Page 1

This document is exclusive property of Cisco Systems, Inc. Permission is granted to print and copy
this document for noncommercial distribution and exclusive use by instructors in the IP Telephony
course as part of an official Cisco Networking Academy Program.
Page 2
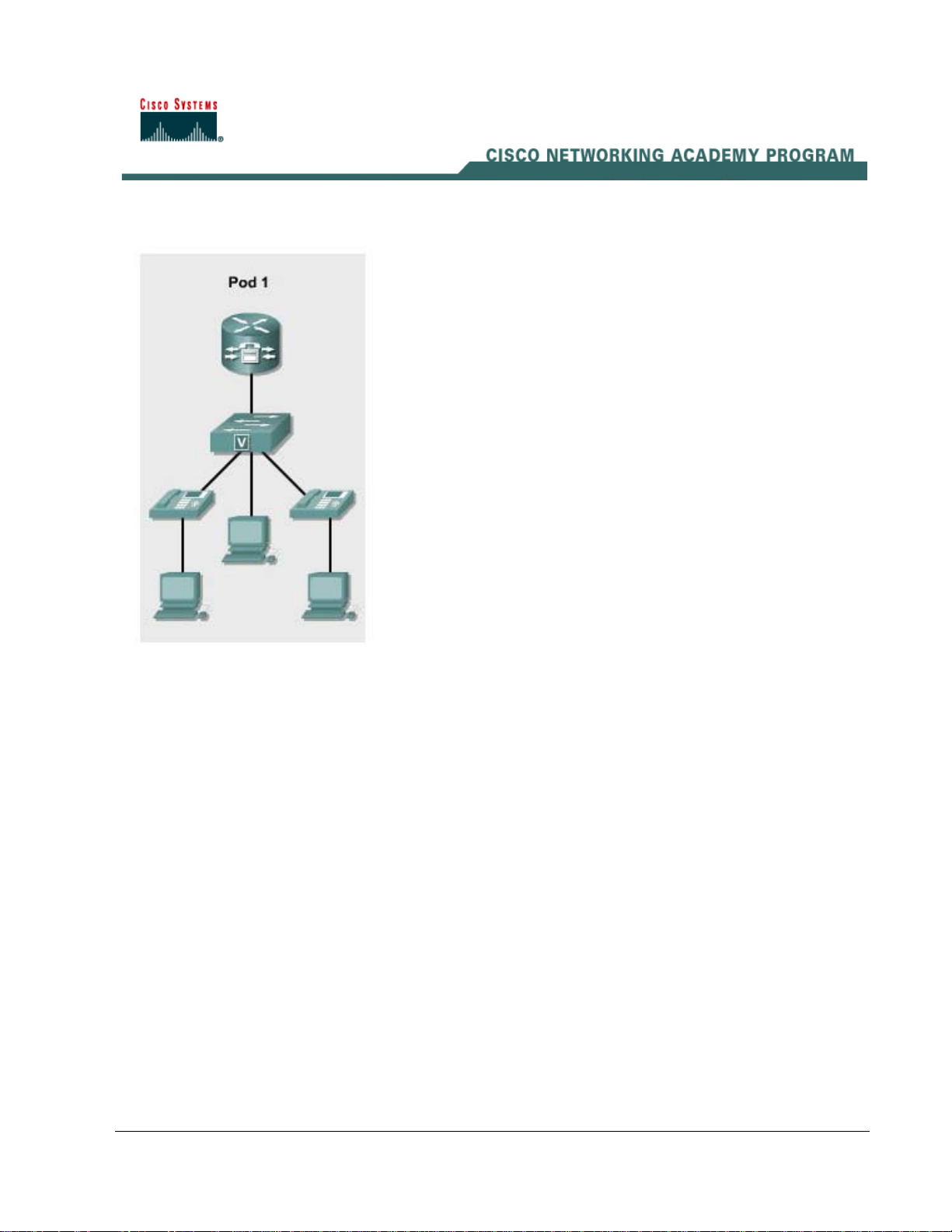
Lab 2.1.1a Basic Setup for the CME Router with Switch Module
Objectives
• Configure a Cisco router in preparation for CallManager Express (CME)
• Configure a switch in preparation for CME
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with switch module
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
In this lab, the ACME.com Company has decided to deploy CallManager Express in the enterprise.
First, the router portion (including the switch module) of CallManager Express must be configured.
The routers and switch module should be configured using the information found in IP Telephony
Table 1.
2 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 3

Step 1 Assign a Pod Number
a. Ask the instructor to assign a pod number to the lab group.
What pod number was the group assigned? ____________________
Step 2 Erasing Configuration and VLANs from the Router
a. The router with a four port switch module stores VLAN information in Flash memory. To ensure
the router does not have a previous configuration, connect a console cable to the router and
power on the router.
b. Erase the switch VLAN database and startup-configuration file by using the delete
flash:vlan.dat, erase startup-config, and reload commands.
Router# delete flash:vlan.dat
Router# erase startup-config
Router# reload
Step 3 Basic CME Router Configuration
a. On the router, enter privilege mode and then configuration mode.
b. Change the hostname of the router. Use the command hostname CMERouterX, where X is the
pod number assigned to the group. Throughout the rest of the lab, use IP Telephony Table 1
parameters based on the pod number assigned.
Router(config)# hostname CMERouterX
c. Set the enable secret password to cisco. (Do not deviate from this password.)
d. Use the command no ip domain-lookup to disable name resolution since there is no DNS
server in the classroom lab.
CMERouterX(config)# no ip domain-lookup
e. Note that router commands are IOS and model specific. Examples given in this lab are the most
common configurations seen. However, the command may vary slightly. For example, on a 1760
router the VTY lines are 0 through 15 instead of 0 through 4. Configure all the router VTY lines
with parameters similar to the following:
CMERouterX(config)# line vty 0 4
CMERouterX(config-line)# password cisco
CMERouterX(config-line)# login
CMERouterX(config-line)# logging synchronous
f. Configure the console port parameters.
CMERouterX(config)# line console 0
CMERouterX(config-line)# password cisco
CMERouterX(config-line)# login
CMERouterX(config-line)# logging synchronous
3 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 4

g. Create two VLANs—one for the voice VLAN and one for the data VLAN. VLAN 1, the
management VLAN, is already created. Note that the X shown in the command is the pod
number.
CMERouterX# vlan database
CMERouterX(vlan)# vlan X0 name Data state active
CMERouterX(vlan)# vlan X5 name Voice state active
h. Go into the configuration mode for the management VLAN by entering global configuration mode
and typing the command interface vlan 1. The management VLAN is the VLAN used to
remotely manage network devices such as routers and switches.
CMERouterX(config)# interface vlan 1
i. Configure the management VLAN interface with an IP address appropriate for the management
VLAN. From the interface configuration mode, enter the IP address for the management VLAN
based on the information found in IP Telephony Table 1. Use the command ip address 10.X.0.1
255.255.255.0 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-if)# ip address 10.X.0.1 255.255.255.0
j. Go into the configuration mode for the data VLAN by entering global configuration mode and
entering the command interface vlan X0 (where X is the pod number). For example, if the group
was assigned to Pod 1, the command would be as follows: interface vlan 10
CMERouterX(config)# interface vlan X0
k. Configure the data VLAN interface with an appropriate IP address. From the interface
configuration mode, enter the IP address for the data VLAN based on the information found in IP
Telephony Table 1. Use the command ip address 10.X0.0.1 255.255.255.0 command (where X
is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-if)# ip address 10.X0.0.1 255.255.255.0
m. If a host was configured on the same data VLAN, what would be the host default gateway IP
address? ________________________________________________________________
n. Go into the configuration mode for the voice VLAN by entering the global configuration mode
and entering the command interface vlan X5 (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config)# interface vlan X5
o. Configure the voice VLAN with the appropriate IP address. Enter the IP address for the voice
VLAN based on the information found in IP Telephony Table 1. Use the ip address 10.X5.0.1
255.255.255.0 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-if)# ip address 10.X5.0.1 255.255.255.0
p. Bring EACH of the created VLAN interfaces to a useable condition.
CMERouterX(config)# interface vlan x
CMERouterX(config-if)# no shutdown
q. Configure the EIGRP routing protocol by using the router eigrp 100 command to start an
EIGRP process with an autonomous system number of 100. Then enter the command
10.0.0.0, which enables and advertises EIGRP updates on all 10.0.0.0-configured interfaces.
network
CMERouterX(config)# router eigrp 100
CMERouterX
(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
4 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 5

Step 4 Configure the Router Switch Ports
a. Verify the slot into which the router switch four port module inserts by (1) viewing the router and
(2) using the show diag command. Look for the words 4 Port FE Switch.
CMERouterX# show diag
b. Based on the previous step, into what slot does the switch module insert? _________________
c. Use the show ip interface brief command to verify the slot and the format used for the
interface. For example in a 2811 ISR, the four ports list as FastEthernet 0/0/0, 0/0/1, 0/0/2, and
0/0/3.
d. Write the format in which the four ports list. _________________________________________
e. Ports 0 and 1 of the switch module will be used to connect the IP phones. These ports must be
configured as trunk modes, must have the trunking protocol configured, must identify the native
VLAN, and must identify the voice VLAN.
Note that the slot/port-adapter/port parameter that is typed depends on the router slot into which
the four port module inserts.
The native keyword defines this VLAN as the one that is not tagged with VLAN information
when a frame (from VLAN X0) crosses the trunk between the IP phone and the switch. This
allows the PC that connects to the IP phone to be on a different subnet than the IP phone and
still receive an IP address from a DHCP server. If a warning message appears, ignore it. If this
command does not work, the proper router is not being used.
IMPORTANT: Note that the following commands must be done on both port 0 and port 1. An
alternative to the interface fastethernet command is interface range fastethernet slot/port-
adapter/port command.
CMERouterX(config)# interface fastethernet slot/port-adapter/port
CMERouterX(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
CMERouterX(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan X0 (where X is
the pod number)
CMERouterX(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
CMERouterX(config-if)# switchport voice vlan X5 (where X is the pod
number)
CMERouterX(config-if)# no shutdown
f. What is the purpose of the dot1q parameter used in the previous step? ___________________
____________________________________________________________________________
Step 5 Verify VLAN Configuration
a. From privileged mode on the router, issue the show ip interface brief command and verify that
VLAN1, X0, and X5 (where X is the pod number) have IP addresses and that their status is up
and up.
CMERouterX# show ip interface brief
b. Are all three VLAN interfaces up and up and have the proper IP address? If not, troubleshoot as
necessary. __________
If the interfaces are not there, do not have an IP address or the correct IP address, or if their
status is not up and up, do not proceed until appropriate troubleshooting has been performed.
5 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 6

c. From privileged mode verify the port is properly configured as a trunk port by using the show
interfaces slot/port-adapter/port switchport command (where interface-id is the switch port
used to connect to the router).
CMERouterX# show interfaces fastethernet slot/port-adapter/port
switchport
d. What is the status of the switch port (shown as switchport in the command output)?
_____________________________________________________________________________
e. What is the status of the Administrative Mode? _____________________________________
f. What is the status of the Operational Mode? _________________________________________
g. What is the Operational Trunking Encapsulation that has been configured? _________________
h. What VLANs are trunked by default? _______________________________________________
i. The show interfaces trunk command can be used to verify trunk operations.
CMERouterX# show interfaces trunk
j. Based on the command output, what port(s) have trunking enabled?
_________________________________________________________________
k. Based on the command output, what VLAN is the native VLAN? (Note: The native VLAN is the
VLAN that does not tag a frame from this VLAN as it traverses the trunk with VLAN information.
It is also the VLAN that continues to cross the link between the router and the switch if the trunk
ever fails for any reason.) _________________________________________
l. Based on the command output, what VLANs are allowed on the trunk? ____________________
m. Based on the command output, what VLANs are participating in spanning tree and are in the
forwarding state? ______________________________
n. Connect a Cisco IP phone using a straight-through cable to the switch port 0. The port on the
bottom of the IP phone is labeled 10/100. Note that the IP phone will not work until CallManager
Express has been configured.
o. Using a second straight-through cable, connect the second phone to switch port 1 on the router.
6 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 7

Step 6 Save the Router Configuration
a. Save the router configuration by typing the following command:
CMERouterX# copy running-config startup-config
Note: Save the router configuration to a text file as well. These configurations will be required in
future labs.
7 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 8

Answers to 2.1.1a lab
1a. The pod number depends on what the instructor assigned.
3m.
10.X0.0.1 (Pod1 is 10.1.0.1; Pod2 is 10.2.0.1, etc.)
4b. Depends on the router being used
4d. Usually this answer will be something similar to the following: FastEthernet 0/0/0, 0/0/1, 0/0/2,
and 0/0/3 OR FastEthernet 1/0/0, 1/0/1, 1/0/2, and 1/0/3.
4f. DOT1Q is the parameter that specifies the IEEE 802.1Q trunking protocol to be used on the
subinterface. The 802.1Q trunking protocol is the most commonly used trunking protocol. The
alternative is ISL. Note many switches do not have both trunking protocols.
5b. Yes
5d. Enabled
5e. trunk
5f. trunk
5g. dot1q
5h. all of the VLANs
5j. The answer depends on the slot number into which the switch module inserts, but an example
is Fa0/0/0 and Fa0/0/1.
5k. VLAN X0 (where X is the pod number)
5l. 1-1005 (all of them)
5m. VLANs 1, X0, and X5 (where X is the pod number)
8 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1a Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 9
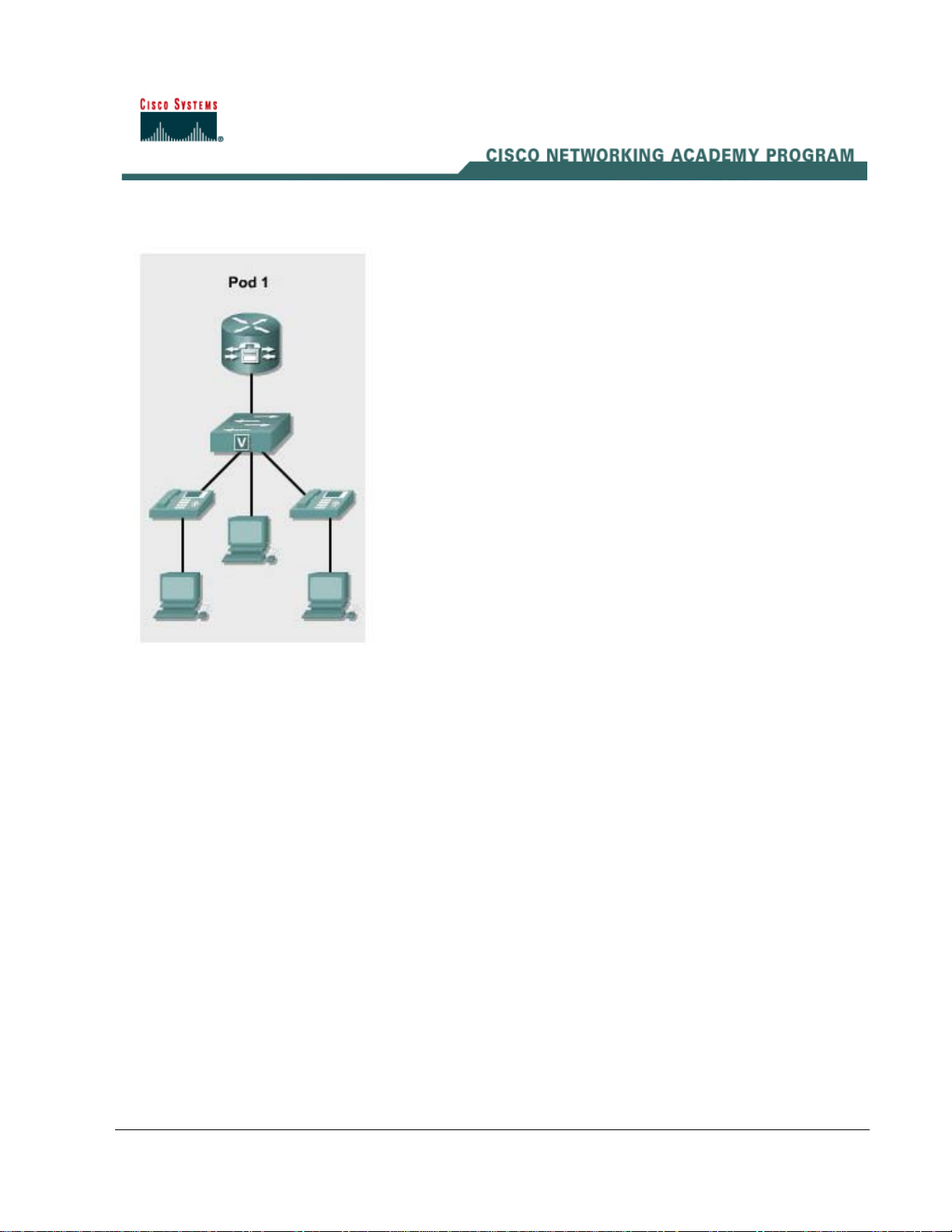
Lab 2.1.1b Basic Setup for the CME Router and Switch
Objectives
• Configure a Cisco router in preparation for CallManager Express (CME)
• Identify the DHCP configuration commands
• Configure a switch in preparation for CME
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline Power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
In this lab, the ACME.com Company has decided to deploy CallManager Express in the enterprise.
First, the router portion of CallManager Express must be configured. The routers and switches
should be configured using the information found in IP Telephony Table 1.
Step 1 Assign a Pod Number
a. Ask the instructor to assign a pod number to the lab group.
What pod number was the group assigned? ____________________
9 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 10

