Cisco Catalyst 4503-E, Catalyst 4506-E, Catalyst 4500X, Catalyst 4500X-F, Catalyst 4507R+E User Manual
...Page 1

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series
Switches (4503-E, 4506-E,
4507R+E, 4510R+E, 4500X and
4500X-F) Running IOS-XE 3.5.2E
Security Target
Revision 1.0
11 March 2014
1
Page 2

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Table of Contents
1 Security Target Introduction ................................................................................................... 6
1.1 Security Target and TOE Identification ............................................................... 6
1.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations ............................................................................... 6
1.3 TOE Overview ..................................................................................................... 8
1.3.1 TOE Evaluated Configuration ...................................................................... 8
1.3.2 TOE Type...................................................................................................... 9
1.3.3 Required non-TOE Hardware/Software/Firmware ....................................... 9
1.4 TOE Description ................................................................................................ 10
1.4.1 TOE Architecture and Security Capabilities............................................... 10
1.5 TOE Environment and Configuration ................................................................ 11
1.6 Physical Scope of the TOE................................................................................. 13
1.6.1 USB Console Port ....................................................................................... 23
1.6.2 Network Ports ............................................................................................. 23
1.6.3 Serial Port.................................................................................................... 23
1.6.4 Compact Flash Slot ..................................................................................... 24
1.6.5 Physical Scope of the TOE ......................................................................... 24
1.7 Logical Scope of the TOE .................................................................................. 24
1.7.1 Security Audit ............................................................................................. 25
1.7.2 Cryptographic Support ................................................................................ 25
1.7.3 User Data Protection ................................................................................... 25
1.7.4 Identification and Authentication ............................................................... 26
1.7.5 Security Management ................................................................................. 26
1.7.6 Protection of the TSF .................................................................................. 27
1.7.7 Resource Utilization.................................................................................... 28
1.7.8 TOE Access ................................................................................................ 28
1.7.9 Trusted Path/Channels ................................................................................ 28
1.8 Excluded Functionality ...................................................................................... 28
2 Conformance Claims ............................................................................................................ 30
2.1 Common Criteria Conformance Claim .............................................................. 30
2.2 Protection Profile Conformance Claim .............................................................. 30
2.3 Protection Profile Conformance Claim Rationale .............................................. 30
2.3.1 TOE Appropriateness.................................................................................. 30
2.3.2 TOE Security Problem Definition Conformance ........................................ 30
2.3.3 Statement of Security Objectives Conformance ......................................... 30
2.3.4 Statement of Security Requirements Conformance .................................... 31
3 Security Problem Definition ................................................................................................. 32
3.1 Introduction ........................................................................................................ 32
3.2 External Entities ................................................................................................. 32
3.3 Assets ................................................................................................................. 32
3.3.1 Primary Assets ............................................................................................ 32
3.3.2 Secondary Assets ........................................................................................ 33
3.4 Assumptions ....................................................................................................... 33
2
Page 3

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
3.5 Threats ................................................................................................................ 34
3.6 Organizational Security Policies ........................................................................ 35
3.6.1 OSPs enforced by TOE ............................................................................... 35
4 Security Objectives ............................................................................................................... 36
4.1 Security Objectives for the TOE ........................................................................ 36
4.2 Security Objectives for the Environment ........................................................... 37
5 Security Requirements .......................................................................................................... 37
5.1 Conventions ........................................................................................................ 38
5.2 TOE Security Functional Requirements ............................................................ 38
5.2.1 Security audit (FAU)................................................................................... 40
5.2.2 Cryptographic Support (FCS) ..................................................................... 43
5.2.3 User data protection (FDP) ......................................................................... 47
5.2.4 Identification and authentication (FIA) ...................................................... 47
5.2.5 Security management (FMT) ...................................................................... 48
5.2.6 Protection of the TSF (FPT) ....................................................................... 49
5.2.7 FRU – Resource Utilization ........................................................................ 50
5.2.8 TOE Access (FTA) ..................................................................................... 51
5.2.9 Trusted Path/Channel (FTP) ....................................................................... 51
5.3 Extended Components Definition ...................................................................... 52
5.4 TOE SFR Dependencies Rationale .................................................................... 54
5.5 Security Assurance Requirements ...................................................................... 56
5.5.1 SAR Requirements...................................................................................... 56
5.5.2 Security Assurance Requirements Rationale .............................................. 57
5.6 Assurance Measures ........................................................................................... 57
6 TOE Summary Specification ................................................................................................ 59
6.1 TOE Security Functional Requirement Measures .............................................. 59
6.2 TOE Bypass and interference/logical tampering Protection Measures .............. 79
7 Rationale ............................................................................................................................... 81
7.1 Rationale for TOE Security Objectives .............................................................. 81
7.2 Rationale for the Security Objectives for the Environment ............................... 83
7.3 Rationale for TOE Security Functional Requirements ...................................... 84
Annex A: References ..................................................................................................................... 88
3
Page 4

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
List of Tables
TABLE 1 ST AND TOE IDENTIFICATION .............................................................................. 6
TABLE 2 ACRONYMS ........................................................................................................... 6
TABLE 3 EVALUATED CONFIGURATION .............................................................................. 8
TABLE 4 IT ENVIRONMENT COMPONENTS ........................................................................... 9
TABLE 5 CATALYST 4500 SERIES SWITCH CHASSIS FEATURES ......................................... 14
TABLE 6 CATALYST 4500 SERIES SWITCH CHASSIS LINE CARDS ...................................... 16
TABLE 7 EXTERNAL ENTITIES INTERACTING WITH TOE ..................................................... 32
TABLE 8 PRIMARY ASSETS TO BE PROTECTED .................................................................... 32
TABLE 9 SECONDARY ASSETS TO BE PROTECTED ............................................................... 33
TABLE 10 OPERATIONAL ASSUMPTIONS ............................................................................ 33
TABLE 11 THREATS ........................................................................................................... 34
TABLE 12 ORGANIZATIONAL SECURITY POLICIES ............................................................. 35
TABLE 13 SECURITY OBJECTIVES FOR THE TOE ................................................................ 36
TABLE 14 SECURITY OBJECTIVES FOR THE ENVIRONMENT ................................................ 37
TABLE 15 SECURITY FUNCTIONAL REQUIREMENTS ........................................................... 38
TABLE 16: AUDITABLE EVENTS ........................................................................................ 41
TABLE 17: SFR DEPENDENCY RATIONALE (FROM NDPP) ................................................. 54
TABLE 18: ASSURANCE MEASURES ................................................................................... 56
TABLE 19: ASSURANCE MEASURES ................................................................................... 57
TABLE 20: HOW TOE SFRS ARE MET ............................................................................... 59
TABLE 21: THREAT/OBJECTIVES/POLICIES MAPPINGS ....................................................... 81
TABLE 22: THREAT/POLICIES/TOE OBJECTIVES RATIONALE ............................................ 82
TABLE 23: ASSUMPTIONS/ENVIRONMENT OBJECTIVES MAPPINGS .................................... 83
TABLE 24: ASSUMPTIONS/THREATS/OBJECTIVES RATIONALE ........................................... 83
TABLE 25: SECURITY OBJECTIVE TO SECURITY REQUIREMENTS MAPPINGS ...................... 84
TABLE 26: OBJECTIVES TO REQUIREMENTS RATIONALE .................................................... 86
TABLE 27: REFERENCES ..................................................................................................... 88
List of Figures
FIGURE 1 TOE ENVIRONMENT ........................................................................................... 12
FIGURE 2 CATALYST 4500 SERIES SWITCH CHASSIS .......................................................... 14
FIGURE 3 CISCO CATALYST 4500-X SERIES CHASSIS AND MODULES ................................ 21
FIGURE 4 32 X 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET PORT SWITCH WITH OPTIONAL UPLINK MODULE
SLOT .......................................................................................................................... 21
FIGURE 5 16 X 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET PORT SWITCH WITH OPTIONAL UPLINK MODULE
SLOT .......................................................................................................................... 21
FIGURE 6 8 X 10 GIGABIT ETHERNET PORT UPLINK MODULE ......................................... 21
FIGURE 7 FRONT-TO-BACK AIRFLOW REAR VIEW ............................................................. 22
FIGURE 8 BACK-TO-FRONT AIRFLOW REAR VIEW ............................................................. 22
4
Page 5

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Prepared By:
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Dr.
San Jose, CA 95134
EDCS-1228241
DOCUMENT INTRODUCTION
This document provides the basis for an evaluation of a specific Target of Evaluation
(TOE), the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E,
4500X and 4500X-F) running IOS-XE 3.5.2E. This Security Target (ST) defines a set of
assumptions about the aspects of the environment, a list of threats that the product intends
to counter, a set of security objectives, a set of security requirements, and the IT security
functions provided by the TOE which meet the set of requirements.
5
Page 6

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
ST Title
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E,
4500X and 4500X-F) Running IOS-XE 3.5.2E Security Target
ST Version
1.0
Publication Date
11 March 2014
ST Author
Cisco Systems, Inc.
Developer of the TOE
Cisco Systems, Inc.
TOE Reference
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E,
4500X and 4500X-F) running IOS-XE 3.5.2E
TOE Hardware Models
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E,
4500X and 4500X-F), including one or more Supervisor cards and one or
more of the line cards as identified in Table 3
TOE Software Version
IOS XE 3.5.2E
Keywords
Audit, Authentication, Encryption, Information Flow, Protection, Switch,
Traffic
Acronyms /
Abbreviations
Definition
AAA
Administration, Authorization, and Accounting
ACL
Access Control List
AES
Advanced Encryption Standard
BGP
Border Gateway Protocol. An exterior gateway protocol. It performs routing
between multiple autonomous systems and exchanges routing and reachability
information with other BGP systems.
EDCS-1228241
1 SECURITY TARGET INTRODUCTION
The Security Target contains the following sections:
Security Target Introduction [Section 1]
Conformance Claims [Section 2]
Security Problem Definition [Section 3]
Security Objectives [Section 4]
IT Security Requirements [Section 5]
TOE Summary Specification [Section 6]
Rationale [Section 7]
The structure and content of this ST comply with the requirements specified in the
Common Criteria (CC), Part 1, Annex A, and Part 3, Chapter 4.
1.1 Security Target and TOE Identification
This section provides information needed to identify and control this ST and its TOE.
Table 1 ST and TOE Identification
1.2 Acronyms and Abbreviations
The following acronyms and abbreviations are used in this Security Target:
Table 2 Acronyms
6
Page 7

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Acronyms /
Abbreviations
Definition
CC
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation
CEM
Common Evaluation Methodology for Information Technology Security
CLI
Command Line Interface
CM
Configuration Management
DH
Diffie-Hellman
EAL
Evaluation Assurance Level
EEPROM
Electrically erasable programmable read-only memory, specifically the memory
in the switch where the Cisco IOS is stored.
EIGRP
Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol
FIPS
Federal Information Processing Standard
HMAC
Hashed Message Authentication Code
HTTPS
Hyper-Text Transport Protocol Secure
IEEE
Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers
IGMP
Internet Group Management Protocol
IOS
The proprietary operating system developed by Cisco Systems.
IP
Internet Protocol
IPSEC
IP Security
IT
Information Technology
MAC
Media Access Control
NTP
Network Time Protocol
NVRAM
Non-volatile random access memory, specifically the memory in the switch
where the configuration parameters are stored.
OS
Operating System
OSPF
Open Shortest Path First. An interior gateway protocol (routes within a single
autonomous system). A link-state routing protocol which calculates the shortest
path to each node.
Packet
A block of data sent over the network transmitting the identities of the sending
and receiving stations, error-control information, and message.
PP
Protection Profile
PRNG
Pseudo Random Number Generator
PVLAN
Private VLAN
RADIUS
Remote Authentication Dial In User Service
RIP
Routing Information Protocol. An interior gateway protocol (routes within a
single autonomous system). A distance-vector protocol that uses hop count as it’s
metric.
RNG
Random Number Generator
RSA
Rivest, Shamir and Adleman (algorithm for public-key cryptography)
SM
Service Module
SSH
Secure Shell
SSHv2
Secure Shell (version 2)
ST
Security Target
TACACS
Terminal Access Controller Access Control System
TCP
Transport Control Protocol
TCP/IP
Transmission Control Protocol/Internet Protocol
TDES
Triple Data Encryption Standard
TLS
Transport Layer Security
TOE
Target of Evaluation
TSC
TSF Scope of Control
TSF
TOE Security Function
TSP
TOE Security Policy
EDCS-1228241
7
Page 8

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Acronyms /
Abbreviations
Definition
UDP
User Datagram Protocol
VACL
Virtual Access Control List
VLAN
Virtual Local Area Network
VSS
Virtual Switching System
TOE
One or more WS-C4503-E, WS-C4506-E, WS-C4507R+E, WS-C4510R+E,
WS-C4500X-32SFP+, WS-C4500X-F-32SFP+, WS-C4500X-16SFP+, WSC4500X-F-16SFP+, WS-C4500X-24X-ES, 4500X-24X-IPB, or WSC4500X-40X-ES Switch Chassis (Two chassis configured support High
Availability)
One or more supervisors cards (WS-X45-SUP7-E, WS-X45-Sup7L-E) or
dual supervisor cards (WS-X45-SUP7-E, WS-X45-Sup7L-E) per chassis
(Two Supervisor cards in one chassis provides failover), each supervisor
card running IOS XE 3.5.2E (FIPS validated) software
With one or more of the following line cards:
WS-X4748-RJ45V+E
WS-X4712-SFP+E
1
EDCS-1228241
1.3 TOE Overview
The TOE is the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E,
4510R+E, 4500X and 4500X-F) running IOS XE 3.5.2E (herein after referred to as
Catalyst Switches). The TOE is a purpose-built, switching and routing platform with OSI
Layer2 and Layer3 traffic filtering capabilities.
Cisco IOS is a Cisco-developed highly configurable proprietary operating system that
provides for efficient and effective routing and switching. Although IOS performs many
networking functions, this Security Target only addresses the functions that provide for
the security of the TOE itself as described in Section 1.7 TOE logical scope below.
1.3.1 TOE Evaluated Configuration
The TOE consists of any one of a number of hardware configurations, each running the
same version of IOS XE software. The Catalyst 4500 Series Switches chassis provides
power, cooling, and backplane for the Supervisor Engine, line cards, and service modules
(SM)1. The Supervisor Engines run the IOS XE software. The evaluated configurations
consist of the following components (e.g. at least one of the listed chassis, at least one
supervisor card running IOS-XE 3.5.2E software and at least one line card):
Table 3 Evaluated Configuration
No specific service modules, such as the Firewall Blade, Wireless Service and Network Analysis being
claimed in the evaluated configuration as they require additional license
8
Page 9
Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
WS-X4640-CSFP-E
WS-X4748-UPOE+E
WS-X4748-RJ45-E
Component
Required
Usage/Purpose Description for TOE performance
Authentication
Server
Yes
This includes any authentication server (RADIUS RFC
2865, 2866, 2869 and RFC 3162 (IPv6) and TACACS+
RFC 1492)) that can be leveraged for remote user
authentication. The AAA server needs to be able of acting
as an IPsec peer or as an IPsec endpoint.
Management
Workstation
with SSH
Client
Yes
This includes any IT Environment Management
workstation with a SSH client installed that is used by the
TOE administrator to support TOE administration through
SSH protected channels. Any SSH client that supports
EDCS-1228241
The TOE can optionally connect to an NTP server on its internal network for time
services. If an NTP server is used, it must only be accessible via the internal network (an
internal network isolated from user traffic and intended for use by TOE administrators
only).
If the TOE is to be remotely administered, SSHv2 must be used for that purpose.
The TOE will transmit syslog message to a remote syslog server through an IPsec tunnel.
The TOE can also be configured to use a remote AAA server (RADIUS or TACACS+)
for centralized authentication, and can also connect to those servers through an IPsec
tunnel.
1.3.2 TOE Type
The Cisco Catalyst Switches are a switching and routing platform used to construct IP
networks by interconnecting multiple smaller networks or network segments. As a
Layer2 switch, it performs analysis of incoming frames, makes forwarding decisions
based on information contained in the frames, and forwards the frames toward the
destination. As a Layer3 switch, it supports routing of traffic based on tables identifying
available routes, conditions, distance, and costs to determine the best route for a given
packet. Routing protocols used by the TOE include BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6,
RIPv2, and OSPFv2. BGPv4, EIGRP, and EIGRPv6 supports routing updates with IPv6
or IPv4, while RIPv2 and OSPFv2 routing protocol support routing updates for IPv4
only. Note, the information flow functionality is not included in the scope of the
evaluation. The evaluated configuration is the configuration of the TOE that satisfies the
requirements as defined in this Security Target (ST).
1.3.3 Required non-TOE Hardware/Software/Firmware
The TOE supports (in some cases optionally) the following hardware, software, and
firmware in its environment:
Table 4 IT Environment Components
9
Page 10
Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Component
Required
Usage/Purpose Description for TOE performance
SSHv2 and a key size of 2048 bits or greater may be used.
Syslog server
Yes
The syslog audit server is used for remote storage of audit
records that have been generated by and transmitted from
the TOE. The TOE would ensure that messages are
encrypted within an IPsec tunnel as they leave the TOE.
The syslog server needs to be able of acting as an IPsec
peer or as an IPsec endpoint.
NTP Server
No
The TOE supports communications with an NTP server to
receive clock updates. Any server that supports NTPv1
(RFC 1059), NTPv2 (RFC 1119), or NTP v3 (RFC 1305)
may be used.
2
2
EDCS-1228241
1.4 TOE Description
The TOE description explains the TOE in more detail than was provided in the TOE
overview.
1.4.1 TOE Architecture and Security Capabilities
The Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series are network devices that protect themselves by offering
only a minimal logical interface to the network and control of that interface. The Switch
IOS subsystem is special purpose software that runs on the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series
Switch hardware. The Catalyst Switches have been designed so that all locally
maintained security relevant data can only be manipulated via the secured management
interface, a CLI and provides no general purpose programming capability. There are no
undocumented interfaces for managing the Catalyst switches.
All network traffic to the TOE protected (internal) network passes through Catalyst
Switches. There are no unmediated traffic flows into or out of the TOE. Once network
traffic is received on one of the network ports, it is always subject to the security policy
rules as applied to each traffic flow. Traffic flows characterized as unauthorized are
discarded and not permitted to circumvent the Catalyst Switch. Configuration and
management of the Catalyst Switch is through an SSHv2 session via Management
workstation or via a local console connection. The management interfaces require user
identification and authentication prior to allowing management operations. As described
in Section 6, all management functions are restricted to the authorized administrator of
the TOE. The term “authorized administrator”
administrative user which has been assigned to a privilege level that is permitted to
perform the relevant action; therefore has the appropriate privileges to perform the
requested functions.
is used in this ST to refer to any
Note, the term ‘authorized administrator’ as used in this ST is synonymous with the ‘Security
Administrator’ referenced in the NDPP.
10
Page 11

