Page 1

Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive
Security Appliance Getting Started
Guide
For the Cisco ASA 5510, ASA 5520, and ASA 5540
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Customer Order Number: DOC-7817611=
Text Part Number: 78-17611-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT
NOTICE. ALL STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT
ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR
THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION
PACKET THAT SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO
LOCATE THE SOFTWARE LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adaptation of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as
part of UCB’s public domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Regents of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE
PROVIDED “AS IS” WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED
OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND
NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL
DAMAGES, INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR
INABILITY TO USE THIS MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH
DAMAGES.
CCSP, CCVP, the Cisco Square Bridge logo, Follow Me Browsing, and StackWise are trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; Changing the Way We
Work, Live, Play, and Learn, and iQuick Study are service marks of Cisco Systems, Inc.; and Access Registrar, Aironet, BPX, Catalyst, CCDA, CCDP,
CCIE, CCIP, CCNA, CCNP, Cisco, the Cisco Certified Internetwork Expert logo, Cisco IOS, Cisco Press, Cisco Systems, Cisco Systems Capital, the
Cisco Systems logo, Cisco Unity, Enterprise/Solver, EtherChannel, EtherFast, EtherSwitch, Fast Step, FormShare, GigaDrive, GigaStack, HomeLink,
Internet Quotient, IOS, IP/TV, iQ Expertise, the iQ logo, iQ Net Readiness Scorecard, LightStream, Linksys, MeetingPlace, MGX, the Networkers
logo, Networking Academy, Network Registrar, Pa cke t, PIX, Post-Routing, Pre-Routing, ProConnect, RateMUX, ScriptShare, SlideCast,
SMARTnet, The Fastest Way to Increase Your Internet Quotient, and TransPath are registered trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates
in the United States and certain other countries.
All other trademarks mentioned in this document or Website are the property of their respective owners. The use of the word partner does not imply
a partnership relationship between Cisco and any other company. (0601R)
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
© 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3

CONTENTS
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
1 Before You Begin 1-1
ASA 5500 1-1
ASA 5500 with AIP SSM 1-2
ASA 5500 with CSC SSM 1-3
ASA 5500 with 4GE SSM 1-4
2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500 2-1
Verifying the Package Contents 2-2
Installing the Chassis 2-3
Rack-Mounting the Chassis 2-4
Ports and LEDs 2-5
What to Do Next 2-9
3 Installing Optional SSMs 3-1
Cisco 4GE SSM 3-1
4GE SSM Components 3-2
Installing the Cisco 4GE SSM 3-3
Installing the SFP Modules 3-4
SFP Module 3-5
Installing the SFP Module 3-6
78-17611-01
Cisco AIP SSM and CSC SSM 3-8
Installing an SSM 3-9
What to Do Next 3-10
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
iii
Page 4

Contents
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
4 Connecting Interface Cables 4-1
Connecting Cables to Interfaces 4-2
What to Do Next 4-10
5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance 5-1
About the Factory-Default Configuration 5-1
About the Adaptive Security Device Manager 5-2
Before Launching the Startup Wizard 5-3
Using the Startup Wizard 5-4
What to Do Next 5-5
6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration 6-1
Example DMZ Network Topology 6-1
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment 6-4
Configuration Requirements 6-5
Starting ASDM 6-6
Creating IP Pools for Network Address Translation 6-7
Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with the DMZ Web
Server
6-12
Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with Devices on the
Internet
6-15
Configuring an External Identity for the DMZ Web Server 6-16
Providing Public HTTP Access to the DMZ Web Server 6-18
CHAPTER
iv
What to Do Next 6-24
7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration 7-1
Example IPsec Remote-Access VPN Network Topology 7-1
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario 7-2
Information to Have Available 7-3
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 5

Starting ASDM 7-4
Configuring the FWSM for an IPsec Remote-Access VPN 7-5
Selecting VPN Client Types 7-6
Specifying the VPN Tunnel Group Name and Authentication Method 7-7
Specifying a User Authentication Method 7-8
(Optional) Configuring User Accounts 7-10
Configuring Address Pools 7-11
Configuring Client Attributes 7-12
Configuring the IKE Policy 7-13
Configuring IPsec Encryption and Authentication Parameters 7-15
Specifying Address Translation Exception and Split Tunneling 7-16
Verifying the Remote-Access VPN Configuration 7-17
What to Do Next 7-18
Contents
CHAPTER
78-17611-01
8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration 8-1
Example Site-to-Site VPN Network Topology 8-1
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario 8-2
Information to Have Available 8-2
Configuring the Site-to-Site VPN 8-3
Starting ASDM 8-3
Configuring the Security Appliance at the Local Site 8-4
Providing Information About the Remote VPN Peer 8-6
Configuring the IKE Policy 8-7
Configuring IPSec Encryption and Authentication Parameters 8-9
Specifying Hosts and Networks 8-10
Viewing VPN Attributes and Completing the Wizard 8-11
Configuring the Other Side of the VPN Connection 8-13
What to Do Next 8-13
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
v
Page 6

Contents
CHAPTER
CHAPTER
9 Configuring the AIP SSM 9-1
AIP SSM Configuration 9-1
Overview of Configuration Process 9-2
Configuring the ASA 5500 to Divert Traffic to the AIP SSM 9-2
Sessioning to the AIP SSM and Running Setup 9-5
What to Do Next 9-7
10 Configuring the CSC SSM 10-1
About the CSC SSM 10-1
About Deploying the Security Appliance with the CSC SSM 10-2
Scenario: Security Appliance with CSC SSM Deployed for Content Security 10-4
Configuration Requirements 10-5
Configuring the CSC SSM for Content Security 10-5
Obtain Software Activation Key from Cisco.com 10-6
Gather Information 10-6
Launch ASDM 10-7
Verify Time Settings 10-8
Run the CSC Setup Wizard 10-9
Divert Traffic to the CSC SSM for Content Scanning 10-14
CHAPTER
APPENDIX
vi
What to Do Next 10-20
11 Configuring the 4GE SSM for Fiber 11-1
Cabling 4GE SSM Interfaces 11-2
Setting the 4GE SSM Media Type for Fiber Interfaces (Optional) 11-3
What to Do Next 11-5
A Obtaining a DES License or a 3DES-AES License A-1
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 7

ASA 5500
CHA P T E R
1
Before You Begin
Use the following table to find the installation and configuration steps that are
required for your implementation of the adaptive security appliance.
The adaptive security appliance implementations included in this document are as
follows:
• ASA 5500, page 1-1
• ASA 5500 with AIP SSM, page 1-2
• ASA 5500 with CSC SSM, page 1-3
• ASA 5500 with 4GE SSM, page 1-4
78-17611-01
To Do This ... See ...
Install the chassis Chapter 2, “Installing the Cisco ASA
5500”
Connect interface cables Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Cables”
Perform initial setup of the adaptive security
appliance
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
Chapter 5, “Configuring the
Adaptive Security Appliance”
1-1
Page 8

ASA 5500 with AIP SSM
To Do This ... (continued) See ...
Configure the adaptive security appliance for
your implementation
Configure optional and advanced features Cisco Security Appliance Command
Operate the system on a daily basis Cisco Security Appliance Command
ASA 5500 with AIP SSM
Chapter 1 Before You Begin
Chapter 6, “Scenario: DMZ
Configuration”
Chapter 7, “Scenario:
Remote-Access VPN Configuration”
Chapter 8, “Scenario: Site-to-Site
VPN Configuration”
Line Configuration Guide
Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
1-2
To Do This .... See ....
Install the chassis Chapter 2, “Installing the Cisco ASA
5500”
Install the AIP SSM Chapter 3, “Installing Optional
SSMs”
Connect interface cables Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Cables”
Perform initial setup the adaptive security
appliance
Configure the adaptive security appliance for
AIP SSM
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
Chapter 5, “Configuring the
Adaptive Security Appliance”
Chapter 9, “Configuring the AIP
SSM”
78-17611-01
Page 9
Chapter 1 Before You Begin
To Do This .... (continued) See ....
Configure IPS software for intrusion
prevention
Refine configuration and configure optional
and advanced features
ASA 5500 with CSC SSM
ASA 5500 with CSC SSM
Configuring the Cisco Intrusion
Prevention System Sensor Using the
Command Line Interface
Cisco Intrusion Prevention System
Command Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Line Configuration Guide
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
78-17611-01
To Do This .... To Do This ....
Install the chassis Chapter 2, “Installing the Cisco ASA
5500”
Install the CSC SSM Chapter 3, “Installing Optional
SSMs”
Connect interface cables Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Cables”
Perform initial setup of the adaptive
security appliance
Configure the adaptive security appliance
for content security
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
Chapter 5, “Configuring the
Adaptive Security Appliance”
Chapter 10, “Configuring the CSC
SSM”
1-3
Page 10
ASA 5500 with 4GE SSM
To Do This .... (continued) To Do This ....
Configure the CSC SSM Cisco Content Security and Control
Refine configuration and configure
optional and advanced features
ASA 5500 with 4GE SSM
To Do This ... See ...
Install the chassis Chapter 2, “Installing the Cisco ASA
Install the 4GE SSM Chapter 3, “Installing Optional
Connect interface cables Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Perform initial setup of the adaptive
security appliance
Install the fiber optic module Chapter 3, “Installing Optional
Refine configuration and configure
optional and advanced features
Chapter 1 Before You Begin
SSM Administrator Guide
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Line Configuration Guide
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
5500”
SSMs”
Cables”
Chapter 5, “Configuring the
Adaptive Security Appliance”
SSMs”
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Line Configuration Guide
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Reference
1-4
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 11

