Page 1

Cisco Active Network Abstraction
Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Corporate Headquarters
Cisco Systems, Inc.
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-1706
USA
http://www.cisco.com
Tel: 408 526-4000
800 553-NETS (6387)
Fax: 408 526-4100
Text Part Number: OL-8842-01
Page 2

THE SPECIFICATIONS AND INFORMATION REGARDING THE PRODUCTS IN THIS MANUAL ARE SUBJECT TO CHANGE WITHOUT NOTICE. ALL
STATEMENTS, INFORMATION, AND RECOMMENDATIONS IN THIS MANUAL ARE BELIEVED TO BE ACCURATE BUT ARE PRESENTED WITHOUT
WARRANTY OF ANY KIND, EXPRESS OR IMPLIED. USERS MUST TAKE FULL RESPONSIBILITY FOR THEIR APPLICATION OF ANY PRODUCTS.
THE SOFTWARE LICENSE AND LIMITED WARRANTY FOR THE ACCOMPANYING PRODUCT ARE SET FORTH IN THE INFORMATION PACKET THAT
SHIPPED WITH THE PRODUCT AND ARE INCORPORATED HEREIN BY THIS REFERENCE. IF YOU ARE UNABLE TO LOCATE THE SOFTWARE
LICENSE OR LIMITED WARRANTY, CONTACT YOUR CISCO REPRESENTATIVE FOR A COPY.
The Cisco implementation of TCP header compression is an adapta tion of a program developed by the University of California, Berkeley (UCB) as part of UCB’s public
domain version of the UNIX operating system. All rights reserved. Copyright © 1981, Rege nts of the University of California.
NOTWITHSTANDING ANY OTHER WARRANTY HEREIN, ALL DOCUMENT FILES AND SOFTWARE OF THESE SUPPLIERS ARE PROVIDED “AS IS”
WITH ALL FAULTS. CISCO AND THE ABOVE-NAMED SUPPLIERS DISCLAIM ALL WARRANTIES, EXPRESSED OR IMPLIED, INCLUDING, WITHOUT
LIMITATION, THOSE OF MERCHANTABILITY, FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE AND NONINFRINGEMENT OR ARISING FROM A COURSE OF
DEALING, USAGE, OR TRADE PRACTICE.
IN NO EVENT SHALL CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS BE LIABLE FOR ANY INDIRECT, SPECIAL, CONSEQUENTIAL, OR INCIDENTAL DAMAGES,
INCLUDING, WITHOUT LIMITATION, LOST PROFITS OR LOSS OR DAMAGE TO DATA ARISING OUT OF THE USE OR INABILITY TO USE THIS
MANUAL, EVEN IF CISCO OR ITS SUPPLIERS HAVE BEEN ADVISED OF THE POSSIBILITY OF SUCH DAMAGES.
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Gu ide, 3.5
© 1999 - 2006 Cisco Systems, Inc. All rights reserved.
Page 3
Important Notice
Important Notice
Cisco ANA 3.5 is a carrier-class, multi-vendor network and service
management platform which builds a real-time virtual model of the network,
serving as a live information base for value-added tools and applications for
integration into an existing OSS environment.
Cisco ANA 3.5 is a limited release by Cisco Systems of the existing features
and functions of the Sheer DNA 4.0.1 software.
As this is a limited release, the naming of the product in the software and the
user documentation remains as Sheer DNA.
Obtaining Documentation
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available on Cisco.com.
Cisco also provides several ways to obtain technical assistance and other
technical resources. These sections explain how to obtain technical
information from Cisco Systems.
Cisco.com
You can access the most current Cisco documentation at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
You can access the Cisco website at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com
You can access international Cisco websites at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/public/countries_languages.shtml
Product Documentation DVD
Cisco documentation and additional literature are available in the Product
Documentation DVD package, which may have shipped with your product.
The Product Documentation DVD is updated regularly and may be more
current than printed documentation.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page iii
Page 4

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
The Product Documentation DVD is a comprehensive library of technical
product documentation on portable media. The DVD enables you to access
multiple versions of hardware and software installation, configuration, and
command guides for Cisco products and to view technical documentation in
HTML. With the DVD, you have access to the same documentation that is
found on the Cisco website without being connected to the Internet. Certain
products also have .pdf versions of the documentation available.
The Product Documentation DVD is available as a single unit or as a
subscription. Registered Cisco.com users (Cisco direct customers) can order
a Product Documentation DVD (product number DOC-DOCDVD=) from
Cisco Marketplace at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Ordering Documentation
Beginning June 30, 2005, registered Cisco.com users may order Cisco
documentation at the Product Documentation Store in the Cisco Marketplace
at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Nonregistered Cisco.com users can order technical documentation from 8:00
a.m. to 5:00 p.m. (0800 to 1700) PDT by calling 1 866 463-3487 in the
United States and Canada, or elsewhere by calling 011 408 519-5055. You
can also order documentation by e-mail at tech-doc-storemkpl@external.cisco.com or by fax at 1 408 519-5001 in the United States
and Canada, or elsewhere at 011 408 519-5001.
Documentation Feedback
You can rate and provide feedback about Cisco technical documents by
completing the online feedback form that appears with the technical
documents on Cisco.com.
You can send comments about Cisco documentation to bug-doc@cisco.com.
You can submit comments by using the response card (if present) behind the
front cover of your document or by writing to the following address:
Cisco Systems
Attn: Customer Document Ordering
170 West Tasman Drive
San Jose, CA 95134-9883
We appreciate your comments.
Page iv Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 5

Important Notice
Cisco Product Security Overview
Cisco provides a free online Security Vulnerability Policy portal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.h
tml
From this site, you can perform these tasks:
• Report security vulnerabilities in Cisco products.
• Obtain assistance with security incidents that involve Cisco products.
• Register to receive security information from Cisco.
A current list of security advisories and notices for Cisco products is
available at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/psirt
If you prefer to see advisories and notices as they are updated in real time,
you can access a Product Security Incident Response Team Really Simple
Syndication (PSIRT RSS) feed from this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_psirt_rss_feed.html
Reporting Security Problems in Cisco Products
Cisco is committed to delivering secure products. We test our products
internally before we release them, and we strive to correct all vulnerabilities
quickly. If you think that you might have identified a vulnerability in a Cisco
product, contact PSIRT:
Emergencies — security-alert@cisco.com
An emergency is either a condition in which a system is under active attack
or a condition for which a severe and urgent security vulnerability should be
reported. All other conditions are considered nonemergencies.
Nonemergencies — psirt@cisco.com
In an emergency, you can also reach PSIRT by telephone:
1 877 228-7302
1 408 525-6532
We encourage you to use Pretty Good Privacy (PGP) or a compatible product
to encrypt any sensitive information that you send to Cisco. PSIRT can work
from encrypted information that is compatible with PGP versions 2.x through
8.x.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page v
Page 6

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Never use a revoked or an expired encryption key. The correct public key to
use in your correspondence with PSIRT is the one linked in the Contact
Summary section of the Security Vulnerability Policy page at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/products_security_vulnerability_policy.h
tml
The link on this page has the current PGP key ID in use.
Obtaining Technical Assistance
Cisco Technical Support provides 24-hour-a-day award-winning technical
assistance. The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website on
Cisco.com features extensive online support resources. In addition, if you
have a valid Cisco service contract, Cisco Technical Assistance Center
(TAC) engineers provide telephone support. If you do not have a valid Cisco
service contract, contact your reseller.
Cisco Technical Support & Documentation
Website
The Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website provides online
documents and tools for troubleshooting and resolving technical issues with
Cisco products and technologies. The website is available 24 hours a day, at
this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport
Access to all tools on the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website
requires a Cisco.com user ID and password. If you have a valid service
contract but do not have a user ID or password, you can register at this URL:
http://tools.cisco.com/RPF/register/register.do
Use the Cisco Product Identification (CPI) tool to locate your product serial
number before submitting a web or phone request for service. You can access
the CPI tool from the Cisco Technical Support & Documentation website by
clicking the Tools & Resources link under Documentation & Tools. Choose
Cisco Product Identification Tool from the Alphabetical Index drop-down
list, or click the Cisco Product Identification Tool link under Alerts & RMAs.
The CPI tool offers three search options: by product ID or model name; by
tree view; or for certain products, by copying and pasting show command
output. Search results show an illustration of your product with the serial
number label location highlighted. Locate the serial number label on your
product and record the information before placing a service call.
Page vi Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 7

Important Notice
Submitting a Service Request
Using the online TAC Service Request Tool is the fastest way to open S3 and
S4 service requests. (S3 and S4 service requests are those in which your
network is minimally impaired or for which you require product
information.) After you describe your situation, the TAC Service Request
Tool provides recommended solutions. If your issue is not resolved using the
recommended resources, your service request is assigned to a Cisco engineer.
The TAC Service Request Tool is located at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/servicerequest
For S1 or S2 service requests or if you do not have Internet access, contact
the Cisco TAC by telephone. (S1 or S2 service requests are those in which
your production network is down or severely degraded.) Cisco engineers are
assigned immediately to S1 and S2 service requests to help keep your
business operations running smoothly.
To open a service request by telephone, use one of the following numbers:
• Asia-Pacific: +61 2 8446 7411 (Australia: 1 800 805 227)
• EMEA: +32 2 704 55 55
• USA: 1 800 553-2447
For a complete list of Cisco TAC contacts, go to this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/techsupport/contacts
Definitions of Service Request Severity
To ensure that all service requests are reported in a standard format, Cisco
has established severity definitions.
• Severity 1 (S1)—Your network is “down,” or there is a critical impact to
your business operations. You and Cisco will commit all necessary
resources around the clock to resolve the situation.
• Severity 2 (S2)—Operation of an existing network is severely degraded,
or significant aspects of your business operation are negatively affected
by inadequate performance of Cisco products. You and Cisco will
commit full-time resources during normal business hours to resolve the
situation.
• Severity 3 (S3)—Operational performance of your network is impaired,
but most business operations remain functional. You and Cisco will
commit resources during normal business hours to restore service to
satisfactory levels.
• Severity 4 (S4)—You require information or assistance with Cisco
product capabilities, installation, or configuration. There is little or no
effect on your business operations.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page vii
Page 8

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Obtaining Additional Publications and
Information
Information about Cisco products, technologies, and network solutions is
available from various online and printed sources.
Cisco Marketplace provides a variety of Cisco books, reference guides,
documentation, and logo merchandise. Visit Cisco Marketplace, the company
store, at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/marketplace/
Cisco Press publishes a wide range of general networking, training and
certification titles. Both new and experienced users will benefit from these
publications. For current Cisco Press titles and other information, go to Cisco
Press at this URL:
http://www.ciscopress.com
Packet magazine is the Cisco Systems technical user magazine for
maximizing Internet and networking investments. Each quarter, Packet
delivers coverage of the latest industry trends, technology breakthroughs, and
Cisco products and solutions, as well as network deployment and
troubleshooting tips, configuration examples, customer case studies,
certification and training information, and links to scores of in-depth online
resources. You can access Packet magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/packet
iQ Magazine is the quarterly publication from Cisco Systems designed to
help growing companies learn how they can use technology to increase
revenue, streamline their business, and expand services. The publication
identifies the challenges facing these companies and the technologies to help
solve them, using real-world case studies and business strategies to help
readers make sound technology investment decisions. You can access iQ
Magazine at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/go/iqmagazine
or view the digital edition at this URL:
http://ciscoiq.texterity.com/ciscoiq/sample/
Page viii Cisco Syste ms, Inc .
Page 9

Important Notice
Internet Protocol Journal is a quarterly journal published by Cisco Systems
for engineering professionals involved in designing, developing, and
operating public and private internets and intranets. You can access the
Internet Protocol Journal at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/ipj
Networking products offered by Cisco Systems, as well as customer support
services, can be obtained at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/index.html
Networking Professionals Connection is an interactive website for
networking professionals to share questions, suggestions, and information
about networking products and technologies with Cisco experts and other
networking professionals. Join a discussion at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/discuss/networking
World-class networking training is available from Cisco. You can view
current offerings at this URL:
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/learning/index.html
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page ix
Page 10

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Page x Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 11

About This Guide
About This Guide
This Administrator’s Guide describes the structure and features of the
Sheer™ Dynamic Network Abstraction (DNA) system. Sheer DNA Manage
is the GUI client application designed to simplify and facilitate Sheer DNA
administration. Sheer DNA Manage enables the System Administrator to
configure and control the DNA system. Sheer DNA Manage interacts with
the Sheer DNA Registry (“Golden Source”) to query and modify
configuration information. This guide is intended for use by trained System
Administrators.
It includes the following chapters:
Chapter 1, Introducing Sheer DNA, page 1, describes the Sheer™ DNA
platform and architecture. In addition, it provides a brief explanation of the
terms used throughout this guide.
Chapter 2, Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage, page 13, describes
the Sheer DNA Manage working environment and how to open and operate
the Sheer DNA Manage application.
Chapter 3, Deploying Sheer DNA, page 57, describes the steps that must be
performed to deploy the Sheer DNA.
Chapter 4, General DNA Manage Tables, page 61, describes how to
perform general Sheer DNA Manage functions when working with tables.
Chapter 5, Managing Sheer DNA Units, page 69, describes how to manage
Sheer DNA Units. This includes adding and removing Sheer DNA Units.
Chapter 6, Managing AVMs and VNEs, page 79, describes how to define
and manage AVMs and VNEs.
Chapter 7,
Managing Global Settings, page 107, describes how to define
and manage the Sheer DNA Manage global settings, including client licenses,
DNA database segments, customizing a message of the day (service
disclaimer), polling groups, and protection groups.
Chapter 8,
Managing Links, page 127, describes how to add and remove a
topological link between two ports of two Network Elements in the network.
Chapter 9, Managing Workflows, page 133, briefly describes the Workflow
Engine branch in the Sheer DNA Manage application.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page xi
Page 12
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Chapter 10, Managing Sheer DNA Security, page 135, describes how
Sheer DNA implements a three-dimensional security engine combining a
role-based security mechanism with scopes that are granted to users. In
addition, it describes managing users in the Sheer DNA platform, including,
defining users and passwords.
Appendix A, Utility Scripts, page 155, describes the Sheer DNA utility
scripts including how to restart the Sheer DNA Platform.
Appendix B, Golden Source Registry, page 157, provides details of the
Golden Source Registry.
Appendix C, Ports Used by Sheer DNA, page 159, provides a list of the
ports used by the various Sheer DNA Server and Client applications.
Appendix D, Drools Rules Engine, page 161, introduces and describes
Drools.
Note: Changes to the Registry should only be carried out with the support of
Cisco Professional Services.
Page xii Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 13

Introducing Sheer DNA
Table of Contents
1 Introducing Sheer DNA ..................................................................1
1.1 The Sheer Solution...................................................................................................1
1.2 Sheer DNA Components..........................................................................................4
1.2.1 Autonomous VNE................................................................................................4
1.2.2 The Sheer DNA Servers......................................................................................4
1.2.3 Sheer DNA Clients...............................................................................................5
1.3 Sheer DNA Manage Control Functionality.............................................................6
1.4 Additional Concepts and Terms.............................................................................7
1.5 Terminology and Conventions..............................................................................11
2 Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage.................................... 13
2.1 Starting Sheer DNA Manage..................................................................................13
2.2 The Sheer DNA Manage Window..........................................................................15
2.2.1 Sheer DNA Manage Tree Pane.........................................................................15
2.2.2 Sheer DNA Manage Window Workspace .........................................................18
2.3 Sheer DNA Manage Window, Menus and Toolbar..............................................19
2.3.1 DNA Servers Branch .........................................................................................20
2.3.2 DNA Server Entities Branch..............................................................................24
2.3.3 AVM Branch.......................................................................................................29
2.3.4 Global Settings Branch......................................................................................33
2.3.5 Scopes Branch ..................................................................................................44
2.3.6 Topology Branch................................................................................................47
2.3.7 Users Branch.....................................................................................................49
2.3.8 Workflow Engine Branch...................................................................................52
2.4 Logging Out............................................................................................................56
3 Deploying Sheer DNA................................................................... 57
3.1 System Setup Flow ................................................................................................57
3.2 User and View Setup Flow.....................................................................................60
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page xiii
Page 14

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
4 General DNA Manage Tables....................................................... 61
4.1 Working with DNA Manage Tables.......................................................................61
4.2 Finding Text in a Table ..........................................................................................63
4.3 Filtering Information ..............................................................................................63
4.4 Setting Selection Filters ........................................................................................65
4.5 Sorting a Table .......................................................................................................67
4.6 Exporting the Table to a File.................................................................................68
5 Managing Sheer DNA Units .........................................................69
5.1 What is a DNA Unit?...............................................................................................70
5.2 Adding New Sheer DNA Units...............................................................................71
5.3 Editing Sheer DNA Unit Properties ......................................................................73
5.4 Removing a Sheer DNA Unit.................................................................................75
5.5 Finding a Unit/AVM/VNE........................................................................................76
6 Managing AVMs and VNEs ..........................................................79
6.1 Creating AVMs........................................................................................................80
6.2 AVM Status..............................................................................................................82
6.2.1 Admin and Oper Mode AVM Status ..................................................................83
6.3 Viewing and Editing an AVM’s Properties...........................................................83
6.4 Deleting an AVM.....................................................................................................84
6.5 Starting and Stopping AVMs.................................................................................85
6.6 Moving AVMs..........................................................................................................86
6.7 VNEs Overview.......................................................................................................87
6.7.1 VNE Status........................................................................................................88
6.7.2 Admin and Oper Mode VNE Status...................................................................89
6.8 Defining VNEs.........................................................................................................89
6.8.1 General Tab.......................................................................................................92
6.8.2 SNMP Tab.........................................................................................................94
6.8.3 Telnet / SSH Tab...............................................................................................96
6.8.4 ICMP Tab...........................................................................................................98
6.8.5 Polling Tab.........................................................................................................99
6.9 Viewing and Editing a VNE’s Properties............................................................101
6.10 Deleting a VNE......................................................................................................103
6.11 Changing the VNE’s State ...................................................................................104
6.12 Moving Multiple and Single VNEs ......................................................................105
Page xiv Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 15

