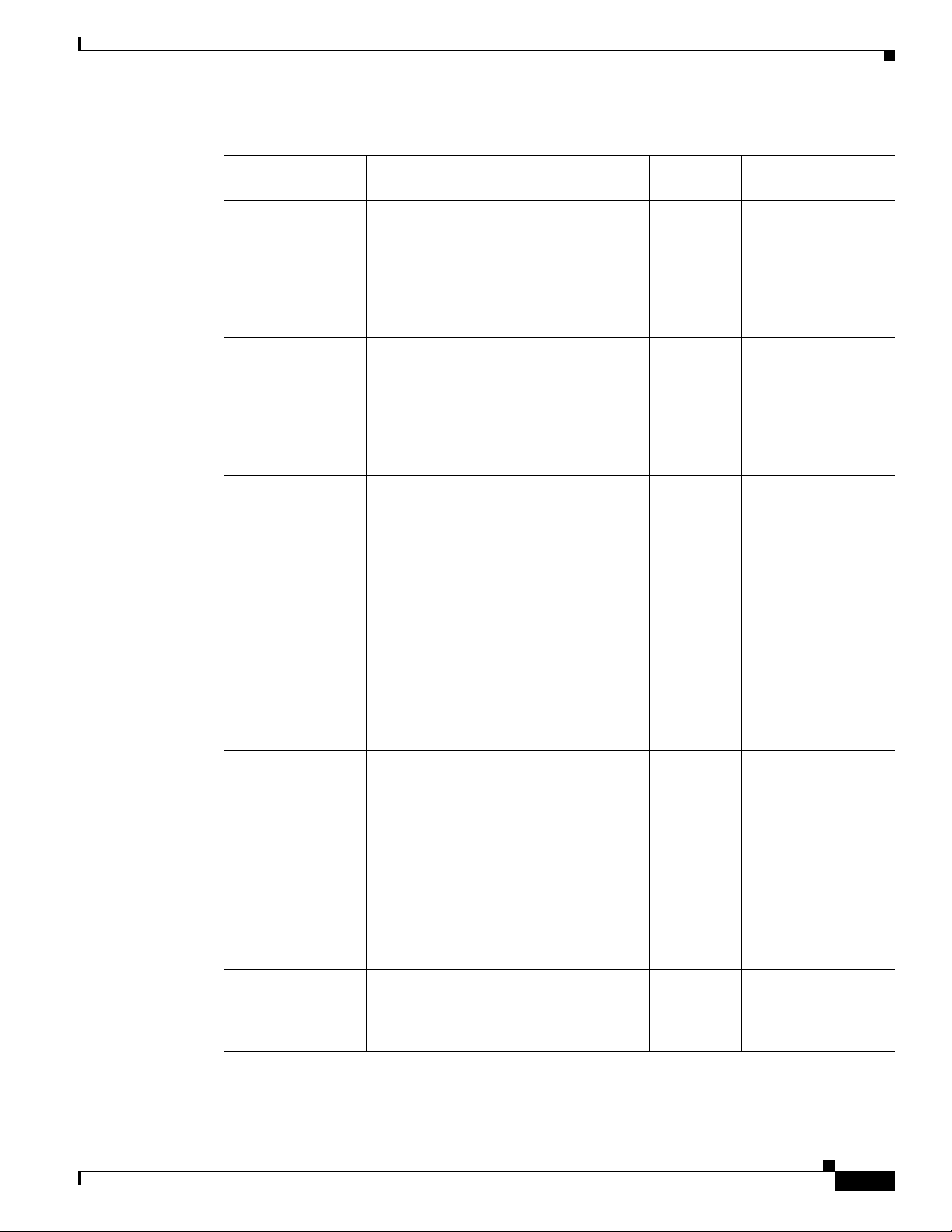
The Cisco MDS 9216i (see Figure 1-2) has a nonremovable supervisor module (in slot 1) with an
integrated 14-port Fibre Channel and 2-port Gigabit Ethernet switching module. See the “Cisco MDS
9216i Integrated Supervisor Module” section on page 1-6.
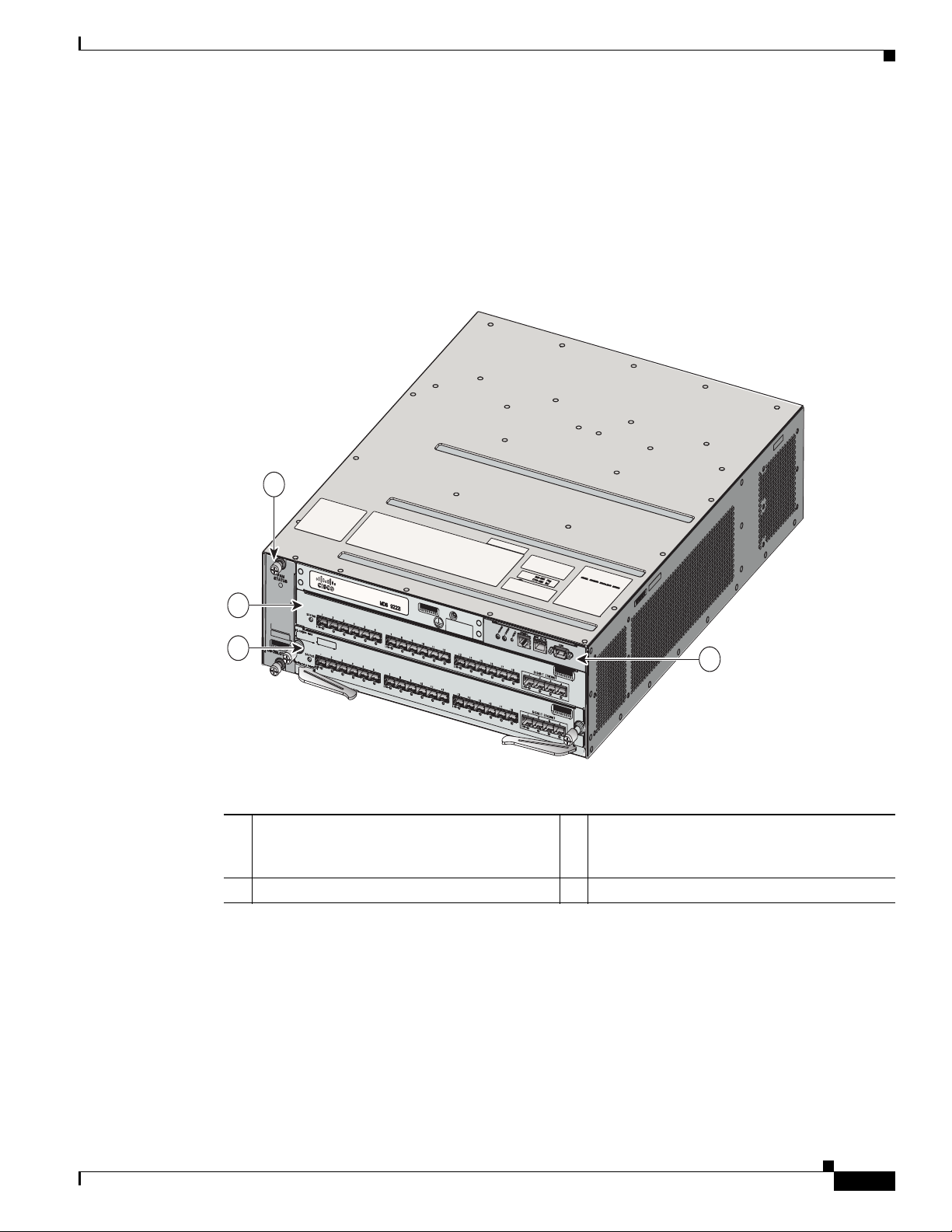
The Cisco MDS 9216A (see Figure 1-3) has a nonremovable supervisor module (in slot 1) with an
integrated 16-port Fibre Channel switching module. See the “Cisco MDS 9216A Integrated Supervisor
Module” section on page 1-7.
Figure 1-1 Cisco MDS 9222i Chassis
1
3
2
1 Fan module 3 Supervisor module with integrated 18-port
Fibre Channel switching and 4-port Gigabit
Ethernet IP Storage Services module
2 Switching module or the services module 4 Interface module
4
184704
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-3
Page 22
Chapter 1 Product Overview
240805
1
4
3
2
Chassis
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-2 Cisco MDS 9216i Chassis
1
M
DS
3
2
9216
1
2
i
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
12
1
3
14
L
I
N
K
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
4
116888
1 Fan module 3 Supervisor module with integrated 14-port
Fibre Channel and 2-port Gigabit Ethernet
switching module
2 Switching module or Services module (such
4 Interface module
as the IPS module)
Figure 1-3 Cisco MDS 9216A Chassis
1 Fan module 3 Supervisor module with integrated 16-port
Fibre Channel switching module
2 Switching module or Services module (such
4 Interface module
as the IPS module)
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-4
OL-17468-02
Page 23

