Page 1

Cisco IE 5000 Hardened Aggregator Hardware
Installation Guide
First Published: September 2015
Last Updated: April 2018
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE
WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE
ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL
RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY
THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR
CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class A devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class A digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
when the equipment is operated in a commercial environment. This equipment generates, uses, and can radiate radio-frequency energy and, if not
installed and used in accordance with the instruction manual, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. Operation of this equipment
in a residential area is likely to cause harmful interference, in which case users will be required to correct the interference at their own expense.
The following information is for FCC compliance of Class B devices: This equipment has been tested and found to comply with the limits for a
Class B digital device, pursuant to part 15 of the FCC rules. These limits are designed to provide reasonable protection against harmful interference
in a residential installation. This equipment generates, uses and can radiate radio frequency energy and, if not installed and used in accordance with
the instructions, may cause harmful interference to radio communications. However, there is no guarantee that interference will not occur in a
particular installation. If the equipment causes interference to radio or television reception, which can be determined by turning the equipment off
and on, users are encouraged to try to correct the interference by using one or more of the following measures:
■ Reorient or relocate the receiving antenna.
■ Increase the separation between the equipment and receiver.
■ Connect the equipment into an outlet on a circuit different from that to which the receiver is connected.
■ Consult the dealer or an experienced radio/TV technician for help.
Modifications to this product not authorized by Cisco could void the FCC approval and negate your authority to operate the product.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB)
as part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of
California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE
PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
Any Internet Protocol (IP) addresses and phone numbers used in this document are not intended to be actual addresses and phone numbers. Any
examples, command display output, network topology diagrams, and other figures included in the document are shown for illustrative purposes
only. Any use of actual IP addresses or phone numbers in illustrative content is unintentional and coincidental.
All printed copies and duplicate soft copies are considered un-Controlled copies and the original on-line version should be referred to for latest
version.
Cisco has more than 200 offices worldwide. Addresses, phone numbers, and fax numbers are listed on the Cisco website at
www.cisco.com/go/offices.
© 2018 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
ii
Page 3

Preface
Audience
This guide is for the networking or computer technician responsible for installing Cisco IE 5000 series switches. We assume that you are
familiar with the concepts and terminology of Ethernet and local area networking.
Purpose
This guide documents the hardware features of the Cisco IE 5000 switches. It describes the physical and performance characteristics of each
switch, explains how to install a switch, and provides troubleshooting information.
This guide does not describe system messages that you might receive or how to configure your switch. For more information, see the
Cisco IE5000 documentation:
http://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/switches/industrial-ethernet-5000-series-switches/tsd-products-support-series-home.html
For information about the standard Cisco IOS commands, see
http://www.cisco.com/cisco/web/psa/configure.html?mode=prod&level0=268438303
Also refer to the printed IE5000 Product Document of Compliance, included with the switch in the packaging, for Hazardous Location and
Compliance information.
Conventions
This document uses the following conventions and symbols for notes, cautions, and warnings.
Note: Means reader take note. Notes contain helpful suggestions or references to materials not contained in this manual.
Caution: Means reader be careful. In this situation, you might do something that could result in equipment damage or loss of data.
Warning: This warning symbol means danger. You are in a situation that could cause bodily injury. Before you work on any
equipment, be aware of the hazards involved with electrical circuitry and be familiar with standard practices for preventing
accidents. Use the statement number provided at the end of each warning to locate its translation in the translated safety warnings
that accompanied this device. Statement 1071
The safety warnings for this product are translated into several languages in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco
IE 5000 Switch that ships with the product. The EMC regulatory statements are also included in that guide.
Related Publications
Before installing, configuring, or upgrading the switch, see the release notes on Cisco.com for the latest information.
These documents provide complete information about the switch and are available on Cisco.com:
Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco IE 5000 Switch
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
iii
Page 4

Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
Release Notes for the Cisco IE 5000 Switch
Cisco IE 5000 Switch Software Configuration Guide
Device Manager Online help (available on the switch)
These compatibility matrix documents are available from this Cisco.com site:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/modules/ps5455/products_device_support_tables_list.html
Cisco Gigabit Ethernet Transceiver Modules Compatibility Matrix (not orderable but available on Cisco.com)
Cisco Small Form-Factor Pluggable Modules Compatibility Matrix (not orderable but available on Cisco.com)
Obtaining Documentation, Obtaining Support, and Security Guidelines
For information on obtaining documentation, obtaining support, providing documentation feedback, security guidelines, and also
recommended aliases and general Cisco documents, see the monthly What’s New in Cisco Product Documentation, which also lists all new
and revised Cisco technical documentation, at:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/docs/general/whatsnew/whatsnew.html
iv
Page 5
Product Overview
The Cisco IE 5000 hardened aggregator provides a rugged and secure switching infrastructure for harsh environments. It is suitable for
industrial Ethernet applications, including process manufacturing, intelligent transportation systems (ITSs), rail transportation, and other
similar deployments.
In industrial environments, you can connect the switch to any Ethernet-enabled industrial communication devices, including programmable
logic controllers (PLCs), human-machine interfaces (HMIs), drives, sensors, and input and output (IO) devices.
For detailed specifications, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
Switch Models, page 1
Cable Side, page 2
Power-Supply Side, page 10
Management Options, page 12
Switch Models
Table 1 Switch Models
Model Total
Ports
IE-5000-16S12P 28 4 GE only 12 12 LAN Base Support for 2 field-replaceable, redundant
IE-5000-12S12P-10G 28 4GE/10GE 12 12 LAN Base Support for 2 field-replaceable, redundant
1. PoE+ = Power over Ethernet.
2. Can be upgraded to IP Services at a fee. IP Services License Product Numbers are the following: L-IE5000-RTU= (Electronic SW License for IE5000
Switches)
SFP/SFP+
Uplinks
FE/GE SFP
Downlinks
Copper
10/100/1000
PoE/PoE+
Ports
Default
Software
1
License
Power Supplies
2
AC or DC power supplies.
For detailed specifications, see the
IE 5000 Data Sheet.
AC or DC power supplies.
For detailed specifications, see the
IE 5000 Data Sheet.
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
1
Page 6
Product Overview
Cable Side
Cable Side
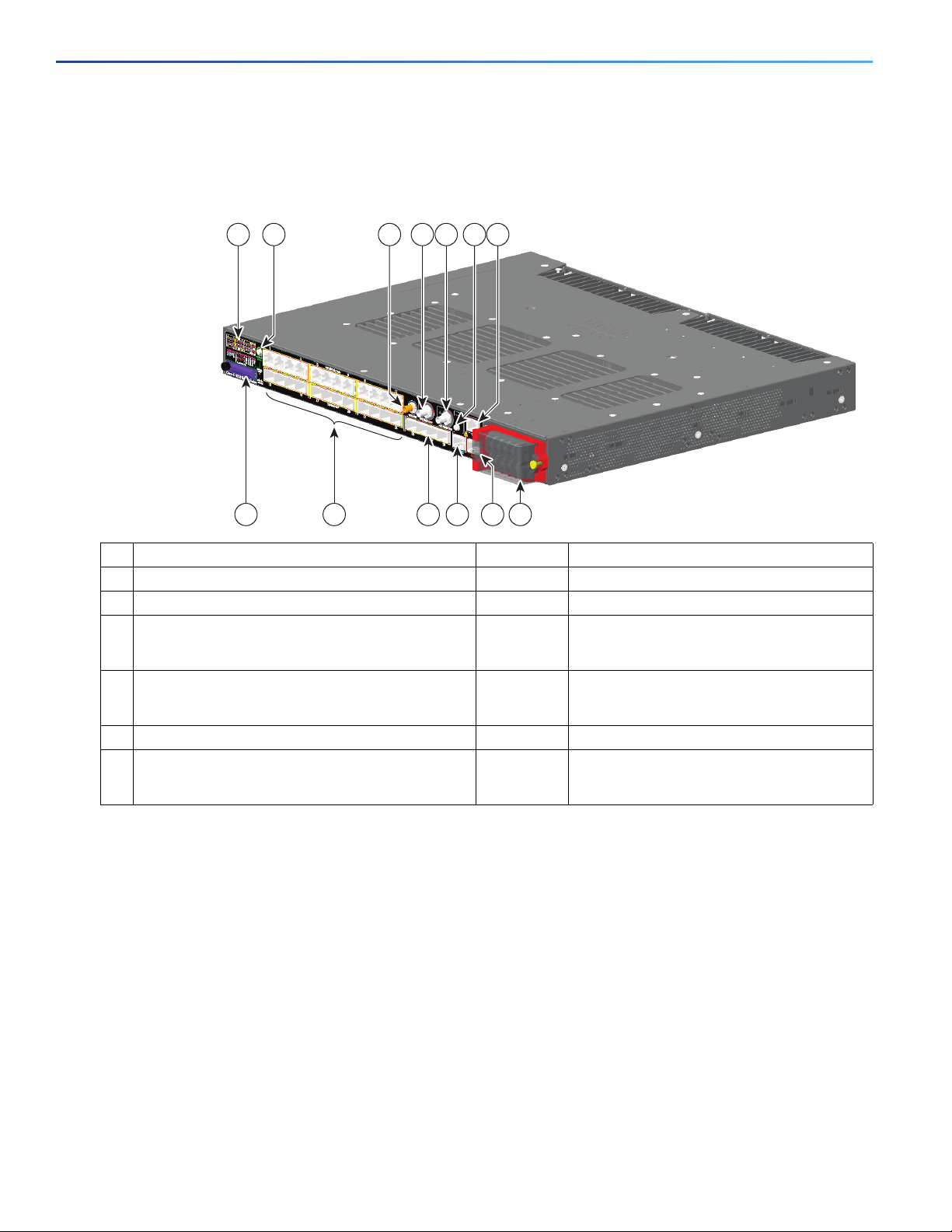
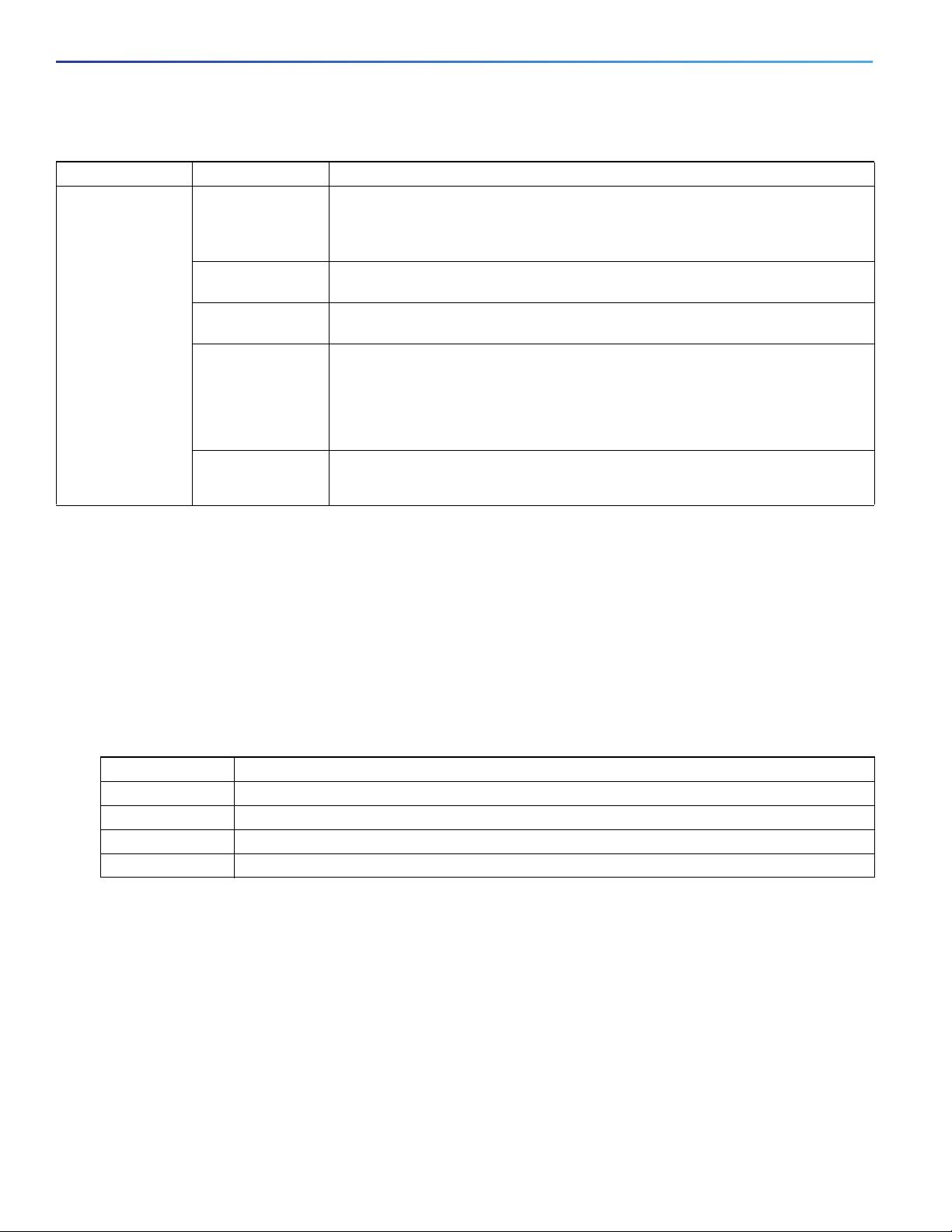
Figure 1 Cisco IE-5000 Cable-Side View
1 4 5
2 6 73
12 11 10 813
1 LEDs 8 Power-input terminal
2 Display mode button 9 Alarm port
3 GPS antenna port 10 Console port
4 Digital Timecode I/O (IRIG)
(Not currently supported by software)
5 Analog Timecode I/O (IRIG)
(Not currently supported by software)
6 USB (mini-Type B) console port 12 (bottom) Twelve 100/1000 SFP Ports (Downlinks)
7 Time of Day (TOD) Port
(Not currently supported by software)
LEDs
For detailed information about LEDs see LEDs, page 5.
Display Mode Button
For detailed functionality see Display Mode Button, page 8.
9
11 Four 1000 SFP/10G SFP+ Ports (Uplinks)
12(top) Twelve 10/100/1000 PoE/PoE+ Ports (Downlinks)
13 Flash memory card slot
349768
GPS Antenna Port
GNSS Module RF Input Requirements
The GPS/GNSS input requires a GPS/GNSS receive antenna with built-in Low-Noise Amplifier (LNA) for optimal performance. The LNA
amplifies the received satellite signals to:
Compensate for cable loss
Increase the signal amplitude to a suitable range for the receiver front-end
2
Page 7

Product Overview
Cable Side
The amplification required is 22dB gain + cable loss + connector loss.
The recommended range of LNA gain (LNA gain minus all cable and connector losses) at the connector of the receiver input is 22dB to
30dB with a minimum of 20dB and a maximum of 35dB.
The GPS/GNSS input on the IE 5000 provides 3.3 or 5VDC (software configurable) to the antenna through the same RF connector.
The antenna should draw between 10 and 100mA. An antenna that draws less than 10mA may wrongly report and "Antenna Open"
fault even though the antenna is operating properly.
Power Requirements
When deployed in a hazardous environment the antenna shall only use power provided by the RF input from a single IE 5000. No additional
power may be supplied to the antenna and associated equipment.
Caution: Supplying additional power, such as with a powered splitter or amplified repeater, may provide enough energy to create
an arc that could ignite the explosive atmosphere.
Surge requirement:
The GPS/GNSS input has built-in ESD protection. If an outdoor antenna is being connected, additional surge protection will be required to
meet the regulations and standards for lightning protection in the countries where the end-product is installed.
The lightning protection must be mounted at the place where the antenna cable enters the building. The primary lightning protection must
be certified for conducting all potentially dangerous electrical energy to PE (Protective Earth). Surge arrestors should support DC-pass and
be suitable for the GPS/GNSS frequency range with low RF attenuation.
Caution: The antenna terminal should be earthed at the building entrance in accordance with the ANSI/NFPA 70, the National Electrical
Code (NEC), in particular Section 820.93, Grounding of Outer Conductive Shield of a Coaxial Cable.
Antenna Sky visibility:
GPS signals require a direct line of sight between antenna and satellite. The antenna should see as much of the sky as possible. Fixed
installations require four satellites in view for an initial time fix, while subsequent updates may be possible with fewer satellites.
Console Ports
You can connect the switch to a PC running Microsoft Windows or to a terminal server through either the RJ-45 console port or the USB
console port.
RJ-45 console port. The RJ-45 connection uses an RJ-45-to-DB-9 female cable.
USB mini-Type B console port (5-pin connector). The USB connection uses a USB Type A-to-5-pin mini-Type B cable.
The USB console interface speeds are the same as the RJ-45 console interface speeds.
To use the USB console port, you must install the Cisco Windows USB device driver on the device that is connected to the USB console
port (device running with Microsoft Windows). See Installing the Cisco Microsoft Windows XP, 2000, Vista, 7, 8, and 10 USB Device
Driver, page 64 for more information.
With the Cisco Windows USB device driver, connecting and disconnecting the USB cable from the console port does not affect Windows
HyperTerminal operations. Mac OS X or Linux require no special drivers.
Note: The 5-pin mini-Type B connectors resemble the 4-pin mini-Type B connectors. They are not compatible. Use only the 5-pin
mini-Type B.
3
Page 8