Introducing Sheer DNA
7 Managing Global Settings.......................................................... 107
7.1 Managing Client Licenses...................................................................................107
7.1.1 Viewing Client License Properties...................................................................109
7.2 Viewing DB Segments .........................................................................................112
7.3 Customizing a Message of the Day....................................................................113
7.4 Managing Polling Groups....................................................................................114
7.4.1 Polling Groups Overview.................................................................................114
7.4.2 Customizing a Polling Group...........................................................................116
7.4.3 Modifying a Polling Group ...............................................................................118
7.4.4 Deleting a Polling Group..................................................................................119
7.4.5 Adaptive Polling...............................................................................................119
7.5 Managing Protection Groups..............................................................................121
7.5.1 Chec k in g A s si g n me n t o f Pr ot e ct i o n G r ou p s t o DN A U n it s ..................................123
7.5.2 Changing Protection Groups for DNA Units.......................................................123
7.5.3 Vi e wi n g a n d E d i t i n g Prot e ct i o n G r o u p Prop e rt i e s...............................................125
7.5.4 De le t in g a P r ot e ct i on G r ou p..............................................................................126
8 Managing Links........................................................................... 127
8.1 Creating a Static Link...........................................................................................127
8.2 Removing a Static Link........................................................................................131
9 Managing Workflows.................................................................. 133
9.1 About the Sheer Workflow Editor.......................................................................133
9.2 Workflow Engine Branch.....................................................................................134
10 Managing Sheer DNA Security..................................................135
10.1 Security Overview................................................................................................135
10.1.1 Scopes.............................................................................................................135
10.1.2 Default Permissions.........................................................................................136
10.1.3 Security Access Roles.....................................................................................136
10.2 Customizing Security Flow .................................................................................139
10.3 Creating Scopes ...................................................................................................140
10.3.1 Editing a Scope and Viewing a Scope Properties...........................................142
10.3.2 Deleting Scopes...............................................................................................142
10.4 Creating New Sheer DNA User Accounts..........................................................143
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page xv
Page 16

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
10.5 Granting or Editing a User’s Rights ...................................................................146
10.5.1 General User’s Rights......................................................................................146
10.5.2 User’s Security Rights.....................................................................................148
10.5.3 Map User Permissions ....................................................................................151
10.6 Deleting a Sheer DNA User Account..................................................................152
10.7 Changing a User’s Password..............................................................................152
A Utility Scripts............................................................................... 155
A.1 Restarting Sheer DNA Gateway..........................................................................155
A.2 Restarting a Sheer DNA Unit...............................................................................155
A.3 Executing a Command on all Sheer DNA Units................................................156
B Golden Source Registry............................................................. 157
C Ports Used by Sheer DNA.......................................................... 159
D Drools Rules Engine................................................................... 161
D.1 Drools Rules Engine Overview...........................................................................161
D.1.1 Drools Components and Terminology.............................................................161
D.2 Drools and ANA Integration................................................................................162
D.3 Drools Definitions in ANA...................................................................................162
D.4 Upgrading Rule Files ...........................................................................................163
Page xvi Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 17

Introducing Sheer DNA
1 Introducing Sheer DNA
About this chapter:
This chapter describes the Sheer™ Dynamic Network Abstraction (DNA)
platform and architecture. In addition, it provides a brief explanation of the
terms used throughout this guide. The Sheer DNA Manage maintenance
application is part of an overall Sheer solution; therefore, in order to better
understand the Sheer DNA Manage environment, a brief overview of Sheer
DNA is required.
The Sheer Solution, page 1, provides an overview of the Sheer DNA, its
platform architecture and functional blocks.
Sheer DNA Components, page 4, describes the Sheer DNA system’s key
components.
Sheer DNA Manage Control Functionality, page 6, describes how Sheer
DNA Manage serves as a tool to manage the Sheer DNA, which enables the
addition, removal and modification of Sheer DNA information.
Additional Concepts and Terms, page 7, explains any additional terms used
within the Sheer DNA Manage application and this guide.
Terminology and Conventions, page 11, describes the conventions used in
the Sheer DNA Administrator’s Guide. In addition, it provides a guide to
related documentation.
1.1 The Sheer Solution
Sheer Dynamic Network Abstraction (DNA) is a carrier class network
management platform, designed to serve as an active mediation layer
between the operation and the network layers. Sheer DNA provides a rich set
of GUI easy to use applications as well as well-defined, APIs for Operation
Support Systems, enabling carriers and service providers to efficiently
respond to the constant market demand for new, reliable and more
sophisticated services, while hiding the complexity of large, multi-vendor,
multi-technology networks.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 1
Page 18

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Sheer DNA provides solutions for diverse network environments and
applications. It offers an integrated network and service auto- discovery for
network modeling, intelligent fault analysis and a highly flexible network
configuration and activation engine. This enables fully correlated
management of global scale networks supporting millions of subscribers and
customers.
Sheer DNA is a network management solution that provides a fully
integrated service-oriented solution offering:
• Multi-vendor, hybrid device support
• Multi-Technology (IP, VPN, MPLS, Ethernet, ATM, DSL)
• Multi-function (Network discovery, Fault, Activation and Configuration)
• Vertical integration with multiple OSS/BSS applications
Based on a patented innovative architecture of Distributed Autonomous
VNEs, Sheer DNA was designed from day one to enable integrated
management, for hybrid network environments, while being extremely
scalable in supporting network growth and evolution.
The Sheer DNA introduces key functional highlights such as:
• Network (Horizontal) Integration: supporting NEs from multiple
vendors, across multiple technologies, forming a unified, end-to-end
synthesis of the network
• Network and Service Discovery, Real-time Inventory and Topology:
discovery of network inventory, services and multi-layer connectivity to
form an accurate, up-to-date network information model
• Network Fault Intelligence: using the auto-discovered network model
for fault correlation and root cause analysis
• Service Impact: the service impact analysis of various network faults
showing affected VPNs and sites
• Activation and Configuration: a flexible, high-performance activation
engine that supports virtually any device configuration required
• Service Verification: real-time verification of configuration health and
consistency
• Service Path Analysis: dynamic isolation and tracing of service paths,
end-to-end across technologies and network layers
• GUI Client Applications: a powerful set of user applications for
Assurance, Fulfillment and Performance management
Page 2 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 19
Introducing Sheer DNA
• OSS/BSS (Vertical) Integration: open, flexible northbound adaptation
framework to OSS/BSS applications, in a wide variety of APIs, protocols
and information models
• Scalability: a fully distributed solution implementing parallel processing
that inherits the scaling properties of the network by creating a virtual
model of it. Adding more Autonomous VNEs and/or more DNA Units
easily supports network growth.
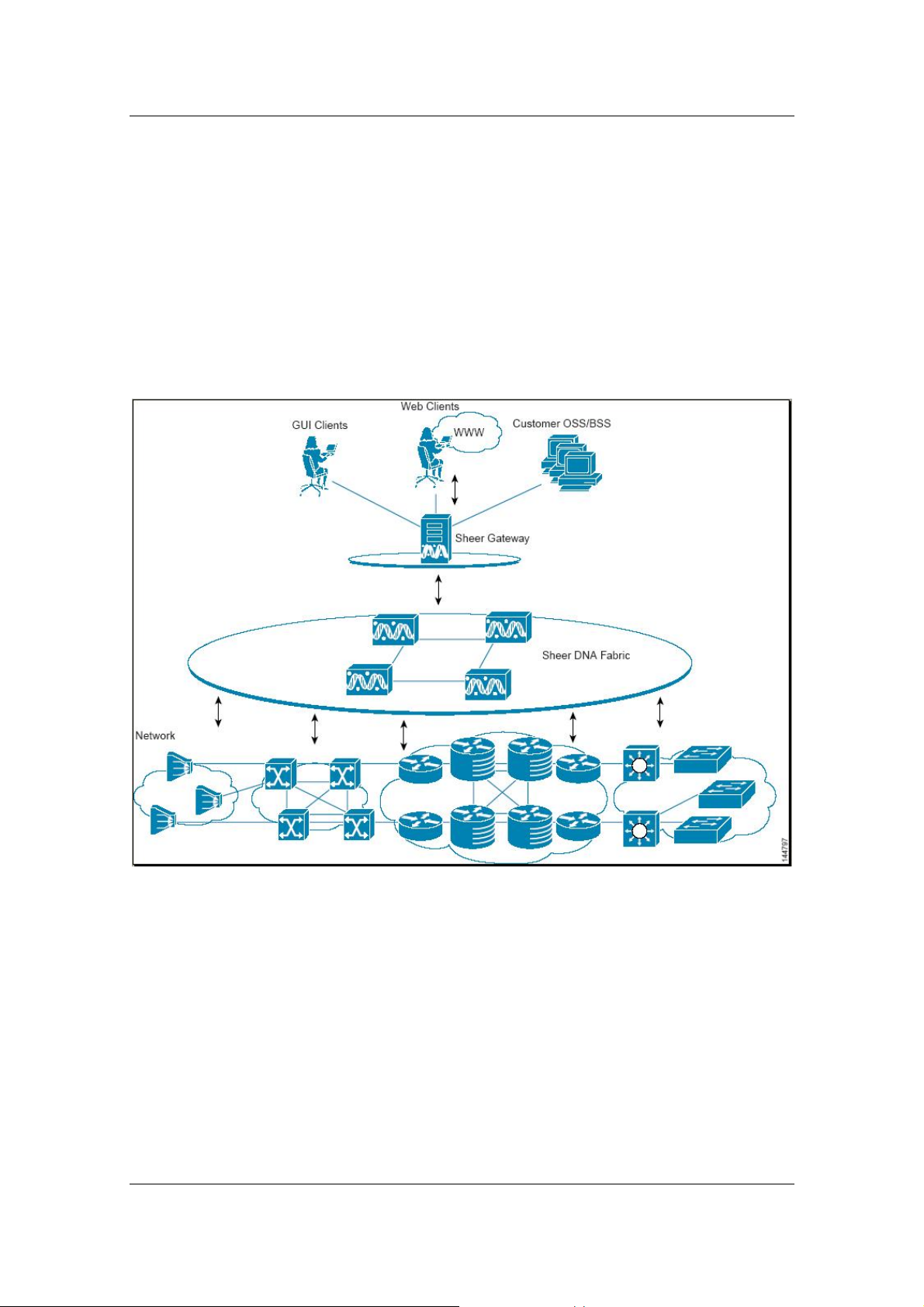
The Sheer™ DNA platform architectural diagram and functional blocks are
displayed below.
Figure 1: Sheer DNA Architecture
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 3
Page 20

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
1.2 Sheer DNA Components
The Sheer DNA system is comprised of several key components, as
described in the sections that follow.
1.2.1 Autonomous VNE
The Autonomous VNEs (Virtual Network Elements) are software entities
that run as a completely autonomous process within the Sheer DNA Units.
Each VNE is assigned to manage a single Network Element (NE) instance
using whatever southbound management interfaces the NE implements (e.g.
SNMP or Telnet). The Autonomous VNEs are the entities that maintain a live
model of each NE and of the entire network.
As the VNE loads, it starts investigating the NE and automatically builds a
live model of the NE, including its physical and logical inventory, its
configuration and its status. Following the device investigation, the VNEs
begin to negotiate with peering VNEs, which represent the peering NEs
determining the connectivity and topology at different layers. This model of
the network topology, device state and device inventory is constantly being
updated by the VNEs, which track every change that occurs in the NE or in
the network.
Messaging between VNEs is used for running different end-to-end flows, in order
to provide information for root cause and impact analysis, service path tracing and
more.
1.2.2 The Sheer DNA Servers
Sheer DNA uses two distinct server types, each performing different activities:
• Sheer DNA Gateway
• Sheer DNA Unit
Sheer DNA Gateway
The Sheer DNA Gateway serves as the gateway through which all clients,
including any OSS/BSS applications as well as the Sheer DNA clients can
access the system. The gateway is an extended Sheer DNA Unit. It enforces
access control and security for all connections and manages client sessions.
In addition it functions as a repository for storing configuration, network and
system events and alarms.
Page 4 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 21

Introducing Sheer DNA
Another important function of the Sheer DNA Gateway is to map network
resources to the business context. This enables Sheer DNA to contain
information that is not directly contained in the network (such as VPNs and
Subscribers) and display it to northbound applications.
Sheer DNA Unit
The main purpose of the Sheer DNA Units is to host the Autonomous VNEs.
The Sheer DNA Units are interconnected to form a fabric of VNEs that can
inter-communicate with other VNEs regardless of which unit they are
running on. Each Sheer DNA Unit can host thousands of Autonomous VNE
processes (depending on the server system size). The Sheer DNA Units also
allow for optimal VNE distribution, ensuring geographic proximity between
the VNE and its managed NE.
The clustered N+m high availability mechanism within the Sheer DNA
Fabric is designed to handle the failure of a Sheer DNA Unit. Sheer DNA
Unit availability is established in the Gateway, running a Protection Manager
process, which continuously monitors all the Sheer DNA Units in the
network. Once the Protection Manager detects a Sheer DNA Unit that is
malfunctioning, it automatically signals one of the m servers in its cluster to
load the configuration of the faulty unit (from the system Registry), taking
over all its managed Network Elements. The switchover to the redundant
standby Sheer DNA Unit does not result in any loss of information in the
system, as all of the information is auto-discovered from the network, and no
persistent storage synchronization is required. When a Sheer DNA Unit is
configured it can be designated as being an active or standby unit.
For more information about high availability, refer to the Cisco Active
Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.
1.2.3 Sheer DNA Clients
Sheer provides a comprehensive suite of GUI applications to manage the
network using the Sheer DNA platform.
• Sheer NetworkVision: The main GUI application of Sheer DNA, used to
visualize every management function supported by the system. For more
information, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction NetworkVision
User’s Guide.
• Sheer EventVision: A tool for viewing all historical events detected by
the Sheer DNA system. For more information, refer to the Cisco Active
Network Abstraction EventVision User’s Guide.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 5
Page 22

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Sheer DNA Manage: A system administration and configuration tool for
managing the entire Sheer DNA platform, as described below.
• Sheer Registry Editor: A tool used for viewing and configuring the
Sheer Registry.
The Sheer DNA Clients support automatic client updates from the Sheer
DNA Gateway using Web Start. When connecting with a Sheer DNA
Gateway application, the system verifies that the client version is the latest
available and if an upgrade is required, the system automatically updates the
Sheer Clients from the Sheer DNA Gateway.
1.3 Sheer DNA Manage Control Functionality
Sheer DNA includes extensive system administration functions for simple
system control. Sheer DNA Manage is the GUI tool used for performing
various system administration activities. It provides an interface to perform
the following:
• Sheer DNA Units: Adding and removing Units.
• Autonomous Virtual Machines (AVMs) and Virtual Network
Elements (VNEs): Adding and removing AVMs and VNEs for the
different Sheer DNA Units. Starting and stopping VNEs, and setting
polling information per VNE.
• Global Settings:
• Clients Licenses: Installing and managing Sheer DNA Client
licenses
• DB Segments: Viewing the storage allocated for all of the database
segments
• Messages of the Day: Generating a message of the day (service
disclaimer)
• Polling Groups: Customizing protection groups
• Protection Groups: Setting up scopes of devices and system users
• Topology: Managing static and persistent topology links.
• Workflow Engine: Enables the administrator to manage workflow
templates and running workflows in runtime.
• Scopes: Enables the administrator to group a collection of managed
Network Elements together in order to enable the user to view and/or
manage the Network Elements based on the user’s role.
• Users: Enables the administrator to define and manage user accounts.
Page 6 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 23

Introducing Sheer DNA
1.4 Additional Concepts and Terms
The sections below include additional concepts and terms used in the Sheer
DNA Manage application and throughout this guide.
AVM
The Sheer DNA Units are divided into AVMs (Autonomous Virtual
Machines). These AVMs are Java processes that provide the necessary
distribution support platform for executing and monitoring multiple VNEs.
AVMs and VNEs should reside on a Sheer DNA Unit (as a common
configuration) but they can also reside on a Sheer DNA Gateway.
There are some types of AVMs that run on the server which do not run
VNEs. These AVMs have reserved ID numbers, namely, AVM 0-100 and these
cannot be used. In addition, there are other reserved AVM ID numbers. The
following AVMs have special roles assigned to them, namely:
• AVM 0 (the switch AVM)
• AVM 11 (the Gateway)
• AVM 66 (the workflows AVM)
• AVM 99 (the management AVM)
• AVM 100 (the trap management AVM)
Device/Network Element
A network component existing in the network, for example, the devices
displayed in Sheer DNA and in Sheer NetworkVision.
Element Management
The base configuration for the creation of the managed element. Sheer DNA
Manage enables the user to create VNEs, for example, by entering the IP
address, SNMP and polling rate information and so on. This is called
Element Management.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 7
Page 24