Step 2 Basic CME Router Configuration
a. Connect to the console port of a Cisco CallManager Express router and power it on. If the router
has a configuration already on it, erase the router and reload it.
b. Enter privilege mode, and then configuration mode.
c. Change the hostname of the router. Use the command hostname CMERouterX, where X is the
pod number assigned to the group. Throughout the rest of the lab, use IP Telephony Table 1
parameters based on the pod number assigned.
Router(config)# hostname CMERouterX
d. Set the enable secret password to cisco. (Do not deviate from this password.)
e. Use the command no ip domain-lookup to disable name resolution since there is no DNS
server in the classroom lab.
CMERouterX(config)# no ip domain-lookup
f. Note that router commands are IOS and model specific. Examples given in this lab are the most
common configurations seen. However, the command man vary slightly. For example, on a 1760
router the VTY lines are 0 through 15 instead of 0 through 4. Configure all the router VTY lines
with parameters similar to the following:
CMERouterX(config)# line vty 0 4
CMERouterX(config-line)# password cisco
CMERouterX(config-line)# login
CMERouterX(config-line)# logging synchronous
g. Configure the console port parameters.
CMERouterX(config)# line console 0
CMERouterX(config-line)# password cisco
CMERouterX(config-line)# login
CMERouterX(config-line)# logging synchronous
h. Create a subinterface for the management VLAN by entering global configuration mode, and
typing the command interface fastethernet 0/0.1. The management VLAN is the VLAN used to
remotely manage network devices such as routers and switches.
Note: Depending on the model and physical configuration of the router, the interface could be a
FastEthernet port or a Gigabit Ethernet port. Also, the router may have a different physical
interface number (i.e., FastEthernet 0 or GigabitEthernet 2/0). If unsure about which interface is
installed, verify the name of the Ethernet ports on the router by using the show running-config
or show ip interface brief command.
CMERouterX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.1
What types of Ethernet interface(s) are on the router? ______________________________
i. Configure the subinterface for trunking by entering the command encapsulation dot1q 1. The 1
is the management VLAN number. The command instructs the router to use this subinterface for
VLAN 1. If a warning message appears, ignore it. If this command does not work, the proper
router is not being used.
CMERouterX(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q 1
10 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 11

j. Configure the management VLAN subinterface with an IP address appropriate for the
management VLAN. From the subinterface configuration mode, enter the IP address for the
management VLAN based on the information found in IP Telephony Table 1. Use the command
ip address 10.X.0.1 255.255.255.0 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-subif)# ip address 10.X.0.1 255.255.255.0
If a switch was configured with an IP address on the same management VLAN, what would be
the default gateway IP address configured on the switch? ________________________
k. Create a subinterface for the data VLAN by entering the global configuration mode and entering
the command interface fastethernet 0/0.X0 (where X is the pod number). For example, if the
group was assigned to Pod 1, the command would be as follows: interface fastethernet 0/0.10
CMERouterX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0.X0
l. Configure the subinterface for trunking by entering the command encapsulation dot1q X0
(where X is the pod number) native. The native keyword defines this VLAN as the one that is
not tagged with VLAN information when a frame (from VLAN X0) crosses the trunk between the
router and the switch. This allows the PC that connects to the IP phone to be on a different
subnet than the IP phone and still receive an IP address from a DHCP server. If a warning
message appears, ignore it. If this command does not work, the proper router is not being used.
CMERouterX(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q X0 native
What is the purpose of the dot1q portion of the command?
___________________________________________________________________
m. Configure the data VLAN subinterface with an IP address appropriate for the data VLAN. From
the subinterface configuration mode, enter the IP address for the data VLAN based on the
information found in IP Telephony Table 1. Use the command ip address 10.X0.0.1
255.255.255.0 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-subif)# ip address 10.X0.0.1 255.255.255.0
If a host was configured on the same data VLAN, what would be the host default gateway IP
address? ________________________________________________________________
n. Create a subinterface for the voice VLAN by entering the global configuration mode, and
entering the command interface fastethernet 0/0.X5 (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-subif)# interface fastethernet 0/0.X5
o. Configure the subinterface for trunking by entering the command encapsulation dot1q X5
(where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-subif)# encapsulation dot1q X5
p. Configure the voice VLAN subinterface with an IP address appropriate for the voice VLAN. Enter
the IP address for the voice VLAN based on the information found in IP Telephony Table 1. Use
the ip address 10.X5.0.1 255.255.255.0 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-subif)# ip address 10.X5.0.1 255.255.255.0
q. Bring the Ethernet interface to a useable condition.
CMERouterX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/0
CMERouterX(config-if)# no shutdown
11 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 12

r. Configure the EIGRP routing protocol by using the router eigrp 100 command to start an
EIGRP process with an autonomous system number of 100. Then enter the command network
10.0.0.0, which enables and advertises EIGRP updates on all 10.0.0.0-configured interfaces.
CMERouterX(config)# router eigrp 100
CMERouterX
s. Connect a straight-through cable between the Ethernet port on the router and port 1 on the
switch.
t. Verify connectivity by viewing the interfaces on the router.
CMERouterX# show ip interface brief
u. Is the Ethernet interface in a functional state?_______
If not, troubleshoot and resolve the problem. Do not proceed until the interface is up and up.
What is the status of the Status and Protocol states for the main Ethernet interface (not the
subinterfaces)? ____________________________________________________________
v. Save the router configuration.
(config-router)# network 10.0.0.0
Step 3 Erasing the CME Switch
Note: The configuration output used in the lab is produced from a 2950 switch. Any other switch or
IOS may produce different output. The following steps are to be executed on each model of switch
unless specifically instructed otherwise.
a. Connect a console cable to the switch and power on the switch.
b. Erase the switch VLAN database and startup-configuration file by using the delete
flash:vlan.dat, erase startup-config, and reload commands.
Switch# delete flash:vlan.dat
Delete filename [vlan.dat]? [Enter]
Delete flash:vlan.dat? [confirm] [Enter]
Switch# erase startup-config
Switch(config)# reload
Step 4 Examine the current switch configuration
a. Examine the running configuration file:
Switch# show running-config
b. How many Ethernet or Fast Ethernet interfaces does the switch have? _____________
c. What is the range of values shown for the VTY lines? _________________________
d. Examine the current contents of NVRAM as follows:
Switch# show startup-config
%% Non-volatile configuration memory is not present
Note that on some switches, the message does not appear.
e. If the switch gave the error message response, why does it appear?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
12 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 13

Step 5 Assign a name to the switch
a. Enter privilege mode and then configuration mode. Use the hostname CMESwitchX command
(where X is the pod number) to name the switch. Throughout the rest of the lab, use IP
Telephony Table 1 parameters based on the pod number assigned.
Switch# configure terminal
Switch(config)# hostname CMESwitchX
Step 6 Examine the current running configuration
a. From privileged mode, exam the current configuration that follows to verify that there is no
configuration except for the hostname:
CMESwitchX# show running-config
b. Are there any passwords set on the console or VTY lines? ______________________________
c. What does the configuration show as the hostname of this switch? _______________________
Step 7 Set access passwords
Enter line configuration mode for the console port. Set the password on the console port to cisco.
Configure the VTY lines with the password of cisco.
CMESwitchX# configure terminal
CMESwitchX(config)# line console 0
CMESwitchX(config-line)# password cisco
CMESwitchX(config-line)# login
CMESwitchX(config-line)# line vty 0 15
CMESwitchX(config-line)# password cisco
CMESwitchX(config-line)# login
Step 8 Set the command mode password
a. Set the enable secret password to cisco.
CMESwitchX(config)# enable secret cisco
b. Which password takes precedence, the enable password or enable secret password?
_____________________________________________________________________________
Step 9 Configure Layer 3 access to the switch
a. Set the IP address of the switch to 10.X.0.4/24 (where X is the pod number). Note: This is done
on the internal virtual interface VLAN 1.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface vlan 1
CMESwitchX(config-if)# ip address 10.X.0.4 255.255.255.0
CMESwitchX(config-if)# description Management VLAN
b. What is the purpose of the management VLAN? _____________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
13 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 14

c. Set the default gateway for the switch to 10.X.0.1 (where X is the pod number).
CMESwitchX(config)# ip default-gateway 10.X.0.1
d. What is the purpose of putting a default gateway on a switch? (Be specific.)
__________________________________________________________________
__________________________________________________________________
Step 10 Verify and activate the management VLANs settings
a. Verify the interface settings on VLAN 1 as follows:
CMESwitchX# show interfaces vlan 1
b. What is the bandwidth on this interface? ____________________________________________
c. What are the VLAN states: VLAN1 is ___________________________________________, line
protocol is _________________________.
d. What is the queuing strategy being used? ___________________________________________
e. Enable the virtual interface using the no shutdown command.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface vlan 1
CMESwitchX(config-if)# no shutdown
Step 11 Save the configuration
a. The basic configuration of the switch has just been completed. Backup the running configuration
file to NVRAM.
Note: This will ensure that the changes made will not be lost if the system is rebooted or
loses power.
CMESwitchX# copy running-config startup-config
Step 12 Configure the switch port as a trunk port
a. From global configuration mode, access switch interface port 1 that connects to the router.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/1
b. From interface configuration mode, set the switch to use the IEEE 802.1Q trunking protocol.
Note: If this command does not work on the switch, the switch only supports the 802.1Q trunking
protocol and does not have to be programmed with this command. The next step may have to be
completed before this step if an older switch is being used.
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
c. From interface configuration mode, set the switch to trunking mode.
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
d. The native VLAN is the one VLAN that does not have the VLAN information tagged onto the
frame as it travels across the trunk. From interface configuration mode, specify which VLAN is
the native VLAN (where X is the pod number).
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan X0
14 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 15

e. Besides trunking, what are the other modes for which a switch port can be configured?
_____________________________________________________________________________
f. From enable mode verify the port is properly configured as a trunk port by using the show
interface interface-id switchport command (where interface-id is the switch port used to
connect to the router).
CMESwitchX# show interfaces fastethernet 0/1 switchport
g. What is the status of the switch port (shown as switchport in the command output)?
_____________________________________________________________________________
h. What is the status of the Administrative Mode? _____________________________________
i. What is the status of the Operational Mode? _________________________________________
j. What is the Operational Trunking Encapsulation that has been configured? _________________
k. What VLANs are trunked by default? _______________________________________________
l. Some switches have another command that can be used to verify trunking operations—show
interfaces trunk.
CMESwitchX# show interfaces trunk
m. If the show interfaces trunk command is available, what port(s) have trunking enabled?
_________________________________________________________________
n. If the show interfaces trunk command is available, what VLAN is the native VLAN? (Note: The
native VLAN is the VLAN that does not tag a frame from this VLAN as it traverses the trunk with
VLAN information. It is also the VLAN that continues to cross the link between the router and the
switch if the trunk ever fails for any reason.) _________________________________________
o. If the show interfaces trunk command is available, what VLANs are allowed on the trunk based
on the output from this command? _____________________________
p. If the show interfaces trunk command is available, what VLANs are participating in spanning
tree and are in the forwarding state? ______________________________
Step 13 Test connectivity across the trunk
a. From enable mode on the switch, ping the router IP address for VLAN1 (the management
VLAN). Refer to IP Telephony Table 1 for this address. (X in the command below refers to the
pod number.)
CMESwitchX# ping 10.X.0.1
b. Was the ping successful from the switch? _____________________________________
If the ping was unsuccessful, do not proceed until appropriate troubleshooting has been
performed and the ping is successful. Note that on some models of routers and switches the
speed and duplex must be manually configured on both ports.
c. Ping the router IP address for the voice VLAN and the data VLAN. Refer to IP Telephony Table
1 for IP addresses, if necessary. All pings should be successful when the trunk is working
correctly. Troubleshoot as necessary.
15 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 16

Step 14 Create VLANs on the switch
a. Manually create the data and voice VLANs in the VLAN database. The X in the VLAN number is
the pod number.
CMESwitchX# vlan database
CMESwitchX(vlan)# vlan X0
CMESwitchX(vlan)# vlan X5
CMESwitchX(vlan)# exit
Step 15 Configure switch ports for IP phones
a. Cable the two IP phones to switch ports 4 and 6 using straight-through cables.
b. Configure the two IP phone ports to use the IEEE 802.1Q trunking protocol using the switchport
trunk encapsulation dot1q command. This command is executed from interface configuration
mode.
Note that the next step may have to be completed before this step if an older switch is being
used.
Configure each switch port for the trunking encapsulation mode.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/4 (and 6)
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk encapsulation dot1q
c. Configure the two IP phone ports to be trunk ports with the switchport mode trunk command.
This command is executed from interface configuration mode.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/4 (and 6)
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport mode trunk
d. For the ports that connect to the IP phones, the switch must be configured so that 802.1Q knows
which VLAN contains voice traffic. This is done with the switchport voice vlan command. The
voice VLAN is X5, where X is the pod number. Refer to IP Telephony Table 1 for the IP
addressing scheme.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/4 (and 6)
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport voice vlan X5
e. The IP phone has a port used to connect a PC. The PC can (and should) be on a separate
VLAN from the IP phone. The IP phone connects to the switch via a trunk port. A trunk port can
carry multiple VLAN information. In order for the phone to operate on a different VLAN from the
phone, the switchport trunk native vlan X0 (where X is the pod number) command must be
used. The native VLAN is the VLAN that does not get tagged with VLAN information as frames
from this VLAN traverse the trunk. The native VLAN must be the same as the data VLAN for this
to work.
This command is done in interface configuration mode. The interface to use is the switch
interface to which one of the IP phones connects (the one that has a PC connected to the PC
port on the back of the IP phone). The X in the switchport command refers to the pod number.
CMESwitchX(config)# interface fastethernet 0/4 (and 6)
CMESwitchX(config-if)# switchport trunk native vlan X0
The IP phones will not register at this point because Call Manager Express has not been
configured on the router yet.
16 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 17

f. Save the switch configuration by typing the following command:
CMESwitchX# copy running-config startup-config
Note: Save the router and switch configurations to a text file as well. These configurations will be
required in future labs.
17 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 18