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM Blade Center
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports the following additional modules:
• The nonremovable interface module (located above the integrated supervisor module), provides the
console port (COM1 port) and the MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port for the integrated supervisor
module. See the “Interface Modules” section on page 1-10.
• An optional module in the open slot (slot 2).
• Two power supplies that are redundant by default and can be configured to be combined if desired.
• A hot-swappable fan module with four fans provides redundancy. See the “Fan Module” section on
page 1-36.
Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM Blade Center
The Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter is designed for IBM BladeCenter
environments. The Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch is based on the Cisco MDS 9000 Family SAN
switching technology, which integrates the Cisco MDS 9000 Family of switches and directors into a
blade-switch architecture. The advanced architecture of the Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for
IBM BladeCenter, along with 4-GB technology, provides outstanding performance between
Bladeswitches and the rest of the Fibre Channel infrastructure.
The Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter provides 4-GB Fibre Channel
performance to blade-server switching. It also provides network intelligence features such as virtual
SANs (VSANs), quality of service (QoS), and N-port interface virtualization (NPIV). It also offers
nondisruptive software upgrades and on-demand port activation and is the most complete embedded
Fibre Channel switching available for the IBM BladeCenter, BladeCenter-T, and BladeCenter-H
platforms.
The Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter provides up to 20 nonblocking 1-, 2-,
and 4-GB Fibre Channel ports that are available in two configurations: 7 internal ports and 3 external
ports, or 14 internal ports and 6 external ports. Each port provides line-rate performance up to 4-GB
without any performance loss for integrated features such as VSANs, QoS, or Network Address
Translation (NAT). The Cisco MDS Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter supports up to 16
VSANs per blade switch.
Each external port on the Cisco MDS FC Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter also provides line-rate
performance up to 4-GB for Inter-Switch Links (ISLs) or additional device connectivity such as storage
or host bus adapters (HBAs).
The Cisco NX-OS software provides role-based access control (RBAC) for management access of the
Cisco Fibre Channel Bladeswitch for IBM BladeCenter command-line interface (CLI) and Simple
Network Management Protocol (SNMP). For more information, see the Cisco 9000 Family Command
Reference.
Integrated Supervisor Modules
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches have nonremovable integrated supervisor modules in each chassis.
These modules include the following:
• Cisco MDS 9222i Integrated Supervisor Module, page 1-6
• Cisco MDS 9216i Integrated Supervisor Module, page 1-6
• Cisco MDS 9216A Integrated Supervisor Module, page 1-7
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-5
Page 24
Chapter 1 Product Overview
184706
1
2
4
3
Integrated Supervisor Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Cisco MDS 9222i Integrated Supervisor Module
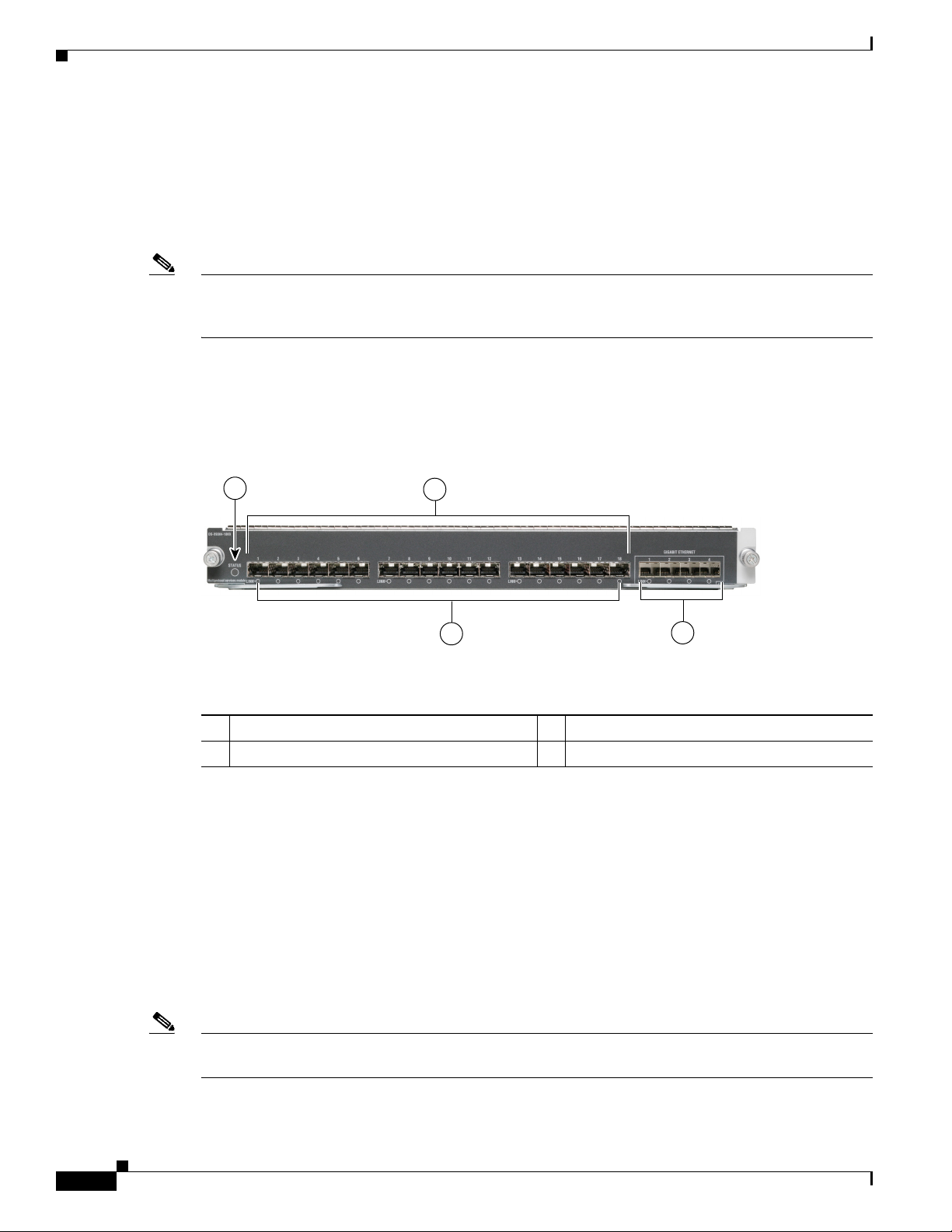
The nonremovable Cisco MDS 9222i integrated supervisor module provides the control and
management functions of the Cisco MDS 9222i Switch, and it includes an integrated 18-port Fibre
Channel switching and 4-port Gigabit Ethernet IP services module. The Cisco MDS 9222i integrated
supervisor module provides multiple communication and control paths to avoid a single point of failure.
Note For description of the integrated 18/4-port Multiservice and the 18/4-port Multiservice FIPS module and
their capabilities, see the “1 8/4-Port Multiservice Module” section on page 1-21 and the “18/4-Port
Multiservice Federal Information Processing Standards Module” section on page 1-22.
Figure 1-4 shows the Cisco MDS 9222i integrated supervisor module with an integrated 18-port Fibre
Channel and 4-port Gigabit Ethernet module.
Figure 1-4 Cisco MDS 9222i Supervisor Module with Integrated 18-Port Fibre Channel and 4-Port
Gigabit Ethernet Module
1 Status LED 3 Gigabit Ethernet ports
2 4-Gbps Fibre Channel ports 4 Link LEDs
The Cisco MDS 9222i integrated supervisor module has a PowerPC PowerQUICC III class processor,
1 GB of DRAM, and an internal CompactFlash card that provides 1 GB of storage for software images.
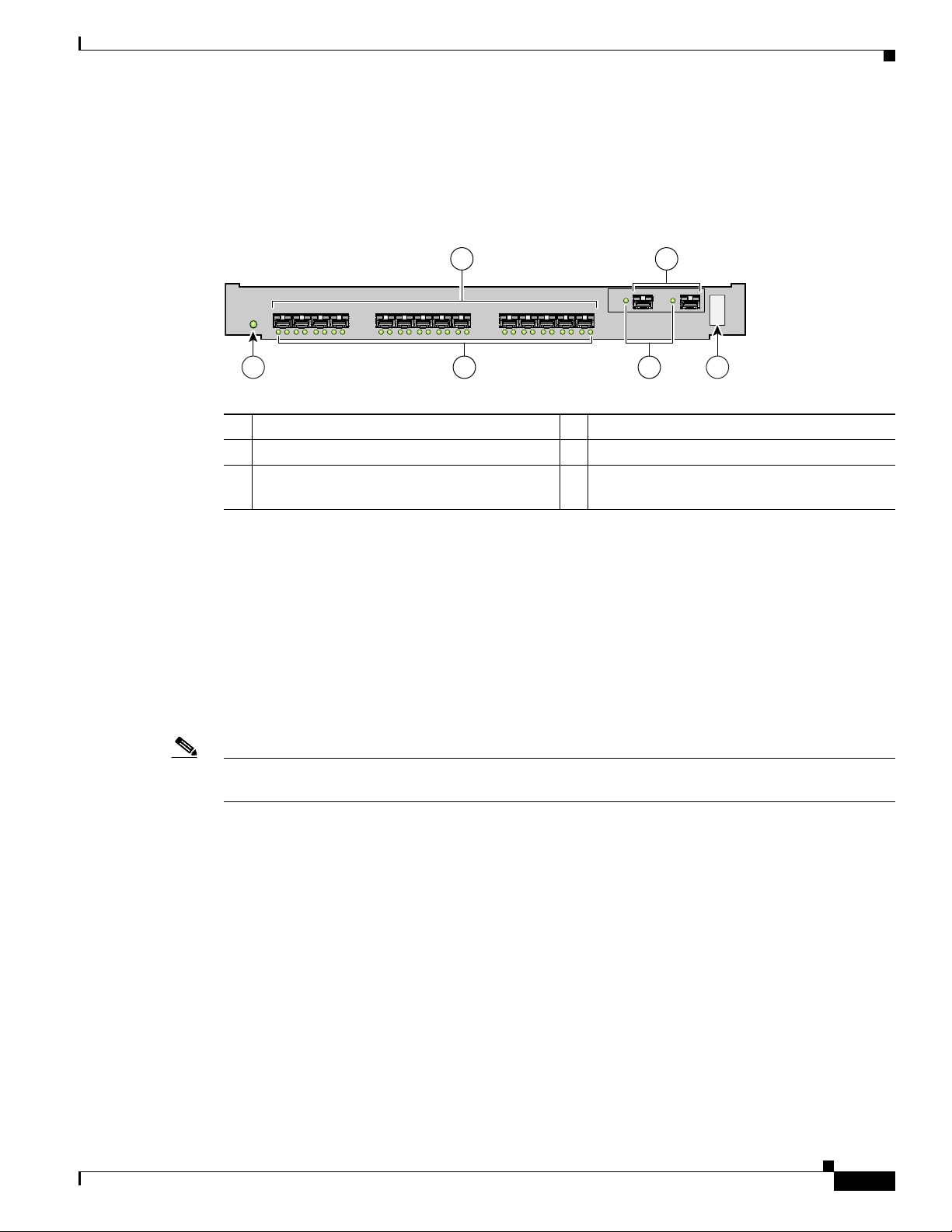
Cisco MDS 9216i Integrated Supervisor Module
The nonremovable Cisco MDS 9216i integrated supervisor module provides the control and
management functions for the Cisco MDS 9216i Switch, and it includes an integrated 14-port Fibre
Channel switching and 2-port Gigabit Ethernet with IP services module. The Cisco MDS 9216i
integrated supervisor module provides multiple communication and control paths to avoid a single point
of failure.
Note For a description of the integrated 14/2-port Multiprotocol Services module and its capabilities, see the
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-6
“14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module” section on page 1-23.
OL-17468-02
Page 25
Chapter 1 Product Overview
—SPEED LINK—
LINK-
—SPEEDLINK—
STATUS
1 56789
LINK— —SPEED
10 11 12 13 14234
12
LINK-
GIGABIT E THERNET
116889
1 6
2 4
3 5
Integrated Supervisor Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-5 shows the Cisco MDS 9216i integrated supervisor module with an integrated 14-port Fibre
Channel and 2-port Gigabit Ethernet module.
Figure 1-5 Cisco MDS 9216i Supervisor Module with Integrated 14-Port Fibre Channel and 2-Port
Gigabit Ethernet Module
1 Status LED 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel ports 5 Link LEDs
3 Link LEDs (under ports, on left) and Speed
LEDs (under ports, on right)
6 Asset tag
The Cisco MDS 9216i integrated supervisor module has a Pentium III class processor, 1 GB of DRAM,
and an internal CompactFlash card that provides 256 MB of storage for software images.
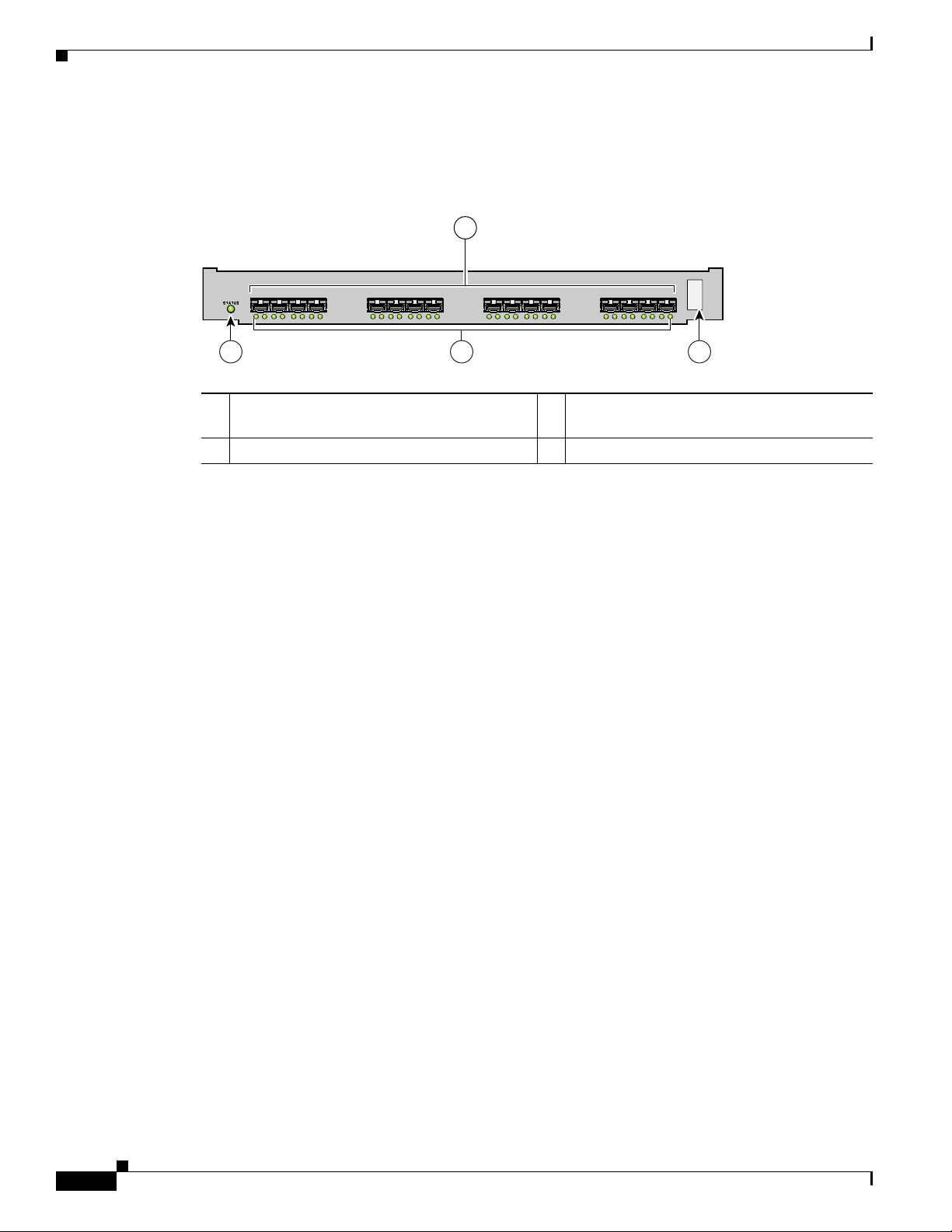
Cisco MDS 9216A Integrated Supervisor Module
The nonremovable Cisco MDS 9216A integrated supervisor module provides the control and
management functions for the Cisco MDS 9216A Switch, and it includes an integrated 16-port switching
module. The Cisco MDS 9216A integrated supervisor module provides multiple communication and
control paths to avoid a single point of failure.
Note For a description of the integrated 16-port switching module and its capabilities, see the “16-Port 2-Gbps
Fibre Channel Switching Module” section on page 1-18.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-7
Page 26
Chapter 1 Product Overview
91670
1 43
LINK- -SPEED LINK- -SPEED LINK- -SPEED LINK- -SPEED
1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4 1 2 3 4
2
Integrated Supervisor Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-6 shows the Cisco MDS 9216A supervisor module with an integrated 16-port Switching
module.
Figure 1-6 Cisco MDS 9216A Supervisor Module with Integrated 16-Port Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LEDs (under ports, on left) and Speed
LEDs (under ports, on right)
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel ports 4 Asset tag
The Cisco MDS 9216A integrated supervisor module has a Pentium III class processor, 1 GB of DRAM,
and an internal CompactFlash card that provides 256 MB of storage for software images.
1-8
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 27
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Integrated Supervisor Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
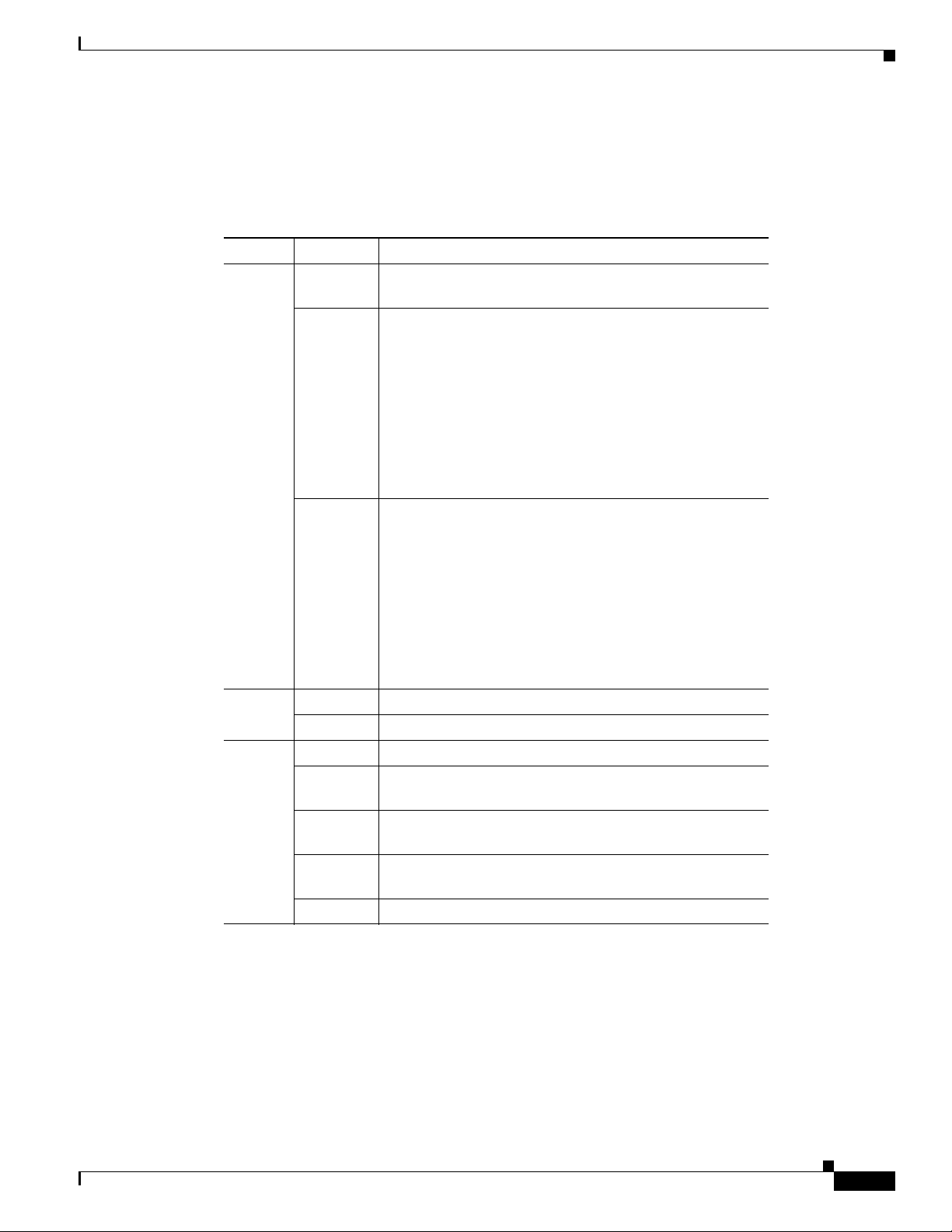
LEDs on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Integrated Supervisor Modules
Table 1-1 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series integrated supervisor modules.
Table 1-1 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Integrated Supervisor Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product
life, you should immediately correct the
environmental temperature and restore the system to
normal operation.
Red One of the following occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not
operational because a fault occurred during the
initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
safe operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to
prevent permanent damage. The system will be shut
down after two minutes if this condition is not cleared.
1
Speed
On 2-Gbps mode.
Off 1-Gbps mode.
Link Solid green Link is up.
Flashing
Link is up (beacon used to identify port).
green
Solid
Link is disabled by software.
yellow
Flashing
A fault condition exists.
yellow
Off No link.
1. The Speed LEDs are available only on Cisco MDS 9216i and Cisco MDS 9216A Supervisor
Modules.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-9
Page 28
Chapter 1 Product Overview
S
T
A
T
U
S
S
Y
S
T
E
M
R
E
S
E
T
CONSOLE
MGMT 10/100
MDS 9216i
9
3
1
5
6
42
116890
COM1
7
8
Interface Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Interface Modules
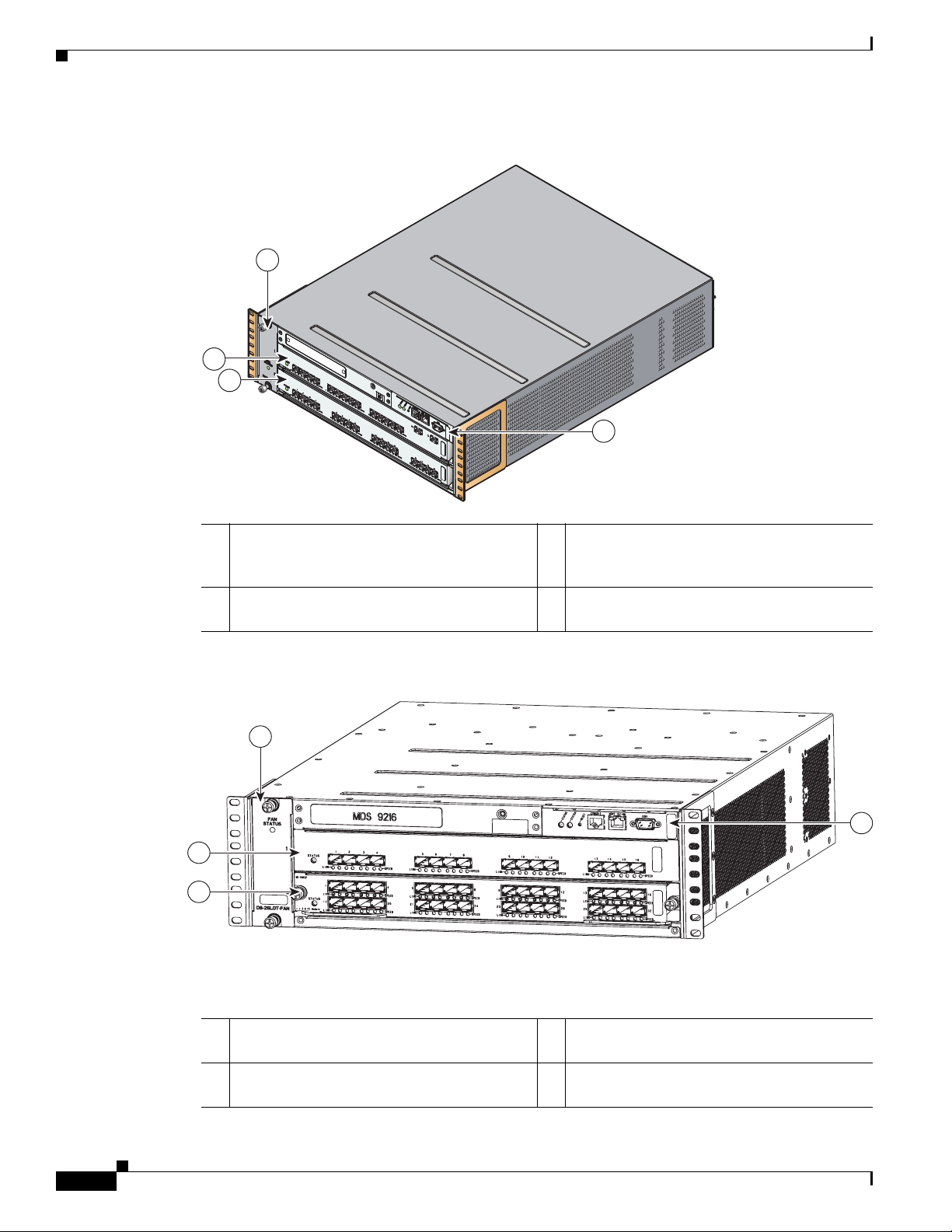
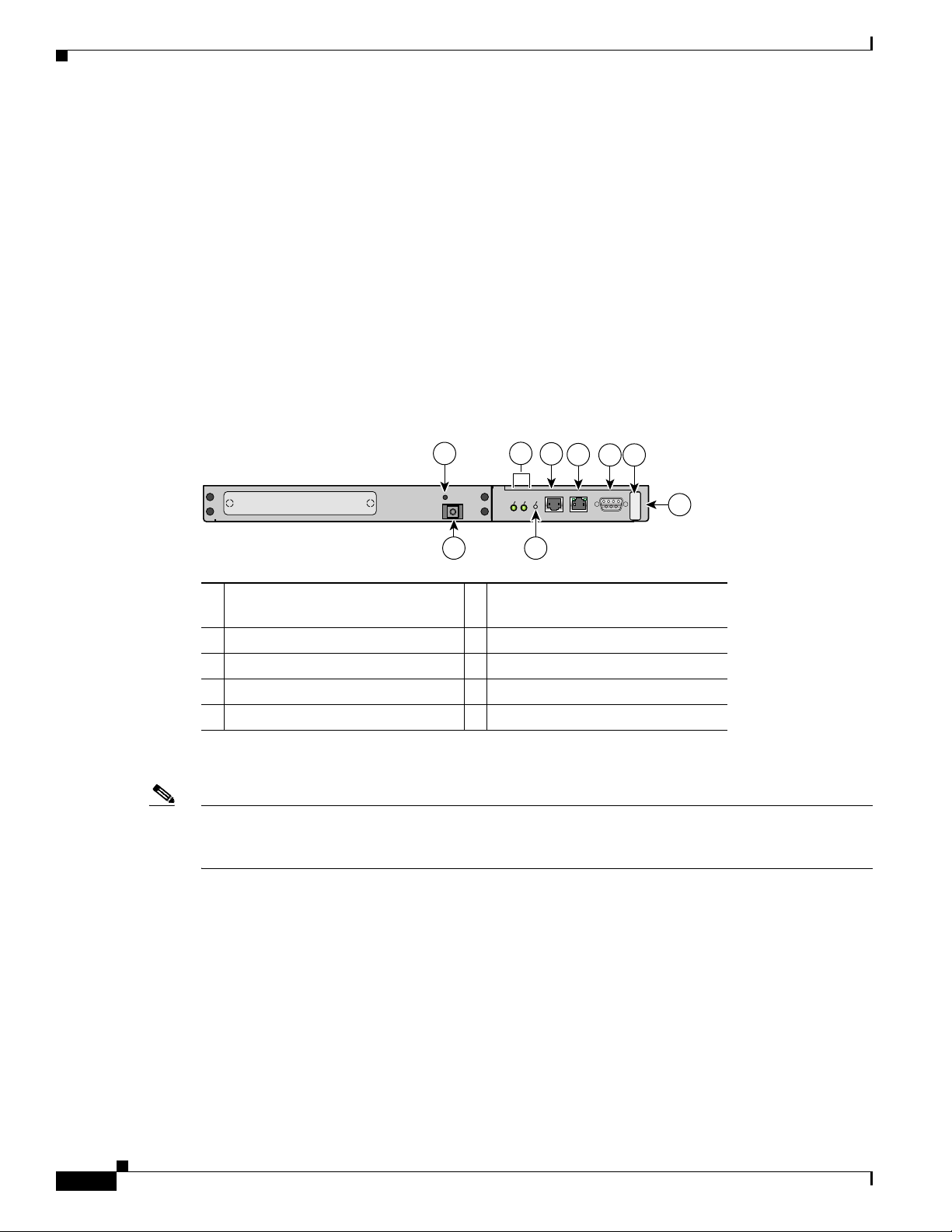
The nonremovable interface module is located above slot 1 (see Figure 1-7) and is identical for all Cisco
MDS 9200 Series switches. It provides the following local and remote management interfaces:
• RS-232 (EIA/TIA-232) console port with an RJ-45 connection that you can use to:
–
Configure the switch from the CLI.
–
Monitor network statistics and errors.
–
Configure SNMP agent parameters.
• MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port with an RJ-45 connection that provides network management
capabilities.
• RS-232 COM1 port with a DB-9 connector that can be attached to a modem.
Figure 1-7 Nonremoveable Interface Module of the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
1 ESD socket (for ESD strap) 6 MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port (with
integrated Link and Activity LEDs)
2 Grounding pad (beneath tape) 7 COM1 port
3 Status and System LEDs 8 Asset tag
4 Reset button 9 Interface module
5 Console port
The clock module is also part of the interface module.
Note The system clocks in the Cisco MDS 9200 Series have a field-measured mean time between failures
(MTBF) of approximately 3.2 million hours or 365 years. In the event of a clock module failure, the
system generates an error message.
1-10
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 29
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Interface Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Interface Module
Table 1-2 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series interface module.
Table 1-2 LEDs on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Interface Module
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational
(normal initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics
(normal initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded
the maximum system operating temperature limit
(a minor environmental warning). To ensure
maximum product life, you should immediately
correct the environmental temperature and
restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not
operational because a fault occurred during the
initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded
the safe operating temperature limits of the card
(a major environmental warning). The card shut
down to prevent permanent damage.
System Green All chassis environmental monitors are reporting OK.
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The power supply failed or the power supply fan
failed.
• Incompatible power supplies are installed.
• The redundant clock failed.
Red The temperature of the supervisor module exceeded
the major threshold.
MGMT 10/100
Ethernet Link
LED
MGMT 10/100
Ethernet
Activity LED
Green Link is up.
Off No link.
Green Traffic is flowing through port.
Off No link or no traffic.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-11
Page 30
Chapter 1 Product Overview
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Module Compatibility
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Module Compatibility
Table 1-3 lists the hardware modules available and the chassis compatibility associated with them.
Table 1-3 MDS 9000 Modules and Platform Compatibility Matrix
Module 9513 9509 9506 9222i 9216A 9216i 9216
Supervisor-2 module X X X
Supervisor-1 module X X
4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel switching
module
48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module XXXXXX
24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module XXXXXX
12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module XXXXXX
4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module XXXXXX
32-port 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel module X X X X X X
16-port 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel module X X X X X X
8-port Gigabit Ethernet IP Storage Services module XXXXXXX
4-port Gigabit Ethernet IP Storage Services module X X X X X X
32-port Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module (ASM) X X X X X
32-port 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel Storage Services
Module (SSM)
Caching Services Module (CSM) X X X X X
18-port Fibre Channel /4-port Gigabit Ethernet Multiservice
(MSM-18/4) module
18-port Fibre Channel /4-port Gigabit Ethernet Multiservice
FIPS (MSFM-18/4) module
14-port Fibre Channel/2-port Gigabit Ethernet Multiprotocol
Services (MPS-14/2) module
XXXX
XXXXXXX
XXXXXX
XXXXXX
XXX XXX
Switching Modules
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports the following hot-swappable Fibre Channel switching modules:
• Generation 3 Modules
–
4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Switching Module
• Generation 2 Modules
–
48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
–
24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
–
12-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
–
4-Port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
• Generation 1 Modules
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-12
OL-17468-02
Page 31