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
License
Sheer DNA Client applications and BQL connectivity is based on installed
license files. Sheer DNA Manage enables the administrator to control and
monitor the number of Sheer DNA Client and BQL connections over a
limited or unlimited period of time based on the client licenses installed. Two
types of licenses are supported, namely, fixed (the number of installed users
are identified by user names or IP addresses or both) or floating (the number
of installed users operating concurrently).
Managed Element
After Sheer DNA Manage installs and runs the process, samples the device
and collects the data a VNE (Managed Element) is created. The VNE
includes logical inventory (tables, for example, forwarding tables) and
physical inventory (for example, modules and ports), and this Managed
Element can be accessed using Sheer NetworkVision.
Network Element Components
Component(s) of a Network Element (NE), such as port(s), blade(s),
context(s) and so on.
Permission
The user’s ability to perform certain tasks. There are two types of
permissions, namely, default and NE related.
• Default: The default permission only applies to the activities that are
related to GUI functionality, not the activities related to Network
Elements. For example, a user with the default permission Viewer can
view maps and the Device List. For more information, refer to page 136.
• Network Element: The NE related permission enables the administrator
to group a collection of managed Network Elements together (in Sheer
DNA Manage) in order to enable the user to view and/or manage the NEs
based on the user’s role or permission. After the user is allocated a scope
(list of Network Elements) and a role, the user can then perform various
activities on the Network Elements, for example, manage alarms in Sheer
NetworkVision. For more information, refer to page 135.
Polling Group
A polling group is defined as a group of polling rates that can be specified for
a device. For more information, refer to page 114.
Page 8 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 25

Introducing Sheer DNA
Protection Group
A Protection Group is a cluster to which Units and Standby Units are related.
In case of Unit failover then the Redundant Unit will be taken from the same
Protection Group.
Redundant Unit
The Sheer DNA Unit comes with built-in redundancy for maximum up time
and automatic switching. A threshold configurable watchdog constantly
monitors the Sheer DNA Units and Sheer DNA Gateway and can make an
automatic or manual (operator approved) switch over when there is no
response from the monitored entity. The system is always up-to-date via real
time investigation of the network. The redundancy mechanism ensures
synchronization of the active and backup Sheer DNA units. Once activated,
the standby Sheer DNA node is immediately synchronized with the network.
Roles
Sheer DNA implements a security engine that combines a role-based security
mechanism that is applied on scopes of Network Elements granted per user.
The system supports user accounts creation, multiple Network Element scope
definition and a set of five pre-defined roles for security and access control to
allow different system functions:
• Administrator: Manage the system configuration and security.
• Configurator: Activate services, and configure the network.
• Operator Plus: Able to fully control alarm life cycle and create maps.
• Operator: Configure business tags and perform most day-to-day
operations.
• Viewer: Read only access to the network and to non-privileged system
functions.
Roles can be granted per scope or at an application level (default permission),
namely, all the activities that are related to GUI functionality, not the
activities related to devices. The default permission includes:
• Application login.
• Manage alarms in Sheer NetworkVision.
• Manage maps: Creating, deleting, and opening.
• Map manipulation: Arrange map, including, aggregations, adding NEs,
NEs placement in map, map background and so on.
• Business tag management.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 9
Page 26

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Scopes
A scope is a named collection of managed Network Elements that have been
grouped together in order to allow a user to view and/or manage the Network
Elements provided a given role. Grouping can be based on geographical
location, Network Element type (such as DSLAM, router, SW, etc.), Network
Element category (such as access, core, etc.) or any other division according
to the network administrator’s requirements.
Using NetworkVision, a user that has been assigned a scope can view and/or
manage the NEs within this scope according to the role assigned to the user
as per the scope. The user cannot view any information regarding NEs that
are outside the user’s scope, including basic properties, inventory, and
alarms.
Static Link
A static link is a physical link that is not automatically discovered by the
system. The user manually creates the static link between Network Elements
by selecting the two end ports from the NE’s physical inventory.
Transport Link
A transport link is a logical link used for communication between the units
and for transferring information.
Users
In order for a user to work with Sheer DNA the following requirements must
be met:
• The user must have a valid license installed.
• The user must have a defined Sheer DNA user account.
• The user must have an assigned permission.
For more information about users, refer to Chapter 10, Managing Sheer DNA
Security.
Page 10 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 27
Introducing Sheer DNA
Workflow
A workflow consists of several tasks grouped together and arranged in a
flowchart. All workflows are stored on the Sheer DNA Gateway. After a
workflow is deployed, it is accessible using Sheer DNA Manage in order to
view properties and status. Deployed workflow templates can be invoked via
the Sheer DNA API using BQL. In addition, the user can view a history of
the invoked workflows using Sheer EventVision. For more information, refer
to this guide and the Cisco Active Network Abstraction Workflow User’s
Guide.
1.5 Terminology and Conventions
This Sheer DNA Administrator’s Guide uses the following conventions:
Convention Description
^ or Ctrl
The ^ and Ctrl symbols represent the Control key. For
example, the key combination ^D or Ctrl-D means hold
down the Control key while pressing the D key. Keys are
indicated in capital letters but are not case sensitive.
Command syntax descriptions use the following conventions:
Convention Description
boldface
Boldface text indicates commands and keywords that the
user enters literally as shown.
italics
Italic text indicates arguments for which the user supplies
values.
[x]
Square brackets enclose an optional element (keyword or
argument).
|
A vertical line indicates a choice within an optional or
required set of keywords or arguments.
[x | y]
Square brackets enclosing keywords or arguments
separated by a vertical line indicate an optional choice.
{x | y}
Braces enclosing keywords or arguments separated by a
vertical line indicate a required choice.
Nested sets of square brackets or braces indicate optional or required choices
within optional or required elements. For example:
Convention Description
[x {y | z}]
Braces and a vertical line within square brackets indicate
a required choice within an optional element.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 11
Page 28
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Examples use the following conventions:
Convention Description
screen
Examples of information displayed on the screen are set
in Courier New font.
Boldface
screen
< >
Examples of text that the user must enter are set in
Courier New bold font.
Angle brackets enclose text that is not printed to the
screen, such as passwords.
[ ]
Square brackets enclose default responses to system
prompts.
{ }
Curly brackets group mandatory parameters together
where there are options.
Related Documentation
For more detailed information, refer to the following publications:
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction NetworkVision User’s Guide
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction EventVision User’s Guide
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction Servers Installation Guide
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction Client Installation Guide
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction Error Messages
• Cisco Active Network Abstraction Workflow User’s Guide
Page 12 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 29

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
2 Getting Started with Sheer DNA
Manage
About this chapter:
This chapter describes the Sheer DNA Manage working environment and
how to access Sheer DNA Manage tools and commands. It also provides
instructions for launching and overviews operating the Sheer DNA Manage
application-using menu and toolbar options.
The Sheer DNA Manage window provides access to all of Sheer DNA
Manage’s functionality.
Starting Sheer DNA Manage, below, describes how to open the Sheer DNA
Manage window.
The Sheer DNA Manage Window, page 15, briefly describes the Sheer
DNA Manage window, including the Tree pane and Workspace.
Sheer DNA Manage Window, Menus and Toolbar, page 19, provides a
detailed description of the Sheer DNA information displayed in the Sheer
DNA Manage window, the menus, and toolbars.
Logging Out, page 56, describes how to log out of Sheer DNA Manage.
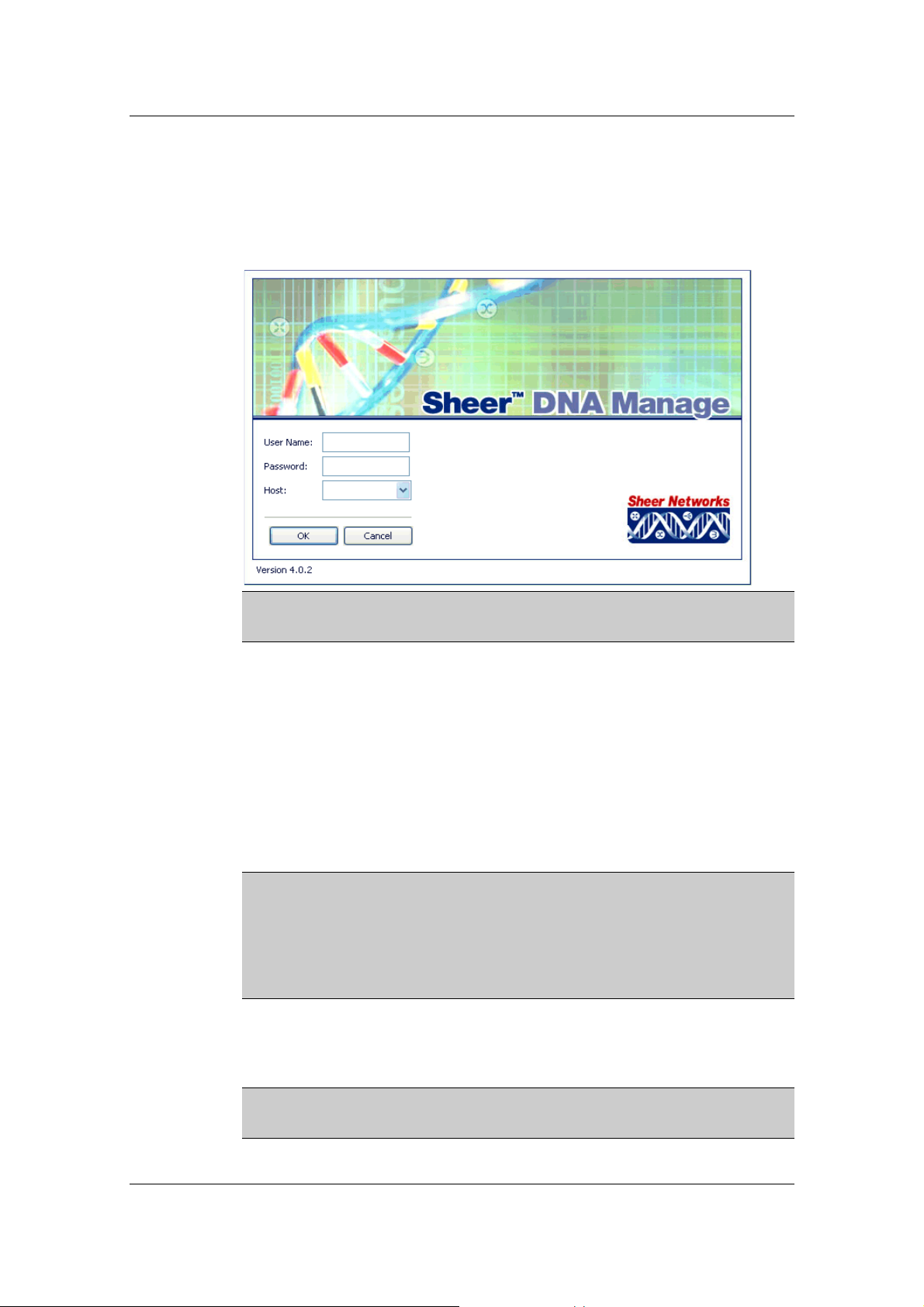
2.1 Starting Sheer DNA Manage
Sheer DNA Manage is password protected to ensure security, and is only
available to users with Administrator privileges. Before you start working
with Sheer DNA Manage, make sure you know the user name, password and
the Sheer DNA Gateway IP address or host name that you require.
Note: If a user does not login to the Sheer DNA Manage, NetworkVision or
EventVision applications during a specified period of time (the default is one
month) the user’s account will be locked automatically. The default period
can be changed in the Sheer DNA Registry. The period of time is measured
from the time the user last logged out of any of the Sheer DNA Client
applications. For information about unlocking a user, refer to page 147.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 13
Page 30
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
To start Sheer DNA Manage
1. From the Start menu, select the Programs folder, then Sheer
DNA/Sheer DNA Manage. The Sheer DNA Manage - Login dialog box
is displayed.
Note: It is recommended that the administrator change the user name and
login password after logging in for the first time.
The last four Sheer DNA Gateways to which the user logged in
successfully are displayed in the Host dropdown list. The list is
displayed in chronological order with the most recent Sheer DNA
Gateway displayed at the top of the list.
2. Enter the required Sheer DNA Gateway’s information in the Host field,
as an IP address or host name,
or
Select a Sheer DNA Gateway from the Host dropdown list.
Note: The Sheer DNA Gateway IP address or host name that was used
when you last logged in is automatically displayed at the top of the Host
dropdown list.
Note: Make sure that you use the leading IP address (the IP on which the
Sheer DNA Gateway was configured) when logging in to the system.
3. Click OK. The Sheer DNA Manage window is displayed. The user name
and host information is displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window
heading.
Note: Some of the Workspaces in the Sheer DNA Manage window may
appear empty when the application is opened for the first time.
Page 14 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 31

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
2.2 The Sheer DNA Manage Window
The Sheer DNA Manage window is displayed below.
Menu bar
Toolbar
Tree pane
Shortcut
menu
Status bar
Workspace
The Sheer DNA Manage window is divided into areas or panes, as follows:
• The Tree pane, as described on page 15.
• The Workspace, as described on page 18.
• The Status Bar, displays the memory usage of the application process
and connection status.
Dragging the borders of the Sheer DNA Manage window adjusts the size of
each area. The two areas are correlated; this means that selecting an option in
the Tree pane affects the information displayed in the Workspace.
2.2.1 Sheer DNA Manage Tree Pane
The Tree pane displays a tree-and-branch representation of the Sheer DNA
Manage folders. The branches can be expanded and collapsed in order to
display and hide information as needed. An example of the Tree pane is
displayed above.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 15
Page 32

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to manage and maintain information in
the Sheer DNA using the following branches in the Sheer DNA Manage
window:
• DNA Servers: Enables the administrator to manage information relating
to the Sheer DNA Gateway, and Sheer DNA Units, including the AVMs
and the VNEs in the Sheer DNA. This includes viewing a list of Sheer
DNA Units, adding, editing and removing AVMs and VNEs, viewing
VNE and AVM properties, starting and stopping AVMs and VNEs, and
moving VNEs to maintenance mode. The DNA Servers branch includes
the DNA Gateway and AVM sub-branches. For more information about
the DNA Servers branch, refer to page 20.
• Global Settings: The Global Settings branch includes the Client
Licenses, DB segments, Message of the Day, Polling Groups and
Protection Groups sub-branches. The Global Settings branch enables the
administrator to:
• Install and manage Sheer DNA Client licenses.
• Enables the administrator to view a table describing the storage
allocated for all the database segments. For more information about
the DB Segments branch, refer to page 37.
• Manage the service disclaimer (message of the day). For more
information about the Service Disclaimer Message of the Day, refer
to page 113.
• Manage the polling groups to be used by a group of devices. The
administrator can define a few polling groups, and the devices will
then be polled according to the polling group. Every polling group
has a different set of polling intervals. For more information about the
Polling Groups branch, refer to page 114.
• Manage and change the default setup of the Sheer DNA Units by
customizing protection groups (clusters) and then assigning Sheer
DNA Units to these protection groups. For more information about
the Protection Groups branch, refer to page 121.
For more information about the Global Settings branch, refer to page 33.
• Scopes: Enables the administrator to group a collection of managed
Network Elements together in order to enable the user to view and/or
manage the Network Elements based on the user’s role. For more
information about the Scopes branch, refer to page 44.
• Topology: Enables the administrator to manage topology-related
parameters, namely, the static links between the devices. For more
information about the Topology branch, refer to page 47.
Page 16 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 33
Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
• Users: Enables the administrator to define and manage user accounts.
For more information about the Users branch, refer to page 49.
• Workflow Engine: Enables the administrator to manage workflow
templates and running workflows in runtime. For more information
about the Workflow Engine branch, refer to page 52.
Clicking on a branch in the Tree pane enables the user to view information
relating to the selected branch in the Workspace. Right-clicking on a branch
in the Tree pane, opens a shortcut menu enabling the user to perform various
functions.
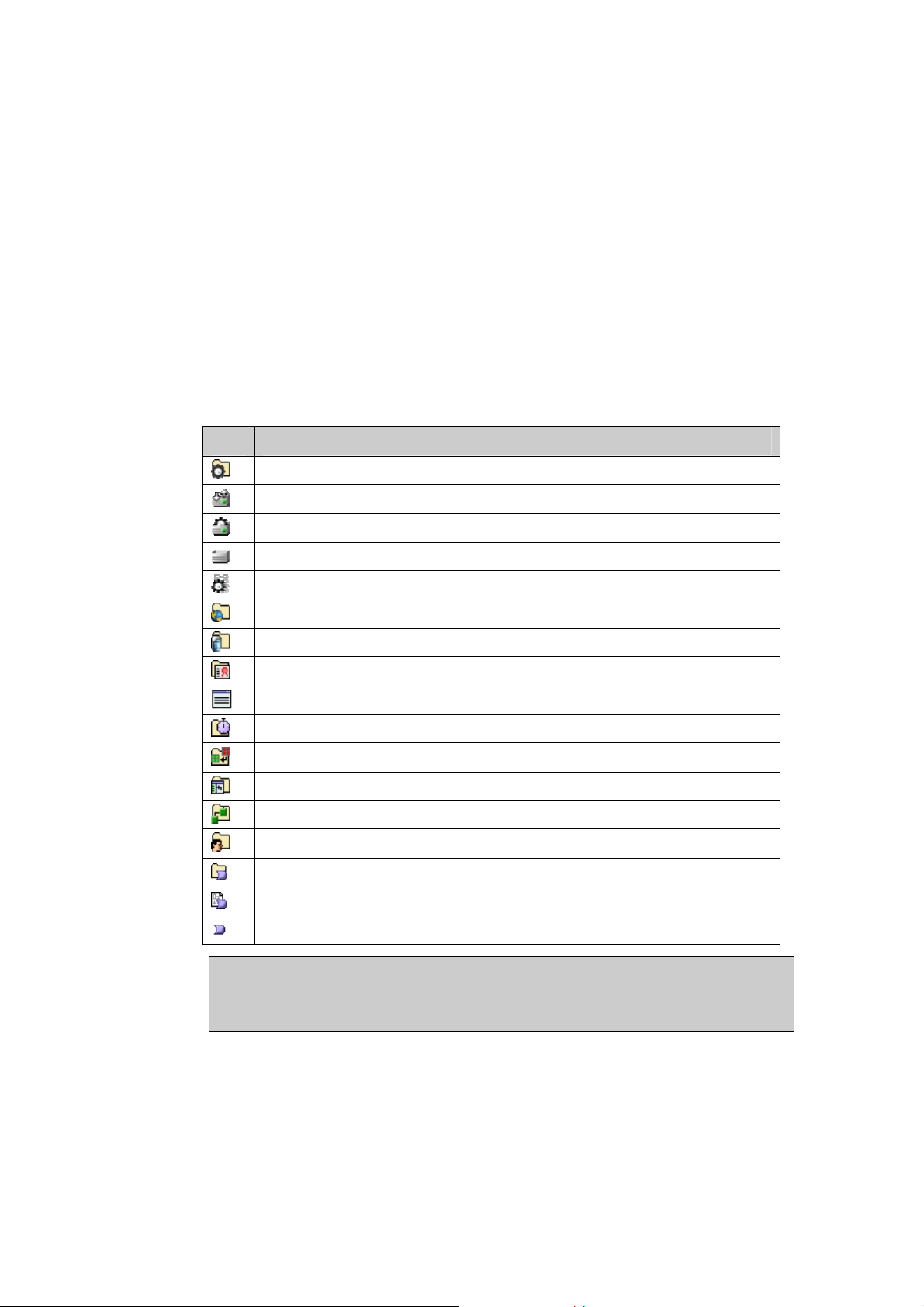
The following icons are displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window:
Icon Description
DNA Servers branch
Sheer DNA Gateway
Sheer DNA Units
Sheer DNA Redundant Unit
AVMs (VNE)
Global Settings branch
DB Segments
Client Licenses
Message of the Day
Polling Groups
Protection Groups
Scopes
Topology
Users
Workflow Engine
Templates
Workflows
Note: The menus and toolbar displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window
are context sensitive; the options vary depending on your selection in the
Tree pane and the Workspace.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 17
Page 34