Product Overview
253163
Cable Side
Figure 2 USB Mini-Type B Port
The configurable inactivity timeout reactivates the RJ-45 console port if the USB console port is activated, but no input activity occurs on
it for a specified time period. When the USB console port deactivates due to a timeout, you can restore its operation by disconnecting and
reconnecting the USB cable. For information on using the CLI to configure the USB console interface, see the switch software guide.
Power-Input Terminal
The power-input terminal provides screw terminals for the AC and DC power connections. The switch can operate with one or two power
supplies. If one of the power sources fail, the other continues to power the switch. See Power Supply Installation, page 33 for information.
Figure 3 Power-Input Terminal
208415
Alarm Ports
The switch has four alarm inputs and one alarm output.
Alarm Input
The alarm input is a dry-contact alarm port. You can connect up to four alarm inputs from devices, such as a door, a temperature gauge, or
a fire alarm, to the alarm port. You can use the CLI to set the alarm severity to minor, or major. An alarm generates a system message and
turns on an LED. See the Alarm LEDs, page 9 for the LED descriptions.
Alarm Output
The alarm output can be configured as a major alarm. Output alarms often control an external alarm, such as a bell or a light. To connect an
external alarm device to the relay, you connect two relay contact wires to complete the electrical circuit. See for information on the alarm
pinouts. see the Alarm Port, page 54.
Four 1000 SFP/10G SFP+ Ports (Uplinks)
Depending on the switch model, the uplink ports support either GE optics and 10G optics, or only GE optics. When using a 1000BaseT SFP,
the port only operates at 1000 mbps.
For more information about SFP/SFP+ modules and cables, see Transceiver Modules. See Switch Models, page 1 for model information.
4
Page 9

Product Overview
Cable Side
100/1000 SFP Ports (Downlinks)
The switch Ethernet SFP modules provide connections to other devices. These field-replaceable transceiver modules provide the downlink
interfaces. The IE 5000 supports both FE and GE optics in the downlinks. SFP modules have local connectors (LCs) for fiber-optic
connections or RJ-45 connectors for copper connections.
For the most up-to-date list of supported SFP models, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
For information about SFP modules, see your SFP module documentation and the Installing and Removing SFP Modules, page 25. For more
information about SFP/SFP+ modules and cables, see Transceiver Modules.
10/100/1000 PoE/PoE+ Ports (Downlinks)
You can set the 10/100/1000 ports on the switch to operate in any combination of half duplex, full duplex, or 10 or 100 Mb/s. You can set
the ports for speed and duplex autonegotiation. The default setting is autonegotiate.
When set for autonegotiation, the switch determines the speed and duplex settings of the attached device and advertises its own capabilities.
If the connected device also supports autonegotiation, the switch negotiates the best connection (the fastest line speed that both devices
support and full-duplex transmission if the attached device supports it) and configures itself accordingly. In all cases, the attached device
must be within 328 feet (100 meters).
Warning: Voltages that present a shock hazard may exist on Power over Ethernet (PoE) circuits if interconnections are made using
uninsulated exposed metal contacts, conductors, or terminals. Avoid using such interconnection methods, unless the exposed metal
parts are located within a restricted access location and users and service people who are authorized within the restricted access
location are made aware of the hazard. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key
or other means of security. Statement 1072
The 10/100/1000 PoE ports on the Cisco IE-5000 switches provide PoE support for devices that are compliant with IEEE 802.3af/802.3at.
The Cisco prestandard PoE is also supported for Cisco IP Phones and Cisco Aironet Access Points. The PoE ports on the switch deliver up
to 30 W of PoE+ power. All twelve ports are PoE ports and can be assigned a port priority.
Refer to Table 15 on page 71 for power supply configuration and PoE power budget information.
On a per-port basis, you control whether or not a port automatically provides power when an IP phone or an access point is connected.
The 10/100/1000 PoE ports use RJ-45 connectors with Ethernet pinouts. The maximum cable length is 328 feet (100 meters). The
100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T traffic requires CA5, CAT5e, or CAT6 unshielded twisted pair (UTP) cable. The 10BASE-T traffic can
use CAT3 or CAT4 UTP cable.
For information about configuring and monitoring PoE ports, see the switch software configuration guide on Cisco.com.
For information about port connections and port specifications, see Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports, page 30.
Note: The output of the PoE circuit has been evaluated as a Limited Power Source (LPS) per IEC 60950-1.
SD Flash Memory Card
The switch supports a flash memory card that makes it possible to replace a failed switch without reconfiguring the new switch. The slot
for the flash memory card is on the front of the switch. The flash card is hot swappable and can be accessed on the front panel in non
hazardous locations only. A cover protects the flash card and holds the card firmly in place. The cover is hinged and closed with a captive
screw. This prevents the card from coming loose and protects against shock and vibration.
For more information on inserting and removing the flash memory card, see Power-Supply Side, page 10.
LEDs
You can use the switch system and port LEDs to monitor switch activity and performance.
5
Page 10
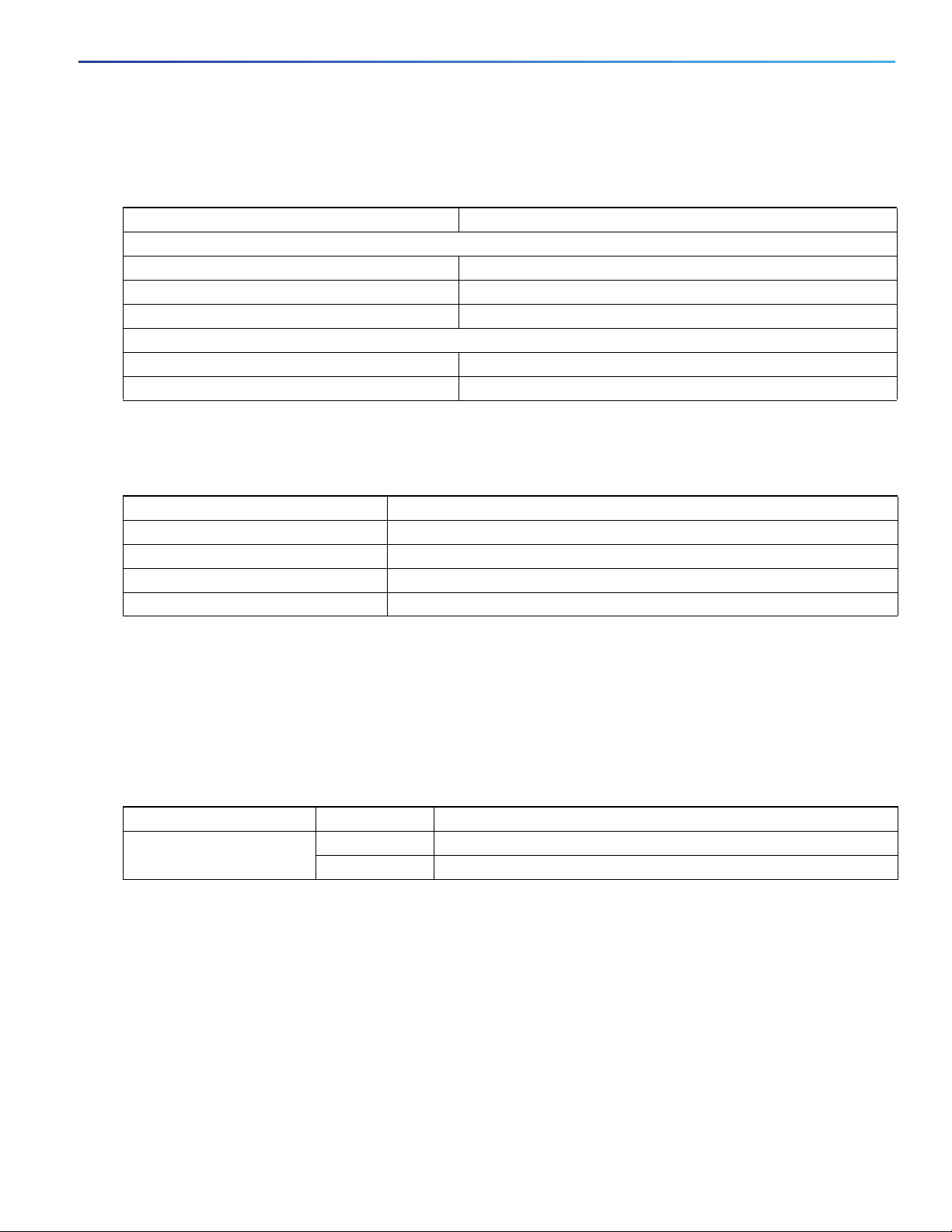
Product Overview
1 2 4
349769
13141516171819
3
5
20
6789101112
Cable Side
Switch Panel LEDs
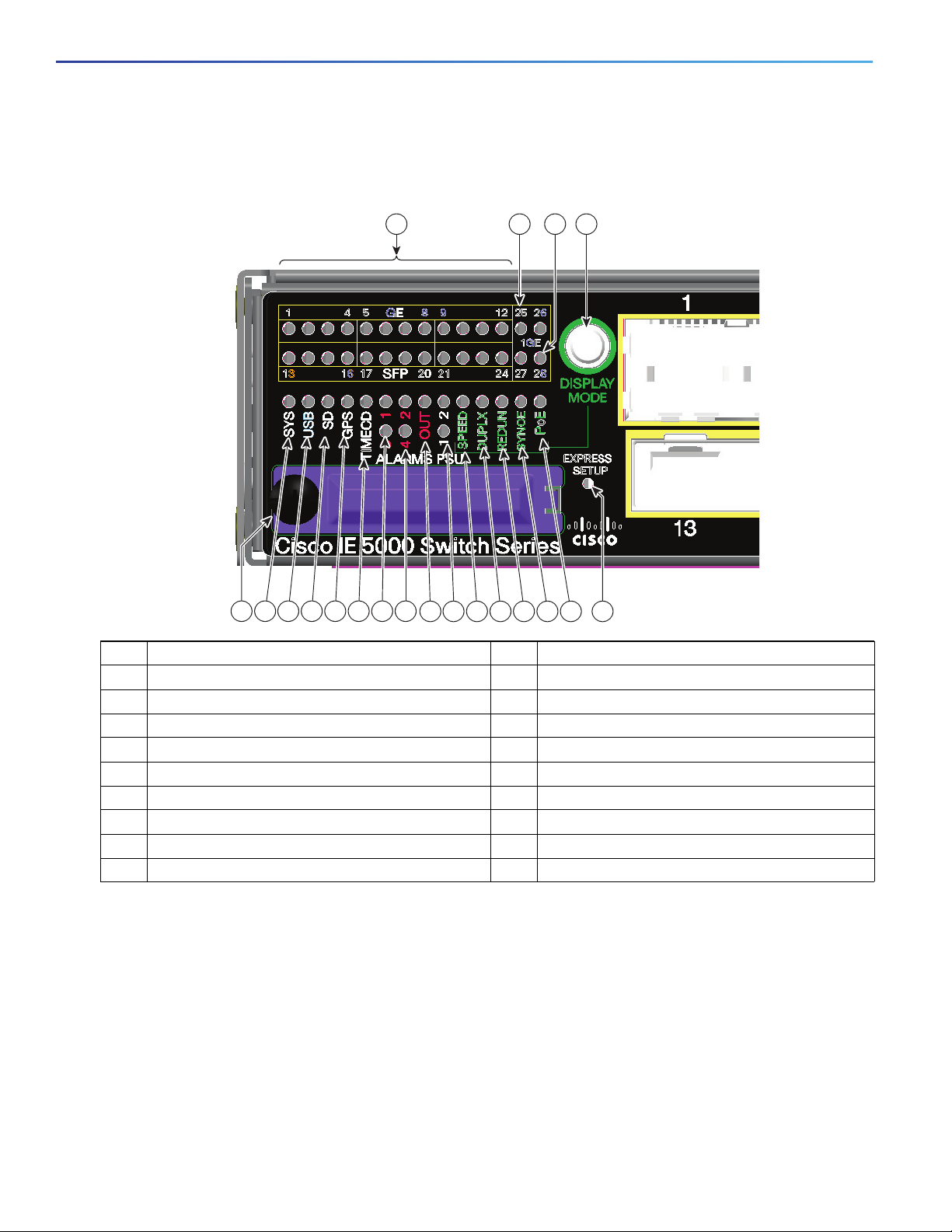
Figure 4 Switch LEDs (Cable Side)
1 Ethernet ports 11 PSU1 and 2 (power supply 1 and 2)
2 10G Ethernet ports 12 OUT (alarm output)
3 10G Ethernet ports 13 Alarms 2 and 4
4 Display mode switch 14 Alarms 1 and 3
5 Express Setup button 15 Timecode status (not currently supported by software)
6 PoE 16 GPS status
7 Synchronous Ethernet status 17 SD (SD flash memory card)
8 Redundancy status 18 USB (mini-USB console)
9 Port duplex status 19 SYS (system)
10 Port speed status 20 SD card slot cover
Port LEDs
Each Ethernet port has a port LED. These port LEDs, display information about the individual ports. The port mode determines the type of
information shown by the port LEDs. Table 2 on page 7 lists the mode LEDs and their associated port modes and meanings.
To select or change a mode, press the Mode button until the desired mode is highlighted. The Mode LED will turn ON solid green when a
mode is selected and turn OFF when timeout (5 seconds) or a different mode is selected. When you change port modes, the meanings of the
port LED colors also change. Table 3 on page 7 explains how to interpret the port LED colors in different port modes.
6
Page 11
Product Overview
Cable Side
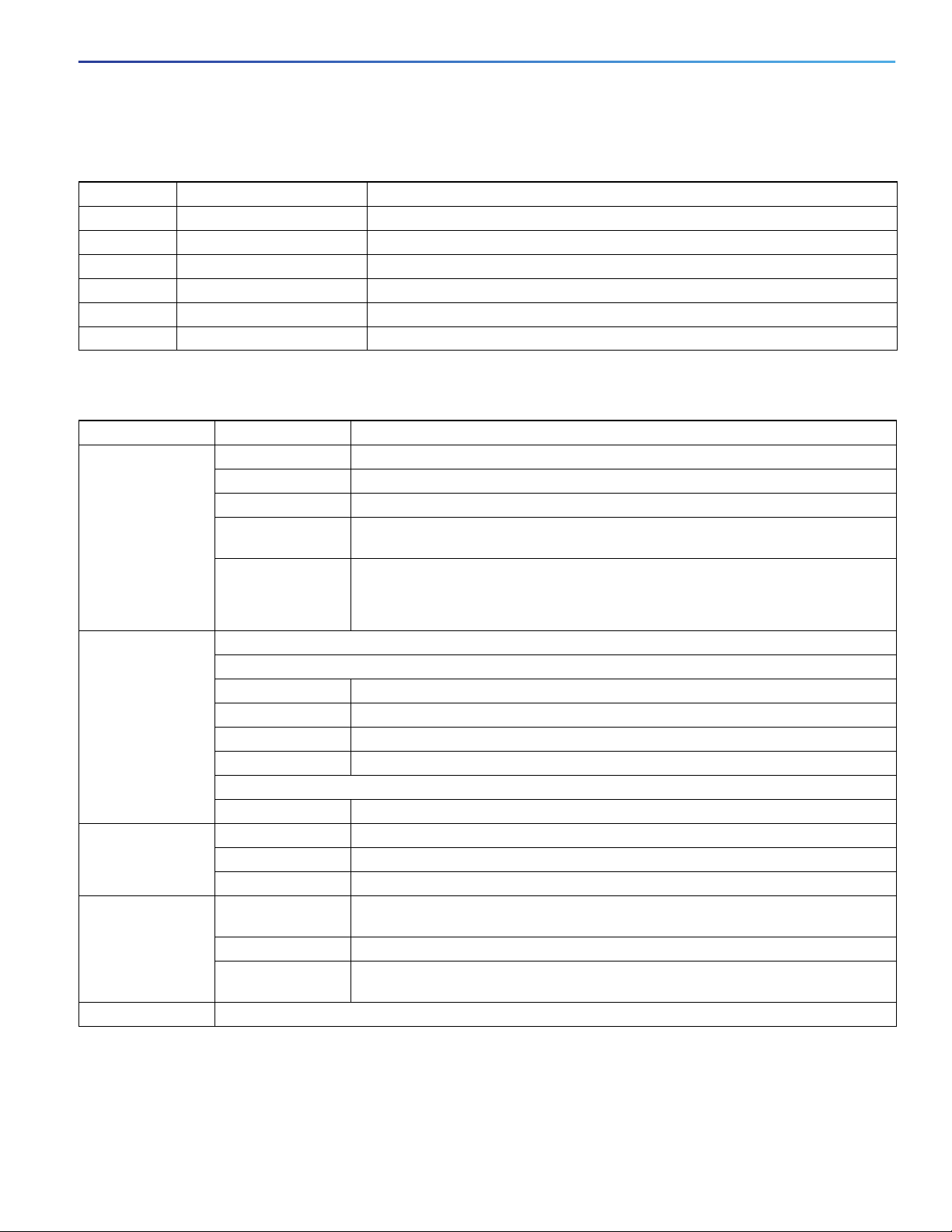
Tabl e 2 Por t Mod e LED s
Mode LED Port Mode Description
All Off Port status The port status. This is the default mode.
SPEED Port speed The port operating speed: 10, 100, 1000 mbps or 10 Gbps.
DUPLX Port duplex mode The port duplex mode: full duplex or half duplex.
REDUN Redundancy status Parallel Redundancy Protocol (PRP) status.
SYNCE Synchronous Ethernet status Not supported by software yet. Mode button skips this LED.
PoE PoE+ port power The PoE+ port status.
Table 3 Meaning of Switch LED Colors in Different Modes
Port Mode LED Port LED Color Meaning
All Off Off No link, or port was administratively shut down.
Green Link present, no activity.
Blinking green Activity. Port is sending or receiving data.
Alternating
green-amber
Amber Port is blocked by Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) and is not forwarding data.
Link fault. Error frames can affect connectivity, and errors such as excessive collisions, CRC
errors, and alignment and jabber errors are monitored for a link-fault indication.
After a port is reconfigured, the port LED can be amber for up to 30 seconds as STP checks the
switch for possible loops.
SPEED 10/100/1000/SFP ports
Downlink Ports
Off Port is not operating.
Amber Port is operating at 10 Mb/s.
Green Port is operating at 100 Mb/s.
Flashing green Port is operating at 1000 Mb/s.
Uplinks Ports
Green Port is operating at 1000 Mb/s.
DUPLX
(duplex)
REDUN Green One or more redundancy protocols are configured and active (for example, HSR, DLR, PRP,
SYNCE Off
Off Port is not operating.
Amber Port is operating in half duplex.
Green Port is operating in full duplex.
etc.)
Blinking amber One or more redundancy protocols are indicating a redundancy fault.
Fast blinking green The port LEDs are showing ports that are participating in a redundancy protocol and the
redundancy fault status of that port.
7
Page 12
Product Overview
Cable Side
Table 3 Meaning of Switch LED Colors in Different Modes (continued)
Port Mode LED Port LED Color Meaning
PoE/PoE+ Off PoE/PoE+ is off.
If the powered device is receiving power from an AC power source, the port LED is off even if
the device is connected to the switch port.
Green PoE/PoE+ is on and all ports function correctly. The port LED is green when the switch port is
providing power.
Alternating green and
amber
Blinking amber PoE/PoE+ is on but one of the high priority ports power is disconnected or failed.
Amber PoE/PoE+ is on with failures.
PoE/PoE+ is on but one of the low priority ports power is disconnected or failed.
PoE+ faults occur when noncompliant cabling or powered devices are connected to a PoE+ port.
Use only standard-compliant cabling to connect Cisco prestandard IP Phones and wireless
access points or IEEE 802.3af/at-compliant devices to PoE+ ports. You must remove from the
network any cable or device that causes a PoE+ fault.
PoE+ is enabled by default.
Display Mode Button
The Display Mode Button allows you to choose the mode you want displayed by the port LEDs (items 1-3 in Figure 4 on page 6). The
LEDs with green text to the left of the Button indicate the chosen display mode. Each time you press the switch, the mode indicator moves
from SPEED, DUPLX, REDUN, SYNCE, and PoE respectively.
Power-Supply Module LEDs
The switch power-supply module LEDs are labeled PSU1 and PSU2 (on the switch) and PSU OK (on the power-supply module). They show
whether power-supply modules 1 and 2 are receiving power.
Table 4 Power Supply Module LEDs
Color System Status
Off Power-supply module (1 or 2) is not installed.
Green Valid input is present, and the output is within the operating range.
Red Valid input is present, and the output is outside the operating range or is not present.
Blinking red Power-supply module (1 or 2) is installed but valid input is not present.
8
Page 13
Product Overview
Cable Side
Alarm LEDs
Table 5 Alarm LEDs
Color System Status
1-4 Input Alarms
Green Alarm not present
Red Minor alarm present
Blinking red Major alarm present
Output Alarm
Green Alarm not present
Red Alarm condition present
SD Flash Memory Card LED
Table 6 SD Flash Card LED
Color System Status
Fast blinking amber Unsupported SD flash memory card is detected.
Slow blinking amber SD flash memory card is not present.
Green SD flash memory card is functioning.
Blinking green SD flash memory card transfer in progress.
USB LED
The USB LED indicates the console port is in use.
If you connect a cable to the console port, the switch automatically uses that port for console communication. If you connect two console
cables, the USB console port has priority.
Table 7 USB LED
LED Color Description
USB console port Green USB console port selected
Off RS232 Console selected
9
Page 14
Product Overview
Power-Supply Side
System LED
Table 8 System LED
Color System Status
Off System is not powered on.
Blinking green Power-On Self-Test (POST) is in progress.
Green System is operating normally.
Red System is receiving power but is not functioning properly.
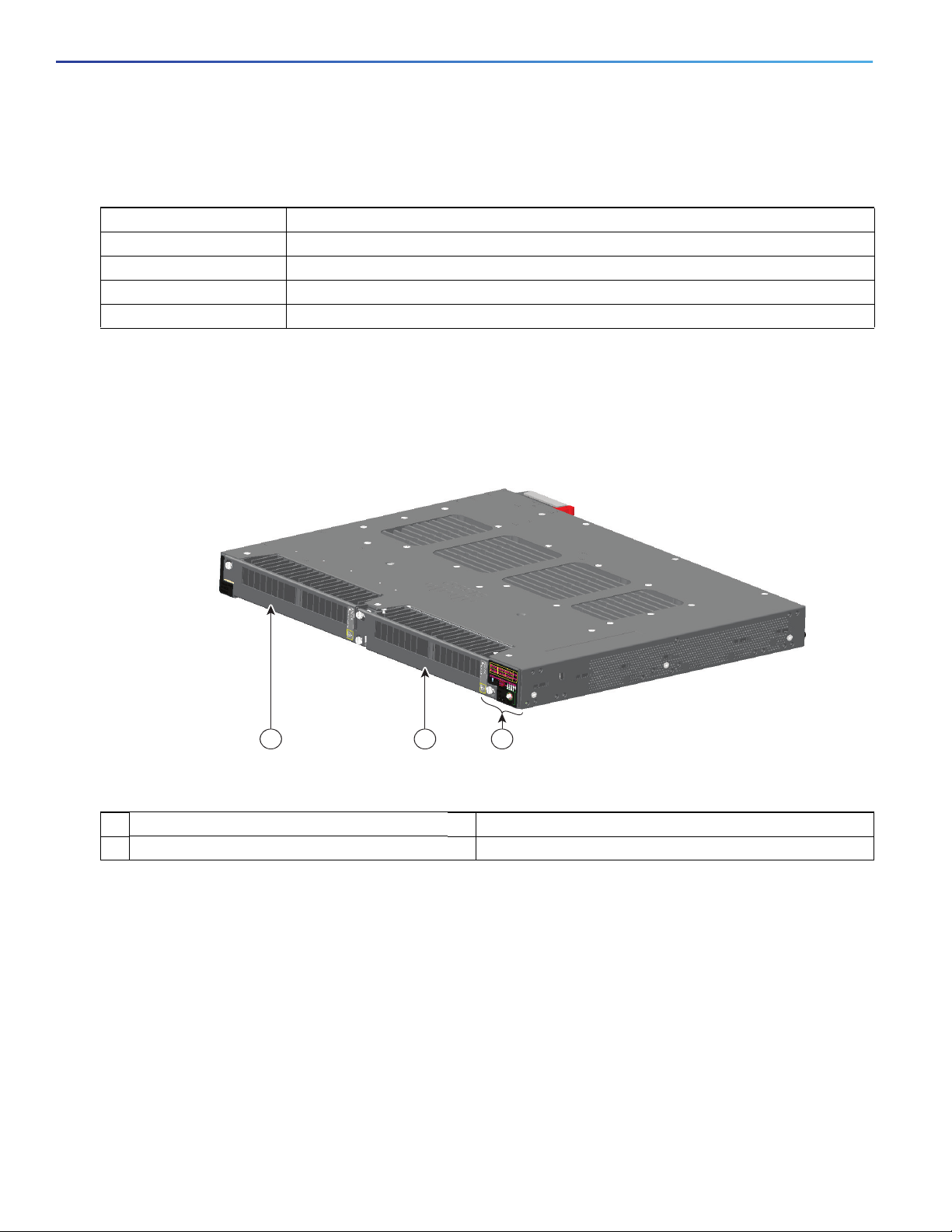
Power-Supply Side
The power-supply side has the LED panel and two power-supply slots for the removable power supplies.
Figure 5 Switch with Both Power-Supply Modules
349771
321
1 Power Supply slot 1 2 Power Supply slot 2
3 LED panel
Note: The 250 W Power Supply is 1.2 in (30 mm) longer than the 150 W versions. Ensure there is adequate space behind the switch for the
extra length.
10
Page 15
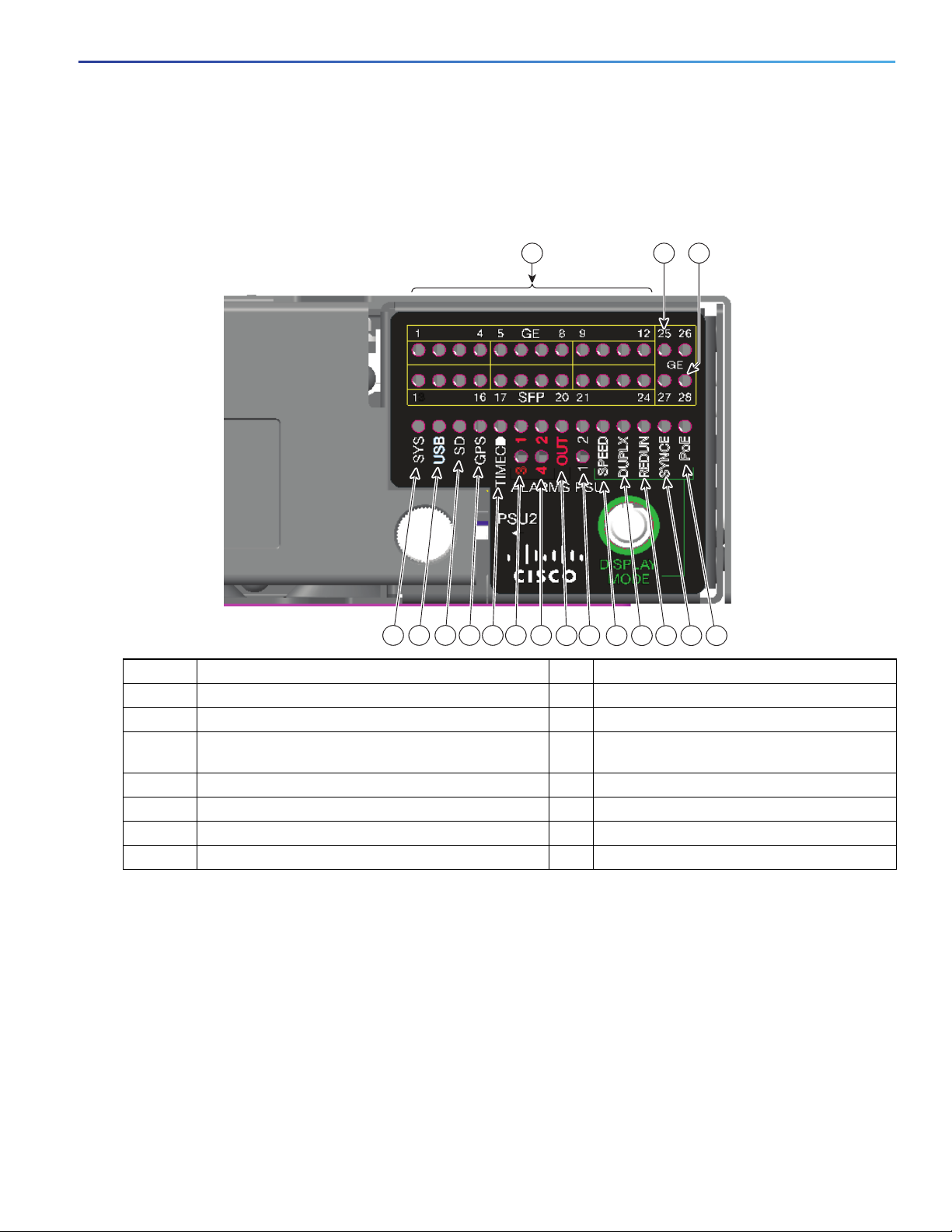
Product Overview
1 2
349772
11121314151617
3
45678910
Power-Supply Side
Power-Supply Side LEDs
Figure 6 Switch LEDs
1 Ethernet ports 10 OUT (alarm output)
2 &3 10G Ethernet ports 11 Alarms 2 and 4
4 PoE 12 Alarms 1 and 3
5 Synchronous Ethernet status 13 Timecode status (not currently supported by
6 Redundancy status 14 GPS status
7 Port duplex status 15 SD (SD flash memory card)
8 Port speed status 16 USB (mini-USB console)
9 PSU1 and 2 (power supply 1and 2) 17 SYS (system)
For more information about these LEDs, see Switch Panel LEDs, page 6.
Power Supply Features
The switch has two slots for power-supply modules:
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H: low-voltage DC
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H: high-voltage AC or DC
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-250: high-voltage AC or DC
Note: For detailed specifications, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
software)
11
Page 16