CHA P T E R
Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
2
Warning
Caution Read the safety warnings in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information
Note The illustrations in this document show the Cisco ASA 5540 adaptive security
Only trained and qualified personnel should be allowed to install, replace, or
service this equipment.
for the Cisco ASA 5500 Series and follow proper safety procedures when
performing these steps.
This chapter describes the product overview, memory requirements and
rack-mount and installation procedures for the adaptive security appliance. This
chapter includes the following sections:
• Verifying the Package Contents, page 2-2
• Installing the Chassis, page 2-3
• Ports and LEDs, page 2-5
• What to Do Next, page 2-9
appliance. The Cisco ASA 5510 adaptive security appliance and Cisco ASA 5520
adaptive security appliance are identical, containing the same back panel features
and indicators.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
2-1
Page 12
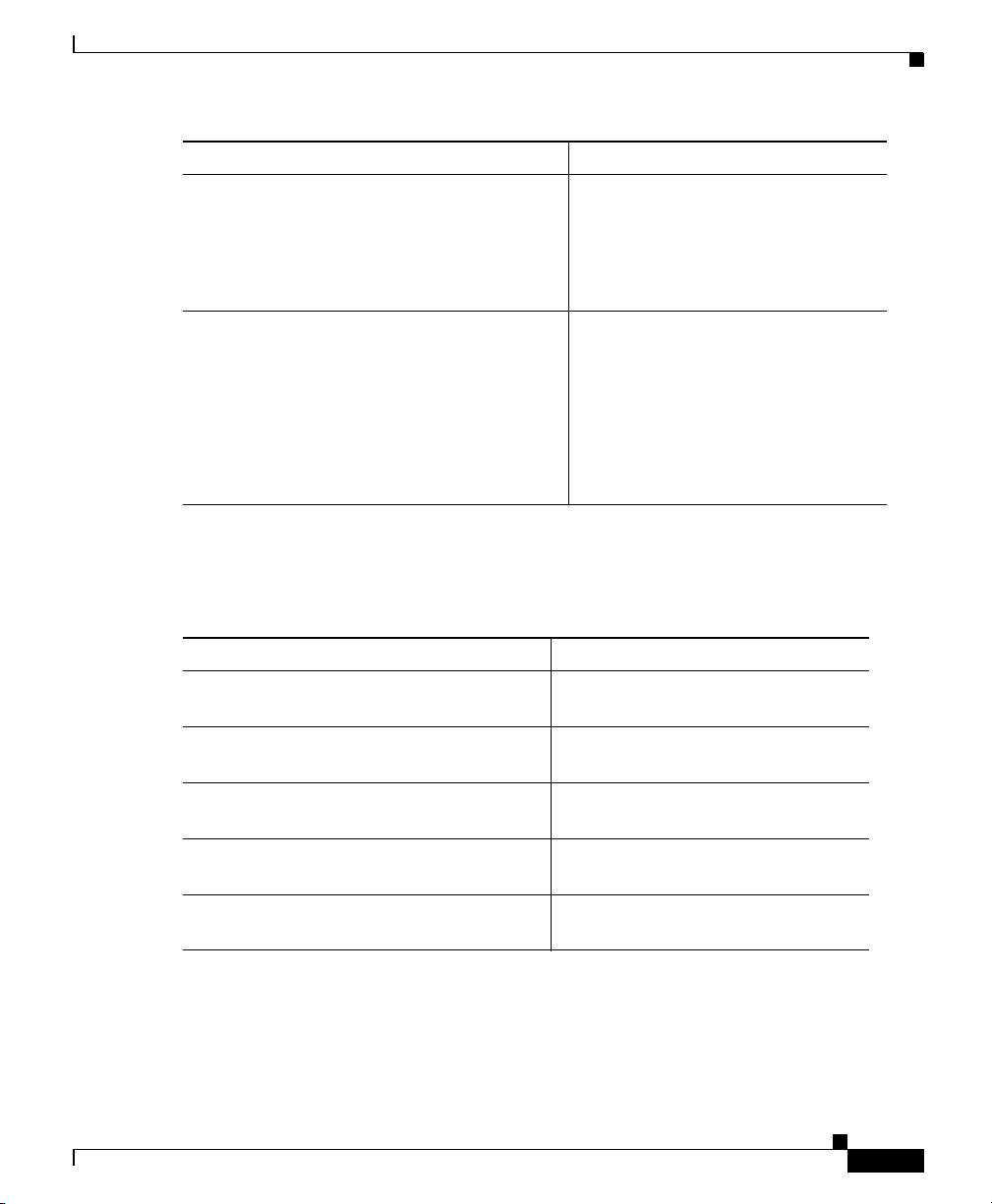
Verifying the Package Contents
Verifying the Package Contents
Verify the contents of the packing box to ensure that you have received all items
necessary to install your Cisco ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance. See
Figure 2-1.
Figure 2-1 Contents of ASA 5500 Package
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LINK SPD
LINK SPD
3
FL
A
SH
LINK SPD
2
LINK SPD
1
ER
0
POW
STATUS
VPN
ACTIVE
FLASH
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
Cisco ASA 5500 adaptive
security appliance
2-2
Mounting brackets
(700-18797-01 AO) right
(700-18798-01 AO) left
2 long cap screws
(48-0654-01 AO)
4 flathead screws
(48-0451-01 AO)
Cable holder
4 cap screws
(48-0523-01 AO)
5500 Adaptive
Security Appliance
Product CD
4 rubber feet
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
Yellow Ethernet cable
(72-1482-01)
Blue console cable
PC terminal adapter
Safety and
Cisco ASA
Compliance
Guide
Documentation
92574
78-17611-01
Page 13
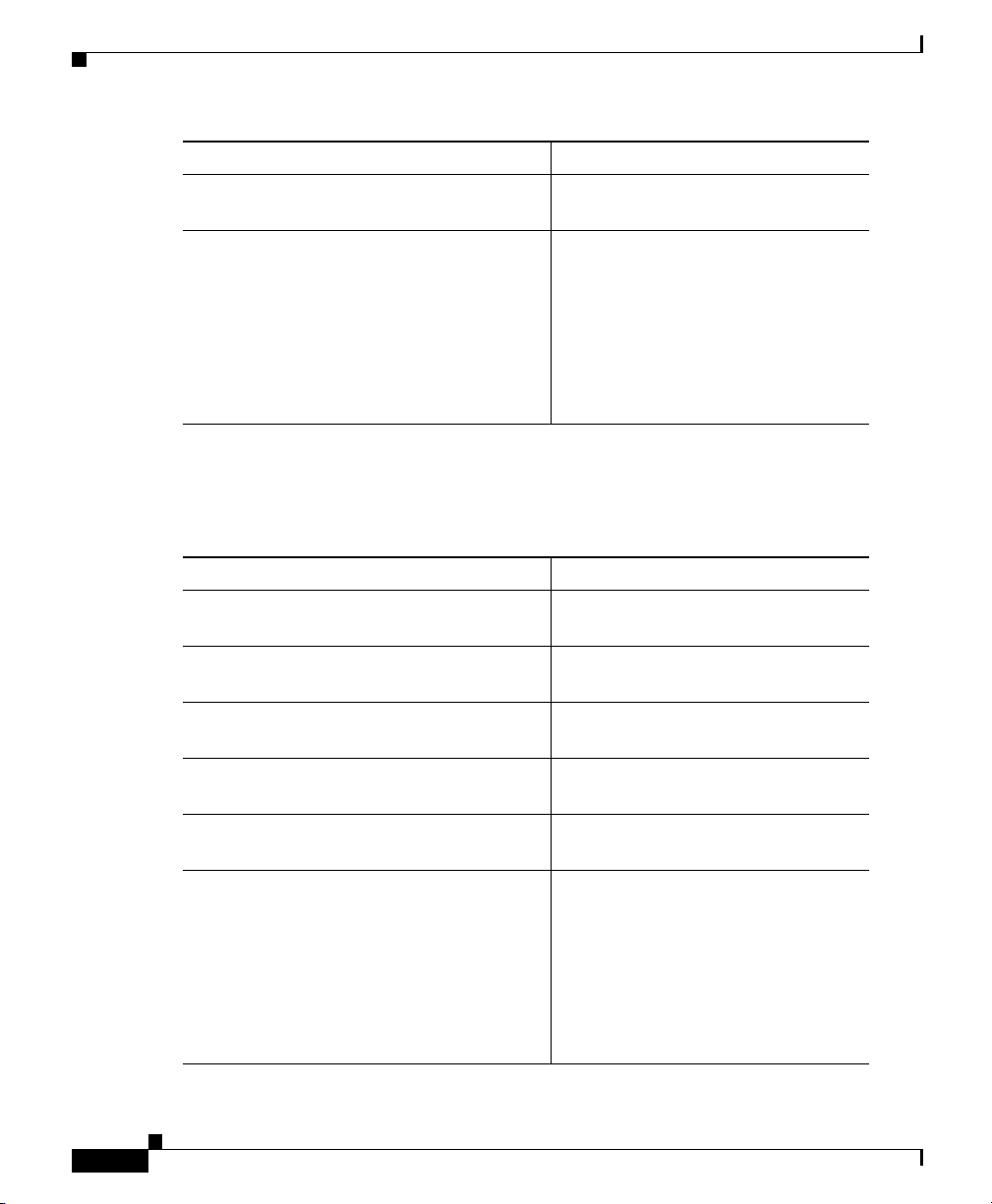
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
Installing the Chassis
This section describes how to rack-mount and install the adaptive security
appliance. You can mount the adaptive security appliance in a 19-inch rack (with
a 17.5- or 17.75-inch opening).
Installing the Chassis
Warning
Warning
To prevent bodily injury when mounting or servicing this unit in a rack, you must
take special precautions to ensure that the system remains stable. The
following guidelines are provided to ensure your safety.
The following information can help plan equipment rack installation:
• Allow clearance around the rack for maintenance.
• When mounting a device in an enclosed rack ensure adequate ventilation. An
enclosed rack should never be overcrowded.
Make sure that the rack is not
congested, because each unit generates heat.
• When mounting a device in an open rack, make sure that the rack frame does
not block the intake or exhaust ports.
• If the rack contains only one unit, mount the unit at the bottom of the rack.
• If the rack is partially filled, load the rack from the bottom to the top, with the
heaviest component at the bottom of the rack.
• If the rack contains stabilizing devices, install the stabilizers prior to
mounting or servicing the unit in the rack.
Before performing any of the following procedures, ensure that power is
removed from the DC circuit. To ensure that all power is OFF, locate the circuit
breaker on the panel board that services the DC circuit, switch the circuit
breaker to the OFF position, and tape the switch handle of the circuit breaker in
the OFF position.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
2-3
Page 14
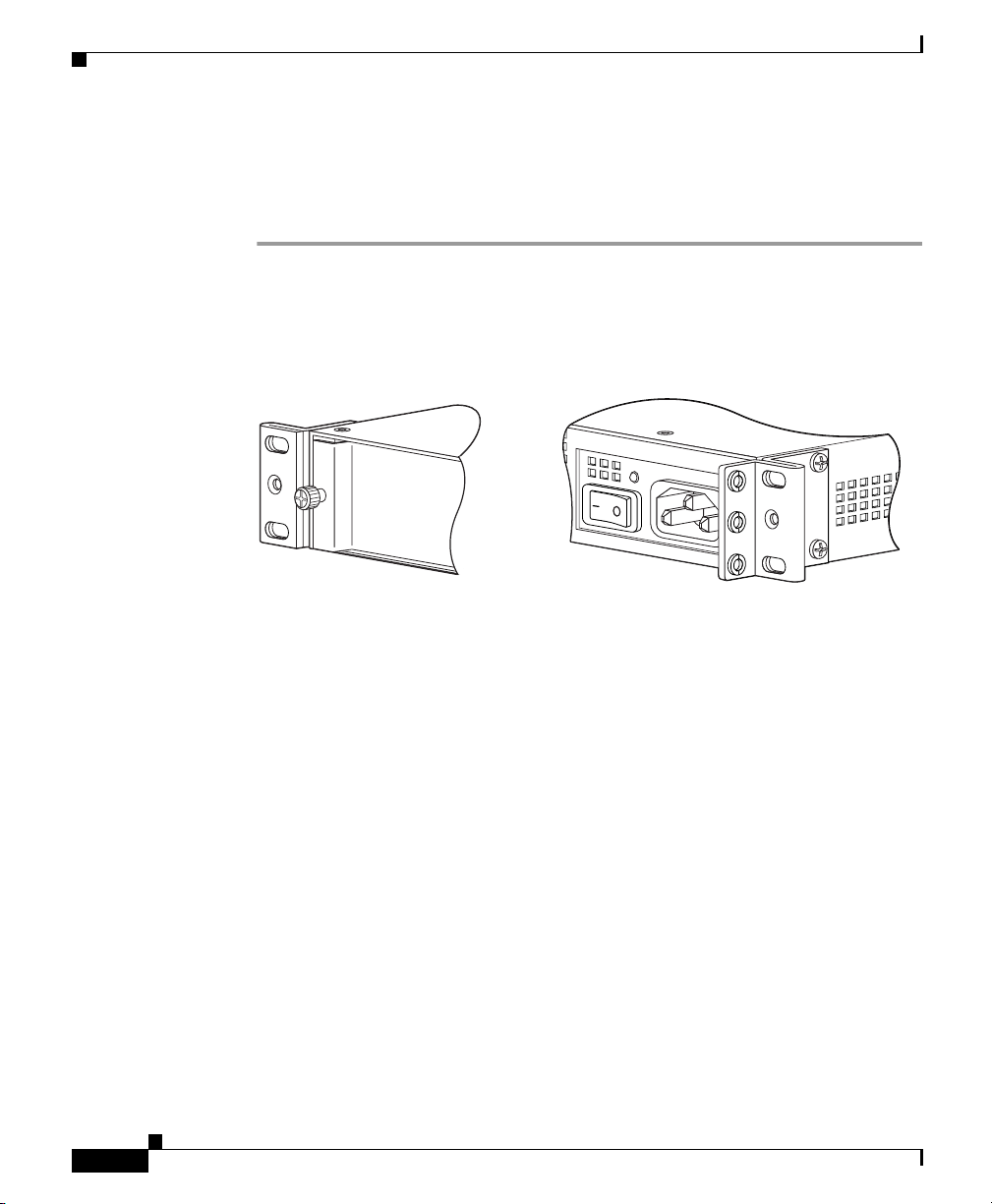
Installing the Chassis
Rack-Mounting the Chassis