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
2.2.2 Sheer DNA Manage Window Workspace
The Workspace is displayed on the right side of the Sheer DNA Manage
window and enables the user to view Sheer DNA Manage information
according to the branch selected in the Tree pane. The information displayed
varies according to the branch selected in the Tree pane.
Note: Multiple rows can be selected using the standard Microsoft® Windows
selection keys when a table is displayed in the Workspace.
The Selection field displayed at the bottom of the Workspace displays the
number of selected rows and the total number of rows in the table, for
example, 6/6 Selected (refer to page 17).
In addition, it displays the location of the selected row(s) in the table, for
example, Line 2.
Table Toolbar
Whenever a table forms part of the Workspace, the same toolbar is displayed,
no matter which branch is selected in the Tree pane.
The table toolbar contains the following tools:
Export to CSV: Enables the user to save the current Sheer DNA
Manage working environment as a file in the Sheer DNA. For more
information, refer to page 68.
Sort Table Values: Enables you to sort the information displayed in
the table, for example, according to status or IP address.
Page 18 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 35

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Filter: Enables the user to define a filter on the information
displayed in the table of the Workspace using the Filter dialog box.
For more information, refer to page 63.
Note: When a filter is applied the Set Selection Filter button and the
Rewind All option under the Previous Selection Filter buttons is
activated.
Set Selection Filter: Applies filters to the selected line or lines.
Note: When the user selects one or multiple lines in a table, the
Previous Selection Filter button is activated.
Previous Selection Filter: Enables the user to undo the last applied
filter selection.
Rewind All option: Enables the user to undo all previous applied
filter selections, and returns all the originally displayed data to the
table displayed in the Workspace.
Opens the online Sheer DNA Manage Help.
For operating instructions on selecting lines and applying filters, refer to the
sections Filtering Information and Setting Selection Filters in Chapter 4,
General DNA Manage Tables.
The Find field enables the user to search for information relating to the
branch selected in the Tree pane. For more information about searching for
information, refer to page 63.
2.3 Sheer DNA Manage Window, Menus and Toolbar
This section provides a detailed description of the Sheer DNA information
displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window depending on the branch
selected, the menus, and toolbars.
For specific information about each branch, refer to:
• DNA Servers, page
• DNA Server Entities, including the DNA Gateway and DNA Units,
page 24.
20.
• AVMs, page 29.
• Global Settings, page
• Scopes, page
44.
33.
• Topology, page 47.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 19
Page 36

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Users, page 49.
• Workflow Engine, page 52.
2.3.1 DNA Servers Branch
Sheer DNA Manage maintains a list of all of the DNA Servers defined in the
system. The DNA Servers branch enables the user to add and remove DNA
Unit Servers.
The user can expand this branch to view a list of the Sheer DNA Units, Sheer
DNA Gateway and AVMs. Each Sheer DNA Gateway, Sheer DNA Unit and
AVM has its own sub-branch. The DNA Servers branch (and associated subbranches) enables the user to manage information relating to the AVMs and
VNEs contained in the Sheer DNA Units.
Note: AVMs and VNEs should reside on a Sheer DNA Unit (as a common
configuration) but they can also reside on a Sheer DNA Gateway.
The DNA Servers branch is displayed below.
The DNA Servers branch contains the following sub-branches:
• DNA Gateway and DNA Unit, namely, DNA Server Entities, refer to
page
24.
• AVMs, refer to page 29.
Page 20 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 37
Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
For more information about DNA Server menu and toolbar options:
• Menu options, refer to page 21.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 23.
The Workspace area of the DNA Servers branch enables the user to view a
list of all of the Sheer DNA Gateways and Sheer DNA Units and their status.
Clicking on a column heading in the table in the Workspace sorts the Sheer
DNA Units in ascending or descending order according to the selected
column.
Note: Any changes that are made to the DNA Servers branch are saved
automatically and registered immediately in the Sheer DNA.
The following columns are displayed in the table in the Workspace:
• IP Address: The IP address of the Sheer DNA Units, and Sheer DNA
Gateways as defined in Sheer DNA Manage.
• Status: The status of the Sheer DNA Unit, as follows:
• Up: The Sheer DNA Unit is up.
• Down: The Sheer DNA Unit is down.
• Unreachable: The Sheer DNA Unit cannot be reached.
• Up Since: The date and time when the DNA Unit was last loaded.
• Physical Memory: The physical memory of the Sheer DNA Unit.
• Used Memory: The memory being used by the Sheer DNA Unit.
• Allocated Memory: The amount of memory allocated to the Sheer DNA
Unit. Allocated memory is the sum of all of the memory settings for all
of the AVMs.
• Protection Group: The protection group to which the Sheer DNA Unit
has been allocated.
• AVM HA: The Sheer DNA Unit is enabled for high availability (true)
or disabled (false). By default this option is enabled for high availability.
For more information about the DNA Servers branch, refer to Chapter 5,
Managing Sheer DNA Units.
Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the DNA Servers branch is selected. The following menus are available:
• File menu, as described in the next section.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 21
Page 38

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 23.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 23.
File Menu – DNA Servers Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New DNA Unit
Creates a new DNA Unit.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage. For more information, refer to page 56.
Tools Menu – DNA Servers Branch
The Tools menu is displayed below.
Change User Password
Enables the user to change the password used, when logging in to the Sheer
DNA Client application suite. The change will take effect the next time that
the user logs in to the application. The Tools menu option is the same
throughout the application.
Help Menu
The Help menu is displayed below.
The Help menu enables the user to display application information, for
example, the version number. The Help menu options are the same
throughout the application.
Page 22 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 39

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Tree Pane Menu – DNA Servers Branch
When the user right-clicks on the DNA Servers branch the following menu is
displayed:
New DNA Unit
The user can add a new Sheer DNA Unit to the Sheer DNA Servers.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – DNA Servers Branch
When the user right-clicks on a Sheer DNA Unit or DNA Gateway in the
table in the Workspace the following menu is displayed:
New AVM
Adds an AVM to the selected Sheer DNA Unit. For more information, refer
to page 80.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected Sheer DNA Unit in a Properties dialog
box. For more information, refer to page 73.
Switch
This option is available when high availability is enabled and is only
available for Sheer DNA Units. Manually switch to the standby Sheer DNA
Unit. For more information, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction
High Availability User’s Guide.
Delete
Deletes the selected Sheer DNA Unit. For more information, refer to page 75.
DNA Manage Toolbar – DNA Servers Branch
The DNA Servers branch contains the following tools (available tool bar
options):
Adds a new Sheer DNA Unit to the Sheer DNA Server.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 23
Page 40

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the Sheer
DNA Servers.
When a Sheer DNA Unit is selected in the table of the Workspace the
following tools are displayed in the toolbar:
Creates a new AVM in the selected Sheer DNA Unit or
Gateway.
Displays the properties of the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Deletes the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the Sheer
DNA Servers.
For more information about the DNA Servers branch, refer to Chapter 5,
Managing Sheer DNA Units.
2.3.2 DNA Server Entities Branch
The DNA Server Entities sub-branch includes the DNA Gateway and DNA
Unit sub-branches. All the options described here refer to both sub-branches.
The DNA Server Entities sub-branch enables the user to manage information
relating to the AVMs and VNEs on a selected Sheer DNA Unit. These
include:
• Adding, editing and removing an AVM
• Switching manually to the standby Sheer DNA Unit
• Viewing AVM properties
• Moving AVMs
• Starting and stopping AVMs and VNEs
• Adding VNEs
Page 24 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 41
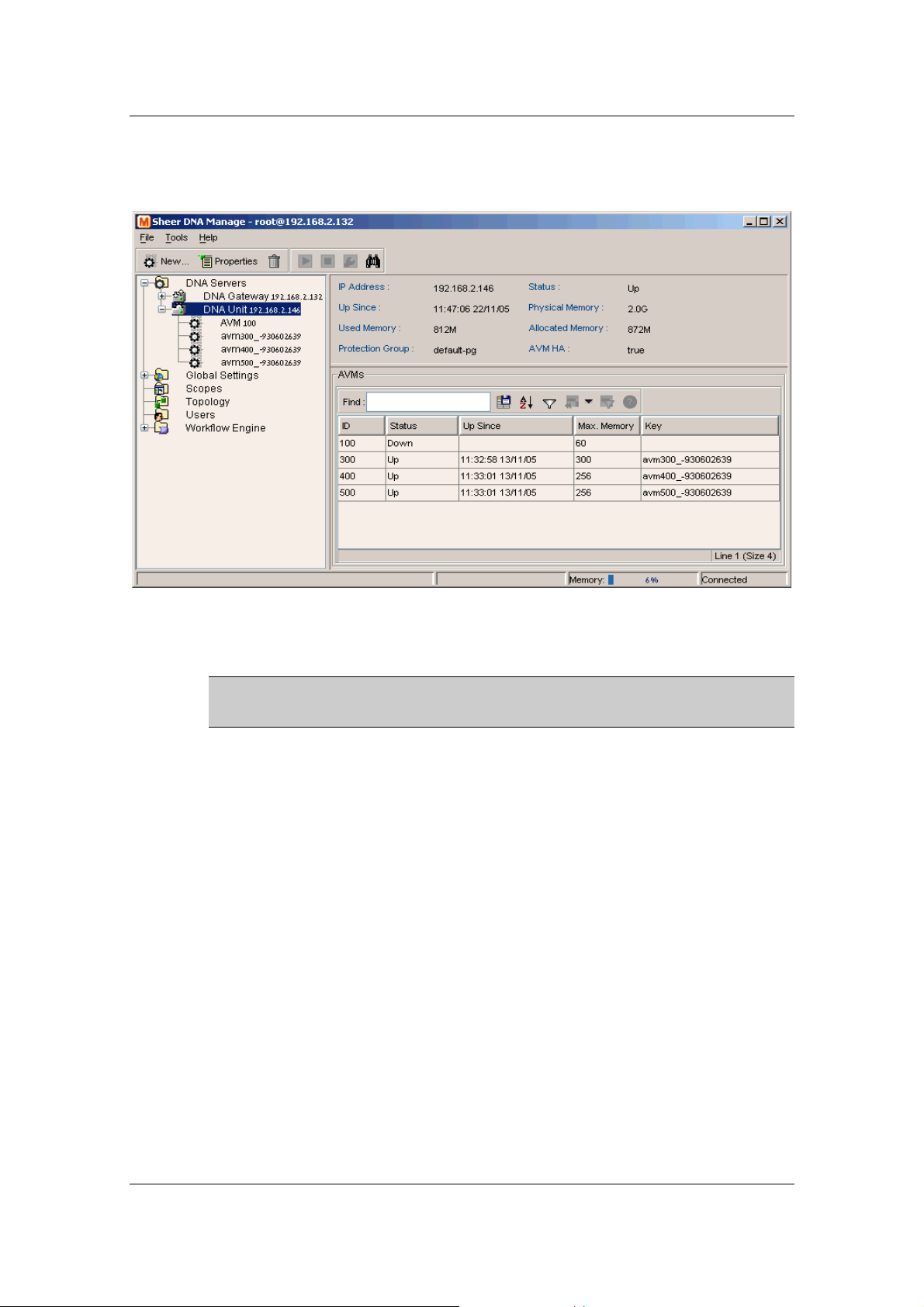
Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
An example of the Sheer DNA Manage window when a DNA Servers Entity
sub-branch is selected is displayed below.
Each row in the table in the Workspace enables the user to view the status of
an AVM. The AVMs can be sorted in ascending or descending order by
clicking on the column heading in the table.
Note: Any changes that are made to the DNA Servers Entity sub-branch are
saved automatically and registered immediately in the Sheer DNA.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table for the AVMs
that are listed or running under the server entity:
• ID: The name of the AVM as defined in Sheer DNA and unique to the
AVM, for example, AVM 18.
• Status: The status of the AVM, as follows:
• Starting Up: When an AVM is started.
• Up: The AVM is up.
• Shutting Down When an AVM is stopped.
• Down: The AVM is down.
• Unreachable: The AVM cannot be reached.
• Up Since: The date and time that the Sheer DNA Unit was last started.
• Max Memory: The maximum allocated memory size as defined when
the AVM was created in Sheer DNA Manage. The default value is
256 MB.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 25
Page 42

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Key: The key of the AVM, which is unique to the system. By default the
key is displayed as “AVM + ID + timestamp”.
For more information about DNA Server specific menu and toolbar options:
• Menu options, refer to page 26.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 28.
DNA Server Entities Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the DNA Server sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• File menu, as described on page 26.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 27.
• Workspace menu, as described on page 27.
File Menu – DNA Servers Entities Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New AVM
Adds an AVM to the selected Sheer DNA Unit. For more information, refer
to page 80.
Properties
Displays the DNA Unit Properties dialog box. This dialog box lists the
properties of the selected Sheer DNA Unit and indicates its status. For more
information, refer to page 73.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage.
Page 26 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 43

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Tree Pane Shortcut Menu – DNA Server Entities Branch
When the user right-clicks on the DNA Server Entities sub-branch in the Tree
pane the following shortcut menu is displayed:
New AVM
Adds an AVM to the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Switch
This option is available when high availability is enabled and is only
available for Sheer DNA Units. Manually switch to the standby Sheer DNA
Unit. For more information, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction
High Availability User’s Guide.
Delete
Deletes the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – DNA Servers Entity Branch
When the user right-clicks an AVM in the Tree pane or in the table in the
Workspace the following menu is displayed:
New VNE
Adds a New VNE to the chosen AVM.
Note: A new VNE cannot be added to the reserved AVMs 0-100.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 27
Page 44

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Actions
Enables the user to start or stop an AVM.
Delete
Deletes an AVM.
Move AVM
Move an entire AVM between DNA Units.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected AVM and its status in the General tab
of a dialog box.
DNA Manage Toolbar – DNA Server Entities Branch
When the DNA Server Entities sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the
following tools are displayed in the toolbar:
Creates a new AVM in the selected Sheer DNA Unit or
Gateway.
Displays the Sheer DNA Server properties and status.
Deletes the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the
Sheer DNA Servers.
When an AVM is selected in the table in the Workspace the following tools
are displayed in the toolbar:
Creates a new VNE in the selected AVM.
Displays the AVM properties and status. For more
information, refer to page
Deletes the selected AVM.
82.
Starts the selected AVM. For more information, refer to
page 85.
Stops the selected AVM. For more information, refer to
page 85.
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the Sheer
Page 28 Cisco Systems, Inc.
DNA Servers.
Page 45

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
For more information on the DNA Servers Entity sub-branch, refer to
Chapter 6, Managing AVMs and VNEs.
2.3.3 AVM Branch
The AVM sub-branch enables the user to manage information relating to the
VNEs in a selected AVM. This includes:
• Adding, editing and removing a VNE
• Viewing VNE or AVM properties
• Deleting an AVM
• Moving AVMs and/or VNEs
• Starting and stopping VNEs or AVMs
• Moving VNEs to maintenance mode
An example of the Sheer DNA Manage window when the AVM sub-branch is
selected is displayed below.
When the user selects the AVM sub-branch the workspace displays the
properties of the AVM and a table with the list of VNEs.
Note: No VNEs are displayed when a special AVM (for example, AVM 66)
that belongs to the Gateway is selected.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 29
Page 46