Answers to 2.1.1b lab
1a. The pod number depends on what the instructor assigned.
2h. The interfaces on the router depends on the router model and physical configuration being
used by the student.
2j. 10.X.0.1 (Pod1 is 10.1.0.1; Pod2 is 10.2.0.1, etc.)
2l. DOT1Q is the parameter that specifies the IEEE 802.1Q trunking protocol to be used on the
subinterface. The 802.1Q trunking protocol is the most commonly used trunking protocol. The
alternative is ISL. Note many switches do not have both trunking protocols.
2m.
10.X0.0.1 (Pod1 is 10.1.0.1; Pod2 is 10.2.0.1, etc.)
2u. Yes or the student needs to troubleshoot.
The status is supposed to be up and up.
4b. The number of interfaces depends on the switch model being used.
4c. The VTY values depends on which switch model is being used, but a common response will be
5 or 15.
4e. Because there is no configuration file located in NVRAM.
6b. No.
6c. CMESwitchX where X is the pod number.
8b. The enable secret command takes precedence over the enable password command.
9b. The management VLAN is the VLAN that is used to access the switch from a remote device.
The management VLAN is where an IP address is assigned to the switch.
9d. The default gateway on a switch allows an administrator to reach remote devices on different
networks from VLAN 1 from the switch command prompt.
10b. The answer depends on the type switch. A common answer is 1,000,000 Kbits.
10c. VLAN1 is administratively down
, line protocol is down.
10d. FIFO
12e. access and dynamic modes
12g. Enabled
12h. trunk
12i. trunk
12j. dot1q
18 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 19

12k. all of the VLANs
12m. If this command can be done, it is the port that the student is using to connect to the router,
port 1.
12n. VLAN X0 (where X is the pod number)
12o. 1-4094 (all of them)
12p. VLAN 1
13b. Yes
19 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.1b Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 20
Lab 2.1.2 Installing Cisco CME Software
Objective
• Install Cisco CallManager Express (CME) software on the router
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Cisco router IOS version that supports CallManager Express
• Workstation with Ethernet 0/100 NIC installed
• TFTP server application
• Access to Table 1 IP Telephony IP Addressing Scheme and VLAN Assignment document
In this lab the ACME.com Company has configured the router with a basic configuration, but the
version of IOS on the router does not support CallManager Express features. The version of IOS will
need to be updated. The router should already be configured. Redo Lab 2.1.1 if necessary.
Note: This lab may not be necessary if the IPVoice IOS is already installed. Use the show flash:
command on the router and see if the words IPVOICE appear in the name of the IOS image. This is
one quick indication that can be used to determine if this lab is necessary.
20 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 21

Step 1 Configure the TFTP server
Note: If the router has multiple Ethernet interfaces use the lowest numbered interface. For example, if
there are two Ethernet interface, 0 and 1, then 0 should be used.
a. Ensure the computer that has the TFTP server application loaded on it is connected to the
Ethernet port of the router. Be sure that the computer has an appropriate IP address and default
gateway assigned. See the IP Telephony Table 1 for IP addressing assignment. An example IP
address is 10.1.0.5 and default gateway of 10.1.0.1, where the 1 in the second octet is equal to
the pod number and the number in the fourth octet is 2, 3 or any number between 5 and 254.
b. Ensure that the appropriate router IOS file that supports CallManager Express is placed in the
default folder for the TFTP server application. Obtain this file from the instructor.
c. Open the TFTP server application.
d. Console to the router. From the router ping the TFTP server. Do not proceed unless the ping is
successful. Troubleshoot as necessary.
e. What address is assigned to the TFTP server? ____________________________________
Step 2 Update and Install Cisco CallManager Express IOS
a. From enable mode, copy the IOS image from the TFTP server to the router. The prompts may
vary depending on the model and IOS.
CMERouterX# copy tftp: flash:
Source filename? [Enter the IOS filename. It is best to copy and
past the filename into this section.]
Address or name of remote host? [Enter the address assigned to the
TFTP server. See step 1e.]
Destination filename? [The filename should be the same as what was
placed in the source filename and Enter can be pressed.]
When and if prompted to overwrite enter y for yes.
(Address or name of remote host is the IP address of the TFTP server. Source filename is
the filename of the Voice IOS located on the TFTP server. Destination filename is the same
name as Source filename. Contact the instructor to obtain the correct router IOS that
supports IP Telephony.)
An example of the process follows:
CMERouter1# copy tftp flash:
Address or name of remote host? 10.10.0.12
Source filename? c2800nm-ipvoice-mz.123-11.T3.bin
Destination filename? c2800nm-ipvoice-mz.123-11.T3.bin
Accessing tftp://10.10.0.12/ c2800nm-ipvoice-mz.123-11.T3.bin...
b. Was the TFTP transfer successful? _______________________
If not, troubleshoot until the transfer is successful. Do not proceed without a successful transfer.
21 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 22

c. Use the show flash command to verify that the IOS file is present in flash memory.
CMERouterX# show flash
For example:
-#- --length-- -----date/time------ path
1 24119024 Mar 24 2005 22:17:00 +00:00 c2800nm-ipvoice-mz.123-
11.T3.bin
32143304 bytes available (24119024 bytes used)
d. The following are the steps to load new system IOS image:
CMERouterX# configure terminal
CMERouterX(config)# boot system flash new_system_image_filename
CMERouterX(config)# exit
CMERouterX# copy running-config startup-config
CMERouterX# reload
When prompted to save the system configuration, enter no.
When prompted to confirm the reload, enter y.
e. Verify the system image file (IOS Image) is the correct one by using the show flash or show
version command. The system image file should match the filename used in step 2a.
CMERouterX# show version
For example:
Cisco IOS Software, 2800 Software (C2800NM-IPVOICE-M), Version
12.3(11)T3, RELEASE SOFTWARE (fc4)
Technical Support: http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Copyright (c) 1986-2005 by Cisco Systems, Inc.
Compiled Wed 26-Jan-05 02:49 by pwade
ROM: System Bootstrap, Version 12.3(8r)T7, RELEASE SOFTWARE
(fc1)
CMERouter1 uptime is 11 minutes
System returned to ROM by power-on
System image file is "flash:c2800nm-ipvoice-mz.123-11.T3.bin"
Cisco 2821 (revision 53.51) with 249856K/12288K bytes of
memory.
Processor board ID FHK0847F0QH
4 FastEthernet interfaces
2 Gigabit Ethernet interfaces
2 Serial(sync/async) interfaces
DRAM configuration is 64 bits wide with parity enabled.
239K bytes of non-volatile configuration memory.
62720K bytes of ATA CompactFlash (Read/Write)
Configuration register is 0x2102
f. Is the image on the router correct? ________________________________
If not, troubleshoot as necessary until this image is on the router.
22 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 23

Answers to 2.1.2 lab
1e. Student’s choice for IP address.
2b. Yes
2f. Yes
23 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 24
Lab 2.1.3 Connecting the IP Phone to a Switch
Objective
• Connect an IP phone to a switch and provide power to it
Equipment Requirements
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Two Cisco IP phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company wishes to implement IP telephony. In order to do so, the phones
must receive power in order to work.
• Cable the two IP phones to a switch
• Provide power to the phones using one or both methods
24 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 25

Step 1 Understanding the two types of switches
a. There are two types of switches that can be used with Cisco IP phones: (1) an inline power
switch and (2) a non-inline power switch. A switch that can provide power to another device such
as an IP phone has the words INLINE POWER stenciled on it as shown below.
A non-inline power switch does not have the words INLINE POWER stenciled on it. An example
of this type of switch is the 2950. The 2950 cannot provide power to other devices such as the
Cisco IP phone.
b. Use the Cisco web site to determine if any model of 29xx switch can provide inline power.
Record the results. __________________________________________________________
Step 2 Cabling the IP phone to an inline power switch
Note: If an inline power switch is not available, skip to Step 3.
a. Locate the two RJ-45 ports on the back of the IP phone.
b. What are the names of the two RJ-45 ports? ______________________________________
c. Connect a power cord to the switch that is to provide the inline power. The switch should power
on.
25 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 26

d. Connect a straight-through Ethernet cable from the 10/100 SW port on the IP phone to any 100
MB port on the inline power switch.
e. What indication is shown that the phone is receiving power? _________________________
__________________________________________________________________________
Step 3 Cabling the IP phone to a non-inline power switch
a. Connect power to the non-inline power switch.
b. In order to connect a Cisco IP phone to a non-inline power switch, a power injector is needed.
Look at the power injector and notice the two RJ-45 jacks on one end of the power injector.
26 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 27

The port on the left labeled 10/100BaseTX to Device is used to connect to the IP phone (via a
straight-through cable).The port on the right labeled 10/100BaseTX to Network is used to
connect to a non-inline power switch such as a 2950 switch (via a straight-through cable).
c. Connect a straight-through cable from the left power injector port labeled 10/100BaseTX To
Device to the IP phone port labeled 10/100 SW.
d. Connect a second straight-through cable from the right power injector port labeled
10/100BaseTX To Network to any non-inline power switch port.
e. At the opposite end of the power injector module there is a cable that goes to the power supply
adapter. The opposite end of the power supply adapter requires an AC power cord.
Plug an AC power cord into the AC adapter. Plug the other end of the AC power cord into an AC
wall outlet.
f. What indication is shown on the phone that power has been applied?
______________________________________________________________________________
_______________________
27 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 28

Answers to 2.1.3 Lab
1b. At the time this lab was written, the 2970 was the most powerful 29xx series switch and it does
not support inline power for all of its ports.
2b. 10/100 SW and 10/100 PC
2e. The phone starts displaying words on the screen. Also, when power is first applied, the buttons
on the bottom start lighting up sequentially.
3f. The phone starts displaying words on the screen. Also, when power is first applied, the buttons
on the bottom start lighting up sequentially.
28 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 29
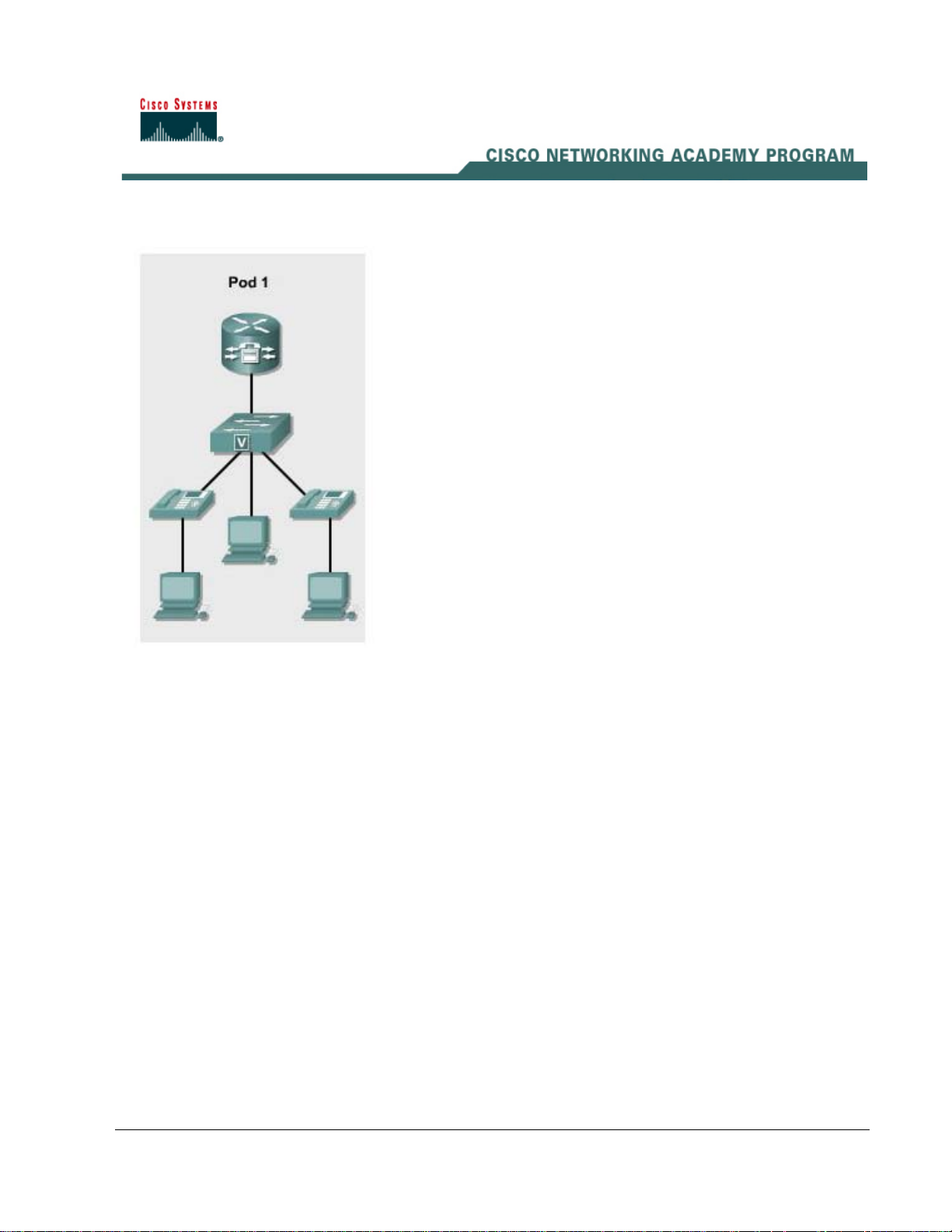
Lab 2.1.4 Resetting a 7900 Series Cisco IP Phone to Factory Defaults
Objective
• Erase the current configuration from an IP phone
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco IP Phone 79xx series
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
In this lab, the ACME.com Company has decided to deploy CallManager Express (CME) in the
enterprise. First, the IP phones must be reset. They were used in a test lab by the network support
staff and currently have various configurations. This process should be used when configuring any IP
phone that could have been previously configured.
Step 1 Provide power to the switch
a. Cable the Cisco IP phone to an inline power switch using a straight-through cable OR cable the
phone (with a straight-through cable) to a power module that connects to a non-inline power
switch.
b. Power on the switch.
c. Which method of providing power to the IP phone was chosen? __________________________
29 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 30

d. What is an advantage of using an in-line power switch? ________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Step 2 Reset the Cisco IP phone
a. On the IP phone press the following keys to unlock the Network Configuration menu: **#. Note:
No feedback will be given on the screen.
b. Press the Settings button on the phone. If the phone buttons are unlabelled, it is the button that
has a checkmark on the button.
c. Press the number 3 on the keypad to select the Network Configuration option.
d. Using the arrow keys scroll up and down to see the network configuration options. How many
options are available? ___________________________________________________________
e. Either scroll to the number 33 options or press the number 33 on the keypad. The Erase
Configuration option should now be displayed on the IP phone.
Note: A key to whether or not this works properly is that the symbol of an unlocked lock is
beside the words Network Configuration. If the symbol is a lock press the following keys: **#.
f. Press the button located under the Yes option.
g. Press the button located under the Save option.
What message appears on the IP phone screen? ___________________________________
h. Press the button that corresponds to Cancel.
i. Press the Save option.
j. What message appears on the IP phone screen? ___________________________________
30 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 31

Answers to 2.1.4 lab
1c. Depends on the equipment available in the classroom.
1d. An inline power switch can provide power to remote devices such as an IP phone through an
Ethernet cable. This saves power outlet in the office where the remote device is located.
2d. Depends on the IP phone being used.
2g. All Fields Saved
2j. All Changes Saved
31 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 2.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 32

Lab 3.1.1 CME Automated Phone Setup
Objectives
• Identify the basic steps to automatically configure Cisco CallManager Express (CME)
• Configure two dual-line phones
• Verify the IP phones register and calls can be placed between two IP phones
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-in-line power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with FastEthernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• Access to Table 1 IP Telephony IP Addressing and VLAN Assignment document
• Access to Table 2 IP Telephony Dial Plan Assignment document
In this lab the ACME.com Company has decided to use the setup utility to configure the Cisco
CallManager Express router and phones. This lab relies on the labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and 2.1.3 being
successfully completed. The lab uses information from Table 2 IP Telephony Dial Plan.
32 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 33