To rack-mount the chassis, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Attach the rack-mount brackets to the chassis using the supplied screws. Attach
the brackets to the holes as shown in Figure 2-2. After the brackets are secured to
the chassis, you can rack-mount it.
Figure 2-2 Installing the Right and Left Brackets
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
132186
132187
2-4
Step 2
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
Attach the chassis to the rack using the supplied screws, as shown in Figure 2-3.
78-17611-01
Page 15
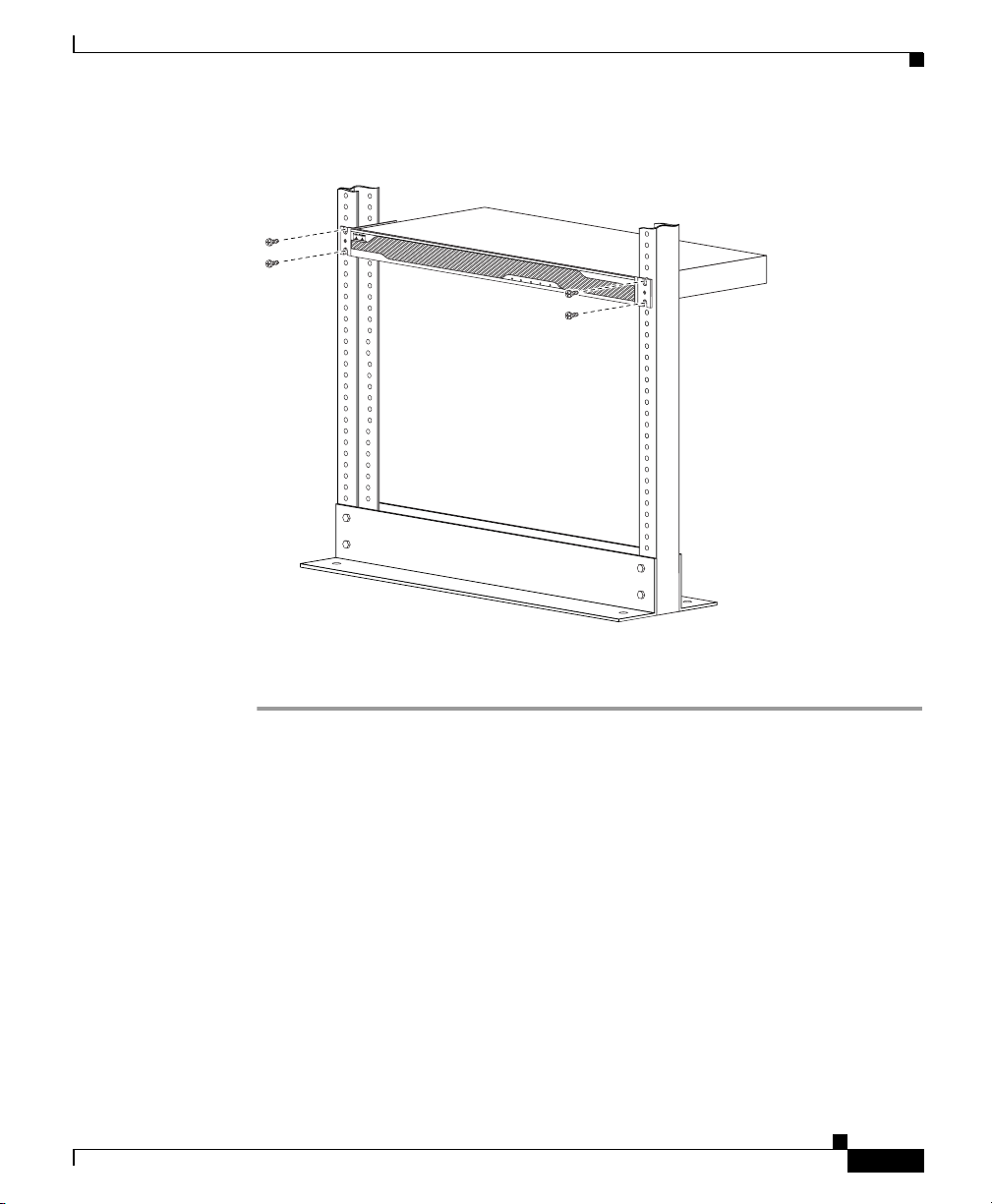
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
Figure 2-3 Rack-Mounting the Chassis
Ports and LEDs
C
IS
CO
A
S
A
POWER
STATUS
ACT
IVE
VP
554
A
0
d
a
S
p
E
tiv
R
I
e
E
S
S
e
c
u
r
ity
A
p
p
N
FLASH
lia
n
c
e
119633
To remove the chassis from the rack, remove the screws that attach the chassis to
the rack, and then remove the chassis.
Ports and LEDs
This section describes the front and rear panels. Figure 2-4 shows the front panel
LEDs.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
2-5
Page 16
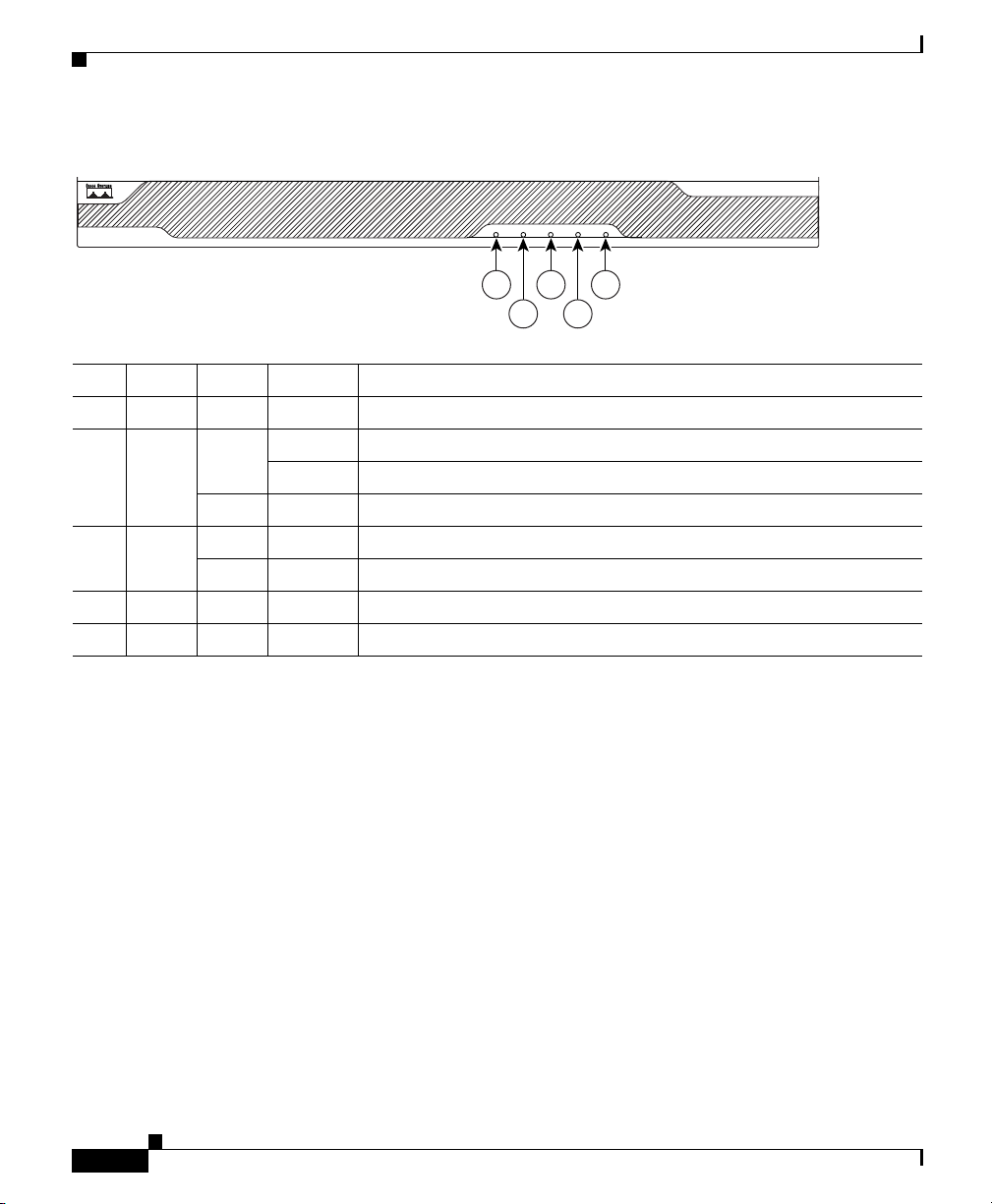
Ports and LEDs
Figure 2-4 Front Panel LEDs
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
POWER STATUS
1
2
ACTIVE
3
CISCO ASA 5540
VPN
FLASH
5
4
SERIES
Adaptive Security Appliance
119638
LED Color State Description
1 Power Green On The system has power.
2 Status Green Flashing The power-up diagnostics are running or the system is booting.
Solid The system has passed power-up diagnostics.
Amber Solid The power-up diagnostics have failed.
3 Active Green Solid This is the active failover device.
Amber Solid This is the standby failover device.
4 VPN Green Solid VPN tunnel is established.
5 Flash Green Solid The CompactFlash is being accessed.
2-6
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 17
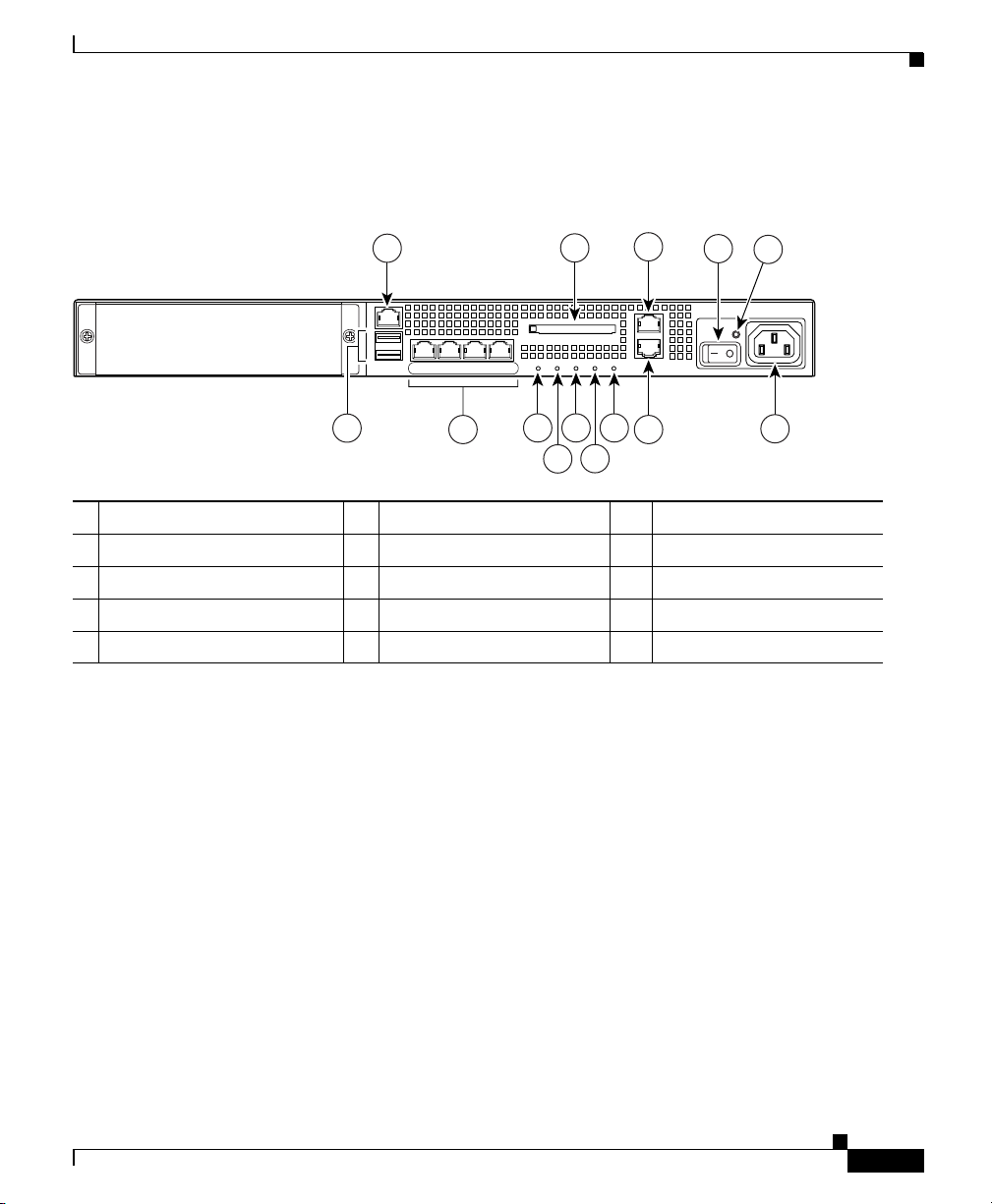
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
Figure 2-5 shows the rear panel features for the adaptive security appliance.
Figure 2-5 Rear Panel LEDs and Ports (AC Power Supply Model Shown)
Ports and LEDs
1
MGMT
USB2
1 Management Port
USB1
6
1
6 USB 2.0 interfaces
LINK SPD2LINK SPD1LINK SPD
LINK SPD
3
0
7
2 External CompactFlash slot 7 Network interfaces
2
FLASH
ACTIVE
POWER
STATUS
8 10 12
9
2
3
3
CONSOLE
AUX
VPN
FLASH
13
11
11 VPN LED
12 Flash LED
4
5
119572
14
3 Serial Console port 8 Power indicator LED 13 AUX port
4 Power switch 9 Status indicator LED 14 Power connector
5 Power indicator LED 10 Active LED
1. The management 0/0 interface is a Fast Ethernet interface designed for management traffic only.
2. Not supported at this time.
3. GigabiteEthernet interfaces, from right to left, GigabitEthernet 0/0, GigabitEthernet 0/1, GigabitEthernet 0/2, and
GigabitEthernet 0/3.
For more information on the Management Port, see the “Management-Only”
section in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Reference.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
2-7
Page 18
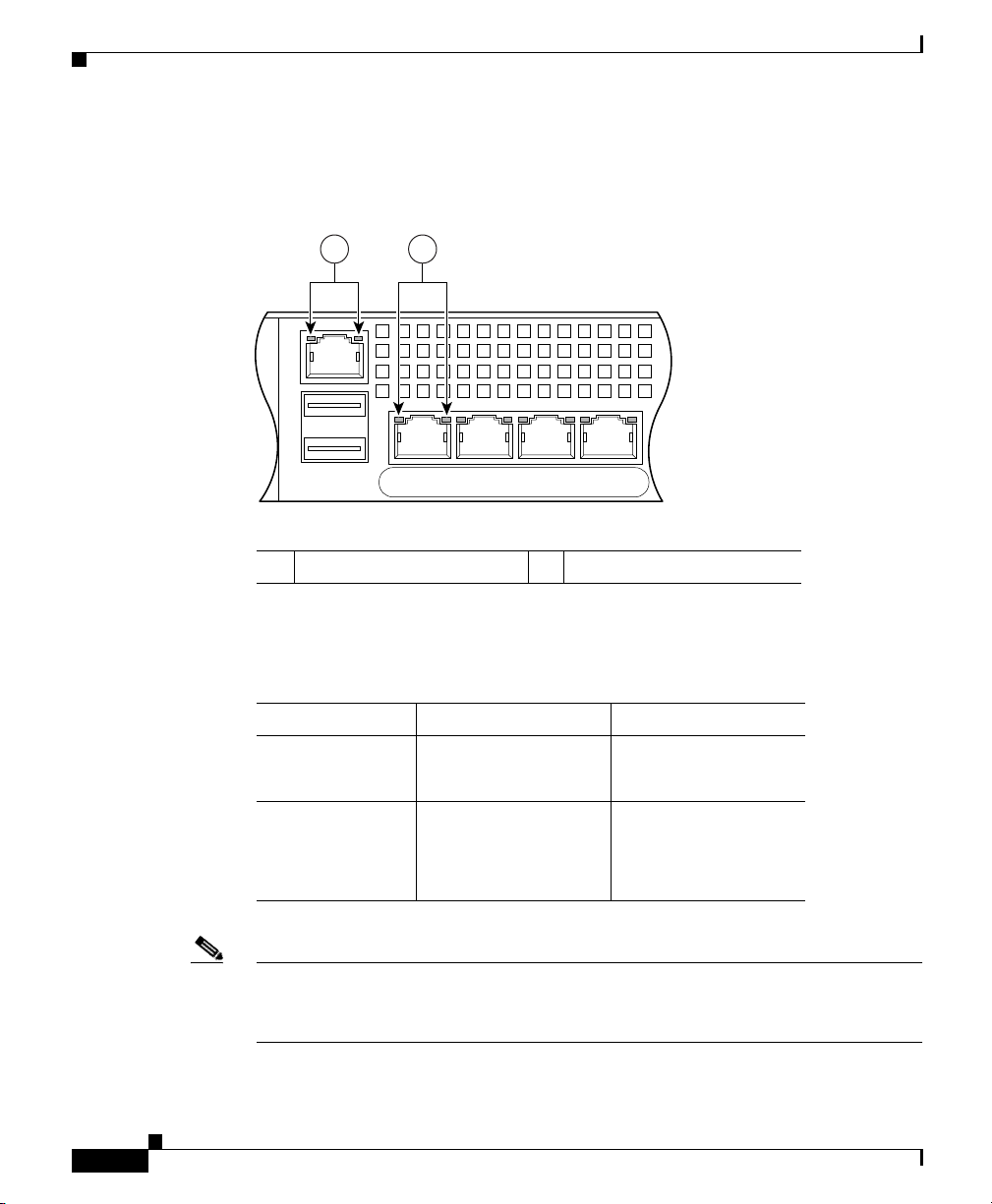
Ports and LEDs
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
Figure 2-6 shows the adaptive security appliance rear panel LEDs.
Figure 2-6 Rear Panel Link and Speed Indicator LEDs
21
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LNK SPD
LNK SPD2LNK SPD1LNK SPD
3
0
126917
1 MGMT indicator LEDs 2 Network interface LEDs
Table 2-1 lists the rear MGMT and Network interface LEDs.
Table 2-1 Link and Speed LEDs
Indicator Color Description
Left side Solid green
Green flashing
Right side Not lit
Green
Amber
Note The ASA 5510 adaptive security appliance only supports 10/100BaseTX. The
Physical link
Network activity
10 Mbps
100 Mbps
1000 Mbps
ASA 5520 adaptive security appliance and the ASA 5540 adaptive security
appliance support 1000BaseT.
2-8
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 19

Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
What to Do Next
Continue with one of the following chapters:
To Do This ... See ...
Install SSMs you purchased but that
have not yet been installed
Continue with connecting interface
cables
What to Do Next
Chapter 3, “Installing Optional SSMs”
Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Cables”
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
2-9
Page 20

What to Do Next
Chapter 2 Installing the Cisco ASA 5500
2-10
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 21

Installing Optional SSMs
This chapter provides information about installing optional SSMs (Security
Services Modules) and their components. You only need to use the procedures in
this chapter if you purchased an optional SSM but it is not yet installed.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Cisco 4GE SSM, page 3-1
• Cisco AIP SSM and CSC SSM, page 3-8
• What to Do Next, page 3-10
Cisco 4GE SSM
The 4GE Security Services Module (SSM) has eight Ethernet ports: four
10/100/1000 Mbps, copper, RJ-45 ports or four optional 1000 Mbps, Small
Form-Factor Pluggable (SFP) fiber ports.
CHA P T E R
3
78-17611-01
This section describes how to install and replace the Cisco 4GE SSM in the
adaptive security appliance. This section includes the following topics:
• 4GE SSM Components, page 3-2
• Installing the Cisco 4GE SSM, page 3-3
• Installing the SFP Modules, page 3-4
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
3-1
Page 22
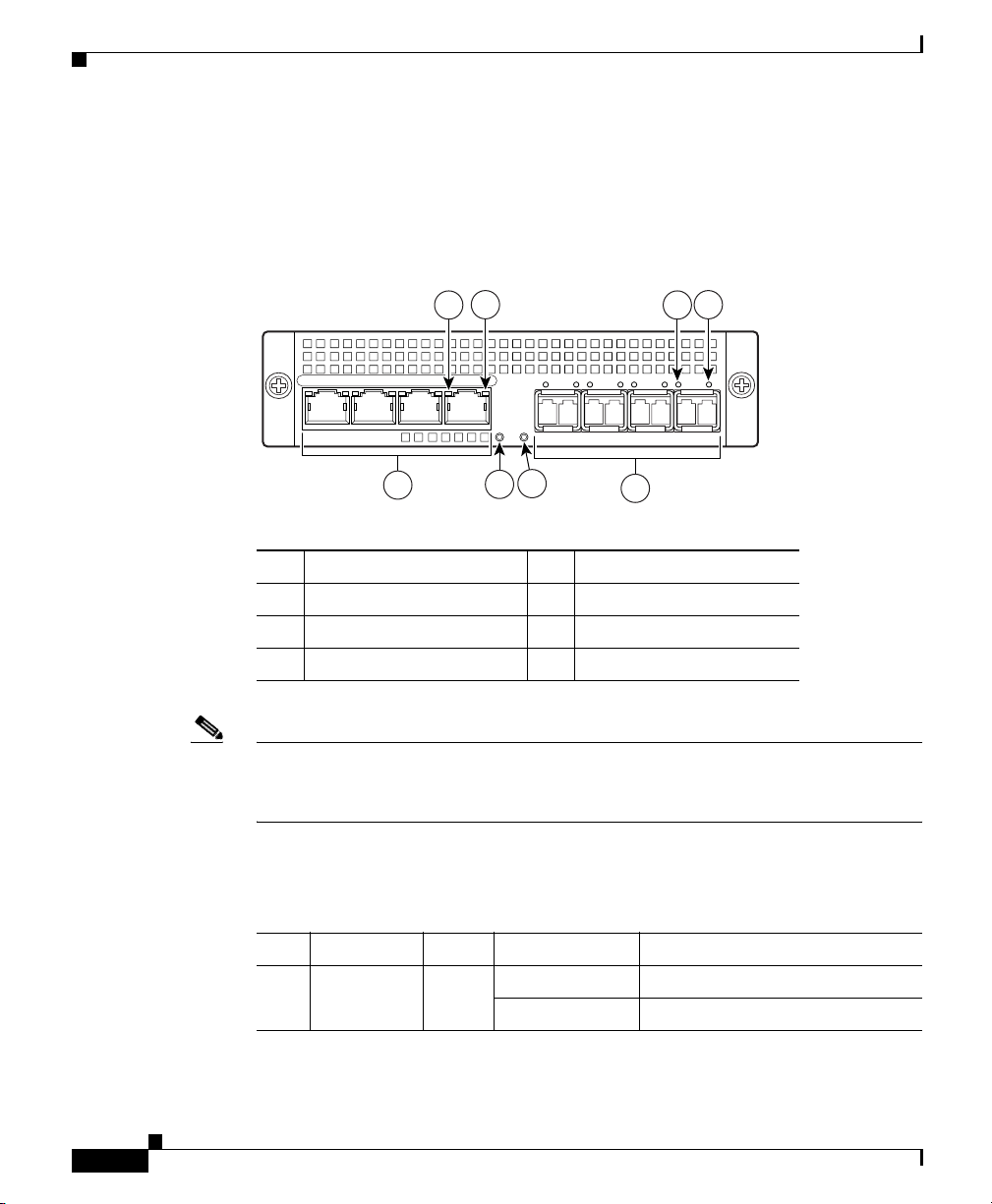
Cisco 4GE SSM
4GE SSM Components
Figure 3-1 lists the Cisco 4GE SSM ports and LEDs.
Figure 3-1 Cisco 4GE SSM Ports and LEDs
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
8
7
132983
LNK
Cisco SSM-4GE
3
2
SPD0123
5
1
4
6
1 RJ-45 ports 5 Status LED
2 RJ-45 Link LED 6 SFP ports
3 RJ-45 Speed LED 7 SFP Link LED
4 Power LED 8 SFP Speed LED
Note Figure 3-1 shows SFP modules installed in the port slots. You must order and
install the SFP modules if you want to use this feature. For more information on
SFP ports and modules, see the “Installing the SFP Modules” section on page 3-4.
Table 3-1 describes the Cisco 4GE SSM LEDs.
3-2
Table 3-1 Cisco 4GE SSM LEDs
LED Color State Description
2, 7 LINK Green Solid There is an Ethernet link.
Flashing There is Ethernet activity.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 23
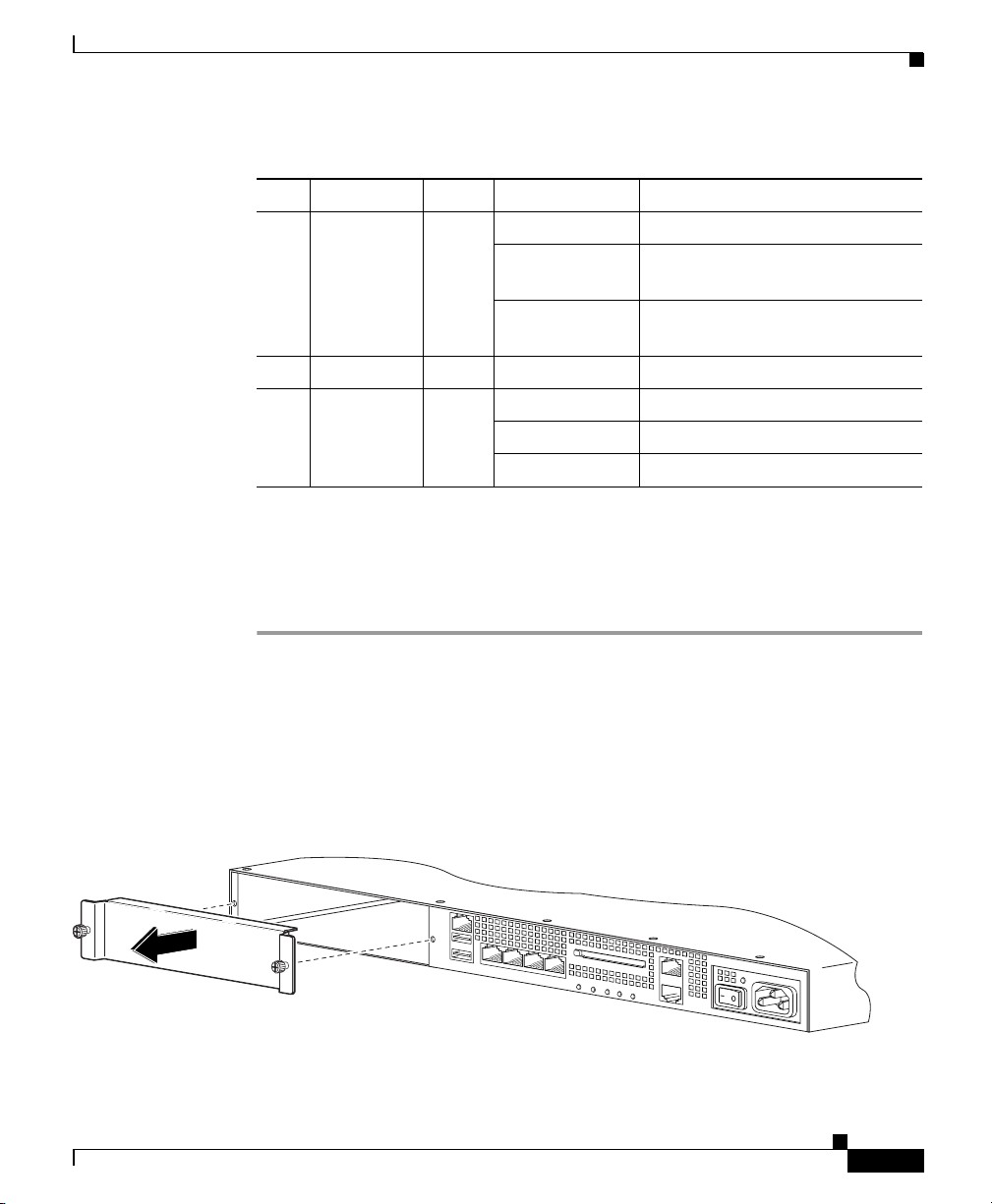
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
Table 3-1 Cisco 4GE SSM LEDs (continued)
LED Color State Description
3, 8 SPEED Off
Green
Amber
4 POWER Green On The system has power.
5 STATUS Green
Green
Amber
Installing the Cisco 4GE SSM
To install a new Cisco 4GE SSM for the first time, perform the following steps:
Cisco 4GE SSM
10 MB There is no network activity.
100 MB There is network activity at
100 Mbps.
1000 MB
(GigE)
There is network activity at
1000 Mbps.
Flashing The system is booting.
Solid The system booted correctly.
Solid The system diagnostics failed.
Step 1 Power off the adaptive security appliance.
Step 2 Locate the grounding strap from the accessory kit and fasten it to your wrist so
that it contacts your bare skin. Attach the other end to the chassis.
Step 3 Remove the two screws (as shown in Figure 3-2) at the left rear end of the chassis,
and remove the slot cover.
Figure 3-2 Removing the Screws from the Slot Cover
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LINK SPD
LINK SPD
3
LINK SPD
2
LINK SPD
1
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
FLASH
R
E
S
0
W
U
O
T
E
P
A
IV
T
N
T
S
P
C
V
A
FLASH
119642
3-3
Page 24
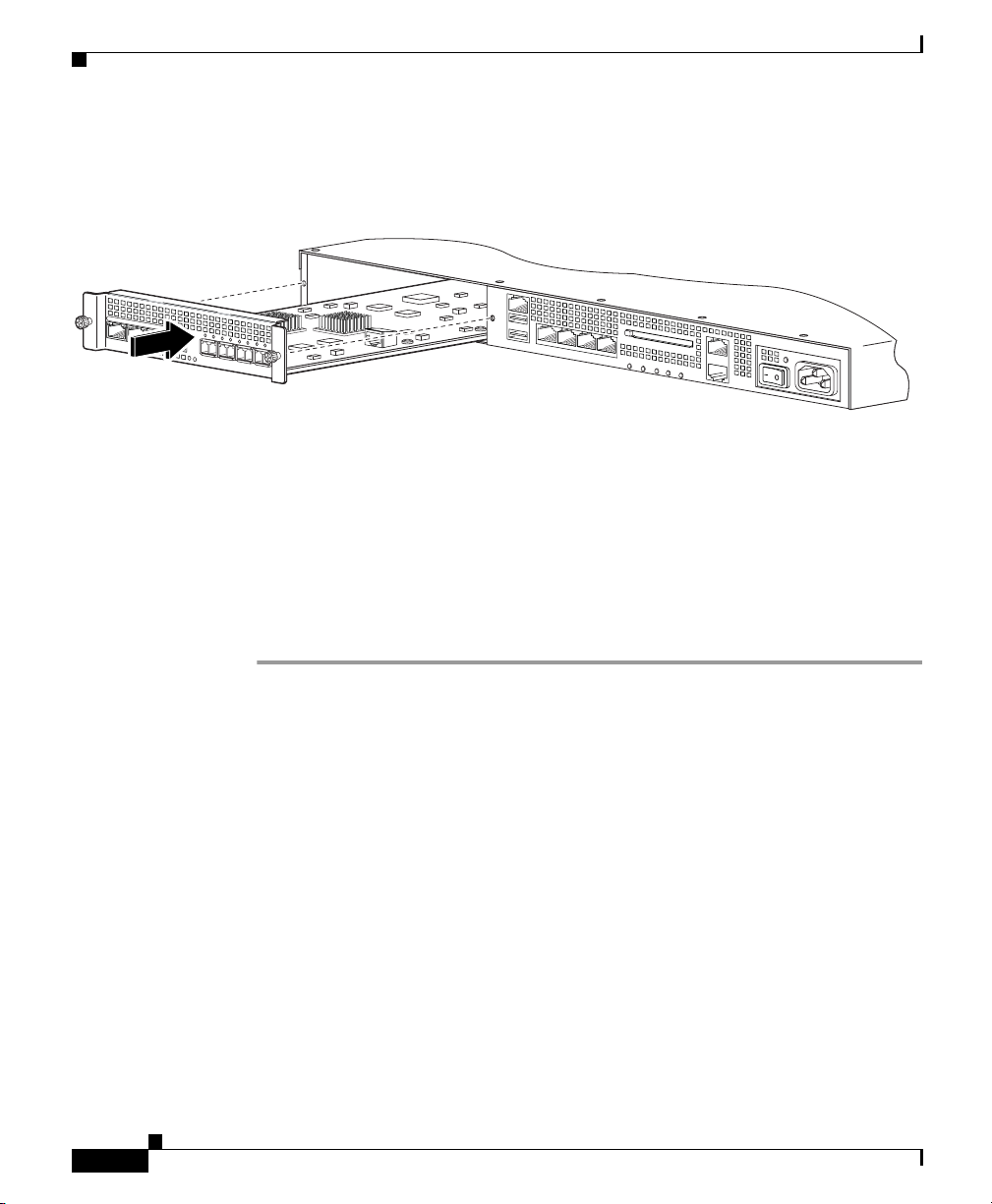
Cisco 4GE SSM
Step 4 Insert the Cisco 4GE SSM through the slot opening as shown in Figure 3-3.
Figure 3-3 Inserting the Cisco 4GE SSM into the Slot
MGMT
MGMT
USB2
LNK
23
1
C
isco
SPD0
S
SM
-4G
S
U
T
E
A
T
POWER
S
USB2
USB1
USB1
L
IN
K
S
P
3
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
F
LA
S
D
L
IN
K
S
P
D
L
IN
K
2
S
P
D
L
IN
K
1
0
H
S
P
D
ER
S
W
PO
STATU
VPN
ACTIVE
FLASH
132984
Step 5
Attach the screws to secure the Cisco 4GE SSM to the chassis.
Step 6 Power on the adaptive security appliance.
Step 7 Check the LEDs. If the Cisco 4GE SSM is installed properly the STATUS LED
flashes during boot up and is solid when operational.
Step 8 Connect one end of the RJ-45 cable to the port and the other end of the cable to your
network devices. For more information, see “Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface
Cables.”
Installing the SFP Modules
The SFP (Small Form-Factor Pluggable) is a hot-swappable input/output device
that plugs into the SFP ports. The following SFP module types are supported:
• Long wavelength/long haul 1000BASE-LX/LH (GLC-LH-SM=)
• Short wavelength 1000BASE-SX (GLC-SX-MM=)
This section describes how to install and remove the SFP modules in the adaptive
security appliance to provide optical Gigabit Ethernet connectivity. This section
contains the following topics:
• SFP Module, page 3-5
3-4
• Installing the SFP Module, page 3-6
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 25
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
SFP Module
The adaptive security appliance uses a field-replaceable SFP module to establish
Gigabit connections.
Note If you install an SFP module after the switch has powered on, you must reload the
adaptive security appliance to enable the SFP module.
Table 3-2 lists the SFP modules that are supported by the adaptive security
appliance.
Table 3-2 Supported SFP Modules
SFP Module Type of Connection Cisco Part Number
1000BASE-LX/LH Fiber-optic GLC-LH-SM=
1000BASE-SX Fiber-optic GLC-SX-MM=
Cisco 4GE SSM
The 1000BASE-LX/LH and 1000BASE-SX SFP modules are used to establish
fiber-optic connections. Use fiber-optic cables with LC connectors to connect to
an SFP module. The SFP modules support 850 to 1550 nm nominal wavelengths.
The cables must not exceed the required cable length for reliable communications.
Table 3-3 lists the cable length requirements.
Table 3-3 Cabling Requirements for Fiber-Optic SFP Modules
SFP Module
62.5/125 micron
Multimode 850
nm Fiber
50/125 micron
Multimode 850
nm Fiber