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table:
• Key: The unique key of the VNE.
• IP Address: The IP address of the device as defined in Sheer DNA
Manage.
• Status: The status of the VNE, as follows:
• Starting Up: When a VNE is started.
• Up: The VNE is up.
• Shutting Down When a VNE is stopped.
• Down: The VNE is down.
• Unreachable: Sheer DNA failed to access the VNE.
• Maintenance: Indicates whether the VNE is or is not in maintenance
mode, namely, true or false.
• Up Since: The date and time that the VNE was last started.
• SNMP: Indicates whether this option is enabled or disabled on the VNE,
namely, true or false.
• Telnet: Indicates whether this option is enabled or disabled on the VNE,
namely, true or false.
• Element Class: Detects the VNE category, namely, Auto Detect, Generic
SNMP, Cloud or ICMP.
• Element Type: The device type (manufacturer name), for example,
Cisco 7204.
• Polling Group: The name of the customized polling group or it is blank
if it is an instance.
For more information about VNEs, refer to Chapter 6, Managing AVMs and
VNEs the section on VNEs Overview.
For more information about AVM menu and toolbar options:
• Menu options, refer to page 30.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 33.
AVM Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the AVM sub-branch is selected. The following menus are available:
• File menu, as described below.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
Page 30 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 47

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 31.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 32.
File Menu – AVM Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New VNE
Adds a VNE to the selected AVM.
Note: A new VNE cannot be added to the reserved AVMs 0-100.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected AVM and its status.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage.
Tree Pane Shortcut Menu – AVM Branch
When the user right-clicks on the AVM sub-branch in the Tree pane the
following menu is displayed:
New VNE
Creates a VNE for the selected AVM. For more information, refer to page 80
Note: A new VNE cannot be added to the reserved AVMs 0-100.
Actions
Starts or stops an AVM. For more information, refer to page 85.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 31
Page 48
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Delete
Deletes an AVM from the Sheer DNA Server.
Note: Reserved AVMs 0-100 cannot be deleted.
Move AVM
Move an entire AVM between DNA Units. For more information, refer to
page 86.
Note: Reserved AVMs 0-100 cannot be moved.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected AVM.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – AVM Branch
When the user right-clicks on a selected VNE in the table the following
shortcut menu (and sub-menu, when required) options are displayed:
Actions
Enables the user to start, stop or delete a VNE. In addition, the VNE can be
moved to maintenance mode.
Delete
Deletes the selected VNE from an AVM.
Move VNEs
Move a single VNE between AVMs.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected VNE.
Page 32 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 49

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
DNA Manage Toolbar – AVM Branch
When the AVM sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the following tools
are displayed in the toolbar:
Creates a new VNE in the selected AVM.
Displays the properties of the selected AVM.
Deletes the selected AVM.
Starts the selected AVM.
Stops the selected AVM.
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the Sheer
DNA Servers.
When a VNE is selected in the table in the Workspace the following tools are
displayed in the toolbar:
Creates a new VNE in the selected AVM.
Displays the properties of the selected VNE.
Deletes the selected VNE from an AVM.
Starts the selected VNE.
Moves the selected VNE to maintenance mode.
Stops the selected VNE.
Search for a Sheer DNA Unit/AVM/VNE amongst all the Sheer
DNA Servers.
For more information on the AVM sub-branch, refer to Chapter 6, Managing
AVMs and VNEs.
2.3.4 Global Settings Branch
The Global Settings branch maintains system-wide settings, for example,
polling and protection groups. Any changes that are made to the settings
affect the configuration throughout the entire system.
The Global Settings branch includes the following sub-branches:
• Client Licenses, refer to page 34
• DB Segments, refer to page 37
• Message of the Day, refer to page 38
• Polling Groups, refer to page 39
• Protection Groups, refer to page
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 33
41
Page 50
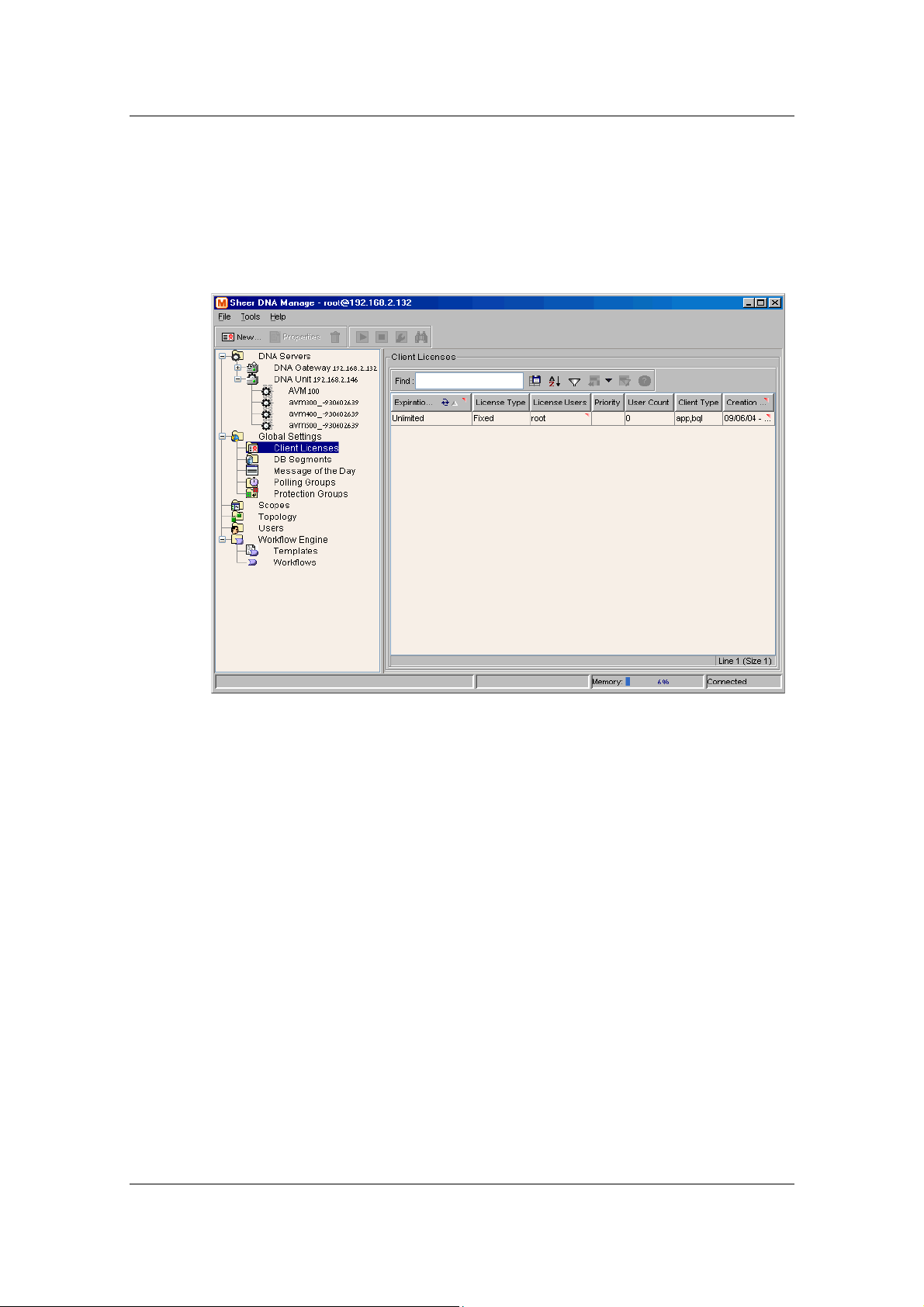
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Client Licenses
The Client Licenses sub-branch enables control and monitoring of the
number of Sheer DNA Client connections over a limited or unlimited period
of time as defined in terms of the client license. The Sheer DNA Manage
window with the Client Licenses sub-branch selected is displayed below.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table when the Client
Licenses sub-branch is selected:
• Expiration Date: Date of the expiration of the license. The license can
be for a limited or unlimited period of time.
• License Type: The license type, namely:
• Fixed: The number of installed users are identified by user names or
IP addresses or both. For example, 5 users with the user names a, b,
c, d and e.
or
• Floating: The number of installed users operating concurrently
(unspecified). For example, 5 users.
• License Users: The user names and/or IP addresses of the users.
• Priority: Available in a future version.
• User Count: The number of users allowed to operate the Sheer DNA
Client applications, as defined in terms of the license. The exact number
of users is displayed if the number is limited or 0 indicates an unlimited
number of users.
Page 34 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 51

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
• Creation Date: The date when the license was implemented.
• Client Type: The applications to which the user is authorized to connect,
namely, BQL and/or Sheer DNA Client applications.
For more information about:
• Menus options, refer to page 35.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 36.
Client Licenses Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Client Licenses sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• File menu, as described below.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 36.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 36.
File Menu – Client Licenses Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New License
Install a new license.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected license.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 35
Page 52

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Tree Pane Menu – Client Licenses Branch
Right clicking on the Client Licenses sub-branch displays the following
menu:
New License
Install a new license.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Client Licenses Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu is displayed:
Delete
Deletes the selected license.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected license.
Toolbar – Client Licenses Branch
When the Client Licenses sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the toolbar
contains the following tools:
Install a new license.
Displays the properties of the selected license.
For more information about client licenses, refer to page
Deletes the selected license.
107.
Page 36 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 53

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
DB Segments Branch
The DB segments branch in Sheer DNA Manage displays a table describing
the storage allocated for all database segments. An example of the Sheer
DNA Manage window when the DB Segments branch is selected is displayed
below.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table when the DB
Segments branch is selected:
• Name: Name of the segment.
• Type: Type of segment, namely, INDEX PARTITION, TABLE
PARTITION, TABLE, CLUSTER, INDEX, ROLLBACK, DEFERRED
ROLLBACK, TEMPORARY, CACHE, LOBSEGMENT and
LOBINDEX
• Tablespace Name: Name of the table space containing the segment.
• Partition Count: Number of partitions.
• Extent Count: Number of extents allocated to the segment where the
data is stored.
• Next Extent Size: Size in bytes of the next extent to be allocated to the
segment.
• Bytes: Size in bytes, of the segment.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 37
Page 54

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Service Disclaimer Message of the Day
The Message of the Day sub-branch enables the user to define a message
(service disclaimer) that will be displayed when a user logs in to the Sheer
Client applications. An example of the Sheer DNA Manage window when the
Message of the Day sub-branch is selected is displayed below.
The following areas are displayed in the Workspace:
• Title: The title of the message, which is displayed as the title of the
dialog box. By default the title “Terms of Use” is displayed.
• Message: A free text message for the user. The message supports HTML
format.
Note: The Abort and Continue buttons are displayed in the message
dialog box by default, so the message must relate to these actions. The
user must accept (Continue) the service disclaimer otherwise the user
will be unable to login.
The following button is displayed in the Workspace:
• Save: Saves the message so that it is displayed when the user logs in to a
Sheer Client application.
For more information about the Message of the Day branch, refer to
page 113.
Page 38 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 55
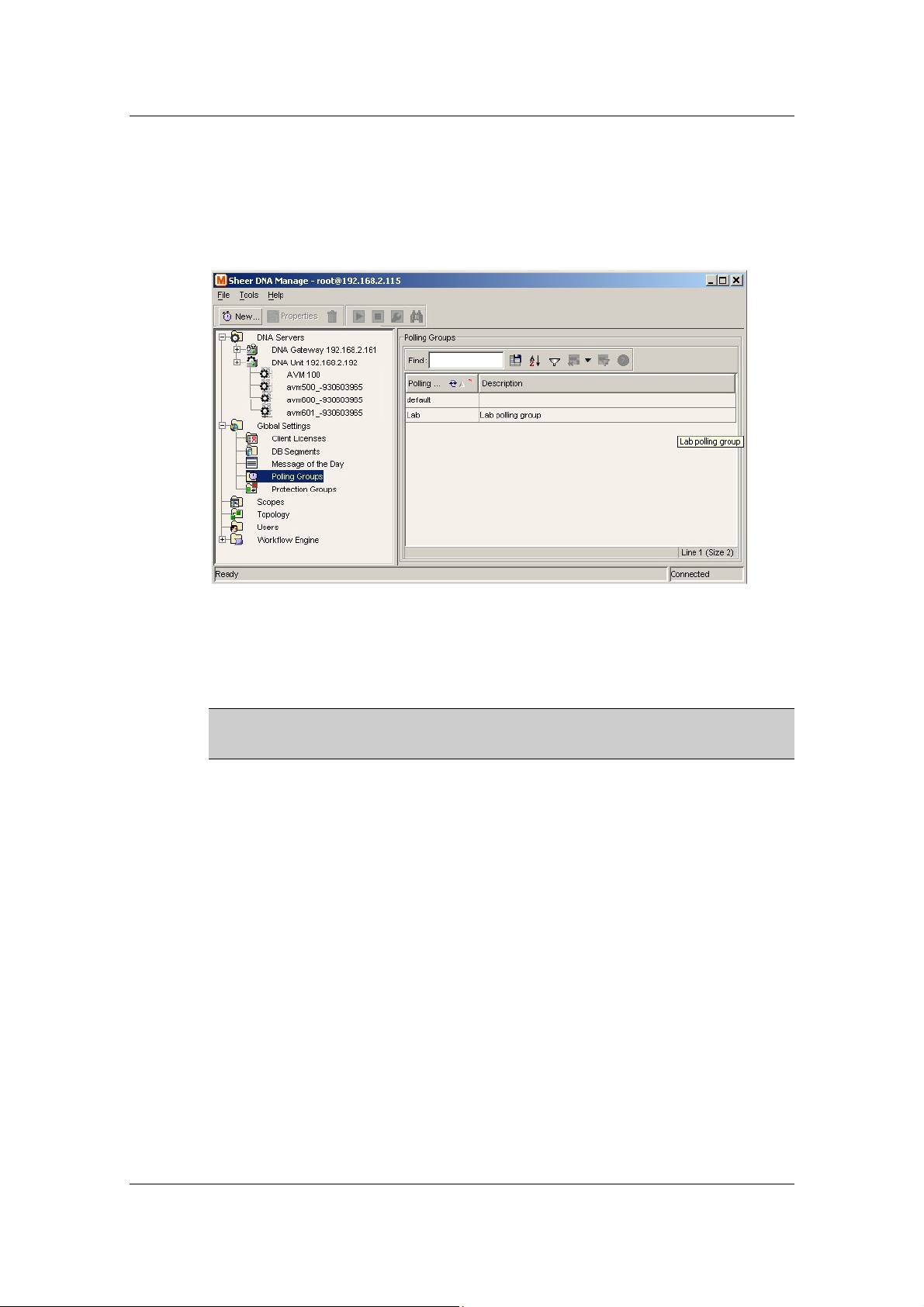
Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Polling Groups
The Polling Groups sub-branch enables the user to manage polling groups,
by categorizing a group of devices to be polled according to pre-set intervals.
The Polling Groups sub-branch is displayed below.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table when the
Polling Groups sub-branch is selected:
• Polling Group: The polling group name defined by the user
• Description: A description of the polling group.
Note: Any changes that are made to the Polling Groups sub-branch are saved
automatically and registered immediately in the Sheer DNA.
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to page 39.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 41.
Polling Group Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Polling Groups sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• File menu, as described on page 40.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 40.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 40.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 39
Page 56
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
File Menu – Polling Groups Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New Polling Group
Creates a new polling group.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected polling group.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage.
Tree Pane Menu – Polling Groups Branch
Right-clicking on the Polling Groups sub-branch displays the following
menu:
New Polling Group
Creates a new polling group.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Polling Groups Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu, is displayed:
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected polling group.
Delete
Deletes the selected polling group.
Page 40 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 57

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Toolbar – Polling Groups Branch
When the Polling Groups sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the toolbar
contains the following tools:
Creates a new polling group.
Displays the properties of the selected polling group.
Deletes the selected polling group.
When a polling group is selected in the table in the Workspace, clicking
Properties in the toolbar displays the properties of the polling group in a
Properties dialog box.
For more information about polling groups, refer to page 114.
Protection Groups
By default all the Sheer DNA Units in the Sheer DNA Fabric belong to one
big cluster. The Protection Groups sub-branch enables the administrator to
change the default setup of the Sheer DNA Units by customizing protection
groups (clusters) and then assigning Sheer DNA Units to these protection
groups.
For more information, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction High
Availability User’s Guide.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 41
Page 58

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
The Sheer DNA Manage window with the Protection Groups sub-branch
selected is displayed below.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table when the
Protection Groups sub-branch is selected:
• Name: The protection group name defined by the administrator.
• Description: A description of the protection group.
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to page 43.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 44.
Protection Group Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Protection Groups sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• File menu, as described on page 43.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 43.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 43.
Page 42 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 59

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
File Menu – Protection Groups Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New Protection Group
Creates a new protection group.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected protection group.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage.
Tree Pane Menu – Protection Groups Branch
Right clicking on the Protection Groups sub-branch displays the following
shortcut menu:
New Protection Group
Creates a new protection group.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Protection Group Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu is displayed:
Delete
Deletes the selected protection group.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected protection group in a Properties dialog
box.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 43
Page 60

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Toolbar – Protection Groups Branch
When the Protection Groups sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the
toolbar contains the following tools:
Creates a new protection group.
Displays the properties of the selected protection group.
Deletes the selected protection group.
For more information about protection groups, refer to the Cisco Active
Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.
2.3.5 Scopes Branch
The Scopes branch enables the administrator to group a collection of
managed Network Elements together in order to enable the user to view
and/or manage the Network Elements based on the role granted to the user
for the scope. For more information on the Scopes branch, refer to Chapter 9,
Managing DNA Security.
The Scopes branch is displayed below.
Each row in the table in the Workspace displays the name of a scope as
defined in Sheer DNA Manage.
Page 44 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 61

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to following section.
• Toolbar, refer to page 46.
Note: The menus and toolbar displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window
are context sensitive; the options vary depending on your selection in the
Tree pane and Workspace.
Scopes Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Scopes branch is selected. The following menus are available:
• File menu, as described in the following section.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 45.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 46.
File Menu – Scopes Branch
The File menu for the Scopes branch is displayed below.
New Scope
Creates a new scope.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected scope.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage. For more information, refer to page 56.
Tree Pane Shortcut Menu – Scopes Branch
When the user right-clicks on the Scopes branch in the Tree pane the
following menu is displayed:
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 45
Page 62