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Protection of the TOE from physical tampering is ensured by its environment. It is
assumed that the switches will remain attached to the physical connections made by an
administrator so that the switch cannot be bypassed. The TOE is completely selfcontained. The hardware, software and firmware provided by Catalyst Switches provide
all of the services necessary to implement the TOE. There are no external interfaces into
the TOE other than the physical ports provided. No general purpose operating system,
user interface, disk storage, or programming interface is provided by the TOE.
The Catalyst Switches that comprise the TOE have common hardware characteristics.
These characteristics affect only non-TSF relevant functions of the switches (such as
throughput, line-card slots, and amount of storage) and therefore support security
equivalency of the switches in terms of hardware:
Central processor that supports all system operations
Dynamic memory, used by the central processor for all system operations
Flash memory (EEPROM), used to store the Cisco IOS image (binary program)
USB slot, used to connect USB devices to the TOE (not relevant as none of the
USB devices are included in the TOE)
Non-volatile read-only memory (ROM) is used to store the bootstrap program and
power-on diagnostic programs
Non-volatile random-access memory (NVRAM) is used to store switch
configuration parameters used to initialize the system at start-up
Physical network interfaces (minimally two) (e.g. RJ45 serial and standard 10/100
Ethernet ports). Some models have a fixed number and/or type of interfaces; some
models have slots that accept additional network interfaces
10 Gigabit Ethernet (GE) uplinks and supports Power over Ethernet Plus (PoE+)
and Universal POEP (UPOE). (Universal POEP is an enhancement to the PoEP
(802.3at) standard to allow powered devices up to 60W to connect over a single
Cat 5e cable. Standard PoEP uses only 2 twisted pairs (out of 4) in the Ethernet
cable. UPOE uses all 4 twisted pairs to deliver 60W to the port.)
Redundant power supplies and fans
Cisco IOS XE is a Cisco-developed highly configurable proprietary operating system that
provides for efficient and effective routing and switching. Although IOS XE performs
many networking functions, this TOE only addresses the functions that provide for the
security of the TOE itself as described in Section 1.7 Logical Scope of the TOE below.
1.5 TOE Environment and Configuration
The TOE consists of one or more physical devices; the Catalyst Switch with Cisco IOS
XE software. The Catalyst Switch has two or more network interfaces and is connected
to at least one internal and one external network. The Cisco IOS configuration determines
how packets are handled to and from the switches’ network interfaces. The switch
configuration will determine how traffic flows received on an interface will be handled.
Typically, packet flows are passed through the network device and forwarded to their
11
Page 12

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
configured destination. BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6, RIPv2, and OSPFv2 Routing
protocols are used on all of the Catalyst Switch models.
The TOE can optionally connect to an NTP server on its internal network for time
services. In addition, if the Catalyst Switch is to be remotely administered, then the
management station must be connected to an internal network, SSHv2 must be used to
connect to the switch. A syslog server can also be used to store audit records. A remote
authentication server can also be used for centralized authentication. If these servers are
used, they must be attached to the internal (trusted) network. The internal (trusted)
network is meant to be separated effectively from unauthorized individuals and user
traffic; one that is in a controlled environment where implementation of security policies
can be enforced.
The following figure provides a visual depiction of an example TOE deployment.
Figure 1 TOE environment
12
Page 13

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
3
Cisco ASR 1006
PWR
STATUS
ASR1000 SIP10
PWR
STATUS
ASR1000 SIP10
PWR
STAT
STBY
ASR1000-ESP20
ACTV
PWR
STAT
STBY
ASR1000-ESP20
ACTV
STAT
ASR1000-RP1
STBY
ACTV
MIN
MAJ
CRIT
A
C 0 CM1
PWR
HD
USB
BF
DISK 1 0
CARRIER
LINK
BITS
CON
AUX
MGMT ETHERNET
CM1
STAT
ASR1000-RP1
STBY
ACTV
MIN
MAJ
CRIT
A C 0
CM1
PWR
HD
USB
BF
DISK 1 0
CARRIER
LINK
BITS
CON
AUX
MGMT ETHERNET
CM1
PWR
STATUS
ASR1000 SIP10
1 0 1
0
2
1
0 2 1 0 P P R
R
Cisco
ETH
ACT
PWR
SLOT 0
0
SLOT 1
0
SLOT 2
0
0K 1 1
1
1700
SERIES
ROUTER
COL
Peer
=
TOE Boundary
Mgt
Workstation
SSH
Connection
Catalyst 4K Switch
Syslog
Server
AAA Server
NTP Server
IPsec
Connection
IPsec
Connection
EDCS-1228241
1.6 Physical Scope of the TOE
The TOE is a hardware and software solution that makes up the following switch models;
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E, 4500X and
4500X-F) running IOS XE 3.5.2E. The following tables further identify the supported
configurations. The network, on which they reside, is part of the environment.
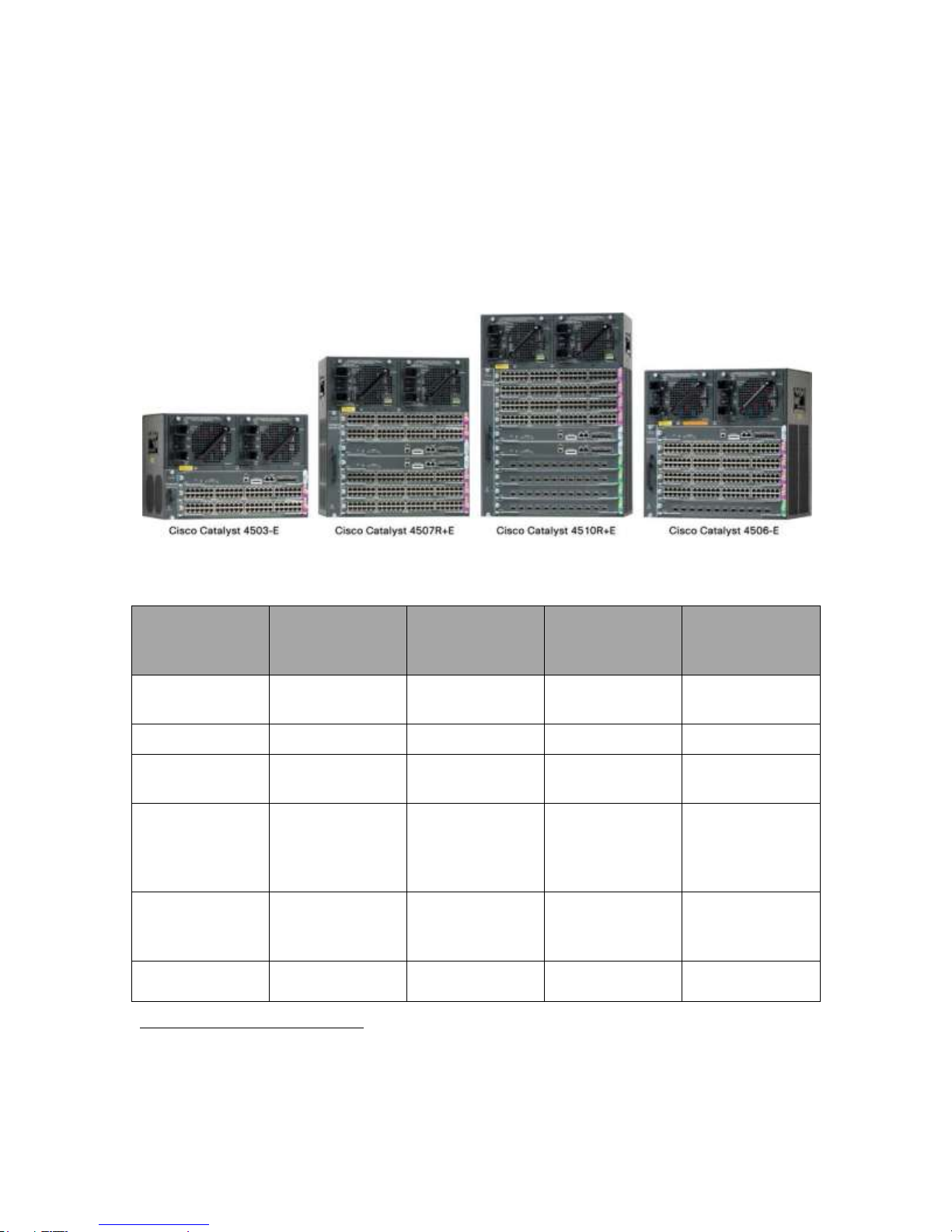
The Cisco Catalyst Switches, 4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E offers four chassis
options and two supervisor engine options and are extremely flexible and support either 6
Gbps, 24 Gbps, or 48 Gbps per line-card slot. The TOE can optionally support any
other line card or service module (SM)3 that is compatible with the supervisors and
chassis models included in the TOE. These line cards and SMs are not security-relevant
No specific service modules, such as the Firewall Blade, Wireless Service and Network Analysis being
claimed in the evaluated configuration as they require additional license
13
Page 14
Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Feature
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4503-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4506-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4507R+E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4510R+E
Chassis
Total number of
slots
3 6 7
10
Line-card slots
2 5 5
8
Supervisor
engine slots
14
12
25
26
Dedicated
supervisor
engine slot
numbers
1 1 3 and 4
5 and 6
Supervisor
engine
redundancy
No
No
Yes
Yes (Supervisor
V-10GE, 6-E and
7-E)
Supervisor
engines
Supervisor 7-E
Supervisor 7-E
Supervisor 7-E
Supervisor 7-E
4
5
6
EDCS-1228241
to the CC-evaluated security functional requirements, however the supervisor cards are
security relevant.
Figure 2 Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Chassis
Table 5 Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Chassis Features
Slot 1 is reserved for supervisor engine only; slots 2 and higher are reserved for line cards.
Slots 3 and 4 are reserved for supervisor engines only in Cisco Catalyst 4507R-E and 4507R+E; slots 1-2 and 5-7 are
reserved for line cards.
Slots 5 and 6 are reserved for supervisor engines only in Cisco Catalyst 4510R-E and 4510R+E; slots 1-4 and 7-10 are
reserved for line cards
14
Page 15

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Feature
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4503-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4506-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4507R+E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4510R+E
Chassis
supported
Supervisor 7L-E
Supervisor 7L-E
Supervisor 7L-E
Maximum PoE
per slot
1,500W
1,500W
1,500W
1,500W slots 1
and 2,
750W slots
3,4,7-10
Bandwidth
scalability per
line-card slot
Up to 48 Gbps
on all slots
Up to 48 Gbps
on all slots
Up to 48 Gbps
on all slots
7
Up to 48 Gbps
on all slots
5
Number of
power supply
bays
2 2 2
2
AC input power
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
DC Input power
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Integrated
Power over
Ethernet
Yes
Yes
Yes
Yes
Minimum
number of
power supplies
1 1 1
1
Power supplies
supported
● 1000W AC
● 1400W AC
● 1300W ACV
● 2800W ACV
● 4200W ACV
● 6000W ACV
● 1400W DC
(triple input)
● 1400W-DC-P
● 1000W AC
● 1400W AC
● 1300W ACV
● 2800W ACV
● 4200W ACV
● 6000W ACV
● 1400W DC
(triple input)
● 1400W-DC-P
● 1000W AC
● 1400W AC
● 1300W ACV
● 2800W ACV
● 4200W ACV
● 6000W ACV
● 1400W DC
(triple input)
● 1400W-DC-P
● 1400W AC
● 2800W ACV
● 4200W ACV
● 6000W ACV
● 1400W DC
(triple input)
● 1400W-DC-P
Number of fantray bays
1 1 1
1
Location of 19inch rack mount
Front
Front
Front
Front
7
EDCS-1228241
WS-C4507R-E and WS-C4510R-E chassis support up to 24G per line-card slot when used with Sup6-E
15
Page 16

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Feature
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4503-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4506-E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4507R+E
Chassis
Cisco Catalyst
WS-C4510R+E
Chassis
Location of 23inch rack mount
Front (option)
Front (option)
Front (option)
Front (option)
Product Number /Description
Cisco Catalyst 4500E Supervisor Cards
Supervisor Engine 7-E
• Performance and capability
– 848 Gbps switching capacity with 250 Mpps of throughput
– 4 nonblocking 10 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks (Small Form-Factor
Pluggable Plus [SFP+])
– SFP support on uplinks to offer flexibility for up to 4 Gigabit
Ethernet ports
– 384 ports of nonblocking 10/100/1000
– PoEP (30W) capabilities on all ports in a line card simultaneously
– UPOE (60W) capabilities on all line-card slots
– Energy Efficient Ethernet (IEEE 802.3az)
– 196 ports of nonblocking Gigabit Ethernet SFP
– 100 ports of 10 Gigabit Ethernet SFP+ (4 uplinks ports + 96 line-
card ports)
– 128,000 FNF entries in hardware
– External USB and Secure Digital (SD) card support for flexible
storage options
– 256,000 routing entries for high-end campus access and
aggregation deployments
– IPv6 support in hardware, providing wire-rate forwarding for IPv6
networks
– Dynamic hardware forwarding-table allocations for ease of IPv4to-IPv6 migration
– Scalable routing (IPv4, IPv6, and multicast) tables, Layer 2 tables,
EDCS-1228241
Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series line cards can be mixed and matched to suit numerous LAN
access, server connectivity, or branch-office deployments. The Cisco Catalyst 4500
Series supports the following supervisor and line cards, by product number:
Table 6 Catalyst 4500 Series Switch Chassis Line Cards
16
Page 17

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Product Number /Description
and access-control-list (ACL) and quality-of-service (QoS) entries to
use 8 queues/port and comprehensive security policies per port
• Infrastructure services
– Cisco IOS XE Software, the modular open application platform for
virtualized borderless services
– Maximum resiliency with redundant components, Nonstop
Forwarding/Stateful Switchover (NSF/SSO), and ISSU support
– Network virtualization through Multi-Virtual Route Forwarding
(VRF) and Easy Virtual Networking (EVN) technology for Layer 3
segmentation
– Automation through Embedded Event Manager (EEM), Cisco
Smart Call Home, AutoQoS, and Auto SmartPorts for fast
provisioning, diagnosis, and reporting
• Cisco Borderless Networks Services
– Optimized application performance through deep visibility with
FNF supporting rich Layer 2/3/4 information (MAC, VLAN, and
TCP Flags) and synthetic traffic monitoring with IP service-level
agreement (IP SLA)
– Medianet capabilities to simplify video QoS, monitoring, and
security
– Energy-efficient design with Cisco EnergyWise technology to
manage network, PoEP, and PC
• Investment protection and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO)
– Full backward compatibility with 6-, 24-, and 48-Gbps slot line
cards with no performance degradation
The Cisco Catalyst 4500E Supervisor Engine 7-E is compatible with
classic Cisco Catalyst 4500 line cards and power supplies, providing
full investment protection. The Supervisor Engine 7-E is not
compatible with classic Cisco Catalyst 4500 chassis. When you
deploy the Cisco Catalyst 4500E Supervisor Engine 7-E with classic
line cards, all of the new features except the 24- and 48-Gbps perslot switching capacity are inherited.
Supervisor Engine 7L-E
• Performance and scalability:
– 520-Gbps switching capacity with 225 mpps of throughput
– 2 nonblocking 10 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks (SFP+) or 4
nonblocking 1 Gigabit Ethernet uplinks (SFP)
EDCS-1228241
17
Page 18

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Product Number /Description
– Supports 3-, 6-, and 7-slot Cisco Catalyst 4500E chassis
– Supports a maximum of 244 ports of 10/100/1000 Base-T and 400
ports of 1000Base-X (CSFP) in a 7-slot chassis
– Supports up to 124 1GE nonblocking fiber ports or 62 10GE fiber
ports in a 7-slot chassis
– Enables next-generation Universal Power Over Ethernet (UPOE,
WS-X4748-UPOE+E) in addition to backward compatibility with
other PoE standards
– Enables EEE (IEEE 802.3az)
– 128,000 Flexible NetFlow entries in hardware
– External USB and SD card support for flexible storage options
– 10/100/1000 RJ-45 console and management port
– 64,000/32,000 IPv4/IPv6 routing entries for campus access and
aggregation deployments
– IPv6 in hardware, providing wire-rate forwarding for IPv6
networks and support for dual stack with innovative resource usage
– Dynamic hardware forwarding-table allocations for ease of IPv4-
to-IPv6 migration
– Scalable routing (IPv4, IPv6, and multicast) tables, Layer 2 tables,
and access-control-list (ACL) and quality-of-service (QoS) entries to
make use of 8 queues per port and comprehensive security policies
per port
• Infrastructure services:
– Cisco IOS XE Software, the modular open application platform for
virtualized borderless services
– Maximum resiliency with redundant components, Nonstop
Forwarding/Stateful Switchover (NSF/SSO), and In-Service
Software Upgrade (ISSU) support
– Network virtualization through Multi-Virtual Route Forwarding
(VRF) technology for Layer 3 segmentation
– Automation through Embedded Event Manager (EEM), Cisco
Smart Call Home, AutoQoS, and Auto SmartPorts for fast
provisioning, diagnosis, and reporting
• Borderless network services:
– Optimized application performance through deep visibility with
Flexible NetFlow supporting rich Layer 2/3/4 information (MAC,
VLAN, TCP Flags) and synthetic traffic monitoring with IP servicelevel agreement (SLA)
– Medianet capabilities to simplify video quality of service,
monitoring, and security. In addition, multicast features such as
Protocol Independent Multicast (PIM) and Source-Specific
EDCS-1228241
18
Page 19