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
–
32-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
–
16-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports one hot-swappable switching or services module in addition to the
integrated module that is part of the supervisor module.
The Fibre Channel switching modules provide system-wide power management and autonegotiation,
which allows ports to negotiate for speed at the other end of the link. Each module has temperature
sensors and an EEPROM that stores serial number and model number information.
The Fibre Channel port interfaces support hot-swappable Fibre Channel SFP and SFP+ transceivers,
which can be short wavelength (SWL) or long wavelength (LWL). The port interfaces also support
coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength-division multiplexing
(DWDM) SFP transceivers, which can be used for extended long wavelength (ELWL) transmission or
for coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) and dense wavelength-division multiplexing
(DWDM). See the “Supported Transceivers” section on page 1-36.
Note The internal bootflash installed on the modules are not field-replaceable units. Do not remove or replace
internal bootflash on the modules. Modifying the factory-installed bootflash is not supported.
4/44-Port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel switching module offers 48 autosensing 1-, 2-,
4-and 8-Gbps Fibre Channel ports and can be used in any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series chassis and in
the Cisco MDS 9222i Switches. The 4/44-port switching module can be configured in one of two
operational modes: shared bandwidth mode (default) and dedicated bandwidth mode.
Figure 1-8 shows a 4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel switching module. The front panel
connectors support standard modular SFP and SFP+ transceivers and the speed detection is autosensing.
Figure 1-8 4/44-port 8-Gbps Host-Optimized Fibre Channel Switching Module
48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module offers 48 autosensing 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbps Fibre
Channel ports and can be used in any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series chassis and in the Cisco MDS 9222i,
9216i, and 9216A Switches. The 48-port switching module can be configured in one of two operational
modes: shared bandwidth mode (default) and dedicated bandwidth mode.
Figure 1-9 shows a 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module. The front panel connectors are
standard modular SFP and the speed detection is autosensing.
188657
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-13
Page 32

Chapter 1 Product Overview
144474
144809
1
2
3
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-9 48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
Figure 1-10 shows the port numbering and LEDs on the 48-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching
module.
Figure 1-10 48-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module LEDs
1 Status LED 3 Fibre Channel ports
2 Link LEDs
24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module offers 24 autosensing 1-, 2-, and 4-Gbps Fibre
Channel ports and can be used in any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series chassis and in the Cisco MDS 9216i
and 9216A Switches. The 24-port switching module can be configured in one of two operational modes:
shared bandwidth mode (default) and dedicated bandwidth mode.
Figure 1-11 shows a 24-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module. The front panel connectors are
standard modular SFP and the speed detection is autosensing.
1-14
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 33

Chapter 1 Product Overview
144471
2
34
1
144470
3
2
1
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-11 24-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Fibre Channel ports
2 Link LEDs 4 Port Group
12-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module can be used in any of the Cisco MDS 9500 Series
chassis and in the Cisco MDS 9216i and 9216A Switches. The 12-port 4-Gbps switching module is a
full-rate mode module providing 12 SFP-based Fibre Channel interfaces. Each interface can support fullline rate operation at 4 Gbps interface speed. The module delivers a sustained data rate of up to 4-Gbps
in each direction, on all ports simultaneously, and up to 96 Gbps of continuous, aggregate bandwidth
when attached to high-performance servers and storage subsystems.
Figure 1-12 shows a 12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module. The front panel connectors are
standard modular SFP and the speed detection is autosensing.
Figure 1-12 12-Port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LEDs
2 Fibre Channel ports
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
1-15
Page 34

Chapter 1 Product Overview
144473
2
3
1
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
4-Port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module offers four dedicated bandwidth Fibre Channel
ports running at 10 Gbps with no oversubscription. This module can be used in any of the Cisco MDS
9500 Series chassis and in the Cisco MDS 9216i and 9216A Switches. The module delivers a sustained
data rate of up to 10 Gbps in each direction, on all ports simultaneously, and up to 80 Gbps of continuous,
aggregate bandwidth.
Figure 1-13 shows a 4-port 10-Gbps switching module. The front panel connectors are standard modular
X2 interfaces and the speed is fixed at 10 Gbps.
Figure 1-13 4-Port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LED
2 X2 port interfaces
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-16
OL-17468-02
Page 35

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Generation 2 Switching Modules
Table 1-4 describes the LEDs for the 48-port, 24-port, and 12-port 4-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching
Modules and the 4-port 10-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module.
Table 1-4 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Generation 2 Fibre Channel Switching Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational
(normal initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics
(normal initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system has
exceeded the maximum system operating
temperature limit (a minor environmental
warning). To ensure maximum product life, you
should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal
operation.
Red One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not
operational because a fault occurred during the
initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system has
exceeded the safe operating temperature limits of
the card (a major environmental warning). The
card has been shut down to prevent permanent
damage.
Link Solid green Link is up.
Intermittent
flashing green
Solid yellow Link is disabled by software.
Flashing
yellow
Off No link.
Link is up (traffic on port).
A fault condition exists.
32-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 32-port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel switching module can be used to allocate bandwidth optimally. The
module is organized into eight four-port groups. Only the first port in each four-port group can be an
ISL. If the first port is an ISL, the other three ports in the group are disabled. The four ports within a port
group share a single internal channel resulting in a subscription ratio of approximately 3.2:1. The 32-port
2-Gbps switching module provides more ports at a lower price per port. Figure 1-14 shows a 32-port
switching module.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-17
Page 36

Chapter 1 Product Overview
91673
2
1 4
3
17 20
4
DS-X9032
5
21 24
89
25 28
12 13
29 32
16
91672
4
3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
2
1
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Tip For a full 2-Gbps bandwidth between two hosts, connect one host to the first port group and the second
host to the second port group.
Figure 1-14 Cisco MDS 9000 Family 32-Port 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LED (to left of port) and
Speed LED (to right of port)
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel port
group
4 Asset tag
16-Port 2-Gbps Fibre Channel Switching Module
The 16-port 2-Gbps switching module is best used for applications requiring high bandwidth; for
example, Inter-Switch Link (ISL) connections between switches and high-performance host or storage
controllers. The 16-port switching module supports a sustained data rate of up to 2 Gbps in each
direction, on all ports simultaneously. Figure 1-15 shows a 16-port 2-Gbps switching module.
The autosensing 1-Gbps/2-Gbps ports of the 16-port Fibre Channel switching module deliver up to
64 Gbps of continuous, aggregate bandwidth when attached to high-performance servers and storage
subsystems.
Figure 1-15 Cisco MDS 9000 Family 16-Port 2-Gbps Switching Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LED (to left of port) and
Speed LED (to right of port)
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel
ports
4 Asset tag
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-18
OL-17468-02
Page 37

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Switching Module Features
Each switching module draws its power from the 42 V supplied on the backplane with local DC/DC
power converters and regulators.
The control processor on the switching module provides power-on, offline, and online diagnostics. The
control processor can be used to configure devices on the switching module and to gather statistical data
from each port.
The control processor can determine which slot it is plugged into, and it can monitor its DC/DC power
source and temperature. The control processor signals the supervisor module and displays an alarm on
its front panel when a problem is detected.
The front panel on the switching module provides basic status information, such as power-on, self-test
running, self-test passed, alarm, and ready.
The binary image for the switching module is downloaded from the supervisor module. Prior to the
image download, the control processor on the switching module runs from code stored on its local
CompactFlash card.
Note Routine software downloads are not required.
The integrated supervisor module can force a reset on the switching module and controls whether power
is applied to the switching module.
If a single component or a set of components on the switching module fails, this does not disable other
switching modules if that is the only failure in the system.
Each switching module has a hardware watchdog timer to detect most component failures. The watchdog
timer resets the card if it is not serviced periodically.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-19
Page 38