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
New Scope
Creates a new scope.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Scopes Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu is displayed:
Delete
Deletes the selected scope.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected scope.
Note: The user cannot delete or edit the All Managed Elements scope in the
table in the Workspace. For more information, refer to the Scopes section on
page 140.
Toolbar – Scopes Branch
When the Scopes branch is selected in the Tree pane the toolbar contains the
following tools:
Creates a new scope. For more information, refer to page 140.
Displays the properties of the selected scope.
Deletes the selected scope.
When a scope is selected in the table in the Workspace, clicking Properties
in the toolbar displays the properties of the selected scope in a Properties
dialog box.
Page 46 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 63

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
2.3.6 Topology Branch
The Topology branch enables the user to define static links between the
Network Elements in order to supplement or override existing autodiscovered topology. The Sheer DNA Manage window with the Topology
branch selected is displayed below.
The Topology branch displays all of the static links defined in the system
including the A Side and Z Side of the link.
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to page 47.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 49.
Topology Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Topology branch is selected. The following menus are available:
• File menu, as described in the following section.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 48.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 48.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 47
Page 64
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
File Menu – Topology Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New Static Link
Creates a new static link.
Properties
This option is unavailable.
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage. For more information, refer to page 56.
Tree Pane Shortcut Menu – Topology Branch
When the user right-clicks on the Topology branch in the Tree pane the
following menu is displayed:
New Static Link
Creates a new static link.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Topology Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following menu
is displayed:
Delete
Deletes the selected static link.
Page 48 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 65

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Toolbar – Topology Branch
The Topology branch contains the following tools:
Opens the New Link dialog box enabling the user to create a link
between two devices. For more information, refer to page 127.
Deletes the selected static link.
For more information about the Topology branch, refer to Chapter 8,
Managing Links.
2.3.7 Users Branch
The Users branch enables the administrator to define and manage user
accounts. For more information about the Users branch, refer to Chapter
Managing Sheer DNA Security.
The Sheer DNA Manage window with the Users branch selected is displayed
below.
10,
Each row in the table in the Workspace displays the user name and a
description of the user.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table:
• User Name: The user name (unique) defined for the current client
station.
• Description: A description of the user.
• Default Permission: The default permission of the user, namely, Viewer
to Administrator. For example, a user with the default permission Viewer
can view maps and the Device List.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 49
Page 66

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Note: The default permission only applies at an application level,
namely, all the activities that are related to GUI functionality, not the
activities related to devices. For more information, refer to Chapter 10,
Managing Sheer DNA Security.
• Last Login: The date and time that the user last logged in.
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to the following section.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 51.
Note: The menus and toolbar displayed in the Sheer DNA Manage window
are context sensitive; the options vary depending on your selection in the
Tree pane and Workspace.
Users Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Users branch is selected. The following menus are available:
• File menu, as described in the following section.
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 51.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 51.
File Menu – Users Branch
The File menu is displayed below.
New User
Creates a new user for the current client station.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected user.
Page 50 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 67

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
Exit
Exits Sheer DNA Manage. For more information, refer to page 56.
Tree Pane Menu – Users Branch
When the user right-clicks on the Users branch in the Tree pane the
following menu is displayed:
New User
Creates a new user for the current client station.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Users Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following menu
is displayed:
Change Password
Displays the Set Password dialog box that enables the administrator to edit a
user’s password.
Delete
Deletes the selected user name from the system.
Note: The user name root cannot be deleted.
Properties
Displays the properties of the selected user.
Toolbar – Users Branch
The Users branch contains the following tools:
Opens the New User dialog box enabling the user to define a
new user for the current client station.
Displays the properties of the selected user.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 51
Deletes the selected user name from the system.
Page 68
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
2.3.8 Workflow Engine Branch
The Workflow Engine branch enables the user to manage workflow templates
and running workflows in runtime. The Workflow Engine branch includes the
following sub-branches:
• Templates: Displays a list of the deployed workflow templates and
enables the user to view the properties of the workflow template. For
more information, refer to the section below.
• Workflows: Displays a list of the running or completed workflows and
enables the user to view and alter their current status. For more
information, refer to page 54.
Templates
The Templates sub-branch enables the user to:
• View a list of the deployed workflow templates
• View the properties (attributes) of a workflow template
• Delete a workflow template
The Sheer DNA Manage window with the Templates sub-branch selected is
displayed below.
The table displays the names of the workflow templates (in the Workspace),
as defined using the Sheer Workflow Editor.
Page 52 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 69

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to the following section.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 54.
Templates Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Templates sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• Tools menu, as described on page
• Help menu, as described on page
22.
22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described the following section.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 53.
Tree Pane Shortcut Menu – Templates Branch
Right clicking on the Templates sub-branch displays the following shortcut
menu:
Properties
Displays a list of the workflow templates available on the Sheer DNA
Gateway.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Templates Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu is displayed:
Properties
Displays the properties (attributes) of the selected workflow template.
Delete
Deletes the selected workflow template.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 53
Page 70
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Toolbar – Templates Branch
When the Templates sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the toolbar
contains the following tools:
Deletes the selected workflow template.
For more information about workflows, refer to the Cisco Active Network
Abstraction Workflow User’s Guide.
Workflows
The Workflows sub-branch enables the user to:
• View the list of running or completed workflows and the status of each
• View the output of a workflow
• Abort a workflow that is being processed or that has been completed, and
initiate rollback
• Delete a workflow
• View the properties of a workflow
The Sheer DNA Manage window with the Workflows sub-branch selected is
displayed below.
The following columns are displayed in the Workspace table when the
Workflows sub-branch is selected:
• ID: A unique sequential number given to the workflow.
Page 54 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 71

Getting Started with Sheer DNA Manage
• Name: The name of the workflow, as defined using the Sheer Workflow
Editor.
• State: The current status of the workflow, namely, Ready, Running,
Done, or Aborted.
For more information about:
• Menu options, refer to the following section.
• Toolbar options, refer to page 56.
Workflows Menus
This section provides a description of each option available in the menus
when the Workflows sub-branch is selected. The following menus are
available:
• Tools menu, as described on page 22.
• Help menu, as described on page 22.
• Tree Pane shortcut menu, as described on page 55.
• Workspace shortcut menu, as described on page 55.
Tree Pane Menu – Workflows Branch
Right clicking on the Workflows sub-branch displays the following shortcut
menu:
Properties
Displays a list of the scripts and their current status.
Workspace Shortcut Menu – Workflows Branch
When the user right-clicks in the table in the Workspace the following
shortcut menu is displayed:
Show Output
View the output of the workflow.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 55
Page 72
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Abort/Rollback
Aborts the workflow and performs rollback if the workflow is running, or if
the workflow has already been completed it performs rollback.
Delete
Deletes the workflow from the database.
Note: A workflow can only be deleted from the database when it is Done or
Aborted. It cannot be deleted while the process is still running.
Properties
Displays the properties (attributes) of the selected workflow, including its
status.
Toolbar – Workflows Branch
When the Workflows sub-branch is selected in the Tree pane the toolbar
contains the following tools:
Deletes the workflow from the database.
For more information about workflows, refer to the Cisco Active Network
Abstraction Workflow User’s Guide.
2.4 Logging Out
When the user has finished working with Sheer DNA Manage the user can
log out of the application. Any changes that were made are automatically
saved when logging out.
To log out of Sheer DNA Manage
1. From the File menu, select Exit,
or
Click to close the Sheer DNA Manage window.
The following message is displayed:
2. Click Yes. The Sheer DNA Manage window is closed.
Page 56 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 73

Deploying Sheer DNA
3 Deploying Sheer DNA
About this chapter:
This chapter describes the steps that must be performed to deploy Sheer DNA
and provides cross-references to the relevant sections in this Administrator’s
Guide.
3.1 System Setup Flow
The flow below describes the steps required to deploy Sheer DNA using
Sheer DNA Manage and the order in which they must be performed.
Step 1: Prepare a deployment plan
Step 4: Customize polling gr oups
Step 1: Prepare a deployment plan: The user must decide the following:
• How many Sheer DNA Unit servers are going to be deployed and
allocate AVMs (Autonomous Virtual Machines) to each server.
• How many and what types of Network Elements will be managed by
each AVM.
Step 2: Set up and manage DNA Servers
Step 2.1: Add Sheer DNA Units
Step 2.2: Create and launch AVMs
Step 2.3: Create and assign VNEs
Step 5: Define static links
(optional)
Step 3: Customize
protection groups
Step 6: Manage and run workflows
(optional)
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 57
Page 74

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• How many protection groups there are going to be and how Sheer DNA
Units are going to be grouped together in protection groups (clusters),
based on the following considerations:
• Device type
• Geographical location
• Importance of device
• Number of devices
Note: The planning of Protection Groups in the deployment plan is
only applicable when high availability is enabled. For more information,
refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction High Availability User’s
Guide.
• How many standby Sheer DNA Units are going to be deployed.
• How Sheer DNA Units, standby Sheer DNA Units and protection groups
are going to be deployed and allocated.
• How many network scopes are required and according to what policy.
• How many users will be defined.
Step 2: Set up and manage DNA Servers: This includes the following:
• Step 2.1: Add Sheer DNA Units: Enables the administrator to add a
Sheer DNA Unit. Transport links are created automatically between the
Sheer DNA Unit and its associated Sheer DNA Gateway in a star
topology or between two Sheer DNA Units. For more information, refer
to the section Adding New Sheer DNA Units on page 71.
In addition, the administrator can configure Sheer DNA Units for high
availability and assign the Sheer DNA Units to protection groups. The
standby Sheer DNA Units can be configured and assigned to protection
groups (optional). For more information, refer to the Cisco Active
Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.
• Step 2.2: Create and launch AVMs: Enables the administrator to add
AVMs to managed Network Elements. For more information, refer to the
section Creating AVMs on page 80.
• Step 2.3: Create and assign VNEs: Enables the administrator to create
a Virtual Network Element (VNE) that corresponds to a Network
Element. For more information, refer to the section Defining VNEs on
page 89.
Note: Additional Units, AVMs, VNEs, Scopes and Users can be added or
edited at any time.
Page 58 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 75

Deploying Sheer DNA
Step 3: Customize protection groups: Enables the administrator to change
the default setup of Sheer DNA Units by customizing protection groups
(clusters) and then assigning Sheer DNA Units to these groups. For more
information, refer to Cisco Active Network Abstraction High Availability
User’s Guide.
Important Note: You must assign a DNA Unit and/or Redundant Unit to a
specific Protection Group.
Step 4: Customize polling groups: Enables the administrator to customize
new polling groups and rates. For more information, refer to the section
Customizing a Polling Group on page 116.
Note: This step can be performed at any time after Step 1.
Step 5: Define static links: Enables the administrator to add a static link
between two ports of two Network Elements in the network (optional). For
more information, refer to the section Creating a Static Link on page 127.
Step 6: Manage and run workflows: Enables the administrator to manage
workflow templates and running workflows in runtime using the Workflow
Engine branch (optional). For more information, refer to Chapter 9,
Managing Workflows.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 59
Page 76

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
3.2 User and View Setup Flow
The flow below describes the steps required to setup Sheer DNA users and
the view using Sheer DNA Manage and the order in which they should be
performed.
Step 1: Insta ll client lice n se(s)
Step 2: Def ine scope(s)
Step 3: Define Sheer DNA user accounts
Step 4: Customize a message of the day
(optional)
Step 1: Install client license(s): Enables the administrator to install and
uninstall the client license provided by Sheer. For more information, refer to
the section Managing Client Licenses on page 107.
Step 2: Define scope(s): Enables the administrator to define and manage
scopes. For more information, refer to the section
Creating Scopes on
page 140.
Step 3: Define Sheer DNA user accounts: Enables the administrator to
define and manage Sheer DNA user accounts. For more information, refer to
section
Creating New Sheer DNA User Accounts on page 143.
Step 4: Customize a message of the day: Enables the administrator to
define a message (service disclaimer) that will be displayed when the user
logs in to the Sheer Client applications. For more information, refer to section
Customizing a Message of the Day on page 113.
For a detailed description about how Sheer DNA implements a role-based
security mechanism with scopes (groups of Network Elements) that are
granted to users and managing users in the Sheer DNA platform, refer to
Chapter
10, Managing Sheer DNA Security.
Page 60 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 77

General DNA Manage Tables
4 General DNA Manage Tables
About this chapter:
This chapter describes how to perform general Sheer DNA Manage functions
when working with tables:
Working with DNA Manage Tables, page 61, describes how to work with
Sheer DNA Manage tables, including finding information, opening filters and
exporting table information.
Finding Text in a Table, page 63, describes how to sort a table by defining
specific criterion.
Filtering Information, page 63, describes how to define a filter for the data
displayed in the Workspace. In addition, it describes how to select lines and
set specific selection filters.
Setting Selection Filters, page 65, describes how to choose a line or specific
set of lines, and display them in the table.
Sorting a Table, page 67, describes how to sort tables by defining specific
criteria.
Exporting the Table to a File, page 68, describes how to export all the
currently displayed data from the Workspace to a CSV file.
All these functions are performed using the Sheer DNA Manage table toolbar
above the displayed table.
4.1 Working with DNA Manage Tables
Various tables are used throughout the application to display different types
of information. Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to perform the
following functions using the toolbar displayed above the table in the
Workspace:
• Find text in a table.
• Define a filter in a table.
• Clear a defined filter from a table.
• Choose lines and set a selection filter in a table
• Undo the previous selection filter in a table
• Undo all selection filters
• Sort the table according to a column
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 61
Page 78

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Export table information.
• Finding specific information in DNA Manage tables
You can also find specific DNA Manage information, such as DNA Units,
AVM/VNE details using the toolbar button and entering criteria into the
Find dialog box. For more information, refer to section Finding a
Unit/AVM/VNE on page 76.
For more information about the Table toolbar, refer to page 18.
The user can open the Filter dialog box by clicking the button and sorting
criteria by table field, operator, and text.
The user can also (multiple) select specific lines and display them in the table
using the
using the
button, and undo the last applied filter, or rewind all filters
buttons.
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to sort a table in one or more of the
following ways:
• According to a column by clicking on the required column heading. The
icon is displayed next to the selected column heading.
• In ascending or descending order by clicking on the column heading.
• By clicking the button in the toolbar of the table and specifying the
criterion by which the table will be sorted. For more information about
sorting a table using the button, refer to page 67.
A triangle is displayed next to the column heading to indicate the column
according to which the table is sorted.
Clicking on a red triangle displayed in a cell expands the cell to display all of
the information in the cell.
Page 62 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 79

General DNA Manage Tables
4.2 Finding Text in a Table
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to search for information in the
Workspace by entering the search criteria, for example, by entering a partial
user name.
Note: The tools displayed in the table are a generic component of Sheer
DNA applications.
To find text in a table
1. In the table toolbar, in the Find field enter the search criteria.
2. Press Enter. The row matching the search criteria is highlighted in the
table.
Note: Click F3 to continue searching the table.
4.3 Filtering Information
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to define a filter for the data displayed
in the Workspace according to a selected column. For example, in the Users
branch information can be filtered according to user name.
To define a filter
1. In the table toolbar, click Filter . An example of the Filter dialog box
with defined field and operator criteria displayed.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 63
Page 80