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Product Number /Description
Multicast (SSM) that provide enterprise customers the additional
scalability to support multimedia applications
– Energy-efficient design with Cisco EnergyWise™ technology
• Investment protection and reduced total cost of ownership (TCO):
– Full backward compatibility with 6 G, 24 G, and 48 Gbps slot line
cards with no performance degradation
The Cisco Catalyst 4500E Supervisor Engine 7L-E is compatible
with classic Cisco Catalyst 4500 line cards and power supplies,
providing full investment protection. Supervisor Engine 7L-E is not
compatible with classic Cisco Catalyst 4500 chassis.
Cisco Catalyst 4500E Series Line Cards
WS-X4748-UPOE+E
• 48 ports nonblocking
• 10/100/1000 module (RJ-45)
• Cisco IOS XE Release 3.1.0SG or later
• UPOE: capable of up to 60 W per port up to 1440 W
• Energy Efficient Ethernet 802.3az
• IEEE 802.3af/at and Cisco prestandard PoE, IEEE 802.3x flow
control
• IEEE 802.1AE and Cisco TrustSec capability in hardware
• L2-4 Jumbo Frame support (up to 9216 bytes)
• Capable of up to 30 W of inline power per port on all ports
simultaneously
• Enterprise and commercial: designed to power next-generation IP
phones, wireless base stations, video cameras, virtual desktop
clients, and other PoE/UPOE devices
• Campus and branch applications requiring enhanced performance
for large file transfers and network backups
WS-X4748-RJ45V+E
• 48 ports nonblocking
• 10/100/1000 module (RJ-45)
• Cisco IOS XE Release 3.1.0SG or later
• IEEE 802.3af/at and Cisco prestandard PoE, IEEE 802.3x flow
control
• IEEE 802.1AE and Cisco TrustSec capability in hardware
• L2-4 Jumbo Frame support (up to 9216 bytes)
• Capable of up to 30 W of inline power per port on all ports
simultaneously
• Enterprise and commercial: designed to power next-generation IP
phones, wireless base stations, video cameras, and other PoE
devices
• Campus and branch applications requiring enhanced performance
for large file transfers and network backups
EDCS-1228241
19
Page 20

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Product Number /Description
WS-X4748-RJ45-E
• 48 ports nonblocking
• 10/100/1000 module (RJ-45)
• Cisco IOS XE Release 3.1.0SG or later
• Energy Efficient Ethernet 802.3az
• IEEE 802.1AE and Cisco TrustSec capability in hardware
• L2-4 Jumbo Frame support (up to 9216 bytes)
• Enterprise and commercial: designed for data only user access
• Campus and branch applications requiring enhanced performance
for large file transfers and network backups
WS-X4712-SFP+E
• 48 gigabits per-slot capacity
• Bandwidth is allocated across four 3-port groups, providing 12
Gbps per port group (2.5:1)
• Up to 12 ports 10GE SFP+ (10GBASE-R) or 12 ports GE SFP
(1GBASE-X)
• SFP+ and SFP can be used simultaneously on the same line card
without any restrictions
• Cisco IOS XE Release 3.1.0SG or later
• IEEE 802.1AE and Cisco TrustSec capability in hardware
• L2-4 Jumbo Frame support (up to 9216 bytes)
• Enterprise and commercial: designed for high-speed backbone
and switch-to-switch applications
• Service provider: 10GE/GE mix aggregation for
DSLAM/PON/mobile data backhaul
• WS-X4712-SFP+E is not supported on 4507R-E and 4510R-E
chassis
WS-X4640-CSFP-E
• 40 modules of Gigabit SFP line card (1000BaseX), providing 24
gigabits per-slot capacity (SFP optional)
• 40 ports with Gigabit SFP (2:1 oversubscribed)
• 80 ports with Gigabit compact SFP (4:1 oversubscribed)
• Customers can mix and match Gigabit SFP and Gigabit compact
SFPs
• 6E/6LE Supports WS-X4640-CSFP-E with IOS version
15.1.(1)SG
• 7E, 7L-E supports WS-X4640-CSFP-E from 15.0(2)SG1 /
3.2.0SG onwards
• Supported on 3, 6, and 7 slot chassis
• IEEE 802.3, IEEE 802.3ah, IEEE 802.3x flow control
• L2-4 Jumbo Frame support (up to 9216 bytes)
• Inherits supervisor engine QoS capability
• Service Provider: Point-to-Point fiber to the home (FTTH) or
building (FTTB) for residential and business applications
• Enterprise: Providing Fiber to the Desktop (FTTD), for
deployments where non-blocking is not a mandatory requirement
EDCS-1228241
20
Page 21

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
The Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series has flexible interface types and port densities that allow
network configurations to be mixed and matched to meet the specific needs of the
organizations network.
The Cisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Switch is a fixed aggregation platform that provides
flexibility through two versions of base switches along with optional uplink module. Both
the 32- and 16-port versions can be configured with optional network modules and offer
similar features. The Small Form-Factor Pluggable Plus (SFP+) interface supports both
10 Gigabit Ethernet and 1 Gigabit Ethernet ports, allowing upgrades to 10 Gigabit
Ethernet when organizational demands change. The uplink module is hot swappable.
Deployment Options include:
32 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port switch with optional Small Form-Factor Pluggable
Plus (SFP+) models
16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port switch with optional Small Form-Factor Pluggable
Plus (SFP+) models
8 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet SFP+ removable uplink module
Dual-redundant AC/DC power supply and five field-replaceable unit (FRU) fans
The figure below shows the Cisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Switch with and without the
optional 8-port uplink module, front-to-back airflow, and the uplink module.
Figure 3 Cisco Catalyst 4500-X Series Chassis and Modules
Figure 4 32 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port Switch with Optional Uplink Module Slot
Figure 5 16 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port Switch with Optional Uplink Module Slot
Figure 6 8 x 10 Gigabit Ethernet Port Uplink Module
21
Page 22

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Figure 7 Front-to-Back Airflow Rear View
Figure 8 Back-to-Front Airflow Rear View
As described above, the physical boundary of the TOE is the switch hardware and
software. The software of the TOE is IOS and other supporting functionality (e.g., SSH
Server). This physical boundary represents the Switch subsystem of the TOE. The
Switch subsystem processes data packets and accepts a management interface connection
to administer the switch. The management interface is either through a secure SSHv2
session or via a local console connection.
The switches are hardware platforms in which all operations in the TOE scope are
protected from interference and tampering by untrusted subjects. All administration and
configuration operations are performed within the physical boundary of the TOE. Also,
all TOE Security Policy (TSP) enforcement functions must be invoked and succeed prior
to functions within the TOE scope of control (TSC) proceeding.
The TOE includes one or more chassis, one or more supervisor engine cards running the
IOS XE software and one or more line cards. Each switch is a physical device with the
following types of communication interfaces provided by the supervisor engine cards
and/or the line cards:
USB ports,
Network port,
22
Page 23

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Serial port, and
Compact Flash Slot
In addition to the communication interfaces above, the TOE includes a number of LEDs
and power connectors. The LEDs are output elements only, and while the power
connectors provide physical input they are not considered TOE interfaces.
1.6.1 USB Console Port
The USB Interface is a physical port on the Supervisor card. The interface allows a
management console to be connected to the TOE as a USB device whereas an
Administrator can authenticate to the TOE and issue commands to the TOEs CLI.
Physical access to the port is protected by operational environment of the switch.
1.6.2 Network Ports
The physical network interfaces to the switch are Ethernet interfaces receiving and
transmitting Internet Protocol datagrams as specified in RFC 0894 [Ethernet], RFC 0791
[IPv4], and RFC 2460 [IPv6]. Over this physical interface network traffic packets are
transferred into and out of the TOE. The physical network interface (ports) can be
located on the supervisor card and/or the line cards.
The network interface is the physical Ethernet interface to the TOE from the internal and
external networks. Within the scope of the evaluation, this interface is used for the
following purposes:
For network traffic entering and leaving the TOE. This could be ‘through traffic’
for example a telnet packet from a user destined from an internal network to an
external network, or ‘to the box traffic’ for example an external ping to the TOE’s
IP address.
To allow a remote Administrator to access the TOE’s CLI over the network using
SSHv2.
To allow the audit log records to be transmitted to the syslog server via IPsec
connection tunnel.
To allow, if configured, time synchronization with the NTP server via secure
transmission (SSHv2, IPsec).
To allow, if configured, the TOE access to the AAA server to authenticate TOE
administrators.
1.6.3 Serial Port
From a directly connected terminal an Administrator can authenticate to the TOE and
issue commands to the TOEs CLI. This interface can also be configured to display
syslog messages to the console.
23
Page 24

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
The primary serial interface into the TOE uses RS-232 signaling over an RJ45 interface.
The serial port is located on the Supervisor card.
1.6.4 Compact Flash Slot
The Supervisor Engine card in the Catalyst 4500 series provides a slot to accept a
compact flash drive. The TOE can accept 64MB, 128 MB, 256 MB, 512 MB compact
flash drives. The storage provided by these drives is used by the TOE as ordinary long
term storage of configuration files and IOS software images.
Because the TOE treats the compact flash storage as an internal storage medium, this
physical interface is considered internal to the TOE and thus, NOT a TSFI.
1.6.5 Physical Scope of the TOE
The physical scope of the TOE comprises a collection of all hardware, firmware,
software and guidance documentation as follows:
The TOE is a hardware and software solution that uses a combination of chassis,
supervisor engine, and line cards as defined in Section 1.3.1, Table 3: the Cisco
Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E, 4500X and
4500X-F) running IOS XE 3.5.2E on the Supervisor Engine.
Installation and Configuration guidance for the Common Criteria NDPP
Evaluated Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E,
4510R+E, 4500X and 4500X-F) with IOS XE 3.5.2E
Cisco IOS Security Command Reference
Cisco IOS Security Configuration Guide
1.7 Logical Scope of the TOE
The TOE includes the following security features that are relevant to the secure
configuration and operation of the TOE.
1. Security audit
2. Cryptographic support
3. User Data Protection
4. Identification and authentication
5. Secure Management
6. Protection of the TSF
7. Resource Utilization
8. TOE access
9. Trusted Path/Channel
These features are described in more detail in the subsections below.
24
Page 25

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
1.7.1 Security Audit
The TOE generates a comprehensive set of audit logs that identify specific TOE
operations. For each event, the TOE records the date and time of each event, the type of
event, the subject identity, and the outcome of the event. Auditable events include: failure
on invoking cryptographic functionality; establishment, termination and failure of an
IPsec SA; establishment, termination and failure of an SSH session; modifications to the
group of users that are part of the authorized administrator roles; all use of the user
identification mechanism; any use of the authentication mechanism; any change in the
configuration of the TOE; detection of replay attacks, changes to time, initiation of TOE
update, indication of completion of TSF self-test, maximum sessions being exceeded,
termination of a remote session and attempts to unlock a termination session; and
initiation and termination of a trusted channel.
The TOE is configured to transmit its audit messages to an external syslog server.
Communication with the syslog server is protected using IPsec and the TOE can
determine when communication with the syslog server fails. If that should occur, the
TOE can be configured to block new permit actions.
The logs can be viewed on the TOE using the appropriate IOS commands. The records
include the date/time the event occurred, the event/type of event, the user associated with
the event, and additional information of the event and its success and/or failure. The
TOE does not have an interface to modify audit records, though there is an interface
available for the authorized administrator to clear audit data stored locally on the TOE.
1.7.2 Cryptographic Support
The TOE provides cryptography support for secure communications and protection of
information when configured in FIPS mode of operation. The crypto module is FIPS
140-2 SL2 validated. The cryptographic services provided by the TOE include:
symmetric encryption and decryption using AES; digital signature using RSA;
cryptographic hashing using SHA1; keyed-hash message authentication using HMACSHA1, and IPsec for authentication and encryption services to prevent unauthorized
viewing or modification of data as it travels over the external network. The TOE also
implements SSHv2 secure protocol for secure remote administration. In the evaluated
configuration, the TOE must be operated in FIPS mode of operation per the FIPS
Security Policy (certificate 1940).
1.7.3 User Data Protection
The TOE supports routing protocols including BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6,
RIPv2, and OSPFv2 to maintain routing tables, or routing tables can configured and
maintained manually (‘static routes’). Since routing tables are used to determine
which egress ACL is applied to the outbound traffic, the authority to modify the
routing tables is restricted to authenticated administrators, and authenticated neighbor
routers. The only aspect of routing protocols that is security relevant in this TOE is
the TOE’s ability to authenticate neighbor routers using shared passwords. Other
25
Page 26

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
security features and configuration options of routing protocols are beyond the scope
of this Security Target and are described in administrative guidance.
The TOE also ensures that packets transmitted from the TOE do not contain residual
information from previous packets. Packets that are not the required length use zeros
for padding the remainder of the packet so that residual data from previous traffic is
never transmitted from the TOE.
1.7.4 Identification and Authentication
The TOE performs local authentication, using Cisco IOS platform authentication
mechanisms, to authenticate access to user EXEC and privileged EXEC command
modes. All users wanting to use TOE services are identified and authenticated prior to
being allowed access to any of the services. Once a user attempts to access the
management functionality of the TOE (via EXEC mode), the TOE prompts the user for a
user name and password. Only after the administrative user presents the correct
identification and authentication credentials will access to the TOE functionality be
granted.
The TOE also supports use of a remote AAA server (RADIUS and TACACS+) as the
enforcement point for identifying and authenticating users attempting to connect to the
TOE’s CLI. Note the remote authentication server is not included within the scope of the
TOE evaluated configuration, it is considered to be provided by the operational
environment.
The TOE can be configured to display an advisory banner when administrators log in and
also to terminate administrator sessions after a configured period of inactivity.
The TOE also supports authentication of other routers using router authentication
supported by BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6, RIPv2, and OSPFv2. Each of these
protocols supports authentication by transmission of MD5-hashed password strings,
which each neighbor router uses to authenticate others. For additional security, it is
recommended router protocol traffic also be isolated to separate VLANs.
1.7.5 Security Management
The TOE provides secure administrative services for management of general TOE
configuration and the security functionality provided by the TOE. All TOE
administration occurs either through a secure session via SSHv2, or a local console
connection (serial port). The TOE provides the ability to perform the following actions:
allows authorized administrators to add new administrators,
start-up and shutdown the device,
create, modify, or delete configuration items,
create, modify, or delete information flow policies,
create, modify, or delete a routing table,
modify and set session inactivity thresholds,
modify and set the time and date,
26
Page 27

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
and create, delete, empty, and review the audit trail
All of these management functions are restricted to authorized administrators of the TOE.
The TOE switch platform maintains administrative privilege levels and supports nonadministrative connections. Non-administrative connections are established with
authenticated neighbor routers for the ability to transmit and receive routing table updates
per the information flow rules. No other access nor management functionality is
associated with non-administrative connections. The administrative privilege levels
include:
Administrators are assigned to privilege levels 0 and 1. Privilege levels 0 and 1
are defined by default and are customizable. These levels have a very limited
scope and access to CLI commands that include basic functions such as login,
show running system information, turn on/off privileged commands, logout.
Semi-privileged administrators equate to any privilege level that has a subset of
the privileges assigned to level 15; levels 2-14. These levels are undefined by
default and are customizable.
Privileged administrators are equivalent to full administrative access to the CLI,
which is the default access for IOS privilege level 15.
All management functions are restricted to the authorized administrator of the TOE. The
term “authorized administrator” is used in this ST to refer to any user account that has
been assigned to a privilege level that is permitted to perform the relevant action;
therefore has the appropriate privileges to perform the requested functions.
1.7.6 Protection of the TSF
The TOE protects against interference and tampering by untrusted subjects by
implementing identification, authentication and access controls to limit configuration to
authorized administrators. Additionally Cisco IOS is not a general-purpose operating
system and access to Cisco IOS memory space is restricted to only Cisco IOS functions.
The TOE provides secure transmission when TSF data is transmitted between the TOE
and other IT entities, such as remote administration via SSH and secure transmission of
audit logs to a syslog server via IPsec.
The TOE is also able to detect replay of information received via secure channels (e.g.
SSH, or IPsec). The detection applied to network packets that terminate at the TOE, such
as trusted communications between the administrators and the TOE, or between an IT
entity (e.g., authentication server) and the TOE. If replay is detected, the packets are
discarded.
In addition, the TOE internally maintains the date and time. This date and time is used as
the timestamp that is applied to audit records generated by the TOE. Administrators can
update the TOE’s clock manually, or can configure the TOE to use NTP to synchronize
27
Page 28

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
8
EDCS-1228241
the TOE’s clock with an external time source. Finally, the TOE performs testing to
verify correct operation of the switch itself and that of the cryptographic module8.
1.7.7 Resource Utilization
The TOE provides the capability of controlling and managing resources so that a denial
of service will not occur. The resource allocations are configured to limit the number of
concurrent administrator sessions.
1.7.8 TOE Access
The TOE can terminate inactive sessions after an authorized administrator configurable
time-period. Once a session has been terminated the TOE requires the user to reauthenticate to establish a new session.
The TOE also provides the authorized administrator with the ability to specify a
notification of use banner on the CLI management interface prior to allowing any
administrative access to the TOE.
1.7.9 Trusted Path/Channels
The TOE establishes a trusted path between the appliance and the CLI using SSHv2, with
the syslog server and if configured with the NTP server and external authentication server
using IPsec.
1.8 Excluded Functionality
The Cisco IOS contains a collection of features that build on the core components of the
system. Those features that are not within the scope of the evaluated configuration
include:
Features that must remain disabled in the evaluated configuration:
HTTP or HTTPS Server - The IOS web server (using HTTPS or HTTP) cannot
satisfy all the NDPP requirements for administrative interfaces and must remain
disabled in the evaluated configuration. The CLI interface is used to manage the
TOE. Not including this feature does not interfere with the management of TOE
as defined in the Security Target or the operation of the TOE.
IEEE 802.11 Wireless Standards requires additional hardware beyond what is
included in the evaluated configuration.
SNMP Server does not enforce the required user-specific authentication. This
feature is disabled by default and must remain disabled in the evaluated
The cryptographic module, which is security relevant, implements support for cryptographic operations
used by other parts of the TOE.
28
Page 29

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
configuration. Including this feature would not meet the security policies as
defined in the Security Target. The exclusion of this feature has no effect on the
operation of the TOE.
Telnet server sends authentication data in the clear. This feature is enabled by
default and must be disabled in the evaluated configuration. Including this feature
would not meet the security policies as defined in the Security Target. The
exclusion of this feature has no effect on the operation of the TOE.
VPN Remote Access requires additional licenses beyond what is included in the
evaluated configuration. Administrative remote access is secured using SSHv2.
Smart Install is a feature to configure IOS Software and switch configuration
without user intervention. The Smart Install uses dynamic IP address allocation to
facilitate installation providing transparent network plug and play. This feature is
not to be used as it could result in settings/configurations that may interfere with
the enforcement of the security policies as defined in the Security Target or the
TOEs operation.
TrustSec is only relevant to RADIUS KeyWrap, which is being represented with
other cryptographic methods identified and described in this Security Target. This
feature is disabled by default and should remain disabled in the evaluated
configuration. Not including this feature does not interfere with the enforcement
of the security policies as defined in the Security Target or the TOEs operation.
Apart from these exceptions, all types of network traffic through and to the TOE are
within the scope of the evaluation.
29
Page 30