62.5/125 micron
Multimode
1310 nm Fiber
— — 550 m at
LX/LH
SX
78-17611-01
275 m at
200 Mhz-km
550 m at
500 Mhz-km
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
500 Mhz-km
———
50/125 micron
Multimode
1310 nm Fiber
550 m at
400 Mhz-km
9/125 micron
Single-mode
1310 nm Fiber
10 km
3-5
Page 26
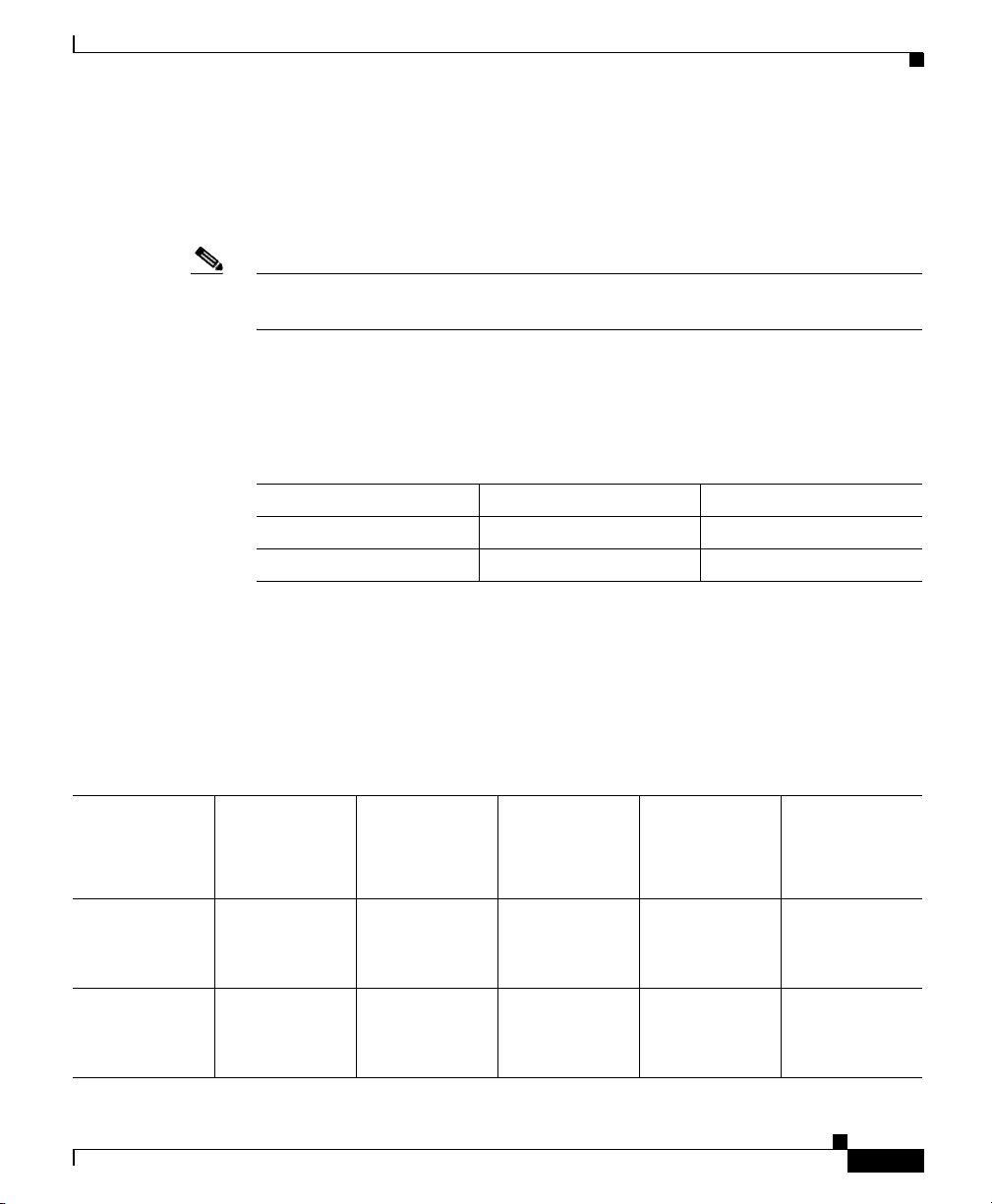
Cisco 4GE SSM
Note Only SFP modules certified by Cisco are supported on the adaptive security
Caution Protect your SFP modules by inserting clean dust plugs into the SFPs after the
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
Use only Cisco-certified SFP modules on the adaptive security appliance. Each
SFP module has an internal serial EEPROM that is encoded with security
information. This encoding provides a way for Cisco to identify and validate that
the SFP module meets the requirements for the adaptive security appliance.
appliance.
cables are extracted from them. Be sure to clean the optic surfaces of the fiber
cables before you plug them back in the optical bores of another SFP module.
Avoid getting dust and other contaminants into the optical bores of your SFP
modules: The optics do not work correctly when obstructed with dust.
Warning
Because invisible laser radiation may be emitted from the aperture of the port
when no cable is connected, avoid exposure to laser radiation and do not stare
into open apertures.
Installing the SFP Module
To install the SFP module in the Cisco 4GE SSM, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Line up the SFP module with the port and slide the SFP module into the port slot
until it locks into position as shown in Figure 3-4.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
3-6
Statement 70
78-17611-01
Page 27
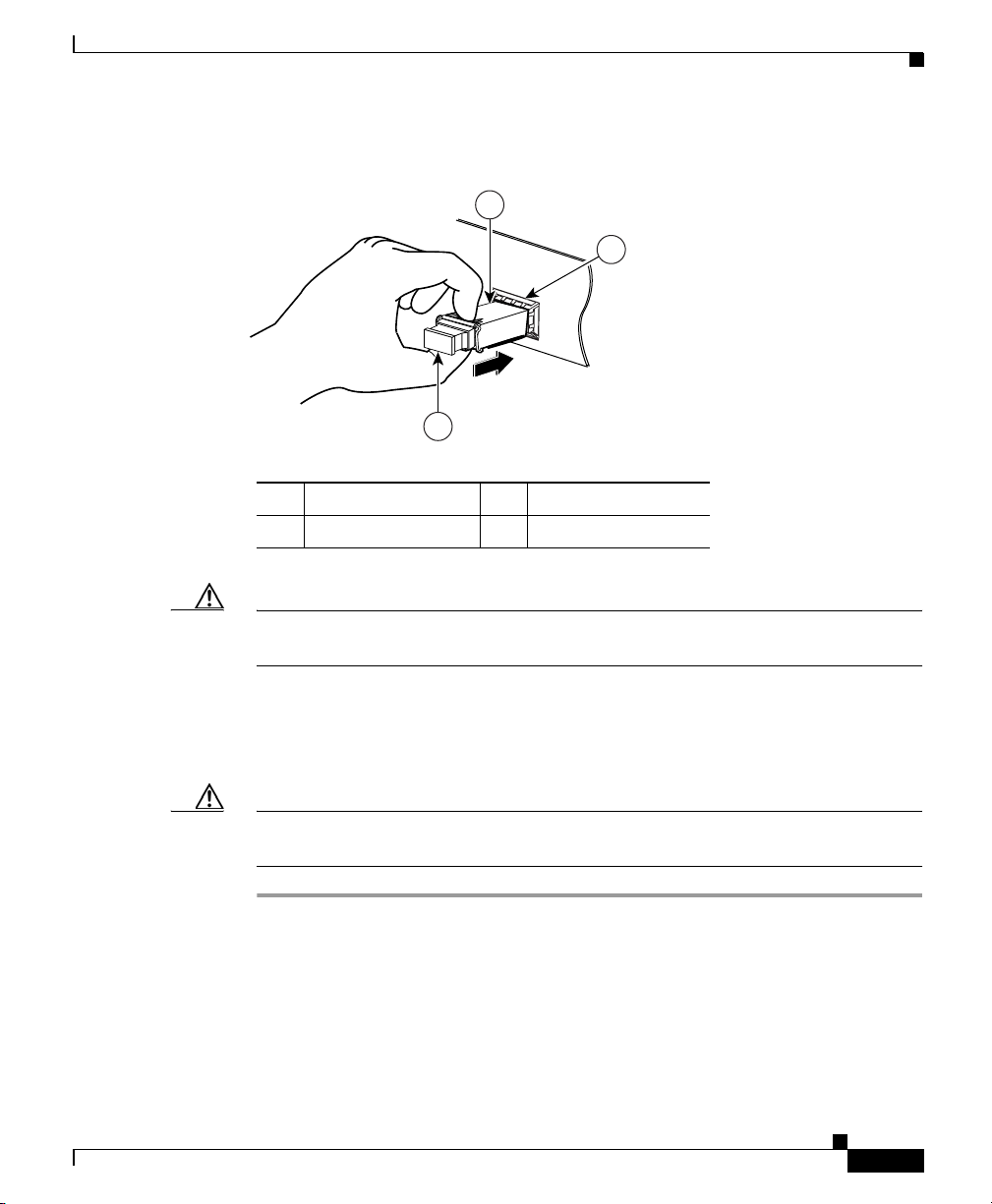
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
Figure 3-4 Installing an SFP Module
1 Optical port plug 3 SFP module
2 SFP port slot
Cisco 4GE SSM
3
2
132985
1
78-17611-01
Caution Do not remove the optical port plugs from the SFP until you are ready to connect
the cables.
Step 2 Remove the Optical port plug; then connect the network cable to the SFP module.
Connect the other end of the cable to your network. For more information on
connecting the cables, see Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface Cables.”
Caution The latching mechanism used on many SFPs locks them into place when cables
are connected. Do not pull on the cabling in an attempt to remove the SFP.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
3-7
Page 28
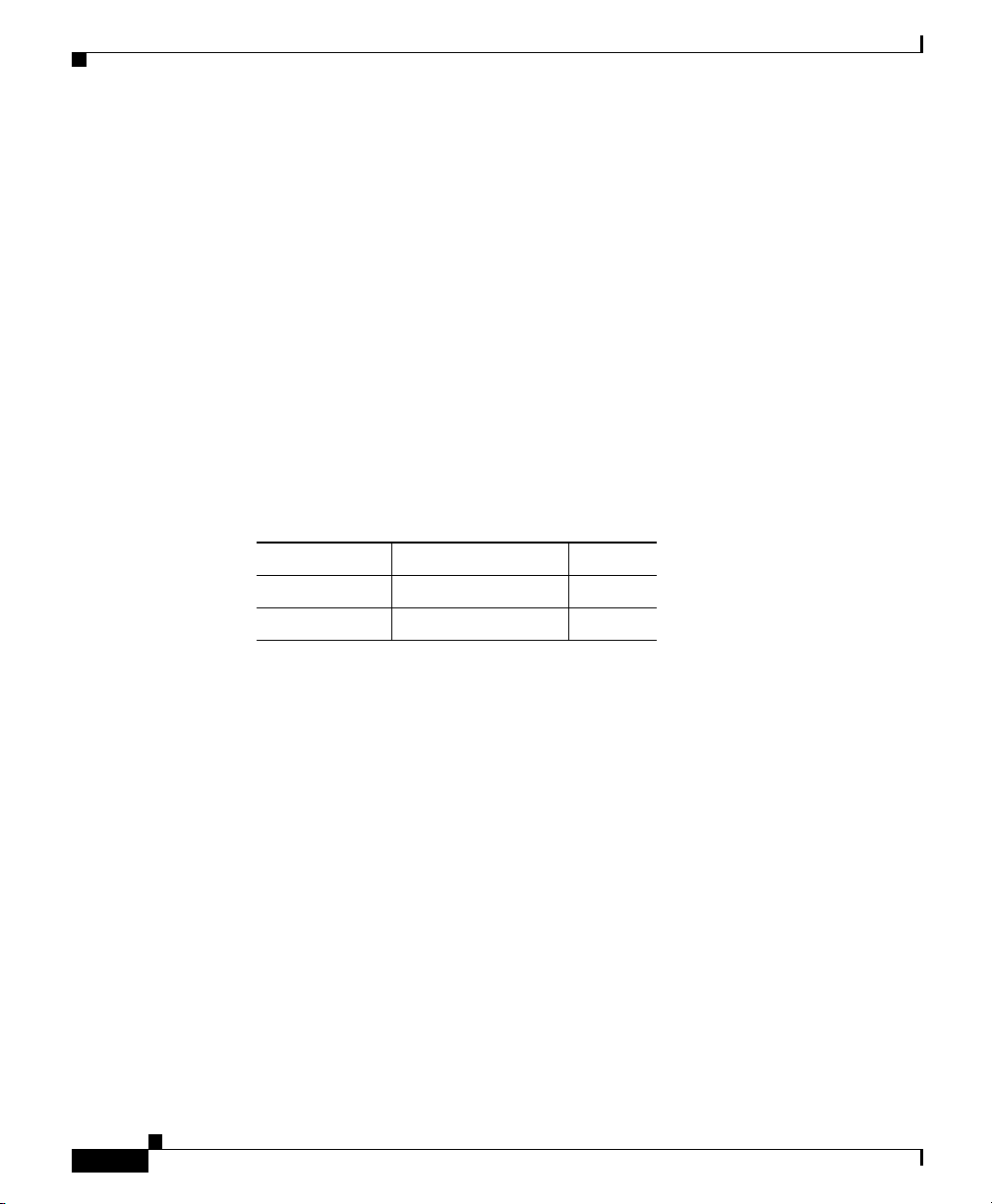
Cisco AIP SSM and CSC SSM
Cisco AIP SSM and CSC SSM
The ASA 5500 series adaptive security appliance supports the AIP SSM
(Advanced Inspection and Prevention Security Services Module) and the CSC
SSM (Content Security Control Security Services Module), also referred to as the
intelligent SSM.
The AIP SSM runs advanced IPS software that provides security inspection.
There are two models of the AIP SSM: the AIP SSM 10 and the AIP SSM 20. Both
types look identical, but the AIP SSM 20 has a faster processor and more memory
than the AIP SSM 10. Only one module (the AIP SSM 10 or the AIP SSM 20) can
populate the slot at a time.
Table 3-4 lists the memory specifications for the AIP SSM 10 and the
AIP SSM 20.
Table 3-4 SSM Memory Specifications
SSM CPU DRAM
AIP SSM 10 2.0 GHz Celeron 1.0 GB
AIP SSM 20 2.4 GHz Pentium 4 2.0 GB
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
3-8
For more information on the AIP SSM, see the “Managing the AIP SSM” section
in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide.
The CSC SSM runs Content Security and Control software. The CSC SSM
provides protection against viruses, spyware, spam, and other unwanted traffic.
For more information on the CSC SSM, see the “Managing the CSC SSM” section
in the Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide.
This section describes how to install and replace the SSM in the adaptive security
appliance. Figure 3-5 lists the SSM LEDs.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 29
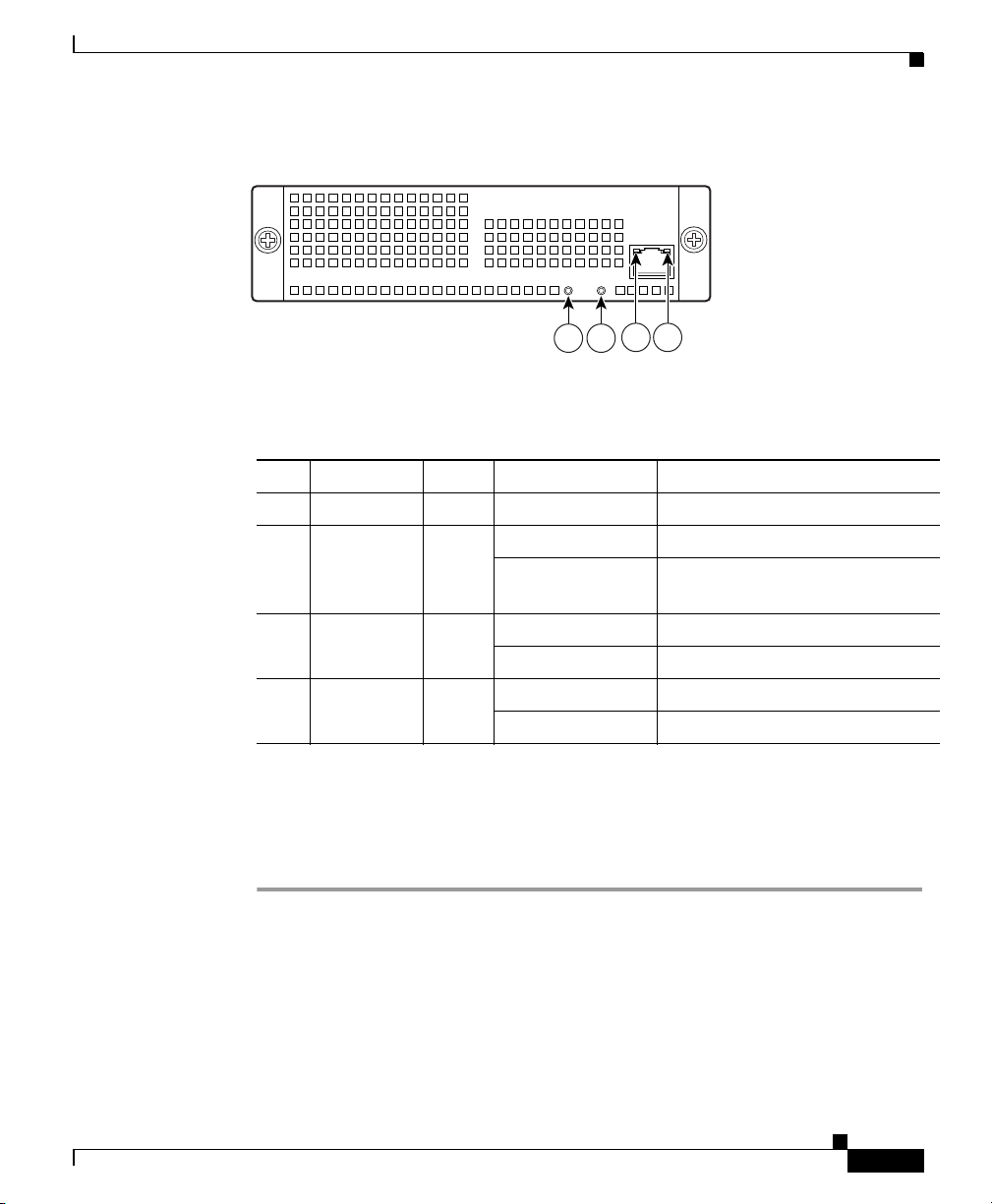
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
Figure 3-5 SSM LEDs
PWR
STATUS
LINK/ACT
Cisco AIP SSM and CSC SSM
SPEED
119644
Table 3-5 describes the SSM LEDs.
Ta b l e 3 - 5 S S M L E D s
1 PWR Green On The system has power.
2 STATUS Green Flashing The system is booting.
3 LINK/ACT Green Solid There is an Ethernet link.
4 SPEED Green
Installing an SSM
To install a new SSM, perform the following steps:
1 2
3 4
LED Color State Description
Solid The system has passed power-up
diagnostics.
Flashing There is Ethernet activity.
100 MB There is network activity.
Amber
1000 MB (GigE) There is network activity.
78-17611-01
Step 1 Power off the adaptive security appliance.
Step 2 Locate the grounding strap from the accessory kit and fasten it to your wrist so
that it contacts your bare skin. Attach the other end to the chassis.
Step 3 Remove the two screws (as shown in Figure 3-6) at the left rear end of the chassis,
and remove the slot cover.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
3-9
Page 30
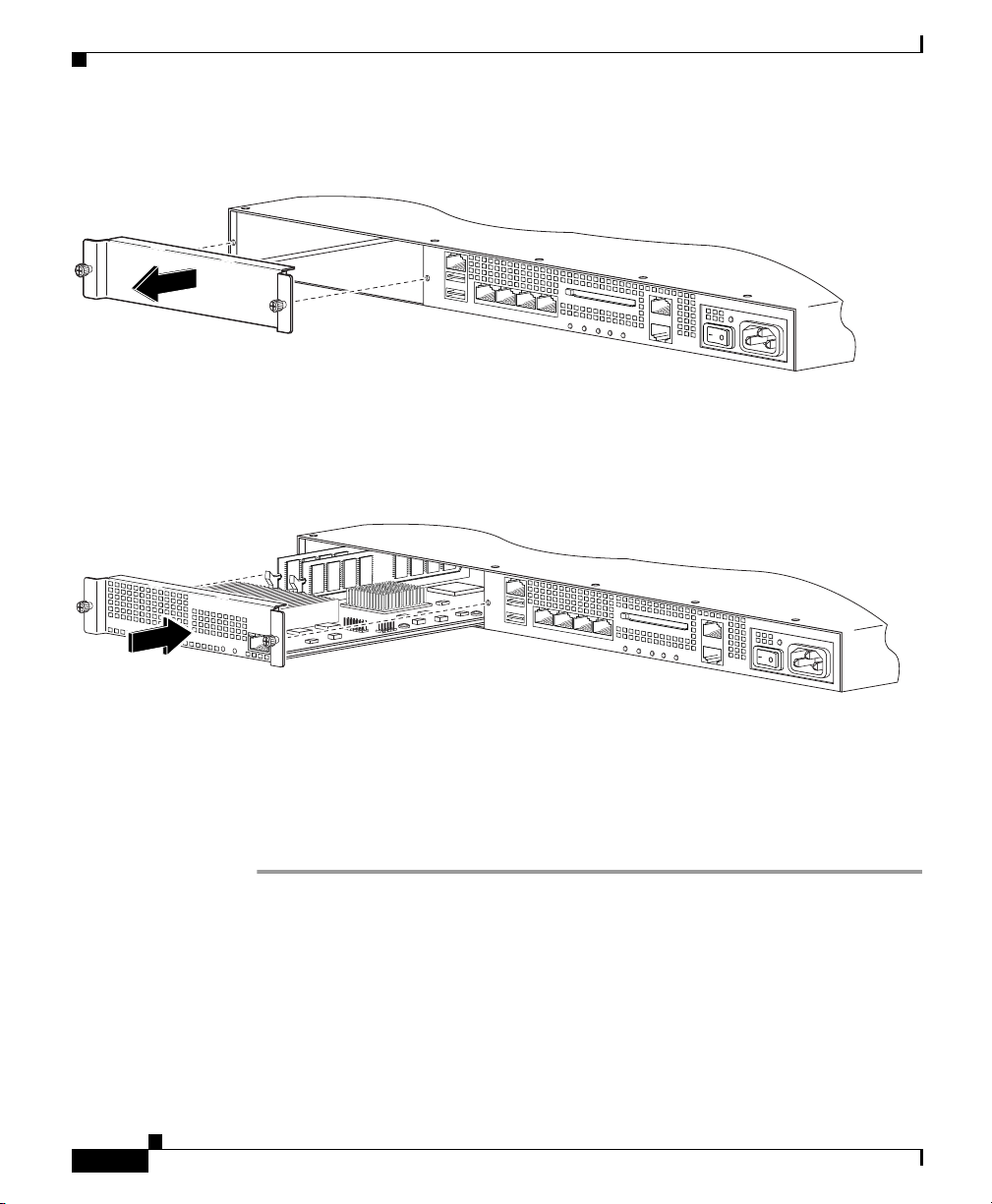
What to Do Next
Figure 3-6 Removing the Screws from the Slot Cover
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LINK SPD
LINK SPD
3
LINK SPD
2
LINK SPD
1
0
Chapter 3 Installing Optional SSMs
FLASH
POWER
H
STATUS
S
VPN
ACTIVE
A
L
F
119642
Step 4
Insert the SSM into the slot opening as shown in Figure 3-7.
Figure 3-7 Inserting the SSM into the Slot
SPEED
LINK/ACT
PWR
STATUS
Step 5 Attach the screws to secure the SSM to the chassis.
Step 6 Power on the adaptive security appliance. Check the LEDs. If the SSM is installed
properly the POWER LED is solid green and the STATUS LED flashes green.
Step 7 Connect one end of the RJ-45 cable to the port and the other end of the cable to your
network devices.
What to Do Next
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LINK SPD
LINK SPD
3
LINK SPD
2
LINK SPD
1
0
POWER
STATUS
VPN
ACTIVE
FLASH
119643
3-10
Continue with Chapter 4, “Connecting Interface Cables.”
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 31