Product Overview
Management Options
Caution: Only the -H and -250 version power supplies are certified safe for hazardous environments.
The switch supports these power-supply module combinations:
Single low-voltage DC
Single high-voltage AC or DC
Two high-voltage AC or DC
Two low-voltage DC
One high-voltage AC or DC and one low-voltage DC
For information on installing the power-supply modules, see Power Supply Installation, page 33.
See Power-Supply Module LEDs, page 8 for information on the power supply LEDs.
Management Options
Cisco IOS CLI
You can configure and monitor the switch from the CLI. Connect your management station to the switch console port or use Telnet
from a remote management station. See the switch command reference on Cisco.com for information.
SNMP network management
You can manage switches from a Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)-compatible management station. The switch
supports a comprehensive set of Management Information Base (MIB) extensions and four Remote Monitoring (RMON) groups. See
the switch software configuration guide on Cisco.com and the documentation that came with your SNMP application for information.
Device Manager
You can use Device Manager, which is in the switch memory, to manage individual and standalone switches. This web interface offers
quick configuration and monitoring. You can access Device Manager from anywhere in your network through a web browser. For more
information, see the Device Manager online help.
Prime Infrastructure
Cisco Prime Infrastructure simplifies the management of wireless and wired networks. It offers Day 0 and 1 provisioning, as well as
Day N assurance from the branch to the data center. We call it One Management. With this single view and point of control, you can
reap the benefits of One Management across both network and compute.
Network Configurations
See the switch software configuration guide on Cisco.com for an explanation of network configuration concepts. The software configuration
guide also provides network configuration examples for creating dedicated network segments that are interconnected through Ethernet
connections.
12
Page 17

Switch Installation
Read the topics and perform the procedures in this order:
Warnings, page 13
Installation Guidelines, page 14
Verifying Switch Operation, page 14
Installing the Switch, page 14
Installing and Removing SFP Modules, page 25
Replacing the SD Flash Memory Card, page 29
Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports, page 30
Where to Go Next, page 30
Warnings
These warnings are translated into several languages in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco IE 5000 Switch
document that ships on the documentation CD.
These warning statements apply to all the switches:
Warning: Before working on equipment that is connected to power lines, remove jewelry (including rings, necklaces, and watches).
Metal objects will heat up when connected to power and ground and can cause serious burns or weld the metal object to the
terminals. Statement 43
Warning: Read the installation instructions before you connect the system to its power source. Statement 1004
Warning: This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the
use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security. Statement 1017
Warning: This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a
suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain
that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024
Warning: This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit.
Statement 1028
Warning: Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Warning: Ultimate disposal of this product should be handled according to all national laws and regulations. Statement 1040
Warning: For connections outside the building where the equipment is installed, the following ports must be connected through an
approved network termination unit with integral circuit protection.
10/100/1000 Ethernet Statement 1044
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
13
Page 18