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Switching Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Generation 1 Switching Module
Table 1-5 describes the LEDs for the 16-port and 32-port switching modules.
Table 1-5 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Generation 1 Fibre Channel Switching Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational
(normal initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics
(normal initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system has
exceeded the maximum system operating
temperature limit (a minor environmental
warning). To ensure maximum product life, you
should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal
operation.
Red One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not
operational because a fault occurred during the
initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system has
exceeded the safe operating temperature limits of
the card (a major environmental warning). The
card has been shut down to prevent permanent
damage.
Speed On 2-Gbps mode.
Off 1-Gbps mode.
Steady
Link is up (beacon used to identify port).
1
flashing green
Link Solid green Link is up.
Intermittent
Link is up (traffic on port).
flashing green
Solid yellow Link is disabled by software.
Flashing
A fault condition exists.
yellow
Off No link.
1. The flashing green light turns on automatically when an external loopback is detected that causes
the interfaces to be isolated. The flashing green light overrides the beacon mode configuration.
The state of the LED is restored to reflect the beacon mode configuration after the external
loopback is removed.
1-20
The Fibre Channel switching modules provide auto-configuring Fibre Channel ports that support Fibre
Channel speeds of 1.0625 Gbps and 2.125 Gbps.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 39

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Services Modules
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports the following hot-swappable services modules:
• 1 8/4-Port Multiservice Module
• 18/4-Port Multiservice Federal Information Processing Standards Module
• 14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module
• IP Storage Services Modules
• 32-Port Fibre Channel Storage Services Module
• 32-Port Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module
• Caching Services Module
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports one hot-swappable switching or services module in addition to the
integrated module that is part of the supervisor module. Each module has temperature sensors and an
EEPROM that stores serial number and model number information.
Note The internal bootflash installed on the modules are not field-replaceable units. Do not remove or replace
internal bootflash on the modules. You cannot modify the factory installed bootflash.
18/4-Port Multiservice Module
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice (MSM-18/4) module provides 18 autosensing
1-, 2-, and 4-Gbps Fibre Channel ports and four Gigabit Ethernet IP services ports. The MSM-18/4
module provides multiprotocol capabilities such as Fibre Channel, Fibre Channel over IP (FCIP), Small
Computer System Interface over IP (iSCSI), IBM Fiber Connectivity (FICON), and FICON Control Unit
Port (CUP) management.
The MSM-18/4 module provides 18 4-Gbps Fibre Channel interfaces for high-performance SAN and
mainframe connectivity and four Gigabit Ethernet ports for FCIP and iSCSI storage services. Individual
ports can be configured with hot-swappable short wavelength, long wavelength, extended-reach, coarse
wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) or dense wavelength-division multiplexing (DWDM) Small
Form-Factor Pluggables (SFPs) for connectivity up to 125 miles (200 km).
The MSM-18/4 module can minimize latency for disk and tape through FCIP write acceleration and
FCIP tape write and read acceleration. The MSM-18/4 module provides up to 16 virtual Inter-Switch
Link (ISL) connections on the four 1-Gigabit Ethernet ports through tunneling, and provides up to 4095
buffer-to-buffer credits that can be assigned to a single Fibre Channel port.
The MSM-18/4 supports hardware-based encryption and it is required to run the Storage Media
Encryption (SME), which is a part of the Cisco NX-OS. For more information on SME, see the Cisco
MDS Storage Media Encryption Guide.
The MSM-18/4 supports SAN extension over IP and is compatible with current SAN extension products,
such as, MPS-14/2, 9216i, and IPS. The MSM-18/4 provides an integrated next generation 4-Gbps FC
platform for SAN extension. The MSM-18/4 module supports Internet Protocol version 6 (IPv6) as
mandated by the U.S. Department of Defense (DoD), Japan, and China. The IPv6 support is provided
for FCIP, iSCSI, and management traffic routed in-band and out-of-band.
The MSM-18/4 module provides intelligent diagnostics, protocol decoding, and network analysis tools
wit h the integrated Call Home capability.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-21
Page 40

Chapter 1 Product Overview
184706
1
2
4
3
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
18/4-Port Multiservice Federal Information Processing Standards Module
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice Federal Information Processing Standards
(MSFM-18/4) module is a FIPS 140-2 Level 3-compliant version of the MSM-18/4 module. The
MSFM-18/4 module is identical to the MSM-18/4 module in form and function, with the exception of
an opaque potting material encapsulating the cryptographic boundary of the MSFM-18/4 module to
prevent unauthorized access and tampering.
Note Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches running Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x, 3.x, and NX-OS 4.1(1b)
support the 18/4-port Multiservice module and the 18/4-Port Multiservice FIPS module.
Figure 1-16 shows the Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice module.
Figure 1-16 Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice Module
1 Status LED 3 Gigabit Ethernet ports
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps/4-Gbps Fibre Channel ports 4 Link LEDs
1-22
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 41

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the 18/4-Port Multiservice Module
Table 1-6 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice module.
Table 1-6 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family 18/4-Port Multiservice Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product
life, you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not operational
because a fault occurred during the initialization
sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the safe
operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
Link Solid
Link is up.
green
Solid
Link is disabled by software.
yellow
Flashing
A fault condition exists.
yellow
Off No link.
14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module
The 14/2-port Multiprotocol Services (MPS-14/2) module provides 14 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel
autosensing ports and two 1-Gigabit Ethernet ports for iSCSI and FCIP over Gigabit Ethernet. The
MPS-14/2 module supports the intelligent features available on other modules, including VSANs,
security, and traffic management.
The 14 1-Gbps/2-Gbps autosensing Fibre Channel ports (labeled 1 through 14) are best used for
applications requiring high bandwidth; for example, Inter-Switch Link (ISL) connections between
switches and high-performance host or storage controllers. Each Fibre Channel port supports a sustained
data rate of up to 2 Gbps in each direction.
The Cisco MDS 9216 Switch supports one MPS-14/2 module. The two Gigabit Ethernet ports (labeled 1
and 2) provide 1-Gbps throughput for IP services, including iSCSI and FCIP over Gigabit Ethernet. The
MPS-14/2 also supports hardware-based encryption and compression for these Gigabit Ethernet ports.
This hardware-based encryption handles the computationally intensive IPsec feature for IP services.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-23
Page 42

Chapter 1 Product Overview
—SPEED LINK—
LINK-
—SPEEDLINK—
STATUS
1 56789
LINK— —SPEED
10 11 12 13 14234
12
LINK-
GIGABIT E THERNET
116889
1 6
2 4
3 5
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The MPS-14/2 modules support FCIP compression to maximize the effective WAN bandwidth of SAN
extension solutions. It achieves up to a 30-to-1 compression ratio, with typical ratios of 2-to-1 over a
wide variety of data sources. With the addition of hardware-based compression, the MPS-14/2 module
is able to provide optimal levels of compressed throughput for implementations across low to
high-bandwidth links.
The Gigabit Ethernet ports on the MPS-14/2 module support iSCSI protocol, FCIP protocol, or both
protocols simultaneously. For information about configuring the ports, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family
CLI Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
The Fibre Channel port interfaces support hot-swappable Fibre Channel SFP transceivers, which can be
short wavelength (SWL) for connectivity up to 1640 feet (500 meters), or long wavelength (LWL) for
connectivity up to 6.2 miles (10 km). All interfaces are autosensing 1-Gbps or 2-Gbps compatible. The
port interfaces also support coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) SFP transceivers, which
can be used for extended long wavelength (ELWL) transmission or for CWDM. See the “Supported
Transceivers” section on page 1-36.
Note Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches running Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x, 3.x, and NX-OS 4.1(1b)
support the MPS-14/2 module.
Figure 1-17 Cisco MDS 9000 Family MPS-14/2 module.
Figure 1-17 Cisco MDS 9000 Family MPS-14/2 Module
1 Status LED 4 Gigabit Ethernet ports
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel
5 Link LEDs
ports
3 Link LEDs (under ports, on left)
6 Asset tag
and Speed LEDs (under ports, on
right)
1-24
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 43

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the 14/2-Port Multiprotocol Services Module
Table 1-7 describes the LEDs for the MPS-14/2 modules.
Table 1-7 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family MPS-14/2 Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product
life, you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not operational
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the safe
Speed On 2-Gbps mode.
Off 1-Gbps mode.
Flashing
Link is up (beacon used to identify port).
green
Link Solid
Link is up.
green
Solid
Link is disabled by software.
yellow
Flashing
A fault condition exists.
yellow
Off No link.
IP Storage Services Modules
because a fault occurred during the initialization
sequence.
operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
OL-17468-02
The 8-port and 4-port IP Storage services (IPS-8 and IPS-4) modules provide eight or four 1-Gigabit
Ethernet ports for iSCSI as well as FCIP over Gigabit Ethernet, and they support the intelligent features
available on other modules, including VSANs, security, and traffic management.
The IPS module ports support the iSCSI protocol, the FCIP protocol, or both protocols simultaneously.
For information about configuring the ports, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide
and the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-25
Page 44

Chapter 1 Product Overview
91694
2
1
4
3
113161
LINK LINK LINK LINK
1234
1
4
3
2
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The Fibre Channel port interfaces support hot-swappable Fibre Channel SFP transceivers, which can be
short wavelength (SWL) for connectivity up to 1640 feet (500 meters), or long wavelength (LWL) for
connectivity up to 6.2 miles (10 km). The port interfaces also support coarse wavelength-division
multiplexing (CWDM) SFP transceivers, which can be used for extended long wavelength (ELWL)
transmission or for CWDM. See the “Supported Transceivers” section on page 1-36.
Figure 1-18 shows an IPS-8 module.
Figure 1-18 Cisco MDS 9000 Family IPS-8 Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LEDs
2 Gigabit Ethernet ports 4 Asset tag
Figure 1-19 shows an IPS-4 module.
Figure 1-19 Cisco MDS 9000 Family IPS-4 Module
1 Status LED 3 Link LEDs
2 Gigabit Ethernet ports 4 Asset tag
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-26
OL-17468-02
Page 45

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on IP Storage Services Module
Table 1-8 describes the LEDs for the IPS module.
Table 1-8 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family IPS Modules
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product
life, you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not
operational because a fault occurred during the
initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
safe operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
Link Solid
Link is up.
green
Flashing
Link is up (beacon used to identify port).
green
Solid
Link is disabled by software.
yellow
Flashing
A fault condition exists.
yellow
Off No link.
32-Port Fibre Channel Storage Services Module
The 32-port Fibre Channel Storage Services Module (SSM) for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family supports
up to 32 Fibre Channel ports, provides distributed intelligent storage services, and supports future
storage services.
OL-17468-02
Note Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches running Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x, 3.x, and NX-OS 4.1(1b)
support the SSM.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-27
Page 46

Chapter 1 Product Overview
120094
2
43
17 20
45
21 24
89
25 28
12 13
29 32
16
Storage Services Module
1
DS-X9032
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The Fibre Channel ports support hot-swappable Fibre Channel SFP transceivers, which can be short
wavelength (SWL) for connectivity up to 1050 feet (500 m), or long wavelength (LWL) for connectivity
up to 6.2 miles (10 km). All interfaces are autosensing 1-Gbps or 2-Gbps compatible. The ports also
support coarse wavelength-division multiplexing (CWDM) SFP transceivers, which can be used for
extended long wavelength (EWL) transmission or for CWDM. For more information about SFP
transceivers, see the “Supported Transceivers” section on page 1-36.
Figure 1-20 shows the SSM, which has the part number DS-X9032-SSM on the left side.
Figure 1-20 Cisco MDS 9000 Family SSM
1 Status LED 3 Link and speed LEDs
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel port group 4 Asset tag
Each module draws power from the 42 V supplied on the backplane with local DC/DC power converters
and regulators.
The control processor on the module provides power-on, offline, and online diagnostics. The control
processor can be used to configure devices on the switching module and to gather statistical data from
each port.
The control processor monitors the DC/DC power source and temperature. The control processor signals
the supervisor module and displays an alarm on its front panel when it detects a problem.
The front panel on the services module provides basic status information, such as power-on, self-test
running, self-test passed, alarm, and ready.
The binary image for the services module is downloaded from the supervisor module. Prior to the image
download, the control processor on the services module runs from the code stored on its local
CompactFlash card. The image for an SSM can be specified using the SSI boot variable. For more
information on how to specify the SSI boot variable, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration
Guide.
Note Software downloads are only necessary when a revision of the code is needed.
The supervisor module can force a reset on the services module and controls whether or not power is
applied to the switching module.
1-28
If a single component or a set of components on the switching module fails, this failure does not disable
another switching module if that is the only failure in the system.
For the detection of most component failures, each switching module has a hardware watchdog timer
that resets the card if it is not serviced periodically.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 47

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Storage Services Module
Table 1-9 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Storage Services Module.
Table 1-9 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Storage Services Module
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass. The module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To assure maximum product life,
you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not operational
because a fault occurred during the initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the safe
operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
Speed On 2-Gbps mode.
Off 1-Gbps mode.
Link Solid green Link is healthy.
Steady flashing
Link is healthy and beacon is enabled.
green
Intermittent
Link is up and traffic is flowing through port.
flashing green
Solid yellow Link is disabled by software.
Flashing yellow A fault condition exists.
Off No link.
32-Port Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module
The Cisco MDS 9000 Family 32-Port Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module (ASM) enables pooling
of heterogeneous storage for increased storage utilization, simplified storage management, and reduced
total cost of storage ownership. The ASM incorporates all the capabilities of the Cisco MDS 9000
DS-X9032 Fibre Channel switching module and also provides scalable, in-band storage virtualization
services. The ASM module makes it possible to allocate bandwidth optimally.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-29
Page 48

Chapter 1 Product Overview
94298
2
1 43
17 20
45
21 24
89
25 28
12 13
29 32
16
DS-X9032
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The Fibre Channel port interfaces support hot-swappable Fibre Channel SFP transceivers, which can be
SWL for connectivity up to 1640 feet (500 meters), or LWL for connectivity up to 6.2 miles (10 km).
All interfaces are autosensing 1-Gbps or 2-Gbps compatible. The port interfaces also support CWDM
SFP transceivers, which can be used for extended long wavelength (ELWL) transmission or for CWDM.
See the “Supported Transceivers” section on page 1-36.
Figure 1-21 shows the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fibre Channel ASM.
Figure 1-21 Cisco MDS 9000 Family ASM
1 Status LED 3 Link and Speed LEDs
2 1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel port group 4 Asset tag
Each module draws power from the 42 V supplied on the backplane with local DC/DC power converters
and regulators.
The control processor on the module provides power-on, offline, and online diagnostics. The control
processor can be used to configure devices on the switching module and to gather statistical data from
each port.
The control processor monitors the DC/DC power source and temperature. The control processor signals
the supervisor module and displays an alarm on its front panel when a problem is detected.
The front panel on the services module provides basic status information, such as power-on, self-test
running, self-test passed, alarm, and ready.
The binary image for the services module is downloaded from the supervisor module. Prior to the image
download, the control processor on the switching module runs from code stored on its local
CompactFlash card. The image for an ASM-SFN can be specified using the ASM-SFN boot variable.
For more information on how to specify the SSI boot variable, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI
Configuration Guide.
Note Software downloads are only necessary when a revision of the code is needed.
The supervisor module can force a reset on the services module and controls whether power is applied
to the switching module.
If a single component or a set of components on the switching module fails, this failure does not disable
another switching module if that is the only failure in the system.
Each ASM has a hardware watchdog timer to detect most component failures. The watchdog timer resets
the card if it is not serviced periodically.
1-30
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 49