Step 1 Configure Cisco IP Telephony Express using the Automated Method
a. From privilege exec (EXEC) mode on the router, use the show running-config command and
view the current configuration. Save or print a copy of the current configuration to compare with
changes later in this lab.
CMERouterX# show running-config
b. From global configuration mode, enter the command
CMERouterX(config)# telephony-service setup
Note: If a mistake is made in the setup program, the mistake can be remedied at the end of the
utility.
c. When prompted with the choice to setup the DHCP service, type y, and press Enter.
d. The IP network of the DHCP pool for voice devices is 10.X5.0.0 (where X is the pod number).
Refer to IP Telephony Table 1 for the DHCP pool information. This command allows the IP
phone to get an IP address from a DHCP pool that will be created on the router.
What pod number is assigned? ___________________________
e. The subnet mask for the DHCP network is 255.255.255.0 for all pods.
f. The TFTP server IP address will be the Cisco CallManager Express router with an IP address of
10.X5.0.1 (where X is the pod number). Option 150 is an optional DHCP option which allows the
IP telephony device to obtain configuration information (files) from the TFTP server.
g. The default router for the pool will also be 10.X5.0.1 (where X is the pod number).
h. Answer yes to the question regarding starting the telephony service setup.
i. For the source IP address, enter 10.X5.0.1 (where X is the pod number).
j. Accept the default port of 2000 by pressing the Enter key. Skinny will be discussed in a later lab.
k. When asked how many phones to configure, respond with 4. Note that even though only two
phones are being configured, selecting 4 will allow up to four IP phones to be configured at this
time. This value can be changed from the command prompt if necessary.
l. When asked whether dual-lines are desired, answer y, and press Enter.
Dual-line IP phones have one voice port with two channels to handle two independent calls. This
capability enables call waiting, call transfer, and conference functions on a phone-line button. In
dual-line mode, each IP phone and its associated line button can support one or two calls.
Selection of one of two calls on the same line is made using the Navigation button located below
the phone display.
m. Select the language that is desired on the phone. (The default of English may be accepted by
simply pressing the Enter key.)
n. Select the country for call progress tones. (If in the United States, the default may be used by
just pressing the Enter key.)
In−band call progress tones (for example, ringback and busy tones) and announcements (for
example, "The number you have dialed is no longer in service") are required to successfully
signal voice calls. Call progress tones can be generated by the originating, terminating or
intermediate devices.
33 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 34

o. Refer to the Table 2 IP Telephony Dial Plan (back of lab manual) to find the appropriate first
extension number. Use the first column in the table to locate the pod being used. The second
column lists extension numbers. From the second column pick the first number in the range
listed for the pod being used. For example, if Pod 1 is being used then the first extension number
is 5000.
p. When asked if DID (Direct-Inward-Dialing) is used, answer y, and press Enter.
DID is a local phone company service that provides a block of phone numbers used to call into a
company's PBX system. With DID, individual phone numbers can be assigned to each person or
PC without having to have a physical line into the PBX for each person’s connection.
q. When asked for the full E.164 number, enter the value from IP Telephony Table 2 that is specific
for the pod. For example, if Pod 1 was being used the E.164 DID number would be 5105555000.
A fully qualified E.164 number contains a country code (issued by the ITU), area code
(sometimes known as a STD code), and the local telephone number. Since the country has been
selected already, it is just the area code and the phone number.
What E.164 number is being used on this router? ____________________________________
r. When asked if forwarding to voicemail (voice message service) is desired, enter y, and press
Enter.
s. Enter the extension number for voicemail based on the pod number assigned. The extension
numbers for voicemail can be seen in the IP Telephone Table 2.
What voicemail extension is being used? _________________________________________
t. Press the Enter key to accept the default of 18 seconds for Call Forward timeout.
u. When asked if any of the information is to be changed, select yes to change an option, or no to
use the current settings and to exit out of the utility. If no mistakes were made in the previous
steps enter n, press Enter, and proceed to the Step1v. If any mistakes were made enter y, press
Enter, and go back to Step 1c.
v. Watch the console output to see if the phones register. Output similar to the following should be
seen on the terminal window. Note that this may take several minutes.
Mar 2 23:57:09.080: %IPPHONE-6-REGISTER: ephone-1 :SEP000F2470F92E
IP:10.15.0.11 Socket:1 DeviceType:Phone has registered.
Note: The power to the phone may need to be removed and reapplied in order to get the phone
to re-request an IP address and register with Call Manager Express.
Step 2 Confirm Correct Setup of CME
a. Place a call between the two IP phones. Pick up the handset on one phone and enter the
number of the second IP phone. Once a connection has been made, reverse the process. Make
a call from the second IP phone to the first one. Calls can also be placed by entering the number
of the other IP phone and pressing the speaker button on the bottom right of the phone. Note
that the speaker button could be pressed first and then the number being dialed.
b. If the phones do connect to one another, perform troubleshoot as necessary. Reset the phone
using steps from a previous exercise if necessary.
34 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 35

Step 3 Review Changes to the Running Configuration
a. From privilege exec (EXEC) mode, enter the show running-config command and view the
changes made in the configuration. Pay particular attention to the telephony-service section.
Compare this configuration with the configuration saved prior to this lab.
CMERouterX# show running-config
b. Write the commands that changed, and the commands that were created as a result of the
automatic telephony-service configuration utility used in this lab. Use additional paper if
needed.______________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
Step 4 Connect a PC to the IP phone port
a. Connect a PC using a straight-through cable to the port labeled 10/100 PC on the bottom of the
IP phone.
b. Configure the PC to receive an IP address from a DHCP server.
c. From privileged mode on the router, create a DHCP pool for the data VLAN (the PC). The X in
the network and default-router commands represents the pod number.
CMERouterX(config)# ip dhcp pool DATA
CMERouterX(dhcp-config)# network 10.X0.0.0 255.255.255.0
CMERouterX(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.X0.0.1
d. In the DHCP pool just created reserve the first 10 IP addresses for networking devices. The X in
the ip dhcp excluded-address command represents the pod number.
CMERouterX(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.X0.0.1 10.X0.0.10
e. Renew the IP address on the PC. It may be necessary to use the commands ipconfig /release
and ipconfig /renew if the PC had already gotten an address in the excluded-address range.
f. Did the PC receive an IP address? If yes, what address did it receive? If no, troubleshoot as
necessary.
35 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 36

Step 5 Reload Router
a. Do NOT save the router configuration. However, it is recommended that you copy the current
configuration to a text file that can be used later.
b. Reload the router so that a manual configuration can be completed in the next task. Do NOT
save the changes.
36 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 37

Answers to 3.1.1 lab
1d. Student dependent
1q. Pod dependent
1s. Pod dependent
3b.
ip dhcp pool ITS
network 10.15.0.0 255.255.255.0
option 150 ip 10.15.0.1
default-router 10.15.0.1
!
tftp-server flash:P00303020214.bin (perhaps)
!
telephony-service
load 7960-7940 P00303020214 (perhaps)
max-ephones 4
max-dn 4
ip source-address 10.15.0.1 port 2000
auto assign 1 to 4
create cnf-files version-stamp Jan 01 2002 00:00:00
dialplan-pattern 1 5105555... extension-length 4
voicemail 6001
max-conferences 4
transfer-system full-consult
!
ephone-dn 1 dual-line
number 5000
call-forward busy 6001
call-forward noan 6001 timeout 18
!
ephone-dn 2 dual-line
number 5001
call-forward busy 6001
call-forward noan 6001 timeout 18
!
ephone-dn 3 dual-line
number 5002
37 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 38

call-forward busy 6001
call-forward noan 6001 timeout 18
!
ephone-dn 4 dual-line
number 5003
call-forward busy 6001
call-forward noan 6001 timeout 18
!
ephone 1
mac-address 0013.C43B.4999
type 7940
button 1:1
!
ephone 2
mac-address 000A.B7B1.33F5
type 7960
button 1:2
!
ephone 3
!
ephone 4
4f. Yes. The PC’s IP address should probably be 10.X0.0.11.
38 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 39

Lab 3.1.2 CME Manual Phone Setup
Objective
• Configure IP Phones using the manual configuration process
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with specific files for IP phone (basic CME .tar
file)
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• One Cisco IP phone
In this lab the ACME.com Company has decided to use the manual setup process to configure the
Cisco CallManager Express router and phones. Use IOS commands to achieve the following goals:
• Manually configure the IP phones with an extension and connect them to the network
• Assign a name to the IP phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and 2.1.3 being successfully completed. The lab uses information
referenced in IP Telephony Table 1 and IP Telephony Table 2.
39 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 40

Step 1 Verify if the Telephony Service is Running
a. If necessary, put the basic configuration from 3.1.1 on the router and switch.
b. Ensure that NO phones are connected to the switch at this time.
c. Access the Cisco CallManager Express router and use the show running-config | begin tele
command to verify that the telephony service has not been configured. The begin tele
parameter will search the running configuration for the first instance of the letter combination of
tele, which is really meant to be telephony-service. If no telephony-service is configured nothing
will be displayed and the CMERouterX prompt will be seen again. If a configuration exists, use
the no telephony-service command to erase any existing configuration.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin tele
CMERouterX(config)# no telephony-service
Step 2 Configure DHCP for the IP Phones
a. Enter ip dhcp exclude-address 10.X5.0.1 10.X5.0.10 (where X is the pod number) to disallow
certain addresses from a DHCP pool that is about to be created in the next step.
CMERouterX(config)# ip dhcp excluded-address 10.X5.0.1 10.X5.0.10
b. Enter the command ip dhcp pool CMEVoiceX (where X is the pod number) to name the DHCP
pool and begin configuration of the parameters that will be served to remote devices.
CMERouterX(config)# ip dhcp pool CMEVoiceX
c. Use the network 10.X5.0.0 255.255.255.0 command to set up the range of addresses that will
be used.
CMERouterX(dhcp-config)# network 10.X5.0.0 255.255.255.0
d. Enter the default-router 10.X5.0.1 (where X is the pod number) to assign a default gateway to
the IP phone.
CMERouterX(dhcp-config)# default-router 10.X5.0.1
e. With CallManager Express, the IP phones receive their initial configuration information and
phone firmware from the TFTP server associated with the CME router. The phones usually get
the IP address of their TFTP server using the DHCP option 150 command. When using CME,
the TFTP server address obtained by the phone should point to the CME router IP address.
Enter option 150 ip 10.X5.0.1 to assign the TFTP server address as the CME router. The Cisco
IP phone downloads the image configuration files from this address (the router). The
configuration files will be located on the voice-capable router.
CMERouterX(dhcp-config)# option 150 ip 10.X5.0.1
Step 3 Verify and Configure Firmware
a. From privileged mode, use the show flash: command to verify the IP phone firmware files that
are present. The firmware files for a 7960 and 7940 will start with “P003.” For example,
P00303020214.bin. Do not continue to Step 4 until the IP phone firmware files are present in
flash.
For a 28x1 router: If these files are not there, there is a file that the instructor must obtain from
the Cisco site that starts with the letters “cme-basic” and has a file extension of “.tar”. An
example of the filename is cme-basic-123-11T.tar.
40 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 41

Note: The .tar file must match the IOS version on the CME router.
The file must be extracted and uploaded to the router Flash memory from a TFTP server. Copy
the .tar file into the appropriate TFTP server folder. From privileged mode, use the archive tar
/xtract tftp://tftp_server_ip_address/.tar_filename flash:. An example of this command is as
follows: archive tar /xtract tftp://10.3.0.33/cme-basic-123-11T.tar flash:.
For a 1760 router (on an older IOS): If these files are not there, the instructor must download
the IOS zip file and the Pxxx files are part of the zip file. For this model of router and this IOS,
upload any and all files that start with P003 from the downloaded file to the router Flash memory
using a TFTP server. An example of this command is copy tftp:P00303020214.bin flash:.
b. In the space provided, write down the firmware files present in flash memory that relate to IP
phones (the P003 files).
CMERouterX# show flash:
_________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________
Step 4 Basic Phone Configuration
a. From global configuration mode, use the tftp-server flash:P003XXXX.XXX command to allow
the firmware files to be accessed through the TFTP server service running on the router. An
example of this command is as follows: tftp-server flash:P00303020214.bin
CMERouterX(config)# tftp-server flash:P003XXXXXXXX.XXX
Note: The filename typed after the flash: parameter is case-sensitive.
Repeat this command for all “P003” firmware files present in Flash memory.
b. From global configuration mode, enter telephony service mode.
CMERouterX(config)# telephony-service
c. To see the maximum allowable number of ephones (another name for IP phones) that this
system can use enter the command max-ephones ?.
d. In the space provided, write the maximum number of phones supported by the current router:
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# max-ephones ?
_________________________________________________________________
e. Set the maximum number of IP phones to two, as this will be sufficient for the classroom lab.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# max-ephones 2
The max-dn command specifies the maximum number of directory numbers or virtual voice
ports supported by the router. The maximum number is IOS and platform-dependent. The
default number is zero.
To see the maximum allowable number of directory numbers that this system can use enter the
command max-dn ?.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# max-dn ?
f. In the space provided, write the maximum number of directory numbers supported by the router
and IOS being used:
41 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 42

CMERouterX(config-telephony)# max-dn ?
_________________________________________________________________
g. Use the max-dn command to configure the maximum number of directory numbers to 20, as this
will be sufficient for the classroom lab.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# max-dn 20
h. The load command updates the Cisco IOS Telephony Services (Cisco ITS) configuration file for
a specific type of IP phone to add the name of the correct firmware file that the phone should
load. This filename also provides the version number for the phone firmware that is in the file.
Cisco IP phones update themselves with new phone firmware whenever they are initially started
or reloaded. When a phone is started or rebooted, the phone reads the configuration file to
determine the name of the firmware file it should load and then looks for that firmware file on a
TFTP server.
Note: A separate load command is needed for each type of phone (although the 7940 and 7960
phones have the same firmware and share the 7960-7940 keyword).
Another keyword used with this command is the name of the firmware file. With the load
command, do not specify the file extension.
Specify the firmware version and associate it with a model of phone by entering the command
load model firmware_filename_without_extension. An example of this command when using
a 7940 and/or 7960 IP phone model is load 7960-7940 P00303020214.
Note: The tar filename used with the load command is entered without the filename extension
(such as .bin). Also, the filename is not case-sensitive with this command. Before using the load
command, view the model numbers available by typing load ?.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# load ?
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# load model filename
Was the 7960-7940 model number used as part of the command? If not, why not? __________
____________________________________________________________________________
i. The IP phone will attempt to transfer a configuration file that it needs called XmlDefault.cnf.xml.
This file is automatically generated by the CME router through the use of the ip source-address
command and is placed in router memory. The XmlDefault.cnf.xml file contains the IP address
that the phones used to register for service. The phones use the SCCP (Skinny Client Control
Protocol) to do this. SCCP is commonly referred to as simply Skinny or the Skinny protocol.
Enter the ip source-address command to define the address and port number where the Cisco
CallManager Express router is listening for registrations (Skinny messages). This address
should correspond to a valid CME router IP address. Note the X in the command is the pod
number.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# ip source-address 10.X5.0.1 port 2000
42 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 43

j. Use the create cnf-files command to build XML configuration files that will be used by the
phones during the boot process.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# create cnf-files
k. What message(s) did the router display when the create cnf-files command was entered?
_________________________________________________________________________
_________________________________________________________________________
l. The keepalive command sets the time interval (in seconds) between messages that are sent
from the phone to the CME router. The default is 30 seconds, which is normally adequate. If the
default is set to too large a value, it is possible that notification will be delayed when a system
goes down.
m. What is the maximum number of seconds that can be set using the keepalive command and
how long is this in hours?
__________________________________________________________________________
n. Set the keepalive interval to 10 seconds.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# keepalive 10
o. Use the show running-config | begin tele command to view the results of the manual
configuration.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin tele
p. Ephone-dn stands for Ethernet phone directory number. It represents a line that connects a
voice channel to a phone so that calls can be made. An ephone-dn has one or more extensions
or phone numbers associated with it to allow calls to be made. An ephone-dn is similar to a
phone line. Each ephone has a number to identify it during the configuration process.
The ephone-dn command creates one virtual voice port and one or more dial peers. This
command automates the process of associating dial peers. The number of ephone-dns that are
created corresponds to the number of simultaneous calls that can be made because each
ephone-dn represents one virtual voice port in the router. This means that if you want more than
one call to the same number to be answered simultaneously, multiple ephone-dns (virtual voice
ports) are needed.
There are two types of ephone-dns: single-line and dual-line. On the most basic level, the single-
line option has one phone number associated to it. A dual-line can have one or two numbers
associated with it. The single-line option should be used when phone buttons have a one-to-one
correspondence to the regular phone lines that come into a CME system. The dual-line option
allows making two call connections at the same time using one phone line button.
Ensure no IP phones are plugged into the switch.
From global configuration command, type ephone-dn 1 ?
q. What two options are available? __________________________________________________
43 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 44

r. Add an ephone-dn for the first line appearance on the first phone in the pod by entering the
ephone-dn 1 dual-line command. The dual-line parameter defines the type of ephone-dn is
being created.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 1 dual-line
In ephone-dn mode enter the number X000 command (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# number X000
s. Enter a name that will be associated with this DN by entering the name firstname lastname
command. Either make up a name or use a student’s name. Example name Ray Hampton.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# name firstname lastname
Exit e-phone-dn configuration mode by typing exit.
t. From global configuration mode, enter the command ephone 1 to enter ephone configuration
mode for the first phone in the pod.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone 1
u. The MAC address of the IP phone will be needed in the next step. The MAC address is on a
sticker on the bottom of the phone. The sticker is normally located in the center. Upon close
inspection, the letters MAC are stenciled directly to the left of the white sticker that contains the
MAC address. In the space provided, write down the MAC of the first IP phone.
_________________________________________________________________
v. Assign the MAC address to ephone 1 with the mac-address H.H.H (where H is the four
hexadecimal characters). Note that the periods must be inserted between each set of four
characters, and the letters are not case-sensitive. An example entry is mac-address
0013.c43b.4999.
CMERouterX(config-ephone)# mac-address H.H.H
44 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 45

w. The button command is used to define properties to the buttons located to the right of the IP
phone’s LCD. The button command has a number that follows it with the number 1 representing
the top button on the IP phone. The number is followed by a separator character that specifies
phone characteristics. For example, the colon separator assigns the phone a normal ring, a
single pulse for internal calls and a double pulse for external calls.
CMERouterX(config-ephone)# button 1:1
Step 5 Verify Phone Registration
a. From privileged mode, enter the debug ephone register command.
CMERouterX# debug ephone register
b. Plug in the IP phone with MAC address configured previously.
c. View the ephone registration debugging output. This may take a few moments. Verify that the
phone has registered and the proper DN appears with the line.
d. Once the phone has registered, what is the last line of the debug output?
___________________________________________________________________________
e. Enter undebug all to turn off all debugging.
CMERouterX(config)# undebug all
f. Save the router configuration. It will be used to complete the next lab.
45 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 46