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
The following dropdown lists are displayed in the Filter dialog box:
• Field: Displays a dropdown list of all the columns displayed in the
current table.
• Operator: Displays a dropdown list of the values included in the
filter operation.
The following checkbox is displayed in the Filter dialog box:
• Not: Select this checkbox to filter the negative of the value in the
Operator field. For example, if the Not checkbox was selected in
the Filter dialog box, the filter operator would be the equivalent of
“does not contain”.
The following free text area is displayed in the Filter dialog box:
• Search for: Enter the required filter value.
2. Select an option from the Field and Operator dropdown lists.
3. Enter th e required filter values in the Search for field.
4. Click OK. The information is displayed in the Workspace using the
defined filter.
Note: The Filter button toggles to indicate that a filter has been
applied.
The filter can be cleared in order to display all the data in the table again.
To clear a filter
1. In the toolbar, click Filter
. The Filter dialog box is displayed.
2. Click Clear. The Workspace displays all of the data.
Important Note: Use the Clear filter option to clear ALL of the filter
settings (refer to the note in the Setting Selection Filters section on
page 65).
Page 64 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 81
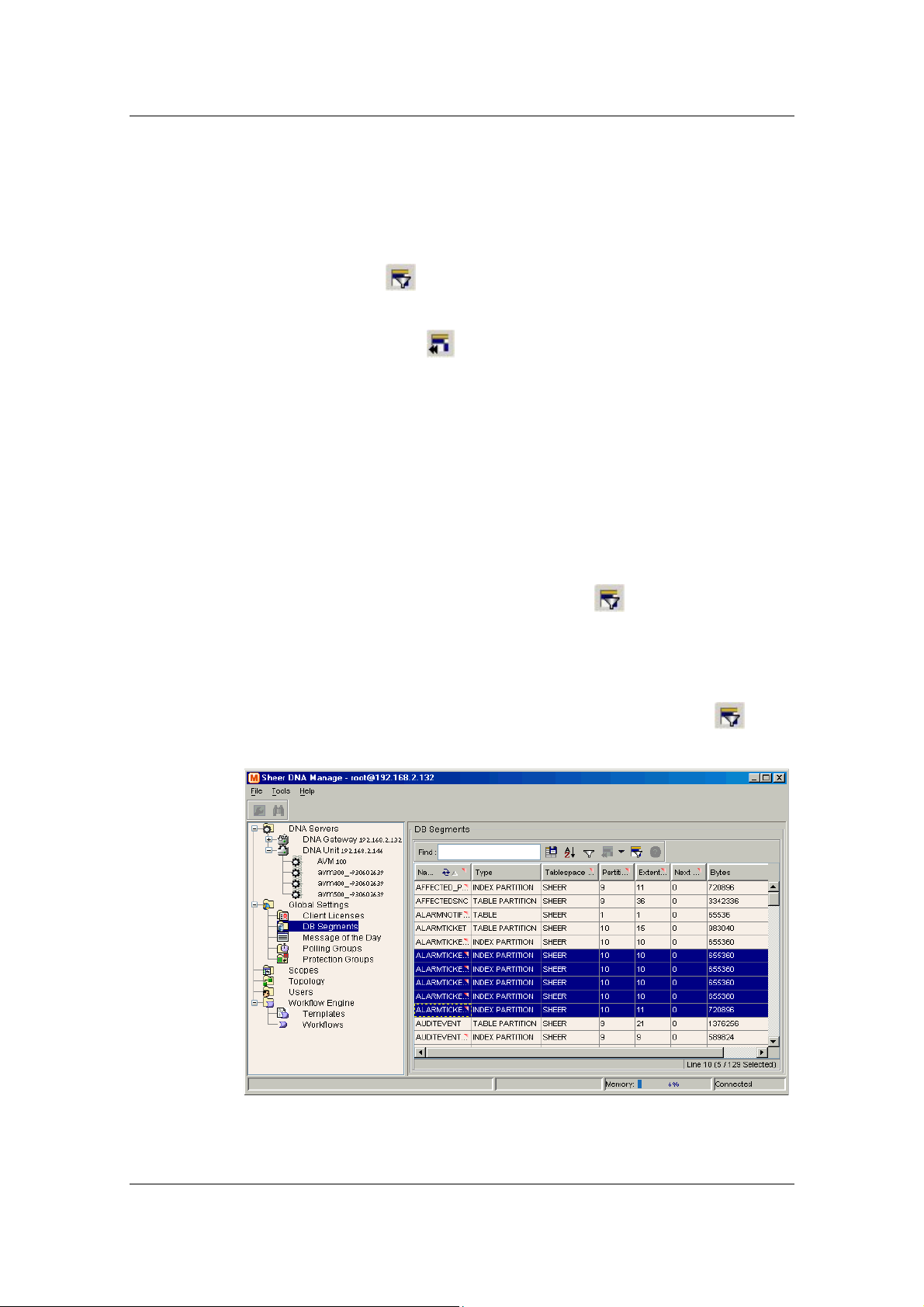
General DNA Manage Tables
4.4 Setting Selection Filters
The user can choose a line or specific set of lines, and display them in the
table (all un-selected lines are hidden). The user may make continuous
multiple line selections, setting the table content after each selection, using
the Set Selection Filter button.
The user can undo the last line selections (one step back), one at a time, using
the Previous Selection Filter button, or undo (rewind) all multiple line
selections, using the Rewind All dropdown menu option.
This powerful Sheer DNA filtering mechanism enables the user sort though
several hundred lines and pinpoint the appropriate line(s) that contain the
required information.
For example, to filter and display seven lines in a 129 line Database Segment
table:
• Select the appropriate lines in the table using standard Windows mouse
and/or keystroke operations
• Apply the filter to the selected line(s) using the button.
To choose multiple lines and apply the set selection filter
1. Select the line(s) in a DNA Manage table using the mouse and standard
Microsoft® Windows selection keys. The Set Selection Filter
button is activated.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 65
Page 82

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
2. Click the button. Only the selected line(s) remain in the table.
To undo the previous filter selection
1. Select one or several lines and filter them out using the appropriate table
toolbar buttons.
2. To undo the last filtering out selection, select the Previous Selection
Filter button. The table will display all lines that appeared before
your last filter selection.
To undo all previous selected filter out options
1. Select, filter out and sort lines as required in the table using the
appropriate table toolbar buttons, such as Previous Selection Filter
button.
2. Click the Previous Selection
button. The Rewind All dropdown
menu option is displayed:
3. Select Rewind All. All the lines in the table are displayed.
Important Note: To clear all manually selected and defined filter
options, use the Clear command button in the Filter dialog box (refer to
page 64 for operating instruction to clear filters).
Page 66 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 83
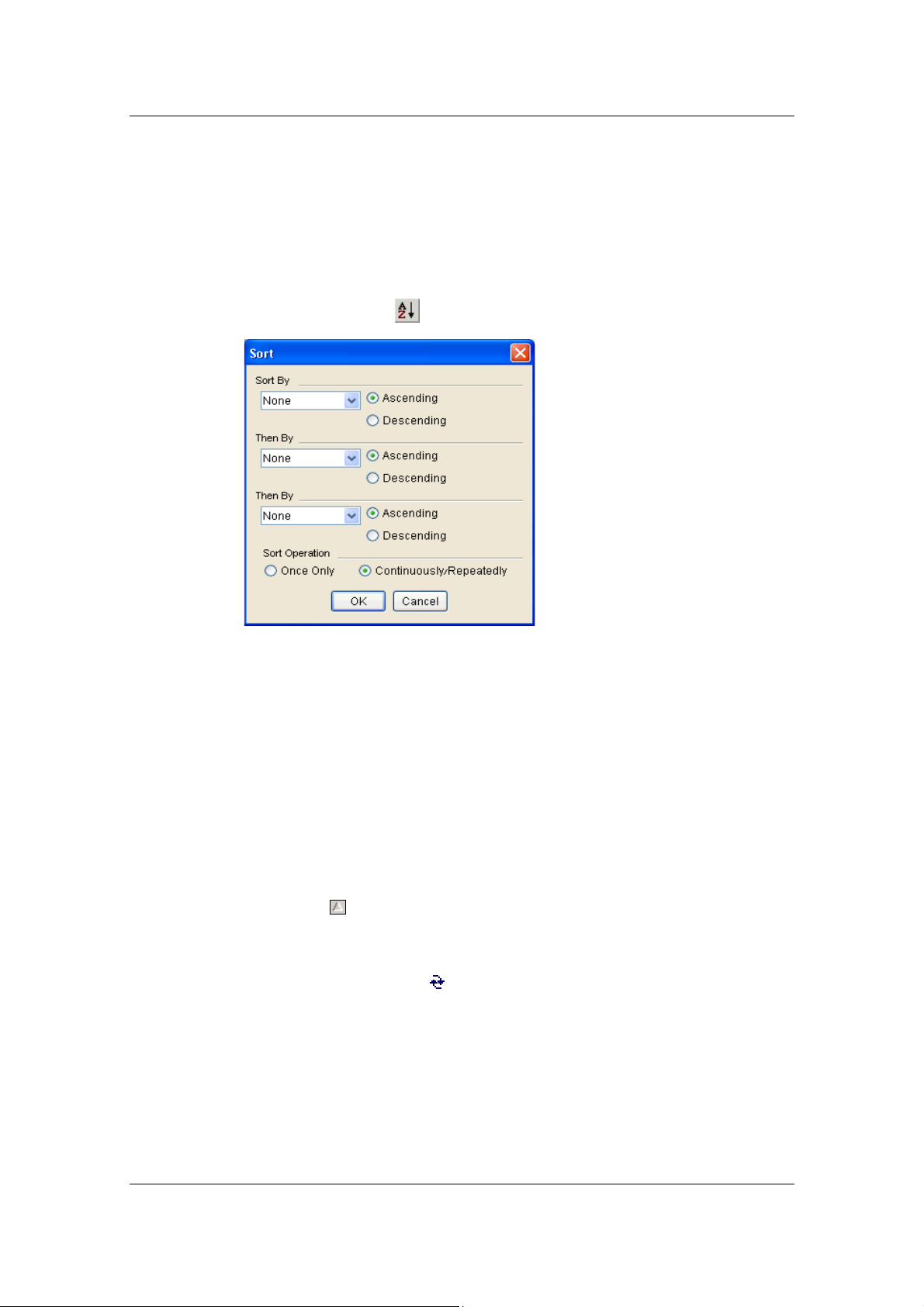
General DNA Manage Tables
4.5 Sorting a Table
The tables displayed in Sheer DNA Manage can be sorted by defining
specific criterion on a one-time only basis or continuously.
To sort a table
1. In the toolbar, click . The Sort dialog box is displayed.
The following dropdown lists are displayed in the Sort By area:
• Sort By: A dropdown list of all of the columns displayed in the
currently displayed table. The table is sorted firstly according to the
selection made here. Select ascending or descending order.
• Then By: Dropdown lists of all of the columns displayed in the table.
The table is sorted secondly and then lastly according to the
selections made here. Select ascending or descending order.
The following radio buttons are displayed in the Sort Operation area:
• Once Only: Sorts the information displayed in the table according to
the specified criterion once only. When this option is selected a
triangle is displayed in the table heading for the selected column.
• Continuously/Repeatedly: Sorts the information displayed in the
table according to the specified criterion continuously. When this
option is selected the icon is displayed next to the selected column
heading.
2. Select an option from the Sort By dropdown list and Ascending or
Descending order.
3. Select an option from the Then By dropdown lists and Ascending or
Descending order (optional).
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 67
Page 84

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
4. Select Once Only or Continuously/Repeatedly.
5. Click OK. The table information is sorted according to the filter defined.
4.6 Exporting the Table to a File
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to export all the currently displayed
data from the Workspace to a CSV file. Either the selected rows are exported
or when nothing is selected the entire table is exported. The data can then be
imported and viewed at a later stage.
Note: This tool occurs throughout the application with the same
functionality.
To export the table to a file
1. In the table toolbar, click the Export to CSV button. The Export
Table To File dialog box is displayed.
2. Browse to the directory where you want to save the table.
3. In the File name field, enter a name for the table.
4. Click Save. The table or selected row(s) is saved in the selected
directory.
Page 68 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 85

Managing Sheer DNA Units
5 Managing Sheer DNA Units
About this chapter:
This chapter describes how to manage Sheer DNA Units. This includes
adding and removing Sheer DNA Units, and viewing Sheer DNA Unit
properties.
What is a DNA Unit?, page 70, provides a description of a DNA Unit.
Adding New Sheer DNA Units, page 71, describes how to add a new Sheer
DNA Unit to the Sheer DNA fabric.
Editing Sheer DNA Unit Properties, page 73, describes how to view the
properties of a Sheer DNA Unit.
Removing a Sheer DNA Unit, page 75, describes how to remove a Sheer
DNA Unit.
Finding a Unit/AVM/VNE, page 76, describes how to locate Sheer DNA
Units, AVMs and VNEs among all Sheer DNA Servers.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 69
Page 86
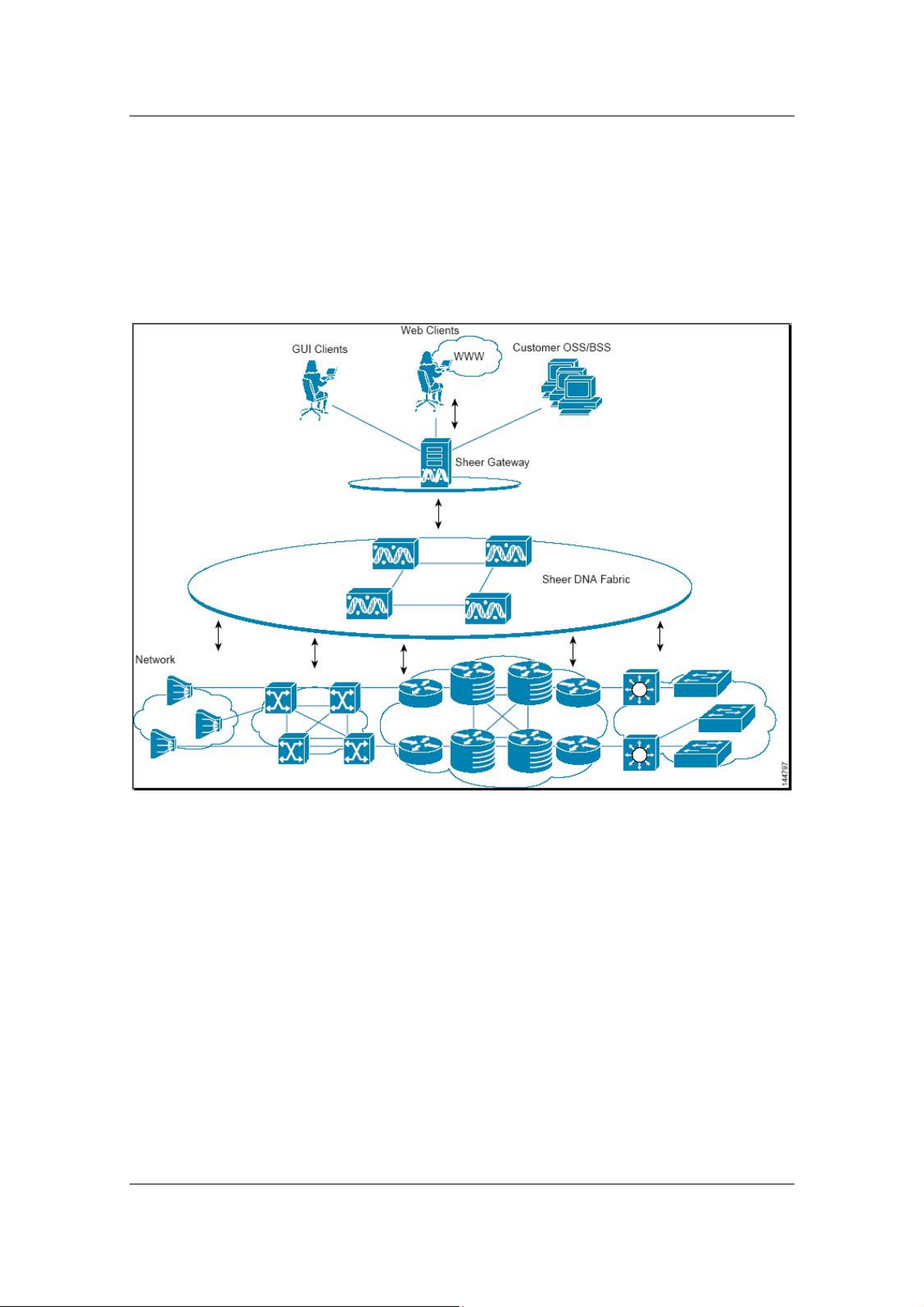
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
5.1 What is a DNA Unit?
The main purpose of the Sheer DNA Units is to host the Autonomous VNEs.
The Sheer DNA Units are interconnected to form a fabric of VNEs that can
inter-communicate with other VNEs regardless of which unit they are
running on. Each Sheer DNA Unit can host thousands of Autonomous VNE
processes (depending on the server system size).
For more information about adding Sheer DNA Units, refer to the section
Adding New Sheer DNA Units on page 71.
The Sheer DNA Units also allow for optimal VNE distribution, ensuring
geographic proximity between the VNE and its managed NE.
Page 70 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 87

Managing Sheer DNA Units
The clustered N+m High Availability mechanism within the Sheer DNA
Fabric is designed to handle the failure of a Sheer DNA Unit. Sheer DNA
Unit availability is established in the Gateway, running a Protection Manager
process, which continuously monitors all the Sheer DNA Units in the
network. Once the Protection Manager detects a Sheer DNA Unit that is
malfunctioning, it automatically signals one of the m servers in its cluster to
load the configuration of the faulty unit (from the system Registry), taking
over all its managed Network Elements. The switchover to the redundant
standby Sheer DNA Unit does not result in any loss of information in the
system, as all of the information is auto-discovered from the network, and no
persistent storage synchronization is required. When a Sheer DNA Unit is
configured it can be designated as being an active or standby unit.
Note: The Sheer DNA system is usually configured with Sheer’s High
Availability mechanism enabled.
For more information about high availability, standby units, and defining a
redundant unit, refer to the Cisco Active Network Abstraction High
Availability User’s Guide.
5.2 Adding New Sheer DNA Units
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to add a Sheer DNA Unit to the Sheer
DNA Fabric. Sheer DNA Manage automatically registers the Sheer DNA
Unit in the registry and creates a transport uplink between the Sheer DNA
Unit and the Sheer DNA Gateway. The Sheer DNA Units are linked to the
Sheer DNA Gateway in a star topology.
In addition, the administrator can enable or disable high availability for a
Sheer DNA Unit. These settings enable the administrator to define to which
protection group a Sheer DNA Unit is assigned and whether it is enabled for
high availability.(For more information on high availability, refer to the
Cisco Active Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.)
Note: By default all Sheer DNA Units in the Sheer DNA Fabric belong to
one big cluster, namely, the default-pg protection group.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 71
Page 88

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
To add a new DNA Unit
1. Select the DNA Servers branch in the DNA Manage window Tree pane.
The DNA Servers branch is displayed.
2. Right-click on the DNA Servers branch to display the shortcut menu and
select New DNA Unit or in the toolbar click New Unit or from the File
menu select New DNA Unit. The New DNA Unit dialog box is
displayed.
The following field is displayed in the New DNA Unit dialog box:
• IP Address: The unique IP address of the Sheer DNA Unit.
Note: If a Sheer DNA Unit is already configured with the same IP
address an error message is displayed.
The following checkboxes are displayed in the New DNA Unit dialog
box:
• Enable Unit Protection: Define whether a Sheer DNA Unit is
enabled (checkbox is selected) for high availability. This option is
selected by default.
Note: It is highly recommended that the user does not disable this
option. When you define the DNA Unit as the “new” Standby Unit,
this option is automatically disabled. For more information about
configuring standby Sheer DNA Units, refer to the Cisco Active
Network Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.
Page 72 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 89