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
2 CONFORMANCE CLAIMS
2.1 Common Criteria Conformance Claim
The ST and the TOE it describes are conformant with the following CC package
specifications:
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation Part 2:
Security Functional Components, Version 3.1, Revision 3, July 2009
o Part 2 Extended
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation Part 3:
Security Assurance Components, Version 3.1, Revision 3, July 2009
o Part 3 Conformant
2.2 Protection Profile Conformance Claim
This ST claims strict conformance to the following Common Criteria validated Protection
Profiles (PP), US Government, Security Requirements for Network Devices
(pp_nd_v1.0), version 1.0, dated 10 December 2010 (from here within referred to as
NDPP). To support the strict conformance claim, as noted below in the PP conformance
claim rationale, the ST includes all claims as indicated in NDPP and makes no additional
claims.
2.3 Protection Profile Conformance Claim Rationale
2.3.1 TOE Appropriateness
The TOE provides all of the functionality at a level of security commensurate with that
identified in the NDPP
2.3.2 TOE Security Problem Definition Conformance
The Assumptions, Threats, and Organization Security Policies included in the Security
Target represent the Assumptions, Threats, and Organization Security Policies specified
in the NDPP for which conformance is claimed verbatim. All concepts covered in the
Protection Profile Security Problem Definition are included in the Security Target.
2.3.3 Statement of Security Objectives Conformance
The Assumptions, Threats, and Organization Security Policies included in the Security
Target represent the Assumptions, Threats, and Organization Security Policies specified
in the NDPP for which conformance is claimed verbatim.
30
Page 31

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
2.3.4 Statement of Security Requirements Conformance
The Security Functional Requirements included in the Security Target represent the
Security Functional Requirements specified in the U.S. Government Protection Profile
for Security Requirements for Network Devices for which conformance is claimed
verbatim. All concepts covered in the Protection Profile’s Statement of Security
Requirements are included in the Security Target. Additionally, the Security Assurance
Requirements included in the Security Target are identical to the Security Assurance
Requirements included in section 4.3 of the NDPP.
31
Page 32

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
External Entities
Entity Definition
Admin
Human who administers the TOE.
Administration tasks include starting the TOE, operating the TOE,
maintaining configuration data and inspection of security audit log
files. In this Security Target there are several levels of
administrators, all which are described in Section 6.1 and all
considered an Admin.
Attacker
A threat agent trying to undermine the security policy of the TOE.
Asset
Asset Description
Audit Data
Primary asset, audit data
EDCS-1228241
3 SECURITY PROBLEM DEFINITION
The security problem definition (SPD) defines the security problem that is to be
addressed.
This document identifies assumptions as A.assumption with “assumption” specifying a
unique name. Threats are identified as T.threat with “threat” specifying a unique name.
3.1 Introduction
This section describes the security environment in which the TOE is intended to be used.
3.2 External Entities
The following human or IT entities possibly interact with the TOE from outside the TOE
boundary.
Table 7 External entities interacting with TOE
3.3 Assets
The owner of the TOE presumably places value upon the following primary and
secondary entities as long as they are in the scope of the TOE.
3.3.1 Primary Assets
The owner of the TOE presumably places value upon the following primary entities. All
these primary assets represent user data in the sense of the CC.
Table 8 Primary assets to be protected
32
Page 33

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Asset
Asset Description
The data which is provided by the TOE during security audit
logging.
Security properties to be maintained by the TOE: confidentiality,
availability, integrity.
Asset
Asset Description
Auth data
Secondary asset, TSF data
The data which is used by the TOE to identify and authenticate the
external entities which interact with the TOE.
Security properties to be maintained by the TOE: confidentiality,
integrity, authenticity.
Crypto data
Secondary asset, TSF data
The data which is used by the TOE for digital signature handling and
encryption/decryption purposes.
Security properties to be maintained by the TOE: confidentiality,
integrity, authenticity.
Ctrl data
Secondary asset, TSF data
The data which is used by the TOE for firmware updates, firmware
registration, and firmware identity checking purposes.
Security properties to be maintained by the TOE: availability,
integrity.
Assumption
Assumption Definition
A.NO_GENERAL_PURPOSE
It is assumed that there are no general-purpose
computing capabilities (e.g., compilers or user
applications) available on the TOE, other than
EDCS-1228241
3.3.2 Secondary Assets
The owner of the TOE presumably places value upon the following secondary entities.
All these secondary assets represent user data in the sense of the CC.
Table 9 Secondary assets to be protected
3.4 Assumptions
The specific conditions listed in the following subsections are assumed to exist in the
TOE’s environment. These assumptions include both practical realities in the
development of the TOE security requirements and the essential environmental
conditions on the use of the TOE.
Table 10 Operational Assumptions
33
Page 34

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Assumption
Assumption Definition
those services necessary for the operation,
administration and support of the TOE.
A.PHYSICAL
Physical security, commensurate with the value of
the TOE and the data it contains, is assumed to be
provided by the environment.
A.TRUSTED_ADMIN
TOE Administrators are trusted to follow and
apply all administrator guidance in a trusted
manner.
Threat
Threat Definition
T.ADMIN_ERROR
An administrator may unintentionally install or
configure the TOE incorrectly, resulting in
ineffective security mechanisms.
T.RESOURCE_EXHAUSTION
A process or user may deny access to TOE services
by exhausting critical resources on the TOE.
T.TSF_FAILURE
Security mechanisms of the TOE may fail, leading
to a compromise of the TSF.
T.UNDETECTED_ACTIONS
Malicious remote users or external IT entities may
take actions that adversely affect the security of the
TOE. These actions may remain undetected and
thus their effects cannot be effectively mitigated.
T.UNAUTHORIZED_ACCESS
A user may gain unauthorized access to the TOE
data and TOE executable code. A malicious user,
process, or external IT entity may masquerade as an
authorized entity in order to gain unauthorized
access to data or TOE resources. A malicious user,
process, or external IT entity may misrepresent
itself as the TOE to obtain identification and
authentication data.
T.UNAUTHORIZED_UPDATE
A malicious party attempts to supply the end user
with an update to the product that may compromise
the security features of the TOE.
T.USER_DATA_REUSE
User data may be inadvertently sent to a destination
not intended by the original sender.
EDCS-1228241
3.5 Threats
The following table lists the threats addressed by the TOE and the IT Environment. The
assumed level of expertise of the attacker for all the threats identified below is Basic.
Table 11 Threats
34
Page 35

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Policy Name
Policy Definition
P.ACCESS_BANNER
The TOE shall display an initial banner describing
restrictions of use, legal agreements, or any other
appropriate information to which users consent by
accessing the TOE.
EDCS-1228241
3.6 Organizational Security Policies
Organizational security policies (OSPs) are security rules, procedures, or guidelines
enforced by the TOE, its operational environment, or a combination of the two.
3.6.1 OSPs enforced by TOE
The following security rules, procedures, or guidelines are enforced by the TOE.
Table 12 Organizational Security Policies
35
Page 36

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE Objective
TOE Security Objective
Definition
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
The TOE will provide protected
communication channels for
administrators, other parts of a
distributed TOE, and authorized IT
entities.
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
The TOE will provide the
capability to help ensure that any
updates to the TOE can be verified
by the administrator to be
unaltered and (optionally) from a
trusted source.
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
The TOE will provide the
capability to generate audit data
and send those data to an external
IT entity.
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
The TOE will display an advisory
warning regarding use of the TOE.
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
The TOE will provide mechanisms
to ensure that only administrators
are able to log in and configure the
TOE, and provide protections for
logged-in administrators.
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEARING
The TOE will ensure that any data
contained in a protected resource
is not available when the resource
is reallocated.
EDCS-1228241
4 SECURITY OBJECTIVES
The security objectives are a concise and abstract statement of the intended solution to
the security problem defined by the SPD.
This document identifies objectives of the TOE as O.objective with objective specifying
a unique name. Objectives that apply to the operational environment are designated as
OE.objective with objective specifying a unique name.
4.1 Security Objectives for the TOE
The security objectives for the TOE consists of a set of objectives the TOE should
achieve to solve its part of the security problem.
Table 13 Security Objectives for the TOE
36
Page 37

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE Objective
TOE Security Objective
Definition
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
The TOE shall provide
mechanisms that mitigate user
attempts to exhaust TOE resources
(e.g., persistent storage).
O.SESSION_LOCK
The TOE shall provide
mechanisms that mitigate the risk
of unattended sessions being
hijacked.
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
The TOE will provide the
capability to test some subset of its
security functionality to ensure it
is operating properly.
Operational Environment
Security Objective
Operational Environment Security
Objective Definition
OE.NO_GENERAL_PURPOSE
There are no general-purpose computing
capabilities (e.g., compilers or user applications)
available on the TOE, other than those services
necessary for the operation, administration and
support of the TOE.
OE.PHYSICAL
Physical security, commensurate with the value of
the TOE and the data it contains, is provided by the
environment.
OE.TRUSTED_ADMIN
TOE Administrators are trusted to follow and apply
all administrator guidance in a trusted manner.
EDCS-1228241
4.2 Security Objectives for the Environment
The security objectives for the environment consist of a set of objectives the environment
should achieve to assist the TOE in correctly providing its security objectives.
Table 14 Security Objectives for the Environment
5 SECURITY REQUIREMENTS
This section identifies the Security Functional Requirements for the TOE. The Security
Functional Requirements included in this section are derived from US Government,
Security Requirements for Network Devices (pp_nd_v1.0), version 1.0, dated 10
December 2010.
37
Page 38

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Functional Component
Requirement Class
Requirement Component
FAU: Security audit
FAU_GEN.1: Audit data generation
FAU_GEN.2: User identity association
FAU_STG_EXT.1: External audit trail storage
FAU_STG_EXT.3: Action in case of loss of audit
server connectivity
EDCS-1228241
5.1 Conventions
The CC defines operations on Security Functional Requirements: assignments, selections,
assignments within selections and refinements. This document uses the following font
conventions to identify the operations defined by the CC:
Where operations were completed in the NDPP itself, the formatting used in the
NDPP has been retained;
Assignment: allows the specification of an identified parameter. Assignments are
indicated using bold and are surrounded by brackets (e.g., [assignment]). Note
that an assignment within a selection would be identified in italics and with
embedded bold brackets (e.g., [[selected-assignment]]).
Selection: allows the specification of one or more elements from a list. Selections
are indicated using bold italics and are surrounded by brackets (e.g., [selection]).
Iteration: allows a component to be used more than once with varying operations.
In the ST, iteration is indicated by a number placed at the end of the component.
For example FDP_IFF.1(1) and FDP_IFF.1(2) indicate that the ST includes two
iterations of the FDP_IFF.1 requirement, (1) and (2).
Refinement: allows the addition of details. Refinements are indicated using bold,
for additions, and strike-through, for deletions (e.g., “… all objects …” or “…
some big things …”).
The Extended SFRs are identified by having a label ‘_EXT’ after the requirement
name for TOE SFRs.
Other sections of the ST use bolding to highlight text of special interest, such as captions.
5.2 TOE Security Functional Requirements
This section identifies the Security Functional Requirements for the TOE that are
specified in the NDPP. The TOE Security Functional Requirements that appear in the
following table are described in more detail in the following subsections.
Table 15 Security Functional Requirements
38
Page 39

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Functional Component
FCS: Cryptographic
support
FCS_CKM.1: Cryptographic key generation (for
asymmetric keys)
FCS_CKM_EXT.4: Cryptographic key zeroization
FCS_COP.1(1): Cryptographic operation (for data
encryption/decryption)
FCS_COP.1(2): Cryptographic operation (for
cryptographic signature)
FCS_COP.1(3): Cryptographic operation (for
cryptographic hashing)
FCS_COP.1(4): Cryptographic operation (for keyedhash message authentication)
FCS_RBG_EXT.1: Cryptographic operation (random
bit generation)
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1: Communications
protection
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1: IPSEC
FCS_SSH_EXT.1: SSH
FDP: User data
protection
FDP_RIP.2: Full residual information protection
FIA: Identification and
authentication
FIA_PMG_EXT.1: Password management
FIA_UIA_EXT.1: User identification and
authentication
FIA_UAU_EXT.5: Password-based authentication
mechanism
FIA_UAU.6: Re-authenticating
FIA_UAU.7: Protected authentication feedback
FMT: Security
management
FMT_MTD.1: Management of TSF data (for general
TSF data)
FMT_SMF.1: Specification of management functions
FMT_SMR.1: Security roles
FPT: Protection of the
TSF
FPT_ITT.1(1): Basic internal TSF data transfer
protection (disclosure)
FPT_ITT.1(2): Basic internal TSF data transfer
protection (modification)
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(1): Management of TSF data (for
reading of authentication data)
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(2): Management of TSF data (for
EDCS-1228241
39
Page 40

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Functional Component
reading of keys)
FPT_RPL.1: Replay detection
FPT_STM.1: Reliable time stamps
FPT_TUD_EXT.1: Trusted update
FPT_TST_EXT.1: TSF testing
FRU: Resource
utilization
FRU_RSA.1: Maximum quotas
FTA: TOE Access
FTA_SSL_EXT.1: TSF-initiated session locking
FTA_SSL.3: TSF-initiated termination
FTA_TAB.1: Default TOE access banners
FTP: Trusted
path/channels
FTP_ITC.1(1): Inter-TSF trusted channel (prevention
of disclosure)
FTP_ITC.1(2): Inter-TSF trusted channel (detection of
modification)
FTP_TRP.1(1): Trusted path
FTP_TRP.1(2): Trusted path
EDCS-1228241
5.2.1 Security audit (FAU)
5.2.1.1 FAU_GEN.1: Audit data generation
FAU_GEN.1.1 The TSF shall be able to generate an audit record of the following
auditable events:
a) Start-up and shutdown of the audit functions;
b) All auditable events for the basic level of audit; and
c) All administrative actions;
d) [Specifically defined auditable events listed in Table 16].
FAU_GEN.1.2 The TSF shall record within each audit record at least the
following information:
a) Date and time of the event, type of event, subject identity, and
the outcome (success or failure) of the event; and
b) For each audit event type, based on the auditable event
definitions of the functional components included in the PP/ST,
[information specified in column three of Table 16].
40
Page 41

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Requirement
Auditable Events
Additional Audit Record
Contents
FAU_GEN.1
None.
FAU_GEN.2
None.
FAU_STG_EXT.1
None.
FAU_STG_EXT.3
Loss of connectivity.
No additional information.
FCS_CKM.1
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_CKM_EXT.4
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_COP.1(1)
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_COP.1(2)
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_COP.1(3)
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_COP.1(4)
Failure on invoking
functionality.
No additional information.
FCS_RBG_EXT.1
Failure of the randomization
process.
No additional information.
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT
.1
None.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1
Failure to establish an IPsec
SA.
Establishment/Termination of
an IPsec SA.
Reason for failure.
Non-TOE endpoint of
connection (IP address) for
both successes and failures.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1
Failure to establish an SSH
Session.
Establishment/Termination of
an SSH Session.
Reason for failure.
Non-TOE endpoint of
connection (IP address) for
both successes and failures.
FDP_RIP.2
None.
FIA_PMG_EXT.1
None.
FIA_UIA_EXT.1
All use of the identification
and authentication
mechanism.
Provided user identity,
origin of the attempt (e.g.,
IP address).
FIA_UAU_EXT.5
All use of the authentication
mechanism.
Origin of the attempt (e.g.,
IP address).
FIA_UAU.6
Attempt to re-authenticate.
Origin of the attempt (e.g.,
IP address).
FIA_UAU.7
None.
EDCS-1228241
Table 16: Auditable Events
41
Page 42

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Requirement
Auditable Events
Additional Audit Record
Contents
FMT_MTD.1
None.
FMT_SMF.1
None.
FMT_SMR.1
None.
FPT_ITT.1(1)
None.
FPT_ITT.1(2)
None.
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(1)
None.
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(2)
None.
FPT_RPL.1
Detected replay attacks.
Origin of the attempt (e.g.,
IP address).
FPT_STM.1
Changes to the time.
The old and new values for
the time.
Origin of the attempt (e.g.,
IP address).
FPT_TUD_EXT.1
Initiation of update.
No additional information.
FPT_TST_EXT.1
Indication that TSF self-test
was completed.
Any additional information
generated by the tests
beyond “success” or
“failure”.
FRU_RSA.1
Maximum quota being
exceeded.
Resource identifier.
FTA_SSL_EXT.1
Any attempts at unlocking of
an interactive session.
No additional information.
FTA_SSL.3
The termination of a remote
session by the session
locking mechanism.
No additional information.
FTA_TAB.1
None.
FTP_ITC.1(1)
Initiation of the trusted
channel.
Termination of the trusted
channel.
Failure of the trusted channel
functions.
Identification of the
initiator and target of failed
trusted channels
establishment attempt.
FTP_ITC.1(2)
Initiation of the trusted
channel.
Termination of the trusted
channel.
Failure of the trusted channel
functions.
Identification of the
initiator and target of failed
trusted channels
establishment attempt.
EDCS-1228241
42
Page 43

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Requirement
Auditable Events
Additional Audit Record
Contents
FTP_TRP.1(1)
Initiation of the trusted
channel.
Termination of the trusted
channel.
Failures of the trusted path
functions.
Identification of the
claimed user identity.
FTP_TRP.1(2)
Initiation of the trusted
channel.
Termination of the trusted
channel.
Failures of the trusted path
functions.
Identification of the
claimed user identity.
EDCS-1228241
5.2.1.1 FAU_GEN.2: User identity association
FAU_GEN.2.1 For audit events resulting from actions of identified users, the TSF
shall be able to associate each auditable event with the identity of the
user that caused the event.
5.2.1.2 FAU_STG_EXT.1: External audit trail storage
FAU_STG_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall be able to [transmit the generated audit data
to an external IT entity over a trusted channel defined in
FTP_ITC.1].
5.2.1.3 FAU_STG_EXT.3: Action in case of loss of audit server connectivity
FAU_STG_EXT.3.1 The TSF shall [store audit records on the TOE and
attempt re-establish connection] if the link to the external
IT entity collecting the audit data generated by the TOE is
not available.
5.2.2 Cryptographic Support (FCS)
5.2.2.1 FCS_CKM.1: Cryptographic key generation (for asymmetric keys)
FCS_CKM.1.1 The TSF shall generate asymmetric cryptographic keys in
accordance with a domain parameter generator and [a random
number generator] that meet the following:
a) All cases: (i.e., any of the above)
43
Page 44