Answers to 3.1.2 lab
3b. Answers will vary according to IOS version, but common answers will be similar to the
following: P00303020214.bin and P00305000301.bin.
4d. 52 (2821 with 12.3.11T); 30 (1760 with 12.3(8)T3. Note that this may vary according to router
model and IOS version.
4f. 192 (2821 with 12.3.11T); 150 (1760 with 12.3(8)T3. Note that this may vary according to
router model and IOS version.
4h. IP phone dependent, but the phone that is part of the lab pack is the 7940 phone which means
the 7960-7940 model is used
4k. Creating CNF files, CNF-FILES: Clock is not set or synchronized, retaining old versionStamps
May 18 22:38:31.308: %IPPHONE-6-REG_ALARM: Name=SEP0013C43B4999 Load=3.1(MF.G2)
Last=CM-NAKed
*May 18 22:38:31.308: %IPPHONE-6-REGISTER_NEW: ephone-1:SEP0013C43B4999 IP:10.15
.0.11 Socket:1 DeviceType:Phone has registered.
*May 18 22:38:31.308: %IPPHONE-6-REG_ALARM: 25: Name=SEP000D2890D043 Load=6.0(4.
0) Last=Initialized
CMERouter3(config-telephony)#
*May 18 22:38:39.644: %IPPHONE-6-UNREGISTER_NORMAL: ephone-1:SEP0013C43B4999
IP:
10.15.0.11 Socket:1 DeviceType:Phone has unregistered normally.
4m. 65535; 18.2
4q. A carriage return (the default) which indicates a single line ephone directory number, and the
parameter dual-line.
4u. The MAC address depends on the IP phone.
5d. ephone-1[1]:Already done SkinnyCompleteRegistration
Instructor notes: The firmware files that are needed for each model of IP phone can be found by
performing a search for Cisco CallManager Express using any of the search engines. (At the time of
thi s wr i t i n g , t h e U RL i s “ www. c i s co . c o m / u n i ver c d / c c / td / d o c / p r oduct/voice/its/cme32/cme322sp.htm”.)
46 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 47

Lab 3.1.3 CME Partially Automated Phone Setup
Objective
• Configure an IP phone using the partially automated process
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with .tar configuration files already extracted
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP Phones (one of which was configured in Lab 3.1.2 lab)
In this lab the ACME.com Company has decided to use the partially automated setup to configure
the Cisco CallManager Express router and phones. Use IOS commands to achieve the following
goals
• Configure the second IP phone through the use of the auto assign command
• Attach the second IP phone to the network
NOTE: This lab relies on lab 3.1.2 being successfully completed. Redo lab 3.1.2 if necessary to
configure one IP phone before starting this lab.
47 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 48

Step 1 Add a Second IP Phone by using the Auto Assign Method
a. Ensure the second IP phone is not connected to the switch. Add a second ephone-dn by using
the ephone-dn 2 dual-line command.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 2 dual-line
b. Use the number X001 command to add a DN (where X is the pod number).
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# number X001
c. Enter telephony service mode by entering the telephony-service command from global
configuration mode.
CMERouterX(config)# telephony-service
d. The auto assign command is used to partially automate the IP phone configuration process.
The auto assign command specifies a range of ephone-dn numbers to assign newly discovered
IP phones. This method is used when there are multiple phones to install and each phone has a
unique extension number.
A phone type can be specified so that all 7940 IP phone models receive an extension in a
particular range and all 7960 models receive an extension in a different range of numbers.
View the models supported by the auto assign command by typing the following command:
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# auto assign 2 to 2 type ?
e. How many IP phone models are listed? _________________________________________
f. For this lab, the basic concept of automatic number assignment is being demonstrated, so
simply enter the command auto assign 2 to 2 from telephony-service configuration mode.
Step 2 Connect an IP Phone
a. From privileged mode, enter the debug ephone pak command, which allows ephone packets to
be displayed.
b. Connect the second IP phone to the appropriate switch port that has been configured for IP
Telephony. Verify the switch configuration if necessary.
c. View the ephone pak debugging output. This may take a few moments. Once the phone has
registered, what is the last line of the debug output?
___________________________________________________________________________
d. Verify that both phones are registered and configured by typing the show ephone command.
e. What indication is shown in the output to prove that both phones are configured properly?
___________________________________________________________________________
f. From one of the IP phones, press the lower right button that has a speaker icon. A dial tone
sounds.
g. After approximately 10 seconds of no input, what sound emits from the phone?
__________________________________________________________________________
h. Is this the sound you normally hear on an analog phone when the phone is taken off the hook
and a number has not been dialed? _________________________
i. Press the lower right button again to cancel the speaker function.
48 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 49

j. Lift the handset of the first IP phone and dial the other IP phone by pressing the four digit
identifier of the second phone. This number is located in the upper right display of the second
phone.
k. If the second IP phone rings, save your configuration by using the copy running-config
startup-config. If unsuccessful, troubleshoot as necessary.
49 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 50

Answers to 3.1.3 lab
1e. IOS dependent, but a common answer is 12.
2c. The message that appears is IOS dependent, but an example of the message is as follows:
%IPPHONE-6-REGISTER: ephone-2:SEP000D2890D043 IP:10.15.0.12. The important thing to
remember is that the message states that a particular phone has registered.
2e. Each ephone lists a section that has the word REGISTERED at the end of the line.
2g. An annoying, repeating tone that sounds like any phone when a number has not been dialed.
2h. Yes (if in the U.S.)
50 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 3.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 51

Lab 4.1.1 Configuring a FXS Port
Objective
• Configure a router FXS port for an analog phone
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with a FXS port
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• One analog phone with RJ-11 cable
• One IP phone
In this lab the ACME.com Company wants to be able to reuse an analog phone for emergency calls.
The analog phone plugs into the router FXS port. A similar configuration could be done for an analog
fax machine or another analog device.
• Configure the router for FXS capability
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and 3.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
51 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 52

Step 1 Verify FXS interface
a. Power on the router and switch.
b. Connect the IP phones. Test them by calling from one phone to another.
c. Use the show hardware privileged mode command to verify a FXS interface is installed in a
router.
d. How many FXS interfaces are installed based on the command output? ___________________
e. Look at the router and notice how the slots where WICs are installed are numbered. On a 2800
series router the slots are numbered to the side of the cards. On a 1760 or 2600 series router,
the slots are numbered below the WIC slot.
f. What slot is the FXS card installed into the router? ______________________________
g. Use the show voice port summary command to see a brief summary of the voice ports
installed on a router. The Ports column shows the slot that the FXS WIC is installed in the router.
The Ports column shows the WIC in a slot/subunit/port format.
h. How are numbers shown for the FXS WIC in the Ports column of the command output?
__________________________
i. Use the show voice port slot/subunit/port command to see detailed information about the
FXS card. For example, if the FXS WIC lists as 0/3/0 and 0/3/1 in the Ports column, the
command would be show voice port 0/3/0 or show voice port 0/3/1.
j. What is the Operation State of the voice port? _________________________________
k. What is the Administrative State of the voice port? ______________________________
l. Use the show running-config | begin voice-port command to see the section of the
configuration that deals with the voice ports. Notice that the syntax following voice-port is the
same as the previous show commands.
m. Using the show running-config command, can you determine whether the voice card is a FXS
or FXO card? ____________
Step 2 Connect Analog Phone
a. Connect an analog phone to FXS port 0 on the router using a phone cable. The FXS ports are
labeled with a 0 or a 1. Reference the photo below.
52 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 53

b. Access global configuration mode on the router and configure the FXS port for connectivity. The
first step is to configure a dial-peer for POTS connectivity.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 1 pots
c. The destination-pattern number command defines the phone number that can be used to
reach the analog phone. Use Table 2 Router FXS Port 0 column to locate a number that
corresponds to the appropriate pod. (For example, Pod 3 would use the command: destination-
pattern 5555088.) Note that the destination-pattern command can be used in other, more
flexible scenarios.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# destination-pattern number
d. The port X/X/0 command associates a dial peer with a specific voice port. Another way of
looking at this is that when someone dials the number listed in the destination-pattern
command, the call is routed to the voice port referenced in this command. The first X is the slot,
the second X is the voice interface subunit, and the 0 is the port number. This slot, subunit, and
port numbers are the same numbers researched in previous questions.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# port X/X/X
e. Save the router configuration.
f. From the analog phone dial the four digits extension of either IP phones. The IP phone should
ring. Troubleshoot if necessary until the IP phone rings.
g. What number shows on the IP phone when the analog phone rings? ______________________
h. From the IP phone, dial the seven digits for the analog phone. This number is the number that
showed on the IP phone display in the previous step.
i. Does the analog phone ring? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. __________________________
53 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 54

Answers to Lab 4.1.1
1d. The answer is router dependent, but the common answer is 2.
1f. The answer is router dependent.
1h. The answer is router model dependent.
1j. Dormant
1k. Up
1m. No.
2g. Pod dependent: Pod 1 5555028; Pod 2 5555058; Pod 3 5555088; Pod 4 5555128
2i. Yes
54 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 55

Lab 4.1.2 Configuring a FXO Port
Objective
• Configure a router FXO port for an analog phone
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with a FXO port
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Adtran
• Two IP phones
• Two analog phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, and 4.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company has configured the IP phones and now wishes to configure the
analog connection to the PSTN. This lab will allow an outbound call only.
55 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 56

Step 1 Configure the FXO Port
a. Connect a RJ-11 phone cable from the lowest numbered FXO port on the router to a port on the
Adtran Octal FXS card.
b. What port on the Adtran was used to connect the FX0 router port? _______________________
c. What slot does the FXO card use on the router? ______________________________________
d. Use the show running-config | begin voice-p command to verify the slot number and the
format of the slot number.
e. Write the format shown in the show running-config command output of the FXO port 0. ______
f. From global configuration mode, use the command voice-port slot/subunit/port to enter the
configuration for the FXO port. The slot/subunit/port is the numbers representing the FXO card
shown in the show running-config command. An example of this command is voice-port 0/2/0
CMERouterX(config)# voice-port slot/subunit/port
g. Enter the ring number 2 command to set the FXO port to answer after two rings. The default
number of rings is one ring. Normally the default is fine so that incoming calls are answered
quickly. If other equipment that can be used to answer incoming calls (such as a fax machine),
the ring number value might want to be set to a higher value to give the equipment sufficient
time to respond. In that case, the FXO interface would answer the call if the other equipment did
not answer the incoming call within the configured number of rings.
This command is not applicable to FXS ports because these types of ports do not receive ringing
on incoming calls.
CMERouterX(config-voiceport)# ring number 2
Step 2 Configure the Dial Peer
a. From global configuration mode, create an analog dial peer with the command dial-peer voice 5
pots.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 5 pots
b. Use the command destination-pattern 5556... to set the digits that will match this dial-peer.
This command sets the pattern to any call that comes in destined for 5556XXX where the X’s are
any numbers from 0 to 9. The periods shown in the command define the dial pattern digit as any
number.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# destination-pattern 5556...
c. Use the command port slot/subunit/port to associate the FXO port being used with dial-peer
number 5.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# port slot/subunit/port
d. The router needs to know which phone number digits to forward for voice calls. Use the
command forward-digits all to forward all the digits (the full length of the destination dial
pattern) to the PSTN (the Adtran).
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# forward-digits all
e. Connect an analog phone to a port on the Adtran Octal FXS card. Ensure a second analog
phone connects to the router FXS port 0.
56 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 57

f. From the analog phone attached to router FXS port, dial the number associated with the analog
phone attached to the Adtran. The phone numbers used on the Adtran Octal FXS ports are as
follows: port 1 phone number is 555-6001; port 2 is 555-6002; port 3 is 555-6003, etc. The
analog phone connected directly to the Adtran port should ring.
g. Does the called analog phone ring? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting before
proceeding. ____________
h. From enable mode on the router, debug the dial peer information.
CMERouterX# debug voice dialpeer all
i. While viewing the debug output, list the line that proves that the dial peer works correctly.
_______________________________________________________________________
j. Turn the debugging off.
CMERouterX# undebug all
k. Test the configuration by calling from an IP Phone to the analog phone attached directly to the
Adtran.
l. Did the call work? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting before proceeding. ___________
57 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 58

Answers to Lab 4.1.2
1b. Student’s choice
1e. Router model dependent. An example on a 2811 router is 0/2/0.
2g. Yes
2i. List of Matched Outgoing Dial-peer(s):
1: Dial-peer Tag=5
2l. Yes
58 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 59

Lab 4.1.3 Configuring PRI Interface and DID
Objective
• Configure a router POTS and PRI interface
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router with a T1 PRI port
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Two IP phones
• Two analog phones
• Adtran
• Special T1 cable
59 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 60

This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, and 4.1.1, being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company has decided that the analog connection to the PSTN is not
sufficient and, as a result, a PRI will be added to give additional capacity and to add DID capability.
The analog connection will be kept for a secondary connection to the PSTN. Configure the PRI with
the following settings.
Note: This lab uses the Adtran for simulating a PBX. Ensure you have the loaded the latest Adtran
IP Telephony configuration for this lab. If you are using the four port Quad T1/PRI card in the Adtran,
ensure the card is in slot four of the Adtran chassis. A special cable is used to connect the router T1
PRI port to the Adtran T1 port; a standard crossover or straight-through cable will not work. If you
have to make a cable, the RJ-45 connector pinouts are 1-4, 2-5, 4-1, 5-2.
There are multiple types of network modules (NMs) that can be used for T1 connections. If the router
has a network module it labeled as NM-DHV2-1T1/E1, the special commands are provided in the
lab.
Step 1 Locate the T1 Port on the CME Router
a. Use the show diag command to view the hardware installed. Locate the T1 card in the
command output and determine what slot it is installed.
b. In what slot does the show diag command show the T1 card? ___________________
c. Perform a show running-config command from enable mode.
d. Does the T1 interface appear in the output? If so, how does it list _______________________
Note that the first number listed in the output is the slot number. This number is important in a
later command.
IMPORTANT: If the T1 interface does not appear, use the global configuration command card
type t1 slot 1 (where slot is the number documented previously). Note that this command is
only needed on the NM–HDV2-1T1/E1 module.
e. Look at the router ports and locate a port that is labeled CTRL T1/E1 or CTRLR T1. This is the
T1 port. The T1 module is integrated into or inserted into the NM-HDV card.
f. Connect a cable from the router T1 port to a T1 port on the Adtran (see table below for correct
Adtran Port number). The Adtran can have just one T1 port, or an optional card can be installed
that provides four more T1s. The optional card is labeled Quad T1/PRI. The cable that is used to
connect the router T1 port to any Adtran T1 port is a special cable. Refer to the note at the
beginning of the lab for connector pinouts.
Pod Number Adtran T1/PRI Port Number
1 T1 Network Module- Port
2 Quad T1/PRI – Port 1
3 Quad T1/PRI – Port 2
4 Quad T1/PRI – Port 3
5 Quad T1/PRI – Port 4
60 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 61