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Fibre Channel Advanced Services Module
Table 1-10 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family ASM.
Table 1-10 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family ASM
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass and the module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product life,
you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurs or occurred:
Speed On 2-Gbps mode.
Link Solid green Link is up.
Caching Services Module
The Caching Services Module (CSM) provides virtualization services that allow the Cisco MDS 9000
Family switches to reallocate physical resources as virtual resources for increased efficiency. The CSM
receives and sends data through the switch backplane. It has two disk drives, two internal batteries for
backup in case of power failure, and no external ports.
CSMs must be implemented in pairs in the fabric to provide redundancy and backup. Only two or more
CSMs in a fabric are supported. However, the CSMs need not to be installed in the same switch.
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not operational
because a fault occurred during the initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the safe
operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
Off 1-Gbps mode.
Steady flashing
Link is up (beacon used to identify port).
green
Intermittent
Link is up (traffic on port).
flashing green
Solid yellow Link is disabled by software.
Flashing yellow A fault condition exists.
Off No link.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-31
Page 50

Chapter 1 Product Overview
91626
STATUS
DS-X9560-SMXX
BATTERY STATUS
NODE 1
NODE 2
DISK STATUS DISK
Cashing Services Module
3 6
852
1 4 7
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The CSM shuts down if the software failure or an external power failure occurs, or if the module is
separated from the backplane while it is still powered on. The CSM automatically backs up the data in
memory to the disk drives and then shuts down. The CSM batteries provide adequate power to back up
data without external power.
Figure 1-22 shows the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CSM.
Figure 1-22 Cisco MDS 9000 Family CSM
1 Status LED 5 Disk 1 Status LED
2 Battery LED 6 Node 2 LEDs
3 Node 1 LEDs 7 Node 2 Status LED
4 Node 1 Status LED 8 Disk 2 Status LED
Figure 1-23 shows the location of the disk drives and batteries on the CSM.
Caution The batteries are shipped fully charged and should be handled accordingly.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-32
OL-17468-02
Page 51

Chapter 1 Product Overview
94038
1
3
4
2
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 1-23 Cisco MDS 9000 Family CSM (Internal View)
1 Disk drive 2 3 Battery 2
2 Disk drive 1 4 Battery 1
See the “Removing and Installing Switching and Services Modules” section on page 2-28 for
information about removing and installing the CSM and maintaining the CSM batteries.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-33
Page 52

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Services Modules
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
LEDs on the Caching Services Module
Table 1-11 describes the LEDs for the CSM.
Table 1-11 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CSM
LED Status Description
Status Green All diagnostics pass, and the module is operational (normal
initialization sequence).
Orange One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The module is booting or running diagnostics (normal
initialization sequence).
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the
maximum system operating temperature limit (a minor
environmental warning). To ensure maximum product life,
you should immediately correct the environmental
temperature and restore the system to normal operation.
Red One of the following occurs or occurred:
• The diagnostic test failed. The module is not operational
because a fault occurred during the initialization sequence.
• The inlet air temperature of the system exceeded the safe
operating temperature limits of the card (a major
environmental warning). The card shut down to prevent
permanent damage.
Node Green Node is fully operational.
Flashing green Node is not yet part of a cluster.
Orange The module is booting or node is administratively down.
Flashing orange Node is in service mode.
Red Node failure.
Off Node does not have power.
Battery Green Battery has sufficient charge to dump cache.
Flashing green Battery is charging and has sufficient charge to dump cache.
Battery conditioning in progress.
Flashing orange Battery is charging but has insufficient charge to dump cache.
Red Battery failure or battery is charged to the extent possible but in-
sufficient to dump cache; replace CSM.
Off Battery does not have power and is not charged.
Disk Solid green Disk is operational.
Flashing orange Dumping cache to disk.
Flashing green Restoring cache from disk.
Red Disk failure.
Off Disk does not have power.
1-34
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 53

Chapter 1 Product Overview
PWR-845-AC
100-240V 12-5A
50/60 Hz
INPUT OK
FAN OK
OUTPUT FAIL
ALL FASTENERS MUST BE FULLY ENGAGED
PRIOR TO OPERATING OF POWER SUPPLY
PWR-845-AC
100-240V 12-5A
50/60 Hz
INPUT OK
FAN OK
OUTPUT FAIL
ALL FASTENERS MUST BE FULLY ENGAGED
PRIOR TO OPERATING OF POWER SUPPLY
4
3
94002
1
2
Power Supplies
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Power Supplies
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports dual hot-swappable 845-W AC power supplies, each of which can
supply sufficient power to the entire chassis should one power supply fail. The power supplies monitor
their output voltage and provide status to the supervisor module. To prevent the unexpected shutdown of
an optional module, power management software only allows a module to power up if adequate power
is available.
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series power supplies can be configured to be redundant or combined. By default,
they are configured as redundant, so that if one fails, the remaining power supply can still power the
entire system. For information on how to configure the power supplies, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family
CLI Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
The power supplies, which are accessed from the rear of the chassis, are illustrated in Figure 1-24.
Figure 1-24 Cisco MDS 9200 Series with 845-W Dual Power Supplies
1 Power supply switch 3 Power supply handle
2 AC power connection 4 Power supply LEDs
Table 1-12 describes the LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series power supplies.
Table 1-12 LEDs for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Power Supplies
LED Status Description
Input OK Green AC input is good and power supply is functioning normally.
Off Power supply is turned off or is not seated properly in the
chassis.
Fan OK Green Power supply fans are operating properly.
Off Fan is not operating or power supply is off.
Output Fail Red Power supply is not in a stable state. If this indication
continues after initial power on, check that all connections
are secure, including the system fan tray.
Off Normal operation or power supply is turned off.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-35
Page 54

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Fan Module
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Fan Module
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports a hot-swappable fan module with four fans. The fan module
provides 80 cfm (cubic feet per minute) of cooling per slot, allowing 400 W of power dissipation per
slot. Sensors on the supervisor module monitor the internal air temperature. If the air temperature
exceeds a preset lower-level threshold, the environmental monitor displays warning messages. If the air
temperature exceeds a preset higher-level threshold, the switch will shut down.
If one or more fans within the fan module fail, the Fan Status LED turns red and the module must be
replaced. Individual fans cannot be replaced, you must replace the entire fan module. If the higher-level
temperature threshold is not exceeded, the switch continues to run for five minutes after the fan module
is removed. This means you can swap out a fan module without having to bring the system down. To
replace a fan module, see the “Removing and Installing the Fan Module” section on page 2-38. The fan
module has one Status LED that indicates the following conditions:
• Green—Fan module is operating normally.
• Red—One or more fans failed. Fan module should be replaced.
• Off—Fan module is not properly seated in the chassis or power supply has failed.
Caution The Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches have internal temperature sensors that are capable of shutting
down the system if the temperature at different points within the chassis exceed certain safety thresholds.
To be effective, the temperature sensors require the presence of airflow; therefore, in the event a fan
module is removed from the chassis, the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches shut down after five minutes
to prevent potentially undetectable overheating. However, the switches shut down sooner if the
higher-level temperature threshold is exceeded.
Supported Transceivers
The following types of transceivers are available from Cisco and are supported on the Cisco MDS 9200
Series:
• X2 Fibre Channel transceivers
• Fibre Channel SFP and SFP+ transceivers, in either SWL or LWL
• Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceivers, in either SWL or LWL
• Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet CWDM SFP transceivers, which can be used for
ELWL transmission or for CWDM
• Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver, 1-Gbps copper
• Fibre Channel DWDM SFP transceiver, which can be used for ELWL transmission or for DWDM
1-36
Note Switches running Cisco MDS SAN-OS Release 2.x, 3.x, and NX-OS 4.1(1b) support combination Fibre
Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceivers.
The transceivers are field-replaceable and hot-swappable. You can use any combination of SFP
transceivers that are supported by the switch. The only restrictions are that SWL transceivers must be
paired with SWL transceivers, and LWL transceivers with LWL transceivers, and the cable must not
exceed the stipulated cable length for reliable communications.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 55

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Supported Transceivers
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
For more information about the X2 transceiver, see the “X2 Transceiver Specifications” section on
page B-7.
For more information about a specific Cisco SFP transceiver, see the “SFP and SFP+ Transceiver
Specifications” section on page B-10. SFP transceivers can be ordered separately or with the Cisco MDS
9200 Series.
Note Use only Cisco transceivers in the Cisco MDS 9200 Series. Each Cisco transceiver is encoded with
model information that enables the switch to verify that the transceiver meets the requirements for the
switch.
X2 Fibre Channel Transceivers
The X2 Fibre Channel transceiver is a small form-factor optimized for 10-Gbps applications and uses an
SC connector. The X2 transceiver is ideally suited for Ethernet, Fibre Channel and telecom switches, and
standard peripheral component interconnect (PCI)-based server and storage connections. The X2
provides robust thermal performance and electromagnetic shielding.
For more information on X2 transceiver specifications, see the “X2 Transceiver Specifications” section
on page B-7.
Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers
Cisco Fibre Channel SFP transceivers are available in SWL or LWL versions. Both of these versions are
1-Gbps/2-Gbps/4-Gbps capable. Cisco Fibre Channel SFP+ transceivers are available in SWL or LWL
versions. Both of these versions are 2-Gbps/4-Gbps/8-Gbps capable.
Cisco Fibre Channel SFP transceivers have LC connectors and comply with 1-Gbps/2-Gbps/4-Gbps
Fibre Channel standards as defined in FC-PI 10.0 2. Cisco Fibre Channel SFP+ transceivers have LC
connectors and comply with 2-Gbps/4-Gbps/8-Gbps Fibre Channel standards as defined in FC-PI-4.
For more information about Fibre Channel SFP and SFP+ transceiver specifications, see the “SFP and
SFP+ Transceiver Specifications” section on page B-10.
Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers
The combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceivers from Cisco Systems are available in
SWL or LWL versions. Both of these versions are 1-Gbps/2-Gbps capable.
The combination SFP transceivers from Cisco Systems have LC connectors and comply with
1-Gbps/2-Gbps Fibre Channel as defined in FC-PI 10.0 2 and Gigabit Ethernet as defined in IEEE
802.3z.
For more information on the Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver specifications, see the
“SFP and SFP+ Transceiver Specifications” section on page B-10.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
1-37
Page 56

Chapter 1 Product Overview
Supported Transceivers
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
CWDM Combination Fibre Channel/Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers
All Fibre Channel and Gigabit Ethernet ports in the Cisco MDS 9200 Series support 1-Gbps/2-Gbps
CWDM SFP transceivers. In addition, the Fibre Channel ports on Cisco MDS 9222i also support 4-Gbps
CWDM SFP transceivers.
The Cisco CWDM SFP transceivers have LC connectors and support both Gigabit Ethernet and Fibre
Channel (1-Gbps/2-Gbps). They match the wavelength plan of Cisco CWDM GBICs and Cisco CWDM
optical add/drop multiplexers (OADMs).
CWDM SFP transceivers can be used in two ways:
• CWDM transmission can send and receive up to eight laser wavelengths carrying different signals
simultaneously on the same optical fiber using an OADM.
• ELWL signals can transmit over longer distances than LWL SFP transceivers.
There are eight different “colors” of CWDM SFP transceivers, one for each fixed wavelength. The fiber
optic cables from the CWDM SFP transceivers must be connected to an OADM. The OADM combines
the wavelengths of the different outgoing signals into one composite send signal. The OADM also
separates the received transmissions into the different wavelengths and sends them to the corresponding
CWDM SFP transceiver.
For more information on the CWDM SFP transceiver specifications, see the “SFP and SFP+ Transceiver
Specifications” section on page B-10.
Gigabit Ethernet SFP Transceivers
The 4-port and 8-port IP Storage services (IPS-4 and IPS-8) modules provide four or eight 1-Gigabit
Ethernet ports that support Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceivers. The Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceivers
have RJ-45 connectors and support Gigabit Ethernet (1-Gbps).
For more information on the Gigabit Ethernet SFP transceiver specifications, see the “SFP and SFP+
Transceiver Specifications” section on page B-10.
DWDM Fibre Channel SFP Transceivers
Fibre Channel ports on Cisco MDS 9222i support 2-Gbps DWDM SFP transceivers. The Cisco DWDM
Fibre Channel SFP transceivers have LC connectors and support Fibre Channel (1-Gbps/2-Gbps). The
DWDM SFP transceivers match the International Telecommunications Union (ITU) 100-Ghz
wavelength grid and the wavelength plan of Cisco 100-Ghz ONS product family.
The DWDM SFP transceivers have the following capabilities:
• DWDM transmission can send and receive up to 32 laser wavelengths carrying different signals
simultaneously on the same optical fiber by using an optical filter.
• ELWL signals can transmit over longer distances than LWL SFP transceivers.
For more information on the DWDM SFP transceiver specifications, see the “SFP and SFP+ Transceiver
Specifications” section on page B-10.
1-38
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 57

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
CHAP T ER
2
Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
This chapter describes how to install the Cisco MDS 9200 Series and its components, and it includes the
following information:
• Preinstallation, page 2-2
• Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack, page 2-5
• Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance, page 2-11
• System Grounding, page 2-19
• Grounding the Chassis, page 2-24
• Starting Up the Switch, page 2-26
• Removing and Installing Components, page 2-28
Note Before you install, operate, or service the system, read the Regulatory Compliance and Safety
Information for the Cisco MDS 9000 Family for important safety information.
OL-17468-02
Warning
Warning
Warning
IMPORTANT SAFETY INSTRUCTIONS
This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you
work on any equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar
with standard practices for preventing accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of
each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings that accompanied this device.
Statement 1071
SAVE THESE INSTRUCTIONS
This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be
accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security.
Statement 1017
Only trained and qualified personnel must be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment.
Statement 1030
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-1
Page 58

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Preinstallation
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Warning
A readily accessible two-poled disconnect device must be incorporated in the fixed wiring.
1022
Note Each new switch requires a license. For information on licensing, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI
Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Preinstallation
This section includes the following topics:
• Installation Options, page 2-2
• Installation Guidelines, page 2-3
• Required Equipment, page 2-4
• Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch, page 2-4
Installation Options
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series can be installed using the following methods:
• In an open EIA rack, using:
–
–
Statement
The rack-mount kit shipped with the switch
The telco and EIA Shelf Bracket Kit (an optional kit, purchased separately) in addition to the
rack-mount kit shipped with the switch
• In a perforated or solid-walled EIA cabinet, using:
–
The rack-mount kit shipped with the switch
–
The telco and EIA Shelf Bracket Kit (an optional kit, purchased separately) in addition to the
rack-mount kit shipped with the switch
• In a two-post telco rack, using:
–
The telco and EIA Shelf Bracket Kit (an optional kit, purchased separately) in addition to the
front brackets shipped with the switch
For instructions on installing the switch using the rack-mount kit shipped with the switch, see the
“Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack” section on page 2-5.
For instructions on installing the switch using the optional, separately purchased telco and EIA Shelf
Bracket Kit, see the “Cisco MDS 9000 Family telco and EIA Shelf Bracket” section on page A-4.
Note The optional telco and EIA Shelf Bracket Kit is not provided with the switch. To order the kit, contact
your switch provider.
2-2
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 59

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Preinstallation
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Installation Guidelines
Follow these guidelines when installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series:
• Plan your site configuration and prepare the site before installing the chassis. Appendix D, “Site
Planning and Maintenance Records,” lists the recommended site planning tasks.
• Record the information listed in Appendix D, “Site Planning and Maintenance Records,” as you
install and configure the switch.
• Ensure that there is adequate space around the switch to allow for servicing the switch and for
adequate airflow (Appendix B, “Technical Specifications,” lists airflow requirements).
• Ensure that the air-conditioning meets the heat dissipation requirements listed in Appendix B,
“Technical Specifications.”
• Ensure that the cabinet or rack meets the requirements listed in Appendix A, “Cabinet and Rack
Installation.”
Note Jumper power cords are available for use in a cabinet. See the “Jumper Power Cord” section on
page C-11.
• Ensure that the chassis is adequately grounded. If the switch is not mounted in a grounded rack,
Cisco recommends connecting both the system ground on the chassis and the power supply ground
to an earth ground.
• Ensure that the site power meets the power requirements listed in Appendix B, “Technical
Specifications.” If available, you can use an uninterruptible power supply (UPS) to protect against
power failures.
Caution Avoid UPS types that use ferroresonant technology. These UPS types can become unstable
with systems like the Cisco MDS 9000 Family, which can have substantial current draw
fluctuations because of fluctuating data traffic patterns.
• Ensure that circuits are sized according to local and national codes. For North America, the 845-W
power supply requires a 15-A or 20-A circuit.
If you are using a 200- or 240-VAC power source in North America, the circuit must be protected
by a two-pole circuit breaker.
Caution To prevent loss of input power, ensure the total maximum loads on the circuits supplying
power to the switch are within the current ratings for the wiring and breakers.
• Use the following screw torques when installing the switch:
–
Captive screws: 4 in-lb
OL-17468-02
–
M3 screws: 4 in-lb
–
M4 screws: 12 in-lb
–
10-32 screws: 20 in-lb
–
12-24 screws: 30 in-lb
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-3
Page 60