Managing Sheer DNA Units
• Standby Unit: Define whether a Sheer DNA Unit is defined
(checkbox is selected) as a standby unit.
• The Protection Group dropdown list displays the currently defined
list of customized protection groups
3. Enter the IP Address of the new Sheer DNA Unit in the IP Address
field.
4. Select the required protection group from the Protection Group
dropdown list.
5. Click OK. The new Sheer DNA Unit is displayed in the Tree pane and
the Workspace of the Sheer DNA Manage window.
If the new Sheer DNA Unit is installed and reachable it will start
automatically. The Sheer DNA Unit is registered with the Sheer DNA
Gateway. Specifically, the command creates the configuration registry for the
new Sheer DNA Unit in the Golden Source. For more information about the
Golden Source Registry, refer to page 157.
In addition, Sheer DNA Manage automatically creates the transport uplinks
between the Sheer DNA Unit and the Sheer DNA Gateway.
5.3 Editing Sheer DNA Unit Properties
The user can view the properties of a Sheer DNA Server, for example,
physical and allocated memory.
To edit a Sheer DNA Unit’s properties
1. Select the DNA Servers branch in the Sheer DNA Manage window Tree
pane. The DNA Servers branch is displayed.
2. Select the Sheer DNA Unit or Sheer DNA Gateway in the Workspace or
expand the DNA Servers branch and select the required Sheer DNA Unit
or Sheer DNA Gateway in the Tree pane.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 73
Page 90

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
3. Right-click on the required Sheer DNA Unit or DNA Gateway branch to
display the shortcut menu and select Properties, or in the toolbar click
Properties or from the File menu, select Properties. The DNA Unit
Properties dialog box is displayed.
The following fields are displayed in the DNA Unit Properties dialog
box:
• IP Address: The IP Address of the Sheer DNA Unit or Sheer DNA
Gateway.
• Status: The status of the Sheer DNA Unit or Gateway, namely, Up or
Down.
• Up Since: The date and time that the Sheer DNA Unit or Sheer DNA
Gateway was started.
• Physical Memory: The physical memory of the Sheer DNA Unit or
Sheer DNA Gateway.
• Allocated Memory: The amount of memory allocated to the Sheer
DNA Unit or Sheer DNA Gateway. Allocated memory is the sum of
all of the memory settings for all of the AVMs.
• Used Memory: The maximum memory used by the Sheer DNA Unit
or Sheer DNA Gateway. (Used memory is the sum total of the
memory used by all the AVMs that are Up.)
The Protection Group dropdown list displays the currently defined list
of customized protection groups.
Page 74 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 91
Managing Sheer DNA Units
4. You can change the assigned DNA Unit protection group, as required, by
selecting an option from the dropdown list.
The Enable Unit Protection checkbox defines whether a Sheer DNA
Unit is enabled (the checkbox is selected) for high availability. This
option is selected by default when high availability is enabled.
Note: If and when you change (disable/enable) the Enable Unit
Protection option (high availability), changes will only become effective
after a delay of about 15 minutes.
5. Click OK. The DNA Unit Properties dialog box is closed.
5.4 Removing a Sheer DNA Unit
The user can remove a Sheer DNA Unit.
Note: The user must first delete all of the VNEs and non-reserved AVMs
before deleting a Sheer DNA Unit. The reserved AVMs cannot be deleted.
For more information about reserved AVMs, refer to page 80.
Note: The Sheer DNA Gateway cannot be deleted.
Note: The Sheer DNA Unit cannot be deleted if it is the Sheer DNA Gateway
to which the user is connected.
To remove a Sheer DNA Unit
1. In the Sheer DNA Manage window Tree pane, select the DNA Servers
branch. The DNA Servers branch is displayed.
2. Expand the DNA Servers branch and select the Sheer DNA Unit you
want to remove in the Tree pane or Workspace.
3. Right-click on the Sheer DNA Unit that you want to remove to display
the shortcut menu, and select Delete. A warning message is displayed.
4. Click Yes to proceed or No to cancel the operation. A confirmation
message is displayed.
5. Click OK. The Sheer DNA Unit is deleted and is no longer displayed in
the Tree pane and Workspace.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 75
Page 92

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
5.5 Finding a Unit/AVM/VNE
A single search in Sheer DNA Manage can locate Sheer DNA Units, AVMs
and VNEs among all Sheer DNA Servers according to specifically defined
search criteria.
To find a Unit/AVM/VNE
1. In the Sheer DNA Manage window Tree pane, select the DNA Servers
branch or any sub-branch. The selected branch or sub-branch is
displayed.
2. In the toolbar, click Find. The Find dialog box is displayed.
The Find field enables the user to enter specific search criteria in order
to find the required DNA Unit/AVM/VNE. For example, the user can
search for an AVM using the ID number or search for a Unit using an IP
address.
The Types dropdown list enables the user to specify whether the user is
searching for a Unit/AVM/VNE by selecting an option from the list.
When an option is selected from the list, then the Property area is
enabled, displaying the properties for the selected option. For example, if
AVM is selected from the Types dropdown list, then the AVM’s
properties are displayed in the Property area and the user can select a
specific property according to which the user wants to conduct the
search.
The Up and Down radio buttons enable the user to search up and down
(you can also use the F3 key).
Page 76 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 93

Managing Sheer DNA Units
The following buttons are displayed in the Find dialog box:
• Find: Searches for the DNA Unit/AVM/VNE from the selected
point in the Tree pane, either up or down.
• Cancel: Cancels the search and clears the Find dialog box.
3. Enter the search criteria in the Find field.
4. From the Types dropdown list select DNA Unit/AVM/VNE (optional).
5. From the Property area select a specific property (optional).
6. Select a direction, namely, Up or Down.
7. Click Find. The DNA Unit/AVM/VNE matching the search criteria is
highlighted in Sheer DNA Manage.
Note: Click F3 to view the next DNA Unit/AVM/VNE matching the
search criteria.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 77
Page 94

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
Page 78 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 95

Managing AVMs and VNEs
6 Managing AVMs and VNEs
About this chapter:
This chapter describes defining and managing AVMs and VNEs.
Creating AVMs, page 80, describes how to define an AVM for a Sheer
DNA Unit Server.
AVM Status, page 82, describes the status of AVMs when they are created
and loaded.
Viewing and Editing an AVM’s Properties, page 83, describes how to
view and edit an AVM’s properties.
Deleting an AVM, page 84, describes how to delete AVMs.
Starting and Stopping AVMs, page 85, describes how to stop and start
AVMs, and the respective changes in AVM status.
Moving AVMs, page 86, describes how to manage AVM before you move
them, and their status after a move.
VNEs Overview, page 87, provides an overview of assigning VNE IP
addresses, the VNE relationship to an AVM, and how to add a VNE to an
AVM.
Defining VNEs, page 89 describes how to open the New VNE dialog box and
provides a description of property options you may define in each tab.
Viewing and Editing a VNE’s Properties, page 101, describes how to view
and edit the properties of a VNE.
Deleting a VNE, page 103, describes how to delete a VNE from an AVM.
Changing the VNE’s State, page 104, describes how to start or stop a VNE
or move a VNE to maintenance mode.
Moving Multiple and Single VNEs, page 105, describes how to move
VNEs between AVMs.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 79
Page 96

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
6.1 Creating AVMs
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to define AVMs for DNA Unit Servers.
Every AVM (Autonomous Virtual Machine) in the Sheer DNA Fabric is by
default managed by the watchdog protocol. Sheer DNA Manage enables the
administrator to define AVMs for Sheer DNA Units and enable or disable the
watchdog protocol on the AVM.
In order to define an AVM:
• The Sheer DNA Unit must be installed.
• The Sheer DNA Unit must be connected to the transport network.
• The default AVMs, namely, AVM 0 (the switch AVM), AVM 99 (the
management AVM) and AVM 100 (the trap management AVM) must be
running.
Note: For more information on the status of AVMs, for example, status
Up when the AVM is running, refer to the AVM Status section on
page 82.
• The new AVM must have a unique ID within the Sheer DNA Unit.
Note: There are certain AVM ID numbers that are reserved, namely, AVM 0100 and these cannot be used. In addition, there may be other reserved AVM
ID numbers. The user will be unable to enter a reserved number.
To create an AVM
1. Select the DNA Servers branch in the Sheer DNA Manage window’s
Tree pane. The DNA Servers branch is displayed.
2. Expand the DNA Servers branch and select the required DNA Servers
Entity sub-branch.
Page 80 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 97

Managing AVMs and VNEs
3. Right-click on the required Sheer DNA Unit to display the menu and
select New AVM or in the toolbar click New AVM or from the File
menu select New AVM. The New AVM dialog box is displayed.
The following fields are displayed in the New AVM dialog box:
• DNA Unit: The IP address of the selected Sheer DNA Unit.
Note: The Sheer DNA Unit does not have to be Up to create a new
AVM.
• ID: The name of the AVM as defined in Sheer DNA Manage, and
unique to the Sheer DNA Unit, for example, AVM 18.
Note: The AVM numbers 0-100 are reserved and cannot be used.
The user will be unable to enter a reserved number. A message is
displayed in the New AVM dialog box advising the user that the
number is reserved.
• Key: The key is a string that uniquely identifies an AVM in the
system (across all DNA Units) thus enabling a transparent failover
scenario in the system. If the user does not enter a key the default
key is used, namely, “ID + timestamp”.
• Allocated Memory: The maximum memory allocated to the AVM.
The following checkboxes are displayed in the New AVM dialog box:
• Activate on creation: Select this option to load the AVM into the
bootstrap of the Sheer DNA Unit. This changes the administrative
status of the AVM to Up and ensures that the AVM is loaded on
subsequent restarts of the Sheer DNA Unit. By default this option is
unchecked and the newly created AVM has an administrative status
of Down.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 81
Page 98

Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
• Enable AVM Protection: By default this option is selected
enabling the watchdog protocol on the AVM when high availability
is enabled. For more information, refer to the Cisco Active Network
Abstraction High Availability User’s Guide.
Note: It is highly recommended that the user does not disable this
option if high availability is enabled.
Note: If this option is selected or unchecked when the AVM is up
then you will need to restart the AVM in order for this change to
take affect.
4. Define the properties of the AVM.
5. Click OK. The new AVM is added to the selected Sheer DNA Unit, is
displayed in the Workspace, and is activated.
Creating the new AVM results in Sheer DNA providing the registry
information of the new AVM in the specified Sheer DNA Unit, and the AVM
can now host VNEs. For more information, refer to the section Defining
VNEs on page 89.
6.2 AVM Status
The status of AVMs (and VNEs) is affected by Admin and Oper mode.
Admin mode is the administrative instructions that are sent to the AVM.
Oper mode is the actual status of the AVM, for example, Up. For more
information about Admin and Oper modes, refer to page 83.
When moving an AVM (file), its status, for example, Up or Down, has a
bearing on whether the file is reloaded (Up) or not (Down). For more
information about moving AVMs, refer to page
about starting and stopping AVMs, refer to page 85.
An AVM can have only one of the following statuses at a time:
• Up: The file (process) is reachable and was loaded and started. When a
Start (command) option is issued, and no problems are encountered, such
as an overloaded server, the AVM is running (has been loaded and
started), and its status is Up.
• Down: The file (process) is reachable and was stopped. When a Stop
(command) option is issued, Sheer DNA issues instructions to shutdown
all of the processes. When all of the processes have been stopped, the
status of the AVM is Down.
86. For more information
• Starting Up: When a Start or upload (command) option is issued, and
for example, the Server cannot execute it due to the fact that it is busy or
overloaded, the status of the AVM is Starting Up.
Page 82 Cisco Systems, Inc.
Page 99

Managing AVMs and VNEs
• Shutting Down: When a Stop (command) option is issued, and while the
command is being executed (some processes may still be running), the
status of the AVM is Shutting Down.
6.2.1 Admin and Oper Mode AVM Status
The table below describes the status of an AVM depending on the Admin and
Oper modes, as displayed in the Status column of the AVMs table. The
Admin mode is the administrative instructions that are sent to the VNE. The
Oper mode is the actual status of the VNE, for example, Up.
Status Admin Mode Oper Mode
Up
Shutting Down
Down
Starting Up Up Down
Up Up
Down Up
Down Down
6.3 Viewing and Editing an AVM’s Properties
Sheer DNA Manage enables the user to view and edit the properties of an
AVM, for example, the key and the allocated memory.
To view and edit an AVM’s properties
1. Select the DNA Servers branch in the Sheer DNA Manage window’s
Tree pane. The DNA Servers branch is displayed.
2. Expand the DNA Servers branch and select the required AVM sub-branch
in the Tree pane.
3. Right-click to display the shortcut menu and select Properties, or from
File menu, select Properties or in the toolbar click Properties.
Cisco Systems, Inc. Page 83
Page 100
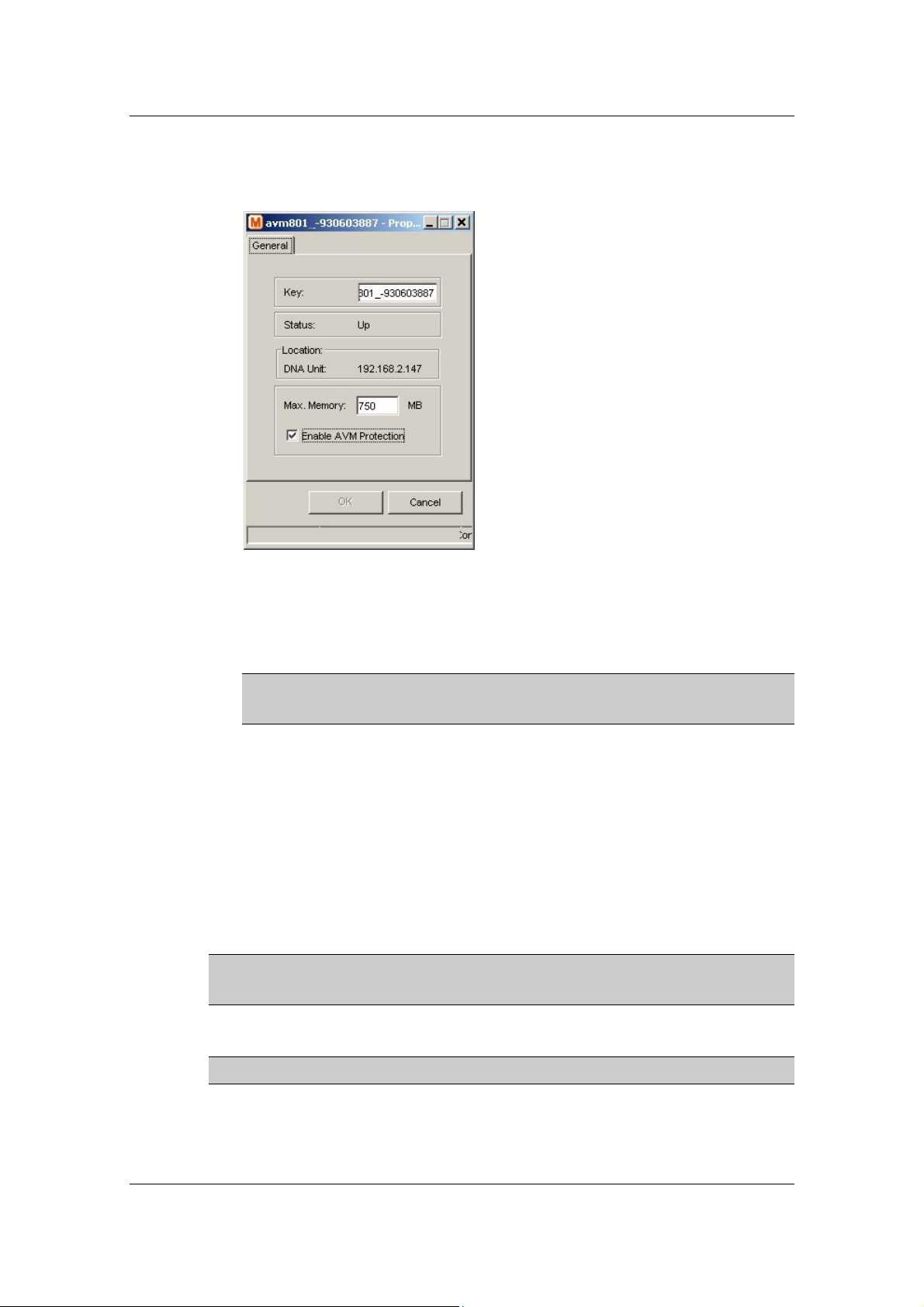
Cisco Active Network Abstraction Administrator’s Guide, 3.5
The AVM Properties dialog box is displayed with the details of the
selected AVM, including, the IP address/key of the Sheer DNA Unit.
The following field is displayed in the AVM Properties dialog box:
• Status: The status of the AVM, namely, Up, Down or Unreachable.
For more information, refer to the section AVM Status on page 82.
4. Edit the details of the AVM, as required.
Note: For more information on the other fields displayed in the AVM
Properties dialog box, refer to page 81.
5. Click OK. The AVM’s new properties are displayed in the Workspace.
6.4 Deleting an AVM
The user can remove an AVM. If the AVM is running it will be stopped
before removal. This procedure deletes the registry information of the AVM
in the specified Sheer DNA Unit. If there are VNEs running in the AVM then
an error message will be displayed and the user will be unable to delete the
AVM.
Important Note: You must remove all of the VNEs before removing their
hosting AVM.
For more information, refer to Deleting a VNE on page 103.
Note: Reserved AVMs 0-100 cannot be deleted.
Page 84 Cisco Systems, Inc.
 Loading...
Loading...