CHA P T E R
4
Connecting Interface Cables
This chapter describes how to connect the cables to the Console, Auxiliary,
Management, Cisco 4GE SSM, and SSM ports. In this document, SSM refers to an
intelligent SSM, the AIP SSM, or the CSC SSM.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Connecting Cables to Interfaces, page 4-2
• What to Do Next, page 4-10
Note The 4GE SSM, AIP SSM, and CSC SSM are optional security services modules.
Skip these steps if your adaptive security appliance does not include these
modules.
78-17611-01
Warning
Caution Read the safety warnings in the Regulatory Compliance and Safety Information for
Only trained and qualified personnel should install, replace, or service this
equipment. Statement 49
the Cisco ASA 5500 Series and follow proper safety procedures when performing
these steps.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-1
Page 32

Connecting Cables to Interfaces
Connecting Cables to Interfaces
To connect cables to the interfaces, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Place the chassis on a flat, stable surface, or in a rack (if you are rack-mounting it).
Step 2 Before connecting a computer or terminal to the ports, check to determine the baud
rate of the serial port. The baud rate must match the default baud rate (9600 baud) of
the Console port of the adaptive security appliance. Set up the terminal as follows:
9600 baud (default), 8 data bits, no parity, 1 stop bits, and Flow Control (FC) =
Hardware.
Step 3 Connect the cables to the ports.
a. Management port–The adaptive security appliance has a dedicated
management interface referred to as the Management0/0 port. The
Management0/0 port is a Fast Ethernet interface with a dedicated port used
only for traffic management. Similar to the Console port, but the Management
port accepts only incoming traffic to the adaptive security appliance.
Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
4-2
Note You can configure any interface to be a management-only interface using
the management-only command. You can also disable management-only
mode on the management interface. For more information about this
command, see the management-only command in the Cisco Security
Appliance Command Reference.
–
Connect one RJ-45 connector to the Management0/0 port, as shown in
Figure 4-1.
–
Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to the Ethernet port on your
computer.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 33

Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
Figure 4-1 Connecting to the Management Port
MGMT
USB2
USB1
1 Management port 2 RJ-45 to RJ-45 Ethernet cable
Connecting Cables to Interfaces
1
LNK SPD2LNK SPD1LNK SPD
LNK SPD
3
0
92684
2
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-3
Page 34

Connecting Cables to Interfaces
b. Console port
Figure 4-2 Connecting the Console Cable
Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
–
Connect the serial console cable as shown in Figure 4-2. The console
cable has a DB-9 connector on one end for the serial port on your
computer, and the other end is an RJ-45 connector.
–
Connect the RJ-45 connector to the Console port on the adaptive security
appliance.
–
Connect the other end of the cable, the DB-9 connector, to the console
port on your computer.
CONSOLE
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FLASH
VPN
FLASH
AUX
1
2
1 RJ-45 Console port 2 RJ-45 to DB-9 console cable
126982
4-4
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 35

Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
c. Auxiliary port
–
Connect the serial console cable as shown in Figure 4-2. The console
cable has a DB-9 connector on one end for the serial port on your
computer, and the other end is an RJ-45 connector.
–
Connect the RJ-45 connector to the Auxiliary port (labeled AUX) on the
adaptive security appliance, as shown in Figure 4-3.
–
Connect the other end of the cable, the DB-9 connector, to the serial port
on your computer.
Figure 4-3 Connecting to the AUX Port
POWER
STATUS
ACTIVE
FLASH
Connecting Cables to Interfaces
CONSOLE
AUX
VPN
FLASH
1
78-17611-01
2
92686
1 RJ-45 AUX port 2 RJ-45 to DB-9 console cable
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-5
Page 36

Connecting Cables to Interfaces
d. Cisco 4GE SSM
• Ethernet port
Note The Cisco 4GE SSM is optional; this connection is necessary only if you
Figure 4-4 Connecting to the RJ-45 port
Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
–
Connect one RJ-45 connector to the Ethernet port of the Cisco 4GE SSM
as shown in Figure 4-4.
–
Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to your network device, such
as a router, switch or hub.
have installed the Cisco 4GE SSM on the adaptive security appliance.
LN
K
Cisco SSM-4GE
123
0
S
PD
S
ER
U
T
A
T
POW
S
MGMT
MGMT
USB1
USB2
USB2
USB1
1
4-6
2
143147
1 Ethernet ports 2 RJ-45 connector
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 37

Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
• SFP modules
–
Insert and slide the SFP module into the SFP port until you hear a click.
The click indicates that the SFP module is locked into the port.
–
Remove the optical port plugs from the installed SFP as shown in Figure 4-5.
Figure 4-5 Removing the Optical Port Plug
1
1 Optical port plug 2 SFP module
–
Connect the LC connector to the SFP module as shown in Figure 4-6.
Connecting Cables to Interfaces
2
S
U
T
A
T
S
143146
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-7
Page 38

Connecting Cables to Interfaces
Figure 4-6 Connecting the LC Connector
1 LC connector 2 SFP module
Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
L
N
K
Cisco SSM-4GE
123
0
S
PD
R
S
E
U
T
A
T
POW
S
MGMT
MGMT
USB1
USB2
USB2
USB1
143148
2
1
4-8
–
Connect the other end to your network devices, such as routers, switches,
or hubs.
e. SSM
–
Connect one RJ-45 connector to the management port on the SSM, as
shown in Figure 4-7.
–
Connect the other end of the RJ-45 cable to your network devices.
Note SSMs are optional; this connection is necessary only if you have installed
an SSM on the adaptive security appliance.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 39

Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
Figure 4-7 Connecting to the Management Port
1 SSM management port 2 RJ-45 to RJ-45 cable
Connecting Cables to Interfaces
MGMT
SPEED
MGMT
USB1
USB2
USB2
USB1
LINK?ACT
ER
W
PO
STATUS
1
2
143149
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-9
Page 40

What to Do Next
Chapter 4 Connecting Interface Cables
f. Ethernet ports
–
Connect the RJ-45 connector to the Ethernet port as shown in Figure 4-8.
–
Connect the other end of the Ethernet cable to your network device, such
as a router, switch or hub.
Figure 4-8 Connecting Cables to Network Interfaces
MGMT
USB2
USB1
LNK SPD2LNK SPD1LNK SPD
LNK SPD
3
1
0
92685
2
1 RJ-45 Ethernet ports 2 RJ-45 connector
Step 4
Connect the power cord to the adaptive security appliance and plug the other end
to the power source.
Step 5 Power on the chassis.
What to Do Next
Continue with Chapter 5, “Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance.”
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
4-10
78-17611-01
Page 41

CHA P T E R
5
Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
This chapter describes the initial configuration of the adaptive security appliance.
You can perform the configuration steps using either the browser-based Cisco
Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) or the command-line interface
(CLI). However, the procedures in this chapter refer to the method using ASDM.
Note To use ASDM, you must have a DES license or a 3DES-AES license. For more
information, see Appendix A, “Obtaining a DES License or a 3DES-AES
License.”
This chapter includes the following sections:
• About the Factory-Default Configuration, page 5-1
• Before Launching the Startup Wizard, page 5-3
• Using the Startup Wizard, page 5-4
• What to Do Next, page 5-5
About the Factory-Default Configuration
Cisco adaptive security appliances are shipped with a factory-default configuration
that enables quick startup. This configuration meets the needs of most small and
medium business networking environments.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
5-1
Page 42

Chapter 5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
About the Adaptive Security Device Manager
By default, the adaptive security appliance Management interface is configured with
a default DHCP address pool. This configuration enables a client on the inside
network to obtain a DHCP address from the adaptive security appliance to connect to
the appliance. Administrators can then configure and manage the adaptive security
appliance using ASDM. Based on your network security policy, you should also
consider configuring the adaptive security appliance to deny all ICMP traffic through
the outside interface or any other interface that is necessary.
About the Adaptive Security Device Manager
5-2
The Adaptive Security Device Manager (ASDM) is a feature-rich graphical
interface that enables you to manage and monitor the adaptive security appliance.
Its web-based design provides secure access so that you can connect to and
manage the adaptive security appliance from any location by using a web browser.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 43

Chapter 5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
Before Launching the Startup Wizard
In addition to its complete configuration and management capability, ASDM
features intelligent wizards to simplify and accelerate the deployment of the
adaptive security appliance.
To use ASDM, you must have a DES license or a 3DES-AES license. In addition,
Java and JavaScript must be enabled in your web browser.
In addition to the ASDM web configuration tool, you can configure the adaptive
security appliance by using the command-line interface. For more information, see
the Cisco Security Appliance Command Line Configuration Guide and the Cisco
Security Appliance Command Reference.
Before Launching the Startup Wizard
Before you launch the Startup Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Obtain a DES license or a 3DES-AES license.
To run ASDM, you must have a DES license or a 3DES-AES license. If you did
not purchase one of these licenses with the adaptive security appliance, see
Appendix A, “Obtaining a DES License or a 3DES-AES License” for information
about how to obtain and activate one.
78-17611-01
Step 2 Enable Java and Javascript in your Web browser.
Step 3 Gather the following information:
• A unique hostname to identify the adaptive security appliance on your
network.
• The IP addresses of your outside interface, inside interface, and any other
interfaces.
• The IP addresses to use for NAT or PAT configuration.
• The IP address range for the DHCP server.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
5-3
Page 44

Using the Startup Wizard
Using the Startup Wizard
ASDM includes a Startup Wizard to simplify the initial configuration of your
adaptive security appliance. With a few steps, the Startup Wizard enables you to
configure the adaptive security appliance so that it allows packets to flow securely
between the inside network (GigabitEthernet0/1) and the outside network
(GigabitEthernet0/0).
To use the Startup Wizard to set up a basic configuration for the adaptive security
appliance, perform the following steps:
Step 1 If you have not already done so, perform one of the following steps:
• If you have an ASA 5520 or 5540, connect the inside GigabitEthernet0/1
interface to a switch or hub by using the Ethernet cable. To this same switch,
connect a PC for configuring the adaptive security appliance.
• If you have an ASA 5510, connect the inside Ethernet 1 interface to a switch
or hub by using the Ethernet cable. To this same switch, connect a PC for
configuring the adaptive security appliance.
Step 2 Configure your PC to use DHCP (to receive an IP address automatically from the
adaptive security appliance), or assign a static IP address to your PC by selecting
an address out of the 192.168.1.0 network. (Valid addresses are 192.168.1.2 through
192.168.1.254, with a mask of 255.255.255.0 and default route of 192.168.1.1.)
Chapter 5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
5-4
Note The inside interface of the adaptive security appliance is assigned
192.168.1.1 by default, so this address is unavailable.
Step 3 Perform one of the following steps:
• If you have an ASA 5520 or 5540, check the LINK LED on the
GigabitEthernet0/1 interface.
• If you have an ASA 5510, check the LINK LED on the Ethernet 1 interface.
When a connection is established, the LINK LED interface on the adaptive security
appliance and the corresponding LINK LED on the switch or hub becomes solid
green.
Step 4 Launch the Startup Wizard.
a. On the PC connected to the switch or hub, launch an Internet browser.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 45

Chapter 5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
b. In the address field of the browser, enter this URL: https://192.168.1.1/.
Note The adaptive security appliance ships with a default IP address of
192.168.1.1. Remember to add the “s” in “https” or the connection
fails. HTTPS (HTTP over SSL) provides a secure connection between
your browser and the adaptive security appliance.
Step 5 In the dialog box that requires a username and password, leave both fields empty.
Press Enter.
Step 6 Click Ye s to accept the certificates. Click Ye s for all subsequent authentication
and certificate dialog boxes.
ASDM starts.
Step 7 From the Wizards menu at the top of the ASDM window, choose Startup Wizard.
Step 8 Follow the instructions in the Startup Wizard to set up your adaptive security
appliance.
For information about any field in the Startup Wizard, click Help at the bottom of
the window.
What to Do Next
What to Do Next
Next, configure the adaptive security appliance for your deployment using one or
more of the following chapters:
To Do This ... See ...
Configure the adaptive security
appliance to protect a DMZ web server
Configure the adaptive security
appliance for remote-access VPN
Configure the adaptive security
appliance for Site-to-Site VPN
78-17611-01
Chapter 6, “Scenario: DMZ
Configuration”
Chapter 7, “Scenario: Remote-Access
VPN Configuration”
Chapter 8, “Scenario: Site-to-Site
VPN Configuration”
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
5-5
Page 46

What to Do Next
Chapter 5 Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance
To Do This ... See ...
Configure the AIP SSM for intrusion
Chapter 9, “Configuring the AIP SSM”
prevention
Configure the CSC SSM for content
security
Chapter 10, “Configuring the CSC
SSM”
5-6
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 47

CHA P T E R
Scenario: DMZ Configuration
This chapter describes a configuration scenario in which the adaptive security
appliance is used to protect network resources located in a demilitarized zone
(DMZ). A DMZ is a separate network located in the neutral zone between a
private (inside) network and a public (outside) network.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Example DMZ Network Topology, page 6-1
• Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment, page 6-4
• What to Do Next, page 6-24
Example DMZ Network Topology
6
78-17611-01
The example network topology shown in Figure 6-1 is typical of most DMZ
implementations of the adaptive security appliance.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-1
Page 48

Example DMZ Network Topology
Figure 6-1 Network Layout for DMZ Configuration Scenario
Security
HTTP client
inside interface
10.10.10.0
(private address)
10.10.10.0
(private address)
Appliance
outside interface
209.165.200.225
(public address)
DMZ interface
10.30.30.0
(private address)
Internet
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
HTTP client
HTTP client
DMZ Web
Server
Private IP address: 10.30.30.30
Public IP address: 209.165.200.226
132064
This example scenario has the following characteristics:
• The web server is on the DMZ interface of the adaptive security appliance.
• HTTP clients on the private network can access the web server in the DMZ
and can also communicate with devices on the Internet.
• Clients on the Internet are permitted HTTP access to the DMZ web server; all
other traffic is denied.
• The network has two routable IP addresses that are publicly available: one for
the outside interface of the adaptive security appliance (209.165.200.225),
and one for the public IP address of the DMZ web server (209.165.200.226).
Figure 6-2 shows the outgoing traffic flow of HTTP requests from the private
network to both the DMZ web server and to the Internet.
6-2
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 49