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Preinstallation
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Required Equipment
Before beginning the installation, ensure that the following items are ready:
• Number 1 and number 2 Phillips screwdrivers with torque capability
• 3/16-in. flat-blade screwdriver
• Tape measure and level
• ESD wrist strap or other grounding device
• Antistatic mat or antistatic foam
The following additional items (not found in the accessory kit) are required to ground the chassis:
• Grounding cable (6 AWG recommended), sized according to local and national installation
requirements; the required length depends on the proximity of the Cisco MDS 9200 Series to proper
grounding facilities
• Crimping tool large enough to accommodate girth of lug
• Wire-stripping tool
Unpacking and Inspecting the Switch
Caution When handling switch components, wear an ESD strap and handle modules by the carrier edges only.
An ESD socket is provided on the chassis. For the ESD socket to be effective, the chassis must be
grounded through the power cable, the chassis ground, or the metal-to-metal contact with a grounded
rack.
Tip Keep the shipping container in case the chassis requires shipping in the future.
Note If you purchased Cisco support through a Cisco reseller, contact the reseller directly. If you purchased
support directly from Cisco Systems, contact Cisco Technical Support at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Note The switch is thoroughly inspected before shipment. If any damage occurred during transportation or
any items are missing, contact your customer representative immediately.
To inspect the shipment, follow these steps:
2-4
Step 1 Compare the shipment to the equipment list provided by your customer service representative and verify
that you have received all items, including the following:
• Print documentation and CD-ROMs
• Grounding lug kit
• Rack-mount kit
• ESD wrist strap
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 61

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
• Cables and connectors
• Any optional items ordered
Step 2 Check for damage and report any discrepancies or damage to your customer service representative. Have
the following information ready:
• Invoice number of shipper (see packing slip)
• Model and serial number of the damaged unit
• Description of damage
• Effect of damage on the installation
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
This section describes how to use the rack-mount kit provided with the switch to install the Cisco MDS
9200 Series into a cabinet or rack that meets the requirements described in Appendix A, “Cabinet and
Rack Installation.” All Cisco MDS 9200 Series switches use the same installation procedure.
Caution If the rack is on wheels, ensure that the brakes are engaged or that the rack is otherwise stabilized.
The rack-mount kit provided with the switch contains the items listed in Ta ble 2-1. If you do not find all
the parts listed in Tab le 2 -1, you may have an older version of the rack-mount kit, which only included
the front rack-mount brackets. If this is the case, you can either install the switch in the rack with just
the front rack-mount brackets, or contact your customer service representative for a current version of
the rack-mount kit.
Note If you purchased Cisco support through a Cisco reseller, contact the reseller directly. If you purchased
support directly from Cisco, contact Cisco Technical Support at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Table 2-1 Contents of Cisco MDS 9200 Series Rack-Mount Kit
Quantity Part Description
Front rack-mount bracket kit
2 Front rack-mount brackets
12 M4 x 6-mm Phillips countersunk screws
Cable management bracket kit
2 Cable guide
6 12-24 x 3/4-inch Phillips binder-head screws
6 10-32 x 3/4-inch Phillips binder-head screws
Rear rack-mount bracket kit
2 Long slider rails
2 Short slider rails
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-5
Page 62

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
116891
M
D
S
9
216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
1
2
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Table 2-1 Contents of Cisco MDS 9200 Series Rack-Mount Kit (continued)
Quantity Part Description
2C brackets
6 12-24 x 3/4-inch Phillips binder-head screws
6 10-32 x 3/4-inch Phillips binder-head screws
4 M4 x 6-mm, Phillips countersunk screws
To install the switch in a cabinet or rack using the rack-mount kit provided with the switch, follow these
steps:
Step 1 Install the front rack-mount brackets as follows:
a. Position a front rack-mount bracket against the chassis and align the screw holes as shown in
Figure 2-1. Then attach the front rack-mount bracket to the chassis with six of the M4 screws.
b. Repeat with the other front rack-mount bracket on the other side of the switch.
Figure 2-1 Attaching Front Rack-Mount Bracket to the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
1 Front rack-mount
2 Screws, M4
bracket
2-6
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 63

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
GE1
LINK
GE2
LINK
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
1 2
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 2 Install the C brackets on the switch as follows:
a. Position one of the C brackets against the side of the switch and align the screw holes as shown in
Figure 2-2 and Figure 2-3. Then attach the bracket to the switch with two of the flat-head
screws.
Note Ensure the C bracket is oriented so that it blocks the fewest airflow holes on the chassis; the holes
should be slightly closer to the bottom of the brackets and the text on the back of the bracket
should be right side up.
b. Repeat with the other C bracket on the other side of the switch.
Figure 2-2 Installing C Brackets onto the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M4
1 C bracket 2 Screws, M4
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-7
Page 64

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-3 C Brackets for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (Close-Up View)
2-8
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 65

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M
DS 9216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
11
1
2
13
14
1
2
3
4
116893
1
3
2
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 3 Position the chassis in the rack, inserting the rear of the chassis between the front mounting rails (see
Figure 2-4). Use the 12-24 x 3/4-in. or 10-32 x 3/4-in. screws (depending on the type of rack) to attach
the front rack-mount brackets to the mounting rails (three per side).
If you are installing the optional cable guides, place the cable guides in front of the front rack-mount
brackets, and then pass the screws through the cable guides, front rack-mount brackets, and mounting
rail. You can install one or both cable guides; if installing a single cable guide, it can be installed on
either side.
Figure 2-4 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series in the Rack
1 Mounting rail 3 Screws, 12-24 or 10-32
2 Front rack-mount
bracket
Step 4
From the back of the rack, position the longer slider rails with the ears away from the chassis and slide
them into the C brackets previously installed on the sides of the chassis (see Figure 2-5).
Step 5 Level the chassis (it may sag slightly towards the back) and attach the slider rails to the mounting rails
OL-17468-02
with the 12-24 x 3/4-in. or 10-32 x 3/4-in. screws, three per side.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-9
Page 66

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
99001
1
2
3
Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-5 Inserting and Installing Slider Rails (Back View)
1 Screws, 12-24 or 10-32 3 C bracket
2 Slider rail
2-10
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 67

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
G
E
1
L
I
N
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
116894
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-6 shows the Cisco MDS 9200 Series completely installed in a rack.
Figure 2-6 Cisco MDS 9200 Series Chassis Installed in the Rack
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front
Clearance
This section describes how to use the rack-mount kit provided with the switch to install the Cisco MDS
9200 Series into a cabinet with insufficient front-facing clearance. The Cisco MDS 9200 Series is
installed rear-facing to provide adequate clearance for the fiber-optic cables. This cabinet meets the
requirements described in Appendix A, “Cabinet and Rack Installation,” except the cabinet has less than
three inches of clearance between the inside of the front door or bezel panel and the front cabinet
mounting rails. This rear-facing installation is necessary to ensure that the minimum bend radius for the
fiber-optic cables is maintained. In these cabinets, the Cisco MDS 9200 Series is mounted backwards,
with the fiber-optic cables facing toward the rear of the cabinet and the power supplies facing the front
of the cabinet.
Caution If the rack is on wheels, ensure that the brakes are engaged or that the rack is otherwise stabilized.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-11
Page 68

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
116891
MDS 9216i
GE1
LINK
GE2
LINK
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
1
2
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
The rack-mount kit provided with the switch contains the items listed in Ta ble 2-1. If you do not find all
of the parts listed in Tab le 2-1, you may have an older version of the rack-mount kit, which only included
the front rack-mount brackets. If this is the case, you can either install the switch in the rack with just
the front rack-mount brackets, or contact your customer service representative for a current version of
the rack-mount kit.
Note If you purchased Cisco support through a Cisco reseller, contact the reseller directly. If you purchased
support directly from Cisco, contact Cisco Technical Support at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml
Installing Front Rack-Mount Brackets for Cabinets with 26 Inches or Greater of Rail Spacings
Before installing the switch into the cabinet, the front rack-mount brackets for the Cisco MDS 9200
Series must be installed onto the switch. To install the brackets for cabinets with front-mounting rail to
rear-mounting rail spacing greater than or equal to 26 inches, follow these steps.
Step 1 Install the front rack-mount brackets as follows:
a. Position a front rack-mount bracket against the chassis and align the screw holes as shown in
Figure 2-7. Then attach the front rack-mount bracket to the chassis with six of the M4 screws.
b. Repeat with the other front rack-mount bracket on the other side of the switch.
Figure 2-7 Attaching Front Rack-Mount Bracket to the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
2-12
1 Front rack-mount bracket 2 Screws, M4
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 69

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
GE1
LIN
K
GE2
LINK
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
116892
1 2
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 2 Install the C brackets on the switch as follows:
a. Position one of the C brackets against the side of the switch and align the screw holes as shown in
Figure 2-8 and Figure 2-9. Then attach the bracket to the switch with two of the flat-head
screws.
Figure 2-8 Installing C Brackets onto the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M4
1 C bracket 2 Screws, M4
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-13
Page 70

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-9 C Brackets for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (Close-Up View)
Note Ensure the C bracket is oriented so that it blocks the fewest airflow holes on the chassis; the holes
should be slightly closer to the bottom of the brackets and the text on the back of the bracket
should be right side up.
b. Repeat with the other C bracket on the other side of the switch.
Installing Front Rack-Mount Brackets for Cabinets with Less Than 26 Inches of Rail Spacings
The front rack-mount brackets for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series switch must be installed onto the switch
prior to installing the switch into the cabinet. For cabinets with less than 26 inches of rail-to-rail spacing,
the front rack-mount bracket must be installed 180 degrees from normal. To install the brackets for
cabinets with front-mounting rail to rear-mounting rail spacing of less than 26 inches that need to be
mounted backwards to maintain adequate fiber-optic clearance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Install the front rack-mount brackets as follows:
a. Position one of the front rack-mount brackets against the side of the switch and align the screw holes
as shown in Figure 2-10. Then attach the bracket to the switch with the six M4 screws originally
provided with the bracket.
2-14
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 71

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
116895
LINK-
GE1
GE2
1
2
3
4
LINK-
10
11
12
13
14
5
6
7
8
9
MDS 9216i
GE1
LINK
GE2
LINK
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
116896
1 2
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-10 Front Rack-Mount Brackets (Rotated) Installed on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
b.
Repeat with the other front rack-mount bracket on the other side of the switch.
Step 2 Install the C brackets on the switch as follows:
a. Position one of the C brackets against the side of the switch and align the screw holes as shown in
Figure 2-11 and Figure 2-12. Then attach the bracket to the switch with two of the flat-head
screws.
M4
Figure 2-11 Installing C Brackets onto the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
1 C bracket 2 Screws, M4
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-15
Page 72

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
94297
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-12 C Brackets for the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (Close-Up View)
Note Ensure the C bracket is oriented so that it blocks the fewest airflow holes on the chassis; the holes
should be slightly closer to the bottom of the brackets and the text on the back of the bracket
should be right side up.
b. Repeat with the other C bracket on the other side of the switch.
Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series Rear-Facing into Cabinet
To install the switch rear-facing in a cabinet using the rack-mount kit provided with the switch, for
cabinets with insufficient front-facing clearance, follow these steps:
Step 1 Position the chassis in the rack, inserting the back of the chassis between the rear mounting rails (see
Figure 2-13). Use the 12-24 x 3/4-in. or 10-32 x 3/4-in. screws (depending on the type of rack) to attach
the front rack-mount brackets to the mounting rails (three per side).
If you are installing the optional cable guides, place the cable guides in front of the front rack-mount
brackets, and then pass the screws through the cable guides, front rack-mount brackets, and mounting
rail. You can install one or both cable guides; if installing a single cable guide, it can be installed on
either side.
2-16
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 73

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
I
N
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
12
13
14
1
2
3
4
116897
1
3
2
Front cabinet
mounting rails
Rear cabinet
mounting rails
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Note Figure 2-13 shows the front rack-mount brackets as rotated. Your chassis may have these
brackets installed in the normal position.
Figure 2-13 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series (Rear-Facing) in the Rack
1 Mounting rail 3 Screws, 12-24 or 10-32
2 Front rack-mount
bracket
Step 2
From the front of the rack, position the longer slider rails with the ears away from the chassis and slide
them into the C brackets previously installed on the sides of the chassis (see Figure 2-14).
Step 3 Level the chassis (it may sag slightly towards the back) and attach the slider rails to the mounting rails
with the 12-24 x 3/4-in. or 10-32 x 3/4-in. screws, three per side.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-17
Page 74

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
1
2
3
Rear cabinet
mounting rails
Front cabinet
mounting rails
Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-14 Inserting and Installing Slider Rails (Front View)
1 Screws, 12-24 or 10-32 3 C bracket
2 Slider rail
Figure 2-15 shows the Cisco MDS 9200 Series completely installed in a rack.
Note Figure 2-15 shows the front rack-mount brackets as rotated. Your chassis may have these
brackets installed in the normal position.
2-18
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 75

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
G
E
1
LIN
K
G
E2
LI
NK
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
Rear cabinet
mounting rails
Front cabinet
mounting rails
System Grounding
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-15 Cisco MDS 9200 Series Installed in the Rack (Back View)
System Grounding
This section describes the need for system grounding and explains how to prevent damage from
electrostatic discharge.
Proper Grounding Practices
Grounding is one of the most important parts of equipment installation. Proper grounding practices
ensure that the buildings and the installed equipment within them have low-impedance connections and
low-voltage differentials between chassis. When you properly ground systems during installation, you
reduce or prevent shock hazards, equipment damage due to transients, and data corruption. Tab l e 2- 2
OL-17468-02
lists some general grounding practice guidelines.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-19
Page 76

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
System Grounding
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Table 2-2 Grounding Best Practices
Electromagnetic Noise Severity
Environment
Commercial building is
subjected to direct lightning
strikes.
For example, some places in the
United States, such as Florida,
are subject to more lightning
strikes than other areas.
Commercial building is located
in an area where lightning
storms frequently occur but is
not subject to direct lightning
strikes.
Commercial building contains a
mix of information technology
equipment and industrial
equipment, such as welding.
Existing commercial building is
not subject to natural
environmental noise or
man-made industrial noise. This
building contains a standard
office environment. This
installation has a history of
malfunction due to
electromagnetic noise.
New commercial building is not
subject to natural environmental
noise or man-made industrial
noise. This building contains a
standard office environment.
Existing commercial building is
not subject to natural
environmental noise or
man-made industrial noise. This
building contains a standard
office environment.
Level Grounding Recommendations
High All lightning protection devices
must be installed in strict
accordance with manufacturer
recommendations. Conductors
carrying lightning current
should be spaced away from
power and data lines in
accordance with applicable
recommendations and codes.
Best grounding practices must
be closely followed.
High Best grounding practices must
be closely followed.
Medium to high Best grounding practices must
be closely followed.
Medium Best grounding practices must
be closely followed. Determine
source and cause of noise if
possible, and mitigate as closely
as possible at the noise source or
reduce coupling from the noise
source to the victim equipment.
Low Best grounding practices should
be followed as closely as
possible. Electromagnetic noise
problems are not anticipated, but
installing a best practice
grounding system in a new
building is often the least
expensive route and the best way
to plan for the future.
Low Best grounding practices should
be followed as much as possible.
Electromagnetic noise problems
are not anticipated, but
installing a best practice
grounding system is always
recommended.
2-20
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 77