Switch Installation
Installation Guidelines
Warning: To prevent the system from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum recommended ambient
temperature of:
140°F (60°C) Statement 1047
Note: Operating temperatures exceeding 60C are not covered by the product safety certifications and approvals. However, the switch can
function in the installations under the environmental conditions listed
Warning: Installation of the equipment must comply with local and national electrical codes. Statement 1074
Note: For U.S. installations, refer to national electrical code ANSI/NFPA 70.
Warning: To prevent airflow restriction, allow clearance around the ventilation openings to be at least:
1.75 in. (4.4 cm). Statement 1076
Warning: Avoid using or servicing any equipment that has outdoor connections during an electrical storm. There may be a risk of
electric shock from lightning. Statement 1088
Switch Specifications, page 70.
Installation Guidelines
Before installing the switch, verify that these guidelines are met:
Cabling is away from sources of electrical noise, such as radios, power lines, and fluorescent lighting fixtures. Make sure that the
cabling is away from other devices that might damage the cables.
Operating environment is within the ranges listed in Technical Specifications, page 69.
Relative humidity around the switch does not exceed 95 percent (non-condensing).
Altitude at the installation site is not higher than 13,800 feet.
For 10/100/1000 fixed ports, cable lengths from the switch to connected devices are not more than 328 feet (100 meters).
For more information about SFP/SFP+ modules and cables, see Transceiver Modules.
Airflow around the switch and through the vents is unrestricted. To prevent overheating, the switch must meet the minimum clearance
of 1.75 in. (4.4 cm) at the top and bottom.
Note: If the switch is installed in a closed or multirack assembly, the temperature around it might be greater than normal room
temperature. Ensure that the internal temperature does not exceed the maximum ambient temperature specifications for the switch.
Verifying Switch Operation
Before installing the switch in a rack or on a wall, you should power the switch and verify that the switch passes the power-on self-test
(POST).
To wire the switch to the power source, see Power-Supply Module Installation, page 35.
When the switch begins POST, the SYS LED blinks green, and the other LEDs stay green. When the switch passes POST, the SYS LED
turns green. The other LEDs turn off and return to their operating status. If the switch fails POST, the SYS LED is amber.
Note: Contact Cisco Systems immediately if your switch fails POST.
After a successful POST, disconnect the power from the switch. For more information, see Wiring the Power Source, page 39. See the
Installing the Switch, page 14 to install the switch in a rack or on a wall.
Installing the Switch
Rack-Mounting, page 15
14
Page 19

Switch Installation
Installing the Switch
Wall-Mounting, page 21
Rack-Mounting
To rack-mount the switch, select the rack size and follow the steps in these sections:
Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks, page 15
Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks for IP-30 Compliance (Optional), page 17
Attaching Brackets for 23-Inch Racks, page 19
Attaching Brackets for ETSI Racks, page 20
Rack-Mounting the Switch, page 20
.
Warning: To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must take special precautions to ensure
that the system remains stable. The following guidelines are provided to ensure your safety:
This unit should be mounted at the bottom of the rack if it is the only unit in the rack.
When mounting this unit in a partially filled rack, load the rack from the bottom to the top with the heaviest
component at the bottom of the rack.
If the rack is provided with stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers before mounting or servicing the unit in the
Statement 1006
rack.
Warning: For mounting railway-application equipment and for EN50155 standard compliance, the switch must be installed only in
a rack mid-mounting position. If you install the switch in a front rack-mounting (cable side or power supply side) position or in a
wall-mounting position, a mechanical failure can occur that results in the switch becoming detached from the rack. Statement 403
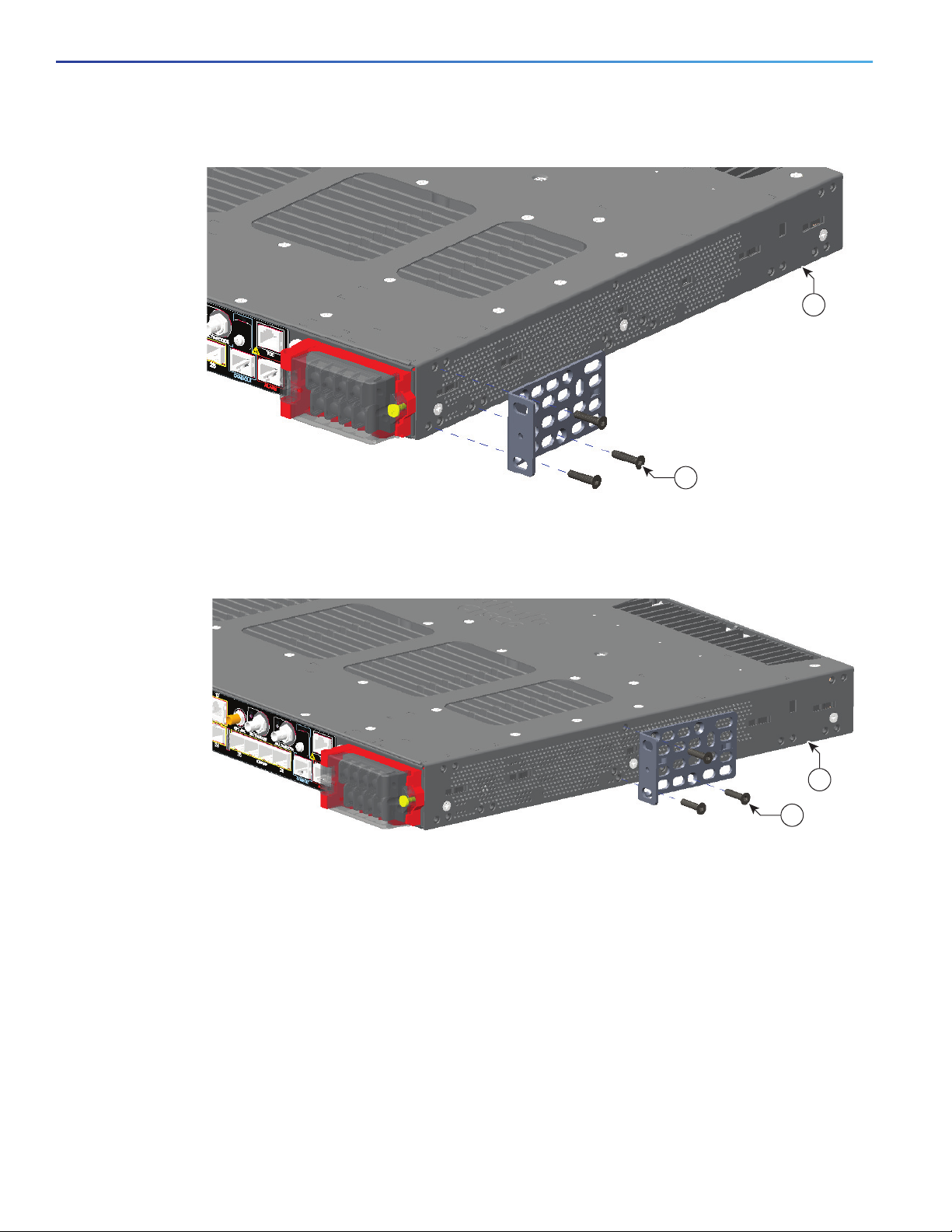
Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks
The following illustrations show how to attach brackets to the switches.
15
Page 20
Switch Installation
1
2
349773
3
2
Installing the Switch
Figure 7 Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks (Front bracket)
Figure 8 Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks (Mid Mount)
16
Page 21

Switch Installation
1
2
Installing the Switch
Figure 9 Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks (Rear Mount)
Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks for IP-30 Compliance (Optional)
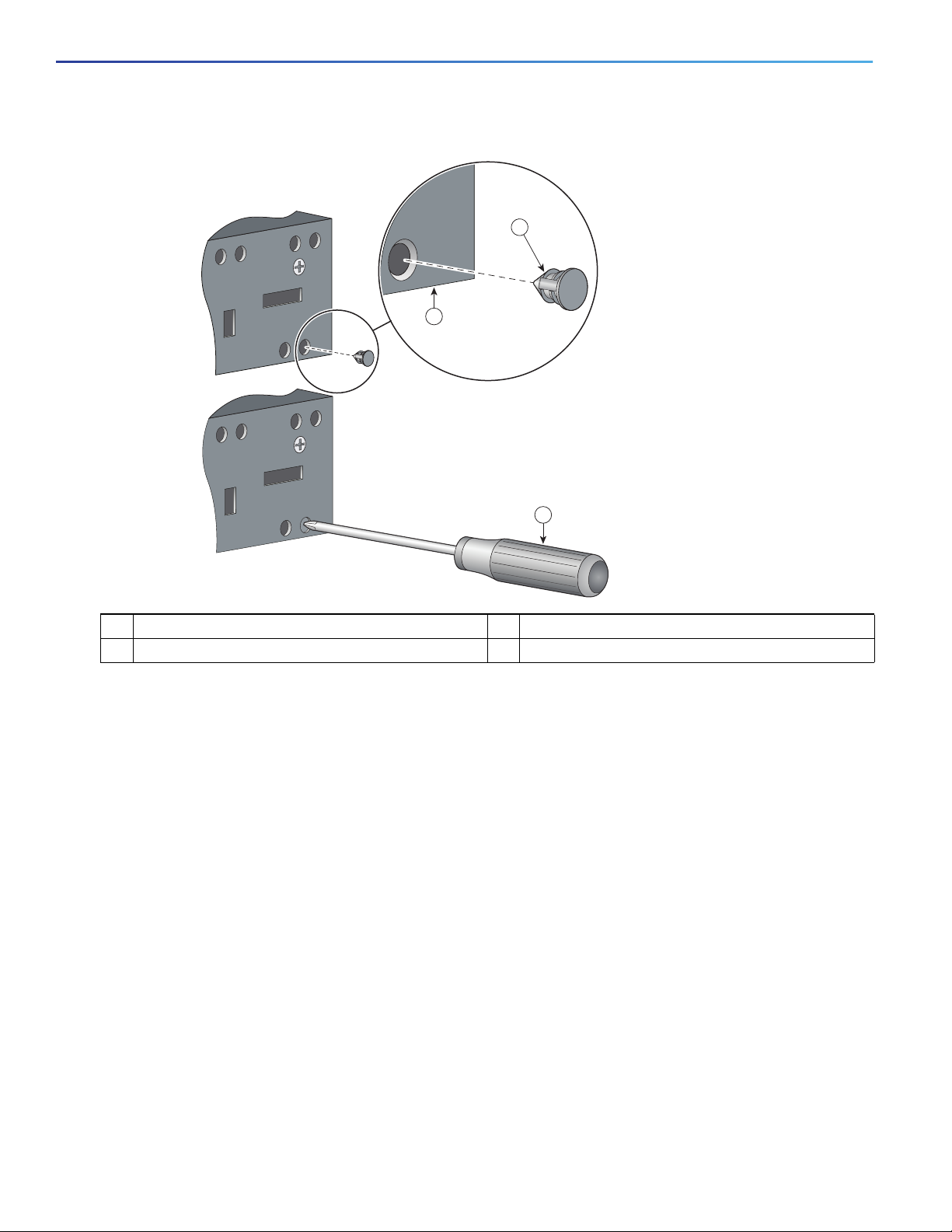
Before installing the mounting brackets, you need to install the rubber plugs in the unused mounting holes. Figure 10 on page 18 shows a
close-up of the rubber plug. You can install the rubber plugs in the holes as shown in Figure 11 on page 19.
17
Page 22
Switch Installation
255738
Installing the Switch
Figure 10 Inserting the Rubber Plug
1
2
3
1 Rubber plug 3 Screwdriver
2 Switch
1. Identify your bracket mounting position. See Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks, page 15.
2. Insert the rubber plugs in the appropriate holes on both sides of the switch. See Figure 11 on page 19.
3. Use a screwdriver or pen to completely push in the rubber plugs. See Figure 10 on page 18.
4. Install the brackets on both sides of the switch. See Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks, page 15 and Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch
Racks for IP-30 Compliance (Optional), page 17.
18
Page 23
Switch Installation
2
3
4
1
1
1
Installing the Switch
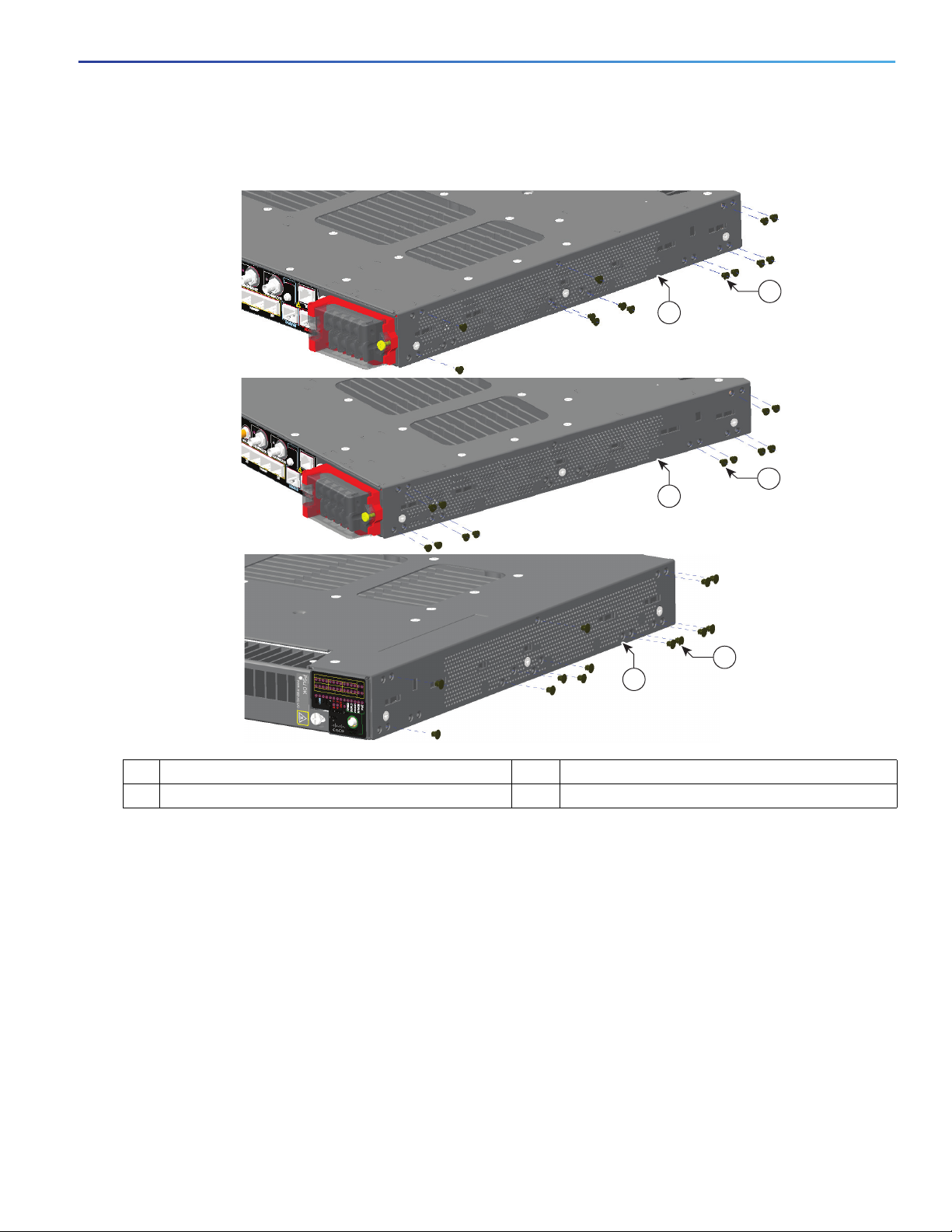
Figure 11 Plug locations by position
1 Rubber plug 3 Mid-mounting position
2 Rear-mounting position 4 Front-mounting position
Note: For IP-30 compliance: If you use 23-inch brackets or ETSI brackets, you can insert the rubber plugs in the same holes as shown in
Figure 11 on page 19 before installing the brackets.
Attaching Brackets for 23-Inch Racks
If 23-inch brackets (RM-RGD-23IN=) are required, follow steps in Figure 12 on page 20 for installation.
Note: 23-inch and ETSI brackets should not be used in high vibration environments, including any railway application (EN50155).
Note: For IP-30 compliance: If you use 23-inch brackets or ETSI brackets, you can insert the rubber plugs in the same holes as shown in
Figure 11 on page 19 before installing the brackets.
19
Page 24

Switch Installation
C
is
co
C
GS 2
5
2
0
C
isco
C
G
S 25
2
0
2
3
1
1
1
2
Installing the Switch
Figure 12 Attaching 23-Inch Brackets
Note: For IP-30 compliance: If you use 23-inch brackets, you can insert the rubber plugs in the same holes as shown in Figure 11 on page 19
before installing the brackets.
Attaching Brackets for ETSI Racks
Figure 13 Attaching Brackets (RM-RGD-ETSI=) for ETSI Racks
1 Phillips flat-head screws 3 Power-supply-side mounting position
2 Cable-side-mounting position
Note: 23-inch and ETSI brackets should not be used in high vibration environments, including any railway application (EN50155).
Note: For IP-30 compliance: If you use ETSI brackets, you can insert the rubber plugs in the same holes as shown in Figure 11 on page 19
before installing the brackets.
Rack-Mounting the Switch
After you attach the brackets on the switch, attach the brackets to the rack. See Figure 14 on page 21.
20
Page 25