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Figure 6-2 Outgoing HTTP Traffic Flow from the Private Network
Internal IP address
translated to address
of outside interface
HTTP client
Security
Appliance
Example DMZ Network Topology
10.10.10.0
(private address)
Internal IP address
translated to address
HTTP request
HTTP request
from IP pool
DMZ network
DMZ Web
Server
outside interface
209.165.200.225
(public address)
Private IP address: 10.30.30.30
Public IP address: 209.165.200.226
Internet
HTTP client
HTTP client
In Figure 6-2, the adaptive security appliance permits HTTP traffic originating
from inside clients and destined for both the DMZ web server and devices on the
Internet. To permit the traffic through, the adaptive security appliance
configuration includes the following:
• Access control rules permitting traffic destined for the DMZ web server and
for devices on the Internet.
• Address translation rules translating private IP addresses so that the private
addresses are not visible to the Internet.
153777
78-17611-01
For traffic destined for the DMZ web server, private IP addresses are
translated to an address from an IP pool.
For traffic destined for the Internet, private IP addresses are translated to the
public IP address of the adaptive security appliance. Outgoing traffic appears
to come from this address.
Figure 6-3 shows HTTP requests originating from the Internet and destined for
the public IP address of the DMZ web server.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-3
Page 50

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Figure 6-3 Incoming HTTP Traffic Flow From the Internet
HTTP request
1
sent to public address
of DMZ web server.
Internet
Security
Appliance
2
Incoming request
destined for public
address of DMZ web
server intercepted.
3
Destination IP address
translated to the private IP
address of the web server.
4
Web server receives
request for content.
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
HTTP client
HTTP client
DMZ Web
Server
Private IP address: 10.30.30.30
Public IP address: 209.165.200.226
153779
To permit incoming traffic to access the DMZ web server, the adaptive security
appliance configuration includes the following:
• An address translation rule translating the public IP address of the DMZ web
server to the private IP address of the DMZ web server.
• An access control rule permitting incoming HTTP traffic that is destined for
the DMZ web server.
The procedures for creating this configuration are detailed in the remainder of this
chapter.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ
Deployment
This section describes how to use ASDM to configure the adaptive security
appliance for the configuration scenario shown in Figure 6-1. The procedure uses
sample parameters based on the scenario.
6-4
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 51

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
This configuration procedure assumes that the adaptive security appliance already
has interfaces configured for the inside interface, the DMZ interface, and the
outside interface. Set up interfaces of the adaptive security appliance by using the
Startup Wizard in ASDM. Be sure that the DMZ interface security level is set
between 0 and 100. (A common choice is 50.)
For more information about using the Startup Wizard, see Chapter 5,
“Configuring the Adaptive Security Appliance.”
The section includes the following topics:
• Configuration Requirements, page 6-5
• Starting ASDM, page 6-6
• Creating IP Pools for Network Address Translation, page 6-7
• Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with the DMZ Web
Server, page 6-12
• Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with Devices on the
Internet, page 6-15
• Configuring an External Identity for the DMZ Web Server, page 6-16
• Providing Public HTTP Access to the DMZ Web Server, page 6-18
The following sections provide detailed instructions for how to perform each step.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Configuration Requirements
Configuring the adaptive security appliance for this DMZ deployment requires the
following configuration tasks:
• For the internal clients to have HTTP access to the DMZ web server, you must
create a pool of IP addresses for address translation and identify which clients
should use addresses from the pool. To accomplish this task, you should
configure the following:
–
A pool of IP addresses for the DMZ interface. In this scenario, the IP pool
is 10.30.30.50–10.30.30.60.
–
A dynamic NAT translation rule for the inside interface that specifies
which client IP addresses can be assigned an address from the IP pool.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
6-5
Page 52

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
• For the internal clients to have access to HTTP and HTTPS resources on the
Internet, you must create a rule that translates the real IP addresses of internal
clients to an external address that can be used as the source address.
To accomplish this task, you should configure a PAT translation rule (port
address translation rule, sometimes called an interface NAT) for the internal
interface that translates internal IP addresses to the external IP address of the
adaptive security appliance.
In this scenario, the internal address to be translated is that of a subnet of the
private network (10.10.10.0). Addresses from this subnet are translated to the
public address of the adaptive security appliance (209.165.200.225).
• For external clients to have HTTP access to the DMZ web server, you must
configure an external identity for the DMZ web server and an access rule that
permits HTTP requests coming from clients on the Internet. To accomplish
this task, you should configure the following:
–
Create a static NAT rule. This rule translates the real IP address of the
DMZ web server to a single public IP address. In this scenario, the public
address of the web server is 209.165.200.226.
–
Create a security access rule permitting traffic from the Internet if the
traffic is an HTTP request destined for the public IP address of the DMZ
web server.
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Starting ASDM
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-6
To run ASDM in a web browser, enter the factory-default IP address in the address
field: https://192.168.1.1/admin/.
Note Remember to add the “s” in “https” or the connection fails. HTTPS
(HTTP over SSL) provides a secure connection between your browser and
the adaptive security appliance.
The Main ASDM window appears.
78-17611-01
Page 53

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Creating IP Pools for Network Address Translation
The adaptive security appliance uses Network Address Translation (NAT) and
Port Address Translation (PAT) to prevent internal IP addresses from being
exposed externally. This procedure describes how to create a pool of IP addresses
that the DMZ interface and outside interface can use for address translation.
A single IP pool can contain both NAT and PAT entries, and it can contain entries
for more than one interface.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
6-7
Page 54

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
To configure a pool of IP addresses that can be used for network address
translation, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the ASDM window, click the Configuration tool.
a. In the Features pane, click NAT.
The NAT Configuration screen appears.
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-8
b. In the right pane, click the Global Pools tab.
c. Click Add to create a new global pool for the DMZ interface.
The Add Global Address Pool dialog box appears.
Note For most configurations, IP pools are added to the less secure, or public,
interfaces.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 55

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
d. From the Interfaces drop-down list, choose DMZ.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
e. To create a new IP pool, enter a unique Pool ID. In this scenario, the Pool ID
is 200.
f. In the IP Addresses to Add area, specify the range of IP addresses to be used
by the DMZ interface:
–
Click the Range radio button.
–
Enter the Starting IP address and Ending IP address of the range. In this
scenario, the range of IP addresses is 10.30.30.50–10.30.30.60.
–
(Optional) Enter the Netmask for the range of IP addresses.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-9
Page 56

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
g. Click Add to add this range of IP addresses to the Address Pool.
The Add Global Pool dialog box configuration should be similar to the
following:
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-10
h. Click OK to return to the Configuration > NAT window.
Step 2 Add addresses to the IP pool to be used by the outside interface. These addresses
are used to translate private IP addresses so that inside clients can communicate
securely with clients on the Internet.
In this scenario, there are limited public IP addresses available. Use Port Address
Translation (PAT) so that many internal IP addresses can map to the same public
IP address, as follows:
a. In the right pane of the NAT Configuration screen, click the Global Pools tab.
b. Under the Global Pools tab, click Add.
The Add Global Pool Item dialog box appears.
c. From the Interface drop-down list, choose Outside.
d. Specify a Pool ID for the Outside interface.
You can add these addresses to the same IP pool that contains the address pool
used by the DMZ interface (in this scenario, the Pool ID is 200).
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 57

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
e. Click the Port Address Translation (PAT) using the IP address of the
interface radio button.
If you select the option Port Address Translation using the IP address of the
interface, all traffic initiated from the inside network exits the adaptive
security appliance using the IP address of the outside interface. To the devices
on the Internet, it appears that all traffic is coming from this one IP address.
f. Click the Add button to add this new address to the IP pool.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
g. Click OK.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-11
Page 58

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
The displayed configuration should be similar to the following:
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Step 3 Confirm that the configuration values are correct.
Step 4 Click Apply in the main ASDM window.
Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with the DMZ Web Server
In the previous procedure, you created a pool of IP addresses that could be used
by the adaptive security appliance to mask the private IP addresses of inside
clients.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-12
78-17611-01
Page 59

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
In this procedure, you configure a Network Address Translation (NAT) rule that
associates IP addresses from this pool with the inside clients so they can
communicate securely with the DMZ web server.
To configure NAT between the inside interface and the DMZ interface, perform
the following steps starting from the main ASDM window:
Step 1 In the main ASDM window, click the Configuration tool.
Step 2 In the Features pane, click NAT.
Step 3 From the Add drop-down list, choose Add Dynamic NAT Rule.
The Add Dynamic NAT Rule dialog box appears.
Step 4 In the Real Address area, specify the IP address to be translated. For this scenario,
address translation for inside clients is done according to the IP address of the
subnet.
a. From the Interface drop-down list, choose the Inside interface.
b. Enter the IP address of the client or network. In this scenario, the IP address
of the network is 10.10.10.0.
c. From the Netmask drop-down list, choose the Netmask. In this scenario, the
netmask is 255.255.255.0.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
Step 5 In the Dynamic Translation area:
a. From the Interface drop-down list, choose the DMZ interface.
b. To specify the address pool to be used for this Dynamic NAT rule, check the
Select check box next to Global Pool ID. In this scenario, the IP pool ID is
200.
In this scenario, the IP pool that we want to use is already created. If it was
not already created, you would click Add to create a new IP pool.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-13
Page 60

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-14
c. Click OK to add the Dynamic NAT Rule and return to the Configuration >
NAT window.
Review the configuration screen to verify that the translation rule appears as you
expected.
Note When you click OK to create this rule, notice that there are actually two
translation rules created:
• A translation rule between the inside and DMZ interfaces to be used when
inside clients communicate with the DMZ web server.
• A translation rule between the inside and outside interfaces to be used when
inside clients communicate with the Internet.
ASDM is able to create both rules because the addresses to be used for translation
are both in the same IP pool.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 61

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
The displayed configuration should be similar to the following:
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Step 6 Click Apply to complete the adaptive security appliance configuration changes.
Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with Devices on the Internet
In the previous procedure, you configured a Network Address Translation (NAT)
rule that associates IP addresses from the IP pool with the inside clients so they
can communicate securely with the DMZ web server.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
6-15
Page 62

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
For many configurations, you would also need to create a NAT rule between the
inside interface and the outside interface to enable inside clients to communicate
with the Internet.
However, in this scenario you do not need to create this rule explicitly. The reason
is that the IP pool (pool ID 200) contains both types of addresses needed for
address translation: the range of IP addresses to be used by the DMZ interface,
and the IP address to be used for the outside interface. This enables ASDM to
create the second translation rule for you.
Configuring an External Identity for the DMZ Web Server
The DMZ web server needs to be accessible by all hosts on the Internet. This
configuration requires translating the private IP address of the DMZ web server
to a public IP address, enabling access to outside HTTP clients that are unaware
of the adaptive security appliance. To map the real web server IP address
(10.30.30.30) statically to a public IP address (209.165.200.226), perform the
following steps:
6-16
Step 1 In the ASDM window, click the Configuration tool.
Step 2 In the Features pane, click NAT.
Step 3 From the Add drop-down list, choose Add Static NAT Rule. The Add Static NAT
Rule dialog box appears.
Step 4 In the Real Address area, specify the real IP address of the web server:
a. From the Interface drop-down list, choose the DMZ interface.
b. Enter the real IP address of the DMZ web server. In this scenario, the IP
address is 10.30.30.30.
c. From the Netmask drop-down list, choose the Netmask 255.255.255.255.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 63

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
Step 5 In the Static Translation area, specify the public IP address to be used for the web
server:
a. From the Interface drop-down list, choose Outside.
b. From the IP Address drop-down list, choose the public IP address of the DMZ
web server.
In this scenario, the public IP address of the DMZ web server is
209.165.200.226.
Step 6 Click OK to add the rule and return to the list of Address Translation Rules.
This rule maps the real web server IP address (10.30.30.30) statically to the public
IP address of the web server (209.165.200.226).
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-17
Page 64

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
The displayed configuration should be similar to the following:
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Step 7 Click Apply to complete the adaptive security appliance configuration changes.
Providing Public HTTP Access to the DMZ Web Server
By default, the adaptive security appliance denies all traffic coming in from the
public network. You must create an access control rule on the adaptive security
appliance to permit specific traffic types from the public network to resources in
the DMZ. This access control rule specifies the interface of the adaptive security
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-18
78-17611-01
Page 65

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
appliance that processes the traffic, whether the traffic is incoming or outgoing,
the origin and destination of the traffic, and the type of traffic protocol and service
to be permitted.
In this section, you create an access rule that permits incoming HTTP traffic
originating from any host or network on the Internet, if the destination of the
traffic is the web server on the DMZ network. All other traffic coming in from the
public network is denied.
To configure the access control rule, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the ASDM window:
a. Click the Configuration tool.
b. In the Features pane, click Security Policy.
c. Click the Access Rules tab, and then from the Add pull-down list, choose
Add Access Rule.
The Add Access Rule dialog box appears.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-19
Page 66

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-20
Step 2 In the Interface and Action area:
a. From the Interface drop-down list, choose Outside.
b. From the Direction drop-down list, choose Incoming.
c. From the Action drop-down list, choose Permit.
Step 3 In the Source area:
a. From the Type drop-down list, choose IP Address.
b. Enter the IP address of the source host or source network. Use 0.0.0.0 to allow
traffic originating from any host or network.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 67

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Alternatively, if the address of the source host or network is preconfigured,
choose the source IP address from the IP Address drop-down list.
c. Enter the netmask for the source IP address or select one from the Netmask
drop-down list.
Step 4 In the Destination area:
a. In the IP address field, enter the public IP address of the destination host or
network, such as a web server. (In this scenario, the public IP address of the
DMZ web server is 209.165.200.226.)
Step 5 In the Protocol and Service area, specify the type of traffic that you want to permit
through the adaptive security appliance.
a. From the Protocol drop-down list, choose tcp.
b. In the Source Port area, click the Service radio button, choose “=” (equal to)
from the Service drop-down list, and then choose Any from the next
drop-down list.
c. In the Destination Port area, click the Service radio button, choose “=” (equal
to) from the Service drop-down list, and then choose HTTP/WWW from the
next drop-down list.
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-21
Page 68

Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
At this point, the entries in the Add Access Rule dialog box should be similar to
the following:
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-22
d. Click OK.
Step 6 The displayed configuration should be similar to the following. Verify that the
information you entered is accurate.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 69

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Configuring the Security Appliance for a DMZ Deployment
78-17611-01
Step 7 Click Apply to save the configuration changes to the configuration that the
adaptive security appliance is currently running.
Clients on both the private and public networks can now resolve HTTP requests
for content from the DMZ web server, while keeping the private network secure.
Note Although the destination address specified is the private address of the DMZ web
server (10.30.30.30), HTTP traffic from any host on the Internet destined for the
public address 209.165.200.226 is permitted through the adaptive security
appliance. The address translation (209.165.200.226 to 10.30.30.30) allows the
traffic to be permitted. For information about creating the translation rule, see the
“Configuring NAT for Inside Clients to Communicate with the DMZ Web Server”
section on page 6-12.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-23
Page 70

What to Do Next
Step 8 If you want the configuration changes to be saved to the startup configuration so
that they are applied the next time the device starts, from the File menu, click
Save.
Alternatively, ASDM prompts you to save the configuration changes permanently
when you exit ASDM.
If you do not save the configuration changes, the old configuration takes effect the
next time the device starts.
What to Do Next
If you are deploying the adaptive security appliance solely to protect a web server
in a DMZ, you have completed the initial configuration. You may want to consider
performing some of the following additional steps:
To Do This ... See ...
Refine configuration and configure
optional and advanced features
Learn about daily operations Cisco Security Appliance Command
Review hardware maintenance and
troubleshooting information
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Line Configuration Guide
Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Hardware
Installation Guide
6-24
You can configure the adaptive security appliance for more than one application.
The following sections provide configuration procedures for other common
applications of the adaptive security appliance.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 71

Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
To Do This ... See ...
Configure a remote-access VPN Chapter 7, “Scenario: Remote-Access
Configure a site-to-site VPN Chapter 8, “Scenario: Site-to-Site
What to Do Next
VPN Configuration”
VPN Configuration”
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
6-25
Page 72