Step 2 Configure the ISDN Switch Type
a. From global configuration mode, use the command isdn switch-type primary-ni to set the PRI
switch type. Note that this type must be the same one being used by the provider. In this lab, the
provider is the Adtran unit, and it has been configured with the primary-ni ISDN switch type.
CMERouterX(config)# isdn switch-type primary-ni
b. What other ISDN switch types are available? ________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
Step 3 Configure the T1 Controller
a. The network-clock-participate command allows the ports on a specific module or voice WAN
interface card (VWIC) to use the network clock for timing. The alternative is to restrict a device to
use its own clocking signals.
b. From global configuration mode, enter the command network-clock-participate wic
slot_number (where slot_number is the physical slot where the T1 port is installed). An
example is as follows: CMERouterX(config)# network-clock-participate wic 1
or CMERouterX(config)# network-clock-participate slot 1
CMERouterX(config)# network-clock-participate wic slot number
c. From global configuration, type controller t1 ? to determine what slot numbers are available. If
there is only one T1 card installed, only one number lists.
d. How many slot numbers are available in the help output? ____________
e. From global configuration mode, enter the mode to control the T1 port by using the controller t1
slot/port_or_subslot/port command. The slot/port_or_subslot/port parameters are the same
as what was researched earlier. An example in the 2811 router would be controller t1 1/0/0 or
controller t1 1/0 (depending on NM-HDV2-1T1/E1 type).
CMERouterX(config)# controller t1 slot/port_or_subslot/port
f. In T1 controller mode, enter the command framing esf to set the type of framing used.
CMERouterX(config-controller)# framing esf
g. In T1 controller mode, enter the command linecode b8zs to set the line coding.
CMERouterX(config-controller)# linecode b8zs
h. Set the clocking to the line with the clock source line command.
CMERouterX(config-controller)# clock source line
i. Use the command pri-group timeslots 1-12 to assign the first 12 channels to the PRI.
CMERouterX(config-controller)# pri-group timeslots 1-12
Note: If an error appears that there are not enough DSP resources, reduce the number of
timeslots to 8 (1-8 in the command).
The B channels on the TI should go up and messages to that effect should be seen on the
console.
61 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 62

j. Use the command show isdn status and verify that Layer 1 is ACTIVE, and that Layer 2 shows
MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHED.
CMERouterX# show isdn status
k. Did the show isdn status command output show the proper states (ACTIVE and
MULTIPLE_FRAME_ESTABLISHED)? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting. __________
l. In the show isdn status output notice on the second line of the output that a serial port is listed.
m. Write the serial interface port number as this number is shown in the command output. This
number is needed in the next step. _______________________
n. Use the show interface serial mod/port_or_subslot/port:23 to verify that the interface status
is up and up. Examples of this command on a 2811 router are show interface serial 1/0/0:23 or
show interface serial 1/0:23 (depending on the hardware being used).
CMERouterX# show interface serial mod/port_or_subslot/port:23
Step 4 Configure the Dial-Peer to Call the Analog Phone
a. Reference Table 2 to test the configuration. Before testing the TI, test standard phone
configuration by calling one of the IP phones from the analog phone attached to the router FXS
port. (Note: only four digits are needed for dialing.)
Note that if any connection exists between the router FX0 port and the Adtran unit, remove that
connection.
b. Does the analog phone to IP phone connection work properly? If not, troubleshoot as necessary.
_________________
c. Connect a second analog phone to the port on the Adtran Octal FXS that corresponds to your
pod number. For example, if pod 2 is being used, connect the analog phone to port 2 of the
Adtran Octal FXS card. Place a call from one of the IP phones to the analog phone connected
directly to the Adtran. (Note: The Adtran analog (FXS) port 1 phone number is 555-6001; port 2
is 555-6002; port 3 is 555-6003, etc.) Note that the call should not connect.
From the analog phone connected to the FXS router port, call the analog phone connected
directly to the Adtran analog (FXS) port. (555-600x, where x is the pod number).
d. Based on what has been learned thus far, why did the phone calls fail? __________________
__________________________________________________________________________
e. What audio and visual indications were shown on the IP phone when the call was made?
____________________________________________________________________________
f. A previous lab configured a dial-peer for the local FXS port. This step and the ones that follow
configure a dial-peer for a phone number on the simulated PBX (Adtran). This dial-peer will use
the PRI port on the router to access the cloud (the analog (FXS) port on the Adtran). The dial-
peer voice command creates a specific dial-peer for an analog connection.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 2 pots
g. Commands in this step tell the router which port to forward the call through for a specific number.
The destination-pattern number command defines the phone number that will be forwarded.
Different symbols can be used to define the number or range of numbers in the destination
62 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 63

pattern. For example, the command destination-pattern 555[4,6]… directs the router to send a
call starting with 5554XXX or 5556XXX out the specified port. The numbers in the brackets
mean either a 4 or a 6. The three periods represent any number 0-9. This step uses this
command syntax to allow any number starting with 5554 or 5556 to send out the port designated
in the next step.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# destination-pattern 555[4,6]…
h. The port X/X/X:23 command references the serial interface associated with the T1 controller
configured earlier on the router. Type do show running config at the command line to verify the
serial interface number, or refer to the earlier question. An example of a serial port interface
number is as follows: port 1/0/0:23 or port 1/0:23 (depending on what model of NM-HDV2-
1T1/E1 is being used).
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# port X/X/X:23
i. The router needs to know which phone number digits to forward for voice calls. Use the
command forward-digits all to forward all the digits (the full length of the destination dial
pattern) to the PSTN (the Adtran).
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# forward-digits all
j. Test the configuration by calling the analog phone attached to the Adtran analog (FXS) port from
an IP phone. The Adtran FXS port 1 phone number is 555-6001; port 2 is 555-6002; port 3 is
555-6003, etc.
k. Was the call successful? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting? _____
l. What message appears on the IP phone when a call is successfully made to the analog phone
connected directly to the Adtran FXS port? _________________________________
m. Save the router configuration.
Step 5 Configure the Dial-Peer to Call from the analog phone on the Adtran
a. Test the current configuration by calling the analog phone (seven digits) connected to the router
FXS port from the analog phone attached to the Adtran analog (FXS) port. The call should fail.
b. Did the call connect?_______ Why not? ____________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
c. A previous step configured a dial peer from the router to the simulated PBX (the Adtran). The
next few steps configure a dial peer that allows a call made from the analog phone connected to
the Adtran into the router using the PRI card.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 3 pots
d. Commands in this step tell the router which numbers to allow from the outside world into the
router for processing. The incoming called-number number command defines the numbers
allowed for an incoming call for a specific dial peer. Note that the three periods that follow the
four fives in this command are part of the command.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# incoming called-number 5555…
e. Use the direct-inward-dial to enable Direct Inward Dialing (DID). DID is a service provided from
the local phone company that provides a block of numbers used to call into a company’s own
PBX. When DID is used, a company can assign a company employee a phone number without
requiring a physical line into the PBX (Adtran) for each person.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# direct-inward-dial
63 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 64

f. Use the port X/X/X:23 command to apply the dial peer to a specific interface. This command
allows calls that come in from the previously defined numbers (5555xxx) to be allowed through a
particular router port. An example of this command is as follows: port 1/0/0:23 or port 1/0:23
(depending on what model of NM-HDV2-1T1/E1 is being used). Use the port parameters
previously documented in a question.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# port X/X/X:23
g. Test the configuration by calling from the analog phone attached to the Adtran analog (FXS) port
to the analog phone connected to the FXS port on the router.
h. Did the call work properly? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting. ____________
i. Save the router configuration.
64 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 65

Answers to Lab 4.1.3
1b. Hardware dependent, but the module is normally inserted into slot 1.
1d. Yes and how it lists is router dependent. An example is controller T1 1/0/0
2b. Other types include the following: primary-4ess, primary-5ess, primary-des100, primary-net5,
primary-ntt, primary-qsig, primary-ts014
3d. Router model dependent, but the normal answer will be 1.
3k. Yes
4d. The router does not know where to send the call. The router uses a dial peer to define a
specific condition that, if met, sends a call through a particular port.
4e. A tone similar to a busy tone sounded, and the display showed Unknown Number.
4k. Yes
4l. “Ring out” is shown followed by “Connected” when the analog phone is answered.
5b. No. The call did not connect because a dial peer has not been defined for this type of
connection.
5h. Yes.
65 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 66

Lab 4.1.4 Configuring VoIP Dial-Peers Across a WAN Link
Objective
• Configure the VoIP dial peers across a WAN link.
Equipment Requirements
• Two Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable routers with a serial port
• Two inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Adtran
• Two IP phones
• Two analog phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and 3.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company has added another site with its own CallManager Express. A
WAN connection to the other site will need to be configured and tested.
66 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 67

Step 1 Configure the Serial Interface
a. In this lab, Pod 1 and Pod 2 will partner, and Pod 3 and Pod 4 will partner.
b. Ensure that a serial cable connects from the lowest serial interface on the lowest pod number
router terminating on the other pod’s lowest number router serial interface.
c. On both pods, use the show ip interface brief command to verify that (1) a serial interface is
installed and (2) the lowest numbered serial interface.
d. What is the port/slot number assigned to the lowest numbered serial interface? ____________
e. On both pods, use the show controllers serial mod/port for the lowest serial interface and
verify if the cable is a DCE or DTE. Examples of this command are show controllers serial 0/0
or show controllers serial 0/1/0.
CMERouterX# show controllers serial mod/port
f. Type the interface serial mod/port command from global configuration mode to access the
serial interface. Examples of this command are interface serial 0/0 or interface serial 0/1/0.
CMERouterX(config)# interface serial mod/port
g. If the pod has the DCE end of the cable, use the command clock rate 115200 to set the clock
rate of the lowest serial interface.
CMERouterX(config-if)# clock rate 64000
h. Use the encapsulation hdlc command to configure the serial link encapsulation to HDLC.
CMERouterX(config-if)# encapsulation hdlc
i. Refer to Table 1 for the appropriate IP address to apply to the serial interface.
CMERouterX(config-if)# ip address 10.X.0.X 255.255.255.0
j. Use the command no shutdown to enable the serial interface.
CMERouterX(config-if)# no shutdown
k. Wait for your partner pod to complete the previous steps. Verify connectivity by using ping to test
the serial connection. Ping the address of your partner pod serial interface. Enter ping 10.Y.0.X
(refer to Table 1 for the partner pod IP address).
l. From an IP phone connected to the pod, attempt to dial a four digit extension numbers of one of
the partner pod IP phones.
m. What was the result, and why is this result? _______________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
n. What message displayed on the IP phone when the call did not complete? _________________
Step 2 Configure the Dial Peer
a. From global configuration mode, create a new dial peer with the command dial-peer voice 6
voip.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 6 voip
67 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 68

b. Associate a pattern to the dial peer by using the global configuration mode command
destination-pattern digits. Refer to Table 2 for the destination patterns being used. Depending
on the pod number, use one of the following commands to configure a destination pattern. Note
that the period(s) at the end of the command is part of the command.
Pod 1- destination-pattern 50[3,4,5].
Pod 2- destination-pattern 50[0,1,2].
Pod 3- destination-pattern 51[0,1,]..
Pod 4- destination-pattern 50[6,7,8].
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# destination-pattern digits_fm_list
c. Use the session target ipv4:10.Y.0.X (where the IP address is the partner pod router’s serial
interface address).
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# session target ipv4:10.X.0.X
d. The G711 codec is what is used to translate analog voice data to a digital format. G711 uses a
64kbps data rate. Manually configure the codec to be used by entering the command codec
g711ulaw. This codec will be used by any call that matches this dial peer.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# codec g711ulaw
Step 3 Test the Configuration
a. Dial a four digit extension numbers of one of the phones in your partner’s pod and stay
connected. The lowest number pod partner should count aloud the numbers one to ten slowly
into the phone.
b. How is the voice call quality? ____________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
c. Is the quality of the voice acceptable? ____________________________________
d. Coordinating with your partner pod, place a second simultaneous call between the pods using a
four digit extension. This will force two calls on the WAN link. The highest number pod partner
counts aloud from number one to number 10. After counting, remain connected.
e. How is the voice quality? Is it the same, better, or worse? _______________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
f. Verify the codec being used by the call is G.711 by quickly pressing blue i or question mark
button (depending on the model of phone) on the IP phones twice while the calls are connected.
g. What does the IP phone display to indicate the codec being used? _______________________
h. Hang up both calls.
Step 4 Reconfigure the Codec
a. From global configuration mode on both pods, access the dial peer with the command dial-peer
voice 6 voip.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 6 voip
68 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 69

b. The G729 codec uses an 8kbps data rate. Reconfigure the codec to use the G729 codec by
entering the command codec g729br8.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# codec g729br8
c. Coordinate with the partner pod to place two simultaneous calls across the WAN link by dialing
the four digit extensions.
d. How is the voice quality? Remain connected._________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
e. On the IP phone, verify the codec is G.729 by quickly pressing the blue i or ? (question mark)
button twice (depending on the model of phone) while the calls are still connected.
f. Save the configuration by using the command copy running-config startup-config.
69 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 70

Answers to Lab 4.1.4
1d. Hardware dependent, but common answers include serial 0/0 or serial 0/1/0.
1m. No the call did not complete because a dial peer has not been defined.
1n. Unknown number is the message that displays.
3b. Voice quality is tolerable. There is a delay.
3c. Yes.
3e. The quality is worse with the second call.
3g. TxType:G711u is the indication shown on the type of codec being used.
4d. Voice quality is OK, but less quality than the first call with the G711 codec.
70 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 71

Lab 4.1.5 Configuring Class of Restriction
Objective
• Configure Class of Service on the IP telephony network.
Equipment Requirements
• Two Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable routers with a serial and PRI ports
• Two inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Adtran
• Two IP phones
• Two analog phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 4.1.1, 4.1.3, and 4.1.4 being successfully completed and
loaded.
In this lab ACME.com wishes to implement Class of Service to restrict access to where certain IP
phones can call.
71 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 72