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
ANSI X9.80 (3 January 2000), “Prime Number
Generation, Primality Testing, and Primality
Certificates” using random integers with deterministic
tests, or constructive generation methods
Generated key strength shall be equivalent to, or
greater than, a symmetric key strength of 112 bits using
conservative estimates.
c) Case: For domain parameters used in RSA-based key
establishment schemes
NIST Special Publication 800-56B “Recommendation
for Pair-Wise Key Establishment Schemes Using
Integer Factorization Cryptography”
5.2.2.2 FCS_CKM_EXT.4: Cryptographic key zeroization
FCS_CKM_EXT.4.1 The TSF shall zeroize all plaintext secret and private
cryptographic keys and CSPs when no longer required.
5.2.2.3 FCS_COP.1(1): Cryptographic operation (for data encryption/decryption)
FCS_COP.1.1(1) The TSF shall perform [encryption and decryption] in
accordance with a specified cryptographic algorithm [AES
operating in [CBC mode]] and cryptographic key sizes 128-
bits, 256-bits, and [no other key sizes] that meets the
following:
FIPS PUB 197, “Advanced Encryption Standard
(AES)”
[NIST SP 800-38A, NIST SP 800-38D].
5.2.2.4 FCS_COP.1(2): Cryptographic operation (for cryptographic signature)
FCS_COP.1.1(2) The TSF shall perform cryptographic signature services in
accordance with a [(2) RSA Digital Signature Algorithm
(rDSA) with a key size (modulus) of 2048 bits or greater] that
meets the following:
Case: RSA Digital Signature Algorithm
[FIPS PUB 186-3, “Digital Signature Standard]
5.2.2.5 FCS_COP.1(3): Cryptographic operation (for cryptographic hashing)
FCS_COP.1.1(3) The TSF shall perform [cryptographic hashing services] in
accordance with a specified cryptographic algorithm [SHA-1,
44
Page 45

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
SHA 256, SHA-512] and message digest sizes [160, 256, 512]
bits that meet the following: FIPS Pub 180-3 “Secure Hash
Standard.”
5.2.2.6 FCS_COP.1(4): Cryptographic operation (for keyed-hash message
authentication)
FCS_COP.1.1(4) The TSF shall perform [keyed-hash message authentication] in
accordance with a specified cryptographic algorithm HMAC[SHA-1, SHA-256, SHA-512], key size [128, 192, 256 bits],
and message digest sizes [160, 256, 512] bits that meet the
following: FIPS Pub 198-1 “The Keyed-Hash Message
Authentication Code”, and FIPS PUB 180-3, “Secure Hash
Standard.”
5.2.2.7 FCS_RBG_EXT.1: Cryptographic operation (random bit generation)
FCS_RBG_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall perform all random bit generation (RBG)
services in accordance with [NIST Special Publication 800-
90 using CTR_DRBG (AES)] seeded by an entropy source
that accumulated entropy from at least one independent TSFhardware-based noise source.
FCS_RBG_EXT.1.2 The deterministic RBG shall be seeded with a minimum of
[256 bits] of entropy at least equal to the greatest length of
the keys and authorization factors that it will generate.
5.2.2.8 FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1: Communications protection
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall protect communications using
[IPsec, SSH] and [no other protocol].
5.2.2.9 FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1: IPSEC
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall implement IPsec using the ESP protocol as
defined by RFC 4303 using the cryptographic algorithms
AES-CBC-128, AES-CBC-256 (both specified by RFC
3602), [no other algorithms] and using IKEv1 as defined
in RFCs 2407, 2408, 2409, and RFC 4109, [no other
methods] to establish the security association.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.2 The TSF shall ensure that IKEv1 Phase 1 exchanges use
only main mode.
45
Page 46

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.3 The TSF shall ensure that IKEv1 SA lifetimes are able to
be limited to 24 hours for Phase 1 SAs and 8 hours for
Phase 2 SAs.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.4 The TSF shall ensure that IKEv1 SA lifetimes are able to
be limited to [an administratively configurable number
of kilobytes including the range from 100 – 200] MB of
traffic for Phase 2 SAs.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.5 The TSF shall ensure that all IKE protocols implement DH
Groups 14 (2048-bit MODP) and [no other DH groups].
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.6 The TSF shall ensure that all IKE protocols implement Peer
Authentication using the [rDSA] algorithm.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.7 The TSF shall support the use of pre-shared keys (as
referenced in the RFCs) for use in authenticating its IPsec
connections.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1.8 The TSF shall support the following:
Pre-shared keys shall be able to be composed of any
combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers,
and special characters (that include: “!”, “@”, “#”, “$”,
“%”, “^”, “&”, “*”, “(“, and “)”);
Pre-shared keys of 22 characters [no other lengths].
5.2.2.10 FCS_SSH_EXT.1: SSH
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall implement the SSH protocol that complies
with RFCs 4251, 4252, 4253, and 4254.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.2 The TSF shall ensure that the SSH connection be rekeyed
after no more than 228 packets have been transmitted using
that key.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.3 The TSF shall ensure that the SSH protocol implements a
timeout period for authentication as defined in RFC 4252 of
[120 seconds], and provide a limit to the number of failed
authentication attempts a client may perform in a single
session to [3] attempts.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.4 The TSF shall ensure that the SSH protocol implementation
supports the following authentication methods as described in
RFC 4252: public key-based, password-based.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.5 The TSF shall ensure that, as described in RFC 4253, packets
greater than [35,000] bytes in an SSH transport connection
are dropped.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.6 The TSF shall ensure that the SSH transport implementation
uses the following encryption algorithms: AES-CBC-128,
AES-CBC-256, [no other algorithms].
46
Page 47

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.7 The TSF shall ensure that the SSH transport implementation
uses SSH_RSA and [no other public key algorithms] as its
public key algorithm(s).
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.8 The TSF shall ensure that data integrity algorithms used in
the SSH transport connection is [hmac-sha1, hmac-sha1-96,
hmac-md5-96].
FCS_SSH_EXT.1.9 The TSF shall ensure that diffie-hellman-group14-sha1 is the
only allowed key exchange method used for the SSH
protocol.
5.2.3 User data protection (FDP)
5.2.3.1 FDP_RIP.2: Full residual information protection
FDP_RIP.2.1 The TSF shall ensure that any previous information content of a
resource is made unavailable upon the [allocation of the resource
to] all objects.
5.2.4 Identification and authentication (FIA)
5.2.4.1 FIA_PMG_EXT.1: Password management
FIA_PMG_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall provide the following password management
capabilities for administrative passwords:
1. Passwords shall be able to be composed of any
combination of upper and lower case letters,
numbers, and special characters (that include: “!”,
“@”, “#”, “$”, “%”, “^”, “&”, “*”, “(“, and “)”);
2. Minimum password length shall be settable by the
Security Administrator, and support passwords of 8
characters or greater;
3. Passwords composition rules specifying the types and
number of required characters that comprise the
password shall be settable by the Security
Administrator.
4. Passwords shall have a maximum lifetime,
configurable by the Security Administrator.
5. New passwords must contain a minimum of 4
character changes from the previous password.
47
Page 48

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
5.2.4.2 FIA_UIA_EXT.1: User identification and authentication
FIA_UIA_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall allow [no services] on behalf of the user to be
performed before the user is identified and authenticated.
FIA_UIA_EXT.1.2 The TSF shall require each user to be successfully identified
and authenticated before allowing any other TSF-mediated
actions on behalf of that user.
5.2.4.3 FIA_UAU_EXT.5: Password-based authentication mechanism
FIA_UAU_EXT.5.1 The TSF shall provide a local password-based authentication
mechanism, [[remote password-based authentication via
RADIUS or TACACS+]] to perform user authentication.
FIA_UAU_EXT.5.2 The TSF shall ensure that users with expired passwords are
[locked out until their password is reset by an
administrator].
5.2.4.4 FIA_UAU.6: Re-authenticating
FIA_UAU.6.1 The TSF shall re-authenticate the user under the conditions: when
the user changes their password, [following TSF-initiated locking
(FTA_SSL)].
5.2.4.5 FIA_UAU.7: Protected authentication feedback
FIA_UAU.7.1 The TSF shall provide only obscured feedback to the user while the
authentication is in progress at the local console.
5.2.5 Security management (FMT)
5.2.5.1 FMT_MTD.1: Management of TSF data (for general TSF data)
FMT_MTD.1.1 The TSF shall restrict the ability to manage the TSF data to the
Security Administrators.
5.2.5.2 FMT_SMF.1: Specification of Management Functions
FMT_SMF.1.1 The TSF shall be capable of performing the following management
functions:
Ability to configure the list of TOE services available before
an entity is identified and authenticated, as specified in
FIA_UIA_EXT.1, respectively.
Ability to configure the cryptographic functionality.
48
Page 49

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
Ability to update the TOE, and to verify the updates using the
digital signature capability (FCS_COP.1(2)) and [no other
functions]
Ability to manage the cryptographic functionality
Ability to manage the audit logs and functions
Ability to manage routing tables
Ability to manage security attributes belonging to
individual users
Ability to manage the default values of the security
attributes
Ability to manage the warning banner message and
content
Ability to manage the time limits of session inactivity.
5.2.5.3 FMT_SMR.1: Security roles
FMT_SMR.1.1 The TSF shall maintain the roles:
[Security Administrator,
[ No other roles]].
FMT_SMR.1.2 The TSF shall be able to associate users with roles.
5.2.6 Protection of the TSF (FPT)
5.2.6.1 FPT_ITT.1(1) Basic Internal TSF Data Transfer Protection (Disclosure)
FPT_ITT.1.1(1) Refinement: The TSF shall protect TSF data from disclosure when
it is transmitted between separate parts of the TOE through the
use of the TSF-provided cryptographic services:
[FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1 IPSEC].
5.2.6.2 FPT_ITT.1(2) Basic Internal TSF Data Transfer Protection (Modification)
FPT_ITT.1.1(2) Refinement: The TSF shall detect modification of TSF data when
it is transmitted between separate parts of the TOE through the
use of the TSF-provided cryptographic services:
[FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1 IPSEC].
5.2.6.3 FPT_PTD_EXT.1(1): Management of TSF data (for reading of
authentication data)
FPT_PTD_EXT.1.1(1) The TSF shall prevent reading of the plaintext passwords.
49
Page 50

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
5.2.6.4 FPT_PTD_EXT.1(2): Management of TSF data (for reading of all
symmetric keys)
FPT_PTD_EXT.1.1(2) The TSF shall prevent reading of all pre-shared keys,
symmetric key, and private keys.
5.2.6.5 FPT_RPL.1: Replay detection
FPT_RPL.1.1 The TSF shall detect replay for the following entities: [network
packets terminated at the TOE].
FPT_RPL.1.2 The TSF shall perform: [reject the data] when replay is detected.
5.2.6.6 FPT_STM.1: Reliable time stamps
FPT_STM.1.1 The TSF shall be able to provide reliable time stamps for its own
use.
5.2.6.7 FPT_TUD_EXT.1: Trusted update
FPT_TUD_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall provide security administrators the ability to
query the current version of the TOE firmware/software.
FPT_TUD_EXT.1.2 The TSF shall provide security administrators the ability to
initiate updates to the TOE firmware/software.
FPT_TUD_EXT.1.3 The TSF shall provide a means to verify firmware/software
updates to the TOE using a [published hash] prior to
installing those updates.
5.2.6.8 FPT_TST_EXT.1: TSF testing
FPT_TST_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall run a suite of self tests during initial start-up
(on power on) to demonstrate the correct operation of the
TSF.
5.2.7 FRU – Resource Utilization
5.2.7.1 FRU_RSA.1: Maximum quotas
FRU_RSA.1.1(1) The TSF shall enforce maximum quotas of the following
resources: [resources supporting the administrative
interface], [no other resource] that [individual user] can use
[simultaneously].
50
Page 51

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
5.2.8 TOE Access (FTA)
5.2.8.1 FTA_SSL_EXT.1: TSF-initiated session locking
FTA_SSL_EXT.1.1 The TSF shall, for local interactive sessions, [terminate the
session] after a Security Administrator-specified time period of
inactivity.
5.2.8.2 FTA_SSL.3: TSF-initiated termination
FTA_SSL.3.1 The TSF shall terminate a remote interactive session after a
[Security Administrator-configurable time interval of session
inactivity].
5.2.8.3 FTA_TAB.1: Default TOE Access Banners
FTA_TAB.1.1 Before establishing a user/administrator session the TSF shall
display a Security Administrator-specified advisory notice and
consent warning message regarding unauthorized use of the TOE.
5.2.9 Trusted Path/Channel (FTP)
5.2.9.1 FTP_ITC.1(1): Inter-TSF trusted channel (prevention of disclosure)
FTP_ITC.1.1(1) The TSF shall use [IPSec] to provide a trusted communication
channel between itself and authorized IT entities that is logically
distinct from other communication channels and provides assured
identification of its end points and protection of the channel data
from disclosure.
FTP_ITC.1.2(1) The TSF shall permit the TSF, or the authorized IT entities to
initiate communication via the trusted channel.
FTP_ITC.1.3(1) The TSF shall initiate communication via the trusted channel for
[all authentication functions), [IPSec]].
5.2.9.2 FTP_ITC.1(2) – Inter-TSF trusted channel (detection of modification)
FTP_ITC.1.1(2) The TSF shall use [IPSec] in providing a trusted
communication channel between itself and authorized IT entities
that is logically distinct from other communication channels and
provides assured identification of its end points and detection of
the modification of data.
FTP_ITC.1.2(2) The TSF shall permit the TSF, or the authorized IT entities to
initiate communication via the trusted channel.
51
Page 52

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
FTP_ITC.1.3(2) The TSF shall initiate communication via the trusted channel for
[all authentication functions, [IPSec]].
5.2.9.3 FTP_TRP.1(1): Trusted path
FTP_TRP.1.1(1) Refinement: The TSF shall provide a communication path
between itself and remote administrators using [SSH as specified
in FCS_SSH_EXT.1 to access the CLI] that is logically distinct
from other communication paths and provides assured
identification of its end points and protection of the
communicated data from disclosure.
FTP_TRP.1.2(1) The TSF shall permit remote administrators to initiate
communication via the trusted path.
FTP_TRP.1.3(1) Refinement: The TSF shall require the use of the trusted path for
all remote administrative actions.
5.2.9.4 FTP_TRP.1(2) – Trusted path
FTP_TRP.1.1(2) Refinement: The TSF shall provide a communication path
between itself and remote administrators using [SSH as specified
in FCS_SSH_EXT.1 to access the CLI] that is logically distinct
from other communication paths and provides assured
identification of its end points and detection of modification of
the communicated data.
FTP_TRP.1.2(2) The TSF shall permit remote administrators to initiate
communication via the trusted path.
FTP_TRP.1.3(2) Refinement: The TSF shall require the use of the trusted path for
all remote administrative actions.
5.3 Extended Components Definition
This Security Target includes Security Functional Requirements (SFR) that is not drawn
from existing CC Part 2. The Extended SFRs are identified by having a label ‘_EXT’
after the requirement name for TOE SFRs. The structure of the extended SFRs is
modeled after the SFRs included in CC Part 2. The structure is as follows:
A. Class – The extended SFRs included in this ST are part of the identified
classes of requirements.
B. Family – The extended SFRs included in this ST are part of several SFR
families
C. Component – The extended SFRs are not hierarchical to any other
components, though they may have identifiers terminating on other than “1”.
52
Page 53

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
The dependencies for each extended component are identified in the TOE
SFR Dependencies section of this ST below.
D. The management requirements, if any, associated with the extended SFRs are
incorporated into the Security management SFRs defined in this ST.
E. The audit requirements, if any, associated with the extended SFRs are
incorporated into the Security audit SFRs defined in this ST.
F. The dependency requirements, if any, associated with the extended SFRs are
identified in the dependency rationale and mapping section of the ST (TOE
SFR Dependencies Rationale).
Extended Requirements Rationale:
FAU_STG_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement to
export audit records outside the TOE.
FAU_STG_EXT.3:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement to
detect, and take a defined action, when an external audit server becomes
inaccessible.
FCS_CKM_EXT.4:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement for
immediate zeroization when keys and CSPs are no longer required.
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement to
identify required protocol-related cryptographic mechanisms.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement specific
to IPSEC.
FCS_RBG_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement specific
to random bit generation.
FCS_SSH_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement specific
to SSH.
FIA_PMG_EXT.1:
53
Page 54

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement for
specific password composition and aging constraints..
FIA_UAU_EXT.5:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement
allowing the identification of required external authentication services.
FIA_UIA_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement
combining both identification and authentication requirements.
FPT_PTD_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP (as FPT_PTD.1(1)) –where it is defined as a
requirement specifically disallowing access to identified TSF data. Note, in the
NDPP this SFR is not represented as an Extended Requirement with the
inclusion of the ‘EXT’ qualifier. However this SFR is not represented in the
Part 2 CC, as such the ST Author has corrected by including the ‘EXT’
qualifier.
FPT_PTD_EXT.2:
This SFR was taken from NDPP (as FPT_PTD.1(2)) – where it is defined as a
requirement specifically disallowing access to identified TSF data. Note, in the
NDPP this SFR is not represented as an Extended Requirement with the
inclusion of the ‘EXT’ qualifier. However this SFR is not represented in the
Part 2 CC, as such the ST Author has corrected by including the ‘EXT’
qualifier.
FPT_TST_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement for TSF
self tests of the TOE during initialization (on bootup).
FPT_TUD_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement for
secure TOE update capabilities.
FTA_SSL_EXT.1:
This SFR was taken from NDPP – where it is defined as a requirement for
behavior after local terminal session inactivity.
5.4 TOE SFR Dependencies Rationale
The following table provides dependency rational for SFRs that were drawn from the
NDPP.
Table 17: SFR Dependency Rationale (from NDPP)
54
Page 55

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
SFR
Dependency
Rationale
FAU_GEN.1
FPT_STM.1
Met by FPT_STM.1
FAU_GEN.2
FAU_GEN.1
FIA_UID.1
Met by FAU_GEN.
Met by FIA_UIA_EXT.1
FAU_STG_EXT.1
FAU_GEN.1
Met by FAU_GEN.1
FAU_STG_EXT.3
FAU_STG_EXT.1
Met by FAU_STG_EXT.1
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_CKM.2 or
FCS_COP.1
FCS_CKM.4
Met by FCS_COP.1(2), (3), and
(4)
Met by FCS_CKM.4
FCS_CKM_EXT.4
FDP_ITC.1 or
FDP_ITC.2 or
FCS_CKM.1
Met by FCS_CKM.1
FCS_COP.1(1)
FDP_ITC.1 or 2 or
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_CKM.4
Met by FCS_CKM.1 and
FCS_CKM_EXT.4
FCS_COP.1(2)
FDP_ITC.1 or 2 or
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_CKM.4
Met by FCS_CKM.1 and
Met by FCS_CKM_EXT.4
FCS_COP.1(3)
FDP_ITC.1 or 2 or
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_CKM.4
Met by FCS_CKM.1 and
Met by FCS_CKM_EXT.4
FCS_COP.1(4)
FDP_ITC.1 or 2 or
FCS_CKM.1
FCS_CKM.4
Met by FCS_CKM.1 and
Met by FCS_CKM_EXT.4
FCS_RBG_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1
FCS_HTTPS_EXT.1 or
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1 or
FCS_SSH_EXT.1 or
FCS_TLS_EXT.1
Met by FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1 and
FCS_SSH_EXT.1
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1
FCS_COP.1
Met by FCS_COP.1
FCS_SSH_EXT.1
FCS_COP.1
Met by FCS_COP.1
FDP_RIP.2
No dependencies
N/A
FIA_PMG_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FIA_UIA_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FIA_UAU_EXT.5
No dependencies
N/A
FIA_UAU.6
No dependencies
N/A
FIA_UAU.7
FIA_UAU.1
Met by FIA_UIA_EXT.1
FMT_MTD.1
FMT_SMF.1
FMT_SMR.1
Met by FMT_SMF.1
Met by FMT_SMR.1
EDCS-1228241
55
Page 56