Switch Installation
Cisco IE 3010
1
Installing the Switch
Figure 14 Rack-Mounting
1 Mid-mounting position
After the switch is mounted in the rack:
1. Wire the switch to a power source. See Wiring the Power Source, page 39.
2. Connect the ports. See Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports, page 30.
3. Attach the cable guide to prevent the cables from obscuring the LED panels on the devices in the rack. Use the supplied black screw
to attach the cable guide to the left or right bracket.
For configuration instructions about the CLI setup program, go to Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program, page 57.
Wall-Mounting
To wall-mount the switch, follow the steps in these sections:
Attaching Brackets, page 22
Attaching Brackets for IP-30 Compliance (Optional), page 23
Wall-Mounting the Switch, page 23
Warning: Read the wall-mounting instructions carefully before beginning installation. Failure to use the correct hardware or to
follow the correct procedures could result in a hazardous situation to people and damage to the system. Statement 378
Warning: For mounting railway-application equipment and for EN50155 standard compliance, the switch must be installed only in
a rack mid-mounting position. If you install the switch in a front rack-mounting (cable side or power supply side) position or in a
wall-mounting position, a mechanical failure can occur that results in the switch becoming detached from the rack. Statement 403
If the switch is wall-mounted in an enclosure, follow these minimum clearances:
Sides of switch (facing up and facing down): 3.75 in. (9.52 cm)
Port side 3.0 in. (7.62 cm)
Power supply side: 5.25 in. (13.33 cm)
Cover side (not facing wall): 1.75 in. (4.44 cm)
Base side (facing wall): 0 in. (0 cm)
21
Page 26

Switch Installation
1
Installing the Switch
Attaching Brackets
Figure 15 Attaching 19-inch Rack Brackets
1 Phillips truss-head screws
22
Page 27

Switch Installation
Installing the Switch
Attaching Brackets for IP-30 Compliance (Optional)
1. Insert the rubber plugs in the appropriate holes on both sides of the switch. See Figure 10 on page 18.
2. Use a screwdriver or pen to completely push in the rubber plugs. See Figure 10 on page 18.
3. Install the brackets on both sides of the switch. See Attaching Brackets for 19-Inch Racks, page 15.
Wall-Mounting the Switch
For the best support of the switch and cables, ensure that the switch is attached securely to wall studs or to a firmly attached plywood
mounting backboard.
Orientation should exactly match the figure below, with power terminal down, the LEDs up, and the venting and Cisco Logo facing away
from the wall. See Figure 16 on page 24 and After the Switch is Mounted on the Wall, page 24.
23
Page 28

Switch Installation
Installing the Switch
Figure 16 Wall-Mounting the Cisco IE-5000
1
1 User-supplied screws
After the Switch is Mounted on the Wall
Wire the switch to a power source. See Wiring the Power Source, page 39.
For configuration instructions about using the CLI setup program, go to Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program, page 57.
Connect the switch ports. See the Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports, page 30.
24
349787
Page 29

Switch Installation
Installing and Removing SFP Modules
Installing and Removing SFP Modules
This section presents procedures to install and remove fiber-optic and 1000BASE-T SFP transceiver modules.
Note: The 10G Uplink SFP+ slots support up to 4 W of total SFP power. Most SFP modules draw 1 W or less and allow all 4 SFP+ Uplinks
to be used. When installing higher power modules, ensure the total rated power draw remains below 4 W. When installing modules that
draw higher than 1 W, leave at least one empty slot between them.
Note: Some 10G SFP+ modules are not rated to work at very low temperatures. To permit such modules to operate in cold environments,
the IE5000 system has a heater on the 4 Uplink SFP slots.
Installing SFP Modules
These sections describe how to install and remove SFP modules. SFP modules are inserted into SFP module slots on the front of the switch.
Field-replaceable SFP modules provide the uplink interfaces, send (TX) and receive (RX).
You can use any combination of rugged SFP modules. Each SFP module must be of the same type as the SFP module on the other end of
the cable, and the cable must not exceed the stipulated cable length for reliable communications.
For more information about SFP modules, see Cisco Transceiver Modules.
Caution: Depending on the SFP module you use, the operating temperature limits may be effected. Choose an SFP module
appropriate to the installed environment.
Caution: To prevent electrostatic-discharge (ESD) damage, follow standard board and component handling procedures.
Warning: Do not insert and remove SFP modules while power is on; an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an explosion in
hazardous location installations. Be sure that power is removed or the area is nonhazardous before proceeding. Statement 1087
Note: Removing and installing an SFP module can shorten its useful life. Do not remove and insert any module more often than is absolutely
necessary.
Caution: Do not install or remove the LC SFP module with fiber-optic cables attached because of potential damage to the cables,
the cable connector, or the optical interfaces in the SFP module. Disconnect all cables before removing or installing an SFP module.
Removing and installing an SFP module can shorten its useful life. Do not remove and insert SFP modules more often than is
absolutely necessary.
Installing Fiber Optic SFP Modules
Warning: Class 1 laser product. Statement 1008
To install and cable an optical SFP transceiver uplink port:
1. Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
2. Find the send (TX) and receive (RX) markings on the module top.
On some SFP modules, the send and receive (TX and RX) markings might be replaced by arrows that show the direction of the connection,
either send or receive (TX or RX).
3. If the module has a bale-clasp latch, move it to the open, unlocked position.
4. Align the module in front of the slot opening, and push until you feel the connector snap into place.
5. If the module has a bale-clasp latch, close it.
6. For fiber-optic SFP modules, remove the dust plugs and save.
25
Page 30

Switch Installation
208370
Cisco IE 3010
Installing and Removing SFP Modules
7. Connect the SFP cables.
Figure 17 Installing an SFP Module
Caution: Do not remove the dust plugs from the fiber-optic SFP module port or the rubber caps from the fiber-optic cable until you
are ready to connect the cable. The plugs and caps protect the SFP module ports and cables from contamination and ambient light.
Installing 100/1000BASE-T SFP Modules
Table 9 100/1000BASE-T SFP Modules
Model Number Downlink Support Uplink Support
GLC-T
GLC-FE-T-I 10/100 Support expected in future Software
The 100/1000BASE-T (copper) SFP transceiver, see Figure 18 on page 27, has a bale-clasp locking mechanism that secures the transceiver
in the module socket. The SFP network interface is an RJ-45 connector.
10/100/1000 1000 Base-T Only
Not Supported
release
26
Page 31

Switch Installation
Installing and Removing SFP Modules
Figure 18 1000BASE-T SFP Transceiver
1
2
3
1 RJ-45 connector 3 Bale-clasp latching mechanism in the open (unlocked) position.
2 Bale-clasp latching mechanism in the closed (locked) position.
273166
Caution: To comply with GR-1089 intrabuilding lightning immunity requirements, you must use grounded, shielded, twisted-pair,
CAT5 cabling.
Note: When connecting to a 100/1000BASE-T-compatible server, workstation, or router, use four twisted-pair, straight-through CAT5
cabling for the SFP transceiver port. When connecting to a 100/1000BASE-T-compatible switch or repeater, use four twisted-pair, crossover
CAT5 cabling.
To install a 100/1000BASE-T SFP transceiver:
1. Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to the ESD ground connector on the chassis or to a properly grounded bare
metal surface.
Caution: To avoid ESD damage, handle the SFP by its sides; do not touch the connector pins.
2. Remove the SFP module from its protective packaging.
3. Check the markings on the SFP transceiver to verify that you have the correct model for your network.
4. Position the SFP transceiver in front of the port socket opening.
Note: Different Cisco devices have different SFP transceiver socket configurations. Your Cisco device might require that the SFP
transceiver be installed with the bale-clasp either in a latch-up or a latch-down orientation. Verify that you have the SFP transceiver
oriented correctly when you position it in front of the port socket.
5. With the bale-clasp closed (locked), slide the SFP transceiver into the socket until you feel it snap in place in the socket. You may hear
an audible click as the SFP transceiver latch engages in the socket (Figure 17 on page 26).
6. Connect the network interface cable RJ-45 plug to the SFP RJ-45 connector.
7. Observe the port status LED:
— Green indicates that the SFP transceiver and the target device established a link.
— Amber indicates that the port is discovering the network topology and searching for loops. This process takes about 30 seconds,
and then the LED turns green.
— Off indicates that the target device might not be turned on, there might be a cable problem, or there might be a problem with the
adapter installed in the target device. Refer to Troubleshooting, page 45 for solutions to cabling problems.
27
Page 32

Switch Installation
Installing and Removing SFP Modules
Connecting to SFP Modules
This section describes how to connect to a fiber-optic or 1000BASE-T SFP port. For instructions on how to install or remove an SFP module,
see Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports, page 30.
Warning: Class 1 laser product. Statement 1008
Warning: Do not connect or disconnect cables to the ports while power is applied to the switch or any device on the network because
an electrical arc can occur. This could cause an explosion in hazardous location installations. Be sure that power is removed from
the switch and cannot be accidentally be turned on, or verify that the area is nonhazardous before proceeding. Statement 1070
Caution: Do not remove the rubber plugs from the SFP module port or the rubber caps from the fiber-optic cable until you are
ready to connect the cable. The plugs and caps protect the SFP module ports and cables from contamination and ambient light.
Before connecting to the SFP module, be sure that you understand the port and cabling guidelines in Installing and Removing SFP
Modules, page 25. See Cable and Connectors, page 53 for information about the LC on the SFP module.
Caution: To prevent ESD damage, follow standard board and component handling procedures.
Connecting to a Fiber Optic SFP Module
To connect a fiber-optic cable to an SFP module:
1. Remove the rubber plugs from the module port and fiber-optic cable, and store them for future use.
2. Insert one end of the fiber-optic cable into the SFP module port.
3. Insert the other cable end into a fiber-optic receptacle on a target device.
4. Observe the port status LED:
— The LED turns green when the switch and the target device have an established link.
— The LED turns amber while the STP discovers the network topology and searches for loops. This process takes about 30 seconds,
and then the port LED turns green.
— If the LED is off, the target device might not be turned on, there might be a cable problem, or there might be a problem with the
adapter installed in the target device. See Troubleshooting, page 45 for solutions to cabling problems.
5. If necessary, reconfigure and restart the switch or the target device.
Connecting to a 1000BASE-T SFP Module
To connect a CAT5 cable to a 1000BASE-T SFP module:
Caution: To prevent ESD damage, follow standard board and component handling procedures.
1. When connecting to servers, workstations, and routers, insert a four twisted-pair, straight-through cable in the RJ-45 connector. When
connecting to switches or repeaters, insert a four twisted-pair, crossover cable.
Note: When connecting to a 1000BASE-T device, use a four twisted-pair CAT5 cable.
2. Insert the other cable end in an RJ-45 connector on a target device.
3. Observe the port status LED.
— The LED turns green when the switch and the target device have an established link.
28
Page 33

Switch Installation
1
Replacing the SD Flash Memory Card
— The LED turns amber while the STP discovers the network topology and searches for loops. This process takes about 30 seconds,
and then the port LED turns green.
— If the LED is off, the target device might not be turned on, there might be a cable problem, or there might be problem with the
adapter installed in the target device. See Troubleshooting, page 45 for solutions to cabling problems.
4. If necessary, reconfigure and restart the switch or target device.
Removing SFP Modules
1. Attach an ESD-preventive wrist strap to your wrist and to a bare metal surface.
2. Disconnect the cable from the SFP module. For reattachment, note which cable connector plug is send (TX) and which is receive (RX).
3. Insert a dust plug into the optical ports of the SFP module.
4. If the module has a bale-clasp latch, pull the bale out and down to eject it. If the latch is obstructed and you cannot use your finger, use
a small, flat-blade screwdriver or other long, narrow instrument.
5. Grasp the SFP module, and carefully remove it from the slot.
6. Place the module in an antistatic bag or other protective environment.
Figure 19 Removing a Bale-Clasp Latch SFP Module
1 Bale clasp
Replacing the SD Flash Memory Card
1. Locate the flash memory card slot on the cable-side of the switch.
2. Loosen the captive thumb screw. (Be careful not to cross-thread or over-tighten the thumb screw.)
3. Pull the cover open, and pull the cover tab from the hinge.
4. Gently push the flash memory card to eject it. Place it in an anti-static bag to protect it from static discharge.
5. Push the replacement card into the slot, and press it firmly in place. The card is keyed so that you cannot insert it the wrong way.
29
Page 34

Switch Installation
Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports
6. Place the flash card slot cover tabs into the hinge.
7. Close the cover, and hand-tighten the screw.
Connecting Devices to the Ethernet Ports
The Ethernet ports use standard RJ-45 connectors with Ethernet pinouts. The maximum cable length is 328 feet (100 meters). The
100BASE-TX and 1000BASE-T traffic requires Category 5, Category 5e, or Category 6 UTP cable. The 10BASE-T traffic uses Category
3 or Category 4 cable.
The autonegotiation feature is enabled by default on the switch. At this setting, the switch ports configure themselves to operate at the speed
of the attached device. If the device does not support autonegotiation, you can set the switch port speed and duplex parameters. To maximize
performance, either let the ports autonegotiate both speed and duplex, or set the port speed and duplex parameters on both ends of the
connection.
For simplified cabling, the automatic medium-dependent interface crossover (auto-MDIX) feature is enabled by default. With auto-MDIX
enabled, the switch detects the required cable type for copper Ethernet connections and configures the interface accordingly. Therefore, you
can use either a crossover or a straight-through cable for connections to a Ethernet port, regardless of the type of connected device.
See the switch software configuration guide or the switch command reference on Cisco.com for more information about autonegotiation
and auto-MDIX.
If auto-MDIX is disabled, use the guidelines in Cables and Adapters, page 55 to select the cable for connecting the Ethernet ports to other
devices.
When using PoE/PoE+, those ports have the same autonegotiation settings and cabling requirements as those in the Connecting Devices to
the Ethernet Ports, page 30. These ports provide PoE power.
See Cable and Connectors, page 53 for information on the cables and connectors.
The ports provide PoE/PoE+ support for devices compliant with IEEE 802.3af/at and also provide Cisco prestandard PoE/PoE+ support for
Cisco IP Phones and Cisco Aironet Access Points.
On a per-port basis, you can control whether or not a port automatically provides power to a connected IP phone or an access point.
To access an advanced PoE planning tool, use the Cisco Power Calculator on Cisco.com:
http://tools.cisco.com/cpc/launch.jsp
You can use this application to calculate the power supply requirements for a specific PoE/PoE+ configuration. The results show output
current, output power, and heat dissipation.
Warning: Voltages that present a shock hazard may exist on Power over Ethernet (PoE) circuits if interconnections are made using
uninsulated exposed metal contacts, conductors, or terminals. Avoid using such interconnection methods, unless the exposed metal
parts are located within a restricted access location and users and service people who are authorized within the restricted access
location are made aware of the hazard. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the use of a special tool, lock and key
or other means of security. Statement 1072
Caution: Category 5e and Category 6 cables can store high levels of static electricity. Always ground the cables to a suitable and
safe earth ground before connecting them to the switch or other devices.
Where to Go Next
You can use the default configuration or use any of the management options described in the Management Options, page 12 to change the
switch settings.
30
Page 35

Power Supply Installation
This chapter describes how to remove and install a new or replacement power supply. Your switch ships with at least one installed
power-supply module (AC or DC, depending on your order).
The power-supply modules are field-replaceable units (FRUs) and are hot-swappable when deployed in non-hazardous locations.
For translations of the safety warnings in this chapter, see the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for the Cisco IE 5000 Switch
on Cisco.com.
Power-Supply Modules, page 34
Installation Guidelines, page 35
Grounding the Switch, page 36
Installing the Power-Supply Module in the Switch, page 37
Wiring the Power Source, page 39
Removing the Power-Supply Module, page 44
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
33
Page 36

Power Supply Installation
207215
1
2
3
207232
1
2
3
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC
Power-Supply Modules
Power-Supply Modules
Table 10 Power Supply Modules
Model Description
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H Low-voltage DC. For detailed specifications, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H High-voltage AC or DC. For detailed specifications, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-250 High-voltage AC or DC. For detailed specifications, see the IE 5000 Data Sheet.
Figure 20 PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H Power-Supply Module
1 Power-supply module 3 Captive screw
2 PSU OK LED
Figure 21 PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H Power-Supply Module
1 Power-supply module 3 Captive screw
2 PSU OK LED
For a description of the PSU OK LEDs, see the Power-Supply Module LEDs, page 8.
34
Page 37