What to Do Next
Chapter 6 Scenario: DMZ Configuration
6-26
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 73

CHA P T E R
7
Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
This chapter describes how to use the adaptive security appliance to accept
remote-access IPsec VPN connections. A remote-access VPN enables you to
create secure connections, or tunnels, across the Internet, thus providing secure
access to off-site users.
If you are implementing an Easy VPN solution, this chapter describes how to
configure the Easy VPN server (sometimes called a headend device).
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Example IPsec Remote-Access VPN Network Topology, page 7-1
• Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario, page 7-2
• What to Do Next, page 7-18
Example IPsec Remote-Access VPN Network Topology
Figure 7-1 shows an adaptive security appliance configured to accept requests
from and establish IPsec connections with VPN clients, such as a Cisco Easy VPN
hardware client, over the Internet.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
7-1
Page 74

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Figure 7-1 Network Layout for Remote Access VPN Scenario
DNS Server
10.10.10.163
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
VPN client
VPN client
VPN client
Internal
network
WINS Server
10.10.10.133
Inside
10.10.10.0
Security
Appliance
Outside
Internet
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN
Scenario
This section describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance to accept
IPsec VPN connections from remote clients and devices. If you are implementing
an Easy VPN solution, this section describes how to configure an Easy VPN
server (also known as a headend device).
(user 1)
(user 2)
(user 3)
132209
7-2
Values for example configuration settings are taken from the remote-access
scenario illustrated in Figure 7-1.
This section includes the following topics:
• Information to Have Available, page 7-3
• Starting ASDM, page 7-4
• Configuring the FWSM for an IPsec Remote-Access VPN, page 7-5
• Selecting VPN Client Types, page 7-6
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 75

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
• Specifying the VPN Tunnel Group Name and Authentication Method,
page 7-7
• Specifying a User Authentication Method, page 7-8
• (Optional) Configuring User Accounts, page 7-10
• Configuring Address Pools, page 7-11
• Configuring Client Attributes, page 7-12
• Configuring the IKE Policy, page 7-13
• Configuring IPsec Encryption and Authentication Parameters, page 7-15
• Specifying Address Translation Exception and Split Tunneling, page 7-16
• Verifying the Remote-Access VPN Configuration, page 7-17
Information to Have Available
Before you begin configuring the adaptive security appliance to accept remote
access IPsec VPN connections, make sure that you have the following information
available:
• Range of IP addresses to be used in an IP pool. These addresses are assigned
to remote VPN clients as they are successfully connected.
• List of users to be used in creating a local authentication database, unless you
are using a AAA server for authentication.
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
78-17611-01
• Networking information to be used by remote clients when connecting to the
VPN, including:
–
IP addresses for the primary and secondary DNS servers
–
IP addresses for the primary and secondary WINS servers
–
Default domain name
–
List of IP addresses for local hosts, groups, and networks that should be
made accessible to authenticated remote clients
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-3
Page 76

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Starting ASDM
To run ASDM in a web browser, enter the factory default IP address in the address
field: https://192.168.1.1/admin/.
Note Remember to add the “s” in “https” or the connection fails. HTTPS
(HTTP over SSL) provides a secure connection between your browser and
the adaptive security appliance.
The Main ASDM window appears.
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
7-4
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 77

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Configuring the FWSM for an IPsec Remote-Access VPN
To begin the process for configuring a remote-access VPN, perform the following
steps:
Step 1 In the main ASDM window, choose VPN Wizard from the Wizards drop-down
menu. The VPN Wizard Step 1 screen appears.
78-17611-01
Step 2 In Step 1 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
a. Click the Remote Access VPN radio button.
b. From the drop-down list, choose Outside as the enabled interface for the
incoming VPN tunnels.
c. Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-5
Page 78

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Selecting VPN Client Types
In Step 2 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Specify the type of VPN client that will enable remote users to connect to this
adaptive security appliance. For this scenario, click the Cisco VPN Client radio
button.
You can also use any other Cisco Easy VPN remote product.
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
7-6
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 79

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Specifying the VPN Tunnel Group Name and Authentication Method
In Step 3 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Specify the type of authentication that you want to use by performing one of the
following steps:
• To use a static preshared key for authentication, click the Pre-Shared Key
radio button and enter a preshared key (for example, “Cisco”). This key is
used for IPsec negotiations between the adaptive security appliances.
• To use digital certificates for authentication, click the Certificate radio
button, choose the Certificate Signing Algorithm from the drop-down list,
and then choose a pre-configured trustpoint name from the drop-down list.
If you want to use digital certificates for authentication but have not yet
configured a trustpoint name, you can continue with the Wizard by using one
of the other two options. You can revise the authentication configuration later
using the standard ASDM screens.
• Click the Challenge/Response Authentication (CRACK) radio button to
use that method of authentication.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-7
Page 80

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Step 2 Enter a Tunnel Group Name (such as “Cisco”) for the set of users that use
common connection parameters and client attributes to connect to this adaptive
security appliance.
Step 3 Click Next to continue.
Specifying a User Authentication Method
Users can be authenticated either by a local authentication database or by using
external authentication, authorization, and accounting (AAA) servers (RADIUS,
TACACS+, SDI, NT, Kerberos, and LDAP).
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-8
78-17611-01
Page 81

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
In Step 4 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 If you want to authenticate users by creating a user database on the adaptive
security appliance, click the Authenticate Using the Local User Database radio
button.
Step 2 If you want to authenticate users with an external AAA server group:
a. Click the Authenticate Using an AAA Server Group radio button.
b. Choose a preconfigured server group from the drop-down list, or click New
to add a new server group.
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
78-17611-01
Step 3 Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-9
Page 82

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
(Optional) Configuring User Accounts
If you have chosen to authenticate users with the local user database, you can
create new user accounts here. You can also add users later using the ASDM
configuration interface.
In Step 5 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 To add a new user, enter a username and password, and then click Add.
7-10
Step 2 When you have finished adding new users, click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 83

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Configuring Address Pools
For remote clients to gain access to your network, you must configure a pool of
IP addresses that can be assigned to remote VPN clients as they are successfully
connected. In this scenario, the pool is configured to use the range of IP addresses
209.165.201.1–209.166.201.20.
In Step 6 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enter a pool name or choose a preconfigured pool from the drop-down list.
Alternatively, click New to create a new address pool.
The Add IP Pool dialog box appears.
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
78-17611-01
Step 2 In the Add IP Pool dialog box:
a. Enter the Starting IP address and Ending IP address of the range.
b. (Optional) Enter the Netmask for the range of IP addresses.
c. Click OK to return to Step 6 of the VPN Wizard.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-11
Page 84

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Step 3 Click Next to continue.
Configuring Client Attributes
To access your network, each remote access client needs basic network
configuration information, such as which DNS and WINS servers to use and the
default domain name. Rather than configuring each remote client individually,
you can provide the client information to ASDM. The adaptive security appliance
pushes this information to the remote client or Easy VPN hardware client when a
connection is established.
Ensure that you specify the correct values, or remote clients will not be able to use
DNS names for resolution or use Windows networking.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-12
78-17611-01
Page 85

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
In Step 7 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enter the network configuration information to be pushed to remote clients.
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Configuring the IKE Policy
IKE is a negotiation protocol that includes an encryption method to protect data
and ensure privacy; it is also an authentication method to ensure the identity of the
peers. In most cases, the ASDM default values are sufficient to establish secure
VPN tunnels.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
7-13
Page 86

Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
To specify the IKE policy in Step 8 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following
steps:
Step 1 Click the Encryption (DES/3DES/AES), authentication algorithms (MD5/SHA),
and the Diffie-Hellman group (1/2/5/7) used by the
during an IKE security association.
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
adaptive security appliance
7-14
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 87

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Configuring IPsec Encryption and Authentication Parameters
In Step 9 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Click the Encryption algorithm (DES/3DES/AES) and authentication algorithm
(MD5/SHA).
78-17611-01
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-15
Page 88

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Specifying Address Translation Exception and Split Tunneling
Split tunneling lets a remote-access IPsec client conditionally direct packets over
an IPsec tunnel in encrypted form or to a network interface in clear text form.
The adaptive security appliance uses Network Address Translation (NAT) to
prevent internal IP addresses from being exposed externally. You can make
exceptions to this network protection by identifying local hosts and networks that
should be made accessible to authenticated remote users. (In this scenario, the
entire inside network 10.10.10.0 is exposed to all remote clients.)
In Step 10 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Specify hosts, groups, and networks that should be in the list of internal resources
made accessible to authenticated remote users.
To add or remove hosts, groups, and networks dynamically from the Selected
Hosts/Networks pane, click Add or Delete, respectively.
7-16
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 89

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
Implementing the IPsec Remote-Access VPN Scenario
Note Enable split tunneling by checking the Enable Split Tunneling check box
at the bottom of the screen. Split tunneling allows traffic outside the
configured networks to be sent out directly to the Internet instead of over
the encrypted VPN tunnel.
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Verifying the Remote-Access VPN Configuration
In Step 11 of the VPN Wizard, review the configuration attributes for the VPN
tunnel you just created. The displayed configuration should be similar to the
following:
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-17
Page 90

What to Do Next
If you are satisfied with the configuration, click Finish to apply the changes to the
adaptive security appliance.
If you want the configuration changes to be saved to the startup configuration so
that they are applied the next time the device starts, from the File menu, click
Save. Alternatively, ASDM prompts you to save the configuration changes
permanently when you exit ASDM.
If you do not save the configuration changes, the old configuration takes effect the
next time the device starts.
What to Do Next
If you are deploying the adaptive security appliance solely in a remote-access
VPN environment, you have completed the initial configuration. In addition, you
may want to consider performing some of the following steps:
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
7-18
To Do This ... See ...
Refine configuration and configure
optional and advanced features
Learn about daily operations Cisco Security Appliance Command
Review hardware maintenance and
troubleshooting information
You can configure the
The following sections provide configuration procedures for other common
applications of the
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
adaptive security appliance for more than one application.
adaptive security appliance.
Cisco Security Appliance Command
Line Configuration Guide
Reference
Cisco Security Appliance Logging
Configuration and System Log
Messages
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Hardware
Installation Guide
78-17611-01
Page 91

Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
To Do This ... See ...
Configure the
appliance
adaptive security
to protect a Web server in a
DMZ
Configure a site-to-site VPN Chapter 8, “Scenario: Site-to-Site
What to Do Next
Chapter 6, “Scenario: DMZ
Configuration”
VPN Configuration”
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
7-19
Page 92

What to Do Next
Chapter 7 Scenario: Remote-Access VPN Configuration
7-20
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 93

CHA P T E R
8
Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
This chapter describes how to use the adaptive security appliance to create a
site-to-site VPN.
Site-to-site VPN features provided by the adaptive security appliance enable
businesses to extend their networks across low-cost public Internet connections to
business partners and remote offices worldwide while maintaining their network
security. A VPN connection enables you to send data from one location to another
over a secure connection, or tunnel, first by authenticating both ends of the
connection, and then by automatically encrypting all data sent between the two
sites.
This chapter includes the following sections:
• Example Site-to-Site VPN Network Topology, page 8-1
• Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario, page 8-2
• Configuring the Other Side of the VPN Connection, page 8-13
• What to Do Next, page 8-13
Example Site-to-Site VPN Network Topology
Figure 8-1 shows an example VPN tunnel between two adaptive security
appliances.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
8-1
Page 94

Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Figure 8-1 Network Layout for Site-to-Site VPN Configuration Scenario
Site A
Inside
10.10.10.0
Security
Appliance 1
209.165.200.226
Outside
Internet
Outside
209.165.200.236
Security
Appliance 2
Creating a VPN site-to-site deployment such as the one in Figure 8-1 requires you
to configure two adaptive security appliances, one on each side of the connection.
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
This section describes how to configure the adaptive security appliance in a
site-to-site VPN deployment, using example parameters from the remote-access
scenario shown in Figure 8-1.
This section includes the following sections:
• Information to Have Available, page 8-2
• Configuring the Site-to-Site VPN, page 8-3
Information to Have Available
Inside
10.20.20.0
Site B
132066
8-2
Before you begin the configuration procedure, gather the following information:
• IP address of the remote adaptive security appliance peer
• IP addresses of local hosts and networks permitted to use the tunnel to
communicate with resources on the remote site
• IP addresses of remote hosts and networks permitted to use the tunnel to
communicate with local resources
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 95

Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
Configuring the Site-to-Site VPN
This section describes how to use the ASDM VPN Wizard to configure the
adaptive security appliance for a site-to-site VPN.
This section includes the following topics:
• Starting ASDM, page 8-3
• Configuring the Security Appliance at the Local Site, page 8-4
• Providing Information About the Remote VPN Peer, page 8-6
• Configuring the IKE Policy, page 8-7
• Configuring IPSec Encryption and Authentication Parameters, page 8-9
• Specifying Hosts and Networks, page 8-10
• Viewing VPN Attributes and Completing the Wizard, page 8-11
The following sections provide detailed instructions for how to perform each
configuration step.
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Starting ASDM
78-17611-01
To run ASDM in a web browser, enter the factory default IP address in the address
field: https://192.168.1.1/admin/.
Note Remember to add the “s” in “https” or the connection fails. HTTPS
(HTTP over SSL) provides a secure connection between your browser and
the adaptive security appliance.
The Main ASDM window appears.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
8-3
Page 96

Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
Configuring the Security Appliance at the Local Site
Note The adaptive security appliance at the first site is referred to as Security
Appliance 1 from this point forward.
To configure the Security Appliance 1, perform the following steps:
Step 1 In the main ASDM window, choose the VPN Wizard option from the Wizards
drop-down menu. ASDM opens the first VPN Wizard screen.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
8-4
78-17611-01
Page 97

Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
In Step 1 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
a. Click the Site-to-Site VPN radio button.
Note The Site-to-Site VPN option connects two IPSec security gateways,
which can include adaptive security appliances, VPN concentrators,
or other devices that support site-to-site IPSec connectivity.
b. From the drop-down list, choose Outside as the enabled interface for the
current VPN tunnel.
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
78-17611-01
c. Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
8-5
Page 98

Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Providing Information About the Remote VPN Peer
The VPN peer is the system on the other end of the connection that you are
configuring, usually at a remote site.
Note In this scenario, the remote VPN peer is referred to as Security Appliance 2 from
this point forward.
In Step 2 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Enter the Peer IP Address (the IP address of Security Appliance 2, in this scenario
209.165.200.236) and a Tunnel Group Name (for example “Cisco”).
Step 2 Specify the type of authentication that you want to use by performing one of the
following steps:
• To use a static preshared key for authentication, click the Pre-Shared Key
radio button and enter a preshared key (for example, “Cisco”). This key is
used for IPSec negotiations between the adaptive security appliances.
8-6
Note When you configure Security Appliance 2 at the remote site, the VPN
peer is Security Appliance 1. Be sure to enter the same preshared key
(Cisco) that you use here.
• Click the Challenge/Response Authentication radio button to use that
method of authentication.
• To use digital certificates for authentication, click the Certificate radio
button, choose the Certificate Signing Algorithm from the drop-down list,
and then choose a preconfigured trustpoint name from the drop-down list.
If you want to use digital certificates for authentication but have not yet
configured a trustpoint name, you can continue with the Wizard by using one
of the other two options. You can revise the authentication configuration later
using the standard ASDM screens.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
Page 99

Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Step 3 Click Next to continue.
Configuring the IKE Policy
IKE is a negotiation protocol that includes an encryption method to protect data
and ensure privacy; it is also an authentication method to ensure the identity of the
peers. In most cases, the ASDM default values are sufficient to establish secure
VPN tunnels between two peers.
In Step 3 of the VPN Wizard, perform the following steps:
Step 1 Click the Encryption (DES/3DES/AES), authentication algorithms (MD5/SHA),
and the Diffie-Hellman group (1/2/5) used by the adaptive security appliance
during an IKE security association.
78-17611-01
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
8-7
Page 100

Implementing the Site-to-Site Scenario
Chapter 8 Scenario: Site-to-Site VPN Configuration
8-8
Note When configuring Security Appliance 2, enter the exact values for each
of the options that you chose for Security Appliance 1. Encryption
mismatches are a common cause of VPN tunnel failures and can slow
down the process.
Step 2 Click Next to continue.
Cisco ASA 5500 Series Adaptive Security Appliance Getting Started Guide
78-17611-01
 Loading...
Loading...