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
System Grounding
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Note In all situations, grounding practices must comply with local National Electric Code (NEC)
requirements or local laws and regulations.
Note Always ensure that all of the modules are completely installed and that the captive installation screws
are fully tightened. In addition, ensure that all I/O cables and power cords are properly seated. These
practices are normal installation practices and must be followed in all installations.
Preventing Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electrostatic discharge (ESD) damage, which can occur when modules or other FRUs are improperly
handled, results in intermittent or complete failures. Modules consist of printed circuit boards that are
fixed in metal carriers. Electromagnetic interference (EMI) shielding and connectors are integral
components of the carrier. Although the metal carrier helps to protect the board from ESD, always use
an ESD grounding strap when handling modules.
Follow these guidelines for preventing ESD damage:
• Always use an ESD wrist strap and ensure that it makes maximum contact with bare skin. ESD
grounding straps are available with banana plugs, metal spring clips, or alligator clips. All MDS
9200 series chassis are equipped with a banana plug connector (identified by the ground symbol next
to the connector) somewhere on the front panel. Cisco recommends that you use a personal ESD
grounding strap equipped with a banana plug.
• If you choose to use the disposable ESD wrist strap supplied with most FRUs or an ESD wrist strap
equipped with an alligator clip, you must attach the system ground lug to the chassis in order to
provide a proper grounding point for the ESD wrist strap.
Note This system ground is also referred to as the network equipment building system (NEBS) ground.
• If your chassis does not have the system ground attached, you must install the system ground lug.
See “Establishing the System Ground” section on page 2-23 for installation instructions and
location of the chassis system ground pads.
Note You do not need to attach a supplemental system ground wire to the system ground lug; the lug provides
a direct path to the bare metal of the chassis.
After you install the system ground lug, follow these steps to correctly attach the ESD wrist strap:
Step 1 Attach the ESD wrist strap to bare skin as follows:
OL-17468-02
a. If you are using the ESD wrist strap supplied with the FRUs, open the wrist strap package and
unwrap the ESD wrist strap. Place the black conductive loop over your wrist and tighten the strap
so that it makes good contact with your bare skin.
b. If you are using an ESD wrist strap equipped with an alligator clip, open the package and remove
the ESD wrist strap. Locate the end of the wrist strap that attaches to your body and secure it to your
bare skin.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-21
Page 78

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M
DS 9216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
1
2
13
14
1
2
3
4
154017
2
1
3
4
5
System Grounding
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 2 Grasp the spring or alligator clip on the ESD wrist strap and momentarily touch the clip to a bare metal
spot (unpainted surface) on the rack. Cisco recommends that you touch the clip to an unpainted rack rail
so that any built-up static charge is then safely dissipated to the entire rack.
Step 3 Attach either the spring clip or the alligator clip to the ground lug screw as follows (See Figure 2-16.):
a. If you are using the ESD wrist strap that is supplied with the FRUs, squeeze the spring clip jaws
open, position the spring clip to one side of the system ground lug screw head, and slide the spring
clip over the lug screw head so that the spring clip jaws close behind the lug screw head.
Note The spring clip jaws do not open wide enough to fit directly over the head of the lug screw or
the lug barrel.
b. If you are using an ESD wrist strap that is equipped with an alligator clip, attach the alligator clip
directly over the head of the system ground lug screw or to the system ground lug barrel.
Figure 2-16 Attaching the ESD Wrist Strap to the System Ground Lug Screw
1 ESD ground strap 3 Side view of grounding lug (clip slid behind
screw)
2 Clip and grounding lug 4 Clip installed (behind screw)
5 System ground connector
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-22
OL-17468-02
Page 79

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
System Grounding
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
In addition, follow these guidelines when handling modules:
• Handle carriers by available handles or edges only; avoid touching the printed circuit boards or
connectors.
• Place a removed component board-side-up on an antistatic surface or in a static shielding container.
If you plan to return the component to the factory, immediately place it in a static shielding
container.
• Never attempt to remove the printed circuit board from the metal carrier.
Caution For safety, periodically check the resistance value of the antistatic strap. The measurement should be
between 1 and 10 megohm (Mohm).
Establishing the System Ground
This section describes how to connect a system ground to the MDS 9200 series switches.
Note This system ground is also referred to as the network equipment building system (NEBS) ground.
You must use the system (NEBS) ground on AC-powered systems if you are installing this equipment in
a U.S. or European Central Office.
The system (NEBS) ground provides additional grounding for EMI shielding requirements and
grounding for the low voltage supplies (DC-DC converters) on the modules and is intended to satisfy the
telcordia Technologies NEBS requirements for supplemental bonding and grounding connections. You
must observe the following system grounding guidelines for your chassis:
• You must install the system (NEBS) ground connection with any other rack or system power ground
connections that you make. The system ground connection is required if this equipment is installed
in a U.S. or European Central Office.
• You must connect both the system (NEBS) ground connection and the power supply ground
connection to an earth ground. The system (NEBS) ground connection is required if this equipment
is installed in a U.S. or European Central Office.
• You do not need to power down the chassis because the MDS 9200 series chassis are equipped with
AC-input power supplies.
Required Tools and Equipment
To connect the ground system, you need the following tools and materials:
• Grounding lug—A two holes standard barrel lug. Supports up to 6 AWG wire. Supplied as part of
accessory kit.
• Grounding screws—Two M4 x 8mm (metric) pan-head screws. Supplied as part of the accessory kit.
• Grounding wire—Not supplied as part of accessory kit. The grounding wire should be sized
according to local and national installation requirements. Depending on the power supply and
system, a 12 AWG to 6 AWG copper conductor is required for U.S. installations. Commercially
available 6 AWG wire is recommended. The length of the grounding wire depends on the proximity
of the switch to proper grounding facilities.
OL-17468-02
• No. 1 Phillips screwdriver.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-23
Page 80

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Grounding the Chassis
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
• Crimping tool to crimp the grounding wire to the grounding lug.
• Wire-stripping tool to remove the insulation from the grounding wire.
Grounding the Chassis
The chassis has a grounding pad with two threaded M4 holes for attaching a grounding lug. Figure 2-17
shows the system ground location on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series.
Warning
Caution Cisco recommends grounding the chassis, even if the rack is already grounded.
Caution All power supplies must be grounded. The receptacles of the AC power cables used to provide power to
When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and
disconnected last.
Statement 1046
the chassis must be the grounding type, and the grounding conductors should connect to protective earth
ground at the service equipment.
2-24
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 81

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
MDS 9216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
11
1
2
1
3
1
4
1
2
3
4
116899
2
3
4
5
6
1
Grounding the Chassis
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-17 Location of System Ground on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
1 ESD socket (on switch) 4 Screws, M4, with square cone
washers
2 ESD plug 5 NRTL listed grounding lug
3 Grounding cable 6 Close-up of grounding pad on
switch
Warning
Caution Grounding the chassis is required if you are using DC power supplies, even if the rack is already
When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and
disconnected last.
Statement 1046
grounded. A grounding pad with two threaded M4 holes is provided on the chassis for attaching a
grounding lug. The ground lug must be NRTL listed. In addition the copper conductor (wires) must be
used and the copper conductor must comply with NEC code for ampacity.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-25
Page 82

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Starting Up the Switch
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
To attach the grounding lug and cable to the chassis, follow these steps:
Step 1 Use a wire-stripping tool to remove approximately 0.75 in. (19 mm) of the covering from the end of the
grounding cable.
Step 2 Insert the stripped end of the grounding cable into the open end of the grounding lug.
Step 3 Use the crimping tool to secure the grounding cable in the grounding lug.
Step 4 Remove the adhesive label from the grounding pad on the chassis.
Step 5 Place the grounding lug against the grounding pad so that there is solid metal-to-metal contact, and insert
the two M4 screws with washers through the holes in the grounding lug and into the grounding pad.
Step 6 Ensure that the lug and cable do not interfere with other equipment.
Step 7 Prepare the other end of the grounding cable and connect it to an appropriate grounding point in your
site to ensure adequate earth ground.
Starting Up the Switch
This section provides instructions for powering up the switch and verifying component installation.
Warning
Warning
Note Do not connect the MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port to the LAN until the initial switch configuration has
Hazardous voltage or energy is present on the backplane when the system is operating. Use caution
when servicing.
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to
hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI)
that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not
operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are in place. During this
procedure, wear grounding wrist straps to avoid ESD damage to the switch.
Statement 1034
been performed. For instructions on configuring the switch, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI
Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide. For
instructions on connecting to the console port, see the “Connecting to the Console Port” section on
page 3-2.
Statement 1029
2-26
Warning
When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and
disconnected last.
Statement 1046
To power up the switch and verify hardware operation, follow these steps:
Step 1 Verify that empty module slots have filler panels installed, the faceplates of all modules are flush with
the front of the chassis, the ejector levers are fully closed and approximately parallel to the front of the
module, and the captive screws of the power supplies, fan module, and all supervisor, switching, or
services modules are tight.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 83

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Starting Up the Switch
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 2 Verify that both power supplies and the fan module are installed.
Step 3 Verify that the power switches on both power supplies are off, and then plug the power cables into the
power supplies and tighten the screws on the power cable retainers to ensure the cables cannot be pulled
out.
Note Depending on the outlet receptacle on your power distribution unit, you may need the optional
jumper power cord to connect the Cisco MDS 9200 Series to your outlet receptacle. See the
“Jumper Power Cord” section on page C-11.
Step 4 Connect the other end of the power cables to an AC power source.
Step 5 Ensure that the switch is adequately grounded as described in the “Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with
Insufficient Front Clearance” section on page 2-11, and that the power cables are connected to outlets
that have the required AC power voltages (see the “Weight of Modules” section on page B-3).
Step 6 Flip the power switches on the power supplies to the on (|) position. The switch boots automatically.
Step 7 Listen for the fans; they should begin operating when the switch is powered on.
Caution Do not operate the switch without a functioning fan module except for during the brief fan
module replacement procedure. Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches can operate for only a few
minutes without any functioning fan modules before they begin to overheat.
Step 8 After the switch boots, verify that the LED behavior is as follows:
• Fan module: Status LED is green.
• Power supplies:
–
Input Ok LED is green.
–
Fan Ok LED is green.
–
Output Fail LED is off.
• Supervisor, switching, or services modules:
–
During initialization, the status LED on the module flashes orange once, remains orange during
diagnostic boot tests, then turns green when the module is operational (online). If the system
software is unable to start up, this LED remains orange or turns red.
–
After initialization, the status LED is green, indicating that all chassis environmental monitors
are reporting that the system is operational. If this LED is orange or red, then one or more
environmental monitor is reporting a problem.
• The Link LEDs for the Ethernet port should not be on unless the cable is connected.
Note The link LEDs for the Fibre Channel ports remain yellow until the ports are enabled, and the
LED for the MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port remains off until the port is connected.
OL-17468-02
Step 9 Try removing and reinstalling a component that is not operating correctly. If it still does not operate
correctly, contact your customer service representative for a replacement.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-27
Page 84

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Note If you purchased this product through a Cisco reseller, contact the reseller directly for technical
support. If you purchased this product directly from Cisco, contact Cisco Technical Support at
this URL: http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml.
Step 10 Verify that the system software has booted and the switch has initialized without error messages. If any
problems occur, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Troubleshooting Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family
System Messages Guide. If you cannot resolve an issue, contact your customer service representative.
Step 11 Complete the worksheets provided in Appendix D, “Site Planning and Maintenance Records” for future
reference.
Note A setup utility automatically launches the first time you access the switch and guides you through the
basic configuration. For instructions on how to configure the switch and check module connectivity, see
the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager
Configuration Guide.
Removing and Installing Components
This section includes the following topics:
• Removing and Installing Switching and Services Modules, page 2-28
• Maintaining a Caching Services Module, page 2-35
• Removing and Installing Power Supplies, page 2-36
• Removing and Installing the Fan Module, page 2-38
• Removing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series, page 2-40
Warning
Caution To prevent ESD damage, wear grounding wrist straps during these procedures and handle modules by
Removing and Installing Switching and Services Modules
Hazardous voltage or energy is present on the backplane when the system is operating. Use caution
when servicing.
Statement 1034
the carrier edges only.
Slot 1 is reserved for the supervisor module with its integrated multiport switching or IP services
module. Slot 2 can contain an optional module. See Figure 1-2 for slot locations.
2-28
Warning
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into
beams or view directly with optical instruments.
Statement 1051
OL-17468-02
Page 85

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Warning
Warning
Caution To prevent ESD damage, wear grounding wrist straps during these procedures and handle modules by
Use of controls, adjustments, or performing procedures other than those specified may result in
hazardous radiation exposure.
Statement 1057
Hazardous voltage or energy is present on the backplane when the system is operating. Use caution
when servicing.
Statement 1034
the carrier edges only.
Note Install the Cisco MDS 9200 Series in the rack before installing modules. For information about installing
the chassis, see the “Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack” section on page 2-5.
This section includes the following topics:
• Removing a Caching Services Module, page 2-31
• Removing Other Switching or Services Modules, page 2-32
• Installing a Switching or Services Module, Including Caching Services Modules, page 2-33
• Verifying Installation of a Switching or Services Module, page 2-34
Figure 2-18 and Figure 2-19 show the positioning of a module in the chassis.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-29
Page 86

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M
DS 9216i
G
E
1
L
IN
K
G
E
2
L
IN
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
14
1
2
3
4
EMI gasket
STATUS
DS-X9032
1/2 G FC Module
EMI gasket
Insert module
between slot guides
4
3
2
1
6
117000
Ejector lever fully
extended
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-18 Positioning the Module in the Chassis
2-30
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 87

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
M
DS 9216i
G
E
1
L
I
N
K
G
E
2
L
I
N
K
5
6
7
8
9
1
0
11
12
13
1
4
1
2
3
4
1mm
Amount of gap
between the
module EMI
gasket and the
module above it
2
1
Press down
Press down
STATUS
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-19 Clearing the EMI Gasket
Removing a Caching Services Module
Note A minimum of two CSMs in each fabric are required for redundancy and data backup.
Warning
Warning
OL-17468-02
Caution Wait for all LEDs to turn off before removing the module from the chassis. If the LEDs are on, the
Do not touch or bridge the metal contacts on the battery. Unintentional discharge of the batteries can
cause serious burns.
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations.
Statement 1040
module still has power.
Statement 341
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-31
Page 88

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
To remove a CSM module from the chassis, follow these steps:
Step 1 Power off the module from the CLI. For information about the correct command to use, see the
Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide.
Step 2 Ensure that the backup process has completed by verifying that all LEDs on the module have turned off.
This requires up to 10 minutes.
Step 3 Loosen the two captive screws on the module.
Step 4 Remove the module from the chassis as follows:
a. Place your thumbs on the left and right ejector levers (shown in Figure 2-18 on page 2-30) and
simultaneously rotate the levers outward to unseat the module from the backplane connector.
b. Grasp the front edge of the module and slide the module part of the way out of the slot. Place your
other hand under the module to support the weight of the module. Do not touch the module circuitry.
Step 5 Place the module on an antistatic mat or antistatic foam if not immediately reinstalling it in another slot.
Step 6 Install a filler panel to keep dust out of the chassis and maintain consistent airflow if the slot will remain
empty.
Warning
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure
to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic
interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling
air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers,
and rear covers are in place.
Removing Other Switching or Services Modules
To remove a switching or services module from the chassis, follow these steps:
Step 1 Disconnect any network interface cables attached to the module.
Step 2 Loosen the two captive screws on the module.
Step 3 Remove the module from the chassis as follows:
a. Place your thumbs on the left and right ejector levers (shown in Figure 2-18 on page 2-30) and
simultaneously rotate the levers outward to unseat the module from the backplane connector.
b. Grasp the front edge of the module and slide the module part of the way out of the slot. Place your
other hand under the module to support the weight of the module. Do not touch the module circuitry.
Step 4 Place the module on an antistatic mat or antistatic foam if not immediately reinstalling it in another slot.
Step 5 Install a filler panel to keep dust out of the chassis and maintain consistent airflow if the slot will remain
empty.
Statement 1029
2-32
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 89