Power Supply Installation
Power-Supply Module Installation
Power-Supply Module Installation
Installation Guidelines, page 35
Installing a Power-Supply Module, page 35
Wiring the Power Source, page 39
Removing the Power-Supply Module, page 44
Installation Guidelines
Observe these guidelines when removing or installing a power-supply module:
A power-supply module that is only partially connected to the switch disrupts the system operation.
Warning: Blank faceplates and cover panels serve three important functions: they prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and
currents inside the chassis; they contain electromagnetic interference (EMI) that might disrupt other equipment; and they direct
the flow of cooling air through the chassis. Do not operate the system unless all cards, faceplates, front covers, and rear covers are
in place.
Statement 1029
Warning: Do not reach into a vacant slot while installing or removing a module. Exposed circuitry is an energy hazard. Statement
206
Warning: Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or service this equipment. Statement 1030
Warning: Avoid using or servicing any equipment that has outdoor connections during an electrical storm. There may be a risk of
electric shock from lightning. Statement 1088
Installing a Power-Supply Module
This procedure is for installing a power-supply module in the PSU1 or PSU2 slot.
Warning: The covers are an integral part of the safety design of the product. Do not operate the unit without the covers installed.
Statement 1077
Warning: This unit might have more than one power supply connection. All connections must be removed to de-energize the unit.
Statement 1028
Caution: Equipment installation must comply with local and national electrical codes.
Equipment That You Need
Torque driver(s) capable of 5 to 35 in-lbs
Ring, spade, or flanged spade terminal (terminals should be insulated)
— Ring terminal (such as Tyco part number 2-34158-1 for 16–14 AWG or 2-34852-1 for 12–10 AWG wire)
— Spade terminal (such as Tyco part number 54367-2 for 16–14 AWG wire)
— Flanged spade terminal (such as Tyco part number 2-324165-1 for 16–14 AWG wire or 1-324581-1 for 12–10 AWG wire)
Use the 16-14 AWG wire and appropriate terminals for the AC or high-voltage DC power supply
Use the12-10 AWG wire and appropriate terminals for the low-voltage DC power supply
35
Page 38

Power Supply Installation
Power-Supply Module Installation
Crimping tool (such as Thomas & Bett part number WT2000, ERG-2001)
6-gauge copper ground wire
12-AWG wire (minimum) for the low-voltage power-supply module and 16-AWG (minimum) wire for the high-voltage power-supply
module
For power source connections, use wires rated for at least 194°F (90°C).
UL- and CSA-rated style 1007 or 1569 twisted-pair copper wire
Wire-stripping tools for stripping 6-, 10-, 12-, 14-, and 16-gauge wires.
Number-2 Phillips screwdriver
Flat-blade screwdriver
Obtain these necessary tools and equipment:
Ratcheting torque screwdriver with a number-2 and a number-1 Phillips head that exerts up to 15 pound-force inches (lbf-in.) or 240
ounce-force inches (ozf-in.) of pressure.
Panduit crimping tool with optional controlled-cycle mechanism (model CT-720, CT-920, CT-920CH, CT-930, or CT-940CH).
Wire-stripping tools.
12-gauge copper ground wire (insulated or noninsulated) when using the single-ground connection.
6-gauge copper ground wire (insulated or noninsulated) when using the dual-ground connection.
For the dual ground connection, also use the supplied dual-hole lug from the accessory kit.
Four leads of 16-gauge copper wire.
Grounding the Switch
Follow the grounding procedures at your site and observe these warnings:
Warning: This equipment must be grounded. Never defeat the ground conductor or operate the equipment in the absence of a
suitably installed ground conductor. Contact the appropriate electrical inspection authority or an electrician if you are uncertain
that suitable grounding is available. Statement 1024
Warning: When installing or replacing the unit, the ground connection must always be made first and disconnected last. Statement
1046
Caution: Follow the grounding procedure instructions, and use an appropriately Listed or certified lug (included with the switch)
for number-6 AWG wire and 10-32 ground-lug screws.
Note: You can use the grounding lug to attach a wrist strap for ESD protection during servicing.
Follow these steps to install a dual-hole lug on the switch. Be sure to follow any grounding requirements at your site.
1. Use a Phillips screwdriver or a ratcheting torque screwdriver with a Phillips head to remove the ground screw from the cable side of
the switch. You need the screw in Step 4.
2. Strip the 6-gauge ground wire to 0.5 inch (12.7 mm) ± 0.02 inch (0.5 mm). See Figure 22 on page 37. Stripping more than the
recommended amount of wire can leave exposed wire from the connector.
36
Page 39

Power Supply Installation
Insulation
Wire lead
0.5 in. (12.7 mm) ± 0.02 in. (0.5 mm)
60528
2
Cisco IE 3010
208335
Power-Supply Module Installation
Figure 22 Stripping the Ground Wire
3. Insert the ground wire into the terminal lug, and crimp the terminal to the wire. (see Figure 23 on page 37).
Figure 23 Crimping the Terminal Lug
4. Slide the ground screw from Step 1 through the terminal lug. Insert the ground screws into the opening on the cable side.
Figure 24 Attaching the Terminal Lug
1 Dual-hole terminal lug
5. Use a ratcheting torque screwdriver to tighten the ground screws to 30 in-lb (± 2 in-lb).
6. Attach the other end of the ground wire to an appropriate ground.
Installing the Power-Supply Module in the Switch
1. Ensure that the power is off at the AC or DC circuits.
80938
Locate the circuit breakers, turn them OFF, and lock out the circuit.
37
Page 40

Power Supply Installation
Cisco IE 3010
Switch Series
208382
208383
Power-Supply Module Installation
Warning: If the power is not off at the AC or DC circuit breaker, do not touch the power-input terminal.
2. Use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the two captive screws of the blank power-supply module and gently pull it out. See Figure 25 on
page 38 and Figure 26 on page 38.
Figure 25 Loosen the Screws on the Power Supply Blank
Figure 26 Remove the Power Supply Blank
Cisco Connected Grid
Switch 2500 Series
3. Insert the power-supply module into the slot, and gently push it in. See Figure 27 on page 39.
Note: Ensure that the power supply module is flush with the switch.
Installing the DC Power Supply in the Switch
To remove and install a DC-powered power supply module, follow these steps:
1. Turn off power at the DC circuits. To ensure that power is removed from the DC circuits, locate the circuit breakers for the DC circuits,
switch the circuit breakers to the OFF position, and tape the circuit-breaker switches in the OFF position.
2. Use a number-2 Phillips screwdriver to remove the plastic safety cover from the power supply terminal blocks.
3. Use a number-1 Phillips screwdriver to remove the DC-input power wires from the power terminals.
Use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the two captive screws at the lower edge that secure the power supply module to the switch chassis
(Figure 27 on page 39).
4. Remove the power supply module from the power slot by pulling on the extraction handle.
5. Insert the new power supply into the power supply slot, and gently apply pressure while pushing the module into the slot (Figure 27
on page 39). When correctly inserted, the power supply is flush with the switch rear panel.
38
Page 41

Power Supply Installation
Power-Supply Module Installation
Figure 27 Insert the Power-Supply Module
6. Use a ratcheting torque screwdriver to torque each screw to 8–10 in-lb (4-6.5 in-lb for 250 W PSU).
Wiring the Power Source
208377
Before you wire the power source, review these warnings:
Warning: This product relies on the building’s installation for short-circuit (overcurrent) protection. Ensure that the protective
device is rated not greater than:
AC: 10 A, DC: 15 A Statement 1005
Warning: A readily accessible two-poled disconnect device must be incorporated in the fixed wiring.
Statement 1022
Warning: Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install or replace this equipment.
Statement 1030
Warning: Hazardous voltage or energy may be present on power terminals. Always replace cover when terminals are not in service.
Be sure uninsulated conductors are not accessible when cover is in place. Statement 1086
1. Ensure that the power is off at the AC or DC circuits.
Locate the circuit breakers, turn them OFF, and lock out the circuit.
Warning: If the power is not off at the AC or DC circuit breaker, do not touch the power-input terminal.
2. Use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the captive screw on the power-input terminal, and open the cover.
39
Page 42

Power Supply Installation
Power-Supply Module Installation
Figure 28 Opening the Power-Input Terminal Cover
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2A
Cisco CGS 2520
5
10A
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2A
2A
5
2A
10A
207426
The terminal screws labels are on the power-input terminal cover. See Figure 29 on page 41.
40
Page 43

Power Supply Installation
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2A
5
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2A
2A2A
10A
10A
5
2
1
4
3
76
98
11
10
14
13
5
12
207241
0.25 in. (6.3 mm) ± 0.02 in. (0.5 mm)
Power-Supply Module Installation
Figure 29 Power-Input Terminal
1 Line connection for high-voltage AC (PSU1) 8 Line connection for high-voltage AC (for PSU2)
2 Neutral connection for high-voltage AC (PSU1) 9 Neutral connection for high-voltage AC (PSU2)
3 Positive connection for high-voltage DC (PSU1) 10 Positive connection for high-voltage DC (PSU2)
4 Negative connection for high-voltage DC (PSU1) 11 Negative connection for high-voltage DC (PSU2)
5 PSU1 (power-supply module 1) 12 PSU2 (power-supply module 2)
6 Positive connection for low-voltage DC (PSU1) 13 Positive connection for low-voltage DC (PSU2)
7 Negative connection for low-voltage DC (PSU1) 14 Negative connection for low-voltage DC (PSU2)
Note: The power-supply module 1 connection is labeled PSU1, and the power-supply module 2 connection is labeled PSU2. Make sure that
you connect the wires to the correct terminal screws.
3. Use twisted-pair copper wire to connect from the power-input terminal to the power source.
4. Strip each of the two wires to 0.25 inch (6.3 mm) ± 0.02 inch (0.5 mm).
Note: Do not strip more than 0.27 inch (6.8 mm) of insulation from the wire. Stripping more than the recommended amount of wire
can leave exposed wire from the connector after installation.
Figure 30 Stripping the Input Power Source Wire
5. Insert the wire into a spade terminal, and crimp it to the wire.
You can also use a ring or flanged spade terminal as listed in Equipment That You Need, page 35.
41
Page 44

Power Supply Installation
207427
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2.2A
100-240V~, 50-60Hz, 2.2A
Cisco IE 3010
208381
C
co IE
3
0
Power-Supply Module Installation
Figure 31 Crimping the Spade Terminal Lug
6. Loosen the terminal screw, and slide the terminal under the screw and washer. See Figure 33 on page 43.
Note: Use the appropriate terminal screws based on power supply type: high-voltage (AC or DC) or low-voltage (DC).
7. Make the power connection:
AC Power Connection
Connect the line wire into the terminal screw labeled L and the neutral wire into the terminal screw labeled N to complete the AC
connection.
Figure 32 Connecting the Wires to the High-Voltage AC Power (PSU1)
DC Power Connection
Connect the positive wire into the terminal screw labeled “+”, and the negative wire into the terminal screw labeled “–”.
Low-voltage DC Power-Supply Module
Connect the wires to the terminals labeled Lo.
42
Page 45

Power Supply Installation
Cisco IE 3010
208380
Ci
s
co IE
301
Power-Supply Module Installation
High-voltage DC Power-Supply Module
Connect the wires to the terminals labeled Hi.
Note: Ensure that you cannot see any wire lead. Only wire with insulation should extend from the terminal screw.
Figure 33 Connecting the Wires to the Low-Voltage DC Power (PSU2)
8. Torque the captive screws (above the wires) to 8.5 in-lb (± 0.5 in-lb).
9. Complete the power connection:
AC Power Connection
Connect the other end of the line wire (the one connected to L) to the line terminal on the AC-power source, and connect the other end
of the neutral wire (the one connected to N) to the neutral terminal on the AC power source.
DC Power Connection
Connect the other end of the positive wire (the one connected to “+”) to the positive terminal on the DC-power source, and connect
the other end of the negative wire (the one connected to “–”) to the negative terminal on the DC power source.
Note: Ensure that you cannot see any wire lead. Only wire with insulation should extend from the terminal screw.
If you have two power supplies, repeat steps 1 through 10.
10. Close the power-input terminal cover.
11. Use a ratcheting torque screwdriver to torque the screw to 7 in-lb (± 1 in-lb).
12. Turn on the power at the AC or DC circuit.
13. Verify that the PSU1 or PSU2 LED on the switch and PSU OK LED on the power-supply module are green.
See the switch software guide for information on how to configure the power supply settings.
43
Page 46

Power Supply Installation
208384
Cisco IE 3010
Switch Series
208385
Removing the Power-Supply Module
Removing the Power-Supply Module
The power-supply modules are hot-swappable. By removing the power-supply modules, you can power off the switch without disconnecting
the wiring from the power-input terminal.
1. Ensure that the power is off at the AC or DC circuits.
Locate the circuit breakers, turn them OFF, and lock out the circuit.
Warning: If the power is not off at the AC or DC circuit breaker, do not touch the power-input terminal.
2. Verify that the PSU LED and PSU OK LED is blinking red or is off.
3. Use a Phillips screwdriver to loosen the captive screws that secure the power-supply module to the switch. See Figure 34 on page 44.
Warning: Hot surface. Statement 1079
Figure 34 Removing the Screws
Cisco IE 3010
Switch Series
4. Remove the power-supply module from the power slot. The power-supply module might be hot. See Figure 35 on page 44.
5. Install a new power-supply module or a blank cover.
Figure 35 Removing the Power-Supply Module
Caution: To prevent exposure to hazardous voltages and to contain electromagnetic interference (EMI), either a power-supply
module or a blank cover must be in each power-supply module slot at all times.
44
Page 47

Troubleshooting
This chapter provides these topics for troubleshooting problems:
Diagnosing Problems, page 45
How to Recover Passwords, page 48
Finding the Switch Serial Number, page 48
Diagnosing Problems
The switch LEDs provide troubleshooting information about the switch. They show boot errors, port-connectivity problems, and overall
switch performance. You can also get statistics from Device Manager, the CLI, or an SNMP workstation. See the Cisco IE 5000 Switch
Software Configuration Guide, or the documentation that came with your SNMP application for details.
Switch Boot Fast
Note: Contact your Cisco TAC representative if your switch does not successfully boot.
Note: You can disable boot fast and run POST by using the Cisco IOS CLI, see the Cisco IE 5000 Switch Software Configuration Guide for
more information.
Switch LEDs
Look at the port LEDs information when troubleshooting the switch. See LEDs, page 5 for a description of the LED colors and their
meanings.
Switch Connections
Bad or Damaged Cable
Always examine the cable for marginal damage or failure. A cable might be just good enough to connect at the physical layer, but it could
corrupt packets as a result of subtle damage to the wiring or connectors. You can identify this problem because the port has many packet
errors or it constantly flaps (loses and regains link).
Exchange the copper or fiber-optic cable with a known good cable.
Look for broken or missing pins on cable connectors.
Rule out any bad patch panel connections or media converters between the source and the destination. If possible, bypass the patch
panel, or eliminate media converters (fiber-optic-to-copper).
Try the cable in another port to see if the problem follows the cable.
Ethernet and Fiber-Optic Cables
Make sure that you have the correct cable:
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
45
Page 48

Troubleshooting
Diagnosing Problems
For Ethernet, use Category 3 or better copper cable for 10 Mb/s UTP connections. Use either Category 5, Category 5e, or Category 6
UTP for 10/100/1000 Mb/s, and PoE connections.
Verify that you have the correct fiber-optic cable for the distance and port type. Make sure that the connected device ports match and
use the same type encoding, optical frequency, and fiber type.
Determine if a copper crossover cable was used when a straight-through was required or the reverse. Enable auto-MDIX on the switch,
or replace the cable.
Link Status
Verify that both sides have a link. A broken wire or a shutdown port can cause one side to show a link even though the other side does not
have a link.
A port LED that is on does not guarantee that the cable is functional. It might have encountered physical stress, causing it to function at a
marginal level. If the port LED does not turn on:
Connect the cable from the switch to a known good device.
Make sure that both ends of the cable are connected to the correct ports.
Verify that both devices have power.
Verify that you are using the correct cable type. See Cable and Connectors, page 53 for information.
Look for loose connections. Sometimes a cable appears to be seated but is not. Disconnect the cable, and then reconnect it.
10/100/1000 Port Connections
If a port appears to malfunction:
Verify the status of all ports by checking the LEDs. For more information, see Switch LEDs, page 45.
Use the show interfaces command to see if the port is error-disabled, disabled, or shut down. Reenable the port if necessary.
Verify the cable type. See Cable and Connectors, page 53.
SFP Module
Use only Cisco SFP modules. Each Cisco module has an internal serial EEPROM that is encoded with security information. This encoding
verifies that the module meets the requirements for the switch.
Inspect the SFP module. Exchange the suspect module with a known good module.
Verify that the module is supported on this platform. (The switch release notes on Cisco.com list the SFP modules that the switch
supports.)
Use the show interfaces command to see if the port or module is error-disabled, disabled, or shutdown. Reenable the port if needed.
Make sure that all fiber-optic connections are clean and securely connected.
Interface Settings
Verify that the interface is not disabled or powered off. If an interface is manually shut down on either side of the link, it does not come up
until you reenable the interface. Use the show interfaces command to see if the interface is error-disabled, disabled, or shut down on either
side of the connection. If needed, reenable the interface.
46
Page 49