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
SFR
Dependency
Rationale
FMT_SMF.1
No dependencies
N/A
FMT_SMR.1
FIA_UID.1
Met by FIA_UIA_EXT.1
FPT_ITT.1(1)
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_ITT.1(2)
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(1)
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(2)
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_RPL.1
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_STM.1
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_TUD_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FPT_TST_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FRU_RSA.1
No dependencies
N/A
FTA_SSL_EXT.1
No dependencies
N/A
FTA_SSL.3
No dependencies
N/A
FTA_TAB.1
No dependencies
N/A
FTP_ITC.1(1)
No dependencies
N/A
FTP_ITC.1(2)
No dependencies
N/A
FTP_TRP.1(1)
No dependencies
N/A
FTP_TRP.1(2)
No dependencies
N/A
Assurance Class
Components
Components Description
DEVELOPMENT
ADV_FSP.1
Basic Functional Specification
GUIDANCE
DOCUMENTS
AGD_OPE.1
Operational user guidance
AGD_PRE.1
Preparative User guidance
EDCS-1228241
5.5 Security Assurance Requirements
5.5.1 SAR Requirements
The TOE assurance requirements for this ST are taken directly from the NDPP which are
derived from Common Criteria Version 3.1, Revision 3. The assurance requirements are
summarized in the table below as identified in the NDPP, Section 4.3. The ST does not
include any changes to the assurance requirements beyond those identified and described
in the NDPP, as such all assurance activities from NDPPv1.0 form the SARs in this ST.
Table 18: Assurance Measures
56
Page 57

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Assurance Class
Components
Components Description
LIFE CYCLE SUPPORT
ALC_CMC.1
Labeling of the TOE
ALC_CMS.1
TOE CM coverage
TESTS
ATE_IND.1
Independent testing – conformance
VULNERABILITY
ASSESSMENT
AVA_VAN.1
Vulnerability analysis
Component
How requirement will be met
ADV_FSP.1
The functional specification describes the external interfaces of
the TOE; such as the means for a user to invoke a service and the
corresponding response of those services. The description
includes the interface(s) that enforces a security functional
requirement, the interface(s) that supports the enforcement of a
security functional requirement, and the interface(s) that does not
enforce any security functional requirements. The interfaces are
described in terms of their purpose (general goal of the interface),
method of use (how the interface is to be used), parameters
(explicit inputs to and outputs from an interface that control the
behavior of that interface), parameter descriptions (tells what the
parameter is in some meaningful way), and error messages
(identifies the condition that generated it, what the message is,
and the meaning of any error codes). The development evidence
also contains a tracing of the interfaces to the SFRs described in
this ST.
EDCS-1228241
5.5.2 Security Assurance Requirements Rationale
This Security Target claims conformance to the NDPP which draws from EAL1 the
Security Assurance Requirements (SARs). This target was chosen to ensure that the TOE
has a low to moderate level of assurance in enforcing its security functions when
instantiated in its intended environment which imposes no restrictions on assumed
activity on applicable networks.
5.6 Assurance Measures
The TOE satisfies the identified assurance requirements. This section identifies the
Assurance Measures applied by Cisco to satisfy the assurance requirements. The table
below lists the details.
Table 19: Assurance Measures
57
Page 58

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Component
How requirement will be met
AGD_OPE.1
The Administrative Guide provides the descriptions of the
processes and procedures of how the administrative users of the
TOE can securely administer the TOE using the interfaces that
provide the features and functions detailed in the guidance.
AGD_PRE.1
The Installation Guide describes the installation, generation, and
startup procedures so that the users of the TOE can put the
components of the TOE in the evaluated configuration.
ALC_CMC.1
The Configuration Management (CM) document(s) describes
how the consumer (end-user) of the TOE can identify the
evaluated TOE (Target of Evaluation). The CM document(s)
identifies the configuration items, how those configuration items
are uniquely identified, and the adequacy of the procedures that
are used to control and track changes that are made to the TOE.
This includes details on what changes are tracked, how potential
changes are incorporated, and the degree to which automation is
used to reduce the scope for error.
ALC_CMS.1
ATE_IND.1
Cisco will provide the TOE for testing.
AVA_VAN.1
Cisco will provide the TOE for testing.
EDCS-1228241
58
Page 59

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
FAU_GEN.1
The TOE generates an audit record whenever an audited event
occurs. The types of events that cause audit records to be
generated include events related to the enforcement of
information flow policies, identification and authentication
related events, and administrative events (the specific events and
the contents of each audit record are listed in the table within the
FAU_GEN.1 SFR, “Auditable Events Table”). Each of the events
is specified in the audit record is in enough detail to identify the
user for which the event is associated (e.g. user identity, MAC
address, IP address), when the event occurred, where the event
occurred, the outcome of the event, and the type of event that
occurred. Additionally, the startup and shutdown of the audit
functionality is audited.
The audit trail consist of the individual audit records; one audit
record for each event that occurred. The audit record can contain
up to 80 characters and a percent sign (%), which follows the
time-stamp information. As noted above, the information
includes [at least] all of the required information. Additional
information can be configured and included if desired. Refer to
the Guidance documentation for configuration syntax and
information.
The logging buffer size can be configured from a range of 4096
(default) to 2147483647 bytes. It is noted, not make the buffer
size too large because the switch could run out of memory for
other tasks. Use the show memory privileged EXEC command to
view the free processor memory on the switch. However, this
value is the maximum available, and the buffer size should not be
set to this amount. Refer to the Guidance documentation for
configuration syntax and information.
The administrator can also configure a ‘configuration logger’ to
keep track of configuration changes made with the command-line
interface (CLI). The administrator can configure the size of the
configuration log from 1 to 1000 entries (the default is 100).
Refer to the Guidance documentation for configuration syntax
and information.
EDCS-1228241
6 TOE SUMMARY SPECIFICATION
6.1 TOE Security Functional Requirement Measures
This section identifies and describes how the Security Functional Requirements identified
above are met by the TOE.
Table 20: How TOE SFRs are Met
59
Page 60

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
The log buffer is circular, so newer messages overwrite older
messages after the buffer is full. Administrators are instructed to
monitor the log buffer using the show logging privileged EXEC
command to view the audit records. The first message displayed
is the oldest message in the buffer. There are other associated
commands to clear the buffer, to set the logging level, etc.; all of
which are described in the Guidance documents and IOS CLI.
The logs can be saved to flash memory so records are not lost in
case of failures or restarts. Refer to the Guidance documentation
for configuration syntax and information.
The administrator can set the level of the audit records to be
displayed on the console or sent to the syslog server. For instance
all emergency, alerts, critical, errors, and warning message can be
sent to the console alerting the administrator that some action
needs to be taken as these types of messages mean that the
functionality of the switch is affected. All notifications and
information type message can be sent to the syslog server,
whereas message is only for information; switch functionality is
not affected.
To configure the TOE to send audit records to a syslog server, the
‘set logging server’ command is used. A maximum of three
syslog servers can be configured. Refer to the Guidance
document for complete guidance and command syntax. The audit
records are transmitted using IPsec tunnel to the syslog server. If
the communications to the syslog server is lost, the TOE
generates an audit record and all permit traffic is denied until the
communications is re-established.
For the FIPS crypto self-tests, the messages are displayed only on
the console during startup. Once the box is up and operational
and the crypto self-test command is entered, then the messages
would be displayed on the console and will also be logged.
For the TSF self-test, successful completion of the self-test is
indicated by reaching the log-on prompt. If there are issues, the
applicable audit record is generated and displayed on the console.
Auditable Event
Rationale
All use of the user
identification
mechanism.
Events will be generated for
attempted identification/
authentication, and the
username attempting to
authenticate will be included
EDCS-1228241
60
Page 61

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
in the log record.
Any use of the
authentication
mechanism.
Events will be generated for
attempted identification/
authentication, and the
username attempting to
authenticate will be included
in the log record, along with
the origin or source of the
attempt.
Management functions
The use of the security
management functions is
logged; modifications of the
behavior of the functions in
the TSF and modifications of
default settings.
Detection of replay
attacks
Attempts of replaying data
previously transmitted and
terminated at the TOE are
logged, along with the origin
or source of the attempt.
Changes to the time.
Changes to the time are
logged.
Updates (software)
An audit record will be
generated on the initiation of
updates (software/firmware)
Failure to establish
and/or
establishment/failure
of an SSH and IPsec
session
Attempts to establish an
SSH and IPsec session or
the failure of an established
SSH and/or IPsec is logged.
Resources quotas are
exceeded
If the threshold for the
number of concurrent
administrative sessions is
exceeded, and audit record
is generated
Locking and
unlocking interactive
sessions
Any attempt to unlock an
inactive sessions is logged,
as is an inactive session
when it exceeds the time
limit of inactivity
Indication that TSF
self-test was
completed.
During bootup, if the self-
test fails, the failure is
logged.
Trusted channels
The initiation, termination,
EDCS-1228241
61
Page 62

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
and failure related to trusted
channel sessions with
peer/neighbor routers and or
the remote administration
console
FAU_GEN.2
The TOE shall ensure that each auditable event is associated with
the user that triggered the event and as a result, they are traceable
to a specific user. For example, a human user, user identity or
related session ID would be included in the audit record. For an
IT entity or device, the IP address, MAC address, host name, or
other configured identification is presented. Refer to the
Guidance documentation for configuration syntax and
information.
FAU_STG_EXT.1
and
FAU_STG_EXT.3
The TOE is configured to export syslog records to a specified,
external syslog server. The TOE protects communications with an
external syslog server via IPsec. If the IPsec connection fails, the
TOE will store audit records on the TOE when it discovers it can
no longer communicate with its configured syslog server.
FCS_CKM.1
The TOE implements a random number generator for RSA key
establishment schemes (conformant to NIST SP 800-56B). The
TOE is also compliant to ANSI X9.80 (3 January 2000), “Prime
Number Generation, Primality Testing, and Primality
Certificates” using random integers with deterministic tests.
Furthermore, the TOE does not implement elliptic-curve-based
key establishment schemes.
FCS_CKM_EXT.4
9
The TOE meets all requirements specified in FIPS 140-2 for
destruction of keys and Critical Security Parameters (CSPs) in
that none of the symmetric keys, pre-shared keys, or private keys
are stored in plaintext form. This requirement applies to the
secret keys used for symmetric encryption, private keys, and
CSPs used to generate key (list them); which are zeroized
immediately after use, or on system shutdown, etc.
The cryptographic module securely administers both
cryptographic keys and other critical security parameters such as
passwords. The tamper evidence seals provide physical protection
for all keys. All keys are also protected by the passwordprotection required by the privileged administrator role login, and
can be zeroized by the privileged administrator. All zeroization
consists of overwriting the memory that stored the key. Keys are
9
EDCS-1228241
Note, the following information may be deemed sensitive and may be removed prior to publically posting
this Security Target.
62
Page 63

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
exchanged and entered electronically. Persistent keys are entered
by the privileged administrator via the console port CLI, transient
keys are generated or established and stored in DRAM. If present,
a VSS link can export all DRAM and NVRAM keys to another
switch over a secure connection for high availability purposes.
The module supports the following critical security parameters
(CSPs). It is noted that there may be keys and CSPs that are not
applicable to this evaluation and should not be reviewed. They
are included for completeness of the module.
ID
Algorit
hm
Size
Description
Storag
e
Zeroizati
on
Method10
General Keys/CSPs
User
Password
Passwo
rd
Variable
(8+
characters)
Used to
authenticate
local users
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
by
overwriti
ng with
new
password
Enable
Password
Passwo
rd
Variable
(8+
characters)
Used to
authenticate
local users at a
higher privilege
level
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
by
overwriti
ng with
new
password
RADIUS
secret
Shared
Secret
Variable
(8+
characters)
The RADIUS
Shared Secret
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
using the
following
command
:
# no
radiusserver key
Overwritt
en with:
0x0d
RADIUS
Key wrap
key
AES
128/256
bits
Used to protect
SAK
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
when data
structure
is freed
TACACS
+ secret
Shared
Secret
Variable
(8+
characters)
The TACACS+
shared secret
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
using the
following
command
:
# no
tacacs-
10
EDCS-1228241
Unless specifically noted, the zeroization method used for secrets, keys, etc is to overwrite with zeros
(0x00).
63
Page 64

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
server key
Overwritt
en with:
0x0d
RNG
Seed
ANSI
X9.31
Append
ix 2.4
using
3-key
TDES
16 bytes
This is the seed
for ANSI
X9.31 RNG
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
upon
power
cycle the
device
RNG
Seed Key
ANSI
X9.31
Append
ix 2.4
using
3-key
TDES
24 bytes
This is the seed
key for ANSI
X9.31 RNG
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
upon
power
cycle the
device
DiffieHellman
private
exponent
DH
1024-4096
bits
The private
exponent used
in DiffieHellman (DH)
exchange.
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
upon
completio
n of DH
exchange.
Overwritt
en with:
0x00
DiffieHellman
Shared
Secret
DH
1024-4096
bits
This is the
shared secret
agreed upon as
part of DH
exchange
DRAM
(plainte
xt0
Automati
cally after
completio
n of DH
exchange.
Overwritt
en with:
0x00
SSH
SSH RSA
private
key
RSA
1024/1536/
2048 bits
modulus
SSH key
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
Zeroized
using the
following
command
:
# crypto
key
zeroize
rsa
Overwritt
en with:
0x00
SSH
session
key
TripleDES/A
ES
168bits/256bits
This is the SSH
session
symmetric key.
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when the
SSH
session is
terminate
EDCS-1228241
64
Page 65
Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
d.
Overwritt
en with:
0x00
SSH
session
authentica
tion key
HMAC
SHA-1
160-bits
This is the SSH
session
authentication
key
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
SSH
session
terminate
d
TLS
TLS
Server
RSA
private
key
RSA
1024/1536/
2048 bits
modulus
Identity
certificates for
module itself
and also used
in TLS
negotiations.
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
# fips
zeroize all
TLS premaster
secret
Shared
Secret
384-bits
Shared secret
created using
asymmetric
cryptography
from which
new HTTPS
session keys
can be created.
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
terminate
d.
TLS
session
key
TripleDES/A
ES
168bits/256bits
This is the TLS
session key
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
terminate
d.
MacSec
MACsec
Security
Associati
on Key
(SAK)
AESGCM
128/256
bits
Used for
creating
Security
Associations
(SA) for
encrypting/decr
ypting the
MACSec
traffic in the
MACSec
hardware.
MACse
c PHY
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
expires
MACsec
Connectiv
ity
Associati
on Key
(CAK)
AESGCM
128/256
bits
A secret key
possessed by
members of a
MACSec
connectivity
association.
MACse
c PHY
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
expires
MACsec
KEK
AESGCM
128/256
bits
Used to
transmit SAKs
to other
members of a
MACSec
connectivity
association
MACse
c PHY
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
expires
EDCS-1228241
65
Page 66

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
MACsec
ICK
secret
128/256
bits
Used to verify
the integrity
and
authenticity of
MPDUs
MACse
c PHY
(plainte
xt)
Automati
cally
when
session
expires
SESA
SESA
Authoriza
tion Key
AES
128 bits
Used to
authorize
members of a
single stack on
Incredible
Units.
Used as input
to SP800-108
derivation
methods to
derive four
additional 128
fields to
transfer the
Master Session
Key and
additional
aggressive
exchange
material
NVRA
M
(plainte
xt)
“no fips
authorizat
ion-key”
SESA
Master
Session
Key
AES
128 bits
Used to derive
SESA session
key
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Upon
completio
n of key
exchange
SESA
Derived
Session
Keys
AES
and
HMAC
-SHA-1
128 bits
and 192
bits
Used to protect
traffic over
stacking ports
DRAM
(plainte
xt)
Upon
bringing
down the
stack
IKE session encrypt key - This structure contains all of the SA
items, including the skeyid, skeyid_d, IKE Session Encryption
Key and IKE Session Authentication Key. All values overwritten
by 0’s (0x00) automatically after IKE session terminated.
IKE session authentication key - This structure contains all of the
SA items, including the skeyid, skeyid_d, IKE Session
Encryption Key and IKE Session Authentication Key. All values
overwritten by 0’s (0x00) automatically after IKE session
terminated.
FCS_COP.1(1)
The TOE provides symmetric encryption and decryption
capabilities using AES in CBC and GCM mode (128, 256 bits) as
described in FIPS PUB 197, NIST SP 800-38A and NIST SP
800-38D.
FCS_COP.1(2)
The TOE will provide cryptographic signature services using
RSA with key size of 2048 and greater as specified in FIPS PUB
186-3, “Digital Signature Standard”.
EDCS-1228241
66
Page 67