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Warning
Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure
to hazardous voltages and currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic
interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct the flow of cooling
air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers,
and rear covers are in place.
Statement 1029
Installing a Switching or Services Module, Including Caching Services Modules
The following warning applies only to the Caching Services Module:
Warning
Note Before installing any modules in the chassis, Cisco recommends installing the chassis in the rack. See
Step 1 Verify that there is enough clearance to accommodate any interface equipment that you connect directly
Step 2 If a filler panel is installed, remove the two Phillips pan-head screws from the filler panel and remove
Do not touch or bridge the metal contacts on the battery. Unintentional discharge of the batteries can
cause serious burns.
Statement 341
the “Installing the Chassis in a Cabinet or Rack” section on page 2-5.
To install a module in slot 2 of the chassis, follow these steps:
to the nearby components.
the panel. To remove a currently installed module, see the “Removing and Installing Switching and
Services Modules” section on page 2-28.
Step 3 Open fully both ejector levers on the new or replacement module (see Figure 2-18 on page 2-30).
Step 4 Position the module in the chassis as follows:
a. Position the module in the slot, aligning the sides of the module carrier with the slot guides on each
side of the slot.
b. Slide the module carefully into the slot until the EMI gasket along the top edge of the module makes
contact with the supervisor module above it and both ejector levers have closed to approximately 45
degrees with respect to the module faceplate (see Figure 2-19 on page 2-31).
c. Grasp the two ejector levers using the thumb and forefinger of each hand and press down to create
a small 0.040-in. (1 mm) gap between the module's EMI gasket and the module above it (see
Figure 2-20).
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-33
Page 90

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
FAN
STATUS
FAN-MOD-2
1
2
122003
Ejector levers flush with
module faceplate
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
TA
TU
S
S
YS
TEM
R
E
SE
T
CONSOLE
MGMT 10/100
MDS 9216i
COM1
—SPEED LINK—
LINK-
—SPEEDLINK—
STATUS
1 56789
LINK— —SPEED
10 11 12 13 14234
GE1
LINK-
GE2
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-20 Closing the Ejector Levers
Caution Do not press down too forcefully on the levers because they can bend.
d. Press down and simultaneously close the left and right ejector levers to fully seat the module in the
backplane connector. The ejector levers are fully closed when they are flush with the module
faceplate.
Note Ensure that the ejector levers are fully closed before tightening the captive screws. Failure to
fully seat the module in the backplane connector can result in error messages.
e. Tighten the two captive screws on the module.
Verifying Installation of a Switching or Services Module
To verify the module installation in slot 2, follow these steps:
Step 1 Verify that the ejector levers of the module are fully closed (parallel to the faceplate) to ensure that the
module is fully seated in the backplane connectors.
Step 2 Check the captive screws of the module, the power supply, and the fan module, and tighten any loose
captive screws.
Step 3 Verify that a filler panel is installed and that the screws holding the panel in place are tightened if the
slot is to remain empty.
Step 4 Turn on the power supply switches to power up the system and check the LEDs on the module.
Note For information on how to check connectivity of the module, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family
CLI Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-34
OL-17468-02
Page 91

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Maintaining a Caching Services Module
Caution Maintenance should only be performed by qualified service personnel.
Note A minimum of two CSMs in each fabric are required for redundancy and data backup.
This section includes the following topics:
• Maintaining the Batteries on the Caching Services Module, page 2-35
• Maintaining the Disk Drives on the Caching Services Module, page 2-35
Maintaining the Batteries on the Caching Services Module
The CSM batteries last approximately three years. The following message displays in the system log
when a battery fails:
Dec 5 17:14:36 sw-90.21 %SVC_BATTERY-SLOT8-4-BATTERY_CAPACITY_LOW:
Battery capacity is below the required threshold.
A message also appears in the output of the show interface command.
If you see this message, contact your support provider for assistance. If a battery fails, the CSM must be
replaced.
Caution The CSM batteries are shipped fully charged and should be handled accordingly.
Warning
Warning
Do not touch or bridge the metal contacts on the battery. Unintentional discharge of the batteries can
cause serious burns.
Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations.
Statement 1040
Statement 341
The batteries are automatically charged on a periodic basis with an SMBus-compliant Level III smart
charger located on the CSM. The smart charger measures the charge and recharges the battery to full if
it is less than 90 percent of capacity.
The batteries are also automatically reconditioned on a periodic basis, one battery at a time. During
reconditioning all power is drained from the battery and the battery is completely recharged, requiring
approximately six hours. The Battery Status LED flashes green during the reconditioning.
Maintaining the Disk Drives on the Caching Services Module
A message displays in the system log when a disk drive requires replacement. If you see this message,
contact your support provider for assistance.
If a disk drive fails, the CSM must be replaced. The other CSM(s) in the fabric contain the same data,
and they can continue to provide caching services during the replacement period.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
2-35
Page 92

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Removing and Installing Power Supplies
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series supports dual 845-W AC power supplies that monitor output voltage and
provide status to the supervisor module.
This section includes the following topics:
• Removing a Power Supply, page 2-36
• Installing a Power Supply, page 2-36
A flat-blade or Phillips screwdriver is required to perform these procedures.
Warning
Warning
Note You can replace a faulty power supply while the system is operating provided the other power supply is
Voltage is present on the backplane when the system is operating. To reduce risk of an electric shock,
keep hands and fingers out of the power supply bays and backplane areas.
Power supply captive installation screws must be tight to ensure protective grounding continuity.
Statement 289
functioning.
Removing a Power Supply
To remove a power supply, follow these steps:
Step 1 Turn the power switch to the off (0) position.
Step 2 Loosen the screw on the power cable retainer and disconnect the power cable from the power supply
being removed.
Step 3 Loosen the captive screw on the power supply.
Step 4 Grasp the power supply handle with one hand and slide it out of the chassis.
Step 5 Install a blank filler panel if the power supply bay is to remain empty.
Statement 166
Installing a Power Supply
To install a power supply, follow these steps:
Step 1 Ensure that the system (earth) ground connection has been made. For ground connection instructions,
see the “Installing the Switch in a Cabinet with Insufficient Front Clearance” section on page 2-11.
Step 2 If the power supply bay has a filler panel, loosen the screws holding the panel and remove the panel.
Step 3 Verify that the power switch is in the off (0) position on the power supply you are installing. See
Figure 2-21 for the location of the power switch.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-36
OL-17468-02
Page 93

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
94976
PWR-845-AC
100-240V 12-5A
50/60 Hz
INPUT OK
FAN OK
OUTPUT FAIL
ALL FASTENERS MUST BE FULLY ENGAGED
PRIOR TO OPERATING OF POWER SUPPLY
5
1
2 3
4
94975
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-21 845-W AC Power Supply Front Panel
1 Power switch 4 AC power connection
2 Power cable retainer 5 Captive screw
3 Power supply LEDs
Step 4
Hold the power supply by the handle and orient it as shown in Figure 2-22, and then slide it into the
power supply bay, ensuring that it is fully seated in the bay.
Figure 2-22 Handling an 845-W AC Power Supply
Step 5
Tighten the power supply captive screws.
Step 6 Plug the power cable into the power supply, and tighten the screw on the power cable retainer to ensure
the cable cannot be pulled out.
Note Depending on the outlet receptacle on your power distribution unit, you may need the optional
jumper power cord to connect the Cisco MDS 9200 Series to your outlet receptacle. See the
“Jumper Power Cord” section on page C-11.
OL-17468-02
Step 7 Connect the other end of the power cable to an AC power source.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-37
Page 94

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Caution In a system with dual power supplies, connect each power supply to a separate power source.
In case of a power source failure, the second source will most likely still be available.
Step 8 Turn the power switch to the on (|) position on the power supply.
Step 9 Verify power supply operation by checking that the power supply LEDs are in the following states:
• Input Ok LED is green.
• Fan Ok LED is green.
• Output Fail LED is off.
Removing and Installing the Fan Module
The fan module is designed to be removed and replaced while the system is operating without presenting
an electrical hazard or damage to the system, provided the replacement is performed promptly.
This section includes the following topics:
• Removing a Fan Module, page 2-39
• Installing a Fan Module, page 2-39
You will need a flat-blade or number 2 Phillips screwdriver to perform these procedures.
Caution The Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches have internal temperature sensors that are capable of shutting
down the system if the temperature at different points within the chassis exceed certain safety thresholds.
To be effective, the temperature sensors require the presence of airflow; therefore, in the event a fan
module is removed from the chassis, the Cisco MDS 9000 Family switches will be shut down after five
minutes to prevent potentially undetectable overheating. However, the switches will shut down sooner if
the higher-level temperature threshold is exceeded.
2-38
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 95

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
LINK-
GE1
GE2
1
2
3
4
LINK-
1
0
1
1
1
2
1
3
1
4
5
6
7
8
9
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
1
6
122002
MDS 9216i
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Figure 2-23 shows a fan module partially installed in the Cisco MDS 9200 Series.
Figure 2-23 Fan Module
Removing a Fan Module
Warning
Step 1 Loosen the two captive screws on the fan module by turning them counterclockwise, using a flat-blade
Step 2 Grasp the fan module with both hands and pull it outward; rock it gently, if necessary, to unseat the power
Step 3 Pull the fan module clear of the chassis.
When removing the fan tray, keep your hands and fingers away from the spinning fan blades. Let the
fan blades completely stop before you remove the fan tray.
To remove a fan module, follow these steps:
or number 2 Phillips screwdriver if required.
connector from the backplane.
Caution If the switch is powered on, you must hot-swap another fan module into this switch within five
Installing a Fan Module
Statement 258
minutes.
OL-17468-02
To install a fan module, follow these steps:
Step 1 Hold the fan module with the Fan Status LED at the top (see Figure 2-23).
Step 2 Place the fan module into the front chassis cavity so it rests on the chassis, lift the fan module up slightly
to align the top and bottom chassis guides, then push the fan module into the chassis until it seats in the
backplane and the captive screws make contact with the chassis, and tighten the captive screws.
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
2-39
Page 96

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Removing and Installing Components
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Step 3 Listen for the fans if the switch is powered on. You should immediately hear them operating. If you do
not hear them, ensure that the fan module is inserted completely in the chassis and the faceplate is flush
with the outside surface of the chassis.
Step 4 Verify that the Fan Status LED is green. If the LED is not green, one or more fans are faulty. If this
occurs, contact your customer service representative for a replacement part.
Note If you purchased this product through a Cisco reseller, contact the reseller directly for technical support.
If you purchased this product directly from Cisco, contact Cisco Technical Support at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/warp/public/687/Directory/DirTAC.shtml.
Removing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
When removing the Cisco MDS 9200 Series from the rack, remove the slider brackets first, and then the
front screws fastening the front rack-mount brackets to the rack.
Note The slider rail and C brackets do not have a stop mechanism when sliding in and out. If the front of the
chassis is unfastened from the rack and the chassis slides forward on the slider rails, it may slip off the
end of the rails and fall out of the rack.
To remove the Cisco MDS 9200 Series from the rack, follow these steps:
Step 1 Remove the screws fastening the slider bracket to the mounting rails.
Step 2 Slide the slider brackets out of the C brackets on the sides of the Cisco MDS 9200 Series.
Step 3 Ensure the weight of the Cisco MDS 9200 Series is supported; for example, being held by another
person.
Step 4 Remove the screws fastening the front rack-mount brackets on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series to the
mounting rails, and remove the Cisco MDS 9200 Series from the rack.
2-40
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 97

Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
CHAP T ER
3
Connecting the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
The Cisco MDS 9200 Series provides the following types of ports:
• Console port (interface module)—An RS-232 port that you can use to create a local management
connection.
• COM1 port (interface module)—An RS-232 port that you can use to connect to an external serial
communication device such as a modem.
• MGMT 10/100 Ethernet port (interface module)—An Ethernet port that you can use to access and
manage the switch by IP address, such as through the CLI or Cisco Fabric Manager.
• Fibre Channel ports (supervisor and switching modules)—Fibre Channel ports that you can use to
connect to the SAN, or for in-band management.
• Other port types provided by the optional module, if installed, such as the iSCSI and/or FCIP over
Gigabit Ethernet ports on the 4-port or 8-port IPS modules.
Caution When running power and data cables in overhead or subfloor cable trays, Cisco strongly recommends
that power cables and other potential noise sources must be located as far away as practical from network
cabling that terminates on Cisco equipment. In situations where long parallel cable runs cannot be
separated by at least 3.3 ft (1 m), Cisco recommends shielding any potential noise sources by housing
them in a grounded metallic conduit.
OL-17468-02
This chapter includes the following topics:
• Preparing for Network Connections, page 3-2
• Connecting to the Console Port, page 3-2
• Connecting to the COM1 Port, page 3-4
• Connecting to the MGMT 10/100 Ethernet Port, page 3-5
• Connecting to a Fibre Channel Port, page 3-6
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
3-1
Page 98

Chapter 3 Connecting the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
FAN
STATUS
FAN-MOD-2
1
2
122004
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
TAT
U
S
SY
S
TE
M
R
ES
ET
CONSOLE
MGMT 10/100
MDS 9216i
COM1
—SPEED LINK—
LINK-
—SPEEDLINK—
STATUS
156789
LINK— —SPEED
10 11 12 13 14234
GE1
LINK-
GE2
Console
Preparing for Network Connections
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Preparing for Network Connections
When preparing your site for network connections to the Cisco MDS 9200 Series, consider the following
for each type of interface, and gather all the required equipment before connecting the ports:
• Cabling required for each interface type
• Distance limitations for each signal type
• Additional interface equipment required
Connecting to the Console Port
The console port (labeled Console) is an RS-232 port with an RJ-45 interface. (See Figure 3-1.) The
console port is an asynchronous (async) serial port; any device connected to this port must be capable
of asynchronous transmission.
Cisco recommends using this port to create a local management connection to set the IP address and
other initial configuration settings before connecting the switch to the network for the first time.
Caution The console port can be used to connect to a modem, however, Cisco recommends using the COM1 port
for this purpose. If you decide to connect the console port to a modem, do not connect it while the switch
is booting; connect either before powering the switch on or after the switch has completed the boot
process.
Figure 3-1 Connecting to the Console Port on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
You can use the console port to perform the following:
• Configure the Cisco MDS 9200 Series from the CLI.
• Monitor network statistics and errors.
• Configure SNMP agent parameters.
• Download software updates.
3-2
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
Page 99

Chapter 3 Connecting the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
Connecting to the Console Port
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Note To connect the console port to a computer terminal, the computer must support VT100 terminal
emulation. The terminal emulation software—frequently an application such as HyperTerminal or
Procomm Plus—makes communication between the Cisco MDS 9200 Series and a computer possible
during setup and configuration.
To connect the console port to a computer terminal, follow these steps:
Step 1 Configure the terminal emulator program to match the following default port characteristics: 9600 baud,
8 data bits, 1 stop bit, no parity.
Step 2 Connect the supplied RJ-45 to DB-9 female adapter or RJ-45 to DB-25 female adapter (depending on
your computer serial port) to the computer serial port. Cisco recommends using the adapter and cable
provided with the switch.
Step 3 Connect the console cable (a rollover RJ-45 to RJ-45 cable) to the console port (see Figure 3-1) and to
the RJ-45 to DB-9 adapter or RJ-45 to DB-25 adapter at the computer serial port.
Note For configuration instructions, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide or the
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
OL-17468-02
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
3-3
Page 100

Chapter 3 Connecting the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
FAN
STATUS
FAN-MOD-2
1
2
122005
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16
S
TA
TU
S
SY
S
TE
M
R
ES
ET
CONSOLE
MGMT 10/100
MDS 9216i
COM1
—SPEED LINK—
LINK-
—SPEEDLINK—
STATUS
156789
LINK— —SPEED
10 11 12 13 14234
GE1
LINK-
GE2
Connecting to the COM1 Port
Send documentation comments to mdsfeedback-doc@cisco.com
Connecting to the COM1 Port
Note The COM1 port is not supported for connection to a console.
The COM1 port (labeled COM1) is an RS-232 port with a DB-9 interface. (See Figure 3-2.) You can use
this port to connect to an external serial communication device such as a modem. For information about
how to turn off hardware flow control, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI Configuration Guide or the
Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide.
Figure 3-2 Connecting to the COM1 Port on the Cisco MDS 9200 Series
To connect the COM1 port to a modem, follow these steps:
Step 1 Connect the DB-9 serial adapter to the COM1 port.
Note Connect the modem to the COM1 port using the adapters and cables provided with the accessory
kit.
Step 2 Connect the RJ-45 to DB-25 modem adapter to the modem.
Step 3 Connect these two adapters using the RJ-45 to RJ-45 rollover cable (or equivalent crossover cable).
Step 4 If the default settings for the COM1 port were modified, see the Cisco MDS 9000 Family CLI
Configuration Guide or the Cisco MDS 9000 Family Fabric Manager Configuration Guide for
information on this feature.
3-4
Cisco MDS 9200 Series Hardware Installation Guide
OL-17468-02
 Loading...
Loading...