Troubleshooting
Resetting the Switch
Ping End Device
Ping from the directly connected switch first, and then work your way back port by port, interface by interface, trunk by trunk, until you
find the source of the connectivity issue. Make sure that each switch can identify the end device MAC address in its Content-Addressable
Memory (CAM) table.
Spanning Tree Loops
STP loops can cause serious performance issues that look like port or interface problems.
A unidirectional link can cause loops. It occurs when the traffic sent by the switch is received by the neighbor, but the traffic from the
neighbor is not received by the switch. A broken cable, other cabling problems, or a port issue can cause this one-way communication.
You can enable UniDirectional Link Detection (UDLD) on the switch to help identify unidirectional link problems. For information about
enabling UDLD on the switch, see the “Understanding UDLD” section in the switch software configuration guide on Cisco.com.
Switch Performance
Speed, Duplex, and Autonegotiation
Port statistics that show a large number of alignment errors, frame check sequence (FCS), or late-collisions errors, might mean a speed or
duplex mismatch.
A common issue occurs when duplex and speed settings are mismatched between two switches, between a switch and a router, or between
the switch and a workstation or server. Mismatches can happen when manually setting the speed and duplex or from autonegotiation issues
between the two devices.
To maximize switch performance and to ensure a link, follow one of these guidelines when changing the duplex or the speed settings.
Let both ports autonegotiate both speed and duplex.
Manually set the speed and duplex parameters for the interfaces on both ends of the connection.
If a remote device does not autonegotiate, use the same duplex settings on the two ports. The speed parameter adjusts itself even if the
connected port does not autonegotiate.
Autonegotiation and Network Interface Cards
Problems sometimes occur between the switch and third-party network interface cards (NICs). By default, the switch ports and interfaces
autonegotiate. Laptops or other devices are commonly set to autonegotiate, yet sometimes issues occur.
To troubleshoot autonegotiation problems, try manually setting both sides of the connection. If this does not solve the problem, there could
be a problem with the firmware or software on the NIC. You can resolve this by upgrading the NIC driver to the latest version.
Cabling Distance
If the port statistics show excessive FCS, late-collision, or alignment errors, verify that the cable distance from the switch to the connected
device meets the recommended guidelines. See the Cable and Connectors, page 53.
Resetting the Switch
These are reasons why you might want to reset the switch to the factory default settings:
You installed the switch in your network and cannot connect to it because you assigned the wrong IP address.
47
Page 50

Troubleshooting
How to Recover Passwords
You want to reset the password on the switch.
Note: Resetting the switch deletes the configuration and reboots the switch.
Caution: If you press the Express Setup button when you power on, the automatic boot sequence stops, and the switch enters
bootloader mode.
To reset the switch:
1. Press and hold the Express Setup button (recessed behind a small hole in the faceplate) for about 10 seconds with a paper clip or similar
object. The switch reboots. The system LED turns green after the switch completes rebooting.
2. Press the Express Setup button again for 3 seconds. A switch 10/100/1000 Ethernet port blinks green.
The switch now behaves like an unconfigured switch. You can configure the switch by using the CLI setup procedure described in
Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program, page 57
How to Recover Passwords
Password recovery is a feature that a system administrator can enable or disable. If password recovery is disabled, the only way to recover
from a lost or forgotten password is to clear the switch configuration entirely. For this procedure, see the How to Recover Passwords,
page 48.
The Cisco IE 5000 Switch Software Configuration Guide provides details about enabling and disabling the password recovery feature and
the procedure for recovering passwords.
Finding the Switch Serial Number
If you contact Cisco Technical Assistance, you need to know the serial number of your switch. The serial number is on the top of the switch.
You can also use the show version command to obtain the switch serial number.
48
Page 51

Hazardous Location Installation Information
This appendix provides hazardous location installation information for the Cisco IE 5000 Hardened Aggregators.
Also refer to the printed IE5000 Product Document of Compliance, included with the switch in the packaging, for Hazardous Location and
Compliance information.
Hazardous Area Installation Warnings
Caution: When installed in a Class I. Div/Zone 2 hazardous location environment, this equipment must be installed in a min. IP54
certified enclosure.
Caution: Airflow around the switch must be unrestricted. To prevent the switch from overheating, there must be the following
minimum clearances:
- Top and bottom: 1.75 in. (4.4 cm)
- Sides: 1.75 in. (4.4 cm)
- Front: 1.75 in. (4.4 cm)
Contact your Cisco Technical Assistance Centre (TAC) if tighter spacings are required.
Caution: When installed in a Class I. Div/Zone 2 hazardous location environment. this equipment must be installed in a pollution
degree 2 environment per IEC 60664-1)
Caution: This equipment is suitable for use in Class I. Division 2 . Groups A, B . C. D. or only nonhazardous locations.
Caution: Do not install or remove SFP or SFP+ modules when an explosive atmosphere may be present.
Caution: Do not install or remove power supplies when an explosive atmosphere may be present.
Caution: Do not use the USB Console Service Port when an explosive atmosphere may be present.
Warning: Exposure to some chemicals could degrade the sealing properties of materials used in the sealed relay device. Statement
381
Warning: This unit is intended for installation in restricted access areas. A restricted access area can be accessed only through the
use of a special tool, lock and key, or other means of security. Statement 1017
Warning: To prevent the system from overheating, do not operate it in an area that exceeds the maximum
recommended ambient temperature of :
Warning: When you connect or disconnect the power and/or alarm connector with power applied, an electrical arc can occur. This
could cause an explosion in hazardous area installations. Be sure that all power is removed from the switch and any other circuits.
Be sure that power cannot be accidentally turned on or verify that the area is nonhazardous before proceeding. Statement 1058
140°F (60°C) Statement 1047
Warning: In switch installations in a hazardous location, the DC power source could be located away from the vicinity of the switch.
Before performing any of the following procedures, locate the DC circuit to ensure that the power is removed and cannot be turned
on accidentally, or verify that the area is nonhazardous before proceeding. Statement 1059
Warning: This equipment is supplied as “open type” equipment. It must be mounted within an enclosure that is suitably designed
for those specific environmental conditions that will be present and appropriately designed to prevent personal injury resulting
from accessibility to live parts. The interior of the enclosure must be accessible only by the use of a tool.
The enclosure must meet IP 54 or NEMA type 4 minimum enclosure rating standards. Statement 1063
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
49
Page 52

Hazardous Location Installation Information
Hazardous Area Installation Warnings
Warning: Use twisted-pair supply wires suitable for 86°F (30°C) above surrounding ambient temperature outside the enclosure.
Statement 1067
Warning: When used in a Class I, Division 2, hazardous location, this equipment must be mounted in a suitable enclosure with a
proper wiring method that complies with the governing electrical codes. Statement 1069
Warning: Explosion Hazard—The area must be known to be nonhazardous before installing, servicing, or replacing the unit.
Statement 1082
Note: This equipment has been tested by UL for the explosion, fire, shock and casualty hazards required by the applicable hazardous
locations standards. UL certification does not cover the performance or reliability of any GPS hardware, GPS operating software, or other
GPS-related aspects of equipment covered under this category. Accordingly, UL makes no representations, warranties or certifications
regarding the performance or reliability of any GPS-related functions of equipment covered under this category.
North American Hazardous Location Approval
The following information applies when operating this equipment in hazardous locations:
English: Products marked "Class I, Div 2, GP A, B, C, D" are suitable for use in Class I Division 2 Groups A, B, C, D,
Hazardous Locations and nonhazardous locations only. Each product is supplied with markings on the rating
nameplate indicating the hazardous location temperature code. When combining products within a system, the
most adverse temperature code (lowest "T" number) may be used to help determine the overall temperature
code of the system. Combinations of equipment in your system are subject to investigation by the local Authority
Having Jurisdiction at the time of installation.
Français: Informations sur l'utilisation de cet équipement en environnements dangereux:
Les produits marqués "Class I, Div 2, GP A, B, C, D" ne conviennent qu'à une utilisation en environnements de
Classe I Division 2 Groupes A, B, C, D dangereux et non dangereux. Chaque produit est livré avec des marquages
sur sa plaque d'identification qui indiquent le code de température pour les environnements dangereux. Lorsque
plusieurs produits sont combinés dans un système, le code de température le plus défavorable (code de
température le plus faible) peut être utilisé pour déterminer le code de température global du système. Les
combinaisons d'équipements dans le système sont sujettes à inspection par les autorités locales qualifiées au
moment de l'installation.
EMC Environmental Conditions for Products Installed in the European Union
This section applies to products to be installed in the European Union.
The equipment is intended to operate under the following environmental conditions with respect to EMC:
A separate defined location under the user’s control.
Earthing and bonding shall meet the requirements of ETS 300 253 or CCITT K27.
AC-power distribution shall be one of the following types, where applicable: TN-S and TN-C as defined in IEC 364-3.
In addition, if equipment is operated in a domestic environment, interference could occur.
50
Page 53

Hazardous Location Installation Information
Hazardous Locations Standards
Hazardous Locations Standards
The following standards were used for the hazardous locations
approvals and certifications:
Les normes suivantes ont été appliquées pour les approbations et
les certifications dans le cadre d'environnements dangereux :
UL 121201, Ed. 9 UL 121201, Ed. 9
CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60079-0-11 Ed. 2 CAN/CSA C22.2 No 60079-0-11 Éd. 2
CAN/CSA C22.2 No. 60079-15-12 Ed. 1 CAN/CSA C22.2 No 60079-15-12 Éd. 1
CSA C22.2 No. 213 Ed. 3 CSA C22.2 No 213 Éd. 3
EN 60079-0:2012+A11:2013 EN 60079-0:2012+A11:2013
EN 60079-15:2010 EN 60079-15:2010
IEC 60079-0 6th Edition IEC 60079-0, 6e édition
IEC 60079-15 4th Edition IEC 60079-15, 4e édition
UL 60079-0, 5th Ed, 2009-10-21 UL 60079-0, 5e éd., 21-10-2009
UL 60079-15, 3rd Ed, 2009-7-17 UL 60079-15, 3e éd., 17-07-2009
The following hazardous locations strings are provided on the
access point:
Class 1, Div 2, Groups A B C D Classe 1, Div 2, Groupes A B C D
Class 1, Zone 2, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc X Classe 1, Zone 2, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc X
II 3 G, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc II 3 G, Ex nA nC IIC T4 Gc
DEMKO 14 ATEX 1435X DEMKO 14 ATEX 1435X
Class 1, Zone 2, AEx nA nC IIC T4 Gc Classe 1, Zone 2, AEx nA nC IIC T4 Gc
Les marques d'homologation relatives aux environnements
dangereux suivantes sont apposées sur le point d'accès :
51
Page 54

Hazardous Location Installation Information
Hazardous Locations Standards
52
Page 55

Cable and Connectors
231 45678Pin Label
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
TP0+
TP0TP1+
TP2+
TP2TP1TP3+
TP3-
Connector Specifications, page 53
Cables and Adapters, page 55
Connector Specifications
10/100/1000 Ports, page 53
SFP Module Connectors, page 53
Alarm Port, page 54
10/100/1000 Ports
The 10/100/1000 Ethernet ports on the switches use RJ-45 connectors. Figure 36 on page 53 shows the pinouts.
Figure 36 10/100/1000 Port Pinouts
Connector pins 1, 2, 3, and 6 are used for PoE.
SFP Module Connectors
Figure 37 on page 54 shows a LC style connector that is used with the SFP Module slots. It is a fiber-optic cable connector.
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
53
Page 56

58476
253163
253405
Cable and Connectors
Connector Specifications
Figure 37 Fiber-Optic SFP Module LC Connector
Warning: Invisible laser radiation may be emitted from disconnected fibers or connectors. Do not stare into beams or view directly
with optical instruments. Statement 1051
Console Port
The switch has two console ports: a USB 5-pin mini-Type B port (see Figure 38 on page 54) and an RJ-45 (RS-232) console port.
Figure 38 USB Mini-Type B Port
The USB console port uses a USB Type A to 5-pin mini-Type B cable, shown in Figure 39 on page 54. The USB Type A-to-USB mini-Type
B cable is not supplied. You can order an accessory kit that contains this cable.
Note: When running Linux, access the USB Console using Minicom instead of Screen.
Figure 39 USB Type A-to-USB 5-Pin Mini-Type B Cable
The RJ-45 console port uses an 8-pin RJ-45 connector . An RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable is used to connect the console port of the switch
to a console PC. You need to provide a RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter if you want to connect the switch console port to a terminal.
You can order a kit (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=) containing that adapter. For console port and adapter pinout information, see Console
Port, page 54.
Alarm Port
The alarm port uses an RJ-45 connector. See Alarm Ports, page 4 for more information. For information on alarm ratings, see the Alarm
Ratings, page 72.
54
Page 57

Cable and Connectors
To Pin 8
Alarm In Common
To Pin 8
Alarm In Common
To Pin 1, 2, 4, or 5
Alarm Input
To Pin 1, 2, 4, or 5
Alarm Input
Normally-Open (NO) Contacts
Normally-Closed (NC) Contacts
Alarm Input Details
Alarm Output Details
Form-C
Normally-Open/Normally-Closed Contacts
To P i n 7
Alarm Out Common
To P i n 3
Alarm Out N/C
To Pin 6
Alarm Out N/O
Cables and Adapters
Figure 40 Alarm Port Details
Cables and Adapters
SFP Module Cables, page 55
Console Port Adapter Pinouts, page 55
SFP Module Cables
Each port must match the wave-length specifications on each end of the cable, and for reliable communications, the cable must not exceed
the allowable length.
For more information about SFP/SFP+ modules and cables, see Transceiver Modules.
Console Port Adapter Pinouts
The console port uses an 8-pin RJ-45 connector. If you did not order a console cable, you need to provide an RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable
to connect the switch console port to a PC console port. You need to provide an RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter if you want to connect
the switch console port to a terminal. You can order an adapter (part number ACS-DSBUASYN=).
Table 11 on page 56 lists the pinouts for the console port, the RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable, and the console device.
55
Page 58

Cable and Connectors
Cables and Adapters
Table 11 Console Port Adapter Pinouts (RJ-45-to-DB-9)
Switch Console
Port (DTE)
Signal DB-9 Pin Signal
RTS 8 CT S
DTR 6 DSR
TxD 2 RxD
GND 5 GND
RxD 3 TxD
DSR 4 DTR
CTS 7 RTS
Note: The RJ-45-to-DB-25 female DTE adapter is not supplied with the switch. You can order this adapter from Cisco (part number
ACS-DSBUASYN=).
Table 12 Console Port Adapter Pinouts (RJ-45-to-DB-25)
Switch
Console
Port (DTE)
Signal DB-25 Pin Signal
RTS 5 CTS
DTR 6 DSR
TxD 3 RxD
GND 7 GND
RxD 2 TxD
DSR 20 DTR
CTS 4 RTS
RJ-45-to-DB-9
Terminal Adapter
RJ-45-to-DB-25
Adapter
Console
Device
Console
Device
56
Page 59

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
This appendix provides a command-line interface (CLI) setup procedure for a standalone switch. Before connecting the switch to a power
source, review the safety warnings in Warnings, page 13 and Installation Guidelines, page 35
Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup
When you first set up the switch, you should use Express Setup to enter the initial IP information. This process enables the switch to connect
to local routers and the Internet. You can then access the switch through the IP address for additional configuration.
Required Equipment
You need this equipment to set up the switch:
Computer with Windows 2000/Vista/2003/XP/Window7/Mac.
A Web browser (IE, Firefox) with JavaScript enabled.
A straight-through or crossover Category 5 Ethernet cable to connect your computer to the switch port.
Do not use the RS232 serial console port for express setup.
A small paper clip to reach to button.
Note: Before running Express Setup, disable any pop-up blockers or proxy settings on your browser and any wireless client running on your
computer.
Express Setup Procedure
To run Express Setup:
1. Make sure that nothing is connected to the switch.
2. Ensure the switch is in default factory mode.
Skip to next step if freshly out of the box.
a. If not freshly out of the package, use a paper clip to reset the switch for 10 seconds until the SYS LED light turns red; then release
the paper clip.
Switch will automatically reboot once the SYS led goes red.
3. Ensure no data port is connected to the switch.
Note: During Express Setup, the switch acts as a DHCP server.
— You can add a serial console cable to monitor the booting sequence. Do not hit [return key] on console screen.
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
57
Page 60