• Configure the lowest numbered IP phone to be able to call over the WAN, but not over the PSTN
• Configure the highest numbered IP phone to be able to call to any destination that the router can
call
• The analog phone should be able to call across the WAN or the analog PSTN
• The digital PSTN should not be available to the analog phone
Step 1 Configure Class of Restriction
a. In this lab do NOT save the changes made to the router. A Class of Restriction (COR) is used to
determine which incoming dial peer can use which outgoing dial peer to make a call. A dial peer
can have one incoming and one outgoing COR list. The cor command is used to set the dial-
peer COR parameter for dial peers and directory numbers. COR allows a company to deny
certain call attempts on the basis of the incoming and outgoing CORs configured on the dial
peers. The COR could be used to block calls to 900 numbers from company phones.
The CME admin guide from Cisco gives another excellent example of a COR.
b. From global configuration mode, enter the command dial-peer cor custom to enter the cor
mode.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor custom
c. Enter the first name by using the command name Analog.
CMERouterX(config-dp-cor)# name Analog
d. Enter the second name by using the command name PRI.
CMERouterX(config-dp-cor)# name PRI
e. Enter the final name by using the command name WAN.
CMERouterX(config-dp-cor)# name WAN
f. Type exit to return to global configuration mode.
g. Define a Class of Restriction (COR) list by using the command dial-peer cor list callAnalog.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor list callAnalog
h. Put a member in the COR list with the command member Analog.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member Analog
i. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Define a COR list by using the command dial-peer
cor list callPRI..
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor list callPRI
j. Put a member in the COR list with the command member PRI.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member PRI
k. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Define a COR list by using the command dial-peer
cor list callWAN.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor list callWAN
l. Put a member in the COR list with the command member WAN.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member WAN
72 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 73

m. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Define a COR list by using the command dial-peer
cor list Type1.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor list Type1
n. Put a member in the COR list with the command member WAN.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member WAN
o. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Define a COR list by using the command dial-peer
cor list Type2.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer cor list Type2
p. Put the first of two members in the COR list with the command member WAN.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member WAN
Put the second of two members in the COR list with the command member Analog.
CMERouterX(config-dp-corlist)# member Analog
q. Type exit to go to global configuration mode.
Step 2 Apply Class of Restriction to a Dial Peer
a. Enter dial-peer voice 2 pots to enter dial peer configuration mode.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 2 pots
b. Assign an outbound COR list to the dial peer with the command corlist outgoing callAnalog.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# corlist outgoing callAnalog
c. Without making a phone call, what phone calls do you expect to work and what phone calls do
you expect to not work? _______________________________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
d. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Enter dial-peer voice 3 pots to enter dial peer
configuration mode.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 3 pots
e. Assign an outbound COR list to the dial peer with the command corlist outgoing callPRI.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# corlist outgoing callPRI
f. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Enter dial-peer voice 6 voip to enter dial peer
configuration mode.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 6 voip
g. Assign an outbound COR list to the dial peer with the command corlist outgoing callWAN.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# corlist outgoing callWAN
h. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Enter ephone directory number mode by entering
the command ephone-dn 1.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 1
73 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 74

i. In ephone-dn mode, enter the command cor incoming Type1.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# cor incoming Type1
j. Type exit to go to global configuration mode. Enter dial-peer voice 1 pots to enter dial peer
configuration mode.
CMERouterX(config)# dial-peer voice 1 pots
k. Assign an outbound COR list to the dial peer with the command cor incoming Type2.
CMERouterX(config-dial-peer)# cor incoming Type2
l. Test the COR settings by attempting to dial a partner pod over the WAN, analog connection to
the PSTN, and the PRI connection to the PSTN. Test on all three phones. Remember that the
highest numbered IP phone should be able to call any destination the router has a dial peer. The
lowest numbered IP phone should not be able to call the phone connected directly to the Adtran.
m. Does the test work as it should? If not, perform appropriate troubleshooting. __________
n. When the test is successful, reload the router making sure you do not save the configuration.
74 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 75

Answers to 4.1.5 lab
2c. Student’s opinion
2m. Yes
75 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 4.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 76

Lab 5.1.1 Configure GUI for System Administrator
Objective
• Configure and use the GUI system administrator interface
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Appropriate .tar file loaded on the router or available from the instructor or student assistant
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• TFTP Server application
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, and 3.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab ACME.com wishes to use a Web GUI instead of the CLI for adds, moves, and changes.
Currently the GUI is not installed or configured. Configure and use the GUI to do various
administrative tasks.
76 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 77

• Enable the GUI on the CallManager Express router using files located on the TFTP server
• Create a username and password
• Use the GUI to create an ephone-dn and assign it to one of the two IP phones
• Use the GUI to add a speed dial to one of the two IP phones
• Use the GUI to change the date and time format on the IP phones
• Use the GUI to change the system time
Step 1 Configure the GUI interface for the System Administrator
a. The router and switch should be configured with the basic configuration. The IP phones should
be plugged into the switch and configured with a basic configuration using any of the methods
previously demonstrated.
b. From one of the phones, dial the other phone. Does the call go through properly? If not,
troubleshoot as necessary. ________________________________________
c. From privileged mode, use the show flash: command to verify the IP phone GUI firmware files
are present. The firmware files for a 7960 and 7940 will include some HTML files such as
admin_user, ephone_admin, and telephony_service.
If these files are not present, there is a file that the instructor must obtain from the Cisco site that
starts with the letters “cme-gui” and has a file extension of “.tar”. An example of the filename is
cme-gui-123-11T.tar. Note that some of the older IOS versions did not combine these files in a
.tar file.
Note: The .tar file must match the IOS version on the CME router.
Once the .tar file is obtained from the Cisco site, the GUI files are extracted from the .tar file and
uploaded to the router Flash memory. This is done from a TFTP server. Copy the .tar file into the
appropriate TFTP server folder. From privileged mode, use the archive tar /xtract
tftp://tftp_server_ip_address/.tar_filename flash:. tftp_server_ip_address is the address of
the TFTP server (that contains the .tar file). .tar_filename is the name of the file that starts with
the letters “cme-gui” and has a filename extension of .tar. An example of this command is as
follows: archive tar /xtract tftp://10.3.0.33/cme-gui-123-11T.tar flash:. A successful extraction
shows an output similar to the following:
Loading cme-gui-123-11T.tar from 10.3.0.33 (via GigabitEthernet0/0.3):
!
extracting CiscoLogo.gif (1602 bytes)
extracting Delete.gif (953 bytes)
extracting Plus.gif (1347 bytes)!
extracting Tab.gif (174 bytes)
extracting admin_user.html (3845 bytes)!
extracting admin_user.js (641134
bytes)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
!!!!!!!!!
!!!!
extracting dom.js (16344 bytes)!!!!
extracting downarrow.gif (864 bytes)
77 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 78

extracting ephone_admin.html (6146 bytes)!
extracting logohome.gif (4658 bytes)!
extracting normal_user.html (3724 bytes)!
extracting normal_user.js (76732 bytes)!!!!!!!!!!!!!!!
extracting sxiconad.gif (843 bytes)!
extracting telephony_service.html (2357 bytes)
extracting uparrow.gif (870 bytes)!
extracting xml-test.html (9968 bytes)!!
extracting xml.template (3311 bytes)!
[OK - 788992 bytes]
d. Was the extraction successful? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. ________________________
Step 2 Configure the GUI interface for the System Administrator
a. The CME GUI interface allows administrators to configure CallManager Express using web
access rather than from a console or Telnet connection. Enter the command ip http server to
enable the Web server on the Cisco CallManager Express router.
CMERouterX(config)# ip http server
b. Enter the command ip http path flash: to define that the location of the HTML files are in Flash
memory of the router. The HTML files on the router are needed to perform GUI administration.
CMERouterX(config)# ip http path flash:
c. Enter ip http authentication local to define that login credentials will be defined locally on the
router. Without this command, the default authentication is the router’s enable secret password,
or the enable password if enable secret is not set.
CMERouterX(config)# ip http authentication local
d. Move to the telephony service mode by using the command telephony-service.
CMERouterX(config)# telephony-service
e. From telephony service mode define a username and password used for web-based access.
The username will be ACMEadmin with a password of cisco.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# web admin system name ACMEadmin
password cisco
f. Enter dn-webedit to allow changes to the Directory Number through the Web interface.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# dn-webedit
g. Enter time-webedit to allow the Cisco CallManager Express time to be set from the Web
interface.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# time-webedit
Currently, the only changes that can be made through the web interface are the directory
number and the time based on the commands just entered, but more can be configured.
h. Return to privileged mode and save the router configuration.
78 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 79

Step 3 Configure a speed dial using the GUI
a. Ensure the PC that will be used to access the CME GUI either (1) connects to a switch port that
has been configured for the data VLAN or (2) connects to the 10/100 PC port on one of the IP
phones. The PC can be configured for DHCP and if so configured, should receive an IP address
from the CME router. Ensure the router has been configured for a data DHCP pool (see previous
lab). If the router has not been configured, the PC can be manually configured with an IP
address in the data VLAN IP address range. See Table 1 for these addresses.
If the PC connects to a switch port, ensure the switch interface is configured for (1) access mode
and (2) the data VLAN (X0 where X is the pod number).
The PC should be able to ping the router interfaces before any other step is attempted.
b. Can the PC ping all of the router interfaces? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. ___________
c. What IP address is assigned to the PC? __________________________________________
d. Open the Web browser on the PC and enter the URL of http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
the pod number). Attempt to log in using a blank username and the enable secret password.
e. Were you able to login using blank username and the enable password? Why or why not?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
f. Try logging in again and when asked for credentials, use ACMEadmin for the username and
cisco for the password.
g. What are the five menu options available through the web interface? ______________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
h. From the Configure menu option, select Extensions. The currently configured extensions are
shown on the screen.
i. How many extensions display on the screen? If none, the phones have not been configured
correctly. Start this lab over. ______________________________________________________
j. From the Configure menu option, select Phones. The two configured phones should be listed. If
none are listed, the phones are not configured correctly. Start this lab over and connect the
phones properly.
k. In the Phone Physical ID(MAC Address) column, click on the first MAC address. The MAC
address is underlined. The phone line buttons list in a separate window in a table. Note that
popups may have to be enabled in order to see this window.
(where X is
l. How many buttons list on the screen? Does this correspond to the correct number of buttons
located to the right of the IP phone’s LCD? _________________________________________
m. Scroll down until the Speed Dial Information section is reached. In the Speed Dial 1: textbox,
type in the four digit extension of the other IP phone. Normally, the number for the phone that is
being accessed is shown as the first button. For example, if configuring this for the IP phone that
currently has the extension of 1001 (shown higher in this web configuration window), type 1000
(the other IP phone extension). In the Label: textbox, type a name or description that will display
on the IP phone. An example is Alyssa.
n. Click on the Change button at the bottom of the screen. When prompted if the changes are to be
saved, click the OK button.
79 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 80

o. What feedback is received as a result of clicking the OK button? _______________________
p. In the message that appears on the screen, click the OK button to clear the message.
q. Look at the IP phone that was being changed. What happens as a result of creating a speed dial
using the GUI? ________________________________________________________________
r. Once the phone has reset, what has changed on the phone display?
_____________________________________________________________________________
s. Press the second button on the phone that was just configured (the one that contains the words
just created with the speed dial). What happens as a result?
____________________________________________________________________________
Step 4 Configure system time using the GUI
a. From the Configure menu, select System Parameters. Notice the different selections that can
be changed.
b. Use the System Time option to change the date and/or time to a different time than is currently
defined. Note that the current time is based on the time of the computer and not the router.
c. Click on the Set button to use the currently configured settings. Click on the OK button to save
the changes and select the OK button to acknowledge the save.
d. Select the Date and Time Format option from the left column. Change the format to a different
selection.
e. Reset the two IP phones by using the Configure drop down menu and selecting the Phones
option. Use the Reset All link to reset the phones. Click OK to reset the phones and OK again to
acknowledge the save.
f. View the changes as they occur on the IP phones. Record your observations.
_____________________________________________________________________________
g. From the Configure menu, select System Parameters again. Click on the Directory Service
option from the left column and select Name Schema.
h. What is the other name schema that can be selected? _________________________________
i. Click on the System Message option from the left column.
j. In the System Message: textbox, type in a message. Click on the Set button and click on OK to
save the changes. Click on the OK button to acknowledge the save.
k. How does the phone change as a result of the last configuration step?
_____________________________________________________________________________
l. How might a system administrator use this option? ____________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
m. Logout of the GUI Web page by clicking on the Logout option from the upper right portion of the
screen.
n. From the router CLI, save the configuration to be used in future labs.
80 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 81

Answers to 5.1.1 Lab
1b. Yes
1d. Yes
3c. Student dependent, but it should be 10.X0.0.X (where the first X is the pod number and the
second X is a number other than 1 or 4—these are used by the router and the switch).
3e. No, the student could not log in because the web admin system command was used to define
the username and password needed to access CallManager Express through a web page.
3g. Configure, Voice Mail, Administration, Reports, and Help
3i. The answer depends on what the student configured the maximum number of extensions to be.
If the automated phone setup lab was used, the response is 4.
3l. The number of buttons on the phone depends on the model. The 7940 model has 2 buttons
and the 7960 model has 6 buttons. Yes, the number of buttons on the screen corresponds to
the number of buttons on the phone.
3o. Configuration has been successfully changed.
3q. The phone resets automatically and the name Alyssa is seen beside the second button on the
IP phone.
3r. The phone now has the message that was chosen displayed directly beside the second phone
button on the right.
3s. The other phone rings.
4f. Even though both phones resets, it does not occur simultaneously. One phone resets and then
the other one resets.
4h. Last name first
4k. A message appears at the bottom of the phone with the words typed in the System Message
textbox.
4l. Answers will vary, but one thought is that a system administrator might send a message about
planned system maintenance or changes using this method.
81 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.1 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 82

Lab 5.1.2 Configure GUI for Customer Administrator
Objective
• Configure and use the GUI interface for the customer administrator
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• TFTP server application
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, and 5.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab ACME.com wants an administrative assistant to have the ability to perform a subset of the
tasks that the system administrator can perform in the GUI web interface. Configure the customer
administrator in CallManager Express to enable this.
• Create the customer administrator credentials using the GUI
• Verify changes using the CLI
82 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 83

• Create credentials of ACMEcust with a password of cisco
• Copy the XML file using a TFTP server
• Examine the context of the XML file
Step 1 Configure a Phone using the GUI interface for the Customer Administrator
a. Ensure the phones can connect to one another. If they cannot, redo previous labs.
b. Use the show running-config | begin tele command to view part of the current configuration.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin tele
c. Open the Web browser on the student PC and enter the URL of http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
(where X is the pod number). Use ACMEadmin for the username and cisco for the password.
This allows access to the GUI as the system administrator.
d. Point to the Configure menu option, and select System Parameters. Ensure the Administrator’s
Login Account option (the first menu option on the left) is selected.
e. From the Admin User Type: drop-down menu, select Customer (instead of System).In the
Admin User Name: textbox, type in ACMEcust. Note that usernames are case sensitive in Call
Manager Express. The Customer Administrator category allows a person to be given rights to
change some of the phone parameters. The account by default has the ability to change the
same things as the administrator, but this account can be customized to remove authority.
f. Set the New Password and Confirm Password to cisco in both textboxes. Passwords are also
case sensitive.
g. Click on the Change button and select OK when asked to confirm the change. A confirmation
window pops up stating the change has been implemented. Click on OK.
h. Logout of the CallManager GUI by clicking on the Logout link in the upper right corner.
Step 2 Review Changes to the Configuration
a. Console into the Cisco CallManager Express router and go to privileged mode.
b. Use the show running-config | begin tele command to view the changes to the configuration.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin tele
c. What changes to the configuration occurred as a result of adding the Customer Administrator?
____________________________________________________________________________
Step 3 Test the New Account
a. Return to the GUI CME Web page by typing the URL http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html (where X is
the pod number) in a web browser.
b. When prompted for a username and password, use the newly-created Customer Administrator
account (ACMEcust for the username and cisco for the password).
c. How many System Parameters can be changed using the Customer Administrator account?
__________
d. Logout of the CallManager GUI by clicking on the Logout link in the upper right corner.
e. Open up another browser window and return to the CallManager Express GUI interface by
typing http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
83 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
in the address line.
Page 84

f. When prompted for a username and password, use the System Administrator account
(ACMEadmin for the username and cisco for the password).
g. How many System Parameters can be changed using the System Administrator account? _____
h. Note that the Customer Administrator and the System Administrator have the same level of
access. Logout of the CallManager GUI by clicking on the Logout link in the upper right corner.
Step 4 Download XML Template
a. Return to the router CLI.
b. Use the show flash: command to view the contents of Flash memory. Notice that there is a file
named xml.template saved in Flash.
c. Start the TFTP server application. The PC that has the TFTP server application should be
connected to the switch and be able to ping the router before any transfers occur.
d. Is there connectivity between the TFTP server and the router? _________________________
e. From the router privileged mode prompt, issue the command to copy the xml.template file in
Flash memory from Flash to the TFTP server.
CMERouterX# copy flash:xml.template tftp:
The transfer should be successful. Troubleshoot as necessary until the file transfers.
f. What indication is given that the TFTP transfer was successful? ________________________
g. Using a text editor such as Notepad, open the downloaded file (xml.template).
h. What is the first word found inside the greater than and less than symbols of the xml.template
file? _______________________________________________________________________
i. The xml.template file can be modified and uploaded to the router to modify what can be seen
through the web interface. The web customize load filename.xml command is used in
telephony-service router configuration mode to specify the new XML file to be used with the web
interface. This file must be copied up to the router Flash memory before it can be used.
Customizing the login is beyond the scope of this lab.
j. Save the router configuration.
84 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 85