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
FCS_COP.1(3)
The TOE provides cryptographic hashing services using SHA-1
SHA-256, SHA-384, and SHA-512 as specified in FIPS Pub 1803 “Secure Hash Standard.”
FCS_COP.1(4)
The TOE uses HMAC-SHA1. SHA-256, and SHA-512 message
authentication as part of the RADIUS Key Wrap functionality as
specified in FIPS Pub 198-1 “The Keyed-Hash Message
Authentication Code” and FIPS PUB 180-3, “Secure Hash
Standard”.
In addition, The TOE provides MD5 hashing for authentication of
neighbor routers via BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6, RIPv2,
and OSPFv2 with shared passwords.
The hash mechanism is implemented as specified in the relevant
RFCs:
BGPv4 uses MD5 for authentication of routing updates as
defined in RFC 2385 (Protection of BGP Sessions via
TCP MD5 Signature Option).
EIGRP and EIGRPv6 (Cisco proprietary) uses MD5 for
authentication of routing updates.
RIPv2 uses MD5 for authentication of routing updates as
defined in Section 2.4 of RFC 2453.
OSPFv2 uses MD5 for authentication of routing updates
as defined in Appendix D of RFC 2328 (OSPF version 2).
Routing tables for IPv4 and IPv6 can be created and maintained
manually using static routes configured by the administrator. Use
of routing protocols in IPv4 or IPv6 is not required to support or
enforce any TOE security functionality including filtering of IPv4
or IPv6 traffic. BGPv4, EIGRP and EIGRPv6 supports MD5authenticated routing updates with IPv6 or IPv4 as does RIPv2
while OSPFv2 routing protocol support MD5-authenticated
routing updates for IPv4 only.
It is noted that per the FIPS Security Policy, that MD5 is not a
validated algorithm during FIPS mode of operation. For
additional security, it is recommended router protocol traffic also
be isolated to separate VLANs.
FCS_RBG_EXT.1
The TOE implements a random bit generator (RBG) based on the
AES-256 block cipher, as specified in FIPS Pub 140-2 Annex C:
X9.31 Appendix 2.4.
EDCS-1228241
67
Page 68

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
The TOE implements a NIST-approved AES-CTR Deterministic
Random Bit Generator (DRBG), as specified in SP 800-90.
The entropy source used to seed the Deterministic Random Bit
Generator (e.g. based on SP 800-90A/B/C) is a random set of bits
or bytes that are regularly supplied to the DRBG from the internal
Quack (ACT) processor which produces a minimum of 256 bits
of entropy.
All RNG entropy source samplings are continuously health tested
by the NIST DRBG as per SP 900-90A before using them as a
seed. Though related to this, the tests are part of the FIPS
validation procedures for the DBRG and are part of the NIST
validations for FIPS 140-2 for the products. Any initialization or
system errors during bring-up or processing of this system causes
a reboot as necessary to be FIPS compliant. Finally, the system
will be zeroizing any entropy seeding bytes, which will not be
available after the current collection.
FCS_COMM_PRO
T_EXT.1
The TOE implements SSHv2 and IPsec either of which can be
used to protect communications for remote administration. IPsec
is also used to protect communications with external servers (e.g.,
syslog server, NTP and if configured an external authentication
server).
FCS_SSH_EXT.1
The TOE implements SSHv2 (telnet is disabled in the evaluated
configuration) in compliance with RFCs 4251, 4252, 4253, and
4254; using SSH RSA public key algorithm.
SSHv2 sessions are limited to a configurable session timeout
period of 120 seconds, a maximum number of failed
authentication attempts limited to 3, and will be rekeyed upon
request from the SSH client (no more than 228 packets). SSH
connections will be dropped if the TOE receives a packet larger
than 35,000 bytes.
The TOE’s implementation of SSHv2 supports hashing
algorithms hmac-sha1, hmac-sha1-96, hmac-md5-96.
The TOE can also be configured to use only one of the identified
DH groups for key exchange. The available groups include Diffie
Hellmen, group 14 (2048 bits) and group 16 (4096 bits).
The network traffic between the remote admin console and the
TOE establish and operate an encrypted session using AES in
CBC mode with key sizes 128 or 256 bits (FIPS 197) supporting
both public key-based and password-based authentication
EDCS-1228241
68
Page 69

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
methods.
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1
The TOE implements IPsec to provide authentication and
encryption services to prevent unauthorized viewing or
modification of data as it travels over the external network. The
TOE implementation of the IPsec standard (in accordance with
the RFCs noted in the SFR) uses the Encapsulating Security
Payload (ESP) protocol to provide authentication, encryption and
anti-replay services.
IPsec Internet Key Exchange, also called ISAKMP, is the
negotiation protocol that lets two peers agree on how to build an
IPsec Security Association (SA). The IKE protocols
implement Peer Authentication using the rDSA algorithm.
IKE separates negotiation into two phases: phase 1 and phase 2.
Phase 1 creates the first tunnel, which protects later ISAKMP
negotiation messages. The key negotiated in phase 1 enables IKE
peers to communicate securely in phase 2. During Phase 2 IKE
establishes the IPsec SA. IKE maintains a trusted channel,
referred to as a Security Association (SA), between IPsec peers
that is also used to manage IPsec connections, including:
The negotiation of mutually acceptable IPsec options
between peers,
The establishment of additional Security Associations to
protect packets flows using ESP, and
The agreement of secure bulk data encryption AES (128
and 256 bit) keys for use with ESP.
After the two peers agree upon a policy, the security parameters
of the policy are identified by an SA established at each peer, and
these IKE SAs apply to all subsequent IKE traffic during the
negotiation.
The TOE support IKEv1 session establishment. As part of this
support, the TOE can be configured to not support aggressive
mode for IKEv1 exchanges and to only use mainmodeusing the
‘crypto isakmp aggressive-mode disable’ command as specified
for the evaluated configuration.
The TOE can be configured to not allow “confidentiality only”
ESP mode by ensuring the IKE Policies configured include ESPencryption.
The TOE supports configuration lifetimes of both Phase 1 SAs
and Phase 2 SAs using “lifetime” command. The default time
value for Phase 1 SAs is 24 hours. The default time value for
Phase 2 SAs is 1 hour, but it is configurable to 8 hours.
The TOE also supports configuration of maximum traffic that is
EDCS-1228241
69
Page 70

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
allowed to flow for a given IPsec SA using the following
command, ‘crypto ipsec security-association lifetime’ as specified
for the evaluated configuration. The default amount is 2560KB,
which is the minimum configurable value. The maximum
configurable value is 4GB. However, the TOE is to be
configured to use a range between 100-200 MB as specified in the
SFR.
Other configuration options include rDSA algorithm for
implementing peer authentication as noted above, pre-shared keys
for authenticating IPsec connections can be 22 characters and be
composed of any combination of upper and lower case letters,
numbers, and special characters using the‘crypto isakmp key’ key
command and may be proposed by each of the peers negotiating
the IKE establishment. The TOE also supports both rekey and
response to rekeyed by the peer for phase 2 (IPSec) SA and the
approved configuration would have only HMAC-SHA1
configured within their IKE policy; no other hash functions will
then be considered. The TOE also supports Diffie-Hellman
Group 14 (2048-bit keys) in support of IKE Key Establishment.
FDP_RIP.2
The TOE ensures that packets transmitted from the TOE do not
contain residual information from previous packets. Packets that
are not the required length use zeros for padding. Residual data is
never transmitted from the TOE. Once packet handling is
completed its content is overwritten before memory buffer which
previously contained the packet is reused. This applies to both
data plane traffic and administrative session traffic.
FIA_PMG_EXT.1
The TOE supports the local definition of users with
corresponding passwords. The passwords can be composed of any
combination of upper and lower case letters, numbers, and special
characters (that include: “!”, “@”, “#”, “$”, “%”, “^”, “&”, “*”,
“(“, and “)”. Minimum password length is settable by the
Authorized Administrator, and support passwords of 8 characters
or greater. Password composition rules specifying the types and
number of required characters that comprise the password are
settable by the Authorized Administrator. Passwords have a
maximum lifetime, configurable by the Authorized
Administrator. New passwords must contain a minimum of 4
character changes from the previous password.
FIA_UIA_EXT.1
The TOE requires all users to be successfully identified and
authenticated before allowing any TSF mediated actions to be
performed. Administrative access to the TOE is facilitated
through the TOE’s CLI. The TOE mediates all administrative
actions through the CLI. Once a potential administrative user
attempts to access the CLI of the TOE through either a directly
EDCS-1228241
70
Page 71

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
connected console or remotely through an SSHv2 connection, the
TOE prompts the user for a user name and password. Only after
the administrative user presents the correct authentication
credentials will access to the TOE administrative functionality be
granted. No access is allowed to the administrative functionality
of the TOE until an administrator is successfully identified and
authenticated.
For neighbor routers, which do not have access to the CLI, the
neighbor router must present the correct hashed password prior to
exchanging routing table updates with the TOE. The TOE
authenticates the neighbor router using its supplied password
hash, and the source IP address from the IP packet header. The
supported routing protocols BGPv4, EIGRP, EIGRPv6 for IPv6,
RIPv2, and OSPFv2 use MD5 hashes to authenticate
communications as specified in FCS_COP.1(4).1. For additional
security, router protocol traffic can also be isolated to separate
VLANs.
FIA_UAU_EXT.5
The TOE can be configured to require local authentication and/or
remote authentication via a RADIUS or TACACS+ server as
defined in the authentication policy for interactive (human) users.
Neighbor routers are authenticated only to passwords stored
locally.
The policy for interactive (human) users (Administrators) can be
authenticated to the local user database, or have redirection to a
remote authentication server. Interfaces can be configured to try
one or more remote authentication servers, and then fail back to
the local user database if the remote authentication servers are
inaccessible.
If the interactive (human) users (Administrators) password is
expired, the user is locked out until the password is reset by the
administrator.
FIA_UAU.6
Users changing their passwords are first prompted to enter their
old password. Users are also required to provide their password
when re-establishing a remote session due to a session
termination of inactivity.
The TOE does not provide the capability for an administrator
(level 1) to change their own password. However the
administrator (level 1) can change their password when required
by the TOE (e.g. when expired). At which time the administrator
is required to enter their current password before entering a new
password. System administrators (level 15) can change any
user’s password, including their own as required for TOE
EDCS-1228241
71
Page 72

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
management, though must be in privilege EXEC mode to perform
the function. When the System Administrator (level 15) attempts
to change their own password, the TOE will enforce the password
expiration policy at which time the System Administrator (level
15) will be required to enter their current password prior to
entering a new password. See the Cisco Catalyst 4500 Series
Switches (4503-E, 4506-E, 4507R+E, 4510R+E, 4500X and
4500X-F) Running IOS-XE 3.5.2E Common Criteria Operational
User Guidance and Preparative Procedures for details and
configuration settings.
FIA_UAU.7
When a user enters their password at the local console, the TOE
displays only ‘*’ characters so that the user password is obscured.
For remote session authentication, the TOE does not echo any
characters as they are entered.
FMT_MTD.1
The TOE provides the ability for authorized administrators to
access TOE data, such as audit data, configuration data, security
attributes, information flow rules, routing tables, and session
thresholds. Each of the predefined and administratively
configured privilege level has a specified set of permissions that
will grant them some level of access to the TOE data, though with
some privilege levels, the access is limited. The TOE performs
role-based authorization, using TOE platform authorization
mechanisms, to grant access to the semi-privileged and privileged
roles. The term “authorized administrator” is used in this ST to
refer to any user which has been assigned to a privilege level that
is permitted to perform the relevant action; therefore has the
appropriate privileges to perform the requested functions.
FMT_SMF.1
The TOE provides all the capabilities necessary to securely
manage the TOE. The administrative user can connect to the
TOE using the CLI to perform these functions via SSHv2, a
terminal server, or at the local console. Refer to the Guidance
documentation for configuration syntax, commands, and
information related to each of these functions.
The management functionality provided by the TOE include the
following administrative functions:
Ability to manage the cryptographic functionality -
allows the authorized administrator the ability to identify
and configure the algorithms used to provide protection
of the data, such as generating the RSA keys to enable
SSHv2, configuration of routing protocols, and if used
the configuration of remote authentication
Ability to manage the audit logs and functions - allows
the authorized administrator to configure the audit logs,
view the audit logs, and to clear the audit logs
EDCS-1228241
72
Page 73

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
Ability to manage routing tables - allows the authorized
administrator the ability to create, modify, and delete the
routing tables to control the routed network traffic
Ability to manage security attributes belonging to
individual users - allows the authorized administrator to
create, modify, and delete other administrative users
Ability to manage the default values of the security
attributes - allows the authorized administrator to specify
the attributes that are used control access and/or manage
users
Ability to manage the warning banner message and
content – allows the authorized administrator the ability
to define warning banner that is displayed prior to
establishing a session (note this applies to the interactive
(human) users; e.g. administrative users
Ability to manage the time limits of session inactivity –
allows the authorized administrator the ability to set and
modify the inactivity time threshold;
Ability to update the TOE and verify the updates are
valid.
FMT_SMR.1
The TOE switch platform maintains administrative privilege level
and non-administrative access. Non-administrative access is
granted to authenticated neighbor routers for the ability to receive
updated routing tables per the information flow rules. There is no
other access or functions associated with non-administrative
access. The administrative privilege levels include:
Administrators are assigned to privilege levels 0 and 1.
Privilege levels 0 and 1 are defined by default and are
customizable. These levels have a very limited scope and
access to CLI commands that include basic functions
such as login, show running system information, turn
on/off privileged commands, logout.
Semi-privileged administrators equate to any privilege
level that has a subset of the privileges assigned to level
15; levels 2-14. These levels are undefined by default
and are customizable. The custom level privileges are
explained in the example below.
Privileged administrators are equivalent to full
administrative access to the CLI, which is the default
access for IOS privilege level 15.
Note, the levels are not hierarchical.
For levels, level 0 is the most restrictive and 15 is the least
restrictive.
EDCS-1228241
73
Page 74

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
For level 0, there are five commands associated with privilege
level 0: disable, enable, exit, help, and logout. However, the level
could be configured to allow a user to have access to the ‘show’
command.
Level 1 is normal EXEC-mode user privileges.
Following is an example of how privileges are set, rules in
setting privilege levels and assigning users to those privilege
levels. Note, that the administrator needs to have the
appropriate privilege level and if required, applicable
password to execute the commands:
When setting the privilege level for a command with multiple
words (commands), the commands starting with the first word
will also have the specified access level. For example, if the show
ip route command is set to level 15, the show commands and
show ip commands are automatically set to privilege level 15—
unless they are individually set to different levels. This is
necessary because a user cannot execute, for example, the show
ip command unless the user also has access to show commands.
To change the privilege level of a group of commands, the all
keyword is used. When a group of commands is set to a privilege
level using the all keyword, all commands which match the
beginning string are enabled for that level, and all commands
which are available in submodes of that command are enabled for
that level. For example, if the show ip keywords is set to level 5,
show and ip will be changed to level 5 and all the options that
follow the show ip string (such as show ip accounting, show ip
aliases, show ip bgp, and so on) will be available at privilege
level 5.
The privilege command is used to move commands from one
privilege level to another in order to create the additional levels of
administration. The default configuration permits two types of
users to access the CLI. The first type of user is a person who is
only allowed to access user EXEC mode. The second type of
user is a person who is allowed access to privileged EXEC
mode. A user who is only allowed to access user EXEC mode is
not allowed to view or change the configuration of the
networking device, or to make any changes to the operational
status of the networking device. On the other hand, a user who
is allowed access to privileged EXEC mode can make any change
to a networking device that is allowed by the CLI.
Following is an example for setting the privilege levels for
EDCS-1228241
74
Page 75

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
staff that are usually not allowed to run all of the commands
available in privileged EXEC mode (privilege level 15) on a
networking device. They are prevented from running commands
that they are not authorized for by not being granted access to the
password assigned to privileged EXEC mode or to other levels
that have been configured on the networking device.
The steps and commands show setting privilege level 7 with
access to two commands, clear counters and reload.
Step 1 enable password
Enters privileged EXEC mode. Enter
the password when prompted.
Router> enable
Step 2 configure terminal
Enters global configuration mode.
Router# configure terminal
Step 3 enable secret level level password
Configures a new enable secret
password for privilege level 7.
Router(config)# enable secret level 7 Zy72sKj
Step 4 privilege exec level level command-string
Changes the privilege level of the clear
counters command from privilege level
15 to privilege level 7.
Router(config)# privilege exec level 7 clear
counters
Step 5 privilege exec all level level command-string
Changes the privilege level of the
reload command from privilege level
15 to privilege level 7.
Router(config)# privilege exec all level 7
reload
Step 6 end
Exits global configuration mode.
Router(config)# end
The following example shows the enforcement of the settings
above and privilege levels.
Step 1 enable level password
Logs the user into the networking
device at the privilege level specified
for the level argument.
Router> enable 7 Zy72sKj
Step 2 show privilege
Displays the privilege level of the
current CLI session
Router# show privilege
Current privilege level is 7
EDCS-1228241
75
Page 76

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
Step 3 clear counters
The clear counters command clears the
interface counters. This command has
been changed from privilege level 15
to privilege level 7.
Router# clear counters
Clear "show interface" counters on all
interfaces [confirm]
Router#
02:41:37: %CLEAR-5-COUNTERS:
Clear counter on all interfaces by
console
Step 4 clear ip route *
The ip route argument string for the
clear command should not be allowed
because it was not changed from
privilege level 15 to privilege level 7.
Router# clear ip route *
^
% Invalid input detected at '^' marker.
Router#
Step 5 reload in time
The reload command causes the
networking device to reboot.
Router# reload in 10
Reload scheduled in 10 minutes by
console
Proceed with reload? [confirm]
Router#
***
*** --- SHUTDOWN in 0:10:00 --***
02:59:50: %SYS-5-SCHEDULED_RELOAD:
Reload requested for 23:08:30 PST Sun Mar 20
Step 6 reload cancel
The reload cancel terminates a reload
that was previously setup with the
reload in time command.
Router# reload cancel
***
*** --- SHUTDOWN ABORTED --***
04:34:08: %SYS-5SCHEDULED_RELOAD_CANCELLED:
Scheduled reload cancelled at 15:38:46 PST
Sun Mar 27 2005
Step 7 disable
Exits the current privilege level and
EDCS-1228241
76
Page 77

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
returns to privilege level 1.
Router# disable
Step 8 show privilege
Displays the privilege level of the
current CLI session
Router> show privilege
Current privilege level is 1
The term “authorized administrator” is used in this ST to refer to
any user that has been assigned to a privilege level that is
permitted to perform the relevant action; therefore has the
appropriate privileges to perform the requested functions. The
privilege level determines the functions the user can perform;
hence the authorized administrator with the appropriate
privileges. Refer to the Guidance documentation and IOS
Command Reference Guide for available commands and
associated roles and privilege levels.
The Switch can and shall be configured to authenticate all access
to the command line interface using a username and password.
FPT_ITT.1(1) and
FPT_ITT.1(2)
The TOE is self-contained and provides all of the claimed
functionality within a single appliance. However if more than
one TOE is used in the configuration, the TOE may be
configured to use the cryptographic services as described in
the FCS SFRs to secure the connection and protect the
transmitted data.
FPT_PTD_EXT.1
and
FPT_PTD_EXT.2
The TOE includes a Master Passphrase features that can be used
to configure the TOE to encrypt all locally defined user
passwords. In this manner, the TOE ensures that plaintext user
passwords will not be disclosed even to administrators.
The TOE stores all private keys in a secure directory that is not
readily accessible to administrators. All pre-shared and symmetric
keys are stored in encrypted form to prevent access.
FPT_RPL.1
By virtue of the cryptographic and path mechanisms implemented
by the TOE, replayed network packets directed (terminated) at the
TOE will be detected and discarded.
Note: The intended scope of this requirement is trusted
communications with the TOE (e.g., administrator to TOE, IT
entity (e.g., authentication server) to TOE). As such, replay does
not apply to receipt of multiple network packets due to network
congestion or lost packet acknowledgments.
FPT_STM.1
The TOE provides a source of date and time information for the
switch, used in audit timestamps and in validating service
requests. This function can only be accessed from within the
EDCS-1228241
77
Page 78