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup
— Ensure the computer connected to switch is configured with DHCP.
4. Web Browser: disable pop-up blockers and proxy settings.
5. Connect power to the switch.
See the wiring instructions in Grounding the Switch, page 36 and Wiring the Power Source, page 39.
6. Power on or reset the switch.
Use LEDs to monitor boot progress:
— Sys blinking: bootloader
— Sysl Blank: POST
— Sys solid: exit post, IOS initializing
— Sys and alarm LEDs green: IOS init done
— ~90 – 100 seconds after power on
— EXP blinking: ready for express setup process
7. Insert paper clip into express setup button (see Figure 4 on page 6) for 1-2 seconds.
When released, port Gig1/1 LED starts flashing green.
8. Connect computer to port Gig1/1.
LED continues to blink.
9. After computer has IP address (169.254.0.2), point browser to http://169.254.0.1.
10. Leave the username blank and enter the default password, cisco.
Note: The switch ignores text in the username field. The Express Setup window appears.
Troubleshooting: If the Express Setup window does not appear, make sure that any pop-up blockers or proxy settings on your browser
are disabled and that any wireless client is disabled on your computer.
Note: The screen capture below shows an IE 4000 series switch, but the functionality is identical for the IE 5000.
58
Page 61

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup
11. Enter all entries in English letters and Arabic numbers.
In the Network Settings (Required for Static IP):
— IP Address: Enter a valid IP address for the switch.
You can later use the IP address to access the switch through Device Manager.
— Switch Username and Password: Enter a password. The password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, can start with a
number, is case sensitive, allows embedded spaces, but does not allow spaces at the beginning or end. In the Confirm Password
field, enter the password again.
Note: You must change the password from the default password, cisco.
— Default Gateway: Enter the IP address of the router.
12. Enter the Control Industrial Protocol (CIP) VLAN settings (optional):
— CIP VLAN: Enter the VLAN on which CIP will be enabled. The CIP VLAN can be the same as the management VLAN, or you
can isolate CIP traffic on another VLAN that is already configured on the switch. The default CIP VLAN is VLAN 1. Only one
VLAN on a switch can have CIP enabled.
— IP Address: Enter the IP address for the CIP VLAN. If the CIP VLAN is different from the management VLAN, you must specify
an IP address for the CIP VLAN. Make sure that the IP address that you assign to the switch is not being used by another device
in your network.
— Subnet Mask: Select a mask from the drop-down list.
For more information about the CIP VLAN settings, click Help on the tool-bar.
13. Optional Settings:
59
Page 62

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through Express Setup
You can enter the optional information now, or enter it later by using Device Manager. For more information about the Express Setup
fields, see the on-line help for the Express Setup window.
Click Submit to save your changes and to complete the initial setup.
For more information about the optional settings, click Help on the tool-bar.
After you click Submit, these events occur:
— The switch is configured and exits Express Setup mode.
— The browser displays a warning message and tries to connect with the earlier switch IP address.
— Typically, connectivity between the computer and the switch is lost because the configured switch IP address is in a different
subnet from the IP address on the computer.
14. Turn off DC power at the source, disconnect all cables to the switch, and install the switch in your network. See Management Options,
page 12 for information about configuring and managing the switch.
15. If you changed the static IP address on your computer in Step 1, change it to the previously configured static IP address.
Note: The screen capture below shows an IE 4000 series switch, but the functionality is identical for the IE 5000.
16. You can now manage the switch by using the Cisco Network Assistant, Device Manager, or both. See Management Options, page 12
for information about configuring and managing the switch.
You can display Device Manager by following these steps:
a. Start a web browser on your computer.
b. Enter the switch IP address, username, and password in the web browser, and press Enter. The Device Manager page appears.
Troubleshooting:
60
Page 63

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port
If the Device Manager page does not appear:
— Confirm that the port LED for the switch port connected to your network is green.
— Confirm that the computer that you are using to access the switch has network connectivity by connecting it to a well known web
server in your network. If there is no network connection, troubleshoot the network settings on the computer.
— Make sure that the switch IP address in the browser is correct.
— If the switch IP address in the browser is correct, the switch port LED is green, and the computer has network connectivity,
continue troubleshooting by reconnecting the computer to the switch. Configure a static IP address on the computer that is in the
same subnet as the switch IP address.
When the LED on the switch port connected to the computer is green, reenter the switch IP address in a web browser to display the Device
Manager. When Device Manager appears, you can continue with the switch configuration.
Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port
You can enter Cisco IOS commands and parameters through the CLI. Use one of these options to access the CLI:
RJ-45 Console Port, page 61
USB Console Port, page 62
RJ-45 Console Port
1. Connect the RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable to the 9-pin serial port on the PC. Connect the other end of the cable to the switch console
port.
2. Start the terminal-emulation program on the PC or the terminal. The program, frequently a PC application such as HyperTerminal or
ProcommPlus, makes communication between the switch and your PC or terminal possible.
61
Page 64

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
2
Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port
Figure 41 Connecting the Console Cable
2
1
Cisco IE 3010
1
1 RJ-45 console port 2 Console cable (RJ-45-to-DB-9 adapter cable)
3. Configure the baud rate and character format of the PC or terminal to match the console port characteristics:
— 9600 baud
— 8 data bits
— 1 stop bit
— No parity
— None (flow control)
4. Connect power to the switch as described in Wiring the Power Source, page 39.
5. The PC or terminal displays the bootloader sequence. Press Enter to display the setup prompt. Follow the steps in the Completing the
Setup Program, page 65.
USB Console Port
08386
1. If you are connecting the switch USB console port to a Windows-based PC for the first time, install a USB driver. See Installing the
Cisco Microsoft Windows XP, 2000, Vista, 7, 8, and 10 USB Device Driver, page 64 for more information.
62
Page 65

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port
Figure 42 Connecting the USB Console Cable
2
2
1
Cisc o IE 3010
1
3
208379
1 USB console port 3 USB port on the PC
2 USB cable
2. Connect an USB cable to the PC USB port, and connect the other end of the cable to the switch mini-B (5-pin-connector) USB console
port. See Figure 42 on page 63.
3. To identify the COM port assigned to the USB console port:
a. Choose Start > Control Panel > Systems
b. Click the Hardware tab and choose Device Manager.
c. Expand the Ports section.
The assigned COM port appears in parenthesis at the end of the line with this entry: Cisco USB System Management Console.
4. Start the terminal-emulation program on the PC or the terminal.
The program, frequently a PC application such as HyperTerminal or ProcommPlus, makes communication possible between the switch
and your PC or terminal.
5. Configure the COM port.
6. Configure the baud rate and character format of the PC or terminal to match the console port characteristics:
— 9600 baud
— 8 data bits
63
Page 66

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Accessing the CLI Through the Console Port
— 1 stop bit
— No parity
— None (flow control)
7. Connect power to the switch as described in Wiring the Power Source, page 39
The PC or terminal displays the bootloader sequence.
8. Press Enter to display the setup prompt.
9. Follow the steps in the Completing the Setup Program, page 65.
Installing the Cisco Microsoft Windows XP, 2000, Vista, 7, 8, and 10 USB Device Driver
A USB device driver must be installed the first time a Microsoft Windows-based PC is connected to the USB console port on the switch.
Use this procedure to install the USB driver on Windows XP, Windows 2000, Windows Vista, Windows 7, Windows 8, and Windows 10.
1. Obtain the file Cisco_usbconsole_driver_3_1.zip from the Cisco.com website
https://software.cisco.com/download/release.html?mdfid=282979369&softwareid=282855122&release=3.1
The file details are as follows:
— Description: Cisco_usbconsole_driver_3_1.zip
— Release: 3.1
— Release Date: 27/Nov/2014
— File Name: Cisco_usbconsole_driver_3_1.zip
— Size: 14.35 MB (15045453 bytes)
— MD5 Checksum: eff2e955edcdc70209e6f9c8f6bd59cd
2. Unzip the file and install the corresponding exe file.
3. Navigate to the Device Manager window by performing a search in WIndows for Device Manager and opening it.
4. Connect the USB cable from the Windows PC to the Cisco switch.
5. From the Device Manager page, expand Ports (COM & LPT). Select USB Serial Port. Right-click and select Update Driver
Software ...
6. In the Update Driver Software window, select Browse my computer for driver software. Then choose Let me pick from a list of
device drivers on my computer and click Next.
7. Enable Show compatible hardware and choose Cisco Serial as the model. Click Next.
After the update is completed, Windows displays Windows has successfully updated your driver software.
8. Click Close.
Uninstalling the Cisco Microsoft Windows XP, 2000, Vista, 7, 8, and 10 USB Driver
Note: Disconnect the switch console terminal before uninstalling the driver.
1. Run setup.exe for Windows 32-bit or setup(x64).exe for Windows-64bit.
2. Click Next.
64
Page 67

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Entering the Initial Configuration Information
3. When the InstallShield Wizard for Cisco Virtual Com appears, click Next.
4. When the Program Maintenance window appears, select the Remove radio button.
5. Click Next.
6. When the Remove the Program window appears, click Remove.
If a User Account Control warning appears, click Allow - I trust this program to proceed.
7. When the InstallShield Wizard Completed window appears, click Finish.
Entering the Initial Configuration Information
To set up the switch, you need to complete the setup program, which runs automatically after the switch powers on. You must assign an IP
address and other configuration information necessary for the switch to communicate with the local routers and the Internet.
IP Settings
You need this information:
Switch IP address
Subnet mask (IP netmask)
Default gateway (router)
Enable secret password
Enable password
Telnet password
Completing the Setup Program
Follow these steps to complete the setup program and to create an initial configuration for the switch:
1. Enter Ye s at these two prompts.
Would you like to enter the initial configuration dialog? [yes/no]: yes
At any point you may enter a question mark '?' for help.
Use ctrl-c to abort configuration dialog at any prompt.
Default settings are in square brackets '[]'.
Basic management setup configures only enough connectivity
for management of the system, extended setup will ask you
to configure each interface on the system.
Would you like to enter basic management setup? [yes/no]: yes
2. Enter a host name for the switch, and press Return.
On a command switch, the host name is limited to 28 characters and on a member switch to 31 characters. Do not use -n, where n is a number,
as the last character in a host name for any switch.
Enter host name [Switch]: host_name
65
Page 68

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Entering the Initial Configuration Information
3. Enter an enable secret password, and press Return.
The password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, can start with a number, is case sensitive, allows spaces, but ignores leading
spaces. The secret password is encrypted, and the enable password is in plain text.
Enter enable secret: secret_password
4. Enter an enable password, and press Return.
Enter enable password: enable_password
5. Enter a virtual terminal (Telnet) password, and press Return.
The password can be from 1 to 25 alphanumeric characters, is case sensitive, allows spaces, but ignores leading spaces.
Enter virtual terminal password: terminal-password
6. (Optional) Configure Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) by responding to the prompts. You can also configure SNMP
later through the CLI. To configure SNMP later, enter no.
Configure SNMP Network Management? [no]: no
7. Enter the interface name (physical interface or VLAN name) of the interface that connects to the management network, and press
Return. For this release, always use vlan1 as that interface.
Enter interface name used to connect to the
management network from the above interface summary: vlan1
8. Configure the interface by entering the switch IP address and subnet mask and pressing Return. The IP address and subnet masks
shown below are examples.
Configuring interface vlan1:
Configure IP on this interface? [yes]: yes
IP address for this interface: 10.4.120.106
Subnet mask for this interface [255.0.0.0]: 255.0.0.0
9. Enter Y to configure the switch as the cluster command switch. Enter N to configure it as a member switch or as a standalone
switch.
If you enter N, you can configure the switch as a command switch later through the CLI. To configure it later, enter no.
Would you like to enable as a cluster command switch? [yes/no]: no
You have completed the initial configuration of the switch, and the switch displays its configuration. This is an example of the configuration
output:
The following configuration command script was created:
hostname switch1
enable secret 5 $1$Ulq8$DlA/OiaEbl90WcBPd9cOn1
enable password enable_password
line vty 0 15
password terminal-password
no snmp-server
!
no ip routing
!
interface Vlan1
no shutdown
ip address 10.4.120.106 255.0.0.0
!
interface FastEthernet1/0/1
!
66
Page 69

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Entering the Initial Configuration Information
interface FastEthernet1/0/2
interface FastEthernet1/0/3
!
...<output abbreviated>
end
10. These choices appear:
[0] Go to the IOS command prompt without saving this config.
[1] Return back to the setup without saving this config.
[2] Save this configuration to nvram and exit.
If you want to save the configuration and use it the next time the switch reboots, select option 2 to
save it in NVRAM.
Enter your selection [2]:2
Make your selection, and press Return.
After you complete the setup program, the switch can run the default configuration that you created. To change this configuration or to
perform other management tasks, enter commands at the
Switch> prompt.
67
Page 70

Configuring the Switch with the CLI Setup Program
Entering the Initial Configuration Information
68
Page 71

Technical Specifications
Switch Specifications, page 70
Power-Supply Module Specifications, page 72
Alarm Ratings, page 72
Cisco Systems, Inc. www.cisco.com
69
Page 72

Technical Specifications
Switch Specifications
Switch Specifications
Table 13 Cisco IE 5000 Switch Specifications
Environmental Ranges
Operating temperature
Storage temperature –40 to 185°F (–40 to 85°C)
Relative humidity 5 to 95% (noncondensing)
Operating altitude Up to 13,800 ft (3049 m)
Storage altitude Up to 15,000 ft (4570 m)
Thermal spacing 1.75 in. (4.4 cm)
Operational shock 50G at 11ms, half sine and 200G ar 2.11ms, half sine.
Non-Operational Shock 65-80G at 9ms, Trapezoidal
Physical Specifications
Weight 13.7 lb (6.2 kg) (no power-supply module)
Dimensions (H x W x D) 1.75 x 17.5 x 15.0 in. (4.45 x 44.5 x 38.1 cm)
1. Operating temperatures exceeding 60°C are not covered by the product safety certifications and approvals. However, the switch can function in
the installations under the environmental conditions listed.
2. The maximum operating temperature of the switch varies depending on the type of SFP module that you use.
1
-40°C to +74°C
-40°C to +70°C (Vented Enclosure Operating)
-40°C to +60°C (Sealed Enclosure Operating)
-34°C to +74°C (100LFM or more Fan or Blower equipped Enclosure
Operating)
-40°C to +85°C (Type Tested to +85°C for 16 hours)
2
Table 14 Cisco IE 5000 Switch Power Requirements
Power Requirements
Nominal input voltage PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H:
100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
100 to 250 VDC
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-250:
100 to 240 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
100 to 250 VDC
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H:
24 to 60 VDC
Absolute maximum (short term) input voltage PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H:
90 to 264 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
90 to 300 VDC
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-250:
90 to 264 VAC, 50 to 60 Hz
90 to 300 VDC
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H:
18 to 75 VDC
70
Page 73

Technical Specifications
Switch Specifications
Table 14 Cisco IE 5000 Switch Power Requirements (continued)
Power consumption with PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H (s) Single Power Supply Module installed:
Power consumption with PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H (s) Single Power Supply Module installed:
No PoE ports on: 76W max/ 259.3 BTUs per hour
148W max / 505 BTUs per hour with maximum (4) PoE
ports on,
Two Power Supply Modules installed:
PoE power consumption alone
(12 ports poe): 215W max / 733.6 BTUs per hour.
Complete system power including 12 ports poe: 291W
max.
No PoE ports on: 76W max/ 259.3 BTUs per hour
148W with maximum (4) PoE ports on, / 505 BTUs per
hour
Two Power Supply Modules installed:
PoE power consumption alone
(12 ports poe): 215W max / 733.6 BTUs per hour.
Complete system power including 12 ports poe: 291W
max.
Table 15 Cisco IE 5000 Switch PoE Power budget
PID System Power Available PoE Power
System
Reserved
IE-5000-12S12P-10G,
IE-5000-16S12P
IE-4010-16S12P 70W 80W 200W 180W 285W 360W
IE-4010-4S24P 70W 80W 200W 180W 285W 385W
85W 65W 185W 165W 270W 360W
One 150W
PSU
Two 150W
PSU
One 250W
PSU
One 150W PS
+ one 250W
PSU
Two 250W
PSU
71
Page 74

Technical Specifications
Power-Supply Module Specifications
Power-Supply Module Specifications
Table 16 Power Supply Module Specifications
Physical Specifications
Weight
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-250
Dimensions (H x W x D)
PWR-RGD-AC-DC-H and PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-H
PWR-RGD-LOW-DC-250
Alarm Ratings
Table 17 Alarm Input and Output Ratings
2.55 lb (1.15 kg)
2.5 lb (1.13 kg)
3.2 lb (1.45 kg)
1.58 x 7 x 5 in. (4 x 17.8 x 12.7 cm) (without mounting
flanges)
1.58 x 7x 6.18 in. (4 x 17.8 x 15.7 cm) (with mounting flanges)
Alarm Ratings
Alarm input electrical specification No external voltage needed to activate alarm inputs. The open circuit voltage between any
Alarm input (1 to 4) and Alarm input Common is 5VDC and the loop current is 2 mA max per
input.
Alarm output electrical specification 30VDC @ 1A, 48VDC @ 0.5A
72
 Loading...
Loading...