Answers to Lab 5.1.2
2c. The following line has been added: web admin customer name ACMEcust password cisco
3c. 17 in 12.3.11T and 16 in 12.3(8)T3 IOS version. Other IOS versions may be different.
3g. 17 in 12.3.11T and 16 in 12.3(8)T3 IOS version. Other IOS versions may be different.
4d. Yes
4f. The following message appears as the transfer occurs and completes successfully:
!!
3311 bytes copied in 0.036 secs (91972 bytes/sec)
4h. Presentation
85 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.2 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 86

Lab 5.1.3 Configure GUI for Phone User
Objective
• Configure and use the GUI for the Phone User
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 5.1.1, and 5.1.2 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company needs to configure user credentials so that the users can make
some settings of their assigned phones through the GUI Web interface. Configure two users as listed
below and test the levels of access.
• Configure a user named EFriend and a password of cisco for the IP phone with a sequence
number of 1 from the GUI
86 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 87

• Configure a user named KHampton and a password of cisco for the IP phone with a sequence
number of 2 from the CLI
• Open the GUI and log in as one of the user accounts created
Step 1 Configure a Phone using the GUI for the Phone User
a. Use the show running-config | begin ephone command to view part of the current
configuration.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin ephone
b. Open the Web browser on the student PC and enter the URL of http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
(where X is the pod number). Use ACMEadmin for the username and cisco for the password.
c. From the main menu, point to Configure and select the Phones option.
d. Locate the Phone Sequence Number column. Select the link for the IP phone with a sequence
number of 1 by clicking on the MAC address located in the first column (Phone Physical ID) of
that same row. Note: Pop-up blocking may need to be disabled for this site.
e. In the window that displays as a result of clicking on the MAC address, what is the default value
for Call Blocking? [Exempt | Non Exempt] _________________________________________
f. Scroll to the Login Account section. In the Login Username textbox, add a username of EFriend
and a password of cisco. Note that the username and password are case sensitive. Click on the
Change button to save the configuration change. When prompted to save the change, click on
OK. When the confirmation message appears, click on OK.
g. From the main menu, point to Administration and select Save Router Config. When prompted
to save the change, click on the OK button. A message may appear that the change is delayed
because a Telnet session is active. This only occurs when a HyperTerminal session is active at
the same time as a Web session. Whether or not this message is displayed, proceed to step 1h.
h. Logout of the GUI Web interface by clicking on the Logout link in the upper right portion of the
screen.
i. Use HyperTerminal to access the Cisco CallManager Express router, and use the command
show running-config | begin ephone to view the changes made through the GUI Web
interface.
j. What changes to the configuration have been made in the ephone 1 section?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
k. From global configuration mode, use the command ephone 2 to enter ephone configuration
mode.
l. Enter the command username KHampton password cisco to configure a phone user for the
second phone.
87 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin ephone
CMERouterX(config)# ephone 2
CMERouterX(config-ephone)# username KHampton password cisco
Page 88

m. Save the router changes.
CMERouterX# copy running-config startup-config
n. Open a Web browser and use the URL http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
number). Authenticate with the EFriend account and a password of cisco.
o. Point to the Configure menu option.
p. What is different from the other Web accounts? ______________________________________
q. Click on the Phone option (under Configure).
r. Does the system allow any phone except for ephone1 to be configured? ___________________
s. Logout of the Web GUI.
(where X is the pod
88 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 89

Answers to 5.1.3 Lab
1e. Non Exempt is the default value.
1j. Answers will vary depending on the type of phone configured, but an example is listed below:
ephone 1
username "EFriend" password cisco
Based on what we did in this lab at this point the only new line in the configuration is username
“EFriend” password cisco.
1p. The only option is Phone. The other options of Extensions and System Parameters are not
available.
1r. No
89 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.3 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 90

Lab 5.1.4 Configuring Call Transfer and Call Forward
Objective
• Transfer calls and set up call forwarding
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• One analog phone
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 4.1.1, 5.1.1, and 5.1.2 being successfully completed and
loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company currently has the system default of blind transfers and wishes to
change to consultative transfers system wide. Configure CallManager Express to use consultative
transfers. However, the ability to forward calls should be restricted and the user should not be able to
forward calls from the IP phones.
90 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 91

• Configure consultative transfer
• Use the IP phone to configure call forward to the other IP phone
• Restrict the ability to forward calls from the IP phone using IOS commands
Step 1 Configure Call Transfer and Call Forward
a. Check connectivity between the analog phone and one of the IP phones. From the analog
phone, dial one of the IP phones.
b. Does the phone connection work between the analog phone and the IP phone? If not,
troubleshoot as necessary.
________________________________________________________
c. Note that a softkey button on the phone is an option selected by one of the four buttons at the
bottom of the IP phone display.
When the analog phone dials one of the IP phones and the IP phone is ringing, press the
Answer softkey button followed by the Trnsfer softkey button. A dial tone emits. Enter the
extension of the other IP phone. The other IP phone should ring.
d. Was the transfer successful? If not, troubleshoot as necessary.
___________________________
e. By default, the phone transfer from one IP phone to the other is blind. What is your best guess
as to what the term blind transfer means?
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
f. Access the router CLI. From global configuration mode, enter telephony-service mode.
CMERouterX(config)# telephony-service
g. Use the command transfer-system full-consult to enable consultative transfers.
CMERouterX(config-telephony)# transfer-system full-consult
h. From the analog phone, dial one of the IP phones. When the IP phone starts ringing, press the
Answer softkey button followed by the Trnsfer softkey button. A dial tone emits. Enter the
extension of the other IP phone. The other IP phone should ring. On the other IP phone (the
target IP phone) press the Answer softkey. Notice that the call is not automatically transferred
and the only connection where a conversation can occur is between the two IP phones. In fact,
the caller on the analog phone is on hold, and even if the analog phone is hung up, the call
transfer between the two IP phones continues.
i. From the IP phone that initiated the transfer press the Trnsfer softkey button a second time to
complete the transfer. Now the analog phone and the second IP phone have a connection. Hang
up all phones.
j. From the second IP phone, press the CFwdAll softkey button then enter the number of the first
IP phone followed by the # key. This forwards all calls to the other IP phone.
91 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 92

k. What message appears when all calls have been forwarded to another IP phone?
____________________________________________________________________________
l. From the analog phone, call the number of the second IP phone. The call should be forwarded to
the first IP phone.
m. Does the first IP phone ring? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. ________________
n. Press the CFwdAll softkey button on the second IP phone to disable the call forwarding.
Step 2 Examining Call Forward Features
a. From global configuration mode, enter ephone-dn 1 to enter ephone-dn mode.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 1
b. Enter the command call-forward max-length 0 to disable call forwarding from the first IP phone.
Note that even though call forwarding is disabling, a phone call can still be placed to the phone
and from the phone.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)#
c. List one example of when a company might disable call forwarding for an employee that has an
IP phone. ____________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
d. Examine the router configuration to determine which IP phone uses ephone-dn 1.
e. What is the phone number assigned to ephone-dn 1 based on the router configuration output?
__________________________________________________________________________
f. From the IP phone with ephone-dn 1 assigned to it, press the CFwdAll softkey button.
g. What is different than before? __________________________________________________
h. Use the GUI Web interface as a phone user (for example, KHampton, cisco). Under the
Configure menu option, select Phone. In the Line Information section click on the hyperlink for
the line being configured (probably Line 1). Configure call forward busy, and call forward no-
answer to forward calls to the other IP phone’s number. In the timeout textbox enter 15 (18
seconds is the default). Click on the Change button. Then on the Configure > Phone page, scroll
down to the end of the page and click on the Save Changes button. Click on the OK button to
save changes, click on the OK button to acknowledge the changes. Notice that the user can still
configure call forward settings from the GUI even though the call-forward max-length 0 is set
from the router prompt.
call-forward max-length 0
i. What happens to incoming calls when call forward busy and call forward no answer options are
active and set to the other IP phone?______________________________________________
j. If a forwarding number was also entered into the call forward all textbox what would then happen
to calls to that number?___________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________
k. Use the analog phone to verify functionality of the call forwards.
l. Remove the call forwarding from the IP phone using any method.
92 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 93

Answers to 5.1.4 Lab
1b. Yes
1d. Yes
1e. Student’s own reasoning, but blind transfer is that the phone where the call is being transferred
to cannot tell the phone number that transferred the call. Only the originating number shows.
Some companies would want to know the person doing the transferring of the call
(administrative assistant versus the general switchboard).
1k. Forwarded to X000 (where X is the pod number)
1m. Yes
2c. Student’s choice. Two sample answers include the following: (1) the employee forwards the IP
phone to their own cell phone and takes off for the golf course, and (2) an employee frequently
forwards their IP phone to another IP phone and does not take calls.
2e. Either X000 or X0001 depending on the pod and configuration.
2g. The CFwdAll button did not work.
2i. The calls forward even though the CFwdAll softkey is disabled. Have the students notice the
icon in the very top right corner of the IP phone display. When the phone is forwarded, this
animation occurs.
2j. All calls to the first IP phone would be automatically forwarded to the second IP phone without
ever ringing the first IP phone.
93 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.4 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 94

Lab 5.1.5 Configuring Call Park
Objective
• Configure the Call Park option
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• One analog phone
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 4.1.1, and 5.1.1 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company has an overhead page that is used by the company operator to
page someone that is not answering a transferred consultative call. The ability to park the call will be
needed so the person being paged can retrieve the call from any phone in the CallManager Express
system.
94 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 95

• Configure the ability to park a call at the extension X800 (where X is the pod number)
• Configure the system to send a reminder after 10 seconds and to repeat this three times
• Retrieve a parked call from a different IP phone
Step 1 Configure Call Transfer and Call Forward
a. From the router CLI global configuration mode, create an ephone to use as a “call park slot”—a
fake ephone that is simply used as a holding spot for a phone call. In this instance, the number
11 is being used.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 11
If a message appears that dn 11 exceeds the max-dn limit, move to the telephony-service
configuration mode and type the command max-dn 15. Return to global configuration and re-
enter the ephone-dn 11 command.
b. What message appears as a result of the ephone-dn 11 command? ___________________
____________________________________________________________________________
c. Use the number X800 (where X is the pod number) command to assign an extension.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# number X800
d. Use the command park-slot timeout 10 limit 3 to set a reminder after 10 seconds and to
terminate the call after three reminders.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# park-slot timeout 10 limit 3
e. What is the maximum amount of time in hours that can be programmed for the call park feature?
_________________________________________________________________
f. Try resetting the IP phones by using the keys on the IP phones and pressing the following
buttons: * * # * *. Note this will work on most 7940 IP phones, however it may not work on 7960
IP phones. If this method does not work then reset the IP phone using the method previously
learned from an earlier lab. Refer to lab 2.1.2 if necessary.
g. From the analog phone, call one of the IP phones and answer the call.
h. Use the more softkey button to find and press the Park softkey button. You may need to press
the more softkey multiple times before the Park softkey is seen.
i. Wait 10 seconds. What is heard on the analog phone and on the IP phone?
____________________________________________________________________________
j. Wait another 20 seconds. What happens to the call?___________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
95 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 96

k. The Park IP phone feature allows a call to be picked up from a remote location. Say that a
hardware store has multiple lines coming into the store. Every phone in every department does
not need every one of these lines to be connected to it. Instead, the Park feature can be used.
When the main office tells a department to pick up on a particular number, it could be the Park
feature that is being used. Another good time to use the Park feature is when someone is taking
a call in their office, the employee needs the boss to hear what the caller is saying. The
employee can park the call and pick the call back up in the supervisor’s office.
From the analog phone, call one of the IP phones and answer the call.
l. On the IP phone, use the more softkey button to find and press the Park softkey button.
m. From the second IP phone, use the more softkey button to find and press the PickUp softkey
button. When dial tone is heard, dial X800 (where X is the pod number) to retrieve the parked
call. Note that the number dialed is the same number that was programmed into the virtual
ephone-dn earlier in this lab.
n. The second IP phone and the analog phone are now connected and can communicate, and the
first IP phone has been disconnected.
o. Did the call connect? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. _______________________________
p. Disconnect the call. The Park feature can also allow the original IP phone that places the call in
Park to pick up the call. From the analog phone, dial one of the IP phones and answer the call.
q. Use the more softkey button to find and press the Park softkey button.
r. From the IP phone that parked the call, use the more softkey button to find and press the
PickUp softkey button. When a dial tone is heard, press * to retrieve the call.
s. Did the call connect? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. ______________________________
96 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 97

Answers to 5.1.5 Lab
1b. May 24 15:10:36.824: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface ephone_dsp DN 11.1, changed state
to up
1e. 18.2 hours (65,535 seconds)
1i. The analog phone beeps three times and the IP phone rings again.
1j. The phone connection disconnects.
1o. Yes
1s. Yes
97 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.5 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 98

Lab 5.1.6 Customize the IP Phone Display
Objective
• Customize the IP Phone Display
Equipment Requirements
• Cisco CallManager Express (CME) capable router
• Inline power capable switch or non-inline power switch with power injectors
• Workstation with an Ethernet 10/100 NIC installed
• Two Cisco IP phones
• IP Telephony Table 2
This lab relies on labs 2.1.1, 2.1.2, 3.1.1, 5.1.1, and 5.1.3 being successfully completed and loaded.
In this lab the ACME.com Company wishes to customize the IP phones with the Direct Inward Dial
(DID) number of the phone, the company name on the display, and a label on the line. Configure the
following with IOS commands or by using the GUI.
98 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.6 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 99

• Configure the top line of the two IP phones
• Configure the system message on the IP phone using the CLI
• Label the first line on the first IP phone with my line X000 (where X is the pod number)
Step 1 Customize the IP Phone Display
a. Ensure the two IP phones can connect to one another before this lab begins. Troubleshoot as
necessary.
b. Browse to the URL http://10.X0.0.1/ccme.html
Web interface. Use the system administrator credentials of ACMEadmin and cisco.
c. Point to Configure and select the System Parameters option.
d. In the list of system parameters on the left, select System Message. Enter a message of ACME
Classroom. Click on the Set button. When asked if the change is to be saved, click on the OK
button. When the change is successful and that message appears, click OK.
If this change was to be completed from the router CLI, telephony-service configuration mode is
used, and the system message command is used The number of characters that can be
displayed on an IP phone system message is not set because the IP phone normally uses a
proportional font rather than a fixed font. Normally, there is room for approximately 30
characters.
e. What change took place on the connected IP phones? _________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________
f. Logout of the Web interface. Access the CME router CLI. From global configuration mode, enter
the ephone directory number configuration mode for the first IP phone.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 1
g. Use the description command to set the label on the IP phone header bar.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# description Phone1
(where X is the pod number) to access the GUI
h. Enter the ephone directory number configuration mode for the second phone by using the
ephone-dn 2 command.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 2
i. Use the description DIDnumber (where DIDnumber is the first E.164 DID number listed for
each pod in IP Telephony Table 2) to set the IP phone header bar. An example for Pod 1 would
be description 5105555000.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# description DIDnumber
j. Return to the ephone directory number configuration mode for the first IP phone.
CMERouterX(config)# ephone-dn 1
k. Use the command label my line X000 (where X is the pod number) to set a label on ephone-dn
1. A label displays on the phone next to the line button associated with an ephone dialer number.
CMERouterX(config-ephone-dn)# label my line X000
99 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.6 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 100

l. Reset both IP phones by pressing * * # * * on the keypad, or by using the method shown in lab
2.1.2. Some IP phone firmware versions may require selecting the “Settings” button prior to
pressing **#**.
m. What visible changes are on the IP phones? _______________________________________
___________________________________________________________________________
n. View the changes made on the router.
CMERouterX# show running-config | begin tele
o. Save the router changes.
CMERouterX# copy running-config startup-config
p. Notice the system message ACME Classroom appears on the bottom of every phone, Phone1
appears in the top right of the first IP phone, the first button on the first IP phone has the label
my line X000 (where X is the pod number), and the number 5105555000 appears at the top of
the second IP phone.
q. Do all four items appear correctly? If not, troubleshoot as necessary. ____________________
100 - 165 IP Telephony v1.0 Lab 5.1.6 Copyright © 2005, Cisco Systems, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...