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
configuration exec mode via the privileged mode of operation of
the switch. The clock function is reliant on the system clock
provided by the underlying hardware. The timestamp is assumed
to be accurate to an official time source, such as Network Time
Protocol (NTP) server. Therefore, the TOE can optionally be set
to receive time from an NTP server. The NTP synchronizes the
TOE clock to the U.S. Naval Observatory Master Clocks in
Washington, DC and Colorado Springs CO. The NTP sends
periodic requests and adjusts the clock as necessary. If an NTP
server is used, the TOE supports signature verification of the
timestamp from the time server.
FPT_TUD_EXT.1
The TOE has specific versions that can be queried by an
administrator. When updates are made available by Cisco, an
administrator can obtain and install those updates. The
cryptographic checksums (i.e., public hashes) are used to verify
software/firmware update files (to ensure they have not been
modified from the originals distributed by Cisco) before they are
used to actually update the applicable TOE components.
FPT_TST_EXT.1
As a FIPS 140-2 validated product, the TOE runs a suite of selftests during initial start-up to verify its correct operation. If any of
the tests fail, the security administrator will have to log into the
CLI to determine which test failed and why. If the tests pass
successfully the login prompt is displayed and the administrator
will be able to login and administer the TOE. Refer to the FIPS
Security Policy for available options and management of the
cryptographic self-test.
For testing of the TSF, the TOE automatically runs checks and
tests at startup and during resets to ensure the TOE hardware and
software components are available and operating correctly. If all
components pass the tests, the login prompt will be displayed. If
any of the tests fail, the TOE will reboot to try to correct the
issue(s). Refer to the Guidance documentation for installation
configuration settings and information and troubling shooting if
issues are identified.
FRU_RSA.1
An administrator can configure a maximum number of
concurrent sessions for remote administrative interfaces.
FTA_SSL_EXT.1
and FTA_SSL.3
An administrator can configure maximum inactivity times for
both local and remote administrative sessions. When a session
is inactive (i.e., not session input) for the configured period of
time the TOE will terminate the session, flush the screen, and
no further activity is allowed requiring the administrator to log
in (be successfully identified and authenticated) again to
establish a new session.
EDCS-1228241
78
Page 79

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
TOE SFRs
How the SFR is Met
The allowable range is from 1 to 65535 seconds.
FTA_TAB.1
The TOE displays a privileged Administrator specified banner on
the CLI management interface prior to allowing any
administrative access to the TOE. This is applicable for both
local and remote TOE administration.
FTP_ITC.1(1) and
FTP_ITC.(2)
The TOE protects communications with authorized IT entities with
IPSec. This protects the data from disclosure by encryption and by
checksums that verify that data has not been modified.
FTP_TRP.1(1) and
FTP_TRP.1(2)
All remote administrative communications take place over a
secure encrypted SSHv2 session. The SSHv2 session is
encrypted using AES encryption. The remote users are able to
initiate SSHv2 communications with the TOE.
EDCS-1228241
6.2 TOE Bypass and interference/logical tampering Protection
Measures
The TOE consists of a hardware platform in which all operations in the TOE scope are
protected from interference and tampering by untrusted subjects. All administration and
configuration operations are performed within the physical boundary of the TOE. Also,
all TSP enforcement functions must be invoked and succeed prior to functions within the
TSC proceeding.
The TOE has been designed so that all locally maintained TSF data can only be
manipulated via the secured management interface, the CLI interface. There are no
undocumented interfaces for managing the product.
All sub-components included in the TOE rely on the main chassis for power, memory
management, and access control. In order to access any portion of the TOE, the
Identification and Authentication mechanisms of the TOE must be invoked and succeed.
No processes outside of the TOE are allowed direct access to any TOE memory. The
TOE only accepts traffic through legitimate TOE interfaces. Specifically, processes
outside the TOE are not able to execute code on the TOE. None of these interfaces
provide any access to internal TOE resources.
The TOE enforces information flow control policies and applies network traffic security
on its interfaces before traffic passes into or out of the TOE. The TOE controls every
ingress and egress traffic flow. Policies are applied to each traffic flow. Traffic flows
characterized as unauthorized are discarded and not permitted to circumvent the TOE.
There are no unmediated traffic flows into or out of the TOE. The information flow
policies identified in the SFRs are applied to all traffic received and sent by the TOE.
Each communication including data plane communication, control plane
communications, and administrative communications are mediated by the TOE. The data
79
Page 80

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
EDCS-1228241
plane allows the ability to forward network traffic; the control plane allows the ability to
route traffic correctly; and the management plane allows the ability to manage network
elements. There is no opportunity for unaccounted traffic flows to flow into or out of the
TOE.
This design, combined with the fact that only an administrative user with the appropriate
role may access the TOE security functions, provides a distinct protected domain for the
TOE that is logically protected from interference and is not bypassable.
80
Page 81

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
T.UNAUTHORIZED_ACCESS
T.UNAUTHORIZED_UPDATE
T.ADMIN_ERROR
T.UNDETECTED_ACTIONS
T.RESOURCE_EXHAUSTION
T.USER_DATA_REUSE
T.TSF_FAILURE
P.ACCESS BANNER
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
X X
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
X
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
X O.DISPLAY_BANNER
X
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
X
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEARING
X
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
X
O.SESSION_LOCK
X
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
X
EDCS-1228241
7 RATIONALE
This section describes the rationale for the Security Objectives and Security Functional
Requirements as defined within this Security Target. The following matrix is the typical
display that is drawn from the information presented in Sections 2 and 3 of the NDPP.
7.1 Rationale for TOE Security Objectives
Table 21: Threat/Objectives/Policies Mappings
81
Page 82
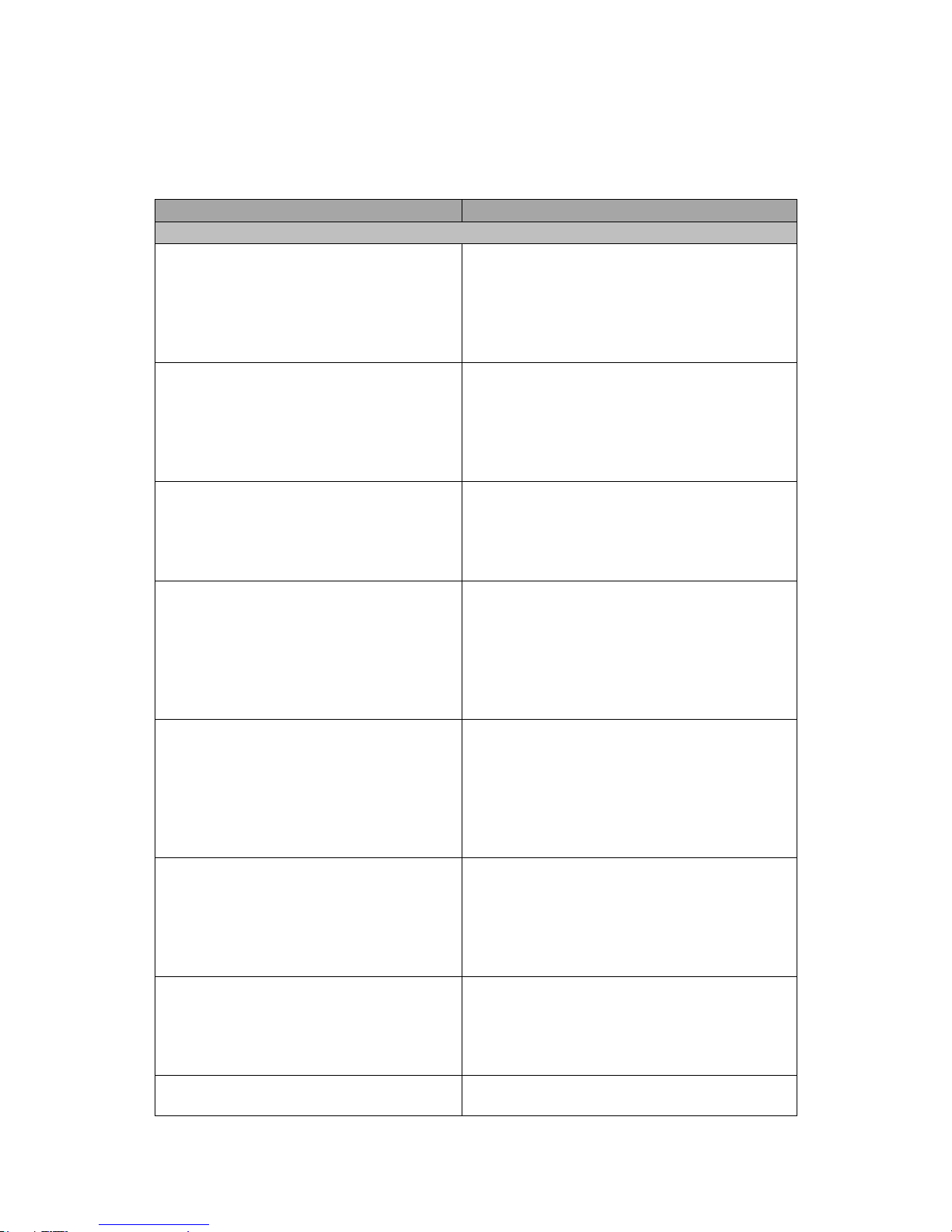
Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Objective
Rationale
Security Objectives Drawn from NDPP
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat: T.UNAUTHORIZED_ACCESS
and T.UNAUTHORIZED_UPDATE to
ensure the communications with the TOE is
not compromised.
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat T.UNAUTHORIZED_UPDATE to
ensure the end user has not installed a
malicious update, thinking that it was
legitimate.
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
This security objective is necessary to counter
the T.UNDETECTED_ACTIONS to ensure
activity is monitored so the security of the
TOE is not compromised.
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
This security objective is necessary to address
the Organization Security Policy
P.ACCESS_BANNER to ensure an advisory
notice and consent warning message
regarding unauthorized use of the TOE is
displayed before the session is established.
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
This security objective is necessary to counter
the T.ADMIN_ERROR that ensures actions
performed on the TOE are logged so that
indications of a failure or compromise of a
TOE security mechanism are known and
corrective actions can be taken.
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEA
RING
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat T.USER_DATA_REUSE so that
data traversing the TOE could inadvertently
be sent to a user other than that intended by
the sender of the original network traffic.
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat: T.RESOURCE_EXHAUSTION to
mitigate a denial of service, thus ensuring
resources are available.
O.SESSION_LOCK
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat: T.UNAUTHORIZED_ACCESS to
EDCS-1228241
Table 22: Threat/Policies/TOE Objectives Rationale
82
Page 83

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Objective
Rationale
ensure accounts cannot be compromised and
used by an attacker that does not otherwise
have access to the TOE.
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
This security objective is necessary to counter
the threat T.TSF_FAILURE to ensure failure
of mechanisms do not lead to a compromise
in the TSF.
OE.NO_GENERAL_PURP
OSE
OE.PHYSICAL
OE.TRUSTED_ADMIN
A.NO_GENERAL_PURPOSE
X
A.PHYSICAL
X
A.TRUSTED_ADMIN
X
Environment Objective
Rationale
OE.NO_GENERAL_PURPOSE
This security objective is necessary to address
the assumption A.NO_GENERAL_PURPOSE
by ensuring there are no general-purpose
computing capabilities (e.g., the ability to
execute arbitrary code or applications)
capabilities on the TOE.
OE.PHYSICAL
This security objective is necessary to address
the assumption A.PHYSICAL by ensuring the
TOE and the data it contains is physically
protected from unauthorized access.
OE.TRUSTED_ADMIN
This security objective is necessary to address
EDCS-1228241
7.2 Rationale for the Security Objectives for the Environment
Table 23: Assumptions/Environment Objectives Mappings
Table 24: Assumptions/Threats/Objectives Rationale
83
Page 84

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Environment Objective
Rationale
the assumption A.TRUSTED_ADMIN by
ensuring the administrators are non-hostile and
follow all administrator guidance.
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEARING
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
O.SESSION_LOCK
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
FAU_GEN.1
X
FAU_GEN.2
X
FAU_STG_EXT.1
X
FAU_STG_EXT.3
X X
FCS_CKM.1
X
FCS_CKM_EXT.4
X
FCS_COP.1(1)
X
FCS_COP.1(2)
X X
FCS_COP.1(3)
X X
FCS_COP.1(4)
X
EDCS-1228241
7.3 Rationale for TOE Security Functional Requirements
The security requirements are derived according to the general model presented in Part 1
of the Common Criteria. Specifically, the tables below illustrate the mapping between the
security requirements and the security objectives and the relationship between the threats,
policies and IT security objectives. The functional and assurance requirements presented
in this Security Target are mutually supportive and their combination meets the stated
security objectives.
Table 25: Security Objective to Security Requirements Mappings
84
Page 85

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEARING
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
O.SESSION_LOCK
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
FCS_RBG_EXT.1
X
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1
X
FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1
X
FCS_SSH_EXT.1
X
FDP_RIP.2
X
FIA_PMG_EXT.1
X
FIA_UIA_EXT.1
X
FIA_UAU_EXT.5
X
FIA_UAU.6
X
FIA_UAU.7
X
FMT_MTD.1
X
FMT_SMF.1
X
FMT_SMR.1
X
FPT_ITT.1(1)
X
FPT_ITT.1(2)
X
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(1)
X X
FPT_PTD_EXT.1(2)
X X
FPT_RPL.1
X
FPT_STM.1
X
FPT_TUD_EXT.1
X
FPT_TST_EXT.1
X
EDCS-1228241
85
Page 86

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICATIONS
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_CLEARING
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
O.SESSION_LOCK
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
FRU_RSA.1
X
FTA_SSL_EXT.1
X X
FTA_SSL.3
X X
FTA_TAB.1
X
FTP_ITC.1(1)
X
FTP_ITC.1(2)
X
FTP_TRP.1(1)
X
FTP_TRP.1(2)
X
Objective
Rationale
Security Functional Requirements Drawn from Security Requirements
for NDPP
O.PROTECTED_COMMUNICA
TIONS
The SFRs, FAU_STG_EXT.3, FCS_CKM.1,
FCS_CKM_EXT.4, FCS_COP.1(1), FCS_COP.1(2),
FCS_COP.1(3), FCS_COP.1(4), FCS_RBG_EXT.1,
FCS_COMM_PROT_EXT.1, FCS_IPSEC_EXT.1,
FCS_SSH_EXT.1, FPT_ITT.1(1), FPT_ITT.1(2),
FPT_PTD.1(1), FPT_PTD.1(2), FPT_RPL.1,
FTP_ITC.1(1), FTP_ITC.1(2), FTP_TRP.1(1),
FTP_TRP.1(2) meet this objective by ensuring the
communications between the TOE and endpoints are
secure by implementing the encryption protocols as
defined in the SFRs and as specified by the RFCs.
O.VERIFIABLE_UPDATES
The SFRs, FPT_TUD_EXT.1, FCS_COP.1(2),
EDCS-1228241
Table 26: Objectives to Requirements Rationale
86
Page 87

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
Objective
Rationale
FCS_COP.1(3) meet this objective by ensuring the
update was downloaded via secure communications, is
from a trusted source, and the update can be verified
by cryptographic mechanisms prior to installation.
O.SYSTEM_MONITORING
The SFRs, FAU_GEN.1, FAU_GEN.2,
FAU_STG_EXT.1, FAU_STG_EXT.3, FPT_STM.1
meet this objective by auditing actions on the TOE.
The audit records identify the user associated with the
action/event, whether the action/event was successful
or failed, the type of action/event, and the date/time the
action/event occurred. The audit logs are transmitted
securely to a remote syslog server. If connectivity to
the remote syslog server is lost, the TOE will block
new permit actions.
O.DISPLAY_BANNER
The SFR, FTA_TAB.1 meets this objective by
displaying an advisory notice and consent warning
message regarding unauthorized use of the TOE.
O.TOE_ADMINISTRATION
The SFRs, FIA_UIA_EXT.1, FIA_UAU_EXT.5,
FIA_UAU.6, FIA_UAU.7, FMT_MTD.1,
FMT_SMF.1, FMT_SFR.1, FPT_PTD.1(1),
FTA_SSL_EXT.1, FTA_SSL.3 meet this objective by
ensuring the TOE supports a password-based
authentication mechanism with password complexity
enforcement such as, strong passwords, password lifetime constraints, providing current password when
changing the password, obscured password feedback
when logging in, and passwords are not stored in
plaintext.
O.RESIDUAL_INFORMATION_
CLEARING
The SFR, FDP_RIP.2 meets this objective by ensuring
no left over user data from the previous transmission is
included in the network traffic.
O.RESOURCE_AVAILABILITY
The SFR, FRU_RSA.1 meets this objective by limiting
the number of amount of exhaustible resources, such
the number of concurrent administrative sessions.
O.SESSION_LOCK
The SFRs, FTA_SSL_EXT.1, FTA_SSL.3 meet this
objective by terminating a session due to
meeting/exceeding the inactivity time limit.
O.TSF_SELF_TEST
The SFR, FPT_TST_EXT.1 meets this objective by
performing self-test to ensure the TOE is operating
correctly and all functions are available and enforced.
EDCS-1228241
87
Page 88

Cisco Cat4K NDPP ST 11 March 2014
[CC_PART1]
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation – Part 1: Introduction and
general model, dated July 2009, version 3.1, Revision 3
[CC_PART2]
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation – Part 2: Security
functional components, dated July 2009, version 3.1, Revision 3
[CC_PART3]
Common Criteria for Information Technology Security Evaluation – Part 3: Security
assurance components, dated July 2009, version 3.1, Revision 3
[CEM]
Common Methodology for Information Technology Security Evaluation – Evaluation
Methodology, dated July 2009, version 3.1, Revision 3
[NDPP]
US Government, Security Requirements for Network Devices (pp_nd_v1.0), version 1.0,
dated 10 December 2010
EDCS-1228241
ANNEX A: REFERENCES
The following documentation was used to prepare this ST:
Table 27: References
88
 Loading...
Loading...